- 1School Of Chinese Materia Medica, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Respiratory, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
This review systematically bridges a critical gap in existing scholarship by re-examining plant interaction principles articulated in ancient Chinese agrarian texts through the lens of contemporary allelopathy research. While prior studies have explored allelochemical mechanisms and molecular interactions, this synthesis uniquely focuses on how classical Chinese theories of “mutual engenderment and restraint” offer actionable insights for sustainable agriculture—a dimension underdeveloped in both historical and modern scientific discourse. By cross-referencing ancient documentation of crop interplanting and weed management strategies with current allelopathic research frameworks, this work identifies synergies between traditional ecological wisdom and cutting-edge phytochemical studies. This dual perspective not only validates the empirical foundations of ancient practices but also uncovers innovative solutions for pest suppression, soil health, and yield optimization in resource-constrained agricultural systems. Unlike conventional reviews that compartmentalize historical and scientific analyses, this study demonstrates the translational potential of cultural heritage by modeling a hybrid research methodology that integrates textual philology, ethnobotany, and molecular ecology. This synthesis repositions ethnobotanical heritage as a dynamic resource for harmonizing productivity with ecological balance.
1 Introduction
The true scientific study of plants began as a consequence and a part of the great intellectual movement of the sixth century BC in Asia Minor and in the Mediterranean Region (Liu et al., 2008), meanwhile parallel traditions of botanical wisdom developed independently across different regions. China has a history of more than 7,000 years in agricultural cultivation (Sylvan et al., 1987), during which pesticides, herbicides, etc., were not widely used until the 1980s (Liu et al., 2008). While lacking various agrochemical techniques, the ancient Chinese people successfully controlled crop weeds and pests through tillage, hand weeding, interplanting, mulching, and crop rotation (Zhaoji, 1998). Over two thousand years ago, Chinese ancestors documented plant synergies and antagonisms, applying these principles to agricultural cultivation — a testament to ethnobotanical wisdom that transcended geographic boundaries. Similarly, indigenous agriculturalists in the Americas developed comparable understandings of plant relationships, preserved through oral traditions and codified in many ancient documents. Collectively, these traditions underscore the universal human capacity to observe and interpret natural patterns, creating resilient agricultural systems long before contemporary scientific frameworks emerged. Traditional knowledge systems, whether transmitted orally across generations in China or recorded in Mesoamerican pictorial manuscripts, remain invaluable archives of ecological insight, challenging modern assumptions about the primacy of chemical solutions in agriculture.
Such a phenomenon of one plant affecting the growth and development of another plant was called “mutual engenderment and restraint” by the ancient Chinese. In the following 2,000 years, these two concept continued to appear in ancient Chinese books and was enriched and expanded. In most cases, the ancestors discussed the engenderment and restraint relationship between plants from a perspective of practical production. The mutual promotion between the two is called “engenderment”, while the mutual inhibition is called “restraint”.
In contemporary times, the most used term in exploring engenderment and restraint is “allelopathy”. The phenomenon of plants influencing neighboring plants through the release of chemicals in the environment has been known as early as c. 370 BC (Willis, 1985). However, it was not until 1938 when Hans Molisch gave it a formal name, allelopathy (Molisch, 1938). Allelopathy now usually refers to the production and release of allelopathic substances by plants, which inhibits the establishment and growth of symbiotic plants (Meiners et al., 2012). The concepts of allelopathy and mutual engenderment and restraint may overlap, but they are not completely consistent.
Avoiding mutual restraint and cleverly utilizing mutual engenderment in production were the basic knowledge of ancient Chinese farmers. Qi Min Yao Shu is the most complete ancient agricultural book in China, which summarized many experiences of mutual influence between plants. The method of using soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) to help melons (do not pertain to a specific botanical species, but rather encompasses multiple melon plants in a general context) take root and sprout (Jia, 1875) has been used for thousands of years, and during the Qing Dynasty, when people applied this method to rice (Oryza sativa L.) production, it became known as the “killing method”. The mechanisms underlying the interactions between plants observed by the ancient are gradually being revealed by modern science, such as the production and release of 1,4-naphthoquinone in black walnuts (Juglans nigra L.), which interferes with the growth of understory plants (Soderquist, 1973); DIMBOA (2,4-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one) is a dominant allelopathic substance applied by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and corn (Zea mays L.) against weeds, pathogens, and herbivores (Niemeyer, 2009), and its production can be induced by various weeds (Zhang et al., 2016). However, the mechanism of mutual influence between plants was not the focus of the ancients. They preferred to use such laws to guide agricultural production. This is also the concept of “harmony between heaven and man” that ancient Chinese scientists have always upheld, which entails exploring the laws of nature and pursuing harmonious coexistence between humans and nature. This concept has unique inspirations for the world today when exploring sustainable development within the framework of modern agricultural production.
In today’s China, the population has reached an enormous 1.44 billion based on the seventh national population census data, with the area of arable land per capita being very small (Yan et al., 2010) and the farmland multi-cropping index high. Intercropping is still used in agriculture and forestry. The situation for world’s arable croplands is no better off, especially with urban expansion and agricultural pollution, the area of arable croplands is decreasing (Pravalie et al., 2021). Increasing temperature, extreme heat days, potential evaporation, and drought severity were associated with higher levels of cropland loss (Kennedy et al., 2023). The results of a research combing spatially explicit projections of urban expansion with datasets on global croplands and crop yields show that urban expansion will result in a 1.8–2.4% loss of global croplands by 2030 (Bren d’Amour et al., 2017). According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), food production has continued to rise, but hunger remains a persistent issue. In 2023, between 713 and 757 million people were undernourished. Considering the mid-range (733 million), this is about 152 million more people than in 2019 (data in Figure 1). Therefore, exploring a way to rationalize the use of land and to increase the yield of cultivated land through technology has become an important topic for sustainable development in the contemporary world.
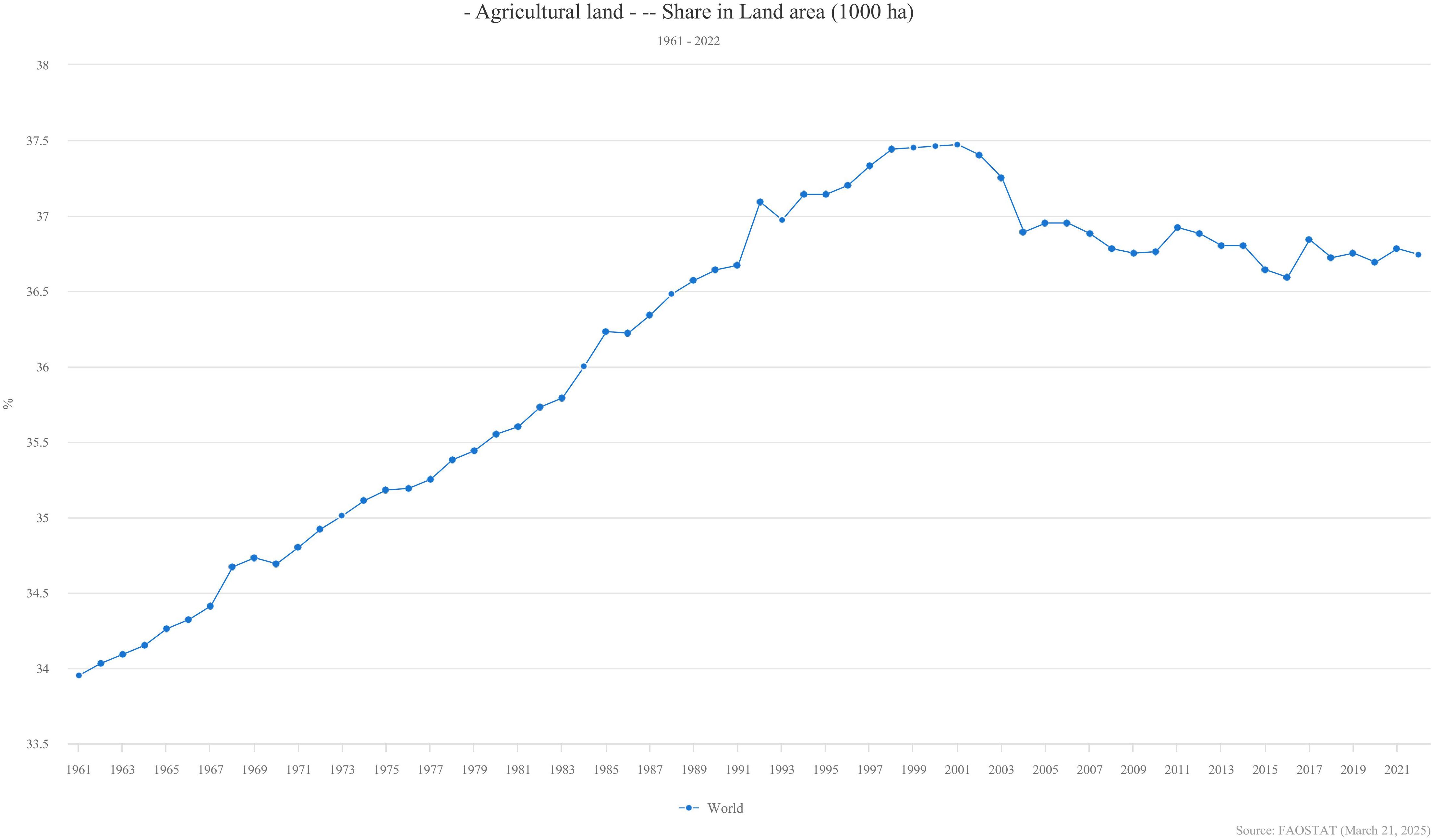
Figure 1. Agricultural land — share in land area (1000 ha) from 1961 to 2022. Despite the relatively stable agricultural land area, the challenge of hunger persists, enhancing agricultural productivity while ensuring sustainability and land conservation is a promising approach.
Allelopathic interactions between plants play an important role in weed management, pest and disease prevention, and planting system selection. Modern “mutual engenderment and restraint” studies not only contribute to a better understanding of structure and succession in a natural community, but also provide an alternative approach to weed management, agricultural sustainability, and new sources of natural herbicides. This paper mainly reviews the records of “mutual engenderment and restraint” in ancient Chinese literature, introduces the wisdom of the Chinese ancestors to readers and provides inspiration for contemporary research in sustainable development.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Research objective
This study seeks to systematically recover the concept of plant interdependence and antagonism as articulated in ancient Chinese agrarian literature—a body of knowledge that remains significantly underutilized in contemporary scientific discourse. By employing interdisciplinary frameworks from plant science, agroecology, and ethnobotany, this research aims to address unresolved questions about the empirical validity of ancient observational practices and their potential contributions to modern plant interaction studies. This endeavor not only recovers lost epistemological traditions but also establishes a foundational framework for integrating indigenous ecological knowledge with cutting-edge biotechnology, thereby bridging a critical gap between cultural heritage and innovation-driven sustainability solutions.
2.2 Research methods
The specific research workflow and results are illustrated in Figure 2. An initial literature review was conducted using keywords including “interdependence”, “antagonism”, “allelopathy”, “inhibition”, “promotion”, “symbiosis”, “traditional agriculture,” and “influence” within the CNKI over the past three decades (primarily focusing on Chinese articles). This process involved extracting references to ancient texts that document instances of plant interdependence and antagonism while establishing a list based on frequency of citation and thematic relevance. A total of 57 significant ancient books were identified for further analysis (refer to Table 1). The selected works were accessed through both online databases and physical libraries.
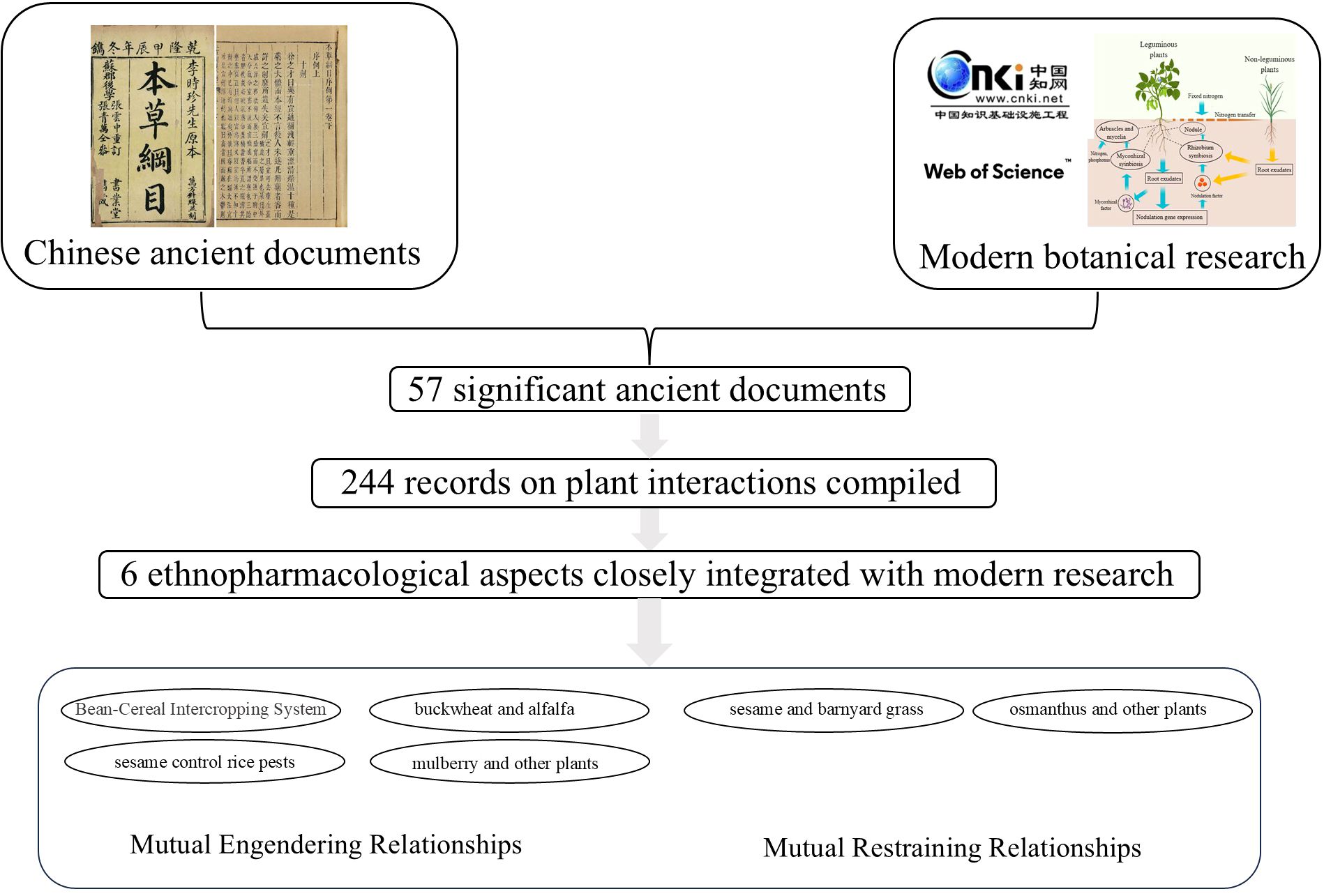
Figure 2. The research flowchart on ancient Chinese classics and modern literature. The results reveal that the potential research value of Chinese ethnobotany and contemporary studies can be categorized into two primary directions: mutual engendering (four plant combinations) and mutual restraining (two plant combinations).
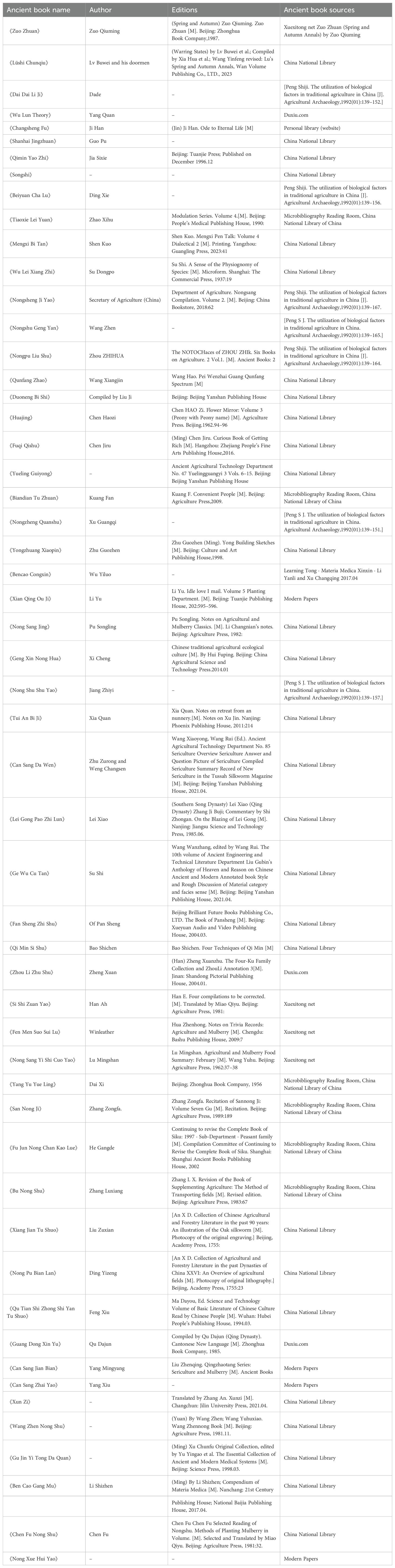
Table 1. Inventory of key ancient Chinese texts documenting plant interactions: this table systematically lists all the 57 ancient Chinese agricultural and philosophical texts studied in this project, which represent foundational sources for understanding ancient Chinese ecological wisdom, with each entry accompanied by source information including author, publishing house, publication era, electronic journals, collection location; forming the primary corpus for subsequent content analysis of traditional plant interaction paradigms.
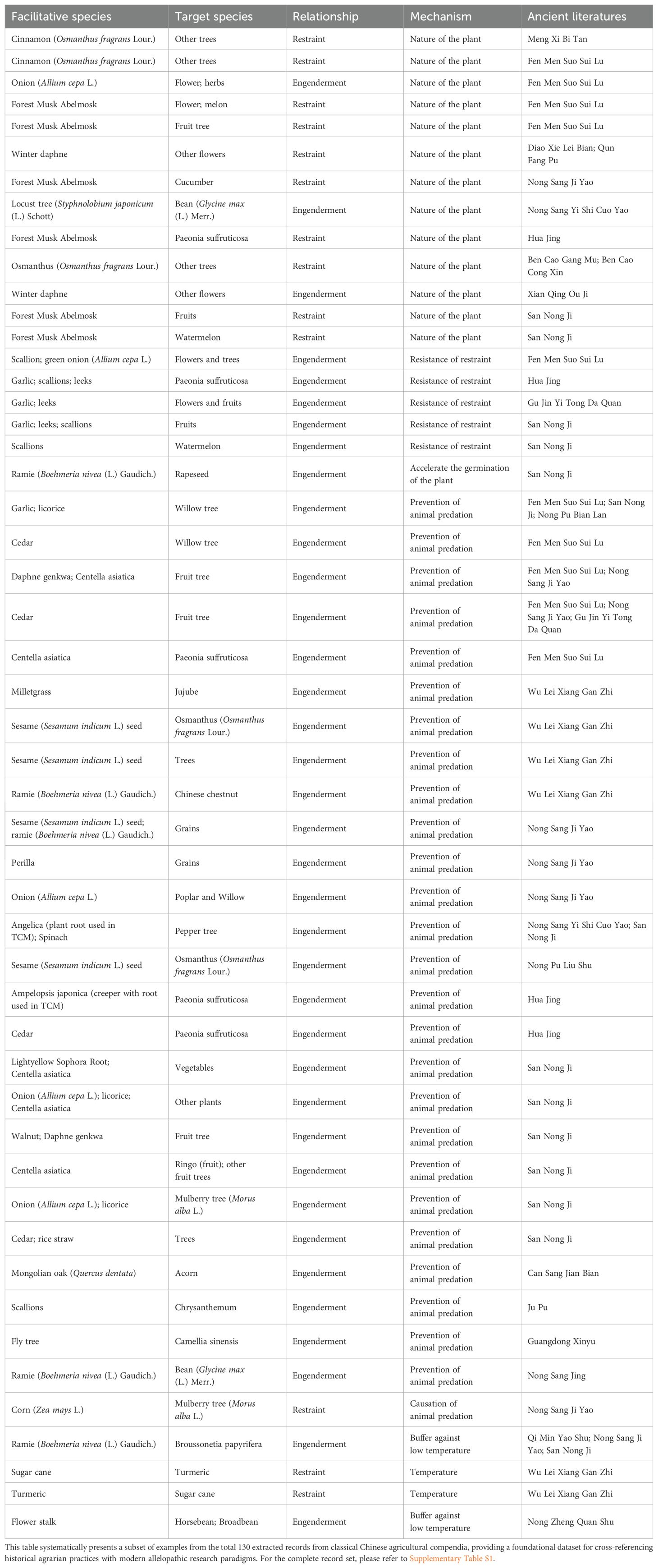
Only those records detailing interactions between two or more plants were included in this study. A total of 244 records on plant interactions have been compiled, many of which contain mutually verifiable content, further substantiating the significance of studying ancient documents. The extracted information was categorized into nine distinct themes: “nature of the plant (ecological niche in traditional Chinese philosophy),” “resistance of restraint,” “acceleration of plant germination,” “prevention of animal predation,” “causation of animal predation,” “buffer against low temperature” “improvement to land nutrition,” “competition for land nutrients,” and “increase of shade/competition for light”. The mechanism of plant interaction and elimination in some records was not clearly documented, resulting in the identification of a total of effective 130 data strips (refer to Table 2 in the paper). All the data and their original Chinese information extracted during the study of ancient literature are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
This integrative approach not only recovers lost agronomic wisdom from cultural heritage but also generates novel hypotheses for future research by connecting fragmented knowledge systems across millennia.
Notably, extensive modern research significance and value have been identified in the relationships between soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) and grass intercropping systems, sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) application for rice (Oryza sativa L.) pest control, crop–halophyte interactions in saline–alkali lands, mulberry’s (Morus alba L.) associations with other plants, sesame and barnyard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) P.Beauv.) relationships, as well as cinnamon’s (Osmanthus fragrans Lour.) interactions with other plants.
3 The relationship between plants
According to the single-factor effect, the interspecific relationship among plants can basically be summarized into three kinds of effects: facilitation, competition, and neutrality (Qing et al., 2016). Mutual engenderment and restraint represent a bidirectional or multilateral effect between plants, which, in modern terms, is also referred to as allelopathy, chemical interference, biochemical antagonism, or biochemical heterosis (Feng et al., 1999).
As early as the 5th and 3rd century BC, Democritus and Theophrastus respectively put forth the existence of mutual chemical reactions between plants (Putnam and Duke, 1978), but did not provide a distinctive definition. It wasn’t until 1937 that Molisch, inspired by the Greek words “Allelon” and “Pathos”, proposed the term “Allelopathy” to describe the concept of mutual engenderment and restraint between plants (Molisch, 1938), which includes both beneficial and unfavorable aspects (Ho and Wen, 1992). In 1974, Rice defined it as: “A process in which one plant, including microorganisms, releases chemicals into the environment that have direct or indirect harmful effects on other plants or microorganisms (Rice, 1984).” In fact, a large number of natural phenomena, data, and experiments indicate that the chemical substances released by plants can produce both inhibitory and stimulatory effects as a result of differences in concentration, environmental factors, and target subjects. Therefore, Rice later pointed out in his classic work Allelopathy: “Allelopathy refers to the process in which plants release chemicals into the environment, leading to direct or indirect beneficial or adverse effects on other plants or microorganisms (Rice, 1984).” This is currently the most classic definition of allelopathy.
Mutual engenderment and restraint, as an ancient philosophical concept, originates from the ancient Chinese theory of Yin–Yang and the Five Elements. Mutual engenderment refers to a relationship of mutual promotion and supplementation, while restraint refers to a relationship of mutual restraint and inhibition. The ancient Chinese’s understanding of allelopathy among plants is referred to as mutual engenderment and restraint. However, there are still differences between “mutual engenderment and restraint” and allelopathy.
Firstly, there is a difference in mechanism. Allelopathy is the release of chemicals from plants into the environment, which affects the growth and germination of the surrounding plants. Due to the high dependence of allelopathy on the chemical substances synthesized by plants themselves, influencing factors include plant density, environmental temperature, etc. Studies have shown that DIMBOA (2,4-dihydroxy-7-methoxy-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one) may induce allelopathic reactions in a density-dependent manner (Kong et al., 2018). The mutual engenderment and restraint of plants mentioned in ancient China is a manifestation of the influence between plants, and its mechanisms are diverse, not all of which are allelopathic effects. Some of the influence principles are physical or accompanying relationships between plants. Qi Min Yao Shu believed that planting locust tree (Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott) must intercrop with ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich.), also known as “planting ramie under locust tree (Jia, 1875).” Locust tree is a leguminous plant with nitrogen fixation function. Ramie relies on locust tree to obtain nutrients, so it grows vigorously (Fu et al., 2020). The experience of planting candlenut (Aleurites moluccanus (L.) Willd.) to protect tea recorded in the Bei Yuan Tea Record utilized the shading and cold protection effect of tall candlenut on tea trees (Yu et al., 1991), providing a good growth environment for tea trees with this high–low physical position, and achieving maximum economic benefits.
In addition, in terms of research scope, mutual engenderment and restraint refers to the interaction between plants, while allelopathy involves the interaction between plants and microorganisms. With the focus of mutual engenderment and restraint on macroscopic interactions and allelopathy on microscopic interactions, which involves the study of specific chemical substances and mechanisms. The fundamental reason is that due to the limitation of scientific and technological level, the microscopic reaction is beyond the cognition of the ancients. In terms of research methods, qualitative research is the main approach for mutual engenderment and restraint, while quantitative research is the main approach for allelopathy. Although there are differences between mutual engenderment and restraint and allelopathy, ancient records of the engenderment and restraint relationship between plants still have certain reference value for modern research on plant allelopathy.
4 Records of engenderment and restraint relationships between plants
China is a nation renowned for its extensive historical background and an abundant collection of canonical publications, including numerous historical documents that document a plethora of interspecies relationships among plants. The majority of these valuable contents are meticulously preserved within the ancient agricultural and ethnobotanical books of China (Qing et al., 2016). The recorded interspecies relationships can be generally divided into two categories: one is favorable to another plant or is mutually beneficial, known as “engenderment”; the other is harmful to another plant or mutually detrimental, known as “restraint” (Jianling, 2011). In order to explore the ancestors’ understanding of “mutual engenderment and restraint” relationship in ancient Chinese plants, we can sort these classics into four initial stages according to the development of agricultural history (Yin, 2023).
The Spring/Autumn and Warring States period (770 BC–221 BC) is a stage of germination and formation. During this period, agriculturalists, agricultural books that serves as a carrier for agricultural science, and related agronomic literature had already appeared, for example, in Zuo Zhuan, it states that “under such a large tree as the pine (Pinus cembra L.) and cypress (Platycladus orientalis (L.) Franco), the grass will not be able to grow luxuriantly (Ming, 2000).”
Subsequently, the period of Jin, Qin, Han, Wei, Jin, and South and North Dynasties was a stage of development and maturation for agricultural books, with plentiful traditional agricultural classics such as Fan Sheng Zhi Shu, Si Min Yue Ling, and Qi Min Yao Shu. At this stage, agricultural production was rapidly restored and developed, with the technology of intensive farming in the north gradually maturing, while the basis of agricultural technology recorded in agricultural books was expanded and enriched, making a more complete system. For example, the representative work of agricultural books in Han Dynasty, Fan Sheng Zhi Shu, has a record of utilizing the interspecific relationships among plants to make horticultural crops more productive—“In addition, you can plant adzuki beans (Vigna angularis (Willd.) Ohwi & H.Ohashi) in melons, four to five liters per acre, which can also be sold. This method is suitable for growing on flat land and can yield an income of about 10,000 copper money per acre from melons (Fan, 2004).” Qi Min Yao Shu of the Wei, Jin, South and North Dynasties period, can be seen as the representing work on dry farming intensive farming techniques in the north. During the Sui, Tang, and Song Dynasties, agricultural development spread to the south, and the amounts of agricultural books reflecting the production experience of the southern region increased, such as Si Shi Zuan Yao of the Tang Dynasty and Chen Fu Nong Shu of the Song Dynasty, and so on. Yuan, Ming and Qing Dynasties is a transitional stage where traditional agricultural books peaked and modernized. During this period, the editing of agricultural books reached an unprecedented peak in terms of quality and quantity. They were focused on the planting methods of mulberry, tea, and other cash crops, and an extensive amount of planting methods of crops in the northern drylands and the southern paddy fields were also included in books such as Sang Can Jian Bian, Nong Sang Jing, Nong Zheng Quan Shu, San Nong Ji, etc.
This paper extracts data on the “mutual engenderment and restraint” relationships among plants from comprehensive agricultural books that have been compiled and published and obtained total 130 records on the “mutual engenderment and restraint” relationship among plants, as illustrated in the Table 2.
After excluding plants that do not explicitly point out the mechanisms behind “mutual engenderment and restraint”, we summarized the mechanisms into nine aspects: nature of the plant, resistance of restraint, acceleration of plant germination, prevention of animal predation, causation of animal predation, buffer against low temperature, improvement to land nutrition, competition for land nutrients, and increase of shade/competition for light (Figure 3). This shows that the ancient Chinese’s understanding of the mechanisms of “mutual engenderment and restraint” between plants is mainly reflected in five factors: interspecific relationships, intraspecific relationships, temperature, soil, and light.
These mechanisms including nine aspects: nature of the plant, resistance of restraint, acceleration of plant germination, prevention of animal predation, causation of animal predation, buffer against low temperature, improvement to land nutrition, competition for land nutrients, and increase of shade/competition for light.
From the data we processed, the ancient Chinese’s understanding of the mutual engenderment and restraint relationship between plants tends to be perceived through how the overall growth environment influence the plants. Unlike the holistic macroscopic view of the mutual engenderment and restraint relationships by these ancestors, modern studies tend to carry on in a more microscopic aspect (Cheng and Cheng, 2015). Various studies use leachate, aqueous extracts, hot water extracts, methanol extracts, etc., as experimental materials to study the components of the extracts that play a role in the relationship of mutual engenderment and restraint, and as a result many new environmentally friendly and resistant herbicides and insecticides have been developed (Ayilara et al., 2023). For example, allelopathic water extracts of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) were applied to manage weed in Wheat (Weston et al., 2013); phenolic acids in rice, such as cinnamic acid and coumaric acid, can be used for weed control (Li et al., 2015). Combined application of allelopathic extract of sorghum and consortium of two allelopathic rhizobacteria significantly increased the wheat growth traits including the biological yield and grain yield (Raza et al., 2021). Several researchers have also suggested the use of allelochemicals extracted in water for weed suppression in the laboratory and also application under field conditions (Jabran et al., 2010) (Cheema et al., 2007; Khawar et al., 2010).
In practical production, the allelopathic effects between plants can be widely used to control weeds. The utilization method can be to directly cover the ground of allelopathic plants, such as returning straw to the field. On the other hand, allelopathic substances can also be manually extracted as herbicides. This article summarizes the ancient Chinese literature on mutual engenderment and restraint, hoping to provide researchers with ideas and experience, and inspire the application and research of the relationship between engenderment and restraint today.
5 Application of the engenderment and restraint relationship among plants
5.1 Mutual engendering relationships
5.1.1 Analysis on the application of the engendering relationship in bean–cereal intercropping systems
The intercropping system of beans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) and cereal was first recorded in Qi Min Yao Shu: “In the method of cultivating beautiful fields, mung beans (Vigna radiata (L.) R.Wilczek) are superior. Adzuki beans (Vigna angularis (Willd.) Ohwi & H.Ohashi) and sesame are secondary (Jia, 1875).” Later, it can be seen in the Compendium of Agriculture and Mulberry: “For any field where millet is accumulated, newly cleared fields are the best, followed by fields where soybeans were grown, and the least preferred are fields where cereals were grown. The land must be ripe (Si, 1982).” Leguminous plants enrich the soil and improve soil environment quality, with soybeans having a better effect than millets (Setaria italica (L.) P.Beauv.). Qi Min Yao Shu further notes: “For cereal fields, the best are those previously planted with green beans or adzuki beans, followed by sesame, millet, and the least preferred are those with rutabaga and soybeans (Jia, 1875).” The engendering relationship between legumes and grass family plants can be reflected on soil condition improvement, which has been subject to more in-depth modern research.
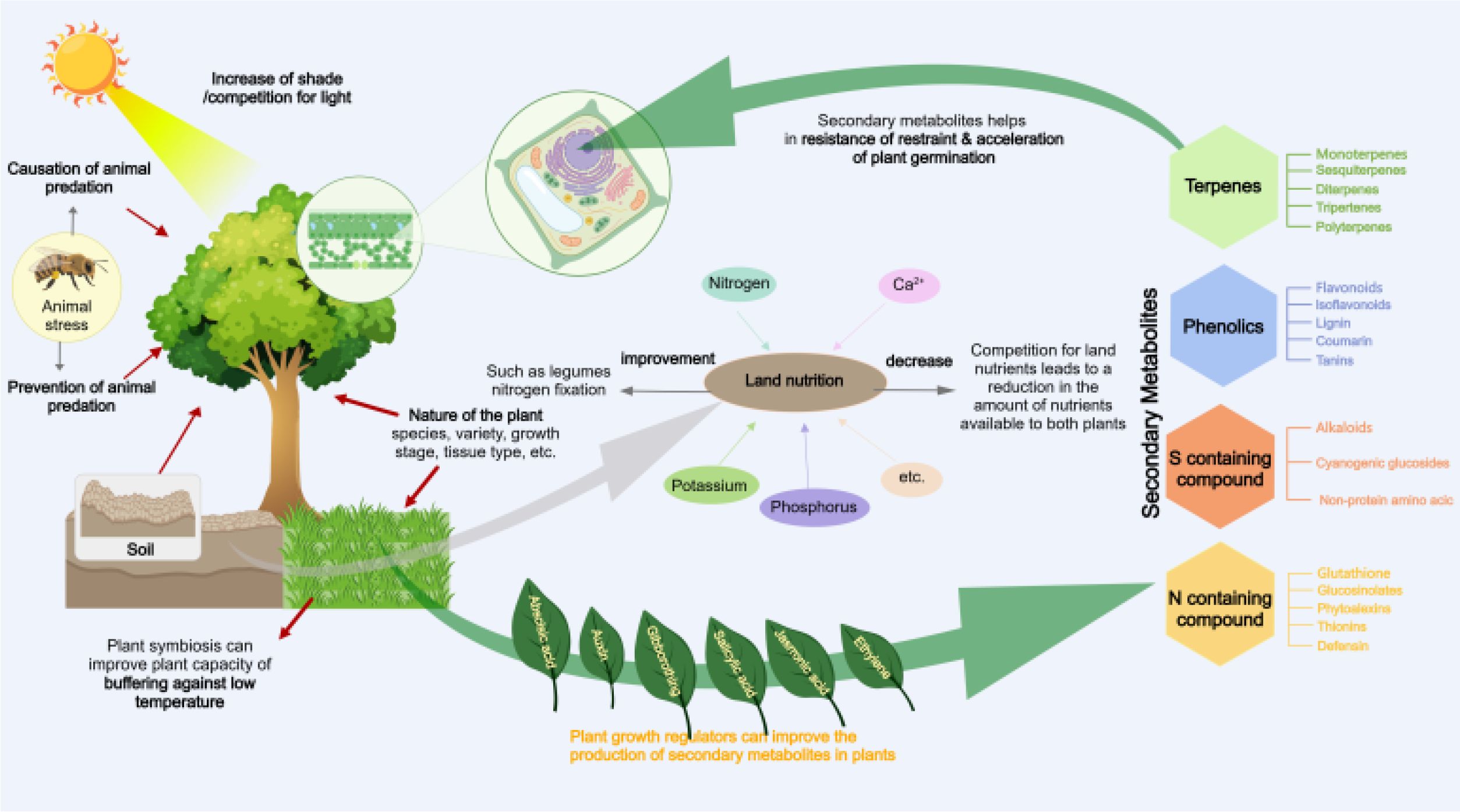
Rhizobia are bacteria that mainly symbiotically form nodules with the roots or stems of leguminous plants and are capable of biological nitrogen fixation (Peix et al., 2015). They fix free nitrogen into bound nitrogen compounds and retain them in the soil (Coskun et al., 2017), reducing atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia and providing them to their host plants for protein synthesis (Wenxin and Wenfeng, 2004). Rhizobia can also draw essential nutrients for growth and development from their host plants (Herridge et al., 2008). This mutually beneficial symbiosis increases crop yields, provides a significant amount of nitrogen fertilizer for subsequent crops, reduces the use of synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, and improves soil nutrient utilization efficiency, offering significant ecological and economic value.
On this basis, some studies have also found that intercropping corn (Zea mays L.) and soybean (Glycine max (L.) not only facilitates the transfer of nitrogen, but also promotes the absorption and utilization of nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium, as well as biological yield. The latter two are higher than intercropping, showing obvious intercropping advantages (Wenxin and Wenfeng, 2004).
In the arid and semi-arid regions of western China, to protect farmland soil and maintain a green ecological environment, policies of returning farmland to forests or grasslands are implemented (Trivedi et al., 2020). The bean–cereal intercropping system can increase nitrogen fertilizer for the soil, not only saving costs but also improving soil conditions, which is a feasible approach to reshape the ecological environment. The mechanism by which legumes enhance soil conditions and reshape the green ecological environment is illustrated in Figure 4.
However, three points should be noted during the implementation process: Firstly, some rhizobia can be symbiotically associated with a category of leguminous plants, while others can only coexist with a specific legume; Secondly, it is necessary to consider the interactions between rhizosphere microorganisms in plants, as nodulation is initiated by soil microorganisms infecting the roots, thus producing a series of hormones that promote or reduce plant growth, and directly acting on the plants to exert their maximum effect; Thirdly, the influence of abiotic factors must be considered, thus selecting rhizobia based on different ecological areas, climate environments, and soil types (Wenxin and Wenfeng, 2004).
5.1.2 Analysis on the application of sesame in the prevention and control of rice pests
The substances secreted by many parts of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) have allelopathic effects capable of preventing and controlling pests and diseases, establishing symbiotic relationships with many crops. For instance, the use of sesame stems on osmanthus trees (Osmanthus fragrans Lour.) is documented in Wu Lei Xiang Gan Zhi (Records of Mutual Sensation Among Different Categories): “For borer infestation in osmanthus, tie and hang sesame stems with husks on the tree (Su, 1937)”; Sesame firewood on trees—“Hanging sesame wood on trees prevents raincoat worms”; For sesame’s application on cinnamon trees (Osmanthus fragrans Lour.), Nong Pu Liu Shu states, “For borer damage, take sesame stems and hang them among the trees to kill various insects (Wang and Wang, 2021).” It is evident that whether for osmanthus or cinnamon trees, the unique aroma and secretions of sesame can achieve a deworming effect.
Modern research has shown that sesame is particularly effective in controlling pest infestations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). On one hand, the decomposition of sesame stalks produces substances like phenols, alkaloids, and sesame toxins, all of which have a certain inhibitory effect on the pathogen of rice sheath blight and parasitic wasps during the egg stage of rice planthoppers, and have a certain toxic effect on some mollusks such as the golden apple snail; On the other hand, the return of sesame to the fields increases the potassium content in the soil, which when absorbed and utilized by rice, enhances the insect resistance of rice plant tissues (Pingyang, 2012).
5.1.3 Analysis on the application of engendering relationships in the intercropping system of crops and halophytes on saline–alkali land
Ancient books have recorded that the combination of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) and alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) is beneficial for the growth of alfalfa. Nong Sang Ji Ya: “The four seasons should be recorded. If alfalfa is not in the field, it can be planted with wheat (Si, 1982)”. There are also relevant records in Nong Pu Bian Lan, San Nong Ji, and Yang Yu Yue Ling. The ancients believed that the combination of buckwheat and alfalfa benefited the growth of alfalfa by promoting its rooting. As stated in Nong Pu Bian Lan, “When planting buckwheat, alfalfa takes root when cutting buckwheat (Yizeng Ding, 1957).”; also in San Nong Ji, “In summer, alfalfa seeds are harvested, mixed with buckwheat, and buckwheat is cut off to promote the growth of alfalfa (Zhang, 1989).”; and as mentioned in Yang Yu Yue Ling, “Alfalfa seeds are taken once a month and planted together with buckwheat. The buckwheat is cut off and the alfalfa roots takes root (Dai, 1956).”
There are two explanations for the increased yield when intercropping buckwheat and alfalfa. One is the improvement of soil salinization. The intercropping of the two can reduce soil salinization, improve soil structure and ion balance, and thus increase yield, in fact, the planting method of intercropping buckwheat and alfalfa has been adopted in the arid areas of northwest China to improve soil salinization. Currently, research has found that its feasible mechanisms include improving soil physical properties, organic acid exudation, and decomposition of dead branches, leaves, and roots. In addition to buckwheat and alfalfa, cotton/Suaeda salsa intercropping (CSSI) and cotton/alfalfa inter cropping (CAI) can also improve soil salinization (Gao et al., 2022). Research has shown that intercropping the two achieved high yields in the first year of planting, which is 2.17 times higher than monoculture control. In the second year, the yield increased by 41.7% compared with that of monoculture control, while alfalfa significantly increased root growth by 26–175%. Changes in root morphology or distribution in intercropping systems are effective means to increase phosphorus absorption and yield, and intercropping inoculation has a significant effect on the sustained increase of alfalfa yield (Zhang et al., 2024).
5.1.4 Application analysis of the engendering relationship between mulberry and other plants
The intercropping between mulberry (Morus alba L.) and beans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) can improve soil salinization and promote more vigorous plant growth. Qi Min Yao Shu, “Mung beans and adzuki beans are often dug and planted under the mulberry tree. Both types of beans are good, nourishing, and beneficial to the mulberry (Jia, 1875).” Fen Men Suo Sui Lu, “A mulberry tree is about five feet tall. Mulberry trees are often dug with a hoe, and mung beans and adzuki beans are planted. Do not pick the leaves in the two years after planting. Leaves should be picked when the trunk is as thick as an arm (Hua, 2009).” Mulberry trees can promote the growth of mung beans and adzuki beans, while also making the stems and roots of legumes more robust. Fan Sheng Zhi Shu, “When millet and mulberry were planted together with three liters per mu (Mu is a municipal unit of land area in China, one mu is about 666.667 square meters.), both millet and mulberry could grow, and the excess mulberry was removed, and the sparsity was adjusted. Wait for the millet to mature and harvest (Fan, 2004).”
In fact, research from Li Xu et al. has confirmed the soil improvement effect of mulberry bean intercropping (Li et al., 2016). The diversity and composition of bacterial communities in intercropped plants growing in saline–alkali soil vary between monoculture and intercropping samples. Some beneficial plant rhizosphere bacteria (phosphate solubilizing bacteria) are more abundant in the soil samples obtained from intercropping, and the pH value of intercropped soil is significantly reduced compared to the control soil. Therefore, from a biological perspective, intercropping mulberry trees and soybean is a good strategy for improving saline–alkali soil.
In addition, there are relevant records showing that the co-cultivation of mulberry and millet is also mutually beneficial. Nong Sang Ji Yao, “Turnip (Brassica rapa L.) seeds are often sown just one step away from the mulberry tree. After harvest, the pigs are let out to eat them, and the land becomes very soft and easy to cultivate (Si, 1982).” The turnip seeds are planted around the tree and then returned to the field, greatly improving the soil environment. Nong Sang Ji Yao, “You can plant millet in mulberry fields, it is beneficial for mulberries”. All this indicates that mulberry–millet intercropping is beneficial for the growth of mulberry trees (Si, 1982).
Tall mulberry trees can provide a suitable environment for crops that prefer shade, such as tea. Nong Sang Ji Yao, “Tea is afraid of sunlight, so it should be planted under a mulberry tree or in the shade of bamboo (Si, 1982).” The roots of mulberry trees are deep, while the roots of ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich.) are only on the surface. The two combined can fully utilize land resources, and ramie metabolites can also nourish mulberry trees. Chen Fu Nong Shu, “If the mulberry garden is close to home, you can build a fence, plant the mulberry trees sparsely, make the ridges wider, and plant ramie all over the bottom. When manure is applied to the ramie, the mulberry tree is also nourished, which kills two birds with one stone. The mulberry roots are deep in soil and the ramie roots are shallow. They don’t harm each other and the benefits are doubled (Chen and Qiyu, 1981).”
The effectiveness of the ancient intercropping method of mulberry–tea has been validated in contemporary research. Firstly, intercropping mulberry and tea greatly improves land use efficiency and economic output. Planting experiments have shown that the production value of three different planting densities of mulberry–tea intercropping gardens are all higher than those of ordinary dense-planting mulberry and tea gardens (Zhenggang and Maozi, 2017). In addition, a more scientific intercropping model that combines contemporary agricultural research is also being completed, which involves factors such as planting density, crown cultivation, fertilization, pest control, and other aspects, allowing ancient mulberry tea intercropping to still play a role in contemporary agricultural production (Chunzhun et al., 2001). How to improve soil pollution and pesticide residues caused by mulberry–tea intercropping is still a direction that needs to be further explored for future green and sustainable agriculture.
5.2 Restraining relationships
5.2.1 Application analysis of the restraining relationship between sesame and barnyard grass
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.), originally known as “Hu Ma” and referred to as “Jiao Ma”, “You Ma”, “Zhi Ma”, etc., is one of the widely cultivated oilseed crops in China and has an inhibitory effect on the growth of some weeds. Wang Zhen’s Agricultural Book states, “In today’s Han Dynasty, in the Mian, Huai, and Ying regions, it’s common to open up new lands for cultivation with planting crops like sesame, which can lead to abundant harvests, filling up the granaries and quickly enriching the farmers.” (Wang, 2009) This indicates that the ancients often planted sesame to reclaim wastelands, making the soil fertile for the subsequent planting of grains, thus achieving great harvests. San Nong Ji (Chronicles of Agriculture) mentioned, “Planting sesame seeds for one season can cause the grass roots to rot (Zhang, 1989).” Nong Pu Bian Lan (Convenient Manual of Agriculture) adds, “Planting sesame for one year rots the weed roots. Planting grains afterward, then, will encounter no problem of weeds (Dong, 2018).” This shows that sesame seeds can cause the roots of weeds to decay, thereby eliminating the issue of weeds when planting grains later. In addition to grains, planting sesame can also increase the yield of mulberry leaves, as Nong Sang Ji Yao (Essential Techniques for Agriculture and Sericulture) notes: “Planting mung beans, black beans, sesame, melons, and taro can produce lush mulberry trees, with leaves increasing by two to three times the next year. Planting millet can also have the same effect (Si, 1982).” It can also facilitate the survival of fir trees, as San Nong Ji suggests, “On barren hills and ridges, first plant sesame seeds for two seasons. In the following year, during the Grain in Ear period (Mangzhong, one of the 24 solar terms.), use a pointed stake to make holes without turning over the original soil, and insert tender fir seedlings next to the fir. Firmly pack the soil around, and space them three to five feet apart in rows. The densely packed rows tend to make fir thrive easier (Zhang, 1989).”
Sesame has a certain preventive and therapeutic effect on weeds. The secretions of its roots, the decomposition substances of plant bodies such as leaves, the volatiles from its above-ground parts, or rainwater leaching substances can affect or poison other substances. The secretions and toxins produced by decomposition, most commonly phenolic and terpenoid compounds (Weilian, 1990), have a inhibitory effect on many dryland weeds such as Cyperus rotundus L., Imperata cylindrica (L.) P. Beauv., and Ageratum conyzoides L., etc (Wang et al., 2008). During growth, it can inhibit root growth, reduce root length and seedling height, though the allelopathic weed-suppressing effect of different sesame varieties varies greatly (Li et al., 2016). In addition, sesame stalks are rich in nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and returning them to the field can improve soil fertility (Li and Xinglu, 1994), which has a positive effect on balancing and enhancing soil fertility.
The inhibitory effect of sesame recorded in ancient literature has enormous potential application value. The allelopathic effect of sesame can be widely used as an herbicide, with the sesame secretions and toxins produced by decomposition directly used as natural herbicides (Pereira et al., 2015). Similarly, natural compounds such as nicotine and pyrethroids have been used in plant protection for a long time (Ren and Chong, 2023). What’s more, for plants with continuous cropping obstacles, they can be rotated with sesame to improve soil environment (Lyu et al., 2023) (Wacal et al., 2019). Interplanting with sesame can improve crop yield and land use of the planting system (Saad et al., 2022) (Meena et al., 2009). In addition, genetic engineering breeding is also a current research hotspot, which can be used to screen for weed resistant genes in sesame, thus cultivating new varieties of crops with weed and fungal pathogens resistance.
5.2.2 Application analysis of the restraining relationship between osmanthus and other plants
Ancient literature records that Osmanthus (Osmanthus fragrans Lour.) has a strong inhibitory effect on the plants and trees growing around it. Similar records have been found in ancient books such as Lü shi Chunqiu, Mengxi Bitan, Tan Yuan Ji, Fenmen Suosuilu, Lei Gong Pao Zhi Lun, and Ben Cao Cong Xin. The relevant records span from the Spring and Autumn Period to the Ming Dynasty. From the literature, it shows that ancient people mostly used the restraining factors of Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Lour., Cinnamomum wilsonii Gamble, etc.) and weeds to control weeds.
According to the Tongzhi, Lü shi Chunqiu states that there are no trivial trees and arbor under the Osmanthus. It was also said in Ge Wu Cu Tan that “the Osmanthus flowers are shredded into pieces and mixed into brick steps, preventing weeds to grow” (Shi, 1995). Yang Wengong’s Tanyuan recorded that “Li Yu, the last emperor of the Southern Tang Dynasty, expressed concern over the proliferation of weeds in the vicinity of the Qingshu Pavilion, and Xu Kai ordered for pieces of the Osmanthus to be stuffed into the cracks of the bricks, thus killing the weeds.” Later on, there were similar statements in the Diao Xie Lei Bian (Zhenyu, 1990) and many other flowers charts and agricultural books that introduce the people’s experience in using Osmanthus fragransto control the growth of weeds. Ancient scientists also discussed the mechanism by which Osmanthus trees inhibit the growth of other plants. Wu Yiluo’s Ben Cao Cong Xin records the phenomenon of “wood withering after coming in contact with the Osmanthus; stuff a piece of the Osmanthus tree into a wood and it will die (Li and Xu, 2017).” Xu Kai believes that it is because the Osmanthus tree attracts pests that affect the growth of other plants, and “because of its spicy and stimulating properties (Hua, 2009).” In his book Lei Gong Pao Zhi Lun, Lei Gong believed that “a nail is too small to maim a great tree, it is only because of its restricting property (Xue, 1985).” It was believed that it is the nature of the Osmanthus tree itself that restricted the growth of other plants.
In recent years, studies have reported that various substances extracted from Osmanthus fragrans (Thunb.) Lour. have allelopathic effects. The allelopathic substances produced by the Osmanthus flower may be released through the process of leaf decomposition into its rhizosphere soil. It accumulates in the soil and inhibits the growth of neighboring competing plants, providing a competitive advantage for its species (Shi, 1995). The leaf extract of Sassafras tzumu (Hemsl.) Hemsl., which belongs to the Lauraceae family, has also been experimentally proven to significantly reduce the seed germination and seedling growth of Brassica rapa chinensis L (Wan et al., 2017). Extracts of other Osmanthus are also being proven to inhibit the growth of other plants (Cavalieri and Caporali, 2010; Daba et al., 2021). These studies confirm the inhibitory effects of the Osmanthus on other plants as recorded in ancient literature, suggesting to modern researchers that Osmanthus and other lauraceae plants, especially their leaf extracts, may contain allelopathic substances that may be useful for weed management in certain agricultural environments. This will help reduce the dependency on commercial herbicides in the development of sustainable agricultural systems.
6 Perspectives and outlooks
At present, diversified intercropping systems have been used to control diseases and improve field productivity. Ancient literature has also recorded many phenomena of mutual restraining in the intercropping of crops. In future sustainable agriculture, utilizing the engendering interaction between plants and avoiding the restraining interaction between crops may also become a research direction for intercropping systems.
Overall, the concept of plant engenderment and restraint in ancient China refers to the promoting or inhibiting effect of one plant on the growth and development of another. The modern study of allelopathy has become a hot topic in the fields of botany, ecology, agriculture, soil science, horticulture, and more in recent years. The concepts of the two have abundant similarities, but they are still not completely the same. The ancient Chinese ethnobotany focused more on observing the phenomenon of promotion or inhibition between plants, explained its mechanism in a relatively simple way in terms of the influence of external light, insect damage, and so on. On the other hand, the modern concept of allelopathy focuses more on the chemical microscopic explanation of the engendering and restricting relationship between plants, while also taking the impact of the environment and ecosystem into account.
Traditional agriculture in China is very different from that in the West. The ancient Chinese did not strive to conquer nature or study and understand it through analysis. Their goal is to “establish agreements” with nature, achieving and maintaining harmony. Many modern scholars have also aimed at this kind of wisdom, combining subjective and objective aspects into one, guiding people to harmonize with nature. Building on the foundation of the ancients, the research on allelopathy in modern China has already advanced in great lengths. In recent years, scholars have integrated allelopathy with technologies from genomics, ecology, chemistry, and other fields, and have made a series of breakthroughs. Standing at this current juncture and looking back at the research of the ancient Chinese, the records of mutual engenderment and restraint look back at us from distant ancient times, telling us how far this scientific journey has come and where the possible direction of global sustainability in the future may be.
Faced with the current complex and severe ecological, environmental problems, Western scholars actively explore the establishment of a balanced relationship between man and nature by ways of critical thinking and self-reflection, mainly as a part of the research attributes of ecological ethics. However, the way in which Chinese ancestors observed and followed nature has allowed them to coexist with it with a gentle attitude. At a time where environmental crises are rapidly growing and maintaining farmland and foods is facing challenges, the ancient Chinese’s experience with mutual engenderment and restraint between plants may provide a unique Chinese solution for crop pest control, weed control, crop yield increase, and the development of natural botany chemicals.
Author contributions
BL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. YD: Investigation, Writing – original draft. HW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. XP: Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by China Environmental Protection Foundation “Green Mountain Public Nature Protection Action” funded project “Under the Forest American Ginseng Ecological Planting Model Integrated Optimization and Demonstration Promotion Project” (CEPFQS202169-19).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fagro.2025.1574846/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table 1 | Ethnobotanical Interactions Documentation compiles all the130 systematically extracted records of plant “mutual engenderment and restraint” relationships from classical Chinese agricultural compendia.
Supplementary Table 2 | Information was extracted from ancient literature research, including all ancient literature and related modern literature, from which the author extracted information about the crosstalk between plants.
Supplementary Table 3 | Chinese traditional culture concept in English comparison glossary table (Based on WHO International Standard Terminologies on Traditional Medicine in the Western Pacific Region).
References
Ayilara M. S., Adeleke B. S., Akinola S. A., Fayose C. A., Adeyemi U. T., Gbadegesin L. A., et al. (2023). Biopesticides as a promising alternative to synthetic pesticides: A case for microbial pesticides, phytopesticides, and nanobiopesticides. Front. IN Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1040901
Bren d’Amour C., Reitsma F., Baiocchi G., Barthel S., Güneralp B., Erb K.-H., et al. (2017). Future urban land expansion and implications for global croplands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 8939–8944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1606036114
Cavalieri A., Caporali F. (2010). Effects of essential oils of cinnamon, lavender and peppermint on germination of Mediterranean weeds. Allelo. J. 25, 441–451.
Cheema Z. A., Farooq M., Wahid A. (2007). Allelopathy–Current Trends and Future Applications (Faisalabad, Pakistan: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, University of Agriculture).
Cheng F., Cheng Z. H. (2015). Research progress on the use of plant allelopathy in agriculture and the physiological and ecological mechanisms of allelopathy. Front. IN Plant Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01020
Chunzhun J., Meiqiu M., Youxiang X. (2001). Mulberry tea intercropping management technology. Silkw. Tea Newslett. 02, 17.
Coskun D., Britto D. T., Shi W., Kronzucker H. J. (2017). How plant root exudates shape the nitrogen cycle. Trends Plant Sci. 22, 661–673. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2017.05.004
Daba A., Berecha G., Tadesse M. (2021). Herbicidal effects of essential oils from selected plant species against common coffee (Coffea arabica L.) weed species. Acta Physiol. Plant. 43, 162. doi: 10.1007/s11738-021-03337-8
Dong A. X. (2018). Collection of Chinese Agricultural and Forestry Literature 25 (Beijing: Xueyuan Publishing House).
Fu S., Xi Y., Zhao P., Liang Y., Song X., Chang H., et al. (2020) Evaluation of the diversity and potential growth-promoting properties of culturable endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in Robinia pseudoacacia (Sophora japonica). Microbiol. Bull. 47, 2458–2470.
Gao Y., Bi Y., Ma S., Zhang Y., Guo Y., Zhou Y., et al. (2022). Yields of buckwheat and alfalfa in an intercropping system inoculated with dark septate endophytes in a coal mining subsidence dryland area. Agronomy 12, 2860. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12112860
Herridge D. F., Peoples M. B., Boddey R. M. (2008). Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s11104-008-9668-3
Ho S. W., Wen Y. S. (1992). The phallic effect and its application. Plant Physiol. Newslett. 28, 81–87.
Jabran K., Cheema Z. A., Farooq M., Hussain M. (2010). Lower doses of pendimethalin mixed with allelopathic crop water extracts for weed management in canola (Brassica napus). Int. J. Agric. Biol. 12, 335–340.
Jianling L. (2011). An introduction to the phylogenetic relationship between plants and its relevance. Inner Mongol. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2, 98–98.
Kennedy J., Hurtt G. C., Liang X. Z., Chini L., Ma L. (2023). Changing cropland in changing climates: quantifying two decades of global cropland changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 18. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/acca97
Khawar J., Muhammad F., Mubshir H., Muhammad A. (2010). Wild oat (Avena fatua L.) and canary grass (Phalaris minor ritz.) management through allelopathy. J. Plant Prot. Res. 50, 41–44.
Kong C.-H., Zhang S.-Z., Li Y.-H., Xia Z.-C., Yang X.-F., Meiners S. J., et al. (2018). Plant neighbor detection and allelochemical response are driven by root-secreted signaling chemicals. Nat. Commun. 9, 3867. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06429-1
Li Q., Liu Z., Li H. (2016). Evaluation of the chemosensitizing effect of sesame on barnyard grass and its ecological value in large fields. Anhui Agric. Sci. 44, 73–77+80.
Li X., Sun M., Zhang H., Xu N., Sun G. (2016). Use of mulberry–soybean intercropping in salt–alkali soil impacts the diversity of the soil bacterial community. Microb. Biotechnol. 9, 293–304. doi: 10.1111/mbt2.2016.9.issue-3
Li W., Xinglu L. (1994). Study on the effect of sesame straw returned to the field to control rice pests and weeds and to improve soil fertility. J. Guangxi Agric. Univ. 03, 228–232.
Li J., Zhang Q., Hu W., Yang X., He H. (2015). Stability of phenolic acids and the effect on weed control activity. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 58, 919–926. doi: 10.1007/s13765-015-0124-9
Liu Y. H., Zeng R. S., An M., Mallik A. U., Luo S. M. (2008). Autotoxicity in agriculture and forestry. Allelo. Sustain. Agric. Forest., 283–301.
Lyu F. J., Zhang W. M., Wang R. Q., Lyu R., Lin H. X., Zhang Z. H., et al. (2023). Rhizosphere bacterial community composition was significantly affected by continuous cropping but not by sesame genotype. RHIZOSPHERE 27. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2023.100750
Meena S. L., Shamsudheen M., Dayal D. (2009). Productivity of clusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) and sesame (Sesamum indicum) intercropping system under different row ratio and nutrient management in arid region. Indian J. OF Agric. Sci. 79, 901–905.
Meiners S. J., Kong C.-H., Ladwig L. M., Pisula N. L., Lang K. A. (2012). Developing an ecological context for allelopathy. Plant Ecol. 213, 1221–1227. doi: 10.1007/s11258-012-0078-5
Molisch H. (1938). Der Einfluss einer Pflanze auf die Andere, Allelopathie. Nature 141, 493–493. doi: 10.1038/141493a0
Niemeyer H. M. (2009). Hydroxamic acids derived from 2-hydroxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one: key defense chemicals of cereals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 1677–1696. doi: 10.1021/jf8034034
Peix A., Ramírez-Bahena M. H., Velázquez E., Bedmar E. J. (2015). Bacterial associations with legumes. Crit. Rev. IN Plant Sci. 34, 17–42. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2014.897899
Pereira V. D., Anese S., Imatomi M., Grisi P. U., Canedo E. M., Gualtieri S. C. J., et al. (2015). Allelopathic potential of Serjania lethalis: Evidence from esamum indicu. Acta Biol. Colombiana 20, 31–37.
Pingyang Z. (2012). Ecological functions of flowering plants in enhancing biological control of key natural enemies on rice planthopper (Zhejiang China: Zhejiang Normal University).
Pravalie R., Patriche C., Borrelli P., Panagos P., Rosca B., Dumitrascu M., et al. (2021). Arable lands under the pressure of multiple land degradation processes. A global perspective. Environ. Res. 194.
Putnam A. R., Duke W. B. (1978). Allelopathy in agroecosystems. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 16, 431–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.16.090178.002243
Qing Z., Zhongyu S., Long Y., Mei W. (2016). The practice of utilizing plant auxiliary effects in our history of ecological agriculture. Chin. J. Ecol. Agric. 24, 1585–1597.
Raza T., Yahya Khan M., Mahmood Nadeem S., Imran S., Nazir Qureshi K., Naeem Mushtaq M., et al (2021). Biological management of selected weeds of wheat through co-application of allelopathic rhizobacteria and sorghum extract. Biol. Control. 164, 104775
Ren L. Y., Chong J. H. (2023). Repellency and Toxicity of Eight Plant Extracts against the Western Flower Thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis. Appl. SCIENCES-BASEL 13. doi: 10.3390/app13031608
Saad A. H., El Naim A. M., Ahmed A. A., Ibrahim K. A., Islam M. S., Al-Qthanin R. N., et al. (2022). Response of sesame to intercropping with groundnut and cowpea. Commun. IN Soil Sci. AND Plant Anal. 53, 2285–2296. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2022.2071438
Soderquist C. J. (1973). Juglone and allelopathy. J. Chem. Educ. 50, 782–783. doi: 10.1021/ed050p782
Sylvan W., Yu Y. T., Sun H. (Eds.) (1987). Feeding a Billion: Frontiers of Chinese Agriculture (Michigan: Michigan State University Press).
Trivedi P., Leach J. E., Tringe S. G., Sa T., Singh B. K. (2020). Plant–microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 18, 607–621. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0412-1
Wacal C., Ogata N., Sasagawa D., Handa T., Basalirwa D., Acidri R., et al. (2019). Seed yield, crude protein and mineral nutrient contents of sesame during a two-year continuous cropping on upland field converted from a paddy. Field Crops Res. 240, 125–133. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.06.004
Wan Z.-g., Zhu C. L., Sun H. G., Wan X. F., Xiong J.-L. (2017). Allelopathic potential of Sassafras tzumu (Lauraceae) on seed germination and seedling growth of Brassica rapa chinensis L. Allelo. J. 41, 25–36. doi: 10.26651/2017-41-1-1081
Wang L. M., Yunping X., Yueliang R., Xiaowen Y., Hongying Z. (2008). Chemosensory effects of sesame and its research progress. Crops Mag. 04, 15–18.
Wang X., Wang R. (2021). Ancient agricultural technology department volume 21 Rich curiosity book 2 farm field six books national vein people day. (Beijing: Beijing Yanshan Publishing House).
Weilian L. (1990). Studies on the biochemical phases of sesame and the effect of sesame straw on field return. Farm. Cultiv. 06, 47–50.
Wenxin C., Wenfeng C. (2004). Reducing chemical nitrogen fertilizers by utilizing biological nitrogen fixation. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Herald 6, 3–6.
Weston L. A., Alsaadawi I. S., Baerson S. R. (2013). Sorghum allelopathy-from ecosystem to molecule. J. Chem. Ecol. 39, 142–153. doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0245-8
Willis R. J. (1985). The historical bases of the concept of allelopathy. J. Hist. Biol. 18, 71–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00127958
Yan Y., Zhao J., Deng H., Luo Q. (2010). Predicting China’s cultivated land resources and supporting capacity in the twenty-first century. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. June 2006, 229–241.
Yin M. P. (2023). Study on the Editing Practice of Ancient Chinese Agricultural Books (Beijing: China Social Science Publishing House).
Yu L., Fan X., Ru H. (1991). The Classic of Tea Xuanhe Beiyuan Tribute Tea Record The Essential Record of Tea Products (Beijing: China Book Council).
Zhang S. Z., Li Y. H., Kong C. H., Xu X. H. (2016). Interference of allelopathic wheat with different weeds. Pest Manag. Sci. 72, 172–178. doi: 10.1002/ps.2016.72.issue-1
Zhang W.-P., Surigaoge S., Yang H., Yu R.-P., Wu J.-P., Xing Y., et al. (2024). Diversified cropping systems with complementary root growth strategies improve crop adaptation to and remediation of hostile soils. Plant Soil. 26 (1), 4–17. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06464-y
Zhaoji Z. (1998). History of Chinese Plant Physiology (Guangzhou: Guangdong Higher Education Press).
Zhenggang W., Maozi Q. (2017). Briefing on mulberry and tea intercropping trials. North. Sericult. 38, 12–14.
Keywords: ancient Chinese document, allelopathy, modern agriculture, sustainable development, ecological sustainability, cultural heritage, plant–plant interaction
Citation: Li B, Jiao Z, Dong Y, Wu H, Peng X and Zhang Z (2025) Ancient insights into plant allelopathy and potential applications: new perspectives for sustainable development. Front. Agron. 7:1574846. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1574846
Received: 11 February 2025; Accepted: 31 March 2025;
Published: 02 May 2025.
Edited by:
Matthias Samuel Geck, World Agroforestry Center, KenyaReviewed by:
Yasir Iftikhar, University of Sargodha, PakistanMargot Schulz, University of Bonn, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Li, Jiao, Dong, Wu, Peng and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zilong Zhang, emhhbmd6aWxvbmc3NkAxNjMuY29t
 Bing Li
Bing Li Ziheng Jiao1
Ziheng Jiao1 Zilong Zhang
Zilong Zhang