- 1Plankton Diversity and Evolution, Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Leiden, Netherlands
- 2Department Freshwater and Marine Ecology, Institute for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Dynamics, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 3Marine Animal Ecology Group, Wageningen University & Research, Wageningen, Netherlands
Shelled holoplanktonic gastropods are among the most vulnerable calcifiers to ocean acidification. They inhabit the pelagic environment and build thin and transparent shells of aragonite, a metastable form of calcium carbonate. While shelled pteropods have received considerable attention and are widely regarded as bioindicators of ocean acidification, atlantids have been much less studied. In the open ocean, atlantids are uniquely positioned to address the effects of ocean acidification at distinct trophic levels. From juvenile to adult, they undergo dramatic metamorphosis. As adults they are predatory, feeding primarily on shelled pteropods, copepods and other zooplankton, while as juveniles they feed on algae. Here we investigated the transcriptome and the impact of a three-day CO2 exposure on the gene expression of adults of the atlantid Atlanta ariejansseni and compared these to results previously obtained from juveniles. Individuals were sampled in the Southern Subtropical Convergence Zone (Atlantic Ocean) and exposed to ocean chemistry simulating past (~mid-1960s), present (ambient) and future (2050) conditions. In adults we found that the changes in seawater chemistry had significantly affected the expression of genes involved in biomineralization and the immune response, although there were no significant differences in shell growth between the three conditions. In contrast, juveniles experienced substantial changes in shell growth and a broader transcriptomic response. In adults, 1170 genes had the same direction of expression in the past and future treatments when compared to the ambient. Overall, this type of response was more common in adults (8.6% of all the genes) than in juveniles (3.9%), whereas a linear response with decreasing pH was more common in juveniles (7.7%) than in adults (4.5%). Taken together, these results suggest that juveniles are more sensitive to increased acidification than adults. However, experimental limitations including short incubation times, one carboy used for each treatment and two replicates for transcriptome analysis, require us to be cautious about these conclusions. We show that distinct transcriptome profiles characterize the two life stages, with less than 50% of shared transcripts. This study provides an initial framework to understand how ocean acidification may affect the molecular and calcification responses of adult and juvenile atlantids.
Introduction
Since the industrial revolution the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere has increased dramatically due to human activities. The ocean absorbs about one third of the human-released CO2 (Le Quéré et al., 2015; Gruber et al., 2019), causing ocean acidification (OA) at unprecedent rates (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2014; Jiang et al., 2019). OA results in the reduction of carbonate ion concentrations ([CO32−]) and saturation states of biologically important minerals such as calcite and aragonite (Doney et al., 2009; Feely et al., 2009; Gattuso et al., 2015; Zeebe et al., 2016). This process has major consequences on biogenic calcification, negatively impacting many marine calcifying organisms (Orr et al., 2005; Fabry et al., 2008; Kroeker et al., 2013). Because marine calcifiers play key roles in marine ecosystems, it is of major importance to gain a better understanding of the impacts of OA on these organisms (Riebesell and Gattuso, 2015).
Shelled holoplanktonic gastropods - atlantids and pteropods - are globally distributed members of the marine zooplankton and reach high abundances especially in the upper ocean (Bednaršek et al., 2012a; Burridge et al., 2017; Wall-Palmer et al., 2018b), which is the location where the largest amount of anthropogenic CO2 is absorbed (Caldeira and Wickett, 2003). They build thin and lightweight shells of aragonite, a metastable polymorph of calcium carbonate (Sun et al., 2015) and are among the most vulnerable marine calcifiers to OA (Bednaršek et al., 2017; Manno et al., 2017; Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). While pteropods are known to play a key role in the carbon cycle and are considered important members of marine food webs (Bednaršek et al., 2012a; Manno et al., 2017; Buitenhuis et al., 2019), atlantids have been much less studied in this regard. They are generally less abundant than pteropods (Burridge et al., 2017) but ecologically very important as they are active predators of other zooplankton, including pteropods. Shelled pteropods are mucus-web feeders throughout their entire life, while atlantids feed primarily on algae as juveniles and transition into being active predators as adults (Lalli and Gilmer, 1989).
Shelled pteropods were reported to decrease calcification rates and suffer extensive shell dissolution under acidified conditions (Feely, 2004; Orr et al., 2005; Fabry et al., 2008; Comeau et al., 2009; Bednaršek et al., 2012b; Moya et al., 2016; Maas et al., 2018; Mekkes et al., 2021), thus they have been proposed as bioindicators of OA (Bednaršek et al., 2014; Bednaršek et al., 2017; Manno et al., 2017). Atlantids are expected to be equally vulnerable to acidification (Wall-Palmer et al., 2016b), but research on this group is scarce. So far, only one study has focused on the influence of changing ocean chemistry upon atlantids, using juveniles of the species Atlanta ariejansseni (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). This species has a circumglobal distribution within a narrow latitudinal band between 35 and 48 degrees South, in the Southern Subtropical Convergence Zone, and is the only atlantid species occurring in these relatively colder waters (Wall-Palmer et al., 2016a; Wall-Palmer et al., 2018a). Because of the increased solubility of CO2 at lower seawater temperatures, A. ariejansseni is expected to be among the first species of atlantids to experience the negative impacts of OA (Orr et al., 2005; Negrete-García et al., 2019).
In the study by Wall-Palmer et al. (2021) a reduction in shell extension and shell volume of juvenile A. ariejansseni was observed from past to ambient ocean chemistry conditions, suggesting that shell production was already compromised in today’s South Atlantic waters. The same study observed an increase in shell extension from present to future ocean chemistry conditions, without significant changes in shell volume or thickness. In addition, the differential gene expression analysis of the juveniles indicated a linear response for genes involved in protein synthesis and organismal development: genes involved in protein synthesis were upregulated whereas genes involved in organismal development were downregulated with decreasing pH (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021).
In the present study, we build on the findings by Wall-Palmer et al. (2021) by investigating the transcriptome and the effects of short-term OA exposure on the calcification and gene expression of adult A. ariejansseni. Adult individuals were exposed to the same experimental conditions as described by Wall-Palmer et al. (2021) using ocean carbonate chemistry representative of present (ambient), near past (mid-1960s) and near future (2050) ocean conditions. The past and future treatments allowed us to compare the effects of small and short-term changes in ocean chemistry with ambient conditions while aragonite saturation was maintained across all treatments (Ω≥1.82). RNAseq was conducted to determine the gene expression patterns of adult A. ariejansseni. The gene expression patterns were then compared to those reported for the juveniles (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). RNAseq is an effective method to quantify the response to OA on a molecular level and, when paired with phenotypic changes, can portray a comprehensive view of the whole organism’s response (Melzner et al., 2020; Strader et al., 2020).
As adults, atlantids have well-developed eyes, and are presumably visually selective predators on pteropods, other atlantids and copepods (Lalli and Gilmer, 1989; Wall-Palmer et al., 2016b). In addition, they have a trunk-like proboscis to reach their preys inside shells and use a sucker on their swimming fin to hold them in place. Atlantids undergo dramatic metamorphosis by digesting their own velum as they transition from juvenile into mature adults (Pilkington, 1970). Therefore, we posit that the molecular and phenotypic responses to a changing ocean chemistry may be quite distinct in the two life stages. It is expected that juveniles will be more susceptible to the decreasing ocean’s pH because they are still growing their shell, having higher calcification rates than mature adults (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). Studying the responses to OA at different developmental stages is critical to characterize the bottlenecks that will determine an organism’s survival in acidifying oceans (Kurihara, 2008; Byrne, 2012; Byrne and Przeslawski, 2013).
Materials and Methods
Sample Collection
Adult and juvenile individuals of Atlanta ariejansseni were collected in October 2017 in the Southern Subtropical Convergence Zone during the Atlantic Meridional Transect AMT27 (DY084/085) cruise of the RRS Discovery. Individuals were collected at 41°09 S, 30°00 W during hours of darkness between 00:38 and 01:44 as described in (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). Collection was carried out at a maximum depth of 100 m using a 1-meter diameter ring net with 200 μm mesh and a closed cod-end for three slow, short (18-22 minute) oblique tows. Adults and juveniles of A. ariejansseni were sorted from the net samples with a light microscope and placed in calcein indicator (MERCK Calcein indicator for metal determination, CAS 1461-15-0, concentration 50 mg/l), covered to maintain dark conditions and left for two hours. Individuals were then rinsed with 0.2 μm filtered seawater and introduced immediately into the experiment carboys.
Experimental Setup
Surface seawater was collected from the same region and filtered at 0.2 μm into four barrels. The seawater was then subjected to three different OA conditions simulating the past (pH 8.19 ± 0.02, mid-1960s), present (pH 8.14 ± 0.02, ambient) and predicted future (8.03 ± 0.00, 2050s) chemistry conditions of the ocean in the study region. The future and past ocean chemistry conditions were achieved by bubbling 795 ppm and 180 ppm CO2 in air through the water for 12 hours, respectively. After 12 hours, pH, temperature and salinity were measured, and samples for Dissolved Organic Carbon (DIC) analysis were collected from each of the four barrels (Supplementary Table S1). The experimental setup for the juveniles is reported in Wall-Palmer et al. (2021). For the adult experiments, one carboy of six litres was then filled for each of the three ocean chemistry conditions and two carboys were filled for the control (5 carboys in total). Dried algae (0.6 mg/l, 3.6 mg per carboy) were added to all five carboys. While the algae were only necessary as a food source for the juveniles, they were also added to the adult incubations and the controls to ensure consistency across all experimental conditions. Between 16 and 17 adult individuals were added to each carboy (49 in total). No specimens were added to the control carboys. All carboys were sealed air-tight and masked with blackout fabric to maintain low light levels. The carboys were incubated for three days within a temperature-controlled room, which maintained the water at ambient ocean temperatures, between 14 and 16°C. After three days, measurements for pH, temperature and salinity were made and samples for DIC analysis were collected for all carboys. Measurements indicated that the overall water conditions remained stable throughout the experiments (Supplementary Table S1). All specimens were collected from the carboys and examined using a light microscope. The mortality rate was extremely low, with only a single adult having died. From each of the three ocean chemistry conditions, five living and undamaged adult A. ariejansseni individuals were preserved in RNAlater (Invitrogen) and frozen for RNAseq analyses while 34 specimens were preserved for shell growth measurements.
Water Chemistry
Seawater pH, temperature and salinity were measured using a research grade benchtop pH meter (HANNA HI5522-02, pH accuracy ±0.002, readable to 0.1 mV and 0.001 pH). pH was measured on the NBS scale with a glass electrode and frequent calibrations using NBS standards were made. Samples for Dissolved Organic Carbon (DIC) analysis were filtered into 5 ml glass vials and poisoned with 15 μl of saturated mercury (II) chloride (HgCl2) with no head space. DIC samples were analysed at the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) Texel, The Netherlands, using a Technicon Traacs 800 autoanalyzer spectrophotometric system following the methodology of Stoll et al. (2001). CO2SYS (Excel v2.3) (Pierrot et al., 2011) was used to calculate other carbonate system parameters from the measured DIC and measured pH (Hoppe et al., 2012), using the constants K1 and K2 from Mehrbach et al. (1973) refitted by Dickson and Millero (1987) and the KHSO4 dissociation constant of Dickson (1990). The concentrations of phosphorus and silicone were measured from surface CTD samples from the study region (Woodward and Harris, 2019).
Shell Extension
Shell extension was determined for adult specimens as described in Wall-Palmer et al. (2021). In brief, after the three-day OA experiments, calcein stained specimens from the past (n=6), ambient (n=7) and future (n=6) conditions were imaged using a Zeiss Axioplan 2 microscope with a Colibri light source and filter (excitation 485/20, FT 510, emission 515–565) producing a final wavelength of 515–565 nm.
The length of shell grown at the aperture was measured in three places in the images using the software FIJI (ImageJ) (Schindelin et al., 2012). The growth measurements were taken in places where the fluorescing of the calcein was clear and there was no damage to the edge of the shell. These places varied among the specimens. Nineteen of the 34 specimens preserved for shell measurements were used. The remaining specimens were damaged during preservation and preparation because adult shells are very fragile at the growing edge. The average of the measurements was tested using a one-way PERMANOVA, including pairwise comparisons to detect differences between treatments (Supplementary Table S2).
RNA Extraction and Sequencing
For each ocean chemistry condition, RNA from two pools of two adult A. ariejansseni individuals were extracted with the RNeasy Plus Micro Kit (QIAGEN). This sampling provided two replicates per condition (6 samples) and was selected to ensure that there was enough RNA for downstream processing. RNA extraction was followed by quantity and quality control using the Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent Technologies) with an RNA 6000 Nano Chip. The RIN (RNA integrity number) scores were between 7,3 and 8,7 (Supplementary Table S3). Libraries were generated with the NEBNext® Ultra II Directional Library Prep Kit for Illumina (New England BioLabs) using the manufacturer’s protocol for Poly(A) mRNA magnetic isolation. To isolate the mRNA, total RNA was added to NEBNext Sample Purification beads. After purification, the mRNA was fragmented into approximately 300 base-pair fragments. Subsequently, dUTPs was used in the synthesis of the second strand to reverse transcribe the mRNA into cDNA. The cDNA fragments were then selected based on size and amplified according to the manufacturer’s instructions using NEBNEXT Multiplex Dual Index kit (New England BioLabs). The Bioanalyzer 2100 using an Agilent DNA High Sensitivity Chip was used as quality and quantity control of the libraries. The library size was approximately between 420 and 450 bps (~300 bp insert +128 bp sequencing adapters). A total of six libraries were sequenced at the BaseClear BV Leiden on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform using paired-end 150 base-pair sequences, which produced between 14,659,290 and 22,606,954 reads per library. FASTQ read sequence files were generated using bcl2fastq2 version 2.18. Initial quality assessment was based on data passing the Illumina Chastity filtering. Subsequently, reads containing PhiX control signal were removed using an in-house filtering protocol. In addition, reads containing (partial) adapters were clipped (up to a minimum read length of 50 bp). The second quality assessment was based on the remaining reads using the FASTQC version 0.11.5 (Andrews, 2010), confirming that no filtering was needed after this.
Transcriptome Assembly, Filtering and Annotation
Paired-end reads of the six libraries of adult A. ariejansseni were pooled and assembled with Trinity (v2.8.4) (Haas et al., 2013) using default parameters. The reads were mapped back to the assembled transcriptome using Bowtie2 (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012). Open reading frames (ORFs) of the de novo transcriptome assembly were predicted using Transdecoder (v5.5.0) (Haas et al., 2013). The longest isoforms from each Trinity locus were blasted against a subset of the NCBI nr database as described in (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021), including all Mollusca (txid6447), Stramenophiles (txid33634) and Viridiplantae (txid33090). Total RNA was extracted from the whole tissue, which also includes foreign RNA as indicated by the skewed GC distribution of the final unfiltered assembly (Supplementary Figure S1). To remove contaminants, all transcripts not having a best hit with a molluscan sequence (e-value <10 e-5) were removed from the assembly resulting in a filtered assembly with a unimodal GC distribution (Supplementary Figure S1). This filtering approach resulted in a final assembly consisting of 93,885 transcripts (contigs) and 26,548 gene loci as predicted by the Trinity assembler (hereafter genes) (Supplementary Table S4). Unfiltered and filtered assemblies were uploaded to the Galaxy web platform (Afgan et al., 2016) and evaluated with Quast (Galaxy v5.0.2) (Mikheenko et al., 2018) and BUSCO (Galaxy v5.0.0) using the set of conserved metazoan orthologs (metazoa_odb9) as reference (Simão et al., 2015). The final assembly represented 15.5% of the unfiltered assembly but the completeness as measured by BUSCO was similar between the two versions (84.1% and 84.0% for the unfiltered and filtered assemblies respectively, Supplementary Table S4). Next, functional annotation of the filtered juvenile assembly from (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021) and the filtered adult assembly from this study were obtained by following the Trinotate (v3.2.1) pipeline. The annotation strategies included homology searches using BLAST+ against Swissprot (release October 2019) and protein domain detection using HMMER (Eddy, 2011) against PFAM (El-Gebali et al., 2019) (release September 2018) using default parameters. The percentage of annotated transcripts in adults was between 58.8 and 65.8 depending on the annotation strategy and was similar to the juveniles (between 59.3 and 68.8%) (Supplementary Table S5). The number of common transcripts between adults and juveniles was estimated using cd-hit on the filtered assemblies (Huang et al., 2010) (CD-HIT-EST-2D, identity cut-off: 0.9).
Differential Gene Expression Analysis and Visualization
Sequence reads of the two life stages were aligned to the filtered transcriptome assemblies using Salmon (Galaxy v1.3.0) (Patro et al., 2017), producing the counts relative to the transcripts and gene loci. All the Trinity genes with an expression lower than 0.5 counts per million (CPM) in at least 2 out of the 6 samples per life stage were filtered out from subsequent analyses. The statistically significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were determined with the Bioconductor package DESeq2 (v1.26.0) (Love et al., 2014) using the negative binomial distribution. Pairwise comparisons were done in the direction of the decreasing pH and included the contrasts future vs present and present vs past using an alpha of 0.05. In DESeq2, a fold change of 0.5 was considered as the appropriate cut-off to look a differential expression patterns between treatments (Schurch et al., 2016). To minimize false positives due to low replicate number, we also removed genes which had a difference in counts of more than 300 and more than 20 times fold difference between replicates. To control the false discovery rate (FDR), multiple testing correction was performed using the Benjamini-Hochberg method (p-adj < 0.05). The statistically significant DEGs in adults were blasted against the nr database of NCBI (June 2021) and InterPro (October 2021). Genes were then categorized in putative biological processes based on the annotations: ‘immune response’, ‘protein synthesis’, ‘protein degradation’, ‘biomineralization’, ‘cell death’ and others (Supplementary Tables S6, S7). To visualize the expression patterns of statistically significant DE genes, the read counts from all adult (n = 6) samples were converted into logCPM values with the R function calculateCPM. The R function scale was used for scaling the row values, whereas the heatmap itself was created with the pheatmap package (1.0.12) (Kolde, 2019). R code used for this analysis and input files can be accessed on Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/Mari-Lee/atlanta.
GO Enrichment Analysis and Correlation Test
GO terms obtained from the juvenile and adult transcriptome annotation were trimmed using the GOslimmer tool (Galaxy v1.0.1) (Faria, 2017) and processed with the ranked-based method GO MWU for enrichment analysis as implemented in (Wright et al., 2015). The GO MWU enrichment analysis uses adaptive clustering of GO terms by testing whether the genes belonging to a certain GO category are significantly clustered near the top or the bottom of the global ranked list of genes. Here, the Mann–Whitney U test was based on the ranking of signed log p-values obtained from DESeq2 after filtering lower expressed genes (< 0.5 CPM) and genes having high expression variation between replicates. The associated GO terms were tested for overrepresentation in the categories of “Biological Process” and “Molecular Function” for adults and juveniles, in the present vs past and future vs present comparisons. Significance thresholds were corrected using Benjamini-Hochberg false discovery rate procedure (p-value <0.05). GO terms that were significantly enriched in at least two of the four comparisons, by either up or downregulated genes, were visualized using the pheatmap package (1.0.12) (Kolde, 2019) and categorized into nine major GO groups: “binding”, “enzymatic activity”, “structural molecule activity”, “transporter activity”, “developmental process”, “cellular component organization”, “multicellular organismal process”, “metabolic process” and “locomotion”.
To further explore the differences in gene expression between the life stages, we carried out a Pearson correlation test to determine the number of genes whose expression patterns were significantly (p < 0.05) correlated with pH in a linear or non-linear way. For each gene, we tested for the linear correlation between its expression patterns and decreasing pH (2-2-1-1-0-0) and for the correlation between its expression pattern and the change in ambient condition (1-1-0-0-1-1) using the cor.test function in R and the counts from Salmon as input, after filtering lower expressed genes (< 0.5 CPM) and genes with high expression variation between replicates. We also tested for gene expression change only occurring in the past (1-1-0-0-0-0) or in the future (0-0-1-1-1-1). R code used for these analyses and input files can be accessed on Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/Mari-Lee/atlanta.
Results
Atlanta ariejansseni: Shell Growth and Transcriptome Comparison
Atlantids took up the calcein indicator prior to the incubation, which was incorporated into their shells as they grew during the three-day experiment (Figures 1A, B) (Mekkes et al., 2021; Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). Overall, shells were transparent and lustrous showing no signs of dissolution. In adults we did not observe significant differences in shell growth across different ocean chemistry conditions (P = 0.2828) (Supplementary Table S2). This is in contrast with the juveniles that had significant differences in shell extension between all conditions (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). Comparison between adult and juvenile transcriptome assemblies was carried out by a sequence clustering method based on a 90% identity cut-off (cd-hit-est-2d). Juveniles had 69,480 unique transcripts (71.3% of the assembly) and 28,003 transcripts that were in common with adults, whereas adults had 48,921 unique transcripts (52.1% of the assembly) and 44,964 transcripts that were in common with juveniles (Figure 1C).
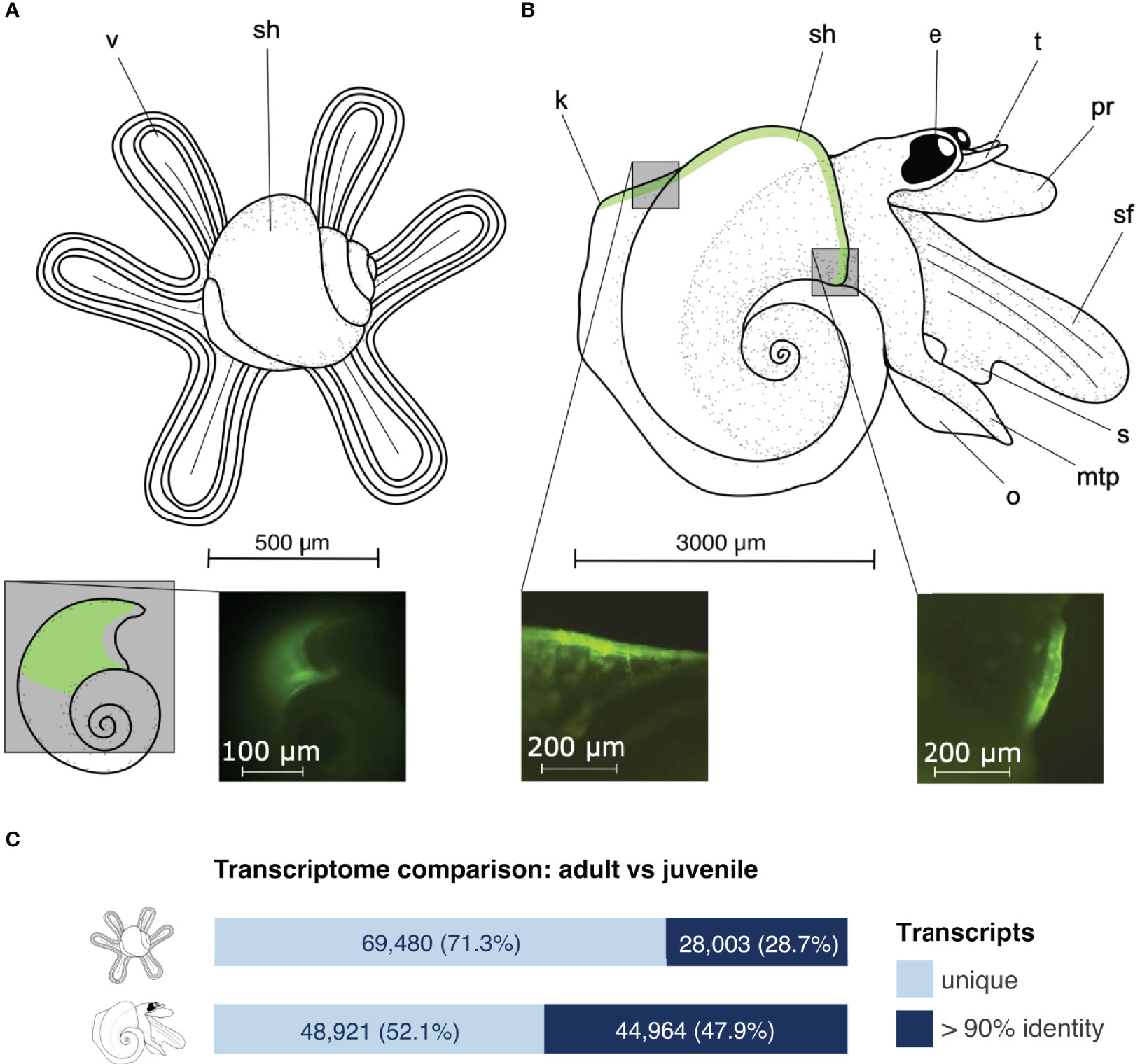
Figure 1 External morphology of Atlanta ariejansseni juveniles (A) and adults (B), supported by fluorescence images of their shells stained with calcein, showing areas of active calcification during the experiments. Key to morphology (from left to right): v, velum; sh, shell; k, keel; e, eye; t, tentacle; pr, proboscis; sf, swimming fin; s, sucker; mtp, metapodium; o, operculum. At an early stage, juveniles have a four-lobed velum, which changes into a long and narrow six-lobed velum at a later stage shown here. When undergoing metamorphosis, the velum is digested. Shells are transparent with unique shell ornamentation and mature adults have a total of 4.5 to 4.75 whorls. Shell sizes range from 500 μm in juveniles to 3000 μm in adults. The soft tissue varies greatly in colour among individuals from mottled white to orange-pink and dark grey (Wall-Palmer et al., 2016a). The green shading in the drawings represents the regions stained with calcein. (C) Clustering between adult and juvenile Atlanta ariejansseni transcriptome assemblies: the fraction of identical transcripts is marked in dark blue, while the fraction of different transcripts is in light blue. Clustering was conducted with cd-hit-est-2d (identity > 90%) on the filtered transcriptome assemblies.
Transcriptomic Response to the Different Ocean Chemistry Conditions in Adults
A total of 33 statistically significant DEGs were identified in the two pairwise comparisons for adult A. ariejansseni: present (ambient) vs past (mid-1960s); and future (2050) vs present (ambient). Most of these genes were putatively involved in biomineralization and immune response, although there were also other biological processes being affected, including protein synthesis, protein degradation and cell death (Supplementary Tables S6, S7). Upregulation of genes was more prominent in the present, followed by the future and past conditions (Figure 2). Four genes were upregulated in both past and future treatments in relation to the ambient condition, including two genes putatively involved in biomineralization (extensin-like, collagen alpha-1) (Ramos-Silva and Marin, 2016; Herlitze et al., 2018). Six genes had the opposite pattern and were downregulated in the past and future treatments, including two genes coding for Complement component 1q (C1q)-related proteins, which are known to be involved in the immune response (Gestal et al., 2010) but may also have roles in biomineralization (Shimizu et al., 2019), and one fucolectin, which may be involved in the immune response (Bianchet et al., 2002). Finally, 14 genes were upregulated in both the present and future conditions when compared to the past, including four candidate biomineralization genes (‘Zona pellucida (ZP)-related protein’, ‘C-type lectin’, ‘coadhesin’ and ‘stanniocalcin-like’) (Marie et al., 2013; Demarchi et al., 2016; Marin, 2020), two genes coding for fucolectin and two for ubiquitin proteins.
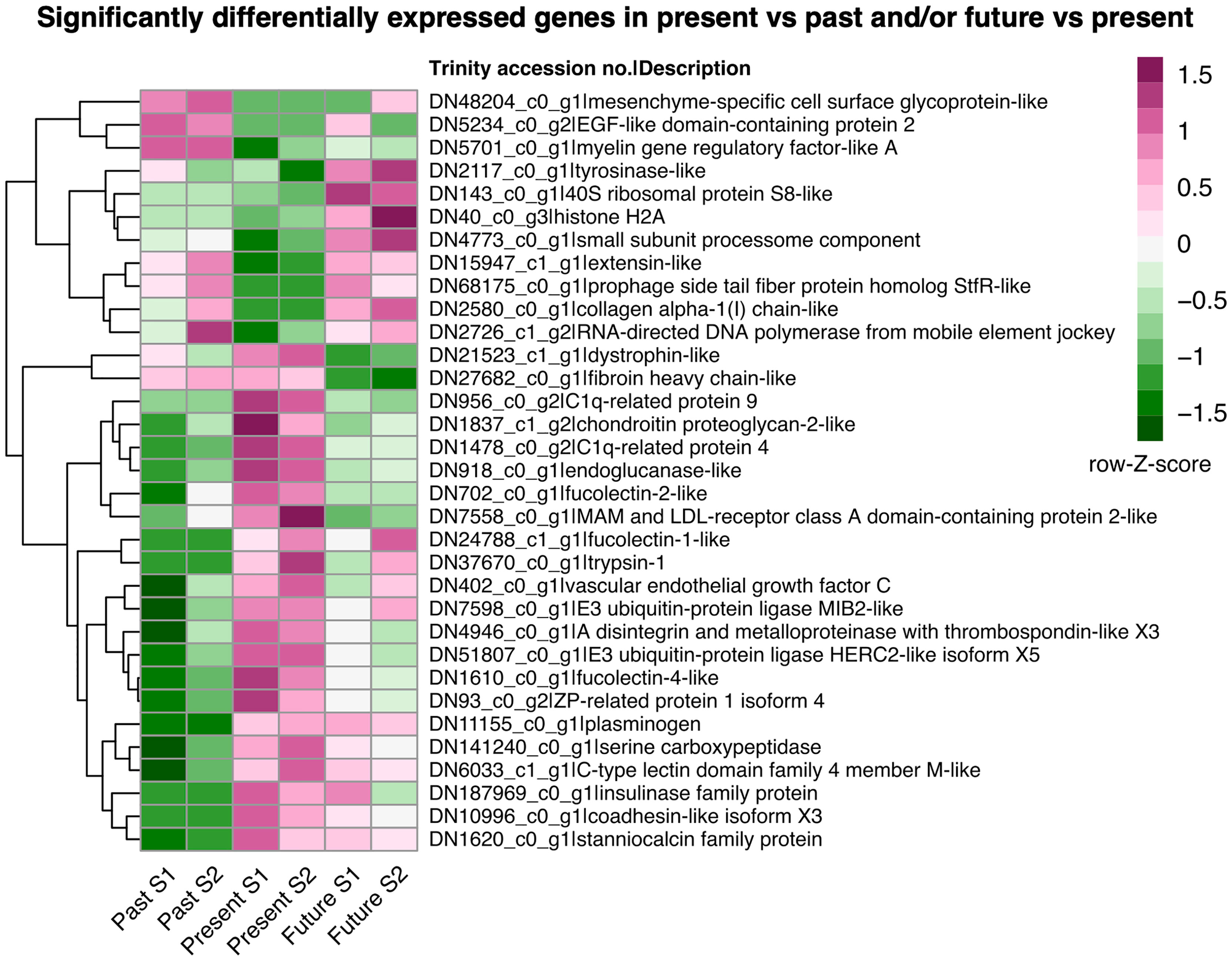
Figure 2 Heatmap illustrating the expression patterns of the statistically significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in adult Atlanta ariejansseni from past (mid-1960s), present (ambient) and future (2050) ocean chemistry conditions. Gene loci as predicted by Trinity are labelled by their accession numbers in the assembly followed by the description of the blast best hit. Visualization is based on the row Z-scores of the log count per million of the genes. The statistically significant DEGs were determined with DESeq2 using the negative binomial distribution. Pairwise comparisons were done in the direction of the decreasing pH and included the contrasts future versus present and present versus past using an alpha of 0.05. Multiple testing correction was performed using the Benjamini-Hochberg method (p-adj < 0.05).
Transcriptomic Responses in Adults versus Juveniles
In adult A. ariejansseni, enriched GO terms in both the present versus past and the future versus present comparisons were inversely up or downregulated (Figure 3). These opposing patterns were observed for the molecular functions: rRNA binding (GO:0019843), nucleotidyltransferase activity (GO:0016779), kinase activity (GO:0016301), cytoskeletal protein binding (GO:00080920), lipid binding (GO:0008289), mRNA binding (GO:0003729), and biological processes: anatomical formation structure involved in morphogenesis (GO:0048646), circulatory system process (GO:0003013), cytoskeleton organization (GO:0007010), cellular protein-containing complex assembly (GO:0034622), cell adhesion (GO:0007155) and cell junction organization (GO:0034330). The same was not observed for the juveniles, where GO terms followed the same direction of regulation in the present vs past and in the future vs present, i.e., in agreement with the decreasing pH (Figure 3). The GO terms structural molecule activity (GO:0005198), kinase activity (GO:0016301), structural constituent of ribosome (GO:0003735) and RNA binding (GO:0003723) were all upregulated in the direction of the decreasing pH whereas peptide metabolic process (GO:0006518) was downregulated.
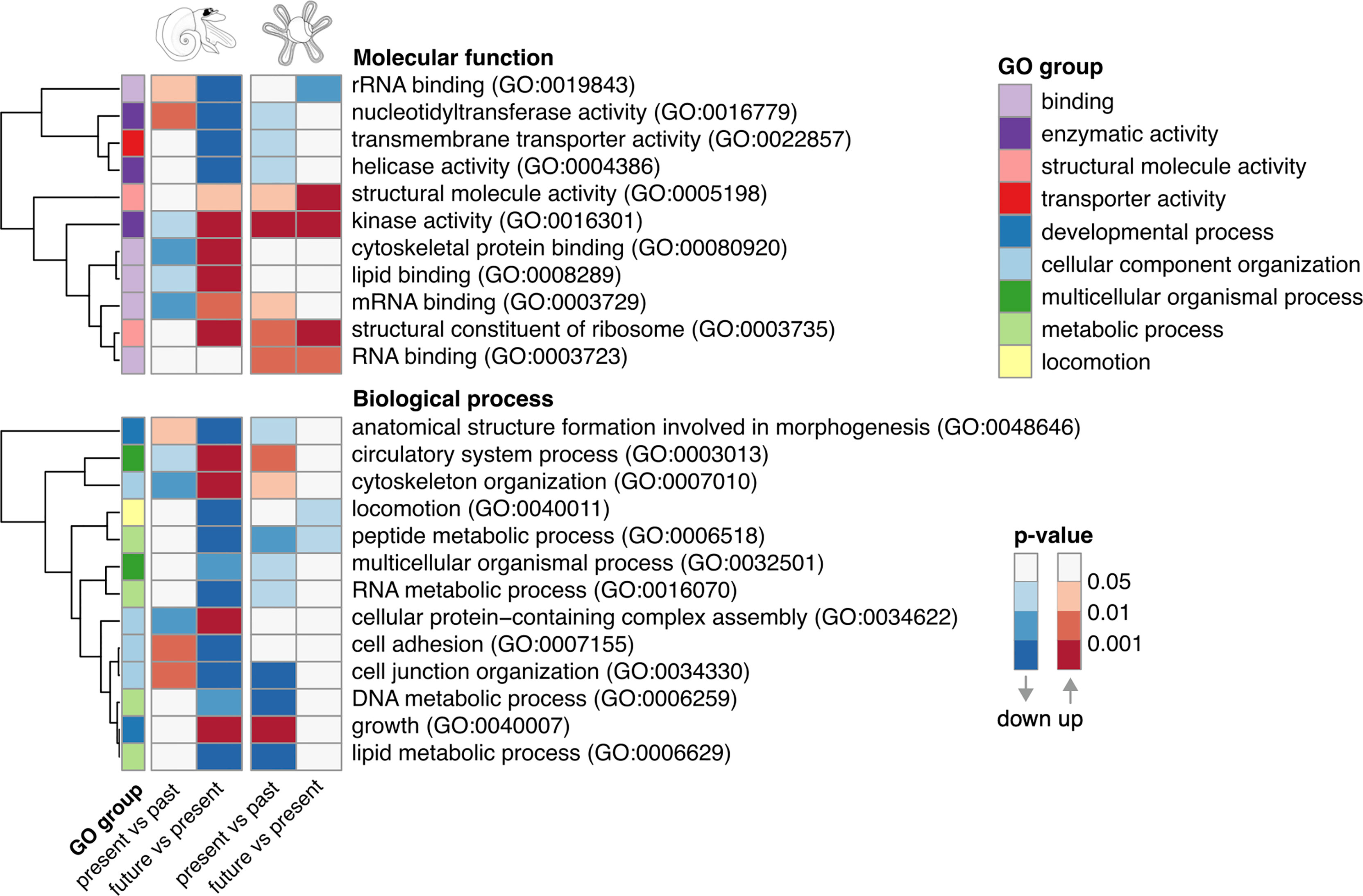
Figure 3 Enriched gene ontology terms among upregulated (red) or downregulated (blue) genes in the pairwise comparisons present versus past and future versus present, for juveniles (right) and adults (left) of the species Atlanta ariejansseni. In juveniles five GO terms are regulated in the same direction (same color: red or blue) for both comparisons. By contrast, 12 GO terms are regulated in opposing directions in adults. The GO terms are grouped by molecular function and biological process. The color sequences indicate that the enriched GO terms passed an adjusted p-value threshold of 0.05 or lower.
To further explore the differences in the responses between life stages, the Pearson correlation test was used to identify genes with expression patterns correlated with the decrease in pH and genes correlated with the changes between ambient vs treatments, i.e., with a ‘U-shaped’ response (Figure 4 and Supplementary Figure S2). In juveniles, a total of 1216 genes (7.7% of all filtered genes) were correlated with the pH, whereas this number was 613 (4.5%) for the adults. In adults, there were 1170 genes (8.6%) whose expression was rather correlated to a change in ambient environment, and for juveniles this number of genes was 623 (3.9%). We also observed a considerable fraction of genes differentially expressed only in the past or future conditions (Figure 4 and Supplementary Figure S3).
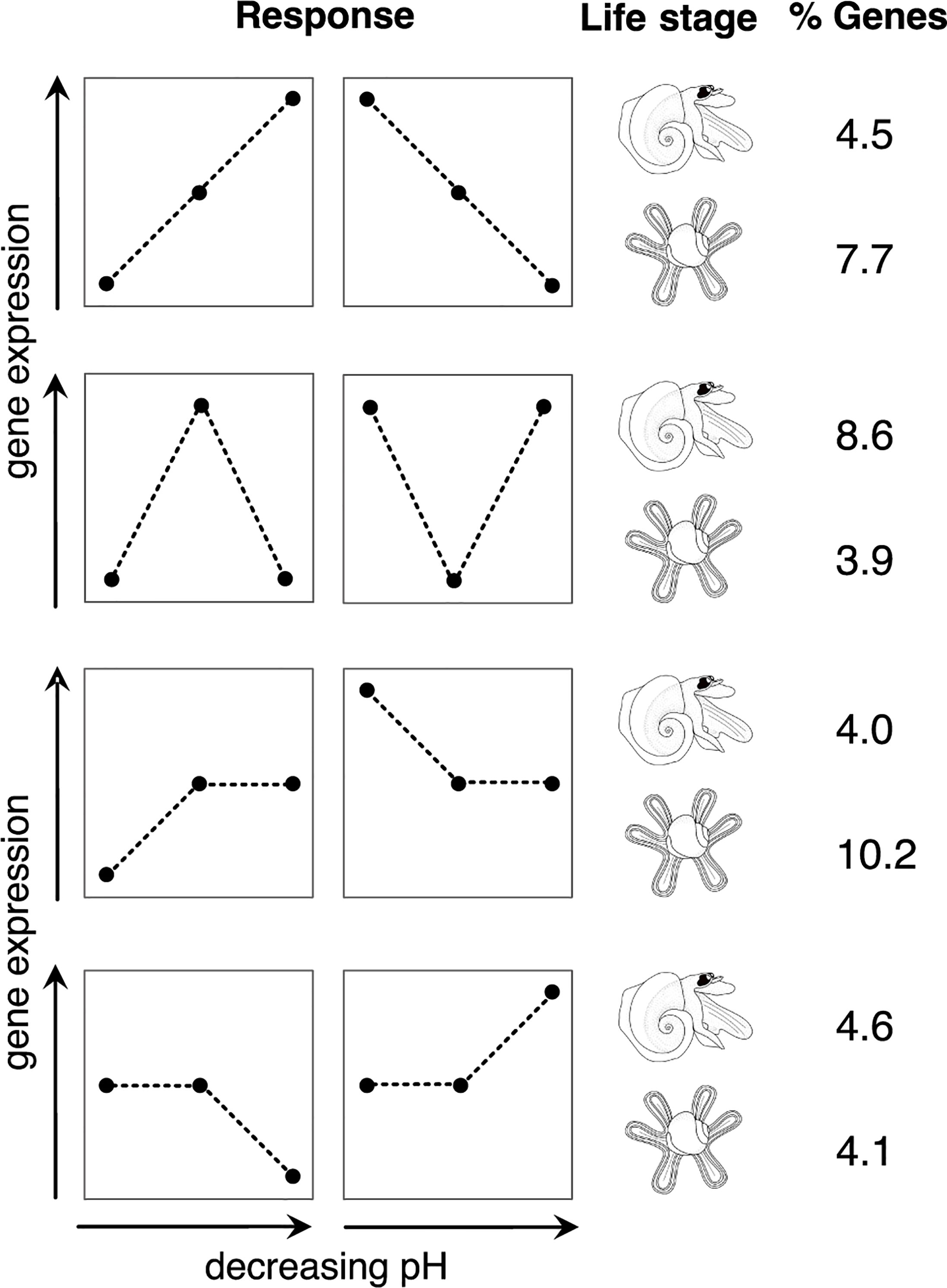
Figure 4 Percentage of genes in adult and juvenile Atlanta ariejansseni following the four main gene expression patterns in response to past, present and future ocean chemistry conditions. Four responses (from top to bottom): gene expression patterns correlated with a decrease in pH (linear response), gene expression patterns in accordance to change of the ambient condition (‘U-shaped’ response), differential expression patterns only in the past condition and differential expression patterns only in the future condition. The horizontal axis of the response plots represents the direction of decreasing pH from past, present and future ocean chemistry conditions. The proportions (%) refer to the genes in the filtered assembly that had a significant correlation (p-value<0.05) with each of the expression patterns using the Pearson correlation test (see also Supplementary Figures S2, S3).
Discussion
Transcriptomic Response in Adult Atlantids
The present study is a follow-up on the first OA experiments on atlantid juveniles (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). Here we provide a first insight into the OA response of adult atlantids, and a basic framework for comparing two very different life stages in the same experimental setup. In adult atlantids there were no significant changes in shell growth across treatments, however, biomineralization may have been affected by the incubation and the changes in seawater chemistry since 12 putative biomineralization genes were significantly up or downregulated (Supplementary Tables S6, S7). Results from our study can also be compared to those obtained from short-term OA exposures on adult shelled pteropods (Koh et al., 2015; Maas et al., 2015; Moya et al., 2016; Maas et al., 2018). However, it is worth noting that adult pteropods in previous studies were exposed to ocean chemistry conditions predicted for the future only, and, with more extreme conditions (pH values of 6.5-7.9) than the ones used here. Significantly DEGs putatively related to biomineralization in adult A. ariejansseni – collagen, c-type lectins and tyrosinase (Figure 2) - were also found to be affected by seawater chemistry in pteropods (Koh et al., 2015; Maas et al., 2015; Moya et al., 2016; Maas et al., 2018). Collagen was upregulated in adult A. ariejansseni under the future ocean chemistry conditions as well as in Limacina retroversa (Maas et al., 2018), Heliconoides inflatus (Moya et al., 2016) and Clio pyramidata (Maas et al., 2015) when exposed to lower pH conditions. Genes coding for c-type lectin (coadhesin-like and C-type lectin domain family 4) were upregulated from the past to the present in A. ariejansseni but did not have a significant fold change from the present to the future. In H. inflatus and C. pyramidata, c-type lectin-coding genes were upregulated (Maas et al., 2015; Moya et al., 2016) while in Limacina helicina they were downregulated (Koh et al., 2015), when exposed to higher CO2 concentrations. Two significantly DEGs involved in protein synthesis, 40S ribosomal protein and small subunit processome component, were upregulated in the future treatment but did not change significantly from the past to the present (Figure 2). This pattern contrasts with the experiments in Heliconoides inflatus (Moya et al., 2016), where similar genes were downregulated in response to low pH. Maas et al. (2018) suggested that differential expression of these genes may be a general stress response due to an interactive effect of captivity. Significant changes were also found in a putative fibrinolysis-related plasma serine protease (plasminogen) which was upregulated in the present and future conditions for adult A. ariejansseni. Plasminogen is associated with the immune response and was also significantly upregulated in adult pteropods under high CO2 treatments (Koh et al., 2015; Maas et al., 2018).
In sum, statistically significant DEGs associated with biomineralization, protein synthesis or degradation and immunity, but also other processes, show similar as well as different expression patterns in A. ariejansseni compared to shelled pteropods subjected to experimental ocean acidification. Some of the observed differences may be species-specific, keeping in mind that pteropods and atlantids are not phylogenetically closely related gastropods and are ecologically very distinct. Moreover, the differences in the experimental setups between studies, including incubation times, feeding and carbonate chemistry parameters, are also likely to influence calcification and the overall organismal response (Maas et al., 2018; Strader et al., 2020; Wall-Palmer et al., 2021).
Distinct Responses in the Two Life Stages
Atlantid juveniles and adults are morphologically very distinct and have unique transcriptomic profiles for each life stage (Figure 1). Hence it is insightful to compare their response to OA within the same experimental framework. During our three-day experiment, adult individuals showed no significant differences in shell extension between treatments (Supplementary Table S2). By contrast, juveniles had increased shell extension in the past and future treatments, and produced greater shell volume at high pH (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). The shell growth differences were accompanied by more genes with a decreasing or increasing expression level along the decreasing pH gradient in juveniles (1011 DEGs – 7.7% of total genes) than in adults (409 DEGs – 4.5% of total genes) (Figure 4). When blasting the two sets of significantly DEGs we found that there were no genes in common between the two life stages but some of their putative functions were similar. These included coadhesin, epidermal growth factor (EGF), complement component 1q (C1q), C-type lectin, extensin-like, MAM and LDL-receptor (meprin, A-5 protein, and receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase mu, low-density lipoprotein), (von Willebrand factor type A) vWFA, RNA-directed DNA polymerase from mobile element jockey-like, endoglucanase, trypsin, and ribosomal proteins. In adult A. ariejansseni, the 33 statistically significant DEGs were mostly associated with biomineralization and the immune response. In juveniles, other processes including morphogenesis, protein synthesis, oxidative metabolism, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism were also significantly affected (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). Taking together the transcriptomic response and the shell growth experiments, we suggest that juveniles are more sensitive to the changes in seawater chemistry than the adults.
GO enrichment analyses showed that genes associated with 12 GO categories were inversely regulated from the past to the present and from the present to the future conditions for adults, whereas in juveniles genes associated to five GO terms were always regulated in the same direction, i.e. congruent with the decrease in pH (Figure 3). The Pearson correlation test further supported these observations by showing that there were more genes having a U-shape pattern in adults (8.6%) than in juveniles (3.9%) (Figure 4). This suggests that adults are better adapted than juveniles to their ambient environment and respond to any change in seawater chemistry, be it to higher or to lower pH. Conversely, juveniles had more genes whose expression was linearly correlated with the decrease in pH and more genes only differentially expressed in the past condition (Figure 4). These results support a higher vulnerability of juveniles to the incubation experiments, and to OA, when compared to adults of the same species. Early life stages have been shown to be more sensitive to OA than adults in many marine invertebrates (Kurihara, 2008; Byrne, 2011; Kroeker et al., 2013), including pteropods (Thabet et al., 2015; León et al., 2019). The juvenile stage is a period in which atlantids are expected to grow a large amount of their aragonite shell before they transition into mature adults and this stage likely constitutes a major bottleneck in the species’ survival in acidifying waters.
Implications and Limitations of Our Experiment
Atlantids were exposed to pH levels ranging from 8.03 to 8.19 for a period of three days mimicking past, present and future ocean chemistry conditions. These short incubation times, without experimental acclimation, cannot predict what will happen in the long term, such as in a multi-generational response or in the field. However, our short-term experiments provide insight into the acute responses of A. ariejansseni to changing ocean chemistry based on general changes in calcification and in the transcriptional profiles. Although some marine zooplankton species have been successfully cultured to look into transgenerational effects of OA (De Wit et al., 2016), similar experiments remain challenging for holoplanktonic gastropods. Several culturing techniques have been attempted with pteropods but they experience high mortality rates in captivity (Howes et al., 2014). Rearing atlantids faces additional problems: as juveniles they can be provided with an algal food source but when metamorphosing into adults, after 9 to 11 days of incubation, they become carnivorous and may show cannibalistic behaviour (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021). A second limitation of our experiment is the lack of biological replicates, with only one carboy per treatment and two replicates for transcriptome analysis. In this case, the possibility of the carboy as a confounding factor cannot be ruled out. However, ocean chemistry conditions of the carboys used for the juvenile calcification experiments, which used the same pre-treated water and were run in parallel to the adult experiment, were consistent across the three replicates (pH 8.186 ± 0.019 for the past, 8.143 ± 0.017 for the present and 8.030 ± 0.002 for the future) (Wall-Palmer et al., 2021) and similar to those of the adults. A third limitation was the difference in pool sizes between adults (two individuals) and juveniles (eight to ten individuals) in order to have enough RNA for downstream processing (Supplementary Table S3). In general, increasing the number of individuals in the pool is expected to minimize the variance between replicates (Takele Assefa et al., 2020) and improve statistical power to detect DEGs. However, variability between biological replicates was shown to be quite high in other wild-caught planktonic gastropods (Maas et al., 2015; Maas et al., 2018; Johnson and Hofmann, 2020), meaning that in this case a small pool size may be more effective. Thus, it is unclear whether the difference in pool sizes had a significant effect on transcriptional noise. Given the limitations of the experimental setup in regard to the low number of replicates, we adopted a conservative approach by including an additional filtering step to remove genes having high expression variation between replicates. Future studies should include at least three biological replicates to ensure more statistical power.
Conclusion
We assessed and compared the calcification and transcriptomic responses to short-term OA exposure in the adult and juvenile stages of the holoplanktonic gastropod A. ariejansseni. Our results show highly distinct transcriptional profiles for each life stage and provide first insights into the development and physiology of atlantids. Adults responded to our perturbation experiments with smaller changes in gene expression than juveniles, suggesting that juveniles are more sensitive to ocean acidification. Thus, more focus should be given to responses at distinct, and especially early, life stages in future studies addressing the impact of OA in calcifying zooplankton. Moreover, our RNAseq data and bioinformatics pipeline for DGE analysis represent a valuable framework for further comparative transcriptomic approaches between distinct developmental stages.
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of this study is provided as supplementary information. Reads used in this study were deposited at NCBI BioProject PRJNA742523. The Transcriptome Shotgun Assembly has been deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the accession GJHI00000000. The version described in this paper is the first version, GJHI00000000. R scripts and input files can be accessed on Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/Mari-Lee/atlanta.
Author Contributions
PR-S Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – Original Draft, Supervision, Funding acquisition. M-LO: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – Original Draft, Visualization. DW-P: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Funding acquisition. LM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation. KP: Conceptualization, Writing - Review & Editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 844345 [EPIC, PRS] and grant agreement No. 746186 [POSEIDoN, DW-P]. Plankton collection on the AMT27 cruise was funded by a Vidi grant (016.161351) from the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) to KTCAP. The Atlantic Meridional Transect is funded by the UK Natural Environment Research Council through its National Capability Long-term Single Centre Science Programme, Climate Linked Atlantic Sector Science (grant number NE/R015953/1).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Elza Duijm for advice and preparation of the RNA libraries, to Vassilis Kitidis and Matthew Humphreys for discussion on carbonate chemistry and checking carbonate system calculations, and to Erica Goetze for advice and support during sampling and the onboard experiments. We would also like to thank the captain, crew and scientists who supported our work during cruise DY084/085 (AMT27) onboard the RRS Discovery (PSO: A. Rees). This study contributes to the international IMBeR project and is contribution number 373 of the Atlantic Meridional Transect programme.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2022.801458/full#supplementary-material
References
Afgan E., Baker D., van den Beek M., Blankenberg D., Bouvier D., Čech M., et al. (2016). The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W3–W10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw343
Bednaršek N., Feely R. A., Reum J. C. P., Peterson B., Menkel J., Alin S. R., et al. (2014). Limacina Helicina Shell Dissolution as an Indicator of Declining Habitat Suitability Owing to Ocean Acidification in the California Current Ecosystem. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 281, 20140123. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.0123
Bednaršek N., Klinger T., Harvey C. J., Weisberg S., McCabe R. M., Feely R. A., et al. (2017). New Ocean, New Needs: Application of Pteropod Shell Dissolution as a Biological Indicator for Marine Resource Management. Ecol. Indic. 76, 240–244. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.01.025
Bednaršek N., Možina J., Vogt M., O’Brien C., Tarling G. A. (2012a). The Global Distribution of Pteropods and Their Contribution to Carbonate and Carbon Biomass in the Modern Ocean. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 4, 167–186. doi: 10.5194/essd-4-167-2012
Bednaršek N., Tarling G. A., Bakker D. C. E., Fielding S., Jones E. M., Venables H. J., et al. (2012b). Extensive Dissolution of Live Pteropods in the Southern Ocean. Nat. Geosci. 5, 881–885. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1635
Bianchet M. A., Odom E. W., Vasta G. R., Amzel L. M. (2002). A Novel Fucose Recognition Fold Involved in Innate Immunity. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 628–634. doi: 10.1038/nsb817
Buitenhuis E. T., Le Quéré C., Bednaršek N., Schiebel R. (2019). Large Contribution of Pteropods to Shallow CaCO3 Export. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 33, 458–468. doi: 10.1029/2018GB006110
Burridge A. K., Goetze E., Wall-Palmer D., Le Double S. L., Huisman J., Peijnenburg K. T. C. A. (2017). Diversity and Abundance of Pteropods and Heteropods Along a Latitudinal Gradient Across the Atlantic Ocean. Prog. Oceanogr. 158, 213–223. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2016.10.001
Byrne M. (2011). Impact of Ocean Warming and Ocean Acidification on Marine Invertebrate Life History Stages: Vulnerabilities and Potential for Persistence in a Changing Ocean. In Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review (CRC Press), 1–42.
Byrne M. (2012). Global Change Ecotoxicology: Identification of Early Life History Bottlenecks in Marine Invertebrates, Variable Species Responses and Variable Experimental Approaches. Mar. Environ. Res. 76, 3–15. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2011.10.004
Byrne M., Przeslawski R. (2013). Multistressor Impacts of Warming and Acidification of the Ocean on Marine Invertebrates’ Life Histories. Integr. Comp. Biol. 53, 582–596. doi: 10.1093/icb/ict049
Caldeira K., Wickett M. E. (2003). Anthropogenic Carbon and Ocean pH. Nature 425, 365–365. doi: 10.1038/425365a
Comeau S., Gorsky G., Jeffree R., Teyssié J.-L., Gattuso J.-P. (2009). Impact of Ocean Acidification on a Key Arctic Pelagic Mollusc (Limacina Helicina). Biogeosciences 6, 1877–1882. doi: 10.5194/bg-6-1877-2009
Demarchi B., Hall S., Roncal-Herrero T., Freeman C. L., Woolley J., Crisp M. K., et al. (2016). Protein Sequences Bound to Mineral Surfaces Persist Into Deep Time. Elife 5. doi: 10.7554/eLife.17092
De Wit P., Dupont S., Thor P. (2016). Selection on Oxidative Phosphorylation and Ribosomal Structure as a Multigenerational Response to Ocean Acidification in the Common Copepod Pseudocalanus acuspes. Evol. Appl. 9, 1112–1123. doi: 10.1111/eva.12335
Dickson A. G. (1990). Thermodynamics of the Dissociation of Boric Acid in Potassium Chloride Solutions From 273.15 to 318.15 K. Deep Sea Res. Part A. Oceanogr. Res., 37. doi: 10.1021/je00061a009
Dickson A. G., Millero F. J. (1987). A Comparison of the Equilibrium Constants for the Dissociation of Carbonic Acid in Seawater Media. Deep Sea Res. Part A. Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 34, 1733–1743. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(87)90021-5
Doney S. C., Fabry V. J., Feely R. A., Kleypas J. A. (2009). Ocean Acidification: The Other CO2 Problem. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 1, 169–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.marine.010908.163834
Eddy S. R. (2011). Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PloS Comput. Biol. 7, e1002195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195
El-Gebali S., Mistry J., Bateman A., Eddy S. R., Luciani A., Potter S. C., et al. (2019). The Pfam Protein Families Database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D427–D432. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky995
Fabry V. J., Seibel B. A., Feely R. A., Orr J. C. (2008). Impacts of Ocean Acidification on Marine Fauna and Ecosystem Processes. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 65, 414–432. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsn048
Faria D. (2017) GOSlimmer. Available at: https://github.com/DanFaria/GOSlimmer.
Feely R. A., Sabine C. L., Lee K., Berelson W., Kleypas J., Fabry V. J., et al (2004). Impact of Anthropogenic CO2 on the CaCO3 System in the Oceans. Science 305, 362–366. doi: 10.1126/science.1097329
Feely R. A., Doney S. C., Cooley S. R., et al (2009). Present Conditions and Future Changes in a High-CO2 World. Oceanography 22, 36–47. doi: 10.5670/oceanog.2009.95
Gattuso J.-P., Magnan A., Billé R., Cheung W. W. L., Howes E. L., Joos F., et al. (2015). Contrasting Futures for Ocean and Society From Different Anthropogenic CO2 Emissions Scenarios. Science 349. doi: 10.1126/science.aac4722
Gestal C., Pallavicini A., Venier P., Novoa B., Figueras A. (2010). MgC1q, a Novel C1q-Domain-Containing Protein Involved in the Immune Response of Mytilus galloprovincialis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 34, 926–934. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2010.02.012
Gruber N., Clement D., Carter B. R., Feely R. A., van Heuven S., Hoppema M., et al. (2019). The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2 From 1994 to 2007. Science 363, 1193–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.aau5153
Haas B. J., Papanicolaou A., Yassour M., Grabherr M., Blood P. D., Bowden J., et al. (2013). De Novo Transcript Sequence Reconstruction From RNA-Seq Using the Trinity Platform for Reference Generation and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 8, 1494–1512. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.084
Herlitze I., Marie B., Marin F., Jackson D. J. (2018). Molecular Modularity and Asymmetry of the Molluscan Mantle Revealed by a Gene Expression Atlas. Gigascience 7, giy056. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giy056
Hoegh-Guldberg O., Cai R., Poloczanska E. S., Brewer P. G., Sundby S., Hilmi K., et al. (2014). “The Ocean” in Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Eds. Barros V. R., Field C. B., Dokken D. J., Mastrandrea M. D., Mach K. J., Bilir T. E., et al (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 1655–1732. doi: 10.1017/CBO9781107415386.010
Hoppe C. J. M., Langer G., Rokitta S. D., Wolf-Gladrow D. A., Rost B. (2012). Implications of Observed Inconsistencies in Carbonate Chemistry Measurements for Ocean Acidification Studies. Biogeosciences 9, 2401–2405. doi: 10.5194/bg-9-2401-2012
Howes E. L., Bednaršek N., Budenbender J., Comeau S., Doubleday A., Gallager S. M., et al. (2014). Sink and Swim: A Status Review of Thecosome Pteropod Culture Techniques. J. Plankton Res. 36, 299–315. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbu002
Huang Y., Niu B., Gao Y., Fu L., Li W. (2010). CD-HIT Suite: A Web Server for Clustering and Comparing Biological Sequences. Bioinformatics 26, 680–682. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq003
Jiang L. Q., Carter B. R., Feely R. A., Lauvset S. K., Olsen A. (2019). Surface Ocean pH and Buffer Capacity: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 9, 18624. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55039-4
Johnson K. M., Hofmann G. E. (2020). Combined Stress of Ocean Acidification and Warming Influence Survival and Drives Differential Gene Expression Patterns in the Antarctic Pteropod, Limacina Helicina antarctica. Conserv. Physiol. 8, coaa013. doi: 10.1093/conphys/coaa013
Koh H. Y., Lee J. H., Han S. J., Park H., Shin S. C., Lee S. G. (2015). A Transcriptomic Analysis of the Response of the Arctic Pteropod Limacina Helicina to Carbon Dioxide-Driven Seawater Acidification. Polar Biol. 38, 1727–1740. doi: 10.1007/s00300-015-1738-4
Kroeker K. J., Kordas R. L., Crim R., Hendriks I. E., Ramajo L., Singh G. S., et al. (2013). Impacts of Ocean Acidification on Marine Organisms: Quantifying Sensitivities and Interaction With Warming. Glob. Change Biol. 19, 1884–1896. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12179
Kurihara H. (2008). Effects of CO2-Driven Ocean Acidification on the Early Developmental Stages of Invertebrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 373, 275–284. doi: 10.3354/meps07802
Lalli C. M., Gilmer R. W. (1989). Pelagic Snails: The Biology of Holoplanktonic Gastropod Mollusks (Stanford University Press).
Langmead B., Salzberg S. L. (2012). Fast Gapped-Read Alignment With Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
León P., Bednaršek N., Walsham P., Cook K., Hartman S. E., Wall-Palmer D., et al. (2019). Relationship Between Shell Integrity of Pelagic Gastropods and Carbonate Chemistry Parameters at a Scottish Coastal Observatory Monitoring Site. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 77, 436–450. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsz178
Le Quéré C., Moriarty R., Andrew R. M., Peters G. P., Ciais P., Friedlingstein P., et al. (2015). Global Carbon Budget 2014. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 7, 47–85. doi: 10.5194/essd-7-47-2015
Love M. I., Huber W., Anders S. (2014). Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data With Deseq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Maas A. E., Lawson G. L., Bergan A. J., Tarrant A. M. (2018). Exposure to CO2 Influences Metabolism, Calcification, and Gene Expression of the Thecosome Pteropod Limacina retroversa. J. Exp. Biol. 221, jeb164400. doi: 10.1242/jeb.164400
Maas A. E., Lawson G. L., Tarrant A. M. (2015). Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of the Response of the Thecosome Pteropod Clio pyramidata to Short-Term CO2 Exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genomics Proteomics 16, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cbd.2015.06.002
Manno C., Bednaršek N., Tarling G. A., Peck V. L., Comeau S., Adhikari D., et al. (2017). Shelled Pteropods in Peril: Assessing Vulnerability in a High CO2 Ocean. Earth-Science Rev. 169, 132–145. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.04.005
Marie B., Jackson D. J., Ramos-Silva P., Zanella-Cléon I., Guichard N., Marin F. (2013). The Shell-Forming Proteome of Lottia gigantea Reveals Both Deep Conservations and Lineage-Specific Novelties. FEBS J. 280, 214–232. doi: 10.1111/febs.12062
Marin F. (2020). Mollusc Shellomes: Past, Present and Future. J. Struct. Biol. 212, 107583. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2020.107583
Mehrbach C., Culberson C. H., Hawley J. E., Pytkowicx R. M. (1973). Measurement of the Apparent Dissociation Constants of Carbonic Acid in Seawater At Atmospheric Pressure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 897–907. doi: 10.4319/lo.1973.18.6.0897
Mekkes L., Sepúlveda-Rodríguez G., Bielkinaitė G., Wall-Palmer D., Brummer G.-J. A., Dämmer L. K., et al. (2021). Effects of Ocean Acidification on Calcification of the Sub-Antarctic Pteropod Limacina Retroversa. Front. Mar. Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.581432
Melzner F., Mark F. C., Seibel B. A., Tomanek L. (2020). Ocean Acidification and Coastal Marine Invertebrates: Tracking CO2 Effects From Seawater to the Cell. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 12, 499–523. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010419-010658
Mikheenko A., Prjibelski A., Saveliev V., Antipov D., Gurevich A. (2018). Versatile Genome Assembly Evaluation With QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 34, i142–i150. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty266
Moya A., Howes E. L., Lacoue-Labarthe T., Forêt S., Hanna B., Medina M., et al. (2016). Near-Future pH Conditions Severely Impact Calcification, Metabolism and the Nervous System in the Pteropod Heliconoides inflatus. Glob. Change Biol. 22, 3888–3900. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13350
Negrete-García G., Lovenduski N. S., Hauri C., Krumhardt K. M., Lauvset S. K. (2019). Sudden Emergence of a Shallow Aragonite Saturation Horizon in the Southern Ocean. Nat. Clim. Change 9, 313–317. doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0418-8
Orr J. C., Fabry V. J., Aumont O., Bopp L., Doney S. C., Feely R., et al. (2005). Anthropogenic Ocean Acidification Over the Twenty-First Century and its Impact on Calcifying Organisms. Nature 437, 681–686. doi: 10.1038/nature04095
Patro R., Duggal G., Love M. I., Irizarry R. A., Kingsford C. (2017). Salmon Provides Fast and Bias-Aware Quantification of Transcript Expression. Nat. Methods 14, 417–419. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4197
Pierrot D. E., Wallace D. W. R., Lewis E. (2011). MS Excel Program Developed for CO2 System Calculations. doi: 10.3334/CDIAC/otg.CO2SYS_XLS_CDIAC105a
Pilkington M. G. (1970). Young Stages and Metamorphosis in an Atlantid Heteropod Occurring Off South-Eastern New Zealand. J. Molluscan Stud. 39, 117–124. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.mollus.a065086
Ramos-Silva P., Marin F. (2016). Proteins as Functional Units of Biocalcification – An Overview. Key Eng. Mater. 672, 183–190. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.672.183
Riebesell U., Gattuso J.-P. (2015). Lessons Learned From Ocean Acidification Research. Nat. Clim. Change 5, 12–14. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2456
Schindelin J., Arganda-Carreras I., Frise E., Kaynig V., Longair M., Pietzsch T., et al. (2012). Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 676–682. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2019
Schurch N. J., Schofield P., Gierliński M., Cole C., Sherstnev A., Singh V., et al. (2016). How Many Biological Replicates Are Needed in an RNA-Seq Experiment and Which Differential Expression Tool Should You Use? RNA 22, 839–851. doi: 10.1261/rna.053959.115
Shimizu K., Kimura K., Isowa Y., Oshima K., Ishikawa M., Kagi H., et al. (2019). Insights Into the Evolution of Shells and Love Darts of Land Snails Revealed From Their Matrix Proteins. Genome Biol. Evol. 11, 380–397. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy242
Simão F. A., Waterhouse R. M., Ioannidis P., Kriventseva E. V., Zdobnov E. M. (2015). BUSCO: Assessing Genome Assembly and Annotation Completeness With Single-Copy Orthologs. Bioinformatics 31, 3210–3212. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351
Stoll M. H. C., Bakker K., Nobbe G. H., Haese R. R. (2001). Continuous-Flow Analysis of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon Content in Seawater. Anal. Chem. 73, 4111–4116. doi: 10.1021/ac010303r
Strader M. E., Wong J. M., Hofmann G. E. (2020). Ocean Acidification Promotes Broad Transcriptomic Responses in Marine Metazoans: A Literature Survey. Front. Zool. 17, 7. doi: 10.1186/s12983-020-0350-9
Sun W., Jayaraman S., Chen W., Persson K. A., Ceder G. (2015). Nucleation of Metastable Aragonite CaCO3 in Seawater. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112, 3199–3204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423898112
Takele Assefa A., Vandesompele J., Thas O. (2020). On the Utility of RNA Sample Pooling to Optimize Cost and Statistical Power in RNA Sequencing Experiments. BMC Genomics 21, 312. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6721-y
Thabet A. A., Maas A. E., Lawson G. L., Tarrant A. M. (2015). Life Cycle and Early Development of the Thecosomatous Pteropod Limacina retroversa in the Gulf of Maine, Including the Effect of Elevated CO2 Levels. Mar. Biol. 162, 2235–2249. doi: 10.1007/s00227-015-2754-1
Wall-Palmer D., Burridge A. K., Goetze E., Stokvis F. R., Janssen A. W., Mekkes L., et al. (2018a). Biogeography and Genetic Diversity of the Atlantid Heteropods. Prog. Oceanogr. 160, 1–25. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2017.11.004
Wall-Palmer D., Burridge A. K., Peijnenburg K. T. C. A. (2016a). Atlanta Ariejansseni, a New Species of Shelled Heteropod From the Southern Subtropical Convergence Zone (Gastropoda, Pterotracheoidea). Zookeys, 13–30. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.604.8976
Wall-Palmer D., Mekkes L., Ramos-Silva P., Dämmer L. K., Goetze E., Bakker K., et al. (2021). The Impacts of Past, Present and Future Ocean Chemistry on Predatory Planktonic Snails. R. Soc. Open Sci. 8, 202265. doi: 10.1098/rsos.202265
Wall-Palmer D., Metcalfe B., Leng M. J., Sloane H. J., Ganssen G., Vinayachandran P. N., et al. (2018b). Vertical Distribution and Diurnal Migration of Atlantid Heteropods. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 587, 1–15. doi: 10.3354/meps12464
Wall-Palmer D., Smart C. W., Kirby R., Hart M. B., Peijnenburg K. T. C. A., Janssen A. W. (2016b). A Review of the Ecology, Palaeontology and Distribution of Atlantid Heteropods (Caenogastropoda: Pterotracheoidea: Atlantidae). J. Molluscan Stud. 82, 221–234. doi: 10.1093/mollus/eyv063
Woodward E. M. S., Harris C. (2019). Atlantic Meridional Transect Cruise AMT27 (DY084) Micro-Molar Nutrient Measurements From CTD Bottle Samples During 2017.
Wright R. M., Aglyamova G. V., Meyer E., Matz M. V. (2015). Gene Expression Associated With White Syndromes in a Reef Building Coral, Acropora hyacinthus. BMC Genomics 16, 371. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1540-2
Keywords: ocean acidification, bioindicator, gene expression, calcification, planktonic gastropods, atlantids, life stages
Citation: Ramos-Silva P, Odendaal M-L, Wall-Palmer D, Mekkes L and Peijnenburg KTCA (2022) Transcriptomic Responses of Adult Versus Juvenile Atlantids to Ocean Acidification. Front. Mar. Sci. 9:801458. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.801458
Received: 25 October 2021; Accepted: 17 March 2022;
Published: 16 May 2022.
Edited by:
Gary H. Dickinson, The College of New Jersey, United StatesReviewed by:
Kanmani Chandra Rajan, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaShiguo Li, Research Center for Eco-environmental Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2022 Ramos-Silva, Odendaal, Wall-Palmer, Mekkes and Peijnenburg. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Paula Ramos-Silva, cGF1bGEuc3JzQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Katja T. C. A. Peijnenburg, a2F0amEucGVpam5lbmJ1cmdAbmF0dXJhbGlzLm5s
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Paula Ramos-Silva
Paula Ramos-Silva Mari-Lee Odendaal
Mari-Lee Odendaal Deborah Wall-Palmer
Deborah Wall-Palmer Lisette Mekkes
Lisette Mekkes Katja T. C. A. Peijnenburg
Katja T. C. A. Peijnenburg