Abstract
Background:
The scaphoid is the most frequently fractured carpal bone, yet its diagnosis remains a significant clinical challenge. A substantial percentage of non-displaced fractures are missed on initial radiographs, leading to delays in treatment and an increased risk of serious long-term complications such as non-union and avascular necrosis. While advanced imaging like CT and MRI are highly accurate, they are associated with higher costs, radiation exposure (CT), and limited immediate availability. High-resolution musculoskeletal ultrasound has emerged as a rapid, non-invasive, and cost-effective alternative. Its unique ability to perform dynamic, real-time assessment of fracture stability offers a significant advantage over static imaging modalities.
Case presentation:
A 29-year-old woman presented to our outpatient clinic with acute left wrist pain following a traction-fall injury. An initial four-view radiographic series of the wrist revealed no definitive evidence of a fracture. Despite the negative imaging, clinical suspicion remained high due to persistent, exquisite point tenderness over the anatomical snuffbox. A point-of-care musculoskeletal ultrasound examination was performed, which revealed a clear hypoechoic cortical breach at the scaphoid waist. To assess mechanical stability, a dynamic stress maneuver—defined as a gentle, controlled “heel-toe” probe rocking that applies focal pressure across the fracture—was performed under real-time sonographic visualization. Gentle probe pressure combined with passive ulnar deviation of the wrist demonstrated visible gapping and micromotion at the fracture site, confirming it as mechanically unstable. Based on this definitive finding, the diagnosis was revised to an unstable occult scaphoid waist fracture, and the management plan was immediately upgraded to a rigid thumb spica splint. Long-term follow-up over 2 years showed radiographic and sonographic evidence of a stable fibrous union.
Conclusion:
This case report highlights the pivotal role of dynamic musculoskeletal ultrasound as an adjunct in the diagnostic algorithm for acute wrist trauma. It demonstrates its ability not only to identify a radiographically occult scaphoid fracture but, more critically, to provide immediate functional information about mechanical stability. This information is paramount for guiding appropriate and timely management to mitigate the risk of long-term complications. We advocate for the broader integration of dynamic ultrasound into the initial assessment of suspected scaphoid fractures.
1 Introduction
The scaphoid bone is the most commonly fractured carpal bone, representing 60–70% of all carpal fractures and 2–7% of all skeletal fractures (1, 2). These injuries predominantly affect young, active individuals (ages 15–29) following a fall onto an outstretched hand (FOOSH), with significant socioeconomic impact including prolonged immobilization, lost work/sport time, and potential long-term disability (3, 4). The scaphoid serves as a critical mechanical link between proximal and distal carpal rows, with its complex, three-dimensional anatomy and articulations with four carpal bones (lunate, capitate, trapezium, trapezoid) enabling essential wrist motions like the dart-thrower’s motion crucial for daily and athletic activities (5, 6). During FOOSH injuries, extreme extension and radial deviation concentrate immense forces across the scaphoid’s slender waist, the site of 70–80% of scaphoid fractures (7).
Despite its prevalence, acute diagnosis of scaphoid fractures remains notoriously difficult. Between 5 and 20% of non-displaced scaphoid fractures are missed on initial four-view radiographs (8), due to the scaphoid’s complex anatomy, oblique orientation, and often subtle, non-displaced nature of initial injury. Clinical findings (anatomical snuffbox tenderness, scaphoid tubercle tenderness, thumb compression pain) are sensitive but lack specificity, leading to over-immobilization of unconfirmed suspected fractures (9). A missed or delayed diagnosis is particularly problematic due to the scaphoid’s unique, retrograde vascularity originating from the dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery. Fractures, especially of the waist or proximal pole, can disrupt blood flow, placing the proximal fragment at high risk of avascular necrosis (AVN) and non-union (10, 11). Scaphoid non-union leads to progressive carpal instability (DISI pattern) and, over years, to scaphoid non-union advanced collapse (SNAC wrist), a debilitating pattern of post-traumatic osteoarthritis often requiring complex surgical salvage (12–14).
The conventional diagnostic algorithm involves cast immobilization followed by repeat radiographs in 10–14 days, but this delays diagnosis and necessitates unnecessary immobilization (15). Advanced imaging (CT, MRI) is highly accurate but has significant drawbacks: radiation exposure (CT), high cost, and limited availability in acute settings (16–18). High-resolution musculoskeletal ultrasonography (MSK-US) has emerged as a cost-effective, radiation-free, point-of-care alternative with high sensitivity and specificity for detecting scaphoid cortical breaches (19–23). However, while static ultrasound identifies fracture presence, dynamic ultrasonography uniquely provides real-time, functional assessment of fracture stability under controlled stress—the single most critical factor determining management, as unstable fractures have markedly higher non-union risk when treated non-operatively (24, 25). Despite its potential, reports demonstrating how dynamic ultrasound findings decisively alter treatment pathways remain limited. This case illustrates diagnosis of a radiographically occult scaphoid fracture classified as mechanically unstable using dynamic point-of-care ultrasound, demonstrating how definitive functional information led to immediate management escalation.
2 Case presentation
2.1 Initial presentation and diagnosis
On June 29, 2019, a 29-year-old right-handed woman presented to our outpatient orthopedic clinic with acute-onset left wrist pain. The injury occurred when she fell onto her outstretched left hand after being pulled by another person. On initial physical examination, there was diffuse swelling, ecchymosis, and significant tenderness to palpation across the entire wrist, with a painfully limited range of motion in all planes. A standard four-view radiographic series of the left wrist was obtained, which did not reveal a definitive fracture line, dislocation, or other acute bony abnormality (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Initial radiographic series of the left wrist (A) Anteroposterior, (B) Lateral, (C) Internal Oblique, (D) External Oblique. No definitive fracture line is observed.
Based on predominant ulnar-sided tenderness on initial presentation, the patient was managed with a short arm ulnar gutter splint. After several days, the initial ulnar-sided pain and swelling resolved completely. However, this clinical improvement unmasked a persistent and now more prominent, exquisite tenderness localized to the radial side. Specifically, palpation of the anatomical snuffbox and the scaphoid tubercle elicited a sharp, focal pain (rated 8/10 on the Visual Analog Scale). Axial compression of the thumb also reproduced this pain, further heightening the clinical suspicion for an occult scaphoid fracture.
Due to these persistent and highly localized signs, a high-resolution musculoskeletal ultrasound examination was performed at the point of care using a high-frequency linear transducer (18-5 MHz, LOGIQ E9, GE Healthcare). The point-of-care ultrasound examination began with a static assessment. With the wrist in slight ulnar deviation to maximize the longitudinal view of the scaphoid, a clear hypoechoic cortical breach was identified at the scaphoid waist. A small, overlying hypoechoic collection consistent with a hematoma was also noted (Figure 2).
Figure 2
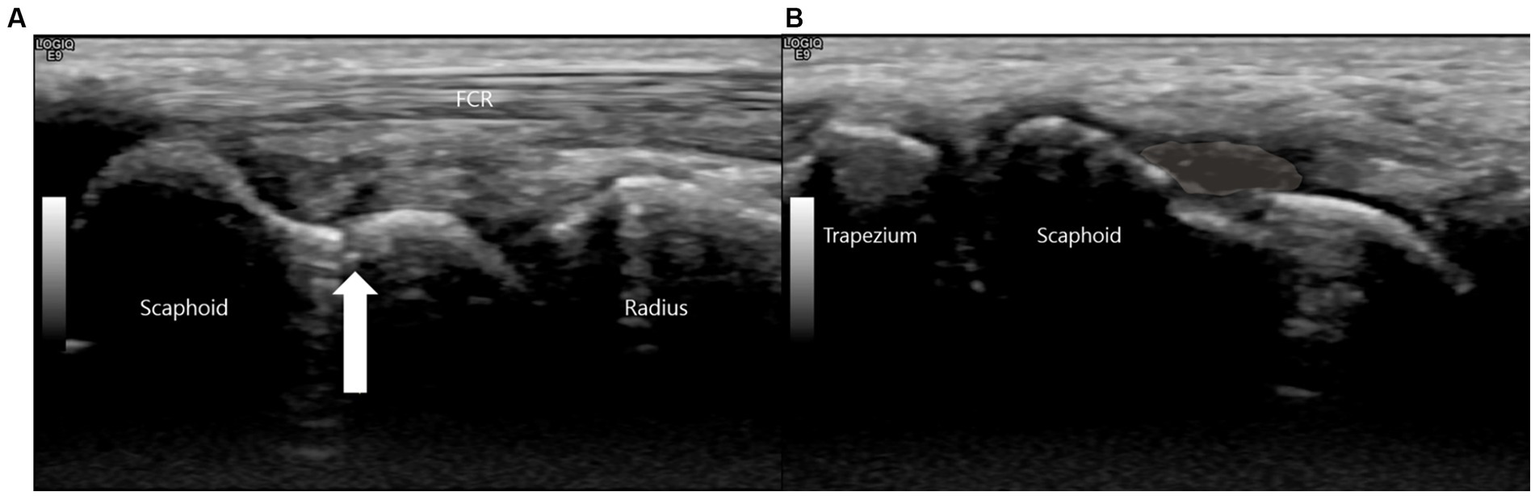
This is a high-resolution ultrasound image of the scaphoid waist. (A) The white arrow indicates the fracture site. (B) A hypoechoic collection consistent with a hematoma (shaded area) is noted superficial to the cortical breach.
This sonographic finding correlated precisely with the point of maximal tenderness elicited during the physical examination, confirming it as the anatomical source of the patient’s symptoms.
To assess functional stability, a dynamic examination was performed. A dynamic stress maneuver is defined as a gentle, controlled “heel-toe” probe rocking that applies focal pressure across the fracture while maintaining a longitudinal view, used to elicit real-time widening of the fracture gap as evidence of mechanical instability (Figure 3). With the wrist in this position, the examiner applied this controlled maneuver. A definitive fracture line, visualized as a hypoechoic cortical breach, was identified. The purpose of this maneuver was to apply shear stress across the fracture site to challenge its integrity. In real-time, this stress resulted in a visible widening of the hypoechoic fracture gap, providing unequivocal evidence of micromotion and confirming the diagnosis of a mechanically unstable fracture (Supplementary Video S1).
Figure 3
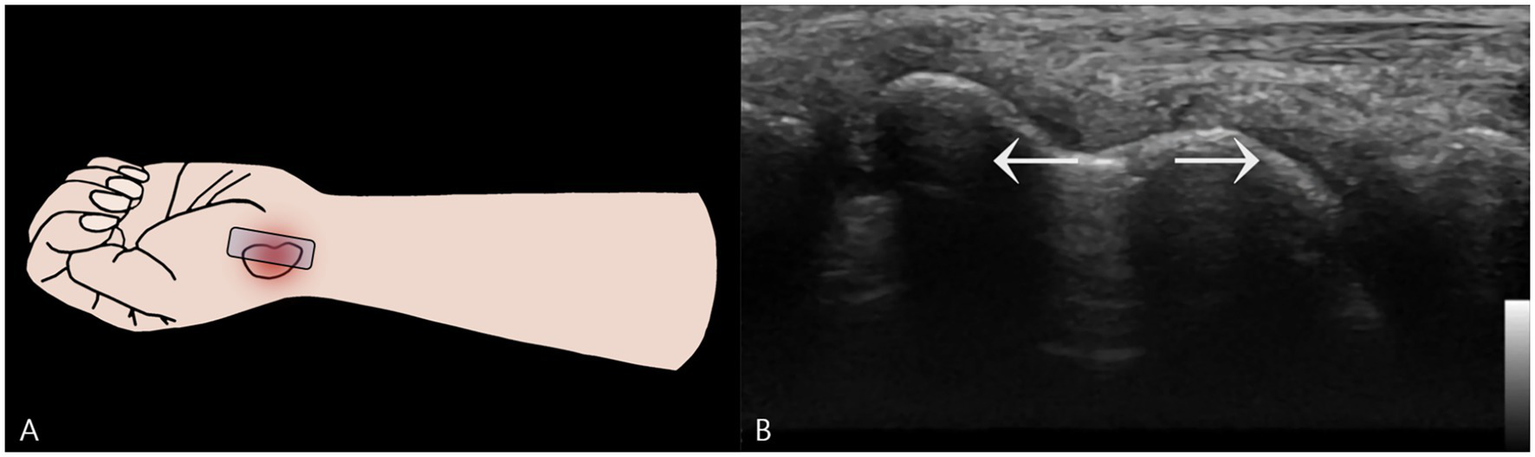
Dynamic Stress Examination of the Scaphoid Waist Fracture. (A) Schematic illustration showing the placement of the ultrasound probe longitudinally over the scaphoid waist. Focal pressure is applied directly onto the distal fragment using a “heel-toe” maneuver to assess for instability. (B) A two-dimensional ultrasound image captured during the application of dynamic stress. This image provides definitive evidence of mechanical instability by demonstrating a visible widening of the hypoechoic fracture gap.
Based on this definitive finding of instability, the management was immediately escalated. The initial splint was replaced with a rigid thumb spica short arm splint. This change was critical, as immobilizing the thumb is necessary to neutralize the forces acting on the scaphoid during thumb motion, thereby providing the robust stabilization required for an unstable waist fracture.
2.2 Follow-up and long-term outcome
Long-term follow-up was complicated by patient-specific circumstances that precluded surgical intervention, the standard recommendation for many unstable scaphoid fractures. Consequently, the patient was managed with prolonged conservative therapy. Radiographs obtained more than one-year post-injury remained inconclusive, showing no substantial interval changes and failing to provide clear evidence of healing.
This created a diagnostic dilemma, as the radiographic findings alone could have been misinterpreted as a persistent non-union. In contrast, the follow-up ultrasound examination provided a definitive assessment. It revealed early callus formation and restoration of cortical continuity across the scaphoid waist. Most critically, a repeat dynamic stress examination was performed, which revealed no widening of the former fracture site under stress, confirming that mechanical stability had been achieved (Figure 4).
Figure 4
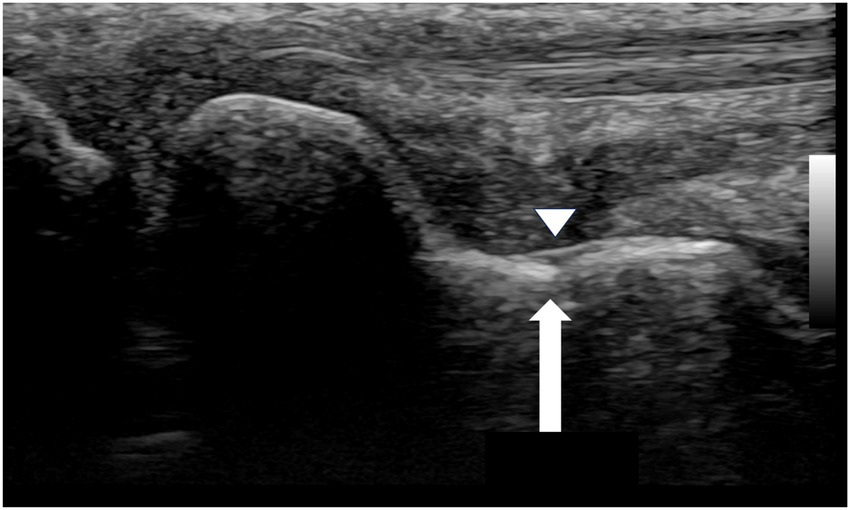
Follow-up ultrasound image of the waist region of the scaphoid (September 1, 2020). The white arrow indicates restoration of cortical continuity and formation of a bony bridge over the fracture site. The arrowhead demonstrates the bony callus formation.
This starkly contrasted with the ambiguous radiographs, demonstrating that the fracture had healed into a stable fibrous union with sufficient integrity to prevent micromotion, thereby allowing for a confident conclusion to the treatment plan.
3 Discussion
3.1 Diagnostic and functional insights from dynamic ultrasound
The accurate and timely diagnosis of scaphoid fractures is paramount to preventing long-term complications such as non-union and SNAC wrist (26). While static high-resolution ultrasound has been extensively validated for detecting cortical breaches (sensitivities and specificities exceeding 90%) (21–23, 27), the unique contribution of this case lies in demonstrating real-time, functional assessment of mechanical instability—a capability under-reported in the literature. We illustrate how this dynamic finding immediately altered the management algorithm in clinical practice, demonstrating value beyond anatomic characterization.
The dynamic maneuver described—applying focal pressure onto the distal fragment with “heel-toe” rocking motion—is a biomechanical stress test performed under direct visualization. Real-time gapping at the fracture site is a direct sonographic correlate of mechanical instability. This finding moves diagnosis from a purely anatomical question (“Is there a fracture?”) to a functional and prognostic one (“Is the fracture stable?”)—the single most important factor guiding treatment. Stable, non-displaced fractures can often be managed successfully with cast immobilization alone (union rates exceeding 90%), whereas unstable fractures have markedly higher non-union risk (approaching 50% or more when treated non-operatively) (28–30). The diagnostic accuracy of our approach was strengthened by multiple concordant findings: precise topographic concordance between maximal clinical tenderness and sonographic lesion, composite imaging signs (cortical breach and hematoma), dynamic gap widening confirming mechanical instability, direct management escalation, and follow-up dynamic testing showing loss of gapping confirming restored stability. This multimodal approach effectively ruled out false positives and anchored diagnosis in both anatomic and functional evidence. The ability to immediately risk-stratify these injuries at the point of care identified this patient for escalated management, with the sonographic diagnosis of instability justifying immediate application of rigid thumb spica splint rather than simple ulnar gutter splint.
Dynamic ultrasound provides real-time, functional information at the point of care, fundamentally distinguishing it from static imaging (CT, MRI, static US) (Table 1). While CT and MRI offer superior detailed anatomical assessment (8, 16), they are static snapshots from which instability must be inferred indirectly. Dynamic ultrasound directly demonstrates instability, transforming diagnosis into a functional biomechanical evaluation that directly answers the clinician’s most pressing question. This capability aligns with value-based care principles: rapid, low-cost, repeatable testing yielding high-impact clinical information. It prevents the common cycle of negative radiographs, uncertain immobilization, patient anxiety, and delayed diagnosis. Long-term follow-up in this case revealed another critical advantage: radiographs obtained over 1 year post-injury remained inconclusive, potentially suggesting non-union warranting surgery, while follow-up ultrasound revealed partial cortical restoration, callus formation, and, most importantly, absence of gapping on dynamic stress testing, confirming stable fibrous union. This highlights dynamic ultrasound’s unique ability to differentiate between symptomatic unstable non-union requiring surgery and asymptomatic stable fibrous union manageable conservatively (31). For fractures initially diagnosed by ultrasound, sonographic stability appears a more clinically relevant healing endpoint than complete radiographic consolidation.
Table 1
| Modality | What it shows best | Typical strengths | Typical limitations | Role in workflow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiographs (4-view) | Gross fracture lines, displacement | Widely available, low cost | Early false-negatives common | First-line screen |
| CT | Cortical detail, displacement, morphology | Precise anatomic quantification; surgical planning | Radiation; cost | Structural clarification |
| MRI | Marrow edema, occult fractures | Highest sensitivity in early phase | Access; cost | Confirmatory when high suspicion persists |
| Static US | Cortical breach; superficial hematoma | Point-of-care; no radiation; high resolution | Operator-dependent; primarily structural | Rapid confirmation in clinic/ED |
| Dynamic US (this report) | Real-time mechanical instability (gap widening) | Functional assessment that directly informs management | Standardization & thresholds needed; operator-dependent | Decision pivot in POCUS-first pathway |
Diagnostic approaches for suspected scaphoid fracture with negative initial radiographs—strengths and typical use.
Successful application requires several considerations. The technique is highly operator-dependent, requiring proficiency in wrist sonography and thorough understanding of scaphoid anatomy. High-frequency linear transducers (≥12 MHz) are essential for adequate spatial resolution (19, 20). The “heel-toe” pressure method, designed to create shear stress across the scaphoid waist, must be controlled to be diagnostic without causing undue pain or iatrogenic displacement. Standardization of dynamic ultrasound protocols represents a critical future development, with research focusing on defining optimal stress maneuvers for different fracture locations and establishing quantitative criteria for instability (e.g., millimetric thresholds for gap widening). This case report has notable strengths, including clear step-by-step illustration of dynamic technique and direct demonstration of its impact on patient management, with long-term follow-up providing insight into natural history of unstable fractures managed conservatively. However, conclusions are tempered by inherent single-case limitations and cannot be generalized. The technique’s operator-dependence and potential for iatrogenic injury with excessive stress require cautious, controlled technique application. Future prospective, multicenter studies are urgently needed to directly compare diagnostic accuracy of dynamic ultrasound against CT and MRI for assessing fracture stability (4, 15), establish inter-rater reliability among operators of varying experience, quantify millimetric thresholds for instability, and conduct formal cost-effectiveness analyses. Based on current evidence, we propose a modified diagnostic algorithm for suspected scaphoid fractures with negative initial radiographs: (1) Detailed clinical examination including anatomical snuffbox palpation and axial thumb compression; (2) If high clinical suspicion, proceed directly to point-of-care ultrasound—first static assessment to confirm cortical discontinuity; (3) If static ultrasound negative, scaphoid fracture is highly unlikely and immobilization can be avoided; (4) If static ultrasound positive, immediately perform dynamic stress testing to assess stability; (5) If dynamic ultrasound reveals instability, urgent orthopedic consultation and consideration of early surgical fixation is warranted; (6) CT or MRI is reserved for anatomic detailing in surgical planning or when ultrasound findings are equivocal. Implementation of this streamlined Clinical Exam → POCUS (Static + Dynamic) pathway could significantly reduce costs and patient morbidity associated with traditional “wait-and-see” approaches. For patients with wrist sprains but no fracture, negative ultrasound could immediately and confidently rule out scaphoid injury, preventing weeks of unnecessary cast immobilization and patient anxiety. For patients with confirmed unstable fractures, it ensures immediate, appropriate treatment, mitigating devastating long-term complications such as AVN and SNAC wrist.
4 Conclusion
This case report describes a patient with a radiographically occult scaphoid fracture in whom dynamic musculoskeletal ultrasound was instrumental for both initial diagnosis and the crucial assessment of mechanical stability. The ability to confirm instability in real-time at the point of care allowed for an immediate and appropriate escalation of conservative management. This case adds to the growing body of literature supporting the use of ultrasound in the evaluation of acute wrist trauma and specifically highlights the unique, value-added information provided by a dynamic examination. We believe that for experienced operators, dynamic MSK-US should be considered a primary imaging tool in the algorithm for suspected scaphoid fractures, offering a rapid, accurate, and radiation-free pathway to definitive diagnosis and optimized patient care.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because This was a retrospective study, using existing data and not including personally identifiable information. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
Y-HY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Supervision. JH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft. KL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JC: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. TS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. AS: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CK: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. HL: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. HK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DC-JS Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to declare that both Yonghyun Yoon and King Hei Stanley Lam are the co-first authors for their equal contribution to this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1711119/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Video S1Dynamic ultrasound examination of the scaphoid waist fracture.
References
1.
Hove LM . Epidemiology of scaphoid fractures in Bergen, Norway. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. (1999) 33:423–6. doi: 10.1080/02844319950159145
2.
Duckworth AD Buijze GA Moran M Gray A Court-Brown CM Ring D et al . Predictors of fracture following suspected injury to the scaphoid. J Bone Joint Surg Br. (2012) 94-B:961–8. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.94B7.28704
3.
Garala K Taub NA Dias JJ . The epidemiology of fractures of the scaphoid: impact of age, gender, deprivation and seasonality. Bone Joint J. (2016) 98-b:654–9. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.98B5.36938
4.
Clementson M Bjorkman A Thomsen NOB . Acute scaphoid fractures: guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. EFORT Open Rev. (2020) 5:96–103. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190025
5.
Amarasooriya M Al-Dirini R Bryant K Bain GI . Scaphoid kinematics in scapholunate instability: a dynamic CT study. Skeletal Radiol. (2023) 52:1557–66. doi: 10.1007/s00256-023-04323-6
6.
Wolfe SW Crisco JJ Orr CM Marzke MW . The dart-throwing motion of the wrist: is it unique to humans?J Hand Surg Am. (2006) 31:1429–37. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2006.08.010
7.
Cooney WP Dobyns JH Linscheid RL . Fractures of the scaphoid: a rational approach to management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (1980) 149:90–7.
8.
Mallee W Doornberg JN Ring D van Dijk CN Maas M Goslings JC . Comparison of CT and MRI for diagnosis of suspected scaphoid fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2011) 93:20–8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.I.01523
9.
Furunes H Vandvik PO . Cast immobilisation for suspected scaphoid fractures. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. (2009) 129:177–9. doi: 10.4045/tidsskr.09.34096
10.
Gelberman RH Menon J . The vascularity of the scaphoid bone. J Hand Surg Am. (1980) 5:508–13. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(80)80087-6
11.
Steinmann SP Adams JE . Scaphoid fractures and nonunions: diagnosis and treatment. J Orthop Sci. (2006) 11:424–31. doi: 10.1007/s00776-006-1025-x
12.
Linscheid RL Dobyns JH Beabout JW Bryan RS . Traumatic instability of the wrist: diagnosis, classification, and pathomechanics. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2002) 84:142. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200201000-00020
13.
Vender MI Watson HK Wiener BD Black DM . Degenerative change in symptomatic scaphoid nonunion. J Hand Surg Am. (1987) 12:514–9. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(87)80198-3
14.
Watson HK Ballet FL . The SLAC wrist: scapholunate advanced collapse pattern of degenerative arthritis. J Hand Surg Am. (1984) 9:358–65. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(84)80223-3
15.
Torabi M Lenchik L Beaman FD Wessell DE Bussell JK Cassidy RC et al . ACR appropriateness criteria® acute hand and wrist trauma. J Am Coll Radiol. (2019) 16:S7–S17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2019.02.029
16.
Adey L Souer JS Lozano-Calderon S Palmer W Lee S-G Ring D . Computed tomography of suspected scaphoid fractures. J Hand Surg Am. (2007) 32:61–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2006.10.009
17.
Fowler C Sullivan B Williams LA McCarthy G Savage R Palmer A . A comparison of bone scintigraphy and MRI in the early diagnosis of the occult scaphoid waist fracture. Skeletal Radiol. (1998) 27:683–7. doi: 10.1007/s002560050459
18.
Brooks S Cicuttini FM Lim S Taylor D Stuckey SL Wluka AE . Cost effectiveness of adding magnetic resonance imaging to the usual management of suspected scaphoid fractures. Br J Sports Med. (2005) 39:75–9. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2003.007435
19.
Herneth AM Siegmeth A Bader TR Ba-Ssalamah A Lechner G Metz VM et al . Scaphoid fractures: evaluation with high-spatial-resolution US initial results. Radiology. (2001) 220:231–5. doi: 10.1148/radiology.220.1.r01jl15231
20.
Kwee RM Kwee TC . Ultrasound for diagnosing radiographically occult scaphoid fracture. Skeletal Radiol. (2018) 47:1205–12. doi: 10.1007/s00256-018-2931-7
21.
Jain R Jain N Sheikh T Yadav C . Early scaphoid fractures are better diagnosed with ultrasonography than X-rays: a prospective study over 114 patients. Chin J Traumatol. (2018) 21:206–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2017.09.004
22.
Herrera Ortiz AF Guevara SZ Ramírez SM Cubillos Rojas J Giraldo Malo R Fernández Beaujon L et al . What is the role of ultrasonography in the early diagnosis of scaphoid fractures?Eur J Radiol Open. (2021) 8:100358. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2021.100358
23.
Fusetti C Poletti PA Pradel PH Garavaglia G Platon A Della Santa DR et al . Diagnosis of occult scaphoid fracture with high-spatial-resolution sonography: a prospective blind study. J Trauma. (2005) 59:677–81. doi: 10.1097/01.ta.0000177467.79282.40
24.
Sinha NK Bhardwaj A Rao AS . Dynamic palpation for diagnosing clinically covert scaphoid fractures. Cureus. (2024) 16:e74537. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74537
25.
Taleisnik J . The ligaments of the wrist. J Hand Surg Am. (1976) 1:110–8. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(76)80004-4
26.
Kawamura K Chung KC . Treatment of scaphoid fractures and nonunions. J Hand Surg Am. (2008) 33:988–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.04.026
27.
Hauger O Bonnefoy O Moinard M Bersani D Diard F . Occult fractures of the waist of the scaphoid: early diagnosis by high-spatial-resolution sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2002) 178:1239–45. doi: 10.2214/ajr.178.5.1781239
28.
Dias JJ Wildin CJ Bhowal B Thompson JR . Should acute scaphoid fractures be fixed? A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2005) 87:2160–8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.D.02305
29.
Bond CD Shin AY McBride MT Dao KD . Percutaneous screw fixation or cast immobilization for nondisplaced scaphoid fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2001) 83:483–8. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200104000-00001
30.
McQueen MM Gelbke MK Wakefield A Will EM Gaebler C . Percutaneous screw fixation versus conservative treatment for fractures of the waist of the scaphoid: a prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. (2008) 90:66–71. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.90B1.19767
31.
Schuind F Moungondo F El Kazzi W . Prognostic factors in the treatment of carpal scaphoid non-unions. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. (2017) 27:3–9. doi: 10.1007/s00590-016-1886-4
Summary
Keywords
scaphoid fracture, occult fracture, dynamic ultrasonography, wrist injury, point-of-care ultrasound, fracture stability
Citation
Yoon Y-H, Hwang J, Lam KHS, De Castro JC, Suryadi T, Suhaimi A, Kang CW, Lee H, Kim H, Kim S and Su DC-J (2025) Unstable occult scaphoid fracture diagnosed by dynamic point-of-care ultrasound: a case report and review. Front. Med. 12:1711119. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1711119
Received
23 September 2025
Accepted
28 October 2025
Published
05 November 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Ganesh Yadagiri, National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Kolkata, India
Reviewed by
Kakarla Ramakrishna, KL University, India
Lohitha Gujjari, The Ohio State University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Yoon, Hwang, Lam, De Castro, Suryadi, Suhaimi, Kang, Lee, Kim, Kim and Su.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yong-Hyun Yoon, mgyyh00@gmail.com; King Hei Stanley Lam, drlamkh@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.