- Division of Cellular and Molecular Biology, Department of Cell and Molecular Biology & Microbiology, Faculty of Biological Sciences and Technologies, University of Isfahan, Isfahan, Iran
Biomarkers are biological molecules found in body fluids or tissues, which can be considered as indications of a normal or abnormal process, or of a condition or disease. There are various types of biomarkers based on their application and molecular alterations. Treatment-sensitivity or drug resistance biomarkers include prognostic and predictive molecules with utmost importance in selecting appropriate treatment protocols and improving survival rates. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most prevalent hematological malignancy diagnosed in children with nearly 80% cure rate. Despite the favorable survival rates of childhood ALL (chALL), resistance to chemotherapeutic agents and, as a consequence, a dismal prognosis develops in a significant number of patients. Therefore, there are urgent needs to have robust, sensitive, and disease-specific molecular prognostic and predictive biomarkers, which could allow better risk classification and then better clinical results. In this article, we review the currently known drug resistance biomarkers, including somatic or germ line nucleic acids, epigenetic alterations, protein expressions and metabolic variations. Moreover, biomarkers with potential clinical applications are discussed.
Introduction
The National Institute of Health (NIH) defines biological markers or biomarkers as biological markers found in body fluids, such as blood or tissues, that are considered as signs of a normal or abnormal process, or of a condition or disease (1–3). Biomarkers typically differentiate patients from persons without the disease. They can be detected in the excretions or secretions including urine, stool, sputum, or nipple discharge, or in the circulation such as whole blood, plasma, or serum, and therefore easily, non-invasively and serially assessed. Biological markers can be tissue-derived and require either special imaging or biopsy for evaluation (Figure 1). They are assuming a growing role in all aspects of oncology including patient assessment, estimation of disease risk, screening for occult primary cancers, distinguishing malignant from benign tumors or one type of tumor from another, prediction and determination of the prognosis for patients who have been diagnosed with malignancy, and monitoring status of the disease either to detect recurrence or progression or determine response to treatment (1).
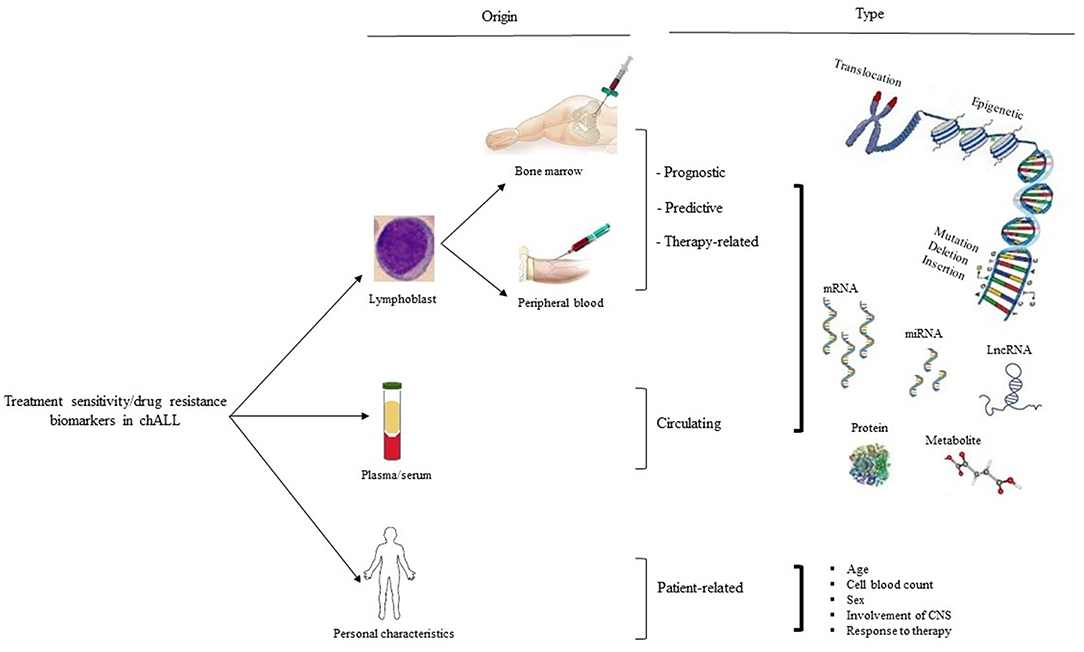
Figure 1. Treatment sensitivity/drug resistance biomarker in chALL. There are three types of treatment sensitivity/drug resistance biological markers based on their origins of detection, including patient lymphoblast, serum/plasma, and personal characteristics (such as age, cell blood count, sex, involvement of CNS, and response to therapy). Biomarkers related to lymphoblastic cells are subdivided into prognostic, predictive, and therapy-related biological markers. CNS, the central nervous system.
There are two major types of biomarkers: (1) Biomarkers of exposure which are used in cancer susceptibility and risk prediction, (2) Biomarkers of disease that are utilized in screening, diagnosis, and monitoring of disease progression (4). Cancer susceptibility and risk stratification biomarkers indicate those individuals at an increased risk of developing malignancy, who can be candidates for prevention investigations, such as: biomarkers of exposure to carcinogens, oxidative stress, inflammation and molecular alterations at DNA level (including some single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and mutations in specific genes) (5). There are many types of disease biomarkers based on their application, including: diagnostic, classification, staging, treatment sensitivity or drug resistance biomarkers, and biomarkers associated with disease aggressiveness and progression used in screening and monitoring of disease progression (3, 6, 7). Personalized medicine methods are being developed based on the cancer diagnostic and treatment sensitivity or resistance biomarkers at cellular levels. Using precise targets for diagnosis of cancers is of importance, since the current treatment approach is based on a targeted therapy (8, 9). Therefore, diagnostic and treatment sensitivity/drug resistance biomarkers are more important in clinical and cure rate of cancers.
Diagnostic biomarkers may be signals of the cancer presence and are recognized by characterizing molecular alterations and main mutations involved in cancer development and proliferation or any substance or process that is indicative of the presence of cancer in the body (2, 6). For example, changes in some protein expression levels can be used as the markers of early detection of B-ALL, including leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein 1 (LRG1), thrombin (F2), alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M), heparin cofactor II (SERPIND1), clusterin (CLU), alpha-1 antitrypsin (SERPINA1), complement C3 (C3), complement factor B (CFB), and alpha-2-antiplasmin (SERPINF2) (10). These biomarkers are useful in targeted therapies and in preventing toxicity related to standard (systemic) therapies. Detection of cancer at the early stages through diagnostic biomarkers significantly increases the chances of successful therapy.
Treatment sensitivity/drug resistance biomarkers can be considered as prognostic, predictive, therapy-related, circulating, and patient-related markers (Figure 1). Prognostic biomarkers assess outcome regardless of therapy type, whereas predictive markers estimate outcome of a specific treatment compared with another one. These biomarkers identify somatic or germ line nucleic acids (i.e., DNA, RNA, microRNA, or other non-coding RNAs such as long non-coding RNAs), epigenetic changes (i.e., DNA methylation), proteins (i.e., enzymes or receptors), antibody expressions, and even metabolic variations (1, 2, 6–8).
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is one of the most common hematologic cancers in children, responsible for 75% of all childhood leukemias (11–13). The contemporary treatment for the childhood ALL (chALL) is based on standard combination chemotherapy and particular preventive treatment of the central nervous system (CNS) (14). Despite the successful treatment rate of about 70-80%, the most difficult challenge in the treatment of chALL is still the risk of relapse in 20-30% of these children (15). The cure rate of chALL is related to early detection and stratification of individual patients into the risk groups of standard, low, intermediate, or high risks, based on the presence of special prognostic factors, genetic findings and response to treatment (14, 16).
Because of the lack of adequate initial symptoms, the clinical diagnosis of chALL requires a bone marrow biopsy/aspiration which is completely invasive, especially for children (17). Considering the laborious and painful nature of bone marrow biopsy/aspiration, reliable biomarkers for disease diagnosis and monitoring is appealing and of paramount importance (18). Appropriate biomarkers allow non-invasive monitoring of the patients and earlier diagnosis of disease, which may contribute to improved outcome. Furthermore, identifying new prognostic biomarkers is useful for the risk stratification of the patients and determining when to treat more aggressively or less intensively. Moreover, it may help developing novel drug targets and designing individualized therapies (5, 6). The current study mainly focuses on the prognostic biomarkers identified in chALL in order to help predicting response to treatment and adopting proper strategy for the disease management.
ALL Prognostic Biomarkers
The development of multidrug resistance (MDR) phenomenon and relapsed ALL is the most common cause of therapy failure and the main cause of the increased morbidity and mortality in children with ALL (19, 20). According to the WHO classification of leukemic neoplasms, ALL patients are categorized into standard, low, intermediate, or high risk groups according to the identified molecular and/or cytogenetic markers (i.e., MLL-AF4 and BCR-ABL rearrangements) and response to treatment (21). Leukemia minimal residual disease (mrd) level quantification is widely used for prediction of impending relapse and clinical outcomes, therapeutic hierarchy of chALL, and guiding clinicians to develop appropriate and efficient therapy options so that patients can avoid unnecessary chemical drug toxicity. Both quantitative polymerase chain reaction (QPCR) and flow cytometry analysis can be used to identify mrd. These techniques are sensitive, with the ability to detect one blast cell among 103 to 106 normal cells; robust; and reproducible. However, allele-specific QPCR is routinely used to detect mrd in chALL, using immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) or T-cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangements (22, 23). Furthermore, the multiplex real time PCR (RT-PCR) is another useful, rapid and flexible molecular technique, which provides additional information for accurate diagnosis and prognosis of chALL, such as identifying translocations and mutations in KRAS gene and the acquired mutations in the ABL1 kinase domain for predicting response to targeted treatments (8, 24). However, the number of identified fusion genes in acute leukemia is still limited.
RT-PCR assays show insufficient standardized cut-offs, and invasiveness of bone marrow aspiration which is painful for patient (25). Therefore, there is a huge interest in determining accurate disease-specific and sensitive biomarkers that are required for better risk assortment, predicting treatment response and distinguishing between indolent and aggressive disease (26). These biomarkers are essential for the assessment of the risk of relapse at diagnosis and could be useful in identification of patients requiring more intensive therapy (5, 16). The exact assignment of patients to various risk groups is critical to determine the premium therapeutic strategy for each patient and results in increased patient survival rate and reduced medical costs (27). Risk-based treatment is emphasized in therapeutic protocols for chALL to decrease the toxicity in low risk children and provide aggressive treatments for those with high risk of disease recurrence (21). Risk stratification adapted treatments using prognostic biomarkers will help to increase the cure rate (25). Remarkable advancement in molecular techniques and high throughput DNA sequencing has provided many nucleic acid-, epigenetic- and protein-based prognostic biomarkers which are described in below sections (9).
Deoxyribonucleic Acid-Based Biomarkers
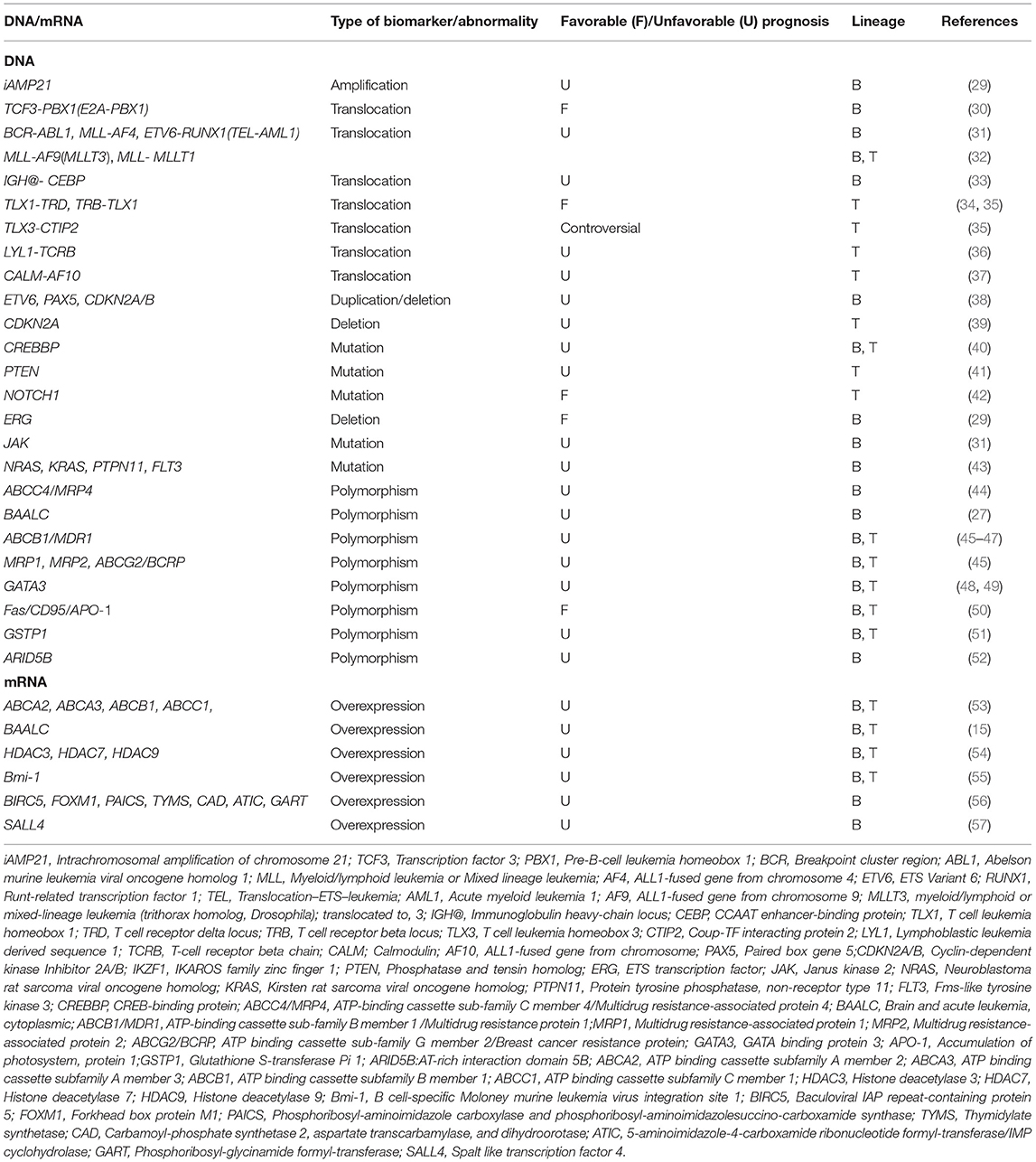
The fact that ALL develops only in a small number of individuals exposed to the specific environmental and lifestyle risk factors, indicates that the host genetic factors may have a key role in the genesis of leukemia (12, 28). Molecular modifications at the DNA level include numerical- and structural-chromosomal abnormalities such as rearrangements/translocations, point mutations/deletions or insertions, SNPs and gene replication (Table 1) (8). These genetic biomarkers can be somatic, recognized as mutations in DNA derived from tumor tissue, or germ line sequence variations, DNA isolated from whole blood, buccal cells, or sputum (1). Unlike protein markers, genetic biomarkers are more reproducible and less affected by intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli (6). Genomic alterations are a composite part of diagnosis and classification of hematological malignancies and have implications in the prognosis, risk stratification and selection of the appropriate therapy protocol based on the molecular changes (8). Currently, a very active area of tumor research is the use of genetic and epigenetic alterations in order to develop targeted therapies (58).
Recurring genomic alterations have a crucial role to induce drug resistance at relapse (59). In fact, differences in clinical features and outcomes observed in chALL patients are thought to be the result of variety in the chromosomal abnormalities, genetic backgrounds, and mutations in leukemic blasts (45). In most therapeutic protocols, different genetic subgroups of chALL are treated following risk-adapted treatment, which is tailored to the children' relative high risk of recurrence (60). Recently, the number of genetic modifications found in ALL patients has been extremely increased by developed multi next-generation sequencing (NGS) methods such as whole-genome sequencing and transcriptome sequencing (31). Several numerical chromosome changes have been recognized in chALL, including hypodiploidy, hyperdiploidy, near-haploidy, and complex karyotypes (61). The prevalence of hyperdiploidy is more than near-haploidy, hypodiploidy, and complex karyotypes in pediatric B cell precursor (BCP)-ALL and it is associated with good treatment response (29, 33, 61). Intrachromosomal amplification is another chromosome abnormality related to the treatment response. For example, intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21) is related to unfavorable prognosis in childhood BCP-ALL (29). iAMP21 is defined as amplification of the 5.1-Mb common region containing genes mapping to the Down Syndrome Critical Region (DSCR), RUNX1 and miR-802. Childhood BCP-ALL with iAMP21 consistently has 3 or more copies of the RUNX1 gene (62). Deletion of IKZF1, CDKN2A, RB1, and PAX5 genes are considered as other genetic alterations related to iAMP21 (30). Translocations, mutations and polymorphisms are the most common DNA level prognostic biomarkers in chALL.
Translocations/Rearrangements
Chromosomal irregularities mostly include non-random chromosomal translocations, which may generate novel fusion genes or cause inopportune gene expression of proto-oncogenes or altered proteins (21). Some of the common genetic events, such as translocations, are used for risk stratification and therapy assignment in chALL. Chromosomal translocations, such as BCR-ABL1, ETV6-RUNX1, and E2A-PBX1, occur in about 80% of childhood B-ALL and can be detected using interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and routine cytogenetic analysis (31). However, ~50% of T-ALL children have normal karyotype and cytogenetic (63). Here, we discuss some frequent chromosomal translocations which are known as prognostic biomarkers in chALL.
E2A, also known as TCF3, is located at chromosome 19p13.3. This basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor is essential for development and differentiation of B-cell. The chromosomal translocation t(1;19)(q23;p13) is the most prevalent translocation in E2A gene and appears in ~5–7% of childhood B-ALL cases. The resulting E2A-PBX1 is a chimeric fusion protein created by the amino-terminal transactivation domains of E2A and the DNA-binding homeodomain of PBX1 (30). Another E2A related translocation, t(17;19)(q22;p13), happens rarely among childhood B-ALL and includes the amino-terminal transactivation domains of E2A and the leucine zipper dimerization domain of HLF (31, 64). In pediatric B-ALL, t(1;19) is related to a favorable outcome, while chromosomal translocation t(17;19) is associated with a poor prognosis (30, 65).
The reciprocal translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11) results in the production of a Philadelphia chromosome and the expression of tyrosine kinase BCR-ABL1 chimeric fusion protein, the ABL1 oncogene on chromosome 9 and the BCR gene on chromosome 22. This translocation rarely occurs in children and the fusion protein has ABL1 kinase activity and localizes in the cell nucleus. Depending on the breakpoint site of the BCR gene, the BCR-ABL chimeric proteins may possess various molecular weights. A shorter form, p190, is observed in childhood Ph+ B-ALL and is associated with a worse outcome and a 5-year overall survival (OS) of <10% (29, 31, 66).
The most frequent chromosomal translocation involving the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) gene in B-ALL is t(4;11)(q21;q23), which is correlated with very poor prognosis for infants under 1 year of age, a great number of whom experience relapse. However, this translocation is associated with more favorable prognosis for children between the ages of 1 and 9 years or those of 10 years of age or older, and results in an MLL-AF4 (AFF1) fusion gene. Additionally, MLL-AF4 consists of more than 50% of the translocations and is more frequent (~24%) in children who have received chemotherapy for other tumors. Generally, this translocation is associated with an increased risk of recurrence in childhood B-ALL (29, 31, 67). Other 11q23 translocations in leukemia are t(9;11)(p22;q23) and t(11;19)(q23;p13.3), which create MLL-AF9(MLLT3) and MLL- MLLT1 fusion genes, respectively. In T-ALL and non-infant B-ALL patients, t(11;19)(q23;p13.3) translocation is correlated with favorable outcome, while in infant B-ALL cases, this genetic abnormality is associated with poor outcome (32).
ETV6, formerly known as TEL, is located at chromosome 12p13 and encodes an ETS family transcriptional repressor protein. It is commonly fused with other genes in human lymphoid or myeloid leukemia (68). RUNX1, previously known as AML1, located at chromosome 21q22, encodes a transcription factor protein that is important for embryonic hematopoiesis as well as B-cell differentiation in adult blood cell progenitors. Chromosomal translocation t(12;21)(p13;q22) leads to the ETV6-RUNX1 fusion protein, consisting of the N-terminal non-DNA-binding domain of ETV6 combined with RUNX1, and is the most common alteration in childhood B-ALL (~30%), but it is rarely observed in T-ALL (69). Children with B-ALL correlated with ETV6-RUNX1 show a highly good response to treatment (31). Despite the favorable prognostic factor of ETV6-RUNX1 translocation, relapse occurs in up to 20% of these subtypes demonstrating this cytogenic abnormality (70). Furthermore, recurrent translocations of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus (IGH@) are relatively rare but have been well-documented in B-ALL. Translocations of IGH@ with each of the five members of the CEBP transcription factor family have been identified in childhood B-ALL. However, the CEBP/IGH fusion, as a result of t(8;14)(q11;q32), is the most frequent translocation reported in pediatric B-ALL. This chromosomal alteration occurs either as a single acquired abnormality, or in conjunction with Down syndrome or t(9;22)(q34;q11). Chromosomal translocation t(8;14)(q24;q32) is correlated with a very inferior outcome and relapse (33).
TLX1 (also known as HOX11), located at chromosome 10q24.31, is a HOX transcription factor, which plays essential role in cell fate and differentiation during normal development. Genetic rearrangement t(10;14)(q24;q11.2) occurs in ~10% of childhood T-ALLs and induces dysregulation of TLX1 expression in these patients (34). Another translocation with aberrant expression of HOX11 is t(7;10)(q35;q24) (35). It has been demonstrated that T-ALL children with HOX11 expression show better survival (35, 71).
Another more frequent translocation in pediatric T-ALL is t(5;14)(q35;q32), observed in ~>20% of these patients. However, this genetic alteration encodes HOX11L2-BCL11B fusion protein (also known as TLX3-CTIP2) and leads to HOX11L2 activation, which is a homeobox transcription factor (72). The prognostic significance of this rearrangement remains controversial. There is an ongoing debate about the prognostic impact of t(5;14)(q35;q32) in T-ALL. Both, positive (35) and negative (73, 74) correlations, even no association (75) between the HOX11L2 expression and T-ALL prognosis are published recently. These controversial data may be due to the sample size of the cohort investigated (35).
Lymphoblastic leukemia-derived sequence 1 (LYL1) gene is mapped at chromosome 19p13 and a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor in T-ALL. The chromosomal translocation t(7;19)(q35; p13) leads to truncation of the LYL1 gene and creates LYL1-TCRB fusion gene. This translocation is associated with poor prognosis in pediatric T-ALL (36). Furthermore, another rare frequent translocation correlated with poor prognosis in pediatric T-ALL is t(10;11)(p13;q14), which creates CALM-AF10 fusion gene (37).
Admittedly, the genetic basis of the disease still remains unknown in a significant fraction of pediatric BCP-ALL and the response to treatment is unpredictable at the time of diagnosis in these patients (29). Therefore, finding of new prognostic biomarkers is critical for better risk assortment and improving the clinical outcome in chALL.
Other Genetic Mutations
Although chromosomal rearrangements are used as predictive factors of chALL, recurrent genetic alterations are associated with ALL response to treatment. The nature of these mutations includes changes of single base pairs to small deletions/insertions, duplications and copy number variation of DNA sequences. Minor deletions and amplifications are more precisely identified using genome wide DNA copy number profiling studies. Until now, more than fifty different recurring genetic abnormalities have been recognized. The most frequently affected genes are involved in lymphocyte differentiation (PAX5, IKZF1, and EBF1), lymphoid signaling (BTLA, CD200, TOX, BLNK, VPREB1), transcriptional regulation (ETV6, ERG), regulation of cell-cycle and tumor suppression (CDKN2A/CDKN2B, RB1, PTEN), and drug responsiveness (the glucocorticoid (GC) receptor NR3C1) (76). These alterations can be also determined by PCR. In this part, the most frequent mutations observed in the prognostic biomarkers of chALL will be reviewed.
Recently, our group demonstrated that BCP-ALL children with at least one of the genetic alterations including ETV6 (12p13.2) duplication, PAX5 (9p13.2) deletion, and CDKN2A/B (9p21.3) deletion must be classified as those with high-risk ALL, which have worse 3-year disease free survival (3-DFS) (38). PAX5 alteration, a B-lineage specific transcription factor, is one of the most common genetic aberrations in B-ALL (~30%). There are various genetic alterations correlated with PAX5 gene, including point mutations, monoallelic deletions, and translocations. PAX5 deletions are more common and correlated with E2A-PBX1, BCR-ABL1 and complex karyotype with secondary genetic changes; while PAX5 rearrangements are relatively rare (2.5% of B-ALL cases). CDKN2A (MTS1) and CDKN2B (MTS2) are well-known tumor suppressor genes that encode p16INK4a/p14ARF and p15INK4b proteins, respectively. Deletion of the 9p21 chromosomal region leads to deletion in these proteins, controlling G1/S cell-cycle progression, and are identified in 21–36% of pediatric B-ALL (consisting of 42 children and 60 adults) (31). Furthermore, CDKN2A deletion is also correlated with poor event-free survival (EFS) in pediatric T-ALL (39).
CREBBP is a transcriptional activator with various functions such as regulation of protein turnover and acetylation of histone and non-histone targets through its E4 polyubiquitin ligase and acetyl transferase activities, respectively. The activated transcription of gene CREBBP is associated with poor response to treatment in chALL (including 82 T-ALL and 88 B-ALL) (40). Besides, deletions in MTA1/14q32.33 and 15q13.2 as well as gain on 1p36.11 are correlated with shorter OS in chALL (including 115 B-ALL and 27 T-ALL) (77).
NOTCH1 gene, located at chromosome 9, encodes a single-pass heterodimeric transmembrane receptor with essential role in T-cell development. Chromosomal translocation t(7;9)(q34;q34.3) involves NOTCH1 gene in a limited number of T-ALL patients. However, activating mutations of NOTCH1 occur in up to 50% of pediatric T-ALL and involve either the heterodimer domain (HD) or the PEST domain of this protein, leading to ligand independent activation of NOTCH1. Interestingly, NOTCH1 activating mutations are associated with a favorable mrd and long-term outcome as well as prednisone response in these children (42).
The majority of PTEN tumor suppressor gene alterations in T-ALL are mutations resulting in truncated membrane binding C2-domain or deletions affecting the entire PTEN locus. A study has shown that small deletions result in inactivated PTEN by affecting only a few exons in about 8% of childhood T-ALL. The PTEN alterations (major deletions or mutations) are correlated with poor prognosis, leading to hyperactive PI3K–AKT signaling that impairs apoptosis and drives increased cell proliferation and metabolism in T-ALL patients (41). It has been suggested that PTEN deletion has more adverse outcome than mutations which preserve the N-terminal phosphatase domain (78).
Somatic genetic alterations of IKZF1, located at 7p13-p11.1 and encoding the lymphoid transcription factor IKAROS, are the most prevalent genetic lesions in high-risk BCP-ALL and are considered as very frequent events in BCR-ABL1–positive ALL (75 to 90%). Rare and frequent IKZF1 deletions, affecting exons 4-7 and exons 1-8, are correlated with poor prognosis, high risk of recurrence and EFS rates of below 50% (79–81). IKZF1 mutations/deletions lead to loss of IKZF1 function and drug resistance by affecting expression of the various molecules in different signaling pathways including cell adhesion (RHO, CTNND1, FAK, CD90(THY1), and ITGA5), metabolic pathways (GLUT1/3/6, INSR, HK2, AMPK, HK3, LKB1, G6PD, TXNIP, NR3C1, and CNR2), GR target gene regulation (NR3C1, EMP1, EMP1, and IK6), and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (PIK3CD and PIK3C2B) (82). Overexpression of cell adhesion molecules, creating aberrant cell-cell and cell-stroma interactions and acquisition of stem cell-like properties, mediates extravascular invasion, residence in the niche, activation of integrin signaling pathways, and reduced sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Overexpression and binding of THY1 at the cell surface lead to Src and FAK activation. FAK activation results in migration, proliferation and survival, due to the activation of various signaling pathways such as Rac/Rho and PI3K/AKT. Furthermore, IKZF1-related dysregulation of NR3C1 gene, encoding GC receptor, involves in GC resistance (83). However, coding IKZF1 mutations have been identified in familial B-ALL and ~0.9% of presumed sporadic pediatric B-ALL, most variants of which adversely affect IKZF1 function and response to treatment. Detection of IKZF1 alterations at diagnosis may be considered as a negative prognostic factor and it can be useful in identifying B-ALL children with high risk of treatment failure (79, 80).
Recent genomic profiling studies of chALL have identified a recurrent V(D)J-mediated intragenic deletion of the ERG gene (ERGdel) in about 7% of pediatric BCP-ALL, coding a member of the ETS transcription factor family with a main role in hematopoiesis (84). It has been observed that ERGdel is associated with older age, aberrant CD2 expression and frequent IKZF1Δ4-7 deletions. In one research, ERGdel chALL showed a favorable outcome, with an 8-year EFS and 8-year OS of 86.4 and 95.6%, respectively. In addition, presence of ERGdel in BCP-ALL children with IKZF1 Δ4-7 deletions showed a better disease outcome. Therefore, ERGdel can be used as a positive prognostic biomarker for patients with IKZF1 status (29).
Mutations of Janus kinases (JAKs), protein tyrosine kinases and key players in the JAK-STAT pathway, were initially identified in B-ALL correlated with Down syndrome. However, about 10% of B-ALLs without Down syndrome is also have the heterozygous somatic mutations of JAKs. These alterations happen in highly conserved residues in the kinase and pseudo-kinase domain, resulting in constitutive kinase activation, and are highly correlated with aberrant expression of the cytokine receptors in B-ALL patients. It has been shown that JAK mutation is correlated with relapse in B-ALL and ~70% of children with JAK mutation carry concomitant deletion of CDKN2A/B and/or IKZF1 (31).
RAS pathway alterations have been associated with chemotherapy resistance and inferior outcome in BCP-ALL and the large majority of aberrations (98%) occur in NRAS, KRAS, PTPN11, and FLT3 genes. High hyperdiploid, MLL-AF4-rearranged, BCR-ABL1-like and B-other cases have high alteration frequencies, while ETV6-RUNX1 cases have moderate frequencies in RAS pathway. Furthermore, researchers found that TCF3-PBX1 and BCR-ABL1-rearranged cases show rare frequencies in this pathway. RAS pathway mutations are related to unfavorable outcome and can be used as prognostic biomarkers in pediatric BCP-ALL (43).
Polymorphisms
Polymorphisms affect clinical outcome in chALL patients and are considered as potential prognostic biomarkers in this regard (45). Different genetic polymorphisms have been recognized as probable risk factors for hematological malignancies. In one study, 102 mrd–associated SNPs are detected in chALL using a genome-wide interrogation (85). Genetic polymorphisms related to genes mediating transportation and metabolism of drug have been indicated to be of importance in the difference in survival after cancer treatment (45). Some of the new polymorphism biomarkers are given below.
In recent years, the main focus of our studies has been placed on chALL and the cellular and molecular factors contributing to ALL MDR. We have identified SNP rs2274407 (G912T; K304N) located in the 3′ splice acceptor site of exon 8 of ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 4 (ABCC4 or MRP4) pre-mRNA and ABCC4 G912T allele carriers (G/T and T/T genotypes), which are correlated with worse 3-DFS in pediatric BCP-ALL. Additionally, it is identified that the T allele of rs2274407 may have functional impact on the aberrant splicing of ABCC4 mRNA. Bioinformatics analyses and in vitro studies suggested that the G912T allele can result in the elimination of about 250–300 bp in exon 8 and reduction of ABCC4 expression in lymphoblastic cells (44). Some other polymorphisms including G2269A, C912A, G559T, T1393C, and A934C have been identified additionally in the ABCC4 gene, which may be associated with outcomes in chALL (including 94 chALL containing B- and T-ALL with unidentified percentage) (86, 87).
Our group has also indicated that the rs62527607 [GT] SNP of Brain and Acute Leukemia, Cytoplasmic (BAALC) gene can be used as a novel negative prognostic biomarker in childhood ALL. The GT genotype may lead to an increase in the risk of drug resistance in pre-B-ALL and T-ALL cases by 2.86 and 8.75 folds, respectively, compared with those with GG genotype. However, patients who have GG genotype show no difference in response to chemotherapy (27).
Evaluating gene polymorphisms in ABC transporters can help predict the outcome of ALL and optimize the efficacy of chemotherapy in ALL patients. In one study, the SNPs related to the genes of MDR1/ABCB1, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP/ABCG2 were investigated in 82 chALL patients (including 6 T-ALL and 76 B-ALL). It has been demonstrated that a combination of MDR1 C1236T, MRP2 G1249A, and/or BCRP G34A SNPs is remarkably correlated with decreased EFS and OS (45). Some other studies have also shown the correlation between polymorphisms of MDR1 and risk of relapse in chALL (including 522 and 207 chALL containing B- and T-ALL with unidentified percentage). The risk of relapse is increased for patients with the 1199GA variant vs. 1199GG, the 3435CC variants vs. 3435CT/TT and the 1236CC variant vs. 1236CT/TT (46, 47). MDR1 gene is a member of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family encoding P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which plays an important role in MDR of cancer cells by promoting cellular efflux of structurally and functionally different chemotherapeutic regimens, such as anthracyclines, taxanes, and vinca alkaloids (88). Some genetic polymorphisms in MDR1 affect the intracellular expression levels of the P-gp protein, thereby resulting in MDR of pediatric ALL. Some MDR1 gene polymorphisms, such as C3435T, observed in exon 26, have been revealed to change the normal conformation of the P-gp protein, which inhibits its substrate-binding properties contributing to worse clinical outcome. Additionally, a number of MDR1 gene polymorphisms, including C3435T and G2677G/A, have been suggested to be correlated with the pharmacokinetics of the P-gp substrates including cyclosporine, digoxin, and fexofenadine. This study suggests a regulatory role for these SNPs in drug metabolism and ALL related SNPs (45).
The possible role of GATA3 rs3824662 polymorphism as a prognostic biomarker has been investigated in chALL (including 98 B-ALL and 18 T-ALL). GATA3 polymorphism which is located around the tissue-specific enhancer, is remarkably associated with the expression level of GATA3. The AA genotype is associated with significantly higher GATA3 mRNA levels and with shorter DFS, which increases incidence of relapse and poor prognosis in chALL. The regulatory network of GATA3 has also been shown in T- and B-ALL (48, 49).
GG genotype at −670 A/G position of Fas gene promoter is correlated with liver involvement in ALL patients (including 142 chALL containing B- and T-ALL with unidentified percentage). Fas or CD95/APO-1, a member of the superfamily of tumor necrosis factor receptors, is one of the significant molecules contributing to the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis (50). Binding apoptotic ligands to Fas receptor leads to homo-trimerization of this receptor, signaling transduction, death complex formation, and cell death (89). It is suggested that A to G substitution at the mentioned position leads to Fas dysregulation and resistance to treatment. As a result, Fas GG genotype at this position can be considered as a good prognostic biomarker in children with ALL (50).
Leonardi et al., studied the predictive value of germline polymorphisms in chALL (including 140 chALL containing B- and T-ALL with unidentified percentage). Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) are enzymes which play role in detoxification. It was proved that patients with a glutathione S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) c.313A>G genotype have an increased risk of relapse, and a shortened Recurrence-Free Survival (RFS) was observed in homozygote G patients. The association was even stronger when the combined genotypes of GSTP1 c.313GG, GSTT1 null and GSTM1 null was considered. In other words, patients who have 2/3 risk-allele genotypes are more prone to the risk of relapse and worse RFS. In fact, GSTP1 c.313A >G SNP modifies the enzyme activity, and GSTT1 and GSTM1 genes with a deletion polymorphism result in no activity of the enzyme. These prognostic biomarkers could improve risk stratification and reduce the number of relapses and deaths in chALL (51). Furthermore, eight ARID5B SNPs are associated with relapse and worse treatment outcome in pediatric BCP-ALL, including rs6479778, rs2893881, rs4948488, rs2393782, rs6479779, rs7923074, rs10821938, and rs17215180 with T, C, C, G, C, T, A and C risk alleles, respectively. The first six SNPs are associated with lower OS and can be considered as prognostic factors in pediatric BCP-ALL (52).
Ribonucleic Acid-Based Biomarkers
Changes at RNA level, occurs during RNA transcription or gene expression (8). Gene expression studies in chALL and the analysis of the DNA level alterations, have emphasized the great heterogeneity of this malignancy and made the possibility for differential diagnosis and identifying new sub-types of leukemia for better risk stratification (76). Various high-throughput methods are used to assess differential gene expression at RNA level in leukemia. Two of the most common methods include microarrays and next generation sequencing (90). Since high-throughput technologies remain prone to systematic errors, their clinical applications are limited and need to be confirmed using alternate methods, which are mostly included northern blot analysis and real time PCR (91, 92). Here, some of the gene expression alterations, known as prognostic biomarkers in chALL are reviewed. The related genes include: ABCA2, ABCA3, ABCB1, ABCC1, BAALC, Survivin (BIRC5), FOXM1, PAICS, TYMS, CAD, ATIC, GART, HDACs, Bmi-1, and Spalt-like transcription factor 4 (SALL4) (Table 1).
Possible association of the patient response to therapy with the mRNA expression levels of several ABC transporters including ABCA2, ABCA3, ABCB1/MDR1, MRP1/ABCC1, MRP3/ABCC3, ABCG2/BCRP, and MVP/LRP, has been previously investigated in chALL (including 21 B-ALL and 6 T-ALL). A significant positive correlation was observed between mRNA expression profiles of ABCA2, ABCA3, MDR1, and MRP1 genes and positive mrd measured a year after treatment. Based on the statistical analyses and performed RT-PCR assays, it was shown that the overexpression of these genes may result in an increased risk of positive mrd by 15-, 6.25-, 12,-and 9-fold, respectively, suggesting a poor prognostic impact (53). Furthermore, BAALC has been introduced as a novel poor prognostic molecular marker in chALL (consisting of 23 B-ALL and 5 T-ALL). Our results demonstrated that the high expression level of BAALC is also associated with the positive mrd measured a year after treatment. Moreover, a positive association was determined between mRNA expression levels of BAALC and MDR1/ABCB1 (15).
Higher expression levels of some histone deacetylases (HDACs) have been detected in chALL including HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC8, HDAC6, and HDAC7. Overexpression of HDAC1 and HDAC4 have been shown in T-ALL, while HDAC5 has higher expression in B-lineage ALL. As well as that, HDAC3 overexpression is associated with a significant lower 5-year EFS in T-ALL patients (54). Increased expression level of HDAC4 is correlated with high initial leukocyte count, T-ALL phenotype and prednisone poor-response in chALL (containing 73 B-ALL and 19 T-ALL) (93). Additionally, high expression levels of two other histone deacetylases, HDAC7 and HADC9, are associated with a decreased 5-year EFS in B-lineage CD10-positive patients. Thus, HDAC7 and HADC9 overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis in chALL (including 78 B-ALL and 16 T-ALL). Therefore, they can be prognostic factors and promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of chALL (54).
It has been recently identified that ALL patients with up-regulated proto-oncogene Bmi-1 at the time of diagnosis, show lower RFS rate (75.8%) than patients with down-regulated expression level of Bmi-1 (94.1%). Furthermore, there is a significant positive association between increased level of Bmi-1 and poor response to prednisone in chALL (consisting of 66 B-ALL and 11 T-ALL). The B cell-specific moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 or Bmi-1 is a member of the Polycomb-group (PcG) family, which is known to be an oncogene and its expression can be a novel prognostic biomarker in children with ALL (55).
Some differential gene expressions are associated with relapse or its timing. As up-regulation of BIRC5 (an apoptosis inhibitor/cell-cycle regulator) and FOXM1 (an oncogenic transcription factor) genes were identified in relapsed BCP-ALL, these genes can be introduced as biomarkers/indicators of poor prognosis. Up-regulation of some genes involved in folate metabolism and nucleotide biosynthesis, including PAICS, TYMS, CAD, ATIC, and GART, has been observed in late relapse (56).
Up-regulation of SALL4 protein due to its CpG island hypomethylation, was reported in pediatric BCP-ALL. SALL4 is a newly identified zinc-finger transcriptional factor which is essential for embryonic development. This protein plays a key role in the B-ALL cell survival and can be considered as a potential novel target in the treatment of B-ALL (57). Furthermore, some studies reported that SALL4 can regulate Bmi-1, as the mRNA expression of Bmi-1 is positively associated with that of SALL4 (55).
miRNA Levels Alteration
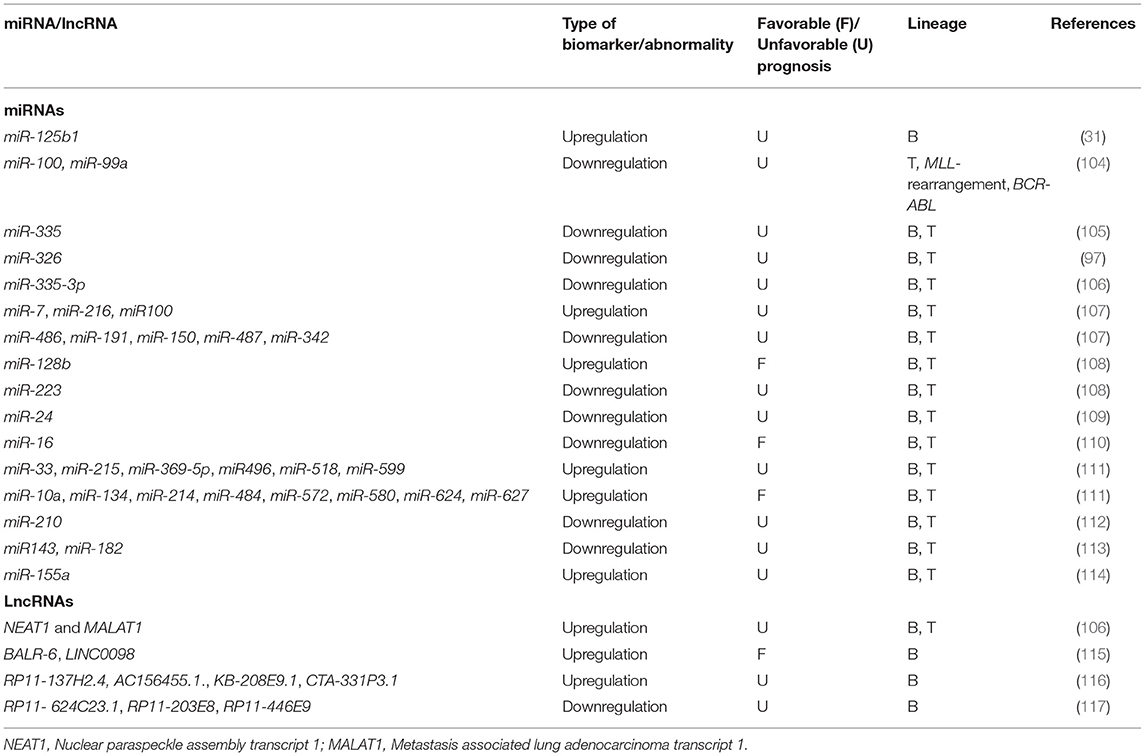
MicroRNAs, recently discovered non-coding endogenous single-stranded RNAs (composed of 19-24 nucleotides), show dysregulation during hematopoiesis and thereby have role in leukemogenesis (14, 94). These micro markers have proven to be very promising chALL biomarkers and have widespread clinical applications because of their stability and resistance to degradation in not only blood, but also various biological specimens (such as tissue, sputum, stool and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens), easily measured, and most importantly, their quantities correlates with the presence of the malignancy or with clinically relevant malignancy features (8, 14, 95–97). Recent studies have revealed that extracellular circulating miRNA levels in secreted membrane vesicles (microvesicles and exosomes), blood serum, and other body fluids can be used as biomarkers to diagnose, classify and predict prognosis of chALL (96, 98–101). miRNA expression dysregulation in cancers is because of different mechanisms, such as deletion or amplification of miRNA related genes, abnormal transcriptional control of miRNAs, epigenetic dysregulation and defects in the biogenesis machinery of miRNA (102). Some miRNAs might be up-regulated in chALL, and thus are suggested to have an oncogenic potential. On the other hand, some of them might be down-regulated in these patients, and are proposed to be tumor suppressors. Some examples of oncogenic miRNAs in chALL are miR-203 and miR-125b. Some tumor suppressor miRNAs are miR-181a, miR-326, and miR-200c, which show frequently down-regulation in chALL (97, 98). MicroRNA profiling can also be correlated with relevant clinical information, such as disease aggressiveness and metastatic potential, patient response to therapy, time-to-relapse and OS, and other clinical markers in chALL (101). Based on some investigations, not only can miRNAs regulate and sensitize the MDR phenotype, but also can be served as prognostic markers with potential implications in therapeutic interventions as drugs or therapeutic targets in chALL (103). Moreover, the identification of some prognostic miRNAs in patients can be used to predict prognosis and monitor cancer recurrence during their follow-up (14). Some new technologies are developed for the high-throughput identification of miRNAs in the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer, such as power-free microfluidic chip, electrically magnetic-controllable electrochemical biosensors, bead-based suspension array and one-step RT-PCR (8). A growing number of publications has revealed many examples of different miRNA profiles that provide potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers in chALL. As it is not plausible for this paper to review all of these studies, some of the critical miRNAs are introduced as follows. More investigated miRNAs are listed in Table 2.
MiRNA-125b1, also known as miR-125-1, is mapped at chromosome 11q24.1, which is the first miRNA identified in B-ALL and inserted into the rearranged IgH in some B-ALL patients. This translocation leads to the overexpression of miR-125b, which may play role as a negative regulator of p53, and can be considered as a poor prognostic micro marker for clinical outcome prediction (31).
Downregulation of miR-100 and miR-994 were found in pediatric T-ALL and children with the MLL-rearrangement and BCR-ABL fusion genes. It has been revealed that dysregulation of these miRNAs was also correlated with worse survival and prognosis in these children. Both miRNAs act as tumor suppressor genes and target FKBP51, involving in cell proliferation and apoptosis by impairing GC receptor translocation and reducing GC receptor activity and signaling pathways (104).
MiRNA-335 downregulation is correlated with worse 5-year EFS and GC resistance in chALL (including 56 B-ALL and 7 T-ALL). Since miR-335 targets MAPK1, its downregulation results in the upregulation of MAPK1, MEK/ERK map kinase pathway-mediated survival, proliferation and drugresistance of lymphoblast cells (105).
Our group has identified that miR-326 was downregulated in chALLs with MDR phenotype (36 B-ALL and 4 T-ALL). Furthermore, we demonstrated downregulation of miR-335-3p in the chALL MDR patients (58 B-ALL and 6 T-ALL). Interestingly, our data revealed that, there is a possibly causative correlation between the downregulation of miR-326 and miR-335-3p, increased risk of drug resistance and ALL relapse, and upregulation of ABCA2 and ABCA3 transporters, respectively (97, 106).
Long Non-coding RNAs
Long non-coding RNAs, also known as lncRNAs (non-coding RNAs longer than 200nt) are emerging key regulators of numerous cellular processes such as gene expression (118). Different studies have already shown that changes in the expression of lncRNAs contribute to malignancies' development and progression, and can be utilized as diagnostic and prognostic markers in many cancers including ALL (Table 2) (119). Since the expression of lncRNAs is more tissue and cell type specific than that of protein coding mRNAs (120), these transcripts are potentially highly specific diagnostic/prognostic biological markers for used for the classification of cancer subtypes and stratify patients for clinical trials and therapeutic protocols (121).
A recent study by our group has shown that NEAT1 and MALAT1 lncRNAs miR-335-3p can be used as prognostic biomarkers in chALL (58 B-ALL and 6 T-ALL) (106). The expression of other four lncRNAs BALR-1, LINC0098, BALR-6, and BALR-2 correlates with cytogenetic abnormalities, disease subgroups, OS and response to treatment in pediatric BCP-ALL. In addition, BALR-6 and LINC0098 up-regulation have been identified in patients with t(12;21) (115).
Another study reported up-regulation of five lncRNAs in BCP-ALL, including RP11-68I18.10, AC156455.1, RP11-137H2.4, CTA-331P3.1, and KB-208E9.1. These lncRNAs have significant effect on hallmark traits of cancer, such as migration, treatment response, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. The two lncRNAs, RP11-137H2.4 and RP11-68I18.10, are correlated with proliferation, while RP11-137H2.4, AC156455.1, KB-208E9.1, or CTA-331P3.1 are associated with apoptosis and drug resistance. In particular, knockout of lncRNA RP11-137H2.4 effectively involves in inhibition of cell proliferation and migration and sensitive GC-resistant BCP-ALL cells to GC. This lncRNA has prognostic role and can be critical for the development of novel therapies to put an end to GC resistance in childhood BCP-ALL (116).
In BCP-ALL, three lncRNAs were reported to be down-regulated, namely RP11-624C23.1, RP11-446E9, and RP11-203E8. Restoring the expression of all these lncRNAs in leukemic cell lines has dramatic effect on cancer hallmark cellular phenotypes. Interestingly, RP11-203E8 and RP11-624C23.1 have a very similar effect on DNA damage response. Cells with up-regulation of RP11-624C23.1 or RP11-203E8 specifically display decreased γ-H2A.X and increased apoptosis levels than control cells in response to genotoxic stress. Therefore, RP11-624C23.1 or RP11-203E8 silencing can result in increasing resistance to genotoxic stress. Since the genotoxic agents are essential parts of chALL treatment, these lncRNAs may be novel prognostic biomarkers and treatment targets in ALL (117).
Epigenetic-Based Biomarkers
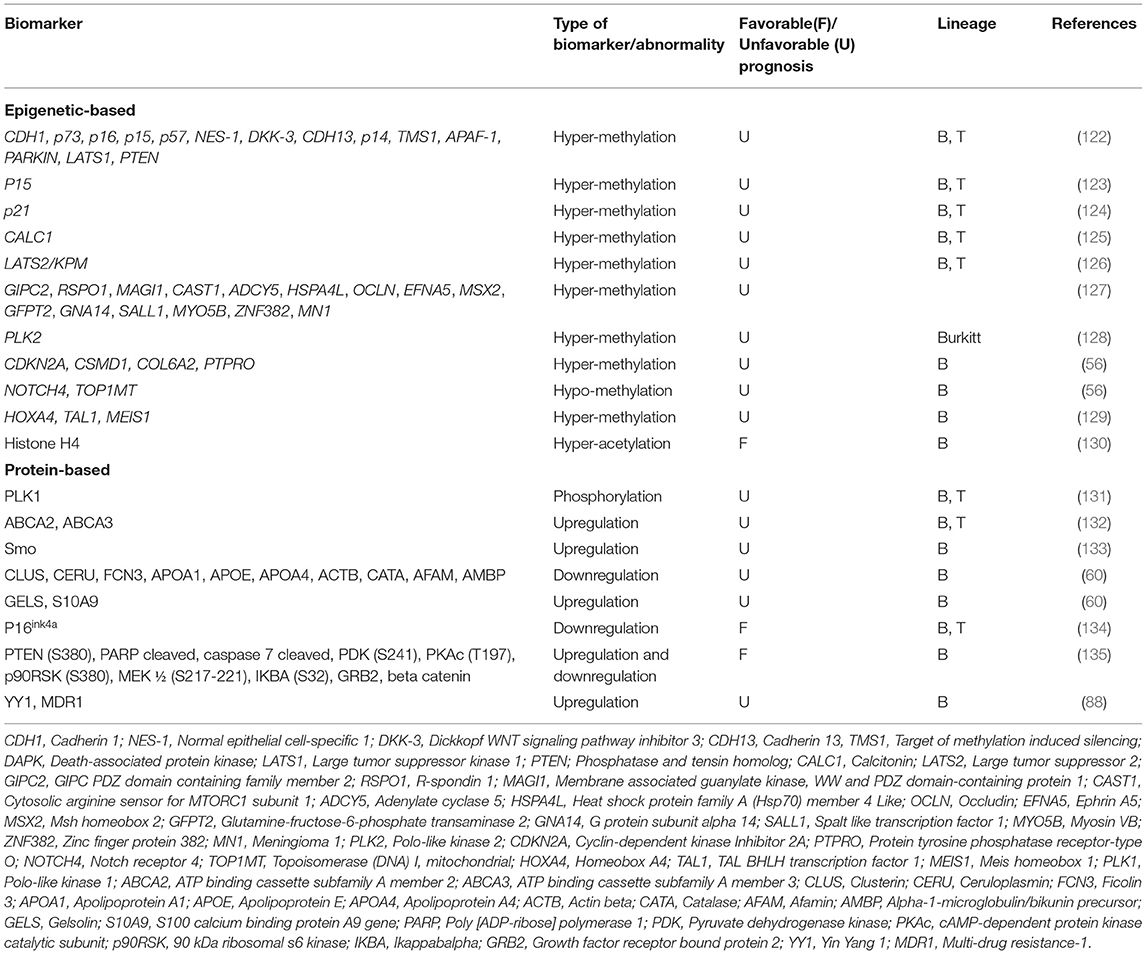
Epigenetic modifications may have an impact on gene expression, and play essential role in the emergence and recurrence of cancer, therefore may be considered as cancer prognostic biomarkers with important clinical implications (18, 59, 122). In order to identify epigenetic alterations, genome-wide methylation profiles were created for example, using methylated CpG island recovery assays followed by NGS (118), through which, technical standardizations are performed to determine useful clinical disease thresholds for the specific DNA methylation biomarkers (18).
Aberrant DNA methylation patterns are identified to occur during the progression of leukemia and correlated with clinical outcome. Methylation profile analysis of some genes including CDH1, p73, p16, p15, p57, NES-1, DKK-3, CDH13, p14, TMS1, APAF-1, DAPK, PARKIN, LATS1, and PTEN demonstrated that children including 88 B-ALLs and 12 T-ALLs, with methylation of 4 or more of these genes had worse DFS and OS. Interestingly, promoter methylation of these genes was correlated with favorable outcome in children with t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation or high white blood cell (WBC) count at diagnosis (122). In addition, it has been demonstrated that hyper-methylation of p15 is related to worse 8-year DFS in chALL (54 B-ALL and 39 T-ALL) (123).
Methylation-dependent silencing of p21 was observed in 109 children with ALL (the percentage of B- and T-ALL is not unidentified in this study). p21 expression is induced by functional p53 protein following apoptosis or cell cycle arrest. Since p21 methylation is correlated with unfavorable 7-year DFS and 9-year OS, hyper-methylation of p21 is suggested as an important factor in predicting the clinical outcome in chALL (124).
Methylation analysis of calcitonin (CALC1) gene identified the association of CALC1 hyper-methylation with a higher relapse and mortality rate in chALL (including 56 chALL with unidentified contribution of B- and T-ALL). Downregulation of p57KIP2 was also shown in patients with CALC1 hyper-methylation. However, hyper-methylation of CALC1 gene is associated with increased risk of relapse and worse clinical outcome in chALL (125). Furthermore, downregulation of human large tumor suppressor 2 (LATS2/KPM) gene following hyper-methylation is found in chALL with increased risk of relapse and mortality (54 B and T-ALL cases) (126).
In one study, a genome-wide analysis of promoter associated CpG island methylation was performed by the use of both methylated CpG island amplification (MCA) and representational differential analysis (RDA) or a DNA promoter microarray in patients with ALL. Methylation of multiple CpG islands, including GIPC2, MAGI1, RSPO1, ADCY5, CAST1, OCLN, HSPA4L, MSX2, EFNA5, GNA14, GFPT2, SALL1, ZNF382, MYO5B, and MN1 genes, was correlated with worse OS. Patients with more than four methylated genes had a remarkably poorer outcome when treated with hyper CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, adriamycin, and dexamethasone) based chemotherapy, used for ALL treatment (127).
It has been identified that Polo-like kinase 2 (PLK2) methylation-dependent transcriptional silencing occurs in B cell lymphomas, 100% of Burkitt lymphoma (BL) cell lines and a similarly high proportion of primary BL. The PLK2 has been lately introduced as a potential prognostic biomarker in response to the chemotherapy. PLK1 can act as an oncogene and indeed is a prominent target for developmental therapeutics in oncology, while PLK2-PLK5 have properties more similar to tumor suppressor genes (128).
In one study, analysis of methylation-dependent transcription regulation identified a subset of hyper-methylated and down-regulated genes in BCP-ALL, including CDKN2A, CSMD1, COL6A2, and PTPRO, whereas other genes were hypo-methylated and overexpressed including NOTCH4 and TOP1MT in relapsed children with BCP-ALL (56).
Aberrant methylation of IRF8, TAL1, MEIS1, IRF4, HOXA4, and HOXA5 has been observed in BCP-ALL patients. MEIS1 and HOXA4 expression and TAL1 methylation are correlated with WBC count, National Cancer Institute (NCI) risk classification and age, respectively. MEIS1 expression is inversely associated with WBC count, HOXA4 expression is down-regulated in patients with high risk based on the NCI classification and TAL1 methylation is rather increased in patients older than 9 years and in patients who show relapse (129). It has also been demonstrated that increased histone H4 acetylation is significantly associated with favorable RFS, EFS, OS in pediatric BCP-ALL (130). The identified epigenetic-based biomarkers are introduced in Table 3.
Protein-Based Biomarkers
The gene expression alterations induced at protein levels may be attributed to post-transcriptional, translational and post-translational modifications (8). The applied post-translational modifications, such as glycosylation or phosphorylation, in addition to the protein up or down regulation, may be considered as protein-based biomarkers in various diseases (7). These alterations may be identified using immunoassay formats, electrophretic techniques and targeted mass spectrometry. The protein-based biomarkers recently introduced in ALL are shown in Table 3.
It has been newly shown that PLK1 protein phosphorylation on Thr210 is prevalent in chALL (including 168 B-ALL and 34 T-ALL) and associated with lower EFS. PLK1 phosphorylation contributes to its binding to p53 and inhibiting its pro-apoptotic function. while, in turn, PLK1 expression is transcriptionally inhibited by p53 upon DNA damage, showing a role for PLK1 in the G2/M phase of proliferation (131).
Based on our previous findings, the overexpression of ABCA2 and ABCA3 transporters at protein levels can have prognostic impact on chALL (60 B-ALL and 9 T-ALL). Tertiary structure and docking analyses showed a possible compensatory mechanism between these two ABC transporters, through which, up-regulation of one of them may lead to drug efflux and multidrug resistance (132). Furthermore, our group has recently identified that overexpression of Smo at the protein level following the downregulation of miR-326 is related to MDR in pediatric B-ALL. Our results revealed a positive correlation between Smo and ABCA3 transcripts in these children (133).
Braoudaki et al. suggested that CLUS, CERU, FCN3, GELS, APOA1, APOE, APOA4, S10A9, ACTB, CATA, AFAM, and AMBP proteins can be considered as potential prognostic markers for aggressive pediatric B-ALL. In this study, aggressive B-ALL patients with high risk of relapse, were those with aged <1 or >10 years old, WBC count > 50 × 109/L, L2 > 20% or L3 blasts and CNS disease at diagnosis. In addition, down-regulation of GELS and S10A9 proteins were introduced as poor prognostic biomarkers in these children. Up-regulation of FCN3, ApoE, ApoA1, ApoA4, AMBP, ACTB, CATA, AFAM, CLUS, and CERU proteins has also been observed in aggressive B-ALL patients (60).
p16ink4a is a tumor suppressor protein and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI), which results in G1 arrest in the presence of a functional pRb. High expression of this protein was shown in chALL with inferior DFS, whereas p16ink4a low expression was a favorable prognostic factor. Therefore, it has been suggested that p16ink4a expression at protein level is a strong prognostic biomarker in chALL. Forty three B-ALL and 15 T-ALL were investigated in this study (134).
One study demonstrated that a subgroup of pediatric B-ALL patients with specific pattern of protein expression including higher level of PTEN (S380), cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase 7, PDK (S241), PKAc (T197), p90RSK (S380), MEK 1/2 (S217-221), IKBA (S32), and GRB2 and lower beta catenin expression have superior survival (135).
Recently, immunocytochemistry analysis revealed that overexpression of YY1 at the protein level is correlated with unfavorable OS via upregulation of MDR1/P-gp in chALL (including 51 B-ALL and 12 T-ALL). Overexpression of MDR1 protein contributes to the resistance to a variety of chemotherapeutic drugs and relapse in chALL (88).
ALL Predictive Biomarkers
Predictive biomarkers give information about the response to a specific treatment and help to select particular treatment over another (Table 4), while prognostic biomarkers provide information about the natural history of the disorder (145). In other words, predictive biomarkers can be used to recognize individuals who are more likely to respond to a particular medical reagent or environmental agent. The aforementioned response can be a symptomatic benefit, better survival, or a detrimental effect (146). More precisely, the predictive biomarkers help to optimize therapy decisions and facilitate personalized chemotherapy (147).
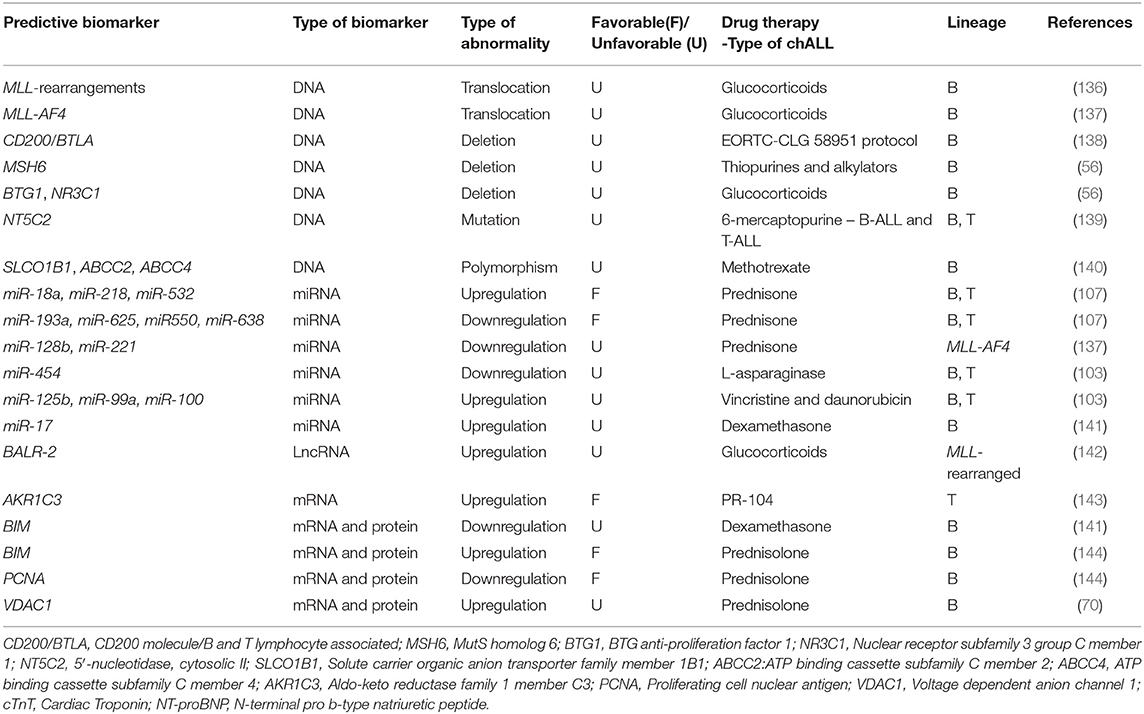
As discussed above, MLL translocation is correlated with poor prognosis in chALL. In one study, it is revealed that patients with MLL rearrangement, specially infants, show GC resistance (136), introducing this translocation as a predictive biomarker.
CD200/BTLA deletions act as predictive biomarkers in pediatric BCP-ALL without any known genetic lesions, and are associated with <8-year EFS. These patients are treated according to the EORTC-CLG 58951 protocol. A strong correlation has been observed between CD200/BTLA deletions and ETV6-RUNX1 positive leukemia as well. ETV6-RUNX1 positive is a good prognostic biomarker in BCP-ALL and CD200/BTLA deletions do not affect prognosis within this genetic subtype (138). It has been found that specific deletions of MSH6, BTG1, and NR3C1 have been related to resistance to thiopurines, alkylators (MSH6) and GCs (BTG1 and NR3C1) in pediatric B-ALL (56). Furthermore, mutations in the cytosolic 5′-nucleotidase II gene NT5C2 lead to proteins with increased nucleotides activity and result in increased nucleoside-analog metabolism and 6-mercaptopurine resistance in chALL (103 T-ALL and 35 BCP-ALL) (139).
Moreover, it has been shown that SLCO1B1 rs11045879, ABCC2rs3740065, and ABCC4rs9516519 polymorphisms are novel predictive biomarkers for Methotrexate (MTX) toxicity and outcome in pediatric B-ALL. The association between these polymorphisms and the toxicity of MTX has been confirmed through analysis of 384 SNPs in twelve MTX transporter genes (SLCO1B1, SLCO1B3, SLCO1A2, ABCG2, ABCB1, ABCC1, ABCC2, ABCC3, ABCC4, SLC19A1, SLC22A6, and SLC22A8 (140).
It has been shown that upregulation of miR-193a, miR-625, miR-550, and miR-638 is associated with resistance to prednisone, while miR-18a, miR-218, and miR-532 were downregulated in children with poor prednisone response (The ALL samples in this study consisted of 48 B-ALL and 1 T-ALL) (107). Downregulation of miR-128b and miR-221 are predictive biomarkers for resistance to GC in pediatric MLL-AF4 ALL cells. MLL-AF4 translocation is correlated with GC resistance and is introduced as a predictive biomarker in chALL carrying this translocation. Restoration of these miRNAs can sensitize MLL-AF4 ALL cells to GC drugs (137). Furthermore, low expression of miR-454 is associated with resistance to L-asparaginase (in 81 patients), while overexpression of miR-125b, miR-99a, and miR-100 is related to vincristine and daunorubicin resistance in chALL (103). It has also been demonstrated that overexpression of miR-17 and downregulation of its target (BIM) result in dexamethasone resistance in childhood B-ALL (141).
LncRNA BALR-2 can promote cell survival via inhibition of downstream genes of the GC receptors, such as Fos, Jun, and BIM. BALR-2 plays a role in resistance to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and up-regulates in MLL-rearranged BCP-ALL. BIM has an indispensable role in the regulation of B-ALL GC response and can be served as a predictive biomarker in pediatric B-ALL (142).
According to the in vivo and in vitro studies, AKR1C3 is introduced as a predictive biomarker for response to PR-104 treatment, in pediatric T-ALL. In patient-derived leukemic blasts, primary T-ALL cells have been proven to be more sensitive to PR-104 than BCP-ALL primary cells, and this sensitivity correlates with AKR1C3 expression. It has been suggested that PR-104 represents a new treatment for refractory/relapsed T-ALL, and expression of AKR1C3 can be served as a predictive biological marker to detect those children who will most likely take advantage of therapy with PR-104 in prospective clinical trials (143).
Early response to 7 days-PRED treatment is one of the most prominent positive prognostic factors in pediatric B-ALL. Patients with up regulation of the two proteins named, BIM and voltage-dependent anion-channel protein1 (VDAC1), at day eight of PRED monotherapy, showed increased EFS compared with those whose gene expression profiles were not changed followed by PRED therapy. Down regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) revealed similar impact on patients EFS. These data introduced three promising predictive biomarkers of BMI, VDAC1, and PCNA in childhood B-ALL (70, 144).
Circulating Biomarkers
Due to the promising characteristics of high stability, low cost, possibility of repeated sampling and noninvasiveness, circulating biomarkers have received extensive attention in molecular medicine nowadays. Compelling evidences have shown that these types of biomarkers are measurable in secreted membrane vesicles (microvesicles and exosomes), blood serum, and other body fluids and can be used as biomarkers to diagnose, classify, follow-up and predict prognosis in chALL (96, 98–101). It has been suggested that extracellular circulating biomarkers play an important role in intracellular communication in both paracrine and endocrine manners (101).
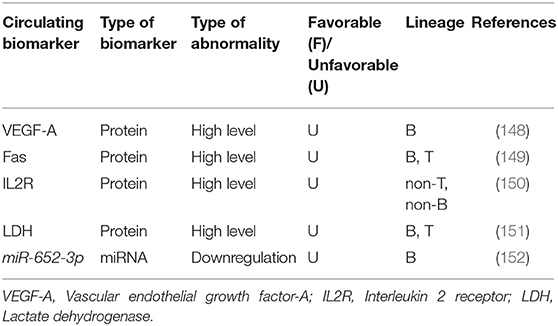
Serum vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) is recently introduced as a circulating biomarker which can be useful for screening high-risk chALL patients and monitoring their response to treatment (148). A study has suggested that low serum levels (≤60 pg/mL) of the VEGF-A, at the end of induction (day 28), is significantly correlated with favorable 6-year EFS in children with standard risk B-ALL. Whereas, children with high VEGF-A serum levels (>100 pg/mL) or a rise in the VEGF-A level during induction (days 0–28) have shown worse 6-year EFS. Furthermore, VEGF-A serum concentration at the entry into induction (day 0) is reported to be related to time of relapse. Another study demonstrated that the mean values of serum Fas at the time of diagnosis is associated with response to treatment in 29 chALL (with unidentified portion of B- and T-ALL). In other words, relapsed children have higher Fas levels compared with patients in CR. Therefore, serum Fas levels are appropriate circulating biomarkers for chALL follow up (149). It has also been demonstrated that higher serum levels of interleukin 2 receptor (IL2R) (>2.000 U/mL) is a useful circulating biomarker for the prediction of response to treatment in children with non-T, non-B ALL, but not in those with T cell disease. However, increased levels of IL2R is related to the worse treatment outcome in these patients (150). Another study revealed that at day 14 and day 29 of induction, significant decreased serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level is associated to increased platelet count and decreased peripheral and bone marrow blast cell percentages in chALL (including 44 patients with unidentified percentage of B- and T-ALL) (151).
To the best our knowledge, only one circulating miRNA has already been introduced to be correlated with response to treatment and outcome in chALL. It has been recently demonstrated that circulating miR-652-3p is downregulated in childhood B-ALL at initial diagnosis and relapse compared with the samples of the same patients at CR. In addition, miR-652-3p upregulation using mimic leads to vincristine- and cytarabine-induced apoptosis in lymphoblast cells via increased sensitivity to these drugs (152) (Table 5).
Patient-Related Biomarkers
Some clinical and hematological factors play important role in chALL patients response to chemotherapy, including age, WBC and leukocyte count at initial diagnosis, immunophenotype, involvement of CNS, the presence or absence of mediastinal tumor, and mrd in different stages of treatment (37, 153). Children between 1 and 10 years of age have a favorable prognosis and better outcome compared to the children younger than 24 months, adolescents and adults. However, these factors are used to classify chALL patients into the different risk groups including standard risk with 90% survival rate, intermediate risk with 60% rate survival and high risk with 30% survival rate (37). For example, children with WBC count under 50,000/μL, at diagnosis, show better response to treatment than patients with WBC count equal to or above 50,000/μL (154). The leukocytosis count >30 × 109L and >100 × 109L is identified as a poor prognostic factor in pediatric B-ALL and T-ALL, respectively.
Children with T-ALL and pro B-ALL immunophenotypes as well as mrd-positive children have worse outcome and EFS (155, 156). It has been demonstrated that pediatric B-ALL patients with CD10− or CD34− have poor outcome compared with those who are CD10+ or CD34+ (157).
Therapy-Related Biomarkers
One of the most important limitations in chALL treatment is acquired resistance to treatment, which is developed after exposure to chemotherapy agents and contributed to MDR and relapse (158). Identification of the biomarkers related to drug resistance may provide novel approaches to targeted therapy and improve patient clinical outcome. Therapy-related biomarkers are shortly introduced in this section.
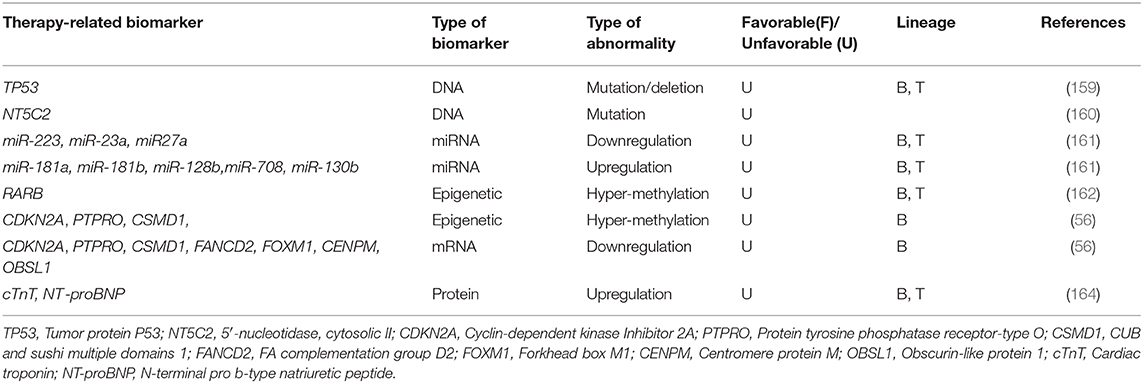
Deletions/Mutations of the tumor suppressor gene TP53 are correlated with poor response to treatment, EFS, and OS in chALL (218 BCP-ALL and 47 T-ALL). Alterations in TP53 gene were shown to be gained in relapsed patients after treatment, using direct sequencing and multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification in 23 matched samples (159).
DNA analysis of paired chALL samples at diagnosis, relapse, or complete remission (CR) revealed that some missense mutations specially occur in relapsed patients after treatment and are not identified at initial diagnosis or CR. These mutations happen in RGS12, LPHN1, CAND1, PRMT2, NIPSNAP1, USP7, TULP4, CBX3, COBRA1, SDF2, FBXO3, SCARF1, NEGR1, NT5C2, DPH5, SMEK2, MIER3, DOPEY1, ZNF192, and NT5C2 genes. RNA sequencing of 10 matched cases demonstrated that novel somatic mutations are acquired in NT5C2 gene at relapse and are not presented at diagnosis. Enzymatic analysis in additional 61 relapsed cases identified that these mutations conferred increased enzymatic activity of the protein cN-II, a 5′-nucleotidase, and resistance to nucleoside analog therapies (160).
MicroRNA expression analysis of paired diagnosis/relapse samples (11 B-ALL and 6 T-ALL patients) revealed that some miRNAs are differentially expressed at diverse stages of the disease. miR-223, miR-23a, and miR27a, are examples of those miRNAs which are downregulated at initial diagnosis, restored at CR, and downregulated once again at relapse. On the other hand, some miRNAs, including miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-128b, and miR-708 are overexpressed at both diagnosis and relapse. These sets of miRNAs may have main roles in leukemogenesis and post-therapy drug resistance (161).
Methylation analysis of some genes in 8 patients with B-ALL and 1 with T-ALL showed hyper methylation of MGMT, and p16 at both diagnostic and relapse status. However, RARB was specifically hyper-methylated at the time of relapse. It is suggested that, RARB hyper-methylation is correlated with chALL progression and should be monitored after chemotherapy (162).
High-throughput analysis of matched diagnosis/relapse childhood BCP-ALL samples revealed more frequent somatic deletions in KZF1, VPREB1, NR3C1, and EBF1 genes at the stage of relapse compared with the disease onset (56). Furthermore, in contrast to T-ALL (163), BCP-ALL showed significantly more hyper-methylated genome at relapse (56). Promotor hyper-methylation, and consequently downregulation of CDKN2A, PTPRO, and CSMD1 tumor suppressor genes was also identified only in relapsed chALLs, but not those at the onset of the disease. Furthermore, some genes including FANCD2, FOXM1, CENPM, and OBSL1 were only expressed at relapse, not diagnostic status of pediatric BCP-ALL (56).
One study has identified that, increased serum levels of cTnT (cardiac injury biomarker) and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP; cardiomyopathy biomarker), followed by treatment with doxorubicin, may act as biomarkers for cardiac injury and cardiomyopathy in children with high-risk ALL (52 T-ALL and 434 B-ALL) (164). Although Doxorubicin chemotherapy is very effective in pediatric ALL, it may also cause damage to myocardial cells and consequently, induce cardiomyopathy (164, 165) (Table 6).
Biomarkers in Personalized Medicine and Immunotherapy
Since the effectiveness and cure rate of conventional chemotherapy depend on many individual factors, such as genetic and protein expression differences in one patient vs. another, the field of precision and personalized medicine is growing incredibly fast (166). Some of the diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive biomarkers are currently used in clinical practice of personalized and targeted oncotherapy, such as: tyrosine kinase inhibitors, e.g., Gleevec® (imatinib; Novartis) in ALL patients with BCR-ABL1 gene rearrangements; FLT3 inhibitor Hydrate® (CEP-701, lestaurtinib; Cephalon Inc.) in ALL patients with MLL rearrangements; and purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitor Mundesine® (forodesine; Mundipharma AG) in pediatric T-ALL with purine nucleoside phosphorylase mutation (167, 168).
Immunotherapy is another more specific and effective class of cancer treatments. Some of the pediatric immune-based approaches have received FDA approval, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), checkpoint inhibitors, bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs), and chimeric antigen receptor-modified T (CAR-T) cells. However, some immunotherapy protocols are still under way to be examined, such as vaccines and oncolytic virotherapies (169). CAR-T cells are genetically engineered to target surface antigens on tumor cells and have exhibited good efficacy for treatment of the hematological malignancies (170). For example, tisagenlecleucel (also known as Kymriah or CTL019) is a CD19 CAR-T cell, which is used for immunotherapy in pediatric B-ALL (169). There are evidences indicating post CR-relapse followed by CD-19 CAR-T infusion. In these cases, transfusion of CD22 and/or CD20 CAR-T cells followed by CD-19 CAR-T cell therapy may decrease the side effects raised by the first round immunotherapy. Although much has been explored to this regard, CAR-T cell therapy requires closer inspection and there is a growing need to determine biomarkers in order to improve response to immunotherapy (171).
Challenges in Clinical Applications of Biomarkers
Due to the important role of biomarkers at all stages of disease, it is essential that they undergo extremely thorough and careful evaluations, such as analytical and clinical validations and clinical utility assessments, before incorporation into a routine clinical care (1). Identification, validation and introduction of a novel biomarker is just as difficult as the development and approval of a new drug. Moreover, ~30–50% of biomarkers are coupled to drug development programs and only 3–5% reach the clinical usage (172). Herein, we point out some challenges in the validation of biomarkers and their application in chALL clinical trials.
A number of biological challenges are encountered during the development of novel biomarkers, including the intrinsic biological differences among distinct individuals, complexity in tumor response to treatment and the complexity of various biological systems, involving diverse interacting molecular pathways and adaptive feedback and cross-talk loops. Besides the aforementioned challenges, various types of measurement errors may occur during the validation of disease biomarkers (4, 173, 174). The fundamental determinant assuring the reliability of biomarkers analyses is the use of standard protocols for sample collection, processing, and storage (172). On the other hand, the statistical analyses of the biomarker data is another main logistical component of the validation process; statistical evaluation is challenging regarding achievement of uniformity in data management, biostatistics, and bioinformatics methodologies (172). In biomarker validation, statistical approach must detect relationships that happen by chance from those reflecting true biological associations (175).
However, omic features (i.e., genomics, proteomics, epigenetics, etc.) and/or environmental and lifestyle factors, may contribute to drug response. It is necessary to recognize biomarkers through either omic data alone or along with environmental/lifestyle factors such as age, gender, diet, and other metabolic factors, studied in personalized medicine, to use the “right drug,” for the “right patient,” at the “right dose,” at the “right time” (4, 176).
In order to identify valid and reliable biomarkers, cohort studies should be performed, evaluating large number of sample collections (177). In this regard, one of the main challenges to identify new biomarkers in chALL is the limited number of children participating in research studies because of the painful or invasive procedures required for sample collection. Another challenge is obtaining age-matching control samples, which is essential to identify normal reference value. In addition to the low number of childhood malignancies compared with adults, parents are reluctant to participate in the trials (178).
Conclusion
In conclusion, MDR is a serious impediment to the treatment of chALL; the most common malignancy in children. Treatment sensitivity/drug resistance depends on many factors, such as genetic, epigenetic, transcriptomic, and proteomic alterations. These modifications can be used as bio-signatures, helping better risk stratification and, predicting patient response to therapy. Some chromosomal translocations are introduced as positive prognostic biomarkers, including t(1;19)(q23;p13), t(12;21)(p13;q22), t(7;10)(q35;q24), and t(10;14)(q24;q11.2), which may predict a favorable outcome; Some others are presented as negative bio-forecasters including t(17;19)(q22;p13), t(9;22)(q34;q11), t(8;14)(q24;q32), and t(7;19)(q35; p13), which anticipate worse response to treatment. Some of the drug resistance biomarkers are currently used for targeted therapy. Examples of these molecules are BCR-ABL1 gene rearrangement which is targeted by Imatinib, the commercially fabricated tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and MLL rearrangement which is potentially hampered by the FLT3 inhibitor, Lestaurtinib. Moreover, pediatric chALL biomarkers may be attacked using immune-based approaches including CAR-T cell therapies. Circulating biomarkers, are promising biological markers which are detected non-invasively, and employed for classification, follow-up and predicting prognosis in chALL.
Author Contributions
NA and EG conceived the ideas and wrote the article. KG reviewed the article and made suggestions. SR conceived the ideas, wrote and reviewed the article, and made suggestions.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Henry NL, Hayes DF. Cancer biomarkers. Molecular oncology. (2012) 6:140–6. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.01.010
2. Summers T, Langan RC, Nissan A, Brücher BL, Bilchik AJ, Protic M, et al. Serum-based DNA methylation biomarkers in colorectal cancer: potential for screening and early detection. J Cancer. (2013) 4:210. doi: 10.7150/jca.5839
3. Hasanzadeh M, Shadjou N, De La Guardia M. Aptamer-based assay of biomolecules: Recent advances in electro-analytical approach. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. (2017) 89:119–32. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.02.003
4. Mayeux R. Biomarkers: potential uses and limitations. NeuroRx. (2004) 1:182–8. doi: 10.1602/neurorx.1.2.182
6. Kalia M. Biomarkers for personalized oncology: recent advances and future challenges. Metab Clin Exp. (2015) 64:S16–21. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.10.027
7. Tainsky MA. Genomic and proteomic biomarkers for cancer: a multitude of opportunities. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2009) 1796:176–93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.04.004
8. Sethi S, Ali S, Philip PA, Sarkar FH. Clinical advances in molecular biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2013) 14:14771–84. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714771
9. Sharma M, Mohanty S. Molecular biomarkers in cytogenetically normal–acute myeloid leukemia: harnessing the targets. J Mol Biomarkers Diagn Sci. (2013) 8:2. doi: 10.4172/2155-9929.S8-009
10. De Souza Cavalcante M, Torres-Romero JC, Lobo MDP, Moreno FBMB, Bezerra LP, Lima DS, et al. A panel of glycoproteins as candidate biomarkers for early diagnosis and treatment evaluation of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biomarker Res. (2016) 4:1. doi: 10.1186/s40364-016-0055-6
11. Aberuyi N, Rahgozar S. Prediction of involved microRNAs in modulation of ABCA2 transporter in order to confront multi drug resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using bioinformatic methods. In: 8th Congress of Iranian Pediatric Hematology and Oncology Society. Tehran (2014).
12. Hunger SP, Mullighan CG. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1541–52. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1400972
13. Hashemi F, Asadi N, Beheshtipour N, Karimi M. The impact of educating parents of leukemic children on the patients' quality of life. Iran Red Cresc Med J. (2011) 13:550.
14. Ferracin M, Negrini M. Micromarkers 2.0: an update on the role of microRNAs in cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Exp Rev Mol Diagn. (2015) 15:1369–81. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1081058
15. Azizi Z, Rahgozar S, Moafi A, Dabaghi M, Nadimi M. mRNA overexpression of BAALC: A novel prognostic factor for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Biomed Rep. (2015) 3:371–4. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.437
16. Szczepanek J, Styczynski J, Haus O, Tretyn A, Wysocki M. Relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children in the context of microarray analyses. Arch Immunol Therap Exp. (2011) 59:61–8. doi: 10.1007/s00005-010-0110-1
17. Bai Y, Zhang H, Sun X, Sun C, Ren L. Biomarker identification and pathway analysis by serum metabolomics of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2014) 436:207–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.05.022
18. Chatterton Z, Burke D, Emslie KR, Craig JM, Ng J, Ashley DM, et al. Validation of DNA methylation biomarkers for diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Chem. (2014) 60:995–1003. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.219956
19. Aberuyi N, Rahgozar S, Moafi A. The role of ATP-binding cassette transporter A2 in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia multidrug resistance. Iranian J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. (2014) 4:118.
20. Giussani P, Tringali C, Riboni L, Viani P, Venerando B. Sphingolipids: key regulators of apoptosis and pivotal players in cancer drug resistance. Int J Mol Sci. (2014) 15:4356–92. doi: 10.3390/ijms15034356
21. López Villar E, Wu D, Cho WC, Madero L, Wang X. Proteomics-based discovery of biomarkers for paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: challenges and opportunities. J Cell Mol Med. (2014) 18:1239–46. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12319
22. Scrideli CA, Assumpção JG, Ganazza MA, Araújo M, Toledo SR, Lee MLM, et al. A simplified minimal residual disease polymerase chain reaction method at early treatment points can stratify children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia into good and poor outcome groups. Haematologica. (2009) 94:781–9. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2008.003137
23. Redwaan S, Abdelraheem H, Eldin TK, Badrawy H, Abdelsalam EMN. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a single-center experience. J Curr Med Res Pract. (2016) 1:31. doi: 10.4103/2357-0121.199351
24. Bader P, Kreyenberg H, Von Stackelberg A, Eckert C, Salzmann-Manrique E, Meisel R, et al. Monitoring of minimal residual disease after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia allows for the identification of impending relapse: results of the ALL-BFM-SCT 2003 trial. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:1275–84. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.4631
25. Bai J, He A, Zhang W, Huang C, Yang J, Yang Y, et al. Potential biomarkers for adult acute myeloid leukemia minimal residual disease assessment searched by serum peptidome profiling. Proteome Sci. (2013) 11:39. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-11-39
26. Hunger SP, Loh ML, Whitlock JA, Winick NJ, Carroll WL, Devidas M, et al. Children's Oncology Group's 2013 blueprint for research: acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2013) 60:957–63. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24420
27. Nadimi M, Rahgozar S, Moafi A, Tavassoli M, Tanha HM. Evaluation of rs62527607 [GT] single nucleotide polymorphism located in BAALC gene in children with acute leukemia using mismatch PCR-RFLP. Cancer Genet. (2016) 209:348–53. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2016.06.005
28. Mullighan CG. Genetic variation and the risk of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia Res. (2010) 34:1269. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2010.05.013
29. Clappier E, Auclerc M, Rapion J, Bakkus M, Caye A, Khemiri A, et al. An intragenic ERG deletion is a marker of an oncogenic subtype of B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a favorable outcome despite frequent IKZF1 deletions. Leukemia. (2014) 28:70. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.277
30. Ou Z, Sherer M, Casey J, Bakos HA, Vitullo K, Hu J, et al. The Genomic Landscape of PAX5, IKZF1, and CDKN2A/B Alterations in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cytogenet Genome Res. (2016) 150:242–52. doi: 10.1159/000456572
31. Kholod O. RNA-Sequencing Analysis in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Reveals Aberrant Gene Expression and Splicing Alterations. University of Missouri—Columbia (2017).
32. Rubnitz JE, Camitta BM, Mahmoud H, Raimondi SC, Carroll AJ, Borowitz MJ, et al. (1999). Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the MLL-ENL fusion and t (11; 19)(q23; p13. 3) translocation. J Clin Oncol. 17:191–6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.1.191
33. Moorman AV, Ensor HM, Richards SM, Chilton L, Schwab C, Kinsey SE, et al. Prognostic effect of chromosomal abnormalities in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: results from the UK Medical Research Council ALL97/99 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. (2010) 11:429–38. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70066-8
34. Van Vlierberghe P, Ferrando A. The molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clini Investig. (2012) 122:3398–406. doi: 10.1172/JCI61269
35. Gottardo N, Jacoby P, Sather H, Reaman G, Baker D, Kees U. Significance of HOX11L2/TLX3 expression in children with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated on Children's Cancer Group protocols. Leukemia. (2005) 19:1705. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403834
36. El-Menshawy N, Shahin D, Ghazi HF. Prognostic Significance of the Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Derived Sequence 1 (LYL1) GeneExpression in Egyptian Patients with AcuteMyeloid Leukemia. Turkish J Hematol. (2014) 31:128. doi: 10.4274/tjh.2012.0063
37. Forero RM, Hernández M, Hernández-Rivas JM. Genetics of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Leukemia. London, UK: IntechOpen (2013).
38. Moafi A, Zojaji A, Salehi R, Najafi SD, Rahgozar S. The correlation between Pax5 deletion and patients survival in Iranian children with precursor B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cell Mol Biol. (2017) 63:19–22. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2017.63.8.4
39. Jang W, Park J, Kwon A, Choi H, Kim J, Lee GD, et al. CDKN2B downregulation and other genetic characteristics in T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Exp Mol Med. (2019) 51:4. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0195-x
40. Mullighan CG, Zhang J, Kasper LH, Lerach S, Payne-Turner D, Phillips LA, et al. CREBBP mutations in relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. (2011) 471:235. doi: 10.1038/nature09727
41. Mendes RD, Sarmento LM, Canté-Barrett K, Zuurbier L, Buijs-Gladdines JG, Póvoa V, et al. PTEN microdeletions in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia are caused by illegitimate RAG-mediated recombination events. Blood. (2014) 124:567–78. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-03-562751
42. Breit S, Stanulla M, Flohr T, Schrappe M, Ludwig W-D, Tolle G, et al. Activating NOTCH1 mutations predict favorable early treatment response and long-term outcome in childhood precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (2006) 108:1151–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-12-4956
43. Jerchel IS, Hoogkamer AQ, Ariës IM, Steeghs EM, Boer JM, Besselink NJ, et al. RAS pathway mutations as a predictive biomarker for treatment adaptation in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. (2018) 32:931. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.303
44. Tanha HM, Rahgozar S, Naeini MM. ABCC4 functional SNP in the 3′ splice acceptor site of exon 8 (G912T) is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. (2017) 80:109–17. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3340-7
45. Zhai X, Wang H, Zhu X, Miao H, Qian X, Li J, et al. Gene polymorphisms of ABC transporters are associated with clinical outcomes in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Arch Med Sci. (2012) 8:659. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2012.30290
46. Gregers J, Green H, Christensen IJ, Dalhoff K, Schroeder H, Carlsen N, et al. Polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene and effect on outcome and toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. (2015) 15:372. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2014.81
47. Pongstaporn W, Pakakasama S, Chaksangchaichote P, Pongtheerat T, Hongeng S, Permitr S. MDR1 C3435T and C1236T polymorphisms: association with high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. (2015) 16:2839–43. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.7.2839
48. Mosaad YM, Elashery R, Darwish A, Sharaf Eldein OA, Barakat T, Marouf S, et al. GATA3 rs3824662 gene polymorphism as possible risk factor in a cohort of Egyptian patients with pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its prognostic impact. Leukemia Lymphoma. (2017) 58:689–98. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2016.1204656
49. Hou Q, Liao F, Zhang S, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Zhou X, et al. Regulatory network of GATA3 in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:36040. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16424
50. Valibeigi B, Amirghofran Z, Golmoghaddam H, Hajihosseini R, Kamazani FM. Fas gene variants in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and association with prognosis. Pathol Oncol Res. (2014) 20:367–74. doi: 10.1007/s12253-013-9705-2
51. Leonardi DB, Abbate M, Riccheri MC, Nuñez M, Alfonso G, Gueron G, et al. Improving risk stratification of patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Glutathione-S-Transferases polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of relapse. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:110–7. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8606
52. Xu H, Cheng C, Devidas M, Pei D, Fan Y, Yang W, et al. ARID5B genetic polymorphisms contribute to racial disparities in the incidence and treatment outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:751. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0345
53. Rahgozar S, Moafi A, Abedi M, Entezar-E-Ghaem M, Moshtaghian J, Ghaedi K, et al. mRNA expression profile of multidrug-resistant genes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia of children, a prognostic value for ABCA3 and ABCA2. Cancer Biol Ther. (2014) 15:35–41. doi: 10.4161/cbt.26603
54. Moreno DA, Scrideli CA, Cortez MA, De Paula Queiroz R, Valera ET, et al. Differential expression of HDAC3, HDAC7 and HDAC9 is associated with prognosis and survival in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. (2010) 150:665–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08301.x
55. Peng H-X, Liu X-D, Luo Z-Y, Zhang X-H, Luo X-Q, Chen X, et al. Upregulation of the proto-oncogene Bmi-1 predicts a poor prognosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:76. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3049-3
56. Hogan LE, Meyer JA, Yang J, Wang J, Wong N, Yang W, et al. Integrated genomic analysis of relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals therapeutic strategies. Blood. (2011) 118:5218–26. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-345595
57. Ueno S, Lu J, He J, Li A, Zhang X, Ritz J, et al. Aberrant expression of SALL4 in acute B cell lymphoblastic leukemia: mechanism, function, and implication for a potential novel therapeutic target. Exp Hematol. (2014). 42:307–316. e308. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2014.01.005
58. Reyjal J, Cormier K, Turcotte S. Autophagy and cell death to target cancer cells: exploiting synthetic lethality as cancer therapies. In: Koumenis C, Hammond E, Giaccia A, editors. Tumor Microenvironment and Cellular Stress. New York, NY: Springer (2014). p. 167–88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5915-6_8
59. Bhatla T, Jones CL, Meyer JA, Vitanza NA, Raetz EA, Carroll WL. The biology of relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia: opportunities for therapeutic interventions. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. (2014) 36:413. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000000179
60. Braoudaki M, Lambrou GI, Vougas K, Karamolegou K, Tsangaris GT, Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou F. Protein biomarkers distinguish between high-and low-risk pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a tissue specific manner. J Hematol Oncol. (2013) 6:52. doi: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-52
61. Safavi S, Paulsson K. Near-haploid and low-hypodiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia: two distinct subtypes with consistently poor prognosis. Blood. (2017) 129:420–3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-743765
62. Garcia DRN, Arancibia AM, Ribeiro RC, Land MGP, Silva MLM. Intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21) detected by ETV6/RUNX1 FISH screening in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report. Rev Brasil Hematol Hemoterapia. (2013) 35:369–71. doi: 10.5581/1516-8484.20130111
63. Mrózek K, Harper DP, Aplan PD. Cytogenetics and molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin. (2009) 23:991–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2009.07.001
64. Hirai M, Yagasaki H, Fujimura J, Inoue M, Shimozawa K, Okuma H, et al. Successful preemptive donor lymphocyte infusions from a haploidentical donor in a boy with E2A-HLF-positive ALL. Leukemia Lymphoma. (2018) 59:746–8. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1347927
65. Lokadasan R, Prem S, Koshy SM, Jayasudha A. Hypercalcaemia with disseminated osteolytic lesions: a rare presentation of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Ecancermedicalscience. (2015) 9. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2015.542
66. Kang Z-J, Liu Y-F, Xu L-Z, Long Z-J, Huang D, Yang Y, et al. The Philadelphia chromosome in leukemogenesis. Chin J Cancer. (2016) 35:48. doi: 10.1186/s40880-016-0108-0
67. Meyer C, Burmeister T, Gröger D, Tsaur G, Fechina L, Renneville A, et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2017. Leukemia. (2018) 32:273. doi: 10.1038/leu.2017.213
68. Zhang MY, Churpek JE, Keel SB, Walsh T, Lee MK, Loeb KR, et al. Germline ETV6 mutations in familial thrombocytopenia and hematologic malignancy. Nat Genet. (2015) 47:180. doi: 10.1038/ng.3177
69. Hakeem A, Shiekh AA, Bhat GM, Lone A. Prognostification of ALL by cytogenetics. Indian J Hematol Blood Transf. (2015) 31:322–31. doi: 10.1007/s12288-014-0483-0
70. Jiang N, Kham SKY, Koh GS, Lim JYS, Ariffin H, Chew FT, et al. Identification of prognostic protein biomarkers in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). J Proteomics. (2011) 74:843–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.02.034
71. Schneider NR, Carroll AJ, Shuster JJ, Pullen DJ, Link MP, Borowitz MJ, et al. New recurring cytogenetic abnormalities and association of blast cell karyotypes with prognosis in childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a pediatric oncology group report of 343 cases. Blood. (2000) 96:2543–9. doi: 10.1182/blood.V96.7.2543
72. Su X-Y, Della-Valle V, Andre-Schmutz I, Lemercier C, Radford-Weiss I, Ballerini P, et al. HOX11L2/TLX3 is transcriptionally activated through T-cell regulatory elements downstream of BCL11B as a result of the t (5; 14)(q35; q32). Blood. (2006) 108:4198–201. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-032953
73. Ballerini P, Blaise A, Busson-Le Coniat M, Su XY, Zucman-Rossi J, Adam M, et al. HOX11L2 expression defines a clinical subtype of pediatric T-ALL associated with poor prognosis. Blood. (2002) 100:991–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-11-0093
74. Ferrando AA, Neuberg DS, Staunton J, Loh ML, Huard C, Raimondi SC, et al. Gene expression signatures define novel oncogenic pathways in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. (2002) 1:75–87. doi: 10.1016/S1535-6108(02)00018-1
75. Cavé H, Suciu S, Preudhomme C, Poppe B, Robert A, Uyttebroeck A, et al. Clinical significance of HOX11L2 expression linked to t (5; 14)(q35; q32), of HOX11 expression, and of SIL-TAL fusion in childhood T-cell malignancies: results of EORTC studies 58881 and 58951. Blood. (2004) 103:442–50. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1495
76. Jiménez-Morales S, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Ramírez-Bello J. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a genomic perspective. Boletín Médico Del Hospital Infantil de México. (2017) 74: 13–26. doi: 10.1016/j.bmhime.2017.11.013
77. Forero-Castro M, Robledo C, Benito R, Abáigar M, Martín AÁ, Arefi M, et al. Genome-wide DNA copy number analysis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia identifies new genetic markers associated with clinical outcome. PloS One. (2016) 11:e0148972. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148972
78. Gutierrez A, Sanda T, Grebliunaite R, Carracedo A, Salmena L, Ahn Y, et al. High frequency of PTEN, PI3K, and AKT abnormalities in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (2009) 114:647–50. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-206722
79. Boer J, Van Der Veer A, Rizopoulos D, Fiocco M, Sonneveld E, De Groot-Kruseman HA, et al. Prognostic value of rare IKZF1 deletion in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: an international collaborative study. Leukemia. (2016) 30:32. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.199
80. Mullighan CG, Su X, Zhang J, Radtke I, Phillips LA, Miller CB, et al. Deletion of IKZF1 and prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. (2009) 360:470–80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808253
81. Van Der Veer A, Zaliova M, Mottadelli F, De Lorenzo P, Te Kronnie G, Harrison CJ, et al. IKZF1 status as a prognostic feature in BCR-ABL1–positive childhood ALL. Blood. (2014) 123:1691–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-509794
82. Marke R, Van Leeuwen FN, Scheijen B. The many faces of IKZF1 in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. (2018) 103:565–74. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.185603
83. Churchman ML, Mullighan CG. Ikaros: exploiting and targeting the hematopoietic stem cell niche in B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Exp Hematol. (2017) 46:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2016.11.002
84. Zaliova M, Zimmermannova O, Dörge P, Eckert C, Möricke A, Zimmermann M, et al. ERG deletion is associated with CD2 and attenuates the negative impact of IKZF1 deletion in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. (2015) 29:1222. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.77
85. Yang JJ, Cheng C, Yang W, Pei D, Cao X, Fan Y, et al. Genome-wide interrogation of germline genetic variation associated with treatment response in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. JAMA. (2009) 301:393–403. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.7
86. Ansari M, Sauty G, Labuda M, Gagné V, Laverdière C, Moghrabi A, et al. Polymorphisms in multidrug resistance-associated protein gene 4 is associated with outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (2009) 114:1383–6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-191098
87. Tanaka Y, Manabe A, Fukushima H, Suzuki R, Nakadate H, Kondoh K, et al. Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) polymorphisms impact the 6-mercaptopurine dose tolerance during maintenance therapy in Japanese childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. (2015) 15:380. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2014.74
88. Antonio-Andrés G, Rangel-Santiago J, Tirado-Rodríguez B, Martinez-Ruiz GU, Klunder-Klunder M, Vega MI, et al. Role of Yin Yang-1 (YY1) in the transcription regulation of the multi-drug resistance (MDR1) gene. Leukemia Lymphoma. (2018) 59:2628–38. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1448083
89. Ramezani G, Pourgheysari B, Shirzad H, Sourani Z. Pterostilbene increases Fas expression in T-lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Res Pharmaceutical Sci. (2019) 14:55. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.251853
90. Handschuh L. Not only mutations matter: molecular picture of acute myeloid leukemia emerging from transcriptome studies. J Oncol. (2019) 2019:7239206. doi: 10.1155/2019/7239206
91. Prokopec SD, Watson JD, Waggott DM, Smith AB, Wu AH, Okey AB, et al. Systematic evaluation of medium-throughput mRNA abundance platforms. RNA. (2013) 19:51–62. doi: 10.1261/rna.034710.112
92. Wilhelm BT, Briau M, Austin P, Faubert A, Boucher G, Chagnon P, et al. RNA-seq analysis of 2 closely related leukemia clones that differ in their self-renewal capacity. Blood. (2011) 117:e27–38. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-293332
93. Gruhn B, Naumann T, Gruner D, Walther M, Wittig S, Becker S, et al. The expression of histone deacetylase 4 is associated with prednisone poor-response in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia Res. (2013) 37:1200–7. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2013.07.016
94. Correia NC, Barata JT. MicroRNAs and their involvement in T-ALL: a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. (2019) 74:100650. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2019.100650
95. Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs: new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. (2013) 57:840–7. doi: 10.1002/hep.26095
96. Allegra A, Alonci A, Campo S, Penna G, Petrungaro A, Gerace D, et al. Circulating microRNAs: new biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer. Int J Oncol. (2012) 41:1897–912. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1647
97. Ghodousi ES, Rahgozar S. MicroRNA-326 and microRNA-200c: Two novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:6024–32. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26800
98. Grobbelaar C, Ford AM. The role of MicroRNA in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: challenges for diagnosis and therapy. J Oncol. (2019) 2019:894. doi: 10.1155/2019/8941471
99. Almeida RS, Costa E Silva M, Coutinho LL, Garcia Gomes R, Pedrosa F, Massaro JD, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles discriminate childhood T-from B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol Oncol. (2019) 37:103–12. doi: 10.1002/hon.2567
100. Ultimo S, Martelli AM, Zauli G, Vitale M, Calin GA, Neri LM. Roles and clinical implications of microRNAs in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:5642–54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26290
101. Carvalho De Oliveira J, Molinari Roberto G, Baroni M, Bezerra Salomão K, Alejandra Pezuk J, Sol Brassesco M. MiRNA dysregulation in childhood hematological cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2688. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092688
102. Peng Y, Croce CM. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Trans Targeted Ther. (2016) 1:15004. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2015.4
103. Gómez-Gómez Y, Organista-Nava J, Illades-Aguiar B, Leyva-Vázquez MA. miRNAs in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: diagnosis, prognosis and target therapeutic. In: Advances in Hematologic Malignancies. London, UK: IntechOpen (2019). doi: 10.5772/intechopen.84318
104. Li X, Luo X, Han B, Duan F, Wei P, Chen Y. MicroRNA-100/99a, deregulated in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, suppress proliferation and promote apoptosis by regulating the FKBP51 and IGF1R/mTOR signalling pathways. Br J Cancer. (2013) 109:2189. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.562
105. Yan J, Jiang N, Huang G, Tay JLS, Lin B, Bi C, et al. Deregulated MIR 335 that targets MAPK 1 is implicated in poor outcome of paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. (2013) 163:93–103. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12489
106. Pouyanrad S, Rahgozar S, Ghodousi ES. Dysregulation of miR-335-3p, targeted by NEAT1 and MALAT1 long non-coding RNAs, is associated with poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Gene. (2019) 692:35–43. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.01.003
107. Zhang H, Luo X-Q, Zhang P, Huang L-B, Zheng Y-S, Wu J, et al. MicroRNA patterns associated with clinical prognostic parameters and CNS relapse prediction in pediatric acute leukemia. PLoS One. (2009) 4:e7826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007826
108. Nemes K, Csóka M, Nagy N, Márk Á, Váradi Z, Dankó T, et al. Expression of certain leukemia/lymphoma related microRNAs and its correlation with prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pathol Oncol Res. (2015) 21:597–604. doi: 10.1007/s12253-014-9861-z
109. Organista-Nava J, Gómez-Gómez Y, Illades-Aguiar B, Del Carmen Alarcón-Romero L, Saavedra-Herrera MV, Rivera-Ramírez AB, et al. High miR-24 expression is associated with risk of relapse and poor survival in acute leukemia. Oncol Rep. (2015) 33:1639–49. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3787
110. Kaddar T, Chien W, Bertrand Y, Pages M, Rouault J, Salles G, et al. Prognostic value of miR-16 expression in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia relationships to normal and malignant lymphocyte proliferation. Leukemia Res. (2009) 33:1217–23. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2008.12.015
111. Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Moqadam FA, Khankahdani LM, Lange-Turenhout E, Chen C, et al. MicroRNAs characterize genetic diversity and drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematol Haematol. (2011) 2010:026138. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.026138
112. Mei Y, Gao C, Wang K, Cui L, Li W, Zhao X, et al. Effect of microRNA-210 on prognosis and response to chemotherapeutic drugs in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Sci. (2014) 105:463–72. doi: 10.1111/cas.12370
113. Piatopoulou D, Avgeris M, Drakaki I, Marmarinos A, Xagorari M, Baka M, et al. Clinical utility of miR-143/miR-182 levels in prognosis and risk stratification specificity of BFM-treated childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Hematol. (2018) 97:1169–82. doi: 10.1007/s00277-018-3292-y
114. El-Khazragy N, Noshi MA, Abdel-Malak C, Zahran RF, Swellam M. miRNA-155 and miRNA-181a as prognostic biomarkers for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Biochem. (2019) 120:6315–21. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27918
115. Lajoie M, Drouin S, Caron M, St-Onge P, Ouimet M, Gioia R, et al. Specific expression of novel long non-coding RNAs in high-hyperdiploid childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0174124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174124
116. Ouimet M, Drouin S, Lajoie M, Caron M, St-Onge P, Gioia R, et al. A childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia-specific lncRNA implicated in prednisolone resistance, cell proliferation, and migration. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:7477. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13936
117. Gioia R, Drouin S, Ouimet M, Caron M, St-Onge P, Richer C, et al. LncRNAs downregulated in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia modulate apoptosis, cell migration, and DNA damage response. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:80645. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20817
118. Almamun M, Levinson BT, Van Swaay AC, Johnson NT, Mckay SD, Arthur GL, et al. Integrated methylome and transcriptome analysis reveals novel regulatory elements in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Epigenetics. (2015) 10:882–90. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1078050
119. Morlando M, Ballarino M, Fatica A. Long non-coding RNAs: new players in hematopoiesis and leukemia. Front Med. (2015) 2:23. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2015.00023
120. Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer A, Djebali S, Tilgner H, et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. (2012) 22:1775–89. doi: 10.1101/gr.132159.111
121. Yarmishyn AA, Kurochkin IV. Long noncoding RNAs: a potential novel class of cancer biomarkers. Front Genet. (2015) 6:145. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00145
122. Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Castillejo JA, Agirre X, Barrios M, Navarro G, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of cancer-related genes: a strong independent prognostic factor in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (2004) 104:2492–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-0954
123. Mai H, Liu X, Chen Y, Li C, Cao L, Chen X, et al. Hypermethylation of p15 gene associated with an inferior poor long-term outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2016) 142:497–504. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2063-6
124. Roman-Gomez J, Castillejo JA, Jimenez A, Gonzalez MG, Moreno F, Del Carmen Rodriguez M, et al. 5′ CpG island hypermethylation is associated with transcriptional silencing of the p21CIP1/WAF1/SDI1 gene and confers poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (2002) 99:2291–6. doi: 10.1182/blood.V99.7.2291
125. Roman J, Castillejo JA, Jimenez A, Bornstein R, Gonzalez MG, Del Carmen Rodriguez M, et al. Hypermethylation of the calcitonin gene in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is associated with unfavourable clinical outcome. Br J Haematol. (2001) 113:329–38. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02764.x
126. Jimenez-Velasco A, Roman-Gomez J, Agirre X, Barrios M, Navarro G, Vázquez I, et al. Downregulation of the large tumor suppressor 2 (LATS2/KPM) gene is associated with poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. (2005) 19:2347. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403974
127. Kuang S, Tong W, Yang H, Lin W, Lee M, Fang Z, et al. Genome-wide identification of aberrantly methylated promoter associated CpG islands in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. (2008) 22:1529. doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.130
128. Coley HM, Hatzimichael E, Blagden S, Mcneish I, Thompson A, Crook T, et al. Polo like kinase 2 tumour suppressor and cancer biomarker: new perspectives on drug sensitivity/resistance in cancer. Oncotarget. (2012) 3:78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.332
129. Musialik E, Bujko M, Kober P, Wypych A, Gawle-Krawczyk K, Matysiak M, et al. Promoter methylation and expression levels of selected hematopoietic genes in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Res. (2015) 50:26–32. doi: 10.5045/br.2015.50.1.26
130. Janczar K, Janczar S, Pastorczak A, Mycko K, Paige AJ, Zalewska-Szewczyk B, et al. Preserved global histone H4 acetylation linked to ETV6-RUNX1 fusion and PAX5 deletions is associated with favorable outcome in pediatric B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia Res. (2015) 39:1455–61. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.10.006
131. Hartsink-Segers SA, Exalto C, Allen M, Williamson D, Clifford SC, Horstmann M, et al. Inhibiting Polo-like kinase 1 causes growth reduction and apoptosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Haematol Haematol. (2013) 2013:084434. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.084434
132. Aberuyi N, Rahgozar S, Dehaghi ZK, Moafi A, Masotti A, Paolini A. The translational expression of ABCA2 and ABCA3 is a strong prognostic biomarker for multidrug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. OncoTargets Ther. (2017) 10:3373. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S140488
133. Sheybani Z, Rahgozar S, Ghodousi ES. The Hedgehog signal transducer Smoothened and microRNA-326: pathogenesis and regulation of drug resistance in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Manage Res. (2019) 11:7621. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S214405
134. Mekki Y, Catallo R, Bertrand Y, Manel A, Ffrench P, Baghdassarian N, et al. Enhanced expression of p16 ink4a is associated with a poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. (1999) 13:181. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2401303
135. Tumino M, Accordi B, Sciro M, Giordan M, te Kronnie G, Basso G, et al. Reverse Phase Protein Assay (RPPA) defines specific patterns in childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Blood. (2008) 112:2510. doi: 10.1182/blood.V112.11.2510.2510
136. Spijkers-Hagelstein JA, Schneider P, Pinhanços SM, Castro PG, Pieters R, Stam RW. Glucocorticoid sensitisation in Mixed Lineage Leukaemia-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by the pan-BCL-2 family inhibitors gossypol and AT-101. Eur J Cancer. (2014) 50:1665–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.03.011
137. Yeh C-H, Moles R, Nicot C. Clinical significance of microRNAs in chronic and acute human leukemia. Mol Cancer. (2016) 15:37. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0518-2
138. Ghazavi F, Clappier E, Lammens T, Suciu S, Caye A, Zegrari S, et al. CD200/BTLA deletions in pediatric precursor-B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated according to the EORTC-CLG 58951 protocol. Haematol Haematol. (2015) 2015:126953. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.126953
139. Tzoneva G, Perez-Garcia A, Carpenter Z, Khiabanian H, Tosello V, Allegretta M, et al. Activating mutations in the NT5C2 nucleotidase gene drive chemotherapy resistance in relapsed ALL. Nat Med. (2013) 19:368. doi: 10.1038/nm.3078
140. Lopez-Lopez E, Ballesteros J, Piñan MA, De Toledo JS, De Andoin NG, Garcia-Miguel P, et al. Polymorphisms in the methotrexate transport pathway: a new tool for MTX plasma level prediction in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenet Genomics. (2013) 23:53–61. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e32835c3b24
141. Harada M, Pokrovskaja-Tamm K, Söderhäll S, Heyman M, Grander D, Corcoran M. Involvement of miR17 pathway in glucocorticoid-induced cell death in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia Lymphoma. (2012) 53:2041–50. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.678004
142. Fernando TR, Rodriguez-Malave NI, Waters EV, Yan W, Casero D, Basso G, et al. LncRNA expression discriminates karyotype and predicts survival in B-lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol Cancer Res Mol. (2015) 6:2015. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0006-T
143. Fulda S. Biomarker of sensitivity to PR-104 in leukemia. Blood. (2015) 126:1153–4. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-655225
144. Jiang N, Koh GS, Lim JY, Kham SK, Ariffin H, Chew FT, et al. BIM is a prognostic biomarker for early prednisolone response in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Exp Hematol. (2011) 39:321–329. e323. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.11.009
145. Walther A, Johnstone E, Swanton C, Midgley R, Tomlinson I, Kerr D. Genetic prognostic and predictive markers in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. (2009) 9:489. doi: 10.1038/nrc2645
146. FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, Endpoints, and Other Tools) Resource. Silver Spring, MD: Food and Drug Administration (US) (2016).
147. Nalejska E, Maczynska E, Lewandowska MA. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers: tools in personalized oncology. Mol Diagn Ther. (2014) 18:273–84. doi: 10.1007/s40291-013-0077-9
148. Avramis IA, Panosyan EH, Dorey F, Holcenberg JS, Avramis VI. Correlation between high vascular endothelial growth factor-A serum levels and treatment outcome in patients with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from Children's Oncology Group Study CCG-1962. Clin Cancer Res. (2006) 12:6978–84. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1140
149. Arslan A, Antmen AB. Serum Fas and Fas ligand levels in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Cukurova Med J. (2009) 44:1–1.
150. Pui C, Ip SH, Iflah S, Behm FG, Grose BH, Dodge RK, et al. Serum interleukin 2 receptor levels in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (1988) 71:1135–7. doi: 10.1182/blood.V71.4.1135.1135
151. Hafiz MG, Mannan M. Serum lactate dehydrogenase level in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Bangladesh Med Res Council Bull. (2007) 33:88–91. doi: 10.3329/bmrcb.v33i3.1139
152. Jiang Q, Lu X, Huang P, Gao C, Zhao X, Xing T, et al. Expression of miR-652-3p and effect on apoptosis and drug sensitivity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BioMed Res Int. (2018) 2018:5724686. doi: 10.1155/2018/5724686
153. Zhou Y, Fan X, Routbort M, Yin CC, Singh R, Bueso-Ramos C, et al. Absence of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase expression identifies a subset of high-risk adult T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Modern Pathology. (2013) 26:1338. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.78
154. Edwards H, Rubenstein M, Dombkowski AA, Caldwell JT, Chu R, Xavier AC, et al. Gene signature of high white blood cell count in b-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0161539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161539
155. Ontario HQ. Minimal residual disease evaluation in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: an economic analysis. Ontario Health Technol Assessment Series. (2016) 16:1–83.
156. Goldberg JM, Silverman LB, Levy DE, Dalton VK, Gelber RD, Lehmann L, et al. Childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute acute lymphoblastic leukemia consortium experience. J Clin Oncol. (2003) 21:3616–22. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.10.116
157. Dakka N, Bellaoui H, Bouzid N, Khattab M, Bakri Y, Benjouad A. CD10 AND CD34 expression in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Morocco: clinical relevance and outcome. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. (2009) 26:216–31. doi: 10.1080/07357900902897557
158. Dehghan-Nayeri N, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Omrani MD, Gharehbaghian A, Pour KG, Eshghi P. Identification of potential predictive markers of dexamethasone resistance in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Commun Signal. (2017) 11:137–45. doi: 10.1007/s12079-016-0357-3
159. Hof J, Krentz S, Van Schewick C, Körner G, Shalapour S, Rhein P, et al. Mutations and deletions of the TP53 gene predict nonresponse to treatment and poor outcome in first relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. (2011) 29:3185–93. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.34.8144
160. Meyer JA, Wang J, Hogan LE, Yang JJ, Dandekar S, Patel JP, et al. Relapse-specific mutations in NT5C2 in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. (2013) 45:290. doi: 10.1038/ng.2558
161. Han B-W, Feng D-D, Li Z-G, Luo X-Q, Zhang H, Li X-J, et al. A set of miRNAs that involve in the pathways of drug resistance and leukemic stem-cell differentiation is associated with the risk of relapse and glucocorticoid response in childhood ALL. Hum Mol Genet. (2011) 20:4903–15. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr428
162. Matsushita C, Yang Y, Takeuchi S, Matsushita M, Van Dongen JJ, Szczepanski T, et al. Aberrant methylation in promoter-associated CpG islands of multiple genes in relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncol Rep. (2004) 12:97–9. doi: 10.3892/or.12.1.97
163. Kunz JB, Rausch T, Bandapalli OR, Eilers J, Pechanska P, Schuessele S, et al. Pediatric T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia evolves into relapse by clonal selection, acquisition of mutations and promoter hypomethylation. Haematologica. (2015) 100:1442–50. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2015.129692
164. Lipshultz SE, Miller TL, Scully RE, Lipsitz SR, Rifai N, Silverman LB, et al. Changes in cardiac biomarkers during doxorubicin treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: associations with long-term echocardiographic outcomes. J Clin Oncol. (2012) 30:1042. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.3404
165. Lipshultz SE, Rifai N, Dalton VM, Levy DE, Silverman LB, Lipsitz SR, et al. The effect of dexrazoxane on myocardial injury in doxorubicin-treated children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. (2004) 351:145–53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa035153
166. Krzyszczyk P, Acevedo A, Davidoff EJ, Timmins LM, Marrero-Berrios I, Patel M, et al. The growing role of precision and personalized medicine for cancer treatment. Technology. (2018) 6:79–100. doi: 10.1142/S2339547818300020
167. Eryilmaz E, Canpolat C. Novel agents for the treatment of childhood leukemia: an update. OncoTargets Ther. (2017) 10:3299. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S126368
168. Ong FS, Das K, Wang J, Vakil H, Kuo JZ, Blackwell W-LB, et al. Personalized medicine and pharmacogenetic biomarkers: progress in molecular oncology testing. Exp Rev Mol Diagn. (2012) 12:593–602. doi: 10.1586/erm.12.59
169. Wedekind MF, Denton NL, Chen C-Y, Cripe TP. Pediatric cancer immunotherapy: opportunities and challenges. Pediatr Drugs. (2018) 20:395–408. doi: 10.1007/s40272-018-0297-x
170. Li D, Li X, Zhou W-L, Huang Y, Liang X, Jiang L, et al. Genetically engineered T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Signal Transd Targeted Ther. (2019) 4:1–17. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0070-9
171. Spencer KR, Wang J, Silk AW, Ganesan S, Kaufman HL, Mehnert JM. Biomarkers for immunotherapy: current developments and challenges. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. (2016) 36:e493–503. doi: 10.14694/EDBK_160766
172. De Gramont A, Watson S, Ellis LM, Rodón J, Tabernero J, De Gramont A, et al. Pragmatic issues in biomarker evaluation for targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2015) 12:197. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.202
173. De Palma M, Hanahan D. The biology of personalized cancer medicine: facing individual complexities underlying hallmark capabilities. Mol Oncol. (2012) 6:111–27. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.01.011
174. Wu L, Qu X. Cancer biomarker detection: recent achievements and challenges. Chem Soc Rev. (2015) 44:2963–97. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00370E
175. Ensor JE. Biomarker validation: common data analysis concerns. Oncologist. (2014) 19:886–91. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0061
176. Wang E, Cho WC, Wong SC, Liu S. Disease biomarkers for precision medicine: challenges and future opportunities. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. (2017) 15:57. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.04.001
177. Pesch B, Brüning T, Johnen G, Casjens S, Bonberg N, Taeger D, et al. Biomarker research with prospective study designs for the early detection of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2014) 1844:874–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.12.007
Keywords: childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia, multidrug resistance, prognostic biomarkers, predictive biomarkers, drug resistance biomarkers
Citation: Aberuyi N, Rahgozar S, Ghodousi ES and Ghaedi K (2020) Drug Resistance Biomarkers and Their Clinical Applications in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 9:1496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01496
Received: 16 July 2019; Accepted: 12 December 2019;
Published: 17 January 2020.
Edited by:
J. Luis Espinoza, Kindai University, JapanReviewed by:
Nirmalya Saha, University of Michigan, United StatesJaira F. de Vasconcellos, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, United States
Copyright © 2020 Aberuyi, Rahgozar, Ghodousi and Ghaedi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Soheila Rahgozar, rahgozar@sci.ui.ac.ir
 Narges Aberuyi
Narges Aberuyi Soheila Rahgozar
Soheila Rahgozar Kamran Ghaedi
Kamran Ghaedi