- 1Yan’an Medical College of Yan’an University, Yan’an, Shaanxi, China
- 2Yan’an Key Laboratory of Northern Shaanxi Tumor Prevention and Treatment, Yan’an Medical College, Yan’an University, Yan’an, Shaanxi, China
The intramembrane aspartic protease, γ-secretase, is a heterotetrameric protein complex composed of four integral membrane proteins: presenilin (PSEN), nicastrin (NCT), Anterior pharynx defective-1 (APH-1), and presenilin enhancer 2 (PEN-2). These components are sequentially assembled into a functional complex. γ-secretase is ubiquitously expressed in all cells and tissues and exhibits enzymatic activity akin to “molecular scissors” by cleaving various type I transmembrane proteins. The primary substrates of this complex include amyloid precursor protein (APP) and Notch. The role of APP in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been extensively investigated. Although γ-secretase inhibitors (GSIs) have been evaluated for their therapeutic potential in AD, their clinical application is limited due to significant toxic side effects. Recently, γ-secretase modulators (GSMs) have emerged as promising alternatives, offering new opportunities for the treatment of AD, especially the inherent γ-secretase modulatory proteins (GSMPs) within cells. Research on GSMPs has ushered in a new era for mitigating the side effects of AD drugs. In this review, we systematically summarize recent advancements in the study of γ-secretase in relation to AD and provide an overview of GSMs and GSMPs, thereby offering potential insights for the development of therapeutic strategies for AD.
1 Introduction
The γ-secretase complex is an intramembrane-cleaving protease (I-CliP) that catalyzes the intramembrane domain (TMD) of its protein substrates and performs a wide variety of essential biological roles (Wolfe, 2019). The γ-secretase has been identified as a heterotetrameric complex consisting of four membrane protein subunits: APH-1, NCT, PSEN, and PEN-2 (Oikawa and Walter, 2019; Figure 1A). It takes a stepwise manner to assemble the four subunits into one complex, the correct assembly of the γ-secretase is tightly regulated, and then the mature γ-secretase complex is transported to the plasma membrane and endosomes to perform its functions (Dries and Yu, 2008; Smolarkiewicz et al., 2013; Figure 1B). Alzheimer disease (AD) is a common cause of cognitive impairment in middle-aged and elderly people. It is a hereditary and sporadic neurodegenerative disorder (Knopman et al., 2021). Excessive phosphorylation of tau protein (Anwar et al., 2024; Adnan et al., 2023), and deposition of beta-amyloid protein (Aβ) are currently the mainstream theories recognized as causing AD (Wolfe, 2024). γ-secretase has various substrates, in AD, γ-secretase produces Aβ by cleaving amyloid precursor protein (APP). The abnormal accumulation and aggregation of these peptides are considered crucial factors in the pathological changes of AD (Kim et al., 2024). Despite the key role γ-secretase plays in AD pathogenesis (Hakem et al., 2024), direct inhibition strategies have not achieved satisfactory outcomes in clinical trials, largely because inhibiting multiple γ-secretase substrates may disrupt normal physiological functions (Dries and Yu, 2021; Caldwell et al., 2022). As a result, researchers are investigating alternative approaches to regulate γ-secretase activity, such as the creation of GSMs, which represent a class of small molecules capable of influencing the activity of γ-secretase (Wolfe, 2024; Hakem et al., 2024). Unlike GSIs, which directly suppress the enzyme’s activity, GSMs modify the cleavage patterns of substrates via allosteric regulation. This process leads to a reduction in the generation of harmful amyloid peptides (Rynearson et al., 2021; Petit et al., 2022). Furthermore, the design of GSMs aims to minimize side effects associated with GSIs observed during clinical trials, such as interference with the Notch signaling pathway (Hur, 2022). In recent years, the growing comprehension of γ-secretase’s structure and function has enhanced our knowledge of GSM mechanisms. Cryo-electron microscopy has played a pivotal role in mapping the structural configuration of γ-secretase when it interacts with GSMs, revealing critical details about how GSMs influence the γ-secretase complex (Dries and Yu, 2021; Yang et al., 2021). Studies on GSMs can help to improve our targeted therapy for AD.
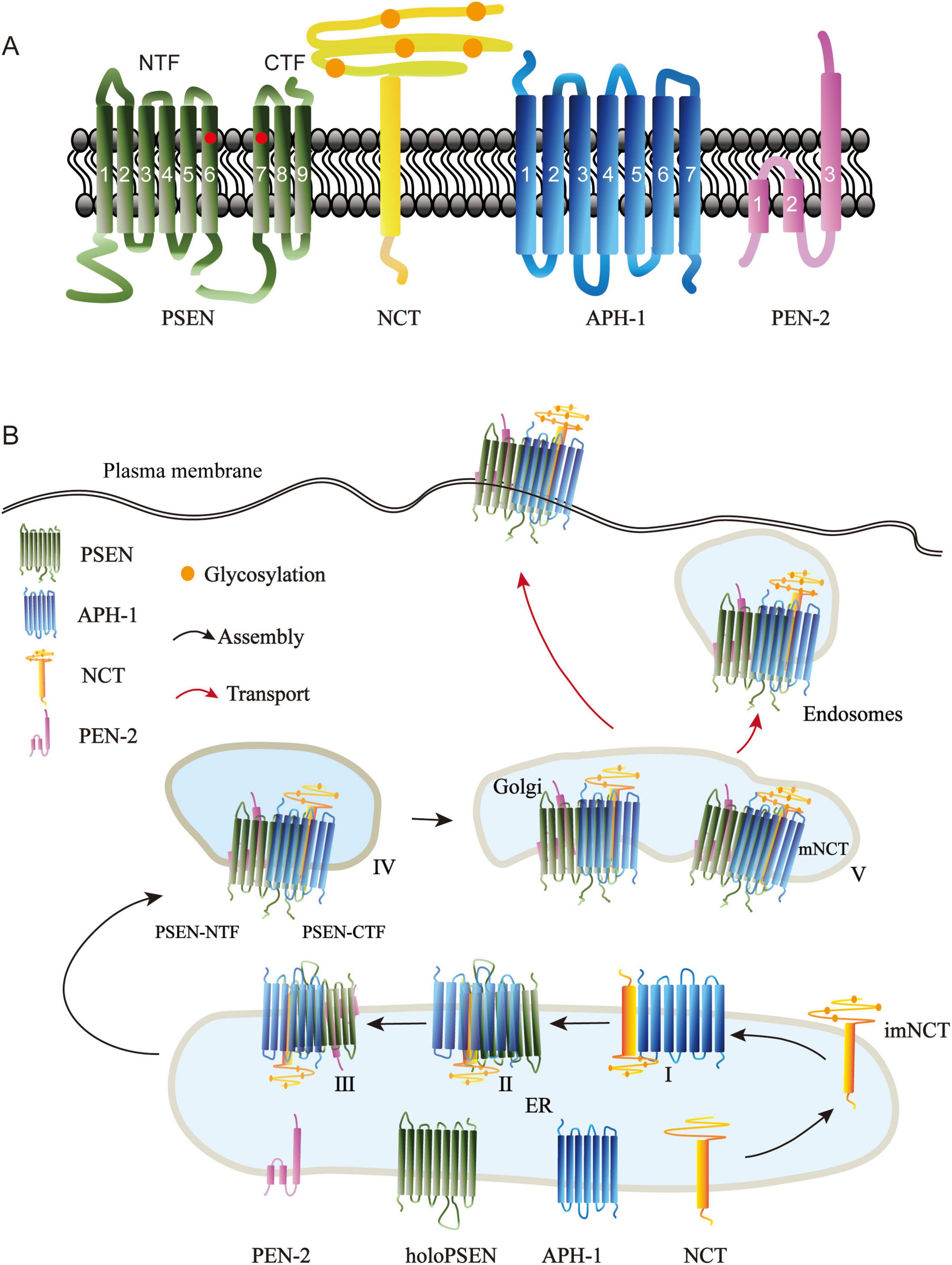
Figure 1. Structure of γ-secretase subunits and their assembly in cells. (A) The γ-secretase complex is composed of four multipass membrane proteins, presenilin (PSEN), nicastrin (NCT), Anterior pharynx defective-1 (APH-1), and presenilin enhancer 2 (PEN-2). PSEN represents the catalytic components in the complex; it consists of nine transmembrane helices, including two catalytic aspartate residues (circled in red) in TM6 and TM7. PSEN is cleaved endoproteolytically between TM6 and TM7 to produce amino terminal fragment (NTF) and carboxyl terminal fragment (CTF). NCT is a cofactor of PSEN; it is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with a large glycosylated extracellular domain (orange circles indicate the glycosalation site). APH-1 is a seven-transmembrane protein required for APH-1/NCT trafficking to the cell surface (Goutte et al., 2002). PEN-2, the smallest component of the -secretase complex, modulates the activity of -secretase. PEN-2 has three membrane-embedded domains, the first two domains traversing only half of the lipid bilayer. (B) The four γ-secretase subunits are biosynthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and taking a stepwise manner to form a complex. Subcomplex I: N-glycosylated Nicastrin forms imNCT, which then binds to APH-1 to create imNCT/APH-1. PSEN holoprotein binds to the imNCT/APH-1 subcomplex. Subcomplex III: PEN-2 is fused to imNCT/APH-1/PSEN holoprotein. Subcomplex IV: PSEN autoproteolysis at theTMD6 and TMD7 producing PSEN-NTF and PSEN-CTF fragments. Subcomplex V: Subcomplex IV is transported to the Golgi, where NCT undergoes further N-glycosylation to generate mature Nicastrin. Then, the mature γ-secretase complex moves on toward the plasma membrane and endosomes.
The activity of γ-secretase is modulated by a variety of factors, including the properties of its substrates and the intracellular microenvironment. In addition to APP, many γ-secretase substrates are associated with AD, such as Notch, CD43, CD44, CD91, CD269, CSF-1R, etc., The study of these substrates related to AD may give us new ideas about whether they regulate the activity of γ-secretase to act together in AD. There is evidence that the enzymatic activity of γ-secretase can also be influenced by interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3), which is upregulated in tissue samples from certain late-onset Alzheimer’s disease patients and exhibits a positive correlation with γ-secretase activity (Hur et al., 2020). Several studies have demonstrated that inhibiting γ-secretase-activating protein (GSAP) effectively reduces Aβ production while leaving other critical γ-secretase substrates unaffected (Kim et al., 2024). Apolipoprotein E (ApoE), the most prominent genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (sAD), interacts with γ-secretase and selectively inhibits its activity in a substrate-dependent manner (Hou et al., 2023). These intracellular proteins, which regulate γ-secretase, are referred to as γ-secretase modulatory proteins (GSMPs). If GSMPs can be effectively modulated to achieve therapeutic effects for AD, this approach may potentially further mitigate the side effects associated with chemical drugs. In summary, γ-secretase and its substrates are intricately associated with the onset and progression of AD. A deeper investigation into the underlying mechanisms is crucial for advancing AD treatment. Notably, targeted therapies involving GSMs and GSMPs hold promise in providing new hope for AD patients.
2 Subunits of γ-secretase and their assembly
2.1 Subunits of γ-secretase
2.1.1 PSEN
Early in the 1990’s, two human early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease (EOFAD) -related loci were discovered on chromosomes 14 (Rogaev et al., 1995) and 1 (Schellenberg et al., 1992). These loci were subsequently identified as two homologous genes: Presenilin1 (psen1) and Presenilin2 (psen2) (Levy-Lahad et al., 1995; Sherrington et al., 1995). PSEN are the catalytic components with aspartyl protease activity, and more than 150 AD causing mutations have been reported in both genes, with the majority occurring in PSEN1 (Zhang et al., 2014). The full-length PSEN consists of nine transmembrane helices (TM1-9) and two catalytic aspartate residues in TM6 (Asp257) and TM7 (Asp385) (Spasic et al., 2006). During γ-secretase complex maturation, the presenilin holoprotein becomes inactive and is rapidly degraded by proteolytic activity. PSEN undergoes autoproteolysis into stable N-terminal fragments (NTF, TM1-6) and C-terminal fragments (CTF, TM7-9) (Fraser et al., 1998; Kim et al., 1997; Thinakaran et al., 1996; Figure 1A). The endoproteolytic fragments of PSEN proteins are predominantly localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus (Annaert et al., 1999), but also found in the plasma membrane (Marambaud et al., 2002), endosomes (Vetrivel et al., 2004), phagosomes (Jutras et al., 2005), lysosomes (Sannerud et al., 2016), mitochondria (Area-Gomez and Schon, 2016; Area-Gomez et al., 2009), and nuclear envelope (Kimura et al., 2001). where they are interacted with NCT, APH-1, and PEN-2 to form a 250kDa complex (Yu et al., 1998).
2.1.2 NCT
A novel protein (Nicastrin, NCT) was found in 2000 by immunoprecipitation of PSEN1 combined with mass spectrometry (Yu et al., 2000). Nicastrin was named after the Italian village of Nicastro, where the PSEN-associated forms of Familial Alzheimer’s disease were discovered (Feldman et al., 1963; Foncin et al., 1985). Human NCT gene maps to chromosomee 1, it has been identified as risk genes for Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility locus in two genome surveys (Zubenko et al., 1998; Owen et al., 2000). NCT is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with 709 amino acids, a putative amino-terminal signal peptide, an N-terminal hydrophilic domain, N-myristoylation and phosphorylation motifs, a transmembrane domain, and a 20-residue hydrophilic carboxy terminus (Yu et al., 2000; Figure 1A). The conserved functions of NCT for Notch signaling have been revealed from studies in Caenorhabditis. Elegans (Goutte et al., 2000), Drosophila melanogaster (Chung and Struhl, 2002; Hu et al., 2002), and mice (Beher et al., 2003). NCT is the first identified PSEN cofactor, and it plays a critical role in PSEN-mediated processing of APP and notch/glp-1 signaling (Yu et al., 2000). The ectodomain of NCT is proposed to recruit substrates into the γ-secretase complex (Shah et al., 2005; Dries et al., 2009).
2.1.3 APH-1
In the genetic screening of Notch, psen, and NCT in C. elegans, two multipass transmembrane proteins, Anterior pharynx defective-1 (APH-1) and Presenilin enhancer-2 (PEN-2), interact strongly with PSEN (SEL-12 in C. elegans) and NCT (APH-2 in C. elegans); APH-1 deficiency caused a comparable phenotype to psen and NCT (Francis et al., 2002; Goutte et al., 2002). In mammals, APH-1 is a seven transmembrane protein of approximately 25 kDa (Figure 1A). The GxxxG motif in the fourth TMD of APH-1 is critical for the formation and activation of the γ-secretase complex. APH-1 physically interacts with immature NCT (imNCT) in ER to form a stable subcomplex (LaVoie et al., 2003; Lee et al., 2004), then binds to the C-terminus of PSEN holoprotein (Morais et al., 2003; Steiner et al., 2008). The ternary complex of imNCT/APH-1/holo-PSEN is then transported to the trans-Golgi, where NCT can fully develop and become extensively N-glycosylated. Human APH-1 is encoded by aph1a and aph1b, of which aph1a appears to be the more studied.
2.1.4 PEN-2
The PEN-2 was identified side-by-side with APH-1 in a C. elegans screening (Francis et al., 2002; Goutte et al., 2002). Human PEN-2 is encoded by a single gene on chromosome 19 (Panmontha et al., 2015). It is the smallest component of γ-secretase with 101 residues, two hydrophobic domains that function as transmembrane spanning domains, and a “U-shaped” structure with the N- and C- termini toward the lumen, according to earlier reports (Crystal et al., 2003; Bergman et al., 2004; Figure 1A). Recent structure research of PEN-2, however, has revealed that there are three membrane-embedded domains, with the C-terminus being luminal and the N-terminus being exposed to the cytoplasm, indicating that the first two domains traverse only half of the lipid bilayer (Zhang et al., 2015). PEN-2 is the last protein to be incorporated into the γ-secretase complex and regulates PSEN auto-hydrolysis and NCT maturation (Francis et al., 2002; Watanabe et al., 2006), and it serves as an ER retention receptor for the immature γ-secretase complex (Fassler et al., 2005). The extracellular region of PEN-2 can interact with the ectodomain of NCT (Sun et al., 2015). The N-terminal extension of PEN-2 can modify the hydrophilic environment of the PSEN catalytic pore (Isoo et al., 2007). Thus, PEN-2 may modulate γ-secretase activity.
2.2 Assembly and activation of γ-secretase complex
The correct assembly of the γ-secretase is tightly regulated. It is now widely acknowledged that it takes a stepwise manner to assemble the four subunits into one complex. First, the Nicastrin is synthesized and modified with N-glycosylated in the ER to form imNCT, which then binds to APH-1 to form the heterodimer imNCT/APH-1 subcomplex I (LaVoie et al., 2003). In order to build subcomplex II, the Proximal C-terminus of the PSEN holoprotein connects to the intermediate heterodimer via the TM domain of NCT (Kaether et al., 2005). Then, PEN-2 and TM4 of PSEN are combined to create subcomplex III (Kornilova et al., 2006; Watanabe et al., 2006). However, it is unclear whether this complex is generated by successive binding of PSEN1 and PEN-2 or by a prefabricated PSEN1/PEN-2 subcomplex (Fraering et al., 2004). Subcomplex III is immediately followed by PSEN autoproteolysis at TMD6 and TMD7 to produce PSEN-NTF and PSEN-CTF fragments, which comprise the active form of PSEN inside subcomplex IV (Fukumori et al., 2010). If PEN-2 is not present, the subcomplex is degraded via proteasomes (Prokop et al., 2004). In a next step, approximately 5% of subcomplex IV traffics to the Golgi, where NCT is further N-glycosylated to form mature Nicastrin (mNCT), and this is the subcomplex V (Moniruzzaman et al., 2018), represents the formation of active γ-secretase in the cell. Finally, the mature active γ-secretase complex is then transported to the plasma membrane and endosomes (Dries and Yu, 2008; Smolarkiewicz et al., 2013; Figure 1B). The four-component intramembrane proteinase gamma-secretase is intricately linked to the development of various diseases. Single-particle electron cryo-microscopy revealed the principle of the assembly of four subunits, with PSEN1 in the central position, its amino terminal fragment (NTF) wrapped by PEN-2, and its carboxyl terminal fragment (CTF) interacting with APH-1. NCT’s unique TM binds to APH-1, and its extracellular domain binds to PEN-2. TM6 and TM7 in PSEN1 are located on the convex side of the TM horseshoe shape and contain catalytic aspartate residues. This structure provides an important framework for understanding the function of γ-secretase (Sun et al., 2015). The complex of γ-secretase with the Notch fragment indicates that three transmembrane domains of PSEN1 surround the transmembrane helix of Notch, and PSEN1 undergoes a significant conformational rearrangement when binding to its substrate. These features reveal structural changes in γ-secretas during substrate recruitment (Yang et al., 2019). Post-translational modifications can further regulate the matured γ-secretase. The phosphorylation of PSEN1, PSEN2 and NCT regulate functions of γ-secretase complex, including the proteolytic processing, γ-secretase activity (Fluhrer et al., 2004; Walter et al., 1999; Kuo et al., 2008), stability (Lau et al., 2002) and subcellular localization (Sannerud et al., 2016). The assembly and activation of the four subunits play an important role in the function of γ-secretase.
γ-secretase complex is ubiquitous in all tissues, the presence of all γ-secretase subunits does not guarantee active complex formation, many evidences suggest that two pools of γ-secretase exist: the long half-life of assembling γ-secretase complex and the short half-life of monomeric subunits, and only a small fraction of γ-secretase is catalytically active (Beher et al., 2003; Lai et al., 2003). A broad range of γ-secretase substrates has been identified, suggesting that additional events and cofactors composition are required to enhance the activity of γ-secretase and substrate specificity (Placanica et al., 2010). Although γ-secretase can cleave a variety of protein substrates, when cells are in different environments and receive different signals, γ-secretase may selectively hydrolyze one or a class of substrates to ensure the normal execution of cell functions. γ-secretase subunits are localized in nearly all endomembrane system compartments, including the endoplasmic reticulum (Kaether et al., 2004), lysosomal membrane (Houser et al., 2023), pre- and post-Golgi compartments (Annaert et al., 1999), phagosome (Jutras et al., 2005), plasma membrane and endosome (Vetrivel et al., 2004). This suggests that in different cellular domains γ-secretase binds to different substrates and plays different roles. Thus, the activity of γ-secretase may be regulated by a variety of mechanisms. For instance, APP is processed by intracellular γ-secretase, while Notch, which acts on the plasma membrane, is processed on the cell surface (Tarassishin et al., 2004). Furthermore, lipid composition also impacts substrate processing, the cholesterol-rich membranes are the major site of Aβ production (Wahrle et al., 2002; Marquer et al., 2014), and γ-secretase partitioning into lipid bilayers remodels membrane components that create a suitable microenvironment for substrate recognition and activity (Barros et al., 2020). Only correct subunit assembly can enable γ-secretase to recognize specific substrates under specific environment and conditions, thus being actived and performing the correct cell biological functions.
3 γ-secretase in Alzheimer’s disease
Over a 100 distinct type I integral membrane proteins have been identified as γ-secretase substrates to date, and more are being continuously discovered (Hemming et al., 2008; Haapasalo and Kovacs, 2011). γ-secretase was originally characterized based on its proteolytic function in cleaving the APP, a process that generates Aβ—a key pathological component in the formation of senile plaques associated with AD. Consequently, γ-secretase is widely regarded as a central player in the pathogenesis of AD. Beyond APP, an expanding repertoire of γ-secretase substrates has been implicated in the molecular mechanisms underlying AD development. In the following sections, we will systematically examine those proteins that demonstrate significant associations with the onset and progression of AD, aiming to elucidate the multifaceted roles of γ-secretase in disease pathology and to lay a foundation for the development of targeted therapeutic interventions.
3.1 Amyloid precursor protein (APP)
Alzheimer’s disease was first officially described by Alois Alzheimer in 1906, which is the most common form of dementia (Small and Cappai, 2006). The excessively aggregates amyloid plaques in the brain majorly contribute to dysfunction and degeneration of neurons that result in AD (Zhang et al., 2012). Although the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease is still the subject of considerable debate, the “amyloid-cascade hypothesis” has remained the prevailing theory over the years (Small and Cappai, 2006; Soria Lopez et al., 2019). This hypothesis suggests that amyloid plaques in the brains of AD patients consisted of fibrils formed by Aβ. The cleavage by γ-secretase requires shedding of the substrate’s extracellular domains by the other secretases. In the Non-Amyloidogenic pathway, APP is cleaved by α-secretase to generate sAPPα and the membrane-associated 83 amino acid C-terminal fragment APP-CTF (C83), γ-secretase further cleaves C83 to produce p3 and AICD (Selkoe, 2001; Figure 2A). Alternatively, in the amyloidogenic pathway, APP is first processed by β-secretase and produces the secreted sAPP-β and APP–C-terminal 99-residue fragment (C99), subsequent γ-Secretase mediated cleavage of C99 at the γ-, ζ-, and ε-sites close to the cytosolic end of TMD to generate APP intracellular domain (AICD) and the extracellular secretion of Aβ peptides (Moser et al., 2024). The cleavage of C99 by γ-secretase results in a variety of peptides (from large Aβ49 peptides to smaller ones with 37 residues), Aβ peptides are cleaved mainly by tripeptide trimming or tetrapeptide trimming via the Aβ40 product line (Aβ49→46→43→40→37) or the Aβ42 product line (Aβ48→45→42→38) (Hur, 2022; Takami et al., 2009; Wang et al., 1996; Figure 2B).
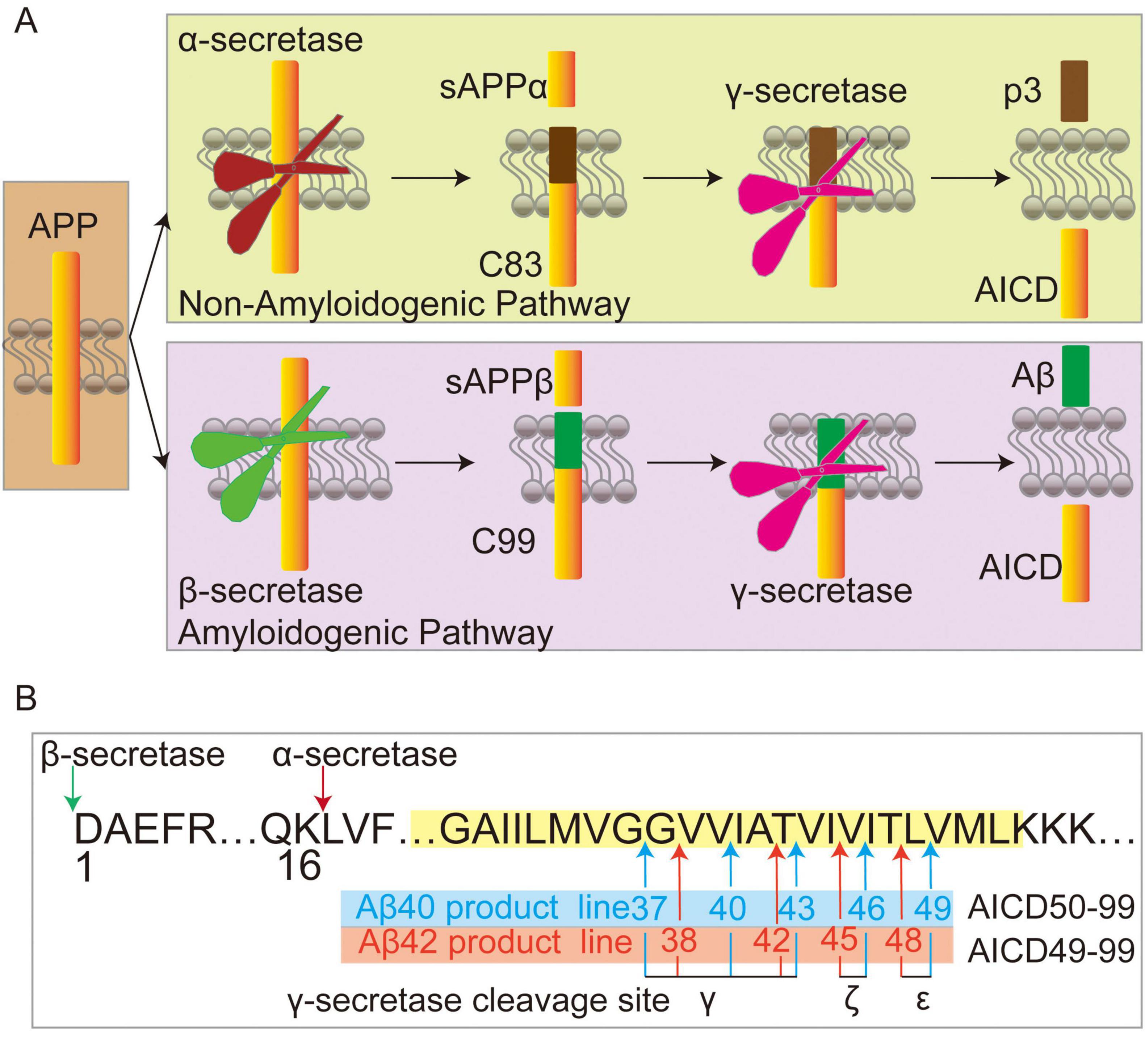
Figure 2. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing. (A) In the non-amyloid and amyloid pathways, APP undergoes cleavage by α-secretase or β-secretase, respectively, releasing sAPPα and C83 in the non-amyloid pathway, or sAPPβ and C99 in the amyloid pathways. Subsequently, γ-secretase cleaves C83 into p3 and APP intracellular domain (AICD), while C99 is processed into Aβ and AICD. (B) Following β-secretase mediated cleavage of APP (where the sequence numbering of Aβ stars at 1), C99 is further cleaved by γ-secretase at ε-sites to generate Aβ49 and AICD50-99, or Aβ48 and AICD49-99. These peptides are subsequently processed through additional cleavages at ζ and γ sites, resulting in the sequential formation of Aβ46→43→40→37 from Aβ49, and Aβ48→45→42→38 from Aβ48. Arrows indicate cleavage sites, and membranes are depicted in yellow.
Approximately 25 mutations in APP are associated with the occurrence of AD, many of which are located in the area of TMD (Devkota et al., 2021). Although there have been numerous debates on whether immune activity is advantageous or detrimental to the progression of AD pathology, it has long been that immune activity is closely related to the pathophysiology of AD (Frost et al., 2019).
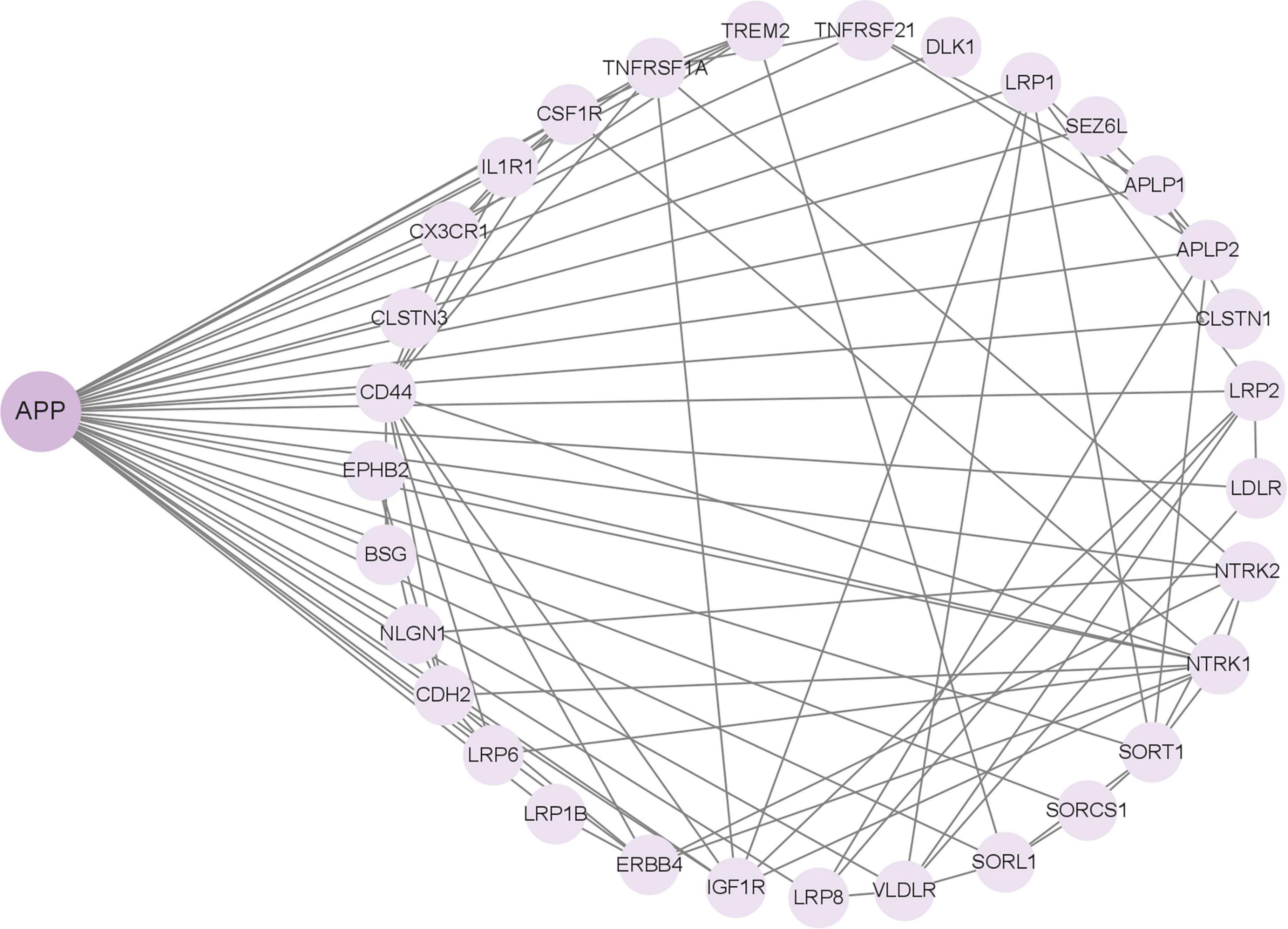
3.2 Other GS substrate proteins related to AD
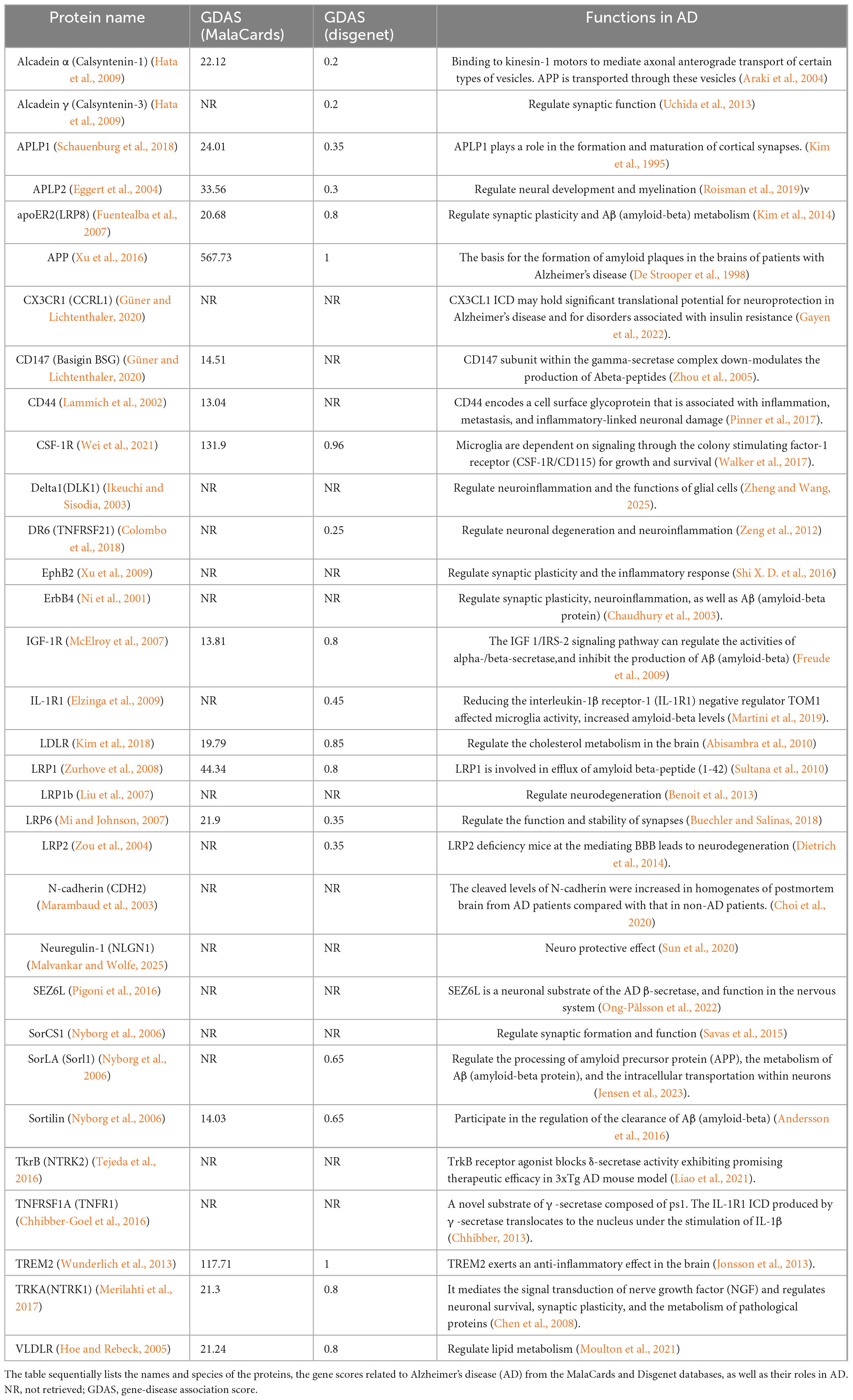
In addition to APP, γ-Secretase has more than 140 substrates, all of which are type 1 transmembrane proteins. Among them, many substrates have been reported to be related to the APP. For instance, the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) directly interacts with the PS1 subunit of γ-secretase and competes with APP for access to the enzyme’s cleavage site. Overexpression of the C-terminal fragment of LRP decreases the production of Aβ peptides derived from APP and suppresses the signaling activity of AICD (Lleó et al., 2005). These findings indicate that LRP functions as a competitive substrate, modulating the cleavage of APP by γ-secretase through occupancy of the enzyme’s active site. Based on the important role of APP in AD, the research on these substrates may be more conducive to our study of the molecular mechanism of AD pathogenesis. We input the 149 substrate proteins of γ-Secretase (Güner and Lichtenthaler, 2020) into the STRING website (STRING: functional protein association networks) to screen the APP-related proteins centered on this APP (Figure 3). The screened proteins were analyzed and compared with AD in the Human Disease Database Retrieval (MalaCards) and the Disgenet database. These proteins are summarized in Table 1.
4 γ-secretase modulators (GSMs)
4.1 GSMs
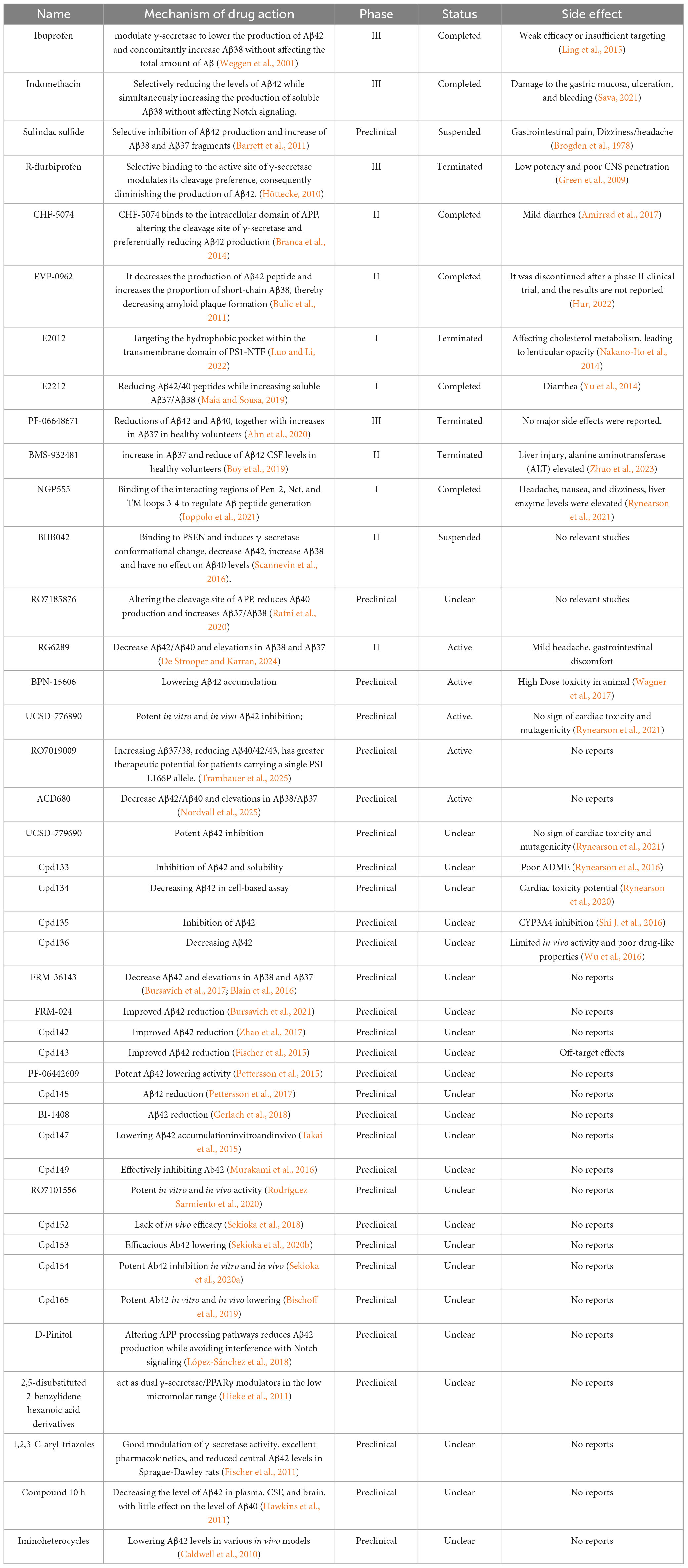
γ-secretase modulators exhibit greater therapeutic potential by modulating enzyme activity to selectively decrease Aβ42 levels while preserving the normal processing of other substrates (Mekala et al., 2020; Wolfe, 2012). Cryo-electron microscopy revealed that GSMs bind to the transmembrane domain of PS1 and change the conformation of γ-secretase, thereby reducing Aβ42 production and enhancing Aβ38 generation (Yang et al., 2021; Mehra and Kepp, 2021; Figure 4). In addition, Petit et al. demonstrated that certain GSMs enhance the efficiency of substrate processing by stabilizing the interaction between γ-secretase and APP, elucidating the mechanism of their selective regulation (Petit et al., 2022). Early GSMs, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), were ineffective due to insufficient potency and unfavorable pharmacokinetic properties. NSAIDs mainly alleviate Aβ-induced neuroinflammation by inhibiting COX-1, COX-2 and prostaglandins (Imbimbo et al., 2010). Ibuprofen, flurbiprofen, and indomethacin can regulate γ-secretase, lowering Aβ42 levels while increasing Aβ38 (Eriksen et al., 2003). However, clinical trials have not confirmed significant efficacy in patients with mild to moderate AD (Miguel-Álvarez et al., 2015). Although studies on indomethacin have shown some positive trends, the results are not convincing due to the small sample size (de Jong et al., 2008). Research indicates that NSAIDs may be effective in the early stage of the disease but ineffective or even harmful in the later stages (Hampel et al., 2020). Moreover, most NSAIDs have difficulty penetrating the blood-brain barrier (BBB), limiting their efficacy (Sastre and Gentleman, 2010), and the effects are also influenced by individual genetic backgrounds (DiBattista et al., 2016). Recently, novel GSMs, including pyridine derivatives, purine compounds, and quinazolinones, have exhibited greater potency and selectivity. The purinergic GSMs developed by Rivkin’s group substantially reduced brain Aβ42 levels in a mouse model (Rivkin et al., 2010). The incorporation of lipophilic groups has been shown to improve membrane permeability and central exposure (Naumann et al., 2013; Sekioka et al., 2020b). The newer-generation GSM BPN-15606 does not inhibit overall γ-secretase activity. Instead, it binds to the PS1 subunit of γ-secretase, allosterically altering APP cleavage to reduce Aβ42/Aβ40 production and promote the generation of more easily cleared fragments Aβ38/Aβ37 (Wagner et al., 2017). In PSAPP transgenic mice, treatment with BPN-15606 before significant plaque formation effectively reduced amyloid deposition and improved cognitive performance. However, when treatment started six months of age—after plagues were already widespread—the drug reduced Aβ pathology but did not improve existing cognitive impairments (Prikhodko et al., 2020). This suggests that once neuronal damage becomes irreversible, lowering Aβ levels alone may not be sufficient to restore cognitive function. Mobley’s team in Down syndrome mice showed that BPN-15606 significantly reduced Aβ42 and Aβ40 levels; improved nerve growth factor signaling; reduced tau hyperphosphorylation, and corrected behavioral deficits, indicating its potential to delay or prevent AD onset in individuals with Down syndrome (Chen et al., 2024). Preclinical studies also demonstrated favorable pharmacokinetics and safety profiles supporting its advancement into clinical trials (Wagner et al., 2017; Gunnar et al., 2023). Although the new generation of GSMs possesses theoretical safety advantages based on their mechanism of action, practical challenges remain for these modulators. Firstly, the substrate diversity of γ-secretase may result in off-target effects, necessitating the development of more precise modulators. Secondly, the activity of γ-secretase in the brains of AD patients varies with disease progression, potentially influencing drug efficacy (Nobuto et al., 2013). Future research should focus on structure-based drug design, combining cryo-electron microscopy and computational chemistry to optimize binding sites. Developing multi-targeted modulators for Aβ and tau pathologies is also crucial (Gunnar et al., 2023; Joanna and Yue-Ming, 2022; Ji-Yeun, 2022). The existing GSMs are summarized in Table 2.
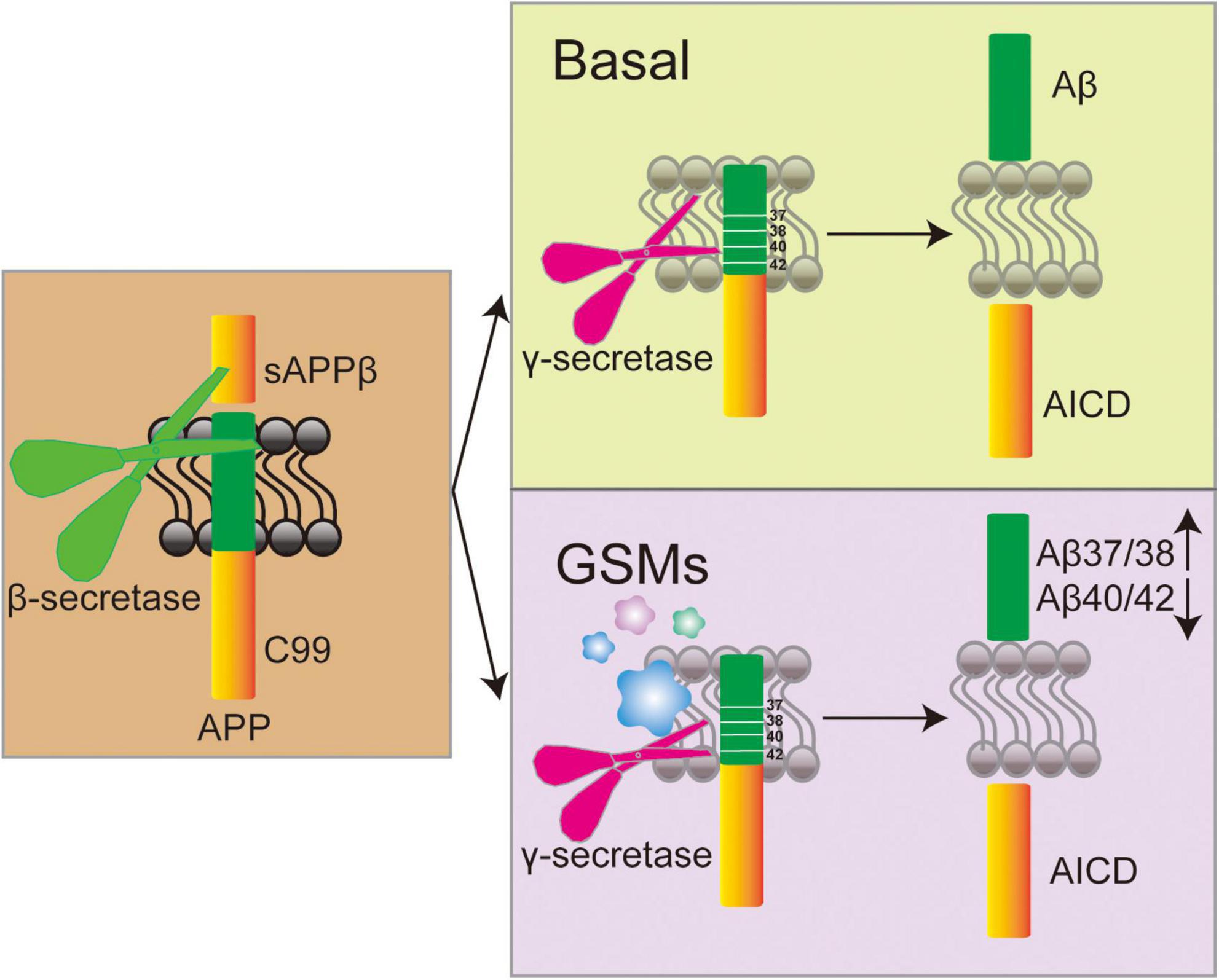
Figure 4. Mechanism diagram of γ-secretase modulators (GSMs) regulating γ-secretase activity and its effect on Aβ peptide generation.
4.2 γ-secretase modulatory proteins (GSMPs)
The aggregation of Aβ-monomers forms the amyloid plaques observed in Alzheimer patients’ brains, which is the key factor in AD (Selkoe, 2013). Increasing evidence has suggested that γ-secretase and its associated proteins could participate in regulating AD, but direct inhibition of γ-secretase has no significant effect on reducing Aβ accumulation and improving cognition in AD’s patients (Shi and Holtzman, 2018). γ-secretase has been a key target for drugs as it facilitates the final cleavages in the production of Aβ. Due to severe adverse effects in clinical trials, GSIs have been discontinued. GSMPs are more secure. It has high efficiency and good safety. Targeting GSMPs can selectively regulate the APP pathway and has tremendous applicability prospects in the treatment of AD. Nowadays, several GSMPs that are closely related to the APP signaling pathway, such as GSAP (Kim et al., 2024; Jin et al., 2022), IFITM3 (Hur, 2021), transmembrane trafficking protein, 21-KD (TMP21) (Ílgün and Çakir, 2025), and stress-associated endoplasmic reticulum protein 1 (SERP1) (Jung et al., 2020). We review the results of a Pubmed search for the keywords “gamma secretase AND (γ-secretase modulatory proteins OR GSMP)” and review recent advances in GSMPs.
4.2.1 γ-secretase activating protein (GSAP)
Lots of γ-secretase interacting proteins have been identified through LCMS analysis. The GSAP was identified as a γ-secretase-interacting partner (Teranishi et al., 2010; Frykman et al., 2012), it could form a complex with γ-secretase and APP-CTF, and an SNP in GSAP has been discovered to be associated with Alzheimer’s disease, giving genetic evidence that links GSAP to AD susceptibility (He et al., 2010). Studies have shown that the inhibition of GSAP can reduce Aβ production without affecting the other key γ-secretase substrates (Kim et al., 2024). GSAP does not interact with Notch, nor does it affect its cleavage (He et al., 2010; Wong et al., 2019). Knockdown of GSAP could reduce Aβ burden and plaque development in the AD model transgenic mice (Kim et al., 2024; He et al., 2010). GSAP specifically promotes γ-secretase–mediated cleavage of APP, the 16-kDa C-terminal fragment of GSAP (GSAP-16K) exerts dual modulation on γ-secretase cleavage: GSAP-16K in dilute phase increases C99 cleavage toward preferred production of Aβ42, but GSAP-16K condensates reduce APP-C99 cleavage through substrate sequestration (Jin et al., 2022). Imatinib is a commonly used anti-cancer drug in the clinic, multiple evidence indicates that imatinib inhibits Aβ but has no effect on Notch signaling (He et al., 2010; Netzer et al., 2003). In AD mouse models, imatinib prevents GSAP from interacting with APP-CTF, thereby reducing Aβ levels and tau phosphorylation (Chu et al., 2014). However, due to the extremely poor BBB penetration ability of imatinib (Brahmachari et al., 2017), it has not yet been applied in Phase II and Phase III clinical trials. Administration of the dimerization of Lep9R3LC (diLep9R3LC) peptide and GSAP siRNA complexes in AD mice can reduce GSAP in the cortex/hippocampus, inhibit Aβ accumulation, reduce tau hyperphosphorylation, and improve cognitive function in AD mice (Kim et al., 2024). In neurons, GSAP interacts with the Fe65–APP complex to modulate APP phosphorylation and its trafficking/partitioning (Xu et al., 2021). Reducing GSAP levels diminishes the partitioning of APP-CTF into lipid rafts, specifically at the mitochondria-associated membrane (MAM), and also decreases γ-secretase activity involved in Aβ production, and decreasing GSAP expression mitigates pathological effects linked to AD (Xu et al., 2021). In addition to contributing to amyloid formation in the brain, GSAP can also promote end-organ dysfunction after bacterial pneumonia. Infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa caused arterial hypoxemia in wild-type rats, but the integrity of the alveolar-capillary barrier was preserved in GSAP knockout rats. Additionally, infection enhanced myocardial infarction after ischemia-reperfusion injury, and this enhancement was eliminated in the GSAP knockout rats (Gwin et al., 2023). This result sheds light on the role of GSAP in innate immunity and highlights the contribution of GSAP to end-organ dysfunction during infection. However, even if GSAP can serve as an amyloid-beta-lowering therapeutic target without affecting other key functions of γ-secretase, but whether it also acts on other substrates and whether its regulation causes other side effects remains to be investigated.
4.2.2 Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3)
Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 is one of the members of the IFITMs family, as interferon-induced genes have been found in human neuroblastoma cells, it is an innate immune response protein involved in preventing the entry of viruses into host cells (Amini-Bavil-Olyaee et al., 2013; Bailey et al., 2014; Kehs et al., 2025). The Aβ peptides have antimicrobial and antiviral activities as part of the innate immune response in the brain (Amini-Bavil-Olyaee et al., 2013; Bailey et al., 2014). Hur et al. (2020) performed photo-crosslinking tests using the γ-secretase modulator E2012-BPyne and found that IFITM3 is a γ-secretase interaction protein. By interacting with neighboring IFITMs or other transmembrane proteins, IFITMs inhibit the formation of viral fusion pores and reduce the fluidity of the host membrane, this prevents viral infection (Yao and Yan, 2020). In the context of AD, IFITM3 was significantly reduced in the PSEN1 and PSEN2 double-knockout mice, and similarly, IFITM3 RNAi also reduced γ-secretase activity. Furthermore, IFITM3 directly binds to γ-secretase near the catalytic site and reduces γ-secretase activity for Aβ40 and Aβ42 (Hur et al., 2020). The expression of IFITM3 is significantly higher in patients with Alzheimer’s disease in the temporal cortex, knockout of IFITM3 in AD mouse significantly reduces plaque deposition (Hur et al., 2020). Other studies have shown that the expression of IFITM3 could be upregulated by the human herpes virus 6B, hepatitis C virus and cytokines interferon-γ (IFNγ), IFNα, IL-6, and IL-1β all significantly induce (Gómez-Herranz et al., 2023; Yánez et al., 2020; Jiménez-Munguía et al., 2022), and when infected COVID- 19, young mice showed higher IFITM3 responses and interferon-induced chemokines than older mice (Subramaniam et al., 2024). As an immune response protein, IFITM3 plays an important role in AD and other immune-related diseases. It has been confirmed that IFITM3 can interact with γ-secretase in AD, but whether γ-secretase is also involved in other immune diseases with IFITM3 remains to be confirmed.
4.2.3 Transmembrane trafficking protein, 21-KD (TMP21)
Transmembrane trafficking protein, 21-KD, also known as TMED10, is expressed in most brain regions, with higher expression in neuronal cells (Vetrivel et al., 2008). Transgenic mice with neuron-specific increases in TMP21 expression exhibit postnatal growth retardation and severe neurological issues like tremors, seizures, ataxia, uncoordinated movements, and premature death, complete deletion of TMP21 results in embryonic lethality at very early stages (Denzel et al., 2000; Gong et al., 2011). TMP21 is co-localized with γ-secretase, its expression is decreased in AD, which is consistent with the previous study that Aβ expression is increased when TMP21 is knocked down (Vetrivel et al., 2008; Pardossi-Piquard et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2006). Importantly, TMP21 binds to γ-secretase and specifically modulates APP cleavage at the γ-site, however, it has no effect on Notch cleavage at the ε-site (Vetrivel et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2006; Bromley-Brits and Song, 2012). Moreover, TMP21 reduction impairs APP’s bidirectional transport in the ER/Golgi, which increases the amount of APP that undergoes amyloidogenic cleavage in endocytic compartments and sAPP, Aβ40, and Aβ42 secretion (Vetrivel et al., 2007). Reducing TMP21 can increase GSK3β activity (Zhang et al., 2019), thereby promoting NF-κB-mediated β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) expression and activity, which further promotes APP processing and Aβ generation (Ly et al., 2013). A study showed that TMP21 could interact with the murine cytomegalovirus immunoevasin gp40 to facilitate virus immune escape (Ramnarayan et al., 2018; Stützer et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2023; Araki et al., 2004; Honda et al., 2024), so does TM21 also defend against foreign invasion in AD like IFITM3? This is also one of the directions that can be explored in the future.
4.2.4 Stress-associated endoplasmic reticulum protein 1 (SERP1)
Through a genome-wide screen for regulators of γ-secretase activity, researchers identified that SERP1 promotes Aβ production in cells undergoing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. The carboxyl-terminal domain of SERP1 interacts with the APH1A/NCT subcomplex of γ-secretase. Under ER stress conditions, SERP1 selectively recruits APP into the γ-secretase and enhances the subcellular localization of this complex within lipid rafts, leading to increased Aβ generation. Moreover, in cells exposed to high glucose levels and in diabetic AD model mice, elevated levels of SERP1, enhanced γ-secretase assembly, and increased Aβ production were observed (Jung et al., 2020). APH1A and NCT play a crucial role in stabilization, maturation and substrate recognition of the γ-secretase complex. The binding of SERP1 to this subcomplex may enhance its enzymatic activity by stabilizing the conformation of the complex or facilitating the entry of substrates into the active site. Although SERP1 has been shown to interact with γ-secretase, no atomic-resolution cryo-EM structures of SERP1 in complex with either the full γ-secretase complex or its APH1A/NCT subcomplex have been reported to date. Cryo-EM technology holds the potential to elucidate the molecular details of the SERP1–γ-secretase interaction at the atomic level, which is critical not only for understanding the unique mechanism of SERP1 as a GSMP, but also for guiding the rational design of therapeutics targeting this interaction.
4.3 The other GSMPs
4.3.1 Hif-1α
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (Hif-1α) serves as a key transcription factor in the cellular adaptation to hypoxic conditions. It plays critical roles in processes such as angiogenesis, metabolism (Masoud and Li, 2015), embryogenesis, and the development and progression of tumors (Peng and Liu, 2015). Numerous studies have shown that Hif-1α can enhance Notch signaling by binding to and stabilizing the intracellular domain of Notch (NICD), thereby activating downstream Notch target genes. Under hypoxic conditions, the interaction between Hif-1α and Notch is essential for maintaining the undifferentiated state of cells (Gustafsson et al., 2005). To counteract the negative feedback effects of Notch signaling in cancer stem cells, Hif-1α can bind to the promoter region of Hes1, a gene targeted by Notch signaling (Wang et al., 2011). In Drosophila models, Hif-1α has been shown to activate Notch signaling independently of ligand interactions, promoting the survival of Drosophila blood cells (Mukherjee et al., 2011). Additionally, research has demonstrated that hypoxia leads to an increase in Aph1a gene expression, which contributes to the upregulation of γ-secretase activity. This effect is mediated through a Hif-1α response element located within the Aph1a gene promoter (Wang et al., 2006). In breast cancer, Hif-1α no longer performs its canonical role as a transcription factor under hypoxic conditions, but instead interacts directly with γ-secretase regulates its activity for Notch cleavage, and enhances cancer cell migration and metastasis (Villa et al., 2014). Microglia-specific BACE-1 deletion enhances autophagolysosome function and Aβ-induced metabolic reprogramming via PI3K-mTOR-HIF-1α signaling, promoting Aβ degradation (Singh et al., 2022). This demonstrates that Hif-1α plays a significant role in AD; however, the molecular mechanism by which Hif-1α and γ-secretase jointly regulate AD requires further elucidation.
4.3.2 CD 147
Coimmunoprecipitation investigations indicated that CD147, a glycoprotein, also referred to as basigin or EMMPRIN (Gabison et al., 2009). Inhibition of CD147 was found to enhance the production of Aβ-peptides, suggesting its function as a regulatory component of γ-secretase in Aβ generation (Zhou et al., 2005). Additionally, CD147 regulates matrix metalloproteinases and is expressed across various human tissues, contributing to both extracellular matrix degradation and fibrosis. This makes it a promising target for cancer therapy via interactions involving cell-matrix and cell-cell connections (Huang et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2016). CD147 undergoes intramembrane cleavage by γ-secretase at lysine 231, leading to the release of its intracellular domains (ICD). The CD147ICD subsequently relocates to the nucleus, where it activates Notch signaling by binding to Notch promoters (Yong et al., 2019). Elevated levels of nuclear CD147ICD correlate with poorer prognoses in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), with patients exhibiting high CD147ICD expression showing significantly reduced overall survival rates compared to those with low CD147ICD expression (Yong et al., 2019). Depletion of CD147 using RNAi increases Aβ-peptide production without altering γ-secretase or APP substrates. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between CD147 and γ-secretase could pave the way for developing innovative therapies for Alzheimer’s disease (Zhou et al., 2005).
5 Concluding remarks and future challenges
The γ-secretase complex is universally present in all cells and tissues, and its ability to cleave multiple type I membrane proteins can be likened to “molecular scissors “(Wong et al., 2020). Initially characterized as a proteolytic activity responsible for the cleavage of APP to generate Aβ, γ-secretase has been extensively studied in the context of FAD due to missense mutations in its subunits (Jarrett et al., 1993). The deposition of Aβ peptide plaques in the cerebral cortex represents a hallmark feature of AD patients (Dominguez-Gortaire et al., 2025). The generation of Aβ peptides is not only dependent on γ-secretase activity but is also critically regulated by β-secretase. Following the cleavage of APP by β-secretase at the β-site, a membrane-bound C99 intermediate is formed. This C99 fragment subsequently undergoes further cleavage by γ-secretase to produce Aβ peptides. Thus, β-secretase plays a pivotal role in controlling the production of Aβ (Cervellati et al., 2021). In AD, β-secretase expression and activity are significantly increased, contributing to excessive Aβ production (Vassar, 2012). β-secretase inhibitors (BSIs) could reduce Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels effectively (Eketjäll et al., 2016). However, β-secretase has dual roles in Aβ, both in its production and degradation. When β-secretase is highly expressed, low-dose inhibitors may instead lead to an increase in Aβ42 and Aβ40 levels, as the Aβ-degrading activity of β-secretase is preferentially weakened (Ulku et al., 2024). Several BSIs have advanced to phase III clinical trials, but none have shown clear clinical benefits. For example, Verubecestat caused reversible cognitive decline (Vassar, 2012); Atabecestat led to dose-dependent liver enzyme elevation (Pleen and Townley, 2022; Evin et al., 2011); Lanabecestat was linked to psychiatric events, weight loss, and skin depigmentation (Patel et al., 2022); and Elenbecestat resulted in dizziness, nightmares, elevated liver enzymes, and hippocampal atrophy Elenbecestat (Patel et al., 2022). Despite the setbacks encountered in phase III clinical trials, the involvement of β-secretase in AD pathology remains widely acknowledged. The complexity of AD pathogenesis and the potential off-target effects of BSIs are considered critical contributors to the development of adverse drug reactions.
After β-secretase cleaves APP, γ-secretase subsequently cleaves the resulting C99 fragment to generate Aβ peptides. Recent studies have shown that the formation of Aβ peptide plaques may serve as a defense mechanism against viral attacks (Hur et al., 2020). Thus, it can be hypothesized that under normal physiological conditions, plaques fulfilling their function are subsequently cleared. However, when this clearance process is impaired, it leads to the development of AD. With an increasing number of identified γ-secretase substrates, it has become evident that, in addition to APP, several substrates play critical roles in AD progression (Yin et al., 2025). The limited clinical progress achieved through targeting APP alone suggests that the interplay between these substrates and APP warrants further investigation. Due to the broad substrate specificity of γ-secretase, GSIs inhibit the processing of multiple substrates, leading to significant side effects (Chen et al., 2023). Particularly the Notch pathway, which plays a critical role in essential cellular processes such as stem cell maintenance and proliferation, cell fate determination, and differentiation (Kovall et al., 2017; Kopan and Ilagan, 2009). Inhibition of Notch has been associated with gastrointestinal disorders (Hur, 2022; Abdallah, 2024); lymphopenia and an elevated risk of infection (Doody et al., 2013; Wong et al., 2004), cognitive decline (Doody et al., 2013), and an increased incidence of skin cancer (Uddin et al., 2020). Recent evidence indicates that γ-secretase inhibitors can impair epithelial cell function, leading to colitis in mice (Erkert et al., 2025). Compared to GSIs, GSMs offer more precise modulation of the γ-secretase cleavage site. They shift the cleavage position within the APP transmembrane region, leading to a decrease in Aβ42 levels and a relative increase in Aβ37 and Aβ38 (Figure 4). This approach provides several benefits over GSIs, including the selective reduction of Aβ42 without fully blocking γ-secretase activity, thereby minimizing adverse effects on Notch signaling and allowing for an expanded therapeutic range. Subsequent research uncovered that γ-secretase exhibits distinct localization patterns within tissues and performs specific functions in various cell types (Houser et al., 2023; Strope and Wilkins, 2023; Kwak et al., 2022). These findings raise questions regarding whether γ-secretase activity is regulated by other proteins or signaling pathways. Studies have demonstrated that only a fraction of the γ-secretase complex possesses catalytic activity, and the regulation of this activity remains an open question. GSMPs have emerged as key regulators of γ-secretase activity and specificity, enabling rapid responses to cellular signals and environmental changes (Antony et al., 2025). Multiple GSMPs direct the ubiquitous γ-secretase to initiate appropriate signaling under specific conditions. Notably, GSMPs do not directly inhibit γ-secretase activity but instead modulate it, thereby targeting GMSPs to treat AD may mitigate adverse reactions. BSIs, GSIs, GSMs, and GSMPs can all play a certain role in targeting Aβ deposition. The research progress among them is summarized in Table 3.
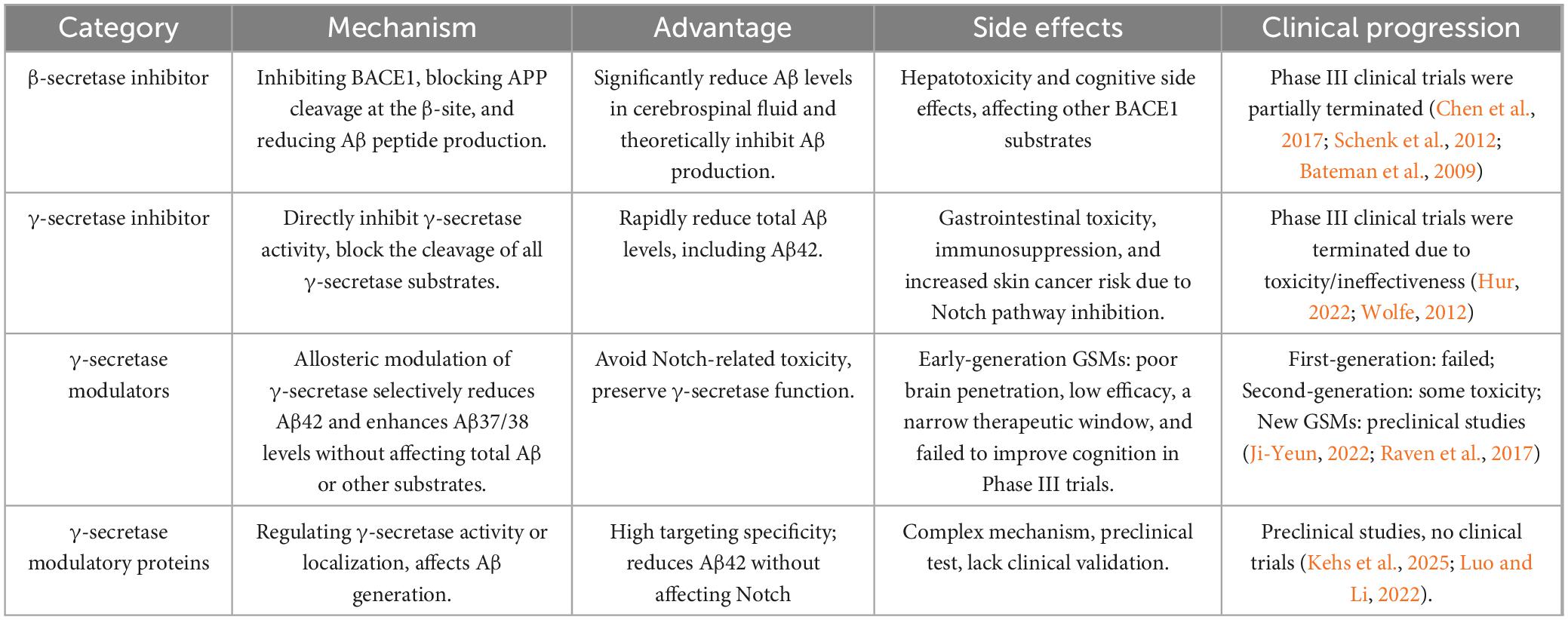
Table 3. The comparison of β-secretase 1 inhibitors, γ-secretase inhibitors (GSIs), γ-secretase modulators (GSMs), and γ-secretase modulatory proteins (GSMPs) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Research on γ-secretase still faces numerous challenges. For example, the mechanism by which GSMs interact with γ-secretase remains unclear. While most studies suggest that GSMs target the PSEN subunit of γ-secretase (Yang et al., 2021), alternative hypotheses propose the formation of a GSM-substrate-γ-secretase ternary complex (Petit et al., 2022). This uncertainty regarding the molecular target hampers the effective optimization of lead compounds. Furthermore, several GSMs have been discontinued from clinical development due to poor BBB penetration and safety concerns such as adverse side effects (Rynearson et al., 2021; Green et al., 2009). These failures underscore the translational gap between animal models and human trials. In addition, the physiological roles of GSM-regulated Aβ37/Aβ38 peptides in humans remain poorly understood, and their potential to cause unintended effects is still undetermined. Furthermore, studies on GSMPs are at an early stage but face multiple challenges. These include determining their precise cellular localization across different cell types, elucidating the mechanisms underlying substrate selectivity, and understanding how specific GSMP subtypes influence substrate processing. Moreover, as protein-based therapeutics, GSMPs are generally large and struggle to cross the BBB, and exogenous proteins may provoke immune responses, compromising both safety and therapeutic efficacy. Finally, biopharmaceuticals typically involve high production costs, complex manufacturing processes, and lower stability compared to small-molecule drugs. Currently, most research efforts are focused on small-molecule GSMs. In contrast, GSMPs represent a promising yet underexplored therapeutic avenue, with unique mechanisms and development hurdles that warrant further investigation. Addressing these gaps could significantly advance our understanding of γ-secretase biology in disease contexts, potentially leading to therapies with improved safety profiles and greater efficacy.
Author contributions
GN: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Software, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Conceptualization. XF: Software, Writing – original draft. DJ: Writing – review & editing. Zw: Writing – original draft. WS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. CM: Software, Writing – review & editing. DX: Writing – review & editing. QY: Software, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 32360162 and 32460232), Scientific Research Project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. 23JK0732), Scientific research project of Yan’an University (Grant No. YDQ2017-25), Doctoral Research Project of Yan’an University (Grant Nos. YDBK 2023-30 and YDBK2019-56), Shaanxi Provincial College Student Innovation Project (Grant No. S202410719094), Science and Technology Plan Project of Yan’an (Grant No. 2023-SFGG-098), and Yan’an Science and Technology Association Youth Talent Lifting Program Project (Grant No. 2023-20-1). Innovation program of university students (Grant No. D2024054)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support provided by the project and express gratitude to the authors for their efforts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdallah, A. (2024). Review on anti-Alzheimer drug development: Approaches, challenges and perspectives. RSC Adv. 14, 11057–11088. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08333k
Abisambra, J., Fiorelli, T., Padmanabhan, J., Neame, P., Wefes, I., and Potter, H. (2010). LDLR expression and localization are altered in mouse and human cell culture models of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 5:e8556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008556
Adnan, M., Anwar, S., DasGupta, D., Patel, M., Elasbali, A., Alhassan, H., et al. (2023). Targeting inhibition of microtubule affinity regulating kinase 4 by harmaline: Strategy to combat Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 224, 188–195. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.115
Ahn, J., Carrieri, C., Dela Cruz, F., Fullerton, T., Hajos-Korcsok, E., He, P., et al. (2020). Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects of a γ-secretase Modulator, PF-06648671, on CSF amyloid-β peptides in randomized phase I studies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 107, 211–220. doi: 10.1002/cpt.1570
Amini-Bavil-Olyaee, S., Choi, Y., Lee, J., Shi, M., Huang, I., Farzan, M., et al. (2013). The antiviral effector IFITM3 disrupts intracellular cholesterol homeostasis to block viral entry. Cell Host Microbe 13, 452–464. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.03.006
Amirrad, F., Bousoik, E., Shamloo, K., Al-Shiyab, H., Nguyen, V., and Montazeri Aliabadi, H. (2017). Alzheimer’s disease: Dawn of a new era? J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 20, 184–225. doi: 10.18433/J3VS8P
Andersson, C., Hansson, O., Minthon, L., Andreasen, N., Blennow, K., Zetterberg, H., et al. (2016). A genetic variant of the sortilin 1 gene is associated with reduced risk of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 53, 1353–1363. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160319
Annaert, W., Levesque, L., Craessaerts, K., Dierinck, I., Snellings, G., Westaway, D., et al. (1999). Presenilin 1 controls gamma-secretase processing of amyloid precursor protein in pre-golgi compartments of hippocampal neurons. J. Cell Biol. 147, 277–294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.2.277
Antony, D., Sheth, P., Swenson, A., Smoller, C., Maguire, K., and Grossberg, G. (2025). Recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease therapy: Clinical trials and literature review of novel enzyme inhibitors targeting amyloid precursor protein. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 26, 63–73. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2024.2438317
Anwar, S., Choudhury, A., Hussain, A., AlAjmi, M., Hassan, M., and Islam, A. (2024). Harnessing memantine in Alzheimer’s disease therapy through inhibition of microtubule affinity-regulating kinase: Mechanistic insights. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 262:130090. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130090
Araki, Y., Miyagi, N., Kato, N., Yoshida, T., Wada, S., Nishimura, M., et al. (2004). Coordinated metabolism of Alcadein and amyloid beta-protein precursor regulates FE65-dependent gene transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 24343–24354. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401925200
Area-Gomez, E., and Schon, E. (2016). Mitochondria-associated ER membranes and Alzheimer disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 38, 90–96. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.04.006
Area-Gomez, E., de Groof, A., Boldogh, I., Bird, T., Gibson, G., Koehler, C., et al. (2009). Presenilins are enriched in endoplasmic reticulum membranes associated with mitochondria. Am. J. Pathol. 175, 1810–1816. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090219
Bailey, C., Zhong, G., Huang, I., and Farzan, M. (2014). IFITM-family proteins: The cell’s first line of antiviral defense. Annu. Rev. Virol. 1, 261–283. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-031413-085537
Barrett, P., Sanders, C., Kaufman, S., Michelsen, K., and Jordan, J. B. (2011). NSAID-based γ-secretase modulators do not bind to the amyloid-β polypeptide. Biochemistry 50, 10328–10342. doi: 10.1021/bi201371j
Barros, M., Houlihan, W., Paresi, C., Brendel, M., Rynearson, K., Lee, C., et al. (2020). γ-Secretase partitioning into lipid bilayers remodels membrane microdomains after direct insertion. Langmuir 36, 6569–6579. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01178
Bateman, R., Siemers, E., Mawuenyega, K., Wen, G., Browning, K., Sigurdson, W., et al. (2009). A gamma-secretase inhibitor decreases amyloid-beta production in the central nervous system. Ann. Neurol. 66, 48–54. doi: 10.1002/ana.21623
Beher, D., Fricker, M., Nadin, A., Clarke, E., Wrigley, J., Li, Y., et al. (2003). In vitro characterization of the presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase complex using a novel affinity ligand. Biochemistry 42, 8133–8142. doi: 10.1021/bi034045z
Benoit, M., Hernandez, M., Dinh, M., Benavente, F., Vasquez, O., and Tenner, A. (2013). C1q-induced LRP1B and GPR6 proteins expressed early in Alzheimer disease mouse models, are essential for the C1q-mediated protection against amyloid-β neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 654–665. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400168
Bergman, A., Hansson, E., Pursglove, S., Farmery, M., Lannfelt, L., Lendahl, U., et al. (2004). Pen-2 is sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum and subjected to ubiquitylation and proteasome-mediated degradation in the absence of presenilin. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 16744–16753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313999200
Bischoff, F., Velter, A., Minne, G., Pieters, S., Berthelot, D., De Cleyn, M., et al. (2019). Design and synthesis of a novel series of cyanoindole derivatives as potent γ-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 29, 1737–1745. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.05.023
Blain, J., Bursavich, M., Freeman, E., Hrdlicka, L., Hodgdon, H., Chen, T., et al. (2016). Characterization of FRM-36143 as a new γ-secretase modulator for the potential treatment of familial Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 8:34. doi: 10.1186/s13195-016-0199-5
Boy, K., Guernon, J., Zuev, D., Xu, L., Zhang, Y., Shi, J., et al. (2019). Identification and preclinical evaluation of the bicyclic pyrimidine γ-secretase modulator BMS-932481. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 10, 312–317. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00541
Brahmachari, S., Karuppagounder, S., Ge, P., Lee, S., Dawson, V., Dawson, T., et al. (2017). c-Abl and Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. J. Parkinsons Dis. 7, 589–601. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171191
Branca, C., Sarnico, I., Ruotolo, R., Lanzillotta, A., Viscomi, A., Benarese, M., et al. (2014). Pharmacological targeting of the β-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain. Sci. Rep. 4:4618. doi: 10.1038/srep04618
Brogden, R., Heel, R., Speight, T., and Avery, G. (1978). Sulindac: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in rheumatic diseases. Drugs 16, 97–114. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197816020-00001
Bromley-Brits, K., and Song, W. (2012). The role of TMP21 in trafficking and amyloid-β precursor protein (APP) processing in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 9, 411–424. doi: 10.2174/156720512800492521
Buechler, J., and Salinas, P. (2018). Deficient Wnt signaling and synaptic vulnerability in Alzheimer’s disease: Emerging roles for the LRP6 receptor. Front. Synapt. Neurosci. 10:38. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00038
Bulic, B., Ness, J., Hahn, S., Rennhack, A., Jumpertz, T., and Weggen, S. (2011). Chemical biology, molecular mechanism and clinical perspective of γ-secretase modulators in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 9, 598–622. doi: 10.2174/157015911798376352
Bursavich, M., Harrison, B., Acharya, R., Costa, D., Freeman, E., Hodgdon, H., et al. (2017). Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a novel series of oxadiazine gamma secretase modulators for familial Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 60, 2383–2400. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01620
Bursavich, M., Harrison, B., Acharya, R., Costa, D., Freeman, E., Hrdlicka, L., et al. (2021). Discovery of the oxadiazine FRM-024: A potent CNS-penetrant gamma secretase modulator. J. Med. Chem. 64, 14426–14447. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00904
Caldwell, A., Liu, Q., Zhang, C., Schroth, G., Galasko, D., Rynearson, K., et al. (2022). Endotype reversal as a novel strategy for screening drugs targeting familial Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 18, 2117–2130. doi: 10.1002/alz.12553
Caldwell, J., Bennett, C., McCracken, T., Mazzola, R., Bara, T., Buevich, A., et al. (2010). Iminoheterocycles as gamma-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 5380–5384. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.121
Cervellati, C., Valacchi, G., and Zuliani, G. (2021). BACE1: From biomarker to Alzheimer’s disease therapeutical target. Aging 13, 12299–12300. doi: 10.18632/aging.203064
Chaudhury, A., Gerecke, K., Wyss, J., Morgan, D., Gordon, M., and Carroll, S. (2003). Neuregulin-1 and erbB4 immunoreactivity is associated with neuritic plaques in Alzheimer disease brain and in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62, 42–54. doi: 10.1093/jnen/62.1.42
Chen, F., Hasegawa, H., Schmitt-Ulms, G., Kawarai, T., Bohm, C., Katayama, T., et al. (2006). TMP21 is a presenilin complex component that modulates gamma-secretase but not epsilon-secretase activity. Nature 440, 1208–1212. doi: 10.1038/nature04667
Chen, G., Xu, T., Yan, Y., Zhou, Y., Jiang, Y., Melcher, K., et al. (2017). Amyloid beta: Structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 38, 1205–1235. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.28
Chen, S., Koch, M., Chávez-Gutiérrez, L., and Zacharias, M. (2023). How modulator binding at the Amyloidβ-γ-secretase interface enhances substrate binding and attenuates membrane distortion. J. Med. Chem. 66, 16772–16782. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01480
Chen, X., Becker, A., Albay, R., Nguyen, P., Karachentsev, D., Roberts, A., et al. (2024). γ-secretase modulator BPN15606 reduced Aβ42 and Aβ40 and countered alzheimer-related pathologies in a mouse model of down syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 96, 390–404. doi: 10.1002/ana.26958
Chen, Z., Simmons, M., Perry, R., Wiener, H., Harrell, L., and Go, R. (2008). Genetic association of neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 2 (NTRK2) With Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 147, 363–369. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30607
Chhibber, J. (2013). Identification and characterization of innate immune receptor substrates of γ-secretase enzyme complex. Cork: University College Cork.
Chhibber-Goel, J., Coleman-Vaughan, C., Agrawal, V., Sawhney, N., Hickey, E., Powell, J., et al. (2016). γ-Secretase activity is required for regulated intramembrane proteolysis of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 and TNF-mediated pro-apoptotic signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 5971–5985. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.679076
Choi, J., Cho, S., Park, J., Yun, S., Jo, C., Kim, E., et al. (2020). Elevated cerebrospinal fluid and plasma N-cadherin in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 79, 484–492. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlaa019
Chu, J., Lauretti, E., Craige, C., and Praticò, D. (2014). Pharmacological modulation of GSAP reduces amyloid-β levels and tau phosphorylation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles. J. Alzheimers Dis. 41, 729–737. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140105
Chung, H., and Struhl, G. (2002). Nicastrin is required for presenilin-mediated transmembrane cleavage in Drosophila. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 1129–1132. doi: 10.1038/ncb1201-1129
Colombo, A., Hsia, H., Wang, M., Kuhn, P., Brill, M., Canevazzi, P., et al. (2018). Non-cell-autonomous function of DR6 in Schwann cell proliferation. EMBO J. 37:e97390. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797390
Crystal, A., Morais, V., Pierson, T., Pijak, D., Carlin, D., Lee, V., et al. (2003). Membrane topology of gamma-secretase component PEN-2. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 20117–20123. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M213107200
de Jong, D., Jansen, R., Hoefnagels, W., Jellesma-Eggenkamp, M., Verbeek, M., Borm, G., et al. (2008). No effect of one-year treatment with indomethacin on Alzheimer’s disease progression: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 3:e1475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001475
De Strooper, B., and Karran, E. (2024). New precision medicine avenues to the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease from insights into the structure and function of γ-secretases. EMBO J. 43, 887–903. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00057-w
De Strooper, B., Saftig, P., Craessaerts, K., Vanderstichele, H., Guhde, G., Annaert, W., et al. (1998). Deficiency of presenilin-1 inhibits the normal cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. Nature 391, 387–390. doi: 10.1038/34910
Denzel, A., Otto, F., Girod, A., Pepperkok, R., Watson, R., Rosewell, I., et al. (2000). The p24 family member p23 is required for early embryonic development. Curr. Biol. 10, 55–58. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)00266-3
Devkota, S., Williams, T., and Wolfe, M. (2021). Familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations in amyloid protein precursor alter proteolysis by γ-secretase to increase amyloid β-peptides of ≤45 residues. J. Biol. Chem. 296:100281. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100281
DiBattista, A., Dumanis, S., Newman, J., and Rebeck, G. (2016). Identification and modification of amyloid-independent phenotypes of APOE4 mice. Exp. Neurol. 280, 97–105. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.04.014
Dietrich, M., Antequera, D., Pascual, C., Castro, N., Bolos, M., and Carro, E. (2014). Alzheimer’s disease-like impaired cognition in endothelial-specific megalin-null mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 39, 711–717. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131604
Dominguez-Gortaire, J., Ruiz, A., Porto-Pazos, A., Rodriguez-Yanez, S., and Cedron, F. (2025). Alzheimer’s disease: Exploring pathophysiological hypotheses and the role of machine learning in drug discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26:1004. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031004
Doody, R., Raman, R., Farlow, M., Iwatsubo, T., Vellas, B., Joffe, S., et al. (2013). A phase 3 trial of semagacestat for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 341–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1210951
Dries, D., and Yu, G. (2008). Assembly, maturation, and trafficking of the gamma-secretase complex in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 5, 132–146. doi: 10.2174/156720508783954695
Dries, D., and Yu, G. (2021). Breathing new life into the rational design of Alzheimer’s therapeutics. Cell 184, 296–298. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.036
Dries, D., Shah, S., Han, Y., Yu, C., Yu, S., Shearman, M., et al. (2009). Glu-333 of nicastrin directly participates in gamma-secretase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 29714–29724. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038737
Eggert, S., Paliga, K., Soba, P., Evin, G., Masters, C., Weidemann, A., et al. (2004). The proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein gene family members APLP-1 and APLP-2 involves alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and epsilon-like cleavages: Modulation of APLP-1 processing by n-glycosylation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 18146–18156. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311601200
Eketjäll, S., Janson, J., Kaspersson, K., Bogstedt, A., Jeppsson, F., Fälting, J., et al. (2016). AZD3293: A novel, orally active BACE1 inhibitor with high potency and permeability and markedly slow off-rate kinetics. J. Alzheimers Dis. 50, 1109–1123. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150834
Elzinga, B., Twomey, C., Powell, J., Harte, F., and McCarthy, J. (2009). Interleukin-1 receptor type 1 is a substrate for gamma-secretase-dependent regulated intramembrane proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 1394–1409. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803108200
Eriksen, J., Sagi, S., Smith, T., Weggen, S., Das, P., McLendon, D., et al. (2003). NSAIDs and enantiomers of flurbiprofen target gamma-secretase and lower Abeta 42 in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 440–449. doi: 10.1172/JCI18162
Erkert, L., Kabisch, M., Gamez-Belmonte, R., Gonzalez-Acera, M., Patankar, J., Schödel, L., et al. (2025). Pharmacological inhibitors of the gamma-secretase enzyme complex disrupt epithelial cell function triggering colitis in mice. J. Crohns Colitis 19:jjaf096. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaf096
Evin, G., Lessene, G., and Wilkins, S. (2011). BACE inhibitors as potential drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Focus on bioactivity. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 6, 91–106. doi: 10.2174/157488911795933938
Fassler, M., Zocher, M., Klare, S., de la Fuente, A. G., Scheuermann, J., Capell, A., et al. (2005). Masking of transmembrane-based retention signals controls ER export of gamma-secretase. Traffic 11, 250–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.01014.x
Feldman, R., Chandler, K., Levy, L., and Glaser, G. H. (1963). Familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 13, 811–824. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.10.811
Fischer, C., Zultanski, S., Zhou, H., Methot, J., Brown, W., Mampreian, D., et al. (2011). Triazoles as γ-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21, 4083–4087. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.04.089
Fischer, C., Zultanski, S., Zhou, H., Methot, J., Shah, S., Hayashi, I., et al. (2015). Discovery of novel triazolobenzazepinones as γ-secretase modulators with central Aβ42 lowering in rodents and rhesus monkeys. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25, 3488–3494. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.003
Fluhrer, R., Friedlein, A., Haass, C., and Walter, J. (2004). Phosphorylation of presenilin 1 at the caspase recognition site regulates its proteolytic processing and the progression of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 1585–1593. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306653200
Foncin, J., Salmon, D., Supino-Viterbo, V., Feldman, R., Macchi, G., Mariotti, P., et al. (1985). [Alzheimer’s presenile dementia transmitted in an extended kindred]. Rev. Neurol. 141, 194–202.
Fraering, P., LaVoie, M., Ye, W., Ostaszewski, B., Kimberly, W., Selkoe, D., et al. (2004). Detergent-dependent dissociation of active gamma-secretase reveals an interaction between Pen-2 and PS1-NTF and offers a model for subunit organization within the complex. Biochemistry 43, 323–333. doi: 10.1021/bi035748j
Francis, R., McGrath, G., Zhang, J., Ruddy, D., Sym, M., Apfeld, J., et al. (2002). Aph-1 and pen-2 are required for Notch pathway signaling, gamma-secretase cleavage of betaAPP, and presenilin protein accumulation. Dev. Cell 3, 85–97. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(02)00189-2
Fraser, P., Levesque, G., Yu, G., Mills, L., Thirlwell, J., Frantseva, M., et al. (1998). Presenilin 1 is actively degraded by the 26S proteasome. Neurobiol. Aging 19, S19–S21. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(98)00029-3
Freude, S., Schilbach, K., and Schubert, M. (2009). The role of IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor signaling for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: From model organisms to human disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 6, 213–223. doi: 10.2174/156720509788486527
Frost, G., Jonas, L., and Li, Y. (2019). Friend, foe or both? Immune activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:337. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00337
Frykman, S., Teranishi, Y., Hur, J., Sandebring, A., Yamamoto, N., Ancarcrona, M., et al. (2012). Identification of two novel synaptic γ-secretase associated proteins that affect amyloid β-peptide levels without altering Notch processing. Neurochem. Int. 61, 108–118. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.03.016
Fuentealba, R., Barría, M., Lee, J., Cam, J., Araya, C., Escudero, C., et al. (2007). ApoER2 expression increases Abeta production while decreasing amyloid precursor protein (APP) endocytosis: Possible role in the partitioning of APP into lipid rafts and in the regulation of gamma-secretase activity. Mol. Neurodegener. 2:14. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-2-14
Fukumori, A., Fluhrer, R., Steiner, H., and Haass, C. (2010). Three-amino acid spacing of presenilin endoproteolysis suggests a general stepwise cleavage of gamma-secretase-mediated intramembrane proteolysis. J. Neurosci. 30, 7853–7862. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1443-10.2010
Gabison, E., Huet, E., Baudouin, C., and Menashi, S. (2009). Direct epithelial-stromal interaction in corneal wound healing: Role of EMMPRIN/CD147 in MMPs induction and beyond. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 28, 19–33. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.11.001
Gao, C., Lu, C., and Chen, J. (2016). Biological characteristics of cluster of differentiation 147 and its relationship with tumour. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 38, 589–593. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2016.05.018
Gayen, M., Benoit, M., Fan, Q., Hudobenko, J., and Yan, R. (2022). The CX3CL1 intracellular domain exhibits neuroprotection via insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 298:102532. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102532
Gerlach, K., Hobson, S., Eickmeier, C., Groß, U., Braun, C., Sieger, P., et al. (2018). Discovery of tetrahydroindazoles as a novel class of potent and in vivo efficacious gamma secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 26, 3227–3241. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.04.053
Gómez-Herranz, M., Taylor, J., and Sloan, R. D. (2023). IFITM proteins: Understanding their diverse roles in viral infection, cancer, and immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 299:102741. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102741
Gong, P., Roseman, J., Fernandez, C., Vetrivel, K., Bindokas, V., Zitzow, L., et al. (2011). Transgenic neuronal overexpression reveals that stringently regulated p23 expression is critical for coordinated movement in mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 6:87. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-87
Goutte, C., Hepler, W., Mickey, K., and Priess, J. (2000). Aph-2 encodes a novel extracellular protein required for GLP-1-mediated signaling. Development 127, 2481–2492. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.11.2481
Goutte, C., Tsunozaki, M., Hale, V., and Priess, J. R. (2002). APH-1 is a multipass membrane protein essential for the Notch signaling pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022523499
Green, R., Schneider, L., Amato, D., Beelen, A., Wilcock, G., Swabb, E., et al. (2009). Effect of tarenflurbil on cognitive decline and activities of daily living in patients with mild Alzheimer disease: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 302, 2557–2564. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1866
Güner, G., and Lichtenthaler, S. (2020). The substrate repertoire of γ-secretase/presenilin. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 105, 27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.05.019
Gunnar, N., Johan, L., and Johan, S. (2023). Gamma-secretase modulators: A promising route for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 16:1279740. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1279740
Gustafsson, M., Zheng, X., Pereira, T., Gradin, K., Jin, S., Lundkvist, J., et al. (2005). Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the undifferentiated cell state. Dev. Cell 9, 617–628. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.09.010
Gwin, M., Alexeyev, M., Geurts, A., Lee, J., Zhou, C., Yang, X., et al. (2023). Gamma secretase activating protein promotes end-organ dysfunction after bacterial pneumonia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 325, L174–L189. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00018.2023
Haapasalo, A., and Kovacs, D. (2011). The many substrates of presenilin/γ-secretase. J. Alzheimers Dis. 25, 3–28. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-101065
Hakem, F., Fouad, Y., and Arafa, R. (2024). Gamma secretase as an important drug target for management of Alzheimer’s disease: A comprehensive review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 24, 109–127. doi: 10.2174/0115680266259174231006070637
Hampel, H., Caraci, F., Cuello, A., Caruso, G., Nisticò, R., Corbo, M., et al. (2020). A path toward precision medicine for neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Immunol. 11:456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00456
Hata, S., Fujishige, S., Araki, Y., Kato, N., Araseki, M., Nishimura, M., et al. (2009). Alcadein cleavages by amyloid beta-precursor protein (APP) alpha- and gamma-secretases generate small peptides, p3-Alcs, indicating Alzheimer disease-related gamma-secretase dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 36024–36033. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.057497
Hawkins, J., Harrison, D., Ahmed, S., Davis, R., Chapman, T., Marshall, I., et al. (2011). Dynamics of Aβ42 reduction in plasma, CSF and brain of rats treated with the γ-secretase modulator, GSM-10h. Neurodegener. Dis. 8, 455–464. doi: 10.1159/000324511
He, G., Luo, W., Li, P., Remmers, C., Netzer, W., Hendrick, J., et al. (2010). Gamma-secretase activating protein is a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 467, 95–98. doi: 10.1038/nature09325
Hemming, M., Elias, J., Gygi, S., and Selkoe, D. (2008). Proteomic profiling of gamma-secretase substrates and mapping of substrate requirements. PLoS Biol. 6:e257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060257
Hieke, M., Ness, J., Steri, R., Greiner, C., Werz, O., Schubert-Zsilavecz, M., et al. (2011). SAR studies of acidic dual γ-secretase/PPARγ modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19, 5372–5382. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.08.003
Hoe, H., and Rebeck, G. (2005). Regulation of ApoE receptor proteolysis by ligand binding. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 137, 31–39. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.02.013
Honda, K., Takahashi, H., Hata, S., Abe, R., Saito, T., Saido, T., et al. (2024). Suppression of the amyloidogenic metabolism of APP and the accumulation of Aβ by alcadein α in the brain during aging. Sci. Rep. 14:18471. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69400-9
Höttecke, N. (2010). Entwicklung und Synthese von γ-Sekretase-Modulatoren zur Behandlung von Morbus Alzheimer. Darmstadt: Technischen Universität Darmstadt.
Hou, X., Zhang, X., Zou, H., Guan, M., Fu, C., Wang, W., et al. (2023). Differential and substrate-specific inhibition of γ-secretase by the C-terminal region of ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4. Neuron 111:1898–1913.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.03.024
Houser, M., Mitchell, S., Sinha, P., Lundin, B., Berezovska, O., and Maesako, M. (2023). Endosome and lysosome membrane properties functionally link to γ-secretase in live/intact cells. Sensors 23:2651. doi: 10.3390/s23052651
Hu, Y., Ye, Y., and Fortini, M. (2002). Nicastrin is required for gamma-secretase cleavage of the Drosophila Notch receptor. Dev. Cell 2, 69–78. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(01)00105-8
Huang, D., Rao, D., Jin, Q., Lai, M., Zhang, J., Lai, Z., et al. (2023). Role of CD147 in the development and diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 14:1149931. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1149931
Hur, J. (2021). Innate immunity protein IFITM3 in Alzheimer’s disease. DNA Cell Biol. 40, 1351–1355. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0585
Hur, J. (2022). γ-Secretase in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 54, 433–446. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00754-8
Hur, J., Frost, G., Wu, X., Crump, C., Pan, S., Wong, E., et al. (2020). The innate immunity protein IFITM3 modulates γ-secretase in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 586, 735–740. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2681-2
Ikeuchi, T., and Sisodia, S. (2003). The Notch ligands, Delta1 and Jagged2, are substrates for presenilin-dependent “gamma-secretase” cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 7751–7754. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200711200
Ílgün, A., and Çakir, T. (2025). Functional specificity of astrocyte subtypes in Alzheimer’s disease: Decoding disease mechanisms through network-based analysis of integrated single-nuclei multi-omic data. Mol. Neurobiol. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04965-8 [Epub ahead of print].
Imbimbo, B., Solfrizzi, V., and Panza, F. (2010). Are NSAIDs useful to treat Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2:19. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00019
Ioppolo, A., Eccles, M., Groth, D., Verdile, G., and Agostino, M. (2021). Evaluation of virtual screening strategies for the identification of γ-secretase inhibitors and modulators. Molecules 27:176. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010176
Isoo, N., Sato, C., Miyashita, H., Shinohara, M., Takasugi, N., Morohashi, Y., et al. (2007). Abeta42 overproduction associated with structural changes in the catalytic pore of gamma-secretase: Common effects of Pen-2 N-terminal elongation and fenofibrate. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 12388–12396. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611549200
Jarrett, J., Berger, E., and Lansbury, P. (1993). The carboxy terminus of the beta amyloid protein is critical for the seeding of amyloid formation: Implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 32, 4693–4697. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a001
Jensen, A., Kitago, Y., Fazeli, E., Vægter, C., Small, S., Petsko, G., et al. (2023). Dimerization of the Alzheimer’s disease pathogenic receptor SORLA regulates its association with retromer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 120:e2212180120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2212180120
Jiménez-Munguía, I., Beaven, A., Blank, P., Sodt, A., and Zimmerberg, J. (2022). Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) and its antiviral activity. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 77:102467. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102467
Jin, C., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Jia, B., Guo, X., Yang, G., et al. (2022). Modulation of amyloid precursor protein cleavage by γ-secretase activating protein through phase separation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119:e2122292119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2122292119
Ji-Yeun, H. (2022). γ-Secretase in Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 54, 433–446. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00754-8
Joanna, E. L., and Yue-Ming, L. (2022). Turning the tide on Alzheimer’s disease: Modulation of γ-secretase. Cell Biosci. 12:2. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00738-7
Jonsson, T., Stefansson, H., Steinberg, S., Jonsdottir, I., Jonsson, P., Snaedal, J., et al. (2013). Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 368, 107–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211103
Jung, S., Hyun, J., Nah, J., Han, J., Kim, S., Park, J., et al. (2020). SERP1 is an assembly regulator of γ-secretase in metabolic stress conditions. Sci. Signal. 13:eaax8949. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aax8949
Jutras, I., Laplante, A., Boulais, J., Brunet, S., Thinakaran, G., and Desjardins, M. (2005). Gamma-secretase is a functional component of phagosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 36310–36317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504069200
Kaether, C., Capell, A., Edbauer, D., Winkler, E., Novak, B., Steiner, H., et al. (2005). The presenilin C-terminus is required for ER-retention, nicastrin-binding and gamma-secretase activity. EMBO J. 23, 4738–4748. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600478
Kaether, C., Capell, A., Edbauer, D., Winkler, E., Novak, B., Steiner, H., et al. (2004). The presenilin C-terminus is required for ER-retention, nicastrin-binding and gamma-secretase activity. EMBO J. 23, 4738–4748. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600478
Kehs, Z., Cross, A., and Li, Y. (2025). From defense to disease: IFITM3 in immunity and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 22:e00482. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00482
Kim, J., Yoon, H., Basak, J., and Kim, J. (2014). Apolipoprotein E in synaptic plasticity and Alzheimer’s disease: Potential cellular and molecular mechanisms. Mol. Cells 37, 767–776. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2014.0248
Kim, K., Goldberg, I., Graham, M., Sundaram, M., Bertaggia, E., Lee, S., et al. (2018). γ-secretase inhibition lowers plasma triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by stabilizing the LDL receptor. Cell Metab. 27:816–827.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.010
Kim, S., Ullah, I., Beloor, J., Chung, K., Kim, J., Yi, Y., et al. (2024). Systemic treatment with siRNA targeting gamma-secretase activating protein inhibits amyloid-β accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomater. Res. 28:0027. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0027
Kim, T., Pettingell, W., Hallmark, O., Moir, R., Wasco, W., and Tanzi, R. (1997). Endoproteolytic cleavage and proteasomal degradation of presenilin 2 in transfected cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11006–11010. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.17.11006
Kim, T., Wu, K., Xu, J., McAuliffe, G., Tanzi, R., Wasco, W., et al. (1995). Selective localization of amyloid precursor-like protein 1 in the cerebral cortex postsynaptic density. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 32, 36–44. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00328-p
Kimura, N., Nakamura, S., Honda, T., Takashima, A., Nakayama, H., Ono, F., et al. (2001). Age-related changes in the localization of presenilin-1 in cynomolgus monkey brain. Brain Res. 922, 30–41. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03146-8
Knopman, D., Amieva, H., Petersen, R., Chételat, G., Holtzman, D., Hyman, B., et al. (2021). Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 7:33. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00269-y
Kopan, R., and Ilagan, M. (2009). The canonical Notch signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 137, 216–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.045
Kornilova, A., Kim, J., Laudon, H., and Wolfe, M. (2006). Deducing the transmembrane domain organization of presenilin-1 in gamma-secretase by cysteine disulfide cross-linking. Biochemistry 45, 7598–7604. doi: 10.1021/bi060107k
Kovall, R., Gebelein, B., Sprinzak, D., and Kopan, R. (2017). The canonical notch signaling pathway: Structural and biochemical insights into shape, sugar, and force. Dev. Cell 41, 228–241. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.04.001
Kuo, L., Hu, M., Hsu, W., Tung, Y., Wang, B., Tsai, W., et al. (2008). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-elicited stimulation of gamma-secretase is mediated by c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent phosphorylation of presenilin and nicastrin. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 4201–4212. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-09-0987
Kwak, M., Southard, K., Kim, W., Lin, A., Kim, N., Gopalappa, R., et al. (2022). Adherens junctions organize size-selective proteolytic hotspots critical for Notch signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 24, 1739–1753. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-01031-6
Lai, M., Chen, E., Crouthamel, M., DiMuzio-Mower, J., Xu, M., Huang, Q., et al. (2003). Presenilin-1 and presenilin-2 exhibit distinct yet overlapping gamma-secretase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 22475–22481. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300974200
Lammich, S., Okochi, M., Takeda, M., Kaether, C., Capell, A., Zimmer, A., et al. (2002). Presenilin-dependent intramembrane proteolysis of CD44 leads to the liberation of its intracellular domain and the secretion of an Abeta-like peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 44754–44759. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206872200
Lau, K., Howlett, D., Kesavapany, S., Standen, C., Dingwall, C., McLoughlin, D., et al. (2002). Cyclin-dependent kinase-5/p35 phosphorylates Presenilin 1 to regulate carboxy-terminal fragment stability. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 20, 13–20. doi: 10.1006/mcne.2002.1108
LaVoie, M., Fraering, P., Ostaszewski, B., Ye, W., Kimberly, W., Wolfe, M., et al. (2003). Assembly of the gamma-secretase complex involves early formation of an intermediate subcomplex of Aph-1 and nicastrin. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 37213–37222. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303941200
Lee, S., Shah, S., Yu, C., Wigley, W., Li, H., Lim, M., et al. (2004). A conserved GXXXG motif in APH-1 is critical for assembly and activity of the gamma-secretase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 4144–4152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M309745200
Levy-Lahad, E., Wasco, W., Poorkaj, P., Romano, D., Oshima, J., Pettingell, W., et al. (1995). Candidate gene for the chromosome 1 familial Alzheimer’s disease locus. Science 269, 973–977. doi: 10.1126/science.7638622
Liao, J., Chen, C., Ahn, E., Liu, X., Li, H., Edgington-Mitchell, L., et al. (2021). Targeting both BDNF/TrkB pathway and delta-secretase for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 197:108737. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108737
Ling, I., Golde, T., Galasko, D., and Koo, E. (2015). Modulation of Aβ42 in vivo by γ-secretase modulator in primates and humans. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 7:55. doi: 10.1186/s13195-015-0137-y
Liu, C., Ranganathan, S., Robinson, S., and Strickland, D. (2007). gamma-Secretase-mediated release of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1B intracellular domain suppresses anchorage-independent growth of neuroglioma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7504–7511. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608088200
Lleó, A., Waldron, E., von Arnim, C., Herl, L., Tangredi, M., Peltan, I., et al. (2005). Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) interacts with presenilin 1 and is a competitive substrate of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) for gamma-secretase. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 27303–27309. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413969200
López-Sánchez, J. L., Moreno, D. A., and García-Viguer, C. (2018). D-pinitol, a highly valuable product from carob pods: Health-promoting effects and metabolic pathways of this natural super-food ingredient and its derivatives. AIMS Agric. Food 3, 41–63. doi: 10.3934/agrfood.2018.1.41
Luo, J., and Li, Y. (2022). Turning the tide on Alzheimer’s disease: Modulation of γ-secretase. Cell Biosci. 12:2. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00738-7
Ly, P., Wu, Y., Zou, H., Wang, R., Zhou, W., Kinoshita, A., et al. (2013). Inhibition of GSK3β-mediated BACE1 expression reduces Alzheimer-associated phenotypes. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 224–235. doi: 10.1172/JCI64516
Maia, M., and Sousa, E. (2019). BACE-1 and γ-secretase as therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmaceuticals 12:41. doi: 10.3390/ph12010041
Malvankar, S., and Wolfe, M. (2025). γ-secretase-mediated endoproteolysis of neuregulin-1 and E-cadherin. Biochemistry 64, 2991–2999. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00095
Marambaud, P., Shioi, J., Serban, G., Georgakopoulos, A., Sarner, S., Nagy, V., et al. (2002). A presenilin-1/gamma-secretase cleavage releases the E-cadherin intracellular domain and regulates disassembly of adherens junctions. EMBO J. 21, 1948–1956. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.8.1948
Marambaud, P., Wen, P., Dutt, A., Shioi, J., Takashima, A., Siman, R., et al. (2003). A CBP binding transcriptional repressor produced by the PS1/epsilon-cleavage of N-cadherin is inhibited by PS1 FAD mutations. Cell 114, 635–645. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2003.08.008
Marquer, C., Laine, J., Dauphinot, L., Hanbouch, L., Lemercier-Neuillet, C., Pierrot, N., et al. (2014). Increasing membrane cholesterol of neurons in culture recapitulates Alzheimer’s disease early phenotypes. Mol. Neurodegener. 9:60. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-60
Martini, A., Gomez-Arboledas, A., Forner, S., Rodriguez-Ortiz, C., McQuade, A., Danhash, E., et al. (2019). Amyloid-beta impairs TOM1-mediated IL-1R1 signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 21198–21206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1914088116
Masoud, G., and Li, W. (2015). HIF-1α pathway: Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 5, 378–389. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.007
McElroy, B., Powell, J., and McCarthy, J. (2007). The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor is a substrate for gamma-secretase-mediated intramembrane proteolysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 358, 1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.062
Mehra, R., and Kepp, K. (2021). Computational prediction and molecular mechanism of γ-secretase modulators. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 157:105626. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105626
Mekala, S., Nelson, G., and Li, Y. (2020). Recent developments of small molecule γ-secretase modulators for Alzheimer’s disease. RSC Med. Chem. 11, 1003–1022. doi: 10.1039/d0md00196a
Merilahti, J., Ojala, V., Knittle, A., Pulliainen, A., and Elenius, K. (2017). Genome-wide screen of gamma-secretase-mediated intramembrane cleavage of receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol. Biol. Cell 28, 3123–3131. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-04-0261
Mi, K., and Johnson, G. (2007). Regulated proteolytic processing of LRP6 results in release of its intracellular domain. J. Neurochem. 101, 517–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04447.x
Miguel-Álvarez, M., Santos-Lozano, A., Sanchis-Gomar, F., Fiuza-Luces, C., Pareja-Galeano, H., Garatachea, N., et al. (2015). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment effect. Drugs Aging 32, 139–147. doi: 10.1007/s40266-015-0239-z
Moniruzzaman, M., Ishihara, S., Nobuhara, M., Higashide, H., and Funamoto, S. (2018). Glycosylation status of nicastrin influences catalytic activity and substrate preference of γ-secretase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 502, 98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.126
Morais, V., Crystal, A., Pijak, D., Carlin, D., Costa, J., Lee, V., et al. (2003). The transmembrane domain region of nicastrin mediates direct interactions with APH-1 and the gamma-secretase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 43284–43291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305685200
Moser, C., Guschtschin-Schmidt, N., Silber, M., Flum, J., and Muhle-Goll, C. (2024). Substrate selection criteria in regulated intramembrane proteolysis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 15, 1321–1334. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00068
Moulton, M., Barish, S., Ralhan, I., Chang, J., Goodman, L., Harland, J., et al. (2021). Neuronal ROS-induced glial lipid droplet formation is altered by loss of Alzheimer’s disease-associated genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118:e2112095118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2112095118
Mukherjee, T., Kim, W., Mandal, L., and Banerjee, U. (2011). Interaction between Notch and Hif-alpha in development and survival of Drosophila blood cells. Science 332, 1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.1199643
Murakami, K., Watanabe, T., Koike, T., Kamata, M., Igari, T., and Kondo, S. (2016). Pharmacological properties of a novel and potent γ-secretase modulator as a therapeutic option for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1633, 73–86. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.016
Nakano-Ito, K., Fujikawa, Y., Hihara, T., Shinjo, H., Kotani, S., Suganuma, A., et al. (2014). E2012-induced cataract and its predictive biomarkers. Toxicol. Sci. 137, 249–258. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft224
Naumann, E., Göring, S., Ogorek, I., Weggen, S., and Schmidt, B. (2013). Membrane anchoring γ-secretase modulators with terpene-derived moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23, 3852–3856. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.04.070
Netzer, W., Dou, F., Cai, D., Veach, D., Jean, S., Li, Y., et al. (2003). Gleevec inhibits beta-amyloid production but not Notch cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 12444–12449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1534745100
Ni, C., Murphy, M., Golde, T., and Carpenter, G. (2001). gamma -Secretase cleavage and nuclear localization of ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Science 294, 2179–2181. doi: 10.1126/science.1065412
Nobuto, K., Kohei, A., Hiroyuki, H., Shigeo, M., and Yasuo, I. (2013). Suspected limited efficacy of γ-secretase modulators. Neurobiol. Aging 34, 1101–1104. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.08.017
Nordvall, G., Yan, P., Agholme, L., Lundkvist, J., Sandin, J., Biverstål, H., et al. (2025). γ-secretase modulation inhibits amyloid plaque formation and growth and stimulates plaque regression in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 392:103400. doi: 10.1016/j.jpet.2025.103400
Nyborg, A., Ladd, T., Zwizinski, C., Lah, J., and Golde, T. (2006). Sortilin, SorCS1b, and SorLA Vps10p sorting receptors, are novel gamma-secretase substrates. Mol. Neurodegener. 1:3. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-1-3
Oikawa, N., and Walter, J. (2019). Presenilins and γ-secretase in membrane proteostasis. Cells 8:209. doi: 10.3390/cells8030209
Ong-Pålsson, E., Njavro, J., Wilson, Y., Pigoni, M., Schmidt, A., Müller, S., et al. (2022). The β-secretase substrate seizure 6-like protein (SEZ6L) controls motor functions in mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 1183–1198. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02660-y
Owen, M., Vrieze, F., Crook, R., Wu, W., Holmans, P., Fenton, I., et al. (2000). A full genome scan for late onset Alzheimers disease. Neurobiol. Aging 21, 138–138. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.2.237
Panmontha, W., Rerknimitr, P., Yeetong, P., Srichomthong, C., Suphapeetiporn, K., and Shotelersuk, V. (2015). A frameshift mutation in PEN-2 causes familial comedones syndrome. Dermatology 231, 77–81. doi: 10.1159/000382122
Pardossi-Piquard, R., Böhm, C., Chen, F., Kanemoto, S., Checler, F., Schmitt-Ulms, G., et al. (2009). TMP21 transmembrane domain regulates gamma-secretase cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 28634–28641. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.059345
Patel, S., Bansoad, A., Singh, R., and Khatik, G. (2022). BACE1: A key regulator in alzheimer’s disease progression and current development of its inhibitors. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 20, 1174–1193. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666211201094031
Peng, G., and Liu, Y. (2015). Hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer stem cells and inflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 36, 374–383. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.03.003
Petit, D., Hitzenberger, M., Koch, M., Lismont, S., Zoltowska, K., Enzlein, T., et al. (2022). Enzyme-substrate interface targeting by imidazole-based γ-secretase modulators activates γ-secretase and stabilizes its interaction with APP. EMBO J. 41:e111084. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022111084
Pettersson, M., Johnson, D., Humphrey, J., Butler, T., Am Ende, C., Fish, B., et al. (2015). Design of pyridopyrazine-1,6-dione γ-secretase modulators that align potency, mdr efflux ratio, and metabolic stability. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 6, 596–601. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00070
Pettersson, M., Johnson, D., Rankic, D., Kauffman, G., Am Ende, C., Butler, T., et al. (2017). Discovery of cyclopropyl chromane-derived pyridopyrazine-1,6-dione γ-secretase modulators with robust central efficacy. Medchemcomm 8, 730–743. doi: 10.1039/c6md00406g
Pigoni, M., Wanngren, J., Kuhn, P., Munro, K., Gunnersen, J., Takeshima, H., et al. (2016). Seizure protein 6 and its homolog seizure 6-like protein are physiological substrates of BACE1 in neurons. Mol. Neurodegener. 11:67. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0134-z
Pinner, E., Gruper, Y., Ben Zimra, M., Kristt, D., Laudon, M., Naor, D., et al. (2017). CD44 splice variants as potential players in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. J. Alzheimers Dis. 58, 1137–1149. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161245
Placanica, L., Chien, J., and Li, Y. (2010). Characterization of an atypical gamma-secretase complex from hematopoietic origin. Biochemistry 49, 2796–2804. doi: 10.1021/bi901388t
Pleen, J., and Townley, R. (2022). Alzheimer’s disease clinical trial update 2019-2021. J. Neurol. 269, 1038–1051. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10790-5
Prikhodko, O., Rynearson, K., Sekhon, T., Mante, M., Nguyen, P., Rissman, R., et al. (2020). The GSM BPN-15606 as a potential candidate for preventative therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 73, 1541–1554. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190442
Prokop, S., Shirotani, K., Edbauer, D., Haass, C., and Steiner, H. (2004). Requirement of PEN-2 for stabilization of the presenilin N-/C-terminal fragment heterodimer within the gamma-secretase complex. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 23255–23261. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401789200
Ramnarayan, V., Hein, Z., Janßen, L., Lis, N., Ghanwat, S., and Springer, S. (2018). Cytomegalovirus gp40/m152 uses TMED10 as ER anchor to retain MHC class I. Cell Rep. 23, 3068–3077. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.017
Ratni, H., Alker, A., Bartels, B., Bissantz, C., Chen, W., Gerlach, I., et al. (2020). Discovery of RO7185876, a highly potent γ-secretase modulator (GSM) as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 1257–1268. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00109
Raven, F., Ward, J., Zoltowska, K., Wan, Y., Bylykbashi, E., Miller, S., et al. (2017). Soluble gamma-secretase modulators attenuate Alzheimer’s β-amyloid pathology and induce conformational changes in presenilin 1. EBioMedicine 24, 93–101. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.08.028
Rivkin, A., Ahearn, S., Chichetti, S., Hamblett, C., Garcia, Y., Martinez, M., et al. (2010). Purine derivatives as potent gamma-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 2279–2282. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.02.008
Rodríguez Sarmiento, R., Bissantz, C., Bylund, J., Limberg, A., Neidhart, W., Jakob-Roetne, R., et al. (2020). Stepwise design of γ-secretase modulators with an advanced profile by judicious coordinated structural replacements and an unconventional phenyl ring bioisostere. J. Med. Chem. 63, 8534–8553. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00909
Rogaev, E., Sherrington, R., Rogaeva, E., Levesque, G., Ikeda, M., Liang, Y., et al. (1995). Familial Alzheimer’s disease in kindreds with missense mutations in a gene on chromosome 1 related to the Alzheimer’s disease type 3 gene. Nature 376, 775–778. doi: 10.1038/376775a0
Roisman, L., Han, S., Chuei, M., Connor, A., and Cappai, R. (2019). The crystal structure of amyloid precursor-like protein 2 E2 domain completes the amyloid precursor protein family. FASEB J. 33, 5076–5081. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802315R
Rynearson, K., Buckle, R., Barnes, K., Herr, R., Mayhew, N., Paquette, W., et al. (2016). Design and synthesis of aminothiazole modulators of the gamma-secretase enzyme. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 3928–3937. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.07.011
Rynearson, K., Buckle, R., Herr, R., Mayhew, N., Chen, X., Paquette, W., et al. (2020). Design and synthesis of novel methoxypyridine-derived gamma-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 28:115734. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115734
Rynearson, K., Ponnusamy, M., Prikhodko, O., Xie, Y., Zhang, C., Nguyen, P., et al. (2021). Preclinical validation of a potent γ-secretase modulator for Alzheimer’s disease prevention. J. Exp. Med. 218:e20202560. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202560
Sannerud, R., Esselens, C., Ejsmont, P., Mattera, R., Rochin, L., Tharkeshwar, A., et al. (2016). Restricted location of PSEN2/γ-secretase determines substrate specificity and generates an intracellular aβ pool. Cell 166, 193–208. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.020
Sastre, M., and Gentleman, S. (2010). NSAIDs: How they work and their prospects as therapeutics in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2:20. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2010.00020
Sava, A. (2021). Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel anti-inflammatory agents / Conception, synt hèse et évaluation biologique de nouveaux agents anti-inflammatoires. Doctoral dissertation, Université d’Orléans and Universitatea de medicină şi farmacie “Grigore T. Popa”. Orléans.
Savas, J., Ribeiro, L., Wierda, K., Wright, R., DeNardo-Wilke, L., Rice, H., et al. (2015). The sorting receptor SORCS1 regulates trafficking of neurexin and AMPA receptors. Neuron 87, 764–780. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.08.007
Scannevin, R., Chollate, S., Brennan, M., Snodgrass-Belt, P., Peng, H., Xu, L., et al. (2016). BIIB042, a novel γ-secretase modulator, reduces amyloidogenic Aβ isoforms in primates and rodents and plaque pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 103, 57–68. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.12.006
Schauenburg, L., Liebsch, F., Eravci, M., Mayer, M., Weise, C., and Multhaup, G. (2018). APLP1 is endoproteolytically cleaved by γ-secretase without previous ectodomain shedding. Sci. Rep. 8:1916. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19530-8
Schellenberg, G., Bird, T., Wijsman, E., Orr, H., Anderson, L., Nemens, E., et al. (1992). Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer’s disease locus on chromosome 14. Science 258, 668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576
Schenk, D., Basi, G., and Pangalos, M. (2012). Treatment strategies targeting amyloid β-protein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2:a006387. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006387
Sekioka, R., Honda, S., Honjo, E., Suzuki, T., Akashiba, H., Mitani, Y., et al. (2020b). Discovery of N-ethylpyridine-2-carboxamide derivatives as a novel scaffold for orally active γ-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 28:115132. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115132
Sekioka, R., Honda, S., Akashiba, H., Yarimizu, J., Mitani, Y., and Yamasaki, S. (2020a). Optimization and biological evaluation of imidazopyridine derivatives as a novel scaffold for γ-secretase modulators with oral efficacy against cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 28:115455. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115455
Sekioka, R., Honjo, E., Honda, S., Fuji, H., Akashiba, H., Mitani, Y., et al. (2018). Discovery of novel scaffolds for γ-secretase modulators without an arylimidazole moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 26, 435–442. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.11.049
Selkoe, D. (2001). Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81, 741–766. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.741
Selkoe, D. (2013). The therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease: Where we stand and where we are heading. Ann. Neurol. 74, 328–336. doi: 10.1002/ana.24001
Shah, S., Lee, S., Tabuchi, K., Hao, Y., Yu, C., LaPlant, Q., et al. (2005). Nicastrin functions as a gamma-secretase-substrate receptor. Cell 122, 435–447. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.05.022
Sherrington, R., Rogaev, E., Liang, Y., Rogaeva, E., Levesque, G., Ikeda, M., et al. (1995). Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 375, 754–760. doi: 10.1038/375754a0
Shi, X. D., Sun, K., Hu, R., Liu, X., Hu, Q., Sun, X., et al. (2016). Blocking the interaction between EphB2 and ADDLs by a small peptide rescues impaired synaptic plasticity and memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 36, 11959–11973. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1327-16.2016
Shi, J., Zuev, D., Xu, L., Lentz, K., Grace, J., Toyn, J., et al. (2016). Design and optimization of tricyclic gamma-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 1498–1502. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.06.020
Shi, Y., and Holtzman, D. (2018). Interplay between innate immunity and Alzheimer disease: APOE and TREM2 in the spotlight. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 18, 759–772. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0051-1
Singh, N., Das, B., Zhou, J., Hu, X., and Yan, R. (2022). Targeted BACE-1 inhibition in microglia enhances amyloid clearance and improved cognitive performance. Sci. Adv. 8:eabo3610. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo3610
Small, D., and Cappai, R. (2006). Alois Alzheimer and Alzheimer’s disease: A centennial perspective. J. Neurochem. 99, 708–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04212.x
Smolarkiewicz, M., Skrzypczak, T., and Wojtaszek, P. (2013). The very many faces of presenilins and the γ-secretase complex. Protoplasma 250, 997–1011. doi: 10.1007/s00709-013-0494-y
Soria Lopez, J., González, H., and Léger, G. (2019). Alzheimer’s disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 167, 231–255. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-804766-8.00013-3
Spasic, D., Tolia, A., Dillen, K., Baert, V., De Strooper, B., Vrijens, S., et al. (2006). Presenilin-1 maintains a nine-transmembrane topology throughout the secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 26569–26577. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600592200
Steiner, H., Winkler, E., and Haass, C. (2008). Chemical cross-linking provides a model of the gamma-secretase complex subunit architecture and evidence for close proximity of the C-terminal fragment of presenilin with APH-1. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 34677–34686. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709067200
Strope, T., and Wilkins, H. (2023). Amyloid precursor protein and mitochondria. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 78:102651. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102651
Stützer, I., Selevsek, N., Esterházy, D., Schmidt, A., Aebersold, R., and Stoffel, M. (2013). Systematic proteomic analysis identifies β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 2 and 1 (BACE2 and BACE1) substrates in pancreatic β-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 10536–10547. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.444703
Subramaniam, S., Kenney, D., Jayaraman, A., O’Connell, A., Walachowski, S., Montanaro, P., et al. (2024). Aging is associated with an insufficient early inflammatory response of lung endothelial cells in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Immunol. 15:1397990. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1397990
Sultana, R., Banks, W., and Butterfield, D. (2010). Decreased levels of PSD95 and two associated proteins and increased levels of BCl2 and caspase 3 in hippocampus from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: Insights into their potential roles for loss of synapses and memory, accumulation of Abeta, and neurodegeneration in a prodromal stage of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 88, 469–477. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22227
Sun, C., Jia, N., Li, R., Zhang, Z., Zhong, Y., and Han, K. (2020). miR-143-3p inhibition promotes neuronal survival in an Alzheimer’s disease cell model by targeting neuregulin-1. Folia Neuropathol. 58, 10–21. doi: 10.5114/fn.2020.94002
Sun, L., Zhao, L., Yang, G., Yan, C., Zhou, R., Zhou, X., et al. (2015). Structural basis of human γ-secretase assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 6003–6008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506242112
Takai, T., Hoashi, Y., Tomata, Y., Morimoto, S., Nakamura, M., Watanabe, T., et al. (2015). Discovery of novel 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridine derivatives as γ-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25, 4245–4249. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.101
Takami, M., Nagashima, Y., Sano, Y., Ishihara, S., Morishima-Kawashima, M., Funamoto, S., et al. (2009). gamma-Secretase: Successive tripeptide and tetrapeptide release from the transmembrane domain of beta-carboxyl terminal fragment. J. Neurosci. 29, 13042–13052. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-09.2009
Tarassishin, L., Yin, Y., Bassit, B., and Li, Y. (2004). Processing of Notch and amyloid precursor protein by gamma-secretase is spatially distinct. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 17050–17055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408007101
Tejeda, G., Ayuso-Dolado, S., Arbeteta, R., Esteban-Ortega, G., Vidaurre, O., and Díaz-Guerra, M. (2016). Brain ischaemia induces shedding of a BDNF-scavenger ectodomain from TrkB receptors by excitotoxicity activation of metalloproteinases and γ-secretases. J. Pathol. 238, 627–640. doi: 10.1002/path.4684
Teranishi, Y., Hur, J., Welander, H., Frånberg, J., Aoki, M., Winblad, B., et al. (2010). Affinity pulldown of γ-secretase and associated proteins from human and rat brain. J. Cell Mol. Med. 14, 2675–2686. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00907.x
Thinakaran, G., Borchelt, D., Lee, M., Slunt, H., Spitzer, L., Kim, G., et al. (1996). Endoproteolysis of presenilin 1 and accumulation of processed derivatives in vivo. Neuron 17, 181–190. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80291-3
Trambauer, J., Sarmiento, R., Garringer, H., Salbaum, K., Pedro, L., Crusius, D., et al. (2025). γ-Secretase modulator resistance of an aggressive Alzheimer-causing presenilin mutant can be overcome in the heterozygous patient state by a set of advanced compounds. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 17:49. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01680-3
Uchida, Y., Gomi, F., Murayama, S., and Takahashi, H. (2013). Calsyntenin-3 C-terminal fragment accumulates in dystrophic neurites surrounding aβ plaques in tg2576 mouse and Alzheimer disease brains: Its neurotoxic role in mediating dystrophic neurite formation. Am. J. Pathol. 182, 1718–1726. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.014
Uddin, M., Kabir, M., Jeandet, P., Mathew, B., Ashraf, G., Perveen, A., et al. (2020). Novel anti-Alzheimer’s therapeutic molecules targeting amyloid precursor protein processing. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020:7039138. doi: 10.1155/2020/7039138
Ulku, I., Leung, R., Herre, F., Walther, L., Shobo, A., Saftig, P., et al. (2024). Inhibition of BACE1 affected both its Aβ producing and degrading activities and increased Aβ42 and Aβ40 levels at high-level BACE1 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 300:107510. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107510
Vassar, R. (2012). BACE1, the Alzheimer’s beta-secretase enzyme, in health and disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 7:L3. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-2-22
Vetrivel, K., Cheng, H., Lin, W., Sakurai, T., Li, T., Nukina, N., et al. (2004). Association of gamma-secretase with lipid rafts in post-Golgi and endosome membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44945–44954. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407986200
Vetrivel, K., Gong, P., Bowen, J., Cheng, H., Chen, Y., Carter, M., et al. (2007). Dual roles of the transmembrane protein p23/TMP21 in the modulation of amyloid precursor protein metabolism. Mol. Neurodegener. 2:4. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-2-4
Vetrivel, K., Kodam, A., Gong, P., Chen, Y., Parent, A., Kar, S., et al. (2008). Localization and regional distribution of p23/TMP21 in the brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 32, 37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2008.06.012
Villa, J., Chiu, D., Brandes, A., Escorcia, F., Villa, C., Maguire, W., et al. (2014). Nontranscriptional role of Hif-1α in activation of γ-secretase and notch signaling in breast cancer. Cell Rep. 8, 1077–1092. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.028
Wagner, S., Rynearson, K., Duddy, S., Zhang, C., Nguyen, P., Becker, A., et al. (2017). Pharmacological and toxicological properties of the potent oral γ-secretase modulator BPN-15606. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 362, 31–44. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.240861
Wahrle, S., Das, P., Nyborg, A., McLendon, C., Shoji, M., Kawarabayashi, T., et al. (2002). Cholesterol-dependent gamma-secretase activity in buoyant cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains. Neurobiol. Dis. 9, 11–23. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2001.0470
Walker, D., Tang, T., and Lue, L. (2017). Studies on colony stimulating factor receptor-1 and ligands colony stimulating factor-1 and interleukin-34 in Alzheimer’s disease brains and human microglia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 9:244. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00244
Walter, J., Schindzielorz, A., Grünberg, J., and Haass, C. (1999). Phosphorylation of presenilin-2 regulates its cleavage by caspases and retards progression of apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 1391–1396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.4.1391
Wang, R., Sweeney, D., Gandy, S., and Sisodia, S. (1996). The profile of soluble amyloid beta protein in cultured cell media. Detection and quantification of amyloid beta protein and variants by immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 31894–31902. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.50.31894
Wang, R., Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, R., Zhang, X., Hong, S., et al. (2006). Transcriptional regulation of APH-1A and increased gamma-secretase cleavage of APP and Notch by HIF-1 and hypoxia. FASEB J. 20, 1275–1277. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-5839fje
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Malek, S., Zheng, P., and Liu, Y. (2011). Targeting HIF1α eliminates cancer stem cells in hematological malignancies. Cell Stem Cell 8, 399–411. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.02.006
Watanabe, N., Tomita, T., Sato, C., Kitamura, T., Morohashi, Y., and Iwatsubo, T. (2006). Pen-2 is incorporated into the gamma-secretase complex through binding to transmembrane domain 4 of presenilin 1. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 41967–41975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509066200
Weggen, S., Eriksen, J., Das, P., Sagi, S., Wang, R., Pietrzik, C., et al. (2001). A subset of NSAIDs lower amyloidogenic Abeta42 independently of cyclooxygenase activity. Nature 414, 212–216. doi: 10.1038/35102591
Wei, Y., Ma, M., Lin, S., Li, X., Shu, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2021). Proteolytic shedding of human colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor and its implication. J. Cell Mol. Med. 25, 4516–4521. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16474
Wolfe, M. (2012). γ-Secretase inhibitors and modulators for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 120, 89–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07501.x
Wolfe, M. (2019). Structure and function of the γ-secretase complex. Biochemistry 58, 2953–2966. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00401
Wolfe, M. (2024). γ-Secretase: Once and future drug target for Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 19, 5–8. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2023.2277350
Wong, E., Frost, G., and Li, Y. (2020). γ-secretase modulatory proteins: The guiding hand behind the running scissors. Front. Aging Neurosci. 12:614690. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.614690
Wong, E., Liao, G., Chang, J., Xu, P., Li, Y., and Greengard, P. (2019). GSAP modulates γ-secretase specificity by inducing conformational change in PS1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 6385–6390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1820160116
Wong, G., Manfra, D., Poulet, F., Zhang, Q., Josien, H., Bara, T., et al. (2004). Chronic treatment with the gamma-secretase inhibitor LY-411,575 inhibits beta-amyloid peptide production and alters lymphopoiesis and intestinal cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 12876–12882. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311652200
Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Toyn, J., Macor, J., and Thompson, L. (2016). Synthesis of pyrimido[4,5-c]azepine- and pyrimido[4,5-c]oxepine-based γ-secretase modulators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 26, 1554–1557. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.02.016
Wunderlich, P., Glebov, K., Kemmerling, N., Tien, N., Neumann, H., and Walter, J. (2013). Sequential proteolytic processing of the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 (TREM2) protein by ectodomain shedding and γ-secretase-dependent intramembranous cleavage. J Biol Chem. 288, 33027–33036. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.517540
Xu, J., Litterst, C., Georgakopoulos, A., Zaganas, I., and Robakis, N. (2009). Peptide EphB2/CTF2 generated by the gamma-secretase processing of EphB2 receptor promotes tyrosine phosphorylation and cell surface localization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 27220–27228. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.048728
Xu, M., Liu, Q., Bi, R., Li, Y., Li, H., Kang, W., et al. (2023). Coexistence of multiple functional variants and genes underlies genetic risk locus 11p11.2 of Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 94, 743–759. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.05.020
Xu, P., Chang, J., Zhou, X., Wang, W., Bamkole, M., Wong, E., et al. (2021). GSAP regulates lipid homeostasis and mitochondrial function associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Exp. Med. 218:e20202446. doi: 10.1084/jem.20202446
Xu, T., Yan, Y., Kang, Y., Jiang, Y., Melcher, K., and Xu, H. (2016). Alzheimer’s disease-associated mutations increase amyloid precursor protein resistance to γ-secretase cleavage and the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio. Cell Discov. 2:16026. doi: 10.1038/celldisc.2016.26
Yánez, D., Ross, S., and Crompton, T. (2020). The IFITM protein family in adaptive immunity. Immunology 159, 365–372. doi: 10.1111/imm.13163
Yang, G., Zhou, R., Guo, X., Yan, C., Lei, J., and Shi, Y. (2021). Structural basis of γ-secretase inhibition and modulation by small molecule drugs. Cell 184:521–533.e14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.049
Yang, G., Zhou, R., Zhou, Q., Guo, X., Yan, C., Ke, M., et al. (2019). Structural basis of Notch recognition by human γ-secretase. Nature 565, 192–197. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0813-8
Yao, A., and Yan, R. (2020). Activity of Alzheimer’s γ-secretase is linked to changes of interferon-induced transmembrane proteins (IFITM) in innate immunity. Mol. Neurodegener. 15:69. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00417-0
Yin, H., Wang, Y., Ren, Z., Xiao, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2025). TDP43 is a newly identified substrate for PS1, enhancing the expression of APP following cleavage. Cell Death Discov. 11:76. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02340-z
Yong, Y., Zhang, R., Liu, Z., Wei, D., Shang, Y., Wu, J., et al. (2019). Gamma-secretase complex-dependent intramembrane proteolysis of CD147 regulates the Notch1 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pathol. 249, 255–267. doi: 10.1002/path.5316
Yu, G., Chen, F., Levesque, G., Nishimura, M., Zhang, D., Levesque, L., et al. (1998). The presenilin 1 protein is a component of a high molecular weight intracellular complex that contains beta-catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 16470–16475. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.26.16470
Yu, G., Nishimura, M., Arawaka, S., Levitan, D., Zhang, L., Tandon, A., et al. (2000). Nicastrin modulates presenilin-mediated notch/glp-1 signal transduction and betaAPP processing. Nature 407, 48–54. doi: 10.1038/35024009
Yu, Y., Logovinsky, V., Schuck, E., Kaplow, J., Chang, M., Miyagawa, T., et al. (2014). Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the novel γ-secretase modulator, E2212, in healthy human subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 54, 528–536. doi: 10.1002/jcph.249
Zeng, L., Li, T., Xu, D., Liu, J., Mao, G., Cui, M., et al. (2012). Death receptor 6 induces apoptosis not through type I or type II pathways, but via a unique mitochondria-dependent pathway by interacting with Bax protein. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 29125–29133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.362038
Zhang, H., Ma, Q., Zhang, Y., and Xu, H. (2012). Proteolytic processing of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid precursor protein. J. Neurochem. 120, 9–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07519.x
Zhang, X., Li, Y., Xu, H., and Zhang, Y. (2014). The γ-secretase complex: From structure to function. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 8:427. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00427
Zhang, X., Wu, Y., Cai, F., and Song, W. (2019). Regulation of global gene expression in brain by TMP21. Mol. Brain 12:39. doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0460-5
Zhang, X., Yu, C., and Sisodia, S. (2015). The topology of pen-2, a γ-secretase subunit, revisited: Evidence for a reentrant loop and a single pass transmembrane domain. Mol. Neurodegener. 10:39. doi: 10.1186/s13024-015-0037-4
Zhao, Z., Pissarnitski, D., Huang, X., Palani, A., Zhu, Z., Greenlee, W., et al. (2017). Discovery of a tetrahydrobenzisoxazole series of γ-secretase modulators. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 8, 1002–1006. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00178
Zheng, Q., and Wang, X. (2025). Alzheimer’s disease: Insights into pathology, molecular mechanisms, and therapy. Protein Cell 16, 83–120. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae026
Zhou, S., Zhou, H., Walian, P., and Jap, B. (2005). CD147 is a regulatory subunit of the gamma-secretase complex in Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta-peptide production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 7499–7504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502768102
Zhuo, X., Howell, B., Shen, H., Woodhead, J., Mosure, K., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Mechanistic investigation of liver injury induced by BMS-932481, an experimental γ-secretase modulator. Toxicol. Sci. 194, 235–245. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfad057
Zou, Z., Chung, B., Nguyen, T., Mentone, S., Thomson, B., and Biemesderfer, D. (2004). Linking receptor-mediated endocytosis and cell signaling: Evidence for regulated intramembrane proteolysis of megalin in proximal tubule. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 34302–34310. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405608200
Zubenko, G., Hughes, H., Stiffler, J., Hurtt, M., and Kaplan, B. B. (1998). A genome survey for novel Alzheimer disease risk loci: Results at 10-cM resolution. Genomics 50, 121–128. doi: 10.1006/geno.1998.5306
Keywords: γ-secretase, Alzheimer’s disease, GSMS, GSMPs, type I transmembrane proteins
Citation: Ning G, Fan X, Juan D, wenxue Z, Sijia W, Meinei C, Xiaolong D and Yiming Q (2025) The manipulator behind “Scissors”: γ -secretase and its modulators in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 17:1637671. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1637671
Received: 29 May 2025; Accepted: 08 August 2025;
Published: 25 August 2025.
Edited by:
Ilya Bezprozvanny, Peter the Great St.Petersburg Polytechnic University, RussiaReviewed by:
Saleha Anwar, Jamia Hamdard University, IndiaYuan Xu, Changzhou First People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Ning, Fan, Juan, wenxue, Sijia, Meinei, Xiaolong and Yiming. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gao Ning, eWFkeGdhb25pbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Gao Ning
Gao Ning Xing Fan
Xing Fan Du Juan1,2
Du Juan1,2