- 1Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-Resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, China
- 2Guangdong Provincial Observation and Research Station for Coastal Upwelling Ecosystem, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology (SCSIO), Shantou, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Biotechnology of Hainan Province, Sanya Institute of Oceanology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology (SCSIO), Sanya, China
- 4College of Earth and Planetary Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Although the adverse effects of increasing atmospheric CO2-induced ocean acidification (OA) on marine calcifying macroalgae have been widely reported, there are limited studies on how daily fluctuations in pCO2 (pH) within shallow ecosystems influence the growth and physiological performance of these calcifiers. Therefore, a 42-day laboratory mimetic experiment to determine how growth, biological performance and related carbon and nitrogen metabolic products of the calcifying macroalga, Halimeda opuntia are generated in response to fluctuating pCO2 under OA conditions (1200 ppmv) was performed. The results of present study showed that the adverse effects of OA were more determined by the adverse influence of elevated acidity (H+) on growth rates, calcification, photosynthesis and the related biotic performance of H. opuntia compared with the positive effects that higher CO2 provided. Moreover, diurnal fluctuations in pCO2 levels [with higher (nearly 8.10) and lower pH (nearly 7.40) values during day and night times, respectively] have amplified these negative influences on H. opuntia. To mitigate elevated pCO2-related stress, higher contents of free amino acids and proline were highly secreted and likely linked to protecting the integrity of algal cellular structures. The above results contribute to increasing our understanding of the biological consequences of pCO2 (pH) variability on calcifying Halimeda species and their physiological plasticity in response to further oceanic pCO2 changes.
Introduction
Atmospheric CO2 reached up to 412.15 ± 0.1 ppm in 2020, and preliminary data for 2021 suggest a rebound in CO2 relative to 2020 of + 4.8% (4.2% to 5.4%) globally, which is thought to be initially and primarily caused by fossil fuel emissions and deforestation (Friedlingstein et al., 2022). The absorption of CO2 has already caused apparent changes in the carbonate chemistry of surface seawater and is predicted to decrease by 0.44 ± 0.005 units from 1870–1899 to 2080–2099 (Masson-Delmotte et al., 2021), thus, resulting in an ongoing process and this trend called ocean acidification (OA) (Caldeira and Wickett, 2003; Gattuso et al., 2015; Masson-Delmotte et al., 2021). To date, there have been considerable studies on the impacts of OA on marine organisms, especially macroalgae, because they are important marine primary producers. Elevated pCO2 would benefit the growth and photosynthesis of some autotrophic macroalgae, such as the economically important macroalgae, Gracilaria lemaneiformis (Chen et al., 2018), and Pyropia yezoensis (Bao et al., 2019), as well as the green macroalga Ulva lactuca (Olischläger and Wiencke, 2013) and U.prolifera (Gao et al., 2017). In addition, no obvious effects of elevated pCO2 on Ulva rigida have been demonstrated (Rautenberger et al., 2015; Gao et al., 2018). However, downward trends in growth rate and pigment accumulation have been observed in Pyropia yezoensis (Mercado et al., 1999) and calcifying macroalgae Halimeda spp. (Campbell et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2020a). Egilsdottir et al. (2013) investigated the lower mMg/Ca ratio of calcite and fewer structures in new fragments produced by the red calcareous coralline alga Corallina elongata under elevated pCO2 (550, 750, and 1,000 ppmv) conditions. A similar phenomenon was reported by Ragazzola et al. (2012), who demonstrated that under elevated pCO2 conditions, the mMg/Ca ratio in the skeletal calcite of the coralline macroalga Lithothamnion glaciale was too small to maintain the stability of skeletal structures by higher ecological niche predators and additional energy to withstand bioerosion and physical erosion. These species-specific responses of macroalgae to OA (elevated pCO2) might be attributed to the efficiency of dissolved inorganic carbon (CO2 utilization and/or elevated acidity) (Egilsdottir et al., 2013; Qu et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2018).
The Halimeda genus of green calcareous macroalgae (Chlorophyta, Bryopsidales) is an ecologically important carbonate macroalgae that is widely distributed in tropical and sub-tropical reefs and lagoons (Hofmann et al., 2014; Wei et al., 2020a; Wei et al., 2020b; Wei et al., 2020c). On a global scale, carbonate sediment production by Halimeda species accounts for nearly 8% of the carbonate budget, at 0.15–0.4 Gt CaCO3 year−1 (Milliman, 1993; Hillis, 2001). Previous studies suggested that CaCO3 biomineralization in some marine organisms, including Halimeda spp., is an enzymatic process that mainly uses bicarbonatefmars.2022.968740, such as the action of a Ca2+/H+-ATPase present in the calicoblastic epithelium (Jury et al., 2010; Wizemann et al., 2015). Studies have documented that biotic CaCO3 precipitation is significantly and adversely affected by the elevation of seawater pCO2, because the CaCO3 saturation (Ω) and pH values are consequently reduced. However, moderate elevations in pCO2 induce a higher availability, which contributes to calcification and photosynthesis processes (Hofmann et al., 2014; Vogel et al., 2015; Campbell et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2020a). For instance, Yildiz et al. (2013) found that low pH (7.7) increased the relative electron transport rates (rETR) of calcified rhodophyte Corallina officinalis. These wide variety of responses by calcifiers is likely due to either taxonomic distinctions (Kroeker et al., 2010; Peach et al., 2017) or the interactive effects of other environmental factors, such as light intensities (Teichberg et al., 2013; Wei et al., 2020a), seawater temperature (Campbell et al., 2016), nutrient regimes (Teichberg et al., 2013) and/or pH fluctuations (Cornwall et al., 2013).
Compared with pelagic oceans, in coastal waters the magnitude of diurnal pH variation always exceeds 0.6 units owing to the CO2 uptake by photosynthesis during the day time and CO2 release via respiration and other biological activities during the night time. Moreover, the large-scale nutrient inputs from human industry and agriculture have aggravated diurnal pH variations in coastal waters (Egilsdottir et al., 2013). Qu et al. (2017) demonstrated that under diurnal pH fluctuation conditions, from approximately 7.83 to approximately 8.44, the adverse effects of acidity (H+) on the photosynthetic performance of the red macroalga Gracilaria lemaneiformis cultivated under high-density conditions that resulted from the CO2 uptake was relatively small. Therefore, the diurnal variability of pH occurring in marine ecosystems is a non-negligible environmental factor affecting the growth and metabolic processes of marine organisms in current oceans and may have characteristic implications for predicting the responses of marine calcifiers to OA in the future (Cornwall et al., 2013). The capacity of marine calcifiers to resist significant diurnal pH/pCO2 fluctuations may be a result of short-term acclimation (due to the phenotypic plasticity of the individual) and/or long-term adaptation (genetic endowment by the population) (Egilsdottir et al., 2013). For instance, Martin and Gattuso (2009) reported that the reduced calcification rate of coralline alga Lithophyllum cabiochae was observed under elevated pCO2 conditions after 1 month, but no obvious effects were observed after acclimatization for 1 year. Thus, to accurately predict how climate changes will affect marine organisms, it is essential to preferentially determine the present detailed effects of specific environmental variabilities on marine species at both local and larger regional scales (Cornwall et al., 2013; Reusch and Boyd, 2013).
Halimeda species may be sensitive to highly variable environments. Teichberg et al. (2013) found that photosynthetic pigment concentrations in Halimeda opuntia were usually higher in deep than shallow waters to enhance light acquisition in areas having low light conditions, whereas carotenoids play a role in photoprotection for mitigating light stress. These phenomena have also been widely found in macroalgae that grow in tropical shallow waters (Beach et al., 2003). To date, however, there are limited studies on how daily fluctuations in pCO2 (pH) within shallow ecosystems influence the growth and physiological performance of marine calcifiers, including Halimeda species. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to examine how abiotic responses of Halimeda to OA are influenced by diurnal fluctuations in seawater pCO2 (pH). It has been hypothesized that (1) periods of relatively lower CO2/higher pH may ameliorate negative influences of OA on marine calcifiers to some degree, by providing short rest intervals that may be beneficial to their calcification (Hurd et al., 2011; Dufault et al., 2012), or (2) amplify the negative effects of OA on biotic performance owing to the extreme mean decreases in pH, especially during the night (Cornwall et al., 2013). These physiological descriptions of accurately mimicked laboratory incubation experiments will provide a better understanding of the responses of marine calcifying organisms to future global climate change-mediated alterations in pH levels.
Materials and methods
Monitoring in situ pH fluctuations and sample collection
For a description of the pH fluctuations at the Halimeda community sampling site located in the Xisha Islands, South China Sea (9.53°–9.60° N, 115.34°–115.46° E), pH values were monitored at 6:00 and 18:00 daily for 30 days (June 1 to 30, 2021) using a YSI meter (YSI Professional Plus, Yellow Springs, OH, USA). The average pH values within the Halimeda community at 6:00 and 18:00 were 8.43 and 7.63, respectively, indicating that the pH variability ranged by 0.80 units during the in situ monitoring period (Figure 1) and contributed to our subsequent experiment design (as described in 2.2). Afterwards, thalli of H. opuntia were sampled in a fore reef lagoon at depths ranging from 1.5–2.5 m and then transported back to the laboratory. To acclimatize the macroalgae to the experimental conditions, they were gently rinsed with filtered seawater and maintained in a large mesocosm tank (2, 000 L) that received a constant fresh sandy-filtered seawater (~45 L/min) under controlled conditions (approximately 27°C, 32 PSU, pH ~8.1, and 80 μmol photons m−2 s−1 with a 12-h: 12-h day: night cycle) for 3 weeks (Hofmann et al., 2014). Irradiance intensities were created using a combination of white FMW39TS and blue FMB5AT5 light bulbs (Arcadia, Redhill, UK) (Wei et al., 2020a). During the acclimation period, H. opuntia samples turned healthy green, indicating that subsequent experiments could be undertaken.
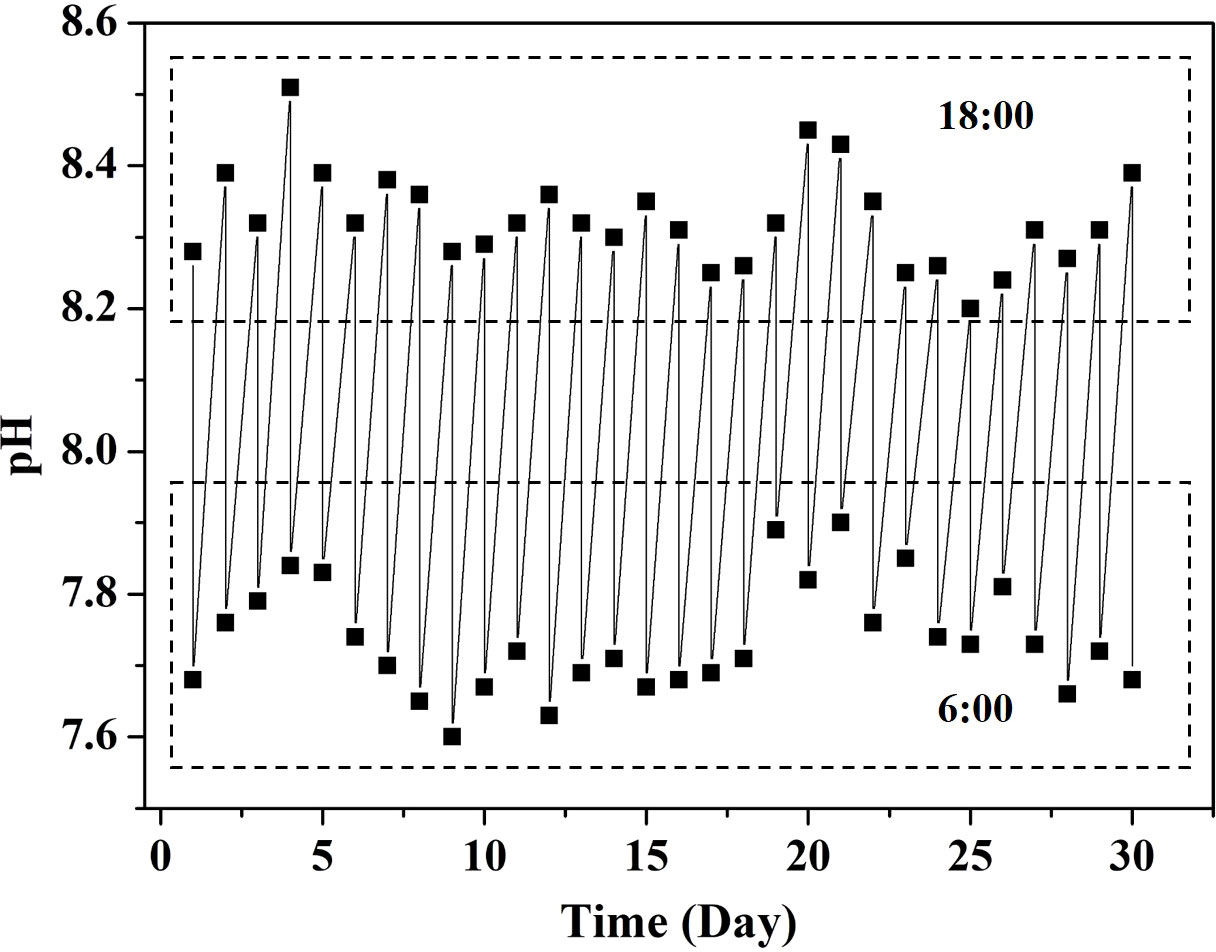
Figure 1 The pH measurements at 6:00 and 18:00 daily over 30 days at an average depth of 2.0 m (1.5–2.5 m) from the sampling site located in the South China Sea.
Experimental design and treatments
After the monitoring in situ pH fluctuations and initial acclimation period, H. opuntia individuals were randomly subjected to experimental manipulations of two static pCO2 levels combined with two fluctuating pCO2 levels within aquaria for 42 days (July 1 to August 11, 2021). For each treatment, there were eight algal thalli [110–120 g fresh weight (FW) in total] in one aquarium (30 L), and three biological replications were prepared per treatment. All the individuals were evenly spaced across the bottom of each aquarium to avoid self-shading, and the 0.45-μm-filtered seawater was replaced every 3 days. The pCO2 (OA) was elevated by bubbling pure CO2 mixed with ambient air automatically into the seawater in each aquarium (CE100C, Wuhan Ruihua Instrument and Equipment Ltd., Wuhan, China). The static elevated pCO2 (OA-ST) was set at 1,200 ppmv, which is the level predicted under extreme conditions by year 2100 (Caldeira and Wickett, 2005). The fluctuations in the elevated pCO2 concentration treatment (OA-FT) were 450 ppmv and 1,800 ppmv during day and night times, respectively. The static ambient pCO2 concentration (AM-ST) was the current local pCO2 level (approximately 450 ppmv), whereas the fluctuation in the ambient pCO2 treatment (AM-FT) during day time was set at 100 ppmv, which was achieved by bubbling post-CO2 mixed with ambient air, and the pCO2 during the night time was set at 1,200 ppmv (Table 1).
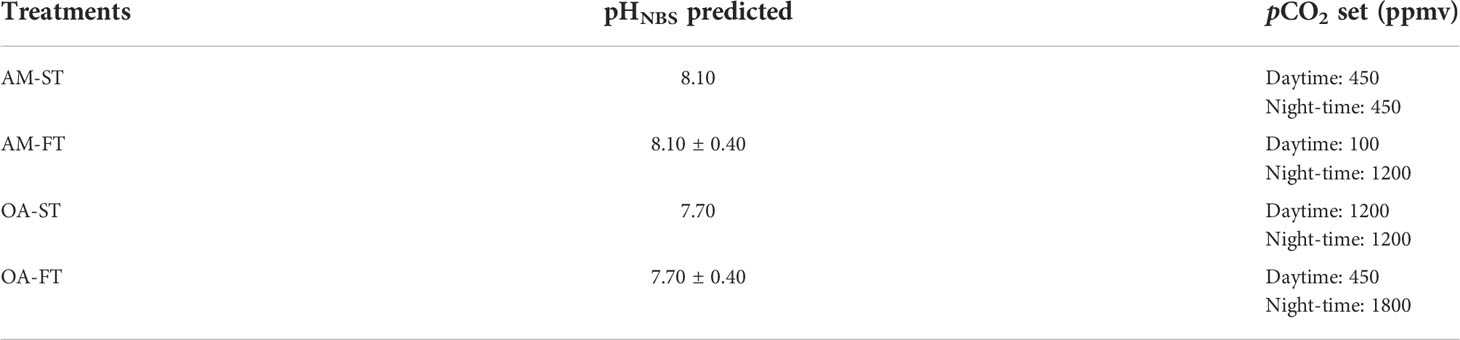
Table 1 Experimental design of static (ST) and fluctuated (FT) current ambient pCO2 (AM), as well as elevated pCO2 (ocean acidification, OA) levels.
Monitoring experimental conditions
To ensure the continuity of the culture conditions among treatments, seawater column chemistry monitoring was conducted daily at the end of the light (18:00) and dark (06:00) periods during the 42-day experiment. Seawater temperature (°C) and salinity (PSU) were determined using a handle YSI meter. The pHNBS valves were obtained using an S220 pH electrode (Thermo Scientific Orion, Waltham, MA, USA) and corrected with standard buffer solution (pH 7 and 10). Total alkalinity (TA) in each aquarium was measured daily using the Gran titration method and corrected by alkalinity reference materials (CRM; Andrew Dickson Lab, Scripps Institute of Oceanography) (Metrohm 877 Titrino Plus, Titrando® Metrohm USA, Inc.) (Dickson et al., 2007). Measured seawater parameters (salinity, temperature, pHNBS, and TA) were used to calculate the levels of dissolved inorganic carbon components using the Excel program CO2SYS (Pierrot et al., 2006).
Growth and calcification rates
The relative growth rate (RGR, % d−1) of H. opuntia was calculated in accordance with the following formula (Wei et al., 2021):
where Wt and Wt-42 represent the FWs obtained on the 42nd and 1st days, respectively, and 42 represents the time interval between the two sampling days.
The instantaneous net calcification rates (Gnet) was estimated using the alkalinity anomaly technique on the 42nd day (Campbell et al., 2016). The algal fragments (5.0 g) were incubated in acrylic transparent bottles (1.0 L) containing filtered seawater under four experimental conditions with an electro-magnetic stirrer. The calculation of Gnet was based on the changes in TA after an 8-h incubation using the following equation:
where Gnet (μmol CaCO3 g FW−1 h−1) represents the net calcification rate of whole thalli H. opuntia, p represents the seawater density (1.025 kg L−1), TA0 and TAn represent the initial TA and TA after n hours of culture (8 h), V represents the seawater volume (1.0 L), and FW and t represent the algal fresh weight (5.0 g) and incubation time (8 h), respectively. When Gnet > 0, calcification occurs, whereas when Gnet < 0, dissolution in CaCO3 mineralogy occurs.
Fv/Fm and pigment contents
The photosystem II (PSII) maximum quantum yield (Fv/Fm) value of H. opuntia was measured by a Diving-PAM II fluorometer (Heinz Walz GmbH, Effeltrich, Germany). After 20 min of dark adaptation, Fv/Fm was obtained using red light as the modulated light (5,000 μmol photons m−2 s−1, 0.6 s). Together with photosynthetic performance, 200 mg FW of fragment (n = 3) was sampled and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen for pigment content measurement. Samples were finely ground in 10 ml 90% acetone and extracted at 4°C for 24 h under dark conditions. Afterwards, the homogenate was centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 10 min (Eppendorf centrifuge 5810 R, Hamburg, Germany). The pigment contents, including chlorophyll (Chl) a, b and carotenoid concentrations, were measured using the supernatant, as described by Ritchie (2008).
Measurement of total carbon and total nitrogen contents
The total organic carbon (TCorg) and total nitrogen (TN) contents (dry weight, % DW) in Halimeda tissues subjected to the four treatments were determined at the end of the experiment. The samples (n = 3) were washed five times and then dried to constant weight at 60°C. Afterwards, all the samples were finely ground and determined by a CHN Elemental Analyzer (Flash EA300, Thermo Scientific, Milan, Italy).
Measurement of enzyme activities
Samples (200 mg FW of each, n = 3) used to determine enzymatic activities, external carbonic anhydrase activity (eCAA) and nitrate reductase activity (NRA), were collected at the end of the experiment. The algal fragments were ground in 5.0 mL 20-M veronal buffer (pH 8.3) for eCAA and 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) for NRA. The eCAA and NRA levels in the supernatant were determined using algal enzymatic ELISA Kits (Mlbio, Shanghai, China) following the appropriate manufacturer’s instructions. Both enzyme activities were corrected using an optical density (OD) standard curve.
Soluble carbohydrate, malondialdehyde, proline and free amino acids
For the determination of the algal soluble carbohydrate (SC) content, 200 mg FW of each sample was collected and ground in 10 ml filtered seawater. After 10 min of centrifuging (5,000 rpm), the SC level in the supernatant was determined using the phenol−sulfuric acid method (Kochert, 1978). The malondialdehyde (MDA) occurrence was measured because it is a potential indicator of lipid peroxidation encountered after environmental stresses (Wei et al., 2020c). In total, 500 mg FW of algal tissues was sampled and ground in 10 ml of 10% trichloroacetic acid, and then centrifuged at 4, 000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was collected and MDA was measured as described by Hodges et al. (1999).
To obtain further insights into the algal physiological regulation after exposure to diurnal fluctuations in seawater pCO2, the proline and free amino acids (FAAs) were analyzed for maintaining the photosynthetic system functioning and protecting the membranes from various damages (Wei et al., 2020a). At the end of the experiment, 500 mg FW of algal tissue for proline was weighed and finely ground in 5 ml 3% sulfosalicylic acid. The homogenate was shaking for 10 min under 100°C conditions. After 10 min of centrifugation (3,000 rpm), the proline content was measured in the supernatant as described by Shan et al. (2007). To determine FAAs, 200 mg FW of each sample was ground in 5 ml PBS buffer (pH 7.4), and FAAs was measured in the supernatant of the aqueous extract using an algal FAAs ELISA Kit (Mlbio, Shanghai, China), as described in the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistical analyses
All the data in this study were presented as a triplicate mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD) (n = 3). The figures were created using Origin 8.0 software (Origin Lab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA). All the statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics 20 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A one-way analysis was conducted to determine the differences among the four treatments. Tukey’s Honestly Significant Differences was used to make post hoc comparisons (95% confidence level). Differences by different uppercase and lowercase letters in Figure 2–7 were considered to be significant at P < 0.05 and extremely significant at P < 0.01.
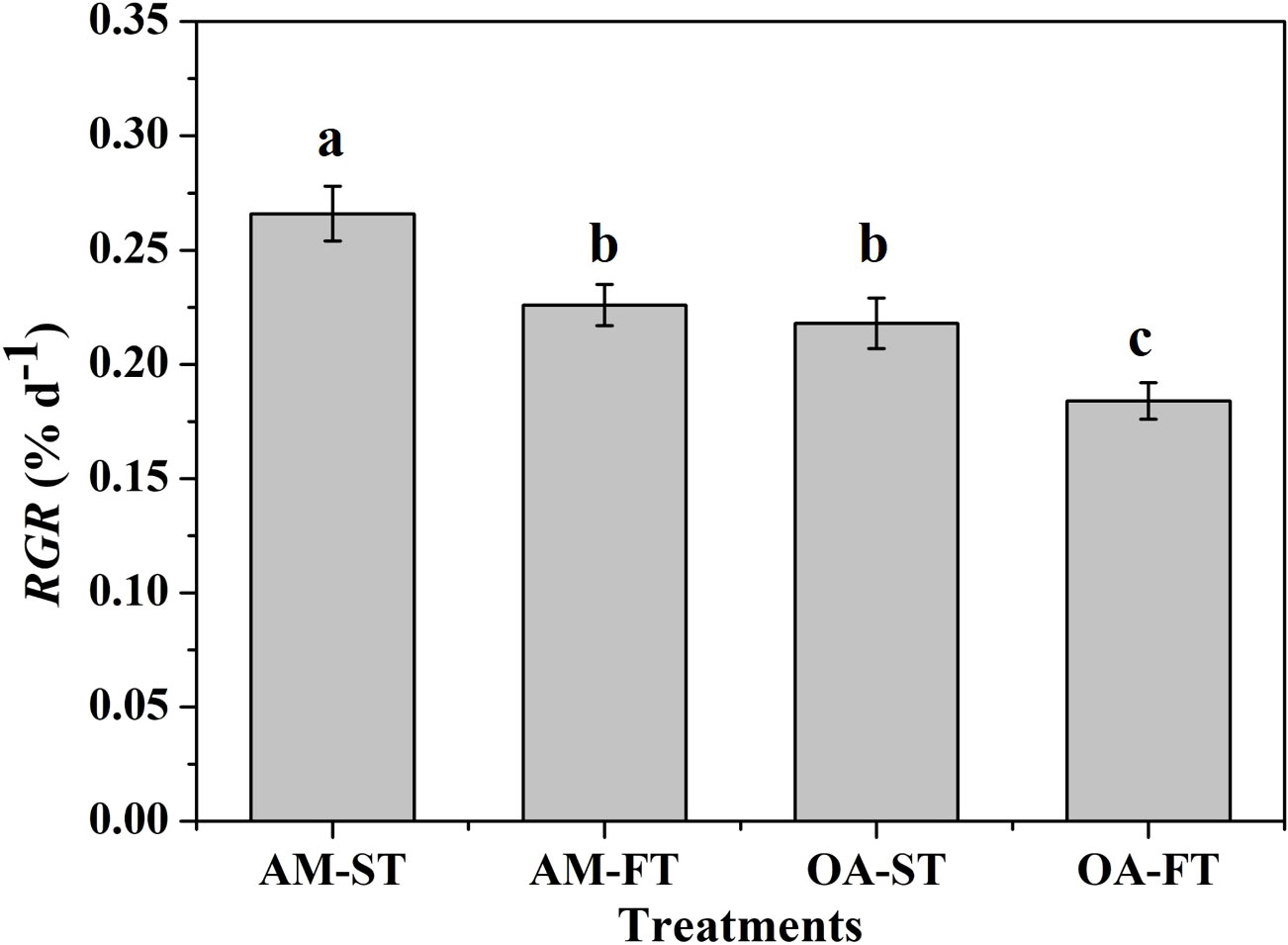
Figure 2 The relative growth rates (RGR, % d−1) of Halimeda opuntia (mean ± SD, n = 3) exposed to the four treatments for 42 days (AM, ambient pCO2 concentration; OA, ocean acidification; ST, static; FT, fluctuating). Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by different uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively (Tukey’s test, P<0.05).
Results
Seawater monitoring
The average pHNBS values in static ambient pCO2 and elevated pCO2 were 8.10 ± 0.01 and 7.71 ± 0.01, respectively, regardless of day or night time, whereas the average pHNBS values for the two fluctuating pCO2 levels were 8.43 ± 0.01 and 7.72 ± 0.02 (P < 0.01), respectively, in day time and 8.08 ± 0.01 and 7.42 ± 0.02 (P < 0.01), respectively, in night time. Nevertheless, the elevated pCO2 altered the DIC components and aragonite saturation state (ΩArag) in seawater (P < 0.01). In contrast with static ambient (AM-ST) pCO2 treatments, the mean CO2 and concentrations in static elevated (OA-ST) pCO2 treatments increased from 14.6–15.3 μmol kg–1 to 39.9–41.5 μmol kg–1 and 1,898.7–1,940.8 μmol kg–1 to 2,172.2–2,196.0 μmol kg–1, respectively, whereas concentrations decreased from 184.2–185.9 μmol kg–1 to 87.4–88.1 μmol kg–1 (P < 0.01). The average CO2, and concentrations in fluctuated ambient (AM-FT) and elevated (OA-FT) pCO2 treatments differed significantly among treatments, as well as between day and night times (P < 0.01) (Table 2). The ΩArag values were lower in elevated pCO2 treatments, ranging from 0.72 to 1.44, and the highest ΩArag values were obtained in AM-FT during the day time (5.47 ± 0.18).
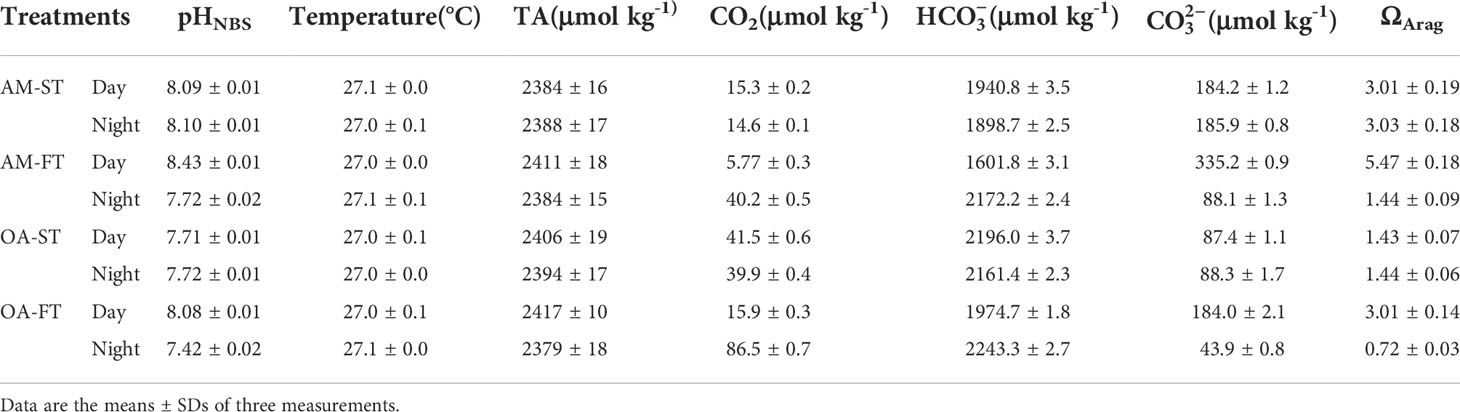
Table 2 Measured seawater parameters of pH (NBS scale), total alkalinity (TA), salinity and temperature, as well as the calculated carbon chemistry of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) components (CO2, and ) using CO2SYS (Pierrot et al., 2006) in each treatment determined at the end of each light (18:00) and dark (06:00) period during the 42-day experiment.
Growth and calcification rates of H. opuntia
After 42-day experimental exposure, the elevated pCO2 and daily fluctuations in the pCO2 of seawater had significant effects on the growth rate of H. opuntia (Figure 2). The highest RGR was recorded in AM-ST, at 0.266% ± 0.012% d−1. The RGR under elevated pCO2 conditions decreased by 22.02%–44.57% in contrast with those in AM-ST. Notably, daily fluctuating pCO2 amplified the negative effects on growth rates at two pCO2 concentration levels. In addition, the RGR values in AM-FT (0.226% ± 0.009% d−1) and OA-ST (0.218% ± 0.011% d−1) were not significantly different (P > 0.05) (Figure 2).
The Gnet differed significantly among the four treatments under both light and dark conditions (P < 0.05) (Figure 3). Under light conditions, the greatest net calcification levels occurred in the four treatments. The Gnet of H. opuntia in AM-ST, AM-FT and OA-FT did not change significantly, ranging from 0.897 to 1.303 μmol CaCO3 g FW−1 h−1 (P > 0.05). The lowest Gnet values were obtained in OA-ST (0.624 ± 0.124 μmol CaCO3 g FW−1 h−1) owing to the elevated pCO2. Under dark conditions, the greatest net dissolution in CaCO3 mineralogy occurred, as shown in Figure 3. The lowest dissolution rate (–0.114 ± 0.054 μmol CaCO3 g FW−1 h−1) was measured in AM-ST. However, elevated pCO2 amplified the negative CaCO3 dissolution rate, and the greatest dissolution rate was –0.517 ± 0.139 μmol CaCO3 g FW−1 h−1 in OA-FT after dark exposure.
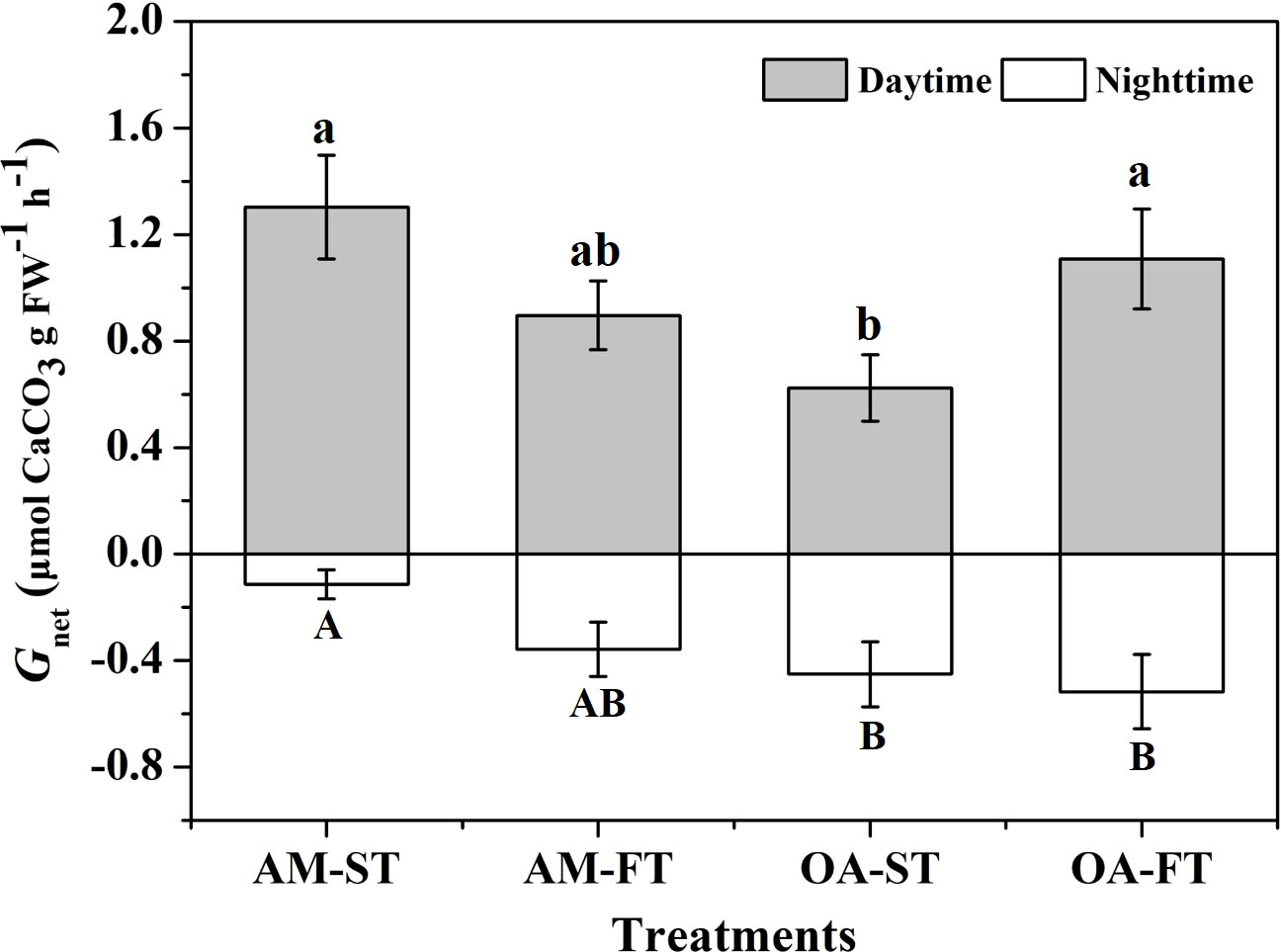
Figure 3 The net calcification rates (Gnet, μmol CaCO3 g FW−1 h−1) of Halimeda opuntia (mean ± SD, n = 3) under light and dark conditions after exposure to four pCO2 treatments for 42 days. Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by different uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively (Tukey’s test, P<0.05).
Chlorophyll fluorescence and pigment contents
There were significant direct effects of elevated pCO2 and daily fluctuating pCO2 on Fv/Fm and Chl-a content (P < 0.05). The lowest Fv/Fm was in AM-FT, with a mean value of 0.562 ± 0.005. Compared with the Fv/Fm (0.630 ± 0.006) in AM-ST, elevated pCO2 decreased the Fv/Fm to the 0.614–0.618 range (Figure 4A). Similar to the Fv/Fm variations, the lowest Chl-a content was in AM-FT, with a mean value of 175.79 ± 12.62 μg g−1 FW, and there were no obvious Chl-a variations in the other three treatments (194.33–225.61 μg g−1 FW) (Figure 4B). Across all the treatments, photosynthetic Chl-b and carotenoid contents were not notably influenced, having 134.99–157.49 μg g−1 FW and 75.33–87.78 μg g−1 FW ranges, respectively (Figures 4C, D).
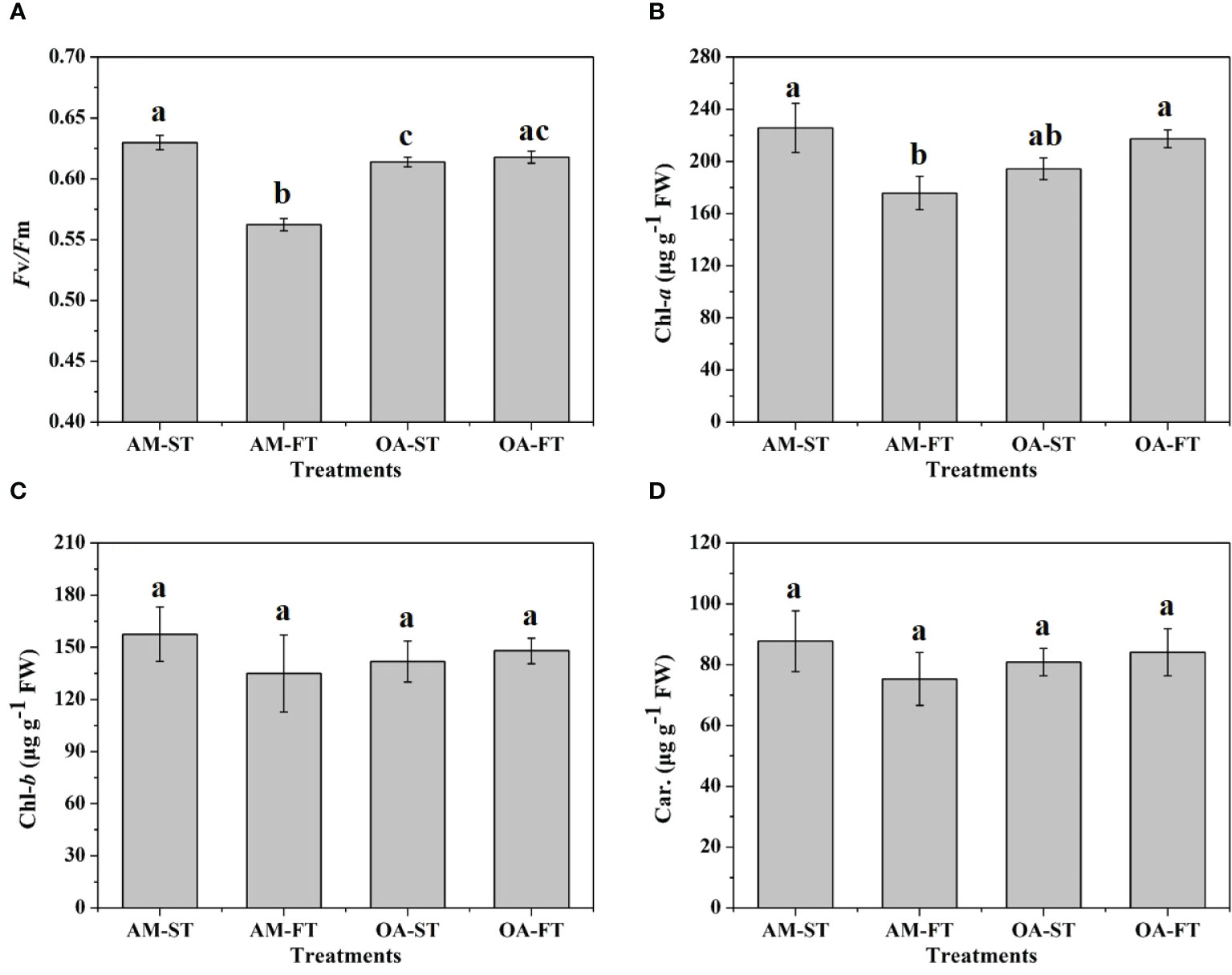
Figure 4 Variations in photosynthetic maximum quantum yields (Fv/Fm) (A) and in chlorophyll (Chl)a (B), b (C) (μg g−1 FW) and carotenoid (Car., μg g−1 FW) contents (D) of Halimeda opuntia (mean ± SD, n = 3) in four pCO2 treatments. Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by different uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively (Tukey’s test, P<0.05).
Tissue total carbon (TCorg) and nitrogen (TN) contents
Total organic carbon (TCorg) and total nitrogen (TN) in H. opuntia tissues were significantly affected by elevated pCO2 and daily fluctuating pCO2 (P < 0.05) (Figure 5). There were no notable differences between the ambient pCO2 treatments, regardless of static or fluctuating pCO2 concentrations (P > 0.05). However, an elevated pCO2 significantly stimulated TCorg accumulation by 8.93%–24.62% compared with the average TCorg in both AM treatments. The highest TCorg content occurred in OA-ST (17.79% ± 0.77% DW). The TN contents did not significantly vary among the AM-ST, AM-FT and OA-ST treatments (1.28%–1.39% DW) (P > 0.05), but it significantly decreased in OA-FT to 0.98% ± 0.07% DW (P < 0.01) (Figure 5).
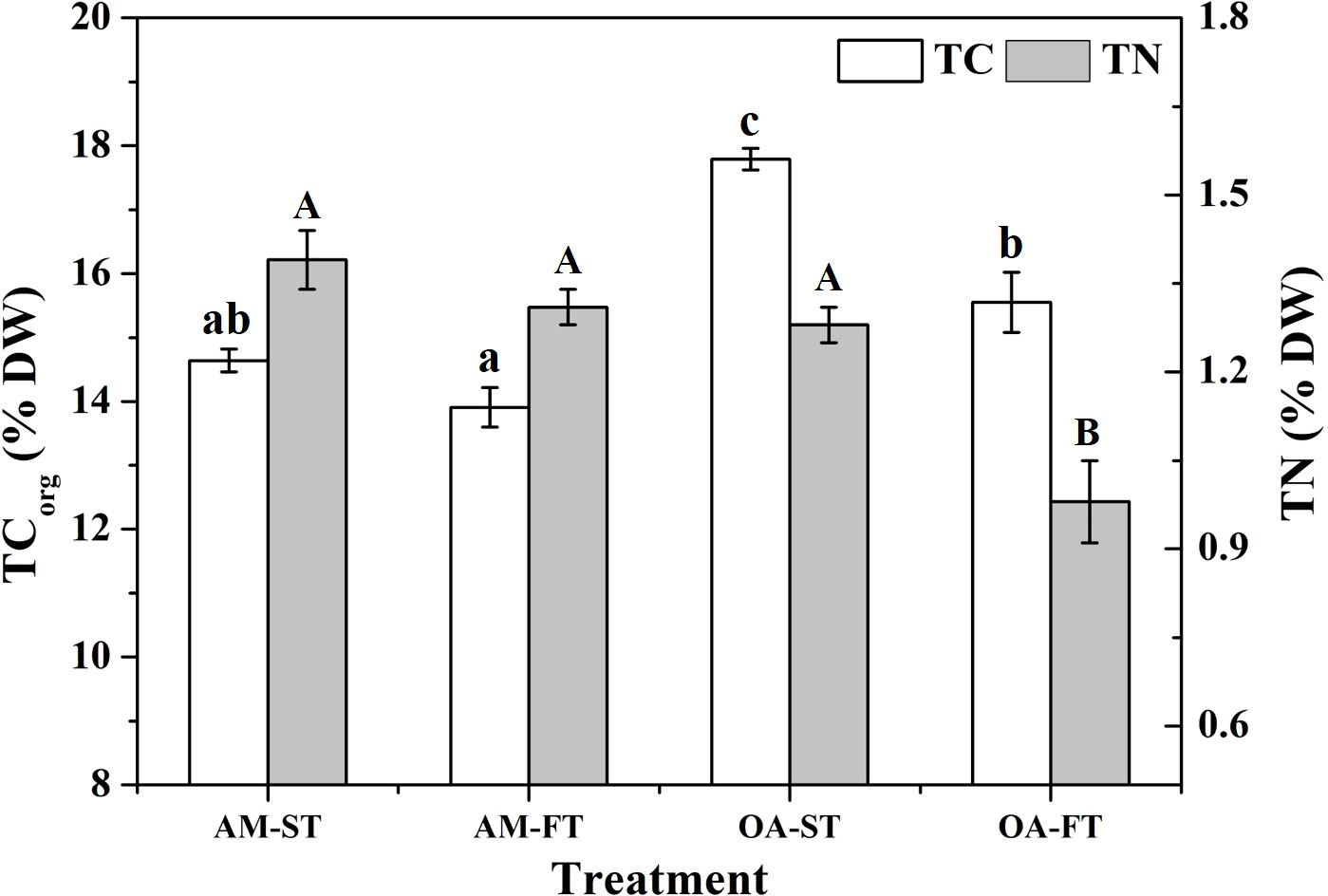
Figure 5 Variations in tissue total organic carbon (TCorg, % DW) and nitrogen (TN, % DW) from the tissues of Halimeda opuntia (mean ± SD, n = 3) in four pCO2 treatments. Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by different uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively (Tukey’s test, P<0.05).
Enzymatic activities (carbonic anhydrase and nitrate reductase)
There were no obvious effects of static and fluctuating pCO2 on the eCAA among the four treatments (3.280–3.828 IU mg−1 FW) (P > 0.05) (Figure 6). Compared with the (NRA in H. opuntia tissues incubated under ambient pCO2 conditions (2.535–2.784 pg mg−1 FW), the NRA decreased under both static and fluctuating elevated pCO2 conditions by 16.63%–34.01%, and the lowest NRA was obtained in OA-FT, having an average value of 1.984 ± 0.298 pg mg−1 FW (P < 0.05) (Figure 6).
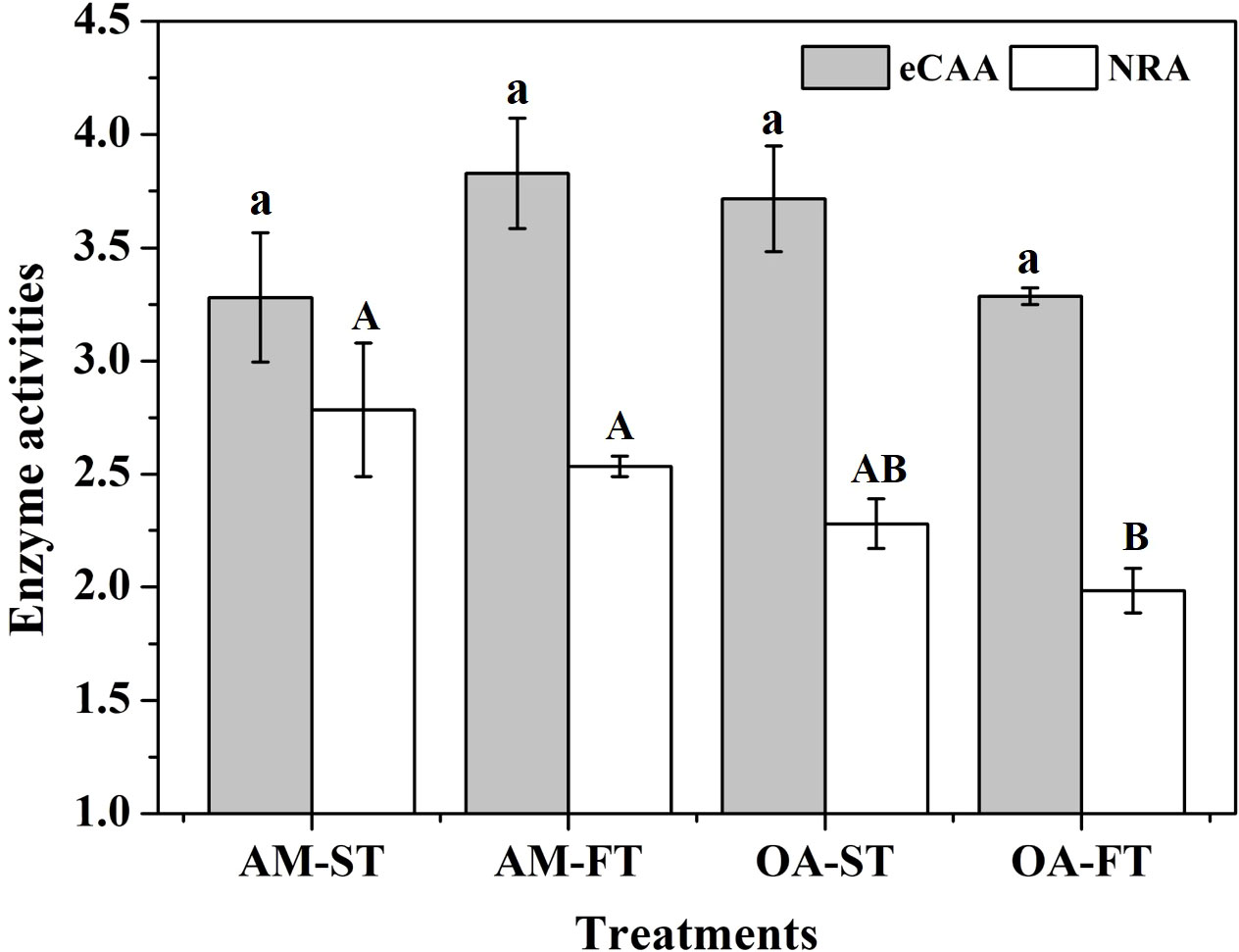
Figure 6 Mean (± SD, n = 3) external carbonic anhydrase activity (eCAA, IU mg−1 FW) and nitrate reductase activity (NRA, pg mg−1 FW) levels in four pCO2 treatments after a 42-day incubation. Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by different uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively (Tukey’s test, P<0.05).
Soluble carbohydrate, malondialdehyde, proline and free amino acids contents
The soluble cellular compositions were significantly affected by elevated pCO2 and daily fluctuations (P < 0.01) (Figure 7). The SC level decreased by 32.38%–67.65% under elevated and fluctuating pCO2 conditions, compared with the SC in AM-ST, and the lowest average SC content occurred in AM-FT at 2.12 ± 0.01 μg mg−1 FW (P < 0.01) (Figure 7A). Under elevated pCO2 conditions (OA-ST), the MDA content increased to 2.74 ± 0.04 μg mg−1 FW (P < 0.01). Moreover, fluctuating pCO2 amplified the effects of abiotic stress on MDA, which increased to 3.98 ± 0.05 μg mg−1 FW and 3.69 ± 0.06 μg mg−1 FW in AM-FT and OA-FT, respectively (Figure 7B). The proline levels increased notably under elevated and fluctuating pCO2 conditions (P < 0.01). The lowest average proline contents was obtained in AM-ST (2.24 ± 0.06 μg mg−1 FW), whereas the highest proline content occurred in OA-FT (4.31 ± 0.08 μg mg−1 FW) (Figure 7C). The FAA content significantly increased in the elevated pCO2 treatment (OA-ST, 3.19 ± 0.09 μg mg−1 FW) compared with in AM-ST (2.50 ± 0.06 μg mg−1 FW). Furthermore, the effects on FAA were enhanced by the two fluctuating pCO2 levels (P < 0.01), and the highest average FAA content occurred in OA-FT (4.46 ± 0.05 μg mg−1 FW) (Figure 7D).
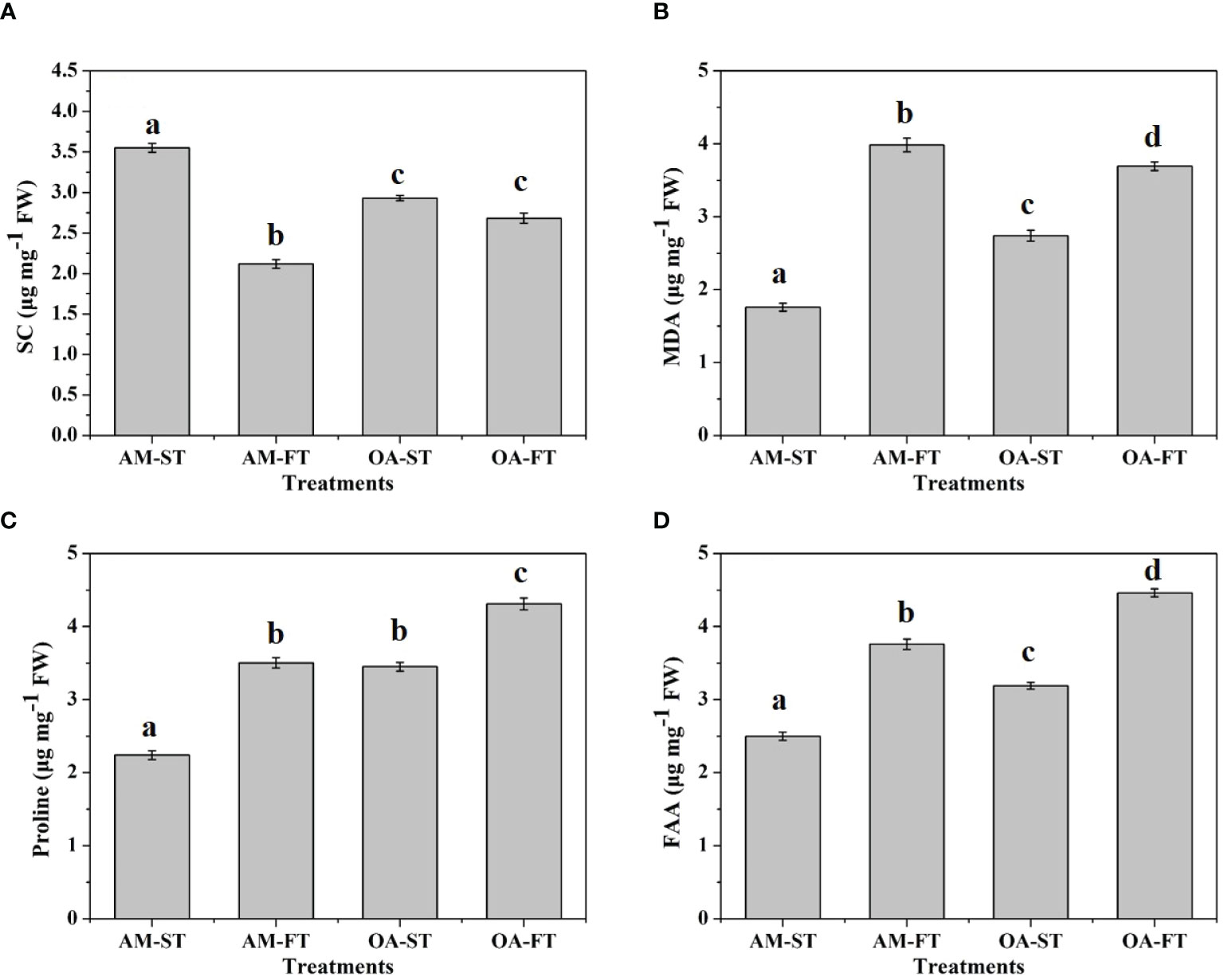
Figure 7 Variations in soluble carbohydrate (SC, μg mg−1 FW) (A), malondialdehyde (MDA, μg mg−1 FW) (B), proline (μg mg−1 FW) (C) and free amino acids (FAA, μg mg−1 FW) (D) contents of Halimeda opuntia (mean ± SD, n = 3) in four pCO2 treatments after a 42-day incubation. Significant differences among the treatments are indicated by different uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively (Tukey’s test, P<0.05).
Discussion
The anthropogenic elevation of atmospheric CO2 induced OA, and a lower aragonite saturation (ΩArag) has been widely reported to negatively affect the growth and calcification processes of marine calcifiers (Campbell et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2020a). Our results demonstrated that the effects of OA were increased by the adverse influence of elevated acidity (H+) on growth rates, calcification, photosynthesis and the related biotic performance of H. opuntia compared with the positive effects of a higher CO2 level. Moreover, diurnal fluctuations in pCO2 levels (with a higher pH during the day time and a lower pH during the night time) amplified these negative influences on H. opuntia. Similar with our previous study, the growth rates of Halimeda cylindracea and Halimeda lacunalis decreased significantly by 6.84%–86.70% under elevated pCO2 (1,000–1,600 ppmv) conditions (Wei et al., 2020a). In contrast with non-calcifying macroalgae, such as G. lemaneiformis (higher pCO2-grown plants), the increased pCO2 under OA conditions alleviates dissolved carbon limitations and leads to an enhancement in RGR (Zou et al., 2004). In this study, H. opuntia exhibited negative growth owing to the extremes in the elevated pCO2 variations. Because the photosynthetic rate of this alga has been completely saturated at the present seawater pCO2 (Zou et al., 2004), the negative effects of elevated pCO2 were mostly attributed to the decreased pH, which disturbs the acid–base balance on the cell surface (Flynn et al., 2012). Subsequently, more metabolic energy has to be expended to resist this interference, resulting in a reduced growth rate (Xu et al., 2017).
The Gnet of H. opuntia was adversely affected by elevated pCO2, which was in keeping with the results of previous studies. Wei et al. (2020a) reported that the Gnet values of H. cylindracea and H. lacunalis decrease by 51.78%–62.29% owing to high pCO2 conditions (1,000–1,600 ppmv). Similarly, Campbell et al. (2016) also demonstrated that the calcification rates of H. opuntia and Halimeda simulans decline by 15% and 50%, respectively, owing to high pCO2 concentration (2,400 ppmv). However, other influences were verified for some calcareous organisms, which displayed inconspicuous changes to cope with elevated pCO2. For instance, Ries et al. (2009) highlighted that the Gnet of Halimeda incrassata only decreases under extremely high pCO2 (2593 ppmv) conditions, with a ΩArag value of 0.9. Such differences may be attributed to species-specific acclimation and anti-stress capabilities (Campbell et al., 2016; Wei et al., 2020a, c). The CO2 enrichment-lowered ΩArag contributes to the dissolution of micro-anhedral calcareous structures among algal interutricular spaces, especially during dark incubation periods (Andersson et al., 2009). This may cause Halimeda to be more susceptible and decomposable than other species (Hofmann et al., 2014). The greatest net dissolution of a calcareous interutricular structure was recorded during a dark period under higher pCO2 conditions owing to a low ΩArag and algal respiration (Raven, 2011). This is consistent with previous findings that CaCO3 dissolution occurs in coralline algal species during dark periods, such as in Corallina pilulifera incubated at 1,600 ppmv (Gao et al., 1993) and in Lithothamnion glaciale grown at 700 ppmv (Budenbender et al., 2011). This addresses the critical influence of ΩArag status on algal mineralogy (Wei et al., 2020a).
An elevated pCO2 concentration in surface seawater can promote the photosynthetic processes for some non-calcifying macroalgae, such as G. lemaneiformis (Wei et al., 2021), Pyropia haitanensis (Chen et al., 2017), Hizikia fusiformis (Zou et al., 2011) and G. chilensis (Gao et al., 1993), owing to the increased availability of DIC resources. Nevertheless, here, H. opuntia showed a negative PSII photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) in response to the effects of OA and daily shifts in pCO2 (pH), which may be caused by the slightly increased the eCAA under high pCO2 conditions. This suggested that CO2 concentration may increase in the periplasmic space and lead to enhancement of DIC uptake from environment, although reduced intracellular Ci (DIC) pools (Raven et al., 2012) and poorly passive CO2 diffusion (Elzenga and Prins, 1989; Miedema and Prins, 1991). Similar conclusions have been made for other Halimeda species. Sinutok et al. (2012) found notable declines (50%–70%) of Fv/Fm values in Halimeda macroloba and H. cylindracea after a 35-day exposure to elevated pCO2 condition (1,200 ppmv, ΩArag: 1.97 ± 0.02). Concurrently, a decline in the Chl-a contents under static/fluctuating low pH conditions indicated the down-regulation of Chl accumulation or pigment degradation, whereas there were limited effects of elevated pCO2 on Chl-b and carotenoid contents. The lack of changes in photosynthetic performance and pigment contents in H. opuntia under fluctuating OA condition was most probably owing to 1) their high tolerance and increased retention of phenotypic plasticity to the dramatic variations in pCO2 (pH), because they regularly experience daily fluctuations in pH in the coastal regions; and/or 2) a higher daytime pH, which provides a period of suitable conditions for macroalgal photosynthesis (Cornwall et al., 2013).
An elevated/fluctuating pCO2 is predicted to modulate TCorg and TN accumulations in H. opuntia tissues. The changes in TCorg and TN contents may be due to variations in the characterizations of enzymatic activities (Wei et al., 2021). At static higher pCO2 levels, the eCAA in chloroplast slightly increased (although there was no statistically significant difference), and this may accelerate the interconversion between CO2 and, guaranteeing soluble carbohydrate synthesis at the carboxylation site (Vidal-Dupiol et al., 2013). Meanwhile, the SC synthesis was enhanced by the positive effects of eCAA activity, which played a role in an improvement in the irradiance harvesting capacity and up-regulation of the photosynthetic electron transport chain (Van Oijen et al., 2004). Moreover, a discrepancy in the average NRA was negatively influenced by diurnal fluctuating pCO2, leading to a noticeable decrease in N accumulations in algal tissues (Figure 6). When NRA decreases, variations in elevated pCO2 can promote the ammonium to nitrate conversion process, leading to the formation of glutamine and thereby inhibiting NRA (Stitt and Krapp, 1999). Such a response would demand less energy for the formation of ammonium than nitrate and allow this macroalga to allocate more energy for regulating eCAA and C acquisition (Losada and Guerrero, 1979; Syrett, 1981). These findings indicate that the elevated pCO2 caused modifications in algal C vs. N metabolism, and the increased variability in pCO2 amplified these influences, which was confirmed by eCAA and NRA driven activities.
The MDA content is used to evaluate lipid peroxidation levels in cell systems (Hodges et al., 1999). Under elevated pCO2 conditions, H. opuntia displayed greater oxidative lipid degradation associated with higher MDA contents, and this adverse physiological performance was amplified in both fluctuating pCO2 treatments. This was in agreement with the decreased algal growth and lower photosynthetic activity (Fv/Fm) levels. The SC synthesis declined sharply under elevated and fluctuating pCO2 conditions due to the depression of PSII activities (Wei et al., 2021), which would in turn down-regulate the irradiance harvesting capacity and photosynthetic activities (Van Oijen et al., 2004). Therefore, it is essential for H. opuntia to undergo appropriate adjustments to cope with the elevated pCO2 pressure (Wei et al., 2020a; Wei et al., 2020c; Wei et al., 2021). Our findings indicate that soluble organic molecules (FAAs and proline) are highly secreted and likely linked to protecting the integrity of cellular structures (Sun et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2018; Wei et al., 2020a; Wei et al., 2020c). Thus, as the experiment progressed, greater contents of proline and FAA were obtained in OA, and these effects were strengthened under the two fluctuating pCO2 conditions, which played a positive role in maintaining the photosynthetic system’s function and in protecting membrane integrity (Xiong et al., 2002). This explanation is corroborated by a previous analysis by Wei et al., (2020a); Wei et al., 2021), who suggested that these modifications give rise to the internal re-partitioning of C and N in Halimeda tissues.
In summary, this study attempted to mimic in situ pH (pCO2) changes, and it demonstrated that a static elevated pCO2 level has adverse effects on the growth, calcification, photosynthesis and other C vs. N metabolic activities of H. opuntia. Moreover, diurnal fluctuations in pCO2 amplified these negative influences of OA, especially during the night time. Under the stress of elevated and/or fluctuating pCO2, higher MDA contents were obtained, which indicates that the cellular membranes were damaged. This generated a dynamic balance in H. opuntia incubated under environmental stress conditions, and it is reasonable to suggest that high contents of proline and FAA, in combination with related-enzymatic activities, play positive roles in protecting cellular structures and mitigating adverse influences. The results of the present study increase our understanding of the biological consequences of pH (pCO2) variability on specific marine calcifiers and their physiological plasticity under future OA conditions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
The authors thank all the staff, and particularly LL who conceived and designed the experiments. ZW performed the experiments and wrote the paper. FY analyzed the data, and YZ contributed materials and analysis tools. LL agrees to serve as the author responsible for contact and communication. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This research was supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (202102021228), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42006129), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2021YFC3100500, 2021YFF0502801), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China (2021B1212050023), Key Programs of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (E1YD5J01), and the Special Research Assistant Grant Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the Tropical Marine Biological Research Station in Hainan, Chinese Academy of Sciences for providing logistical support. Thanks are also due to the editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Andersson A. J., Kuffner I. B., Mackenzie F. T., Jokiel P. L., Rodgers K. S., Tan A. (2009). Net loss of CaCO3 from coral reef communities due to human induced seawater acidification. Biogeosciences 6, 2163–2182. doi: 10.5194/bg-6-1811-2009
Bao M., Wang J., Xu T., Wu H., Li H., Xu J. (2019). Rising CO2 levels alter the responses of the red macroalga pyropia yezoensis under light stress. Aquaculture 501, 325–330. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.11.011
Beach K., Walters L., Vroom P., Smith C., Coyer J., Hunter C. (2003). Variability in the ecophysiology of halimeda spp. (Chlorophyta, bryopsidales) on conch reef, Florida keys, USA. J. Phycol. 39 (4), 633–643.
Budenbender J., Riebesell U., Form A. (2011). Calcification of the Arctic coralline red algae lithothamnion glaciale in response to elevated CO2. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 441, 79–87. doi: 10.3354/meps09405
Caldeira K., Wickett M. E. (2003). Oceanography: anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature. 425 (6956), 365. doi: 10.1038/425365a
Caldeira K., Wickett M. E. (2005). Ocean model predictions of chemistry changes from carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere and ocean. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans. 110 (C9), C09S04. doi: 10.1029/2004JC002671
Campbell J. E., Fisch J., Langdon C., Paul V. J. (2016). Increased temperature mitigates the effects of ocean acidification in calcified green algae (Halimeda spp.). Coral Reefs. 35, 357–368. doi: 10.1007/s00338-015-1377-9
Chen B., Zou D., Du H., Ji W. (2018). Carbon and nitrogen accumulation in the economic seaweed gracilaria lemaneiformis affected by ocean acidification and increasing temperature. Aquaculture. 482, 176–182. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.09.042
Chen B., Zou D., Yang Y. (2017). Increased iron availability resulting from increased CO2 enhances carbon and nitrogen metabolism in the economical marine red macroalga pyropia haitanensis (Rhodophyta). Chemosphere 173, 444–451. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.073
Cornwall C. E., Hepburn C. D., McGraw C. M., Currie K. I., Pilditch C. A., Hunter K. A., et al. (2013). Diurnal fluctuations in seawater pH influence the response of a calcifying macroalga to ocean acidification. Proc. R. Soc B-Biol. Sci. 280 (1772), 20132201. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.2201
Dickson A. G., Sabine C. L., Christian J. R. (2007). Guide to best practices for ocean CO2 measurements, in PICES special publication (Sidney, Canada: North Pacific Marine Science Organization), 67–81.
Dufault A. M., Cumbo V. R., Fan T. Y., Edmunds P. J. (2012). Effects of diurnally oscillating pCO2 on the calcification and survival of coral recruits. Proc. R. Soc B-Biol. Sci. 279, 2951–2958. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2011.2545
Egilsdottir H., Noisette F., Noël L. M. L. J., Olafsson J., Martin S. (2013). Effects of pCO2 on physiology and skeletal mineralogy in a tidal pool coralline alga corallina elongata. Mar. Biol. 160, 2103–2112. doi: 10.1007/s00227-012-2090-7
Elzenga J. T. M., Prins H. B. A. (1989). Light-induced polar pH changes in leaves of elodea canadensis. i. effects of carbon concentration and light intensity. Plant Physiol. 91, 62–67. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.62
Flynn K. J., Blackford J. C., Baird M. E., Raven J. A., Clark D. R., Beardall J., et al. (2012). Changes in pH at the exterior surface of plankton with ocean acidification. Nat. Clim. Change 2, 510–513. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1489
Friedlingstein P., Jones M., O’Sullivan M. W., Andrew R. M., Bakker D. C. E., Hauck J., et al. (2022). Global carbon budget 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 14, 1917–2005. doi: 10.5194/essd-14-1917-2022
Gao K., Aruga Y., Asada K., Kiyohara M. (1993). Influence of enhanced CO2 on growth and photosynthesis of the red algae gracilaria sp. and g. chilensis. J. Appl. Phycol. 5, 563–571. doi: 10.1007/BF02184635
Gao G., Clare A. S., Rose C., Caldwell G. S. (2018). Ulva rigida in the future ocean: potential for carbon capture, bioremediation, and biomethane production. GCB. Bioenergy. 10, 39–51. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12465
Gao G., Liu Y., Li X., Feng Z., Xu Z., Wu H., et al. (2017). Expected CO2-induced ocean acidification modulates copper toxicity in the green tide alga ulva prolifera. Environ. Exp. Bot. 135, 63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.12.007
Gattuso J. P., Magnan A., Billé R., Cheung W. W. L., Howes E. L., Joos F., et al. (2015). Contrasting futures for ocean and society from different anthropogenic CO2 emissions scenarios. Science. 349 (6243), 45–55.
Hillis L. W. (2001). The calcareous reef alga halimeda (Chlorophyta, byropsidales): a cretaceous genus that diversified in the Cenozoic. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 166 (1–2), 89–100. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(00)00203-0
Hodges D. M., DeLong J. M., Forney C. F., Prange R. K. (1999). Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta. 207, 604–611. doi: 10.1007/s004250050524
Hofmann L. C., Heiden J., Bischof K., Teichberg M. (2014). Nutrient availability affects the response of the calcifying chlorophyte halimeda opuntia (L.) J.V. lamouroux to low pH. Planta. 239 (1), 231–242.
Hurd C. L., Cornwall C. E., Currie K. I., Hepburn C. D., McGraw C. M., Hunter K. A., et al. (2011). Metabolically-induced pH fluctuations by some coastal calcifiers exceed projected 22nd century ocean acidification: a mechanism for differential susceptibility? Glob. Change Biol. 17 (10), 3254–3262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02473.x
Jury C. P., Whitehead R. F., Szmant A. M. (2010). Effects of variations in carbonate chemistry on the calcification rates of madracis auretenra (= madracis mirabilis sensu well: bicarbonate concentrations best predict calcification rates). Glob. Change Biol. 16 (5), 1632–1644. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02057.x
Kochert G. (1978). “Protein determination by dye binding,” in Handbook of phycological methods: Physiological and biochemical methods. Eds. Hellebust J. A., Craigie J. S. (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press), 92–93.
Kroeker K. J., Kordas R. L., Crim R. N., Singh G. G. (2010). Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecol. Lett. 13, 1419–1434. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01518.x
Losada M., Guerrero M. G. (1979). “The photosynthetic reduction of nitrate and its regulation,” in Photosynthesis in relation to model systems (Amsterdam: Elsevier), 365–408.
Martin S., Gattuso J. P. (2009). Response of Mediterranean coralline algae to ocean acidification and elevated temperature. Glob. Change Biol. 15 (8), 2089–2100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.01874.x
Masson-Delmotte V., Zhai P., Pirani A., Connors S. L., Péan C., Berger S., et al., eds. (2021). IPCC, 2021: Climate Change 2021: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press.
Mercado J. M., Javier F., Gordillo L., Niell F. X., Figueroa F. L. (1999). Effects of different levels of CO2 on photosynthesis and cell components of the red alga porphyra leucosticta. J. Appl. Phycol. 11 (5), 455–461. doi: 10.1023/A:1008194223558
Miedema H., Prins H. B. A. (1991). pH-dependent proton permeability of the plasma membrane is a regulating mechanism of polar transport through the submerged leaves of potamogeton lucens. Can. J. Bot.-Rev. Can. Bot. 69, 1116–1122. doi: 10.1139/b91-143
Milliman J. D. (1993). Production and accumulation of calcium carbonate in the ocean: budget of a nonsteady state. Glob. Biogeochem Cycle 7 (4), 927–957. doi: 10.1029/93GB02524
Olischläger M., Wiencke C. (2013). Ocean acidification alleviates low-temperature effects on growth and photosynthesis of the red alga neosiphonia harveyi (Rhodophyta). J. Exp. Bot. 64, 5587–5597. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert329
Peach K. E., Koch M. S., Blackwelder P. L., Manfrino C. (2017). Calcification and photophysiology responses to elevated pCO2 in six halimeda species from contrasting irradiance environments on little Cayman island reefs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 486, 114–126. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2016.09.008
Pierrot D., Lewis E., Wallace D. W. R. (2006). “MS excel program developed for CO2 systems calculations: ORNL/CDIAC-105a,” in Carbon dioxide information analysis center oak ridge national laboratory (Tennessee: U.S. Department of Energy, Oak Ridge).
Qu L., Xu J., Sun J., Li X., Gao K. (2017). Diurnal pH fluctuations of seawater influence the responses of an economic red macroalga gracilaria lemaneiformis to future CO2-induced seawater acidification. Aquaculture. 473, 383–388. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.03.001
Ragazzola F., Foster L. C., Form A., Anderson P. S. L., Hansteen T. H., Fietzke J. (2012). Ocean acidification weakens the structural integrity of coralline algae. Glob. Change Biol. 18, 2804–2812. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2012.02756.x
Rautenberger R., Fernández P. A., Strittmatter M., Heesch S., Cornwall C. E., Hurd C. L., et al. (2015). Saturating light and not increased carbon dioxide under ocean acidification drives photosynthesis and growth in ulva rigida (Chlorophyta). Ecol. Evol. 5 (4), 874–888. doi: 10.1002/ece3.1382
Raven J. A. (2011). Effects on marine algae of changed seawater chemistry with increasing atmospheric CO2. Biol. Environ.-Proc. R. Irish Acad. 111B, 1–17. doi: 10.3318/bioe.2011.01
Raven J. A., Giordano M., Beardall J., Maberly S. C. (2012). Algal evolution in relation to atmospheric CO2: carboxylases, carbon concentrating mechanisms and carbon oxidation cycles. Philos. Trans. R. Soc B-Biol. Sci. 367, 493–507. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0212
Reusch T. B. H., Boyd P. W. (2013). Experimental evolution meets marine phytoplankton. Evolution. 67 (7), 1849–1859. doi: 10.1111/evo.12035
Ries J. B., Cohen A. L., McCorkle D. C. (2009). Marine calcifiers exhibit mixed responses to CO2-induced ocean acidification. Geology 37, 1131–1134. doi: 10.1130/G30210A.1
Ritchie R. J. (2008). Universal chlorophyll equations for estimating chlorophylls a, b, c, and d and total chlorophylls in natural assemblages of photosynthetic organisms using acetone, methanol, or ethanol solvents. Photosynthetica. 46, 115–126. doi: 10.1007/s11099-008-0019-7
Shan D., Huang J., Yang Y., Guo Y., Wu C., Yang G., et al. (2007). Cotton GhDREB1 increases plant tolerance to low temperature and is negatively regulated by gibberellic acid. New Phytol. 176, 70–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02160.x
Sinutok S., Hill R., Doblin M. A., Kuhl M., Ralph P. J. (2012). Microenvironmental changes support evidence of photosynthesis and calcification inhibition in halimeda under ocean acidification and warming. Coral Reefs. 31, 1201–1213. doi: 10.1007/s00338-012-0952-6
Stitt M., Krapp A. (1999). The interaction between elevated carbon dioxide and nitrogen nutrition: the physiological and molecular background. Plant Cell Environ. 22, 583–621. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3040.1999.00386.x
Sun Y., Wang B., Jin S., Qu X., Li Y., Hou B. (2013). Ectopic expression of arabidopsis glycosyltransferase UGT85A5 enhances salt stress tolerance in tobacco. PloS One 8 (3), e59924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059924
Syrett P. J. (1981). Nitrogen metabolism of microalgae. Can. J. Fish Aquat Sci. 210, 182–210. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(81)90166-6
Teichberg M., Fricke A., Bischol K. (2013). Increased physiological performance of the calcifying green macroalga halimeda opuntia in response to experimental nutrient enrichment on a Caribbean coral reef. Aquat. Bot. 104, 25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2012.09.010
Van Oijen T., Van Leeuwe M. A., Gieskes W. W. C., De Baar H. J. W. (2004). Effects of iron limitation on photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism in the Antarctic diatom. Eur. J. Phycol. 39, 161–171. doi: 10.1080/0967026042000202127
Vidal-Dupiol J., Zoccola D., Tambutte E., Grunau C., Cosseau C., Smith K. M., et al. (2013). Genes related to ion-transport and energy production are unregulated in response to CO2-driven pH decrease in corals: new insights from transcriptome analysis. PloS One 8 (3), e58652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058652
Vogel N., Fabricius K. E., Strahl J., Noonan S. H. C., Wild C., Uthicke S. (2015). Calcareous green alga halimeda tolerates ocean acidification conditions at tropical carbon dioxide seeps. Limnol. Oceanogr. 60, 263–275. doi: 10.1002/lno.10021
Wei Z., Long C., Yang F., Long L., Huo Y., Ding D., et al. (2020a). Increased irradiance availability mitigates the physiological performance of species of the calcifying green macroalga halimeda in response to ocean acidification. Algal Res. 48, 101906. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2020.101906
Wei Z., Long C., Yang F., Long L., Mo J., Hu Q., et al. (2020b). Effects of plant growth regulators on physiological performances of three calcifying green macroalgae halimeda species (Bryopsidales, chlorophyta). Aquat. Bot. 161, 103186. doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2019.103186
Wei Z., Mo J., Huang R., Hu Q., Long C., Ding D., et al. (2020c). Physiological performance of three calcifying green macroalgae halimeda species in response to altered seawater temperatures. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 39 (02), 89–100. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1471-3
Wei Z., Zhang Y., Yang F., Liang J., Long L. (2021). Increased light availability modulates carbon and nitrogen accumulation in the macroalga gracilariopsis lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta) in response to ocean acidification. Environ. Exp. Bot. 187, 104492. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104492
Wizemann A., Meyer F. W., Hofmann L. C., Wild C., Westphal H. (2015). Ocean acidification alters the calcareous microstructure of the green macro-alga halimeda opuntia. Coral Reefs. 34, 941–954. doi: 10.1007/s00338-015-1288-9
Xiong L., Schumaker K. S., Zhu J. (2002). Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell. 14, S165–S183. doi: 10.1105/tpc.000596
Xu Z., Gao G., Xu J., Wu H. (2017). Physiological response of a golden tide alga (Sargassum muticum) to the interaction of ocean acidification and phosphorus enrichment. Biogeosciences. 14, 671–681. doi: 10.5194/bg-14-671-2017
Yildiz G., Hofmann L. C., Bischof K., Dere S. (2013). Ultraviolet radiation modulates the physiological responses of the calcified rhodophyte corallina officinalis to elevated CO2. Bot. Mar. 56, 161–168. doi: 10.1515/bot-2012-0216
Zou D., Gao K., Luo H. (2011). Short- and long term effects of elevated CO2 on photosynthesis and respiration in the marine macroalga hizikia fusiformis (Sargassaceae, phaeophyta) grown at low and high n supplies. J. Phycol. 47, 87–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2010.00929.x
Keywords: ocean acidification, diurnal pH fluctuations, calcifying macroalgae, biotic performance, soluble organic molecules
Citation: Wei Z, Zhang Y, Yang F and Long L (2022) Diurnal fluctuations in seawater pCO2 amplify the negative effects of ocean acidification on the biotic performance of the calcifying macroalga Halimeda opuntia. Front. Mar. Sci. 9:968740. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.968740
Received: 14 June 2022; Accepted: 04 July 2022;
Published: 26 July 2022.
Edited by:
Dilip Kumar Jha, National Institute of Ocean Technology, IndiaReviewed by:
Du Hong, Shantou University, ChinaRuiping Huang, Xiamen University, China
Hailong Wu, Jiangsu Ocean University, China
Copyright © 2022 Wei, Zhang, Yang and Long. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fangfang Yang, eWN1eWFuZ0BzY3Npby5hYy5jbg==; Lijuan Long, bG9uZ2xqQHNjc2lvLmFjLmNu
 Zhangliang Wei1,2,3
Zhangliang Wei1,2,3 Fangfang Yang
Fangfang Yang Lijuan Long
Lijuan Long