- Department of Entomology, University of Georgia, Griffin, GA, United States
Systena frontalis (F) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) is a serious polyphagous pest in containerized ornamental nurseries in the central, mid-west, and eastern United States. Adults feed on plant foliage, causing shothole damage, and the affected plants are rarely salable. We studied the exogenous application of double-standard RNA (dsRNA) on the adult S. frontalis by targeting three vATPase subunit genes (A, D, and E). To evaluate RNAi efficacy, we measured adult feeding damage, survival, and gene expression levels using quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). Six concentrations-10, 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 µg/cm2 of dsRNA were applied to panicled hydrangea leaves. The dsRNA was designed to inhibit the expression of three vATPase genes, A, D, and E subunits, and assessed how different amounts of cognate dsRNA affect the silencing of these genes. Adult S. frontalis feeding damage was significantly reduced with dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E at 3 d post-exposure. Up to 50% reduction in feeding damage was observed at 70 µg per cm2. The survival of adult S. frontalis was not reduced after ingestion of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E treatment. When the pre-exposed adult S. frontalis to dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E was transferred to nontreated foliage for 1 d, a significant reduction in feeding damage was observed across different tested concentrations of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E. A dose-response in the expression of dsRNA was observed in S. frontalis adults exposed to dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E treated foliage after 4 d. The results suggest that these three RNAi products can potentially manage S. frontalis in ornamental nurseries.
1 Introduction
Systena frontalis (F) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) is a serious pest on ornamental plants in containerized nurseries in the Mid-West, central and eastern USA (Joseph et al., 2021; Arshad et al., 2023). As a polyphagous pest, S. frontalis causes feeding damage to ornamental plants across multiple families. Major host plants include panicled hydrangea [Hydrangea paniculata Siebold (Hydrangeaceae)], Virginia sweetspire [Itea virginica L. (Iteaceae)], weigelas [Weigela spp. (Caprifoliaceae)], roses [Rosa sp. (Rosaceae)], and azaleas [Rhododendron spp. (Ericaceae)] (Joseph et al., 2021; Arshad et al., 2023). In the USA, ornamental deciduous shrubs, including hydrangeas, roses, and weigelas, were valued at $675 million USD (wholesale and retail) in 2017 (USDA NASS, 2019). The economic damage to plants is mostly caused by adults feeding on the foliage (Arshad et al., 2023).
Systena frontalis adults feed on the plant foliage and cause damage as shotholes and skeletonization (Joseph and Hudson, 2020). The affected plants are rarely marketed. Instead, they are maintained in the nursery with additional input until they are ready for sale in the later market window. These additional maintenance costs, including labor, agricultural input, and equipment repairs, account for the reduced profit in ornamental nurseries as they reduce the profitability (Joseph et al., 2021; Arshad et al., 2023). Females of S. frontalis oviposit in the soil (Guédot and McIntosh, 2023) or growing media (Lauderdale, 2017) and overwinter in the egg stage (Jaffe et al., 2021). The larvae develop in the soil or growing media, likely feeding on roots. They pupate in the same soil or growing media and emerge as adults (Arshad et al., 2023). Adults are small, shiny, oval-shaped beetles, about 0.2 inches in length, with metallic-black colored bodies and red-colored heads, which is a unique identification character that distinguishes these beetles from other similar species. Females are slightly larger than males. A pair of light-brown serrate antennae originates below the eyes, with dark-brown distal segments. On the last pair of legs, the femur is wider and swollen, which enables S. frontalis to jump. Adults are active during the growing season, undergoing 1-3 generations depending on the region in the USA (Arshad et al., 2023).
Among many insecticides evaluated to mitigate the damage, foliar applications of tetraniliprole, cyclaniliprole, sulfoxaflor + spinetoram, isocycloseram, and carbaryl were the most effective on S. frontalis adults (Lane and Del Pozo-Valdivia, 2022; Joseph, 2023a; Arshad and Joseph, 2024). Similarly, growing media drench application with tetraniliprole, cyclaniliprole, sulfoxaflor + spinetoram, and isocycloseram (Joseph and Pozo-Valdivia, 2023; Joseph, 2023b), as well as top dressing, the application of granular insecticide to the soil surface around the base of the plant with imidacloprid effectively reduced S. frontalis adult emergence and damage on containerized plants (Lauderdale, 2021). Despite the availability of some effective insecticides, there is a pressing need for additional control options with new modes of action to provide season-long protection against S. frontalis in ornamental nurseries. Relying on a limited number of chemical classes increases the risk of resistance development, making it vital for stakeholders to rotate active ingredients with different mechanisms of action. Although repeated foliar applications at short intervals are often recommended to maintain residual activity (ACES, 2020; Arshad and Joseph, 2024), many insecticide labels restrict the number of applications per season due to regulatory limits on the amount of active ingredient allowed per unit area (Lauderdale, 2021). These constraints, along with the labor and cost associated with frequent applications, emphasize the urgent need for innovative, sustainable pest management strategies. Targeted approaches, such as RNA interference (RNAi), offer a promising alternative by enabling species-specific gene silencing, reducing non-target effects, and potentially providing longer-lasting control with fewer applications.
RNA interference (RNAi) is a gene-silencing mechanism conserved across many eukaryotes, including insects. It is a natural defense system against viruses and mobile genetic elements, such as transposons (Whyard et al., 2009). RNAi is triggered when double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is recognized and processed by the enzyme Dicer into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). These siRNAs then guide a protein complex to degrade or suppress specific messenger RNA (mRNA), thereby silencing the corresponding gene (Palli, 2014). RNAi technology is widely studied on various insect Orders, including Orthoptera, Dictyoptera, Isoptera, Hemiptera, Coleoptera, Neuroptera, Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Lepidoptera (Tomoyasu et al., 2008; Terenius et al., 2011; Xue et al., 2012; Rinker et al., 2016). It has also been explored as a pest management strategy for many economically important insect pests due to its gene-specific mode of action (Baum et al., 2007). The progress of RNAi as a management tool hinges on developing efficient and reliable production methods and delivery of dsRNA to the target pest (Huvenne and Smagghe, 2010). The demonstration of systemic RNAi following the ingestion of dsRNA was initially established on a free-living nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans Maupas (Chromadorea: Rhabditida). Currently, this technology is being investigated in silencing genes of many insect species (Huvenne and Smagghe, 2010). In most of these initial studies, dsRNA was directly injected into the organism to initiate systemic gene silencing (Palli, 2014; Ramkumar et al., 2021).
Vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (vATPase) is a proton translocating pump present in the internal membranes of all eukaryotic cells (Wieczorek et al., 1999, 2009; Abbas et al., 2020). By hydrolyzing ATP to ADP and phosphate, vATPases transport protons across the cell membrane to generate a membrane potential (Vm) as high as 120 mV (Harvey et al., 2009). The Vm can make the transmembrane movement of Cl− through a Cl− channel and maintain pH gradients in specific organelles, such as Golgi apparatus, endosomes, lysosomes, or secretory vesicles in eukaryotic cells (O’Donnell, 2017). Insect vacuolar ATPase synthase genes have been extensively compared across various insect Orders (Pan et al., 2017). Transcript orthologs of 50 selected genes were analyzed in Western corn rootworm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera (DIABVI) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) diet-based RNAi bioassays; 21 and 36 of these RNAi targets showed mortality, and growth inhibition, respectively. The low-dose injection- and diet-based dsRNA assays in T. castaneum and D. v. virgifera, respectively. In the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum Herbst (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), a high concentration produces 80% of larval mortality, and 1.5% of gene expression has been observed after exposure to dsRNA targeting vATPase subunit A (Baum et al., 2007; Knorr et al., 2018). These studies suggest that RNAi-based tools can potentially be developed and used to control adults of other coleopteran pests, including S. frontalis. Systena frontalis is a chrysomelid similar to D. v. virgifera, and vATPase could be targeted using RNAi technology. The A, D, and E subunits of vATPase were selected based on their critical roles in ATP-driven proton transport and intracellular pH regulation. Previous RNAi studies in coleopterans, such as T. castaneum and D. virgifera virgifera, demonstrated that silencing these subunits leads to significant physiological disruption and mortality, making them promising targets for RNAi-based pest control. Thus, the objective of this study was to target three promising vATPase genes in adults of S. frontalis using dsRNA in laboratory settings. We cloned and sequenced the three vATPase genes (vATPase-A, vATPase-D, and vATPase-E) and assessed how different amounts of cognate dsRNAs affect the silencing of the genes. This new knowledge of this target gene will help us develop an effective pest management tool for S. frontalis in ornamental nurseries.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Insects and plants
2.1.1 Insect collection and maintenance
During the summer and fall of 2022 and 2023, Systena frontalis adults were collected using aspirators from Hydrangea paniculata plants at a wholesale nursery in McDuffie County, Georgia, USA. The field-collected adults were transported to the University of Georgia, Griffin Campus, and introduced into 47.5 × 47.5 × 93.0 cm (width × depth × height) cages (BugDorm, BugDorm-4E4590 Insect Rearing Cage, https://shop.bugdorm.com/index.php) placed in a greenhouse. Adults were maintained on 11.4 L container-grown ‘Lime Light’ H. paniculata plants. The beetles were used in laboratory bioassays within 72 hours of collection. The age and sex of the adults were not determined before the bioassays. Greenhouse conditions were maintained at ~30°C, 16:8 h (light:dark) photoperiod, and 75% ± 5% relative humidity. The caged plants used to sustain the beetles were not treated with insecticides and were replaced when foliage damage exceeded 60%.
2.1.2 Plant preparation and leaf disc sourcing
All H. paniculata plants used in this study were grown in containers and obtained from the same commercial nursery. A separate set of H. paniculata plants was maintained without beetles in greenhouse cages to serve as a consistent and insect-free source of foliage for experimental use. These plants were used to prepare leaf discs for dsRNA treatments in the bioassays. Irrigation was provided through overhead sprinklers for 5 minutes every 8 hours, with additional deep watering thrice weekly for 20 minutes.
In 2022 and 2023, S. frontalis adults were collected from H. paniculata plants in a wholesale nursery in Georgia, USA (McDuffie County) during the summer and fall using aspirators. The field-collected S. frontalis adults were transported to the laboratory and temporarily maintained on 11.4 L ‘Lime Light’ H. paniculata container plants in 47.5 × 47.5 × 93.0 cm (width × depth × height) cages (BugDorm, BugDorm-4E4590 Insect Rearing Cage, https://shop.bugdorm.com/index.php) in a greenhouse. When foliage damage exceeded 60%, plants were replaced with fresh ones. The caged H. paniculata plants were not exposed to any insecticides. These field-collected S. frontalis adults were used for various laboratory bioassays within 72 h after introduction. The age and sex of the S. frontalis adults were unknown. These caged plants were maintained in the greenhouse under ~30°C, 16:8 h (light: dark), 75% ± 5% RH. The caged H. paniculata plants were irrigated every 8 h for 5 min using overhead sprinklers in the greenhouse. The plants were irrigated thrice per week for 20 min. The H. paniculata containerized plants were transported from the nursery to the University of Georgia, Griffin Campus, Griffin, Georgia, and temporally maintained in a shade house (50:50; light: shade). These plants served as a food source for field-collected S. frontalis adults in the greenhouse. To ensure continuous host plant availability, additional H. paniculata plants were maintained in greenhouse cages without S. frontalis adults.
2.2 Genomic DNA extraction, total RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
Genomic DNA was isolated from three individual S. frontalis adults, and the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (mtCOI) gene was amplified using a thermocycler (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Francisco, CA, USA) with universal primers for Systena spp. genetic identification (Ellango et al., 2015). Total RNA from five individual S. frontalis adults were extracted using the ISOLATE II RNA Mini Kit (BIOLINE, Wilfong Rd Memphis, Tennessee, USA) after following the protocol from the manufacturer. The purity of the RNA was quantified using NanoDrop™ 2000 (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). A 500 ng aliquot of RNA was used for cDNA synthesis with RevertAid First Strand cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The synthesized cDNA was stored at –20°C until further use.
These steps were essential for identifying and validating the target gene sequences for dsRNA synthesis and ensuring successful downstream gene silencing. High-quality DNA and RNA were critical for accurate amplification, cloning, and transcript quantification, which underscores the effectiveness of RNAi.
2.3 Identification of dsRNA region
The selected genes from S. frontalis were vATPase subunits A, D, and E and were amplified, cloned, and sequenced. The full-length gene sequences were translated from the nucleotide sequence to a protein sequence using a website (https://web.expasy.org/translate). The resulting protein sequences were incorporated into the InterProScan database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence/) to identify the important protein domains and functional sites to characterize their function. The predicted domain was selected and subjected to find the precise small interference RNA (siRNA) regions using SiDirect2.0 software (http://sidirect2.rnai.jp/). The highly predicted siRNA regions were selected for the dsRNA construct. The selected highly predicted siRNA regions were further subjected to the online software “dsCheck” to acquire the Off-target minimized region for synthesizing dsRNA. Using NCBI-BLAST, the chosen dsRNA region was examined for short, perfect nucleotide matches with nontarget species, such as pollinators, predators, and human genomes (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
2.4 In vitro dsRNA synthesis
The template for dsRNA against the respective gene (vATPase A, D, and E; Supplementary Table 1) was amplified from the confirmed plasmids using gene-specific primers having T7 promoter sequence (5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG-3′) at the 5′ of both reverse and forward primers, respectively. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used to create the template for dsRNA synthesis in a reaction volume of 50 μL. The PCR product was resolved in ethidium bromide pre-stained 1.2% agarose gel, and the desired band was excised and eluted with a Nucleospin Extract II kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany). The dsRNA was synthesized by in vitro transcription of 2 μg of the eluted PCR product with T7 RNA Polymerase following manufacturer protocol (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). The in vitro synthesized dsRNA was treated with DNAse I (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) and followed by Phenol: Chloroform purification and ethanol precipitation. Finally, the concentration and integrity of the dsRNA were assessed using NanoDrop and agarose gel electrophoresis, respectively. The synthesized dsRNA was used in the oral feeding bioassay.
2.5 Oral delivery of in vitro synthesized dsRNA
Systena frontalis adults were randomly collected from caged H. paniculata plants in the greenhouse using an aspirator. The collected adults were introduced to 20 mL scintillation vials (Wheaton Science Products, Millville, New Jersey, USA) and were subjected to 3 h starvation before bioassay under laboratory conditions (~25°C, 75% ± 5% RH).
The non-damaged first true leaves of H. paniculata were collected from the greenhouse-caged plants, washed with nuclease-free deionized water in the laboratory, and then dried for 30 min at ~25°C, 75% ± 5% RH in laminar airflow. The synthesized dsRNAs were prepared to 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 µg per cm2 concentrations against the selected target genes. However, 10 and 20 µg per cm2 concentrations of dsvATPase-A were only included in trial 1. For all other trials, trial 2 of dsvATPase-A, and both trials of dsvATPase-D and E, were conducted at 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 µg per cm2 concentrations. The low concentrations, 10 and 20 µg per cm2, were dropped after dsvATPase-A because of poor expression of dsRNA. These concentrations were considered as treatment levels in the bioassays. The dsRNA treatments were applied homogenously on both the abaxial and adaxial sides of leaves using a 0.5 mm paintbrush. The paintbrush was washed thoroughly using RNAse-free water and wiped using Kimwipes® before being used again.
The assay was conducted in a 90 mm plastic Petri dish (Falcon, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, USA). A wet cotton was placed at the bottom of each Petri dish to prevent desiccation, and the cotton was covered with Whatman filter paper (Sigma–Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). A single dsRNA-treated leaf was placed at the center of each dish, and five S. frontalis adults were introduced. Adults were not sexed before introduction. The experimental unit was a Petri dish containing five S. frontalis adults. Each treatment (dsRNA dose) was replicated five times. Each Petri dish included a leaf disc treated with dsRNA. The entire experiment was repeated twice (hereafter mentioned as Trial 1 and Trial 2), with five replicates per treatment for feeding damage and survival assays. After the adult introduction, the Petri dishes were closed with lids, sealed with Parafilm® M (Darmstadt, Germany), and maintained in the environmentally controlled chamber under the same conditions. The treatments were arranged inside the chamber in a completely randomized design.
Adult mortality was assessed at 24, 48, and 72 h post-introduction. To confirm mortality, adults that appeared immobile were gently prodded multiple times with a fine paintbrush to elicit a response. Individuals that remained unresponsive were recorded as dead. After 72 h, surviving adults were transferred to new Petri dishes prepared as described previously. Nontreated, non-damaged H. paniculata leaves were provided to these adults for 24 h. The experiment was repeated twice. Leaf damage from adult feeding was quantified using ImageJ software (Abramoff et al., 2004; Schneider et al., 2012), measuring both the treated and untreated leaf areas consumed.
2.6 Total RNA extraction and gene expression analysis via qRT-PCR
In each trial, three independent biological replicates (live adults) were randomly collected from five Petri dishes and processed per treatment to ensure reproducibility of the qRT-PCR data. Total RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis were carried out as previously described. The synthesized cDNA was diluted to 10 ng per μL, and each qPCR reaction contained 30ng of cDNA, 1 μL of forward and reverse primer (10 μM), and 10 μL of TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNaseH Plus, TaKaRa, Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) in a total volume of 20 μL. The following qPCR parameters were used: One cycle at 95°C for 60 s, 40 cycles at 59°C for 30 s, and 95°C for 5 s (ramp rate 4.4°C per s acquisition mode: Single), followed by a melting curve analysis at 95°C for 5 s (ramp rate 4.4°C per s), 59°C for 60 s (ramp rate 2.2°C per s), and 95°C (ramp rate 0.11°C per s; acquisition mode: Continuous for 1 cycle; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied Biosystems, QuantStudio 3, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). β-actin was used as a housekeeping gene to normalize the expression data as a nontarget control. The relative quantification of genes was conducted using the 2–ΔΔCT method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).
2.7 Statistical analysis
The survival data of adult S. frontalis were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with a generalized linear model (PROC GLIMMIX) in SAS (SAS Institute, 2024). The model employed a log-link function and a negative binomial distribution. Treatment was treated as a fixed effect, and the Petri dish as a random effect within the model. Means were compared using the Tukey-Kramer test (α < 0.05). Means and standard errors were calculated from non-transformed data with the PROC MEAN procedure in SAS for the figures.
The proportion data of S. frontalis feeding damage area on H. paniculata leaves, 3-d post-exposure, and the proportion of S. frontalis feeding damage on fresh untreated leaves were analysed in two separate models. The two response variables for each vATPase-A, -D, and -E were arcsin square root transformed to normalise them. The transformed data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using two general linear models (PROC GLM) in SAS as in Arshad and Joseph (2024). In both models, the treatment was treated as a fixed effect, and Petri dish as a random effect. Tukey’s test separated the least significant (LS) means of damage on H. paniculata leaves post-3 d and 1 d exposure data (α < 0.05). Means and standard errors were calculated from non-transformed data using the PROC MEAN procedure in SAS for the figures.
The relative expression of mRNA data 3-d post-exposure to dsRNA concentrations for each vTAPase A, D, and E were not transformed after checking for normality. The non-transformed data were subjected to a one-way ANOVA using a general linear model (PROC GLM) in SAS as in Joseph and Pozo-Valdivia (2023). Treatment was treated as a fixed effect, and beetles as a random effect within the model. For S. frontalis expression of mRNA data, Tukey’s test was conducted for the LS means of treatment (α < 0.05). Means and standard errors were calculated from non-transformed data using the PROC MEANS procedure in SAS for the figures.
3 Results
3.1 S. frontalis adult survival
For dsvATPase-A, D and Etrials, there were no significant difference between alive S. frontalis adults regardless of dsRNA concentration (Table 1, Figures 1A-F).
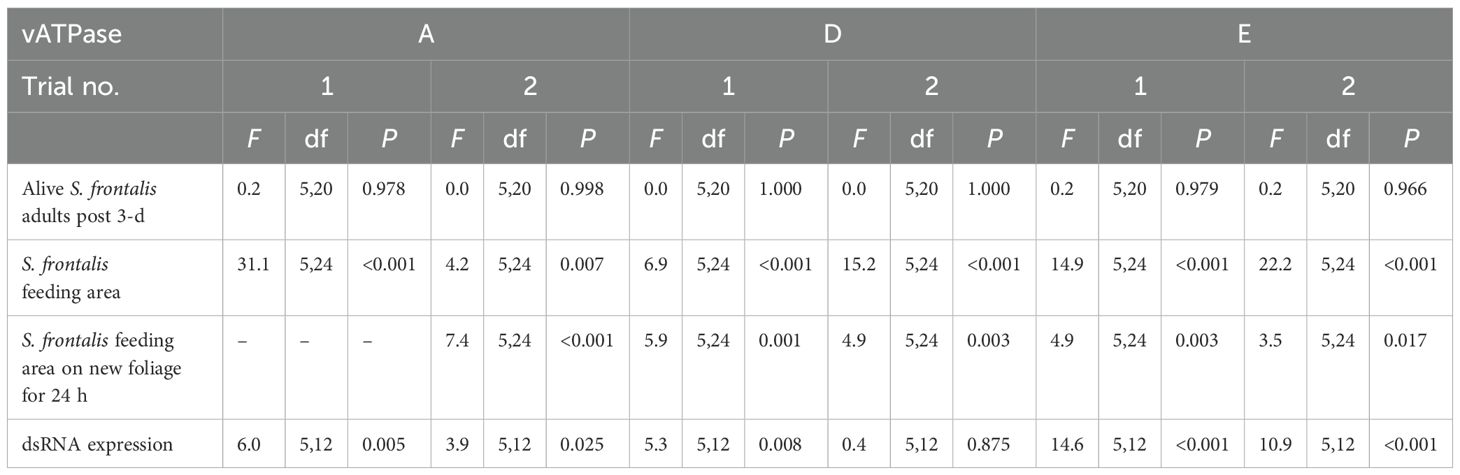
Table 1. Analysis of variance for feeding area, alive S. frontalis adults, and dsRNA expression after coating various concentrations dsvATPase-A, D and E on panicled hydrangea leaves.
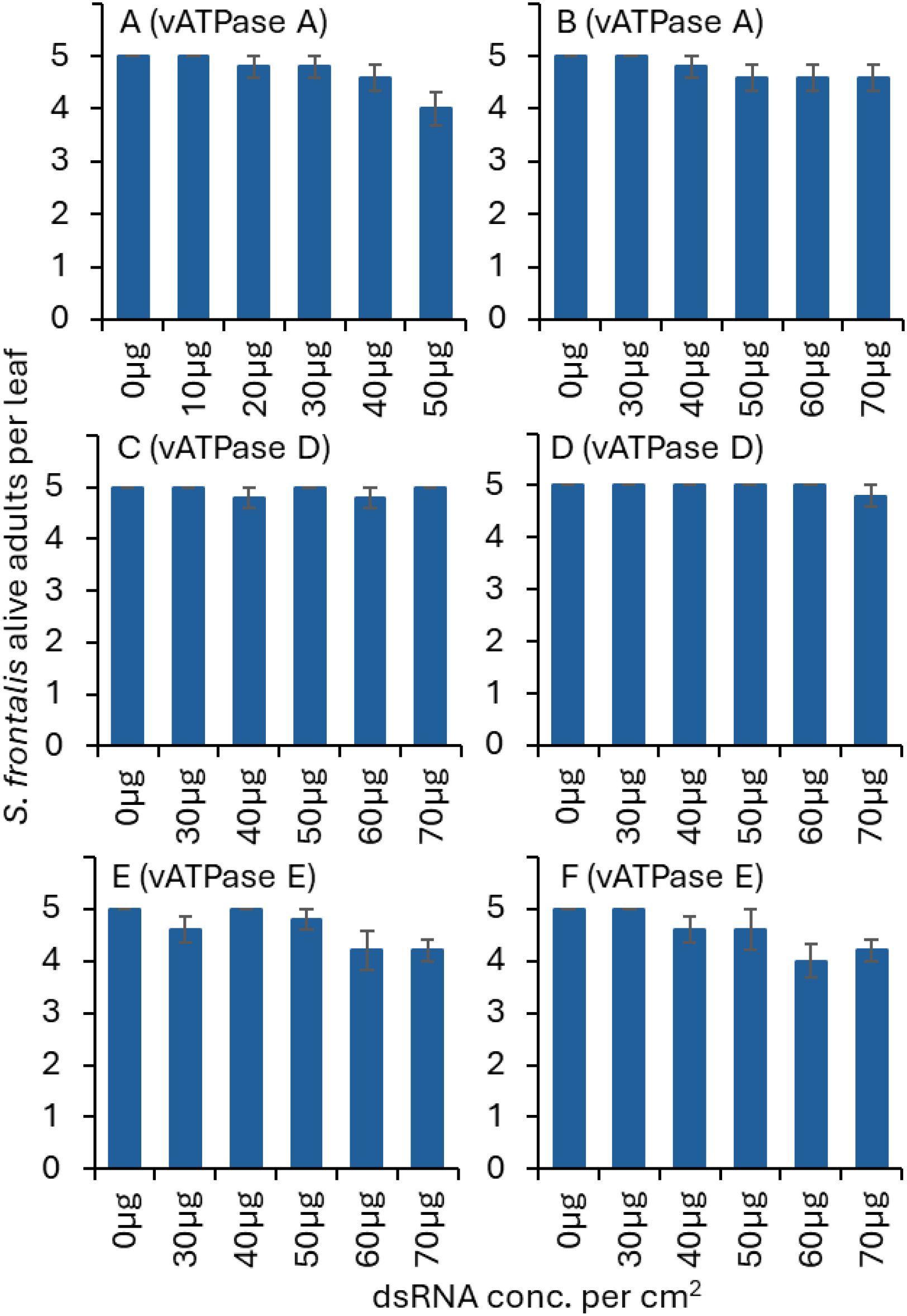
Figure 1. Mean (± SE) numbers of live S. frontalis adults exposed to various concentrations of dsvATPase-A in (A) trial 1 and (B) trial 2; dsvATPase-D in (C) trial 1, (D) trial 2; and dsvATPase-E in (E) trial 1, (F) trial 2 for 3 d post-application. Bars with the same letters within a figure are not significantly different (Tukey-Kramer test, P < 0.05). When not significantly different among treatments (P > 0.05), no letters are given.
3.2 S. frontalis feeding damage 3-d post-exposure
In dsvATPase-A trial 1, the S. frontalis feeding damage area was significantly lower for the 40 and 50 µg dsRNA treatments than for the 10, 20, and 30 µg dsRNA treatments, followed by the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 2A). For trial 2, a significantly lower feeding damage area was observed for the 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 2B). The S. frontalis feeding damage area was not significantly different between 30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 µg dsRNA treatments in trial 1 or between 0, 30, 40, 50, and 60 µg dsRNA treatments in triall 2.
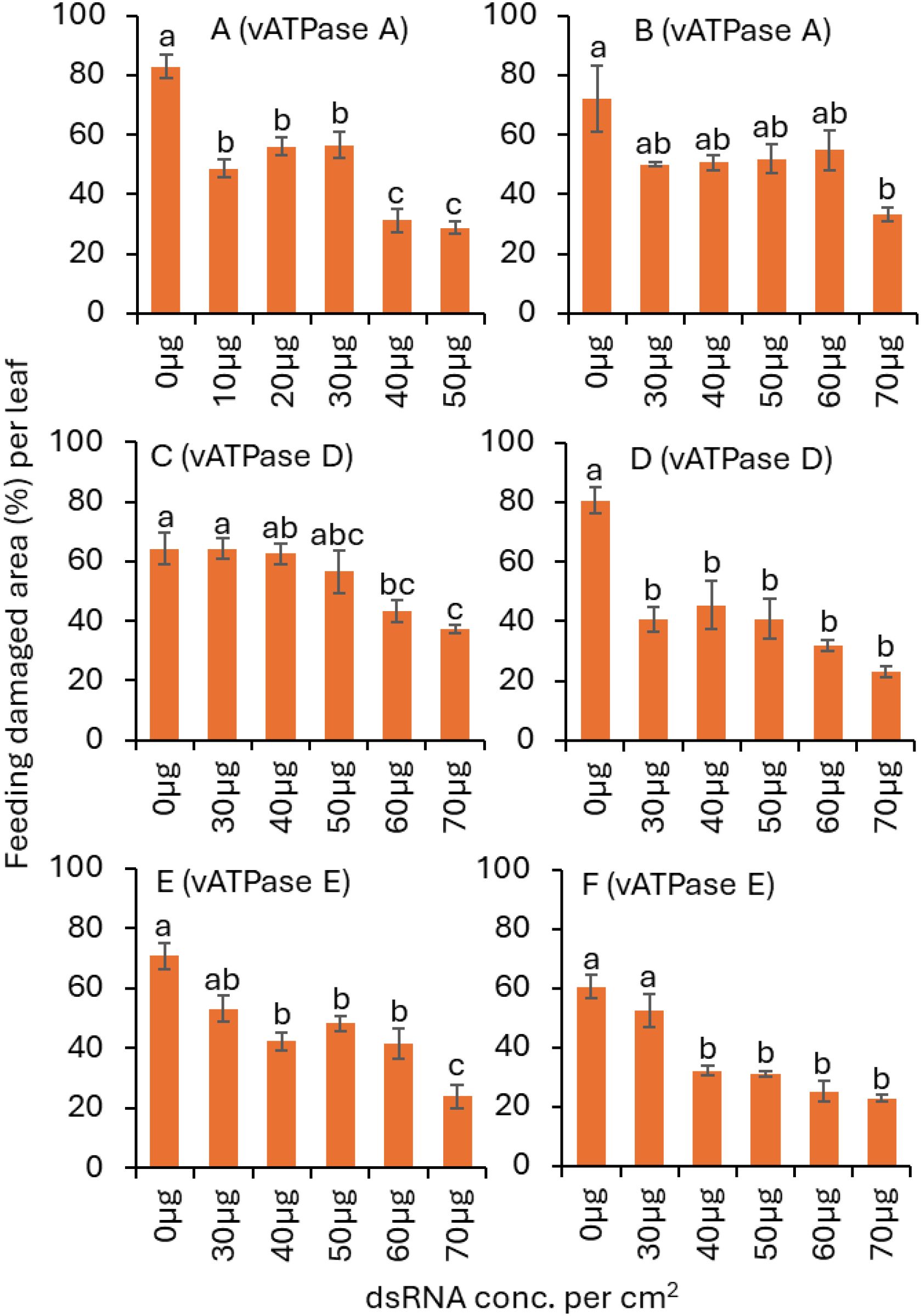
Figure 2. Mean (± SE) area damaged by adult S. frontalis feeding after exposed to various concentrations of dsvATPase-A in (A) trial 1 and (B) trial 2; dsvATPase-D in (C) trial 1, (D) trial 2; and dsvATPase-E in (E) trial 1, (F) trial 2 for 3 d post-application. Bars with the same letters within a figure are not significantly different (Tukey’s test for Least Significant (LS) means, P < 0.05).
In dsvATPase-D trial 1, the S. frontalis feeding damage area was significantly lower for the 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatments than for the 0 and 30 µg dsRNA treatments (Table 1; Figure 2C). For trial 2, a significantly lower feeding damage area was observed for the 30, 40, 50, 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatments than for the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 2D).
In dsvATPase-E trial 1, a significantly lower S. frontalis feeding damage area was observed for the 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the 40, 50, and 60 µg dsRNA treatments, followed by the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 2E). For trial 2, the feeding damage area was significantly lower for the 40, 50, 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatments than for the 30 µg dsRNA and nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 2F).
3.3 Pre-exposed S. frontalis feeding damage 24-h post-exposure
For dsvATPase-A trial 2, when the S. frontalis feeding damage after 24-h exposure was assessed from the pre-exposed adults, significantly lower feeding damage was observed for the 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 3A). There was no significant difference in feeding damage between 50, 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatments. The dsvATPase-A trial 1 was not assessed.
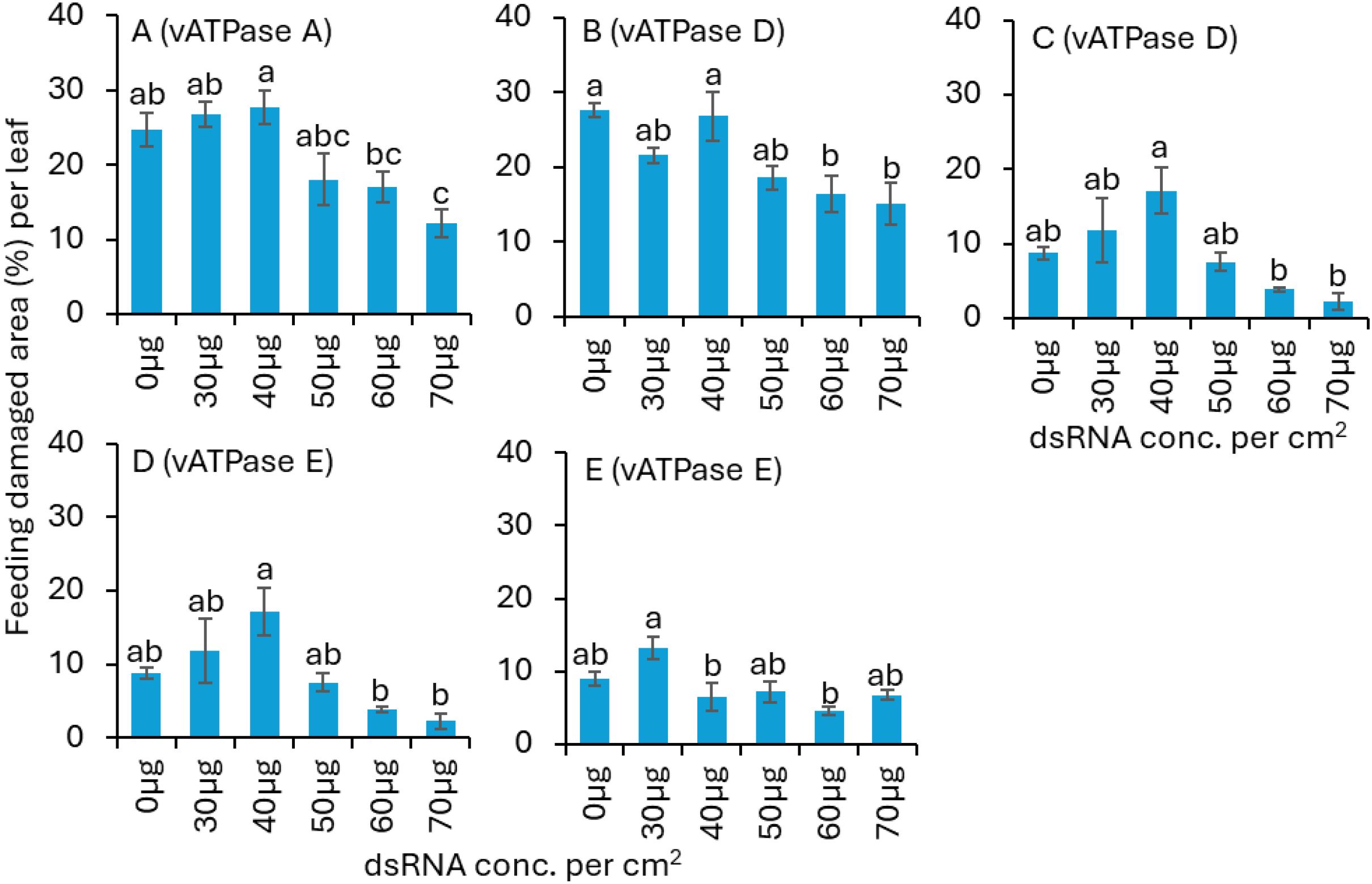
Figure 3. Mean (± SE) area damaged by pre-exposed adult S. frontalis feeding on nontreated panicled hydrangea leaves. Before introducing to nontreated panicled hydrangea leaves, S. frontalis adults were exposed to various concentrations of dsvATPase-A in (A) trial 2; dsvATPase-D in (B) trial 1, (C) trial 2; and dsvATPase-E in (D) trial 1, (E) trial 2 for 3 d post-application. Bars with the same letters within a figure are not significantly different (Tukey’s test for Least Significant (LS) means, P < 0.05).
For dsvATPase-D trial 1, the S. frontalis feeding damage area was significantly lower for the 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatments than for the 0 and 40 µg dsRNA treatments (Table 1; Figure 3B). Similarly, for trial 2, a significantly lower feeding damage area was observed for the 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the 40 µg dsRNA treatment (Table 1; Figure 3C). For dsvATPase-E trial 1, a significantly lower feeding damage area was observed for the 60 and 70 µg dsRNA treatments than for the 40 µg dsRNA treatment (Table 1; Figure 3D). For trial 2, the S. frontalis feeding damage area was significantly lower for the 40 and 60 µg dsRNA treatments than for the 30 µg dsRNA treatment (Table 1; Figure 3E).
3.4 mRNA expression
For dsvATPase-E trial 1, a significantly greater relative mRNA expression was observed for the 30, 40 and 50 µg dsRNA treatments than for the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 4A). For trial 2, the relative expression was significantly greater for the 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 4B). For dsvATPase-D trial 1, the relative expression was significantly greater for the 60 µg dsRNA treatment than for the 0, 40, and 50 µg dsRNA treatments (Table 1; Figure 4C). For trial 2, there was no significant difference relative expression in between dsRNA treatments (Table 1; Figure 4D). For dsvATPase-E trial 1, the relative mRNA expression was significantly greater for the 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the 30 and 40 µg dsRNA treatments followed by the nontreated treatment (Table 1; Figure 4E). For trial 2, relative expression was significantly greater for the 70 µg dsRNA treatment than for the nontreated control treatment (Table 1; Figure 4F).
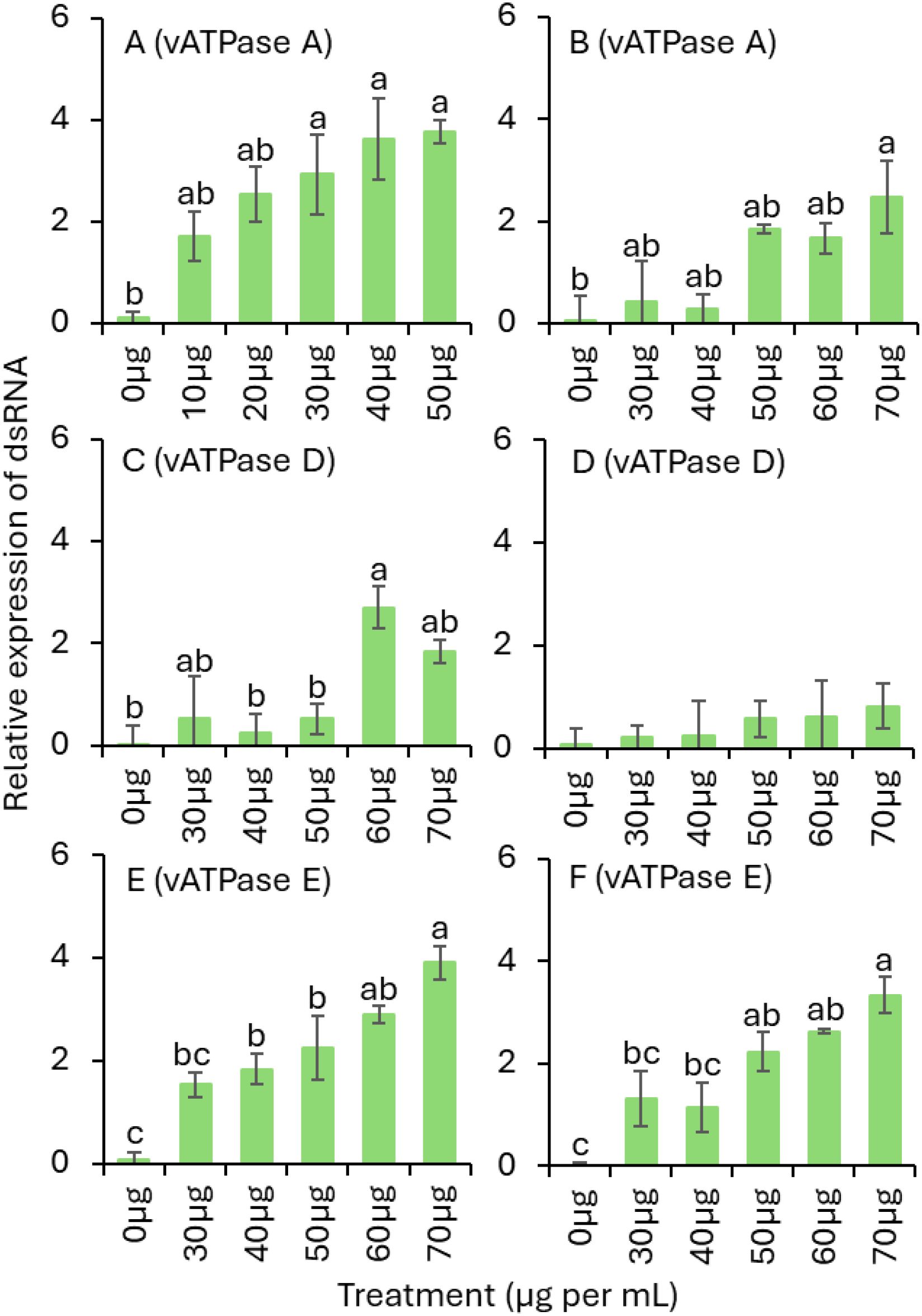
Figure 4. Mean (± SE) relative expression of dsRNA in pre-exposed live S. frontalis adults to feeding panicled hydrangea leaves coated with various concentrations of dsvATPase-A in (A) trial 1 and (B) trial 2; dsvATPase-D in (C) trial 1, (D) trial 2; and dsvATPase-E in (E) trial 1, (F) trial 2 for 3 d post-application. Bars with the same letters within a figure are not significantly different (Tukey’s test for Least Significant (LS) means, P < 0.05). When not significantly different among treatments (P > 0.05), no letters are given.
4 Discussion
In this study, we explored the potential and limitations of a foliar RNAi-based strategy targeting the v-ATPase gene in adult Systena frontalis. Exposure to dsv-ATPase-A, -D, and -E significantly reduced feeding activity, with the greatest reduction—up to ~50%—observed at the 70 µg concentration in select treatments. Importantly, this feeding suppression persisted even after beetles were transferred to untreated foliage, indicating that dsRNA uptake continued to affect behavior beyond the initial exposure period. These results are consistent with previous studies in chrysomelid beetles, where v-ATPase gene silencing demonstrated high sensitivity and measurable phenotypic effects (Pereira et al., 2019; Willow and Veromann, 2021; Li et al., 2022). However, dsRNA exposure did not significantly affect adult S. frontalis mortality, indicating that RNAi primarily impaired feeding behavior rather than inducing lethal effects. The observed persistence of dsRNA effects in S. frontalis implies stable uptake and sustained activity of the RNAi trigger, similar to findings in other insect species where dsRNA remains functional for extended periods (San Miguel and Scott, 2016). The longevity of RNAi-induced gene silencing presents a promising avenue for pest management by enabling prolonged suppression of pest activity, potentially reducing the need for repeated chemical applications in ornamental nurseries.The feeding activity of adult S. frontalis decreased with increased concentrations of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E. This result was consistent with previous research where feeding activity was reduced after exposure to dsvATPase subunits. For example, on South American pinworm, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) larvae, dsvATPase-B reduced the feeding activity of larvae as concentrations of dsvATPase increased in a single leaf assay (Ramkumar et al., 2021). Similarly, dsvATPase-G reduced the feeding of Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata (F.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) larvae (Zeng et al., 2021).
Additionally, in the current study, the dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E expression in recovered live adult S. frontalis increased with an increase in concentrations of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E coated on the single panicle hydrangea leaf assay. Thus, the levels of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E possibly interfered with regulatory pathways (Collins and Forgac, 2020) that affected the normal feeding activity of adult S. frontalis. Poor food intake can negatively impact critical activities, such as dispersal, mating, and oviposition, as they develop energy deprivation over time and are likely to succumb to starvation (Niitepõld, 2019).
Previous studies showed that high mortality was observed after dsvATPase subunits were delivered orally. For example, the mortality rate of melon thrips, Thrips palmi Karny (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), increased by 5.4-fold when exposed to dsvATPase-B (Rakesh et al., 2024). When exposed to dsvATPase-A and -E, researchers noted 100% mortality in both larvae and adults of the willow leaf beetle, Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) (Li et al., 2022). In the current study, however, no or limited mortality of adult S. frontalis was recorded when ingesting dsvATPase-A, D, and E-treated panicled hydrangea leaves. The adults of S. frontalis were observed for only up to three days, and a longer observation period might be necessary to identify potential treatment effects on survival or mortality. Mortality of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster Meigen (Diptera: Drosophilidae), flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), pea aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Hemiptera: Aphididae), and tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta (L.) (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae), was observed by seven days (Whyard et al., 2009). Although using 10 mixed-age beetles (two Petri dishes with five beetles each) per treatment is not ideal for precise mortality measurement, it reflects a practical context where S. frontalis populations vary naturally in age and condition in container ornamental nurseries. This method allowed us to evaluate RNAi effects under semi-realistic nursery conditions. Future studies with larger, age-synchronized groups and longer observation periods are recommended to better assess treatment-related mortality.
We observed dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E overexpression when adult S. frontalis was exposed to leaves coated with dsRNA. The exact reasons for the overexpression of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E in adults were unclear. A previous study suggested that dsRNA produced through endogenous sources evokes alarm signals that can trigger innate immune responses to broken cellular processes, which can result in overexpression of dsRNA, similar to the response of a viral attack (Chen and Hur, 2022). Thus, the overexpression of dsRNA may be related to an immune response that reduces adult S. frontalis feeding. The vATPase is a complex enzyme with several subunits and delivers various regulatory functions in eukaryotic cells (Stevens and Forgac, 1997). It is unclear if the RNA interference of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E modified the integrity or levels of the enzyme, leading to underperformance. Similarly, the interaction of the vATPase enzyme with other enzymes should be evaluated.
Effective pest management often emphasizes concentration and the temporal dependence of mortality rates. Although limited effects of dsvATPase on adult S. frontalis mortality were observed, the beetles showed reduced feeding on dsvATPase-treated panicle hydrangea leaves in this study. Most previous studies provided quantifiable measurements of the molecular effects of dsRNA therapies through the downregulation of dsvATPase expression. However, in this study, the expressions of dsvATPase-A, D, and E increased with higher concentrations in live adult S. frontalis. Because the effectiveness of dsRNA can be time-dependent, it is essential to thoroughly understand the kinetics of gene silencing to develop effective pest management techniques. Despite limited mortality, the feeding inhibition observed at higher dsRNA concentrations suggests potential for integration into IPM programs, particularly for managing dispersal and reproduction in S. frontalis populations. Therefore, further research is warranted to refine the mRNA construct of dsvATPase-A, -D, and -E or to target new subunits not evaluated in this study. Data also suggest that a protocol with an extended observation period, along with dsRNA delivered to beetles via various methods, could yield more robust data on its efficacy. Additionally, future research could explore whether the overexpression of dsRNA in live beetles is linked to immune system activation or other stress responses.
Data availability statement
The raw data are available at doi: 10.5063/F1J67FDW (https://knb.ecoinformatics.org/view/doi:10.5063/F1J67FDW).
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
RG: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. RV: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SVJ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study received funding from the University of Georgia Hatch Project.
Acknowledgments
We thank C. Hardin, A. Chapman, and the nursery grower for helping collect adults for various experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fagro.2025.1613851/full#supplementary-material
References
Abbas Y. M., Wu D., Bueler S. A., Robinson C. V., and Rubinstein J. L. (2020). Structure of V-ATPase from the mammalian brain. Science 367, 1240–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.aaz2924
Abramoff M. D., Magalhaes P. J., and Ram S. J. (2004). Image processing with imageJ. Biophotonics Internat. 11, 36–42.
ACES Alabama Cooperative Extension System (2020). Redheaded flea beetles in Alabama nurseries. Available online at: https://www.growingamerica.com/news/2020/07/redheaded-fleabeetles-alabama-nurseries (Accessed November 9 2023).
Arshad R., Chong J. H., Lauderdale D., Kunkel B., and Joseph S. V. (2023). Biology and management of Systena frontalis (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in ornamental plant nurseries. J. Integr. Pest Manage 14, 7. doi: 10.1093/jipm/pmad007
Arshad R. and Joseph S. V. (2024). Residual activity of insecticides against adult Systena frontalis (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) under semi-field conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 117, 251–258. doi: 10.1093/jee/toad227
Baum J. A., Bogaert T., Clinton W., Heck G. R., Feldmann P., Ilagan O., et al. (2007). Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotech. 25, 1322–1326. doi: 10.1038/nbt1359
Chen Y. G. and Hur S. (2022). Cellular origins of dsRNA, their recognition and consequences. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 286–301. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00430-1
Collins M. P. and Forgac M. (2020). Regulation and function of V-ATPases in physiology and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1862, 183341. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183341
Ellango R., Singh S. T., Rana V. S., Gayatri Priya N., Raina H., Chaubey R., et al. (2015). Distribution of Bemisia tabaci genetic groups in India. Environ. Entomol. 44, 1258–1264. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvv062
Guédot C. and McIntosh H. (2023).Redheaded flea beetle. Available online at: https://fruit.wisc.edu/2023/07/18/red-headed-flea-beetle/ (Accessed January 27 2025).
Harvey W. R., Boudko D. Y., Rheault M., and Okech B. A. (2009). NHEVNAT: An H+ V-ATPase electrically coupled to a Na+:nutrient amino acid transporter (NAT) forms an Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE). J. Exp. Biol. 212, 347–357. doi: 10.1242/jeb.026047
Huvenne H. and Smagghe G. (2010). Mechanisms of dsRNA uptake in insects and potential of RNAi for pest control: A review. J. Insect Physiol. 56, 227–235. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2009.10.004
Jaffe B. D., Rink S., and Guédot C. (2021). Life history and damage by Systena frontalis F. (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Vaccinium macrocarpon Ait. J. Insect Sci. 21, 11. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieab004
Joseph S. V. (2023a). Efficacy of insecticides against Systena frontalis in containerized panicled hydrangea in nursery 2023. Arthr. Manage. Tests 48, tsad092. doi: 10.1093/amt/tsad092
Joseph S. V. (2023b). Evaluation of drench application of insecticides against larvae of Systena frontalis in panicled hydrangea 2023. Arthr. Manage. Tests 48, tsad121. doi: 10.1093/amt/tsad121
Joseph S. V., Chong J. H., Campbell B., Kunkel B., Lauderdale D., Jones S., et al. (2021). Current pest status and management practices for Systena frontalis (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in ornamental plants in the eastern United States: An online survey. J. Integr. Pest Manage 12, 17. doi: 10.1093/jipm/pmab012
Joseph S. V. and Hudson W. (2020). Redheaded flea beetle: An ornamental nursery pest (University of Georgia Extension). Available at: https://extension.uga.edu/publications/detail.html?number=C1187 (Accessed July 7, 2025).
Joseph S. V. and Pozo-Valdivia A. D. (2023). Effects of insecticide drench application against immatures of Systena frontalis in containerized Hydrangea paniculata. J. Environ. Hortic. 41, 161–169. doi: 10.24266/0738-2898-41.4.161
Knorr E., Fishilevich E., Tenbusch L., Frey M. L. F., Rangasamy M., Billionet A., et al 2018)Gene silencing in Tribolium castaneum as a tool for the targeted identification of candidate RNAi targets in crop pests. Sci. Rep. 8, 2061. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20416-y
Lane E. L. and Del Pozo-Valdivia A. I. (2022). Bioassays comparing different insecticides against Systena frontalis adults on Hydrangea paniculata 2022. Arthr. Manage. Tests 47, 129. doi: 10.1093/amt/tsac129
Lauderdale D. (2017). “Red-headed flea beetle biology and management,” in Winter 2017, Nursery and Landscape Notes 35. Available online at: https://wilson.ces.ncsu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/2017-Nursery-Landscape-Notes-RHFB-Article.pdf?fwd=no.
Lauderdale D. (2021).Topdressing granular imidacloprid to reduce red-headed flea beetle injury. Available online at: https://wilson.ces.ncsu.edu/2021/12/topdressing-granular-imidacloprid-to-reduce-red-headed-flea-beetle-injury/ (Accessed August 10 2022).
Li Y., Ze L.-J., Liu F.-J., Liao W., Lu M., and Liu X.-L. (2022). RNA interference of vATPase subunits A and E affects survival of larvae and adults in Plagiodera versicolora (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Pesticide Biochem. Physiol. 188, 105275. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105275
Livak K. J. and Schmittgen T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Niitepõld K. (2019). Effects of flight and food stress on energetics, reproduction, and lifespan in the butterfly Melitaea cinxia. Oecologia 191, 271–283. doi: 10.1007/s00442-019-04489-8
O’Donnell M. (2017). The V-ATPase in insect epithelia. J. Exp. Biol. 220, 3201–3203. doi: 10.1242/jeb.160564
Palli S. R. (2014). RNA interference in Colorado potato beetle: steps toward development of dsRNA as a commercial insecticide. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 6, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2014.09.011
Pan H., Yang X., Bidne B., Hellmich R. L., Siegfried B. D., and Zhou X. (2017). Dietary risk assessment of V-ATPase A dsRNAs on monarch butterfly larvae. Front. Plant Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00242
Pereira A. E., Tenhumberg B., Meinke L. J., and Siegfried B. D. (2019). Southern corn rootworm (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) adult emergence and population growth assessment after selection with vacuolar ATPase-A double-stranded RNA over multiple generations. J. Econ. Entomol. 112, 1354–1364. doi: 10.1093/jee/toz008
Rakesh V., Singh A., and Ghosh A. (2024). Suppression of Thrips palmi population by spray-on application of dsRNA targeting V-ATPase-B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 280, 135576. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135576
Ramkumar G., Asokan R., Prasannakumar N. R., Kariyanna B., Karthi S., Alwahibi M. S., et al. (2021). RNA interference suppression of v-ATPase B and juvenile hormone binding protein genes through topically applied dsRNA on tomato leaves: Developing biopesticides to control the South American pinworm, Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Front. Physiol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.742871
Rinker D. C., Pitts R. J., and Zwiebel L. J. (2016). Disease vectors in the era of next generation sequencing. Genome Biol. 17, 95. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0966-4
San Miguel K. and Scott J. G. (2016). The next generation of insecticides: dsRNA is stable as a foliar-applied insecticide. Pest Manage. Science. 72, 801–809. doi: 10.1002/ps.4056
Schneider C. A., Rasband W. S., and Eliceiri K. W. (2012). NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675. Available online at: https://imagej.net/ij/docs/guide/index.html (Accessed July 7, 2025).
Stevens T. H. and Forgac M. (1997). Structure, function and regulation of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPase. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 779–808. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.13.1.779
Terenius O., Papanicolaou A., and Garbutt J. S. (2011). RNA interference in Lepidoptera: An overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 57, 231–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.11.006
Tomoyasu Y., Miller S. C., Tomita S., Schoppmeier M., Grossmann D., and Bucher G. (2008). Exploring systemic RNA interference in insects: A genome-wide survey for RNAi genes in Tribolium. Genome Biol. 9, R10. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-1-r10
USDA NASS (2019). Census of horticulture. Available online at: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Publications/AgCensus/2017/Online_Resources/Census_of_Horticulture_Specialties/index.php (Accessed January 14 2025).
Whyard S., Singh A. D., and Wong S. (2009). Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species specific insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39, 824–832. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2009.09.007
Wieczorek H., Beyenbach K. W., Huss M., and Vitavska O. (2009). Vacuolar-type proton pumps in insect epithelia. J. Exp. Biol. 212, 1611–1619. doi: 10.1242/jeb.030007
Wieczorek H., Brown D., Grinstein S., Ehrenfeld J., and Harvey W. R. (1999). Animal plasma membrane energization by proton-motive V-ATPases. Bioessays 21, 637–648. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199908)21:8<637::AID-BIES3>3.0.CO;2-W
Willow J. and Veromann E. (2021). Highly variable dietary RNAi sensitivity among Coleoptera. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.790816
Xue X. Y., Mao Y. B., and Tao X. Y. (2012). “New approaches to agricultural insect pest control based on RNA interference,” in Advances in Insect Physiology. Ed. Jockusch E. L. (Academic Press, London), 73–117.
Keywords: VATPase, redheaded flea beetle, DsRNA delivery, gene silencing, RNAi
Citation: Govindaraju R, Vavilapalli R and Joseph SV (2025) Evidence of vacuolar-ATPase gene mediated RNA interference on Systena frontalis (F) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) adults. Front. Agron. 7:1613851. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1613851
Received: 22 April 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 01 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dhandapani Gurusamy, Kongunadu Arts and Science College, IndiaReviewed by:
Vijay Sheri, Texas Tech University, United StatesThibault Costaz, Agroscope, Switzerland
Copyright © 2025 Govindaraju, Vavilapalli and Joseph. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shimat V. Joseph, c3Zqb3NlcGhAdWdhLmVkdQ==
 Ramkumar Govindaraju
Ramkumar Govindaraju Rajesh Vavilapalli
Rajesh Vavilapalli Shimat V. Joseph
Shimat V. Joseph