- 1 Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2School of Mathematical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
It has been demonstrated that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in a variety of biological processes associated with human diseases. However, the identification of lncRNA–disease associations by experimental methods is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Computational methods provide an effective strategy to predict more potential lncRNA–disease associations to some degree. Based on the hypothesis that phenotypically similar diseases are often associated with functionally similar lncRNAs and vice versa, we developed an improved diffusion model to predict potential lncRNA–disease associations (IDLDA). As a result, our model performed well in the global and local cross-validations, which indicated that IDLDA had a great performance in predicting novel associations. Case studies of colon cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer were also implemented, all lncRNAs which ranked top 10 in both databases were verified by databases and related literature. The results showed that IDLDA might play a key role in biomedical research.
Introduction
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a kind of RNA molecule that is not translated into protein (Bertone et al., 2004; Wilusz et al., 2009). In decades past, lncRNA was considered as transcriptional noise and few people studied it. Nowadays, accumulating evidence has proved the key regulatory role of lncRNAs in many significant biological processes (Esteller, 2011). For example, some mutated and dysfunctional lncRNAs were implicated in a lot of human diseases such as renal cancer (Meng et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2015), breast cancer (Barsyte-Lovejoy et al., 2006; Gupta et al., 2010), hepatocellular cancer (Calin et al., 2007; Panzitt et al., 2007), prostate cancer (De Kok et al., 2002; Széll et al., 2008), lung cancer (Ji et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2003), colon cancer (Pibouin et al., 2002), leukemia (Calin et al., 2007)and cardiovascular diseases (Congrains et al., 2012). There are many well-known lncRNA-related biological databases such as NRED (Dinger et al., 2009), NONCODE (Liu et al., 2005; Xie et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2016), LncRNADisease (Chen et al., 2013), Lnc2Cancer (Ning et al., 2016) and lncRNAdb (Quek et al., 2015), including the information about lncRNA and little lncRNA–disease associations.
Recently, exploiting potential lncRNA–disease associations have become a growing significant research area. Many associations between lncRNA and human diseases have been identified by medical experiments, but which is costly and time-consuming. Predicting potential associations by the mathematical method and computational inference for experimental verification is a quite certain well-selected alternative (Chen et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2019).
Chen and Yan (2013) presented the Laplacian Regularized Least Squares for LncRNA–Disease Association (LRLSLDA), which is a semi-supervised learning framework to identify potential associations by integrating known associations and lncRNA expression profiles. Liu et al. (2014) put forward a computational model to predict potential lncRNA–disease associations by integrating many types of data such as gene expression profiles, human lncRNA expression profiles, and human disease-associated gene data. Li J, et al. (2014) presented a prediction method based on genome location information to discover potential vascular disease-related lncRNAs. Sun et al. (2014) established a lncRNA functional similarity network and used the random walk model to predict potential lncRNA–disease associations. However, this method cannot be applied to the lncRNAs without any known associated diseases. Yang et al. (2014) also proposed a network-based method to identify lncRNA–disease associations. And Yang’s method had a great performance to predict lncRNA–disease associations but it did not take into account various similarities. Chen (2015a) constructed a Katz measure model (KATZLDA) to predict lncRNAs associated with diseases, especially isolated disease-related lncRNAs. However, the method relies excessively on a network topology structure. Ping et al. (2019) constructed a lncRNA–disease bipartite network to infer potential lncRNA–disease associations by integrating two similarity calculation methods for lncRNAs and diseases. Gao et al. (2019) developed a dual sparse collaborative matrix factorization method based on gaussian kernel function (DSCMF) to predict novel lncRNA–disease associations. They considered the sparsity of lncRNA–disease association and used the L2,1-norm to ensure its sparsity in optimization.
In this paper, we developed an improved diffusion model for predicting lncRNA–disease associations (IDLDA) based on the hypothesis that phenotypically similar diseases are often associated with functionally similar lncRNAs and vice versa. IDLDA achieved reliable predictions with global and local cross-validations and it obtained higher AUROC than some previously proposed methods. Our results showed that the predicted top 10 lncRNAs in both databases were confirmed by databases and literature, and there were only 2, 2, and 1 lncRNAs which ranked top 50 by IDLDA in both databases that were not confirmed. All these results demonstrated the effectiveness and value of IDLDA in identifying potential lncRNA–disease associations. Data and code are freely available for research purposes only, you can email the author for it.
Materials and Methods
Data Collection and Pre-Processing
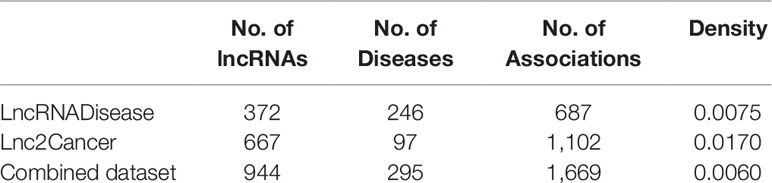
LncRNADisease (Chen et al., 2013) and Lnc2Cancer (Ning et al., 2016) are two well-known databases that we can apply to extract known lncRNA–disease associations. We got 687 experimentally verified lncRNA-disease associations (Supplementary Tables 1 and 3) including 372 lncRNAs and 246 diseases in the LncRNADisease, and 1,102 experimentally verified lncRNA-disease associations (Supplementary Tables 2 and 4) including 667 lncRNAs and 97 cancers in the Lnc2Cancer. These datasets were utilized as not only the gold standard datasets in the cross-validation but also the training datasets in novel lncRNA–disease association prediction. In addition, we also combined the data from the two datasets to make a complete training data set for validation which named combined dataset. There are 1669 experimentally verified lncRNA–disease associations including 944 lncRNAs and 295 diseases. This dataset (Supplementary material Data Sheet 1) can better illustrate the credibility of the model. To the author’s knowledge, this is the first article to combine the data of these two databases for model validation.
We constructed lncRNA–disease associations as a bipartite graph G(V,E) as follows. V=L∪D is the vertex set, where L is the lncRNA set { l1,l2,…,lNl }, D is the disease set { d1,d2,…,dNd }, and denote the edge set E={ eij:di∈D,lj∈L }. Nd and Nl represent the number of diseases and the number of lncRNAs, respectively. Here, the lncRNA–disease association can be represented by an adjacency matrix A={aij}Nd×Nl, where aij=1 if disease di and lncRNA lj have experimentally validated relation in the databases, while the unknown associations are set to 0 indicating that they will be ranked.
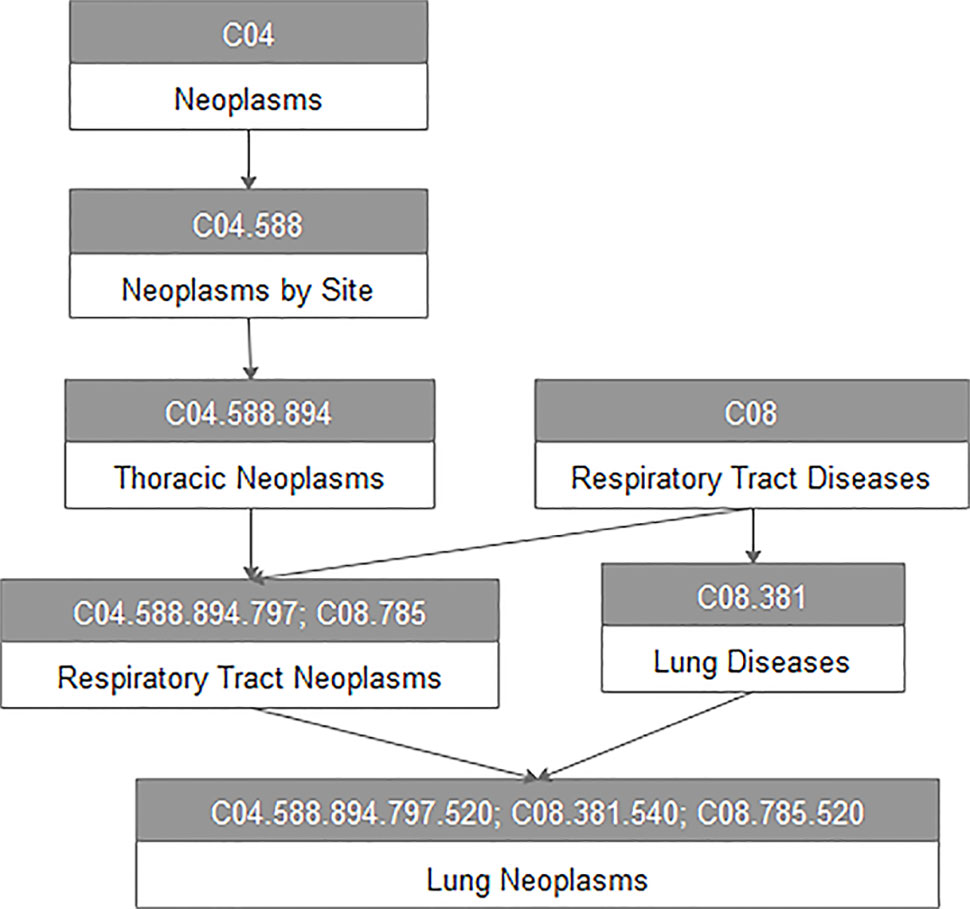
For every disease term dj in the MeSH database, we constructed a directed acyclic graph DAG(dj) based on the MeSH descriptors of Category C downloaded from the National Library of Medicine. For example, Figure 1 represents the DAG of lung neoplasms. All vertices in the DAG are connected by a direct edge from a more general term, we call it parent, to a more specific term, and we call it child (Chen et al., 2015). Here, V(DAG(dj)) indicated the vertex set including vertex dj and its ancestor vertices, and E(DAG(dj)) was the edge set of corresponding direct links from a parent vertex to a child vertex, which represented the relationship between different diseases.
Ensemble Similarity
Disease Ensemble Similarity
For a given disease dj, in the DAG(dj), the contribution of each disease semantic term Cdj(di) of disease di was defined as follows (Wang et al., 2010):
where Δ was a decay factor of semantic contribution, which should be between 0 and 1. According to some previous studies (Wang et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2015; Chen, 2015a), this value was 0.5 here. Accordingly, the contribution to the semantic value of disease dj itself was defined as 1. Meanwhile, the contribution of its ancestor disease should be multiplied by Δ.
According to this way to measure disease semantic similarity, we thought that two diseases di and dj which had a larger DAG(di) ∩ DAG(dj) should have a higher semantic similarity. Thus, the semantic score of disease dj was acquired by adding up all the contributions from ancestor diseases and disease dj itself. Define the semantic score (C) of disease dj as follows:
Thus, disease semantic similarity (SS) between disease di and disease dj can be written as (Chen et al., 2018):
Based on the basic assumption that two lncRNAs with more functional similarity prefer to be more related to similar diseases and vice versa (Lu et al., 2008), we could obtain disease similarity by the topologic information of the known lncRNA–disease association network. Accordingly, we introduced the Gaussian interaction profile kernel for calculating the similarity between diseases as a part of the disease similarity (van Laarhoven et al., 2011; Chen and Yan, 2013). Then we utilized the following equation to obtain disease Gaussian kernel similarity (KD) between disease di and disease dj.
where IP(di) was the i-th column of matrix A. The parameter γd was a parameter for adjusting the bandwidth of the kernel, which should be updated by using a new bandwidth parameter divided by the average value of the associations with lncRNAs for all diseases. According to the previous study (Cheng et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2016), was set to 1 to control thekernel bandwidth.
Thus, γd could be defined as follows:
Define the disease ensemble similarity (DS) between disease di and disease dj as follows:
LncRNA Ensemble Similarity
For a disease di and a group of diseases D, their similarity score S between them was defined as (Chen et al., 2015):
Let D(li) and D(lj) be the set of diseases related to lncRNA li and lncRNA lj, respectively. Define similarity score S between D(li) and D(lj) as follows:
Usually, most of researchers believe that lncRNAs with similar functions are more likely related to similar diseases and vice versa (Yang et al., 2009; Chen and Yan, 2013; Liu et al., 2014; Sun et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2015; Chen, 2015a; Gu et al., 2017). Therefore, the functional similarity between lncRNA li and lncRNA lj was calculated as follows:
where | D(li) | and | D(lj) | were the numbers of diseases associated with lncRNA li and lncRNA lj, respectively.
Similarly, the Gaussian kernel similarity between lncRNA li and lncRNA lj was defined as follows (van Laarhoven et al., 2011; Chen and Yan, 2013):
where = 1 (Cheng et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2016).
Define the lncRNA ensemble similarity (LS) between lncRNA li and lncRNA lj as follows:
Ensemble Associations
On the basis of the ensemble similarity matrix DS and LS, we could obtain two ensemble associations DA={ DAij }Nd×Nl and LA={ LAij }Nd×Nl. DAij and LAij can be written as:
An Improved Diffusion Model on the Network
We applied an improved diffusion model to calculate the information transmitted in the bipartite graph, which was quantified to solve the correlation between lncRNAs and diseases.
First of all, we selected one disease Du as seed, so the initial resources were located on each lncRNA, which associated with disease Du. Based on the hypothesis that lncRNAs with similar functions are usually related to similar diseases and vice versa. All the initial resources in L flowed to D by LA and DA. Thus, the comprehensive index (resources) of the dj vertex was shown as follows:
Each disease scattered the received resources to its associated lncRNAs, the resources located on the dj vertex returned back to L by LA and DA. Then the final comprehensive index (resources) of the li vertex as shown below:
Here the parameters α, β were used to balance the contribution between LA and DA. Therefore, for a given disease Du, we could obtain the comprehensive index IDLDA-score of every lncRNA. Accordingly, we got the predicted ranks of all lncRNAs for every disease. This predicted result can be represented by a rank matrix R={rij}Nd×Nl, where rij indicated the relevance score between disease di and lncRNA lj. The larger the value of rij, the more likely disease di and lncRNA lj are to be related. Thus, IDLDA can predict not only new disease-related lncRNAs but new lncRNA-related diseases. The flow chart of IDLDA is shown in Figure 2.
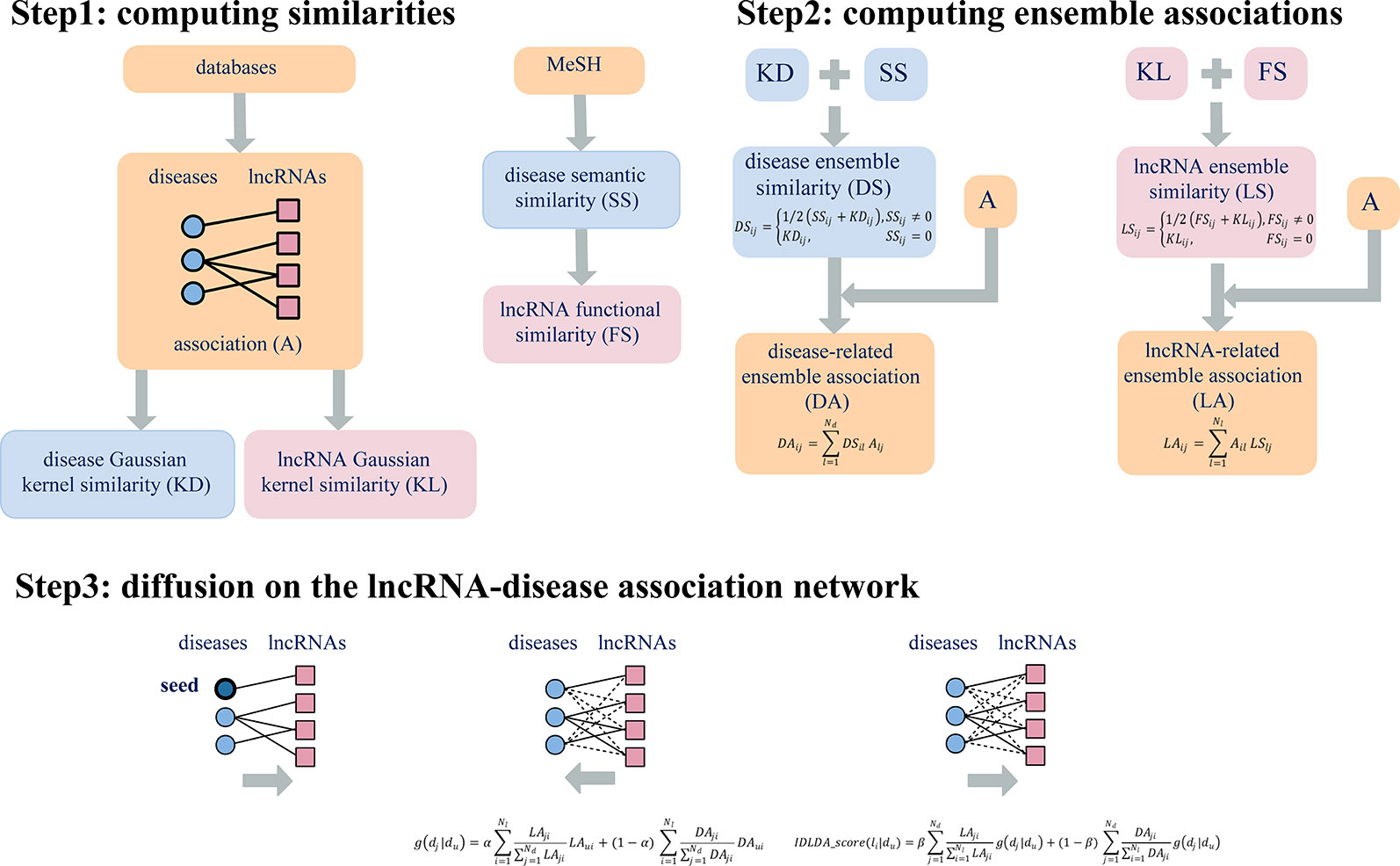
Figure 2 Flowchart of IDLDA. Nd and Nl represent the number of diseases and the number of lncRNAs, respectively.
Results
In this section, we first analyzed some properties of the lncRNA–disease association network. Next, we used global and local cross-validations and performed enrichment analysis to evaluate the performance of IDLDA. Then, we conducted case studies to verify the efficiency of IDLDA in discovering some potential disease-related lncRNAs.
Properties of the lncRNA–Disease Association Network
We analyzed the lncRNA–disease association network’s characteristics to obtain a whole view of it (Table 1). Among them, density denotes the number of edges divided by the number of possible edges. As we can see from Table 1, there are very few associations available, so it is very important to predict potential associations.
Cross-Validation Tests
A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve is a graphical plot that shows the diagnostic ability of the binary classifier system because its recognition thresholds are different (Fawcett, 2006). AUROC (Area Under Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve) is the area under the ROC curve with a value between 0 and 1. AUROC can intuitively evaluate the quality of classifier, the larger the value, the better. The similarities between diseases and lncRNAs rely on known associations. Therefore, the disease ensemble similarity and lncRNA ensemble similarity should be recalculated in each repetition of the experiment. The IDLDA method had two parameters, i.e. α and β. Here, when the values of α and β took 0, 0.1, 0.2, …,1 the values in the leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV), the AUROC were calculated. The highest AUROC value was 0.9513 (α=0.3, β=0.5) in the combined dataset. As a result, the parameters (α, β) in the combined dataset was (0.3, 0.5).
Our model could predict not only new lncRNAs but also new diseases. Here, we adopt three cross-validations to evaluate the prediction accuracy of the model from global and local perspectives. The first cross-validation is LOOCV, some elements in the matrix A were randomly selected as the training set and the remaining elements as the test set; the second cross-validation is CVr, selected some rows of the matrix A randomly as the training set and the remaining data as the test set; the third cross-validation is CVc, selected some columns of the matrix A randomly as a training set and the remaining data as a test set.
Among the three cross-validations, LOOCV was global cross-validation, which could test the prediction accuracy of the model on the original data set. For LOOCV, each known lncRNA–disease association was taken in turn as a testing sample and the remaining associations were used as training samples. And the baseline indicated random performance. In order to ensure the consistency of input data, the similarities of diseases and lncRNAs in other methods is consistent with the similarity of the IDLDA, which can better compare the predictive ability of the model itself. The AUROC of the combined dataset was 0.9513. We demonstrated that our approach significantly outperforms great performance (Supplementary Table 5). CVr and CVc were local cross-validations, which could test the prediction accuracy of the model for newly added diseases and lncRNAs respectively. The results of CVr (Figure 3, Left) and CVc (Figure 3, Right) showed that IDLDA had great performance in predicting novel lncRNA-related diseases and disease-related lncRNAs.
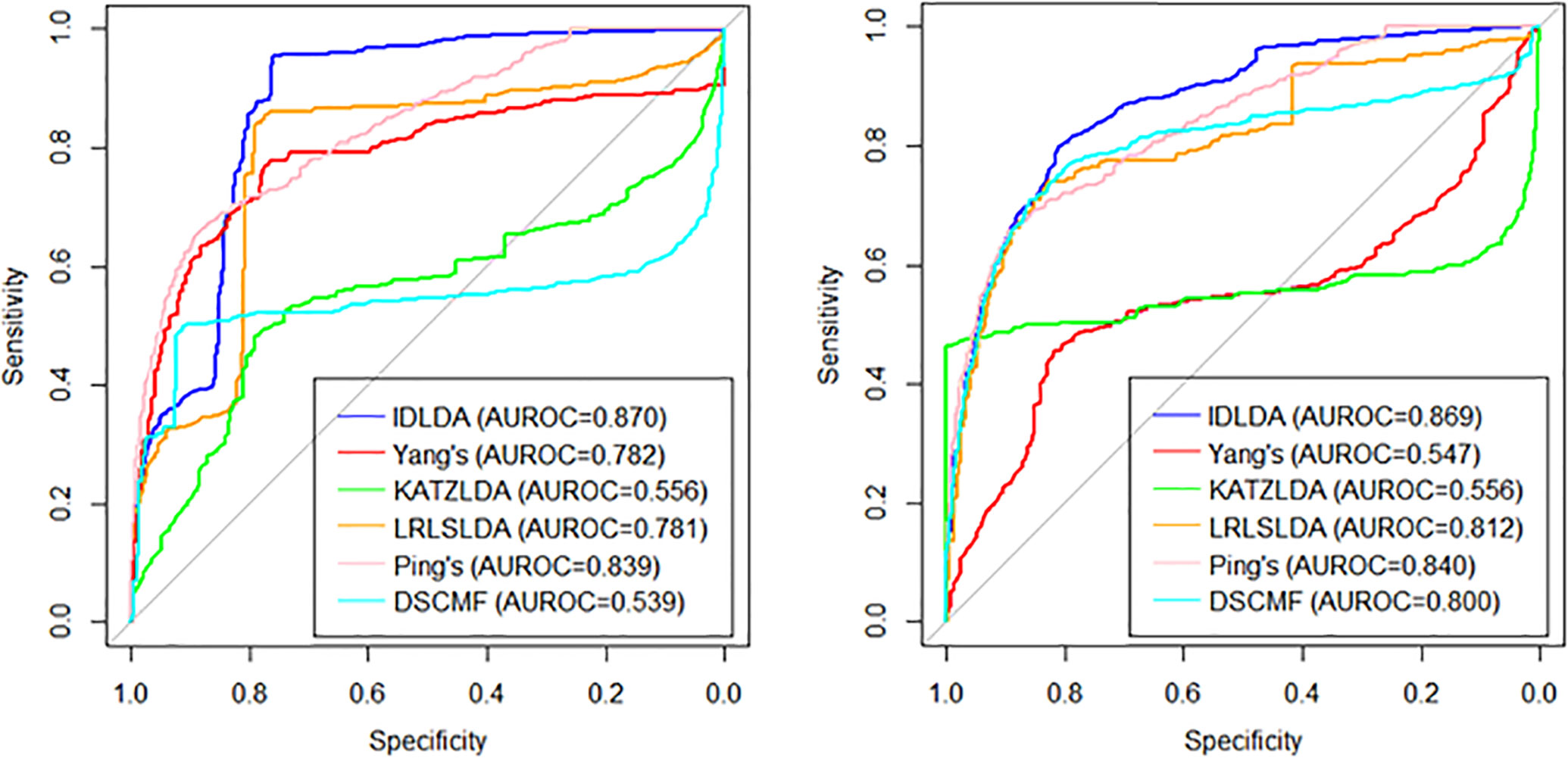
Figure 3 The ROC curves of the different methods with local cross-validation by row (Left) and by column (Right).
Enrichment Analysis
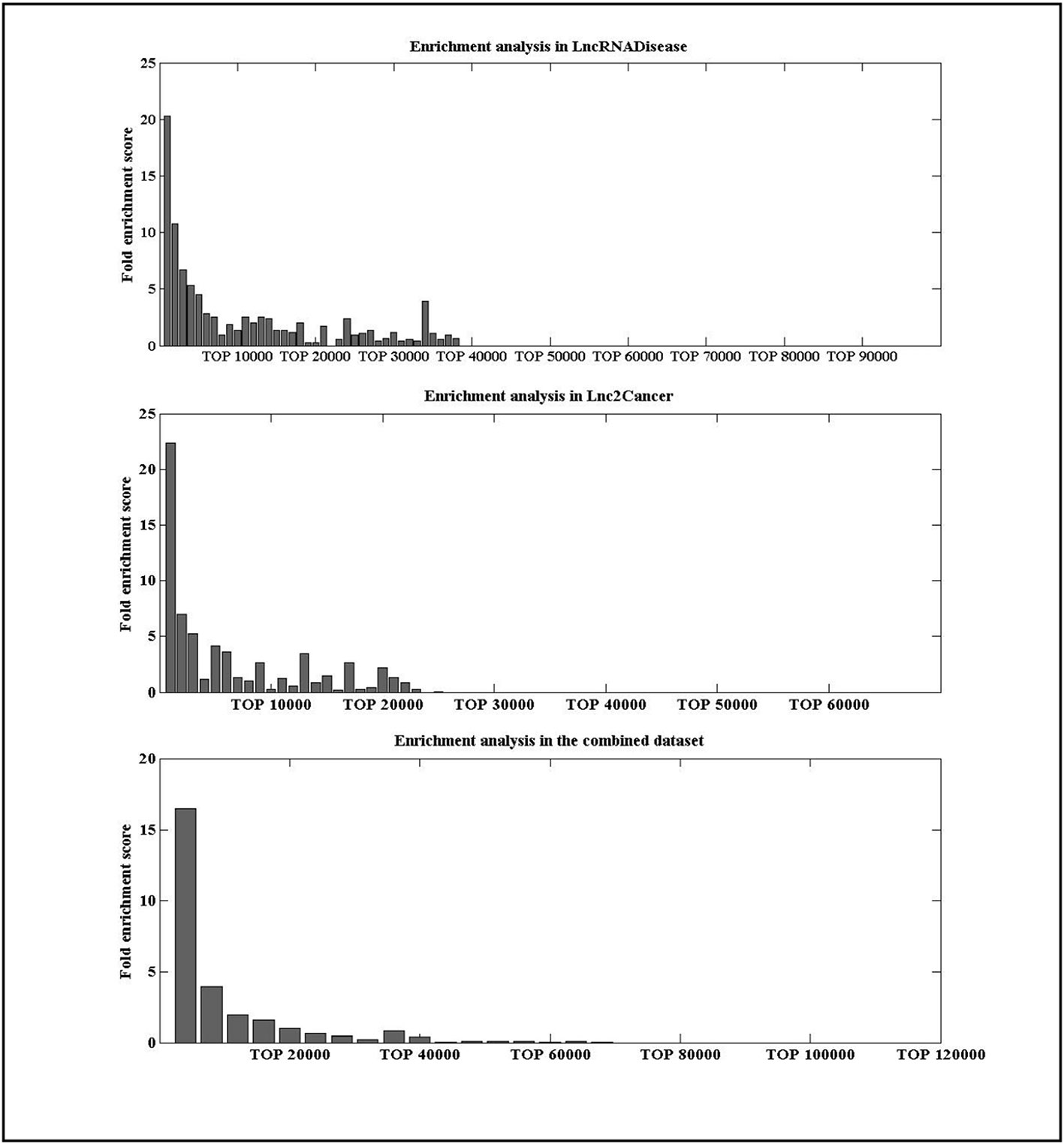
To check whether the lncRNAs with high IDLDA-score were more likely to be disease-related, all candidate lncRNA–disease pairs in two databases were ranked by IDLDA and binned into groups of x. Here, we took x as 1000 for the data in the LncRNADisease and Lnc2Cancer, and as 10000 for the data in the combined dataset. A fold enrichment score was defined as (Huang et al., 2013), where m was the number of distinct experimentally verified associations within one certain bin of x, M was the number of all distinct experimentally verified lncRNA–disease associations, and N was the number of all possible lncRNA–disease associations. For an lncRNA–disease pair, if its fold enrichment score was high for certain bin, it represented this pair was more likely to be related. As shown in Figure 4, lncRNAs with high IDLDA-score were more likely to be disease-related in three datasets.
Case Studies
Case studies were implemented to examine the capability of IDLDA in discovering potential lncRNA–disease associations. For some special diseases, we ranked those candidate lncRNAs based on their corresponding IDLDA-scores. Case studies included three common human diseases (colon cancer, gastric cancer, and breast cancer). Prediction results were verified based on not only the recent updates in the Lnc2Cancer and LncRNADisease but recently published experimental literature. Then we observed the number of the verified lncRNAs in the top 10 and 50 predictions in both databases, all the ranking results have been listed in Tables 2–4.
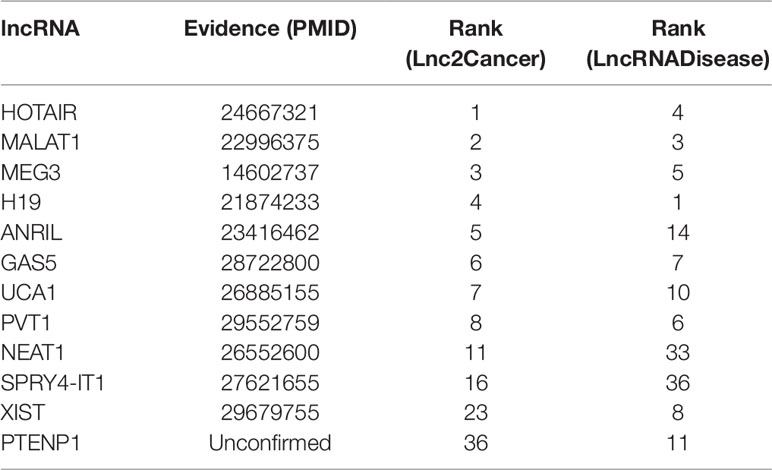
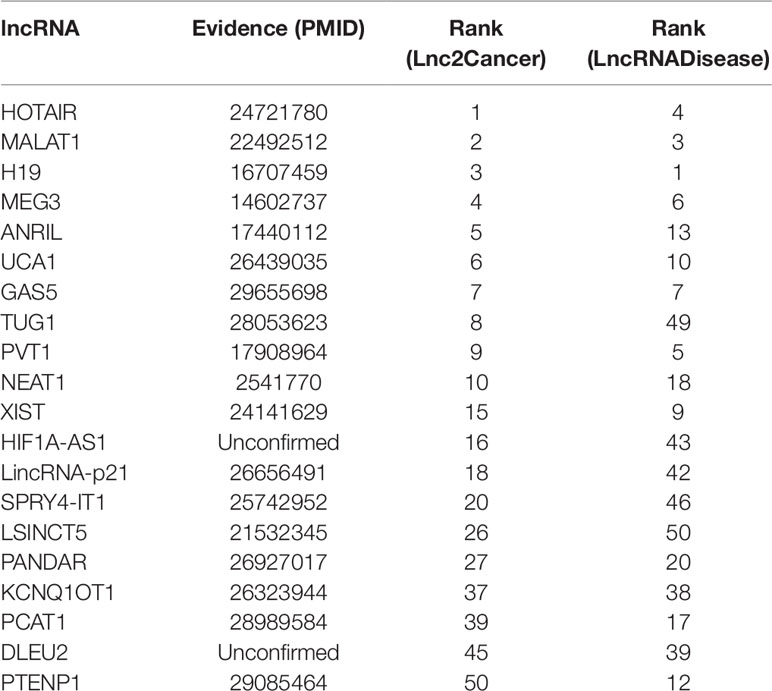
Colon cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in the world (Xue et al., 2015), killing almost seven hundred thousand people every year (Gu et al., 2017), even the disease-specific mortality rate is close to 33% in the developed countries (Han et al., 2015). In 2018, there are 97220 estimated new cases and 50,630 estimated deaths from Colon Neoplasms in U.S. (Siegel et al., 2018). Some associations between colon cancer and lncRNAs have been discovered by biological experiments (Chen et al., 2015), IDLDA can also predict more colon cancer-related lncRNAs. Consequently, all potentially related lncRNAs which ranked top 10 in both databases had been validated by databases and recent experimental literature. Meanwhile, only PTENP1 which ranked top 50 in both databases was not verified. Some research showed that PTENP1 pseudogene may act as “decoy” by protecting PTEN mRNA from binding to common miRNA and allowing expression of the tumor suppressor protein (Li G, et al., 2014). This indicated that PTENP1 was associated with cancer.
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in women, accounting for 22% of all cancer deaths in women (Donahue and Genetos, 2013; Karagoz et al., 2015). Some researchers announced that a number of lncRNAs are associated with the formation of breast cancer (Meng et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2015). In this paper, we used IDLDA to discover the potential breast cancer-related lncRNAs. From Table 3, we could know that all the potential related lncRNAs which ranked top 40 in both databases had been validated. For example, HOTAIR was ranked first in Lnc2Cancer, recent research had confirmed that HOTAIR was strongly expressed in numerous cancers like breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and lung cancer (Gupta et al., 2010; Li G, et al., 2014; Hrdlickova et al., 2014). Only HIF1A-AS1 and DLEU2 in both databases had not been validated by the same resources.
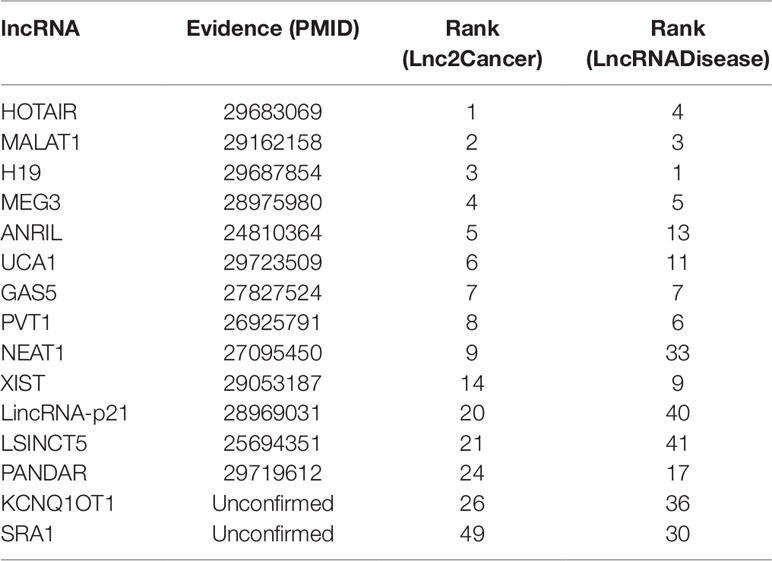
Gastric cancer is the second major reason for cancer-related death in the world (Guo et al., 2014). A myriad of studies has proved that lncRNAs have played crucial roles in the development of gastric cancer (Zhao et al., 2015). It is clear that the associations between breast cancer and HOTAIR, MALAT1, H19, MEG3, ANRIL, UCA1, GAS5, PVT1, NEAT1, XIST, LincRNA-p21, LSINCT5, PANDAR were validated by databases and related literature from Table 4. Only KCNQ1OT1 and SRA1 were not confirmed. But there is a potential relationship between SRA1 and breast cancer (Yan et al., 2011), SRA RNA expression is altered during breast tumorigenesis. The semantic similarity between gastric cancer and breast cancer is very large, perhaps future research could explain the relationship between SRA1 and gastric cancer.
Discussion
According to previous literature, lncRNAs are associated with a mass of diseases. With the emergence of many biological data about lncRNA, it is urgent to design a powerful and effective computing method to predict the underlying disease-related lncRNAs. In this paper, disease semantic similarity, lncRNA functional similarity, disease/lncRNA Gaussian kernel similarity, and lncRNA–disease associations were integrated on a large scale. We developed a computational model named IDLDA, which based on the diffusion model to predict potential lncRNA–disease associations. IDLDA achieved higher AUROC than other methods in the combined dataset. Meanwhile, local cross-validation, enrichment analysis could also show the reliability of the model. Moreover, case studies of colon cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer were also implemented, all lncRNAs which ranked top 10 in both databases were verified, only 2, 2, and 1 lncRNAs which ranked top 50 in both databases were not confirmed by databases and related literature. What is more, the results of local cross-validation showed IDLDA can predict not only new disease-related lncRNAs but new lncRNA-related diseases.
Here are the reasons why IDLDA performs better than some aforementioned methods. Firstly, the lncRNA ensemble similarity and disease ensemble similarity can make full use of the information about known lncRNA–disease associations by integrating lncRNA functional similarity, disease semantic similarity, and the Gaussian kernel similarity. Secondly, both disease ensemble similarity and lncRNA ensemble similarity are used in the diffusion process, IDLDA could predict not only new lncRNAs but also new diseases, overcoming some limitations of previous methods. Thirdly, IDLDA as a semi-supervised method is superior to the supervised methods when the data is incomplete. In particular, semi-supervised method could be implemented without any negative lncRNA–disease associations, which are closer to reality. In short, IDLDA will be an important and powerful bioinformatics tool in biomedical research of the lncRNA–disease association prediction, and even disease treatment.
Although IDLDA is effective, this work has several limitations. Firstly, IDLDA contains two parameters, and finding suitable parameters for different datasets is a challenging task. Additionally, some specific lncRNAs are not associated with certain diseases. If this kind of data can be added to the model in the future, it will certainly be helpful to improve the predictive ability. Successfully established models in the other computational fields would inspire the development of lncRNA–disease association prediction. Perhaps we can improve the predictive performance of IDLDA by integrating more information, such as lncRNA–miRNA information (Chen, 2015b) and disease–drug information (Chen et al., 2016).
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: http://www.cuilab.cn/lncrnadisease , http://www.bio-bigdata.net/lnc2cancer.
Author Contributions
QW conceived the project, developed the prediction method, designed the experiments, implemented the experiments, analyzed the result, and wrote the paper. GY analyzed the result and revised the paper.
Funding
GY was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11631014.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2019.01259/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | List_of_lncRNA_disease_associations_of_lncRNAdisease.
Supplementary Table 2 | Adjacency_matrix_of_Lnc2Cancer.
Supplementary Table 3 | Adjacency_matrix_of_LncRNADisease.
Supplementary Table 4 | List_of_lncRNA_disease_associations_of_Lnc2Cancer.
Supplementary Table 5 | Performance_comparison_of_different_methods.
Supplementary Data Sheet 1 | List_of_lncRNA_disease_associations_of_Combined_dataset.
References
Barsyte-Lovejoy, D., Lau, S. K., Boutros, P. C., Khosravi, F., Jurisica, I., Andrulis, I. L., et al. (2006). The c-Myc oncogene directly induces the H19 noncoding RNA by allele-specific binding to potentiate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 66, 5330–5337. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0037
Bertone, P., Stolc, V., Royce, T. E., Rozowsky, J. S., Urban, A. E., Zhu, X., et al. (2004). Global identification of human transcribed sequences with genome tiling arrays. Sci. (New York N.Y.) 306, 2242–2246. doi: 10.1126/science.1103388
Calin, G. A., Liu, C.-g., Ferracin, M., Hyslop, T., Spizzo, R., Sevignani, C., et al. (2007). Ultraconserved regions encoding ncRNAs are altered in human leukemias and carcinomas. Cancer Cell 12, 215–229. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.027
Chen, X., Yan, G.-Y. (2013). Novel human lncRNA-disease association inference based on lncRNA expression profiles. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 29, 2617–2624. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt426
Chen, G., Wang, Z., Wang, D., Qiu, C., Liu, M., Chen, X., et al. (2013). LncRNADisease: a database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D983–D986. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1099
Chen, X., Yan, C. C., Luo, C., Ji, W., Zhang, Y., Dai, Q. (2015). Constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on lncRNA-disease associations and disease semantic similarity. Sci. Rep. 5, 11338. doi: 10.1038/srep11338
Chen, X., Ren, B., Chen, M., Wang, Q., Zhang, L., Yan, G. (2016). NLLSS: Predicting Synergistic Drug Combinations Based on Semi-supervised Learning. PloS Comput. Biol. 12, e1004975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004975
Chen, X., Yan, C. C., Zhang, X., You, Z.-H. (2017). Long non-coding RNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Briefings Bioinf. 18, 558–576. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw060
Chen, X., Wang, L., Qu, J., Guan, N.-N., Li, J.-Q. (2018). Predicting miRNA-disease association based on inductive matrix completion. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 34, 4256–4265. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty503
Chen, X., Sun, Y.-Z., Guan, N.-N., Qu, J., Huang, Z.-A., Zhu, Z.-X., et al. (2019). Computational models for lncRNA function prediction and functional similarity calculation. Briefings Funct. Genomics 18, 58–82. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely031
Chen, X. (2015a). KATZLDA: KATZ measure for the lncRNA-disease association prediction. Sci. Rep. 5, 16840. doi: 10.1038/srep16840
Chen, X. (2015b). Predicting lncRNA-disease associations and constructing lncRNA functional similarity network based on the information of miRNA. Sci. Rep. 5, 13186. doi: 10.1038/srep13186
Cheng, F., Liu, C., Jiang, J., Lu, W., Li, W., Liu, G., et al. (2012). Prediction of drug-target interactions and drug repositioning via network-based inference. PloS Comput. Biol. 8, e1002503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002503
Congrains, A., Kamide, K., Oguro, R., Yasuda, O., Miyata, K., Yamamoto, E., et al. (2012). Genetic variants at the 9p21 locus contribute to atherosclerosis through modulation of ANRIL and CDKN2A/B. Atherosclerosis 220, 449–455. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.11.017
De Kok, J. B., Verhaegh, G. W., Roelofs, R. W., Hessels, D., Kiemeney, L. A., Aalders, T. W., et al. (2002). DD3(PCA3), a very sensitive and specific marker to detect prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 62, 2695–2698. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-5394.10.s.1.15.x
Dinger, M. E., Pang, K. C., Mercer, T. R., Crowe, M. L., Grimmond, S. M., Mattick, J. S. (2009). NRED: a database of long noncoding RNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, D122–D126. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn617
Donahue, H. J., Genetos, D. C. (2013). Genomic approaches in breast cancer research. Briefings. Funct. Genomics 12, 391–396. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elt019
Esteller, M. (2011). Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 12, 861–874. doi: 10.1038/nrg3074
Fawcett, T. (2006). An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 27, 861–874. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Gao, M.-M., Cui, Z., Gao, Y.-L., Li, F., Liu, J.-X. (2019). “Dual Sparse Collaborative Matrix Factorization Method Based on Gaussian Kernel Function for Predicting LncRNA-Disease Associations,” in Intelligent Computing Methodologies. Eds. D.-S. Huang, Z.-K. Huang, and A. Hussain (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 318–326.
Gu, C., Liao, B., Li, X., Cai, L., Li, Z., Li, K., et al. (2017). Global network random walk for predicting potential human lncRNA-disease associations. Sci. Rep. 7, 12442. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12763-z
Guo, X., Xia, J., Deng, K. (2014). Long non-coding RNAs: emerging players in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol.: J. Int. Soc Oncodev. Biol. Med. 35, 10591–10600. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2548-y
Gupta, R. A., Shah, N., Wang, K. C., Kim, J., Horlings, H. M., Wong, D. J., et al. (2010). Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 464, 1071–1076. doi: 10.1038/nature08975
Han, D., Wang, M., Ma, N., Xu, Y., Jiang, Y., Gao, X. (2015). Long noncoding RNAs: novel players in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 361, 13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.03.002
Hrdlickova, B., Almeida, R. C., Borek, Z., Withoff, S. (2014). Genetic variation in the non-coding genome: Involvement of micro-RNAs and long non-coding RNAs in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842, 1910–1922. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.03.011
Huang, J., Niu, C., Green, C. D., Yang, L., Mei, H., Han, J.-D. J. (2013). Systematic prediction of pharmacodynamic drug-drug interactions through protein-protein-interaction network. PloS Comput. Biol. 9, e1002998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002998
Ji, P., Diederichs, S., Wang, W., Böing, S., Metzger, R., Schneider, P. M., et al. (2003). MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 22, 8031–8041. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206928
Karagoz, K., Sinha, R., Arga, K. Y. (2015). Triple negative breast cancer: a multi-omics network discovery strategy for candidate targets and driving pathways. Omics: J. Integr. Biol. 19, 115–130. doi: 10.1089/omi.20140135
Li, G., Zhang, H., Wan, X., Yang, X., Zhu, C., Wang, A., et al. (2014). Long noncoding RNA plays a key role in metastasis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 780521. doi: 10.1155/2014/780521
Li, J., Gao, C., Wang, Y., Ma, W., Tu, J., Wang, J., et al. (2014). A bioinformatics method for predicting long noncoding RNAs associated with vascular disease. Sci. China. Life Sci. 57, 852–857. doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4692-4
Liu, C., Bai, B., Skogerbø, G., Cai, L., Deng, W., Zhang, Y., et al. (2005). NONCODE: an integrated knowledge database of non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D112–D115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki041
Liu, M.-X., Chen, X., Chen, G., Cui, Q.-H., Yan, G.-Y. (2014). A computational framework to infer human disease-associated long noncoding RNAs. PloS One 9, e84408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084408
Lu, M., Zhang, Q., Deng, M., Miao, J., Guo, Y., Gao, W., et al. (2008). An analysis of human microRNA and disease associations. PloS One 3, e3420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003420
Meng, J., Li, P., Zhang, Q., Yang, Z., Fu, S. (2014). A four-long non-coding RNA signature in predicting breast cancer survival. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.: CR 33, 84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0084-7
Ning, S., Zhang, J., Wang, P., Zhi, H., Wang, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2016). Lnc2Cancer: a manually curated database of experimentally supported lncRNAs associated with various human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D980–D985. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1094
Panzitt, K., Tschernatsch, M. M. O., Guelly, C., Moustafa, T., Stradner, M., Strohmaier, H. M., et al. (2007). Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA. Gastroenterology 132, 330–342. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.08.026
Pibouin, L., Villaudy, J., Ferbus, D., Muleris, M., Prospéri, M.-T., Remvikos, Y., et al. (2002). Cloning of the mRNA of overexpression in colon carcinoma-1 . Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 133, 55–60. doi: 10.1016/s0165-4608(01)00634-3
Ping, P., Wang, L., Kuang, L., Ye, S., Iqbal, M. F. B., Pei, T. (2019). A Novel Method for LncRNA-Disease Association Prediction Based on an lncRNA-Disease Association Network. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 16, 688–693. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2018.2827373
Quek, X. C., Thomson, D. W., Maag, J. L. V., Bartonicek, N., Signal, B., Clark, M. B., et al. (2015). lncRNAdb v2.0: expanding the reference database for functional long noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D168–D173. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku988
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Jemal, A. (2018). Cancer statistics, 2018 . CA: Cancer J. Clin. 68, 7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442
Sun, J., Shi, H., Wang, Z., Zhang, C., Liu, L., Wang, L., et al. (2014). Inferring novel lncRNA-disease associations based on a random walk model of a lncRNA functional similarity network. Mol. Biosyst. 10, 2074–2081. doi: 10.1039/c3mb70608g
Sun, D., Li, A., Feng, H., Wang, M. (2016). NTSMDA: prediction of miRNA-disease associations by integrating network topological similarity. Mol. Biosyst. 12, 2224–2232. doi: 10.1039/C6MB00049E
Széll, M., Bata-Csörgo, Z., Kemény, L. (2008). The enigmatic world of mRNA-like ncRNAs: their role in human evolution and in human diseases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 18, 141–148. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.01.007
van Laarhoven, T., Nabuurs, S. B., Marchiori, E. (2011). Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug-target interaction. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 27, 3036–3043. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr500
Wang, D., Wang, J., Lu, M., Song, F., Cui, Q. (2010). Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases. Bioinf. (Oxford England) 26, 1644–1650. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241
Wilusz, J. E., Sunwoo, H., Spector, D. L. (2009). Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 23, 1494–1504. doi: 10.1101/gad.1800909
Xie, C., Yuan, J., Li, H., Li, M., Zhao, G., Bu, D., et al. (2014). NONCODEv4: exploring the world of long non-coding RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, D98–103. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1222
Xu, N., Wang, F., Lv, M., Cheng, L. (2015). Microarray expression profile analysis of long non-coding RNAs in human breast cancer: a study of Chinese women. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 69, 221–227. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2014.12.002
Xue, Y., Ma, G., Gu, D., Zhu, L., Hua, Q., Du, M., et al. (2015). Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA signature in human colorectal cancer. Gene 556, 227–234. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.060
Yan, Y., Cooper, C., Leygue, E. (2011). The roles of SRA1 gene in breast cancer. Atlas Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 12, 1186–1191. doi: 10.4267/2042/44929
Yang, X., Feng, M., Jiang, X., Wu, Z., Li, Z., Aau, M., et al. (2009). miR-449a and miR-449b are direct transcriptional targets of E2F1 and negatively regulate pRb-E2F1 activity through a feedback loop by targeting CDK6 and CDC25A. Genes Dev. 23, 2388–2393. doi: 10.1101/gad.1819009
Yang, X., Gao, L., Guo, X., Shi, X., Wu, H., Song, F., et al. (2014). A network based method for analysis of lncRNA-disease associations and prediction of lncRNAs implicated in diseases. PloS One 9, e87797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087797
Zhang, X., Zhou, Y., Mehta, K. R., Danila, D. C., Scolavino, S., Johnson, S. R., et al. (2003). A pituitary-derived MEG3 isoform functions as a growth suppressor in tumor cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 5119–5126. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030222
Zhao, J., Liu, Y., Huang, G., Cui, P., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y. (2015). Long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: versatile mechanisms and potential for clinical translation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 5, 907–927. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5411
Keywords: long non-coding RNA, disease, association prediction, computational prediction model, diffusion model
Citation: Wang Q and Yan G (2019) IDLDA: An Improved Diffusion Model for Predicting LncRNA–Disease Associations. Front. Genet. 10:1259. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01259
Received: 26 May 2019; Accepted: 14 November 2019;
Published: 06 December 2019.
Edited by:
Alfredo Pulvirenti, University of Catania, ItalyReviewed by:
Suman Ghosal, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United StatesMin Chen, Hunan Institute of Technology, China
Copyright © 2019 Wang and Yan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guiying Yan, eWFuZ3lAYW1zcy5hYy5jbg==
 Qi Wang
Qi Wang Guiying Yan1,2*
Guiying Yan1,2*