Abstract
While the overall ATP level in neurons remains relatively stable, local fluctuations in synaptic compartments - driven by synaptic potentials - necessitate rapid ATP adjustments. The energy supply for synaptic activity in neurons must be under precise homeostatic control: increased ATP consumption in active synapses requires continuous replenishment, whereas in periods of inactivity, excess ATP production may occur. Overproduction of ATP in thousands of individual synapses is metabolically wasteful, while underproduction threatens to disrupt molecular cascades associated with ongoing synaptic bursts, ion homeostasis, protein synthesis, and neural plasticity. Fine-tuned regulation of ATP synthesis must therefore be controlled locally and dynamically, ensuring metabolic efficiency while preventing disruptions in synaptic bursts, ion homeostasis, and neuronal plasticity. This review summarizes the intricate molecular mechanisms through which mitochondria (MT) interact with their postsynaptic environment to maintain energy balance. We examined the fundamental features of mitochondria in conjunction with their unique properties and roles in nervous tissue, highlighting their ability to dynamically adjust energy production based on local demand rather than maintaining a strictly uniform ATP output. The regulation of ATP synthesis may involve mitochondrial transport, fusion, and fission, as well as changes in mitochondrial shape and molecular structure. This review describes the activity of ATP synthase, the mitochondrial calcium uniporter and other signaling cascades in the context of their uneven distribution within mitochondria. Furthermore, we discuss rapid calcium influxes from postsynaptic membranes and the endoplasmic reticulum into mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs), their buffering mechanisms, and the generation of dynamic responses. We focus on the role of calcium ion (Ca2+) as a precise regulator of ATP production, particularly in mitochondria located near synaptic regions, where it ensures an adequate energy supply for local activity. Overall, we propose potential pathways of interaction between mitochondria and their postsynaptic microdomains. Given that some of the mechanisms discussed remain hypothetical, we emphasize the urgent need for experimental validation to refine understanding of mitochondrial function in synaptic transmission.
1 Introduction
Energy is a fundamental necessity for all cells, enabling their functional activity, growth, and survival. Neurons, however, differ significantly from other cell types due to their unique characteristics: they do not undergo cell division and possess exceptionally long processes—axons and dendrites—that extend across considerable distances to facilitate complex communication networks. This structural specialization demands substantial energy, particularly at synaptic sites where neurotransmission occurs. The primary source of cellular energy is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is predominantly synthesized by mitochondria (MT)—symbiotic organelles present in most eukaryotic cells. MT perform multiple functions, some of which remain incompletely understood. Their energy-producing role is closely tied to ATP synthases, which facilitate ATP generation by harnessing proton gradients across mitochondrial membranes. However, mitochondrial functions are dynamic and depend on their structural organization, which undergoes continuous remodeling in response to physiological changes. These alterations affect mitochondrial transport, docking, fusion, and fission (McCarron et al., 2013; Trigo et al., 2022). Notably, elongated MT enhance oxidative capabilities, whereas spherical or ovoid forms are often associated with increased calcium (Ca2+) levels in cytosol, adaptive mechanisms, or pathology (Glancy et al., 2020).
Beyond mitochondrial ATP synthesis, additional mechanisms contribute to maintaining energy homeostasis. Membrane-associated ATP synthases can support localized ATP production, ensuring energy availability in specific subcellular compartments (Xing et al., 2011; Chang et al., 2023). Astrocytes also play a crucial role in metabolic support through the astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle, a mechanism that links astrocytic glycolysis to neuronal oxidative metabolism (Chih and Roberts, 2003; Roumes et al., 2023). Particularly, such shuttle mechanism may appear during memory formation (Drulis-Fajdasz et al., 2018) and some forms of synaptic plasticity (Marty-Lombardi et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2025).
Cytosolic ([Ca2+]c) and mitochondrial ([Ca2+]m) calcium signaling play a critical role in regulating ATP synthesis and cellular energy balance. The voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) serves as the primary gateway for Ca2+ entry into the MT from the cytosol (Rajendran et al., 2023). Once inside, Ca2+ transport is facilitated by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex, which governs mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and influences enzymatic activity within the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA, also known as the Krebs cycle), thereby enhancing ATP production (De Mario et al., 2023). While this mechanism is particularly vital in neurons, it also operates in highly active cells such as cardiac myocytes and endocrine cells, where precise control of energy metabolism is essential for physiological function. Additionally, ATP synthase (F-ATPase), responsible for ATP production, undergoes conformational changes driven by the proton gradient, with its rotor-stator architecture optimizing energy conversion. Tertiary structures of MCU, VDAC and ATP synthase have been resolved and successfully used for structure-function link (see for review: Najbauer et al., 2021; Zhuo et al., 2021; Vlasov et al., 2022).
Ca2+ directly modulates ATP synthase activity by influencing its conformational states, potentially enhancing enzyme efficiency and mitochondrial energy output. However, disruptions in [Ca2+]m handling are implicated in various pathological conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, cardiovascular disorders, and metabolic syndromes (see for review: Walters and Usachev, 2023; Balderas et al., 2024; Zong et al., 2024; Borbolis et al., 2025; Sun et al., 2025). Dysregulated Ca2+ uptake through the VDAC-MCU complex can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, excessive oxidative stress, and even apoptosis, highlighting the need for maintaining [Ca2+]m homeostasis for overall cellular health (Giorgio et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2025).
In neurons, Ca2+ signaling mechanisms and alternative energy supply pathways are particularly crucial in the context of postsynaptic mitochondria in neurons, where fluctuations in energy demands closely interact with neuronal activity. Ca2+ dynamics regulate mitochondrial function by influencing ATP synthesis and metabolic coupling, ensuring that synaptic compartments maintain adequate energy levels for neurotransmission and plasticity (Groten and MacVicar, 2022). Additionally, Ca2+ plays a key role in shaping mitochondrial distribution, morphology, ion balance, and functional modulation under both normal and pathological conditions. This review will explore these aspects in detail, highlighting their significance in cellular health and disease.
2 Morphology and ultrastructure of mitochondria
2.1 Mitochondrial morphologies in different cell types
MT exhibit diverse morphologies and mobility, ranging from spherical to elongated structures, with their distribution and movement regulated according to cell type and metabolic requirements (Figure 1; Table 1). MT size ranges from 0.5 to more than 2 μm, in cross section (Frey and Mannella, 2000; Perkins and Frey, 2000). Their morphology and distribution vary significantly depending on cellular function. Thus, in fibroblasts, mitochondria are approximately the same size and dispersed evenly, supporting anabolic processes (Figure 1A; Brantová et al., 2006), whereas in skeletal muscle cells, they are categorized into two main populations: intermyofibrillar (IMF) mitochondria, which are located between myofibrils and primarily support oxidative metabolism, and subsarcolemmal (SSM) mitochondria, which cluster beneath the plasma membrane and are more involved in localized energy supply (Figure 1B; Wahwah et al., 2020; Pekkurnaz and Wang, 2022). The SSM mitochondria tend to align in chain-like structures, optimizing ATP distribution for membrane-associated functions and signaling processes (Holmuhamedov et al., 2012). In brain tissue, the morphological differences between MT in neurons and glial cells become increasingly complex depending on the cellular compartment. Thus, in astrocytes, MT are relatively abundant within the soma, where they display diverse orientations, supporting the cell’s metabolic and regulatory functions. As astrocytic processes extend and thin, mitochondrial morphology transitions from a more branched and disorganized network in the soma to elongated, parallel structures within finer outgrowths, particularly in perivascular endfeet, where they often appear more compact and fragmented, likely reflecting localized energy demands and dynamic Ca2+ signaling (Figure 1C; Popov et al., 2023; Salazar et al., 2024). In neurons, MT exhibit the highest degree of compartmental specialization, adapting their morphology and dynamics to meet distinct metabolic requirements: in the soma, mitochondria form elongated, interconnected networks with diverse orientations, while in dendrites, mitochondria are more linear and tubular, with some exceeding 1 μm3 in volume, whereas shorter forms are occasionally observed within dendritic spines. In axons, mitochondria are highly mobile, typically punctate, and rarely surpass 1 μm3, ensuring efficient energy distribution along thin but exceptionally long axonal projections (Figure 1D; Faitg et al., 2021; Pekkurnaz and Wang, 2022). The heterogeneity in mitochondrial volume reflects the overall complexity of the cell, with highly differentiated cells requiring precise spatial and morphological adaptations.
FIGURE 1

Schematic illustration of mitochondrial morphological variations across cell types and subcellular compartments. (A) Mitochondria (MT) of fibroblasts have elongated form with less density of cristae arrangement. (B) MT of skeletal muscle fibers have small and short sizes with high density of cristae arrangement. The MT categorized into two populations: intermyofibrillar (IMF) mitochondria located between myofibrils and subsarcolemmal (SSM) mitochondria clustered beneath the plasma membrane. (C) MT of astrocytes have diverse morphological properties; MT of astrocytic somata have elongated, twisted form with less density of cristae arrangement, whereas MT of astrocytic endfeet have small, elongated thin structure under endfeet base. (D) MT of neurons have great diversity of size and shape; MT of the axon and the axon bulb have small size and short and globular form with high density of cristae arrangement. MT of neuron’s soma have elongated, twisted form with less density of cristae arrangement. MT of dendrites and within spine cluster have elongated form with less density of cristae arrangement. Scale bar: 1 μm. References to electron microscope images of MT in fibroblasts (Brantová et al., 2006), skeletal muscle cells (Wahwah et al., 2020), astrocytes (Pysh and Khan, 1972; Bergami and Motori, 2020), pyramidal neurons (Faitg et al., 2021).
TABLE 1
Comparison of some mitochondrial characteristics in different cell types.
2.2 Mitochondrial ultrastructure
At the ultrastructural level, MT are surrounded by two phospholipid membranes with massive protein insertions (Figure 2). OMM is abundantly equipped with integral beta-barrel channels or porins to transport hydrophilic molecules. These porins include the VDAC, which is the most abundant protein on OMM and is involved in the transport of ATP and ADP anions, Ca2+, and other metabolites, as well as playing a key role as a switch in mitochondrial functions (Rostovtseva and Bezrukov, 2008; Noskov et al., 2013; Rajendran et al., 2023). There is an intermembrane space (∼ 8 nm) between OMM and the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) (Neupert, 1997). The ion concentration within this space is similar to that of the cytosol. In contrast, the IMM provides a high level of impermeability, which is crucial for maintaining a stable proton gradient across the membrane. The impermeability of the IMM is primarily provided by the phospholipids cardiolipin and phosphatidylethanolamine, which have double hydrophobic “tails” of fatty acids (Ikon and Ryan, 2017). The proton gradient is maintained by the energy derived from aerobic respiration, which is a system of redox reactions in transmembrane protein complexes called electron-transport chain (ETC). Additionally, there are transmembrane proteins in the IMM that support metabolic connections with the space within IMM, called the matrix, including a critically important protein that mediates the entry of Ca2+ into the matrix—MCU. The IMM has a highly folded structure in the form of creases called cristae to increase the surface area. The ionic and molecular composition of the narrow space between the cristae may differ compared to the rest of the matrix.
FIGURE 2
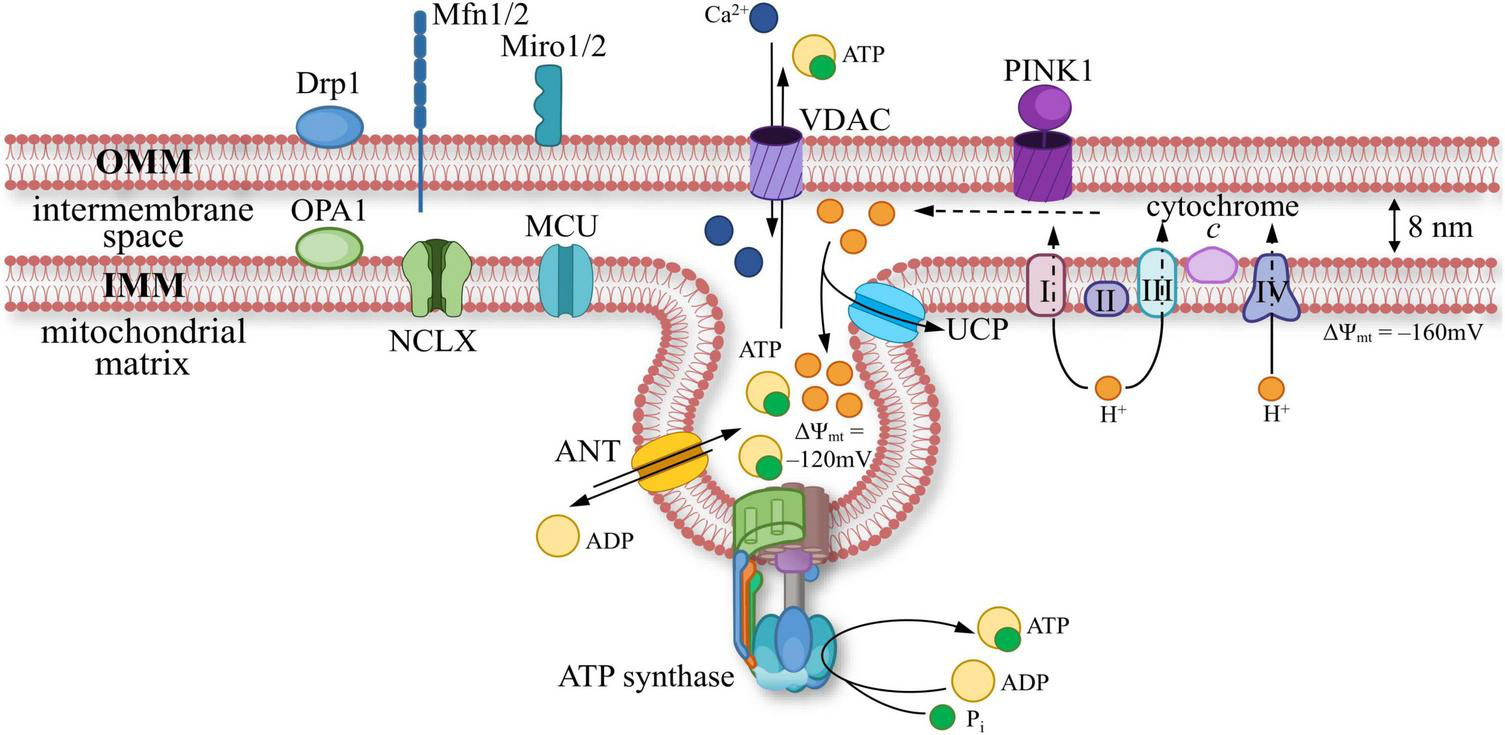
A scheme of mitochondrial membrane ultrastructure: components of the outer (OMM) and inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). Proteins present in OMM: dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1, responsible for mitochondrial fission); dynamin-like GTPase mitofusins 1/2 (Mfn1/2, facilitate physical connections between OMM and other membranes); mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1/2 (Miro1/2, acts as a calcium (Ca2+) sensor; PINK1 (PTEN-induced kinase 1, initiates mitophagy); voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC, responsible for the transport of ions and nucleotides). IMM is equipped with proteins such as: dynamin-like GTPase optic atrophy 1 (OPA1, facilitates mitochondrial fusion); electron transport chain (ETC) components, includes complexes I, II, III, IV, and cytochrome c; ATP synthase (catalyzes the synthesis of ATP), adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT, enables ADP/ATP exchange); mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU, facilitates Ca2+ transport); uncoupling protein (UCP, capable of dissipating the proton gradient); Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCLX).
2.3 Structure and location of mitochondrial ATP synthase
ATP molecules are synthesized in the mitochondrial matrix from ADP and inorganic phosphate by using electrochemical energy produced by the proton gradient (Neupane et al., 2019; Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020b). The process of ATP synthesis is generated by a specific enzyme, also anchored in the IMM, known as ATP synthase. In a broad sense, ATP synthase is related to the superfamily of rotary ATPases. Rotary ATPases can catalyze ATP hydrolysis to perform useful work, such as ion transfer across cellular membranes. Conversely, they can synthesize ATP through directed ion flow, more specifically via proton leakage along the concentration gradient, while protons re-enter the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase (Watson and McStay, 2020). Thus, ATP synthase can operate in both directions—synthesizing ATP or hydrolyzing it—depending on the current local needs of the cell (Figure 3). Eukaryotic ATPases are divided into two types: F-ATPase and V-ATPase (Jonckheere et al., 2012). F-ATPase has the ability to synthesize and hydrolyze ATP (Jonckheere et al., 2012; Pinke et al., 2020). Nevertheless, in MT, F-ATPase primarily functions as an ATP synthase. In contrast, V-ATPase exclusively hydrolyzes ATP to obtain energy for proton pumping across membranes. V-ATPase is present not only in the IMM, but also in various cellular membranes, where it is essential for the acidification of endosomes, lysosomes, and the trans-Golgi network (Abbas et al., 2020; Zubareva et al., 2020).
FIGURE 3

A scheme of mitochondrial ATP synthase composition during ATP synthesis (A) and hydrolysis. (B) ATP synthase converts the energy of the proton electrochemical transmembrane gradient into ATP through mechanical rotation. F1 complex is a hexamer composed of α- and β-subunits, connected to the peripheral stalk (PS), which includes b-, d-,and h (F6 in mammals)-subunits, and the central stalk (CS), containing γ-, ε-, and δ-subunits. F0 is a transmembrane complex composed of the c-ring and the a-subunit. OSCP (oligomycin-sensitivity conferring protein) — connects F1 with PS, provides structural stability and coupling the rotary action of the F0 domain to ATP synthesis in F1. (A) The proton electrochemical gradient (H+) drives the rotation of the c-ring within the F0 complex. This motion initiates conformational changes in the β-subunits of the F1 complex, leading to the sequential binding of ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) and ATP release. (B) In conditions of low membrane potential, ATP is utilized to drive the reverse rotation of the c-ring within the F0 complex. This motion initiates conformational changes in the β-subunits of the F1 complex, leading to sequential ATP cleavage into ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi), leading to proton translocation across the membrane.
The composition of F-ATPase is presented in Figures 3A,B. It consists of two components: the transmembrane proton pore F0 and the inner component F1. The hexamer structure of F1 consists of α- and β-subunits, which alternate with each other and surround the γ-subunit. The central stalk (CS) and the peripheral stalk (PS) connect through the δ and ε subunits and oligomycin-sensitivity conferring protein (OSCP), b, d, and h (F6 in mammals) subunits (Walker and Dickson, 2006; Gerle, 2020). Proton transfer into the matrix is achieved through the rotation of the c-ring composed of several c-subunits and the a-subunit, which contains a proton channel, all coupled with the rotation of the γ-subunit. The CS passes through the center of the F1 hexamer, connecting the transmembrane part of F0 with the catalytic part of F1. The PS acts as a stator, preventing the co-rotation of the F1 domain (Giorgio et al., 2017; Gerle, 2020). The height of the transmembrane domain F0 reaches ∼6.4 nm and the diameter of ∼10–12 nm (Hatefi, 1993). The F1 reaches a length of ∼11–12 nm and a diameter of ∼7.4 nm, the CS has length of approximately ∼4.3–4.5 nm (Hatefi, 1993; Nirody et al., 2020; Nesterov and Yaguzhinsky, 2023). The F1 domain plunges into mitochondrial matrix due to its hydrophilic properties. Specifically, this domain is responsible for the synthesis and/or hydrolysis of ATP (Walker and Dickson, 2006; Nirody et al., 2020; Frasch et al., 2022).
As discussed above, although the eukaryotic F-ATPase (a member of the ATPase family) is typically associated with ATP synthesis, it can work in opposite directions: using the proton gradient for synthesis (Figure 3A) or hydrolyzing ATP to create a proton gradient (Figure 3B).
ATP production is achieved by the transmembrane electrochemical proton gradient generated by the ETC, resulting in the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨmt). The threshold level of ΔΨmt in IMM required to initiate the rotation of ATP synthase’s rotor is –65 mV in mammals (Wescott et al., 2019). The value of ΔΨmt can vary up to –170 mV, with the rate of ATP synthesis increasing nonlinearly with increasing potential (Wescott et al., 2019; Kaim and Dimroth, 1999). Effective ATP generation occurs when ΔΨmt is around –100 to –120 mV (Lee et al., 2002). In addition to the transmembrane electrochemical proton gradient (ΔΨmt), the reduced form of NADH (TCA product) is required for ATP generation (Meléndez-Hevia et al., 1996; Sonenshein, 2001; Bonora et al., 2012). Some of the TCA dehydrogenases are Ca2+-dependent enzymes. Therefore, activation of these dehydrogenases requires Ca2+ influx into mitochondria and the presence of a Ca2+ buffer (to be discussed later) (Bonora et al., 2012; Markovinovic et al., 2022).
The maintenance of ΔΨmt, ETC, and ATP synthase function is supported by several key messengers and factors that are universal in eukaryotic cells. Among these are the ATPase Inhibitory Factor 1 (IF1) (García-Bermúdez and Cuezva, 2016; Glancy and Balaban, 2012; Gore et al., 2022) and Ca2+ (Glancy and Balaban, 2012; Wescott et al., 2019), which regulate mitochondrial bioenergetics, and nitric oxide (NO) produced by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) within the IMM (Finocchietto et al., 2009; Kohlhaas et al., 2017; Godoy et al., 2021). In neuronal cells in particular Ca2+ can enter the mitochondria from the extracellular space via various pathways, such as activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs), a subtype of glutamate receptors (Garthwaite, 2008; Negri et al., 2021), highlighting the specialized role of these receptors in regulating mitochondrial function in the postsynaptic region, opening of voltage-gated calcium channels, engaging store-operated calcium currents, and activating other pathways (see for review: Nanou and Catterall, 2018; Chin and Kaeser, 2024). We will discuss this issue in more detail in section 6.
3 Mitochondria in central neurons
3.1 Features of neuronal mitochondria
Despite the similarities in physiology and functional principles of mitochondria across all tissue types, there are unique characteristics and specific patterns of mitochondrial structure, dynamics, form and localization that are tailored to the energy demands and functions of specific cell types. In the central nervous system tissue, there are several cell types, including neurons and glial cells such as astrocytes, microglia, and oligodendrocytes (Garman, 2011; Herculano-Houzel, 2014; Liu et al., 2023). In comparison with glial cells (Kann and Kovács, 2007; Jackson and Robinson, 2018), cardiomyocytes and skeletal muscle fibers (Kuznetsov et al., 2009), neuronal MT are more motile in both ratio (for instance, the number of mobile MTs in neurons is approximately twice as high as in glia (Jackson and Robinson, 2018) and velocity of the motion: ∼0.3 μm/s in neurons and ∼0.1 μm/s in astrocytes (Stephen et al., 2015; Table 1). Moreover, the speed of mitochondrial movement in neurons and astrocytes varies depending on the direction, either anterograde (from the soma) or retrograde (toward the soma), but the speed of neuronal MT is around three times greater than astrocytes’ one (Jackson et al., 2014; Table 1). Furthermore, in comparison with astrocytes, dysfunctional mitochondria elimination is more developed in neurons (Sukhorukov et al., 2021), which may impact the functionality of these cells (see in the next chapter). MT features within different types of neurons also possess some differences. As an example, MT of fast-spiking [∼ 30–100 Hz (Kann et al., 2014; Kann, 2016)] inhibitory interneurons are distinct from MT of cortical neurons. The unique physiological properties of interneuronal MT require the enhancement of ETC in the IMM, enriched in a number of proteins such as cytochrome c oxidase and the ETC complex I (Whittaker et al., 2011; Kann et al., 2014; Kann, 2016) which ensure the dynamics of ATP synthase and cell survival. As for MT velocity in the neurons of different origins, it may be affected by multiple factors, for example, by activity, stages of cell development (Silva et al., 2021) or by activating modulatory pathways (Pekkurnaz et al., 2014; Jenkins et al., 2024), for example by the AKT–glycogen synthase kinase 3β pathway in serotoninergic and dopaminergic neurons (Pekkurnaz and Wang, 2022).
Little is known about ΔΨmt in neurons, which differ in morphology, origin, and the main transmitter released. One study showed that dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra keep relatively low ΔΨmt, ∼ –94 mV (Huang et al., 2004). Higher values were found in several types of cultured neurons: –100 mV in hippocampal culture (Korkotian et al., 2019), –139 mV in cortical neurons (Gerencser et al., 2012) and –150 mV in cerebellar granule cells (Ward et al., 2000). Several physiological factors, including depolarization, hyperpolarization and overall activity are believed to influence ΔΨmt, contributing to its volatility and dynamic instability. In general, it should be noted that neuronal ΔΨmt fluctuates within a fairly wide range, comparable to the potential in astrocytes and myocytes, but exceeding it in fibroblasts (Table 1).
Thus, neuronal and especially dendritic MT possess a set of unique features that shape their specialized metabolic properties, which will be explored in the context of Ca2+ buffering and ATP production in the following sections.
3.2 Mechanisms of mitochondria motility in neurons
As mentioned above, neuron is a type of cell that exhibits a spatially polarized and elongated form. The MT structure, clustering, and distribution in neurons are highly distinct due to the differentiation of neuronal compartments (Perkins et al., 2001; Kann and Kovács, 2007) and the significant length of their processes, which can extend several meters from the cell soma (Cai and Sheng, 2009a). Neuronal MT mobility occurs through their movement along cytoskeletal elements such as microtubules and actin filaments (Shah et al., 2021; Alberti et al., 2022; Zaninello and Bean, 2023). There is a specific principle for microtubule orientation in neurons: in axons and distal dendrites, microtubules are strictly oriented such that their dynamic ends, or plus-ends, are conditionally directed toward the terminals, while their stable ends, or minus-ends, are directed toward the cell soma. Different motor proteins provide movement in anterograde (toward the terminals) or retrograde (toward the soma) directions (Figure 4A). Thus, the superfamily of kinesin provides mostly for anterograde transport, while dynein provides retrograde transport. In proximal dendrites, the orientation of microtubules could be mixed, with both minus- and plus- ends present, so the direction of motility in dendrites is not solely dependent on motor proteins (Hirokawa and Takemura, 2005; Kapitein et al., 2010; Kruppa and Buss, 2021). In the neuronal soma, mitochondria exhibit specific orientations related to the microtubule network, contributing to the overall cellular architecture and function (Petersen et al., 2014; Seager et al., 2020).
FIGURE 4
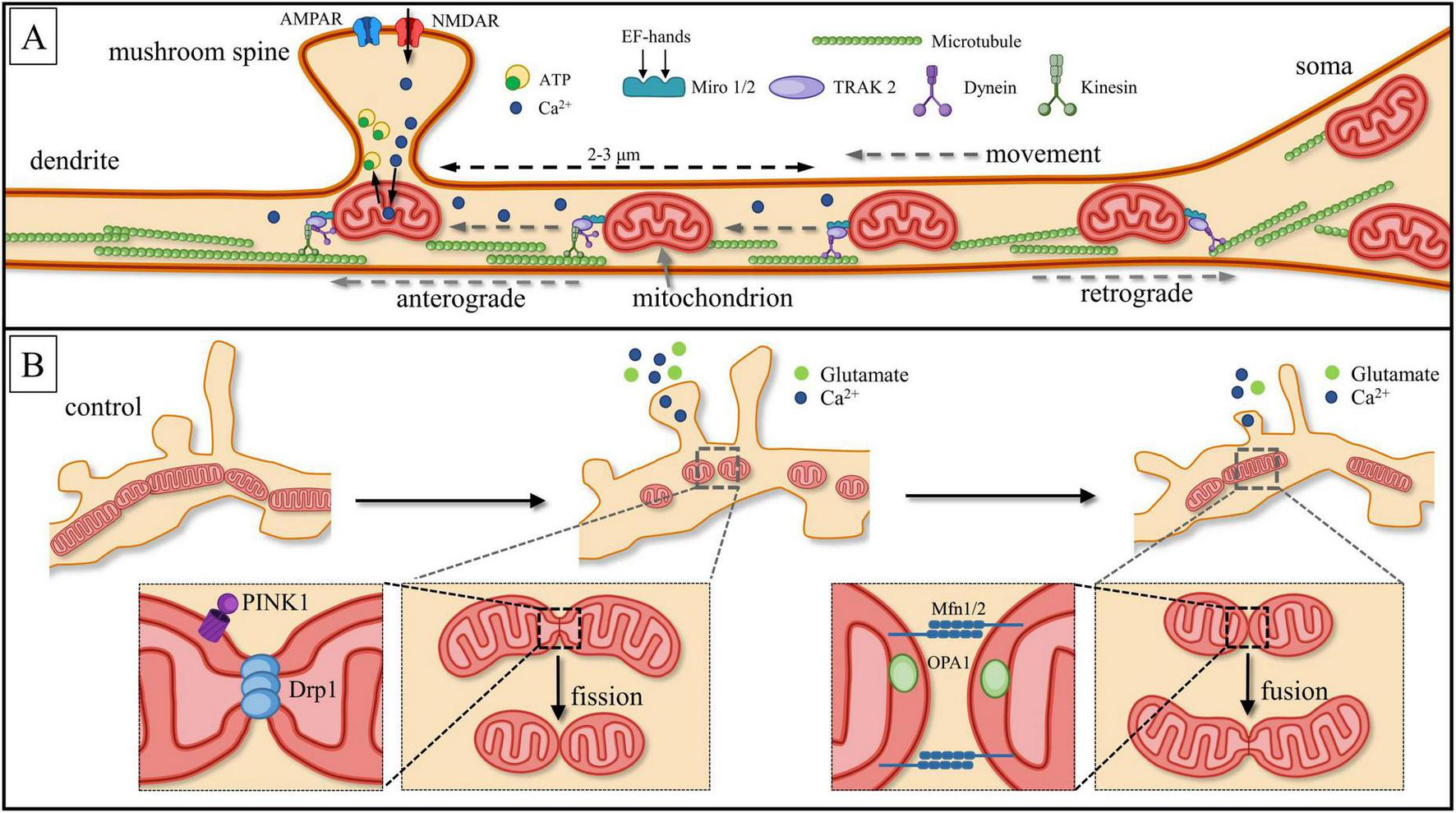
Schematic description of neuronal mitochondria motility. (A) Miro1/2 (Mitochondrial Rho GTPase1/2) acts as a Ca2+ sensor. Through binding with the motor-adaptor protein TRAK2, Miro1/2 inhibits the interaction between dynein and microtubules. This inhibition allows mitochondria to remain within the local Ca2+ burst region (dotted line), which occurs due to the activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). The presence of four EF-hand domains in Miro1/2 facilitates this process. Local Ca2+ bursts are restricted to ∼2–3 μm from the site of origin (dashed line). As a result, mitochondria are anchored beneath the base of dendritic spines, optimizing ATP production and enabling efficient Ca2+ buffering. Different motor proteins provide movement in anterograde (toward the terminals) or retrograde (toward to the soma) directions: kinesin provides anterograde transport, while dynein provides retrograde transport. (B) Another form of mitochondrial motility involves mitochondrial “fission,” which separates organelles, and “fusion,” where they merge into a single cluster. Fission is regulated by the GTPase Dynamin-1-like protein, Drp1, while mitochondrial fusion is controlled by Mitofusins (Mfn) and the dynamin-like GTPase Optic Atrophy 1 (OPA1). During local synaptic glutamate release, high concentrations of [Ca2+]c can induce mitochondrial fission, whereas low concentrations of [Ca2+]c promote fusion. This scheme is based on unpublished confocal images generated by the authors.
Mitochondria are attached to motor proteins through specific adaptor proteins such as Miro1/2 and TRAK1 (Trafficking Kinesin Protein 1) and TRAK2, both homologues of Milton (MacAskill et al., 2010; Misgeld and Schwarz, 2017; Kruppa and Buss, 2021; Duarte et al., 2023). TRAK1 is responsible for axonal transport and binds with both kinesin and dynein, while TRAK2 binds exclusively with dynein, promoting dendritic mitochondrial transport (Sheng, 2014; Seager et al., 2020). It was established that Miro1/2 works not only as GTPases, acting as molecular switchers by binding and hydrolyzing guanosine triphosphatases (GTP) but is also Ca2+ sensitive (Cai and Sheng, 2009b; Lee et al., 2018; Duarte et al., 2023). Miro EF-hands act as Ca2+ sensors and inhibit kinesin, leading to the inactivation of the Miro-TRAK-kinesin complex.
Local Ca2+ gradients play an essential, though not fully understood, role in the mitochondrial movement. On the one hand, the increase in [Ca2+]c in the active zones should attract MT, causing their movement toward the activation site, specifically to the presynaptic bouton and/or the active spine. On the other hand, the movement of MT should halt due to the rise in [Ca2+]c concentration at the activation site. The Ca2+ sensors are in the OMM whereby mitochondria connect not only with motor protein but move along microtubules towards local Ca2+ gradients caused by ongoing synaptic activity (MacAskill et al., 2010; Lin and Sheng, 2015; Rangaraju et al., 2019b; Kushnireva and Korkotian, 2022). Neuronal activity, cytosolic calcium rises, and synaptic glutamate release contribute to a reduction of speed of mitochondrial movement (MacAskill et al., 2009). The growth of synaptic activity reduces dendritic mitochondrial mobility along microtubules and enhances their density at the spine base, especially in mushroom-type spines, where mitochondria organize into stable tubular elongated clusters (Lee et al., 2018; Thomas et al., 2023). Inhibiting the connection between mitochondria and motor kinesin within the mitochondrial motor-adaptor complex leads to the undocking of the mobile fraction of MT from microtubules and their docking in areas of local [Ca2+]c spikes (Figure 4A; Sheng, 2014; Duarte et al., 2023). It is assumed that Ca2+-induced mitochondrial transport arrest near active synapses provides alternate energy to glutamatergic synapses (Colgan and Yasuda, 2014; Duarte et al., 2023).
The largest difference in MT shape and dynamics is observed between axonal and dendritic compartments, favoring larger sizes (with some exceptions) and slower dynamics for the latter. For example, the volume of dendritic mitochondria exceeds that of axons and soma in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, but not in the CA1 region (Faitg et al., 2021). Also, layer 2/3 of cortical neurons exhibit elongated mitochondrial morphology in dendrites (range from 1.31 to 13.28 μm) compared to axonal MT (ranging from 0.45 to 1.13 μm), both in vivo and in vitro (Lewis et al., 2018; Seager et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2020). Axonal mitochondria exhibit greater velocity and longer-range motility and a generally globular or ovoid shape (Seager et al., 2020; Chang et al., 2006). In dendrites, mitochondria exist as extended tubular clusters with high density (Li et al., 2004). A particularly high density of mitochondria is observed in postsynaptic areas, where it supplies local protein synthesis by ribosomal complex, support ionic, or more precisely Ca2+ homeostasis and cytoskeleton structural re-modeling (Chang et al., 2006; Palikaras and Tavernarakis, 2020; Murali Mahadevan et al., 2021; Duarte et al., 2023; Thomas et al., 2023; Bapat et al., 2024). Occasionally, postsynaptic MT can invade dendritic spine head (Bosch and Hayashi, 2012; Thomas et al., 2023), however, typically it is concentrated in the parent dendrites under the spine neck (Nimchinsky et al., 2002; Chang et al., 2006; Bourne and Harris, 2008; von Bohlen Und Halbach, 2009; Thomas et al., 2023).
Furthermore, greater mobility is typical of newly formed mitochondria, created by fission (see below). This MT pool maintains high mobility within the transport motor/adaptor complex due to its small size (Gu et al., 1994; Sheng and Cai, 2012; Segal and Korkotian, 2014; Green et al., 2022). It has been shown that this complex moves directly to areas of elevated [Ca2+]c concentration (Colgan and Yasuda, 2014; Duarte et al., 2023).
3.3 Mechanisms of mitochondria motility in dendrites
It is generally assumed that synaptic activity determines the topography and dynamics of mitochondria associated with the relevant dendritic spines, as well as the total length of mitochondrial clusters (Bereiter-Hahn and Jendrach, 2010; Leung et al., 2021; Thomas et al., 2023). This depends on two types of opposing processes: cluster division or “fission” to separate organelles and merging or “fusion” into one cluster (Figure 4B). Fission is controlled by GTPase from the dynamin superfamily: DNM1L (Dynamin-1-like protein) or Drp1 (dynamin-related protein 1) (Pekkurnaz and Wang, 2022; Duarte et al., 2023). Disruption or delay in fission caused by Drp1 dysfunction prevents mitophagy of damaged mitochondria, which negatively impacts synaptic function. Drp1-dependent modulation of anti-apoptotic proteins Blc-w and Blc-xL expression exerts influence on MT location and is correlated with an increase in protein number in the postsynaptic density (MacAskill et al., 2010). Drp1-dependent mitochondrial division has been increased by the influence of PTEN-induced kinase 1 (Phosphatase and tensin homolog PINK1) and Ca2+ leak following synaptic potentiation (Duarte et al., 2023; Thomas et al., 2023). Enhanced mitochondrial fission promotes structural morphological alterations of dendritic spines in turn (Duarte et al., 2023).
Mitofusins (Mfn) and the dynamin-like GTPase Optic Atrophy 1 (OPA1), which facilitate mitochondrial fusion, play a crucial role in stabilizing mitochondrial morphology (Williams et al., 2010; Emery and Ortiz, 2021). Their dysfunction can result in pathological fragmentation of the organelle and various degenerative conditions (Pellegrini and Scorrano, 2007; Knott and Bossy-Wetzel, 2008; Santos et al., 2015). The mutual and balanced work of Mfn2 and Drp1 is required to maintain physiological function and balance between fission and fusion (MacAskill et al., 2010; Misgeld and Schwarz, 2017). Moreover, the proteins’ connection with transport proteins such as Miro and TRAK are necessary to maintain different forms of synaptic plasticity (MacAskill et al., 2010; Eberhardt et al., 2020).
The loss of functional mitochondria in postsynaptic areas leads to an energy deficit, which blocks morphological plasticity. Ultimately, this process results in dendritic spine pruning and synapse loss (MacAskill et al., 2010; Dromard et al., 2021). Therefore, maintaining a “healthy” pool of mitochondria in the postsynaptic area is essential. However, MT are often damaged there due to increased functional load. The removal of defective mitochondria, which have accumulated improperly folded proteins and lost mitochondrial potency—through a process called mitophagy—is necessary to replace the damaged organelles with new ones (Figure 5). The PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway is primarily involved in the realization of mitophagy (Misgeld and Schwarz, 2017; Palikaras and Tavernarakis, 2020; Figure 5). When the serine/threonine-protein kinase PINK1 accumulates on OMM, it phosphorylates and activates Miro and GTPase protein Mfn2, as well as E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin and ubiquitin itself. Activated Parkin binds to Miro or ubiquitin to attach to the OMM, where Parkin continues to bind and append phosphorylated ubiquitin, recruiting additional mitophagy adapters. As Parkin is ubiquitinated, the autophagosome degrades the damaged or dysfunctional mitochondria (Misgeld and Schwarz, 2017; Quinn et al., 2020). Disturbances in mitophagy processes may trigger synaptic failure, and cell death (Dagda et al., 2009; Makarov and Korkotian, 2023).
FIGURE 5
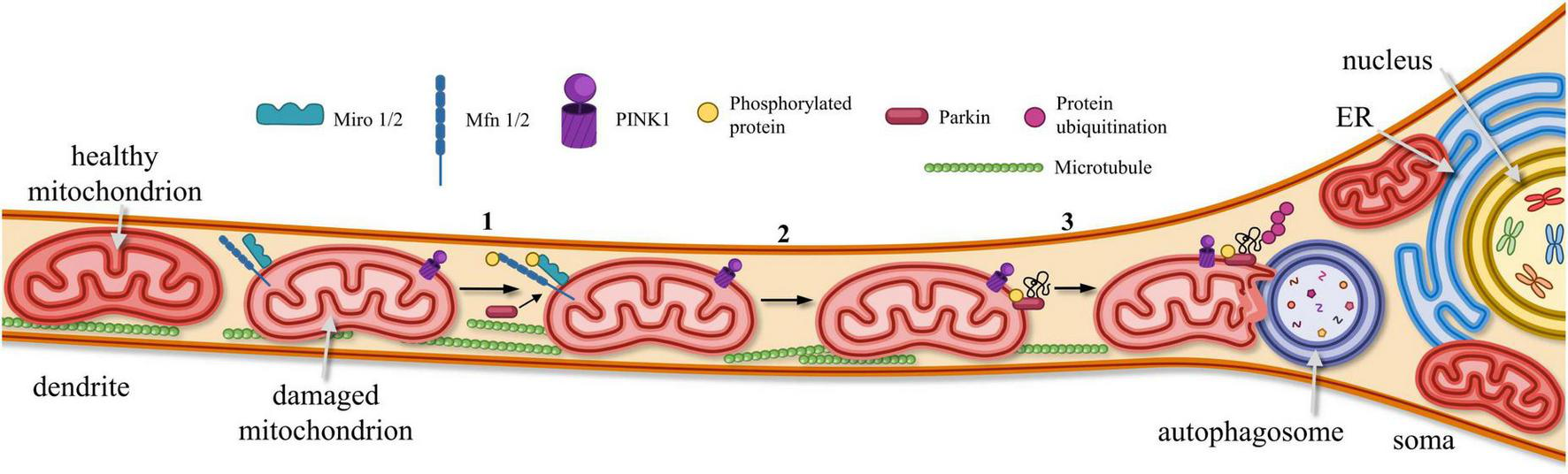
Elimination of dysfunctional MTs from postsynaptic sites. In dendrites, dysfunctional MTs are removed via PINK1-Parkin signaling pathway: (1) PINK1 accumulates on OMM, promoting phosphorylation of Miro1/2, mitofusin proteins (Mfn1/2) and Parkin. (2) Phosphorylated Parkin becomes anchored to OMM, where it binds and recruits phosphorylated ubiquitin. (3) As a result of Parkin-mediated ubiquitination, damaged and dysfunctional mitochondria are targeted for degradation by autophagosomes.
In summary, neuronal mitochondria, that are located away from the cell body, should work with higher level of self-sufficiency and sustain essential functional load. Furthermore, MTs are required to have instantaneous reaction due to the high-speed kinetic (milliseconds) of the major part of electrochemical events along dendritic branches and/or synaptic micro- compartments. The same way signaling pathways getting energetic requests should act. It is possible that mitochondrial dynamic relocation along calcium gradients and changes in the length and shape of mitochondrial clusters can be considered as possible solutions to the functional task. However, it is still unclear whether organelle mobility alone is sufficient to meet the complex energetic demands in neuronal and glial cells, or if more molecular tunings are required. In the next chapters, we will discuss which molecular mechanisms are potentially not only fast but also accurately direct ATP secretion in appropriate compartments.
4 Mitochondria in postsynaptic regions of central neurons
4.1 Mitochondria and local activity at postsynaptic sites
After the completion of the intense phase of synaptogenesis associated with neuronal development, dendritic mitochondria of mature neurons form spatially stable compartments about 30 μm in length (Rossi and Pekkurnaz, 2019; Palikaras and Tavernarakis, 2020; Pekkurnaz and Wang, 2022). Excitatory presynaptic terminals tend to contact dendritic spines, whereas most inhibitory inputs are localized on somatic and proximal dendritic areas (Leung and Peloquin, 2006; Jadi et al., 2012). Frequently, neighboring spines form spatial functional groups or clusters (see an example on Figure 6C; Nimchinsky et al., 2002; Dromard et al., 2021). Likewise, increased activity in such a clusters causes mitochondrial relocation toward presynaptic terminals (Lees et al., 2020; Seager et al., 2020), where energetically the mitochondria support the increased secretion of neurotransmitters, calcium maintenance, and presynaptic plasticity (Li et al., 2004; Chang et al., 2006; Obashi and Okabe, 2013). As mentioned earlier, the mitochondrial protein Miro functions as a Ca2+ sensor, inhibiting the connection between mitochondria and motor kinesin within the mitochondrial motor-adaptor complex. This leads to the undocking of the mobile fraction of mitochondria from microtubules and their docking in areas of local [Ca2+]c spikes (Figure 4A; Sheng, 2014; Duarte et al., 2023). It is assumed that Ca2+-induced mitochondrial transport arrest near active synapses provides alternate energy to glutamatergic synapses (Colgan and Yasuda, 2014; Duarte et al., 2023).
FIGURE 6
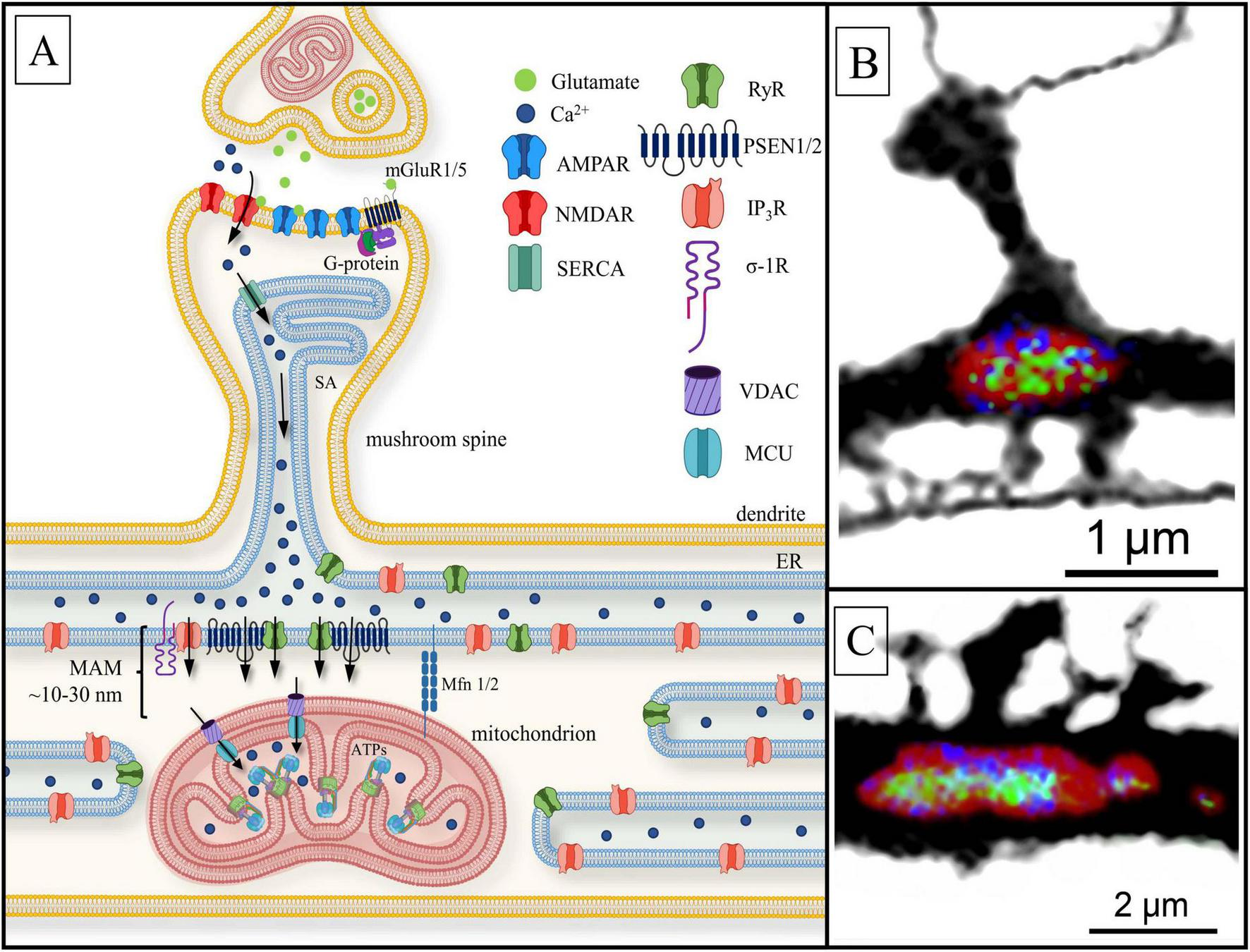
Postsynaptic Ca2+ signaling pathway to the mitochondria. (A) Black arrows present calcium currents. Ca2+ penetrates dendritic spine head via the activation of ionotropic glutamate receptors: N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor NMDAR and AMPAR. The sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) allows Ca2+ to enter the spine apparatus (SA). Ca2+ is released into the mitochondria-associated membranes (MAM) space through ryanodine-sensitive receptors (RyR), presenilin proteins (PSEN1/2) and inositol- 3-phosphate receptors (IP3R) located at the dendritic base on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). PSEN1/2 and sigma-1-receptor (σ-1R) stabilize RyR and IP3R, respectively. Subsequently, calcium ions flux into the mitochondrial matrix through voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) and the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU), located on OMM and IMM, respectively, where Ca2+ influences ATP synthase (ATPs) activity. Mitofusins (Mfn1/2) physically connects the organelles, keep free space between them with a length of 10–30 nm. Other abbreviations: mGluR1/5—the I and V type metabotropic glutamate receptor coupled with G-protein. (B) Confocal image of a single mitochondrion (MT) (red; MT morphology marker) located under dendritic spine base of a hippocampal dendrite, with immunolabeled ATP synthase (green) and MCU (blue); (C) the same as (B). A cluster of dendritic spines with underlying MT. Note non-uniform distribution of MCU and ATP synthase along the MT surface (unpublished observation).
The MT located under the spine bases with synchronized synaptic inputs are not only influenced by them but also exert influence on the structure of new dendritic spine groups themselves within ∼5 (Dromard et al., 2021) to 30 μm (Bapat et al., 2024) from the plasticity induction focus. The appearance of new spines around the potentiation focus is perhaps related to the fission and extension of the mitochondrial network (Dromard et al., 2021). Despite the evident significance, the connection between the local volume and morphology of mitochondria and synaptic functional activity remains apparently unclear. In the study by Thomas et al. (2023), it was discovered that the dendritic spine head volume and its postsynaptic density size do not correlate with the volume of adjacent MT. Instead, mitochondria are preferably concentrated around heterogeneous spine clusters receiving structurally and functionally diverse inputs in dendritic areas undergoing structural dynamics.
4.2 Mitochondria-driven modulation of synaptic plasticity
In the context of synaptic plasticity [long-term potentiation, (LTP) and/or long-term depression, (LTD)], free MT retain motility, allowing them to move along cytoskeleton elements, sometimes over quite long distances (Chang et al., 2006; Colgan and Yasuda, 2014). In postsynaptic compartments, MT do not only react to the current synaptic activity but are also able to affect synaptic currents, specifically by long-term regulation of synaptic strength. It is assumed that MT can exert a modulating effect on LTP/LTD in different ways (see chapter 6.2). For instance, with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) they form mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs). These specialized regions emerge in narrow areas where the two structures take close positions, with a distance of approximately 10–30 nm (Li et al., 2004; Rangaraju et al., 2019a). MAM-contacts facilitate Ca2+ transfer from the ER to nearby MT, which maintains Ca2+ homeostasis in dendrites (Colgan and Yasuda, 2014; García-Bermúdez and Cuezva, 2016; Kushnireva and Korkotian, 2022; Kuijpers et al., 2024). MAM-contacts are regulated by Miro through clustering along OMM (Duarte et al., 2023). In addition, mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) acts as a MAM-contact protein and influences mitochondrial transport along microtubules by associating Miro (Johri and Chandra, 2021).
MT are able to buffer ions over physiological [Ca2+]c range, within certain limits (around ∼100 μM; MacAskill et al., 2010) immediately in response to a local increase in [Ca2+]c levels, thereby restricting Ca2+ spread along the dendrite in lateral directions (MacAskill et al., 2010; Kushnireva et al., 2022). Moreover, MT, having collected Ca2+, provide gradual, slow release of the ions to control the basal Ca2+ level and restrict functional interactions between neighboring dendritic spines (MacAskill et al., 2010). In the absence of synaptic transmission, [Ca2+]m concentration is approximately equal to [Ca2+]c concentration and is around 100 nM (Segal and Korkotian, 2014; Seager et al., 2020). Postsynaptic depolarization leads to a rapid increase in [Ca2+]c (Gu et al., 1994; Pivovarova et al., 1999), and calcium is sequestered by calcium stores when [Ca2+]c reaches 500 nM (Gu et al., 1994; Garbincius and Elrod, 2022). It has been established that changes in [Ca2+]m follow local fluctuations in [Ca2+]c with a slight delay not exceeding a few milliseconds (Kushnireva et al., 2022). Moreover, changes in [Ca2+]m significantly correlate with fluctuations in [Ca2+]c, while the latter are framed by physiological conditions. Presumably, the mechanism ensures selective postsynaptic potentiation for neighboring spines at a distance around ∼2–5 μm (Kushnireva et al., 2022). Thus, if mitochondria-buffered cytosolic calcium has a direct or indirect relationship with mitochondrial activity in space, it is expected that Ca2+ is also be distributed unevenly in the cluster. Indeed, direct measurements indicate that [Ca2+]m reactions are higher in area clusters under the spine base in comparison to more “lateral” clusters (Kushnireva et al., 2022). There is a high detection probability of [Ca2+]m events under the spine base, compared to the probability in lateral zones of the same cluster (Kushnireva et al., 2022). Furthermore, it has been established that during mitochondrial depolarization related to functional activation, there is a short-term increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by mitochondria (ΔΨmt on IMM ≈ –140 mV and lower) (Kaim and Dimroth, 1999; Lee et al., 2002). ROS could act as trigger to LTP induction (Thiels et al., 2000; Massaad and Klann, 2011) (see section 7).
In conclusion, mitochondria are directed to local Ca2+ bursts regions within dendrites to ensure the supply of ATP, proximal to dendritic spines. Dysfunctional mitochondria are eliminated through the mitophagy process to preserve dendritic spine functionality. However, a critical question remains: is there a distinct distribution of ATP synthase within IMM? Specifically, if mitochondria exhibit a non-uniform ATP synthase distribution, what impact does this have on ATP dynamics within the MT and on the surrounding cellular processes reliant on ATP?
5 Regulation of ATP synthesis
5.1 ATP as a glial signaling molecule
It is assumed that precise spatial organization and regulation of ATP synthase activity play significant roles both on presynaptic and postsynaptic sites. However, these roles remain largely unknown. One complicating factor is the fact that the synaptic region is engulfed by astrocytes and microglia which assume important roles in isolating the synapse. During heightened neuronal activity, astrocytes extensively release ATP to neurons while simultaneously increasing the amplitude and frequency of their calcium waves (see for review: Lezmy, 2023; Illes et al., 2025). This process is central to the concept of the tripartite synapse, where astrocytes not only support neurons but also regulate synaptic communication. ATP is released through pannexin and connexin channels and then converted into adenosine, modulating synaptic transmission (Dahl, 2015; Boué-Grabot and Pankratov, 2017; Illes et al., 2019). Additionally, astrocytes are involved in the glutamate shuttle, absorbing excess glutamate from the synaptic cleft and converting it into glutamine, which is then transported back to neurons for reuse (Rose et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2023). This mechanism maintains excitatory signal balance and prevents neurotoxicity. Research indicates that astrocytic calcium waves can propagate to nearby cells, coordinating activity across neuronal networks (Fujii et al., 2017; Letellier and Goda, 2023). This highlights astrocytes as crucial modulators of synaptic plasticity and neuronal communication.
In addition to the effect on ion balance and neurotransmitter control, there is evidence of energy support of the most active synapses by astrocytes. They carry highly specialized structures, endfeet, through which glucose is absorbed from the cerebrovascular network. As hepatocytes, astrocytes are able to reserve glucose in the form of glycogen. It is believed that the mobilization of these reserves correlates with current neuronal activity. The targeted supply of synapses occurs through thin processes in the tripartite synapses mentioned above. For the implementation of this mechanism, the local process must be “aware of” the level of local synaptic activity. Moreover, the branched network of the astrocytic ER can serve as a carrier for intracellular glucose transport. However, it is not glucose but its derivative lactate that is released to the extrasynaptic space (Müller et al., 2018; Pellerin, 2018; Beard et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). In this process, astrocytes metabolize glucose via glycolysis, producing lactate, which is transported to neurons via monocarboxylate transporters. Neuronal mitochondria then convert lactate to pyruvate, which serves as a substrate for ATP production (Beard et al., 2022; Pekkurnaz and Wang, 2022). However, the efficacy of astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle may be affected by aging (Drulis-Fajdasz et al., 2018; Bonvento and Bolaños, 2021) because of glycogen metabolism enzymes concentration increasing in neurons’ MT (Drulis-Fajdasz et al., 2018).
In pathological conditions, astrocytes and microglia can shift from metabolic support to an inflammatory profile, altering their interactions with neurons. Instead of supplying ATP and maintaining neurotransmitter balance, they begin to release pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α), which can impair neuronal function. Microglial purinergic P2X7 receptors become highly active in response to excess ATP, exacerbating inflammation and promoting neurotoxicity (see for review: Giovannoni and Quintana, 2020; López-Teros et al., 2024). Meanwhile, astrocytes may lose their ability to efficiently recycle glutamate, leading to excitotoxicity. This metabolic-inflammation switch contributes to the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting the dual role of glial cells in both support and dysfunction.
5.2 Regulation of local ATP synthesis in neuronal mitochondria
ATP in both presynaptic and postsynaptic MT is regulated by synaptic activity, and aberrant synaptic activity may lead to mitochondrial dysfunction. It has been established that under normal conditions action potentials (AP) stimulate local ATP production in axons (van Hameren et al., 2019). It is reasonable to assume that an analogous effect on ATP regulation may occur not only in the presynaptic terminal of an activated synapse but also in postsynaptic structures. Generally, because of increased [Ca2+]c, a number of local events take place: (1) Buffering of Ca2+ by MT increases [Ca2+]m, which regulates the entry of glutamate and pyruvate into the TCA cycle and enhances ATP production within the range of approximately –130 to –170 mV. This enhancement is due to a greater number of protons moving through the IMM voltage field per ATP synthase cycle, possibly as a consequence of adaptive stoichiometry or increased c-ring turnover (Wescott et al., 2019); (2) Intense mitochondrial fission takes place within 7–8 μm from the active dendritic spines as a result of NMDA-dependent LTP involving Ca2+ /calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), Drp1 and actin polymerization (Divakaruni et al., 2018). Hyperpolarization enables Ca2+ uptake into the mitochondrial matrix, which leads to an increase in ATP production. This can occur during mitochondrial fusion (Klotzsch et al., 2015; Divakaruni et al., 2018). However, it is likely that ATP synthesis, increased after mitochondrial fission, is contributory to sustaining LTP, which is facilitated by intensified Ca2+ buffering because of new divided mitochondria is presented (Divakaruni et al., 2018).
There is just fragmentary evidence for ATP synthase distribution in neurons. Thus, it is known that ATP synthase competes in proton motive force with proteins such as UCP4 (uncoupling protein) concentrated on IMM as well (Klotzsch et al., 2015). UCP4 is included in the family of mitochondrial anion carrier proteins (MACP) (Smorodchenko et al., 2011). The notable feature of UCP4 relates to its expression in neuronal tissue (Ledesma et al., 2002; Crivelli et al., 2024). UCP4 utilizes oxidative phosphorylation energy similar to ATP synthase, however, not for ATP synthesis but for heat generation. Due to the proton gradient charge, the functioning of both proteins causes mitochondrial depolarization. We assume that their activity and expression could differ spatially as well as temporally. Spatial separation of ATP synthase and UCP4 is observed within MT and between the mitochondria of different sections of a neuron. ATP synthase is more expressed in cristae, while UCP4 is expressed in IMM regions adjacent to OMM (Klotzsch et al., 2015). Meanwhile, the proteins anchored in cristae are influenced by a higher ΔΨmt than the proteins adjoining the OMM. The maximal transmembrane proton gradient is limited by rapid lateral proton diffusion from cristae to UCP4 (Klotzsch et al., 2015). However, ATP synthase molecules are able to relocate from cristae to the inner boundary membrane (Weissert et al., 2021). Likewise, it has been observed that ATP synthase expression is mostly typical for dendritic branches, where local events requiring high energy leakage occur (Mironov, 2009), while UCP expression is pronounced in the neuron’s soma (Smorodchenko et al., 2009; Klotzsch et al., 2015). Both enzymes’ expressions are partly separated in time. Thus, ATP synthase is actively expressed in more mature, postnatal neurons, while UCP4 and ATPase as enzymes that hydrolyze ATP are more typical for mitochondria in embryonic cells when ΔΨmt does not reach –100 mV, thereby hindering ATP production by the synthase at this stage (Surin et al., 2013). ATP synthase molecules in mitochondria are typically concentrated at the cristae rims (Ježek et al., 2023). However, mitochondrial ATP synthases in all eukaryotic cells can form dimer or tetramer complexes across the crista surface, which are arranged in linear rows forming helical patterns (Acehan et al., 2011; Davies et al., 2011, 2012). The same can be said about neuronal mitochondria cristae (Nirody et al., 2020). The average distance between neighboring rows is around ∼28–30 nm, and the mean interval between neighboring dimer centers in a row is approximately ∼12–18 nm (Acehan et al., 2011; Davies et al., 2011). Dimerization and oligomerization also contribute to the high-degree curvature of cristae (Acehan et al., 2011; Domínguez-Zorita et al., 2022). The angle between the axis of rotation of ATP synthase V-shaped dimers in mammalian cells is dynamic, which permits the enzyme to function and/or contribute to the structural changes of cristae (Nirody et al., 2020; Domínguez-Zorita et al., 2022).
5.3 Ultrastructural and functional features of ATP synthase in dendrites
Neuronal mitochondrial ATP synthase localization, its distribution on cristae, its oligomerization, and structure are influenced by IF1. It has been established that the absence of IF1 reduces the quantity of neuronal mitochondrial cristae, making them shorter and wider (Romero-Carramiñana et al., 2023). IF1 also regulates ATP synthase activation in neuronal mitochondria, promoting the delicate adjustment of ATP production and the distribution of the ΔΨmt proton gradient within and between cristae (Campanella et al., 2009).
The conversion of ATPase from hydrolyzing to synthesizing ATP is accompanied by a shift in the F0-complex c-ring direction and a conformational alteration of the entire synthase (Surin et al., 2013), particularly the β-subunit of the F1-complex (Weber and Senior, 2003; Nath, 2023), (see Figure 3B). The conformation of ATP synthase can change due to the influx of Ca2+ into the mitochondrial matrix through MCU and the subsequent binding of ions to the β-subunit of ATP synthase (Hubbard and McHugh, 1996; Giorgio et al., 2017).
Although ATP synthase molecules are concentrated in mitochondrial cristae, a number of studies have described the ability of ATP synthase to move from MT to the plasma membrane of excitable cells (Xing et al., 2011; Chang et al., 2023). ATP synthase located in plasmatic membrane, called ectopic (eATPase) is capable of generating and secreting ATP into an extracellular environment to regulate extracellular ATP/ADP ratio and intracellular pH level (Xing et al., 2011). Before anchoring in the plasma membrane, the future eATPase complex is located in the mitochondria. Its transport to the mitochondria occurs as follows: kinesin family member 5B (KIF5B) interacts with Drp1 and binds to Miro and TRAK proteins, directing the bound complex along microtubules within mitochondrial fragments, or mitochondrial “vesicles,” to the plasma membrane (Chang et al., 2023). It has been established that both mitochondrial membranes can attach to the cell’s plasma membrane to anchor eATPase in it (Chang et al., 2023).
Nowadays, there is a consensus that the cytosolic calcium gradient precisely regulates ATP synthesis and/or secretion in eukaryotic cells (Boyman et al., 2020), including neuronal cells (Giorgio et al., 2017). This is especially relevant in the postsynaptic neuronal zone, where calcium signaling plays a key role in synaptic strength regulation. Additionally, there is a significant open question: how exactly is the local ATP level regulated, and is this regulation connected with the spatial distribution of ATP synthase in the postsynaptic zone? In other words, what signaling mechanisms provide the initiation of ATP synthesis and its secretion on a fast dynamic timescale, around milliseconds?
6 Calcium gradients in dendrites
6.1 Calcium signaling in mushroom spines
As mentioned above, the AP-evoked Ca2+ influx into the synaptic area and dendritic cytosol occurs through NMDAR in response to glutamate release from the presynaptic terminal, which is triggered by postsynaptic activation of AMPAR (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors) current (Jonas et al., 2004; Keller et al., 2008; Ashhad and Narayanan, 2013; Strobel et al., 2017). AMPAR and NMDAR are two major subtypes of glutamate receptors that play distinct roles in synaptic transmission and plasticity. AMPARs mediate fast excitatory synaptic transmission by quickly responding to glutamate binding, while NMDARs are voltage-dependent and require both glutamate and membrane depolarization to activate, leading to Ca2+ influx that influences synaptic modulation and plasticity (Figures 6A, 7).
FIGURE 7
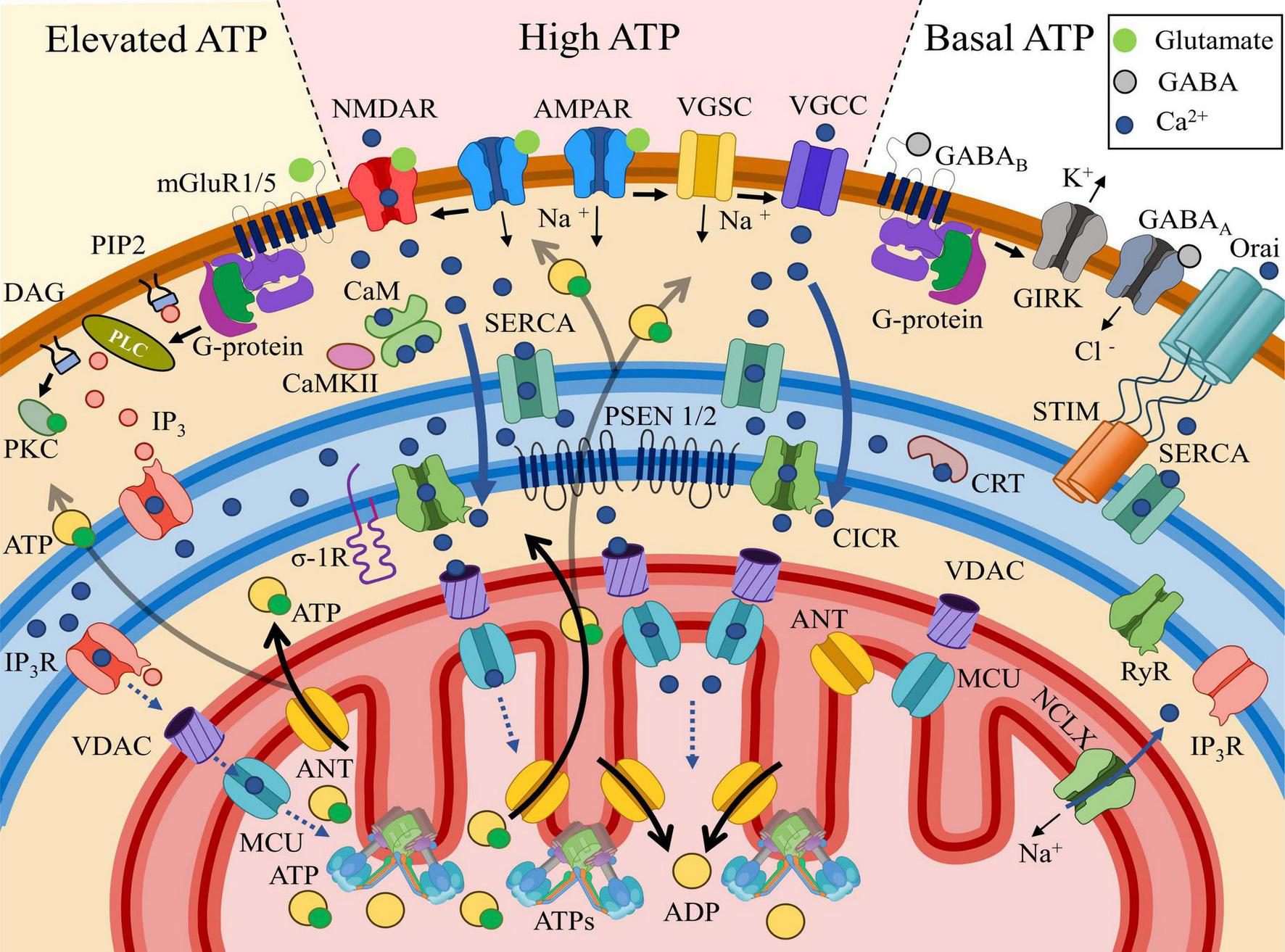
General trends of postsynaptic Ca2+ distribution and the associated ATP concentrations. High ATP section: AMPAR (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors, placed in the middle at the top) activation by glutamate triggers plasma membrane depolarization. NMDAR (N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, on the left in the center) requires both glutamate binding and membrane depolarization for activation. NMDAR efficiently conducts Ca2+, which is taken up by the SERCA pump and transported to the local compartment of the endoplasmic reticulum (blue field), where Ca2+ is buffered by calreticulin (CRT). Voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs) are activated due to membrane depolarization, which in turn opens voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs), allowing Ca2+ to leak from the intracellular space into the cytosol. Localized in the ER (endoplasmic reticulum), RyRs (ryanodine receptors) open due to interaction with elevated cytosolic Ca2+ via the calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) mechanism, leading to a high level of Ca2+ release within the MAM (mitochondria-associated membrane, space between the ER and the mitochondria) region. Ca2+ release is also facilitated by PSEN 1/2 modulating RyRs and/or serving as leak channels. From the MAM, Ca2+ penetrates through the OMM via VDAC (voltage-dependent anion channel) and MCU (mitochondrial calcium uniporter), which may facilitate ATP synthase (ATPs), leading to increased ATP production from ADP exchanged across the IMM via ANT (adenine nucleotide translocator). Activation of the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCLX) facilitates Ca2+ efflux from MT into the cytosol, regulate MT Ca2+ homeostasis. Elevated ATP section: upon activation, the G-protein bound to type I and V metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1/5) dissociates into subunits. The α-subunit of the G-protein activates phospholipase C (PLC), which cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacylglycerol (DAG), which remains membrane-bound, and inositol trisphosphate (IP3), which diffuses into the cytosol. DAG subsequently activates protein kinase C (PKC), initiating signaling cascades involved in long-term plasticity. IP3 binds to the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R), facilitating its opening and Ca2+ leakage into the cytosol. IP3Rs, oriented toward the MAM region, release Ca2+ toward mitochondria (MT) in lower amounts compared to the previously described pathway, contributing to a moderate ATP increase. Basal ATP section: The interaction of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) with ionotropic GABAA (GABA type A) or metabotropic GABAB (GABA type B) receptors conducts Cl– (chloride) anions into the cytosol or removes K+ (potassium) via GIRK (G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels), thereby hyperpolarizing the membrane without creating an influx of Ca2+. As a result, cytosolic Ca2+ levels remain low. The only source of Ca2+ store replenishment in this case is the activation of Orai (voltage-independent calcium release-activated protein), which connects with oligomerized STIM (stromal interaction molecules) located near the plasma membrane and facilitates Ca2+ influx into the store/ER. The absence of increased Ca2+ and IP3 in the cytosol prevents Ca2+ release from the store, as RyR and IP3R remain closed. Under these conditions, ATP levels remain at the basal level.
Excitatory synapses are located on both dendritic spines and dendritic shafts. Shaft synapses are typical of developing neurons (Papa et al., 1995; Cottrell et al., 2000; Bucher et al., 2020). In more mature neurons, non-spine contact types are not able to form spatially bounded Ca2+ gradients due to the relative freedom of ion diffusion along the dendrite. However, why is the calcium gradient so crucial? The gradient is able to influence enzymatic chains, local protein synthesis, maintenance, and ATP production (Korkotian and Segal, 2006; Higley and Sabatini, 2012). In this context, it is essential to consider the factors influencing the uneven dynamic Ca2+ distribution in dendrites.
First, a synaptic Ca2+ gradient appears around the base of the dendritic spine. One of the forms of a mature dendritic protrusions is the mushroom-shaped spine, which consists of a head and a narrow neck connecting it to the dendritic shaft. However, there are other morphological types of dendritic spines, in particular thin spines that lack a distinct head and stubby spines, that are virtually neckless. The role and degree of functional maturity of these morphologies are still under debate (see for review Hering and Sheng, 2001). Briefly, thin spines, due to the lack of sufficient surface area, do not carry a significant receptor complex. In addition, branches of the ER rarely penetrate them. In contrast, stubby spines are too closely associated with the parent dendrite and do not actually represent an isolated chemical and electrical compartment. Hence, we will focus on mushroom spines.
Due to the synaptic current, [Ca2+]c in the spine head may be significantly higher compared to the dendritic [Ca2+]c (Holcman et al., 2005; Segal, 2010; Yuste, 2013). This deviation is achieved by the following factors: (1) the head volume is not large, approximately 1 × 10–18 – 10–20 L (Koch and Zador, 1993; Harris and Kater, 1994); (2) the head contains significant concentrations of Ca2+-binding proteins, such as CaMKII and calmodulin (Yuste et al., 2000); (3) free diffusion from the head through the neck, with a diameter of ∼0.1–0.2 μm (Arellano et al., 2007; Ofer et al., 2021), is hindered, creating an effect of ion compartmentalization (Arellano et al., 2007). Due to this accumulation of Ca2+ in the spine head, related to its buffering and diffusion obstruction from the neck, the transition process duration in the postsynaptic area increases (Hayashi and Majewska, 2005). Thus, Ca2+ gradient appearances around the spine neck base (Yuste et al., 2000; Korkotian and Segal, 2007). This is possibly one of the reasons that 90–95% of excitatory synapses are changed over to spines during the development of most brain structures (Nimchinsky et al., 2002; Bucher et al., 2020; Kandel, 2021).
In comparison with excitatory synapses, most inhibitory ones are located on proximal dendrites and the soma surface (Megías et al., 2001; Bucher et al., 2020), where they repress Ca2+- and Na+-currents responsible for synaptic plasticity and AP-evoked spikes, respectively, through membrane hyperpolarization (Miles et al., 1996; Megías et al., 2001). This location of inhibitory synapses relative to excitatory inputs is required for effective enhanced inhibition (Kandel, 2021). However, in several cases, inhibitory synapses are observed around dendritic spines (Müllner et al., 2015), or on the spines themselves. This occurrence is especially common for pyramidal neurons of neocortex (Marlin and Carter, 2014; Bucher et al., 2020) and CA1 hippocampal neurons (Huang et al., 2005). Inhibitory dendritic synapses are located on proximal dendrites (Chalifoux and Carter, 2011; Gidon and Segev, 2012; Ravasenga et al., 2022), as well as on apical ones (Chalifoux and Carter, 2011; Marlin and Carter, 2014). The main receptors involved in these synapses are the metabotropic gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors (GABABRs) (Huang et al., 2005; Chalifoux and Carter, 2011). There is evidence that dendritic and spine GABABRs receptors are regulated by G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK) channels, as well as NMDARs, which mediate Ca2+ influx into the postsynaptic area, leading to CaMKII activation (Huang et al., 2005; Schulz et al., 2021). It is possible that synaptic GABABRs play a key role in dendritic plasticity and excitability (Huang et al., 2005), by maintaining local Ca2+ homeostasis (Chalifoux and Carter, 2011; Figures 6A, 7).
Some forms of spines (for instance, stubby spines) do not contain a thin neck, which provides a Ca2+ gradient. In the case of mushroom-like structures, the neck functions as a link rather than a barrier for Ca2+ diffusion into the dendrite (Korkotian and Segal, 2000). Diffusion kinetics of Ca2+ through the neck are also influenced by ER tubules (Segal and Korkotian, 2016). In the case of complete separation from the rest of the reticulum, the ER assumes an isolated structure in the form of the spine apparatus (SA), which possesses an actin-associated complex based on proteins such as synaptopodin. Local ER (Sheng and Cai, 2012) and SA (Vlachos et al., 2009; Segal, 2010) control [Ca2+]c levels in response to ion influx from the outside. Ca2+ received through NMDAR into the spine head is accumulated into the local ER storage, while being secreted through ryanodine receptor (RyR) or inositol trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) anchored on ER into dendrite (Kushnireva and Korkotian, 2022; Figure 6).
Ca2+ released from ER acts as a messenger, particularly in MAM-contacts (Johri and Chandra, 2021; Figure 6). There are major proteins related to MAM: (1) RyRs, located on ER/SA under the spine base and facing the dendritic shaft (Basnayake et al., 2021, 2022); (2) presenilins (PSEN1/2) (Korkotian et al., 2019) acted as RyR regulators (Rybalchenko et al., 2008) and (3) sigma-1 receptors (σ1Rs) that regulate and stabilize IP3R-MAM contacts (Hayashi and Su, 2007; Raturi and Simmen, 2013; Johri and Chandra, 2021). It is assumed that PSENs influence Ca2+-leakage from ER in two ways. Firstly, PSEN1/2 modulates RyR conductance by interacting with the receptor’s cytosolic domain at the N-terminus (Rybalchenko et al., 2008; Payne et al., 2015). In this regard, there is experimental evidence that RyR levels are increased in the presence of mutant PSENs (Lerdkrai and Garaschuk, 2018), possibly serving as a compensatory mechanism for PSEN1 regulation deficit (Kushnireva and Korkotian, 2022; Makarov et al., 2023). Secondly, there is evidence that PSEN1 can function as an ion leak channel through the large hydrophilic loop located on the cytosolic side (Tu et al., 2006; Bagaria et al., 2022). MAM-contact proteins also include resident ER proteins such as calnexin or calbindin, the chaperone protein glucose-regulated protein 75 and deglycase, which together with IP3R and VDAC regulate the transfer of Ca2+ from the ER to the mitochondrial matrix through MCU (Johri and Chandra, 2021; Markovinovic et al., 2022). Additionally, the role of mitofusins (Mfn1/2) in the organization of MAM-contacts should be noted (Barazzuol et al., 2021; Markovinovic et al., 2022). Mfn1/2 is involved in anchoring mitochondria under the active spine base: the proteins physically hold ER/SA and the mitochondria at quite a close distance, ∼10–30 nm (Markovinovic et al., 2022). MAM-contacts are involved in Ca2+ level maintenance, as well as in the regulation of apoptosis, mitochondrial dynamics, mobility, and autophagy (Vance, 2014; Johri and Chandra, 2021; Zhao and Sheng, 2024). The alteration of distances within MAM by Mfn1/2 can affect the rate and efficiency of Ca2+ buffering, which in turn influences mitochondrial energy metabolism and signaling pathway regulation. Ca2+ released by RyR, PSEN1/2, and/or IP3R enters the mitochondrial matrix through VDAC and MCU, located just under MAM-contacts on the OMM and IMM, respectively (Garbincius and Elrod, 2022; Markovinovic et al., 2022; Kuijpers et al., 2024). Below, we will discuss how this mechanism is able to provide directed ATP secretion. Dendritic spine(-s) with MT are imaged on the confocal microscope in Figures 6B,C, respectively. Panel B represents a single mushroom spine in contact with an axon. Panel C contains a cluster of spines. MT (single on B and clastered on C) are seen at the base of both examples (red) along with ATP synthase (green) and MCU (blue). Possibly the larger spine on C is assocoated with higher concentrations of ATP synthase and MCU.
6.2 Regulation of ATP levels by ongoing synaptic activity
In Figure 7, the general trends in postsynaptic Ca2+ distribution and the associated ATP concentrations are illustrated. In the excitatory synapses, AMPARs depolarize the membrane after binding to the excitatory transmitter, presynaptic glutamate which allows NMDAR activation, dependent on both ligand binding and membrane potential. NMDAR efficiently conducts Ca2+, which can be taken up by the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) pump and moved to the local compartment of the ER or to the stand-alone SA. In addition, sufficient depolarization of the plasma membrane transmits excitation to the voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSC). The entry of Na+ ions involves the voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC). The following influx of Ca2+ is also absorbed into the depot and calreticulin (CRT) internal buffer protein. MAM-localized RyRs open due to interaction with elevated cytosolic Ca2+ via the calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) mechanism, after which calcium is released towards MT. This is also facilitated by PSEN1/2 modulating RyRs and/or serving as leak channels, as well as by the σ-1 receptor. From the MAM, where [Ca2+]c can reach 20–40 μM (Hajnóczky et al., 2000), Ca2+ penetrates through the OMM via VDAC and into and through the IMM via the MCU uniporter. In the internal environment of the MT, Ca2+ may directly facilitate the Krebs cycle and ATP synthesis, leading to increased ATP production from ADP, which is transported across the IMM via ANT. The released ATP diffuses into the postsynaptic zone, where its increased concentration (“High ATP”) is formed, for example, to maintain short-term plasticity/long-term plasticity mechanisms associated with the buffer protein calmodulin (CaM) and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). Following heavy Ca2+ influx into MT Na+/Ca2+ exchanger plays a key role in Ca2+ extrusion (Rodrigues et al., 2022), but the mechanism depends on Na+ cytosolic and mitochondrial concentration (Boyman et al., 2013).
Metabotropic receptors, which are coupled to a G-protein, for instance, mGluR 1/5 can activate phospholipase C (PLC). Activated PLC cleaves the phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into lipophilic diacylglycerol (DAG) and hydrophilic IP3. DAG can interact with protein kinase C (PKC), triggering long-term plasticity chains. IP3 interacts with IP3R, another calcium depot receptor that creates a local calcium release. This released Ca2+ enters MT in significantly smaller quantities via the pathway described above, creating a zone of moderate ATP increase in the cytosol (“Elevated ATP”) (see Table 2 for half-activation constants).
TABLE 2
| Receptor type | Half-activation Ca2+ concentration* | Source |
| SERCA | ≤0.4 μM | Pancreatic β-cells (Fridlyand et al., 2003) |
| RyR | Activated by low concentrations (1–10 μM) | Cardyomyocites (Laver and Curtis, 1996; Laver, 2007; Seidlmayer et al., 2016) |
| VDAC | Ca2+ permeabolity in open state 20 ions/s (1 μM), in closed state 80 ions/s (4 μM) | Rat liver (Tan and Colombini, 2007) |
| MCU | 10 μM | Isolated MT (Graier et al., 2007) |
| IP3R | 150 nM | Cardyomyocites (Ju et al., 2012) Brain cells (Verkhratsky, 2005) |
| NCLX | 20 — 40 μM | Bacteria (Besserer et al., 2012) |
| IF1+CaM | 5 μM | Cardiac myocytes (Saucerman and Bers, 2012) |
| DRP1 + Calcineurin | 1 μM | Brain cells (Klee et al., 1979) DRP1 dependent on calcineurin (Lai et al., 2023) |
Half-activation Ca2+ concentration of calcium regulatory proteins.
*All values are mean or approximate.
Finally, the interaction of the inhibitory transmitter GABA with the ionotropic GABAA or metabotropic GABAB receptors conducts Cl– anions into the cytosol or removes K+ from it via GIRK, thereby hyperpolarizing the membrane without creating an influx of Ca2+. The only source of depot replenishment in this case remains the store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) mechanism via the plasma channel Orai and the associated depot Ca2+ sensor STIM. In this case, Ca2+ is immediately pumped into the depot by the SERCA pump located nearby, without entering the cytosol (see Basnayake et al., 2022). The absence of an increased Ca2+ and IP3 in the cytosol does not cause ion release from the depot, since RyR and IP3R remain closed. In this case, the ATP level remains at the basal level (“Basal ATP”).
The relationship between local postsynaptic Ca2+ concentrations and ATP production or delivery remains unclear, as no precise data is available in literature. Fink et al. (2017) reported that in skeletal muscle, Ca2+ levels above basal (up to 450 nM) effectively enhanced mitochondrial respiration. With further increases, ATP production slowed down, and after 10 μM, it began to decline. Similar or close values were obtained in mathematical modeling of mitochondrial respiration (Tarraf et al., 2021). In addition, Kushnireva et al. (2022) showed that mitochondrial clusters in the postsynaptic zone effectively regulate local Ca2+ levels and strictly limit their spreading along the dendritic axis to 3–5 μm. In this context, tight local control over Ca2+ not only modulates ATP production but also finely tunes mitochondrial dynamics.
Thus, the emergence of significant calcium gradients extending beyond the postsynaptic compartment is possible only with massive synaptic potentiation. Under resting conditions, [Ca2+]c levels in dendrites typically remain low (approximately 50–100 nM; Verma et al., 2022), and although backpropagating action potentials (bAPs) can evoke global calcium transients reaching 30–90 μM (Sterratt et al., 2012), these supraphysiological concentrations do not appear to affect mitochondrial mobility (Silva et al., 2021). In sharp contrast, local synaptic activation produces modest yet highly localized Ca2+ elevations often in the range from 100 to 200 nM (Gunter and Sheu, 2009) to only up to 10 μm inside dendritic spines during activation (Verma et al., 2022) which are sufficient to reduces the movement of dendritic MT and leads to the grouping of them at the base of the spines and even entry into them (Seager et al., 2020) by the EF-hand domains of the MT adaptor protein Miro, leading to uncoupling of motor proteins and promoting MT arrest near active synapses. Meanwhile, higher concentrations of Ca2+ can further disrupt MT-microtubule interactions. Thus, a concentration of 50 μM free Ca2+ has been shown to cause a 50% reduction in MT binding to microtubules (Wang and Schwarz, 2009). Consequently, mitochondria undock from microtubules and move directly to local Ca2+ spike areas (Figure 4A; Sheng, 2014; Alberti et al., 2022; Zaninello and Bean, 2023), triggered, for example, by NMDAR activity (Duarte et al., 2023; Kuijpers et al., 2024).
Moreover, pathological conditions associated with Ca2+ dysregulation can profoundly disturb mitochondrial transport. In particular, mutations in presenilin-encoding genes—which underlie many familial Alzheimer’s disease cases—result in aberrant Ca2+ release from ER, initiating their physiological imbalance (Sarasija et al., 2018)
These dysfunctional dynamics are believed to disrupt synaptic homeostasis and have been linked not only to Alzheimer’s disease but also to other neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (Sheng and Cai, 2012; Zaninello and Bean, 2023), in which imbalances in Ca2+ homeostasis exacerbate synaptic dysfunction and neuronal loss.
Thus, while modest local Ca2+ elevations (in the range of 100–200 nM) appear to fine-tune mitochondrial positioning for optimal ATP delivery at synaptic sites, excessive Ca2+—whether due to intense synaptic activity or pathological mutations—can instead derail mitochondrial trafficking, thereby contributing to neurodegenerative disease cascades.
In fact, mitochondria are not the only source of ATP in neurons, including their postsynaptic microdomains. It is well known that aerobic glycolysis can serve as an important, albeit secondary, energy pathway, especially in the soma and areas of increased metabolism. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that oxidizes glucose to pyruvate, generating ATP and NADH. Although glycolysis does not appear to be directly dependent on calcium concentration, this ion may act as an indicator of increased synaptic load (Díaz-García et al., 2021). Ca2+ may act as a trigger for increased glycolysis by activating pathways such as the Aralar/malate-aspartate shuttle, indirectly affecting mitochondrial function. In addition, increased intracellular calcium may act as a signal for activation of the glycolytic pathway. Thus, some G-protein coupled metabotropic receptors can activate PKC protein kinase via PLC-DAG-IP3 pathway with following release of Ca2+ from stores (Figure 7). In addition, some PKC isoforms are Ca2+-dependent. It has been established that in astrocytes, PKC regulates glycolysis by phosphorylation of the glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase (Horvat et al., 2021).
7 Calcium signaling within the mitochondria
7.1 Regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential by calcium ions
Ca2+ can permeate the mitochondrial matrix via the MCU, driven by its steep electrochemical gradient, and is regulated by the significant electric potential across the IMM (ΔΨmt ∼−150 mV) (Gu et al., 1994; Walters and Usachev, 2023). Early studies reported that during physiological [Ca2+]c signaling, [Ca2+]m uptake modulates the amplitude and duration of Ca2+ signals without significantly affecting ΔΨmt (Chalmers and McCarron, 2008). Depolarization of ΔΨmt is expected only if [Ca2+]c fluctuations are repetitive and sustained: during AP and backpropagation AP (bAP) (Stoler et al., 2022); no effect is anticipated during single [Ca2+]c transients triggered by calcium influx or release from intracellular stores (Chalmers and McCarron, 2008). However, the occurrence of transient depolarizations of ΔΨmt during cellular Ca2+ signaling may significantly depend on the cell type. For instance, in the study by Huang et al. (2004), distinct types of neurons and other cell types exhibited variations in ΔΨmt: the mean ΔΨmt of fibroblasts was approximately −112 ± 2 mV, while that of neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells was around −87 ± 2 mV. The mean ΔΨmt within different neuronal structures also varied: in primary cultured neurons, it ranged from −111 to −78 mV in cell somata and from −113 to −84 mV in axonal growth cones. Similarly, the mean ΔΨmt of differentiated PC12 line cells ranged from −121 to −89 mV in cell bodies and from −130 to −69 mV in growth cones (Huang et al., 2004). However, in neurons, ΔΨmt in general (Dayal et al., 2024) and specifically dendritic (Zheng et al., 2013) ΔΨmt, can reach higher values than those observed in the aforementioned cell types (∼−150 to −180 mV). Moreover, it has been shown that axonal MT exhibit significantly higher sensitivity to Ca2+ for the activation of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake compared to non-neuronal mitochondria (Ashrafi et al., 2020). A recent study demonstrated that APs induced by a series of synaptic stimuli elicit stronger [Ca2+]m responses in dendrites compared to those triggered by a series of current pulse injections (Stoler et al., 2022).
Detection of coincident synaptic inputs and enhanced mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake accelerates the rates of NADH production and consumption through the TCA cycle (see details below) and the electron transport chain, respectively, increasing ATP synthesis (Stoler et al., 2022). This positions mitochondria as finely tuned contributors to the processes of synaptic plasticity in neurons. Research on neurons shows that mitochondrial calcium uptake can be triggered by an increase in [Ca2+]c as small as 200–300 nM above basal levels ([Ca2+]c ≈ 50–100 nM; [Ca2+]m ≈ 100–200 nM at rest) (Gu et al., 1994; Pivovarova et al., 2002; Stanika et al., 2012; Hu et al., 2018; Walters and Usachev, 2023; Murphy and Eisner, 2024). The rate of Ca2+ efflux from MT is significantly lower than the rate of Ca2+ uptake (∼23 μM/s in neurons). However, [Ca2+]m typically does not exceed 1–5 μM in neurons, even after intense stimulation, due to the ability of incoming calcium to be buffered in the mitochondrial matrix by forming phosphate complexes (Walters and Usachev, 2023). Thus, MT Ca2+ transients typically lag and persist longer than cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+]c) spikes, whether induced or spontaneous (Lin et al., 2019; Kushnireva et al., 2022; Stoler et al., 2022). It has been suggested that the prolonged release of buffered calcium from MT may influence Ca2+ signaling during recovery periods following stimulation or spontaneous activity, effectively preserving a “historical record”of prior activity (Gellerich et al., 2010; Pivovarova and Andrews, 2010).
7.2 Calcium regulation of metabolic cycles
Fluxing into the mitochondrial matrix, Ca2+ can influence ATP synthase activity through two mechanisms: indirectly, via the Krebs cycle, and directly, by binding to the β-subunit of the ATP synthase F1 complex. Concerning Ca2+’s influence on the TCA/Krebs cycle, it is important to note that some of the dehydrogenases involved in the TCA cycle are Ca2+-dependent (Figure 8). For example, pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase exhibit Ca2+ sensitivity, with a Ca2+ half-activation concentration of approximately 0.8 μM (Walters and Usachev, 2023). Isocitrate dehydrogenase is also Ca2+-dependent; however, its Ca2+ half-activation concentration is significantly higher, at around 40 μM (Walters and Usachev, 2023). Elevated Ca2+ concentrations within the mitochondrial matrix stimulate the enzymatic activity of these dehydrogenases, leading to increased flux through the TCA cycle. During a single Krebs cycle, two molecules of CO2, three molecules of NADH, one molecule of FADH2, and one molecule of GTP are produced. Electrons supplied by NADH and FADH2 are both critical for driving the respiratory chain, which encompasses the key stages of oxidative phosphorylation responsible for ATP production. Enhanced NADH generation increases the supply of electrons to the respiratory chain, further supporting ATP synthesis during heightened neuronal activity.
FIGURE 8
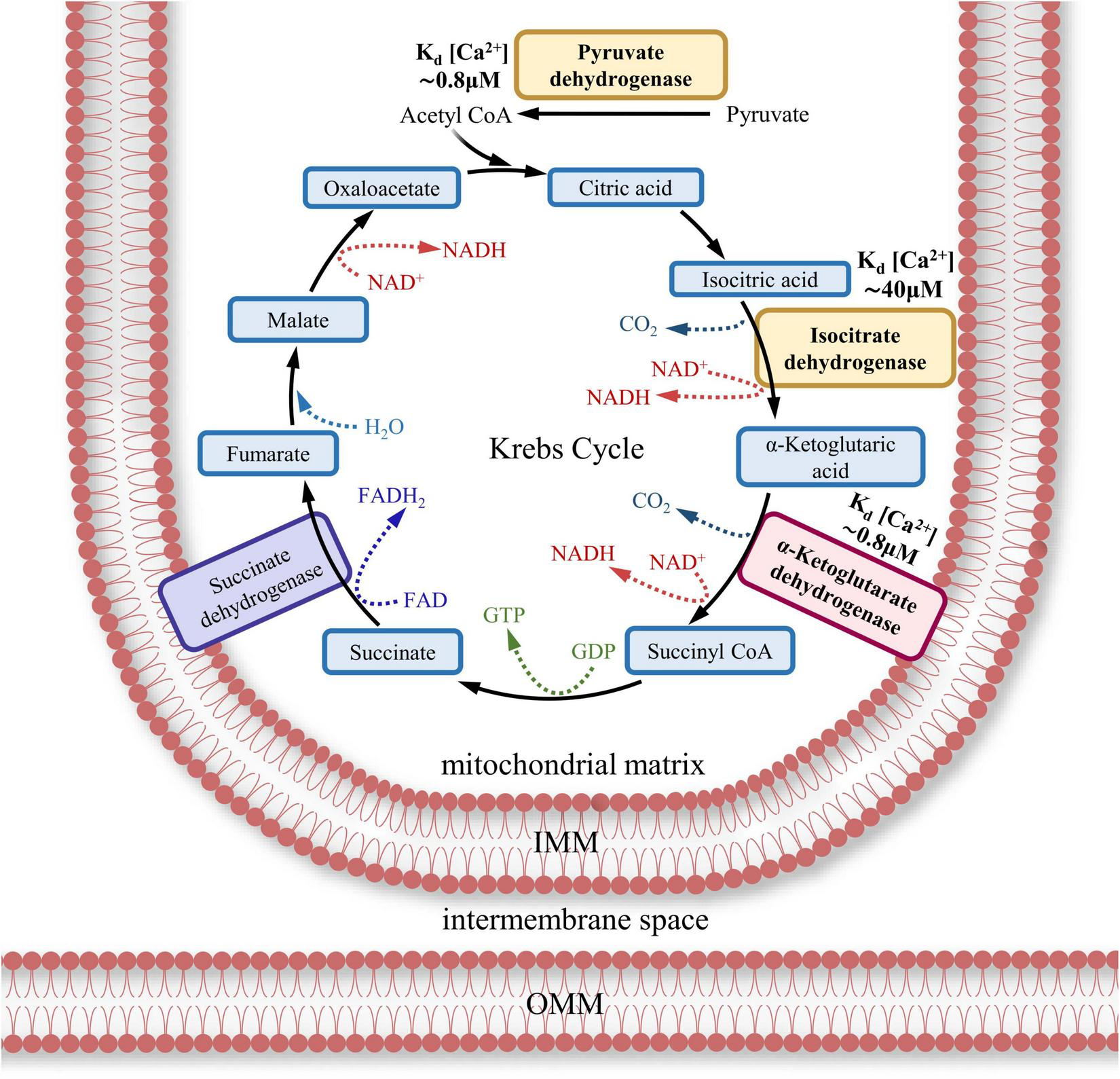
Ca2+-dependent dehydrogenases of the Krebs cycle (TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle). Three Ca2+-dependent dehydrogenases (bold font) of Krebs cycle are represented in the scheme. Half-activation concentration of Ca2+ for pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is approximately 0.8 μM and around 40 μM for isocitrate dehydrogenase (mentioned as Kd). α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is included in I complex of ETC.
The direct influence of Ca2+ on ATP synthase function and dynamics remains a subject of debate (Gellerich et al., 2010). It has been suggested that the ion binds to the β-subunit of the ATP synthase F1 complex directly (Hubbard and McHugh, 1996), inducing conformational changes in the entire ATP synthase (Territo et al., 2000; Nesci, 2022). An increase in [Ca2+]m caused by Ca2+ influx through the MCU leads to enhanced proton intake by accelerating the c-ring rotation. However, to date, there is no conclusive evidence for such direct interaction (Territo et al., 2000; Nesci et al., 2016; Wescott et al., 2019).
The highest activity of ATP synthase in eukaryotic cells is achieved when the Km for Ca2+ ranges from ∼200 nM (Territo et al., 2000) to ∼600 nM in the presence of ADP (Km ≈ 20 μM) (Wescott et al., 2019). Thus, it is arguable that the key condition for maintaining energetic balance in neuronal synaptic zones is the optimal concentration of [Ca2+]m and the efficient import of ADP from the cytosol into the mitochondrial matrix, coupled with the rapid export of ATP from the mitochondrial matrix into the cytosol (Klingenberg, 2008; Kawamata et al., 2010). The effect of Ca2+ might be attributed to the direct activation of the most widespread member of the IMM protein transporter family involved in metabolite exchange, Adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT), also known as the ADP/ATP carrier (AAC) (Territo et al., 2000; Kunji et al., 2016; Wescott et al., 2019). ANT utilizes the energy stored in ΔΨmt to exchange ADP for ATP through an antiport mechanism (Wescott et al., 2019). Its submolecular structure consists of three homologous domains. Each domain contains two transmembrane α-helices connected by a helical bridge. It is hypothesized that the transporter performs a cyclic half-turn in the horizontal plane, parallel to the IMM, in two opposite directions. During the first half-turn, captured ADP is transferred into the mitochondrial matrix, and during the next half-turn, the synthesized ATP is exported from the matrix to the cytosol. In other words, the transporter alternates between two states: one opens to the matrix and the other opens to the intermembrane space (Kunji et al., 2016; Ruprecht et al., 2019). Thus, ANT exports mitochondrial ATP through IMM in exchange for cytosolic ADP at a 1:1 ratio (Pfaff and Klingenberg, 1968; Klingenberg, 1980).
In brain tissue two ANT isoform are expressed: ANT1 is maintained at a high-expression level (Mentel et al., 2021; Mishra et al., 2023), while ANT4 has comparatively the low-expression one (Mishra et al., 2023). Except for ANT, phosphate carrier protein is also involved in ATP transport. It catalyzes phosphate ion (Pi) transport into mitochondrial matrix as a symporter (in collaboration with the proton) or as antiporter in exchange for hydroxyl ion. Without free access of nonorganic phosphate ATP synthesis is not possible. For another thing, there is evidence to suggest that Pi influences Ca2+ level in the mitochondria. Pi can not only stimulate Ca2+ influx (Zoccarato and Nicholls, 1982) by MCU but inhibit Ca2+ efflux to enhance [Ca2+]m (Seifert et al., 2015). Another significant transporter is ATP-Mg2+/Pi carrier (short calcium-binding mitochondrial carriers (SCaMC), that is also Ca2+-dependent transporter having EF-hand structure in its compound to bind the Ca2+ (Mentel et al., 2021; Mishra et al., 2023). Thus, except for ADP and Pi availability in mitochondrial matrix, Ca2+ affects ATP synthesis (Wescott et al., 2019).
The function of ANT can be modulated by cardiolipin, a lipid also detected in neurons (Bradshaw et al., 2024). It is proposed that cardiolipin binds ANT monomers within a dimeric structure, thereby regulating ANT’s role as an ATP/ADP carrier (Paradies et al., 2014). However, this hypothesis remains unsupported (Paradies et al., 2009), as several studies describe cardiolipin as a Ca2+-dependent molecule, whose interaction with ANT may be unstable under certain conditions (Hwang et al., 2014; Miranda et al., 2020). Evidence also suggests that ANT is a Ca2+-sensitive carrier, and its function may be influenced by mitochondrial proteins such as cyclophilin D (CyD) (Calì et al., 2012; Bernardi et al., 2022).
7.3 Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
Oxidation of cardiolipin affected by Ca2+ can impair ANT’s ATP/ADP exchange function, potentially triggering the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) (Paradies et al., 2011, 2014; Miranda et al., 2020; Bradshaw et al., 2024). The opening of mPTP alters the permeability of the mitochondrial membrane (Karch et al., 2019; Figure 9).
FIGURE 9
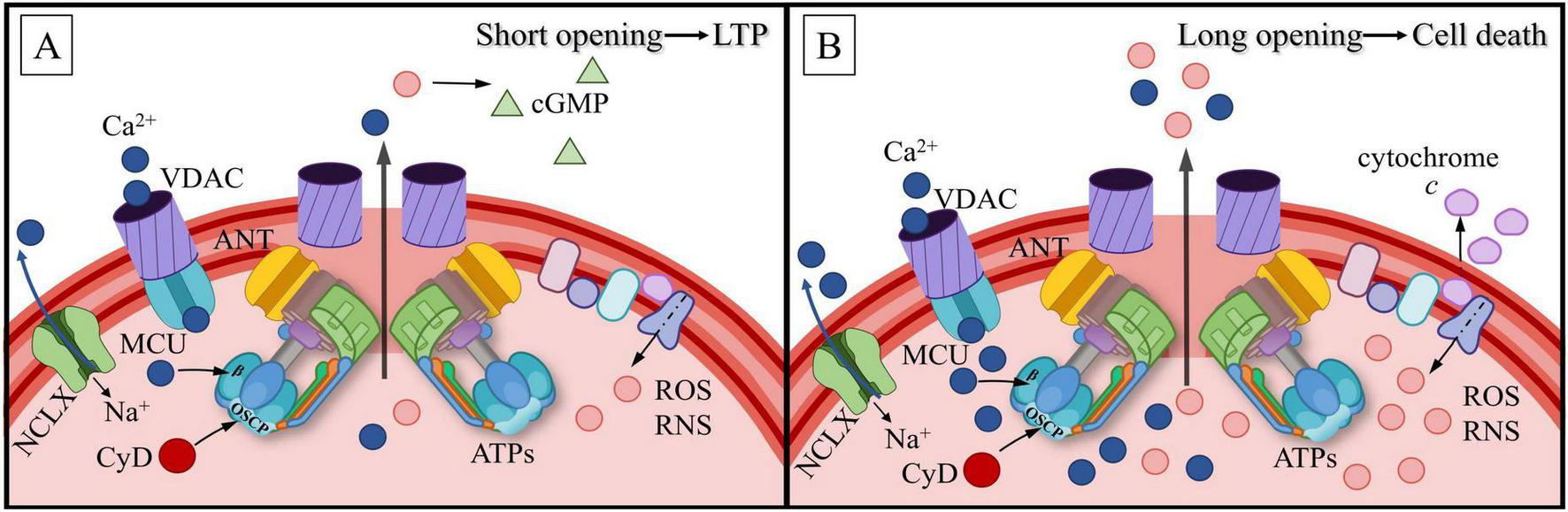
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) structure in physiolodical (A) and pathological (B) conditions. The mPTP is formed by voltage-dependent anion channels (VDAC) on the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT) together with the ATP synthase c-ring on the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). Ca2+ enters the mitochondrial matrix via VDAC and the mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU). Once inside, Ca2+ with cyclophilin D (CyD) modulate the permeability of ANT and ATP synthase. Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCLX) plays a key role in Ca2+ maintenance within mitochondrial matrix. (A) Physiological condition where short openings of the mPTP allow a low-level leak of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). This modest release activates cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) signaling, which contributes to long-term potentiation (LTP). (B) Pathological condition associated with prolonged mPTP opening and high [Ca2+]m levels. In this state, a substantial leak of ROS and RNS occurs, leading to cytochrome c release and cell death.
mPTP opening results in the leakage of Ca2+ from mitochondria (Kinnally et al., 2011; Kaufman and Malhotra, 2014; De Marchi et al., 2014). The role of mPTP remains controversial: while calcium release under physiological conditions primarily occurs via the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, mPTP is thought to play a crucial role in maintaining physiological levels of [Ca2+]m, without necessarily leading to mitochondrial dysfunction. Many studies link mPTP opening to mitochondrial damage and cell death, suggesting that mPTP activation occurs when [Ca2+]m approaches toxic levels. This can cause mitochondrial depolarization and a reduction in ATP production. However, other research highlights the reversibility of [Ca2+]m accumulation and mitochondrial swelling (Pivovarova and Andrews, 2010). Some researchers suggest that mPTP may consist of several components, including ANT (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020b; Bradshaw et al., 2024), the c-ring of ATP synthase dimers (Bernardi et al., 2022), and VDAC (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020b). Others propose that mPTP primarily comprises ANT and ATP synthase monomers (Bernardi et al., 2022). The following molecular chain has been proposed: CyD binds to OSCP (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020a), which accelerates the dissociation of ATP synthase dimers (Bernardi et al., 2022) and contributes to the structural disintegration of ATP synthase (Murphy, 2022; Endlicher et al., 2023). These changes facilitate the formation of mPTP.
The physiological effects of mPTP are as follows: Ca2+ entering the mitochondrial matrix triggers transient mPTP opening, leading to short-term IMM depolarization (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020a) and cristae remodeling (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020b; Bonora et al., 2022). The specific mechanisms underlying depolarization remain unclear. In the open state, the pore diameter is approximately 2–4 nm (Novgorodov and Gudz, 1996; Mironova and Pavlov, 2021). Prolonged mPTP opening, however, results in mitochondrial potential dissipation, ionic imbalance, and ROS generation (Lippe et al., 2019; Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020a). Moreover, the ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) produced in this context do not only contribute to oxidative stress; when generated at sub-toxic levels, as observed beneath the base of dendritic spines or near spineless synapses on the dendritic shaft, they may diffuse across the plasma membrane and stimulate guanylate cyclase or cGMP-dependent protein kinase. This signaling feedback can modulate neurotransmitter release and postsynaptic potentiation (Hidalgo et al., 2007; Massaad and Klann, 2011; Beckhauser et al., 2016), with physiologically relevant [H2O2] typically exceeding 1 μM (Hidalgo et al., 2007). It is hypothesized that mPTP’s physiological role is maintained as long as [Ca2+]m does not exceed 10–40 μM, beyond which ATP production is inhibited (Fink et al., 2017). In this state, the Krebs cycle dehydrogenases are activated. The molecular cascade involves Ca2+ binding to β-subunits, inducing conformational changes in the ATP synthase stalks and the c-ring of the F0 complex (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020a). Prolonged conformational alterations in the c-ring transform it into a nonselective channel, ultimately leading to dissociation of the ATP synthase F1-F0 complex, OMM disruption, and cytochrome c release (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020a).
As mentioned, the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) system consists of an electron transport chain and ATPs. In addition to ATP synthesis, OXPHOS generates ROS. This occurs due to proton leakage with the formation of a superoxide radical as a by-product, which is then transformed into H2O2. It is known that ROS act as an important second messengers, but when OXPHOS function is disrupted, ROS hyperproduction takes on dangerous forms, leading to oxidative stress. Among the OXPHOS regulators, IF1 attracts special attention. Its activity is manifested in MT damage and energy metabolism imbalance. In neurons IF1 acts by inhibiting the hydrolase and synthetic activity of ATPase, shifting energy metabolism towards glycolysis (Formentini et al., 2014). It may be assumed that such shift may occur during local energy deficiency, associated with elevated synaptic activity or with adjacent mitochondrial dysfunctions. The role of IF1 in ROS overload is still debated (Gore et al., 2022).
It is possible that mPTP formation can lead to wide spectrum of pathologies development to ATP synthase dysfunction initiating a number of neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease (Coluccino et al., 2023; Baev et al., 2024), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and more rarely Huntington’s disease, Wilson’s disease and Friedreich’s ataxia (Galber et al., 2021). In all the listed diseases, there is a disruption in ATP synthesis, which can lead to the death of energy-dependent neurons (Calì et al., 2012). There is evidence to suggest that OSCP synthesis is reduced in young and old brains in some animal models of Alzheimer’s disease as well as in old brains without any disorders (Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020b). The cellular mechanisms that inhibit Ca2+ binding to the ATP synthase β-subunit are demonstrated during the progress of the early stages of neurodegeneration (Calì et al., 2012; Pchitskaya et al., 2018; Mnatsakanyan and Jonas, 2020a; Verma et al., 2022).
8 Conclusion
Generalization and analysis of a large body of data related to mitochondrial mechanisms in neurons allow us to make several preliminary conclusions with respect to the high kinetics of energy-intensive processes in synaptic zones associated with neurotransmitter secretion and postsynaptic mechanisms, including the receptor’s balance, its modulation and plasticity. It is remarkable that all the events occur with high speeds in the millisecond range and within an extremely limited volume of a fraction of μm3. These factors make calcium ions an ideal agent in signaling transmission, accounting for their high mobility and the difficulty of their regulation by intracellular storage compartments, including the SA (probably a local Ca2+-store in the necks of dendritic spines) and thin ER branches. Furthermore, cytosolic calcium is essentially a detector of synaptic activity and synaptic strength due to its influx through NMDAR and other specific channels. In the cytosol, Ca2+ are buffered by numerous endogenous sensors including calmodulin. The ions are also captured by storage through the SERCA pump and removed from neurons by different ionic pumps and transporters. Considering all the above-mentioned, it is not surprising that the mitochondria located near synaptic zones, or even directly within them, utilize calcium ions in different ways, but primarily as universal, high precision, fast, local, and functional regulators of ATP production.
In the present review, the potential mechanism of Ca2+ interaction with postsynaptic mitochondria in the context of the ion’s dynamics and its influence on ATP production was described. A few brief conclusions should be drawn:
-
(1)
Neuronal mitochondria can be relocated from the soma to distal parts of the cell. Their functioning requires a high level of self-sufficiency and rapid reactions to energy requests. Synaptic mitochondria experience considerable functional load. This is why mitochondria requires a reliable detector for the activation of local ATP production.
-
(2)
In dendrites, mitochondria form spatially fixed clusters. Mitochondrial distribution depends on local dendritic Ca2+ spikes; in other words, the distribution occurs in the dendritic compartments associated with a specific synapse. Because of the energetic requirement for local plasticity, dendrites need new mitochondria to be attracted, as well as the removal of dysfunctional ones by mitophagy.
-
(3)
It is hypothesized that ATP synthase distribution and activity depend on postsynaptic Ca2+-transients. ATP synthase monomers form dimer or tetramer complexes, which arrange into linear rows forming a helical structure on cristae. This arrangement suggests the possibility of varying ATP synthase concentrations in specific mitochondrial cluster zones.
-
(4)
There are some, albeit currently insufficient, grounds to believe that locally occurring Ca2+ gradients stimulate not only local but also direct ATP synthesis required for activation maintenance in the postsynaptic area (more frequently, this is a dendritic spine).
-
(5)
Entering the mitochondrial matrix through VDAC and MCU, Ca2+ could modulate ATP synthase activity. For instance, the ions’ indirect influence may occur through the Krebs cycle dehydrogenases, while their direct influence could occur through ATP synthase binding to the F1 complex β-subunit. ATP secretion into the cytosol via the ATP/ADP carrier also shows evidence of Ca2+-dependence.
Direct measurements of ATP levels and calcium regulation of synthesis in MTs remain a challenging experimental task. The limitations arise from several factors. First, mitochondrial events typically occur in extremely small volumes, complicating any direct measurements. Second, the inner membrane of intact MTs is an insurmountable barrier for many water-soluble markers. Third, proteins such as genetically encoded calcium probes are sources of experimental artifacts during measurement. Fourth, neurons exhibit millisecond dynamics of electrical and ionic fluctuations, which requires high-speed detection, while it is difficult to combine high imaging resolution and high speed. Finally, physiological ATP levels are maintained at 1–5 mM, making it extremely difficult to measure local fluctuations of these molecules, which probably do not exceed a few percent of the baseline level. A good way out may be mathematical modeling, which does not suffer from the listed limitations. However, there has been little progress in this area so far.
Thus, the model by Pokhilko et al. (2006), describes the rapid kinetics of calcium infusion into mitochondria. The model shows that at concentrations below 140 nM, all available Ca2+ ions are accumulated in the matrix without permeability transition pore activation, while levels above 140 nM promote periodic or continuous pore opening and system oscillations (see Figure 9). The model by Tarraf et al. (2021) predicts the rate of ATP generation in accordance with homeostatic needs. One of the important factors through which calcium may affect ATP levels is the kinetics of the uniporter. The model proposed by Dash et al. (2009) describes the kinetics of Ca2+ transport through the uniporter at different ΔΨ and ion concentrations. Despite the apparent attractiveness, the large number of partly uncertain parameters limit the mathematical modeling of mitochondrial dynamics in the postsynaptic area.
Many mechanisms described in our review remain hypothetical, unproven and require further experimental verification. Thus, possible uneven distribution of ATPs, MCU and ANT in postsynaptic mitochondria requires the use of super-resolution or expansion microscopy, since conventional confocal imaging does not provide sufficient resolution. Crispr/Cas methods, the use of transgenic animals and plasmids carrying mutant genes can indicate whether the lack/malfunction of a set of key proteins, such as PSEN1/2, MCU, RyR/IP3R will affect ATP production. Functional dynamic experiments (electrophysiology, live imaging, glutamate uncaging) along with stimulation or suppression of local synaptic activity can best link synapse function with ATP production. An adequate correlate could be the measurement of mitochondrial potential (using tetramethylrhodamine, TMRM) or intraorganellar calcium (e.g., MT-linked CaMPs). Still, the most effective indication seems to be the direct measurement of ATP postsynaptic fluctuations using recently developed genetically encoded ATP sensors.
In conclusion, the hypothetical nature of some of our suppositions should be emphasized, and new experimental evidence is required to test these assumptions. Future research focusing on the intricacies of ATP synthase distribution, local calcium gradients, and their influence on mitochondrial processes in the postsynaptic zone could unveil new horizons in understanding the mechanisms of neuronal plasticity and energy regulation. Such knowledge will contribute to a deeper comprehension of the foundations of cognitive processes and the development of therapeutic approaches to neurodegenerative diseases.
Statements
Author contributions
TF: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LK: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EK: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
| AAC | ADP/ATP carrier |
| ADP | Adenosine diphosphate |
| AMPAR | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors |
| ANT | Adenine nucleotide translocator |
| AP | Action potential |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| ATPs | ATP synthase |
| CaM | Calmodulin |
| CaMKII | Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| CICR | Calcium-induced calcium release |
| CRT | Calreticulin |
| CS | central stalk of ATP synthase |
| CyD | Cyclophilin D |
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| DJ-1 | Deglycase |
| Drp1 | GTPase Dynamin-1-like protein |
| eATPase | Ectopic ATPase |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ETC | Electron-transport chain |
| IF1 | ATPase Inhibitory Factor 1 |
| IMF | Intermyofibrillar |
| IMM | Inner mitochondrial membrane |
| IP3R | Inositol trisphosphate receptor |
| IP3 | Inositol trisphosphate |
| GABABRs | Gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor |
| GIRK | G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels |
| Grp75 | Protein glucose-regulated protein 75 |
| GTP | Guanosine triphosphatases |
| KIF5B | Kinesin family member 5B |
| LTD | Long-term depression |
| LTP | Long-term potentiation |
| MACP | Mitochondrial anion carrier proteins |
| MAM | Mitochondria-associated membranes of ER |
| MCU | Mitochondrial calcium uniporter |
| Mfn | Mitofusin |
| mPTP | Mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| Miro 1/2 | Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1/2 |
| MT | Mitochondria |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| OSCP | Oligomycin-sensitivity conferring protein |
| OMM | Outer mitochondrial membrane |
| OPA1 | Dynamin-like GTPase Optic Atrophy 1 |
| OXPHOS | Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation |
| PINK | PTEN-induced kinase 1 |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PS | Peripheral stalk of ATP synthase |
| PSEN1/2 | Presenilins 1/2 |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RyR | Ryanodine receptor |
| SA | Spine apparatus |
| SCaMC | Short calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier |
| SERCA | Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase |
| SSM | Subsarcolemmal |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic acid |
| TRAK | Trafficking kinesin protein |
| UCP4 | Uncoupling protein |
| VDAC | Voltage-dependent anion channel |
| VGCC | Voltage-gated calcium channels |
| VGSC | Voltage-gated sodium channels |
| ΔΨmt | Mitochondrial membrane potential |
| [Ca2+]c | Cytosolic calcium concentration |
| [Ca2+]m | Mitochondrial calcium concentration |
| σ1R | Sigma-1 receptor |
References
1
Abbas Y. M. Wu D. Bueler S. A. Robinson C. V. Rubinstein J. L. (2020). Structure of V-ATPase from the mammalian brain.Science3671240–1246. 10.1126/science.aaz2924
2
Acehan D. Malhotra A. Xu Y. Ren M. Stokes D. L. Schlame M. (2011). Cardiolipin affects the supramolecular organization of ATP synthase in mitochondria.Biophys. J.1002184–2192. 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.03.031
3
Alberti P. Semperboni S. Cavaletti G. Scuteri A. (2022). Neurons: The interplay between cytoskeleton, ion channels/transporters and mitochondria.Cells11:2499. 10.3390/cells11162499
4
Arellano J. I. Benavides-Piccione R. DeFelipe J. Yuste R. (2007). Ultrastructure of dendritic spines: Correlation between synaptic and spine morphologies.Front. Neurosci.1:131–143. 10.3389/neuro.01.1.1.010.2007
5
Ashhad S. Narayanan R. (2013). Quantitative interactions between the A-type K+ current and inositol trisphosphate receptors regulate intraneuronal Ca2+ waves and synaptic plasticity.J. Physiol.5911645–1669. 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.245688
6
Ashrafi G. de Juan-Sanz J. Farrell R. J. Ryan T. A. (2020). Molecular tuning of the axonal mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter ensures metabolic flexibility of neurotransmission.Neuron10678–687. 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.020
7
Baev A. Y. Vinokurov A. Y. Potapova E. V. Dunaev A. V. Angelova P. R. Abramov A. Y. (2024). Mitochondrial permeability transition, cell death and neurodegeneration.Cells13:648. 10.3390/cells13070648
8
Bagaria J. Bagyinszky E. An S. S. A. (2022). Genetics, functions, and clinical impact of Presenilin-1 (PSEN1) gene.Int. J. Mol. Sci.23:10970. 10.3390/ijms231810970
9
Balderas E. Lee S. H. Rai N. K. Mollinedo D. M. Duron H. E. Chaudhuri D. (2024). Mitochondrial calcium regulation of cardiac metabolism in health and disease.Physiology39247–268. 10.1152/physiol.00014.2024
10
Bapat O. Purimetla T. Kruessel S. Shah M. Fan R. Thum C. et al (2024). VAP spatially stabilizes dendritic mitochondria to locally support synaptic plasticity.Nat. Commun.15:205. 10.1038/s41467-023-44233-8
11
Barazzuol L. Giamogante F. Calì T. (2021). Mitochondria associated membranes (MAMs): Architecture and physiopathological role.Cell Calcium94:102343. 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102343
12
Basnayake K. Mazaud D. Bemelmans A. Rouach N. Korkotian E. Holcman D. (2022). Fast calcium transients in dendritic spines driven by extreme statistics.PLoS Biol.20:e2006202. 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006202
13
Basnayake K. Mazaud D. Kushnireva L. Bemelmans A. Rouach N. Korkotian E. et al (2021). Nanoscale molecular architecture controls calcium diffusion and ER replenishment in dendritic spines.Sci. Adv.7:abh1376. 10.1126/sciadv.abh1376
14
Beard E. Lengacher S. Dias S. Magistretti P. J. Finsterwald C. (2022). Astrocytes as key regulators of brain energy metabolism: New therapeutic perspectives.Front. Physiol.12:825816. 10.3389/fphys.2021.825816
15
Beckhauser T. F. Francis-Oliveira J. De Pasquale R. (2016). Reactive oxygen species: Physiological and physiopathological effects on synaptic plasticity: Supplementary issue: Brain plasticity and repair.J. Exp. Neurosci.1023–48. 10.4137/JEN.S39887
16
Bereiter-Hahn J. Jendrach M. (2010). Mitochondrial dynamics.Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol.2841–65. 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)84001-8
17
Bergami M. Motori E. (2020). Reweaving the fabric of mitochondrial contact sites in astrocytes.Front. Cell Dev. Biol.8:592651. 10.3389/fcell.2020.592651
18
Bernardi P. Carraro M. Lippe G. (2022). The mitochondrial permeability transition: Recent progress and open questions.FEBS J.2897051–7074. 10.1111/febs.16254
19
Besserer G. M. Nicoll D. A. Abramson J. Philipson K. D. (2012). Characterization and purification of a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger from an archaebacterium.J. Biol. Chem.2878652–8659. 10.1074/jbc.M111.331280
20
Bonora M. Giorgi C. Pinton P. (2022). Molecular mechanisms and consequences of mitochondrial permeability transition.Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.23266–285. 10.1038/s41580-021-00433-y
21
Bonora M. Patergnani S. Rimessi A. De Marchi E. Suski J. M. Bononi A. et al (2012). ATP synthesis and storage.Purinergic Signal.8343–357. 10.1007/s11302-012-9305-8
22
Bonvento G. Bolaños J. P. (2021). Astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation shapes brain activity.Cell Metab.331546–1564. 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.07.006
23
Borbolis F. Ploumi C. Palikaras K. (2025). Calcium-mediated regulation of mitophagy: Implications in neurodegenerative diseases.NPJ Metab. Health Dis.3:4. 10.1038/s44324-025-00049-2
24
Bosch M. Hayashi Y. (2012). Structural plasticity of dendritic spines.Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.22383–388. 10.1016/j.conb.2011.09.002
25
Boué-Grabot E. Pankratov Y. (2017). Modulation of central synapses by astrocyte-released ATP and postsynaptic P2X receptors.Neural Plast.2017:9454275. 10.1155/2017/9454275
26
Bourne J. N. Harris K. M. (2008). Balancing structure and function at hippocampal dendritic spines.Ann. Rev. Neurosci.3147–67. 10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125646
27
Boyman L. Karbowski M. Lederer W. J. (2020). Regulation of mitochondrial ATP production: Ca2+ signaling and quality control.Trends Mol. Med.2621–39. 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.10.007
28
Boyman L. Williams G. S. Khananshvili D. Sekler I. Lederer W. J. (2013). NCLX: The mitochondrial sodium calcium exchanger.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.59205–213. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.03.012
29
Bradshaw P. C. Aldridge J. L. Jamerson L. E. McNeal C. Pearson A. C. Frasier C. R. (2024). The role of cardiolipin in brain bioenergetics, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration.Mol. Neurobiol.627022–7040. 10.1007/s12035-024-04630-6
30
Brantová O. Tesařová M. Hansíková H. Elleder M. Zeman J. Sládková J. (2006). Ultrastructural changes of mitochondria in the cultivated skin fibroblasts of patients with point mutations in mitochondrial DNA.Ultrastructural Pathol.30239–245. 10.1080/01913120600820112
31
Bucher M. Fanutza T. Mikhaylova M. (2020). Cytoskeletal makeup of the synapse: Shaft versus spine.Cytoskeleton7755–64. 10.1002/cm.21583
32
Cai Q. Sheng Z. H. (2009a). Mitochondrial transport and docking in axons.Exp. Neurol.218257–267. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.03.024
33
Cai Q. Sheng Z. H. (2009b). Moving or stopping mitochondria: Miro as a traffic cop by sensing calcium.Neuron61493–496. 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.02.003
34
Calì T. Ottolini D. Brini M. (2012). Mitochondrial Ca2+ and neurodegeneration.Cell Calcium5273–85. 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.04.015
35
Campanella M. Parker N. Tan C. H. Hall A. M. Duchen M. R. (2009). IF1: Setting the pace of the F1Fo-ATP synthase.Trends Biochem. Sci.34343–350. 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.03.006
36
Chalifoux J. R. Carter A. G. (2011). GABAB receptor modulation of voltage-sensitive calcium channels in spines and dendrites.J. Neurosci.314221–4232. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4561-10.2011
37
Chalmers S. McCarron J. G. (2008). The mitochondrial membrane potential and Ca2+ oscillations in smooth muscle.J. Cell Sci.12175–85. 10.1242/jcs.014522
38
Chang D. T. Honick A. S. Reynolds I. J. (2006). Mitochondrial trafficking to synapses in cultured primary cortical neurons.J. Neurosci.267035–7045. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1012-06.2006
39
Chang Y. W. Tony Yang T. Chen M. C. Liaw Y. G. Yin C. F. Lin-Yan X. Q. et al (2023). Spatial and temporal dynamics of ATP synthase from mitochondria toward the cell surface.Commun. Biol.6:427. 10.1038/s42003-023-04785-3
40
Chih C. P. Roberts E. L. Jr. (2003). Energy substrates for neurons during neural activity: A critical review of the astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle hypothesis.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.231263–1281. 10.1097/01.WCB.0000081369.51727.6F
41
Chin M. Kaeser P. S. (2024). On the targeting of voltage-gated calcium channels to neurotransmitter release sites.Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.89:102931. 10.1016/j.conb.2024.102931
42
Colgan L. A. Yasuda R. (2014). Plasticity of dendritic spines: Subcompartmentalization of signaling.Ann. Rev. Physiol.76365–385. 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170400
43
Coluccino G. Muraca V. P. Corazza A. Lippe G. (2023). Cyclophilin D in mitochondrial dysfunction: A key player in neurodegeneration?Biomolecules13:1265. 10.3390/biom13081265
44
Cottrell J. R. Dubé G. R. Egles C. Liu G. (2000). Distribution, density, and clustering of functional glutamate receptors before and after synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons.J. Neurophysiol.841573–1587. 10.1152/jn.2000.84.3.1573
45
Crivelli S. M. Gaifullina A. Chatton J. Y. (2024). Exploring the role of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 4 in brain metabolism: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease.Front. Neurosci.18:1483708. 10.3389/fnins.2024.1483708
46
Dagda R. K. Cherra S. J. Kulich S. M. Tandon A. Park D. Chu C. T. (2009). Loss of PINK1 function promotes mitophagy through effects on oxidative stress and mitochondrial fission.J. Biol. Chem.28413843–13855. 10.1074/jbc.M808515200
47
Dahl G. (2015). ATP release through pannexon channels.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: biol. Sci.370:20140191. 10.1098/rstb.2014.0191
48
Dash R. K. Qi F. Beard D. A. (2009). A biophysically based mathematical model for the kinetics of mitochondrial calcium uniporter.Biophys. J.961318–1332. 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.11.005
49
Davies K. M. Anselmi C. Wittig I. Faraldo-Gómez J. D. Kühlbrandt W. (2012). Structure of the yeast F1Fo-ATP synthase dimer and its role in shaping the mitochondrial cristae.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.10913602–13607. 10.1073/pnas.1204593109
50
Davies K. M. Straussa M. Daum B. Kief J. H. Osiewaczc H. D. Rycovskad A. et al (2011). Macromolecular organization of ATP synthase and complex I in whole mitochondria.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.10814121–14126. 10.1073/pnas.1103621108
51
Dayal A. A. Parfenteva O. I. Wang H. Gebreselase B. A. Gyoeva F. K. Alieva I. B. et al (2024). Vimentin intermediate filaments maintain membrane potential of mitochondria in growing neurites.Biology13:995. 10.3390/biology13120995
52
De Marchi E. Bonora M. Giorgi C. Pinton P. (2014). The mitochondrial permeability transition pore is a dispensable element for mitochondrial calcium efflux.Cell Calcium561–13. 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.03.004
53
De Mario A. D’Angelo D. Zanotti G. Raffaello A. Mammucari C. (2023). The mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex–A play in five acts.Cell Calcium112:102720. 10.1016/j.ceca.2023.102720
54
Di Lisa F. Blank P. S. Colonna R. Gambassi G. Silverman H. S. Stern M. D. et al (1995). Mitochondrial membrane potential in single living adult rat cardiac myocytes exposed to anoxia or metabolic inhibition.J. Physiol.4861–13. 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020786
55
Díaz-García C. M. Meyer D. J. Nathwani N. Rahman M. Martínez-François J. R. Yellen G. (2021). The distinct roles of calcium in rapid control of neuronal glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle.eLife10:e64821. 10.7554/eLife.64821
56
Divakaruni S. S. Van Dyke A. M. Chandra R. LeGates T. A. Contreras M. Dharmasri P. A. et al (2018). Long-term potentiation requires a rapid burst of dendritic mitochondrial fission during induction.Neuron100860–875. 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.025
57
Domínguez-Zorita S. Romero-Carramiñana I. Cuezva J. M. Esparza-Moltó P. B. (2022). The ATPase inhibitory factor 1 is a tissue-specific physiological regulator of the structure and function of mitochondrial ATP synthase: A closer look into neuronal function.Front. Physiol.13:868820. 10.3389/fphys.2022.868820
58
Drabik K. Piecyk K. Wolny A. Szulc-Dąbrowska L. Dębska-Vielhaber G. Vielhaber S. et al (2021). Adaptation of mitochondrial network dynamics and velocity of mitochondrial movement to chronic stress present in fibroblasts derived from patients with sporadic form of Alzheimer’s disease.FASEB J.35:e21586. 10.1096/fj.202001978RR
59
Dromard Y. Arango-Lievano M. Fontanaud P. Tricaud N. Jeanneteau F. (2021). Dual imaging of dendritic spines and mitochondria in vivo reveals hotspots of plasticity and metabolic adaptation to stress.Neurobiol. Stress15:100402. 10.1016/j.ynstr.2021.100402
60
Drulis-Fajdasz D. Gizak A. Wojtowicz T. Wiśniewski J. R. Rakus D. (2018). Aging-associated changes in hippocampal glycogen metabolism in mice. Evidence for and against astrocyte-to-neuron lactate shuttle.Glia661481–1495. 10.1002/glia.23319
61
Duarte F. V. Ciampi D. Duarte C. B. (2023). Mitochondria as central hubs in synaptic modulation.Cell. Mol. Life Sci.80:173. 10.1007/s00018-023-04814-8
62
Eberhardt E. L. Ludlam A. V. Tan Z. Cianfrocco M. A. (2020). Miro: A molecular switch at the center of mitochondrial regulation.Protein Sci.291269–1284. 10.1002/pro.3839
63
Emery J. M. Ortiz R. M. (2021). Mitofusin 2: A link between mitochondrial function and substrate metabolism?Mitochondrion61125–137. 10.1016/j.mito.2021.09.003
64
Endlicher R. Drahota Z. Štefková K. Červinková Z. Kučera O. (2023). The mitochondrial permeability transition pore—Current knowledge of its structure, function, and regulation, and optimized methods for evaluating its functional state.Cells12:1273. 10.3390/cells12091273
65
Faitg J. Lacefield C. Davey T. White K. Laws R. Kosmidis S. et al (2021). 3D neuronal mitochondrial morphology in axons, dendrites, and somata of the aging mouse hippocampus.Cell Rep.36:109509. 10.1101/2021.02.26.433056
66
Feeney C. J. Pennefather P. S. Gyulkhandanyan A. V. (2003). A cuvette-based fluorometric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential measured in cultured astrocyte monolayers.J. Neurosci. Methods12513–25. 10.1016/S0165-0270(03)00027-X
67
Fink B. D. Bai F. Yu L. Sivitz W. I. (2017). Regulation of ATP production: Dependence on calcium concentration and respiratory state.Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiol.313C146–C153. 10.1152/ajpcell.00086.2017
68
Finocchietto P. V. Franco M. C. Holod S. Gonzalez A. S. Converso D. P. Arciuch V. G. A. et al (2009). Mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase: A masterpiece of metabolic adaptation, cell growth, transformation, and death.Exp. Biol. Med.2341020–1028. 10.3181/0902-MR-81
69
Formentini L. Pereira M. P. Sánchez-Cenizo L. Santacatterina F. Lucas J. J. Navarro C. et al (2014). In vivo inhibition of the mitochondrial H+-ATP synthase in neurons promotes metabolic preconditioning.EMBO J.33762–778. 10.1002/embj.201386392
70
Frasch W. D. Bukhari Z. A. Yanagisawa S. (2022). F1FO ATP synthase molecular motor mechanisms.Front. Microbiol.13:965620. 10.3389/fmicb.2022.965620
71
Frey T. G. Mannella C. A. (2000). The internal structure of mitochondria.Trends Biochem. Sci.25319–324. 10.1016/S0968-0004(00)01609-1
72
Fridlyand L. E. Tamarina N. Philipson L. H. (2003). Modeling of Ca2+ flux in pancreatic β-cells: Role of the plasma membrane and intracellular stores.Am. J. Physiology-Endocrinol. Metab.285E138–E154. 10.1152/ajpendo.00194.2002
73
Fujii Y. Maekawa S. Morita M. (2017). Astrocyte calcium waves propagate proximally by gap junction and distally by extracellular diffusion of ATP released from volume-regulated anion channels.Sci. Rep.7:13115. 10.1038/s41598-017-13243-0
74
Galber C. Carissimi S. Baracca A. Giorgio V. (2021). The ATP synthase deficiency in human diseases.Life11:325. 10.3390/life11040325
75
Garbincius J. F. Elrod J. W. (2022). Mitochondrial calcium exchange in physiology and disease.Physiol. Rev.102893–992. 10.1152/physrev.00041.2020
76
García-Bermúdez J. Cuezva J. M. (2016). The ATPase Inhibitory Factor 1 (IF1): A master regulator of energy metabolism and of cell survival.Biochim. Biophys. Acta18571167–1182. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.02.004
77
Garman R. H. (2011). Histology of the central nervous system.Toxicol. Pathol.3922–35. 10.1177/0192623310389621
78
Garthwaite J. (2008). Concepts of neural nitric oxide-mediated transmission.Eur. J. Neurosci.272783–2802. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06285.x
79
Gellerich F. N. Gizatullina Z. Trumbeckaite S. Nguyen H. P. Pallas T. Arandarcikaite O. et al (2010). The regulation of OXPHOS by extramitochondrial calcium.Biochim. Biophys. Acta17971018–1027. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.02.005
80
Gerencser A. A. Chinopoulos C. Birket M. J. Jastroch M. Vitelli C. Nicholls D. G. et al (2012). Quantitative measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential in cultured cells: Calcium-induced de-and hyperpolarization of neuronal mitochondria.J. Physiol.5902845–2871. 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.228387
81
Gerle C. (2020). Mitochondrial F-ATP synthase as the permeability transition pore.Pharmacol. Res.160:105081. 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105081
82
Gidon A. Segev I. (2012). Principles governing the operation of synaptic inhibition in dendrites.Neuron75330–341. 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.05.015
83
Giorgio V. Burchell V. Schiavone M. Bassot C. Minervini G. Petronilli V. et al (2017). Ca2+ binding to F-ATP synthase β subunit triggers the mitochondrial permeability transition.EMBO Rep.181065–1076. 10.15252/embr.201643354
84
Giovannoni F. Quintana F. J. (2020). The role of astrocytes in CNS inflammation.Trends Immunol.41805–819. 10.1016/j.it.2020.07.007
85
Glancy B. Balaban R. S. (2012). Role of mitochondrial Ca2+ in the regulation of cellular energetics.Biochemistry512959–2973. 10.1021/bi2018909
86
Glancy B. Kim Y. Katti P. Willingham T. B. (2020). The functional impact of mitochondrial structure across subcellular scales.Front. Physiol.11:541040. 10.3389/fphys.2020.541040
87
Godoy J. A. Rios J. A. Picón-Pagès P. Herrera-Fernández V. Swaby B. Crepin G. et al (2021). Mitostasis, calcium and free radicals in health, aging and neurodegeneration.Biomolecules11:1012. 10.3390/biom11071012
88
Goldstein S. Moerman E. J. Porter K. (1984). High-voltage electron microscopy of human diploid fibroblasts during ageing in vitro: Morphometric analysis of mitochondria.Exp. Cell Res.154101–111. 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90671-2
89
Gore E. Duparc T. Genoux A. Perret B. Najib S. Martinez L. O. (2022). The multifaceted ATPase inhibitory factor 1 (IF1) in energy metabolism reprogramming and mitochondrial dysfunction: A new player in age-associated disorders?Antioxidants Redox Signal.37370–393. 10.1089/ars.2021.0137
90
Graier W. F. Frieden M. Malli R. (2007). Mitochondria and Ca 2+ signaling: Old guests, new functions.Pflügers Archiv-Eur. J. Physiol.455375–396. 10.1007/s00424-007-0296-1
91
Green A. Hossain T. Eckmann D. M. (2022). Mitochondrial dynamics involves molecular and mechanical events in motility, fusion and fission.Front. Cell Dev. Biol.10:1010232. 10.3389/fcell.2022.1010232
92
Groten C. J. MacVicar B. A. (2022). Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake by the MCU facilitates pyramidal neuron excitability and metabolism during action potential firing.Commun. Biol.5:900. 10.1038/s42003-022-03848-1
93
Gu X. Olson E. C. Spitzer N. C. (1994). Spontaneous neuronal calcium spikes and waves during early differentiation.J. Neurosci.146325–6335. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06325.1994
94
Gunter T. E. Sheu S. S. (2009). Characteristics and possible functions of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport mechanisms.Biochim. Biophys. Acta17871291–1308. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.12.011
95
Gurm G. S. Danik S. B. Shoup T. M. Weise S. Takahashi K. Laferrier S. et al (2012). 4-[18F]-tetraphenylphosphonium as a PET tracer for myocardial mitochondrial membrane potential.JACC Cardiovas. Imag.5285–292. 10.1016/j.jcmg.2011.11.017
96
Hajnóczky G. Csordás G. Madesh M. Pacher P. (2000). The machinery of local Ca2+ signalling between sarco-endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.J. Physiol.52969–81. 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00069.x
97
Harris K. Kater S. B. (1994). Dendritic spines: Cellular specializations imparting both stability and flexibility to synaptic function.Ann. Rev. Neurosci.17341–371. 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002013
98
Hatefi Y. (1993). ATP synthesis in mitochondria.Eur. J. Biochem.218759–767. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18431.x
99
Hayashi T. Su T. P. (2007). Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca2+ signaling and cell survival.Cell131596–610. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036
100
Hayashi Y. Majewska A. K. (2005). Dendritic spine geometry: Functional implication and regulation.Neuron46529–532. 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.05.006
101
Herculano-Houzel S. (2014). The glia/neuron ratio: How it varies uniformly across brain structures and species and what that means for brain physiology and evolution.Glia621377–1391. 10.1002/glia.22683
102
Hering H. Sheng M. (2001). Dentritic spines: Structure, dynamics and regulation.Nat. Rev. Neurosci.2880–888. 10.1038/35104061
103
Hidalgo C. Carrasco M. A. Muñoz P. Núñez M. T. (2007). A role for reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and iron on neuronal synaptic plasticity.Antioxidants Redox Signal.9245–255. 10.1089/ars.2007.9.245
104
Higley M. J. Sabatini B. L. (2012). Calcium signaling in dendritic spines.Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.4:a005686. 10.1101/cshperspect.a005686
105
Hirokawa N. Takemura R. (2005). Molecular motors and mechanisms of directional transport in neurons.Nat. Rev. Neurosci.6201–214. 10.1038/nrn1624
106
Holcman D. Korkotian E. Segal M. (2005). Calcium dynamics in dendritic spines, modeling and experiments.Cell Calcium37467–475. 10.1016/j.ceca.2005.01.015
107
Holmuhamedov E. L. Oberlin A. Short K. Terzic A. Jahangir A. (2012). Cardiac subsarcolemmal and interfibrillar mitochondria display distinct responsiveness to protection by diazoxide.PLoS One7:e44667. 10.1371/journal.pone.0044667
108
Horvat A. Muhič M. Smolič T. Begić E. Zorec R. Kreft M. et al (2021). Ca2+ as the prime trigger of aerobic glycolysis in astrocytes.Cell Calcium95:102368. 10.1016/j.ceca.2021.102368
109
Hu E. Mergenthal A. Bingham C. S. Song D. Bouteiller J. M. Berger T. W. (2018). A glutamatergic spine model to enable multi-scale modeling of nonlinear calcium dynamics.Front. Comp. Neurosci.12:58. 10.3389/fncom.2018.00058
110
Huang C. S. Shi S. H. Ule J. Ruggiu M. Barker L. A. Darnell R. B. et al (2005). Common molecular pathways mediate long-term potentiation of synaptic excitation and slow synaptic inhibition.Cell123105–118. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.033
111
Huang H. M. Fowler C. Zhang H. Gibson G. E. (2004). Mitochondrial heterogeneity within and between different cell types.Neurochem. Res.29651–658. 10.1023/B:NERE.0000014835.34495.9c
112
Hubbard M. J. McHugh N. J. (1996). Mitochondrial ATP synthase F1-β-subunit is a calcium-binding protein.FEBS Lett.391323–329. 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00767-3
113
Hwang M. S. Schwall C. T. Pazarentzos E. Datler C. Alder N. N. Grimm S. (2014). Mitochondrial Ca2+ influx targets cardiolipin to disintegrate respiratory chain complex II for cell death induction.Cell Death Differ.211733–1745. 10.1038/cdd.2014.84
114
Ikon N. Ryan R. O. (2017). Cardiolipin and mitochondrial cristae organization.Biochim. Biophys. Acta18591156–1163. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.03.013
115
Illes P. Burnstock G. Tang Y. (2019). Astroglia-derived ATP modulates CNS neuronal circuits.Trends Neurosci.42885–898. 10.1016/j.tins.2019.09.006
116
Illes P. Rubini P. Ulrich H. Yin H. Y. Tang Y. (2025). Dysregulation of astrocytic ATP/Adenosine release in the hippocampus cause cognitive and affective disorders: Molecular mechanisms, diagnosis, and therapy.MedComm6:e70177. 10.1002/mco2.70177
117
Iqbal S. Hood D. A. (2014). Oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and movement in skeletal muscle myoblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 306, C1176–83. 10.1152/ajpcell.00017.2014
118
Jackson J. G. Robinson M. B. (2018). Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in astrocytes: Mechanisms, consequences, and unknowns.Glia661213–1234. 10.1002/glia.23252
119
Jackson J. G. O’Donnell J. C. Takano H. Coulter D. A. Robinson M. B. (2014). Neuronal activity and glutamate uptake decrease mitochondrial mobility in astrocytes and position mitochondria near glutamate transporters.J. Neurosci.341613–1624. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3510-13.2014
120
Jadi M. Polsky A. Schiller J. Mel B. W. (2012). Location-dependent effects of inhibition on local spiking in pyramidal neuron dendrites.PLoS Comp. Biol.8:e1002550. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002550
121
Jenkins J. E. Fazli M. Evans C. S. (2024). Mitochondrial motility modulators coordinate quality control dynamics to promote neuronal health.Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.89:102383. 10.1016/j.ceb.2024.102383
122
Ježek P. Jabůrek M. Holendová B. Engstová H. Dlasková A. (2023). Mitochondrial cristae morphology reflecting metabolism, superoxide formation, redox homeostasis, and pathology.Antioxidants Redox Signal.39635–683. 10.1089/ars.2022.0173
123
Johri A. Chandra A. (2021). Connection lost, MAM: Errors in ER–Mitochondria connections in neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Sci.11:1437. 10.3390/brainsci11111437
124
Jonas P. Bischofberger J. Fricker D. Miles R. (2004). Interneuron diversity series: Fast in, fast out – temporal and spatial signal processing in hippocampal interneurons.Trends Neurosci.230–40. 10.1016/j.tins.2003.10.010
125
Jonckheere A. I. Smeitink J. A. M. Rodenburg R. J. T. (2012). Mitochondrial ATP synthase: Architecture, function and pathology.J. Inherited Metab. Dis.35211–225. 10.1007/s10545-011-9382-9
126
Ju Y. K. Woodcock E. A. Allen D. G. Cannell M. B. (2012). Inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptors and pacemaker rhythms.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.53375–381. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.06.004
127
Kaim G. Dimroth P. (1999). ATP synthesis by F-type ATP synthase is obligatorily dependent on the transmembrane voltage.EMBO J.184118–4127. 10.1093/emboj/18.15.4118
128
Kandel E. R. (2021). “Synaptic integration in the central nervous system,” in Principles of neural science, 6th Edn, edsKandelE. R.KoesterJ. D.MackS. H.SiegelbaumS. A. (New York, NY: McGraw Hill / Medical), 273–300.
129
Kann O. (2016). The interneuron energy hypothesis: Implications for brain disease.Neurobiol. Dis.9075–85. 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.08.005
130
Kann O. Kovács R. (2007). Mitochondria and neuronal activity.Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiol.292C641–C657. 10.1152/ajpcell.00222.2006
131
Kann O. Papageorgiou I. E. Draguhn A. (2014). Highly energized inhibitory interneurons are a central element for information processing in cortical networks.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.341270–1282. 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.104
132
Kapitein L. C. Schlager M. A. Kuijpers M. Wulf P. S. van Spronsen M. MacKintosh F. C. et al (2010). Mixed microtubules steer dynein-driven cargo transport into dendrites.Curr. Biol.20290–299. 10.1016/j.cub.2009.12.052
133
Karch J. Bround M. J. Khalil H. Sargent M. A. Latchman N. Terada N. et al (2019). Inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition by deletion of the ANT family and CypD.Sci. Adv.5:eaaw4597. 10.1126/sciadv.aaw4597
134
Kassab S. Albalawi Z. Daghistani H. Kitmitto A. (2021). Mitochondrial arrest on the microtubule highway–a feature of heart failure and diabetic cardiomyopathy?Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8:689101. 10.3389/fcvm.2021.689101
135
Kaufman R. J. Malhotra J. D. (2014). Calcium trafficking integrates endoplasmic reticulum function with mitochondrial bioenergetics.Biochim. Biophys. Acta18432233–2239. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.03.022
136
Kawamata H. Starkov A. A. Manfredi G. Chinopoulos C. (2010). A kinetic assay of mitochondrial ADP–ATP exchange rate in permeabilized cells.Anal. Biochem.40752–57. 10.1016/j.ab.2010.07.031
137
Keller D. X. Franks K. M. Bartol T. M. Jr. Sejnowski T. J. (2008). Calmodulin activation by calcium transients in the postsynaptic density of dendritic spines.PLoS One3:e2045. 10.1371/journal.pone.0002045
138
Kim Y. Dube S. E. Park C. B. (2025). Brain energy homeostasis: The evolution of the astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle hypothesis.Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol.291–8. 10.4196/kjpp.24.388
139
Kinnally K. W. Peixoto P. M. Ryu S. Y. Dejean L. M. (2011). Is mPTP the gatekeeper for necrosis, apoptosis, or both?Biochim. Biophys. Acta1813616–622. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.013
140
Klee C. B. Crouch T. H. Krinks M. H. (1979). Calcineurin: A calcium-and calmodulin-binding protein of the nervous system.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.766270–6273. 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6270
141
Klingenberg M. (1980). The ADP-ATP translocation in mitochondria, a membrane potential controlled transport.J. Membrane Biol.5697–105. 10.1007/BF01875961
142
Klingenberg M. (2008). The ADP and ATP transport in mitochondria and its carrier.Biochim. Biophys. Acta17781978–2021. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.04.011
143
Klotzsch E. Smorodchenko A. Löfler L. Moldzio R. Parkinson E. Schütz G. J. et al (2015). Superresolution microscopy reveals spatial separation of UCP4 and F0F1-ATP synthase in neuronal mitochondria.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.112130–135. 10.1073/pnas.1415261112
144
Knott A. B. Bossy-Wetzel E. (2008). Impairing the mitochondrial fission and fusion balance: A new mechanism of neurodegeneration.Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.1147283–292. 10.1196/annals.1427.030
145
Koch C. Zador A. (1993). The function of dendritic spines: Devices subserving biochemical rather than electrical compartmentalization.J. Neurosci.13:413. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00413.1993
146
Kohlhaas M. Nickel A. G. Bergem S. Casadei B. Laufs U. Maack C. (2017). Endogenous nitric oxide formation in cardiac myocytes does not control respiration during β-adrenergic stimulation.J. Physiol.5953781–3798. 10.1113/JP273750
147
Korkotian E. Segal M. (2000). Structure-function relations in dendritic spines: Is size important?Hippocampus10587–595. 10.1002/1098-1063200010:5<587::AID-HIPO9<3.0.CO;2-C
148
Korkotian E. Segal M. (2006). Spatially confined diffusion of calcium in dendrites of hippocampal neurons revealed by flash photolysis of caged calcium.Cell Calcium40441–449. 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.08.008
149
Korkotian E. Segal M. (2007). Morphological constraints on calcium dependent glutamate receptor trafficking into individual dendritic spine.Cell Calcium4241–57. 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.11.006
150
Korkotian E. Meshcheriakova A. Segal M. (2019). Presenilin 1 regulates [Ca2+] i and mitochondria/ER interaction in cultured rat hippocampal neurons.Oxid. Med. Cell. Long.2019:7284967. 10.1155/2019/7284967
151
Kruppa A. J. Buss F. (2021). Motor proteins at the mitochondria–cytoskeleton interface.J. Cell Sci.134:jcs226084. 10.1242/jcs.226084
152
Kuijpers M. Nguyen P. T. Haucke V. (2024). The endoplasmic reticulum and its contacts: Emerging roles in axon development, neurotransmission, and degeneration.Neuroscientist30545–559. 10.1177/10738584231162810
153
Kunji E. R. Aleksandrova A. King M. S. Majd H. Ashton V. L. Cerson E. et al (2016). The transport mechanism of the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier.Biochim. Biophys. Acta18632379–2393. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.03.015
154
Kushnireva L. Korkotian E. (2022). “Mitochondria-Endoplasmic reticulum interaction in central neurons,” in Updates on endoplasmic reticulum, ed.FaveroG. (Brescia: IntechOpen).
155
Kushnireva L. Basnayake K. Holcman D. Segal M. Korkotian E. (2022). Dynamic regulation of mitochondrial [Ca2+] in hippocampal neurons.Int. J. Mol. Sci.23:12321. 10.3390/ijms232012321
156
Kuznetsov A. V. Hermann M. Saks V. Hengster P. Margreiter R. (2009). The cell-type specificity of mitochondrial dynamics.Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.411928–1939. 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.03.007
157
Lai Y. S. Chang C. C. Chen Y. Y. Nguyen T. M. H. Xu J. Chen Y. C. et al (2023). Optogenetically engineered Ca2+ oscillation-mediated DRP1 activation promotes mitochondrial fission and cell death.J. Cell Sci.136:jcs260819. 10.1242/jcs.260819
158
Laver D. R. (2007). Ca2+ stores regulate ryanodine receptor Ca2+ release channels via luminal and cytosolic Ca2+ sites.Biophys. J.923541–3555. 10.1529/biophysj.106.099028
159
Laver D. R. Curtis B. A. (1996). Response of ryanodine receptor channels to Ca2+ steps produced by rapid solution exchange.Biophys. J.71732–741. 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79272-X
160
Ledesma A. Lacoba M. G. D. Arechaga I. Rial E. (2002). Modeling the transmembrane arrangement of the uncoupling protein UCP1 and topological considerations of the nucleotide-binding site.J. Bioenerget. Biomembr.34473–486. 10.1186/gb-2002-3-12-reviews3015
161
Lee A. Hirabayashi Y. Kwon S. K. Lewis T. L. Jr. Polleux F. (2018). Emerging roles of mitochondria in synaptic transmission and neurodegeneration.Curr. Opin. Physiol.382–93. 10.1016/j.cophys.2018.03.009
162
Lee I. Bender E. Kadenbach B. (2002). Control of mitochondrial membrane potential and ROS formation by reversible phosphorylation of cytochrome c oxidase.Mol. Cell. Biochem.23463–70. 10.1023/A:1015921513720
163
Lees R. M. Johnson J. D. Ashby M. C. (2020). Presynaptic boutons that contain mitochondria are more stable.Front. Synap. Neurosci.11:37. 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00037
164
Lerdkrai C. Garaschuk O. (2018). Role of presynaptic calcium stores for neural network dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease.Neural Regenerat. Res.13977–978. 10.4103/1673-5374.233435
165
Letellier M. Goda Y. (2023). Astrocyte calcium signaling shifts the polarity of presynaptic plasticity.Neuroscience52538–46. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.05.032
166
Leung A. Ohadi D. Pekkurnaz G. Rangamani P. (2021). Systems modeling predicts that mitochondria ER contact sites regulate the postsynaptic energy landscape.NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl.7:26. 10.1038/s41540-021-00185-7
167
Leung L. S. Peloquin P. (2006). GABAB receptors inhibit backpropagating dendritic spikes in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells in vivo.Hippocampus16388–407. 10.1002/hipo.20168
168
Lewis T. L. Jr. Kwon S. K. Lee A. Shaw R. Polleux F. (2018). MFF-dependent mitochondrial fission regulates presynaptic release and axon branching by limiting axonal mitochondria size.Nat. Commun.9:5008. 10.1038/s41467-018-07416-2
169
Lezmy J. (2023). How astrocytic ATP shapes neuronal activity and brain circuits.Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.79:102685. 10.1016/j.conb.2023.102685
170
Li A. Shami G. J. Griffiths L. Lal S. Irving H. Braet F. (2023). Giant mitochondria in cardiomyocytes: Cellular architecture in health and disease.Basic Res. Cardiol.118:39. 10.1007/s00395-023-01011-3
171
Li Z. Okamoto K. I. Hayashi Y. Sheng M. (2004). The importance of dendritic mitochondria in the morphogenesis and plasticity of spines and synapses.Cell119873–887. 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.003
172
Ligon L. A. Steward O. (2000). Movement of mitochondria in the axons and dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons.J. Comp. Neurol.427340–350. 10.1002/1096-9861(20001120)427:3<340::AID-CNE2<3.0.CO;2-Y
173
Lin M. Y. Sheng Z. H. (2015). Regulation of mitochondrial transport in neurons.Exp. Cell Res.33435–44. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.01.004
174
Lin Y. Li L. L. Nie W. Liu X. Adler A. Xiao C. et al (2019). Brain activity regulates loose coupling between mitochondrial and cytosolic Ca2+ transients.Nat. Commun.10:5277. 10.1038/s41467-019-13142-0
175
Lippe G. Coluccino G. Zancani M. Baratta W. Crusiz P. (2019). Mitochondrial F-ATP synthase and its transition into an energy-dissipating molecular machine.Oxid. Med. Cell. Long.2019:8743257. 10.1155/2019/8743257
176
Liu Y. Shen X. Zhang Y. Zheng X. Cepeda C. Wang Y. S. et al (2023). Interactions of glial cells with neuronal synapses, from astrocytes to microglia and oligodendrocyte lineage cells.Glia711383–1401. 10.1002/glia.24343
177
López-Teros M. Alarcón-Aguilar A. Castillo-Aragón A. Königsberg M. Luna-López A. (2024). Cytokine profiling in senescent and reactive astrocytes: A systematic review.Neurobiol. Aging13828–35. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2024.02.012
178
MacAskill A. F. Atkin T. A. Kittler J. T. (2010). Mitochondrial trafficking and the provision of energy and calcium buffering at excitatory synapses.Eur. J. Neurosci.32231–240. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07345.x
179
MacAskill A. F. Rinholm J. E. Twelvetrees A. E. Arancibia-Carcamo I. L. Muir J. Fransson A. et al (2009). Miro1 is a calcium sensor for glutamate receptor-dependent localization of mitochondria at synapses.Neuron61541–555. 10.3389/10.1016/j.neuron.2009.01.030
180
Makarov M. Korkotian E. (2023). Differential role of active compounds in mitophagy and related neurodegenerative diseases.Toxins15:202. 10.3390/toxins15030202
181
Makarov M. Kushnireva L. Papa M. Korkotian E. (2023). Presenilins and mitochondria—An intriguing link: Mini-review.Front. Neurosci.17:1249815. 10.3389/fnins.2023.1249815
182
Markovinovic A. Greig J. Martín-Guerrero S. M. Salam S. Paillusson S. (2022). Endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria signaling in neurons and neurodegenerative diseases.J. Cell Sci.135:jcs24853. 10.1242/jcs.248534
183
Marlin J. J. Carter A. G. (2014). GABA-A receptor inhibition of local calcium signaling in spines and dendrites.J. Neurosci.3415898–15911. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0869-13.2014
184
Marty-Lombardi S. Lu S. Ambroziak W. Schrenk-Siemens K. Wang J. DePaoli-Roach A. A. et al (2024). Neuron–astrocyte metabolic coupling facilitates spinal plasticity and maintenance of inflammatory pain.Nat. Metab.6494–513. 10.1038/s42255-024-01001-2
185
Massaad C. A. Klann E. (2011). Reactive oxygen species in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and memory.Antioxid. Redox Signal.142013–2054. 10.1089/ars.2010.3208
186
Mathur A. Hong Y. Kemp B. K. Barrientos A. A. Erusalimsky J. D. (2000). Evaluation of fluorescent dyes for the detection of mitochondrial membrane potential changes in cultured cardiomyocytes.Cardiovas. Res.46126–138. 10.1016/S0008-6363(00)00002-X
187
McCarron J. G. Wilson C. Sandison M. E. Olson M. L. Girkin J. M. Saunter C. et al (2013). From structure to function: Mitochondrial morphology, motion and shaping in vascular smooth muscle.J. Vascular Res.50357–371. 10.1159/000353883
188
Megías M. Emri Z. S. Freund T. F. Gulyas A. I. (2001). Total number and distribution of inhibitory and excitatory synapses on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells.Neuroscience102527–540. 10.1016/S0306-4522(00)00496-6
189
Meléndez-Hevia E. Waddell T. G. Cascante M. (1996). The puzzle of the Krebs citric acid cycle: Assembling the pieces of chemically feasible reactions, and opportunism in the design of metabolic pathways during evolution.J. Mol. Evol.43293–303. 10.1007/BF02338838
190
Mentel M. Chovančíková P. Zeman I. Polčic P. (2021). Learning from yeast about mitochondrial carriers.Microorganisms9:2044. 10.3390/microorganisms9102044
191
Miles R. Toth K. Gulyas A. I. Hfijos N. Freund T. F. (1996). Differences between somatic and dendritic inhibition in the hippocampus.Neuron16815–823. 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80101-4
192
Miranda ÉG. Araujo-Chaves J. C. Kawai C. Brito A. M. Dias I. W. Arantes J. T. et al (2020). Cardiolipin structure and oxidation are affected by Ca2+ at the interface of lipid bilayers.Front. Chem.7:930. 10.3389/fchem.2019.00930
193
Mironov S. L. (2009). Complexity of mitochondrial dynamics in neurons and its control by ADP produced during synaptic activity.Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.412005–2014. 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.04.009
194
Mironova G. D. Pavlov E. V. (2021). Mitochondrial cyclosporine A-independent palmitate/Ca2+-induced permeability transition pore (PA-mPT Pore) and its role in mitochondrial function and protection against calcium overload and glutamate toxicity.Cells10:125. 10.3390/cells10010125
195
Misgeld T. Schwarz T. L. (2017). Mitostasis in neurons: Maintaining mitochondria in an extended cellular architecture.Neuron96651–666. 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.055
196
Mishra G. Coyne L. P. Chen X. J. (2023). Adenine nucleotide carrier protein dysfunction in human disease.IUBMB Life75911–925. 10.1002/iub.2767
197
Mnatsakanyan N. Jonas E. A. (2020a). ATP synthase c-subunit ring as the channel of mitochondrial permeability transition: Regulator of metabolism in development and degeneration.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.144109–118. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.05.013
198
Mnatsakanyan N. Jonas E. A. (2020b). The new role of F1Fo ATP synthase in mitochondria-mediated neurodegeneration and neuroprotection.Exp. Neurol.332:113400. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113400
199
Müller M. S. Fouyssac M. Taylor C. W. (2018). Effective glucose uptake by human astrocytes requires its sequestration in the endoplasmic reticulum by glucose-6-phosphatase-β.Curr. Biol.283481–3486. 10.1016/j.cub.2018.08.060
200
Müllner F. E. Wierenga C. J. Bonhoeffer T. (2015). Precision of inhibition: Dendritic inhibition by individual GABAergic synapses on hippocampal pyramidal cells is confined in space and time.Neuron87576–589. 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.003
201
Murali Mahadevan H. Hashemiaghdam A. Ashrafi G. Harbauer A. B. (2021). Mitochondria in neuronal health: From energy metabolism to Parkinson’s disease.Adv. Biol.5:2100663. 10.1002/adbi.202100663
202
Murphy E. (2022). Cyclophilin D regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore.Curr. Opin. Physiol.25:100486. 10.1016/j.cophys.2022.100486
203
Murphy E. Eisner D. A. (2024). How does mitochondrial Ca2+ change during ischemia and reperfusion? Implications for activation of the permeability transition pore.J. General Physiol.157:e202313520. 10.1085/jgp.202313520
204
Nadalutti C. A. Wilson S. H. (2020). Using human primary foreskin fibroblasts to study cellular damage and mitochondrial dysfunction.Curr. Protocols Toxicol.86:e99. 10.1002/cptx.99
205
Najbauer E. E. Becker S. Giller K. Zweckstetter M. Lange A. Steinem C. et al (2021). Structure, gating and interactions of the voltage-dependent anion channel.Eur. Biophys. J.50159–172. 10.1007/s00249-021-01515-7
206
Nanou E. Catterall W. A. (2018). Calcium channels, synaptic plasticity, and neuropsychiatric disease.Neuron98466–481. 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.03.017
207
Narayanareddy B. R. J. Vartiainen S. Hariri N. O’Dowd D. K. Gross S. P. (2014). A biophysical analysis of mitochondrial movement: differences between transport in neuronal cell bodies versus processes. Traffic15, 762–771. 10.1111/tra.12171
208
Nath S. (2023). Beyond binding change: The molecular mechanism of ATP hydrolysis by F1-ATPase and its biochemical consequences.Front. Chem.11:1058500. 10.3389/fchem.2023.1058500
209
Negri S. Faris P. Maniezzi C. Pellavio G. Spaiardi P. Botta L. et al (2021). NMDA receptors elicit flux-independent intracellular Ca2+ signals via metabotropic glutamate receptors and flux-dependent nitric oxide release in human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Cell Calcium99:102454. 10.1016/j.ceca.2021.102454
210
Nesci S. (2022). What happens when the mitochondrial H+-translocating F1FO-ATP (hydrol) ase becomes a molecular target of calcium? The pore opens.Biochimie19892–95. 10.1016/j.biochi.2022.03.012
211
Nesci S. Trombetti F. Ventrella V. Pagliarani A. (2016). The c-Ring of the F 1 FO-ATP Synthase: Facts and Perspectives.J. Membr. Biol.24911–21. 10.1007/s00232-015-9860-3
212
Nesterov S. V. Yaguzhinsky L. S. (2023). Directed proton transfer from Fo to F1 extends the multifaceted proton functions in ATP synthase.Biophys. Rev.15859–873. 10.1007/s12551-023-01132-y
213
Neupane P. Bhuju S. Thapa N. Bhattarai H. K. (2019). ATP synthase: Structure, function and inhibition.Biomol. Concepts101–10. 10.1515/bmc-2019-0001
214
Neupert W. (1997). Protein import into mitochondria.Ann. Rev. Biochem.66863–917. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.66.1.863
215
Niescier R. F. Kwak S. K. Joo S. H. Chang K. T. Min K. T. (2016). Dynamics of mitochondrial transport in axons.Front. Cell. Neurosci.10:123. 10.3389/fncel.2016.00123
216
Nimchinsky E. A. Sabatini B. L. Svoboda K. (2002). Structure and function of dendritic spines.Ann. Rev. Physiol.64313–353. 10.1146/annurev.physiol.64.081501.160008
217
Nirody J. A. Budin I. Rangamani P. (2020). ATP synthase: Evolution, energetics, and membrane interactions.J. General Physiol.152:e201912475. 10.1085/jgp.201912475
218
Noskov S. Y. Rostovtseva T. K. Bezrukov S. M. (2013). ATP transport through VDAC and the VDAC–tubulin complex probed by equilibrium and Nonequilibrium MD simulations.Biochem.529246–9256. 10.1021/bi4011495
219
Novgorodov S. A. Gudz T. I. (1996). Permeability transition pore of the inner mitochondrial membrane can operate in two open states with different selectivities.J. Bioenerget. Biomembr.28139–146. 10.1007/BF02110644
220
Obashi K. Okabe S. (2013). Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics and distribution by synapse position and neuronal activity in the axon.Eur. J. Neurosci.38350–2363. 10.1111/ejn.12263
221
Ofer N. Berger D. R. Kasthuri N. Lichtman J. W. Yuste R. (2021). Ultrastructural analysis of dendritic spine necks reveals a continuum of spine morphologies.Dev. Neurobiol.81746–757. 10.1002/dneu.22829
222
Palikaras K. Tavernarakis N. (2020). Regulation and roles of mitophagy at synapses.Mechan. Ageing Dev.187:111216. 10.1016/j.mad.2020.111216
223
Papa M. Bundman M. C. Greenberger V. Segal M. (1995). Morphological analysis of dendritic spine development in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons.J. Neurosci.151–11. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-01-00001.1995
224
Paradies G. Paradies V. Ruggiero F. M. Petrosillo G. (2014). Cardiolipin and mitochondrial function in health and disease.Antioxid. Redox Signal.201925–1953. 10.1089/ars.2013.5280
225
Paradies G. Petrosillo G. Paradies V. Ruggiero F. M. (2009). Role of cardiolipin peroxidation and Ca2+ in mitochondrial dysfunction and disease.Cell Calcium45643–650. 10.1016/j.ceca.2009.03.012
226
Paradies G. Petrosillo G. Paradies V. Ruggiero F. M. (2011). Mitochondrial dysfunction in brain aging: Role of oxidative stress and cardiolipin.Neurochem. Int.58447–457. 10.1016/j.neuint.2010.12.016
227
Payne A. J. Kaja S. Koulen P. (2015). Regulation of ryanodine receptor-mediated calcium signaling by presenilins.Recep. Clin. Invest.2:e449. 10.14800/rci.449
228
Pchitskaya E. Popugaeva E. Bezprozvanny I. (2018). Calcium signaling and molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Calcium7087–94. 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.06.008
229
Pekkurnaz G. Wang X. (2022). Mitochondrial heterogeneity and homeostasis through the lens of a neuron.Nat. Metab.4802–812. 10.1038/s42255-022-00594-w
230
Pekkurnaz G. Trinidad J. C. Wang X. Kong D. Schwarz T. L. (2014). Glucose regulates mitochondrial motility via Milton modification by O-GlcNAc transferase.Cell15854–68. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.007
231
Pellegrini L. Scorrano L. (2007). A cut short to death: Parl and Opa1 in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ.141275–1284. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402145
232
Pellerin L. (2018). Neuroenergetics: Astrocytes have a sweet spot for glucose.Curr. Biol.28R1258–R1260. 10.1016/j.cub.2018.09.042
233
Pelletier-Galarneau M. Guehl N. Ptaszek L. Wooten D. Ma C. Takahashi K. et al (2017). Assessment of mitochondrial status in skeletal muscle: First studies.J. Nuclear Med.58 (Suppl. 1):310.
234
Perkins G. A. Frey T. G. (2000). Recent structural insight into mitochondria gained by microscopy.Micron3197–111. 10.1016/S0968-4328(99)00065-7
235
Perkins G. A. Renken C. W. Frey T. G. Ellisman M. H. (2001). Membrane architecture of mitochondria in neurons of the central nervous system.J. Neurosci. Res.66857–865. 10.1002/jnr.10050
236
Petersen J. D. Kaech S. Banker G. (2014). Selective microtubule-based transport of dendritic membrane proteins arises in concert with axon specification.J. Neurosci.344135–4147. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3779-13.2014
237
Pfaff E. Klingenberg M. (1968). Adenine nucleotide translocation of mitochondria: 1. Specificity and control.Eur. J. Biochem.666–79. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00715.x
238
Picard M. White K. Turnbull D. M. (2013). Mitochondrial morphology, topology, and membrane interactions in skeletal muscle: A quantitative three-dimensional electron microscopy study.J. Appl. Physiol.114161–171. 10.1152/japplphysiol.01096.2012
239
Pinke G. Zhou L. Sazanov L. A. (2020). Cryo-EM structure of the entire mammalian F-type ATP synthase.Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.271077–1085. 10.1038/s41594-020-0503-8
240
Pivovarova N. B. Andrews S. B. (2010). Calcium-dependent mitochondrial function and dysfunction in neurons.FEBS J.2773622–3636. 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07754.x
241
Pivovarova N. B. Hongpaisan J. Andrews S. B. Friel D. D. (1999). Depolarization-induced mitochondrial Ca accumulation in sympathetic neurons: Spatial and temporal characteristics.J. Neurosci.196372–6384. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06372.1999
242
Pivovarova N. B. Pozzo-Miller L. D. Hongpaisan J. Andrews S. B. (2002). Correlated calcium uptake and release by mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum of CA3 hippocampal dendrites after afferent synaptic stimulation.J. Neurosci.2210653–10661. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-24-10653.2002
243
Pokhilko A. V. Ataullakhanov F. I. Holmuhamedov E. L. (2006). Mathematical model of mitochondrial ionic homeostasis: Three modes of Ca2+ transport.J. Theoret. biol.243152–169. 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.05.025
244
Popov A. Brazhe N. Morozova K. Yashin K. Bychkov M. Nosova O. et al (2023). Mitochondrial malfunction and atrophy of astrocytes in the aged human cerebral cortex.Nat. Commun.14:8380. 10.1038/s41467-023-44192-0
245
Pysh J. J. Khan T. (1972). Variations in mitochondrial structure and content of neurons and neuroglia in rat brain: An electron microscopic study.Brain Res.361–18. 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90762-7
246
Quinn P. M. J. Moreira P. I. Ambrósio A. F. Alves C. H. (2020). PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation.Acta Neuropathol. Commun.8:189. 10.1186/s40478-020-01062-w
247
Rajendran M. Bezrukov S. M. Rostovtseva T. K. (2023). Role of VDAC isoforms in bioenergetics and metabolism.Biophys. J.122:93a. 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.11.699
248
Rangaraju V. Lauterbach M. Schuman E. M. (2019a). Spatially stable mitochondrial compartments fuel local translation during plasticity.Cell17673–84. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.013
249
Rangaraju V. Lewis T. L. Hirabayashi Y. Bergami M. Motori E. Cartoni R. et al (2019b). Pleiotropic mitochondria: The influence of mitochondria on neuronal development and disease.J. Neurosci.398200–8208. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1157-19.2019
250
Raturi A. Simmen T. (2013). Where the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitochondrion tie the knot: The mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM).Biochim. Biophys. Acta1833213–224. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.04.013
251
Ravasenga T. Ruben M. Regio V. Polenghi A. Petrini E. M. Barberis A. (2022). Spatial regulation of coordinated excitatory and inhibitory synaptic plasticity at dendritic synapses.Cell Rep.38:110347. 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110347
252
Rodrigues T. Piccirillo S. Magi S. Preziuso A. dos Santos, Ramos V. et al (2022). Control of Ca2+ and metabolic homeostasis by the Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCXs) in health and disease.Biochem. Pharmacol.203:115163. 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115163
253
Romero-Carramiñana I. Esparza-Moltó P. B. Domínguez-Zorita S. Nuevo-Tapioles C. Cuezva J. M. (2023). IF1 promotes oligomeric assemblies of sluggish ATP synthase and outlines the heterogeneity of the mitochondrial membrane potential.Commun. Biol.6:836. 10.1038/s42003-023-05214-1
254
Rose J. Brian C. Pappa A. Panayiotidis M. I. Franco R. (2020). Mitochondrial metabolism in astrocytes regulates brain bioenergetics, neurotransmission and redox balance.Front. Neurosci.14:536682. 10.3389/fnins.2020.536682
255
Rossi M. J. Pekkurnaz G. (2019). Powerhouse of the mind: Mitochondrial plasticity at the synapse.Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.57149–155. 10.1016/j.conb.2019.02.001
256
Rostovtseva T. K. Bezrukov S. M. (2008). VDAC regulation: Role of cytosolic proteins and mitochondrial lipids.J. Bioenerget. Biomembr.40163–170. 10.1007/s10863-008-9145-y
257
Roumes H. Pellerin L. Bouzier-Sore A. K. (2023). Astrocytes as metabolic suppliers to support neuronal activity and brain functions.Essays Biochem.6727–37. 10.1042/EBC20220080
258
Ruprecht J. J. King M. S. Zögg T. Aleksandrova A. A. Pardon E. Crichton P. G. et al (2019). The molecular mechanism of transport by the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier.Cell176435–447. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.025
259
Rybalchenko V. Hwang S. Y. Rybalchenko N. Koulen P. (2008). The cytosolic N-terminus of presenilin-1 potentiates mouse ryanodine receptor single channel activity.Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.4084–97. 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.06.023
260
Salazar M. P. R. Kolanukuduru S. Ramirez V. Lyu B. Sejourne G. Sesaki H. et al (2024). Mitochondrial fission controls astrocyte morphogenesis and organization in the cortex.bioRxiv [Preprint]10.1101/2024.10.22.619706
261
Santos D. Esteves A. R. Silva D. F. Januário C. Cardoso S. M. (2015). The impact of mitochondrial fusion and fission modulation in sporadic Parkinson’s disease.Mol. Neurobiol.52573–586. 10.1007/s12035-014-8893-4
262
Sarasija S. Laboy J. T. Ashkavand Z. Bonner J. Tang Y. Norman K. R. (2018). Presenilin mutations deregulate mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis and metabolic activity causing neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans.eLife7:e33052. 10.7554/eLife.33052
263
Saucerman J. J. Bers D. M. (2012). Calmodulin binding proteins provide domains of local Ca2+ signaling in cardiac myocytes.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.52312–316. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.06.005
264
Schulz J. M. Kay J. W. Bischofberger J. Larkum M. E. (2021). GABA B receptor-mediated regulation of dendro-somatic synergy in layer 5 pyramidal neurons.Front. Cell. Neurosci.15:718413. 10.3389/fncel.2021.718413
265
Seager R. Lee L. Henley J. M. Wilkinson K. A. (2020). Mechanisms and roles of mitochondrial localisation and dynamics in neuronal function.Neuronal Signal.4:NS20200008. 10.1042/NS20200008
266
Segal M. (2010). Dendritic spines, synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival: Activity shapes dendritic spines to enhance neuronal viability.Eur. J. Neurosci.312178–2184. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07270.x
267
Segal M. Korkotian E. (2014). Endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores in dendritic spines.Front. Neuroanat.8:64. 10.3389/fnana.2014.00064
268
Segal M. Korkotian E. (2016). Roles of calcium stores and store-operated channels in plasticity of dendritic spines.Neuroscientist22477–485. 10.1177/1073858415613277
269
Seidlmayer L. K. Kuhn J. Berbner A. Arias-Loza P. A. Williams T. Kaspar M. et al (2016). Inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate-mediated sarcoplasmic reticulum–mitochondrial crosstalk influences adenosine triphosphate production via mitochondrial Ca 2+ uptake through the mitochondrial ryanodine receptor in cardiac myocytes.Cardiovas. Res.112491–501. 10.1093/cvr/cvw185
270
Seifert E. L. Ligeti E. Mayr J. A. Sondheimer N. Hajnóczky G. (2015). The mitochondrial phosphate carrier: Role in oxidative metabolism, calcium handling and mitochondrial disease.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.464369–375. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.031
271
Shah M. Chacko L. A. Joseph J. P. Ananthanarayanan V. (2021). Mitochondrial dynamics, positioning and function mediated by cytoskeletal interactions.Cell. Mol. Life Sci.783969–3986. 10.1007/s00018-021-03762-5
272
Sheng Z. H. (2014). Mitochondrial trafficking and anchoring in neurons: New insight and implications.J. Cell Biol.2041087–1098. 10.1083/jcb.201312123
273
Sheng Z. H. Cai Q. (2012). Mitochondrial transport in neurons: Impact on synaptic homeostasis and neurodegeneration.Nat. Rev. Neurosci.1377–93. 10.1038/nrn3156
274
Silva C. A. Yalnizyan-Carson A. Fernández Busch M. V. van Zwieten M. Verhage M. Lohmann C. (2021). Activity-dependent regulation of mitochondrial motility in developing cortical dendrites.eLife10:e62091. 10.7554/eLife.62091
275
Smorodchenko A. Rupprecht A. Fuchs J. Gross J. Pohl E. E. (2011). Role of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 4 in rat inner ear.Mol. Cell. Neurosci.47244–253. 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.03.002
276
Smorodchenko A. Rupprecht A. Sarilova I. Ninnemann O. Bräuer A. U. Franke K. et al (2009). Comparative analysis of uncoupling protein 4 distribution in various tissues under physiological conditions and during development.Biochim. Biophys. Acta17882309–2319. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.07.018
277
Sonenshein A. L. (2001). “The krebs citric acid cycle,” in Bacillus subtilis and its closest relatives: From Genes to Cells, edsSonensheinA. L.HochJ. A.LosickR. (New York, NY: Wiley), 151–162.
278
Stanika R. I. Villanueva I. Kazanina G. Andrews S. B. Pivovarova N. B. (2012). Comparative impact of voltage-gated calcium channels and NMDA receptors on mitochondria-mediated neuronal injury.J. Neurosci.326642–6650. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6008-11.2012
279
Stephen T. L. Higgs N. F. Sheehan D. F. Al Awabdh S. López-Doménech G. Arancibia-Carcamo I. L. et al (2015). Miro1 regulates activity-driven positioning of mitochondria within astrocytic processes apposed to synapses to regulate intracellular calcium signaling.J. Neurosci.3515996–16011. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2068-15.2015
280
Sterratt D. C. Groen M. R. Meredith R. M. Van Ooyen A. (2012). Spine calcium transients induced by synaptically-evoked action potentials can predict synapse location and establish synaptic democracy.PLoS Comp. Biol.8:e1002545. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002545
281
Stoler O. Stavsky A. Khrapunsky Y. Melamed I. Stutzmann G. Gitler D. et al (2022). Frequency-and spike-timing-dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ signaling regulates the metabolic rate and synaptic efficacy in cortical neurons.eLife11:e74606. 10.7554/eLife.74606
282
Strobel C. Sullivan R. K. Stratton P. Sah P. (2017). Calcium signalling in medial intercalated cell dendrites and spines.J. Physiol.5955653–5669. 10.1113/JP274261
283
Sukhorukov V. Voronkov D. Baranich T. Mudzhiri N. Magnaeva A. Illarioshkin S. (2021). Impaired mitophagy in neurons and glial cells during aging and age-related disorders.Int. J. Mol. Sci.22:10251. 10.3390/ijms221910251
284
Sun J. Gao G. Wang S. Liu H. Tang T. S. (2025). Decoding the influence of mitochondrial Ca2+ regulation on neurodegenerative disease progression.Mitochondrial Commun.31–15. 10.1016/j.mitoco.2025.01.001
285
Surin A. M. Khiroug S. Gorbacheva L. R. Khodorov B. I. Pinelis V. G. Khiroug L. (2013). Comparative analysis of cytosolic and mitochondrial ATP synthesis in embryonic and postnatal hippocampal neuronal cultures.Front. Mol. Neurosci.5:102. 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00102
286
Tan W. Colombini M. (2007). VDAC closure increases calcium ion flux.Biochim. Biophys. Acta17682510–2515. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.06.002
287
Tarraf B. Suraniti E. Colin C. Arbault S. Diolez P. Leguèbe M. et al (2021). A simple model of cardiac mitochondrial respiration with experimental validation.Mathemat. Biosci. Eng.185758–5789. 10.3934/mbe.2021291
288
Territo P. R. Mootha V. K. French S. A. Balaban R. S. (2000). Ca2+ activation of heart mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation: Role of the F0/F1-ATPase.Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiol.278C423–C435. 10.1152/ajpcell.2000.278.2.C423
289
Thiels E. Urban N. N. Gonzalez-Burgos G. R. Kanterewicz B. I. Barrionuevo G. Chu C. T. et al (2000). Impairment of long-term potentiation and associative memory in mice that overexpress extracellular superoxide dismutase.J. Neurosci.207631–7639. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-20-07631.2000
290
Thomas C. I. Ryan M. A. Kamasawa N. Scholl B. (2023). Postsynaptic mitochondria are positioned to support functional diversity of dendritic spines.eLife12:R89682. 10.7554/eLife.89682.3
291
Trigo D. Avelar C. Fernandes M. Sá J. da Cruz e Silva O. (2022). Mitochondria, energy, and metabolism in neuronal health and disease.FEBS Lett.5961095–1110. 10.1002/1873-3468.14298
292
Tu H. Nelson O. Bezprozvanny A. Wang Z. Lee S. F. Hao Y. H. et al (2006). Presenilins form ER Ca2+ leak channels, a function disrupted by familial Alzheimer’s disease-linked mutations.Cell126981–993. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.059
293
van Hameren G. Campbell G. Deck M. Berthelot J. Gautier B. Quintana P. et al (2019). In vivo real-time dynamics of ATP and ROS production in axonal mitochondria show decoupling in mouse models of peripheral neuropathies.Acta Neuropathol. Commun.7:86. 10.1186/s40478-019-0740-4
294
Vance J. E. (2014). MAM (mitochondria-associated membranes) in mammalian cells: Lipids and beyond.Biochim. Biophys. Acta1841595–609. 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.11.014
295
Verkhratsky A. (2005). Physiology and pathophysiology of the calcium store in the endoplasmic reticulum of neurons.Physiol. Rev.85201–279. 10.1152/physrev.00004.2004
296
Verma M. Lizama B. N. Chu C. T. (2022). Excitotoxicity, calcium and mitochondria: A triad in synaptic neurodegeneration.Trans. Neurodegenerat.11:3. 10.1186/s40035-021-00278-7
297
Vlachos A. Korkotian E. Schonfeld E. Copanaki E. Deller T. Segal M. (2009). Synaptopodin regulates plasticity of dendritic spines in hippocampal neurons.J. Neurosci.291017–1033. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5528-08.2009
298
Vlasov A. V. Osipov S. D. Bondarev N. A. Uversky V. N. Borshchevskiy V. I. Yanyushin M. F. et al (2022). ATP synthase FOF1 structure, function, and structure-based drug design.Cell. Mol. Life Sci.79:179. 10.1007/s00018-022-04153-0
299
von Bohlen Und Halbach O. (2009). Structure and function of dendritic spines within the hippocampus.Ann. Anat.191518–531. 10.1016/j.aanat.2009.08.006
300
Wahwah N. Kras K. A. Roust L. R. Katsanos C. S. (2020). Subpopulation-specific differences in skeletal muscle mitochondria in humans with obesity: Insights from studies employing acute nutritional and exercise stimuli.Am. J. Physiology-Endocrinol. Metab.318E538–E553. 10.1152/ajpendo.00463.2019
301
Walker J. E. Dickson V. K. (2006). The peripheral stalk of the mitochondrial ATP synthase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta1757286–296. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.01.001
302
Walters G. C. Usachev Y. M. (2023). Mitochondrial calcium cycling in neuronal function and neurodegeneration.Front. Cell Dev. Biol.11:1094356. 10.3389/fcell.2023.1094356
303
Wang J. Jiang J. Hu H. Chen L. (2025). MCU complex: Exploring emerging targets and mechanisms of mitochondrial physiology and pathology.J. Adv. Res.68271–298. 10.1016/j.jare.2024.02.013
304
Wang X. Schwarz T. L. (2009). The mechanism of kinesin regulation by Ca++ for control of mitochondrial motility.Cell136:163. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.046
305
Ward M. W. Rego A. C. Frenguelli B. G. Nicholls D. G. (2000). Mitochondrial membrane potential and glutamate excitotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule cells.J. Neurosci.207208–7219. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07208.2000
306
Watson S. A. McStay G. P. (2020). Functions of cytochrome c oxidase assembly factors.Int. J. Mol. Sci.21:7254. 10.3390/ijms21197254
307
Weber J. Senior A. E. (2003). ATP synthesis driven by proton transport in F1F0-ATP synthase.FEBS Lett.54561–70. 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00394-6
308
Weissert V. Rieger B. Morris S. Arroum T. Psathaki O. E. Zobel T. et al (2021). Inhibition of the mitochondrial ATPase function by IF1 changes the spatiotemporal organization of ATP synthase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta1862:148322. 10.1016/j.bbabio.2020.148322
309
Wescott A. P. Kao J. P. Lederer W. J. Boyman L. (2019). Voltage-energized calcium-sensitive ATP production by mitochondria.Nat. Metab.1975–984. 10.1038/s42255-019-0126-8
310
Whittaker R. G. Turnbull D. M. Whittington M. A. Cunningham M. O. (2011). Impaired mitochondrial function abolishes gamma oscillations in the hippocampus through an effect on fast-spiking interneurons.Brain134:e180. 10.1093/brain/awr018
311
Williams P. A. Morgan J. E. Votruba M. (2010). Opa1 deficiency in a mouse model of dominant optic atrophy leads to retinal ganglion cell dendropathy.Brain1332942–2951. 10.1093/brain/awq218
312
Xing S. L. Yan J. Yu Z. H. Zhu C. Q. (2011). Neuronal cell surface ATP synthase mediates synthesis of extracellular ATP and regulation of intracellular pH.Cell Biol. Int.3581–86. 10.1042/CBI20090441
313
Yao P. J. Eren E. Petralia R. S. Gu J. W. Wang Y. X. Kapogiannis D. (2020). Mitochondrial protrusions in neuronal cells.iscience23:101514. 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101514
314
Yuste R. (2013). Electrical compartmentalization in dendritic spines.Annu. Rev. Neurosci.36429–449. 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150455
315
Yuste R. Majewska A. Holthoff K. (2000). From form to function: Calcium compartmentalization in dendritic spines.Nat. Neurosci.3653–659. 10.1038/76609
316
Zaninello M. Bean C. (2023). Highly specialized mechanisms for mitochondrial transport in neurons: From intracellular mobility to intercellular transfer of mitochondria.Biomolecules13:938. 10.3390/biom13060938
317
Zhang Y. M. Qi Y. B. Gao Y. N. Chen W. G. Zhou T. Zang Y. et al (2023). Astrocyte metabolism and signaling pathways in the CNS.Front. Neurosci.17:1217451. 10.3389/fnins.2023.1217451
318
Zhao W. B. Sheng R. (2024). The correlation between mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs) and Ca2+ transport in the pathogenesis of diseases.Acta Pharmacol. Sinica46271–291. 10.1038/s41401-024-01359-9
319
Zheng W. Watts L. T. Holstein D. M. Wewer J. Lechleiter J. D. (2013). P2Y1R-initiated, IP3R-dependent stimulation of astrocyte mitochondrial metabolism reduces and partially reverses ischemic neuronal damage in mouse.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.33600–611. 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.214
320
Zhuo W. Zhou H. Guo R. Yi J. Zhang L. Yu L. et al (2021). Structure of intact human MCU supercomplex with the auxiliary MICU subunits.Prot. Cell12220–229. 10.1007/s13238-020-00776-w
321
Zoccarato F. Nicholls D. (1982). The role of phosphate in the regulation of the independent calcium-efflux pathway of liver mitochondria.Eur. J. Biochem.127333–338. 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06875.x
322
Zong Y. Li H. Liao P. Chen L. Pan Y. Zheng Y. et al (2024). Mitochondrial dysfunction: Mechanisms and advances in therapy.Signal Transduct. Targeted Therapy9:124. 10.1038/s41392-024-01839-8
323
Zorova L. D. Popkov V. A. Plotnikov E. Y. Silachev D. N. Pevzner I. B. Jankauskas S. S. et al (2018). Mitochondrial membrane potential.Anal. Biochem.55250–59. 10.1016/j.ab.2017.07.009
324
Zubareva V. M. Lapashina A. S. Shugaeva T. E. Litvin A. V. Feniouk B. A. (2020). Rotary ion-translocating ATPases/ATP synthases: Diversity, similarities, and differences.Biochem. Moscow851613–1630. 10.1134/S0006297920120135
Summary
Keywords
mitochondria, mitophagy, dendritic spine, ATP synthase, endoplasmic reticulum, MCU, MAM, Ca2+ signaling
Citation
Feofilaktova T, Kushnireva L, Segal M and Korkotian E (2025) Calcium signaling in postsynaptic mitochondria: mechanisms, dynamics, and role in ATP production. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 18:1621070. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1621070
Received
30 April 2025
Accepted
14 June 2025
Published
21 July 2025
Volume
18 - 2025
Edited by
Sara Baldelli, Università telematica San Raffaele, Italy
Reviewed by
Laura M. Harrison, Tulane University, United States
Jiho Yoo, Chung-Ang University, Republic of Korea
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Feofilaktova, Kushnireva, Segal and Korkotian.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eduard Korkotian, eduard.korkotian@weizmann.ac.il
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.