- 1Geosciences and Natural Resources Laboratory, Department of Geology, Faculty of Sciences, Ibn Tofail University, Kenitra, Morocco
- 2Geology, Environment, Mineral and Energy Resources, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Nouakchott, Nouakchott, Mauritania
- 3National Center for Energy Sciences and Nuclear Techniques (CNESTEN), Rabat, Morocco
As a critical resource for both livelihoods and economic progress, groundwater is increasingly endangered by nitrate contamination stemming from intensive agriculture, landfill leachates, wastewater effluents, soil nitrogen leaching, sewage discharge, and other anthropogenic influences. Stable isotopes (δ15N–NO₃−, δ18O–NO₃−, δ11B) have emerged as powerful tools to distinguish pollution sources, including synthetic fertilizers, animal manure, domestic wastewater, and atmospheric deposition. In regions with intensive agriculture and urban sprawl, nitrate concentrations frequently exceed safe thresholds, underscoring the need for precise source identification to guide mitigation strategies. While traditional vulnerability mapping elucidates contamination pathways, it often fails to resolve specific sources. The integration of multi-isotope tracers (e.g., δ11B with δ15N–NO₃−, δ18O–NO₃−) alongside hydrochemical data has emerged as an effective approach to address this gap, particularly in complex hydrogeological settings. While previous reviews have addressed nitrate contamination and isotope applications, this study adds value through its updated scope (2015–2025), global comparison, emphasis on multi-isotope integration, and the presentation of a unified framework and best practices for source identification. The findings highlight actionable insights for groundwater protection and advocate for the widespread adoption of isotopic tools in sustainable water management worldwide.
Introduction
Groundwater is a vital resource, sustaining life by supplying drinking water and supporting irrigation systems (Subba Rao et al., 2020; Gugulothu et al., 2022). However, its quality is deteriorating globally, jeopardizing agricultural productivity and human health. Nearly half of the world’s population relies on groundwater for daily needs (Mukherjee and Singh, 2018; Adimalla and Qian, 2019), yet this critical resource is increasingly threatened by rapid agricultural expansion, industrial activities, and urbanization (Zhaoshi et al., 2021). The overuse of fertilizers and pesticides, along with untreated sewage and industrial effluents, has severely degraded both surface and subsurface water quality (Suthar et al., 2009). Moreover, dynamic groundwater–surface water exchanges influence the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of aquatic ecosystems (Valett and Sheibley, 2009). In this context, a thorough understanding of aquifer geochemistry becomes essential for diagnosing contamination processes and supporting effective groundwater management strategies (Wu et al., 2021; Eid et al., 2023).
In recent decades, groundwater extraction has surged in response to growing agricultural, industrial, and domestic demands, accompanied by rising contamination from organic, inorganic, and emerging pollutants (Sharma et al., 2022). Among these, nitrate (NO₃−) contamination has emerged as one of the most widespread and persistent challenges affecting groundwater quality. Key anthropogenic sources include atmospheric deposition, chemical fertilizers, animal manure, and untreated urban or industrial waste (Kelepertzis et al., 2023).
To address this growing concern, the concept of groundwater vulnerability—which assesses the susceptibility of aquifers to contamination—has become central to sustainable water resource management (Bera et al., 2021; Paul and Das, 2021). Various assessment techniques, such as DRASTIC, GOD (Arauzo, 2017), SINTACS (Meng et al., 2020), and GALDIT (Boufekane et al., 2022), integrate hydrogeological parameters to delineate areas at risk of contamination. While these models are effective in identifying zones of heightened vulnerability, they often fall short in accurately determining specific nitrate pollution sources, particularly in regions with complex land use and overlapping anthropogenic activities.
To address this limitation, stable isotope techniques have emerged as powerful tools. In particular, nitrogen (δ15N) and oxygen (δ18O) isotopes in nitrate can distinguish between pollution from fertilizers, wastewater, and manure (Kendall, 1998; Panno et al., 2001; Bu et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2022; Li et al., 2025). Boron isotopes (δ11B) further enhance source discrimination, especially in complex hydrogeological and land-use settings (Komor, 1997; Sankoh et al., 2021).
This review aims to provide a comprehensive synthesis of global applications of stable isotopes in identifying nitrate sources in groundwater. It is structured around six thematic components: (1) methodological approaches for data collection and the spatial distribution of studies; (2) patterns and severity of nitrate contamination at a global scale; (3) environmental and anthropogenic drivers influencing nitrate dynamics; (4) roles and developments of isotopic techniques in groundwater research; (5) specific applications of δ15N, δ18O, and δ11B in nitrate source discrimination; and (6) implications for groundwater protection and future directions for research and management.
Data collection and geographic distribution of studies
This review employed a systematic approach to collect and analyze global literature on groundwater nitrate contamination and isotopic tracing techniques. An extensive literature search was conducted using academic databases such as Scopus and Web of Science, supplemented by Google Scholar and ResearchGate. To ensure a focus on recent methodological advances, emerging isotope tracers, and updated hydrochemical applications, the review specifically targeted peer-reviewed publications from 2015 to 2025. This period reflects a decade marked by significant growth in multi-isotope integration, the use of δ11B, and the incorporation of isotopic tools into groundwater management frameworks. Keywords focused on core concepts such as “groundwater nitrate contamination,” “stable isotopes,” “pollution sources,” and isotopic markers (“δ15N–NO₃−,” “δ18O–NO₃−,” “δ11B”), along with related terms like “hydrochemical parameters” and “groundwater vulnerability.” The selection process prioritized articles indexed in Web of Science and Scopus, applying a two-stage screening: initial relevance based on isotope use in source identification, followed by methodological quality control to remove duplicates and redundant studies. Emphasis was placed on research integrating multi-isotope approaches with hydrochemical data for complex contamination scenarios.
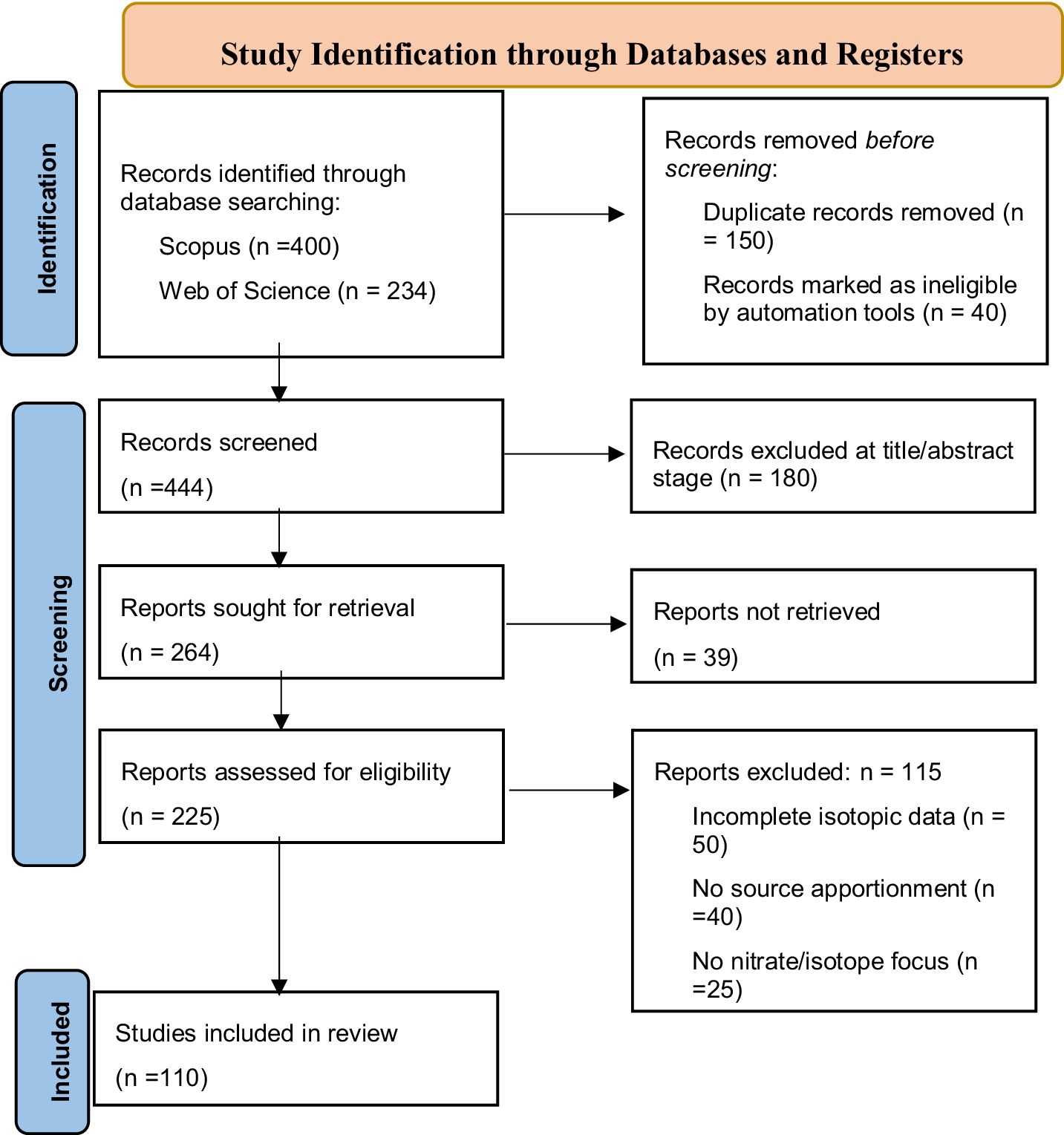
The systematic review followed the PRISMA 2020 guidelines (Page et al., 2021), with the study selection process summarized in Figure 1. A total of 634 records were identified through database searches (Scopus = 400, Web of Science = 234). After the removal of 150 duplicate records and 40 flagged by automation tools, 444 articles remained for screening. Of these, 180 were excluded during the title and abstract review. The remaining 264 reports were sought in full text, of which 225 were successfully retrieved and assessed for eligibility. At this stage, 115 reports were excluded due to incomplete isotopic data (n = 50), lack of source apportionment analysis (n = 40), or absence of a nitrate/isotope focus (n = 25). The final 110 studies met all inclusion criteria and were incorporated into the synthesis.
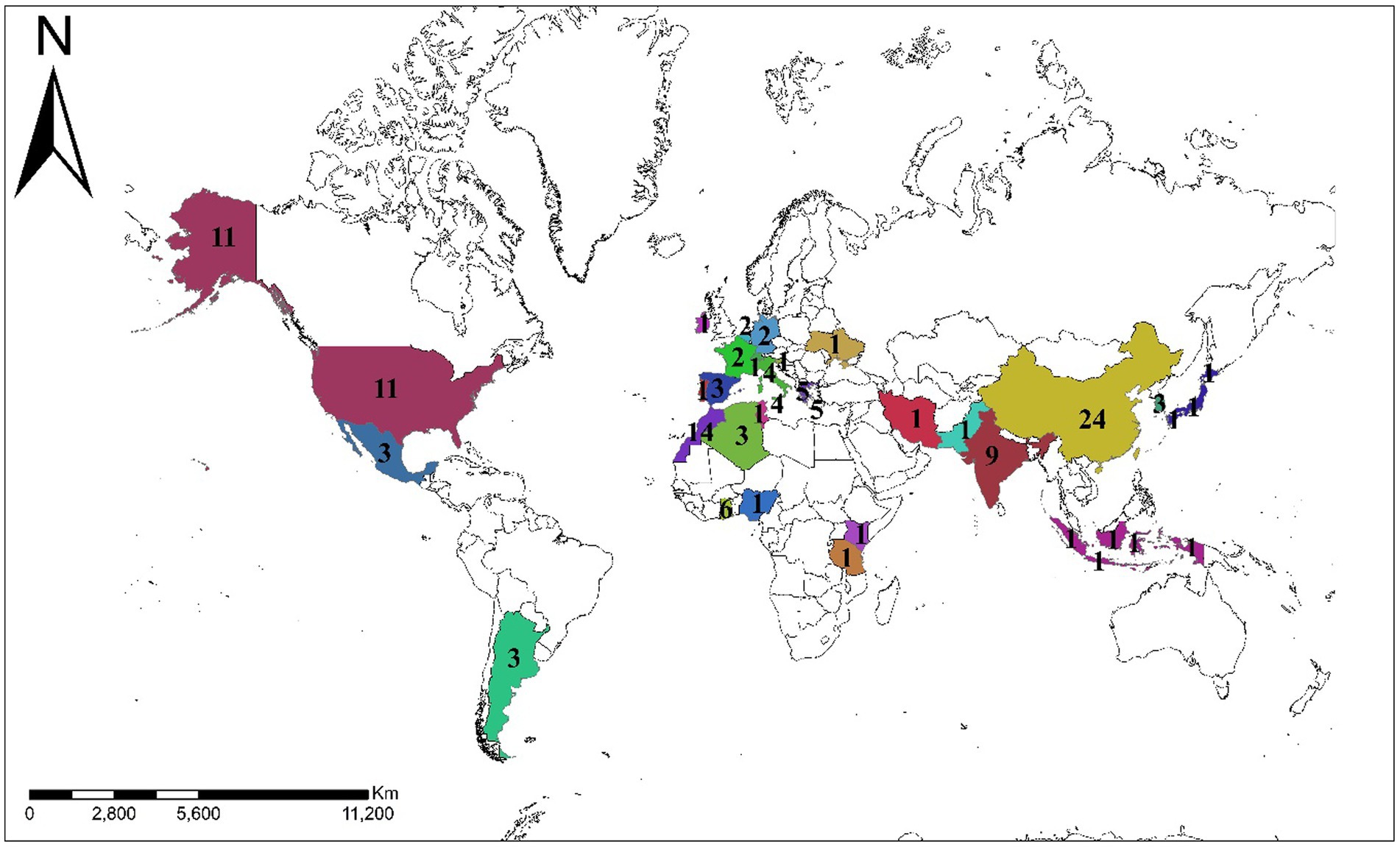
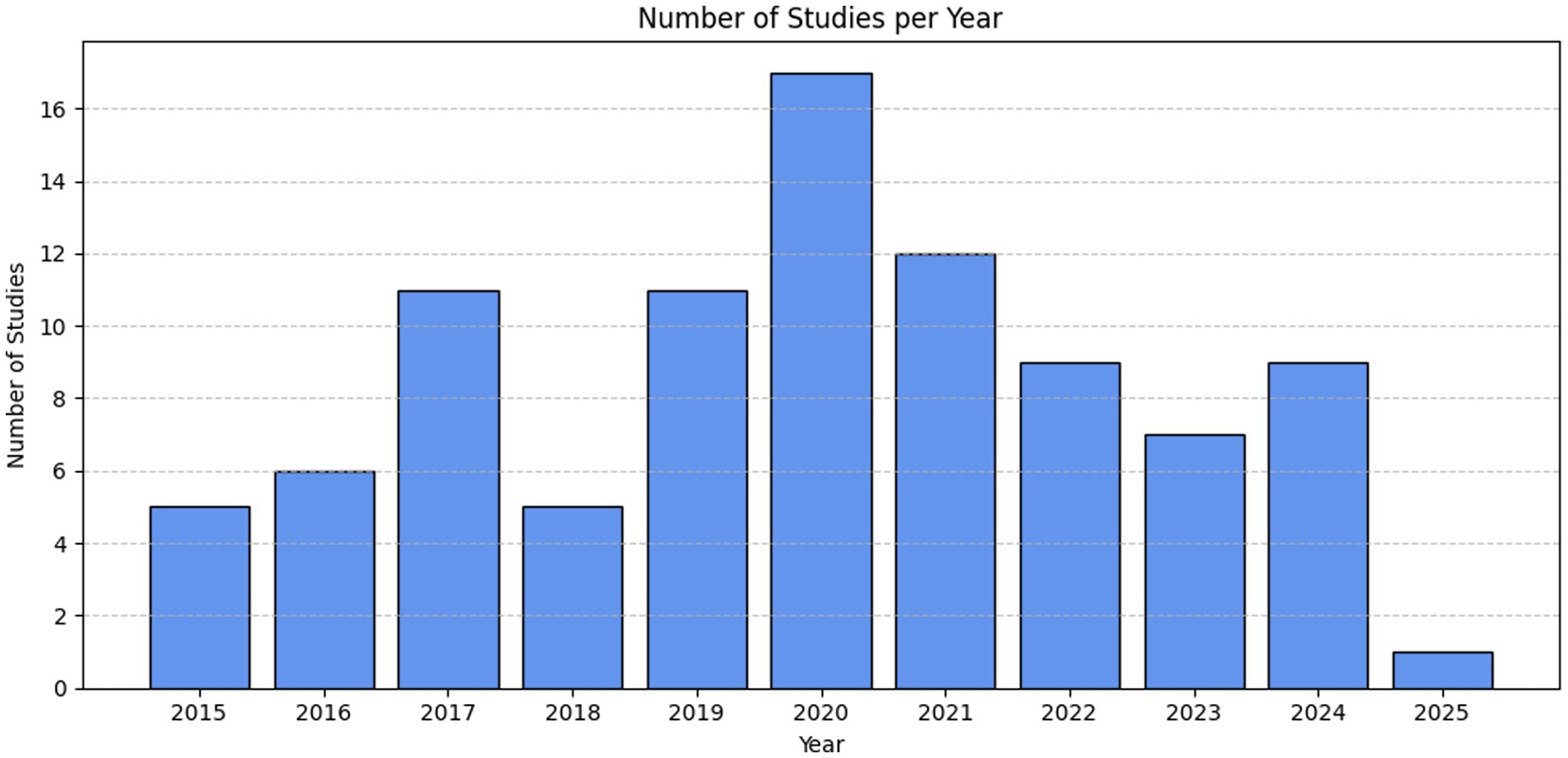
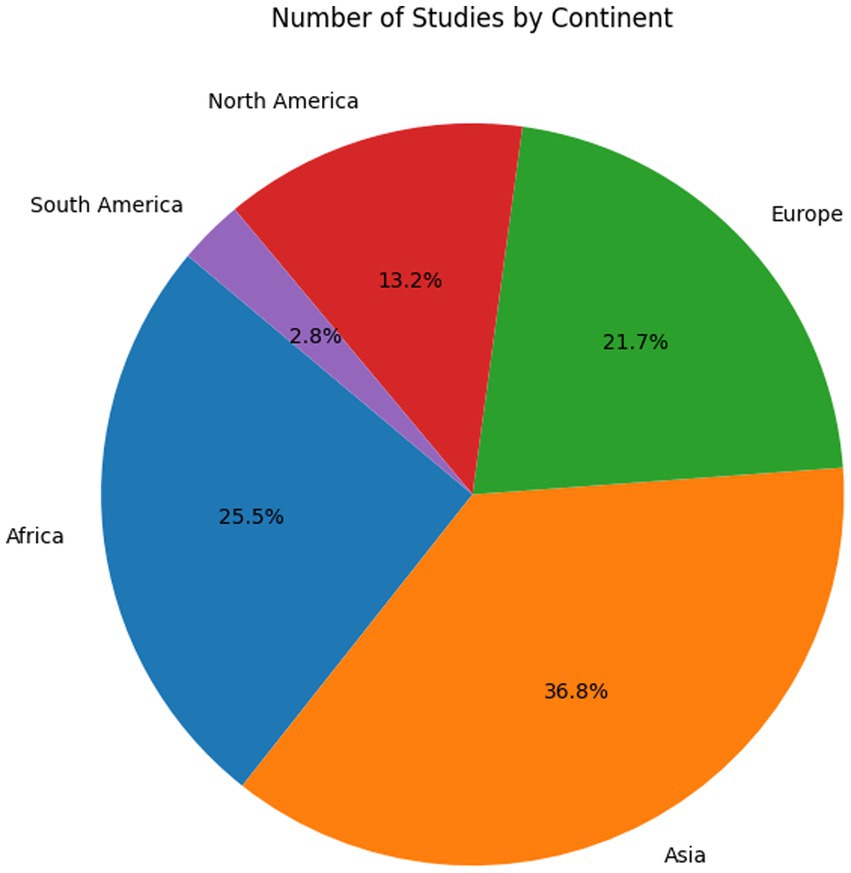
The systematic review reveals a varied global distribution of studies (Figure 2) focusing on nitrate isotopes in groundwater. China leads with the highest number of relevant studies (n = 24), followed by the United States (n = 11) and India (n = 9), reflecting strong research engagement in these regions. Other countries with moderate representation include Ghana (n = 7), Greece (n = 5), Italy (n = 4), and Israel (n = 2), as well as several countries with three studies each, such as Algeria, Argentina, South Korea, and Mexico. European countries like France, Germany, Belgium, and Spain contributed one to two studies each. Notably, Morocco appears with 14 studies, which, while not employing stable isotope techniques, were included to illustrate the widespread and persistent nitrate pollution in the region. Their inclusion serves to emphasize the lack of isotopic applications in Moroccan groundwater research and highlights a significant regional research gap. Some countries, such as Indonesia, Kenya, Nigeria, and Pakistan, are represented by only one study. This underscores both the global relevance of nitrate-related issues and the uneven distribution of isotopic research across regions. The temporal and geographical distributions of studies are shown in Figure 3 (by year) and Figure 4 (by continent), respectively.
Global assessment of nitrate contamination in groundwater systems
Groundwater constitutes the principal water source for drinking and agricultural purposes in arid and semi-arid regions, where surface water availability is severely limited (Zazouli et al., 2024). Over recent years, reliance on groundwater has increased significantly (Zhou et al., 2020; Subba Rao et al., 2020). However, groundwater contamination has emerged as a pressing environmental challenge with significant regional and global implications (Gao et al., 2020; He et al., 2020). This contamination is driven by various factors, including erratic rainfall, rapid urbanization, intensive irrigation, excessive fertilizer use, unregulated industrial activities, population growth, and both anthropogenic and geogenic pollution (Gao et al., 2020; Kumar et al., 2021; Subba Rao et al., 2020). Among the most concerning groundwater pollutants is nitrate (NO₃−), which has become a global issue due to its elevated concentrations. High levels of nitrate in groundwater pose serious risks to human health, particularly through drinking water exposure (Adimalla and Qian, 2021).
Agriculture is the primary source of nitrate pollution, with excessive nitrogen fertilizer use and animal waste contributing significantly. In addition, poorly designed septic systems also lead to nitrate leaching into the water Table. NO₃− pollution originates from both point sources—such as domestic sewage discharges, cesspools, and dairy lagoons—and non-point sources, including agricultural runoff from synthetic fertilizers and manure, soil nitrogen leaching, and atmospheric nitrogen deposition. These sources vary in spatial and temporal patterns, complicating efforts to trace and manage nitrate contamination in groundwater systems (Gao et al., 2020; He et al., 2020). In intensively farmed regions, groundwater nitrate (NO₃−) concentrations frequently reach alarming levels, with recorded values exceeding 250 mg/L (Hilal et al., 2024)—five times the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommended limit of 50 mg/L for drinking water. Studies in various agricultural zones have documented a steady increase in nitrate pollution over recent decades (Nouzha et al., 2016; Aziane et al., 2020; El Khodrani et al., 2020).
In areas with high agricultural activity, particularly those cultivating vegetables and industrial crops, nitrate concentrations in groundwater often exceed safe thresholds (Nouzha et al., 2016). These elevated levels are primarily attributed to livestock waste discharge, excessive chemical fertilizer use, and pesticide infiltration. River basins in agricultural regions frequently experience nitrate pollution due to farming practices, urban expansion, and industrial processes (Kanga et al., 2020).
Inefficient irrigation practices significantly worsen groundwater contamination, contributing to both water resource depletion and environmental degradation through nitrate leaching and eutrophication processes (El Khodrani et al., 2020). Research has shown that nitrate levels are often higher in wells near irrigated farmlands, where excess water application facilitates nitrate transport into the subsurface (Benkaddour et al., 2020).
Additionally, studies have detected agricultural chemicals in a significant proportion of monitored wells, with insecticides and nitrogen-based fertilizers being major contributors (El Bouzaidi et al., 2023). These findings underscore the urgent need for improved agricultural practices, stricter pollution controls, and sustainable groundwater management strategies worldwide.
Factors influencing nitrate contamination in groundwater
Nitrate contamination in groundwater is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, making the relationship between surface nitrogen sources and subsurface nitrate levels highly intricate (Malki et al., 2017). A significant portion of nitrogen from fertilizers can leach into groundwater due to irrigation or precipitation (Van Meter et al., 2016). Excessive fertilizer application increases soil nitrate levels and organic matter, which stimulates microbial processes such as nitrification and denitrification. These biological activities alter the soil’s capacity to retain pesticides by affecting microbial degradation rates and chemical interactions (Oumara and El Youssfi, 2022). When nitrogen inputs surpass crop uptake, soluble nitrate compounds infiltrate groundwater, leading to contamination (El Khodrani et al., 2020).
Studies have shown that reducing fertilizer application does not immediately lower groundwater nitrate levels due to legacy nitrogen in the subsurface (Wang et al., 2015). Key determinants of nitrate contamination include climate conditions, such as rainfall patterns, temperature, and seasonal variability that influence nitrate leaching and microbial processes, as well as fertilizer type, manure management practices, and soil properties (El Khodrani et al., 2020). Aquifer depth also plays a critical role, with shallow aquifers being more vulnerable to nitrate leaching due to their proximity to surface processes, while deeper aquifers often exhibit delayed or reduced contamination (Aziane et al., 2020).
Additional factors influencing nitrate transport include soil texture, permeability, rainfall intensity, recharge rates, water table depth, evapotranspiration, and irrigation efficiency (Barakat et al., 2020). Regions with high precipitation require careful groundwater management to minimize nitrate leaching and associated risks, as increased rainfall can both dilute nitrate concentrations in groundwater and enhance nitrate transport through soil, potentially spreading contamination over a larger area (Wang et al., 2015).
Research in agricultural areas has documented widespread nitrate exceedances of the World Health Organization’s recommended limits, particularly in regions with sandy soils and shallow water tables (Marouane et al., 2015). Seasonal variations further affect nitrate dynamics, with spring rainfall promoting pollutant transport to deeper layers and summer conditions accelerating nitrification, leading to seasonal nitrate peaks (Aziane et al., 2020).
Heavy rainfall events often lead to a rapid increase in nitrate concentrations in groundwater due to accelerated infiltration of nitrate-rich surface water and soil solutions into the aquifer (Wang et al., 2015). This initial spike is typically followed by a gradual decline as hydrological conditions stabilize and dilution occurs. Several interrelated factors influence these dynamics, including soil texture and permeability, which control water movement; land use and fertilizer application timing; and microbial processes such as nitrification and denitrification that modify nitrate concentrations within the subsurface. Additionally, climate variables like precipitation intensity, frequency, and seasonal distribution play a critical role in modulating nitrate transport and transformation. Understanding these complex interactions is essential for developing adaptive land-use practices and targeted mitigation strategies, such as controlled fertilizer application schedules, buffer zones, and improved manure management, to effectively reduce nitrate pollution in vulnerable aquifers and optimize groundwater resource management.
Overview of isotope applications in groundwater research
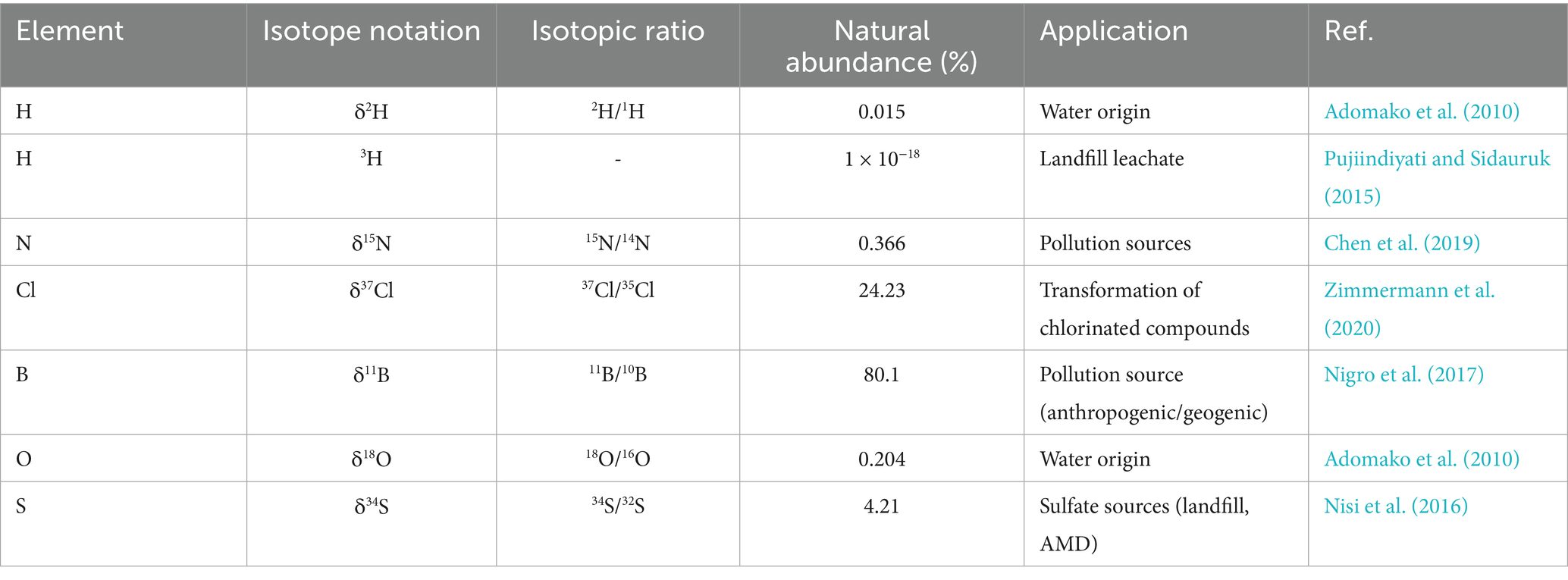
Nisi et al. (2016) emphasize that effective groundwater quality management depends on accurately identifying pollution sources. In many countries, traditional groundwater assessments have predominantly used hydrochemical analysis, geophysical techniques, and evaluation indices to measure pollutant levels in water samples and leachates. Although these approaches offer important data on contamination extent and aquifer vulnerability, they frequently fall short in pinpointing specific pollution origins. The advent and application of isotope techniques have revolutionized groundwater studies by enabling researchers to trace pollution sources and gain a clearer understanding of the origin of surface and groundwater recharge (Jia et al., 2020). Stable isotopes have broad applications in hydrological investigations. From their use, we gain crucial insights into aquifer–aquifer interconnections, groundwater age, and sources of contamination, among other important aspects (Oteng Mensah et al., 2014; Yidana et al., 2015). These techniques, some of which operate on the principle of tracer analysis, track the transport and transformation of key contaminants, such as nitrates, chlorinated compounds, and other anthropogenic pollutants, within aquatic systems. Isotopic composition is quantified using delta (δ) notation, representing the ratio of isotope abundances relative to a standard reference (Xu et al., 2016; Sankoh et al., 2021), as shown in Equation (1).
where: RSample are the heavy (rare) to light (abundant) isotope ratios of the sample; RStandard are the heavy (rare) to light (abundant) ratios of the standard. Oxygen (O), hydrogen (H), carbon (C), sulfur (S), and nitrogen (N) are among the most widely used isotopes in environmental studies (Sankoh et al., 2021). For over eight decades, environmental isotopes (Table 1) have been extensively applied in water bodies and other materials to enhance our understanding of hydrogeological and environmental processes.
Tracing nitrate pollution sources using dual isotopes (δ15N, δ18O) and δ11B
Groundwater contamination arises from both natural sources, such as soil nitrogen and atmospheric deposition, and anthropogenic sources, including synthetic fertilizers, manure, sewage, industrial waste, excessive fertilizer leaching, uncontrolled landfill disposal, sewage infiltration, and seawater intrusion. Except for seawater intrusion, which primarily introduces saline water rather than nitrate contaminants, these sources contribute nitrates with distinct isotopic signatures. This variability in isotopic fingerprints makes stable isotope analysis a powerful tool for identifying the origins and pathways of nitrate pollution in groundwater (Sankoh et al., 2021). Nitrogen, a key tracer for nitrate sources, has two stable isotopes: δ14N (99.63% abundance) and δ15N (0.37% abundance). Since different nitrate (NO₃−) sources exhibit unique isotopic signatures, δ15N and δ18O analysis helps pinpoint contamination pathways (Sankoh et al., 2021).
When tracing nitrate sources in freshwater, understanding the processes affecting δ15N and δ18O is critical. Major nitrate contributors include agricultural runoff and industrial discharges, with microbial processes, such as ammonia volatilization, denitrification, and nitrification that play a pivotal role in nitrogen cycling (Figure 5). Notably, ammonia volatilization and denitrification can significantly enrich δ15N in residual groundwater nitrate (Sankoh et al., 2021).
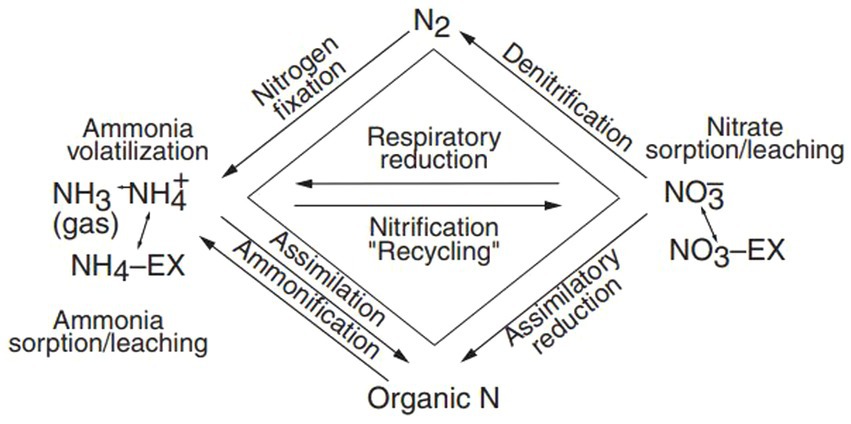
Figure 5. Biochemical cycles of nitrogen (Sankoh et al., 2021).
Application of δ15N and δ18O isotopic signatures for tracing nitrate contamination sources
The use of nitrogen isotopes, specifically δ15N, has been explored in several recent studies (Bu et al., 2017; Peters et al., 2019; Ren et al., 2014) to trace the sources of nitrate (NO₃−) pollution. Despite its effectiveness in distinguishing between various nitrate sources, the δ15N method faces challenges. Specifically, it struggles to differentiate between atmospheric nitrate, soil nitrate, inorganic fertilizers, manure, and landfill waste, as the multiple nitrogen transformations involved cause overlapping δ15N values. To address this uncertainty, researchers have turned to the use of oxygen isotopes (δ18O–NO₃−), which can complement δ15N data. However, the application of δ18O–NO₃− also presents difficulties, as its values tend to overlap for sources such as ammonium fertilizers, soil nitrogen, and manure, complicating the identification of nitrate sources (Minet et al., 2012). In response to these challenges, the combination of δ18O and δ15N, forming a dual isotope approach, has been applied by (Lasagna et Luca; 2019) to improve the accuracy of identifying nitrate sources. This dual isotope technique has become a widely adopted method to trace and characterize nitrate pollution in different environments by analyzing the distinct δ18O–NO₃− and δ15N − NO₃− signatures (Jiang et al., 2016; Puig et al., 2017; Wen et al., 2018; Fernandes et al., 2019; Nyilitya et al., 2020; Weitzman et al., 2021; Ju et al., 2023).
Isotopic fingerprints of δ15N and δ18O in nitrate from manure and septic waste
Septic tanks, landfills, animal manure, sewage, and sludge are significant contributors of nitrate pollution in aquatic systems. These waste sources typically contain organic nitrogen compounds, such as urea and organic nitrate, which undergo microbial transformations, primarily ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification leading to enriched δ15N–NO₃− and δ18O–NO₃− isotopic signatures.
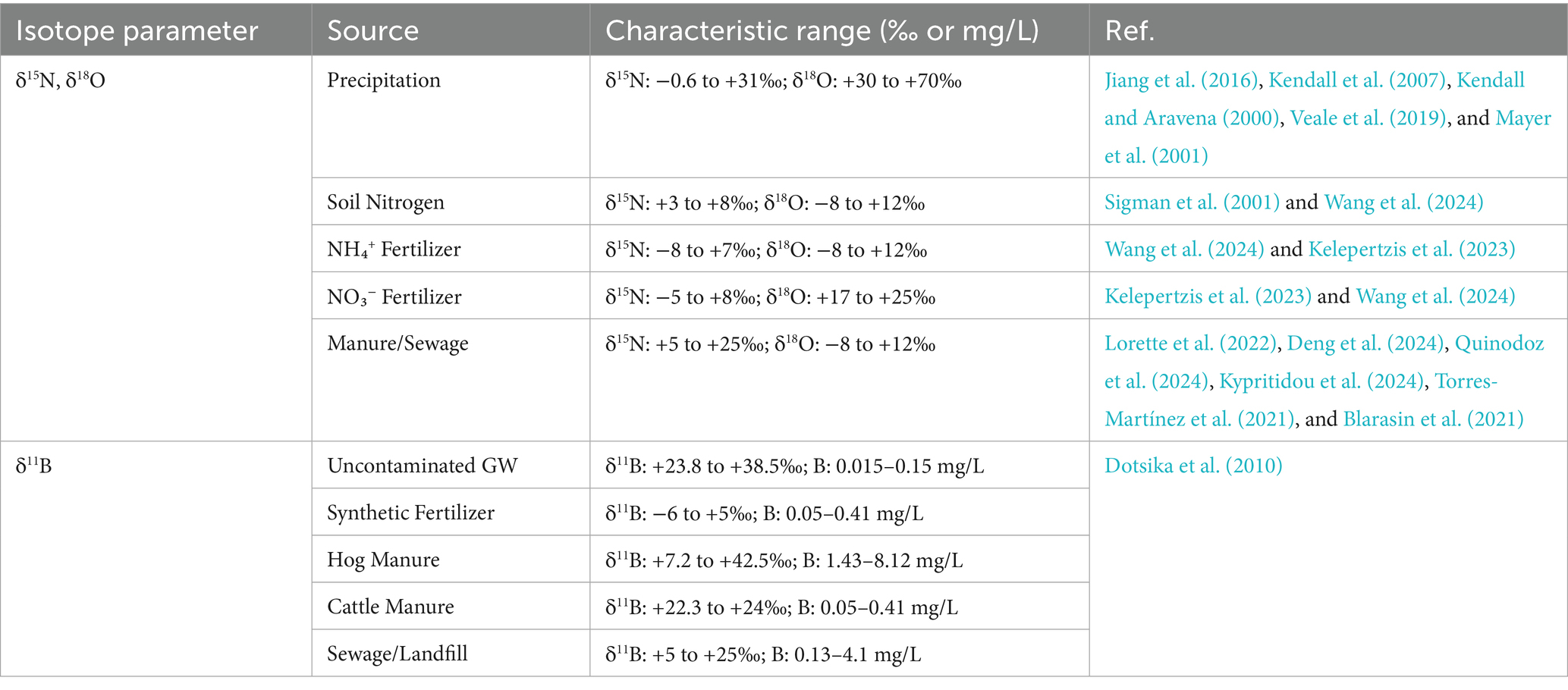
Between 2015 and 2025, a wide range of studies conducted across Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas utilized stable isotope techniques to trace nitrate contamination sources. In groundwater systems, δ15N values from 0 to +9‰ and δ18O values from +2.5 to +7.5‰ were linked to inputs from fertilizers, soil organic matter, excreta, and wastewater (Deng et al., 2024). Seasonal variations were also observed in river systems, with higher δ18O values in summer and lower δ15N in winter, reflecting shifts in nitrate sources throughout the year (Wang et al., 2024).
In the Liao River Basin, isotopic signatures (δ15N–NO₃−: +7.7‰ to +14.6‰; δ18O–NO₃−: +0.6‰ to +11.2‰) were attributed to domestic, industrial, and agricultural effluents (Zhang et al., 2024). Downstream increases in δ15N–NO₃−, averaging +13.1 ± 2.2‰, in industrialized areas of Greece also indicated intensified organic pollution (Kypritidou et al., 2024). Wastewater samples tended to display lower and more variable isotope values, as seen in δ15N–NO₃− values of +4.7‰ to +12.6‰ and δ18O–NO₃− of +1.7‰ to +5.7‰, consistent with mixed inputs from soils and manure (Quinodoz et al., 2024). In Tunisia, δ15N and δ18O ranged from +0.9‰ to +23.8‰ and +5.3‰ to +21.5‰ respectively, again pointing to wastewater and manure as dominant sources (Boumaiza et al., 2022). High δ15N and δ18O values in aquifers adjacent to streams in South Korea (up to +28.0‰ and +23.0‰, respectively) suggested strong inputs from animal waste and sewage (Ju et al., 2023). Similarly, seasonal changes in isotopic values (δ15N: +1.05‰ to +15.47‰; δ18O: −7.92‰ to +22.94‰) were consistent with variable contributions from manure, sewage, and fertilizers (Wang et al., 2023). Evidence of mixed anthropogenic sources is further supported by isotope ranges of δ15N: +2.0‰ to +14.5‰ and δ18O: +0.3‰ to +11.0‰ (Kelepertzis et al., 2023). Sewage sludge, in particular, has shown highly enriched isotopic values, with δ15N reaching +33.8‰ and δ18O up to +57.5‰ due to processes like nitrification and partial denitrification (Lorette et al., 2022).
In Mexico, nitrate in groundwater showed δ15N–NO₃− values between +8.86‰ and +39.67‰, and δ18O–NO₃− values up to +14.89‰, indicating a strong influence from domestic wastewater and manure (Torres-Martínez et al., 2021). Comparable findings were noted in Argentina, where δ15N values above +12.8‰ were attributed to septic tank seepage (Blarasin et al., 2021). In Ghana, Lartsey et al. (2024) investigated nitrate contamination sources in groundwater and surface water of the north-western Volta River Basin using hydrochemical and multi-isotopic approaches, showing that the dominant sources of nitrate are manure and sewage, with a smaller contribution from soil nitrogen. Isotopic analysis (δ15N and δ18O of NO₃−) and mixing models revealed that manure accounts for an average of 74% of nitrate in groundwater, while soil nitrogen contributes about 10%. Recharge primarily originates from rainfall, with some influence from the Black Volta River, and biological processes such as nitrification and denitrification affect nitrate concentrations. Although about 80% of samples were classified as pollution-free based on the Nitrate Pollution Index, anthropogenic inputs were evident near discharge zones, highlighting the significant role of agricultural and domestic waste in groundwater nitrate contamination in the region. Similarly, groundwater in northern Ghana displayed δ15N values of +5.8‰ to +7.0‰ and δ18O values near +17‰, indicative of contamination from domestic and animal waste (Gibrilla et al., 2020), while seasonal variations in Greece also revealed δ15N values between +4.6‰ and +17.7‰, again pointing to inputs from soil and organic waste (Kazakis et al., 2020).
In Kenyan urban centers, δ15N values soared to +51.8‰ during the dry season, clearly implicating sewage and manure (Nyilitya et al., 2020). Multi-source river systems displayed extremely variable nitrate isotope signatures, with δ15N from −23.5‰ to +32.0‰ and δ18O from −12.7‰ to +39.2‰, depending on pollution sources and hydrological conditions (Peters et al., 2019). Urban groundwater studies in Eastern Europe revealed δ15N values between +12.6‰ and +18.0‰, and δ18O from −0.1‰ to +8.7‰, both consistent with anthropogenic waste inputs (Vystavna et al., 2017). In the White Volta River in Ghana, δ15N values up to +22.1‰ were also linked to sewage and animal waste (Anornu et al., 2017). Similarly, values up to +32.5‰ for δ15N–NO₃− and +18.1‰ for δ18O were recorded in Spanish waters, pointing to manure and wastewater under denitrifying conditions (Puig et al., 2017).
In northern China, groundwater showed isotope values ranging from −0.6‰ to +31‰ for δ15N–NO₃− and from +16.3‰ to +37.4‰ for δ18O–NO₃−, suggesting diverse sources including manure and volatilized ammonia (Jiang et al., 2016). Foundational data by Li et al. (2007) established that δ15N values from +10‰ to +25‰ are typical of animal manure and ammonia volatilization. The primary sources of nitrate pollution identified in these studies include animal manure, sewage, ammonia volatilization from urea, agricultural activities, farming, and denitrification processes influenced by precipitation.
In Israel, Shalev et al. (2015) report that nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Central Arava Valley is primarily linked to agricultural sources, with isotopic and chemical analyses indicating that all applied fertilizers (synthetic nitrate, synthetic ammonium, and manure) contribute to contamination, generally in proportion to their use in local fertilization schemes, alongside occasional inputs from leaking sewage reservoirs. Similarly, in the Gaza Strip, Shomar et al. (2008) found that groundwater is mainly impacted by manure and, to a lesser extent, by septic effluents and sludge, while synthetic fertilizers play only a minor role. Isotopic signatures (δ15N and δ18O) confirm these patterns: manure and sludge exhibit enriched δ15N values (+4.6 to +11.9‰), whereas synthetic fertilizers are near 0‰, corresponding to the ranges observed in groundwater (+3.2 to +12.8‰). No significant denitrification was detected in Gaza, and in both regions, irrigation practices and recharge dynamics strongly influence nitrate leaching. These findings underscore the utility of isotope-based approaches for distinguishing contamination sources and guiding sustainable groundwater management.
Isotopic fingerprints of δ15N and δ18O in ammonia from fertilizers and precipitation
The intensive and often poorly regulated use of nitrogen-based fertilizers in agriculture has significantly elevated nitrate (NO₃−) concentrations in groundwater systems. Synthetic fertilizers such as urea, potassium nitrate (KNO₃), and ammonium nitrate (NH₄NO₃), derived from industrial nitrogen fixation, typically exhibit δ15N values between −4‰ and +4‰, reflecting their atmospheric nitrogen origin. In the Erhai Basin, nitrate isotopic compositions revealed δ15N–NO₃− values ranging from −0.64‰ to +17.67‰ (mean: +6.89‰) and δ18O–NO₃− from −1.87‰ to +24.43‰ (mean: +7.88‰), with microbial nitrification dominating approximately 60% of samples particularly in oxygen-rich upstream and littoral zones while denitrification was identified in only 13.56% of cases (She et al., 2024).
Seasonal isotopic shifts further illustrate the dynamic nature of nitrate inputs. During the dry season, δ18O–NO₃− values ranged from −5‰ to +16.85‰ (mean: +2.68‰), and δ15N–NO₃− from −1.17‰ to +8.40‰ (mean: +2.28‰). Conversely, the wet season displayed δ18O–NO₃− values from −4.78‰ to +11.59‰ (mean: −0.52‰) and δ15N–NO₃− from −0.63‰ to +27.06‰ (mean: +1.83‰), suggesting additional inputs from organic fertilizers and domestic effluents (Su et al., 2024).
Isotopic compositions typical of synthetic fertilizers were also documented elsewhere. For example, δ15N and δ18O values of approximately +0.5‰ and +7‰, respectively, were reported in a wastewater-influenced context (Quinodoz et al., 2024). In agricultural areas, Kim et al. (2023) recorded broader δ15N–NO₃− values (+3.0‰ to +27.5‰) and δ18O–NO₃− values (−2.4‰ to +7.7‰), indicating a mixture of sources, including livestock waste, synthetic fertilizers, and soil-derived nitrogen. In riverine systems, dominant nitrification processes were inferred from δ15N–NO₃− values around +5‰ and δ18O–NO₃− around +4‰, with over 70% of δ18O–NO₃− values aligning with microbial nitrate production (Zhou et al., 2022).
Despite their typically low δ15N signatures (−8‰ to +7‰), synthetic nitrate fertilizers can exhibit enriched δ15N–NO₃− values following post-application transformations such as nitrification (Piatek et al., 2005). The δ18O of nitrate formed via nitrification reflects a combination of oxygen from atmospheric O₂ (≈ + 23.9‰) and water (≈ − 25‰ to +4‰), producing δ18O–NO₃− values that generally lie between −10‰ and +10‰ (Kendall, 1998; Kendall and Aravena, 2000; Mayer et al., 2001; Veale et al., 2019). This trend was evident in the observations by Weitzman et al. (2021), who reported δ18O–NO₃− values ranging from −3.2‰ to +17.4‰, and by Wen et al. (2018), who found δ18O–NO₃− between +0.07‰ and +1.77‰both consistent with agricultural inputs.
In regions of Nebraska, groundwater nitrate concentrations ranged from 6.5 to 53 mg/L, with δ15N–NO₃− values between −0.3‰ and +7.8‰, and δ18O–NO₃− values from −1.4‰ to +7.8‰, reflecting predominant inputs from ammonium nitrification and soil organic nitrogen (Spalding et al., 2019). Although synthetic nitrate fertilizers are characterized by higher δ18O–NO₃− values due to their exclusive reliance on atmospheric oxygen (typically +17‰ to +25‰), such values are rarely observed in field settings (Mayer et al., 2001; Veale et al., 2019). For example, δ18O–NO₃− values reported in boreholes, wells, and surface waters across Ghana ranged from +5.1‰ to +8.83‰ (Anornu et al., 2017), well below the levels typical of atmospheric nitrate deposition (≈ + 60‰ to +70‰) or synthetic fertilizers. Similarly, groundwater nitrate in Mexico showed δ18O–NO₃− values between +3.84‰ and +10.96‰ (Pastén-Zapata et al., 2014). These findings, supported by Kendall (1998) and Mayer et al. (2001), further underscore that nitrification can elevate δ18O–NO₃− values by up to 5‰ above theoretical estimates, reinforcing the role of microbial activity in shaping isotopic profiles.
Isotopic fingerprints of δ15N and δ18O in atmospheric deposition
Atmospheric nitrate originates from nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), which are primarily produced through fossil fuel combustion in power plants, vehicles, and industrial processes. These NOₓ compounds undergo various atmospheric transformations, including nitrification, denitrification, and ammonia volatilization, depending on whether nitrogen is present as ammonium (NH₄+) or nitrate (NO₃−), and on the nature of anthropogenic inputs in precipitation. As a result, atmospheric nitrate exhibits highly variable δ15N values, typically ranging from −0.6‰ to +31‰ (Jiang et al., 2016).
However, δ15N alone may not reliably distinguish atmospheric nitrate from other anthropogenic sources due to overlaps in isotopic signatures. In contrast, δ18O–NO₃− provides a more definitive tracer. Atmospheric deposition of nitrate is generally characterized by highly enriched δ18O values, typically ranging from +60‰ to +70‰ (Kendall et al., 2007). This contrasts with biologically derived nitrate in soils and water, which usually exhibits δ18O values between 0.8‰ and 5.8‰ (Chen et al., 2019) or between −15‰ and +15‰ (Shi et al., 2014).
For instance, Jiang et al. (2016) reported δ18O–NO₃− values exceeding +30‰ in atmospheric nitrate. Similarly, Ogrinc et al. (2019) recorded δ18O–NO₃− values as high as +34.6‰ in groundwater from the Sava River aquifer, implicating atmospheric deposition as the dominant nitrate source. These findings are consistent with observations in areas lacking significant land-based anthropogenic pollution. Moreover, Shi et al. (2014) noted that rainfall nitrate can initially present δ18O values between +65‰ and +70‰, but these values rapidly decline to 2–5‰ after biological processing in the soil.
The elevated δ18O values in atmospheric nitrate are attributed to photochemical reactions and incomplete fossil fuel combustion (Kendall et al., 2007). During these reactions, atmospheric molecular oxygen naturally enriched in δ18O is incorporated into nitrate molecules, leading to pronounced isotopic enrichment. As Ogrinc et al. (2019) explain, photochemical processes driven by sunlight enhance the δ18O content of atmospheric compounds, thereby producing nitrate with distinctive δ18O signatures.
Combining δ11B and δ15N isotopic analysis to identify groundwater contamination sources
The non-conservative behavior of nitrogen can interfere with isotopic fractionation, making it challenging to accurately identify the sources of NO₃− in groundwater (Widory et al., 2005). This challenge can be addressed by combining δ15N and δ11B isotopic analyses, as suggested by Bronders et al. (2012) and Saccon et al. (2013).
Boron exists in nature as two isotopes, 10B and 11B, which exhibit significant mass differences. This mass disparity leads to a broad natural variability in δ11B values, enabling the differentiation of various boron sources in groundwater.
In industrial applications, boron compounds such as boric acid and borate minerals are extensively used in manufacturing glass, porcelain, carpets, leather, photographic chemicals, cosmetics, fertilizers, and metals (Vengosh et al., 1998). Sodium perborate, commonly found in household cleaning products as a bleaching agent, also contributes to boron accumulation in wastewater. When these products are released into the environment, boron-containing effluents can infiltrate water resources (Vengosh et al., 1998).
Conventional wastewater treatment processes are ineffective at removing elemental boron, making δ11B a reliable and conservative tracer for identifying wastewater contamination (Saccon et al., 2013). Due to its stability, widespread use in agriculture and industry (Saccon et al., 2013), and natural occurrence in saline waters, δ11B is a valuable tool for pinpointing pollution sources. These sources include fertilizers, septic system effluents, wastewater discharges, animal manure, and seawater intrusion.
Boron isotope variations (δ11B) in natural and anthropogenic sources
Boron isotope ratios (δ11B) reliably trace both natural and anthropogenic water contamination sources, from seawater intrusion to agricultural impacts (Reed and Duranceau, 2016). Initial applications by Komor (1997) introduced δ11B as a co-tracer for nitrate pollution, complementing its prior use in hydrogeochemical assessments (Vengosh et al., 1998; Bassett, 1990).
Natural waters such as pristine groundwater are typically characterized by enriched δ11B values (~30‰) and low boron concentrations (0.01–0.13 mg/L) (Vengosh et al., 1998; Widory et al., 2005). Seawater shows even higher δ11B values (+33‰ to +60‰) with boron concentrations averaging 1.9 mg/L and reaching up to 5.04 mg/L (Vengosh et al., 1998; Tirez et al., 2010).
Animal manure exhibits source-specific δ11B signatures. Hog manure ranges from 7.2‰ to 42.4‰ with boron concentrations as high as 8.12 mg/L, while cattle manure shows δ11B values between 6.2‰ and 24‰ but with lower boron concentrations (0.05–0.41 mg/L) (Komor, 1997; Widory et al., 2005; Tirez et al., 2010). Interestingly, groundwater impacted by pig manure retains similar δ11B values to the manure itself, while cattle manure–impacted groundwater becomes more enriched (32.5–38.6‰), possibly due to isotopic fractionation (Komor, 1997).
Sewage and detergents contribute significantly to anthropogenic boron in water bodies, largely due to sodium borate (NaBO₃) used in cleaning products. Sewage effluents generally display δ11B values from −2.8‰ to +12.9‰ and boron concentrations ranging from 0.13 to 4.1 mg/L (Vengosh et al., 1998; Widory et al., 2005; Tirez et al., 2010). The overlap in δ11B values between sewage and natural borate minerals (e.g., sodium perborate) highlights the difficulty in distinguishing some anthropogenic inputs. Furthermore, municipal solid waste leachates show δ11B values of +3‰ to +10‰, similar to sewage sources (Nigro et al., 2017), suggesting overlapping contamination signatures.
Inorganic fertilizers display variable δ11B compositions. Komor (1997) reported δ11B values of ~0.7‰ for NH₄NO₃, ~0.4‰ for urea, and ~14.8‰ for phosphate fertilizers, with boron concentrations ranging from 0.46 to 13.3 mg/L. In contrast, Tirez et al. (2010) observed different δ11B values for urea (20.6‰) and NPK fertilizers (0.2–7.2‰), highlighting formulation-dependent variability.
Postigo et al. (2021) integrated δ11B with δ15N and δ18O isotopes to trace nitrate sources in the Llobregat Basin. Elevated δ15N–NO₃− values (up to +13.2‰) and δ11B signatures pointed to dominant inputs from wastewater and manure, while chemical fertilizers contributed to select samples.
Overall, δ11B values help differentiate between natural sources, pig and cattle manure, sewage, and fertilizers. However, overlaps—particularly between sewage and landfill leachates—limit δ11B’s discriminative power in some cases. In such contexts, additional tracers like tritium isotopes are recommended to confirm the origin of nitrate pollution.
δ11B as a tracer for pollution source identification
Research conducted across several European countries—including Spain, Portugal, and Italy—has shown that the integrated use of δ15N–NO₃−, δ18O–NO₃−, and δ11B isotopes provides an effective means of identifying nitrate pollution sources, such as organic and inorganic fertilizers, animal manure, and domestic and septic waste (Sankoh et al., 2021).
In Spain, Puig et al. (2017) investigated the Baix Ter Aquifer to trace the origins of nitrate contamination and the geochemical processes influencing its distribution. Their analysis revealed δ15N–NO₃− values ranging from +5.0 to +32‰ and δ18O–NO₃− values from +8.9 to +18.1‰, suggesting significant contributions from sewage, animal manure, and leachates from dumpsites. Similarly, Fernandes et al. (2019) reported elevated δ15N–NO₃− and δ18O–NO₃− values in Portugal, pointing to contamination primarily from animal waste and sewage.
Both studies also utilized δ11B isotopes to further refine the identification of pollution sources. For example, Puig et al. (2017) found δ11B values between +1.4 and +9.0‰ in two samples, indicating sewage input, while 10 samples showed values from +23.5 to +34.5‰, consistent with pig manure signatures. Likewise, Fernandes et al. (2019) observed δ11B values ranging from +28.5 to +44‰, supporting the identification of pig manure as a dominant source.
In Italy, Lasagna and De Luca (2019) conducted a study in the Turin-Cuneo plain using δ15N–NO₃− and δ18O–NO₃− isotopes to distinguish between synthetic and organic pollution sources. They also applied δ11B isotopic analysis to trace anthropogenic inputs, reporting values from +8.37 to +18.05‰. These isotopic signatures suggested sewage contamination at the lower end and potential overlap of cattle and pig manure at the higher end. When boron concentrations were considered (0.06–0.09 mg/L), the results aligned more closely with cattle manure, as earlier studies (Widory et al., 2005; Vengosh et al., 1998; Komor, 1997) indicated higher boron levels (1.43–8.12 mg/L) in pig manure and lower levels (0.05–0.41 mg/L) in cow manure.
Overall, the combined application of δ15N–NO₃−, δ18O–NO₃−, and δ11B isotopes proves to be a valuable and reliable tool for accurately tracing nitrate sources in complex hydrogeological settings.
Rapid guide to identifying pollution sources through isotope analysis
Tracing groundwater pollution sources using isotopic techniques is essential for effective water quality management. However, interpreting and applying these methods can be complex for researchers, policymakers, and environmental professionals. To facilitate this process, (Table 2) presents a structured overview of key isotopic parameters, their characteristics, and corresponding ranges. This multi-isotope approach, incorporating δ15N, δ18O, and δ11B, enhances pollution source identification by distinguishing between nitrate from precipitation, fertilizers, manure, and sewage contamination. By providing a clear reference, this guide supports informed decision-making and the implementation of targeted pollution mitigation strategies.
Conclusions and perspectives for future groundwater management
Groundwater nitrate contamination continues to pose a significant global challenge, exacerbated by agricultural intensification, urban expansion, and inadequate wastewater treatment practices. This review underscores the growing relevance of stable isotope techniques—particularly δ15N–NO₃−, δ18O–NO₃−, and δ11B—in accurately identifying the sources of nitrate pollution. While traditional methods such as vulnerability mapping and hydrochemical analyses provide valuable information on contamination pathways, they often fall short in resolving specific pollution origins, especially in complex hydrogeological settings.
The combined use of multi-isotope approaches and hydrochemical data has proven to be a powerful tool for nitrate source apportionment. The inclusion of δ11B enhances the reliability of isotopic analysis by addressing key limitations related to denitrification and the overlapping signatures of different nitrogen sources. This integrative approach allows for more accurate assessments of groundwater quality and supports the development of targeted mitigation strategies.
Looking toward the future, the adoption of advanced isotopic techniques should be prioritized in groundwater monitoring and management efforts worldwide. Expanding global and regional datasets, refining analytical methodologies, and fostering collaboration among scientists, water managers, and policymakers will be essential for advancing these tools from research to practical application. Incorporating isotope-based methods into water governance frameworks can significantly improve the precision and effectiveness of pollution control measures, especially in areas facing high nitrate loads.
Ultimately, stable isotope techniques offer a promising pathway toward more informed, science-based groundwater management. Their broader implementation will be crucial to protecting water resources, preserving public health, and ensuring long-term groundwater sustainability in an increasingly vulnerable global environment.
Author contributions
AO: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IH: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AK: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MS: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The publication fees for this article were covered by Ibn Tofail University, Kenitra, Morocco.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI (ChatGPT, OpenAI) was used to assist in editing and improving the English language of the manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adimalla, N. , and Qian, H. (2019). Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 176, 153–161. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.066
Adimalla, N. , and Qian, H. (2021). Geospatial distribution and potential noncarcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate contaminated groundwater in southern India: a case study. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 80, 107–119. doi: 10.1007/s00244-020-00762-7
Adomako, D. , Maloszewski, P. , Stumpp, C. , Osae, S. , and Akiti, T. T. (2010). Estimating groundwater recharge from water isotope (δ2H, δ18O) depth profiles in the Densu River basin, Ghana. Hydrol. Sci. J. 55, 1405–1416. doi: 10.1080/02626667.2010.527847
Anornu, G. , Gibrilla, A. , and Adomako, D. (2017). Tracking nitrate sources in groundwater and associated health risk for rural communities in the white Volta River basin of Ghana using isotopic approach (δ15N, δ18ONO3 and 3H). Sci. Total Environ. 603, 687–698. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.219
Arauzo, M. (2017). Vulnerability of groundwater resources to nitrate pollution: a simple and effective procedure for delimiting nitrate vulnerable zones. Sci. Total Environ. 575, 799–812. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.139
Aziane, N. , Larif, M. , Khaddari, A. , and Khaddari, A. (2020). State of nitric pollution of the Mnasra aquifer, coastal zone of the Gharb plain (Morocco). Moroccan J. Chem. 8, 965–981.
Barakat, A. , Mouhtarim, G. , Saji, R. , and Touhami, F. (2020). Health risk assessment of nitrates in the groundwater of Beni Amir irrigated perimeter, Tadla plain, Morocco. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 26, 1864–1878. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2019.1613631
Bassett, R. L. (1990). A critical evaluation of the available measurements for the stable isotopes of boron. Appl. Geochem. 5, 541–554. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(90)90054-9
Benkaddour, R. , Merimi, I. , Szumiata, T. , and Hammouti, B. (2020). Nitrates in the groundwater of the Triffa plain eastern Morocco. Mater Today Proc 27, 3171–3174. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.120
Bera, A. , Mukhopadhyay, B. P. , Chowdhury, P. , Ghosh, A. , and Biswas, S. (2021). Groundwater vulnerability assessment using GIS-based DRASTIC model in Nangasai River basin, India with special emphasis on agricultural contamination. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 214:112085. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112085
Blarasin, M. , Matiatos, I. , Cabrera, A. , Lutri, V. , Giacobone, D. , Quinodoz, F. B., et al. (2021). Characterization of groundwater dynamics and contamination in an unconfined aquifer using isotope techniques to evaluate domestic supply in an urban area. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 110:103360. doi: 10.1016/j.jsames.2021.103360
Boufekane, A. , Maizi, D. , Madene, E. , Busico, G. , and Zghibi, A. (2022). Hybridization of GALDIT method to assess actual and future coastal vulnerability to seawater intrusion. J. Environ. Manag. 318:115580. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115580
Boumaiza, L. , Walter, J. , Chesnaux, R. , Zahi, F. , Huneau, F. , Garel, É., et al. (2022). Combined effects of seawater intrusion and nitrate contamination on groundwater in coastal agricultural areas: a case from the plain of the El-Nil River (north-eastern Algeria). Sci. Total Environ. 851:158153. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158153
Bronders, J. , Tirez, K. , Desmet, N. , Widory, D. , Petelet-Giraud, E. , Bregnot, A., et al. (2012). Use of compound-specific nitrogen (d15N), oxygen (d18O), and bulk boron (d11B) isotope ratios to identify sources of nitrate-contaminated waters: a guideline to identify polluters. Environ. Forensic 13, 32–38. doi: 10.1080/15275922.2011.643338
Bu, H. , Song, X. , Zhang, Y. , and Meng, W. (2017). Sources and fate of nitrate in the Haicheng River basin in Northeast China using stable isotopes of nitrate. Ecol. Eng. 98, 105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.052
Chen, F. , Zhou, X. , Lao, Q. , Wang, S. , Jin, G. , Chen, C., et al. (2019). Dual isotopic evidence for nitrate sources and active biological transformation in the northern South China Sea in summer. PLoS One 14:e0209287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209287
Deng, Y. , Ye, X. , Feng, J. , Guo, H. , and Du, X. (2024). Assessment of soil-groundwater nitrogen cycling processes in the agricultural region through flux model, stable isotope. J. Hydrol. 639:131604. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2024.131604
Dotsika, E. , Poutoukis, D. , Kloppmann, W. , Guerrot, C. , Voutsa, D. , and Kouimtzis, T. H. (2010). The use of O, H, B, Sr and S isotopes for tracing the origin of dissolved boron in groundwater in Central Macedonia, Greece. Appl. Geochem. 25, 1783–1796. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.09.006
Eid, M. H. , Elbagory, M. , Tamma, A. A. , Gad, M. , Elsayed, S. , Hussein, H., et al. (2023). Evaluation of groundwater quality for irrigation in deep aquifers using multiple graphical and indexing approaches supported with machine learning models and GIS techniques, Souf Valley, Algeria. Water 15:182. doi: 10.3390/w15010182
El Khodrani, N. , Omrania, S. , Nouayti, A. , Zouahri, A. , Douaik, A. , Iaaich, H., et al. (2020). Comparative study of groundwater pollution of M’nasra and Sfafaa zones (Gharb, Morocco) by nitrates. In E3S web of conferences, No. 150. EDP Sciences, p. 01006.
El Bouzaidi, H. , Hafiane, F. Z. , Loukili, M. , Kotrasova, K. , EI Azzouzi, E. H. , Purcz, P., et al. (2023). Inssecticides in the typical agricultural groundwater in the Gharb plain (Morocco): Spatial distribution and health risks. Acta Montanistica Slovaca, 27, 1040–1050.
Fernandes, P. , Carvalho, M. R. , Silva, M. C. , Rebelo, A. , and Zeferino, J. (2019). Application of nitrogen and boron isotopes for tracing sources of anthropogenic contamination in Monforte-Alter do Chão aquifer system, Portugal. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 5, 249–266. doi: 10.1007/s40899-018-0265-1
Gao, Y. , Qian, H. , Ren, W. , Wang, H. , Liu, F. , and Yang, F. (2020). Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J. Clean. Prod. 260:121006. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121006
Gibrilla, A. , Fianko, J. R. , Ganyaglo, S. , Adomako, D. , Anornu, G. , and Zakaria, N. (2020). Nitrate contamination and source apportionment in surface and groundwater in Ghana using dual isotopes (15N and 18O-NO3) and a Bayesian isotope mixing model. J. Contam. Hydrol. 233:103658. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103658
Gugulothu, S. , Subbarao, N. , Das, R. , and Dhakate, R. (2022). Geochemical evaluation of groundwater and suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation purpose in an agricultural region of South India. Appl Water Sci 12:142. doi: 10.1007/s13201-022-01583-w
He, X. , Li, P. , Ji, Y. , Wang, Y. , Su, Z. , and Elumalai, V. (2020). Groundwater arsenic and fluoride and associated arsenicosis and fluorosis in China: occurrence, distribution and management. Expo. Health 12, 355–368. doi: 10.1007/s12403-020-00347-8
Hilal, I. , Oubeid, A. M. , Qurtobi, M. , Aqnouy, M. , Amenzou, N. , Saadi, R., et al. (2024). Groundwater vulnerability mapping using the susceptibility index (SI) method and tritium isotopes: a case study of the Gharb aquifer in northwestern Morocco. In E3S web of conferences, No. 489. EDP Sciences, p. 07001.
Jia, H. , Howard, K. , and Qian, H. (2020). Use of multiple isotopic and chemical tracers to identify sources of nitrate in shallow groundwaters along the northern slope of the Qinling Mountains, China. Appl. Geochem. 113:104512. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104512
Jiang, W. , Wang, G. , Sheng, Y. , Zhao, D. , Liu, C. , and Guo, Y. (2016). Enrichment and sources of nitrogen in groundwater in the Turpan-Hami area, northwestern China. Expo. Health 8, 389–400. doi: 10.1007/s12403-016-0209-7
Ju, Y. , Koh, D. C. , Kim, D. H. , Mayer, B. , and Kwon, H. I. (2023). Evaluating the sources and fate of nitrate in riparian aquifers under agricultural land using in situ-measured noble gases, stable isotopes, and metabolic genes. Water Res. 231:119601. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119601
Kanga, I. S. , Naimi, M. , and Chikhaoui, M. (2020). Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index and geographic information system based in Sebou River Basin in the North-West region of Morocco. International Journal of Energy and Water Resources, 4, 347–355.
Kazakis, N. , Matiatos, I. , Ntona, M. M. , Bannenberg, M. , Kalaitzidou, K. , Kaprara, E., et al. (2020). Origin, implications and management strategies for nitrate pollution in surface and ground waters of Anthemountas basin based on a δ15N-NO3− and δ18O-NO3− isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 724:138211. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138211
Kelepertzis, E. , Matiatos, I. , Botsou, F. , Antonopoulou, C. , Lappas, I. , Dotsika, E., et al. (2023). Assessment of natural and anthropogenic contamination sources in a Mediterranean aquifer by combining hydrochemical and stable isotope techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 858:159763. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159763
Kendall, C. (1998). “Tracing nitrogen sources and cycling in catchments” in Isotope tracers in catchment hydrology. eds. C. Kendall and J. J. McDonnell (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 519–576.
Kendall, C. , and Aravena, R. (2000). “Nitrate isotopes in groundwater systems” in Environmental tracers in subsurface hydrology. eds. P. G. Cook and A. L. Herczeg (Boston, MA: Springer US), 261–297.
Kendall, C. , Elliott, E. M. , and Wankel, S. D. (2007). “Tracing anthropogenic inputs of nitrogen to ecosystems” in Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. eds. K. Lajtha and R. Michener (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley), 375–449.
Kim, M. S. , Lim, B. R. , Jeon, P. , Hong, S. , Jeon, D. , Park, S. Y., et al. (2023). Innovative approach to reveal source contribution of dissolved organic matter in a complex river watershed using end-member mixing analysis based on spectroscopic proxies and multi-isotopes. Water Res. 230:119470. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.119470
Komor, S. C. (1997). Boron contents and isotopic compositions of hog manure, selected fertilizers, and water in Minnesota, No. 26. American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America, pp. 1212–1222.
Kumar, R. , Mittal, S. , Sahoo, P. K. , and Sahoo, S. K. (2021). Source apportionment, chemometric pattern recognition and health risk assessment of groundwater from southwestern Punjab, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 43, 733–755. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00518-1
Kypritidou, Z. , Kelepertzis, E. , Kritikos, I. , Kapaj, E. , Skoulika, I. , Kostakis, M., et al. (2024). Geochemistry and origin of inorganic contaminants in soil, river sediment and surface water in a heavily urbanized river basin. Sci. Total Environ. 927:172250. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172250
Lartsey, P. E. , Ganyaglo, S. Y. , Adomako, D. , Sakyi, P. A. , Gibrilla, A. , Barbecot, F., et al. (2024). Tracing nitrate contamination sources and apportionment in North-Western Volta River basin of Ghana using a multi-isotopic approach. Water Air Soil Pollut. 235:633. doi: 10.1007/s11270-024-07418-5
Lasagna, M. , and De Luca, D. A. (2019). Evaluation of sources and fate of nitrates in the western Po plain groundwater (Italy) using nitrogen and boron isotopes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 2089–2104. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-0792-6
Li, B. , Han, D. , Yang, L. , Song, X. , Qin, M. , and Diamantopoulos, E. (2025). New insights into nitrate sources and transformations in riparian groundwater of a sluice-controlled river: an integrated approach using major ions, stable isotopes and microbial gene methods. Environ. Res. 271:121065. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2025.121065
Lorette, G. , Sebilo, M. , Buquet, D. , Lastennet, R. , Denis, A. , Peyraube, N., et al. (2022). Tracing sources and fate of nitrate in multilayered karstic hydrogeological catchments using natural stable isotopic composition (δ15N-NO3− and δ18O-NO3−). Application to the Toulon karst system (Dordogne, France). J. Hydrol. 610:127972. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127972
Li, X. , Masuda, H. , Koba, K. , and Zeng, H. (2007). Nitrogen isotope study on nitrate-contaminated groundwater in the Sichuan Basin, China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. 178:145–156.
Malki, M. , Bouchaou, L. , Hirich, A. , Brahim, Y. A. , and Choukr-Allah, R. (2017). Impact of agricultural practices on groundwater quality in intensive irrigated area of Chtouka-Massa, Morocco. Sci. Total Environ. 574, 760–770. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.145
Marouane, B. , Dahchour, A. , Dousset, S. , and El Hajjaji, S. (2015). Monitoring of nitrate and pesticide pollution in Mnasra, Morocco soil and groundwater. Water Environ. Res. 87, 567–575. doi: 10.2175/106143015X14212658614711
Mayer, B. , Bollwerk, S. M. , Mansfeldt, T. , Hütter, B. , and Veizer, J. (2001). The oxygen isotope composition of nitrate generated by nitrification in acid forest floors. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 65, 2743–2756. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00612-3
Meng, L. , Zhang, Q. , Liu, P. , He, H. , and Xu, W. (2020). Influence of agricultural irrigation activity on the potential risk of groundwater pollution: a study with DRASTIC method in a semi-arid agricultural region of China. Sustainability 12:1954. doi: 10.3390/su12051954
Minet, E. , Coxon, C. E. , Goodhue, R. , Richards, K. G. , Kalin, R. M. , and Meier-Augenstein, W. (2012). Evaluating the utility of 15N and 18O isotope abundance analyses to identify nitrate sources: a soil zone study. Water Res. 46, 3723–3736. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.004
Mukherjee, I. , and Singh, U. K. (2018). Groundwater fluoride contamination, probable release, and containment mechanisms: a review on Indian context. Environ. Geochem. Health 40, 2259–2301. doi: 10.1007/s10653-018-0096-x
Nigro, A. , Sappa, G. , and Barbieri, M. (2017). Application of boron and tritium isotopes for tracing landfill contamination in groundwater. J. Geochem. Explor. 172, 101–108. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.10.011
Nisi, B. , Raco, B. , and Dotsika, E. (2016). “Groundwater contamination studies by environmental isotopes: a review” in Threats to the quality of groundwater resources: Prevention and control. eds. A. Scozzari and E. Dotsika (Berlin: Springer), 115–150.
Nouzha, B. , Kacem, S. A. , Ferdaouss, L. , Abrerrahim, L. , and Mohammed, B. (2016). Evaluation De L’impact De La Pollution Agricole Sur La Qualite Des Eaux Souterraines De La Nappe Du Gharb. Eur. Sci. J. 12:509. doi: 10.19044/esj.2016.v12n11p509
Nyilitya, B. , Mureithi, S. , and Boeckx, P. (2020). Tracking sources and fate of groundwater nitrate in Kisumu City and Kano Plains, Kenya. Water 12:401. doi: 10.3390/w12020401
Ogrinc, N. , Tamše, S. , Zavadlav, S. , Vrzel, J. , and Jin, L. (2019). Evaluation of geochemical processes and nitrate pollution sources at the Ljubljansko Polje aquifer (Slovenia): a stable isotope perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 646, 1588–1600. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.245
Oteng Mensah, F. , Alo, C. , and Yidana, S. M. (2014). Evaluation of groundwater recharge estimates in a partially metamorphosed sedimentary basin in a tropical environment: application of natural tracers. Sci. World J. 2014:419508. doi: 10.1155/2014/419508
Oumara, N. G. G. , and El Youssfi, L. (2022). Salinization of soils and aquifers in Morocco and the alternatives of response. Environ. Sci. Proc. 16:65. doi: 10.3390/environsciproc2022016065
Page, M. J. , McKenzie, J. E. , Bossuyt, P. M. , Boutron, I. , Hoffmann, T. C. , Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
Panno, S. V. , Hackley, K. C. , Hwang, H. H. , and Kelly, W. R. (2001). Determination of the sources of nitrate contamination in karst springs using isotopic and chemical indicators. Chem. Geol. 179, 113–128. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00318-7
Pastén-Zapata, E. , Ledesma-Ruiz, R. , Harter, T. , Ramírez, A. I. , and Mahlknecht, J. (2014). Assessment of sources and fate of nitrate in shallow groundwater of an agricultural area by using a multi-tracer approach. Sci. Total Environ. 470, 855–864. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.043
Paul, S. , and Das, C. S. (2021). An investigation of groundwater vulnerability in the north 24 Parganas district using DRASTIC and hybrid-DRASTIC models: a case study. Environ. Adv. 5:100093. doi: 10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100093
Peters, M. , Guo, Q. , Strauss, H. , Wei, R. , Li, S. , and Yue, F. (2019). Contamination patterns in river water from rural Beijing: a hydrochemical and multiple stable isotope study. Sci. Total Environ. 654, 226–236. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.423
Piatek, K. B. , Mitchell, M. J. , Silva, S. R. , and Kendall, C. (2005). Sources of nitrate in snowmelt discharge: evidence from water chemistry and stable isotopes of nitrate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 165, 13–35. doi: 10.1007/s11270-005-4641-8
Postigo, C. , Ginebreda, A. , Barbieri, M. V. , Barceló, D. , Martín-Alonso, J. , de la Cal, A., et al. (2021). Investigative monitoring of pesticide and nitrogen pollution sources in a complex multi-stressed catchment: the lower Llobregat River basin case study (Barcelona, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 755:142377. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142377
Puig, R. , Soler, A. , Widory, D. , Mas-Pla, J. , Domènech, C. , and Otero, N. (2017). Characterizing sources and natural attenuation of nitrate contamination in the Baix Ter aquifer system (NE Spain) using a multi-isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 580, 518–532. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.206
Pujiindiyati, E. R. , and Sidauruk, P. (2015). Study of leachate contamination in Bantar Gebang landfill to its shallow groundwater using natural isotope tracers of 18O, 2H and 3H. Atom Indones. 41, 31–39. doi: 10.17146/aij.2015.353
Quinodoz, F. B. , Cabrera, A. , Blarasin, M. , Matteoda, E. , Pascuini, M. , Prámparo, S., et al. (2024). Chemical and isotopic tracers combined with mixing models for tracking nitrate contamination in the Pampa de Pocho aquifer, Argentina. Environ. Res. 259:119571. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119571
Reed, E. M. , and Duranceau, S. J. (2016). Chemical and isotopic composition of nitrogen and boron in septic tank wastewater samples. Environ. Earth Sci. 75, 1–7. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6283-0
Ren, Y. , Xu, Z. , Zhang, X. , Wang, X. , Sun, X. , Ballantine, D. J., et al. (2014). Nitrogen pollution and source identification of urban ecosystem surface water in Beijing. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 8, 106–116. doi: 10.1007/s11783-012-0474-z
Saccon, P. , Leis, A. , Marca, A. , Kaiser, J. , Campisi, L. , Böttcher, M. E., et al. (2013). Multi-isotope approach for the identification and characterisation of nitrate pollution sources in the Marano lagoon (Italy) and parts of its catchment area. Appl. Geochem. 34, 75–89. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.02.007
Sankoh, A. A. , Derkyi, N. S. A. , Frazer-Williams, R. A. , Laar, C. , and Kamara, I. (2021). A review on the application of isotopic techniques to trace groundwater pollution sources within developing countries. Water 14:35. doi: 10.3390/w14010035
Shalev, N. , Burg, A. , Gavrieli, I. , and Lazar, B. (2015). Nitrate contamination sources in aquifers underlying cultivated fields in an arid region–the Arava Valley, Israel. Appl. Geochem. 63, 322–332. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.09.017
Sharma, K. , Raju, N. J. , Singh, N. , and Sreekesh, S. (2022). Heavy metal pollution in groundwater of urban Delhi environs: pollution indices and health risk assessment. Urban Clim. 45:101233. doi: 10.1016/j.uclim.2022.101233
She, W. , Jiao, Y. , Lu, R. , Chai, Y. , Chen, F. , Shen, J., et al. (2024). Quantification of nitrate sources and its spatial heterogeneity by dual isotopes. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 10:0201. doi: 10.34133/ehs.0201
Shi, J. , Ohte, N. , Tokuchi, N. , Imamura, N. , Nagayama, M. , Oda, T., et al. (2014). Nitrate isotopic composition reveals nitrogen deposition and transformation dynamics along the canopy–soil continuum of a suburban forest in Japan. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 28, 2539–2549. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7050
Shomar, B. , Osenbrück, K. , and Yahya, A. (2008). Elevated nitrate levels in the groundwater of the Gaza strip: distribution and sources. Sci. Total Environ. 398, 164–174. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.02.054
Sigman, D. M. , Casciotti, K. L. , Andreani, M. , Barford, C. , Galanter, M. , and Böhlke, J. K. (2001). A bacterial method for the nitrogen isotopic analysis of nitrate in seawater and freshwater. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 4145–4153.
Spalding, R. F. , Hirsh, A. J. , Exner, M. E. , Little, N. A. , and Kloppenborg, K. L. (2019). Applicability of the dual isotopes δ15N and δ18O to identify nitrate in groundwater beneath irrigated cropland. J. Contam. Hydrol. 220, 128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2018.12.004
Su, D. , Zhou, Z. , Gong, X. , Yan, L. , Ding, S. , Dong, H., et al. (2024). Identification of nitrate sources and transformation in karst cave water using hydrochemistry and NO3− isotopes (δ15N/δ18O) combined with a Bayesian mixing model. All Earth 36, 1–17. doi: 10.1080/27669645.2024.2356138
Subba Rao, N. , Sunitha, B. , Adimalla, N. , and Chaudhary, M. (2020). Quality criteria for groundwater use from a rural part of Wanaparthy District, Telangana state, India, through ionic spatial distribution (ISD), entropy water quality index (EWQI) and principal component analysis (PCA). Environ. Geochem. Health 42, 579–599. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00393-5
Suthar, S. , Bishnoi, P. , Singh, S. , Mutiyar, P. K. , Nema, A. K. , and Patil, N. S. (2009). Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 171, 189–199. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.111
Tirez, K. , Brusten, W. , Widory, D. , Petelet, E. , Bregnot, A. , Xue, D., et al. (2010). Boron isotope ratio (δ11B) measurements in water framework directive monitoring programs: comparison between double focusing sector field ICP and thermal ionization mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 25, 964–974. doi: 10.1039/c001840f
Torres-Martínez, J. A. , Mora, A. , Mahlknecht, J. , Daesslé, L. W. , Cervantes-Avilés, P. A. , and Ledesma-Ruiz, R. (2021). Estimation of nitrate pollution sources and transformations in groundwater of an intensive livestock-agricultural area (Comarca Lagunera), combining major ions, stable isotopes and MixSIAR model. Environ. Pollut. 269:115445. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115445
Valett, H. M. , and Sheibley, R. W. (2009). “Ground water and surface water interaction” in Encyclopedia of inland waters. ed. H. M. Valett (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 691–702.
Van Meter, K. J. , Basu, N. B. , Veenstra, J. J. , and Burras, C. L. (2016). The nitrogen legacy: emerging evidence of nitrogen accumulation in anthropogenic landscapes. Environ. Res. Lett. 11:035014. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/11/3/035014
Veale, N. , Visser, A. , Esser, B. , Singleton, M. J. , and Moran, J. E. (2019). Nitrogen cycle dynamics revealed through δ18O-NO3− analysis in California groundwater. Geosciences 9:95. doi: 10.3390/geosciences9020095
Vengosh, A. , Kolodny, Y. , and Spivack, A. J. (1998). Groundwater pollution determined by boron isotope systematics. In Isotope Techniques in the Study of Environmental Change (pp. 17–37). International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna.
Vystavna, Y. , Diadin, D. , Yakovlev, V. , Hejzlar, J. , Vadillo, I. , Huneau, F., et al. (2017). Nitrate contamination in a shallow urban aquifer in East Ukraine: evidence from hydrochemical, stable isotopes of nitrate and land use analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 76, 1–13.
Wang, K. , Chen, X. , Wu, Z. , Wang, M. , and Wang, H. (2023). Traceability and biogeochemical process of nitrate in the Jinan karst spring catchment, North China. Water 15:2718. doi: 10.3390/w15152718
Wang, H. , Gao, J. E. , Li, X. H. , Zhang, S. L. , and Wang, H. J. (2015). Nitrate accumulation and leaching in surface and ground water based on simulated rainfall experiments. PLoS One 10:e0136274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136274
Wang, F. , Liu, L. , Xu, W. , Li, Y. , Ruan, Q. , and Cao, W. (2024). Multiple stable isotopic approaches for tracing nitrate contamination sources: implications for nitrogen management in complex watersheds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 269:115822. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115822
Weitzman, J. N. , Brooks, J. R. , Mayer, P. M. , Rugh, W. D. , and Compton, J. E. (2021). Coupling the dual isotopes of water (δ2H and δ18O) and nitrate (δ15N and δ18O): a new framework for classifying current and legacy groundwater pollution. Environ. Res. Lett. 16:045008. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abdcef
Wen, X. , Feng, Q. , Lu, J. , Wu, J. , Wu, M. , and Guo, X. (2018). Risk assessment and source identification of coastal groundwater nitrate in northern China using dual nitrate isotopes combined with Bayesian mixing model. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 24, 1043–1057. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2017.1405722
Widory, D. , Petelet-Giraud, E. , Négrel, P. , and Ladouche, B. (2005). Tracking the sources of nitrate in groundwater using coupled nitrogen and boron isotopes: a synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 539–548. doi: 10.1021/es0493897
Wu, C. , Fang, C. , Wu, X. , Zhu, G. , and Zhang, Y. (2021). Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater using self-organizing maps in the Hangjinqi gasfield area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Geosci. Front. 12, 781–790. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.09.012
Xu, S. , Kang, P. , and Sun, Y. A. (2016). A stable isotope approach and its application for identifying nitrate source and transformation process in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23, 1133–1148. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5309-6
Yidana, S. M. , Alo, C. , Addai, M. O. , Fynn, O. F. , and Essel, S. K. (2015). Numerical analysis of groundwater flow and potential in parts of a crystalline aquifer system in northern Ghana. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 12, 3805–3818. doi: 10.1007/s13762-015-0805-2
Zazouli, M. A. , Dashtban, N. , Jalalvand, M. A. , Kheilgavan, S. J. , Kholerdi, F. M. , Mohammadpour, A., et al. (2024). Unveiling nitrate contamination and health risks: insights from groundwater quality assessment and Monte Carlo simulation along the southern Caspian Sea coasts. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 27:101340. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2024.101340
Zhang, X. , Liu, Z. , Xin, Z. , Zhang, C. , and Song, C. (2024). Tracing nitrogen sources and transformation characteristics in a large basin with spatially heterogeneous pollution distribution. Environ. Res. 262:119859. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119859
Zhaoshi, W. , Xijun, L. , and Kuanyi, L. (2021). Water quality assessment of rivers in Lake Chaohu Basin (China) using water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 121:107021. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107021
Zhou, J. , Hu, M. , Liu, M. , Yuan, J. , Ni, M. , Zhou, Z., et al. (2022). Combining the multivariate statistics and dual stable isotopes methods for nitrogen source identification in coastal rivers of Hangzhou Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 82903–82916. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-21116-x
Zhou, Y. , Li, P. , Chen, M. , Dong, Z. , and Lu, C. (2020). Groundwater quality for potable and irrigation uses and associated health risk in southern part of Gu\u2019an county, North China plain. Environ. Geochem. Health 43, 813–835. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00553-y
Keywords: groundwater pollution, nitrate, contamination, stable isotopes, pollution sources, isotope hydrology
Citation: Oubeid AMA, Hilal I, Kebd A and Sadiki M (2025) Global applications of stable isotopes for identifying nitrate pollution sources in groundwater: a comprehensive review. Front. Water. 7:1666498. doi: 10.3389/frwa.2025.1666498
Edited by:
Venkatramanan Senapathi, National College, IndiaReviewed by:
Gabriella Balacco, Politecnico di Bari, ItalyPriscilla Esinu Selase Lartsey, Université du Québec à Montréal, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Oubeid, Hilal, Kebd and Sadiki. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ahmed Mahmoud Ahmed Oubeid, YWhtZWRvdWJlaWQuYWhtZWRtYWhtb3VkQHVpdC5hYy5tYQ==
 Ahmed Mahmoud Ahmed Oubeid
Ahmed Mahmoud Ahmed Oubeid Ismail Hilal3
Ismail Hilal3