Abstract
Background:
Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (P. lactiflora) has long been used in traditional medicine for pain relief. Paeoniflorin as the main glucoside of P. lactiflora root extract could determine its pharmacological effects. Thus, the research was aimed at investigation of P. lactiflora root extract as a natural modulator of LPS-induced inflammation and I type collagen synthesis in skin and oral gingival cells.
Methods:
The study was conducted using Paeonia lactiflora root extract standardized for paeoniflorin by HPLC-UV method. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channel and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) were chosen as the main targets for paeoniflorin in the P. lactiflora extract in silico. Maximum tolerated concentration was evaluated on keratinocytes as 0.5 mg/mL through MTT assay. In vitro study was conducted to determine the effects of P. lactiflora extract on LPS-induced inflammation and tissue destruction markers in skin keratinocytes, dermal and gingival fibroblasts using ELISA.
Results:
Firstly, the standardized extract at concentrations of 0.03 mg/mL, 0.1 mg/mL and 0.5 mg/mL reduced TRPV1 amount in skin keratinocytes by 38.06%, 52.24% and 67.05% (P < 0.001). Secondly, it was demonstrated that the extract at concentration of 0.5 mg/mL eliminated inflammatory stress induced by LPS reducing the production of TNF-α and production of IL-6 and IL-13 up to 25% (P < 0.01) and 55% (P < 0.001). Moreover, the extract demonstrated a protective effect on tissues destruction by reducing MMP-9 production by 70.27% in dermal fibroblasts and MMP-8 production by 39.32% in gingival fibroblasts.
Conclusion and discussion:
The study underscores the beneficial contribution of P. lactiflora extract on LPS-induced inflammation in skin and oral gingival cells. Specifically, P. lactiflora extract containing paeoniflorin is a promising natural modulator of inflammation, providing complex protection against I type collagen destruction in both cells. The identified phytochemical could be targeted for future investigations including in vivo studies on different aspects of skin inflammation process, followed by the development of novel formulations with it.
1 Introduction
Skin inflammation is a protective biological mechanism against tissue destruction, mediated by various inflammatory factors, such as transient receptor potential vaniloid (TRPV) channels, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and characterized by the dysfunction of both immune and non-immune cells (Bagood and Isseroff, 2021; Lee and Kim, 2022; Shirley et al., 2024). Advances in understanding inflammation biology are rapidly being recognized as pharmacological opportunities for treatment of skin diseases especially, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, eczema and others (Shirley et al., 2024). In this context, it is important that these inflammation-related targets are tightly regulated to alleviate the inflammatory reaction in skin and gingival cells.
Transient receptor potential vaniloid (TRPV) channels are one of seven types of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels characterized by the presence of ankyrin repeats as part of the intracellular N-terminal structural domains and sensitivity to vanilloid and capsaicin (Zhang et al., 2023). Structurally, TRPVs are tetramers where each monomer consists of six transmembrane helices (Hellmich and Gaudet, 2014). These channels are widely distributed in various human tissues and organs, including kidney, liver, neurons, intestine, and skin tissues: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. They play an important role in maintaining skin homeostasis and in the transmission of sensations, especially pain regulation (Zhang et al., 2023; Okada et al., 2021).
TRPV1 channels play one of the main roles in pain signaling in the skin (Iftinca et al., 2021). For example, TRPV1 has been shown to be involved in skin itching (Feng et al., 2017), severe skin redness like a rosacea (Lee et al., 2023) and apparently herpes zoster (Han et al., 2016). TRPV1 is also involved in inflammatory and pain processes in periodontitis and mediates pain signal transmission through the trigeminal nerve (Evangeliou et al., 2023).
It is known that TRPV1 activity can be significantly increased under the action of inflammatory mediators, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) (Wang et al., 2018), interleukin-6 (IL-6) (Fang et al., 2015), interleukin-13 (IL-13) (Rehman et al., 2013) due to the activation of phospholipase C as well as protein kinase A and protein kinase C signaling pathways (Planells-Cases et al., 2005). Bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), being one of the major inducers of the innate immune response with associated inflammation, also contribute to increased TRPV1 expression (Luo et al., 2021; Diogenes et al., 2011; Sattler et al., 2021). Moreover, TRPV1 itself can also enhance the inflammatory process by promoting IL-6 production (Obi et al., 2017). It was established that the local application of capsaicin in the alveolar mucosa has been shown to cause a TRPV1-mediated increase in the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8), which is one of the key markers of periodontitis, gingivitis and carious lesions (Avellan et al., 2006; Al-Majid e al., 2018; Kuula et al., 2009; Atanasova et al., 2023). In addition to oral inflammatory diseases, the association of MMP-8 with acne, skin xerosis and dermatoses has been established (Tsaousi et al., 2016; Tominaga et al., 2011). It is possible that TRPV1 similarly modulates the secretion of MMP-9, another important metalloproteinase associated with inflammatory skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis (Li et al., 2015; Michalak-Stoma et al., 2021; Harper et al., 2010).
As the most abundant proteinases in periodontal tissues, MMP-8 and MMP-9 are actively involved in the degradation of I type collagen type in oral inflammatory processes such as periodontitis and gingivitis (Luchian et al., 2022; Li et al., 2012). In addition, MMP-9 is expressed by human skin cells during wound injury and can probably also induce I type collagen degradation during the concomitant inflammatory process (Cecchi et al., 2024). To summarize, TRPV1 can be not only a key participant in the transmission of pain signals in skin and oral inflammation, but also modulator of MMP-8 and MMP-9 activity in skin and gingival cells.
Due to this fact, the development of drugs that block TRPV1 is one of the topical areas of pharmaceutics. For example, a new drug substance named MK-2295 (Merck Sharp and Dohme Corp., New Jersey, United States) as a TRPV1 antagonist is currently being studied in the context of combating postoperative dental pain (ClinicalTrials, 0038). TRPV1 antagonists are being developed for the treatment of chronic pain due to knee osteoarthritis and postherpetic neuralgia (ClinicalTrials, 0168). In experimental models, spilanthol, a natural alkaloid from Acmella oleracea (Yien et al., 2023), and eucalyptol, one of the main components of eucalyptus oil (Yin et al., 2020), blocks TRPV1, contributing to the reduction of pain sensation during inflammation. However, both molecules are lipophilic and cannot be dissolved in aqueous media, which imposes certain limitations on the convenience of their use in cosmetic products (Boonen et al., 2010; Hoch et al., 2023). According to the published data, all TRPV1 antagonists are currently at the stage of clinical trials and there are no TRPV1-targeting drugs on the market (ClinicalTrials.gov, 2025a; ClinicalTrials.gov, 2025b; ClinicalTrials.gov, 2025c).
Another promising molecule in this field is paeoniflorin, a water-soluble monoterpene glycoside derived from Paeonia lactiflora (P. lactiflora). This compound is known for a wide range of anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects (Gong et al., 2024). In particular, the positive pharmacological properties of paeoniflorin have been demonstrated in models of epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, depression, cerebral ischemia, and anti-pain therapy (Hong et al., 2022). It is reported that paeoniflorin significantly reduced the degree of inflammation in the skin and had an anti-allergic effect in the treatment of contact dermatitis (Wu et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2024).
Paeonia lactiflora itself is a well-known plant since ancient times in the traditional medicine of China, Korea and Japan for pain relief (Wiegand et al., 2024; Zangooei Pourfard et al., 2021; Shu-yun, 1988). In addition to monoterpene glycosides, P. lactiflora contains many other beneficial compounds, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, with an excellent safety profile (Parker et al., 2016). The total glycosides of P. lactiflora (which include paeoniflorin) have been reported to have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects, which have applications in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (He and Dai, 2011).
Thus, considering that the activity of TRPV1 channels and amount of MMPs are closely associated with inflammatory processes and the development of pain syndrome, it seems promising to study P. lactiflora extract as a natural modulator of LPS-induced inflammation. In the present study, the effects of P. lactiflora extract on TRPV1 channels, MMPs, associated pro-inflammatory cytokines and related to inflammation collagen destruction were investigated in an in vitro model in both epidermal and gingival cells for the first time.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Molecular screening of paeoniflorin with TRPV1, MMP-8 and MMP-9
Using DiffDock (Corso et al., 2022) for pose generation and GNINA 1.0 (McNutt et al., 2021) for affinity calculations, the minimal score of Gibbs free energy was predicted for paeoniflorin’s binding to TRPV-1, MMP-8, and MMP-9 active sites (Figures 1a–d). The results indicated a strong affinity of peoniflorin toward the active sites of TRPV1 (−10.79 kcal/mol) and MMP-9 (−9.99 kcal/mol), while it showed a relatively mild affinity to MMP-8 (−6.82 kcal/mol).
FIGURE 1
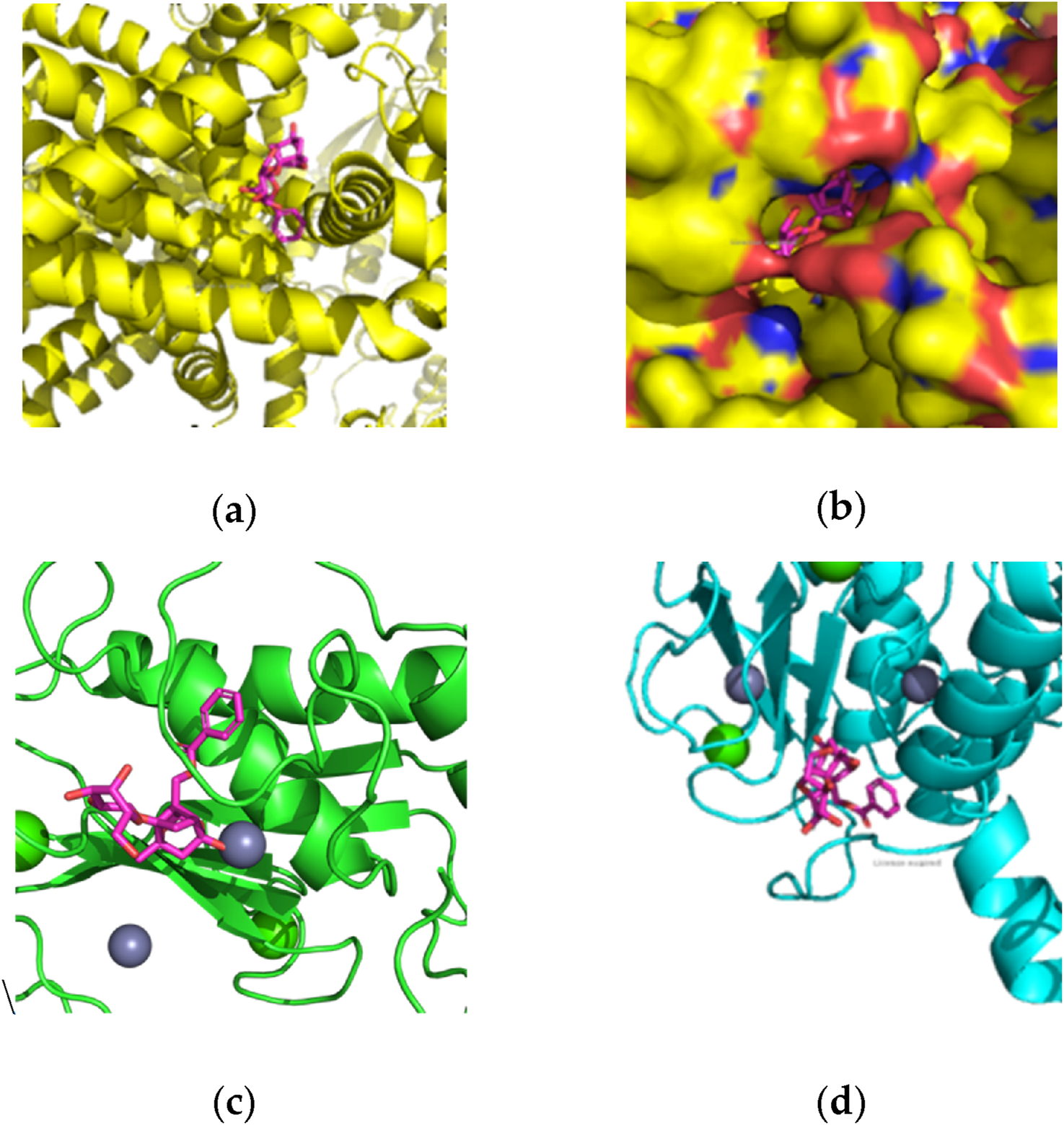
Molecular docking of paeoniflorin with TRPV1, MMP-8 and MMP-9: (a) TRPV1 domain with paeoniflorine pose; (b) TRPV1 domain with paeoniflorine pose in detail; (c) MMP-8 active site with paeoniflorine pose; (d) MMP-9 active site with paeoniflorine pose.
Subsequently, MM/PBSA analysis using the Poisson-Boltzmann method yielded binding free energies of −10.72 ± 2.62 kcal/mol for TRPV1, −7.62 ± 1.43 kcal/mol for MMP-9, and −8.43 ± 0.82 kcal/mol for MMP-8, showing non-linear correlation with the initial docking scores. According to the represented positions after molecular dynamics (Figure 2), paeoniflorin stayed at the corresponding docking site of interaction with significant TRPV1-ligand binding free energy. This complex of in silico methods has improved the results of virtual screening and docking of paeoniflorin with chosen target in skin.
FIGURE 2
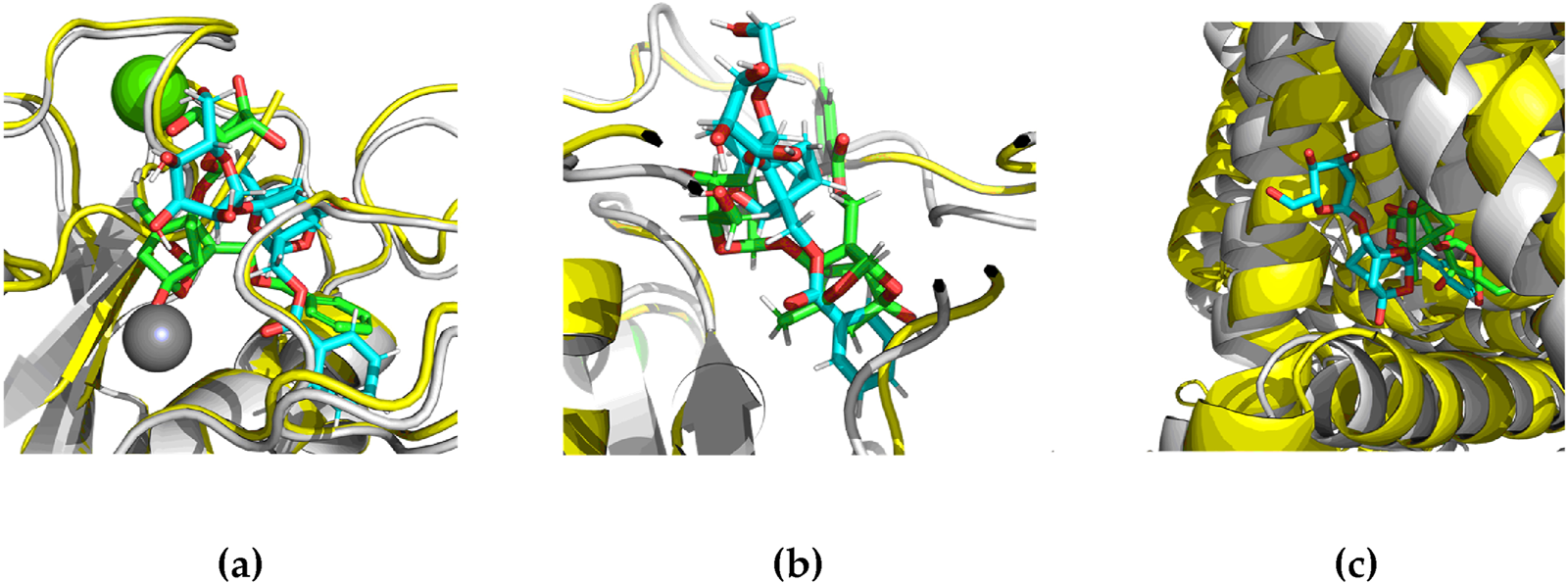
Positions of paeoniflorin in TRPV1, MMP-8 and MMP-9 after MD: (a) MMP-8 domain with paeoniflorine pose; (b) MMP-9 domain with paeoniflorine pose in detail; (c) TRPV1 active site with paeoniflorine pose. Green color represents docking position, blue represents stable ligand position in MD, yellow represents crystal structure of protein, gray represents stable protein position in MD.
Position of paeoniflorin was allocated to the same position of capsaicin in TRPV1 pocket (Figure 3a), therefore this phenomenon probably could demonstrate the same antinociceptive effect as capsaicin (Nadezhdin et al., 2021; Capsaicin, 2023). In case of MMP-9 pocket (Figure 3b), paeoniflorin probably works as an antagonist in the same position of active site (Nishikawa-Shimono et al., 2024).
FIGURE 3
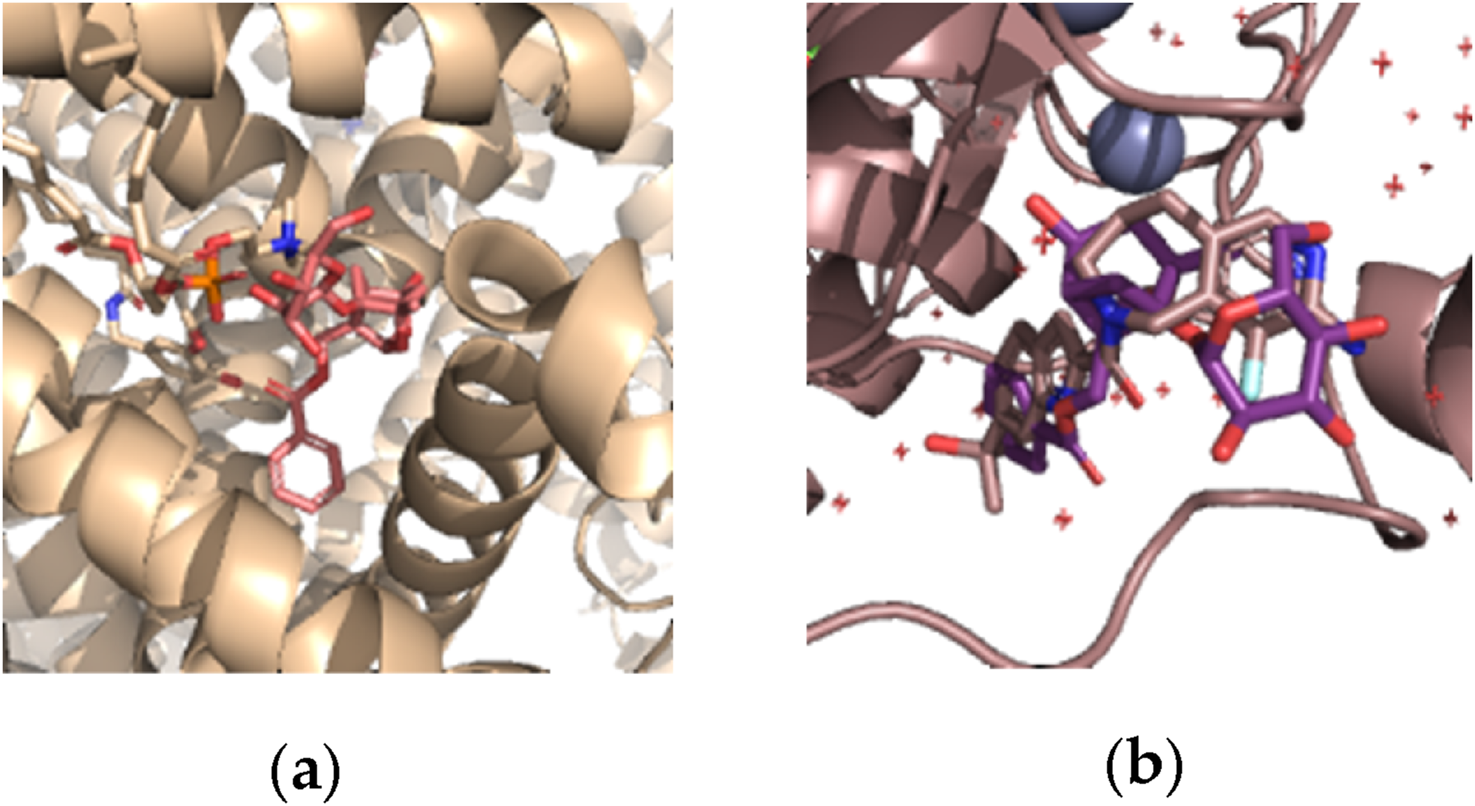
Best position of paeoniflorin (red) and capsaicin (beige color) by DiffDock docking: (a) in TRPV1 pocket; (b) in MMP-9 pocket.
2.2 Quantification of TRPV1, IL-6, IL-13 and TNF-α in skin keratinocytes
In this experiment human keratinocytes cultures were treated with the paeoniflorin-enriched extract of P. lactiflora at three noncytotoxic concentrations, determined by the MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) assay. After subsequent exposure to inflammatory stress, TRPV-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-13 amount were quantified by ELISA immunoassay. In Figure 4 the non-cytotoxic concentrations of paeoniflorin are presented. It was established that 100% of the cell survival rate was observed at the P. lactiflora extract concentration of 0.1 mg/mL (equal to 0.01 weight %).
FIGURE 4
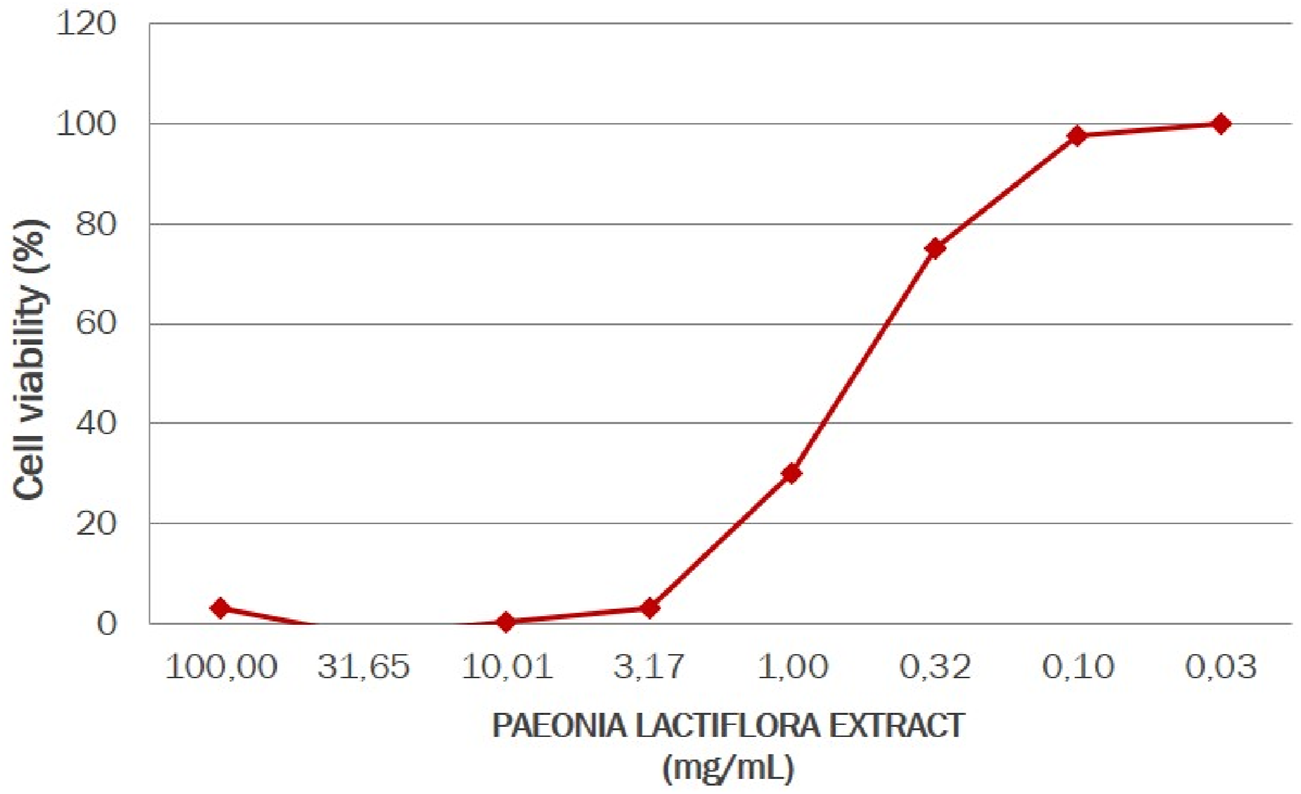
Cell viability of human keratinocytes under Paeonia lactiflora extract treatment.
In cell viability tests, P. lactiflora extract enriched by paeoniflorin showed very high activity, which agrees with literature data (Nishikawa-Shimono et al., 2024; Napolitano et al., 2023). Thus, for a favorable effect on cells, this compound should be used in very low concentrations, which contributes to cost-effectiveness and is an undeniable advantage in the production of paeoniflorin-containing pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
Exposure of the cell culture with 50 μg/mL LPS promoted an increase of 144.45% (P < 0.001) in TRPV-1 amount. Meanwhile, P. lactiflora extract showed a protective effect, decreasing overproduced TRPV1 amount by 113.47%, 88.40% and 64.41% at concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL (0.05%), 0.1 mg/mL (0.01%), and 0.03 mg/mL (0.003%), respectively (P < 0.001) (Figure 5). These results highlighted the role of P. lactiflora extract as targeted substance in action to TRPV1 channels related to itch, increased sensitivity, and pain sensation.
FIGURE 5
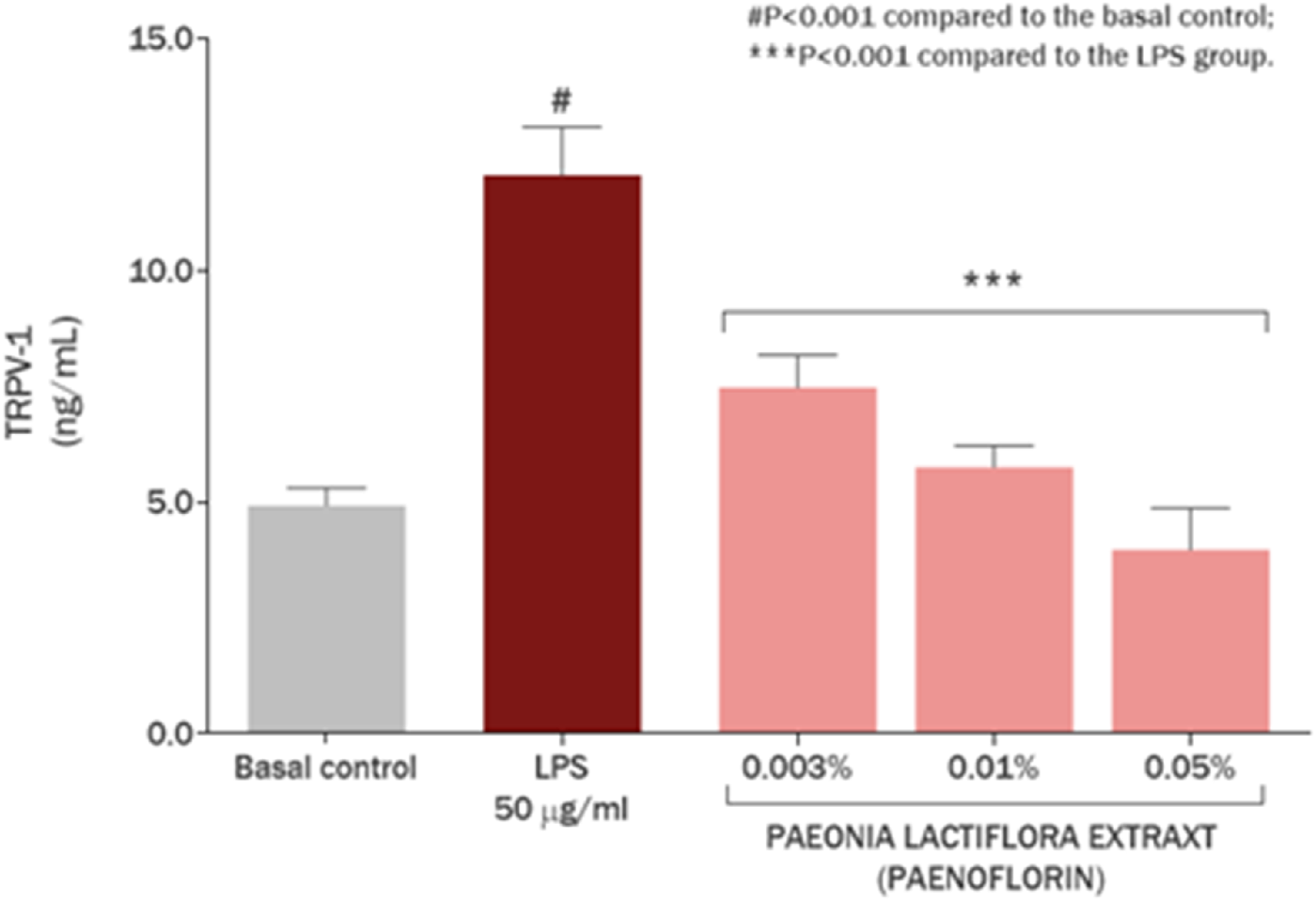
TRPV1 modulation in skin keratinocytes by Paeonia lactiflora root extract.
Figure 6 represents the effect of the P. lactiflora extract on the production of IL-6 in cultured skin keratinocytes. Exposure of the cell culture with 50 μg/mL LPS promoted an increase of 194.20% in IL-6 synthesis, imitating immune reaction and skin inflammation (P < 0.001). Remarkably, P. lactiflora extract showed a protective effect, reducing IL-6 overproduction by 37.78% and 28.70% at concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL (0.05%; P < 0.01) and 0.1 mg/mL (0.01%; P < 0.05), respectively, considering the baseline condition without exposure to bacterial LPS.
FIGURE 6
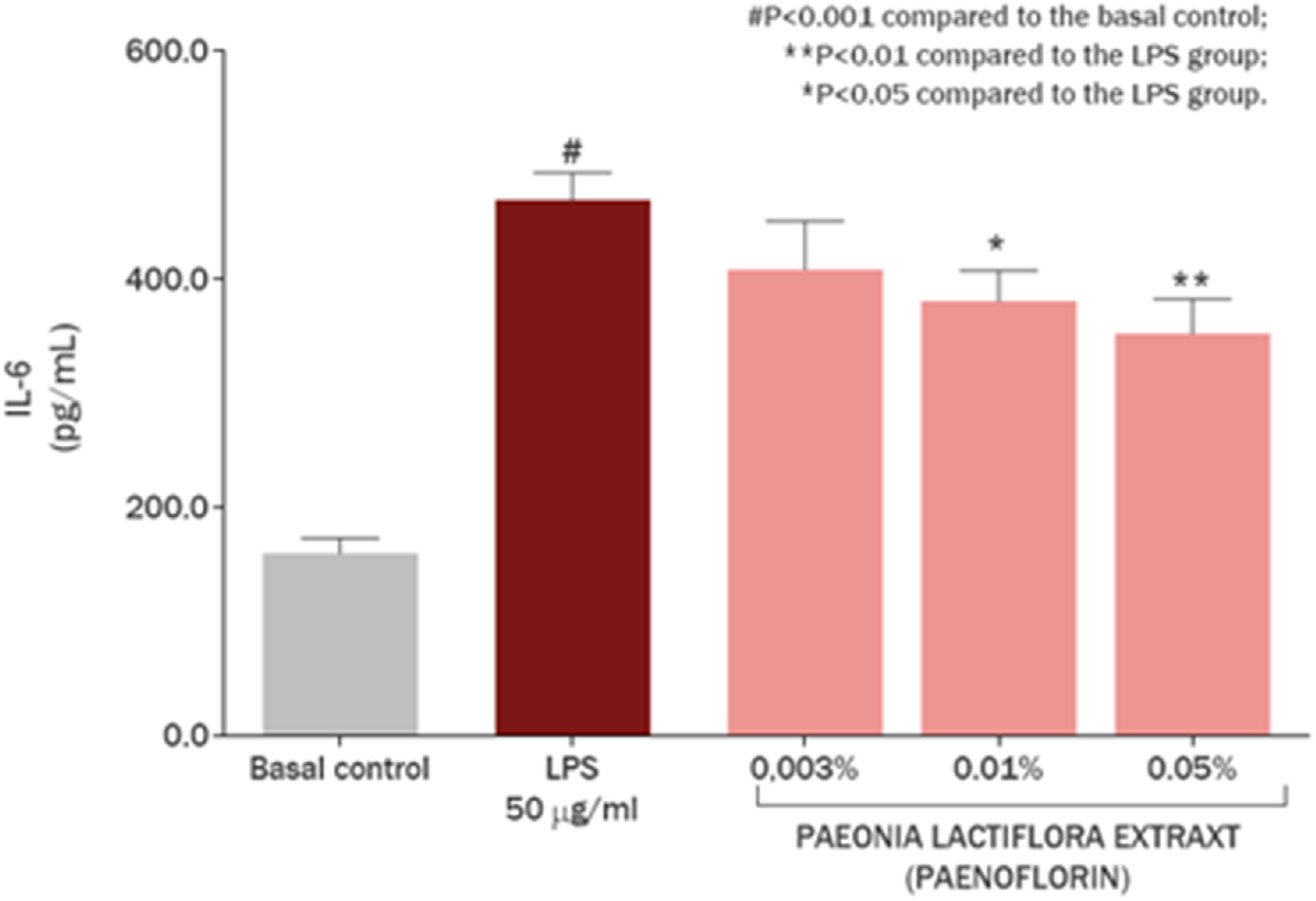
IL-6 modulation in skin keratinocytes by Paeonia lactiflora root extract.
P. lactiflora extract also showed significant anti-inflammatory effect, reducing IL-13 overproduction in skin keratinocytes by 68.63% and 32.61% at concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL (0.05%) and 0.1 mg/mL (0.01%), respectively (P < 0.001) (Figure 7). This action is due to the varied composition of peoniflorin, P. lactiflora glucosides, flavonoids and complexes of other biologically active molecules. Exposure of the cell culture with 50 μg/mL LPS promoted an increase of 409.75% (P < 0.001) in IL-13 synthesis in comparison with basal control in skin keratinocytes, revealing immune response to bacteria cell wall compounds. IL-13 is a key inflammatory marker of atopic dermatitis (Mitroi et al., 2024) in combination with IL-4 inducing chronic inflammation, immune cells involvement, and suppression of skin barrier proteins expression. Therefore, the modulation of IL-13 level in skin keratinocytes by P. lactiflora extract has a beneficial effect on skin recovery and normalization of inflammatory reaction.
FIGURE 7
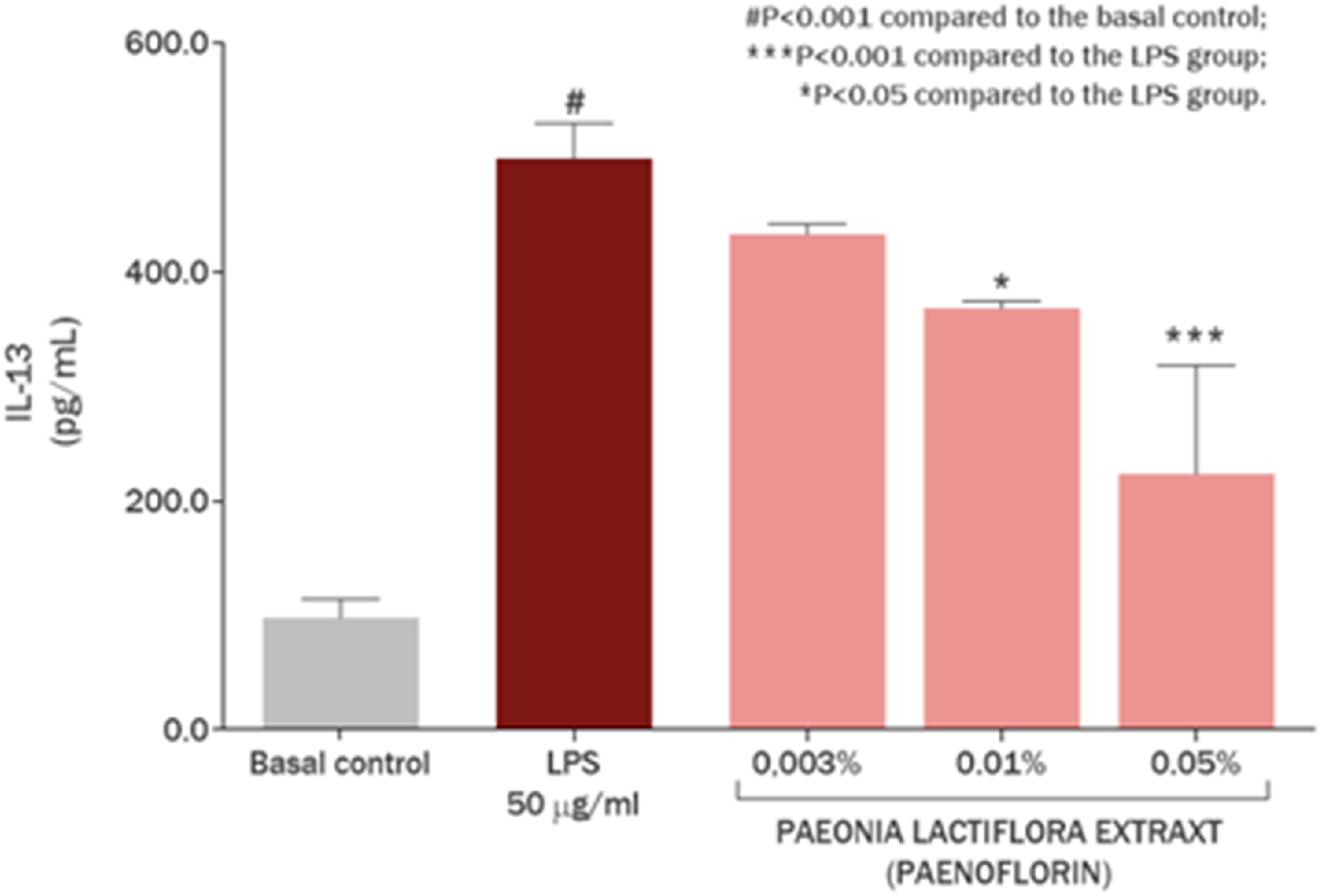
IL-13 modulation in skin keratinocytes by Paeonia lactiflora root extract.
The anti-inflammatory effect of the P. lactiflora extract on the production of TNF-α in cultured keratinocytes was also investigated (Figure 8). Exposure of the cell culture with 50 μg/mL LPS promoted an increase of 25.64% (P < 0.01) in TNF-α production as marker of immediate inflammatory reaction. P. lactiflora extract enriched by paeoniflorin reduced TNF-α overproduction by 148.82% (P < 0.001), 105.49% (P < 0.01) and 100.00% (P < 0.01) at concentrations of 0.5 mg/mL (0.05%), 0.1 mg/mL (0.01%) and 0.03 mg/mL (0.003%), respectively.
FIGURE 8
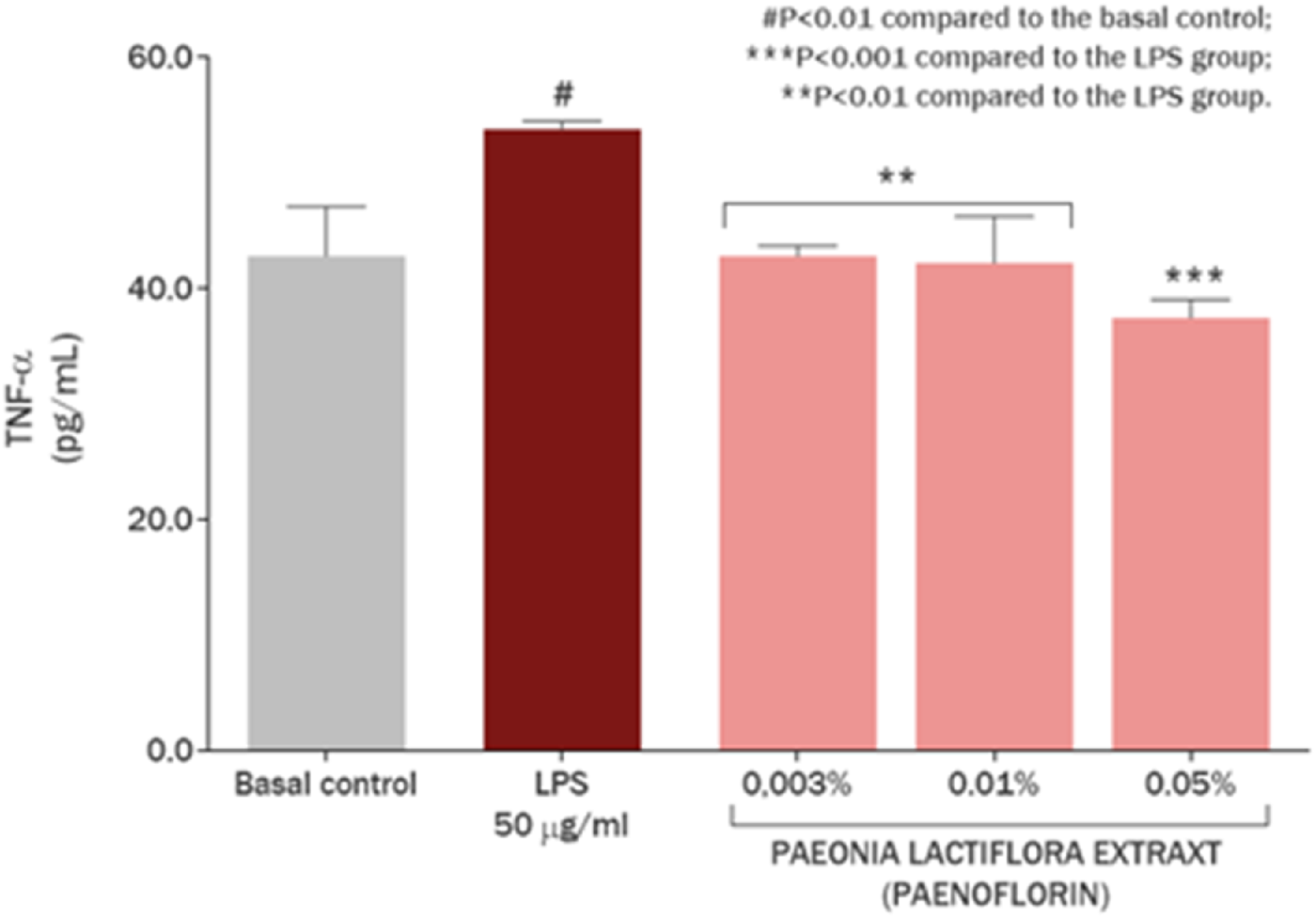
Regulation of TNF-α production in skin keratinocytes by Paeonia lactiflora root extract.
The significant increase in TRPV1, IL-6, IL-13 and TNF-α in the presence of bacterial LPS fully corresponds to the in vivo processes during the inflammatory response of the organism to bacterial infection (Luo et al., 2021; Diogenes et al., 2011; Sattler et al., 2021). Bacterial LPS is one of the main inducers of the innate immune response, and the observed pattern indicates that our experimental model correctly reflects the real in vivo processes.
In the presence of P. lactiflora extract, a decrease in the expression of TRPV1 and then pro-inflammatory cytokines as IL-6, IL-13 and TNF-α was established, which clearly shows the dual anti-inflammatory effects of this paeoniflorin. First, paeoniflorin in the P. lactiflora root extract is capable of binding to TRPV1 transmembrane domain for predicted blocking the pain sensitization and subsequent inflammatory response, e.g., TRPV1-mediated IL-6 release (Obi et al., 2017). Secondly, a decrease in the amount of TRPV1 in keratinocytes was observed. This may be a consequence of the decrease in IL-6, IL-13 and TNF-α, as it is known that the presence of these cytokines can promote TRPV1 expression (Wang et al., 2018; Fang et al., 2015; Figure 9). In addition, decreased TRPV1 expression may be associated with some other unknown epigenetic mechanisms, which may be further investigated in a series of in vitro studies.
FIGURE 9
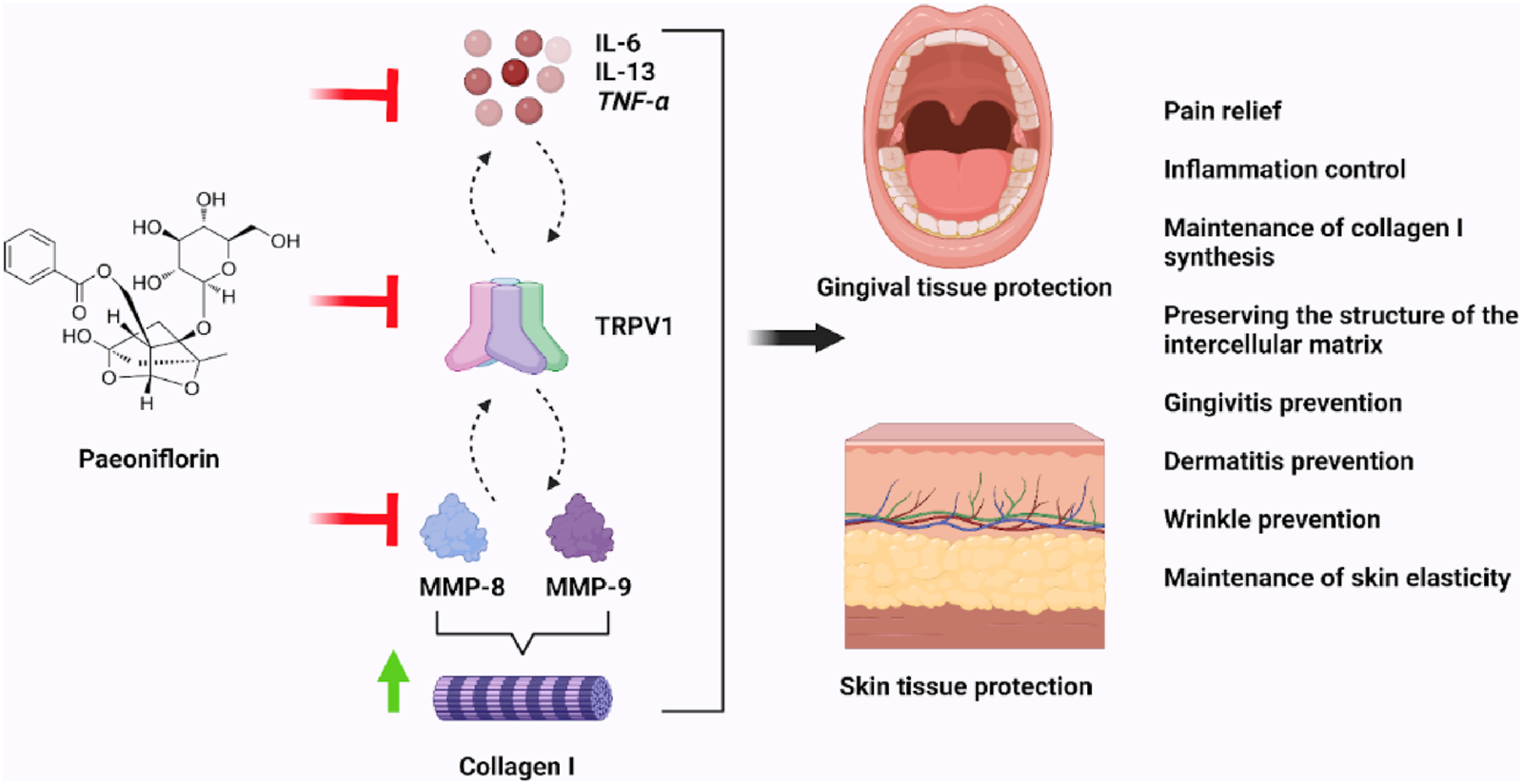
The modulation of LPS-induced inflammation by the Paeonia lactiflora root extract.
It is worth noting that the pro-inflammatory cytokines studied in this experiment play a central role in the development of inflammatory diseases of the skin and oral cavity. For example, IL-13 is one of the main mediators in atopic dermatitis (Lytvyn and Gooderham, 2023), and the development of its antagonists is a well-known strategy for the treatment of this disease (Zhang et al., 2022; Danso et al., 2014). Paeoniflorin, therefore, is also another targeted IL-13 modulator and therefore can be used for the therapy of atopic dermatitis and other inflammatory skin diseases. TNF-α is also involved in the development of inflammation in atopic dermatitis, and its inhibition may also have a positive therapeutic effect (Noh et al., 2013). The expression of IL-6 and TNF-α is significantly increased in the gingival tissue of patients with active periodontitis (Salim et al., 2023). There is also ample evidence for the central role of IL-6 in the development of gingivitis (Holla et al., 2008; Yu et al., 2021). Like IL-13, inhibition of these cytokines may contribute to the treatment of these oral inflammatory diseases.
Thus, in the experiment with keratinocytes the P. lactiflora root extract demonstrated its high activity and complex effect on inflammatory processes in skin keratinocytes. Considering the role of TRPV1 in the transmission of pain sensations, the results of this experiment suggest a favorable effect of paeoniflorin and the P. lactiflora extract in gingival or skin cells in LPS-induced inflammation.
2.3 Quantification of MMP-8 and type I collagen on gingival fibroblast culture
The potential protective effect of P. lactiflora root extract on periodontal extracellular matrix structure was evaluated by quantifying type I collagen and MMP-8 in human gingival fibroblast cultures. The Camellia sinensis extract standardized for epigallocatechin gallate as a positive control because this substance is known for its strengthening effect on type I collagen structure (Sun et al., 2024). The P. lactiflora extract at concentrations of 0.50, 0.10 and 0.03 mg/mL used in the experiment were taken from literature data (Napolitano et al., 2023; Lytvyn and Gooderham, 2023) and results of cytotoxicity assay.
The addition of LPS of Staphylococcus aureus caused active inflammatory process in the oral cavity cells. Moreover, in the presence of LPS, the amount of type I collagen decreased significantly, while the amount of MMP-8 increased for type I collagen destruction. The non-cytotoxic concentration range of C. sinensis extract on human gingival fibroblast culture was established (Figure 10). A 100% cell survival was observed at a concentration of 0.0008 mg/mL; the starting concentration used for the study was 0.0079 mg/mL.
FIGURE 10
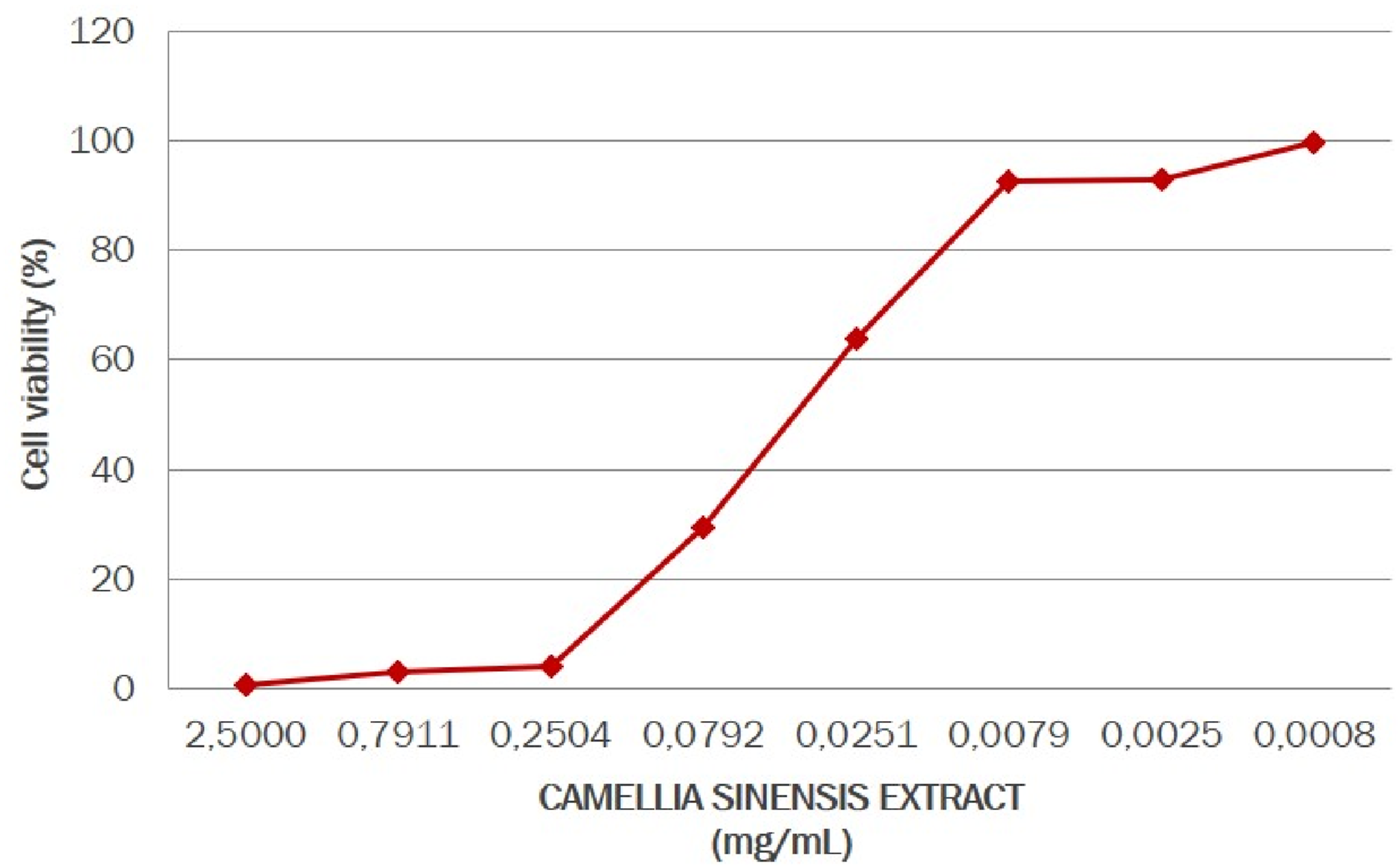
Evaluation of non-cytotoxic concentrations of the Camellia sinensis extract in human gingival fibroblasts.
The effect of the P. lactiflora extract on the production of collagen type I in cultured human gingival fibroblasts is presented at Figure 11. There was no significant difference between all the groups at day 3 (P > 0.05), before treatment and incubation with LPS. The exposure of cell culture to LPS promoted a decrease of 44.78% in collagen type I production (P < 0.001), compared to the basal control group. However, P. lactiflora root extract showed an increase on collagen type I production by 92.16% (P < 0.001), 87.50% (P < 0.001) and 52.82% (P < 0.001) at the concentrations of 0.50, 0.10 and 0.03 mg/mL, respectively, compared to the LPS group (Figure 10). On another side, it is possible to express the observed results in percentage recovery after the LPS exposure. That would mean that the P. lactiflora extract standardized for paeoniflorin showed a percentage of collagen type I recovery of 113.64%, 107.89% and 65.13% at the concentrations of 0.50, 0.10 and 0.03 mg/mL, respectively (Figure 11). These values are calculated depending on decrease of type I collagen amount between the LPS group and basal control.
FIGURE 11
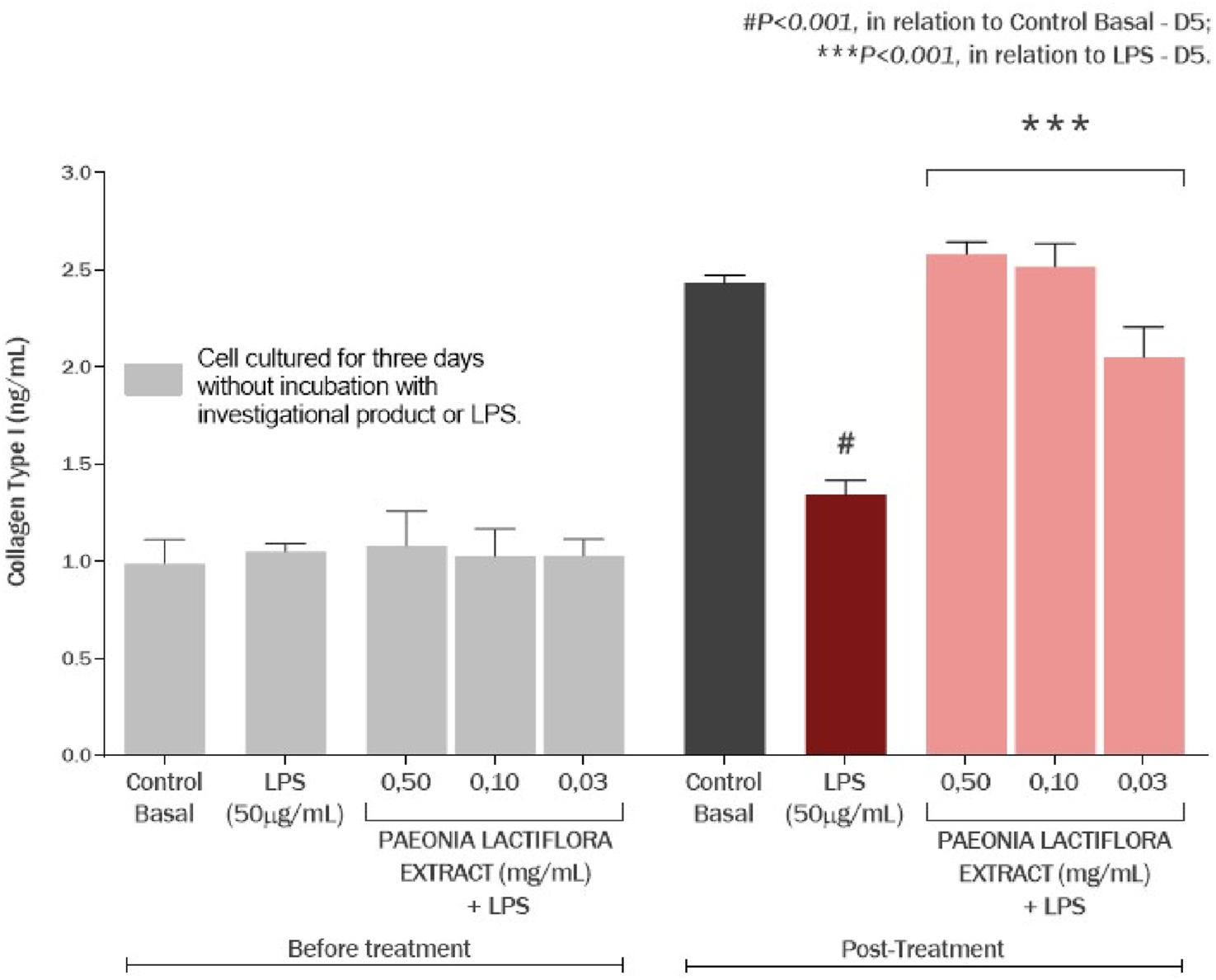
Effect of the Paeonia lactiflora extract on the production of collagen type I in human gingival fibroblasts exposed to LPS. Data represents the mean ± standard deviation of three replicates (ANOVA).
The effects of the P. lactiflora extract and Camellia sinensis extract on MMP-8 production in cultured human gingival fibroblasts are presented in Figure 12. Exposure of cell culture to LPS promoted an increase in MMP-8 production by 69.87% (P < 0.001) compared to the basal control group. P. lactiflora extract showed a protective effect, reducing MMP-8 production by 39.32% (P < 0.001), 39.05% (P < 0.001), and 45.75% (P < 0.001) at concentrations of 0.50, 0.10, and 0.03 mg/mL, respectively, compared with the LPS group. The percentage of prevention of MMP-8 overproduction by paeoniflorin-enriched extract was 95.60%, 94.93% and 111.22%, respectively. Similarly, the C. sinensis extract demonstrated a protective effect by reducing MMP-8 formation by 47.36% (P < 0.001), 46.09% (P < 0.001) and 54.78% (P < 0.001) at concentrations of 0.0079, 0.005 and 0.0008 mg/mL, respectively, compared to the LPS group. The percentage of prevention of MMP-8 overproduction by the C. sinensis extract was 115.14%, 112.06% and 133.17%, respectively (Figure 12).
FIGURE 12
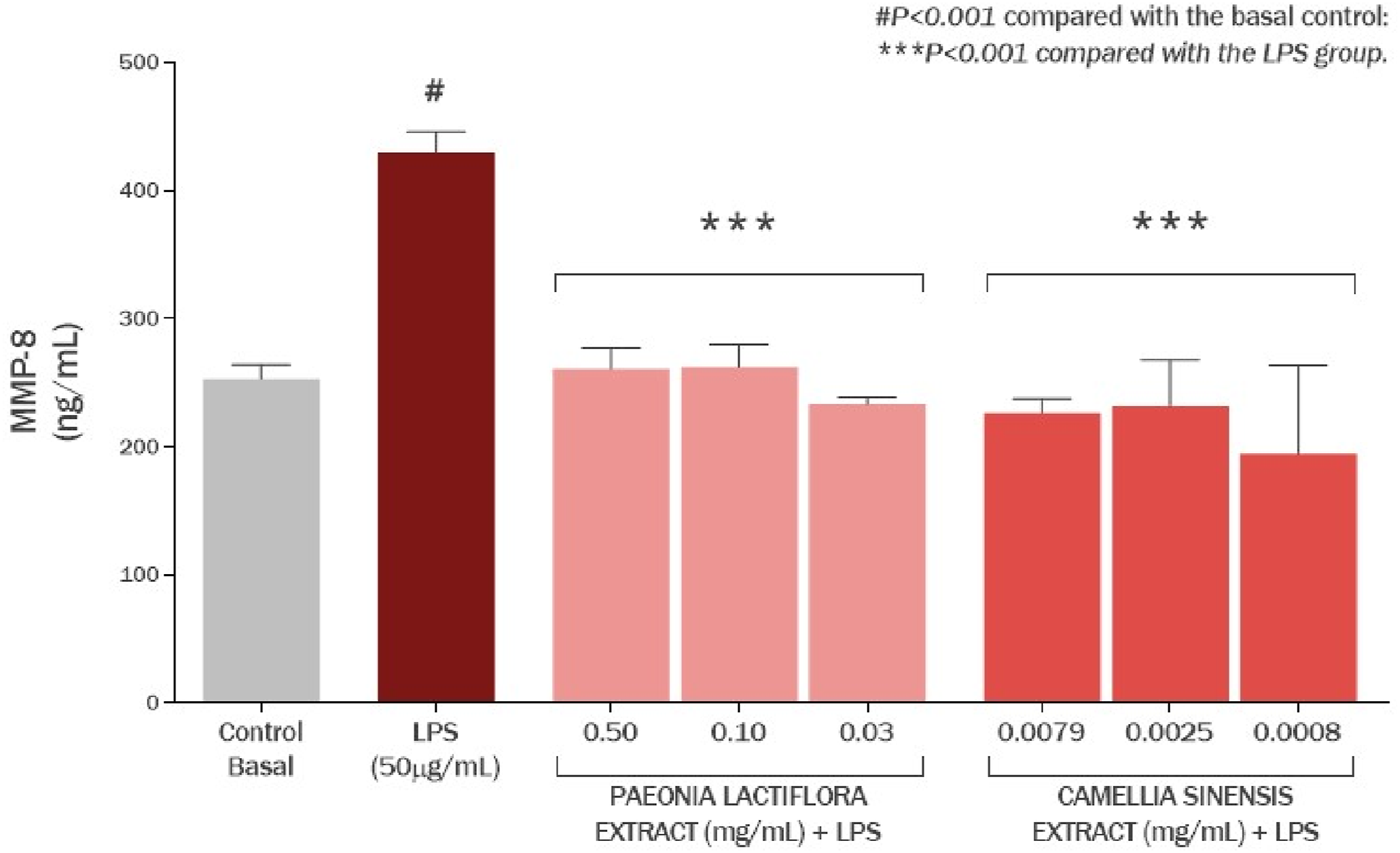
Effect of the Paeonia lactiflora extract and Camellia sinensis extract on the production of MMP-8 in human gingival fibroblasts exposed to LPS. Data represents the mean ± standard deviation of three replicates (ANOVA).
It turned out that P. lactiflora root extract has a protective effect on type I collagen comparable to that of Camellia sinensis leaf extract due to decrease of MMP-8 amount. This metalloproteinase is the most abundant in periodontal tissues and contributes to the destruction of the gingival matrix in periodontitis and gingivitis (Luchian et al., 2022; Li et al., 2012). It has been previously reported that TRPV1 may contribute to the increased activity of MMP-8 in the alveolar mucosa (Avellan et al., 2006). Considering that, according to our data, paeoniflorin modulates TRPV1 amount and promotes a decrease in their number on keratinocytes, we can assume that similar processes occur in gingival fibroblasts. Then the decrease in MMP-8 activity in this experiment may be a consequence of the suppression of primary TRPV1 activity. It is also possible that there is a complex process and synergetic effect here, when decrease of metalloproteinases amount hypothetically occurs through two pathways: TRPV1-related and unrelated.
These are completely new data on the protective effect of P. lactiflora root extract on extracellular matrix degradation in case of inflammatory response induced by oral bacterial LPS and mediated by TRPV1 channels. The exposure of P. lactiflora extract promotes the restoration of type I collagen synthesis and ensures the maintenance of its amount in case of inflammatory response, which is important for the prevention of gingivitis and gingival prolapse in the gingival pocket (Figure 9).
2.4 Quantification of MMP-9 and type I collagen on dermal fibroblast culture
In this experiment, the effect of paeoniflorin-enriched P. lactiflora root extract and EGCG-enriched C. sinensis leaf extract on human dermal fibroblast culture in terms of anti-aging effect, skin elasticity and maintenance of extracellular matrix structure was investigated by quantifying type I collagen and MMP-9. The protective properties of C. sinensis leaf extract on type I collagen type are particularly well studied in the context of preventing skin aging, so in this experiment green tea extract with EGCG also acted as a positive control (Jia et al., 2023; González-González et al., 2022). The P. lactiflora extract at concentrations of 0.50, 0.10, and 0.03 mg/mL used in the experiment were taken from literature data (Napolitano et al., 2023; Lytvyn and Gooderham, 2023) and results of cytotoxicity assay. By adding bacterial LPS, the inflammatory process in the skin caused by bacterial infection was simulated. Finally, in the presence of LPS, the amount of type I collagen decreased significantly, while the amount of MMP-9 increased.
The non-cytotoxic concentration range of C. sinensis leaf extract on human skin fibroblast culture was established as on human gingival fibroblasts as well. The initial concentration used for the study was 2.50 mg/mL; at concentration of 0.0008 mg/mL, 100% cell survival was observed.
Figure 12 reflects the effect of the P. lactiflora extract on the production of type I collagen in cultured human skin fibroblasts. There was no significant difference between all the groups after 3 days (P > 0.05). Meanwhile, exposure of the cell culture to LPS promoted a decrease of 35.87% (P < 0.001) in type I collagen production, compared to the basal control group. As presented in Figure 13, P. lactiflora extract standardized for paeoniflorin showed an increase on type I collagen production by 92.16% (P < 0.001), 87.50% (P < 0.001) and 52.82% (P < 0.001) at the concentrations of 0.50, 0.10 and 0.03 mg/mL, respectively, compared to the LPS group.
FIGURE 13
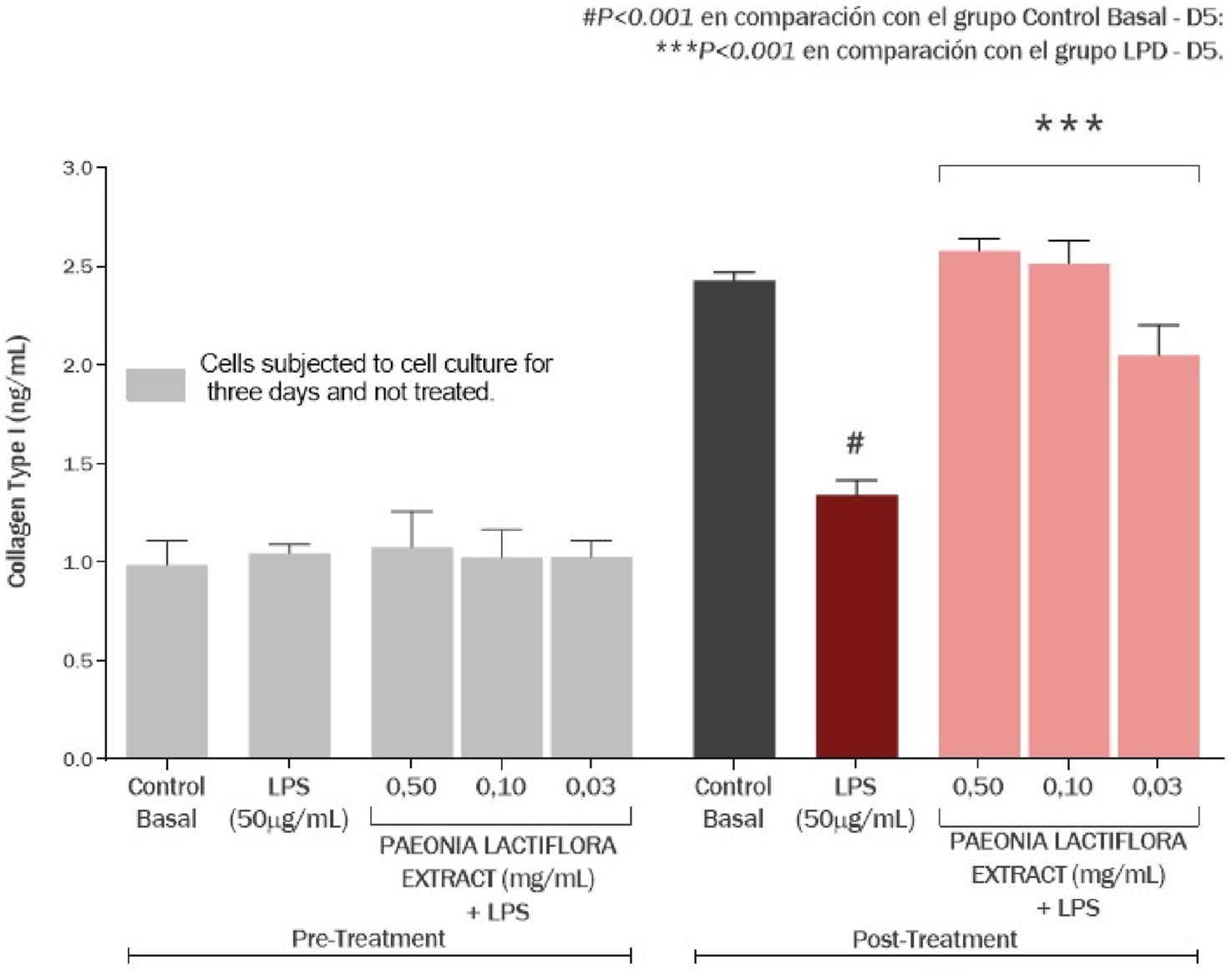
Effect of the Paeonia lactiflora root extract on the production of collagen type I in human skin fibroblasts exposed to LPS. Data represents the mean ± standard deviation of three replicates (ANOVA).
P. lactiflora root extract enriched by paeoniflorin showed an anti-inflammatory effect, reducing MMP-9 amount by 70.27% (P < 0.001) and 57.91% (P < 0.01) at concentrations of 0.50 and 0.10 mg/mL, respectively, compared to the LPS group (Figure 14). Exposure of cell culture to LPS increased MMP-9 production by 401.99% (P < 0.001) compared to the basal control group. Similarly, Camellia sinensis leaf extract enriched by EGCG also decreased the production of MMP-9 by 84.92% (P < 0.001), 61.67% (P < 0.01) and 58.72% (P < 0.01) at concentrations of 0.0079, 0.005 and 0.0008 mg/mL, respectively, compared to the LPS group.
FIGURE 14
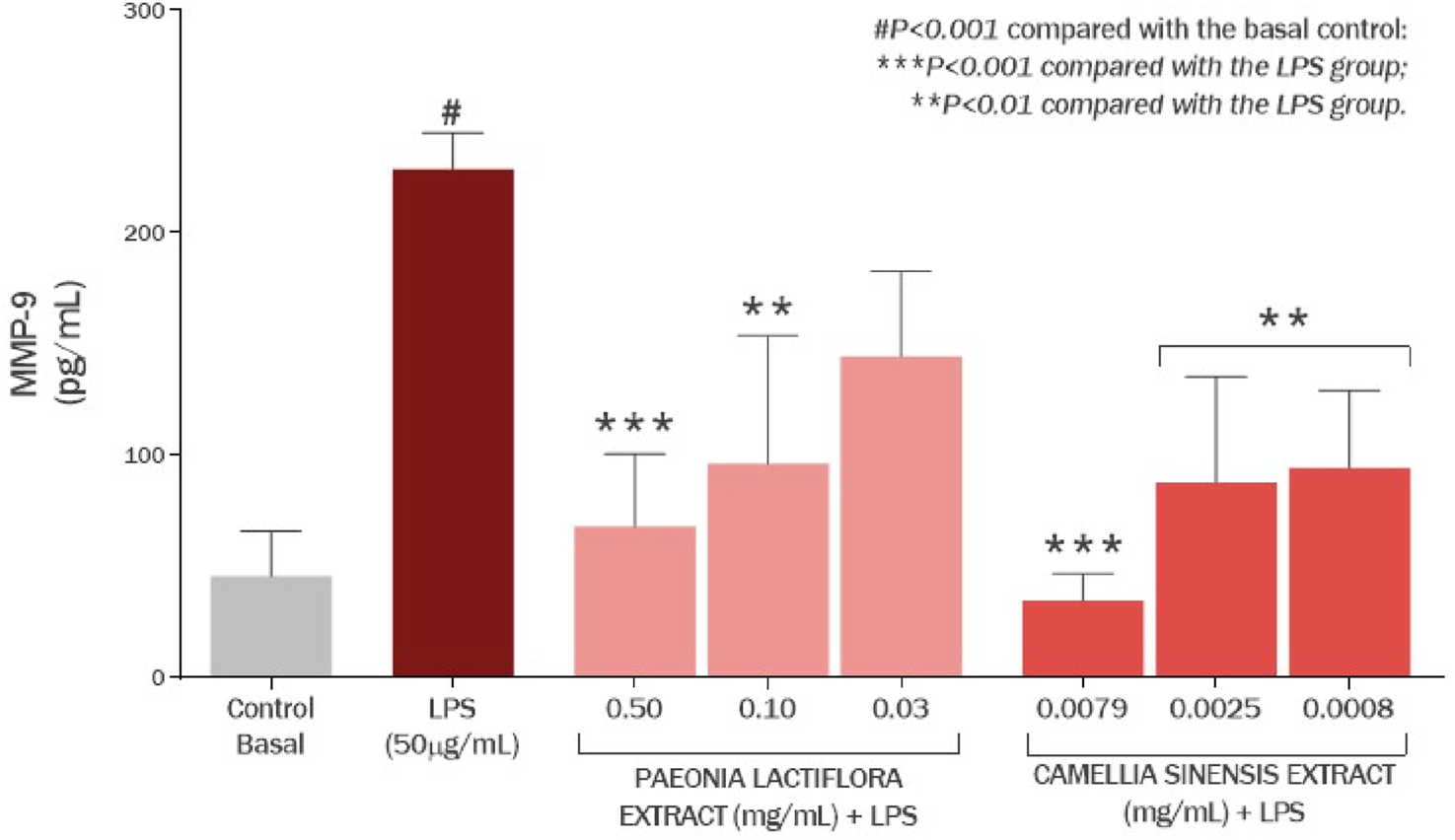
Effect of the Paeonia lactiflora extract and Camellia sinensis extract on the production of MMP-8 in human skin fibroblasts exposed to LPS. Data represents the mean ± standard deviation of three replicates (ANOVA).
P. lactiflora extract showed protective properties comparable to those of green tea extract, promoting type I collagen repair by reducing the activity of MMP-9. This metalloproteinase is one of the key markers of skin inflammation such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis (Michalak-Stoma et al., 2021; Harper et al., 2010). In addition, MMP-9 is the second most abundant metalloproteinase in gingival tissue, so the findings further support the efficacy of paeoniflorin against oral inflammatory diseases (Luchian et al., 2022; Li et al., 2012).
To date, to the best of our knowledge from scientific literature, there is no data on the effect of TRPV1 on MMP-9 activity. Based on the hypothesis in the experiment with gingival fibroblasts, it could be assumed that the reduction of MMP-8 may also be a consequence of the modulation of TRPV1 channels and proinflammatory cytokines in the skin. This is completely new data on the protective effect of paeoniflorin in the destruction of extracellular matrix in case of inflammatory skin response induced by LPS bacteria such as S. aureus, which is particularly important in atopic dermatitis. The action of P. lactiflora extract restores the synthesis of type I collagen and maintains its quantity in case of inflammatory reaction, which is important for the prevention of atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, and wrinkles formation due to a decrease in skin elasticity (Figure 9).
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Substances and materials
Paeonia lactiflora Pall. root extract was standardized for 50% paeoniflorin in the composition by TLC (thin-layer chromatography) and HPLC-UV (high-performance liquid chromatography with UV-Visible detector) at 232 nm using Agilent 1200 containing a vacuum degasser, quaternary pump, autosampler, and diode array detector. The HPLC column was a Zorbax SB-C8 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5.0 μm). In addition, an auxiliary gradient elution program with LC-MS grade acetonitrile (Fisher Chemicals, Cat. No А/0627/17), trifluoroacetic Acid (TFA) of 99.5% purity (Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., Cat. No 65415) and HPLC grade methanol (Fisher Chem-icals, Cat. No M/4056/17) was developed to remove residual hydrophobic solubilizers from the sample matrix and ensure efficient separation of the target components, such as paeoniflorin and its isomers from flavonoids. Experimental procedures and chromatographic data collection were performed in Agilent ChemStation in a fully automated manner using ACD/AutoChrom (2022.2.3) application.
Paeonia lactiflora Pall. root extract was obtained from Organic Herb Inc., China (OHI product code: W015.S50000). Camellia sinensis leaf extract standardized for 90% EGCG by HPLC was also obtained from Organic Herb Inc., China (OHI product code: G003.S91100) as an active control for in vitro research.
Staphylococcus aureus LPS (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat. No. L2515) was used to model the inflammatory process induced by the presence of lipopolysaccharides of the bacterial cell wall. Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 4.5 g/L glucose (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, United States), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Thermo Fisher) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin/amphotericin (Lonza Walkerville Inc., Salisbury, MD, United States) was used for cell cultivation.
3.2 Molecular docking of paeoniflorin with TRPV1, MMP-8, MMP-9 active sites
The protein data was retrieved in.pdb format from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). The structures of TRPV1 (PDB: 7LPE), MMP-8 (PDB: 1KBC), and MMP-9 (PDB: 8K5Y) were employed to construct the three-dimensional model of proteins and were docked with paeoniflorine using DiffDock (Corso et al., 2022), and the binding affinities were calculated with GNINA 1.0 (McNutt et al., 2021) software. The model was prepared by removing water molecules, eliminating redundant chains, and adding polar hydrogens and charges. Finally, the processed structure was saved in.pdb format for further in silico analysis. Initially, the native protein ligand was employed in the molecular docking process to validate the protocol, achieving a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of less than 2 Å. The docking grid was centered at coordinates (X, Y, Z) = (28.73, 58.834, 63.068) with dimensions of 40 × 40 × 40. During docking, the ligand was treated as flexible while the macromolecule remained rigid. The analysis was conducted on a personal computer featuring an Intel Core i7-12700U CPU (2.3 GHz), an RTX 4090 GPU, and 64 GB of RAM, running a 64-bit version of Windows 11.
3.3 Performing molecular dynamics and MM/PBSA analysis
The top-ranked docking poses of paeoniflorin were subjected to molecular dynamics (MD) simulations using GROMACS v.2023.1 (Abraham et al., 2015) with MPI support implementation. Each protein-ligand complex was prepared for MD simulation using the CHARMM36 force field for proteins and CGenFF parameters for the ligand. The systems were solvated in a cubic box with TIP3P water molecules, maintaining a minimum distance of 1.0 nm from the protein surface. Counterions were added to neutralize the system charge.
Energy minimization was performed using the steepest descent algorithm, followed by NVT (100 ps) and NPT (100 ps) equilibration phases. Production MD runs were conducted for 20 ns under NPT (Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty) conditions at 298.15 K and 1 bar pressure, using the Nosé-Hoover thermostat and Parrinello-Rahman barostat, respectively. Trajectory frames were saved every 10 ps for subsequent analysis.
MM/PBSA (Molecular Mechanic/Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area) calculations were performed using gmx_MMPBSA v.1.6.4 (Valdés-Tresanco et al., 2021) to estimate binding free energies. The analysis utilized the last 10 ns of the MD trajectory with frames extracted every 100 ps. Both Generalized Born (GB) and Poisson-Boltzmann (PB) solvation models were employed, with the PB method using a grid spacing of 0.5 Å and ionic strength of 0.1 M.
3.4 Evaluation of cytotoxicity of Paeonia lactiflora extract and Camellia sinensis extract
The cell lines present in this study were purchased from American Type Cultures Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, United States) and MatTek (MatTek Europe, Bratislava, Slovak Republic). Cell viability was determined by a colorimetric method using MTT dye (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, Mo, United States). To perform the test, the products were prepared in culture medium and applied to a 96-well plate in a serial dilution in the range of 100 to 0.03 mg/mL using a dilution factor for keratinocytes cell culture or 3.16 for fibroblasts cell cultures. The cells were incubated for a period of 48 h. MTT was then added to the culture at a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL (100 µL/well) and incubated for 4 h. The contents of the well were removed and 100 µL of isopropanol was added to solubilize the formazan crystals. The absorbance of each well was determined at 570 nm on a Multiskan GO monochromator (Thermo Scientific, Finland).
Upon reaching confluence, the cells were seeded in 96-well plate (Corning, United States) to determine the non-cytotoxic concentrations of the evaluated product. Cells were treated for 4 days with the P. lactiflora extract or C. sinensis extract at three non-cytotoxic concentrations together with inflammatory stress as LPS in a concentration of 50 µg/mL. Cell viability was expressed as a percentage and calculated according to the equation:
3.5 Quantification of TRPV1, IL-6, IL-13, TNF-α in human keratinocytes
The experiment was performed using HaCaT line of human keratinocytes purchased from MatTek (MatTek Europe, Bratislava, Slovak Republic). The cells were seeded in 75 cm2 bottles (Corning, United States) and expanded into an incubator at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2, using a medium specific crop. After treatment, supernatants were collected for TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-13 quantification and the TRPV-1 was measured on the cell lysate. TRPV-1, TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-13 concentrations were measured in the cell lysate and supernatant of the cultures by means of the sandwich ELISA assay, using commercially purchased kits (TRPV-1: Biorbyt; TNF-α: R&D systems; IL-6: R&D systems; IL-13: R&D systems). The absorbance reading was carried out at 450 nm in a Multiskan GO monochromator (Thermo Scientific, Finland). For the statistical evaluation, the ANOVA test was used, which allowed measuring the variation of the results, comparing the data between the groups. Then the Bonferroni posttest was applied, which reinforced and made the result presented in the ANOVA test even more precise. The 5% significance level was used (GraphPad Prism v8).
3.6 Quantification of MMP-8 and I type collagen in gingival fibroblast culture
For this experiment human primary gingival fibroblasts HGF were purchased from American Type Cultures Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, United States) (ATCC: PCS-201-018 ™). Cells were cultivated in 75 cultivated cm2 bottles (Corning, United States) and expanded in an incubator at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2. The P. lactiflora extract concentrations used in this study were 0.50, 0.10 and 0.03 mg/mL according to cytotoxicity profile on human keratinocytes and available toxicological data (Nadezhdin et al., 2021; Capsaicin, 2023; Nishikawa-Shimono et al., 2024).
For the cell treatment and exposure experiment fibroblast cultures were seeded and kept for 48 h in a specific cultivation medium and expanded in an incubator at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2. After 3 days, the supernatant of the cultures was collected for collagen type I quantification. After that the fibroblast culture was treated with 0.50, 0.10 and 0.03 mg/mL of the P. lactiflora extract and with 0.0079, 0.005 and 0.0008 mg/mL of the C. sinensis extract and exposed to LPS in a concentration of 50 ug/mL for additional 48 h. After 5 days, the cells supernatant and lysate were collected for collagen type I and MMP-8 quantification. ELISA for collagen type I and MMP-8 quantification was performed using commercially purchased kits (Abclonal, United States; R&D Systems, United States, respectively). The 450 nm absorbance reading of the immunoenzymatic assay (ELISA) for all mediators was performed in Multiskan GO monochromator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Finland). The ANOVA test was used to evaluate ELISA quantification. Then we applied the Bonferroni post-test, which reinforces and makes the result presented in the ANOVA test even more precise. The significance level of 5% will be used (GraphPad Prism v8).
3.7 Quantification of MMP-9 and I type collagen in dermal fibroblast culture
For this experiment human dermal fibroblasts CCD-1064sk were purchased from American Type Cultures Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, United States) (ATCC: CRL-2076). The cells were cultivated in 75 cm2 bottles (Corning, United States) and expanded into an incubator at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2. Cell treatment and exposure experiments were realized using the same sample preparation and the same concentrations of the P. lactiflora extract and the C. sinensis extract as for the gingival fibroblast experiment described above.
4 Conclusion
In this research, the data of complex anti-inflammatory effect of P. lactiflora extract on LPS-induced inflammation in skin on skin and gingival cells was presented for the first time. Paeoniflorin in the extract is not only able to bind to TRPV1, modulating their activity as evidenced by our in silico modeling, but probably to promote a reduction in the number of TRPV1 on the cell surface. In addition, a decrease in IL-6, IL-13 and TNF-α was observed under the influence of the whole P. lactiflora extract. It is possible that the reduction of TRPV1 is a consequence of the decrease in proinflammatory cytokines or is due to some other epigenetic mechanisms. It was also demonstrated that in addition to the above properties, P. lactiflora extract has a noticeable protective effect on type I collagen in human gingival and skin cells. In the presence of P. lactiflora extract, there was a decrease in the activity of metalloproteinases of MMP-8 and MMP-9, due to which type I collagen production was normalized up to initial level. It is possible that the decrease in metalloproteinases is a consequence of the TRPV1 reduction. Thus, due to its chemical properties as well as its complex effects on TRPV1, pro-inflammatory cytokines and metalloproteinases, P. lactiflora extract standardized for paeoniflorin is a promising natural modulator for the control of LPS-induced inflammation and type I collagen destruction in the skin and oral gingival cells.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
VF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. EI: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. EP: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. VT: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. EK: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude for the and for the resources and expertise offered by the Faculty of Fundamental Medicine and Department of Chemistry in Lomonosov Moscow State University.
Conflict of interest
Authors VF and AY were employed by SkyLab AG.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abraham M. J. Murtola T. Schulz R. Páll S. Smith J. C. Hess B. et al (2015). GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX1-2, 19–25. 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
2
Al-Majid A. Alassiri S. Rathnayake N. Tervahartiala T. Gieselmann D.-R. Sorsa T. (2018). Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 as an inflammatory and prevention biomarker in periodontal and peri-implant diseases. Int. J. Dent.2018, 1–27. 10.1155/2018/7891323
3
Atanasova T. Stankova T. Bivolarska A. Vlaykova T. (2023). Matrix metalloproteinases in oral health-special attention on MMP-8. Biomedicines11, 1514. 10.3390/biomedicines11061514
4
Avellan N.-L. Kemppainen P. Tervahartiala T. Vilppola P. Forster C. Sorsa T. (2006). Capsaicin-induced local elevations in Collagenase-2 (matrix Metalloproteinase-8) levels in human gingival crevice fluid. J. Periodontal Res.41, 33–38. 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2005.00836.x
5
Bagood M. D. Isseroff R. R. (2021). TRPV1: role in skin and skin diseases and potential target for improving wound healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22, 6135. 10.3390/ijms22116135
6
Boonen J. Baert B. Roche N. Burvenich C. De Spiegeleer B. (2010). Transdermal behaviour of the N-Alkylamide spilanthol (af-finin) from spilanthes Acmella (compositae) extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol.127, 77–84. 10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.046
7
Capsaicin M. G. Mózsik G. (2023). Capsaicin, the vanilloid receptor TRPV1 agonist in neuroprotection: mechanisms involved and significance. Neuro-chem Res.48, 3296–3315. 10.1007/s11064-023-03983-z
8
Cecchi R. Ikeda T. Camatti J. Nosaka M. Ishida Y. Kondo T. (2024). Expression of matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in Hu-man skin within 1 hour after injury through immunohistochemical staining: a pilot study. Int. J. Leg. Med.138, 1985–1990. 10.1007/s00414-024-03243-x
9
Chen J. He Q. Jin J. (2024). Targeting dendritic cell activation: the therapeutic impact of paeoniflorin in Cortosteroid-Dependent dermatitis management. Arch. Derm. Res.316, 348. 10.1007/s00403-024-03002-3
10
ClinicalTrials.gov (2025a). ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online at: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00387140 (Accessed on February 17, 2025).
11
ClinicalTrials.gov (2025b). ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online at: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01688934 (Accessed on February 17, 2025).
12
ClinicalTrials.gov (2025c). ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online at: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01688947 (Accessed on February 17, 2025).
13
Corso G. Stärk H. Jing B. Barzilay R. Jaakkola T. (2022). DiffDock: diffusion steps, twists, and turns for molecular docking. arXiv, 01776. 10.48550/arXiv.2210.01776
14
Danso M. O. van Drongelen V. Mulder A. van Esch J. Scott H. van Smeden J. et al (2014). TNF-α and Th2 cytokines induce atopic dermatitis-like features on epidermal differentiation proteins and stratum corneum Li-pids in human skin equivalents. J. Invest. Dermatol.134, 1941–1950. 10.1038/jid.2014.83
15
Diogenes A. Ferraz C. C. R. Akopian A. N. Henry M. A. Hargreaves K. M. (2011). LPS sensitizes TRPV1 via activation of TLR4 in trigeminal sensory neurons. J. Dent. Res.90, 759–764. 10.1177/0022034511400225
16
Evangeliou E. Plemmenos G. Chalazias A. Piperi C. (2023). Impact of TRP channels in oral pathology and therapeutic targeting options: a narrative review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem.23, 1559–1573. 10.2174/1568026623666230331110443
17
Fang D. Kong L.-Y. Cai J. Li S. Liu X.-D. Han J.-S. et al (2015). Interleukin-6-Mediated functional upregulation of TRPV1 receptors in dorsal root ganglion neurons through the activation of JAK/PI3K signaling pathway: roles in the development of bone cancer pain in a rat model: roles in the development of bone cancer pain in a rat model. Pain156, 1124–1144. 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000158
18
Feng J. Yang P. Mack M. R. Dryn D. Luo J. Gong X. et al (2017). Sensory TRP channels contribute differentially to skin inflammation and persistent itch. Nat. Commun.8, 980. 10.1038/s41467-017-01056-8
19
Gong P. Long H. Guo Y. Wang Z. Yao W. Wang J. et al (2024). Chinese herbal medicines: the modulator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease targeting oxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmacol.318, 116927. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116927
20
González -González O. Ramirez I. O. Ramirez B. I. O’Connell P. Ballesteros M. P. Torrado J. J. et al (2022). Drug stability: ICH versus accelerated predictive stability studies. Pharmaceutics14, 2324. 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112324
21
Han S. B. Kim H. Cho S. H. Lee J. D. Chung J. H. Kim H. S. (2016). Transient receptor potential Vanilloid-1 in epidermal keratinocytes may contribute to acute pain in Herpes zoster. Acta Derm. Venereol.96, 319–322. 10.2340/00015555-2247
22
Harper J. I. Godwin H. Green A. Wilkes L. E. Holden N. J. Moffatt M. et al (2010). A study of matrix metalloproteinase expression and activity in atopic dermatitis using a novel skin wash sampling assay for functional biomarker analysis: matrix metalloproteinases in atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol.162, 397–403. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09467.x
23
He D.-Y. Dai S.-M. (2011). Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of Paeonia lactiflora pall., a traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Front. Pharmacol.2, 10. 10.3389/fphar.2011.00010
24
Hellmich U. A. Gaudet R. (2014). Structural biology of TRP channels. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol.223, 963–990. 10.1007/978-3-319-05161-1_10
25
Hoch C. C. Petry J. Griesbaum L. Weiser T. Werner K. Ploch M. et al (2023). 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol): a versatile phytochemical with therapeutic applications across multiple diseases. Pharmacother167, 115467. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115467
26
Holla L. I. Musilova K. Vokurka J. Klapusová L. Pantuckova P. Kukletova M. et al (2008). Association of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) haplotypes with plaque-induced gingivitis in children. Acta Odontol. Scand.66, 105–112. 10.1080/00016350802004664
27
Hong H. Lu X. Wu C. Chen J. Chen C. Zhang J. et al (2022). A review for the pharmacological effects of paeoniflorin in the nervous system. Front. Pharmacol.13, 898955. 10.3389/fphar.2022.898955
28
Iftinca M. Defaye M. Altier C. (2021). TRPV1-Targeted drugs in development for human pain conditions. Drugs81, 7–27. 10.1007/s40265-020-01429-2
29
Jia Y. Mao Q. Yang J. Du N. Zhu Y. Min W. (2023). (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate protects human skin fibroblasts from ultraviolet a induced photoaging. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol.16, 149–159. 10.2147/ccid.s398547
30
Kuula H. Salo T. Pirilä E. Tuomainen A. M. Jauhiainen M. Uitto V.-J. et al (2009). Local and systemic responses in matrix metalloproteinase 8-Deficient mice during porphyromonas gingivalis-induced periodontitis. Infect. Immun.77, 850–859. 10.1128/iai.00873-08
31
Lee H. S. Kim W. J. (2022). The role of matrix metalloproteinase in inflammation with a focus on infectious diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23, 10546. 10.3390/ijms231810546
32
Lee S. G. Kim J. Lee Y. I. Kim J. Choi Y. S. Ham S. et al (2023). Cutaneous neurogenic inflammation mediated by TRPV1-NGF-TRKA pathway activation in rosacea is exacerbated by the presence of demodex mites. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol.37, 2589–2600. 10.1111/jdv.19449
33
Li G. Yue Y. Tian Y. Li J.-L. Wang M. Liang H. et al (2012). Association of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1, 3, 9, interleukin (IL)-2, 8 and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 gene polymorphisms with chronic periodontitis in a Chinese population. Cytokine60, 552–560. 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.06.239
34
Li S.K.-L. Banerjee J. Jang C. Sehgal A. Stone R. A. Civan M. M. (2015). Temperature oscillations drive cycles in the activity of MMP-2,9 secreted by a human trabecular meshwork cell line. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.56, 1396–1405. 10.1167/iovs.14-15834
35
Luchian I. Goriuc A. Sandu D. Covasa M. (2022). The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13) in periodontal and peri-implant pathological processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23, 1806. 10.3390/ijms23031806
36
Luo Y. Suttle A. Zhang Q. Wang P. Chen Y. (2021). Transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels in orofacial pain. Mol. Neurobiol.58, 2836–2850. 10.1007/s12035-021-02284-2
37
Lytvyn Y. Gooderham M. (2023). Targeting interleukin 13 for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Pharmaceutics15, 568. 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020568
38
McNutt A. T. Francoeur P. Aggarwal R. Masuda T. Meli R. Ragoza M. et al (2021). GNINA 1.0: molecular docking with deep learning. J. Cheminformatics13 (1), 43. 10.1186/s13321-021-00522-2
39
Michalak-Stoma A. Bartosińska J. Raczkiewicz D. Kowal M. Krasowska D. Chodorowska G. (2021). Assessment of selected matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and correlation with cytokines in psoriatic patients. Mediat. Inflamm.2021, 1–8. 10.1155/2021/9913798
40
Mitroi G. G. Pleşea E. L. Mitroi G. F. Mitroi M. R. Neagoe C. D. Ianoşi S. L. (2024). Exploring the potential of IL-4 and IL-13 plasma levels as biomarkers in atopic dermatitis. Life14, 352. 10.3390/life14030352
41
Nadezhdin K. D. Neuberger A. Nikolaev Y. A. Murphy L. A. Gracheva E. O. Bagriantsev S. N. et al (2021). Extracellular cap domain is an essential component of the TRPV1 gating mechanism. Nat. Commun.12, 2154. 10.1038/s41467-021-22507-3
42
Napolitano M. di Vico F. Ruggiero A. Fabbrocini G. Patruno C. (2023). The hidden sentinel of the skin: an overview on the role of Interleukin-13 in atopic dermatitis. Front. Med. (Lausanne)10, 1165098. 10.3389/fmed.2023.1165098
43
Nishikawa-Shimono R. Kuwabara M. Fujisaki S. Matsuda D. Endo M. Kamitani M. et al (2024). Discovery of novel indole derivatives as potent and selective inhibitors of proMMP-9 activation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.97, 129541. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2023.129541
44
Noh M. K. Jung M. Kim S. H. Lee S. R. Park K. H. Kim D. H. et al (2013). Assessment of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α levels in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis. Exp. Ther. Med.6, 847–851. 10.3892/etm.2013.1222
45
Obi S. Nakajima T. Hasegawa T. Kikuchi H. Oguri G. Takahashi M. et al (2017). Heat induces Interleukin-6 in skeletal muscle cells via TRPV1/PKC/CREB pathways. J. Appl. Physiol.122, 683–694. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00139.2016
46
Okada Y. Sumioka T. Reinach P. S. Miyajima M. Saika S. (2021). Roles of epithelial and mesenchymal TRP channels in mediating inflammatory fibrosis. Front. Immunol.12, 731674. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731674
47
Parker S. May B. Zhang C. Zhang A. L. Lu C. Xue C. C. (2016). A pharmacological review of bioactive constituents of Paeonia lactiflora pallas and Paeonia veitchii lynch: review of P. lactiflora pallas and P. Veitchiilynch. Phytother. Res.30, 1445–1473. 10.1002/ptr.5653
48
Planells-Cases R. Garcìa-Sanz N. Morenilla-Palao C. Ferrer-Montiel A. (2005). Functional aspects and mechanisms of TRPV1 involvement in neurogenic inflammation that leads to thermal hyperalgesia. Pflugers Arch.451, 151–159. 10.1007/s00424-005-1423-5
49
Rehman R. Bhat Y. A. Panda L. Mabalirajan U. (2013). TRPV1 inhibition attenuates IL-13 mediated asthma features in mice by reducing airway epithelial injury. Int. Immunopharmacol.15, 597–605. 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.02.010
50
Salim A. Angelova S. Roussev B. Sokrateva T. Kiselova-Kaneva Y. Peev S. et al (2023). Salivary Interleukin-6, Inter-leukin-1β, and C-Reactive protein as a diagnostic tool for plaque-induced gingivitis in children. Appl. Sci. (Basel)13, 5046. 10.3390/app13085046
51
Sattler K. El-Battrawy I. Cyganek L. Lang S. Lan H. Li X. et al (2021). TRPV1 activation and internalization is part of the LPS-induced inflammation in human iPSC-Derived cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep.11, 14689. 10.1038/s41598-021-93958-3
52
Shirley S. N. Watson A. E. Yusuf N. (2024). Pathogenesis of inflammation in skin disease: from molecular mechanisms to pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25, 10152. 10.3390/ijms251810152
53
Shu-yun X. (1988). Analgesic effect of total glucosides of Paeonia lactiflora. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol.
54
Sun J. Jiang Y. Fu J. He L. Guo X. Ye H. et al (2024). Beneficial effects of Epigallocatechin gallate in pre-venting skin photoaging: a review. Molecules29, 5226. 10.3390/molecules29225226
55
Tominaga M. Tengara S. Kamo A. Ogawa H. Takamori K. (2011). Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 is involved in dermal nerve growth: implications for possible application to Pruritus from in vitro models. J. Invest. Dermatol.131, 2105–2112. 10.1038/jid.2011.173
56
Tsaousi A. Witte E. Witte K. Röwert-Huber H.-J. Volk H.-D. Sterry W. et al (2016). MMP8 is increased in lesions and blood of acne inversa patients: a potential link to skin destruction and metabolic alterations. Mediat. Inflamm.2016, 1–8. 10.1155/2016/4097574
57
Valdés-Tresanco M. S. Valdés-Tresanco M. E. Valiente P. A. Moreno E. (2021). gmx_MMPBSA: a new tool to perform end-state free energy calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput.17 (10), 6281–6291. 10.1021/acs.jctc.1c00645
58
Wang Y. Feng C. He H. He J. Wang J. Li X. et al (2018). Sensitization of TRPV1 receptors by TNF-α orchestrates the development of vincristine-induced pain. Oncol. Lett.15, 5013–5019. 10.3892/ol.2018.7986
59
Wiegand V. Gao Y. Teusch N. (2024). Pharmacological effects of Paeonia Lactiflora focusing on painful diabetic neuropathy. Planta Med.90, 1115–1129. 10.1055/a-2441-6488
60
Wu X. Qi X. Wang J. Zhang Y. Xiao Y. Tu C. et al (2021). Paeoniflorin Attenuates the allergic contact dermatitis response via inhibiting the IFN-γ production and the NF-κB/IκBα signaling pathway in T lymphocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol.96, 107687. 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107687
61
Yien R. M. K. Gomes A. C. C. Goetze Fiorot R. Miranda A. L. P. Neves G. A. Andrade B. da S. et al (2023). Alkylamides from Acmella oleracea: antinociceptive effect and molecular docking with cannabinoid and TRPV1 receptors. Nat. Prod. Res.37, 3136–3144. 10.1080/14786419.2022.2142221
62
Yin C. Liu B. Wang P. Li X. Li Y. Zheng X. et al (2020). Eucalyptol alleviates inflammation and pain responses in a mouse model of Gout arthritis. Br. J. Pharmacol.177, 2042–2057. 10.1111/bph.14967
63
Yu X. Li J. Yang M. Chen C. Munir S. You J. et al (2021). Role of epigallocatechin gallate in collagen hydrogels modification based on physicochemical characterization and molecular docking. Food Chem.360, 130068. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130068
64
Zangooei Pourfard M. Mirmoosavi S. J. Beiraghi Toosi M. Rakhshandeh H. Rashidi R. Mohammad-Zadeh M. et al (2021). Efficacy and tolerability of hydroalcoholic extract of Paeonia officinalis in children with In-tractable epilepsy: an open-label pilot study. Epilepsy Res.176, 106735. 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106735
65
Zhang Y. Jing D. Cheng J. Chen X. Shen M. Liu H. (2022). The efficacy and safety of IL-13 inhibitors in atopic dermatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol.13, 923362. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.923362
66
Zhang M. Ma Y. Ye X. Zhang N. Pan L. Wang B. (2023). TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.8, 261. 10.1038/s41392-023-01464-x
Summary
Keywords
paeoniflorin, Paeonia lactiflora extract, TRPV1, MMP-8, MMP-9, collagen I, inflammation, tissue destruction
Citation
Filatov V, Yarovaya A, Ilin E, Patronova E, Tashlitsky V and Kalenikova E (2025) Novel prospectives of Paeonia lactiflora root extract as a natural modulator of LPS-induced inflammation and collagen I synthesis in skin and oral gingival cells. Front. Nat. Prod. 4:1625451. doi: 10.3389/fntpr.2025.1625451
Received
08 May 2025
Accepted
04 August 2025
Published
29 August 2025
Volume
4 - 2025
Edited by
Pankaj Kumar, Hemwati Nandan Bahuguna Garhwal University, India
Reviewed by
Abdel Qawasmeh, Hebron University, Palestine
Pragati Dubey, Institute of Medical Sciences, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Filatov, Yarovaya, Ilin, Patronova, Tashlitsky and Kalenikova.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Viktor Filatov, viktor.filatov@fbm.msu.ru
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.