Abstract
In the Indian Ayurvedic system, Tinospora cordifolia is highly prized for its distinct phytochemical components. While the sun-dried portions of this herb have been less examined, the shade-dried stem has been thoroughly investigated for its potential to prevent diabetes. Hence, the present study assesses the anti-diabetic efficacy of the sun-dried stem of T. cordifolia using streptozotocin and a high-fat-diet (HFD)-induced diabetic rat model. GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry) analysis revealed that anti-diabetic components like octacosanol, oleic acid, and palmitoleic acid were present in its methanolic extract. The in vivo investigation showed that the induction of diabetes evoked some physical alterations, such as weight loss and reduction in gonad size, in male Wistar rats, which were improved after supplementation with T. cordifolia. The 900 mg/kg wt dose showed the strongest capacity to lower fasting blood glucose (FBG) (71%), whereas triglyceride (<60 mg/dL) and total cholesterol (<80 mg/dL) were significantly lowered in treated groups compared to the controls. Though FBG levels were lowered in the treatment groups, serum insulin levels (26.09 pg/mL) did not show any elevation in values. Simultaneously, leptin hormone was improved along with serum vitamin D levels, and no improvement or major changes in pancreatic tissues were found. This study is the first to report that T. cordifolia extract can increase serum vitamin D levels in diabetic rats and may have a role in vitamin D regulation.
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is not merely a single disease entity but a complex and heterogeneous group of metabolic disorders characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. This persistent elevation in blood glucose levels serves as a precursor to numerous debilitating complications, including cardiovascular disease, renal dysfunction, neuropathy, and retinopathy (Forbes and Cooper, 2013). Despite a century of advances in diabetes management since the introduction of insulin therapy, the global burden of diabetes continues to escalate at an alarming rate. In 2021, the global prevalence of diabetes among individuals aged 20–79 years was estimated at 10.5%, accounting for 536.6 million people—a statistic that translates to one in ten individuals living with diabetes (Sun et al., 2022). This prevalence is projected to rise further, reaching 643 million by 2030 and 783.2 million by 2045, accentuating the urgent need for effective preventive and therapeutic interventions (Sun et al., 2022). Current therapeutic strategies for diabetes management primarily rely on oral hypoglycemic agents such as sulfonylureas, metformin, and thiazolidinediones, along with insulin therapy (Furman, 2021). While these treatments are effective in controlling blood glucose levels, their long-term use is often associated with pharmacokinetic limitations, secondary treatment failures, and adverse effects (Mandlik et al., 2008). Consequently, the search for alternative or adjunct therapies with improved safety profiles has garnered significant attention. Recognizing this need, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended the exploration of traditional medicine as a complementary approach to diabetes management (Mandlik et al., 2008). Herbal medicines, with their rich reservoir of bioactive compounds, have emerged as promising candidates, offering therapeutic efficacy with minimal toxicity compared to conventional pharmacological agents (Pavana et al., 2007).
Among the plethora of medicinal plants, Tinospora cordifolia (Thunb.) Miers, commonly known as Guduchi or Giloy, holds a prominent position in traditional Indian medicine (Gupta, et al., 2024). This large, glabrous, deciduous climbing shrub belongs to the Menispermaceae family and thrives throughout the tropical regions of the Indian subcontinent and China, often at altitudes of up to 300 m (Singh and Chaudhuri, 2017). Historically, various parts of T. cordifolia have been integral to Ayurvedic formulations for treating a wide array of ailments, including general debility, dyspepsia, fever, urinary disorders, and hepatic dysfunction (Singh et al., 2003). Its pharmacological repertoire extends to diuretic, anti-spasmodic, anti-inflammatory, anti-arthritic, anti-allergic, and anti-diabetic properties, as documented in both ancient texts and contemporary research (Manoharachary and Nagaraju, 2016; Gupta et al., 2024). The anti-diabetic potential of T. cordifolia has been attributed to its phytochemical constituents, which include alkaloids, diterpenoid lactones, glycosides, steroids, and phenolic compounds (Singh et al., 2003). These bioactive compounds are believed to exert their effects through multiple mechanisms, such as enhancing insulin secretion, improving insulin sensitivity, modulating glucose metabolism, and mitigating oxidative stress (Sharma, et al., 2019a). Several studies have investigated the efficacy of T. cordifolia in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rat models, a widely used experimental system for mimicking diabetes. However, the use of STZ alone often results in the destruction of pancreatic β-cells (\u03b2 cells), closely resembling type-1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). This raises concerns about the suitability of STZ-induced models for studying type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), which is characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency rather than β-cell destruction (Furman, 2021; Bonnevie-Nielsen et al., 1981). To address this limitation, modified diabetic models incorporating both STZ and a high-fat diet (HFD) have been developed. These models more accurately simulate the pathophysiology of T2DM by inducing and sustaining a state of chronic hyperglycemia through a combination of insulin resistance and partial β-cell dysfunction (Furman, 2021). Such models provide a more robust platform for evaluating the therapeutic efficacy of anti-diabetic agents over an extended period, allowing for the assessment of both glycemic control and secondary metabolic effects.
An additional layer of complexity arises from variations in the preparation and use of T. cordifolia across different regions and traditions. While shade-dried stems are commonly employed in laboratory studies, certain communities in eastern India prefer sun-dried mature stems for their purported enhanced anti-diabetic efficacy. Despite anecdotal evidence supporting the use of T. cordifolia stems for DM, systematic scientific investigations on sun-dried stems for their phytochemical composition and therapeutic potential seem scarce.
Materials and methods
Plant material and extraction method
Mature T. cordifolia (accession no. Deeptimayee 5,477 (21.12.2022) Cuttack, Odisha [AAU-Weed Herbarium]) stems (diameter ≥1 cm) were collected from a local healer situated in Cuttack district, Odisha state, Eastern India. They were thoroughly washed, cut into small pieces, dried, reduced to a coarse powder, and finally passed through mesh size 14#. The powdered drug was subjected to Soxhlet extraction using 80% methanol solvent. The extract was concentrated under reduced temperature (<50 °C) and pressure (10 mbar) to avoid the loss of secondary metabolites (Katara et al., 2021).
Preliminary phytochemical screening
Preliminary analysis for the presence of phytochemicals was performed on 80% methanolic extract of T. cordifolia by using protocols cited by Bakir Çilesizoğlu et al.; the results are presented in Table 1.
TABLE 1
| Sl. No. | Phyto-chemicals | Tests | Methanol (80%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alkaloids | Mayer’s test | + |
| Hager’s test | + | ||
| 2 | Flavonoids | Alkaline reagent test | + |
| Shinod’s test | + | ||
| 3 | Phenolic compounds and tannins | Ferric chloride test | + |
| Lead tetra acetic acid test | + | ||
| 4 | Proteins | Biuret test | + |
| Ninhydrin test | + | ||
| 5 | Carbohydrate | Molish test | + |
| Benedict’s test | + | ||
| Fehling’s test | + | ||
| 6 | Cardiac glycosides | Keller killiani test | - |
| 7 | Saponins | Saponin test | - |
| 8 | Triterpenoids | Horizon test | - |
| 9 | Steroids | Salkowski test | + |
| 10 | Coumarin | Coumarin test | - |
Phytochemical prescreening of Tinospora cordifolia extracts.
“+” and “−“ indicate “present” and “absent”, respectively.
GC-MS analysis of Tinospora cordifolia
GC-MS analysis of the extracts of the samples was carried out with a PerkinElmer (United States) GCMS instrument (models Clarus 680 GC and Clarus 600C MS) comprising a liquid auto-sampler. The software used in the system was Turbo Mass Ver. 6.4.2. The capillary column used was Elite- 5M, with length of 60 m, ID of 0.25 mm, and film thickness of 0.25 µm. The stationary phase was 5% diphenyl and 95% dimethyl polysiloxane. An injection volume of 1 µL was used in split-less mode. The injector temperature was set at 280 °C and ion-source temperature at 180 °C. The oven temperature was programmed at 60 °C (for 1 min), with an increase at a rate of 7 °C/min to 200 °C (hold for 3 min), then again at an increased rate of 10 °C/min to 300 °C (hold for 5 min). The total run time was approximately 39 min, and solvent delay was kept for 7 min. In the next step during mass spectrometry (MS) analysis, the spectra were taken at 70 eV. The mass range (m/z range) was 50–600 amu. The mass spectra of the unknown components were compared with the spectrum-known components of the NIST library (NIST, 2014), and the compounds were identified with name, molecular weight, and empirical formula.
Induction of type-II diabetes
Male Wistar albino rats weighing 100–150 g were procured, acclimatized, and exclusively fed on a high-fat-diet (60% of its calorific value from fat) during the first 2 weeks of the experiment. At the end of second week, all the rats were fasted for 6–8 h (only water was allowed), and they were injected with STZ. The commercially procured STZ powder was first dissolved in 0.5 M freshly prepared citrate buffer of pH 4.5. Then, a single dose of freshly prepared 40 mg/kg wt STZ was injected intra-peritoneally into the experimental animals. The rats were returned to their cages and provided the high-fat or control diet food as before and normal drinking water. To confirm the development of diabetes, blood samples were collected from the tail vein of the rats, and blood glucose levels were determined 48 h post injection of STZ through a digital blood glucometer. Rats that showed a fasting blood glucose level of >270 mg/dL (>15 mmol/L) were selected for the study (Furman, 2021). Ethical clearance for the experiment was obtained from the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (Approval No.-770/GO/Re/S/03/CPCSEA/FVSc/AAU/IAEC/21-22/944), Assam Agricultural University, Assam, India.
Acute oral toxicity study
The acute oral toxicity test was carried out according to OECD guidelines (OECD, 2001). A group containing six albino Wistar rats was procured and acclimatized (7 days) for an oral toxicity test. The group was fasted (3–4 h) before and 1–2 h after administration of the methanolic extract. A single dose of 2000 mg/kg was administered to all mice of the acute toxicity group, and the animals were observed for behavioral changes (tremor, lethargy, and paralysis), toxicity (redness in eyes, diarrhea, and weight loss), and mortality up to 24 h (Meharie et al., 2020).
Experimental design
The experimental animals were divided randomly into six groups of five animals each (n = 5).
Group I served as the normal control and was fed a normal pellet diet for 1 month.
Group II served as the negative control and was fed a high-fat diet continuously, but no drug was administered.
Group III served as the positive control and was administered standard drug metformin at 100 mg/kg body weight p. o. daily and fed on a high-fat diet continuously.
Group IV was administered a methanolic extract of Tinospora at a dose of 100 mg/kg body weight p. o. daily and fed on a high-fat diet continuously.
Group V was administered methanolic extract of Tinospora at a dose of 600 mg/kg body weight p. o. daily and fed on a high-fat diet continuously.
Group VI was administered methanolic extract of Tinospora at a dose of 900 mg/kg body weight p. o. daily and fed on a high-fat diet continuously.
The experiment was carried out for 30 days; changes like body weight were recorded every week, food and water intake were recorded daily, and FBG was recorded on every tenth day of the experimental period.
Blood and organ collection
Blood samples of each group were collected on the initial (before induction of diabetes) and 30th days of the experiment in commercially available (EDTA and Vit-K3) blood collection vials for blood glucose estimation and other biochemical estimations. For plasma preparation, collected blood samples were centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 15 min, and the supernatant was collected in Eppendorf tubes through micropipette and stored frozen at −20 °C awaiting biochemical analyses. The separated plasma was used for the estimation of different biochemical tests such as blood lipid profile (total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol/HDL-C, and triglyceride/TG), fasting blood glucose levels (FBG), and obesity-related hormones (insulin and leptin). All biochemical tests were conducted in commercially procured ELIZA kits.
Experimental animals from each group were subject to chloroform inhalation to minimize stress and pain during decapitation and organ collection. The pancreas of each mouse was collected in sterilized transparent airtight containers. Each organ was washed twice in distilled water, then submerged in 10% formaldehyde solution, and stored at room temperature for histopathological examination.
Histopathological study
Formalin-fixed organs and tissue were washed under tap water. Ethanol was then used to dehydrate them, followed by clearing through xylene. Finally, the xylene-cleared tissue and organs were embedded in paraffin wax. Sections of tissue and organs 5 mm thick were prepared using a rotary microtome machine. Lastly, the sectioned and embedded tissues were stained with H (hematoxylin) and E (eosin) stains for histopathological observations (Meharie, et al., 2020). The prepared microscopic slides were then investigated under a microscope, and images were captured using a camera at ×40 magnification.
Statistical analysis
The results of the present study were processed and statistically analyzed through GraphPad PRISM (Version-9) and SPSS-2.0 software. All values were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed followed by Duncan post hoc multiple comparison test. Significant differences were set at p values <0.05.
Results
Preliminary phytochemical screening
The phytochemical study of the methanolic extract of T. cordifolia stem revealed a broad variety of phytochemicals. The key phytochemical components, found in 80% methanol extract, were flavonoids, alkaloids, proteins, carbohydrates, glycosides, steroids, saponins, phenolic compounds, and tannins (Table 1).
GC-MS results
The GC-MS analysis results revealed the presence of 18 phytochemical compounds with various therapeutic potentials. The identified phytochemical compounds at various retention times are given in Table 2 along with their reverse value, molecular wt., and therapeutic properties. The major phytochemical components present in the methanolic extract of T. cordifolia with high therapeutic potential were octacosanol, oleic acid, Z,Z-6,28-heptatriactontadien-2-one, retinal, villosin, 3-methyl-2-(2-oxopropyl)furan, calcitriol, and palmitoleic acid.
TABLE 2
| Sl no. | RT (min) | Reverse value | Matched compound name | Mol. Wt | Formula | Therapeutic properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 1 | 15.042 | 759 | Octacosanol | 410 | C28H58O | Anti-Parkinsonian effects (Wang et al., 2012) Regulates lipid and glucose metabolism, (Nies, et al., 2006) Reduces fatigue (Zhou et al., 2021) Promotes cardiovascular health (Thippeswamy, et al., 2008) Protects the liver (Noa, et al., 2003) Relieves constipation (Jiang et al., 2020); anti-inflammatory (Guo et al., 2017; Pushpangadan et al., 2015); anti-nociceptive (de Oliveira et al., 2012) |
| 2 | 17.828 | 892 | 2-methoxy-4-vinylphenol | 150 |
C9H10O2 |
- |
| 3 | 18.503 | 763 | Phenol, 2,6-dimethoxy- | 154 |
C8H10O3 |
- |
| 4 | 19.048 | 860 | Trans-2-methyl-4-N-pentylthiane, S,S-dioxide | 218 |
C11H22O2S |
- |
| 5 | 19.624 | 689 | Diphenyl ether | 170 | C12H10O | - |
| 6 | 21.409 | 679 | Oleic acid | 282 | C18H34O2 | Antioxidant (Ruiz-Núñez et al., 2016) Improve blood lipid profile (Hlais et al., 2013) Maintain body weight (Pérez-Martínez et al., 2011) Prevent palmitic saturated fatty acid; promoted mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance, and inflammation-related signaling in neuronal cells (Kwon et al., 2014) and skeletal muscle (Salvadó et al., 2013) Lower risk of atherosclerosis (Jones et al., 2014) |
| 7 | 22.445 | 725 | 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-isopropyl-benzoquinone | 180 | C10H12O3 | - |
| 8 | 24.540 | 829 | Z,Z-6,28-heptatriactontadien-2-one | 530 | C37H70O | Vasodilator (Paulsamy et al., 2012) |
| 9 | 25.306 | 669 | Retinal | 284 | C20H28O | Essential in human retinal pigment epithelial cells |
| 10 | 26.286 | 778 | Villosin | 300 | C20H28O2 | Antioxidative, NO production inhibitory, and antitumor activities (Zhou et al., 2024) |
| 11 | 27.091 | 912 | 3-methyl-2-(2-oxopropyl)furan | 138 | C8H10O2 | Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities; inhibition of non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation (Xu et al., 2017) |
| 12 | 28.322 | 665 | Calcitriol | 416 | C29H48O | Active form of vitamin D |
| 13 | 28.987 | 920 | Tetradecanoic acid, 10,13-dimethyl-, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | - |
| 14 | 30.303 | 671 | Trans-sinapyl alcohol | 210 | C11H14O4 | - |
| 15 | 31.413 | 869 | Palmitoleic acid | 254 | C16H30O2 | Anti-diabetic, anti-obesity action, suppression of fat synthesis, enhanced energy expenditure, reduced fat storage, and improved glucose metabolism (Morse, 2015a; Novikova et al., 2015) Reduced blood LDL: cholesterol and triglycerides (Morse, N., 2015a; Morse, N., 2015b; Bernstein, et al., 2014; Viollet, et al., 2007) Reduced liver weight and lipid content (Morse, 2015b; Bernstein, et al., 2014) |
| 16 | 31.338 | 874 | 11,14-octadecadienoic acid, methyl ester | 294 | C19H34O2 | - |
| 17 | 31.708 | 871 | Heptacosanoic acid, 25-methyl-, methyl ester | 438 | C29H58O2 | - |
| 18 | 31.593 | 893 | 3-methyl-2-(2-oxopropyl)furan | 138 | C8H10O2 | Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities; inhibition of non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation (Xu et al., 2017) |
List of phytochemicals with their retention time, molecular formula, molecular weight, and therapeutic potentials.
Acute toxicity study
No signs of mortality or toxicity were observed in the experimental group after 6h, 12h, 24h, or 48 h s of toxicity study. Hence, an oral dose of 2000mg//kg body weight was concluded as safe, and three doses (100, 600, and 900 mg/kg body weight) of methanolic extract were chosen for further study.
Effect of methanolic extract of TCE on physical changes
Certain peculiar physical changes were observed among the experimental groups such as weight reduction (Figure 2) and gonadal size reduction (Figure 1). After induction of DM in rats, gonad size was visibly reduced , which then improved after treatment with methanolic extract of TC commenced. Similar observations were previously mentioned in in vivo studies regarding the effect of DM on male reproductive organs and fertility (Kotian et al., 2019).
FIGURE 1
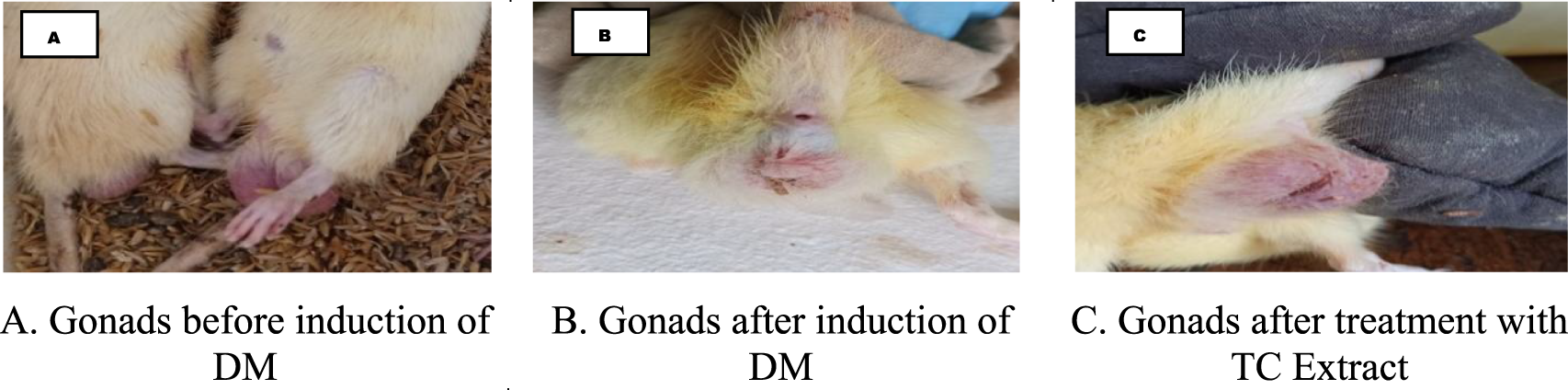
Changes in male reproductive organ before and after induction of DM-II. (A) Gonads before induction of DM. (B) Gonads after induction of DM. (C) Gonads after treatment with TC extract.
All experimental groups showed increased weight gain due to the constant feeding of HFD before induction (Day 0–14) of DM except normal control (G-I) fed on normal pellet diet. After induction of DM-II in the third week only G-I showed no significant weight reduction whereas other groups showed significant (p < 0.05) reduction in weight, which were later improved for G-III, G-IV, G-V, and G-VI due to the administration of metformin and TCE extracts. No weight reduction was observed for G-I animals throughout the experimental period; rather, it non-significantly increased with each progressing week (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2
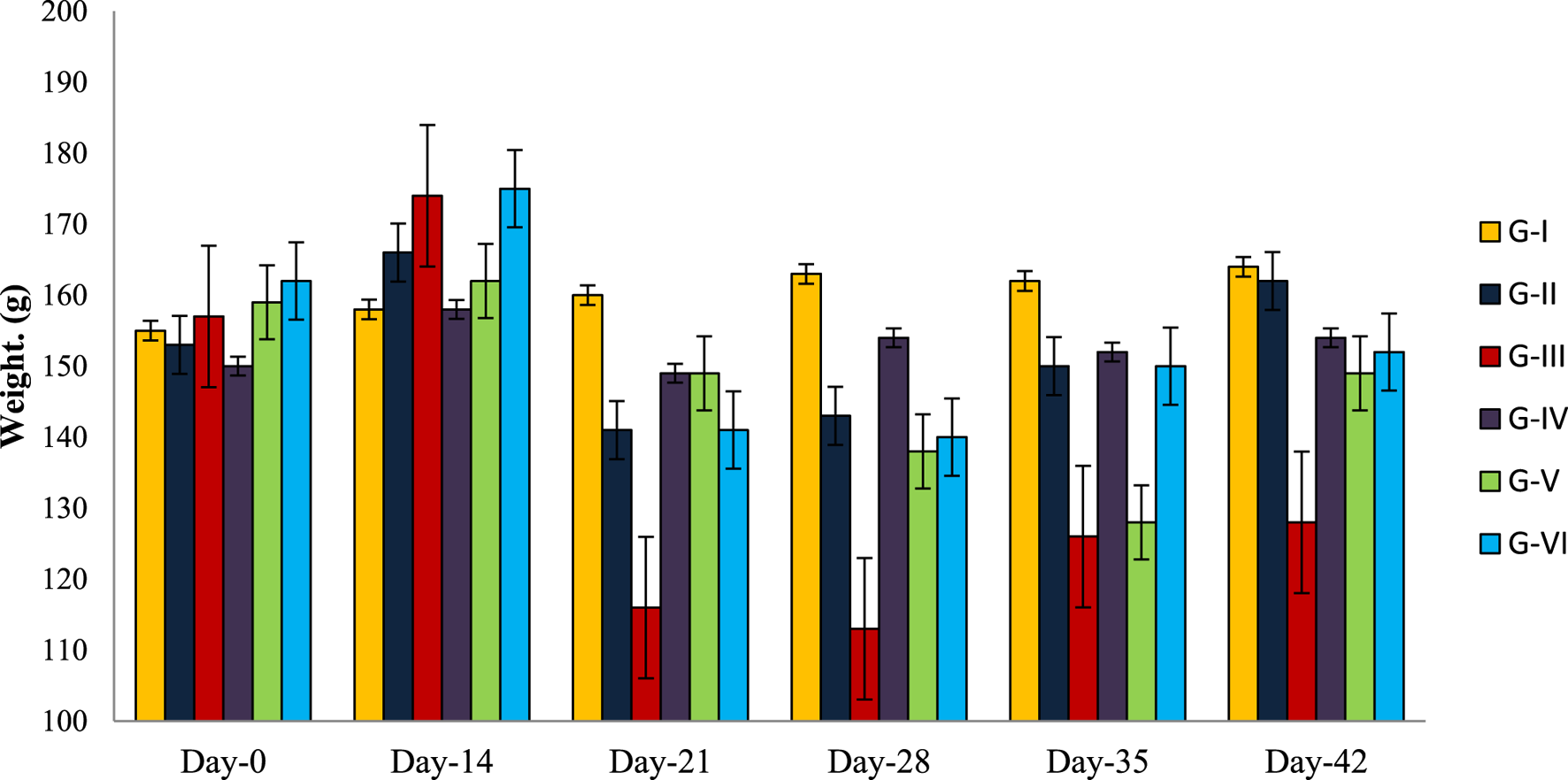
Average weight change observed in experimental animals of each experimental group.
Effect of methanolic extract of TCE on fasting blood glucose levels
The weekly FBG levels of all diabetic groups were significantly (p < 0.05) higher than the normal control group (Figure 3A). However, supplementation with all three doses (100, 600, and 900 mg/kg wt) of TCE resulted in decreased FBG levels compared to the normal control group. The highest efficacy for FBG level reduction was recorded for G-III (74%), which received the standard drug metformin. Among all doses of TCE, 900 mg/kg wt (G-VI) showed maximum efficacy in the reduction of FBG, followed by 600 and 100 mg/kg wt., respectively. However, the negative control group/G-II which was diabetic but not given any drug also showed reduced FBG levels, but the mean blood glucose value remained >250 mg/dL. This may suggest that the use of both STZ and HFD can mimic the hyperglycemic conditions of type-II DM for more than 4 weeks. Although the standard drug showed higher efficacy in reducing FBG levels, methanolic TCE extract also proved to be a potent hypoglycemic agent in this study.
Effect of methanolic extract of TCE on insulin and leptin levels
The mean insulin levels of all groups, including normal control, recorded between 30 and 40 pg/mL before induction of DM-II. After this, insulin levels declined, but the lowest reduction was shown by Group VI rats which were given the highest dose of TCE extract for 30 days. However, in the case of the normal control group, the insulin levels of the rats significantly increased throughout the experimental period (Figure 3B). The mean serum leptin level of the diabetic groups ranged 1.4–1.8 ng/mL before induction of DM-II. However, leptin levels declined after induction of DM-II in all diabetic groups. The highest reduction of circulating leptin level was observed in G-VI (Figure 3C). However, these results are contradictory to previous studies where leptin levels increased with the induction of DM-II (Zhang et al., 2013; Levin et al., 2003).
FIGURE 3
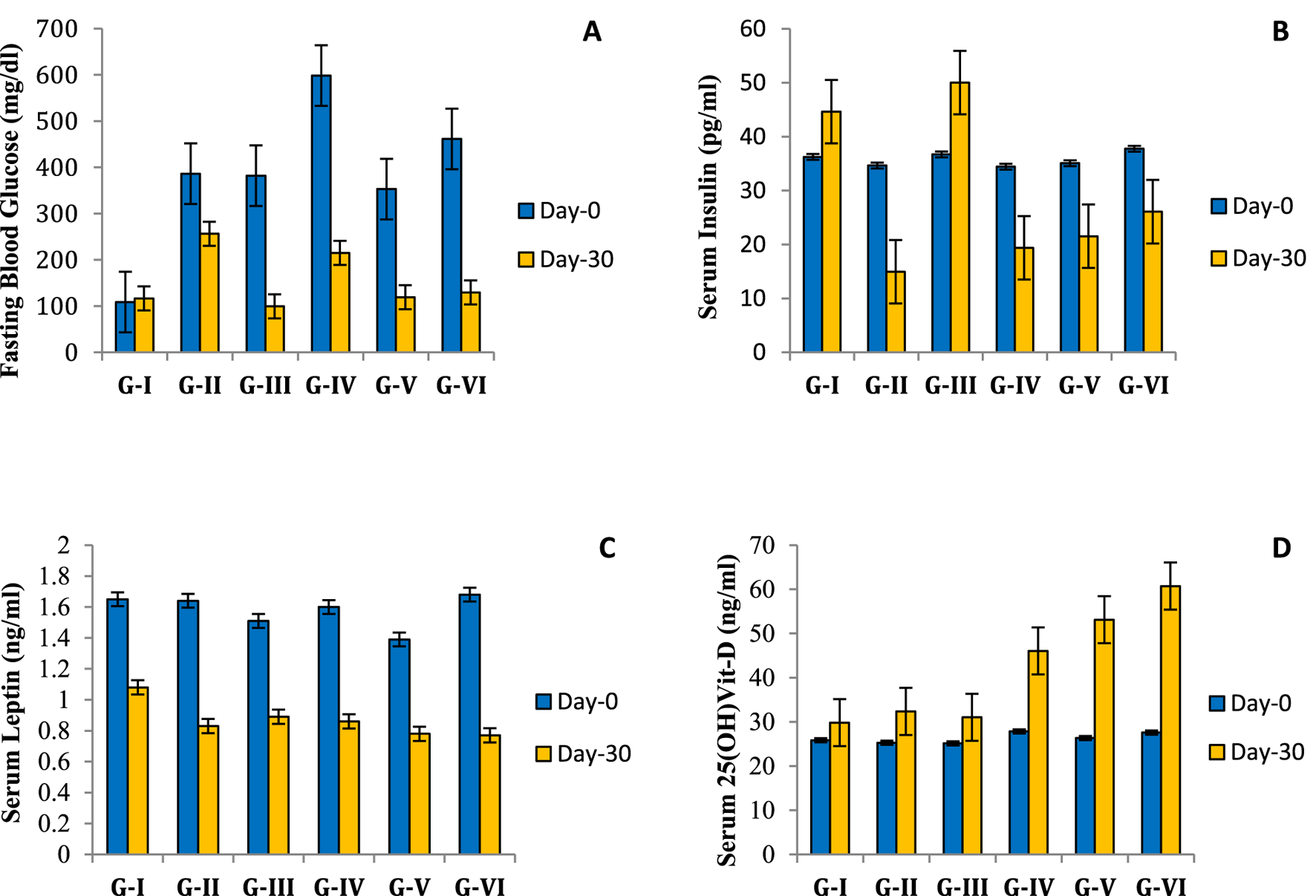
Effect of Tinospora cordifolia extract on hematological parameters of experimental groups. (A) Effect of Tinospora extract on fasting blood glucose (FBG); (B) effect of Tinospora extract on serum insulin; (C) effect of Tinospora extract on serum leptin; (D) effect of Tinospora extract on serum vitamin-D.
Effect of methanolic extract of TCE on serum vitamin-D level
As per the results, the serum vitamin D levels of all diabetic groups ranged between 25 and 28ng/mL before the supplementation of TCE. However, the serum vitamin D levels of the treatment groups (G-IV, G-V, G-VI) increased to 45–60 ng/mL in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3D). The normal control group also showed an increase in serum vitamin D level from 25.85 ± 0.66 ng/mL to 29.83 ± 0.89 ng/mL at the end of the experimental period, but the percent increase was higher in the TCE supplemented groups.
Effect of methanolic extract of TCE on the lipid profile
A significant decrease was recorded in the total cholesterol levels of G-IV, G-V, and G-VI animals receiving 100, 600, and 900 mg/kg wt TCE extract, respectively. However, neither of the group’s total cholesterol values reached >150 mg/dL during the entire experimental period (Figure 4A). The serum triglyceride levels showed a decreasing trend for all diabetic groups (Figure 4B). The maximum reduction of serum triglyceride was observed for 900 mg/kg wt (G-VI) of TCE. The HDL-cholesterol levels for each group were very low, and a non-significant increase was shown by the groups (G-IV, V, and VI) fed on Tinospora extract.
FIGURE 4
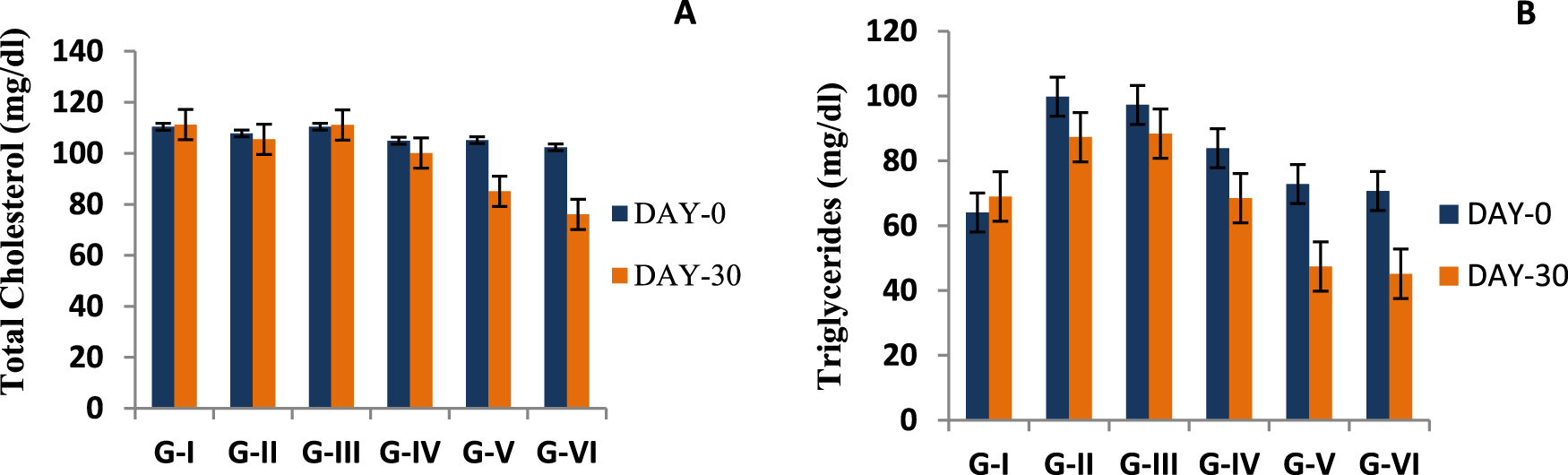
Effect of Tinospora cordifolia stem extract (TCE) on total cholesterol (A) and serum triglyceride (B) levels of the experimental groups. Values plotted in graphs are mean of each group (n = 5) with significance level at 95%.
Effect of the methanolic extract of TCE on histology of the pancreas
STZ is widely known for selective beta cell cytotoxicity, and it has been shown to lower beta cell/islet count and blood insulin levels in STZ-induced diabetic mice (Mitra et al., 1996). In the current investigation, the histological analysis of the pancreas in TCE-treated diabetic rats of groups V and VI revealed no indication of beta cell regeneration in the islets of Langerhans. According to the investigation, group IV animals treated with the lowest dose of TCE (100 mg/kg wt) showed signs of beta cell degeneration and cytoplasmic vacuolation. Similarly, pancreatic cell degeneration was observed in groups V (600 mg/kg wt) and VI (900 mg/kg wt) as well, but cytoplasmic vacuolation was absent in these groups. In contrast, no such beta cell degradation was seen in NC (Figure 5). However these findings contradict previous studies in which Tinospora extract demonstrated beta cell preservation and regenerating activities (Sharma et al.,2019b; Banerjee et al., 2019; Rajalakshmi et al., 2009), although certain studies support the current findings (Puranik et al., 2010). However, cytoplasmic vacuolation was not detected in any of the comparable studies.
FIGURE 5
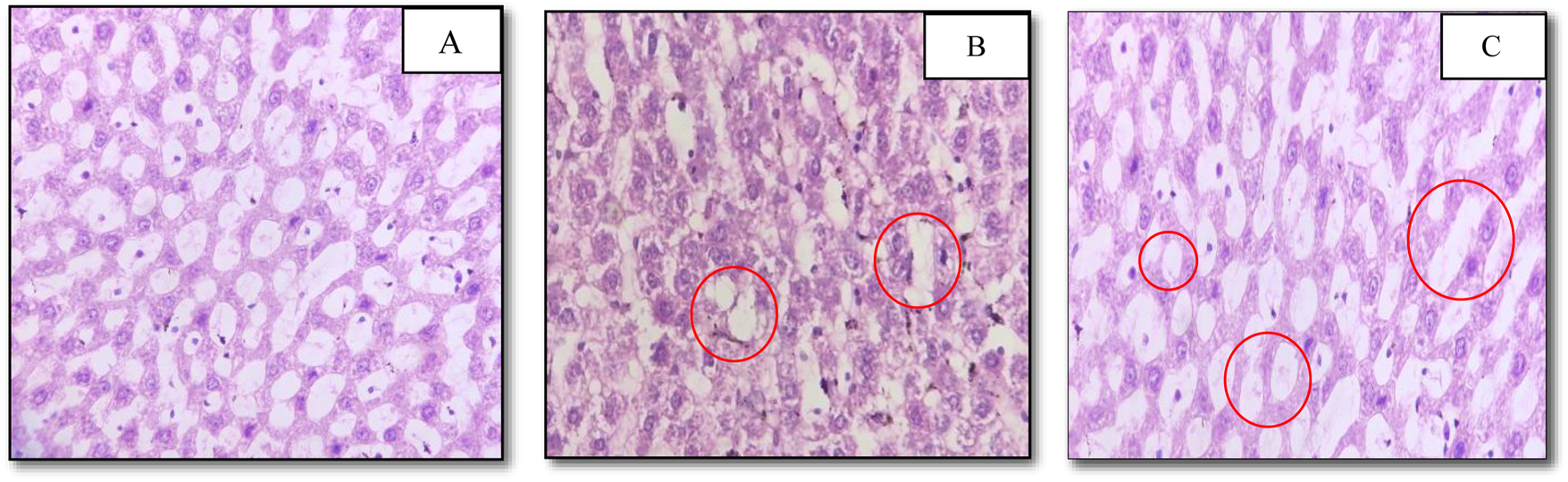
Photomicrographs of pancreatic sections of experimental rats stained with haematoxylin and eosin (10 × 40). (A) No change noted in histological section of normal control group; (B) cytoplasmic vacuolation and beta cell degeneration noted in histological section of Group-IV; (C) beta cell degeneration noted in histological section of Group-V.
Discussion
In the methanolic extract of TCE, antidiabetic phytochemicals such as octacosanol, stigmasterol, palmitoleic acid, oleic acid, and docosanoic acid were found, which substantiates the anti-diabetic activities of Tinospora. However the presence of antioxidants (oleic acid, 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, villosin, stigmasterol, calcitriol, and retinal) and anti-inflammatory (stigmasterol, hexadecanoic acid, docosanoic acid, octacosanol) and immune-modulatory (calcitriol and stigmasterol) phytochemicals can also be considered contributing to the antidiabetic effects of TCE.
The in vivo study established the hypoglycemic efficacy of T. cordifolia extract for all three doses. Out of all the experimental treatments, the standard drug metformin produced the highest reduction (73%) in FBG levels, followed by group-VI/highest TCE dose (71%) in diabetic rats. In case of insulin secretion, the values reduced for all the experimental groups except NC, as compared to their values estimated before the induction of diabetes. However, TCE supplementation improved insulin levels for all groups in a dose-dependent manner. The observed reduction in gonadal size was due to the induction of diabetes, not due to T. cordifolia extract, as described by Gupta and Sharma (2003). The 70% methanolic TCE did induce infertility in male rats, but the change in gonad size was non-significant, which means that the changes observed in this study were not related to Tinospora extract (Gupta and Sharma, 2003) but to type-II diabetes mellitus (Kotian et al., 2019). Hence the improved gonadal size after TCE supplementation can be understood as a sign of improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. The relationship of leptin and type-II diabetes has always been controversial, with some studies supporting an increasing trend of leptin (Zhang et al., 2013; Levin et al., 2003) and some supporting a decreasing trend (Onyemelukwe et al., 2020) in diabetic rats. However, in the present study, serum leptin results showed a decreasing trend after the induction of type-II diabetes in all diabetic groups. After TCE treatment, serum leptin levels started improving for all three doses in a dose-dependent manner; however, Groups III (metformin) and VI showed similar levels of improvement compared to other groups, and the serum leptin levels in normal control rats non-significantly (p > 0.05) increased with time. Our recorded results establish a direct relationship of serum leptin concentration to serum insulin concentration and an inverse relationship of leptin concentration to FBG level. As per our results, STZ-induced diabetes significantly decreased serum leptin concentration along with serum insulin concentration and body weight, which rapidly improved after TCE treatment in diabetic groups, signifying the protective nature of Tinospora stem extract against diabetes mellitus.
The current study’s findings also showed that giving diabetic rats T. cordifolia extract as a supplement raised their serum vitamin D levels from 25–28 ng/mL to 45–60 ng/mL. Even while the normal control group’s serum vitamin D level increased at the end of the trial, the TCE-supplemented groups experienced a larger percentage increase. As supported by the GC-MS results presented here, these results indicate that T. cordifolia extract elevates the serum vitamin D levels in Groups IV, V, and VI and contains vitamin D precursors. Furthermore, our findings are supported by the fact that the presence of vitamin D precursors (calciferol-D) in T. cordifolia stems was previously noted in Kumar and Singh (2021). It was also noteworthy that Group VI had the greatest vitamin D levels and the highest FBG level reduction among the other experimental groups following TCE treatment. Therefore, it makes sense that the rise in vitamin D levels, in addition to the action of other bioactive anti-diabetic chemicals in the extract, may have contributed to the improvement of the diabetes indices in the experimental rats. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked in a number of studies to a series of endocrine alterations, including the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, a decrease in insulin synthesis, and a blockage in the peripheral tissues’ ability to absorb glucose, all of which contribute to insulin resistance (Zhang et al., 2016). Vitamin D supplementation improves glucose regulation and reduced insulin resistance (Guareschi et al., 2019; Krisnamurti et al., 2023). This is because vitamin D interacts with the pancreatic beta-cells to modify extracellular calcium or calcium flow, facilitating the release of insulin from these cells. Additionally, vitamin D activates calcium-dependent endopeptidase, which facilitates the conversion of proinsulin to insulin (Pittas et al., 2007; Lee et al., 1994). As far as we are aware, this work is the first to show that stem extract from T. cordifolia can raise serum vitamin D levels in diabetic rats and that the plant contains some form of vitamin D precursor in it.
Conclusion
The investigation of traditional remedies for the treatment of complicated illnesses like diabetes is essential to the development of novel plant-based medications. The current investigation showed that when administered at a level of 900 mg/kg body weight, T. cordifolia extract exhibited anti-diabetic potency nearly equal to metformin. Although it had no positive effect on serum insulin levels, it was able to lower blood glucose levels by 71%. These findings spark debate about whether T. cordifolia extract influences alternative pathways to exercise its anti-diabetic effects rather than acting on pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin. This in vivo study revealed that Tinospora stem extract improved the two key conditions of Type-II diabetes: insulin and leptin resistance. This, in turn, prevented the diabetic rats from losing a significant amount of weight and assisted them in managing it. Furthermore, early data showing elevated vitamin D levels in diabetic rats after taking T. cordifolia supplementation suggested that T. cordifolia contains precursors to vitamin D. Despite the calcitriol detection in the GC-MS analysis of this investigation, it is still at an early stage. Therefore, in order to determine whether calcitriol or any other type of vitamin D precursor is present in T. cordifolia stem extract and to determine its direct effect on diabetic patients, more thorough procedures and research are needed.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (Approval No.-770/GO/Re/S/03/CPCSEA/FVSc/AAU/IAEC/21-22/944), Assam Agricultural University, Assam, India. The study was conducted in accordance with local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
DM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AB: Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. AS: Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. SG: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. MD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the Guwahati BioTech Park, Guwahati, Assam, India, for providing laboratory facilities to conduct preliminary analyses.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Banerjee A. Singh S. Prasad S. K. Kumar S. Banerjee O. Seal T. et al (2019). Protective efficacy of Tinospora sinensis against streptozotocin induced pancreatic islet cell injuries of diabetic rats and its correlation to its phytochemical profiles. J. Ethnopharmacol.248, 112356. 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112356
2
Bernstein A. M. Roizen M. F. Martinez L. (2014). RETRACTED: purified palmitoleic acid for the reduction of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and serum lipids: a double-blinded, randomized, placebo controlled study. J. Clin.Lipidol.8 (6), 612–617. 10.1016/j.jacl.2014.08.001
3
Bonnevie-Nielsen V. Steffes M. W. &Lernmark A. (1981). A major loss in islet mass and B-cell function precedes hyperglycemia in mice given multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Diabetes30, 424–429. 10.2337/diab.30.5.424
4
de Oliveira A. M. Conserva L. M. de Souza Ferro J. N. de Almeida Brito F. Lyra Lemos R. P. Barreto E. (2012). Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of octacosanol from the leaves of Sabicea grisea Var. grisea in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci.13 (2), 1598–1611. 10.3390/ijms13021598
5
Forbes J. M. Cooper M. E. (2013). Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol. Rev.93 (1), 137–188. 10.1152/physrev.00045.2011
6
Furman B. L. (2021). Streptozotocin-induced diabetic models in mice and rats. Curr. Curr. Protoc.1, 78. 10.1002/cpz1.78
7
Guareschi Z. M. Valcanaia A. C. Ceglarek V. M. Hotz P. Amaral B. K. de Souza D. W. et al (2019). The effect of chronic oral vitamin d supplementation on adiposity and insulin secretion in hypothalamic Obese rats. Br. J. Nutr.121 (12), 1334–1344. 10.1017/S0007114519000667
8
Guo T. Lin Q. Li X. Nie Y. Wang L. Shi L. et al (2017). Octacosanol attenuates inflammation in both RAW264.7 macrophages and a mouse model of colitis. J. Agric. Food Chem.65 (18), 3647–3658. 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05465
9
Gupta R. S. Sharma A. (2003). Antifertility effect of Tinospora cordifolia (willd.) stem extract in Male rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol.41, 885–889.
10
Gupta A. Gupta P. Bajpai G. (2024). Tinospora cordifolia (giloy): an insight on the multifarious pharmacological paradigms of a Most promising medicinal ayurvedic herb. Heliyon10 (4), e26125. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26125
11
Hlais S. El-Bistami D. El Rahi B. Mattar M. A. Obeid O. A. (2013). Combined fish oil and high oleic sunflower oil supplements neutralize their individual effects on the lipid profile of healthy men. Lipids48 (9), 853–861. 10.1007/s11745-013-3819-x
12
Jiang M. Y. Lu H. Pu X. Y. Li Y. H. Tian K. Xiong Y. et al (2020). Laxative metabolites from the leaves of Moringa oleifera. J. Agric. Food Chem.68 (30), 7850–7860. 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01564
13
Katara A. Garg N. Mathur M. (2021). Separation and identification of anti-diabetic compounds in Tinospora cordifolia extract and Ayurvedic formulation guduchi satva by GCMS and FTIR study with subsequent evaluation of in-vitro hypoglycemic potential. IJPSDR13 (2), 183–189. 10.25004/IJPSDR.2021.130211
14
Kotian S. R. Kumar A. Souza A. D. (2019). Effect of diabetes on the Male reproductive system — a histomorphological study. J. Morphol. Sci.36(1), 17–23. 10.1055/s-0039-1683405
15
Krisnamurti D. G. Louisa M. Poerwaningsih E. H. Tarigan T. J. Soetikno V. Wibowo H. et al (2023). Vitamin D supplementation alleviates insulin resistance in prediabetic rats by modifying IRS-1 and PPARγ/NF-κB expressions. Front. Endocrinol.14, 1089298. 10.3389/fendo.2023.1089298
16
Kumar K. Singh A. (2021). Identification of phytochemicals from Tinospora cordifolia using anti ageing specific receptor. Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/10603/465881.
17
Kwon B. Lee H. K. &Querfurth H. W. (2014). Oleate prevents palmitate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance and inflammatory signaling in neuronal cells. Biochim. Acta1843 (7), 1402–1413. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.004
18
Lee S. Clark S. A. Gill R. K. Christakos S. (1994). 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and pancreatic beta-cell function: vitamin D receptors, gene expression, and insulin secretion. Endocrinology134 (4), 1602–1610. 10.1210/endo.134.4.8137721
19
Levin B. E. Dunn-Meynell A. A. Ricci M. R. Cummings D. E. (2003). Abnormalities of leptin and ghrelin regulation in obesity-prone juvenile rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.285, 949–957. 10.1152/ajpendo.00186.2003
20
Mandlik R. V. Desai S. K. Naik S. R. Sharma G. Kohli R. K. (2008). Antidiabetic activity of a polyherbal formulation (DRF/AY/5001). IJEB46, 599–606.
21
Manoharachary C. Nagaraju D. (2016). Medicinal plants for human health and welfare. Ann. phytomedicine5 (1), 24–34.
22
Meharie B. G. Amare G. G. Belayneh Y. M. (2020). Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of the crude extract and solvent fractions of clutiaabyssinica (euphorbiaceae) leaf against CCl4-Induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J. Exp. Pharmacol., 137–150. 10.2147/JEP.S248677
23
Mitra S. K. Gopumadhavan S. Muralidhar T. S. Anturlikar S. D. Sujatha M. B. (1996). Effect of a herbomineral preparation D-400 in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol.54, 41–46. 10.1016/0378-8741(96)01439-0
24
Morse N. (2015a). Lipid-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects of palmitoleic acid: evidence from preclinical and epidemiological studies. Lipid Technol.27 (5), 107–111. 10.1002/lite.201500019
25
Morse N. (2015b). Lipid-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects of palmitoleic acid: evidence from human intervention studies. Lipid Technol.27 (7), 155–160. 10.1002/lite.201500033
26
Nies L. K. Cymbala A. A. Kasten S. L. Lamprecht D. G. Olson K. L. (2006). Complementary and alternative therapies for the management of dyslipidemia. Ann. Pharmacother.40 (11), 1984–1992. 10.1345/aph.1H040
27
Noa M. Mendoza S. Mas R. Mendoza N. (2003). Effect of policosanol on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver damage in sprague-dawley rats. Drugs R and D.4 (1), 29–35. 10.2165/00126839-200304010-00003
28
Novikova D. S. Garabadzhiu A. V. Melino G. Barlev N. A. Tribulovich V. G. (2015). AMP-Activated protein kinase: structure, function, and role in pathological processes. Biochem. (Mosc).80, 127–144. 10.1134/S0006297915020017
29
OECD (2001). OECD guideline for testing of chemicals: acute oral toxicity-fixed dose procedure 420. Available online at: http://www.oecd.org/document/22/0.2340,en.2649.34377.1916054.1.1.1.1.00.html.
30
Onyemelukwe O. U. Ogoina D. &Onyemelukwe G. C. (2020). Leptin concentrations in type 2 diabetes and non-diabetes Nigerian-Africans. Am. J. Cardiovasc.10 (4), 444–454.
31
Pavana P. Sethupathy S. Manoharan S. (2007). Antihyperglycemic and antilipidperoxidative effects of Tephrosia purpurea seed extract in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Indian J. Clin. biochem.22 (1), 77–83. 10.1007/bf02912886
32
Pérez-Martínez P. García-Ríos A. Delgado-Lista J. Pérez-Jiménez F. López-Miranda J. (2011). Mediterranean diet rich in olive oil and obesity, metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus. Curr. Pharm. Des.17 (8), 769–777. 10.2174/138161211795428948
33
Pittas A. G. Lau J. Hu F. B. Dawson-Hughes B. (2007). The role of vitamin D and calcium in type 2 diabetes. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.92 (6), 2017–2029. 10.1210/jc.2007-0298
34
Puranik N. Kammar K. F. Devi S. (2010). Anti-diabetic activity of Tinospora cordifolia (willd.) in streptozotocin diabetic rats; does it act like sulfonylureas?Turkish J. Med. Sci.40 (2), 265–270. 10.3906/sag-0802-40
35
Pushpangadan P. Ijinu T. P. George V. (2015). Plant based anti-inflammatory secondary metabolites. Ann. Phytomedicine4 (1), 17–36.
36
Rajalakshmi M. Eliza J. Priya C. E. Nirmala A. Daisy P. (2009). Anti-diabetic properties of Tinospora cordifolia stem extracts on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.3 (5), 171–180. Available online at: http://www.academicjournals.org/ajpp.
37
Ruiz-Núñez B. Dijck-Brouwer D. A. J. &Muskiet F. A. J. (2016). The relation of saturated fatty acids with low-grade inflammation and cardiovascular disease. J. NutrBiochem36, 1–20. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.12.007
38
Salvadó L. Coll T. Gómez-Foix A. M. Salmerón E. Barroso E. Palomer X. et al (2013). Oleate prevents saturated-fatty-acid-induced ER stress, inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells through an AMPK-Dependent mechanism. Diabetologia56 (6), 1372–1382. 10.1007/s00125-013-2867-3
39
Sharma B. R. Park C. M. Kim H. A. Kim H. J. Rhyu D. Y. (2019a). Tinospora cordifolia preserves pancreatic beta cells and enhances glucose uptake in adipocytes to regulate glucose metabolism in diabetic rats. Phytotherapy research:PTR33 (10), 2765–2774. 10.1002/ptr.6462
40
Sharma P. Dwivedee B. P. Bisht D. Dash A. K. Kumar D. (2019b). The chemical constituents and diverse pharmacological importance of Tinospora cordifolia. Heliyon5 (9), e02437. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02437
41
Singh D. Chaudhuri P. K. (2017). Chemistry and pharmacology of Tinospora cordifolia. Nat. Product. Commun.12 (2), 1934578X1701200240. 10.1177/1934578x1701200240
42
Singh S. S. Pandey S. C. Srivastava S. Gupta V. S. Patro B. Ghosh A. C. (2003). Chemistry and medicinal properties of Tinospora cordifolia (guduchi). Indian J. Pharmacol.35, 83–91.
43
Sun H. Saeedi P. Karuranga S. Pinkepank M. Ogurtsova K. Duncan B. B. et al (2022). IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract.183, 109119–119. 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
44
Thippeswamy G. Sheela M. L. &Salimath B. P. (2008). Octacosanol isolated from Tinospora cordifolia downregulates VEGF gene expression by inhibiting nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB and its DNA binding activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol.588 (2–3), 141–150. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.04.027
45
Viollet B. Mounier R. Leclerc J. Yazigi A. Foretz M. &Andreelli F. (2007). Targeting AMP-Activated protein kinase as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Diabetes Metab. J.33 (6), 395–402. 10.1016/j.diabet.2007.10.004
46
Wang T. Liu Y. Yang N. Ji C. Chan P. Zuo P. (2012). Anti-parkinsonian effects of octacosanol in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6 tetrahydropyridine-treated mice. Neural Regen. Res.7 (14), 1080–1087. 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.14.006
47
Zhang S. Zhang Q. Zhang L. Li C. Jiang H. (2013). Expression of ghrelin and leptin during the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rat model. Mol. Med. Rep.7, 223–228. 10.3892/mmr.2012.1154
48
Zhang J. Ye J. Guo G. Lan Z. Li X. Pan Z. et al (2016). Vitamin D status is negatively correlated with insulin resistance in Chinese type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Endocrinol.2016, 1–7. 10.1155/2016/1794894
49
Zhou Y. Cao F. Wu Q. Luo Y. Guo T. Han S. et al (2021). Dietary supplementation of octacosanol improves exercise-induced fatigue and its molecular mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem.69 (27), 7603–7618. 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01764
50
Zhou J. Yan M. Shi X. Wang Y. Shen H. Mao X. et al (2024). Total synthesis of -villosin C and teuvincenone B. Org. Chem. Front.11, 472–476. 10.1039/D3QO01841E
Summary
Keywords
Tinospora cordifolia , GC-MS, phytochemicals, type-II diabetes, gonad size
Citation
Mahapatra D, Beniwal A, Sarma J, Shome A, Goswami S and Das M (2025) Evaluation of the anti-diabetic potency of Tinospora cordifolia stem against streptozotocin and high-fat diet-induced diabetic rats. Front. Nat. Prod. 4:1689287. doi: 10.3389/fntpr.2025.1689287
Received
20 August 2025
Revised
16 October 2025
Accepted
21 October 2025
Published
27 November 2025
Volume
4 - 2025
Edited by
Argyrios Periferakis, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Reviewed by
Ankanahalli N. Nanjaraj Urs, Washington University in St. Louis, United States
Lamprini Troumpata, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Mahapatra, Beniwal, Sarma, Shome, Goswami and Das.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mamoni Das, correspondingmdas@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.