Previous Radiotherapy Increases the Efficacy of IL-2 in Malignant Pleural Effusion: Potential Evidence of a Radio-Memory Effect?
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Shandong Cancer Hospital affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Internal Medicine-Oncology, Shandong Cancer Hospital affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 3School of Medicine and Life Sciences, University of Jinan-Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, China
- 4Department of oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University, Weifang, China
- 5Weifang People’s Hospital, Weifang, China
- 6Laiwu Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Laiwu, China
- 7Laiwu People’s Hospital, Laiwu, China
- 8Linyi City People’s Hospital, Linyi, China
A Corrigendum on
Previous Radiotherapy Increases the Efficacy of IL-2 in Malignant Pleural Effusion: Potential Evidence of a Radio-Memory Effect?
By Chen D, Song X, Wang H, Gao Z, Meng W, Chen S, Ma Y, Wang Y, Li K, Yu J, Yue J (2018). Front. Immunol. 9:2916. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02916
In the original article, there were mistakes in Figure 1 and Tables 1–3 as published.
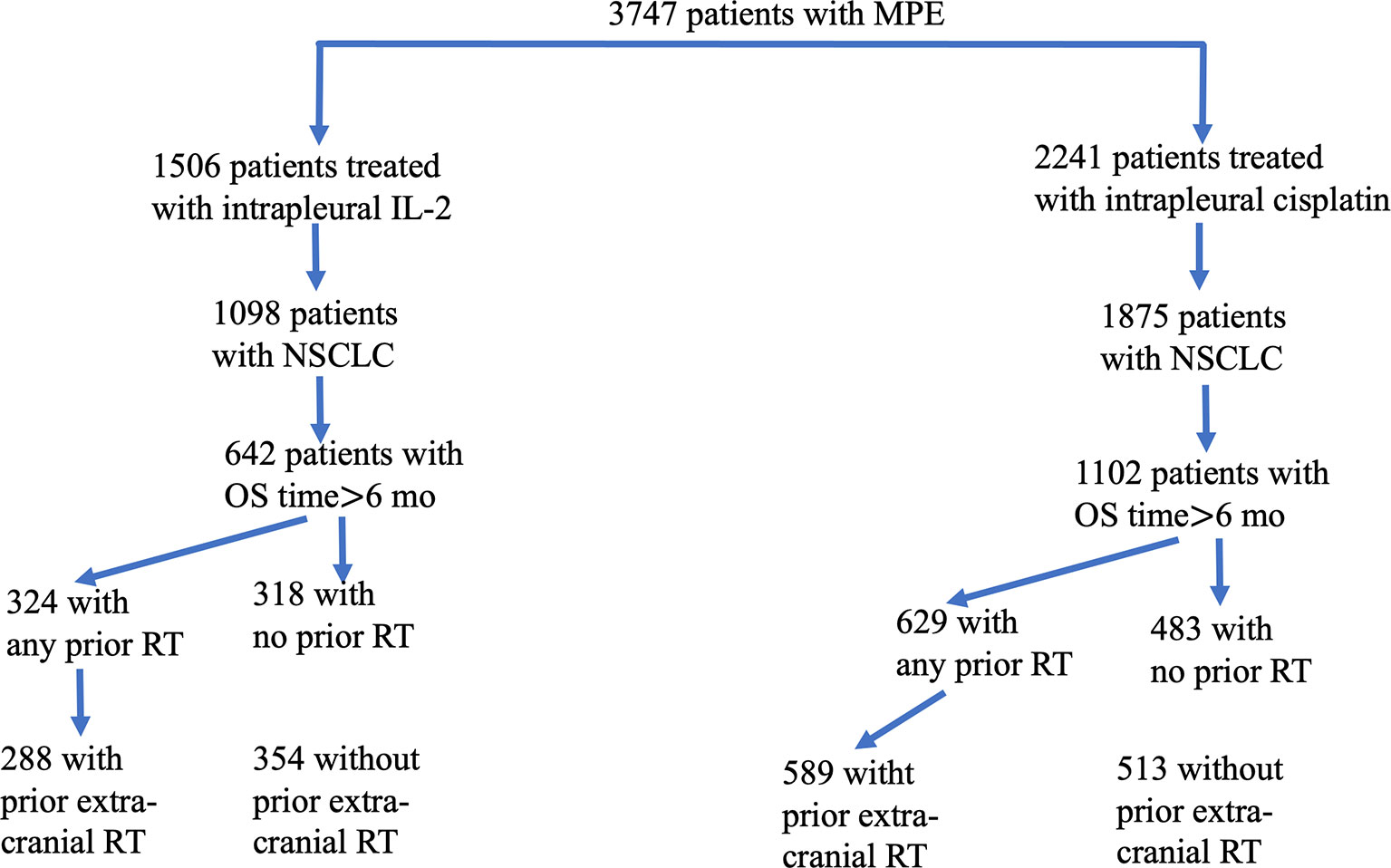
Figure 1 Flowchart of eligible patients enrolled in this study. From a total of 3,747 patients with malignant pleural effusion (MPE), we identified 1,506 who had been treated with interpleural interleukin-2 (IL-2) and 2,241 who had been treated with intrapleural cisplatin. Of the 1,098 patients given IL-2 (and the 1,875 patients given cisplatin) who had non-small cell lung cancer, 642 who had received IL-2 survived for more than 6 months, and 1,102 who had received cisplatin survived for more than 6 months. Patients in each group were subdivided according to whether they had any vs. no radiotherapy (RT), or extracranial vs. no extracranial RT.
In Figure 1, instead of “354 with any prior RT”, “288 with no prior RT”, “324 with prior extra-cranial RT” and “318 without prior extra-cranial RT”, it should be “324 with any prior RT”, “318 with no prior RT”, “288 with prior extra-cranial RT” and “354 without prior extra-cranial RT”, respectively.
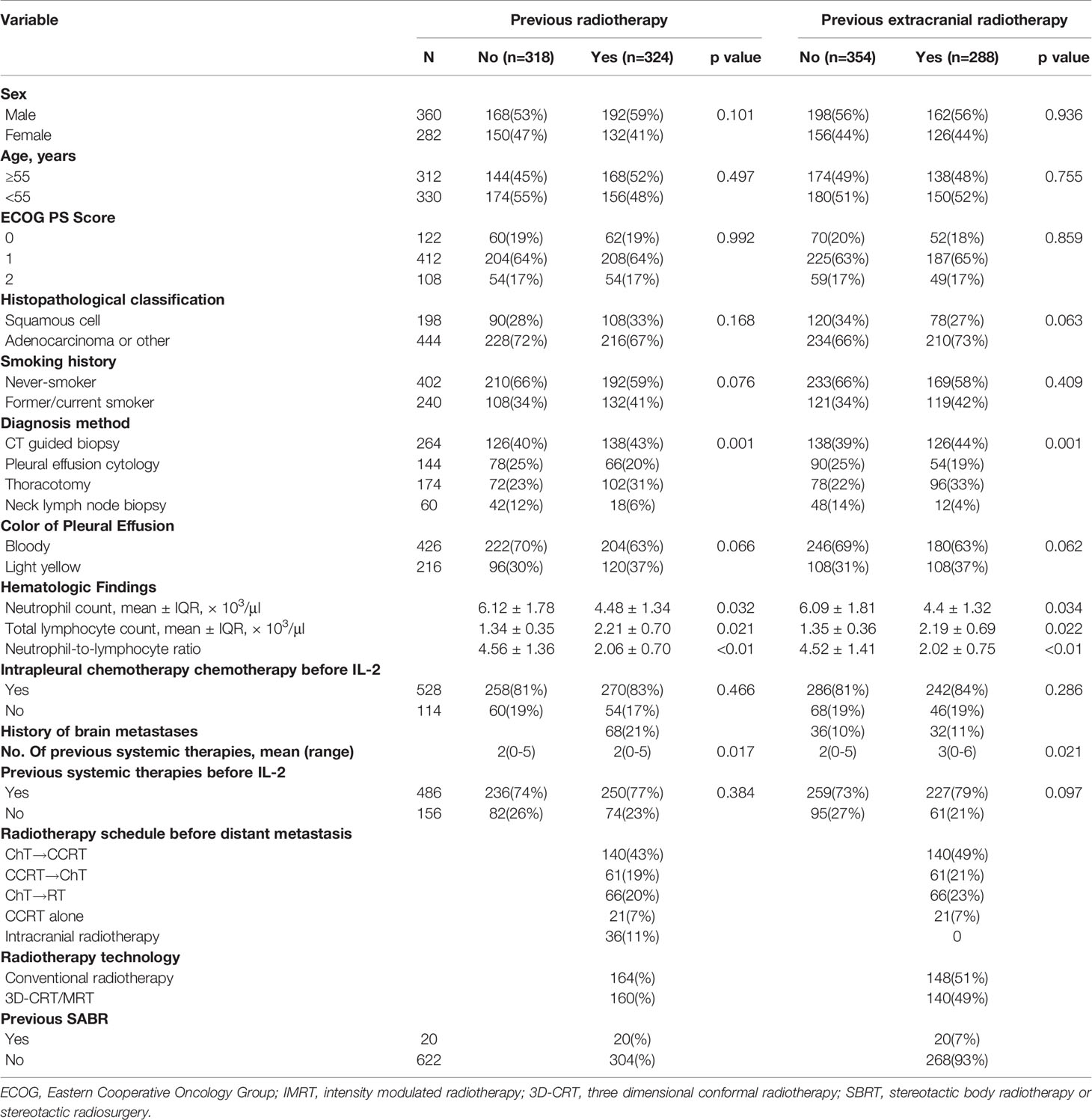
Meanwhile, there were mistakes in Table 1 due to some incorrect statistical results. Consequently, Tables 2 and 3 also need to be revised as, after rechecking the data, ECOG score is not significant in Table 2 These errors were caused by the carelessness and mis-operation in statistics and have been identified by the authors so that this would not happen in the future. The corrected Figure 1 and Table 1 to 3 appear below.
Consequently, a correction has been made to “RESULTS”, “Survival Outcomes”: paragraphs 1 and 2:
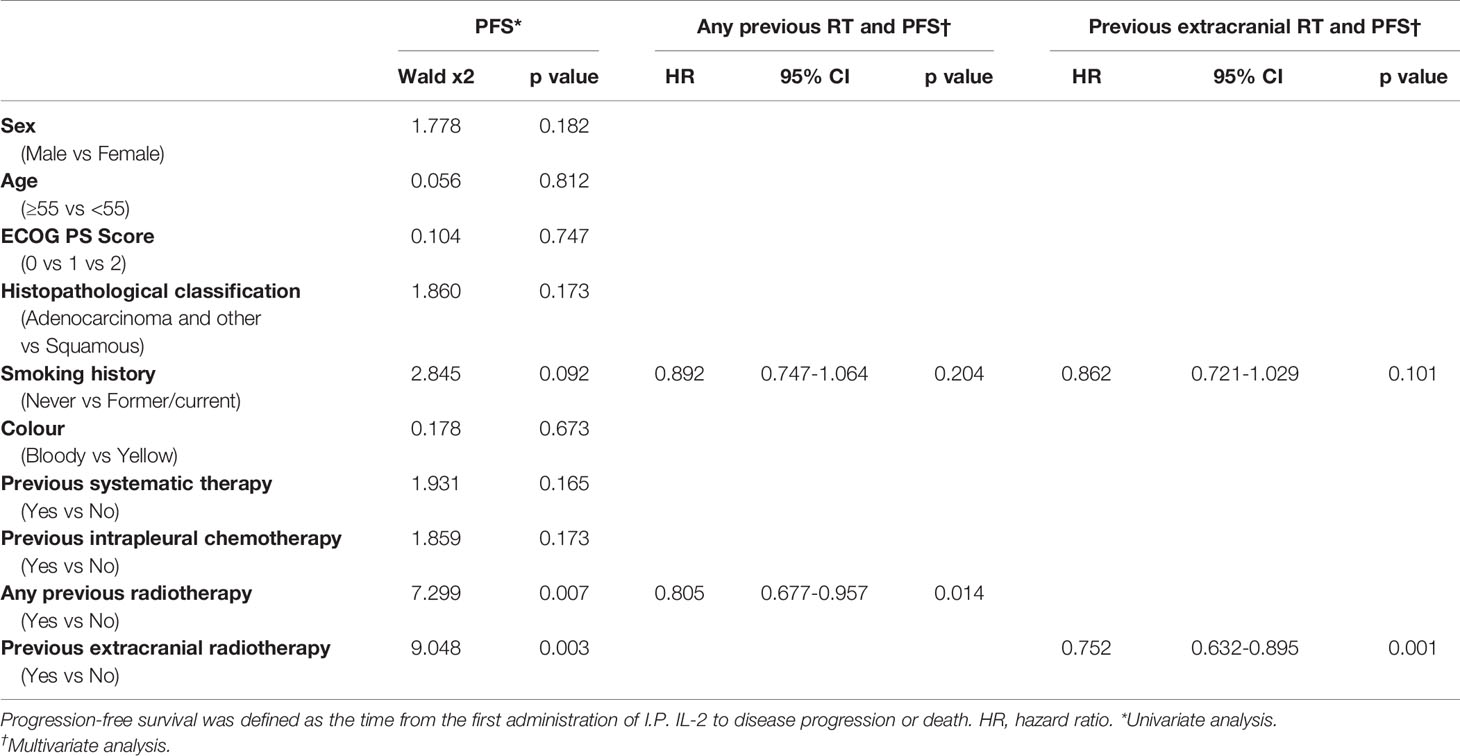
“In univariate analysis of the 642 patients who received intrapleural IL-2, having had any prior radiotherapy (p = 0.007) and having had extracranial radiotherapy (p = 0.003) were associated with longer PFS. Multivariate analysis revealed that having had any radiotherapy and extracranial radiotherapy were independent predictors of PFS (Table 2).”
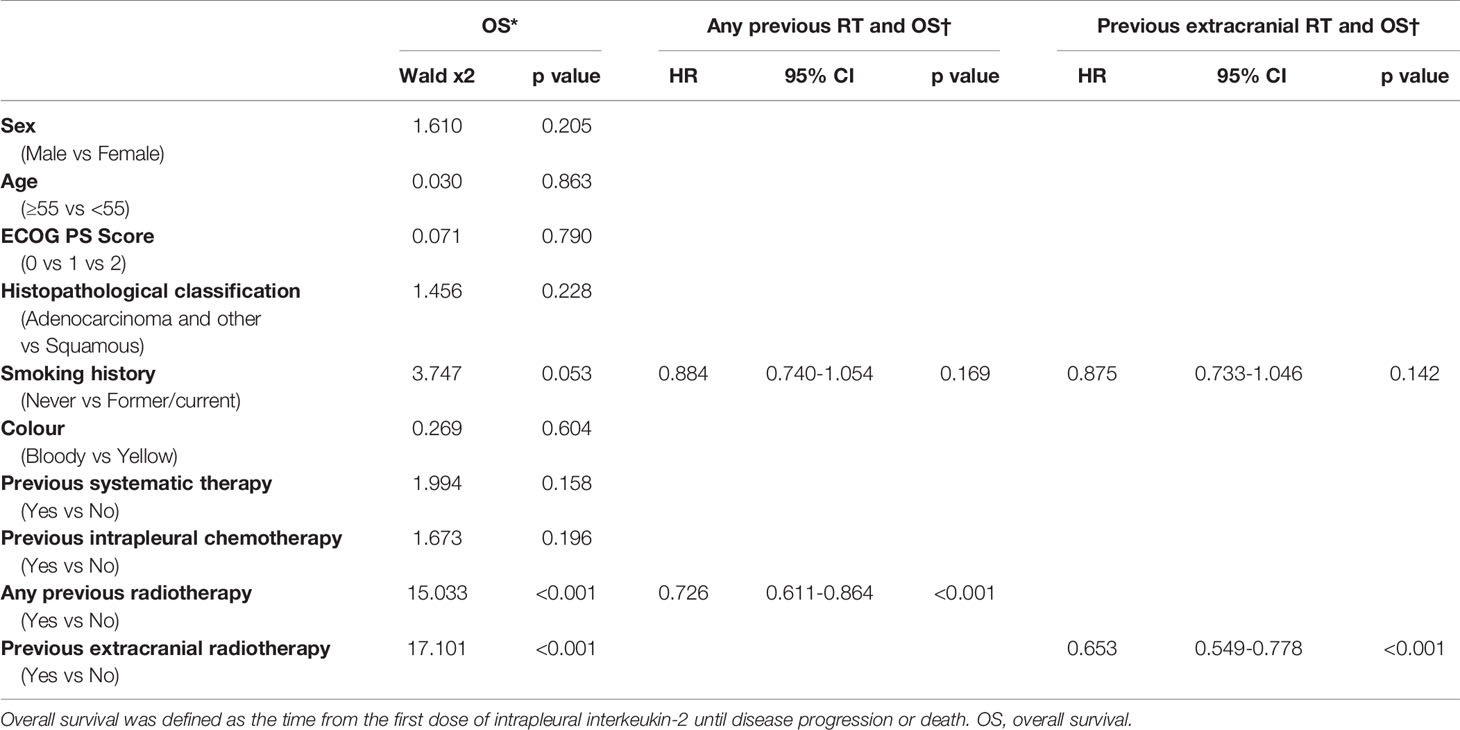
“In univariate analysis of the 642 patients who received intrapleural IL-2, having had any prior radiotherapy (p < 0.001) and extracranial radiotherapy (p < 0.001) were associated with longer OS. Multivariate analysis revealed that having had any radiotherapy and extracranial radiotherapy were independent predictors of OS (Table 3).”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), radiotherapy, radio-memory effect, immunotherapy, interleukin-2 (IL-2), malignant pleural effusion (MPE)
Citation: Chen D, Song X, Wang H, Gao Z, Meng W, Chen S, Ma Y, Wang Y, Li K, Yu J and Yue J (2021) Corrigendum: Previous Radiotherapy Increases the Efficacy of IL-2 in Malignant Pleural Effusion: Potential Evidence of a Radio-Memory Effect? Front. Immunol. 12:649620. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.649620
Received: 05 January 2021; Accepted: 05 March 2021;
Published: 23 March 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Patrik Andersson, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United States
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Song, Wang, Gao, Meng, Chen, Ma, Wang, Li, Yu and Yue. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinming Yu, sdyujinming@163.com; Jinbo Yue, yuejinbo@hotmail.com
 Dawei Chen
Dawei Chen Xinyu Song2,3
Xinyu Song2,3 Jinming Yu
Jinming Yu Jinbo Yue
Jinbo Yue