- 1Shanghai Mental Health Center, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Psychotic Disorders, Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai, China
- 3Brain Science and Technology Research Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 4Departament de Genètica, Microbiologia i Estadística, Facultat de Biologia, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
- 5Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Raras, Valencia, Spain
- 6Institut de Biomedicina de la Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
- 7Institut de Recerca Sant Joan de Déu, Esplugues de Llobregat, Barcelona, Spain
Neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders are a highly disabling and heterogeneous group of developmental and mental disorders, resulting from complex interactions of genetic and environmental risk factors. The nature of multifactorial traits and the presence of comorbidity and polygenicity in these disorders present challenges in both disease risk identification and clinical diagnoses. The genetic component has been firmly established, but the identification of all the causative variants remains elusive. The development of next-generation sequencing, especially whole exome sequencing (WES), has greatly enriched our knowledge of the precise genetic alterations of human diseases, including brain-related disorders. In particular, the extensive usage of WES in research studies has uncovered the important contribution of de novo mutations (DNMs) to these disorders. Trio and quad familial WES are a particularly useful approach to discover DNMs. Here, we review the major WES studies in neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders and summarize how genes hit by discovered DNMs are shared among different disorders. Next, we discuss different integrative approaches utilized to interrogate DNMs and to identify biological pathways that may disrupt brain development and shed light on our understanding of the genetic architecture underlying these disorders. Lastly, we discuss the current state of the transition from WES research to its routine clinical application. This review will assist researchers and clinicians in the interpretation of variants obtained from WES studies, and highlights the need to develop consensus analytical protocols and validated lists of genes appropriate for clinical laboratory analysis, in order to reach the growing demands.
Introduction
The susceptibility to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric (NDP) disorders involves polygenic, multi-effect, and complex genetic structures. Large-scale twin and population-based studies were able to show that genetics accounts for 30–80% of disease liability for many neuropsychiatric disorders (Gandal et al., 2016). An early indication of the genetic involvement in major NDP disorders was their association with rare Mendelian disorders, each with distinctive morphologic, cognitive, and neuropsychiatric phenotypes, such as Fragile X, Angelman, or Rett syndromes (De Boulle et al., 1993; De Hert et al., 1996; Inoue and Lupski, 2003; Betancur, 2011; Blair et al., 2013). Due to the limited power and systematic confounders such as population stratification bias, the early linkage and candidate gene studies often yielded disperse findings (Kohler and Bickeboller, 2006; Price et al., 2010). In contrast, the unbiased large-scale genome-wide interrogation, such as genome-wide association studies (GWAS), of common genetic variation in large cohorts has become a popular detection methodology and study design to identify risk factors in neuropsychiatric diseases, such as autism spectrum disorders (ASD), schizophrenia (SCZ), intellectual disability, and/or developmental delay (ID/DD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorder (BD) and has yielded more robust results (Epi4k Consortium et al., 2013; Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium et al., 2014; Hou et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2016a; The Autism Spectrum Disorders Working Group of The Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, 2017; Trampush et al., 2017; Ikeda et al., 2018; Pasman et al., 2018). Interesting GWAS discoveries have been made on a wide variety of neuropsychiatric disorders and clinical traits, many of which have been covered in other in-depth reviews (Sullivan, 2010; Visscher et al., 2012, 2017; Collins and Sullivan, 2013; Horwitz et al., 2018). Therefore, the scope of our review is mainly focused on the usage of next generation sequencing (NGS) technology, specifically whole exome sequencing (WES), as an additional approach in neuropsychiatric disorder studies, in an attempt to uncover the missing genetic basis of the disease etiology. There are two commonly used study strategies for discovering disease-associated variants using WES. One is the exome case-control study to find the rare inherited variants, which usually require a large sample size to identify the significant variants, such as in SCZ (Genovese et al., 2016), BD (Goes et al., 2016), and OCD (McGrath et al., 2014). A comprehensive review has been done by Gratten et al. (2014) on exome case-control studies and has contributed greatly to our understanding of neuropsychiatric diseases. The other one, is the de novo variants (DNV) discovery, based on trio/quad studies with relatively smaller sample sizes as an alternative strategy with great success in disorders, such as ASD (De Rubeis et al., 2014; Iossifov et al., 2014; O'Roak et al., 2014) and ID/DD (Gilissen et al., 2014; Short et al., 2018). Thus, in this review, we focus on the DNV studies, their significance and clinical translations. Here, we summarize the recent repertoire of de novo events detected from WES family-based trio (two unaffected biological parents and the affected child) or quad (two unaffected biological parents, the affected child, and one unaffected sibling) studies in NDP disorders and provide a detailed overview of some of the most successful integrative methods for DNM analyses. Finally, we also review the current state of WES application in NDP disorder clinical diagnosis.
Dissecting Neurodevelopmental and Psychiatric Disorders by Identifying de novo Rare Genetic Variants
Usage of Whole Exome Sequencing in NDP Disorders to Detect DNMs
Over the past decade, NGS has become increasingly popular for estimating the genetic etiology of Mendelian, complex, and undiagnosed disorders due to its scale and comprehensiveness (Bamshad et al., 2011; Goldstein et al., 2013; MacArthur et al., 2014; Zhu et al., 2014). In WES, the ~1.5% of the genome, encoding for proteins, is captured and then sequenced at lower costs and increases the interpretability of the identified variants, in contrast to the much more expensive whole genome sequencing (WGS) that surveys the entire genome space. To facilitate interpretation and decrease the cost of the whole genome sequencing (WGS), the portion of the genome related to protein coding regions is captured and sequenced in WES. Notably, studies of NDP disorders using WES and WGS have indicated that de novo mutations (DNMs) detected from trio- or quad-based familiar studies have important roles (Table 1), despite the genetic heterogeneity of types of disorders (Sullivan et al., 2012a; Gratten et al., 2013). Filtering DNV in a proband against unaffected parents, facilitates the interpretation of potential de novo pathogenic variants among all the detected ones (Figure 1A). For example, Neale and colleagues (Neale et al., 2012) performed one of the four first large WES cohort studies using a trio-based design to investigate the contribution of DNMs to ASD (Iossifov et al., 2012; Neale et al., 2012; O'Roak et al., 2012b; Sanders et al., 2012), which showcased the important role of DNMs in the pathogenesis of ASD. More importantly, Neale and colleagues also proposed a statistical framework to analyze whether individual genes carry significantly more DNMs than expected by chance. Furthermore, Sanders et al. estimated that penetrant DNMs in genes contribute to autism risk in ~11% of parent-child trio families (Sanders et al., 2015).
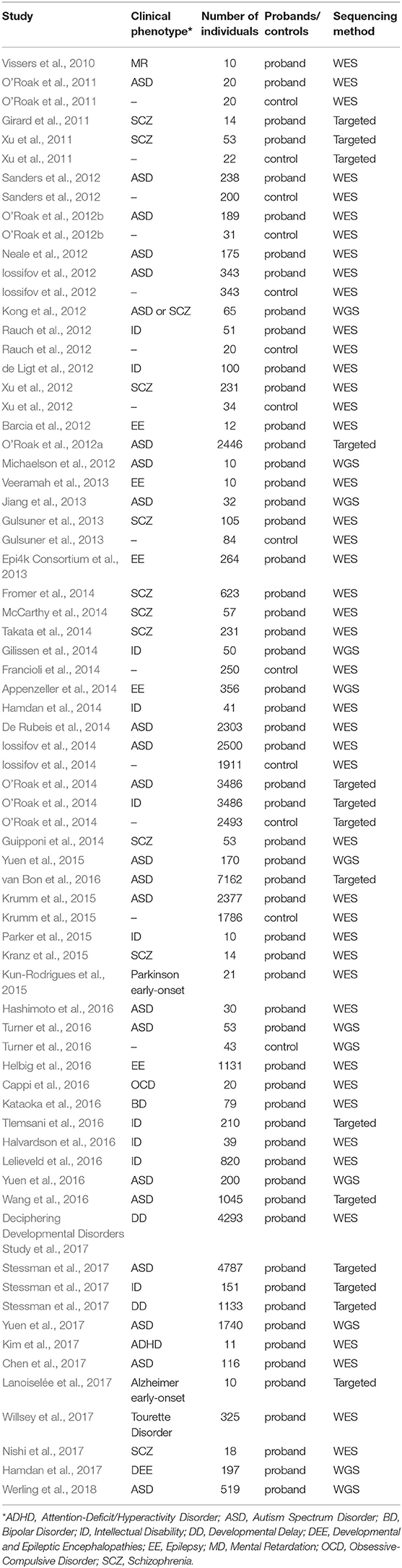
Table 1. Summary of published studies of DNMs found in large cohorts of patients with psychiatric disorders.
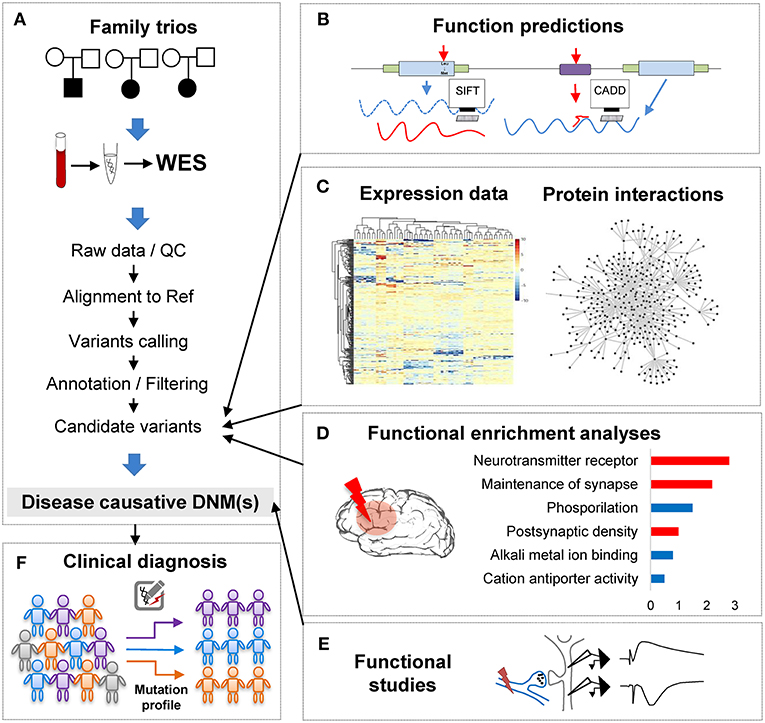
Figure 1. The analytical pipeline for DNMs detected from exome studies in psychiatric disorders. (A) The discovery flow of DNMs from trios, including sample collection, data Quality Control (QC), alignment, variants calling, annotation. (B) The functional annotation step, e.g., applying computational tools, such as SIFT and CADD to predict the functional consequences of the detected mutation. (C) The large-scale data integration step to investigate the underlying disease genetics. (D) The functional enrichment analyses and interpretation step, which help understand the disease etiology. (E) The functional studies phase is the experimental validation step. (F) The clinical application step of the DNM pipeline, which can utilize the verified DNMs as the mutation screening profile for clinical diagnosis in psychiatric patients.
Summary of Published Exome DNMs in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
In the past few years, 66% of the large cohort studies that investigate DNMs of early onset psychiatric disorders published were carried out by WES, compared to only 18% by WGS and the remaining 16% by targeted sequencing, demonstrating the prominent role of the WES in mutation discovery (Table 1). These studies have identified, by the end of 2018 in denovo-db (Turner et al., 2017), more than 57,300 DNMs in 44,200 individuals with a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders estimating a rate of ~1.3 DNMs/individual (Table 1). Also, the decrease in cost of NGS over the years has resulted in an explosion of small WES studies from limited collections or index cases from all over the world (Smedemark-Margulies et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2018). Manual curation and time are needed for all these variants to progressively be introduced in variant databases, such as 1000 Genomes (Gibbs et al., 2015), the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute's Exome Sequencing Project (ESP) (Exome Variant Server (http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/), Database of Short Genetic Variations (dbSNP) (Sherry et al., 2001), expert-curated databases focused on variant information (locus-specific databases; LSDB) (Fokkema et al., 2011) or clinical information e.g., GeneReviews (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1116/) and ClinVar (Landrum et al., 2016), where mutations are deposited by submitters, or collected by the private Human Mutation Database (HGMD) (Stenson et al., 2017). As for DNMs, a few databases are being developed hosting the collection of the DNMs across developmental and neuropsychiatric disorders and controls, such as denovo-db (Turner et al., 2017) and NPdenovo (Li et al., 2016). The same team also developed mirDNMR, a gene-centered database of background DNM rates in humans (Jiang et al., 2017). Still, these databases focus on the variant information, such as locations and frequencies. Therefore, a freely available unified systematic variance repository collecting the results from all the currently published variants fast, including medically relevant information, is needed to ensure the rapid translation of novel information to researchers and clinicians.
DNMs including single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions/deletions (indels) in exonic regions, are rare and generally considered to have a stronger disruptive effect on biological functions than inherited variants (Crow, 2000). Thus, DNMs provide a valuable insight into the genetic understanding and clinical interpretation of sporadic cases in which inheritance may be limited to explain disease etiology (Veltman and Brunner, 2012; MacArthur et al., 2014; Samocha et al., 2014). As a result, the number of WES studies and identified DNMs have increased rapidly over the past few years (Figure 2A). To facilitate the interpretation of DNMs from exonic and exon-flanking regions, they are usually categorized by their functional impacts (Figure 2B) as synonymous (23%) or non-synonymous variants (77%). As the former mutations typically have a silent effect, even some of them may contribute to alternative splicing and protein fold change (Sauna and Kimchi-Sarfaty, 2013), but their predictions are limited except biological experiments showing the results of these variants. Thus, we chose to focus on the non-synonymous DNMs. The latter is further classified into likely gene-damaging loss-of-function (LoF) variants (15%) (nonsense, frameshift indels, and splice-site mutations) and missense variants (62%). However, only a fraction of these DNMs is responsible for the clinical phenotypes. In an extensive study of >2,500 simplex families with ASD, 43% of LoFs, and 13% of the missense DNMs were estimated to be pathogenic (Iossifov et al., 2014). We observe that mutations from ASD and ID/DD contribute the most (86.6%) to the current repertoire of WES DNMs (Figure 2A), which is not surprising since 85% of the trio/quad samples presented these disorders and have been more systematically interrogated than others. Also, the distribution of variant types identified is similar across disorders (Figure 2B).
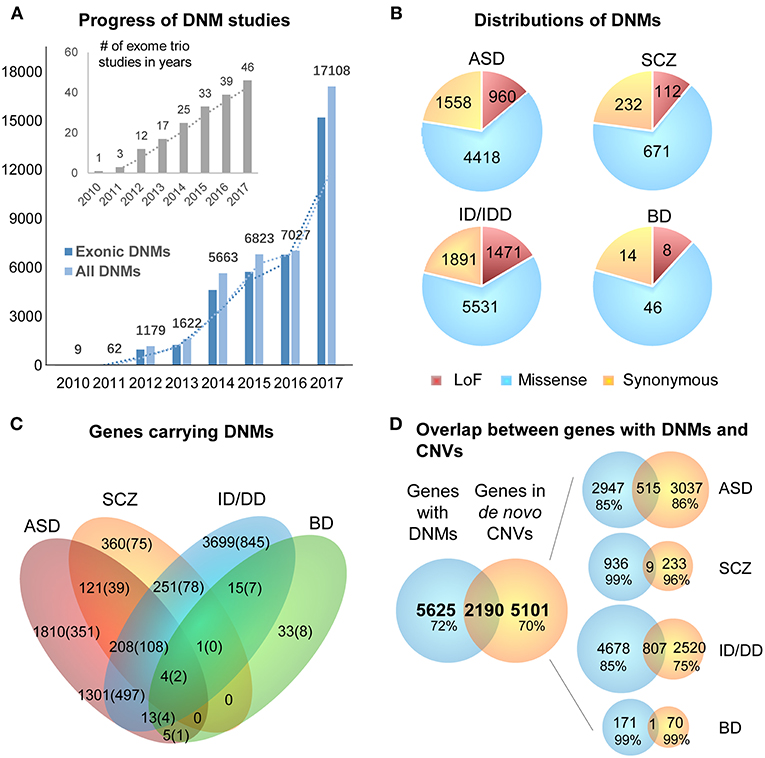
Figure 2. Summary of DNMs detected from exome studies in psychiatric disorders. (A) The overview of the numbers of WES studies in psychiatric disorders increased over the past few years (until the end of 2017). (B) The distribution of de novo LoF, missense, and synonymous mutations detected in four different disorders across large studies (Table 1). (C) Venn Diagram of the overlap of genes hit by DNMs from major studies of patients with psychiatric disorders. (D) The overlap between the genes carrying DNMs and genes hit by the de novo CNVs in four different disorders. ASD, Autism Spectrum Disorder; ID/DD, Intellectual Disability, Developmental Delay; SCZ, Schizophrenia; BD, Bipolar Disorder.
The excessive comorbidity between various neuropsychiatric diagnoses, such as ASD, ID/DD, SCZ, BD, OCD, Tourette syndrome, and ADHD makes the interpretation of the underlining disease etiology extremely difficult (Ronald et al., 2008; Lichtenstein et al., 2010; Rommelse et al., 2010; Faraone et al., 2012; Sullivan et al., 2012b; Chen et al., 2016; Hirschtritt et al., 2018; Liu and Wu, 2018; Shen et al., 2018). Another limiting factor is the large polygenicity of these diseases. Almost all NDP disorders are associated with potentially thousands of disease risk genes, each conferring variable effects. To this extent, accumulation of the genes carrying DNMs from WES in multiple NDP disorder studies provides an excellent opportunity for interrogating the underlying shared genetic component among various disorders. We used pLI scores (Lek et al., 2016) to prioritize and summarize the overlapped genes. The pLI score of a given gene indicates the probability that it belongs in the haploinsufficient category, wherein a single functional copy of a gene is insufficient to maintain its normal function and is extremely intolerant of LoF variation. Thus, we summarized the overlapped genes (Supplementary Table 1) with high pLI scores (pLI ≥ 0.9, extremely LoF intolerant) carrying DNMs between four different disorders, ASD, SCZ, ID/DD, and BP, in Figure 2C.
The disorders that shared the larger number of genes are ASD and ID/DD, but these observations could be explained by the extensive shared clinical phenotypes. These observations need to be considered with caution due to a large number of WES studies performed in these disorders. There are some noticeable genes carrying DNMs in patients from at least three different disorders, such as Chromodomain Helicase DNA Binding Protein 8 CHD8 (ASD, ID/DD, SCZ), Lysine Methyltransferase 2C KMT2C (ASD, BP, ID/DD, SCZ), Chromodomain Helicase DNA Binding Protein 5 CHD5 (ASD, ID/DD, SCZ), Sodium Voltage-Gated Channel Alpha Subunit 2 SCN2A (ASD, ID/DD, SCZ), Neurexin 1 NRXN1 (ASD, ID/DD, SCZ), or Period Circadian Regulator 1 PER1 (ASD, BP, ID/DD), suggesting that some biological processes are probably shared between neuropsychiatric disorders.
Unique Contribution of de novo Events to the Understanding of Disease Etiology
A chromosomal structural variation (SV) is usually a rearrangement of a genomic region with variable size (50 bp−5 Mb) that can cause Mendelian disease and contribute to complex diseases (Stankiewicz and Lupski, 2010; Girirajan et al., 2011). It includes different types of alternations, such as inversions and balanced translocations or genomic imbalances (duplications and deletions), the latter commonly known as copy number variants (CNVs) (Weckselblatt and Rudd, 2015). The advent of chromosomal microarrays enabled the detection of large genomic de novo structural variants such as recurrent de novo (or inherited) CNV in trio studies (e.g., 1q21.1, 16p11.2, or 22q11.21) or ultra-rare or unique de novo CNVs. These discoveries provided an additional aspect of disease etiology and brought rare variants with large effect sizes to the forefront (Malhotra and Sebat, 2012). Especially with the advent of the high sequencing coverage, CNV calling from WES/WGS became more reliable (Trost et al., 2018), and a machine-learning algorithm based software (SV2) improved performance of the SV detection, including CNV, for genotyping deletions and duplications from paired-end sequencing data (Antaki et al., 2018; Brandler et al., 2018). It has been estimated that CNVs are responsible for a considerable percentage of the genetic causes in some psychiatric disorders such as ~10% of simplex cases of ASD (Sebat et al., 2007). However, de novo CNVs discovered in NDP disorders pose many challenges for interpretations, such as pleiotropy, incomplete penetrance, and difficulty to directly identify the pathogenic genes due to the fact that the affected region may contain no known gene (potentially affecting regulatory elements) or, on the contrary, a large and diverse set of genes. When overlapping the genes carrying DNMs from WES to the genes hit by de novo CNVs from arrays of four different disorders (ASD, BD, ID/DD, and SCZ), only <30% of them are shared (Figure 2D). These issues emphasize the need for different detection methods for interrogating the differential impact of molecular pathologies by different types of disease mutations. In consequence, WGS that covers the entire genome in trio or quad family-based studies is more comprehensive and capable of detecting a complete set of SNPs, SNVs, indels, and CNVs of an individual at the same time. Also, it could be a choice to replace the usual strategy of using multiple sequencing technologies to investigate all the variants in neuropsychiatric disorders.
Interpreting rare genetic variants from exome studies
With the abundance of the genomic variants obtained from WES and WGS studies, one of the most significant challenges is to systematically interrogate the functional impact of the detected variants and identify the underlying affected pathway. Though the ultimate proof of DNMs contribution to the phenotypes is functional assays (Figure 1E), these tests are generally difficult to implement in such large scales systematically. To overcome this limitation, computational methods have been developed to investigate DNMs consequences and involve typically multiple steps: evaluation of the DNMs potential pathogenicity; incorporation of other variants such as CNVs or inherited DNMs; and finally, integrative analyses of data from other sources of evidence to enhance the understanding of the disease functional pathways (Figures 1B–D).
Prediction of Functional Consequences of DNMs
One of the most important steps when the variants are obtained, is to functionally annotate them to distinguish deleterious variants from a considerable number of variants from the neutral background. Numerous efforts have been carried out to develop computational tools to functionally interpret both coding and non-coding genomic elements and to estimate the variants pathogenicity, such as SIFT (Ng and Henikoff, 2003), PolyPhen-2 (Adzhubei et al., 2010), GERP (Davydov et al., 2010), or CADD (Kircher et al., 2014) (Figure 1B). Pathogenicity evaluation can be a challenging task as the estimated results of different methods sometimes lack of the consistency, and functional assays are not systematically performed. To this end, several studies (Gnad et al., 2013; Dong et al., 2015; Miosge et al., 2015; Ionita-Laza et al., 2016) have extensively reviewed these computational annotation tools. Some of these studies divide the multiple tools according to the variant types predictions (Richards et al., 2015), while others compared non-coding genome pathogenicity scores using calculation methods based on machine learning approaches (Telenti et al., 2018). These summaries often include widely used tools such as SIFT (Ng and Henikoff, 2003), PolyPhen-2 (Adzhubei et al., 2010), or MutationTaster2 (Schwarz et al., 2014), which are based on the evolutionary conservation, which predicts the impacts by determining the conservation of an amino acid across species or based on protein 3D structures features, or both. Li et al. conducted a comprehensive evaluation of 23 methods for annotating missense variants using three independent benchmark datasets with 12 different performance measures (Li et al., 2018) and indicated that ReVe, a combination of REVEL (Ioannidis et al., 2016) and VEST3 (Carter et al., 2013a), had the best performance in prediction. However, comparative results should be often interpreted casually since the evaluation of these tools can be hindered by the problem of circularity (Grimm et al., 2015), such as different variants from the same protein occurring both in the datasets used for training and for evaluation. Nevertheless, these predictors are limited to estimate the impacts of SNVs on coding regions. Other computational tools, such as CADD (Kircher et al., 2014), LINSIGHT (Huang et al., 2017), FATHMM (Shihab et al., 2015), etc. have shown certain but limited power in predicting consequences of non-coding variants. Some have developed integrative tools that incorporate several of these algorithms. For example, dnNSFP (Liu et al., 2016b) integrated various computation tools such as SIFT (Ng and Henikoff, 2003), PolyPhen-2 (Adzhubei et al., 2010), and CADD (Kircher et al., 2014), and was developed to be a one-stop database for variant functional predictions and annotations. ANNOVAR (Wang et al., 2010) is another comprehensive annotation tool, which incorporates functional deleteriousness prediction scores from the dbNSFP, variants reported in the ClinVar database, variants reported in dbSNP, etc. These tools intend to interpret SNVs and indels through evaluating their functional impacts on genes, reporting all functional relevance scores from different computational tools, assessing conservation levels of the impacted region, and interrogating the position variability frequency in databases such as 1000 Genomes Project (Gibbs et al., 2015), dbSNP (Sherry et al., 2001), and ExAC (Lek et al., 2016). Since their development, both dnNSFP and ANNOVAR have become popular and widely used variants annotation applications.
Furthermore, applying neural networks (LeCun et al., 2015; Salakhutdinov, 2015) in annotating genomics information by sequences has become prevalent in recent years and indicates the start of the deep learning era for computational biology (Jones et al., 2017). Several WES studies have reported some small sets of DNMs hitting the non-coding regions of the genes along with exonic DNMs (Supplementary Table 2), which would require additional interpretations. Two recent methods, DeepSEA (Zhou and Troyanskaya, 2015) and DeepBind (Alipanahi et al., 2015), are great examples of applying the deep learning to model the sequence specificity in various level, particularly on variants hitting at non-coding regions. DeepSEA reached at the single nucleotide resolution to predict transcription factor binding and DNAse sensitivity. DeepBind can forecast the sequence specificity of DNA/RNA- protein binding. Their performance is found to be better than any existing conventional method for predicting non-coding variants consequences. DeepSEA predicts chromatin effects of sequence variations with single-nucleotide sensitivity, by directly learning a regulatory sequence code from large-scale chromatin-profiling data, including transcription factors binding, DNase I sensitivity and histone-mark profiles. DeepBind interrogates the sequence variants by integrating experimental data with a deep convolutional neural network to indicate how variations affect binding within a specific sequence. Compared to DeepSEA, DeepBind analyzes the binding affinity between proteins and DNA/RNA and determines whether mutations could disrupt cellular processes. Overall, the successful implementation of both DeepSEA and DeepBind methods undoubtedly illustrates the advances in non-coding mutations effect annotations.
Also, approximately 10% of disease-causing mutations are mutations within splice site sequences at the intron-exon junctions (Krawczak et al., 2007). Thus, splice-site mutations have been generally considered deleterious (Daguenet et al., 2015). Several computational tools, such as Human Splicing Finder (HSF) (Desmet et al., 2009), GeneSplicer (Pertea et al., 2001), MaxEntScan (http://genes.mit.edu/burgelab/maxent/Xmaxentscan_scoreseq.html), NNSplice (Reese et al., 1997), and MutPred Splice (Mort et al., 2014), have been developed to interpret splice-site mutations and discriminate pathogenic and tolerated ones. One of the most widely used tools, HSF (Desmet et al., 2009), contains more than 10 algorithms including position weight matrices (PWM), maximum entropy principle, and motif comparison method, to identify splicing motifs across the imputed human sequence. It evaluates the disrupted prediction of the natural discovered splice sites. MutPred Splice, more recent developed machine learning-based (random forest) prediction tool with 21 features, targets substitutions that disrupt pre-mRNA splicing (Mort et al., 2014). A survey of the in silico tools that predict potential consequences of splicing mutations has been carried out by Jian et al. (2014).
Furthermore, some researchers have developed tools to investigate the effects of mutations from their protein structures using the resolved or predicted protein structures, and the protein-protein interaction (PPI) information. For example, Meyer et al. (2018) developed Interactome INSIDER (INtegrated Structural Interactome and genomic Data browsER), which is a structurally resolved, multi-scale, proteome-wide human interactome allowing to explore human disease mutations functionally. This useful network enables users to analyze disease mutations from databases or from their studies to identify enrichments in protein interaction domains, residues, and atomic 3D clustering in protein interfaces.
In conclusion, when combining computational annotation tools of different purposes, researchers can thoroughly annotate the detected mutations with comprehensive genetic information and ensure having the first step toward a global interrogation of the variant effects (Figure 1B). A proper prioritization of the variants to detect the one with functional effect is therefore crucial to translate the basic research into the clinical intervention for patients' personalized medicine treatment.
Integrating Inherited and Common Variants to Interpret Rare Genetic Variation From Exome Studies
One of the most popular ways to interpret exome data is to analyze DNMs directly. However, only ~1 to 3 de novo events are usually identified in exonic regions in every individual (Iossifov et al., 2014; Turner et al., 2016; Yuen et al., 2016) and there are a plethora of inherited variants also detected by trio WES that might contribute to the disease etiology. One way to gain a more systematic view of variants effects is to combine the de novo and the inherited variants effectively. For this purpose, He et al. (2013) developed a statistical method, later improved by Sanders et al. (2015), the Transmission and De novo Association Analysis (TADA), which identifies disease risk genes by combining de novo and transmitted SNVs and small indels, with case-control variants data from the same samples to provide a unified statistical quantification of disease association. TADA weights multiple types of variaions differently, e.g., a LoF mutation weights more than a missense mutation, which in turn weights more than a transmitted LoF mutation. By combining de novo and transmitted variants in its analysis, TADA (He et al., 2013; Sanders et al., 2015) assumes that candidate genes for neuropsychiatric disorders would give different types of risks to the disease. Some variants may be causative, while others may be transmitted and play roles as contributors or modifiers. Therefore, by including the information on the inherited variants, one may be able to discover pathogenic genes in cases when DNM information is insufficient. TADA has already been successfully applied in neuropsychiatric disorder studies, such as ASD (He et al., 2013; Sanders et al., 2015; Werling et al., 2018), SCZ (Takata et al., 2014; Nguyen et al., 2017), and can easily be applied to other datasets as well.
Besides assessing whether a particular variant is associated with disease by comparing the observed frequency in cases vs. controls, it is also important to consider the mutation rate of the gene carrying DNMs. Samocha et al. (2014) introduced a statistical metric measure to assess expected vs. observed DNMs by estimating the statistical likelihood of a DNM occurring spontaneously in a gene. The model first calculates the mutation rate for a gene from SNPs in non-coding regions of the genome for all possible trinucleotide to trinucleotide changes, such as AGA evolving to ATA, ACA, or AAA. Then sequence context is considered to determine separate rates for each base changing to each other base for all bases across from the coding region and the annotated conserved splice site. By applying this approach, the consequence of various types of mutation change (e.g., loss-of-function, missense, synonymous) on the corresponding amino acid coded for is determined, and the probabilities for each outcome occurring in a gene are evaluated to create a likelihood per gene for each type of DNMs. With this, Samocha et al. was able to identify 1,003 genes that are estimated to be significantly intolerant to variations that change the coding sequence of the gene (Samocha et al., 2014).
Another approach to consider mutation rate of the risk gene carrying DNMs is by incorporating the imputation-based rare variant burden test using a follow-up cohort after the DNM identification. It has been shown that the discovery of a rare variant near a common variant might be particularly informative to clarify which of the candidate gene is pathogenic (Teslovich et al., 2010; Voight et al., 2010; Momozawa et al., 2011). Thus, applying the common variant burden test imputed to the reference SNP panel on genes carrying DNMs can be an alternative approach to assess the pathogenicity of the variants. Recently, Browning et al. (Pullabhatla et al., 2018) has implemented a DNM study pipeline that includes variant discovery and burden test with imputation to reference SNP panel across coding regions of genes. In addition to discover confident candidates, it shows the SNP with genotype imputation mainly implemented for GWAS still can be a powerful supplementary annotation to the rare variant analysis.
Network Approaches to Enhance Understanding of the Disease Functional Pathways
With various forms of large-scale genetic association studies, researchers have detected hundreds to thousands of genetic loci that are involved in NDP disorder risk (Gratten et al., 2014). As a consequence, many works adopting rigorous data-driven integrative network methods have been carried out to understand how all these genetic variants contribute to the disease etiology of NDP disorders (Geschwind and Konopka, 2009; Parikshak et al., 2015). The network approaches use the experimentally measured or predicted relationships between genes to link them to each other and provide an organized structural system for placing each gene in the context of its molecular framework. Networks usually model genome-wide data by displaying molecular entities, such as genes carrying DNMs from WES or protein products of the impacted genes, as nodes and the associations between nodes as network edges. Edges can be the statistical similarities between genes, such as brain-expression correlations, or physical interactions between proteins. Edges define the network connectivity and consequently define the hierarchical structures of the nodes, which can usually be organized into a relatively small group of highly interconnected modules expected to represent functional module entities. Both the inter-modular connectivity and intra-modular connectivity are used to reflect the important biological relationships: the first one reveals a higher-order organization of the network and the latter one can identify which genes are biological modulators within modules. They are often employed in the integrative analysis pipeline to identify causal functional pathways and molecular drivers of cellular and brain-wide pathology in disorders (Carter et al., 2013b; Furlong, 2013; Mitra et al., 2013).
Here, we describe two main network approaches (Figure 1C), co-expression and protein-protein interaction (PPI), to illustrate the network analysis of genes in NDP disorders (Gilman et al., 2012; O'Roak et al., 2012b; Gulsuner et al., 2013; Parikshak et al., 2013; Willsey et al., 2013). Gene expression has been widely used to investigate biological and functional relationships between human genes. The co-expression analysis was mainly designed to explore shared expression patterns in data from different experiments, tissues, or species (Stuart et al., 2003; Zhang and Horvath, 2005; Prifti et al., 2010). As results, the co-expression network utilizes the gene expression pattern correlation between genes to generate links between nodes to relate disease genes to each other (e.g., DNM genes) for the systems-level analysis, followed by the module discovery to identify topologically highly connected network modules (Cline et al., 2007; Amar et al., 2013; van Dam et al., 2017). Next, one can perform the module functional enrichment analysis to identify possible disease or brain-related pathways by using pathway databases such as the Gene Ontology (GO) (Ashburner et al., 2000), the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes, and Genome Elements (KEGG) (Kanehisa and Goto, 2000), with the aim to facilitate the discovery of potential therapeutic targets or biomarkers. The multiple publications in different disorders have demonstrated the effectiveness of this method in identifying disease related pathways, such ASD (Parikshak et al., 2013, 2016; Gupta et al., 2014) or SCZ (Fromer et al., 2014). For instance, Fromer et al. (2014) has applied the co-expression network approach on the set of genes hit by DNMs in patients and identified co-expression modules related to neuronal functions, including axon guidance, postsynaptic membrane, which supported the significance of the findings. Also, co-expression network analysis has also been successfully applied in cross-psychiatric-disorder studies which analyzed collective DNMs to investigate the genetic convergence among psychiatric disorders (Shohat et al., 2017; Gandal et al., 2018). For example, Gandal et al. found an astrocyte-related module significantly up-regulated in ASD, BD, and SCZ, and enriched for glial cell differentiation and fatty-acid metabolism pathways.
Another important characteristic of the biological systems is that proteins function in pairs and groups by interacting with other molecules (e.g., DNA, RNA) to regulate metabolic and signaling pathways, cellular processes, even organismal systems. As a result, PPI integrative network methods can be used to relate disease risk genes (e.g., DNM genes) to each other and their topological locations within the network modules in order to identify the potential diseases pathways. An essential organized network can be constructed by using experimentally measured or predicted associations to place each gene carrying DNM in the context of its molecular system (Geschwind and Konopka, 2009). Thus, PPI networks have emerged as a powerful resource, together with other information, to complement genetic data such as DNMs to elucidate causal molecular drivers of cellular, circuit level, and brain-wide alterations in pathology (Bergholdt et al., 2007; Lage et al., 2008; Neale et al., 2012; O'Roak et al., 2012b) (Figure 1D). For example, DAPPLE (Rossin et al., 2011) was developed to search for the significant physical connectivity among proteins encoded by disease risk genes according to PPIs reported in the literature. Neale et al. (2012) and Xu et al. (2012) have applied DAPPLE to determine whether there is an over-represented of PPIs among the genes hit by a functional de novo event in their results from trio WES studies in NDP disorders. The fact that different types of mutations, such as de novo SNVs and de novo CNVs, can be discovered from genome-scale studies, a network-based analysis that considers all types of mutations can be a powerful strategy for system-level understanding of the disease. To this end, NETBAG+ (Gilman et al., 2012), has been developed to consider multiple lines of mutational data from diseases, such as de novo SNVs, de novo CNVs, and SNP data from GWAS studies, and performed the PPI network-based integrative analysis to investigate the convergence of heterogeneous neuropsychiatric genetic variation on a functional system level.
In addition, some studies have combined PPIs and gene expressions to perform an integrative network analysis to better elucidate the underlining genetic basis of sets of interested genes, such as the significance of the interconnection between detected genes hits by DNMs and the overall impact of the variants in NDP disorders and have achieved successful results (Gulsuner et al., 2013; Hamdan et al., 2014; O'Roak et al., 2014; Lin et al., 2015). Supplementary Table 3 shows the characteristics and differences between different network-based methods.
Progress and limitations in translating NGS from research to clinical implementation
Traditionally, diagnosing individuals with neuropsychiatric disorders is a very long and tedious process, and includes a large set of clinical assessments, such as dysmorphology evaluation, development monitoring, intellectual function assessment. With increasing acknowledgment of a strong genetic influence to the psychiatric disorders, especially in ASD and ID/DD, with subset of cases with an underlying genetic syndrome, clinical laboratory testing to find genomic variants in risk genes is now an important part of the diagnostic work. Genomic risk variants scanning would be considered when the clinical symptoms and test results suggest a suspected diagnose. This strategy resulted in a diagnosis rate from 5 to 50% in cases (Battaglia et al., 1999; Battaglia and Carey, 2003; Challman et al., 2003; Moog, 2005; van Karnebeek et al., 2005). However, clinicians often tussle with the diseases' phenotypic diversity and are challenged to select a proper genetic testing for complex cases.
Current NGS Gene-Panels Commercially Available for Clinical Genetic Testing
Currently, the recommended laboratory genetic test for disorders, such as ASD and ID/DD, is the chromosomal microarray (Miller et al., 2010), targeting deleted and duplicated segments of DNA (CNVs) that only account for 5–25% of cases (Tammimies et al., 2015). In contrast, the NGS technology provides in-depth view of genomic landscape and can be used to target a selection of genes of interest by targeted gene panels, the entire coding portions of all genes by WES, or the entire genome by WGS to gain a comprehensive map of the genomic variants. Compared with the sequential testing of multiple genes historically, NGS allows the rapid sequencing of various genes simultaneously at a lower cost and is expected to improve clinical diagnosis of disorders and patients' management. NGS has proven indispensable to discover new neuropsychiatric disorder risk genes. In addition, integrative analyses of NGS data have been fruitful in illuminating the underlining genetic basis of disease etiology. It has also been commercially available as a second-tier genetic test and has demonstrated to be a powerful supplementary technique for both risk gene discovery and clinical application in disease diagnosis (Figure 1F) (Bainbridge et al., 2011; Kingsmore et al., 2011; Boycott et al., 2013).
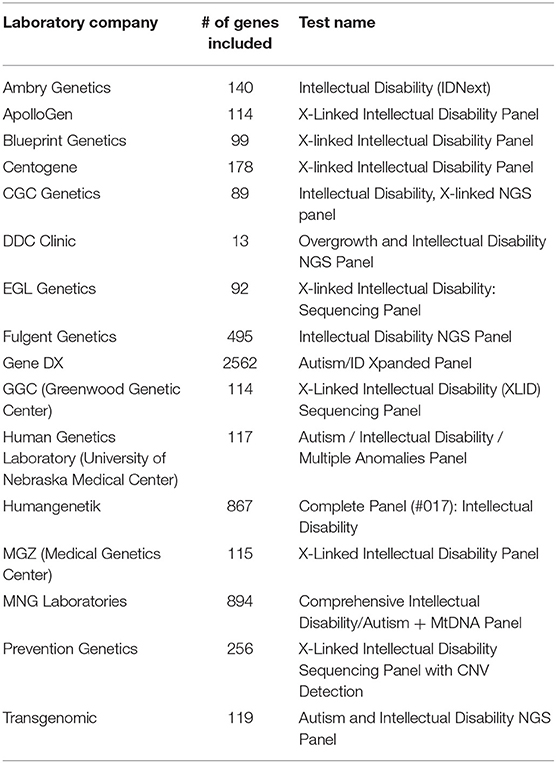
As result, a number of NGS-based clinical testing panels have been developed and are available as NGS-based Laboratory Developed Tests (LDTs) for a set of neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Fragile X syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, and Angelman syndrome. These panels are useful to target a limited number of well-demonstrated causative genes involved in these disorders. However, for many psychiatric disorders with complex genetic basis, the number of genes involved is very large and the degree of confidence of the implication of these genes in disorders is in constant re-evaluation. Currently, most of available commercial genetic testing panels are for two types of complex psychiatric diseases: autism and intellectual disability. Hoang et al. (2018) has performed a comprehensive survey in the clinical sequencing panel test for ASD and found a significant heterogeneity among different laboratories with respect to the tests they offer. Their most striking finding was the number of tested genes on panels used for ASD vary from 11 to 2,562, with little overlap. Here, we performed a similar comparison on NGS-based clinical testing panel used for ID/DD and looked at the number of genes included in panels. We also found a large difference between different panels and included genes can range from 13 to 2,562 (Table 2), which is not surprised since the genetic predisposition may be different in almost every individual in these complex psychiatric disorders due to their heterogeneous nature. This shows that it is still a challenging task to reach consensus gene lists for testing panels in complex psychiatric disorders currently; and indicates that WES might be a better alternative for genetic testing when casual variants are not known since it targets all coding regions of the genome without biases in the gene pre-selection. Thus, targeted gene panels would be ideal for analyzing specific mutations or genes that have suspected associations with disease, while WES could be a better choice when one is uncertain what genes need to be tested.
It is worth mentioning that WGS starts to show its advantage over WES, such as providing a more uniformed coverage, able to identify more variants covering both coding, and non-coding regions of the genome (Wilfert et al., 2017). It is important to extend the interrogation to non-coding variants as these represent the majority of DNMs per genome. A relevant role in neurodevelopmental disorders of these regions such as the non-coding RNAs has already been established (Wanke et al., 2018). Although the current sequencing cost of WGS is still at least three times higher than WES per sample using NovaSeq technology as of January 2019 (Supplementary Table 4; https://genohub.com/), the implementation of WGS has the potential to ultimately replace WES both in research and clinical settings with a decreasing cost in whole genome sequencing and a rapid maturation of its analytical platforms.
Translation of WES for Diagnostic of Neuropsychiatric Disorders From Research to Clinical Practice
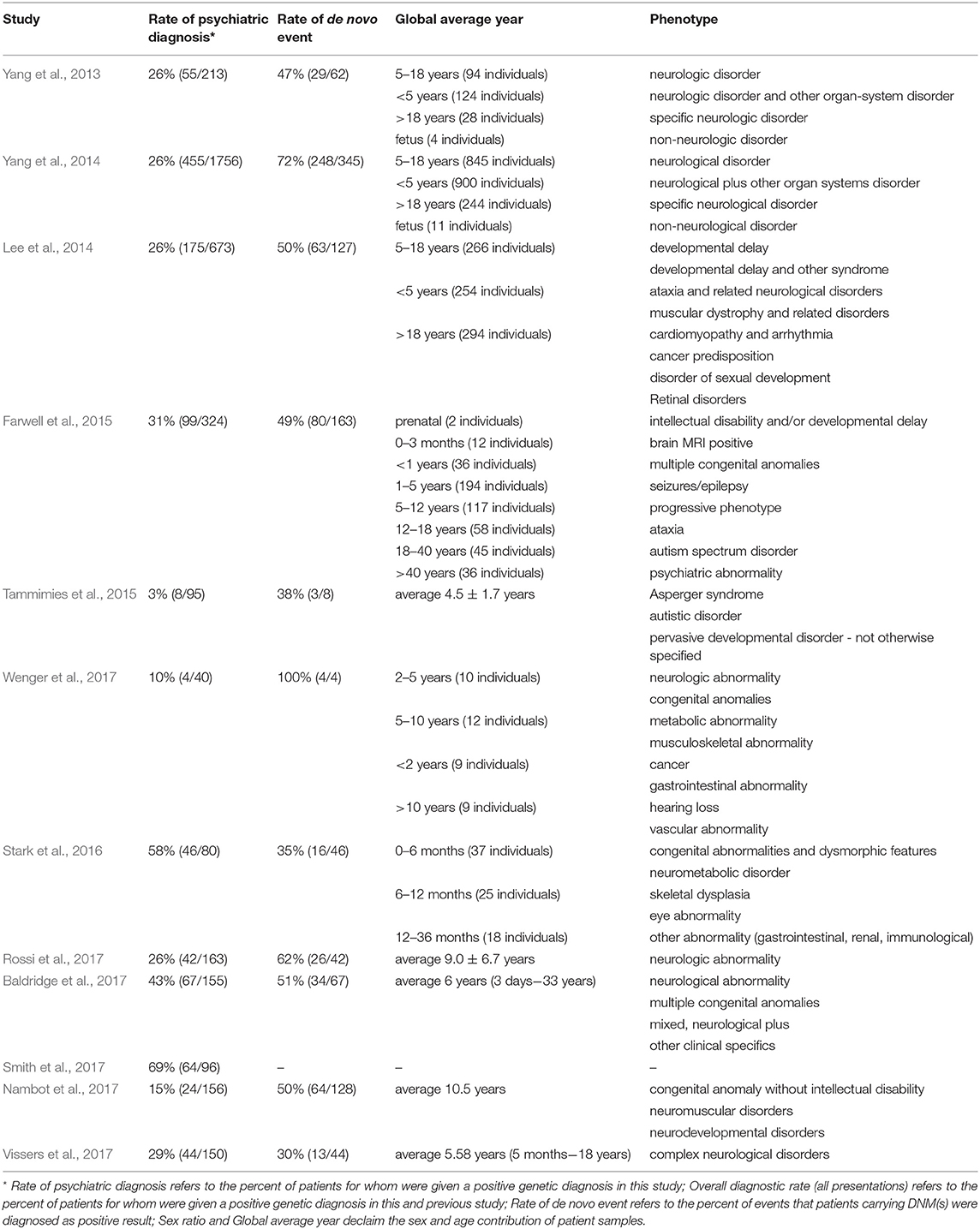
As described above, an alternative strategy is needed that could take advantage of the recent advance of large-scale sequencing techniques and yield faster and higher diagnostic rates. The unbiased nature of WES can reduce the impact of disease variability on genetic testing strategies by equally weighing all genes and making assessments for all identified variants simultaneously in one clinical context (Shashi et al., 2014; Lencz and Malhotra, 2015). Hence, the true exonic phenotypic variability of genetic disorders can be assessed by WES. There are cases in the literature of pathogenic variants identified in patients that would never have been considered for a genetic testing based on their phenotypes (Fogel et al., 2014; Guerreiro et al., 2014; Lu et al., 2014). This also underlines a vital role for clinical input in bioinformatics analysis when estimating the likely contributions of new genetic variations in disorders of a particular patient. Several large studies have already demonstrated a diagnostic yield of 25–45% for clinical WES (Dixon-Salazar et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2013, 2014; Lee et al., 2014; Stark et al., 2016). Moreover, Stark et al. (2016) found that singleton WES as a first-tier screening method, outperforms the standard care in infants with suspected Mendelian disorders (57.5 vs. 13.75% diagnosis rate).
Several large diagnostic sequencing laboratories/institutions, such as Ambry Genetics Laboratory (Rossi et al., 2017), have published studies on the efficacy of diagnosis in patients with suspected genetic disorders using the exome sequencing. They have shown particularly effective diagnosis rates in patients with neuropsychiatric or neurodevelopmental diseases based on Mendelian traits, as shown in Table 3. For instance, in the field of psychiatric disorders of early onsets, such as ASD, the genetic diagnostic yield was almost doubled when WES was used in addition to chromosomal microarrays (Tammimies et al., 2015; Rossi et al., 2017). The implementation of WES in the field of rare pediatric disorders has already shown encouraging success rates, 28–40% when proband-only or trio WES were considered (Wright et al., 2018). Moreover, a pediatric neurology study obtained a higher rate of conclusive diagnoses not exceeding the economic cost supporting the usage of WES as the first-tier diagnostic test (Vissers et al., 2017). Overall, the promising results regarding time and diagnostic rates from these psychiatric studies are genuinely encouraging.
Challenges of NGS Application in NDP Disorders Clinical Diagnosis
The step toward the implementation of NGS technologies in large-scale clinical practice is still limited and variable across countries. The evaluation of the cost-effectiveness and management of these test remains extremely difficult (Payne et al., 2018). The application of WES in clinical practice as a diagnostic tool for neuropsychiatric disorders is challenging, overall. It is well-known that NDP disorders have strong genetic components (Gandal et al., 2016), hold a high degree of genetic and clinical heterogeneity, and present with variable expressivity and penetrance. Also, it has been demonstrated that diverse NDP disorders share genetic etiology (Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium et al., 2013). Hence, using WES is a promising approach to elucidate the genetic causes of NDP disorders, however, multiple concerns remain to be addressed.
A major concern for WES, in general, is the interpretation of the results. The first challenge is how to elucidate the pathogenic effects of the identified variant(s). Multiple prediction tools and algorithms have been developed (section Interpreting Rare Genetic Variants From Exome Studies), but no gold standard interpretation guide could undoubtedly explain the causality or benignity of variants. Enormous databases of large populations' sequencing data are available, such as 1000 Genome Project (Gibbs et al., 2015) or ExAC (Lek et al., 2016), to filter out variants that are common in the population and to rank the mutation tolerance of genes. However, large datasets of multiple populations still need to be compiled. The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) published guidelines that have helped to manage clinical molecular genetic cases (Richards et al., 2015; Nykamp et al., 2017; Strovel et al., 2017). In particular, recommendations on reporting incidental findings are essential in the clinical application of global genomic approaches.
Our current knowledge of NDP disorders' biological mechanisms is still limited, and the contribution of the majority of the genes in the genome to these phenotypes remains unclear. Some disease-related gene databases as ASD genes database SFARI (Abrahams et al., 2013) have introduced a scoring parameter that ranks from high confidence to hypothesized but untested, which is extremely useful to evaluate the association of a variant within these genes to the neuropsychiatric phenotype. Besides, the contributing effect of susceptibility or modifier genes remains to be systematically quantified. Therefore, advancements in knowledge moving toward these types of gene and disease potential associations will be an excellent way to help the variant classification.
WES per se presents some technical limitations. For example, WES has a low efficiency in detecting microsatellite expansions, which nowadays, can only be overcome using alternative techniques such as PCR or Southern blot. WES also presents a limited power to detect small CNVs and mosaic events, which require a much deeper read coverage than the regular clinical WES. Another limitation in neuropsychiatric disorders is the types of tissues studies, as brain tissues from the living individuals are not possible to obtain, the detection of brain-specific mosaic events particular to these tissues would be missed. Therefore, the complete picture of the genomic alterations of neuropsychiatric disorders will be difficult to achieve.
Elucidating the complex nature of the underlying genetics of neuropsychiatric disorders will ultimately require sophisticated mathematical models that include a large number of parameters extracted from genomic, phenotypic information, pharmacogenomics interactions, and environmental factors, among others. These complex approaches will only be reached when systematic high throughput multi-omic studies are applied to each patient, and consensus annotation terms and pipelines are used (precision medicine). Compared to difficulty in characterizing the underlying genetics of neuropsychiatric disorders, some efforts toward regulating the phenotypic terms encountered in human diseases have been made. Human Phenotype Ontology (Köhler et al., 2017) initiative and gene-associated phenotypes database as Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man® (OMIM®) are still struggling to build a standardized vocabulary of phenotypic abnormalities and its likely genetic causes. Furthermore, recently developed platforms of phenotype-genotype relationship sharing, by The Matchmaker Exchange (Philippakis et al., 2015), are already connecting worldwide clinicians and researchers with the aim to link clinical and genetic information and to identify novel genes causative of rare disease phenotypes.
Finally, the extended consequences of reaching a genetic diagnosis in neuropsychiatric disorders are especially relevant for family members and caretakers. Besides a better selection of therapeutic strategies, more accurate prognosis, appropriate support, and surveillance, risk estimation and counseling are essential for the future familial organization and reproductive planning not only for parents but also for other siblings. The application of WES requires multidisciplinary teams with a core of medical geneticist and genetic counselors who will help patients to understand the overwhelming information derived from these complex tests and ensure they make informed decisions (Paneque et al., 2017).
Limitation of the Current Review
We acknowledge that there are many areas of WES in neuropsychiatric disorders that were not deeply addressed within this review, such as certain statistical parameters like effect size, and comparison between different statistical methods used by different tools, since they could not be easily summarized and compared, as not all studies used the same criteria. In writing this review, we relied primarily on the DNM data from denovo-db (Turner et al., 2017), which collects DNMs from large cohort studies from the past 10 years and might be missing data from some small cohort studies. In addition, the impact of DNMs in disease etiology might vary in different disorders, it exerts a large contribution for ASD and ID/DD and have smaller contributions from other disorders, such as BD and OCD, which might be because of a lack of studies or data. Therefore, how the exome case-control study might be used as a complementary strategy to the trio-based study for those disorders can be an excellent topic for a future review.
The current review is intended to serve as a broad summary, analysis, and application of neurodevelopmental and psychiatric DNVs from WES. We believe that future studies and reviews that approach genomic variants from a different angle with different NGS technologies, such as WGS or by focusing on the finer statistical details, even going so far as to scrutinize clinical data from individuals, and to link them to the variants for the interpretation, would lead to interesting and important findings.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Despite many complications and challenges associated with NDP disorders, increasing implications of de novo event's contribute to the disease etiology, together with downstream functional analyses to explore the disrupted biological process by these de novo events, indicate the advent of the application of WES in potential treatments. Moreover, a large number of ASD drugs currently in the pipeline (Sung et al., 2014) keeps us optimistic about the future. The application of WES in clinical practice has the potential to generate an extraordinarily large dataset for multiple disorders. Obtaining large cohorts in research studies, particularly for rare neuropsychiatric diseases, is very difficult or even impossible. As a consequence, it is imperative that clinicians and researchers find a comprehensive protocol to share the genetic information and perform powerful genetic and genomic studies of diseases, always under strict data sharing protocols preserving patients' confidentiality. In the foreseeable future, we will see the development of well-established and tested systematic computational pipelines to integrate genetic and genomic data with expression, interaction and other data that will ultimately facilitate the implementation of NGS into the clinical practice.
Author Contributions
GL designed the concept. GL and WW researched the data. GL, WW, and RC all contributed to the content discussion, writing, and editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0909200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81671328), the Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning (No. 1610000043) and the Innovation Research Plan supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (ZXWF082101).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2019.00258/full#supplementary-material
References
Abrahams, B. S., Arking, D. E., Campbell, D. B., Mefford, H. C., Morrow, E. M., Weiss, L. A., et al. (2013). SFARI Gene 2.0: a community-driven knowledgebase for the autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Mol. Autism 4:36. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-4-36
Adzhubei, I. A., Schmidt, S., Peshkin, L., Ramensky, V. E., Gerasimova, A., Bork, P., et al. (2010). A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 7, 248–249. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0410-248
Alipanahi, B., Delong, A., Weirauch, M. T., and Frey, B. J. (2015). Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA- and RNA-binding proteins by deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 831–838. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3300
Amar, D., Safer, H., and Shamir, R. (2013). Dissection of regulatory networks that are altered in disease via differential co-expression. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9:e1002955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002955
Antaki, D., Brandler, W. M., and Sebat, J. (2018). SV2: accurate structural variation genotyping and de novo mutation detection from whole genomes. Bioinformatics 34, 1774–1777. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx813
Appenzeller, S., Balling, R., Barisic, N., Baulac, S., Caglayan, H., Craiu, D., et al. (2014). De novo mutations in synaptic transmission genes including DNM1 cause epileptic encephalopathies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 95, 360–370. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.08.013
Ashburner, M., Ball, C. A., Blake, J. A., Botstein, D., Butler, H., Cherry, J. M., et al. (2000). Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 25, 25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556
Bainbridge, M. N., Wiszniewski, W., Murdock, D. R., Friedman, J., Gonzaga-Jauregui, C., Newsham, I., et al. (2011). Whole-Genome sequencing for optimized patient management. Sci. Transl. Med. 3:87re3. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002243
Baldridge, D., Heeley, J., Vineyard, M., Manwaring, L., Toler, T. L., Fassi, E., et al. (2017). The exome clinic and the role of medical genetics expertise in the interpretation of exome sequencing results. Genet. Med. 19, 1040–1048. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.224
Bamshad, M. J., Ng, S. B., Bigham, A. W., Tabor, H. K., Emond, M. J., Nickerson, D. A., et al. (2011). Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 745–755. doi: 10.1038/nrg3031
Barcia, G., Fleming, M. R., Deligniere, A., Gazula, V.-R., Brown, M. R., Langouet, M., et al. (2012). De novo gain-of-function KCNT1 channel mutations cause malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy. Nat. Genet. 44, 1255–1259. doi: 10.1038/ng.2441
Battaglia, A., Bianchini, E., and Carey, J. C. (1999). Diagnostic yield of the comprehensive assessment of developmental delay/mental retardation in an institute of child neuropsychiatry. Am. J. Med. Genet. 82, 60–66. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19990101)82:1<60::AID-AJMG12>3.0.CO;2-4
Battaglia, A., and Carey, J. C. (2003). Diagnostic evaluation of developmental delay/mental retardation: an overview. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 117, 3–14. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.10015
Bergholdt, R., Størling, Z. M., Lage, K., Karlberg, E. O., Ólason, P. Í., Aalund, M., et al. (2007). Integrative analysis for finding genes and networks involved in diabetes and other complex diseases. Genome Biol. 8:R253. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r253
Betancur, C. (2011). Etiological heterogeneity in autism spectrum disorders: more than 100 genetic and genomic disorders and still counting. Brain Res. 1380, 42–77. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.11.078
Blair, D. R., Lyttle, C. S., Mortensen, J. M., Bearden, C. F., Jensen, A. B., Khiabanian, H., et al. (2013). A nondegenerate code of deleterious variants in mendelian loci contributes to complex disease risk. Cell 155, 70–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.030
Boycott, K. M., Vanstone, M. R., Bulman, D. E., and MacKenzie, A. E. (2013). Rare-disease genetics in the era of next-generation sequencing: discovery to translation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 681–691. doi: 10.1038/nrg3555
Brandler, W. M., Antaki, D., Gujral, M., Kleiber, M. L., Whitney, J., Maile, M. S., et al. (2018). Paternally inherited cis-regulatory structural variants are associated with autism. Science 360, 327–331. doi: 10.1126/science.aan.2261
Cappi, C., Brentani, H., Lima, L., Sanders, S. J., Zai, G., Diniz, B. J., et al. (2016). Whole-exome sequencing in obsessive-compulsive disorder identifies rare mutations in immunological and neurodevelopmental pathways. Transl. Psychiatry 6:e764. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.30
Carter, H., Douville, C., Stenson, P. D., Cooper, D. N., and Karchin, R. (2013a). Identifying mendelian disease genes with the variant effect scoring tool. BMC Genomics 14:S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S3-S3
Carter, H., Hofree, M., and Ideker, T. (2013b). Genotype to phenotype via network analysis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 23, 611–621. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.10.003
Challman, T. D., Barbaresi, W. J., Katusic, S. K., and Weaver, A. (2003). The yield of the medical evaluation of children with pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 33, 187–192. doi: 10.1023/A:1022995611730
Chen, J., Calhoun, V. D., Perrone-Bizzozero, N. I., Pearlson, G. D., Sui, J., Du, Y., et al. (2016). A pilot study on commonality and specificity of copy number variants in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 6:e824. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.96
Chen, R., Davis, L. K., Guter, S., Wei, Q., Jacob, S., Potter, M. H., et al. (2017). Leveraging blood serotonin as an endophenotype to identify de novo and rare variants involved in autism. Mol. Autism 8:14. doi: 10.1186/s13229-017-0130-3
Cline, M. S., Smoot, M., Cerami, E., Kuchinsky, A., Landys, N., Workman, C., et al. (2007). Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using cytoscape. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2366–2382. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.324
Collins, A. L., and Sullivan, P. F. (2013). Genome-wide association studies in psychiatry: what have we learned? Br. J. Psychiatry 202, 1–4. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.112.117002
Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, Lee, S. H., Ripke, S., Neale, B. M., Faraone, S. V., Purcell, S. M., et al. (2013). Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nat. Genet. 45, 984–994. doi: 10.1038/ng.2711
Crow, J. F. (2000). The origins, patterns and implications of human spontaneous mutation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 1, 40–47. doi: 10.1038/35049558
Daguenet, E., Dujardin, G., and Valcárcel, J. (2015). The pathogenicity of splicing defects: mechanistic insights into pre-mRNA processing inform novel therapeutic approaches. EMBO Rep. 16, 1640–1655. doi: 10.15252/embr.201541116
Davydov, E. V., Goode, D. L., Sirota, M., Cooper, G. M., Sidow, A., and Batzoglou, S. (2010). Identifying a high fraction of the human genome to be under selective constraint using GERP++. PLoS Comput. Biol. 6:e1001025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001025
De Boulle, K., Verkerk, A. J. M. H., Reyniers, E., Vits, L., Hendrickx, J., Van Roy, B., et al. (1993). A point mutation in the FMR-1 gene associated with fragile X mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 3, 31–35. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-31
De Hert, M., Steemans, D., Theys, P., Fryns, J.-P., and Peuskens, J. (1996). Lujan-Fryns syndrome in the differential diagnosis of schizophrenia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 67, 212–214. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960409)67:2<212::AID-AJMG13>3.0.CO;2-M
de Ligt, J., Willemsen, M. H., van Bon, B. W., Kleefstra, T., Yntema, H. G., Kroes, T., et al. (2012). Diagnostic exome sequencing in persons with severe intellectual disability. N. Engl. J. Med. 20367, 1921–1929. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1206524
De Rubeis, S., He, X., Goldberg, A. P., Poultney, C. S., Samocha, K., Ercument Cicek, A., et al. (2014). Synaptic, transcriptional and chromatin genes disrupted in autism. Nature 515, 209–215. doi: 10.1038/nature13772
Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study., McRae, J. F., Clayton, S., Fitzgerald, T. W., Kaplanis, J., Prigmore, E., et al. (2017). Prevalence and architecture of de novo mutations in developmental disorders. Nature 542, 433–438. doi: 10.1038/nature21062
Desmet, F.-O., Hamroun, D., Lalande, M., Collod-Béroud, G., Claustres, M., and Béroud, C. (2009). Human splicing finder: an online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:e67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp215
Dixon-Salazar, T. J., Silhavy, J. L., Udpa, N., Schroth, J., Bielas, S., Schaffer, A. E., et al. (2012). Exome sequencing can improve diagnosis and alter patient management. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:138ra78. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003544
Dong, C., Wei, P., Jian, X., Gibbs, R., Boerwinkle, E., Wang, K., et al. (2015). Comparison and integration of deleteriousness prediction methods for nonsynonymous SNVs in whole exome sequencing studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 2125–2137. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu733
Epi4k Consortium, E., Allen, A. S., Berkovic, S. F., Cossette, P., Delanty, N., Dlugos, D., et al. (2013). De novo mutations in epileptic encephalopathies. Nature 501, 217–221. doi: 10.1038/nature12439
Faraone, S. V., Biederman, J., and Wozniak, J. (2012). Examining the comorbidity between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and bipolar I disorder: a meta-analysis of family genetic studies. Am. J. Psychiatry 169, 1256–1266. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12010087
Farwell, K. D., Shahmirzadi, L., El-Khechen, D., Powis, Z., Chao, E. C., Tippin Davis, B., et al. (2015). Enhanced utility of family-centered diagnostic exome sequencing with inheritance model–based analysis: results from 500 unselected families with undiagnosed genetic conditions. Genet. Med. 17, 578–586. doi: 10.1038/gim.2014.154
Fogel, B. L., Lee, H., Deignan, J. L., Strom, S. P., Kantarci, S., Wang, X., et al. (2014). Exome sequencing in the clinical diagnosis of sporadic or familial cerebellar ataxia. JAMA Neurol. 71, 1237–1246. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1944
Fokkema, I. F. A. C., Taschner, P. E. M., Schaafsma, G. C. P., Celli, J., Laros, J. F. J., and den Dunnen, J. T. (2011). LOVD v.2.0: the next generation in gene variant databases. Hum. Mutat. 32, 557–563. doi: 10.1002/humu.21438
Francioli, L. C., Menelaou, A., Pulit, S. L., van Dijk, F., Palamara, P. F., Elbers, C. C., et al. (2014). Whole-genome sequence variation, population structure and demographic history of the Dutch population. Nat. Genet. 46, 818–825. doi: 10.1038/ng.3021
Fromer, M., Pocklington, A. J., Kavanagh, D. H., Williams, H. J., Dwyer, S., Gormley, P., et al. (2014). De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nature 506, 179–184. doi: 10.1038/nature12929
Furlong, L. I. (2013). Human diseases through the lens of network biology. Trends Genet. 29, 150–159. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2012.11.004
Gandal, M. J., Haney, J. R., Parikshak, N. N., Leppa, V., Ramaswami, G., Hartl, C., et al. (2018). Shared molecular neuropathology across major psychiatric disorders parallels polygenic overlap. Science 359, 693–697. doi: 10.1126/science.aad6469
Gandal, M. J., Leppa, V., Won, H., Parikshak, N. N., and Geschwind, D. H. (2016). The road to precision psychiatry: translating genetics into disease mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1397–1407. doi: 10.1038/nn.4409
Genovese, G., Fromer, M., Stahl, E. A., Ruderfer, D. M., Chambert, K., Landén, M., et al. (2016). Increased burden of ultra-rare protein-altering variants among 4,877 individuals with schizophrenia. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1433–1441. doi: 10.1038/nn.4402
Geschwind, D. H., and Konopka, G. (2009). Neuroscience in the era of functional genomics and systems biology. Nature 461, 908–915. doi: 10.1038/nature08537
Gibbs, R. A., Boerwinkle, E., Doddapaneni, H., Han, Y., Korchina, V., Kovar, C., et al. (2015). A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526, 68–74. doi: 10.1038/nature15393
Gilissen, C., Hehir-Kwa, J. Y., Thung, D. T., van de Vorst, M., van Bon, B. W. M., Willemsen, M. H., et al. (2014). Genome sequencing identifies major causes of severe intellectual disability. Nature 511, 344–347. doi: 10.1038/nature13394
Gilman, S. R., Chang, J., Xu, B., Bawa, T. S., Gogos, J. A., Karayiorgou, M., et al. (2012). Diverse types of genetic variation converge on functional gene networks involved in schizophrenia. Nat. Neurosci. 15, 1723–1728. doi: 10.1038/nn.3261
Girard, S. L., Gauthier, J., Noreau, A., Xiong, L., Zhou, S., Jouan, L., et al. (2011). Increased exonic de novo mutation rate in individuals with schizophrenia. Nat. Genet. 43, 860–863. doi: 10.1038/ng.886
Girirajan, S., Campbell, C. D., and Eichler, E. E. (2011). Human copy number variation and complex genetic disease. Annu. Rev. Genet. 45, 203–226. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-102209-163544
Gnad, F., Baucom, A., Mukhyala, K., Manning, G., and Zhang, Z. (2013). Assessment of computational methods for predicting the effects of missense mutations in human cancers. BMC Genomics 14 (Suppl. 3):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S3-S7
Goes, F. S., Pirooznia, M., Parla, J. S., Kramer, M., Ghiban, E., Mavruk, S., et al. (2016). Exome sequencing of familial bipolar disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 73, 590–597. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.0251
Goldstein, D. B., Allen, A., Keebler, J., Margulies, E. H., Petrou, S., Petrovski, S., et al. (2013). Sequencing studies in human genetics: design and interpretation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 460–470. doi: 10.1038/nrg3455
Gratten, J., Visscher, P. M., Mowry, B. J., and Wray, N. R. (2013). Interpreting the role of de novo protein-coding mutations in neuropsychiatric disease. Nat. Genet. 45, 234–238. doi: 10.1038/ng.2555
Gratten, J., Wray, N. R., Keller, M. C., and Visscher, P. M. (2014). Large-scale genomics unveils the genetic architecture of psychiatric disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 782–790. doi: 10.1038/nn.3708
Grimm, D. G., Azencott, C.-A., Aicheler, F., Gieraths, U., MacArthur, D. G., Samocha, K. E., et al. (2015). The evaluation of tools used to predict the impact of missense variants is hindered by two types of circularity. Hum. Mutat. 36, 513–523. doi: 10.1002/humu.22768
Guerreiro, R., Bras, J., Hardy, J., and Singleton, A. (2014). Next generation sequencing techniques in neurological diseases: redefining clinical and molecular associations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23, R47–R53. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu203
Guipponi, M., Santoni, F. A., Setola, V., Gehrig, C., Rotharmel, M., Cuenca, M., et al. (2014). Exome sequencing in 53 sporadic cases of schizophrenia identifies 18 putative candidate genes. PLoS ONE 9:e112745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112745
Gulsuner, S., Walsh, T., Watts, A. C., Lee, M. K., Thornton, A. M., Casadei, S., et al. (2013). Spatial and temporal mapping of de novo mutations in schizophrenia to a fetal prefrontal cortical network. Cell 154, 518–529. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.049
Gupta, S., Ellis, S. E., Ashar, F. N., Moes, A., Bader, J. S., Zhan, J., et al. (2014). Transcriptome analysis reveals dysregulation of innate immune response genes and neuronal activity-dependent genes in autism. Nat. Commun. 5:5748. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6748
Halvardson, J., Zhao, J. J., Zaghlool, A., Wentzel, C., Georgii-Hemming, P., Månsson, E., et al. (2016). Mutations in HECW2 are associated with intellectual disability and epilepsy. J. Med. Genet. 53, 697–704. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103814
Hamdan, F. F., Myers, C. T., Cossette, P., Lemay, P., Spiegelman, D., Laporte, A. D., et al. (2017). High rate of recurrent de novo mutations in developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 101, 664–685. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.09.008
Hamdan, F. F., Srour, M., Capo-Chichi, J.-M., Daoud, H., Nassif, C., Patry, L., et al. (2014). De novo mutations in moderate or severe intellectual disability. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004772. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004772
Hashimoto, R., Nakazawa, T., Tsurusaki, Y., Yasuda, Y., Nagayasu, K., Matsumura, K., et al. (2016). Whole-exome sequencing and neurite outgrowth analysis in autism spectrum disorder. J. Hum. Genet. 61, 199–206. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2015.141
He, X., Sanders, S. J., Liu, L., De Rubeis, S., Lim, E. T., Sutcliffe, J. S., et al. (2013). Integrated model of de novo and inherited genetic variants yields greater power to identify risk genes. PLoS Genet. 9:e1003671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003671
Helbig, K. L., Farwell Hagman, K. D., Shinde, D. N., Mroske, C., Powis, Z., Li, S., et al. (2016). Diagnostic exome sequencing provides a molecular diagnosis for a significant proportion of patients with epilepsy. Genet. Med. 18, 898–905. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.186
Hirschtritt, M. E., Darrow, S. M., Illmann, C., Osiecki, L., Grados, M., Sandor, P., et al. (2018). Genetic and phenotypic overlap of specific obsessive-compulsive and attention-deficit/hyperactive subtypes with Tourette syndrome. Psychol. Med. 48, 279–293. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717001672
Hoang, N., Buchanan, J. A., and Scherer, S. W. (2018). Heterogeneity in clinical sequencing tests marketed for autism spectrum disorders. NPJ Genomic Med. 3:27. doi: 10.1038/s41525-018-0066-3
Horwitz, T., Lam, K., Chen, Y., Xia, Y., and Liu, C. (2018). A decade in psychiatric GWAS research. Mol. Psychiatry 24, 378–389. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0055-z
Hou, L., Bergen, S. E., Akula, N., Song, J., Hultman, C. M., Landén, M., et al. (2016). Genome-wide association study of 40,000 individuals identifies two novel loci associated with bipolar disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 25, 3383–3394. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw181
Huang, Y.-F., Gulko, B., and Siepel, A. (2017). Fast, scalable prediction of deleterious noncoding variants from functional and population genomic data. Nat. Genet. 49, 618–624. doi: 10.1038/ng.3810
Ikeda, M., Takahashi, A., Kamatani, Y., Okahisa, Y., Kunugi, H., Mori, N., et al. (2018). A genome-wide association study identifies two novel susceptibility loci and trans population polygenicity associated with bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 23, 639–647. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.259
Inoue, K., and Lupski, J. R. (2003). Genetics and genomics of behavioral and psychiatric disorders. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13, 303–309. doi: 10.1016/S0959-437X(03)00057-1
Ioannidis, N. M., Rothstein, J. H., Pejaver, V., Middha, S., McDonnell, S. K., Baheti, S., et al. (2016). REVEL: an ensemble method for predicting the pathogenicity of rare missense variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 99, 877–885. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.08.016
Ionita-Laza, I., Mccallum, K., Xu, B., and Buxbaum, J. (2016). A spectral approach integrating functional genomic annotations for coding and noncoding variants HHS public access. Nat. Genet. 48, 214–220. doi: 10.1038/ng.3477
Iossifov, I., O'Roak, B. J., Sanders, S. J., Ronemus, M., Krumm, N., Levy, D., et al. (2014). The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 515, 216–221. doi: 10.1038/nature13908
Iossifov, I., Ronemus, M., Levy, D., Wang, Z., Hakker, I., Rosenbaum, J., et al. (2012). De novo gene disruptions in children on the autistic spectrum. Neuron 74, 285–299. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.009
Jian, X., Boerwinkle, E., and Liu, X. (2014). In silico tools for splicing defect prediction: a survey from the viewpoint of end users. Genet. Med. 16, 497–503. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.176
Jiang, Y., Li, Z., Liu, Z., Chen, D., Wu, W., Du, Y., et al. (2017). mirDNMR: a gene-centered database of background de novo mutation rates in human. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D796–D803. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1044
Jiang, Y., Yuen, R. K. C., Jin, X., Wang, M., Chen, N., Wu, X., et al. (2013). Detection of clinically relevant genetic variants in autism spectrum disorder by whole-genome sequencing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 93, 249–263. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.06.012
Jones, W., Alasoo, K., Fishman, D., and Parts, L. (2017). Computational biology: deep learning. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 1, 257–274. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20160025
Kanehisa, M., and Goto, S. (2000). KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kataoka, M., Matoba, N., Sawada, T., Kazuno, A.-A., Ishiwata, M., Fujii, K., et al. (2016). Exome sequencing for bipolar disorder points to roles of de novo loss-of-function and protein-altering mutations. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 885–893. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.69
Kim, D. S., Burt, A. A., Ranchalis, J. E., Wilmot, B., Smith, J. D., Patterson, K. E., et al. (2017). Sequencing of sporadic Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) identifies novel and potentially pathogenic de novo variants and excludes overlap with genes associated with autism spectrum disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 174, 381–389. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32527
Kingsmore, S. F., Saunders, C. J., Miller, N. A., Hateley, S. L., Ganusova, E. E., Mudge, J., et al. (2011). Deep sequencing of patient genomes for disease diagnosis: when will it become routine? Sci. Transl. Med. 3:87ps23. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002695
Kircher, M., Witten, D. M., Jain, P., O'Roak, B. J., Cooper, G. M., and Shendure, J. (2014). A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 46, 310–315. doi: 10.1038/ng.2892
Kohler, K., and Bickeboller, H. (2006). Case-Control association tests correcting for population stratification. Ann. Hum. Genet. 70, 98–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00214.x
Köhler, S., Vasilevsky, N. A., Engelstad, M., Foster, E., McMurry, J., Aymé, S., et al. (2017). The human phenotype ontology in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D865–D876. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1039
Kong, A., Frigge, M. L., Masson, G., Besenbacher, S., Sulem, P., Magnusson, G., et al. (2012). Rate of de novo mutations and the importance of father's age to disease risk. Nature 488, 471–475. doi: 10.1038/nature11396
Kranz, T. M., Harroch, S., Manor, O., Lichtenberg, P., Friedlander, Y., Seandel, M., et al. (2015). De novo mutations from sporadic schizophrenia cases highlight important signaling genes in an independent sample. Schizophr. Res. 166, 119–124. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2015.05.042
Krawczak, M., Thomas, N. S. T., Hundrieser, B., Mort, M., Wittig, M., Hampe, J., et al. (2007). Single base-pair substitutions in exon-intron junctions of human genes: nature, distribution, and consequences for mRNA splicing. Hum. Mutat. 28, 150–158. doi: 10.1002/humu.20400
Krumm, N., Turner, T. N., Baker, C., Vives, L., Mohajeri, K., Witherspoon, K., et al. (2015). Excess of rare, inherited truncating mutations in autism. Nat. Genet. 47, 582–588. doi: 10.1038/ng.3303
Kun-Rodrigues, C., Ganos, C., Guerreiro, R., Schneider, S. A., Schulte, C., Lesage, S., et al. (2015). A systematic screening to identify de novo mutations causing sporadic early-onset Parkinson's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 6711–6720. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv376
Lage, K., Hansen, N. T., Karlberg, E. O., Eklund, A. C., Roque, F. S., Donahoe, P. K., et al. (2008). A large-scale analysis of tissue-specific pathology and gene expression of human disease genes and complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 20870–20875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810772105
Landrum, M. J., Lee, J. M., Benson, M., Brown, G., Chao, C., Chitipiralla, S., et al. (2016). ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D862–D868. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1222
Lanoiselée, H.-M., Nicolas, G., Wallon, D., Rovelet-Lecrux, A., Lacour, M., Rousseau, S., et al. (2017). APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 mutations in early-onset Alzheimer disease: a genetic screening study of familial and sporadic cases. PLoS Med. 14:e1002270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002270
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539
Lee, H., Deignan, J. L., Dorrani, N., Strom, S. P., Kantarci, S., Quintero-Rivera, F., et al. (2014). Clinical exome sequencing for genetic identification of rare mendelian disorders. JAMA 312, 1880–1887. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.14604
Lek, M., Karczewski, K. J., Minikel, E. V., Samocha, K. E., Banks, E., Fennell, T., et al. (2016). Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 536, 285–291. doi: 10.1038/nature19057
Lelieveld, S. H., Reijnders, M. R. F., Pfundt, R., Yntema, H. G., Kamsteeg, E.-J., de Vries, P., et al. (2016). Meta-analysis of 2,104 trios provides support for 10 new genes for intellectual disability. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1194–1196. doi: 10.1038/nn.4352
Lencz, T., and Malhotra, A. K. (2015). Targeting the schizophrenia genome: a fast track strategy from GWAS to clinic. Mol. Psychiatry 20, 820–826. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.28
Li, J., Cai, T., Jiang, Y., Chen, H., He, X., Chen, C., et al. (2016). Genes with de novo mutations are shared by four neuropsychiatric disorders discovered from NPdenovo database. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 290–297. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.40
Li, J., Zhao, T., Zhang, Y., Zhang, K., Shi, L., Chen, Y., et al. (2018). Performance evaluation of pathogenicity-computation methods for missense variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, 7793–7804. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky678
Lichtenstein, P., Carlström, E., Råstam, M., Gillberg, C., and Anckarsäter, H. (2010). The genetics of autism spectrum disorders and related neuropsychiatric disorders in childhood. Am. J. Psychiatry 167, 1357–1363. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10020223
Lin, G. N., Corominas, R., Lemmens, I., Yang, X., Tavernier, J., Hill, D. E., et al. (2015). Spatiotemporal 16p11.2 protein network implicates cortical late mid-fetal brain development and KCTD13-Cul3-RhoA pathway in psychiatric diseases. Neuron 85, 742–754. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.01.010
Liu, X., Shimada, T., Otowa, T., Wu, Y.-Y., Kawamura, Y., Tochigi, M., et al. (2016a). Genome-wide association study of autism spectrum disorder in the east asian populations. Autism Res. 9, 340–349. doi: 10.1002/aur.1536
Liu, X., Wu, C., Li, C., and Boerwinkle, E. (2016b). dbNSFP v3.0: a one-stop database of functional predictions and annotations for human nonsynonymous and splice-site SNVs. Hum. Mutat. 37, 235–241. doi: 10.1002/humu.22932
Liu, X., and Wu, Y. (2018). Switch from previous major depression comorbid with CLIPPERS to mania-like episode following glucocorticosteroid therapy: a case report. Gen. Psychiatry 31:e000007. doi: 10.1136/gpsych-2018-000007
Lu, J. T., Campeau, P. M., and Lee, B. H. (2014). Genotype–Phenotype correlation — promiscuity in the era of next-generation sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 593–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1400788
MacArthur, D. G., Manolio, T. A., Dimmock, D. P., Rehm, H. L., Shendure, J., Abecasis, G. R., et al. (2014). Guidelines for investigating causality of sequence variants in human disease. Nature 508, 469–476. doi: 10.1038/nature13127
Malhotra, D., and Sebat, J. (2012). CNVs: harbingers of a rare variant revolution in psychiatric genetics. Cell 148, 1223–1241. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.039
McCarthy, S. E., Gillis, J., Kramer, M., Lihm, J., Yoon, S., Berstein, Y., et al. (2014). De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate chromatin remodeling and support a genetic overlap with autism and intellectual disability. Mol. Psychiatry 19, 652–658. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.29
McGrath, L. M., Yu, D., Marshall, C., Davis, L. K., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., Li, B., et al. (2014). Copy number variation in obsessive-compulsive disorder and tourette syndrome: a cross-disorder study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 53, 910–919. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2014.04.022
Meyer, M. J., Beltrán, J. F., Liang, S., Fragoza, R., Rumack, A., Liang, J., et al. (2018). Interactome INSIDER: a structural interactome browser for genomic studies. Nat. Methods 15, 107–114. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4540
Michaelson, J. J., Shi, Y., Gujral, M., Zheng, H., Malhotra, D., Jin, X., et al. (2012). Whole-Genome sequencing in autism identifies hot spots for de novo germline mutation. Cell 151, 1431–1442. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.019
Miller, D. T., Adam, M. P., Aradhya, S., Biesecker, L. G., Brothman, A. R., Carter, N. P., et al. (2010). Consensus statement: chromosomal microarray is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with developmental disabilities or congenital anomalies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 86, 749–764. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.04.006
Miosge, L. A., Field, M. A., Sontani, Y., Cho, V., Johnson, S., Palkova, A., et al. (2015). Comparison of predicted and actual consequences of missense mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, E5189–E5198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511585112
Mitra, K., Carvunis, A.-R., Ramesh, S. K., and Ideker, T. (2013). Integrative approaches for finding modular structure in biological networks. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 719–732. doi: 10.1038/nrg3552
Momozawa, Y., Mni, M., Nakamura, K., Coppieters, W., Almer, S., Amininejad, L., et al. (2011). Resequencing of positional candidates identifies low frequency IL23R coding variants protecting against inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Genet. 43, 43–47. doi: 10.1038/ng.733
Moog, U. (2005). The outcome of diagnostic studies on the etiology of mental retardation: considerations on the classification of the causes. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 137A, 228–231. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30841
Mort, M., Sterne-Weiler, T., Li, B., Ball, E. V., Cooper, D. N., Radivojac, P., et al. (2014). MutPred splice: machine learning-based prediction of exonic variants that disrupt splicing. Genome Biol. 15:R19. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r19
Nambot, S., Thevenon, J., Kuentz, P., Duffourd, Y., Tisserant, E., Bruel, A.-L., et al. (2017). Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of rare disorders with congenital anomalies and/or intellectual disability: substantial interest of prospective annual reanalysis. Genet. Med. 20, 645–654. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.162
Neale, B. M., Kou, Y., Liu, L., Ma'ayan, A., Samocha, K. E., Sabo, A., et al. (2012). Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 485, 242–245. doi: 10.1038/nature11011
Ng, P. C., and Henikoff, S. (2003). SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3812–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg509
Nguyen, H. T., Bryois, J., Kim, A., Dobbyn, A., Huckins, L. M., Munoz-Manchado, A. B., et al. (2017). Integrated Bayesian analysis of rare exonic variants to identify risk genes for schizophrenia and neurodevelopmental disorders. Genome Med. 9:114. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0497-y
Nishi, A., Numata, S., Tajima, A., Zhu, X., Ito, K., Saito, A., et al. (2017). De novo non-synonymous TBL1XR1 mutation alters Wnt signaling activity. Sci. Rep. 7:2887. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02792-z
Nykamp, K., Anderson, M., Powers, M., Garcia, J., Herrera, B., Ho, Y.-Y., et al. (2017). Sherloc: a comprehensive refinement of the ACMG–AMP variant classification criteria. Genet. Med. 19, 1105–1117. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.37
O'Roak, B. J., Deriziotis, P., Lee, C., Vives, L., Schwartz, J. J., Girirajan, S., et al. (2011). Exome sequencing in sporadic autism spectrum disorders identifies severe de novo mutations. Nat. Genet. 43, 585–589. doi: 10.1038/ng.835
O'Roak, B. J., Stessman, H. A., Boyle, E. A., Witherspoon, K. T., Martin, B., Lee, C., et al. (2014). Recurrent de novo mutations implicate novel genes underlying simplex autism risk. Nat. Commun. 5:5595. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6595
O'Roak, B. J., Vives, L., Fu, W., Egertson, J. D., Stanaway, I. B., Phelps, I. G., et al. (2012a). Multiplex targeted sequencing identifies recurrently mutated genes in autism spectrum disorders. Science 338, 1619–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.1227764
O'Roak, B. J., Vives, L., Girirajan, S., Karakoc, E., Krumm, N., Coe, B. P., et al. (2012b). Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature 485, 246–250. doi: 10.1038/nature10989
Paneque, M., Serra-Juhé, C., Pestoff, R., Cordier, C., Silva, J., Moldovan, R., et al. (2017). Complementarity between medical geneticists and genetic counsellors: its added value in genetic services in Europe. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 25, 918–923. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2017.76
Parikshak, N. N., Gandal, M. J., and Geschwind, D. H. (2015). Systems biology and gene networks in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 16, 441–458. doi: 10.1038/nrg3934
Parikshak, N. N., Luo, R., Zhang, A., Won, H., Lowe, J. K., Chandran, V., et al. (2013). Integrative functional genomic analyses implicate specific molecular pathways and circuits in autism. Cell 155, 1008–1021. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.031
Parikshak, N. N., Swarup, V., Belgard, T. G., Irimia, M., Ramaswami, G., Gandal, M. J., et al. (2016). Genome-wide changes in lncRNA, splicing and regional gene expression patterns in autism. Nature 540, 423–427. doi: 10.1038/nature20612
Parker, M. J., Fryer, A. E., Shears, D. J., Lachlan, K. L., McKee, S. A., Magee, A. C., et al. (2015). De novo, heterozygous, loss-of-function mutations in SYNGAP1 cause a syndromic form of intellectual disability. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 167A, 2231–2237. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37189
Pasman, J. A., Verweij, K. J. H., Gerring, Z., Stringer, S., Sanchez-Roige, S., Treur, J. L., et al. (2018). GWAS of lifetime cannabis use reveals new risk loci, genetic overlap with psychiatric traits, and a causal influence of schizophrenia. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 1161–1170. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0206-1
Payne, K., Gavan, S. P., Wright, S. J., and Thompson, A. J. (2018). Cost-effectiveness analyses of genetic and genomic diagnostic tests. Nat. Rev. Genet. 19, 235–246. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.108
Pertea, M., Lin, X., and Salzberg, S. L. (2001). GeneSplicer: a new computational method for splice site prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 1185–90. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.5.1185
Philippakis, A. A., Azzariti, D. R., Beltran, S., Brookes, A. J., Brownstein, C. A., Brudno, M., et al. (2015). The matchmaker exchange: a platform for rare disease gene discovery. Hum. Mutat. 36, 915–921. doi: 10.1002/humu.22858
Price, A. L., Zaitlen, N. A., Reich, D., and Patterson, N. (2010). New approaches to population stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 459–463. doi: 10.1038/nrg2813
Prifti, E., Zucker, J.-D., Clément, K., and Henegar, C. (2010). Interactional and functional centrality in transcriptional co-expression networks. Bioinformatics 26, 3083–3089. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq591
Pullabhatla, V., Roberts, A. L., Lewis, M. J., Mauro, D., Morris, D. L., Odhams, C. A., et al. (2018). De novo mutations implicate novel genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 27, 421–429. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx407
Rauch, A., Wieczorek, D., Graf, E., Wieland, T., Endele, S., Schwarzmayr, T., et al. (2012). Range of genetic mutations associated with severe non-syndromic sporadic intellectual disability: an exome sequencing study. Lancet 380, 1674–1682. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61480-9
Reese, M. G., Eeckman, F. H., Kulp, D., and Haussler, D. (1997). Improved splice site detection in genie. J. Comput. Biol. 4, 311–323. doi: 10.1089/cmb.1997.4.311
Richards, S., Aziz, N., Bale, S., Bick, D., Das, S., Gastier-Foster, J., et al. (2015). Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genet. Med. 17, 405–423. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30
Rommelse, N. N. J., Franke, B., Geurts, H. M., Hartman, C. A., and Buitelaar, J. K. (2010). Shared heritability of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 19, 281–295. doi: 10.1007/s00787-010-0092-x
Ronald, A., Simonoff, E., Kuntsi, J., Asherson, P., and Plomin, R. (2008). Evidence for overlapping genetic influences on autistic and ADHD behaviours in a community twin sample. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 49, 535–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01857.x
Rossi, L., El-Khechen, D., Black, M. H., Farwell Hagman, K. D., Tang, S., and Powis, Z. (2017). Outcomes of diagnostic exome sequencing in patients with diagnosed or suspected autism spectrum disorders. Pediatr. Neurol. 70, 34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2017.01.033
Rossin, E. J., Lage, K., Raychaudhuri, S., Xavier, R. J., Tatar, D., Benita, Y., et al. (2011). Proteins encoded in genomic regions associated with immune-mediated disease physically interact and suggest underlying biology. PLoS Genet. 7:e1001273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001273
Salakhutdinov, R. (2015). Learning deep generative models. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl. 2, 361–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev-statistics-010814-020120
Samocha, K. E., Robinson, E. B., Sanders, S. J., Stevens, C., Sabo, A., McGrath, L. M., et al. (2014). A framework for the interpretation of de novo mutation in human disease. Nat. Genet. 46, 944–950. doi: 10.1038/ng.3050
Sanders, S. J., He, X., Willsey, A. J., Ercan-Sencicek, A. G., Samocha, K. E., Cicek, A. E., et al. (2015). Insights into autism spectrum disorder genomic architecture and biology from 71 risk loci. Neuron 87, 1215–1233. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.016
Sanders, S. J., Murtha, M. T., Gupta, A. R., Murdoch, J. D., Raubeson, M. J., Willsey, A. J., et al. (2012). De novo mutations revealed by whole-exome sequencing are strongly associated with autism. Nature 485, 237–241. doi: 10.1038/nature10945
Sauna, Z. E., and Kimchi-Sarfaty, C. (2013). “Synonymous Mutations as a Cause of Human Genetic Disease,” in eLS (Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd). doi: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0025173
Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, Ripke, S., Neale, B. M., Corvin, A., Walters, J. T. R., et al. (2014). Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 511, 421–427. doi: 10.1038/nature13595
Schwarz, J. M., Cooper, D. N., Schuelke, M., and Seelow, D. (2014). MutationTaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 11, 361–362. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2890
Sebat, J., Lakshmi, B., Malhotra, D., Troge, J., Lese-Martin, C., Walsh, T., et al. (2007). Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism. Science 316, 445–449. doi: 10.1126/science.1138659
Shashi, V., McConkie-Rosell, A., Rosell, B., Schoch, K., Vellore, K., McDonald, M., et al. (2014). The utility of the traditional medical genetics diagnostic evaluation in the context of next-generation sequencing for undiagnosed genetic disorders. Genet. Med. 16, 176–182. doi: 10.1038/gim.2013.99
Shen, H., Zhang, L., Xu, C., Zhu, J., Chen, M., and Fang, Y. (2018). Analysis of misdiagnosis of bipolar disorder in an outpatient setting. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 30, 93–101. doi: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217080
Sherry, S. T., Ward, M. H., Kholodov, M., Baker, J., Phan, L., Smigielski, E. M., et al. (2001). dbSNP: the NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 308–311. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.308
Shihab, H. A., Rogers, M. F., Gough, J., Mort, M., Cooper, D. N., Day, I. N. M., et al. (2015). An integrative approach to predicting the functional effects of non-coding and coding sequence variation. Bioinformatics 31, 1536–1543. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv009
Shohat, S., Ben-David, E., and Shifman, S. (2017). Varying intolerance of gene pathways to mutational classes explain genetic convergence across neuropsychiatric disorders. Cell Rep. 18, 2217–2227. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.007
Short, P. J., McRae, J. F., Gallone, G., Sifrim, A., Won, H., Geschwind, D. H., et al. (2018). De novo mutations in regulatory elements in neurodevelopmental disorders. Nature 555, 611–616. doi: 10.1038/nature25983
Smedemark-Margulies, N., Brownstein, C. A., Vargas, S., Tembulkar, S. K., Towne, M. C., Shi, J., et al. (2016). A novel de novo mutation in ATP1A3 and childhood-onset schizophrenia. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2, a001008. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a001008
Smith, E. D., Radtke, K., Rossi, M., Shinde, D. N., Darabi, S., El-Khechen, D., et al. (2017). Classification of genes: standardized clinical validity assessment of gene-disease associations aids diagnostic exome analysis and reclassifications. Hum. Mutat. 38, 600–608. doi: 10.1002/humu.23183
Stankiewicz, P., and Lupski, J. R. (2010). Structural variation in the human genome and its role in disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 61, 437–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-100708-204735
Stark, Z., Tan, T. Y., Chong, B., Brett, G. R., Yap, P., Walsh, M., et al. (2016). A prospective evaluation of whole-exome sequencing as a first-tier molecular test in infants with suspected monogenic disorders. Genet. Med. 18, 1090–1096. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.1
Stenson, P. D., Mort, M., Ball, E. V., Evans, K., Hayden, M., Heywood, S., et al. (2017). The human gene mutation database: towards a comprehensive repository of inherited mutation data for medical research, genetic diagnosis and next-generation sequencing studies. Hum. Genet. 136, 665–677. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1779-6
Stessman, H. A. F., Xiong, B., Coe, B. P., Wang, T., Hoekzema, K., Fenckova, M., et al. (2017). Targeted sequencing identifies 91 neurodevelopmental-disorder risk genes with autism and developmental-disability biases. Nat. Genet. 49, 515–526. doi: 10.1038/ng.3792
Strovel, E. T., Cowan, T. M., Scott, A. I., and Wolf, B. (2017). Laboratory diagnosis of biotinidase deficiency, 2017 update: a technical standard and guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet. Med. 19:1079. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.84
Stuart, J. M., Segal, E., Koller, D., and Kim, S. K. (2003). A gene-coexpression network for global discovery of conserved genetic modules. Science 302, 249–255. doi: 10.1126/science.1087447
Sullivan, P. F. (2010). The psychiatric GWAS consortium: big science comes to psychiatry. Neuron 68, 182–186. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.10.003
Sullivan, P. F., Daly, M. J., and O'Donovan, M. (2012a). Genetic architectures of psychiatric disorders: the emerging picture and its implications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 537–551. doi: 10.1038/nrg3240
Sullivan, P. F., Magnusson, C., Reichenberg, A., Boman, M., Dalman, C., Davidson, M., et al. (2012b). Family history of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder as risk factors for autism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 69, 1099–1103. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.730
Sung, M., Chin, C. H., Lim, C. G., Liew, H. S. A., Lim, C. S., Kashala, E., et al. (2014). What's in the pipeline? Drugs in development for autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 10, 371–381. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S39516
Takata, A., Xu, B., Ionita-Laza, I., Roos, J. L., Gogos, J. A., and Karayiorgou, M. (2014). Loss-of-Function variants in schizophrenia risk and SETD1A as a candidate susceptibility gene. Neuron 82, 773–780. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.043
Tammimies, K., Marshall, C. R., Walker, S., Kaur, G., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., Lionel, A. C., et al. (2015). Molecular diagnostic yield of chromosomal microarray analysis and whole-exome sequencing in children with autism spectrum disorder. JAMA 314, 895–903. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.10078
Telenti, A., Lippert, C., Chang, P.-C., and DePristo, M. (2018). Deep learning of genomic variation and regulatory network data. Hum. Mol. Genet. 27, R63–R71. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy115
Teslovich, T. M., Musunuru, K., Smith, A. V., Edmondson, A. C., Stylianou, I. M., Koseki, M., et al. (2010). Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 466, 707–713. doi: 10.1038/nature09270
The Autism Spectrum Disorders Working Group of The Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (2017). Meta-analysis of GWAS of over 16,000 individuals with autism spectrum disorder highlights a novel locus at 10q24.32 and a significant overlap with schizophrenia. Mol. Autism 8:21. doi: 10.1186/s13229-017-0137-9
Tlemsani, C., Luscan, A., Leulliot, N., Bieth, E., Afenjar, A., Baujat, G., et al. (2016). SETD2 and DNMT3A screen in the Sotos-like syndrome French cohort. J. Med. Genet. 53, 743–751. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103638
Trampush, J. W., Yang, M. L. Z., Yu, J., Knowles, E., Davies, G., Liewald, D. C., et al. (2017). GWAS meta-analysis reveals novel loci and genetic correlates for general cognitive function: a report from the COGENT consortium. Mol. Psychiatry 22, 336–345. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.244
Trost, B., Walker, S., Wang, Z., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., MacDonald, J. R., Sung, W. W. L., et al. (2018). A Comprehensive workflow for read depth-based identification of copy-number variation from whole-genome sequence data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 102, 142–155. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.12.007
Turner, T. N., Hormozdiari, F., Duyzend, M. H., McClymont, S. A., Hook, P. W., Iossifov, I., et al. (2016). Genome sequencing of autism-affected families reveals disruption of putative noncoding regulatory DNA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 98, 58–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.023
Turner, T. N., Yi, Q., Krumm, N., Huddleston, J., Hoekzema, K., F. Stessman, H. A., et al. (2017). denovo-db: a compendium of human de novo variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D804–D811. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw865
van Bon, B. W. M., Coe, B. P., Bernier, R., Green, C., Gerdts, J., Witherspoon, K., et al. (2016). Disruptive de novo mutations of DYRK1A lead to a syndromic form of autism and ID. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 126–132. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.5
van Dam, S., Võsa, U., van der Graaf, A., Franke, L., and de Magalhães, J. P. (2017). Gene co-expression analysis for functional classification and gene–disease predictions. Brief. Bioinform. 19:bbw139. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw139
van Karnebeek, C. D. M., Jansweijer, M. C. E., Leenders, A. G. E., Offringa, M., and Hennekam, R. C. M. (2005). Diagnostic investigations in individuals with mental retardation: a systematic literature review of their usefulness. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 13, 6–25. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201279
Veeramah, K. R., Johnstone, L., Karafet, T. M., Wolf, D., Sprissler, R., Salogiannis, J., et al. (2013). Exome sequencing reveals new causal mutations in children with epileptic encephalopathies. Epilepsia 54, 1270–1281. doi: 10.1111/epi.12201
Veltman, J. A., and Brunner, H. G. (2012). De novo mutations in human genetic disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 565–575. doi: 10.1038/nrg3241
Visscher, P. M., Brown, M. A., McCarthy, M. I., and Yang, J. (2012). Five years of GWAS discovery. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 90, 7–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.029
Visscher, P. M., Wray, N. R., Zhang, Q., Sklar, P., McCarthy, M. I., Brown, M. A., et al. (2017). 10 years of GWAS Discovery: biology, function, and translation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 101, 5–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.06.005
Vissers, L. E. L. M., de Ligt, J., Gilissen, C., Janssen, I., Steehouwer, M., de Vries, P., et al. (2010). A de novo paradigm for mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 42, 1109–1112. doi: 10.1038/ng.712
Vissers, L. E. L. M., van Nimwegen, K. J. M., Schieving, J. H., Kamsteeg, E.-J., Kleefstra, T., Yntema, H. G., et al. (2017). A clinical utility study of exome sequencing versus conventional genetic testing in pediatric neurology. Genet. Med. 19, 1055–1063. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.1
Voight, B. F., Scott, L. J., Steinthorsdottir, V., Morris, A. P., Dina, C., Welch, R. P., et al. (2010). Twelve type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci identified through large-scale association analysis. Nat. Genet. 42, 579–589. doi: 10.1038/ng.609
Wang, K., Li, M., and Hakonarson, H. (2010). ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:e164. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq603
Wang, T., Guo, H., Xiong, B., Stessman, H. A. F., Wu, H., Coe, B. P., et al. (2016). De novo genic mutations among a Chinese autism spectrum disorder cohort. Nat. Commun. 7:13316. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13316
Wanke, K. A., Devanna, P., and Vernes, S. C. (2018). Understanding neurodevelopmental disorders: the promise of regulatory variation in the 3'UTRome. Biol. Psychiatry 83, 548–557. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.11.006
Weckselblatt, B., and Rudd, M. K. (2015). Human structural variation: mechanisms of chromosome rearrangements. Trends Genet. 31, 587–599. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2015.05.010
Wenger, A. M., Guturu, H., Bernstein, J. A., and Bejerano, G. (2017). Systematic reanalysis of clinical exome data yields additional diagnoses: implications for providers. Genet. Med. 19, 209–214. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.88
Werling, D. M., Brand, H., An, J.-Y., Stone, M. R., Zhu, L., Glessner, J. T., et al. (2018). An analytical framework for whole-genome sequence association studies and its implications for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 50, 727–736. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0107-y
Wilfert, A. B., Sulovari, A., Turner, T. N., Coe, B. P., and Eichler, E. E. (2017). Recurrent de novo mutations in neurodevelopmental disorders: properties and clinical implications. Genome Med. 9:101. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0498-x
Willsey, A. J., Fernandez, T. V., Yu, D., King, R. A., Dietrich, A., Xing, J., et al. (2017). De Novo coding variants are strongly associated with tourette disorder. Neuron 94, 486–499.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.04.024
Willsey, A. J., Sanders, S. J., Li, M., Dong, S., Tebbenkamp, A. T., Muhle, R. A., et al. (2013). Coexpression networks implicate human midfetal deep cortical projection neurons in the pathogenesis of autism. Cell 155, 997–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.020
Wright, C. F., FitzPatrick, D. R., and Firth, H. V. (2018). Paediatric genomics: diagnosing rare disease in children. Nat. Rev. Genet. 19, 253–268. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.116
Xu, B., Ionita-Laza, I., Roos, J. L., Boone, B., Woodrick, S., Sun, Y., et al. (2012). De novo gene mutations highlight patterns of genetic and neural complexity in schizophrenia. Nat. Genet. 44, 1365–1369. doi: 10.1038/ng.2446
Xu, B., Roos, J. L., Dexheimer, P., Boone, B., Plummer, B., Levy, S., et al. (2011). Exome sequencing supports a de novo mutational paradigm for schizophrenia. Nat. Genet. 43, 864–868. doi: 10.1038/ng.902
Yang, Y., Muzny, D. M., Reid, J. G., Bainbridge, M. N., Willis, A., Ward, P. A., et al. (2013). Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of mendelian disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 1502–1511. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1306555
Yang, Y., Muzny, D. M., Xia, F., Niu, Z., Person, R., Ding, Y., et al. (2014). Molecular findings among patients referred for clinical whole-exome sequencing. JAMA 312, 1870–1879. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.14601
Yuen, R. K. C, Merico, D., Bookman, M., Howe, L. J., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., et al. (2017). Whole genome sequencing resource identifies 18 new candidate genes for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 602–611. doi: 10.1038/nn.4524
Yuen, R. K. C., Merico, D., Cao, H., Pellecchia, G., Alipanahi, B., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., et al. (2016). Genome-wide characteristics of de novo mutations in autism. NPJ Genomic Med. 1, 160271–1602710. doi: 10.1038/npjgenmed.2016.27
Yuen, R. K. C., Thiruvahindrapuram, B., Merico, D., Walker, S., Tammimies, K., Hoang, N., et al. (2015). Whole-genome sequencing of quartet families with autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Med. 21, 185–191. doi: 10.1038/nm.3792
Zhang, B., and Horvath, S. (2005). A General framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 4:17. doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1128
Zhou, J., and Troyanskaya, O. G. (2015). Predicting effects of noncoding variants with deep learning-based sequence model. Nat. Methods 12, 931–934. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3547
Zhu, W., Li, J., Chen, S., Zhang, J., Vetrini, F., Braxton, A., et al. (2018). Two de novo novel mutations in one SHANK3 allele in a patient with autism and moderate intellectual disability. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 176, 973–979. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.38622
Keywords: whole exome sequencing, neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorder, de novo mutation, network analysis, clinical implementation
Citation: Wang W, Corominas R and Lin GN (2019) De novo Mutations From Whole Exome Sequencing in Neurodevelopmental and Psychiatric Disorders: From Discovery to Application. Front. Genet. 10:258. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00258
Received: 09 July 2018; Accepted: 08 March 2019;
Published: 03 April 2019.
Edited by:
Prashanth N. Suravajhala, Birla Institute of Scientific Research, IndiaReviewed by:
Apostolos Zaravinos, European University Cyprus, CyprusAshwani Mishra, Independent Researcher, New Delhi, India
Copyright © 2019 Wang, Corominas and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guan Ning Lin, bmlja2dubGluQHNqdHUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Weidi Wang
Weidi Wang Roser Corominas
Roser Corominas Guan Ning Lin
Guan Ning Lin