Abstract
The underlying mechanisms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are still not fully understood, creating significant obstacles for developing effective therapeutic strategies. Recently, ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of regulated cell death, has been shown to play a role in several psychiatric disorders, such as major depressive disorder (MDD), stress-induced anxiety, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and Parkinson’s disease (PD). While direct evidence for the role of ferroptosis in PTSD is still limited, an increasing number of studies suggest that the pathological features of PTSD may trigger the ferroptosis cascade. Additionally, the typical hallmarks of ferroptosis, such as iron dysregulation, lipid peroxidation, and failure of antioxidant defense systems, may intersect with the pathogenesis of PTSD. Importantly, some treatments for PTSD, such as antioxidants and free radical scavengers, have been proven to inhibit ferroptosis, which further supports the case for ferroptosis as a potential pathogenic mechanism in PTSD. To thoroughly investigate the mechanistic links between ferroptosis and PTSD, we analyze the relevant literature on ferroptosis and PTSD in this review. Our aim is to elucidate the potential relationships between ferroptosis and PTSD, thereby providing novel insights for future research directions. Furthermore, we call for more experimental and clinical studies to explore this relationship further, with the ultimate goal of developing more effective therapeutic strategies for PTSD.
Graphical Abstract

The potential connections between ferroptosis and PTSD. It illustrates the connections between the two, including iron dysregulation, lipid peroxidation, neuroinflammation, and mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction. Each element includes related biochemical changes and effects, such as oxidative stress and neuron apoptosis. Additionally, it explores some potential therapeutic strategies targeting ferroptosis in PTSD, encompassing free radical scavengers, antioxidants, and acupuncture.
1 Introduction
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a psychiatric condition characterized by the re-experiencing of traumatic events, heightened vigilance, anxiety, depression, and other psychological challenges, all of which significantly impact patients’ mental health (Ressler et al., 2022). Research has confirmed that the prevalence of PTSD ranges from 1 to 8% in the general population and rises to 50% in mental health institutions (Maercker et al., 2022). Notably, more than one-third of PTSD patients suffer from chronic and treatment-resistant symptoms, often due to delayed diagnoses. The pathogenesis of PTSD is extremely complex and it involves multiple biological processes, including inflammatory responses, alterations in neuroplasticity, and dysregulation of neurotransmitter systems (Zhang et al., 2014; Hori and Kim, 2019; López-López and Crespo, 2025). Notably, lipid peroxidation dysfunction, a hallmark of ferroptosis, and alterations in lipid-related cascades have been identified as crucial factors in the pathogenesis of PTSD (Atli et al., 2016; Pope and Dixon, 2023). Additionally, the changes in the function, structure, and chemical processes of fear learning and memory circuits are closely associated with the development of PTSD and also pose considerable challenges for its treatment (Harnett et al., 2020). Given the limited efficacy of existing pharmacological treatments for PTSD, there is an urgent need for further research to uncover the underlying mechanisms of PTSD and identify new therapeutic targets.
2 Overview of ferroptosis
Ferroptosis, a distinctive form of regulated cell death (RCD), was first defined by Dixon et al. (2012). Morphologically, ferroptosis is quite different from necrosis, apoptosis, and autophagy on cellular morphology and function. It lacks the characteristic features of classical necrosis, including cytoplasmic and organelle swelling, as well as rupture of the plasma membrane. Similarly, it does not exhibit features of traditional apoptosis, including cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, apoptotic body formation, and cytoskeletal disintegration. Notably, ferroptosis is primarily characterized by pronounced mitochondrial shrinkage, increased membrane density, and reduction or loss of mitochondrial cristae (Xie et al., 2016; Li et al., 2020). These morphological and ultrastructural changes are important markers that distinguish ferroptosis from other forms of RCD. Biochemically, the core mechanism of ferroptosis lies in the iron-dependent accumulation of lipid peroxides, which can be summarized as a cascade reaction of “iron overload-lipid oxidation-antioxidant failure”. Specifically, excessive redox-active iron in cells can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) through pathways such as the Fenton reaction. These ROS preferentially attack phospholipid molecules containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), triggering large-scale lipid peroxidation reactions, which in turn disrupt intracellular redox homeostasis and ultimately initiate the ferroptosis process (Jiang et al., 2021). Genetically, ferroptosis is controlled by genes in multiple pathways (Xie et al., 2016; Tang et al., 2021). For example, the system Xc– pathway transports cystine into cells to supply precursors for GSH synthesis. In this pathway, downregulation of pathway-related genes, such as SLC7A11, reduces GSH production and indirectly promotes ferroptosis. Despite these findings, the intricate genetic and regulatory mechanisms underlying ferroptosis remain to be fully elucidated.
Initially identified in cancer research, ferroptosis has been shown to exert impact on tumor growth, progression, and chemotherapy resistance (Jiang et al., 2021). Accumulating evidence further indicates that ferroptosis significantly regulates the onset and progression of various other diseases (Figure 1), including many central nervous system (CNS) disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and ischemic brain injury (Bao et al., 2021; Mahoney-Sánchez et al., 2021; Li C. et al., 2022; Gleason and Bush, 2021). These findings have positioned ferroptosis as a research focus and a promising therapeutic target for improving the treatment and prognosis of related diseases. While direct studies investigating the role of ferroptosis in PTSD remain limited. Notably, individuals with PTSD have been confirmed to exhibit elevated oxidative stress and disrupted iron metabolism (Zhao et al., 2016; Miller et al., 2018), which are central pathological features of ferroptosis. Moreover, postmortem human studies have further revealed altered transcription of oxidative stress-related genes in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) of PTSD patients (Watling et al., 2023). Furthermore, existing research has identified three key genes that predict the risk of developing PTSD, namely ACSL4, ACO1, and GSS. These genes are involved in regulating lipid, iron, cysteine, and glutathione metabolism and they are not only critical components of ferroptosis but also participate in its associated biological networks (Zhu et al., 2022). Collectively, this evidence suggests that ferroptosis may play a significant role in the development and progression of PTSD, potentially offering new therapeutic strategies for its treatment.
FIGURE 1

The relationship between ferroptosis and various diseases. This figure illustrates the widespread impact of ferroptosis across multiple system diseases, such as tumor diseases, CNS diseases, digestive system diseases, respiratory system diseases, heart diseases, kidney diseases, pancreatic diseases, and so on. This suggests that ferroptosis could serve as a potential therapeutic target in a wide range of diseases.
3 Methodology
To identify key research findings on the association between ferroptosis and PTSD in existing literature, a comprehensive literature search was conducted. First, the search employed targeted keywords and phrases to capture relevant studies, including “ferroptosis and PTSD,” “iron and PTSD,” “PTSD and oxidative stress,” and “PTSD and lipid.” Notably, these terms were specifically selected to cover core biological processes linked to ferroptosis and their potential connections to PTSD. Second, the search was expanded across three major academic databases: PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science, ensuring broad coverage of both clinical and preclinical research. After screening for relevance and direct evidence of the ferroptosis-PTSD relationship, a total of 15 articles were included in this review (Table 1). The ultimate goal of this study is to synthesize the key findings from these 15 included articles, with the aim of providing foundations for advancing the novel treatment strategies for PTSD. The core objective of this study is to conduct an integrated analysis of the key research findings from these 15 included literatures, thereby providing a theoretical basis and practical foundation for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for PTSD.
TABLE 1
| Publication year | Study type | Markers evaluated | Inclusion criteria | Boolean operators | Keywords | References |
| 2003 | Research study | GSH-Px, CAT, MDA, SOD | PTSD patients, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, free radicals | Tezcan et al., 2003 |
| 2015 | Research study | GPX, SOD | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, oxidative stress | Borovac Štefanović et al., 2015 |
| 2016 | Research study | TfR1, Fn | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, iron | Zhao et al., 2016 |
| 2016 | Research study | MDA | PTSD patients, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress | Atli et al., 2016 |
| 2018 | Research study | GSH, GSSG, TBAR | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, oxidative stress | Alzoubi et al., 2018b |
| 2018 | Review | oxidative stress, inflammation | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, oxidative stress, inflammation | Miller et al., 2018 |
| 2019 | Research study | GSH, GSSG, GPX, TBARS | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, oxidative stress | Alzoubi et al., 2019 |
| 2019 | Research study | Nrf2, keap1, HO-1 | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, keap1/Nrf2 | Zhou et al., 2019 |
| 2020 | Research study | GSH, GSSG, GPX | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, oxidative stress | Ahmed et al., 2020 |
| 2021 | Research study | FPN1 | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, FPN1 | Wu et al., 2021 |
| 2022 | Research study | PUFA | PTSD models, oxidative and lipid homeostasis are altered in PTSD models | And | PTSD, lipids | Kelley et al., 2022 |
| 2022 | Research study | ACSL4, ACO1, GSS | Studies evaluating ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, Ferroptosis, inflammatory pathways | Zhu et al., 2022 |
| 2023 | Research study | GSH | PTSD models, ferroptosis-related markers | And | PTSD, GSH, Psychiatric Disorder | Watling et al., 2023 |
| 2023 | Review | Mitochondria | PTSD models, changes related to ferroptosis | And | PTSD, inflammation, mitochondria | Kim et al., 2023 |
| 2024 | Review | Lipid peroxidation | PTSD models, changes related to ferroptosis | And | PTSD, fatty acids, sphingomyelins, triglycerides | Bhargava et al., 2024 |
Characteristics of include studies in the review.
GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; CAT, catalase; MDA, malondialdehyde; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPX, glutathione peroxidase; TfR1, transferrin receptor 1; Fn, ferritin; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; TBAR, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; FPN1, ferroportin 1; Keap1, kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; ACSL4, Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; ACO1, Aconitase 1; GSS, glutathione synthetase.
4 The mechanisms of ferroptosis
The regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis are complicated, encompassing a diverse array of signaling molecules and metabolic pathways (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2
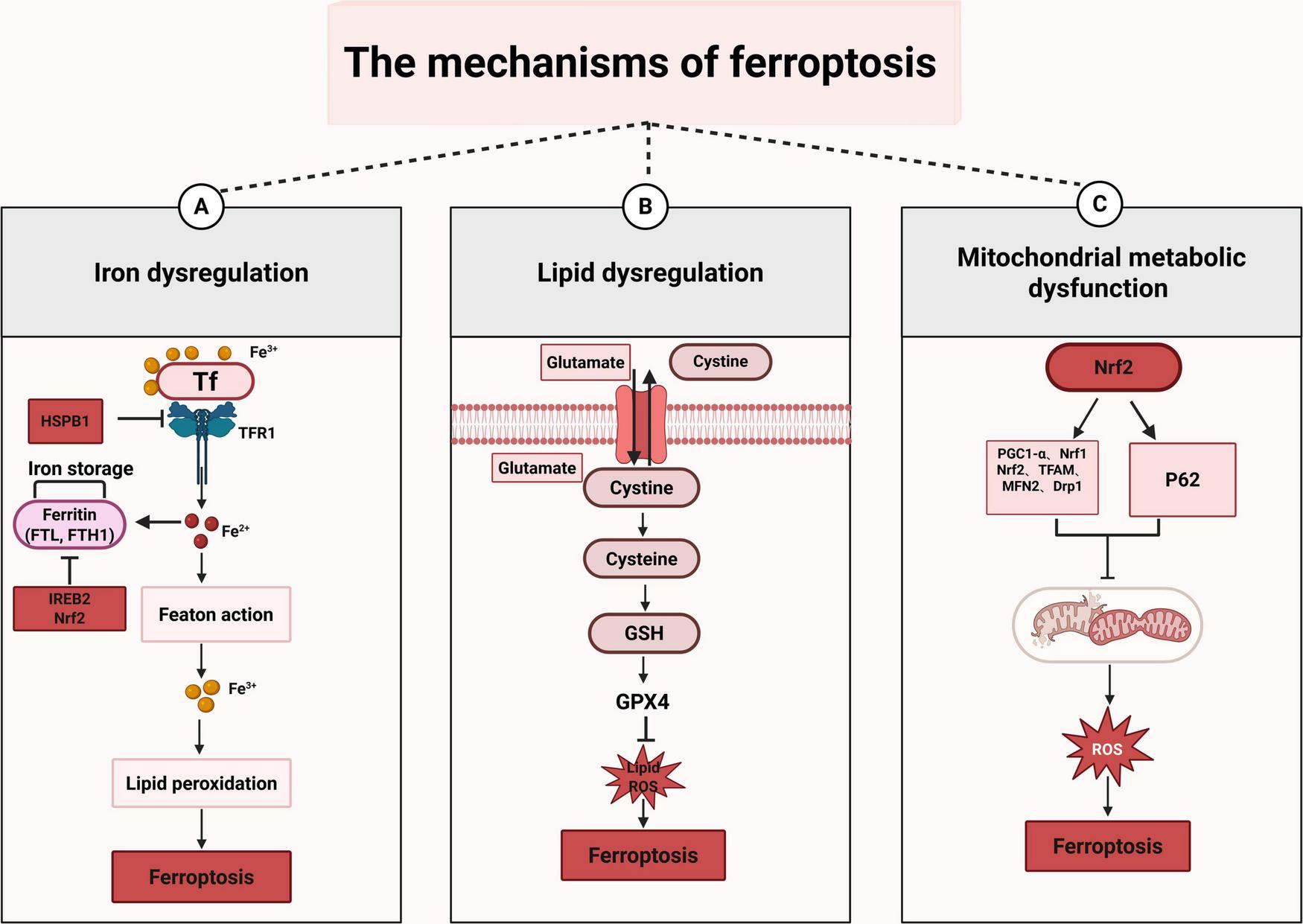
The mechanisms of ferroptosis. This figure illustrates the three primary mechanisms of ferroptosis. (A) Iron dysregulation: when TF binds to Fe3+, it enters the cell through TFR1, leading to the conversion of Fe3+ into Fe2+, which can initiate the Fenton reaction. Moreover, Fe3+ participates in lipid peroxidation and ultimately triggers ferroptosis. In this process, HSPB1 inhibits ferroptosis by suppressing TFR1; while IREB2 and Nrf2 can inhibit ferroptosis by inhibiting FTH1. (B) Lipid dysregulation: cystine is transported into cells and subsequently converted into cysteine. Cysteine then participates in the synthesis of GSH. GSH, under the action of GPX4, inhibits the generation of lipid and ROS. When the function of GPX4 is impaired, the lipid and ROS accumulate, which can trigger ferroptosis. (C) Mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction: Nrf2 is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of a series of genes to influence mitochondrial function, including PGC1-α, Nrf1, Nrf2 itself, TFAM, MFN2, and Drp1. When mitochondrial function is impaired, it leads to excessive production of ROS. This overabundance of ROS can damage cells and ultimately result in ferroptosis.
4.1 Iron dysregulation
Iron metabolism is a tightly regulated process that encompasses iron uptake, distribution, storage, utilization, and efflux (Gao et al., 2019). Generally, cellular iron acquisition primarily depends on the coordinated action of transferrin (TF) and transferrin receptor 1 (TFR1). Specifically, TF transports iron from storage sites to the extracellular environment, where it binds to TFR1. TFR1 is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed in mammalian cells and is critical for iron uptake. Notably, TFR1 expression is dynamically regulated by intracellular iron levels: iron deficiency upregulates TFR1 to enhance iron uptake, while iron excess downregulates TFR1 to prevent overload (Kawabata, 2019).
Beyond the canonical pathway, multiple intracellular molecules precisely control iron metabolism to regulate ferroptosis progression. For instance, heat shock protein family B member 1 (HSPB1) lowers intracellular iron levels by downregulating TFR1, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (Sun et al., 2015). Similarly, iron-responsive element-binding protein 2 (IREB2) maintains iron homeostasis and enhances antioxidant defense by increasing the levels of ferritin heavy chain (FTH1) and ferritin light chain (FTL), ultimately exerting an effect that resists ferroptosis (Lv et al., 2022). Furthermore, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a core regulator of oxidative stress responses, suppresses ferroptosis through promoting FTH1 transcription, which helps maintain iron balance and improve antioxidant capacity (Qian et al., 2024). Conversely, when intracellular iron homeostasis is disrupted, excess iron generates ROS via the Fenton reaction, activates iron-dependent enzymes, induces lipid peroxidation and membrane oxidative damage, and eventually initiates ferroptosis (Dixon et al., 2012). These findings underscore that the accurate regulation of iron metabolism is vital for preserving cellular homeostasis, preventing ferroptosis, and safeguarding organismal health.
4.2 Lipid dysregulation
Lipid peroxidation serves as a pivotal factor in ferroptosis, occurring via both enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanisms (Lee et al., 2021; Zuo et al., 2023). In the non-enzymatic pathway, free ferrous iron in cells triggers the Fenton reaction, which catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and produces highly reactive hydroxyl radicals (●OH). These radicals initiate lipid peroxidation by abstracting hydrogen atoms from the bis-allylic position of PUFAs, leading to the accumulation of lipid peroxides and subsequent cell membrane damage. In contrast, the enzymatic pathway relies on specific catalytic proteins (Lee et al., 2021). Lipoxygenases (ALOXs), which are key drivers of lipid peroxidation, convert PUFAs into lipid peroxides, such as arachidonic acid hydroperoxide. These peroxides increase cell membrane fluidity and permeability, disrupt cellular functions, and eventually induce ferroptosis. Evidence confirms that reducing ALOXs levels can alleviate cell death induced by ferroptosis inducers (Liu et al., 2022). Furthermore, compounds like vitamins and flavonoid-based drugs can suppress ALOX activity, acting as ferroptosis inhibitors (Shah et al., 2018). Additionally, cytochrome P450 reductase facilitates ferroptosis through the lipid peroxidation process, which begins with the peroxidation of PUFAs via electron transfer, a mechanism closely associated with the lipid peroxidation cascade (Feng and Stockwell, 2018). These findings underscore the crucial role of lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis.
Notably, molecules that regulate lipid peroxidation are critical in ferroptosis, as dysfunction of these regulators profoundly influences cellular fate. For instance, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) is a critical factor that facilitates lipid peroxidation by catalyzing the esterification of PUFAs with CoA to generate PUFA-CoA. Studies have demonstrated that ACSL4 deficiency disrupts intracellular PUFA metabolism, significantly reducing lipid peroxide levels and consequently decreasing cellular susceptibility to ferroptosis (Ding et al., 2023). Importantly, ACSL4 is also linked to the risk of PTSD and regulates the metabolism of lipid, iron, cysteine, and GSH, all of which are core pathways implicated in ferroptosis (Zhu et al., 2022). Therefore, further investigation into ACSL4 and its regulatory metabolic network is essential for elucidating the mechanisms of ferroptosis and developing therapeutic strategies for related diseases. Another key mediator of ferroptosis is lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3), which plays a vital role by incorporating oxidation-sensitive PUFAs into cellular membranes. Specifically, LPCAT3 mediates the re-esterification of PUFA-CoA into membrane phospholipids, thereby providing substrate pools for lipid peroxidation. In contrast, genetic ablation or knockdown of LPCAT3 impairs this process, resulting in decreased production of membrane lipid peroxides and subsequent inhibition of ferroptosis (Liu et al., 2022). Collectively, these findings indicate that both ACSL4 and LPCAT3 are pivotal for orchestrating lipid metabolism and controlling ferroptosis.
4.3 Mitochondrial metabolic dysfunction
Ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death, originates and propagates across multiple organelles, including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes (Gan, 2021). Among these, mitochondria play a pivotal role in cellular energy metabolism, performing key biological functions such as ATP production through oxidative phosphorylation and maintaining redox and calcium homeostasis (Yapa et al., 2021). Notably, mitochondrial energy metabolism is significantly altered during ferroptosis, with increased oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production, and a decreased glycolysis rate. Moreover, excessive oxidative stress also causes irreversible damage to mitochondrial structural. Beyond energy metabolism and structure stability, mitochondria also contribute to iron balance regulation within the nervous system. Specifically, they facilitate cell death signals induced by increased lipid peroxidation in neuronal cells (Gao and Chang, 2014). Notably, some ferroptosis inhibitors specifically target mitochondrial pathways. For instance, Cotticelli et al. (2019) has reported that mitochondrial iron overload occurs in Friedreich ataxia (FRDA), and the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant XJB-5–131 significantly reduces ferroptosis in cells. This further confirms that targeting mitochondrial pathways is a promising strategy for regulating ferroptosis.
Notably, multiple intracellular molecules regulate mitochondrial metabolism to modulate ferroptosis. Among them, the antioxidant transcription factor Nrf2 is a crucial regulator of mitochondrial function and ferroptosis process (Han et al., 2024). Specifically, Nrf2 can influence mitochondrial biogenesis by modulating the expression of molecules like PGC-1α, Nrf1 and TFAM, and mitochondrial genes. Additionally, it can regulate mitophagy through a PINK1/Parkin-independent mechanism. Nrf2 also controls mitochondrial fission and fusion processes by regulating the expression of fission-related proteasome genes and fusion-related MFN2 (Li et al., 2023). Another important molecule is AMPK, which is a critical sensor of cellular energy status and regulates an adaptive response under energy stress. Recent study has shown that energy stress activates AMPK, which inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), thereby restraining fatty acid synthesis (FAS) and inhibiting ferroptosis (Lee et al., 2020). Moreover, FoxO3a activity, which is activated by the AMPK pathway, plays a unique role in the energy stress response and ROS regulation. It has been indicated that AMPK phosphorylates FoxO3a at serine 413 under energy stress. This phosphorylation enhances FoxO3a-dependent transcription and confers resistance to erastin-induced ferroptosis (Zhong et al., 2023). Therefore, a deeper understanding of the interactions and mechanisms of these molecules in ferroptosis is important for developing therapeutic strategies for related diseases.
5 Hallmarks of ferroptosis interact with PTSD pathogenesis
5.1 Iron metabolic disturbance
Significant disturbances in iron metabolism have been confirmed in PTSD. Existing evidence has confirmed that single prolonged stress (SPS), a common PTSD model (Souza et al., 2017), significantly elevates plasma cortisol levels and increases iron content in critical brain areas, such as the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and striatum. Meanwhile, stress also induces region-specific changes in both protein and mRNA levels of transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) and ferritin (Fn). Notably, fn serves as an important protein responsible for the iron storage and iron detoxification (Joshi and Clauberg, 1988). These findings suggest that iron metabolism abnormalities may be a key factor in the pathogenesis and development of PTSD. Further research has revealed that brain areas with iron accumulation exhibit mitochondrial swelling and neuronal apoptosis (Zhao et al., 2016). Given that mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid peroxidation are hallmarks of ferroptosis, these findings suggest that iron accumulation in specific brain regions may not only disrupt normal cellular functions but also potentially trigger ferroptosis.
Notably, the pathophysiology of PTSD is closely linked to the dysregulation of multiple neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate, norepinephrine and dopamine (Zhang et al., 2014). Specifically, PTSD patients often exhibit persistent activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which not only enhances excitatory glutamatergic neurotransmission but also leads to hyperactivity of the noradrenergic system (Nutt, 2000). These abnormalities in neurotransmitter systems are directly linked to the heightened vigilance and exaggerated fear responses observed in PTSD patients. Meanwhile, PTSD patients frequently show decreased 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) function, which impairs the inhibitory control of emotions and impulsive behaviors. Additionally, alterations in dopaminergic signaling may occur in specific brain regions, such as the reward circuit, in PTSD patients (Zhang et al., 2014). Collectively, these neurochemical imbalances constitute a key mechanism underlying the core symptoms of PTSD, including hypervigilance, anxiety and traumatic re-experiencing. Notably, iron is essential for the normal function of multiple neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Among these interactions, a significant toxic interplay exists between iron and dopamine. On one hand, dopamine can promote intracellular iron accumulation, which further triggers oxidative stress responses (Dichtl et al., 2018). On the other hand, excessive iron can exacerbate the toxic effect of specific neurotoxic metabolites generated during dopamine metabolism, thereby forming a toxic cycle (Hare and Double, 2016). Furthermore, iron and glutamate exhibit a close bidirectional regulatory relationship. Iron participates in glutamate synthesis through activating cytosolic aconitase, while glutamate enhances cellular iron uptake capacity by upregulating the expression of divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1). This regulatory loop ultimately leads to an increase in total brain iron levels, which further disrupts the homeostasis of nerve cells (McGahan et al., 2005). Given that research has already confirmed the presence of iron metabolic disturbances in PTSD, it is plausible that disturbances in iron metabolism may interact with the dysregulation of the neurotransmitter system, thereby contributing to the development of core symptoms of PTSD. This further underscores the potential importance of iron homeostasis management in PTSD treatment. Moreover, research has demonstrated that the conditional knockout of FPN1 in mouse neurons disrupts iron homeostasis, resulting in iron deficiency in the cortex and hippocampus. This iron deficiency subsequently affects contextual fear responses in mice (Wu et al., 2021). Collectively, these findings underscore the importance of managing iron homeostasis and understanding the mechanisms of ferroptosis, which may offer innovative therapeutic strategies for addressing PTSD.
5.2 Lipid oxidative damage
Lipid peroxidation, a key driver of ferroptosis, has been widely recognized for its significant role in PTSD pathophysiology. Research has indicated that PTSD patients exhibit downregulated expression of GPX and pronounced oxidative stress imbalance. Specifically, decreased levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and GPX have been observed in the bloodstream of PTSD patients (Borovac Štefanović et al., 2015; Hassan et al., 2016). Further studies have shown that malondialdehyde (MDA), a lipid peroxidation byproduct, is significantly elevated in both military personnel and earthquakes survivors with PTSD. The degree of SOD and GPX dysfunction positively correlates with symptom severity (Tezcan et al., 2003). Beyond oxidative stress, PTSD patients also exhibit lipid metabolism abnormalities, including alterations in sphingolipids and phospholipids in both plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (Zieker et al., 2007; Atli et al., 2016; Bhargava et al., 2024). The elevation of these biomarkers is an important signal indicating the occurrence of ferroptosis. Consequently, these findings suggest that significant pathological mechanisms underlying PTSD may involve dysregulated lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress pathways, which are central to the process of ferroptosis.
Supporting evidence from animal models further indicates that traumatic stress can lead to disrupted lipid metabolism. In PTSD models, disturbances in hippocampal lipid and oxidative homeostasis have been confirmed, including elevated cholesterol levels, altered lipid profiles, increased free radical generation, and abnormal levels of oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) (Kelley et al., 2022). These changes may contribute to PTSD development and potentially trigger the ferroptosis cascade. Furthermore, elevated levels of ROS, peroxynitrite, and superoxide have been detected. Chronic ROS accumulation has been shown to impair hippocampal neurogenesis in mice deficient in SOD (Wilson et al., 2013). Moreover, excessive ROS production can lead to mitochondrial swelling and calcium leakage, thereby initiating a cycle of neuroinflammation that exacerbates PTSD symptoms (Lushchak et al., 2022; Kmita et al., 2023). Additionally, significantly increased levels of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARs), which are lipid peroxidation byproducts, have been reported in PTSD models (Alzoubi et al., 2018a). Given that ferroptosis is characterized by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, the observed lipid metabolic disturbances and oxidative stress in PTSD patients and PTSD animal models strongly suggest that ferroptosis may be a significant pathological mechanism in PTSD.
5.3 Vicious circle of inflammation
Inflammation is a protective response of the body to injury or infection, which typically involves activating immune cells and releasing various cytokines. Studies have consistently demonstrated that PTSD patients exhibit higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β (Hori and Kim, 2019; Pivac et al., 2023). Notably, these cytokines may not only directly contribute to neuronal damage but also exacerbate ferroptosis by dysregulating iron metabolism and promoting lipid peroxidation. Moreover, lipid peroxidation products generated during ferroptosis, sch as MDA, may further stimulate inflammatory responses, creating a vicious cycle. This cycle underscores the potential for ferroptosis to perpetuate and amplify neuroinflammation in PTSD. Furthermore, increased activity of the NF-κB pathway has been observed in PTSD patients (Gupta and Guleria, 2022). Importantly, NF-κB activation triggers a cascade of signaling events, which leads to the production of pore-forming proteases, the activation of alarmins, and the stimulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). These enzymes play a crucial role in degrading both cellular and extracellular components of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), such as tight junction and adherens junction proteins. Eventually, this results in increased BBB permeability in vulnerable brain regions (Welcome and Mastorakis, 2020). Notably, iron accumulation has been confirmed in these some brain regions in PTSD models (Zhao et al., 2016). Iron overload may not only directly promote lipid peroxidation but also indirectly amplify neuroinflammatory responses via NF-κB activation, forming another deleterious feedback loop that collectively exacerbates neuronal injury and BBB disruption. Importantly, whole transcriptome analyses of peripheral blood from PTSD patients reveal broad dysregulation in immune-related pathways (Zhu et al., 2022). This suggests that ferroptosis may serve both as a consequence and a driver of immune dysfunction in PTSD.
5.4 Mitochondrial dysfunction
As a central regulator of cellular metabolism and death, mitochondrial play a pivotal role in ferroptosis (Gan, 2021). Specifically, mitochondrial dysfunction exacerbates oxidative stress and increases intracellular ROS levels, thereby promoting ferroptotic cell death. Additionally, mitochondrial dysfunction is frequently accompanied by significant morphological alterations, including increased mitochondrial fission and cristae enlargement, which are closely associated with increased cellular susceptibility to ferroptosis (Song et al., 2024). Notably, MitoQ, an effective mitochondrial ROS scavenger, can improve mitochondrial function by inhibiting ferroptosis (Jelinek et al., 2018), offering a promising therapeutic strategy for ferroptosis-related diseases. Further research has underscored the significance of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in the progression of PTSD. For instance, elevated ROS levels can disrupt calcium homeostasis, leading to mitochondrial swelling and Ca2+ leakage. This disruption may create a vicious cycle of mutual reinforcement between ROS and Ca2+, potentially aggravating PTSD symptoms (Lushchak et al., 2022; Kmita et al., 2023). Additionally, disturbances in iron metabolism have been confirmed in PTSD models, which are closely intertwined with oxidative stress. However, abnormal iron accumulation may further exacerbate oxidative stress and activate ferroptosis-related pathways, thereby increasing the vulnerability of neural cells to ferroptosis. Moreover, studies have revealed that PTSD models exhibit marked mitochondrial impairment. Specifically, increased expression of fission-related proteins FIS1 and DRP1, alongside reduced levels of fusion regulators OPA1 and MFN2, have been detected in the amygdala. Transmission electron microscopy further confirms the presence of swollen and damaged mitochondria in this brain region among stressed rats (Papageorgiou and Filiou, 2024; Prajapati et al., 2024). Collectively, these findings suggest that mitochondrial alterations constitute a key pathological mechanism in PTSD, contributing to ferroptosis and disease progression.
5.5 Role of P53 in ferroptosis and PTSD pathophysiology
The transcription factor p53 is a tumor suppressor that regulates multiple oncogenes expression and their downstream signaling pathways, thereby mediating diverse biological effects (Liu et al., 2019; Levine, 2020). In tumor tissues, mutations or deletions in the p53 gene may contribute to cancer initiation and progression. Notably, the p53 gene is widely expressed in the brain, where it participates in various cellular processes, including dendritogenesis, oxidative stress response, cell death, autophagy, DNA repair, and cell cycle arrest (Lei et al., 2022). Therefore, it has been termed the guardian of the genome. Notably, accumulating evidence reveals a close relationship between p53 and ferroptosis. As a key regulator, p53 can modulate intracellular iron metabolism by regulating related genes. In lipid metabolism, p53 can affect ferroptosis susceptibility through influencing lipid synthesis, degradation, and transport, thereby altering the composition and fluidity of the cell membrane. Furthermore, p53 can regulate both ROS production and clearance, as well as amino acids metabolism through multiple mechanisms, highlighting its important role in modulating ferroptosis (Ji et al., 2022; Liu and Gu, 2022). Given the broad neurobiological functions of p53 described above, it is plausible that p53-mediated pathways may also play a significant role in the pathophysiology of PTSD. For example, the p53-mediated regulation of iron metabolism and ROS production could potentially influence the oxidative stress and neuronal damage observed in PTSD. Further studies have indicated that the ROS-JNK-p53 pathway is involved in neuronal apoptosis in PTSD models. In vitro experiments have demonstrated that electrical stimulation triggers neuronal apoptosis through activating the ROS/JNK/p53 signaling pathway. However, the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) can attenuate ROS generation, suppresses JNK/p53 activation, and decrease the apoptotic rate in HT-22 cells. These findings imply that the ROS-JNK-p53 pathway may serve as a critical mediator of neuronal apoptosis in PTSD (Lv et al., 2024), highlighting the exploration of p53-mediated ferroptosis as a promising avenue for novel therapeutic strategies.
6 Therapeutic strategies targeting ferroptosis in PTSD
Several ferroptosis modulators have been explored for their possible therapeutic benefits in PTSD treatment (Table 2).
TABLE 2
| Intervention | Mechanism | Potential effect | References |
| NAC | Antioxidant, scavenges ROS, inhabits ferroptosis | Reduces oxidative stress, alleviates PTSD symptoms | Maier et al., 2020 |
| Tempol | Antioxidant, modulates catalase and SOD activity, maintains GSH/GSSG ratio | Prevents lipid peroxidation, alleviates PTSD symptoms | Alzoubi et al., 2018b |
| EDA | Suppresses oxidative stress and neuroinflammation | Alleviates depression | Dang et al., 2022 |
| NaHS | Antioxidant | Alleviates anxiety and depression symptoms, reduces iron accumulation | Wang et al., 2021 |
| Cerebrolysin | Maintains GSH, GSSG and GSH/GSSG ratio, prevents oxidative damage | Reduces oxidative stress, lowers ferroptosis risk | Alzoubi et al., 2018b |
| Taurine | Antioxidant, inhibits ferroptosis | Mitigates oxidative stress, improves mitochondrial function | Bhattacharjee et al., 2021 |
| Vitamin E | Reduces oxidative stress biomarkers, protects neurons | Reduces oxidative stress, prevents ferroptosis, supports neuronal survival and function | Ahmed et al., 2020 |
| Etazolate | Regulates GSH, GSSG, GPX4 and TBARs levels | Mitigates oxidative stress, antidepressant effects | Alzoubi et al., 2019 |
| Acupuncture | Increases Nrf2, HO-1 and BDNF levels, inhibits ferroptosis | Reduces oxidative stress and improves PTSD symptoms | Zhou et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2024 |
Therapeutic interventions targeting ferroptosis in PTSD.
NAC, N-acetylcysteine; EDA, edaravone; NaHS, sodium hydrosulfide; BDNF, brain derived neurotrophic factor; GSH, glutathione; GSSH, glutathione disulfide; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPX, glutathione peroxidase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4.
6.1 free radical scavenger
As a thiol compound and a precursor to L-cysteine and reduced GSH, NAC functions as a free radical scavenger. Specifically, it reduces oxidative stress by neutralizing ROS and protecting cells from oxidative damage (Li J. et al., 2022). This is particularly pertinent in PTSD, where oxidative stress is frequently implicated in the pathophysiology of the disorder. Beyond its antioxidant role, NAC may also inhibit ferroptosis by activating Nrf2, which regulates the expression of metallothioneins, ferritins, and ferroportin to prevent iron accumulation (Kerins and Ooi, 2018). Notably, treatment with NAC has been shown to alleviate symptoms in veterans diagnosed with PTSD (Maier et al., 2020). Further research has confirmed that NAC treatment significantly improves cognitive function and reduces apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in PTSD model mice (Zhou et al., 2025). Collectively, these findings indicate that NAC may effectively counteract the oxidative pathologies associated with PTSD, thereby offering a promising avenue for this debilitating condition. Similarly, Tempol (4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl), a nitroxide radical compound that has demonstrated potent antioxidant properties in PTSD models. Specifically, it modulates catalase and SOD activity while maintaining reduced GSH-to-glutathione disulfide (GSH/GSSG) ratio (Alzoubi et al., 2018b). This holds significant importance in the context of ferroptosis, as maintaining the GSH/GSSG ratio is crucial for preventing lipid peroxidation and the cell death associated with ferroptosis. Furthermore, edaravone (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one, EDA), another free radical scavenging, has been shown to alleviate anxiety and depressive-like behaviors in mouse models by regulating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation (Dang et al., 2022). Given that PTSD is a psychiatric disorder characterized by anxiety and depression, edaravone may provide therapeutic benefits for PTSD patients.
Evidence indicates that GPX4 is crucial for protecting cells against ferroptosis by reducing lipid peroxides (Zhang et al., 2024). Additionally, the solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) also plays a key role in regulating the cystine-glutamate antiporter system, which maintains intracellular GSH levels and effectively prevents ferroptosis (Wang et al., 2023). Notably, sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS), a prominent scavenger of free radicals, has been shown to alleviate anxiety and behaviors symptoms. This effect is probably linked to its capacity to reduce iron accumulation and oxidative stress while enhancing the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 (Wang et al., 2021). Given the persistent oxidative stress, iron metabolism abnormalities, and anxiety or depression symptoms in PTSD patients. NaHS may represent a novel and effective strategy for the treatment of PTSD, warranting further investigation in clinical settings. Furthermore, strategies involving iron chelators and free radical scavengers have emerged as promising approaches to inhibit ferroptosis. Therefore, these strategies may potentially improve therapeutic efficacy, thereby providing a more effect strategies for PTSD treatment.
6.2 Antioxidants
Therapies targeting oxidative stress have shown significant potential in alleviating PTSD symptoms. For example, cerebrolysin is a mixture of low molecular weight neuropeptides sourced from porcine brain, and it has been demonstrated to effectively prevent abnormal alterations in GSH, GSSG, and the GSH/GSSG ratio in PTSD models induced by SPS (Alzoubi et al., 2018b). Given that ferroptosis is driven by oxidative stress-mediated lipid peroxidation, cerebrolysin’s ability to sustain antioxidant homeostasis could potentially reduce the risk of ferroptosis in PTSD. Similarly, taurine exerts therapeutic effects through its antioxidant properties, which help stabilize the mitochondrial membrane potential and influence the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) (Palmi et al., 2000). Additionally, research in PTSD models has shown that treatment with taurine can improve mitochondrial function (Bhattacharjee et al., 2021). Given that mitochondrial dysfunction plays a significant role in both inducting oxidative stress and progressing ferroptosis, taurine’s role in maintaining mitochondrial health may help mitigate oxidative stress and thereby inhibit ferroptosis.
Moreover, vitamin E, a fat-soluble vitamin that readily crosses the blood-brain barrier (BBB), has shown potential in reducing oxidative stress (Miyazawa et al., 2019). Studies have indicated that treatment with vitamin E can prevent cognitive decline in individuals affected by various neurodegenerative disorders associated with ferroptosis, including PD and AD (La Fata et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2017). In individuals with PTSD, vitamin E has also been found to effectively lower oxidative stress biomarkers, including the decreased GSH/GSSG ratio and diminished activity of GPX and catalase. Additionally, it protects against the decline in global histone 3 acetylation and antioxidant defense gene named brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels (Ahmed et al., 2020). Notably, histone acetylation is an important epigenetic modification that has been shown to regulate the expression of ferroptosis-related genes, such as GPX4 and SLC7A11, thereby reducing the sensitivity of cells to ferroptosis and playing a crucial role in regulating this cell death process (Yang et al., 2023). These findings suggest that vitamin E may exert its therapeutic effects in PTSD by preventing ferroptosis and preserving neuronal survival and function. Additionally, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors have garnered attention for their ability to reduce oxidative stress and the risk of ferroptosis by increasing intracellular cAMP levels. Etazolate, a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor specific for cAMP, has garnered attention for its anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. Research has confirmed that treatment with etazolate can effectively restore the levels and activities of GSH, GSSG, GPX, and TBARs in PTSD models (Alzoubi et al., 2019). This restoration suggests that etazolate may mitigate oxidative stress and thereby reduce the risk of ferroptosis, contributing to its therapeutic potential in PTSD. In summary, antioxidants such as Cerebrolysin, taurine, vitamin E, and etazolate have shown promise in reducing the risk of ferroptosis in PTSD by mitigating oxidative stress, maintaining antioxidant balance, and preserving mitochondrial health. These findings offer new insights into the treatment of PTSD and provide valuable references for future research and clinical applications.
6.3 Acupuncture
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) encompasses a range of therapeutic approaches, including herbal medicines, acupuncture, and moxibustion, and is known for its multi-pathway, multi-target, and high safety profile (Zhou et al., 2024). Among these, acupuncture, an external therapeutic approach, has been proven effective for various conditions. One important modality of acupuncture therapy is electroacupuncture, which combines traditional acupuncture with modern electrical stimulation to enhance therapeutic effects. Specifically, electroacupuncture has been shown to promote the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 within neurons (Chen et al., 2024). Notably, Nrf2, a key transcription factor, is crucial for coordinating antioxidant responses and significantly contributes to the reduction of ferroptosis (Ma, 2013). Specifically, Nrf2 not only modulates the expression and functionality of GPX4 but also regulates the expression of genes encoding proteins essential for GSH synthesis, including System Xc– and the catalytic/modulatory subunits of glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCLC/GCLM), and glutathione synthetase (GSS). Importantly, elevated Nrf2 levels enhance xCT expression and modify GPX4 synthesis and function, ultimately inhibiting ferroptosis (Anandhan et al., 2020). Research has indicated that electroacupuncture treatment can effectively inhibit ferroptosis by activating Nrf2, increasing protein expression of solute carrier family 7 member 11 (xCT) and GPX4, thereby reducing cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (Zhu et al., 2024). Similar in PTSD, pretreatment with electroacupuncture provides therapeutic benefits for PTSD by increasing Nrf2, HO-1, and BDNF levels, thereby activating antioxidant pathways (Zhou et al., 2019). However, these therapeutic benefits of electroacupuncture pretreatment are negated when Nrf2 is knocked down in the hippocampus. These findings suggest that electroacupuncture’s therapeutic benefits may be mediated through its protective effects against ferroptosis. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the underlying mechanisms and explore the potential clinical applications of electroacupuncture in treating PTSD and other neurodegenerative disorders.
7 Conclusion and future perspective
In this review, we analyzed numerous studies focusing on the role of ferroptosis in PTSD. This hypothesis that ferroptosis might contribute to the intricate pathogenic processes of PTSD is supported by some critical findings. Firstly, the ACSL4, ACO1, and GSS genes have been verified to serve as two key functions: they are not only key predictors of PTSD risk but also play essential roles in the development of the disorder. Secondly, the hallmark features of ferroptosis, including iron dysregulation, lipid peroxidation, neuroinflammation as well as mitochondrial dysfunction, are clearly observed in PTSD patients. Additionally, many therapeutic approaches for PTSD have been found to exhibit anti-ferroptotic effects. Based on these established associations, we encourage more in-depth research to further explore the interplay between ferroptosis and PTSD.
Although there is increasing attention on ferroptosis and its possible involvement in PTSD, the existing literature has certain methodological limitations that require to be addressed. Firstly, most of the existing studies rely on animal models to explore the mechanisms underlying ferroptosis in PTSD. While these models offer valuable insights, they may not fully capture the complexity of PTSD in humans. Therefore, these findings from animal models should be interpreted with caution and validated in human studies. Moreover, the use of different animal species and genetic backgrounds can introduce variability in the results. This variability can complicate the interpretation of results and the generalizability of findings across different studies. In conclusion, while the current literature provides a foundation for understanding the potential role of ferroptosis in PTSD, significant gaps remain. Addressing the methodological limitations of existing studies will be crucial for advancing our knowledge and developing effective therapeutic strategies for PTSD.
Statements
Author contributions
QZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. J-DM: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HC: Investigation, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. Y-MW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82374077), Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Innovation Talent of Shaanxi Province (TZKN-CXRC-02), and the Science and Technology Innovation Talents of Xianyang City (L2024-CXNL-KJRCTD-KJRC-0003).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ACO1, aconitate hydratase 1; ACSL4, Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BBB, blood-brain barrier cAMP, cyclic AMP; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; EDA, edaravone; FAS, fatty acid synthesis; FPN1, ferroportin 1; FoxO3a, forkhead box O3a; FTH1, ferritin heavy chain; FTL, ferritin light chain; GCLC/GCLM, glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic/modulatory subunits; GSH, glutathione; GSS, glutathione synthetase; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; GPX, glutathione peroxidase; HSPB1, heat shock protein family B member 1; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; IREB2, iron-responsive element-binding protein 2; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; MDA, malondialdehyde; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; NaHS, sodium hydrosulfide; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PD, Parkinson’s disease; PUFA-CoA, polyunsaturated fatty acid-CoA; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; PINK1, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; Parkin, Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin protein ligase; PTSD, post-traumatic stress disorder; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SPS, single prolonged; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11 stress; TBARs, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TfR1, transferrin receptor 1; xCT, system Xc–.
References
1
Ahmed M. Alzoubi K. H. Khabour O. F. (2020). Vitamin E prevents the cognitive impairments in post-traumatic stress disorder rat model: Behavioral and molecular study.Psychopharmacology237599–607. 10.1007/s00213-019-05395-w
2
Alzoubi K. H. Al Subeh Z. Y. Khabour O. F. (2019). Molecular targets for the interactive effect of etazolate during post-traumatic stress disorder: Role of oxidative stress, BDNF and histones.Behav. Brain Res.369:111930. 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.111930
3
Alzoubi K. H. Al-Ibbini A. M. Nuseir K. Q. (2018a). Prevention of memory impairment induced by post-traumatic stress disorder by cerebrolysin.Psychiatry Res.270430–437. 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.10.008
4
Alzoubi K. H. Rababa’h A. M. Al Yacoub O. N. (2018b). Tempol prevents post-traumatic stress disorder induced memory impairment.Physiol. Behav.184189–195. 10.1016/j.physbeh.2017.12.002
5
Anandhan A. Dodson M. Schmidlin C. J. Liu P. Zhang D. D. (2020). Breakdown of an ironclad defense system: The critical role of NRF2 in mediating ferroptosis.Cell Chem. Biol.27436–447. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.03.011
6
Atli A. Bulut M. Bez Y. Kaplan İ Özdemir P. G. Uysal C. et al (2016). Altered lipid peroxidation markers are related to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and not trauma itself in earthquake survivors.Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci.266329–336. 10.1007/s00406-015-0638-5
7
Bao W.-D. Pang P. Zhou X.-T. Hu F. Xiong W. Chen K. et al (2021). Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease.Cell Death Differ.281548–1562. 10.1038/s41418-020-00685-9
8
Bhargava A. Knapp J. D. Fiehn O. Neylan T. C. Inslicht S. S. (2024). An exploratory study on lipidomic profiles in a cohort of individuals with posttraumatic stress disorder.Sci. Rep.14:15256. 10.1038/s41598-024-62971-7
9
Bhattacharjee A. Prajapati S. K. Krishnamurthy S. (2021). Supplementation of taurine improves ionic homeostasis and mitochondrial function in the rats exhibiting post-traumatic stress disorder-like symptoms.Eur. J. Pharmacol.908:174361. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174361
10
Borovac Štefanović L. Kalinić D. Mimica N. Beer Ljubić B. Aladrović J. et al (2015). Oxidative status and the severity of clinical symptoms in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder.Ann. Clin. Biochem.5295–104. 10.1177/0004563214528882
11
Chen Y. Li Y. Wu M. Li Z. (2024). Electroacupuncture improves cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice by inhibiting oxidative stress related hippocampal neuronal ferroptosis. Brain Res. 1831:148744. 10.1016/j.brainres.2023.148744
12
Cotticelli M. G. Xia S. Lin D. Lee T. Terrab L. Wipf P. et al (2019). Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for friedreich’s ataxia.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.36947–54. 10.1124/jpet.118.252759
13
Dang R. Wang M. Li X. Wang H. Liu L. Wu Q. et al (2022). Edaravone ameliorates depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1/Gpx4 pathway.J. Neuroinflamm.19:41. 10.1186/s12974-022-02400-6
14
Dichtl S. Haschka D. Nairz M. Seifert M. Volani C. Lutz O. et al (2018). Dopamine promotes cellular iron accumulation and oxidative stress responses in macrophages.Biochem. Pharmacol.148193–201. 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.001
15
Ding K. Liu C. Li L. Yang M. Jiang N. Luo S. et al (2023). Acyl-CoA synthase ACSL4: An essential target in ferroptosis and fatty acid metabolism.Chin. Med. J.1362521–2537. 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002533
16
Dixon S. J. Lemberg K. M. Lamprecht M. R. Skouta R. Zaitsev E. M. Gleason C. E. et al (2012). Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death.Cell1491060–1072. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
17
Feng H. Stockwell B. R. (2018). Unsolved mysteries: How does lipid peroxidation cause ferroptosis?PLoS Biol.16:e2006203. 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006203
18
Gan B. (2021). Mitochondrial regulation of ferroptosis.J. Cell Biol.220:e202105043. 10.1083/jcb.202105043
19
Gao G. Chang Y.-Z. (2014). Mitochondrial ferritin in the regulation of brain iron homeostasis and neurodegenerative diseases.Front. Pharmacol.5:19. 10.3389/fphar.2014.00019
20
Gao G. Li J. Zhang Y. Chang Y.-Z. (2019). Cellular iron metabolism and regulation.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.117321–32. 10.1007/978-981-13-9589-5_2
21
Gleason A. Bush A. I. (2021). Iron and ferroptosis as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease.Neurotherapeutics18252–264. 10.1007/s13311-020-00954-y
22
Gupta S. Guleria R. S. (2022). Involvement of nuclear Factor-κB in inflammation and neuronal plasticity associated with post-traumatic stress disorder.Cells11:2034. 10.3390/cells11132034
23
Han H. Zhang G. Zhang X. Zhao Q. (2024). Nrf2-mediated ferroptosis inhibition: A novel approach for managing inflammatory diseases.Inflammopharmacology322961–2986. 10.1007/s10787-024-01519-7
24
Hare D. J. Double K. L. (2016). Iron and dopamine: A toxic couple.Brain1391026–1035. 10.1093/brain/aww022
25
Harnett N. G. Goodman A. M. Knight D. C. (2020). PTSD-related neuroimaging abnormalities in brain function, structure, and biochemistry.Exp. Neurol.330:113331. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113331
26
Hassan W. Noreen H. Castro-Gomes V. Mohammadzai I. da Rocha J. B. T. Landeira-Fernandez J. (2016). Association of oxidative stress with psychiatric disorders.Curr. Pharm. Des.222960–2974. 10.2174/1381612822666160307145931
27
Hori H. Kim Y. (2019). Inflammation and post-traumatic stress disorder.Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci.73143–153. 10.1111/pcn.12820
28
Jelinek A. Heyder L. Daude M. Plessner M. Krippner S. Grosse R. et al (2018). Mitochondrial rescue prevents glutathione peroxidase-dependent ferroptosis.Free Radic. Biol. Med.11745–57. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.01.019
29
Ji H. Wang W. Li X. Han X. Zhang X. Wang J. et al (2022). p53: A double-edged sword in tumor ferroptosis.Pharmacol. Res.177:106013. 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106013
30
Jiang X. Stockwell B. R. Conrad M. (2021). Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease.Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22266–282. 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
31
Joshi J. G. Clauberg M. (1988). Ferritin: An iron storage protein with diverse functions.Biofactors1207–212.
32
Kawabata H. (2019). Transferrin and transferrin receptors update.Free Radic. Biol. Med.13346–54. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.037
33
Kelley D. P. Chaichi A. Duplooy A. Singh D. Gartia M. R. Francis J. (2022). Labelfree mapping and profiling of altered lipid homeostasis in the rat hippocampus after traumatic stress: Role of oxidative homeostasis.Neurobiol. Stress20:100476. 10.1016/j.ynstr.2022.100476
34
Kerins M. J. Ooi A. (2018). The roles of NRF2 in modulating cellular iron homeostasis.Antioxid. Redox Signal.291756–1773. 10.1089/ars.2017.7176
35
Kim J. W. Lee J.-Y. Oh M. Lee E.-W. (2023). An integrated view of lipid metabolism in ferroptosis revisited via lipidomic analysis.Exp. Mol. Med.551620–1631. 10.1038/s12276-023-01077-y
36
Kmita H. Pinna G. Lushchak V. I. (2023). Potential oxidative stress related targets of mitochondria-focused therapy of PTSD.Front. Physiol.14:1266575. 10.3389/fphys.2023.1266575
37
La Fata G. Weber P. Mohajeri M. H. (2014). Effects of vitamin E on cognitive performance during ageing and in Alzheimer’s disease.Nutrients65453–5472. 10.3390/nu6125453
38
Lee H. Zandkarimi F. Zhang Y. Meena J. K. Kim J. Zhuang L. et al (2020). Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis.Nat. Cell Biol.22225–234. 10.1038/s41556-020-0461-8
39
Lee J.-Y. Kim W. K. Bae K.-H. Lee S. C. Lee E.-W. (2021). Lipid metabolism and ferroptosis.Biology10:184. 10.3390/biology10030184
40
Lei L. Lu Q. Ma G. Li T. Deng J. Li W. (2022). P53 protein and the diseases in central nervous system.Front. Genet.13:1051395. 10.3389/fgene.2022.1051395
41
Levine A. J. (2020). p53: 800 million years of evolution and 40 years of discovery.Nat. Rev. Cancer20471–480. 10.1038/s41568-020-0262-1
42
Li C. Wu Z. Xue H. Gao Q. Zhang Y. Wang C. et al (2022a). Ferroptosis contributes to hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats: Role of the SIRT1/Nrf2/GPx4 signaling pathway.CNS Neurosci. Ther.282268–2280. 10.1111/cns.13973
43
Li J. Cao F. Yin H.-L. Huang Z.-J. Lin Z.-T. Mao N. et al (2020). Ferroptosis: Past, present and future.Cell Death Dis.11:88. 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
44
Li J. Jia B. Cheng Y. Song Y. Li Q. Luo C. (2022b). Targeting molecular mediators of ferroptosis and oxidative stress for neurological disorders.Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2022:3999083. 10.1155/2022/3999083
45
Li J. Jia Y.-C. Ding Y.-X. Bai J. Cao F. Li F. (2023). The crosstalk between ferroptosis and mitochondrial dynamic regulatory networks.Int. J. Biol. Sci.192756–2771. 10.7150/ijbs.83348
46
Liu J. Kang R. Tang D. (2022). Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis.FEBS J.2897038–7050. 10.1111/febs.16059
47
Liu Y. Gu W. (2022). p53 in ferroptosis regulation: The new weapon for the old guardian.Cell Death Differ.29895–910. 10.1038/s41418-022-00943-y
48
Liu Y. Tavana O. Gu W. (2019). p53 modifications: Exquisite decorations of the powerful guardian.J. Mol. Cell Biol.11564–577. 10.1093/jmcb/mjz060
49
López-López B. Crespo I. (2025). Neuroplasticity in post-traumatic stress disorder.Rev. Neurol.80:33478. 10.31083/RN33478
50
Lushchak O. Strilbytska O. Koliada A. Storey K. B. (2022). An orchestrating role of mitochondria in the origin and development of post-traumatic stress disorder.Front. Physiol.13:1094076. 10.3389/fphys.2022.1094076
51
Lv J. Hou B. Song J. Xu Y. Xie S. (2022). The relationship between ferroptosis and diseases.J. Multidiscip. Healthc.152261–2275. 10.2147/JMDH.S382643
52
Lv Y. Zhao X. Zhang R. He Z. Xu Y. Tu L. et al (2024). Oxidative stress mediates hippocampal neuronal apoptosis through ROS/JNK/P53 pathway in rats with PTSD triggered by high-voltage electrical burn.Folia Morphol.83300–313. 10.5603/fm.95727
53
Ma Q. (2013). Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity.Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.53401–426. 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320
54
Maercker A. Cloitre M. Bachem R. Schlumpf Y. R. Khoury B. Hitchcock C. et al (2022). Complex post-traumatic stress disorder.Lancet40060–72. 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00821-2
55
Mahoney-Sánchez L. Bouchaoui H. Ayton S. Devos D. Duce J. A. Devedjian J.-C. (2021). Ferroptosis and its potential role in the physiopathology of Parkinson’s Disease.Prog. Neurobiol.196:101890. 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101890
56
Maier A. Dharan A. Oliver G. Berk M. Redston S. Back S. E. et al (2020). A multi-centre, double-blind, 12-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to assess the efficacy of adjunctive N-Acetylcysteine for treatment-resistant PTSD: A study protocol.BMC Psychiatry20:397. 10.1186/s12888-020-02793-9
57
McGahan M. C. Harned J. Mukunnemkeril M. Goralska M. Fleisher L. Ferrell J. B. (2005). Iron alters glutamate secretion by regulating cytosolic aconitase activity.Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol.288C1117–C1124. 10.1152/ajpcell.00444.2004
58
Miller M. W. Lin A. P. Wolf E. J. Miller D. R. (2018). Oxidative stress, inflammation, and neuroprogression in chronic PTSD.Harv. Rev. Psychiatry2657–69. 10.1097/HRP.0000000000000167
59
Miyazawa T. Burdeos G. C. Itaya M. Nakagawa K. Miyazawa T. (2019). Vitamin E: Regulatory redox interactions.IUBMB Life71430–441. 10.1002/iub.2008
60
Nutt D. J. (2000). The psychobiology of posttraumatic stress disorder.J. Clin. Psychiatry61 (Suppl. 5):24–29; discussion 30-32.
61
Palmi M. Youmbi G. T. Sgaragli G. Meini A. Benocci A. Fusi F. et al (2000). The mitochondrial permeability transition and taurine.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.48387–96. 10.1007/0-306-46838-7_8
62
Papageorgiou M. P. Filiou M. D. (2024). Mitochondrial dynamics and psychiatric disorders: The missing link.Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.165:105837. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105837
63
Pivac N. Vuic B. Sagud M. Nedic Erjavec G. Nikolac Perkovic M. Konjevod M. et al (2023). PTSD, immune system, and inflammation.Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.1411225–262. 10.1007/978-981-19-7376-5_11
64
Pope L. E. Dixon S. J. (2023). Regulation of ferroptosis by lipid metabolism.Trends Cell Biol.331077–1087. 10.1016/j.tcb.2023.05.003
65
Prajapati S. K. Ahmed S. Rai V. Gupta S. C. Krishnamurthy S. (2024). Suvorexant improves mitochondrial dynamics with the regulation of orexinergic and mTOR activation in rats exhibiting PTSD-like symptoms.J. Affect. Disord.35024–38. 10.1016/j.jad.2024.01.045
66
Qian Z. Zhang Q. Li P. Li Y. Zhang Y. Li R. et al (2024). A disintegrin and metalloproteinase-8 Protects against erastin-induced neuronal ferroptosis via activating Nrf2/HO-1/FTH1 signaling pathway.Mol. Neurobiol.613490–3502. 10.1007/s12035-023-03782-1
67
Ressler K. J. Berretta S. Bolshakov V. Y. Rosso I. M. Meloni E. G. Rauch S. L. et al (2022). Post-traumatic stress disorder: Clinical and translational neuroscience from cells to circuits.Nat. Rev. Neurol.18273–288. 10.1038/s41582-022-00635-8
68
Shah R. Shchepinov M. S. Pratt D. A. (2018). Resolving the role of lipoxygenases in the initiation and execution of ferroptosis.ACS Cent. Sci.4387–396. 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00589
69
Song X. Hao X. Zhu B. T. (2024). Role of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in chemically-induced ferroptosis.Free Radic. Biol. Med.223473–492. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.07.006
70
Souza R. R. Noble L. J. McIntyre C. K. (2017). Using the single prolonged stress model to examine the pathophysiology of PTSD.Front. Pharmacol.8:615. 10.3389/fphar.2017.00615
71
Sun X. Ou Z. Xie M. Kang R. Fan Y. Niu X. et al (2015). HSPB1 as a novel regulator of ferroptotic cancer cell death.Oncogene345617–5625. 10.1038/onc.2015.32
72
Tang D. Chen X. Kang R. Kroemer G. (2021). Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications.Cell Res.31107–125. 10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
73
Tezcan E. Atmaca M. Kuloglu M. Ustundag B. (2003). Free radicals in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder.Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci.25389–91. 10.1007/s00406-003-0413-x
74
Wang C. Liu H. Xu S. Deng Y. Xu B. Yang T. et al (2023). Ferroptosis and neurodegenerative diseases: Insights into the regulatory roles of SLC7A11.Cell Mol. Neurobiol.432627–2642. 10.1007/s10571-023-01343-7
75
Wang Y. Wang S. Xin Y. Zhang J. Wang S. Yang Z. et al (2021). Hydrogen sulfide alleviates the anxiety-like and depressive-like behaviors of type 1 diabetic mice via inhibiting inflammation and ferroptosis.Life Sci.278:119551. 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119551
76
Watling S. E. Rhind S. G. Warsh J. Green D. McCluskey T. Tong J. et al (2023). Exploring brain glutathione and peripheral blood markers in posttraumatic stress disorder: A combined [1H]MRS and peripheral blood study.Front. Psychiatry14:1195012. 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1195012
77
Welcome M. O. Mastorakis N. E. (2020). Stress-induced blood brain barrier disruption: Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways.Pharmacol. Res.157:104769. 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104769
78
Wilson C. B. McLaughlin L. D. Nair A. Ebenezer P. J. Dange R. Francis J. (2013). Inflammation and oxidative stress are elevated in the brain, blood, and adrenal glands during the progression of post-traumatic stress disorder in a predator exposure animal model.PLoS One8:e76146. 10.1371/journal.pone.0076146
79
Wu Q. Hao Q. Li H. Wang B. Wang P. Jin X. et al (2021). Brain iron deficiency and affected contextual fear memory in mice with conditional Ferroportin1 ablation in the brain.FASEB J.35:e21174. 10.1096/fj.202000167RR
80
Xie Y. Hou W. Song X. Yu Y. Huang J. Sun X. et al (2016). Ferroptosis: Process and function.Cell Death Differ.23369–379. 10.1038/cdd.2015.158
81
Yang F. Wolk A. Håkansson N. Pedersen N. L. Wirdefeldt K. (2017). Dietary antioxidants and risk of Parkinson’s disease in two population-based cohorts.Mov. Disord.321631–1636. 10.1002/mds.27120
82
Yang M. Luo H. Yi X. Wei X. Jiang D.-S. (2023). The epigenetic regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis and its implications for biological processes and diseases.MedComm4:e267. 10.1002/mco2.267
83
Yapa N. M. B. Lisnyak V. Reljic B. Ryan M. T. (2021). Mitochondrial dynamics in health and disease.FEBS Lett.5951184–1204. 10.1002/1873-3468.14077
84
Zhang G.-Q. Yang J.-X. Zhang Y.-Q. Liang X. Hu M. Fan J. (2014). Altered neurotransmitter levels with post-traumatic stress disorder.Turk. Neurosurg.24844–848. 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.8723-13.1
85
Zhang W. Liu Y. Liao Y. Zhu C. Zou Z. (2024). GPX4, ferroptosis, and diseases.Biomed. Pharmacother.174:116512. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116512
86
Zhao M. Yu Z. Zhang Y. Huang X. Hou J. Zhao Y. et al (2016). Iron-induced neuronal damage in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder.Neuroscience33090–99. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.05.025
87
Zhong S. Chen W. Wang B. Gao C. Liu X. Song Y. et al (2023). Energy stress modulation of AMPK/FoxO3 signaling inhibits mitochondria-associated ferroptosis.Redox Biol.63:102760. 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102760
88
Zhou C.-H. Xue F. Xue S.-S. Sang H.-F. Liu L. Wang Y. et al (2019). Electroacupuncture pretreatment ameliorates PTSD-Like behaviors in rats by enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis via the Keap1/Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway.Front. Cell Neurosci.13:275. 10.3389/fncel.2019.00275
89
Zhou Y. Yuan X. Guo M. (2025). Unlocking NAC’s potential ATF4 and m6A dynamics in rescuing cognitive impairments in PTSD.Metab. Brain Dis.40:129. 10.1007/s11011-024-01485-7
90
Zhou Z. Yu Y. Miao J. Wang G. Wang Y. Wang T. et al (2024). Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in treating central nervous system diseases by modulating ferroptosis.Am. J. Chin. Med.521989–2019. 10.1142/S0192415X24500770
91
Zhu J. Zhang Y. Ren R. Sanford L. D. Tang X. (2022). Blood transcriptome analysis: Ferroptosis and potential inflammatory pathways in post-traumatic stress disorder.Front. Psychiatry13:841999. 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.841999
92
Zhu W. Dong J. Han Y. (2024). Electroacupuncture downregulating neuronal ferroptosis in MCAO/R rats by activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis.Neurochem. Res.492105–2119. 10.1007/s11064-024-04185-x
93
Zieker J. Zieker D. Jatzko A. Dietzsch J. Nieselt K. Schmitt A. et al (2007). Differential gene expression in peripheral blood of patients suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder.Mol. Psychiatry12116–118. 10.1038/sj.mp.4001905
94
Zuo H.-L. Huang H.-Y. Lin Y.-C.-D. Liu K.-M. Lin T.-S. Wang Y.-B. et al (2023). Effects of natural products on enzymes involved in ferroptosis: Regulation and implications.Molecules28:7929. 10.3390/molecules28237929
Summary
Keywords
post-traumatic stress disorder, ferroptosis, lipid peroxidation, iron dysregulation, inflammatory responses, therapeutic target
Citation
Zhang Q, Mao J-D, Chen H, Wang M, Wu Y-M and Wang C (2025) Ferroptosis as a potential therapeutic target for post-traumatic stress disorder. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 18:1648047. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1648047
Received
17 June 2025
Accepted
25 September 2025
Published
23 October 2025
Volume
18 - 2025
Edited by
Pavlo Petakh, Uzhhorod National University, Ukraine
Reviewed by
Amanda Alves Marcelino Da Silva, Universidade de Pernambuco, Brazil
Chayan Munshi, Ethophilia Research Foundation, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Mao, Chen, Wang, Wu and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chuan Wang, wangchuan@sntcm.edu.cnYu-Mei Wu, yumeiwu@fmmu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.