- 1Academy of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, Qinghai University, Qinghai Academy of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, Xining, Qinghai, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Qinghai Province Superior Forage Germplasm in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Laboratory for Research and Utilization of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Germplasm Resources, Xining, Qinghai, China
Introduction: Grass species are crucial for grassland ecological restoration; however, native grass species suitable for ecological restoration are scarce on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Therefore, the collection and screening of local native grass species are of great significance for their ecological adaptability in alternative habitats and introduction into new habitats.
Methods: We evaluated the ecological adaptability and yield dynamics of 10 wild Elymus nutans germplasms. It analyzed the agronomic traits and forage yield of different Elymus nutans varieties and uses a piecewise structural equation model to explore how years, varieties, and their interactions affect forage yield by influencing agronomic traits. The TOPSIS model was employed to comprehensively evaluate the tested materials to select high-quality Elymus nutans varieties suitable for planting in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone, thereby providing better grass species varieties for the ecological restoration of degraded grasslands in this zone.
Results: Agronomic traits and grass yield of the tested Elymus nutans resources were best in the third year, followed by the second year, and worst in the fourth year. During the field trials period, variety 18-023 had a relatively high plant height (99.00–128.83 cm), high grass yield of per plant (79.33–82.83 g), high grass height (19.00–34.67 cm), high number of tillers (52.51–433.32 per plant), large leaf size with leaf length (13.17–17.61 cm) and leaf width (0.91–1.03 cm). Variety 15-010 had a large crown breadth (87.51–127.53 cm), and variety 17-213 had a high dry-fresh ratio (0.41–0.49).
Conclusion: The piecewise structural equation model analysis indicated that plant height, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio are the key factors affecting the forage yield of Elymus nutans. The TOPSIS model comprehensive evaluation showed: 18-023 and 15-010 had the best comprehensive production performance and are ideal materials for promotion and planting in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone. They are also parental materials in line with the concept of breeding high-yielding and stable new varieties. Therefore, it is necessary to collect and screen China’s unique plant germplasm resources, aiming to supply high-quality materials for the ecological restoration of degraded grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone.
1 Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau is an important ecological barrier and pastoral production base in China (Li et al., 2024). In recent years, due to climate change and irrational development and utilization by humans, the alpine meadows in this region have been severely degraded, leading to prominent seasonal contradictions between forage and livestock. These issues are threatening the ecological security and socio-economic development of the region (Li et al., 2019). Therefore, it is urgent to restore degraded grassland ecosystems, increase grassland productivity, and promote a balance between forage and livestock supply and demand (Zhang et al., 2019).
Elymus nutans, also known as hook-headed and bay-panicle grass, is a perennial herb that is both forage and ecologically valuable. It is a dominant species in the alpine meadows of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and is widely used for slope protection, vegetation restoration, and reconstruction of degraded grasslands. It is characterized by tall plants, abundant leaves, long panicles, high seed production, and ease of cultivation. It is highly palatable to livestock and has considerable economic value. It also has strong drought resistance, cold tolerance, alkali tolerance, and wind-sand resistance, making it an ideal grass for ecological restoration (Zhou et al., 2022; Ren et al., 2025; Song et al., 2025).
With the implementation of the ecological restoration and management project of the “black soil beach” in the Sanjiangyuan region, the demand for grass species adapted to local ecological conditions has increased (Ferrigno, 2015; Wang et al., 2025). Moreover, owing to the unique natural environment of the Tibetan Plateau, characterized by low temperatures and strong radiation (Sun et al., 2025), introduced grass species find it difficult to adapt, and the progress of ecological restoration projects is slow. Therefore, collecting local grass germplasm resources specific to this zone, conducting adaptability evaluations of germplasm resources, and screening high-quality grass germplasm resources suitable for the natural environment of this zone are of great significance for advancing the progress of ecological restoration and management projects, improving project quality, and maintaining the stability of the alpine meadow plant communities. Studies have shown that Elymus nutans has good ecological and productive advantages in alpine meadow plant communities (Wang et al., 2014; Ringselle et al., 2016). Given the intricate relationship between the growth of Elymus nutans and its complex growth environment, it is crucial to select suitable cultivation sites and conduct cultivation evaluations to comprehensively assess its growth and select superior grass species resources (Johnson et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2025a). Relevant studies have shown that in artificial grasslands of Elymus nutans aged 0–3 years, plant biomass, plant biomass traits, and community cover significantly increase with the extension of establishment years. This process not only enriches the quantity and quality of forage for livestock and wildlife but also provides a better habitat for soil biota (Hou et al., 2023). Moreover, Elymus nutans performs well in the ecological restoration of degraded grasslands, effectively improving soil quality, preventing desertification, and increasing soil moisture and nutrient content through its root systems (Wu et al., 2010). It is worth noting that the carbon sequestration intensity of artificial Elymus nutans grasslands peaks in the third year (He et al., 2019). Therefore, Elymus nutans is the preferred grass species for the ecological restoration of degraded grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. These findings have greatly promoted ecological restoration and pastoral development in high-altitude areas. However, these achievements are far from meeting current production needs. In particular, there is still a shortage of high-quality Elymus nutans germplasm resources with strong adaptability and comprehensive performance, and the supply and demand contradiction still exists (Wang et al., 2025). Collecting and screening high-quality wild grass germplasm resources can help improve the quality of ecological restoration of “black soil beach” degraded grasslands, making newly established artificial grassland communities more stable and achieving better ecological restoration results. It also helps enrich the forage germplasm resource gene bank in alpine areas and lays the foundation for breeding high-quality grass species with better adaptability, productivity, and ecological performance. Moreover, the key factors affecting the forage production performance of artificial Elymus nutans grasslands and their regulatory pathways are still unclear, which is not conducive to the exploration of high-quality Elymus nutans germplasm resources. Therefore, it is urgent to conduct scientific research on the collection and evaluation of wild germplasm resources.
Based on current studies, the present study used ten excellent Elymus nutans germplasm resources as research objects. By constructing a TOPSIS model and a piecewise structural equation model, a comprehensive evaluation of the agronomic traits and forage production performance of the tested materials was conducted. The study also revealed the factors and pathways by which varieties, years, and their interactive effects influence the forage yield of the tested materials, with the aim of screening out high-yielding and stable Elymus nutans germplasm resources with good adaptability. This will provide high-quality grass species resources for promoting the ecological restoration and reconstruction of degraded grasslands and the development of animal husbandry in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental site description
The experimental site was located at the National Forage Germplasm Nursery in Haibei County, Qinghai Province (on the Tibetan Plateau) (100eau)mtal E, 3600eau)m N) at an altitude of 3156 m. The region has a typical plateau continental climate, characterized by thin air, abundant sunshine, strong solar radiation, and highly variable weather conditions. There are only two seasons: cold and warm, with a large diurnal temperature range. The average annual temperature is 8.9 °C, with no absolute frost-free period; the frost-free period is approximately 30 d per year, and the growing season for plants is about 120 d. Precipitation and heat occur in the same period, with an average annual precipitation of approximately 375 mm, mainly concentrated from July to September. From June 2022 to September 2024, the average monthly temperature and precipitation were 2.6 °C and 95.9 mm, respectively (Figure 1). The average annual sunshine duration is approximately 2980 hours, and the average annual evaporation is approximately 1400 mm. The chestnut soil is the main soil type, with soil organic matter, total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and available phosphorus contents of 32.5 g/kg, 1.6 g/kg, 1.4 g/kg, and 2.2 mg/kg, respectively, and a soil pH of 8.4 (Shi et al., 2024).
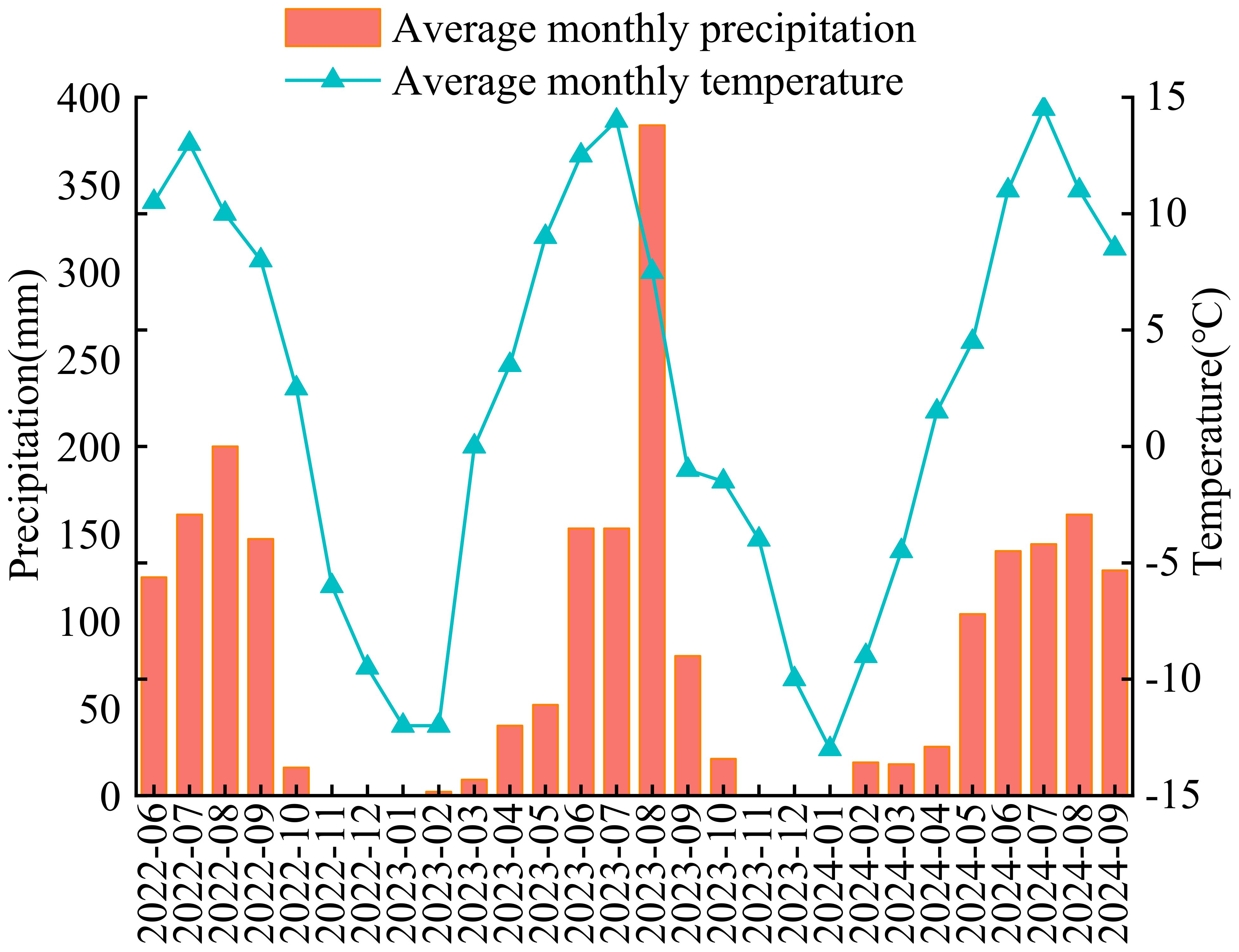
Figure 1. Distribution of monthly average temperature and precipitation at the experimental site from June 2022 to September 2024.
2.2 Materials and experimental design
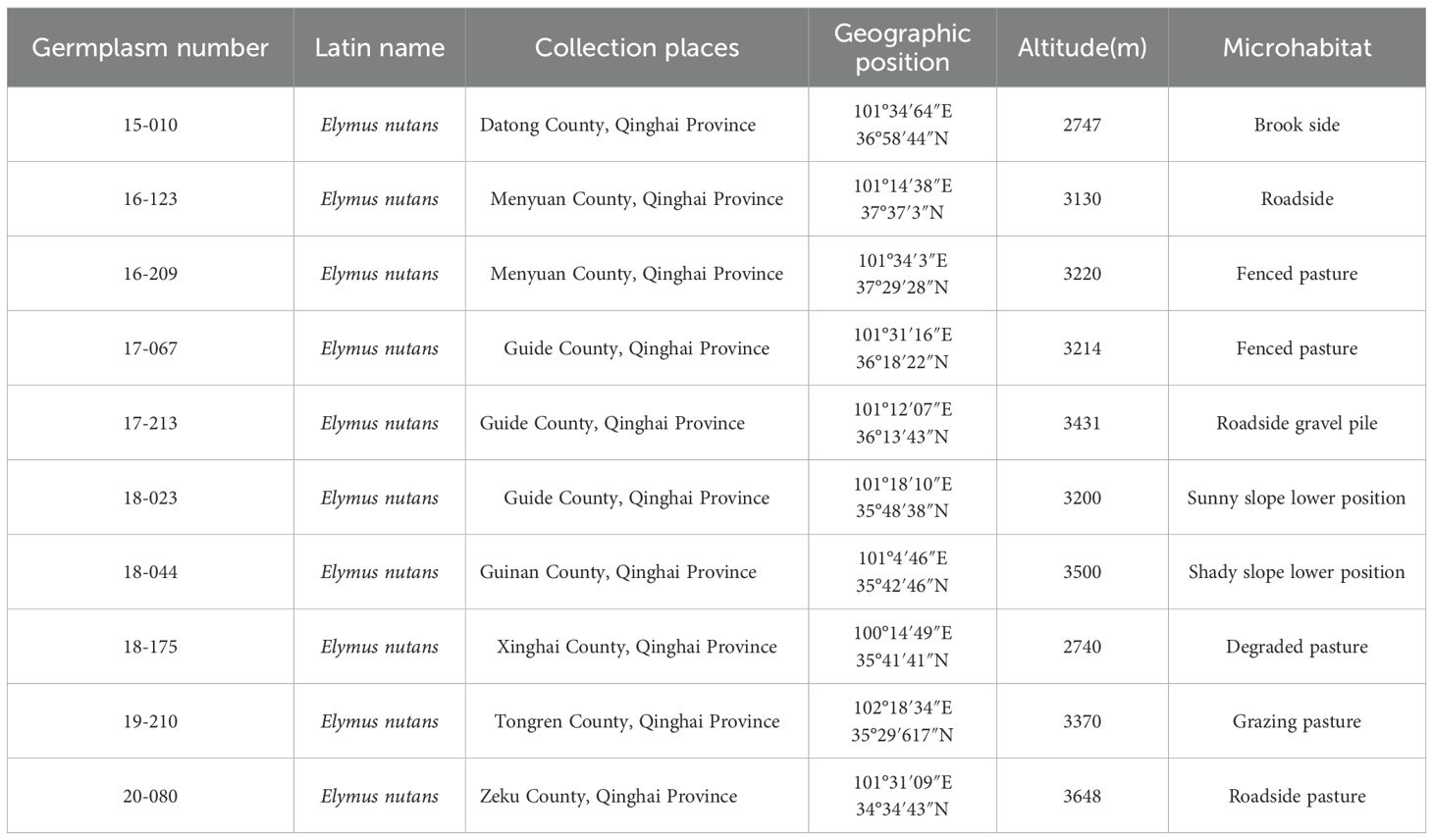
The experimental materials were sourced from different ecological regions of the Tibetan Plateau (Table 1). After field classification and screening, 10 Elymus nutans varieties with better productivity and stronger adaptability were selected from 600 wild resources for the experiment (15-010, 16-123, 16-209, 17-067, 17-213, 18-023, 18-044, 18-175, 19-210, and 20-080). The experiment was initiated by sowing in early June 2021. Prior to sowing, the experimental site was deeply plowed and leveled, and stones, roots, and other debris were removed.
The experiment was conducted continuously for three years, using a completely randomized block design with six replications. To fully exploit the productivity of the tested materials, a single-plant cultivation method was employed. Seeds were first placed in seedling trays for germination (model: external dimensions 540 mm × 280 mm, 105-hole tray, hole diameter 35 mm at the top, 10 mm at the bottom, depth 40 mm, and individual hole volume 25 ml). The seedling trays were filled with field soil and nutrient soil mixture (1:1) and germinated in a greenhouse. To improve seedling survival rates, the seedling trays were transferred to the experimental site after germination for acclimatization. When the seedlings reached the two-leaf-one-heart stage, they were transplanted into the field. The plant and row spacing in the experimental field were both set at 80 cm, with each experimental plot measuring 3 m × 5 m. A 1.5 m wide protective border was established around the experimental field, using Elymus sibiricus cv. Qingmu No. 1 as the planting material for the protective border. The pathways between plots were set at 1 m wide. Compound phosphate fertilizer ((NH4)2HPO4) was used as the base fertilizer, applied at a rate of 75 kg/hm2. After the experimental seedlings survived, irrigation, fertilization, and grazing were prohibited. Conventional field management was carried out in the experimental field. In the 1-year (2021), weeding was performed three times. In the second (2022), third (2023), and fourth (2024) years, intertillage and weeding were conducted twice each (after regreening and before jointing), along with plant disease, pest, and rodent control.
2.3 Sampling methods and index measurement
Sampling and index measurements were conducted during the flowering period of Elymus nutans in August 2022 (second year), 2023 (third year), and 2024 (fourth year). In each experimental plot, 10 plants with similar growth vigor and no obvious pests and diseases were randomly selected. For each resource, plant height (natural height), crown breadth (average width of forage in the north-south and east-west directions), and grass height (height of basal leaves) were measured using a tape measure. The number of tillers (number of branches growing from the base of the main stem) per plant was counted, and the size of the leaf (flag leaf) was measured in terms of length and width. The plants were then weighed to calculate the dry grass yield per plant.
Forage yield: During the early flowering stage of Elymus nutans, 10 individual plants with consistent growth vigor were randomly selected in each plot (excluding marginal effects) and cut at the ground level. After removing weeds, the samples were immediately weighed to record the fresh weight. The Elymus nutans samples were then placed in large envelopes and brought back to the laboratory. They were first dehydrated at 105 °C for 30 min, followed by drying at 75 °C until a constant weight was achieved, which was recorded as the dry weight (Wang et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2025).
2.4 Data analysis
The data were initially analyzed using Excel 2019. Normality (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test) and homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test) were assessed for plant height, leaf length, leaf width, crown breadth, grass height, number of tillers, dry-fresh ratio, and dry grass yield per plant of different Elymus nutans resources using SPSS 19.0 (SPSS 19.0, Chicago, IL, USA) (Edgington, 1965; Odzimierz Bryc, 1995). Subsequently, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with least significant difference (LSD) multiple comparisons was used to analyze the significance of these indices at the 0.05 level of significance. Two-way ANOVA was employed to evaluate the effects of years, varieties, and their interactions on the agronomic traits and forage yield of Elymus nutans.
K-means clustering analysis was conducted on the key traits of Elymus nutans resources using the factoextra and ggplot2 packages in R. Based on the K-means clustering results, the TOPSIS model, was applied using the plyr package to comprehensively evaluate the agronomic traits and forage yield per plant of Elymus nutans resources.
The Random Forest model was constructed using the randomForest package in R 4.0.2 (R Development Core Team) to rank the importance of the factors influencing forage yield. The significance of the model and individual factors was assessed using the rfUtilities and rfPermute packages. To further elucidate the factors affecting the forage production performance of individual Elymus nutans plants, a piecewise structural equation model (SEM) was built using the piecewiseSEM package in R 4.0.2, based on the Random Forest analysis, to explore the processes and pathways influencing forage yield in different Elymus nutans resources. All figures were generated using the Origin 2021 software.
Piecewise Structural Equation Model (Piecewise SEM): Piecewise SEM decomposes complex causal relationships into multiple simple linear models. Each model corresponds to a path in the path diagram and can be fitted and evaluated independently of the others.
We applied piecewise structural equation modeling to analyze the interactions and pathways between agronomic traits (plant height, number of tillers, crown breadth, grass height, and dry-fresh ratio) and dry grass yield per plant in Elymus nutans.
TOPSIS model: The TOPSIS model is a multi-criteria decision-making tool. It determines the best option by comparing the distance of each alternative to the ideal and anti-ideal solutions. It is widely used for evaluation and selection tasks.
The weighting procedure of the TOPSIS model with the entropy-weight method was executed in four steps (n = number of accessions, m = number of indicators).
Normalization – construct matrix P
pij = xij / Σi xij (i = 1…n, j = 1…m)
Entropy value ej
qij = pij / Σi pij
ej = −(ln n)−1 Σi(qij ln qij)
Dispersion coefficient
dj = 1 − ej
Weight determination
wj = dj / Σj dj (Σj wj = 1)
Weights were then applied to generate the weighted normalized matrix V = pij wj for the subsequent TOPSIS ranking.
The TOPSIS model was applied to evaluate Elymus nutans accessions. This includes data standardization of agronomic traits (plant height, grass height, leaf length, leaf width, crown breadth, and number of tillers) and dry grass yield per plant. Subsequently, we constructed a weighted standardized matrix. The ideal and anti-ideal solutions were determined. Distances of each accession to both solutions were calculated. Finally, closeness coefficients (0-1, closer to 1 is better) were computed to identify the optimal germplasm resources.
3 Results
3.1 Agronomic traits and forage yield
The phenotypic characteristics and dry grass yield per plant of Elymus nutans resources varied significantly among the different years (Figure 2). Plant height, grass height, leaf length, leaf width, crown breadth, number of tillers, and dry grass yield per plant were highest in the third year, followed by the second year, and lowest in the fourth year, with significant differences among years (P < 0.05). In the second year, 18–023 had the highest plant height and leaf length (P < 0.05), widest leaf width (P < 0.05), most tillers per plant (P < 0.05), and highest dry grass yield per plant (P < 0.05), which were 109.00 cm, 15.67 cm, 1.02 cm, 62.50 tillers per plant, and 81.32 g, respectively (Figures 2A, C, D, F, G). It also had the highest grass height, at 22.00 cm (Figure 2B). 15-010, 16-123, and 18–023 had the largest crown breadth, 95.83–102.50 cm (Figure 2E). 17–213 had the highest dry-fresh ratio, at 0.41 (Figure 2H). In the third year, 15–010 and 18–023 had the highest plant and grass heights (P < 0.05), measuring 120.83–128.83 cm and 32.50–34.66 cm, respectively (Figures 2A, B). 18–023 had the longest leaf length and widest leaf width, at 17.60 cm and 1.03 cm, respectively (Figures 2C, D). 15–010 had the largest canopy width, at 127.53 cm (Figure 2E). 18–023 had the most tillers per plant and highest dry grass yield per plant (P < 0.05), with 433.33 tillers per plant and 82.83 g, respectively (Figure 2F, G). 17–213 had the highest dry-fresh ratio, at 0.49 (Figure 2H). In the fourth year, 18–023 had the highest plant height, grass height, leaf length, crown breadth, number of tillers, and dry grass yield per plant, which were 99.03 cm, 19.01 cm, 13.16 cm, 86.67 cm, 52.51 tillers per plant, and 79.33 g, respectively (Figures 2A, B, C, E, F, G).
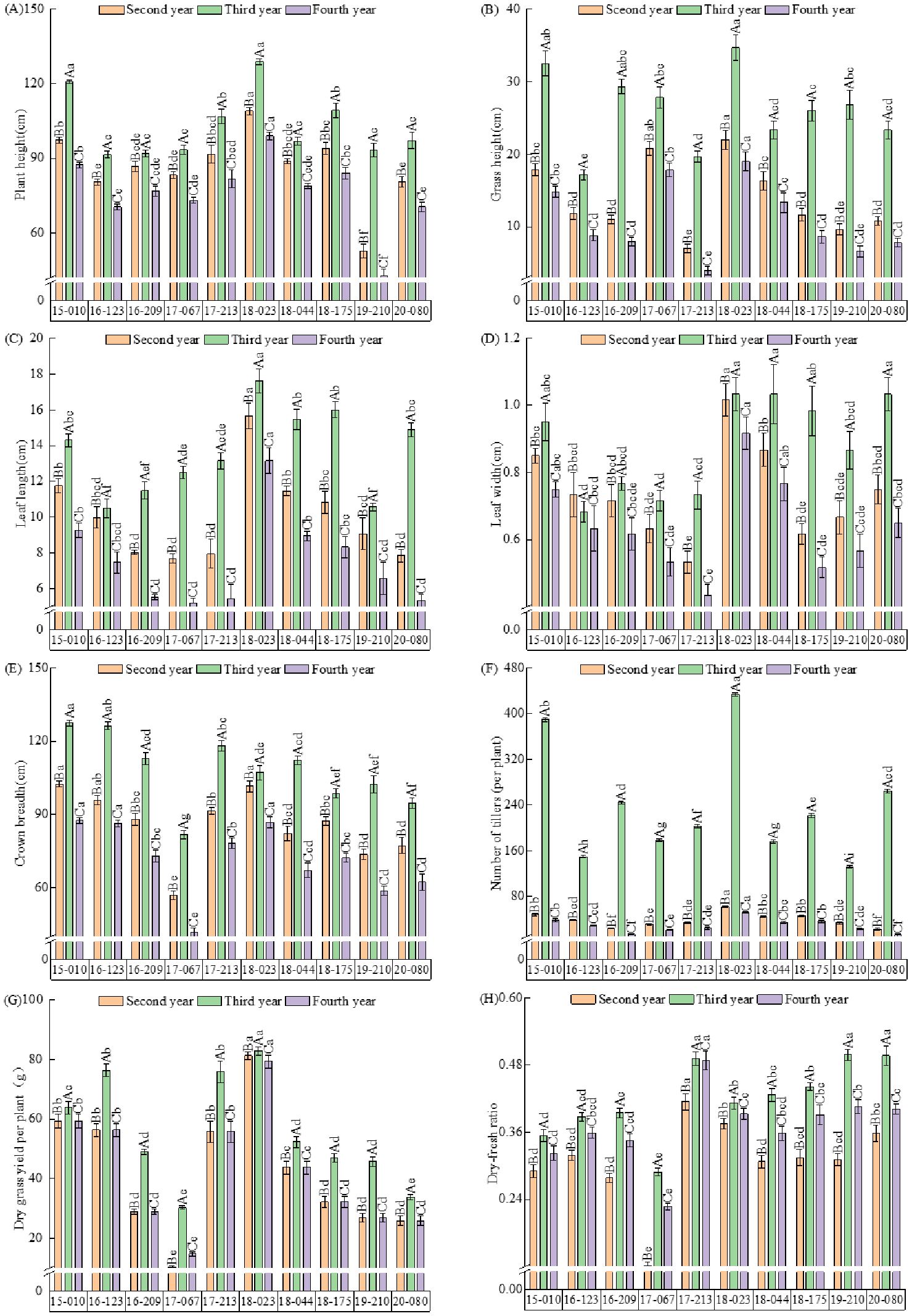
Figure 2. Agronomic trait characteristics and production performance of 10 varieties Elymus nutans accessions. (A) Plant height. (B) Grass height. (C) Leaf length. (D) Leaf width. (E) Crown breadth. (F) number of Tillers (per plant). (G) Dry grass yield per plant. (H) Dry-fresh ratio. Capital letters indicate individual traits measured across the 3 cultivation years. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; different lowercase letters denote significant differences among years within the same accession (P < 0.05, Tukey’s test).
The results of the two-way ANOVA (Table 2) indicated that year and variety, as well as their interaction, had highly significant effects on plant height, grass height, leaf length, leaf width, crown breadth, number of tillers, and dry grass yield per plant of the experimental materials (P < 0.01).
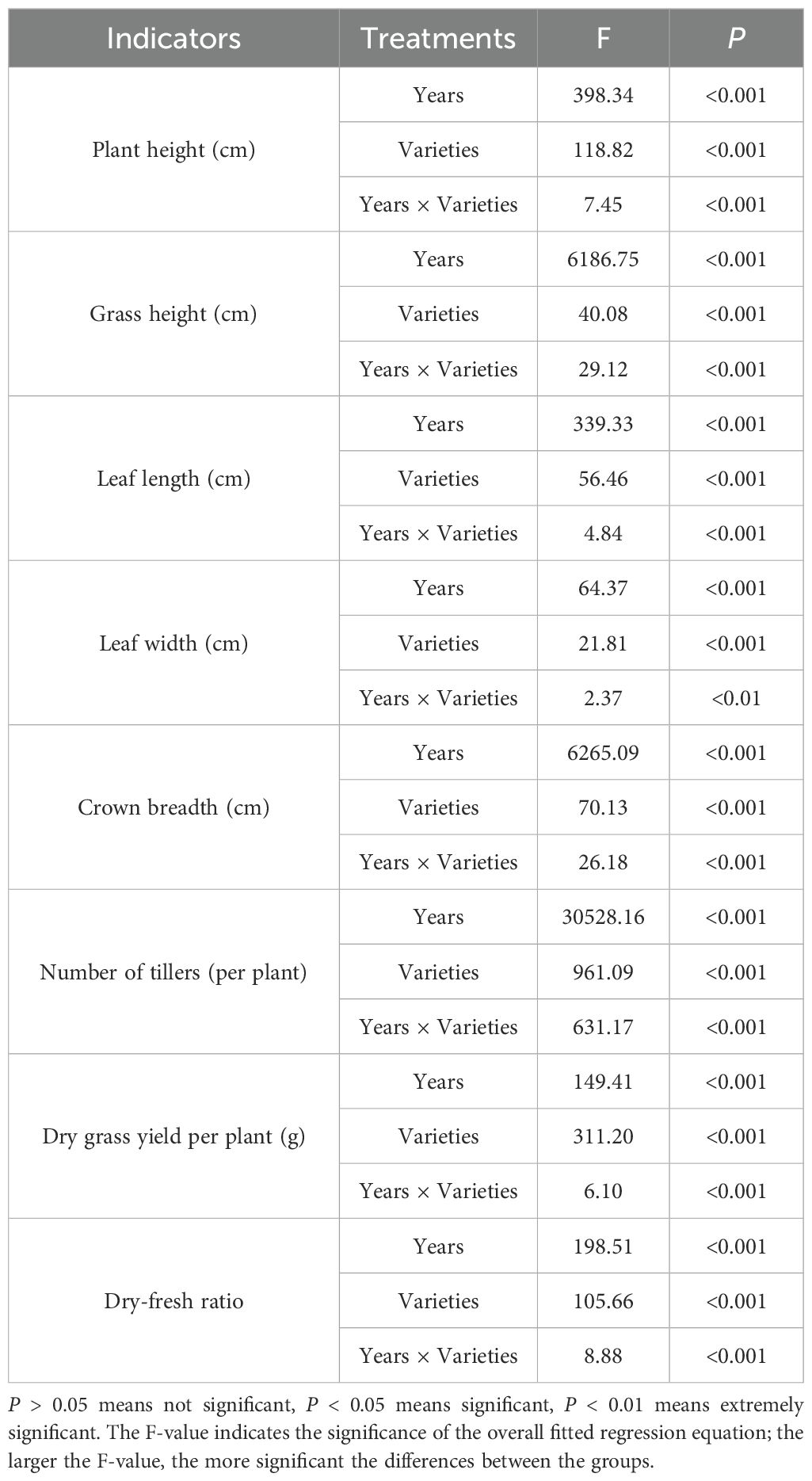
Table 2. Two-factor variance analysis of effects of years and varieties on agronomic traits and production performance of Elymus nutans.
3.2 Comprehensive evaluation of different Elymus nutans resources
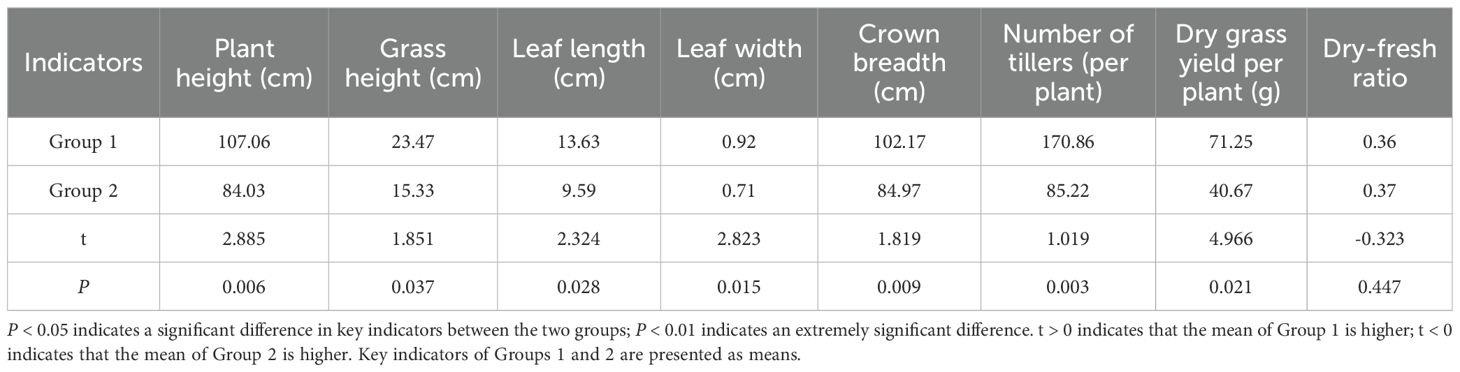
To effectively evaluate the comprehensive performance of the 10 excellent Elymus nutans resources, K-means clustering analysis was conducted based on key agronomic traits and yield-related characteristics of the resources. The 10 Elymus nutans resources were clustered into two groups. The P-values between the two groups were 0.006 for plant height, 0.037 for grass height, 0.028 for leaf length, 0.015 for leaf width, 0.009 for crown breadth, 0.003 for number of tillers, and 0.021 for dry grass yield per plant. Among these, plant height, crown breadth, and number of tillers showed extremely significant differences (Table 3). Group 1 accounted for 48% of the resources, whereas group 2 accounted for 52%. The resources in the second group mainly included 18-023, 15-010. The resources in the second group mainly included 16-123, 17-067, 18-175, 18-044, 17-209, 20-080, 19-210, and 17-213 (Figure 3A).
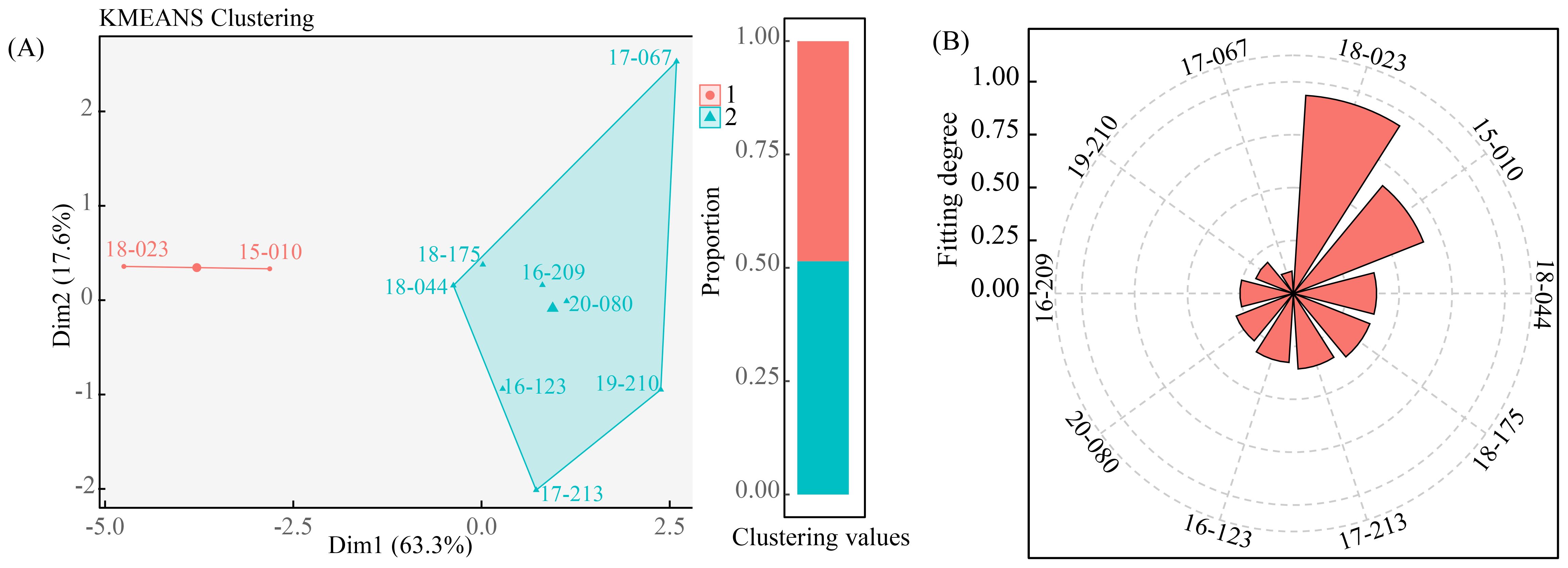
Figure 3. Comprehensive evaluation of forage performance based on the K-means clustering analysis and TOPSIS model. (A) represents the clustering results of 10 varieties Elymus nutans, derived from their agronomic traits and production performance during 3 years cultivation period. (B) represents the ranking results of the test materials obtained via the TOPSIS model.
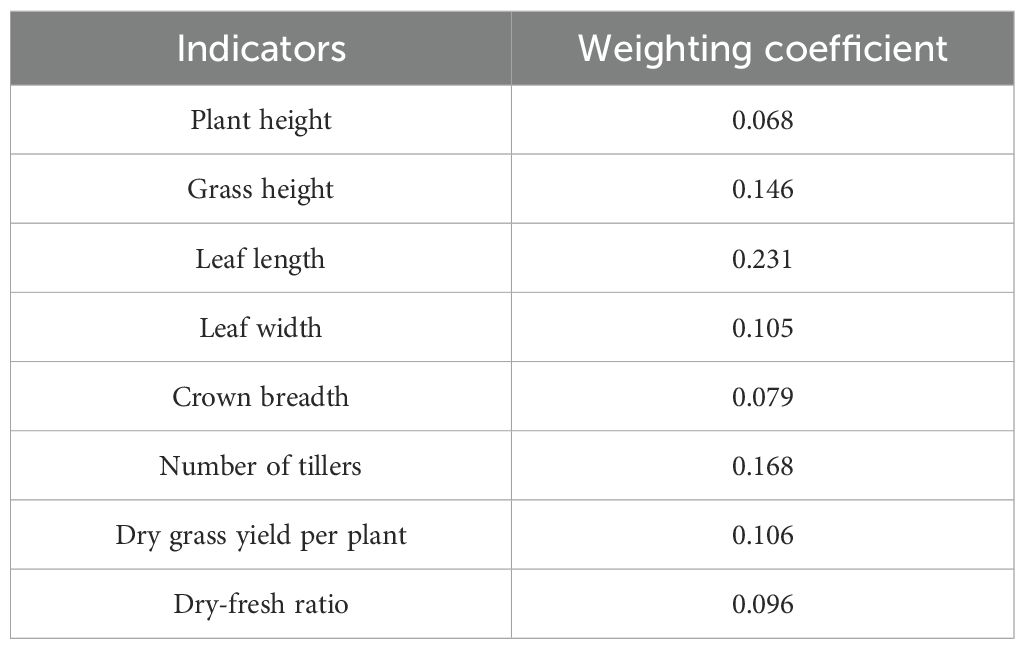
To further identify the Elymus nutans resources with the best overall performance, the TOPSIS model (Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution) was applied to comprehensively evaluate the dry grass yield per plant, plant height, grass height, leaf length, leaf width, crown breadth, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio of different Elymus nutans resources. The respective weight coefficients were 0.068 for plant height, 0.146 for grass height, 0.231 for leaf length, 0.105 for leaf width, 0.079 for crown breadth, 0.168 for number of tillers, 0.106 for dry grass yield per plant, and 0.096 for dry-fresh ratio (Table 4). The results showed that the degree of fit, from highest to lowest, was 18-023, 15-010, 18-044, 18-175, 17-213, 16-123, 20-080, 16-209, 19-210, and 17-067. Among them, 18–023 had the highest degree of fit at 0.93, while 17–067 had the lowest degree of fit at 0.11 (Figure 3B). Comprehensive evaluation results indicated that 18–023 had the best overall performance and was the optimal Elymus nutans resource for cultivation.
3.3 Key factors influencing the production performance of Elymus nutans resources
To determine the effects of plant height, grass height, leaf size (leaf length, leaf width), crown breadth, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio on the dry grass yield per plant, a Random Forest model was used to rank the importance of these factors (Figure 4). The results indicated that these factors collectively explained 79.17% of the variation in dry grass yield. Plant height, number of tillers, dry-fresh ratio, grass height, crown breadth, leaf length, and leaf width all had highly significant effects on forage yield (P < 0.01).
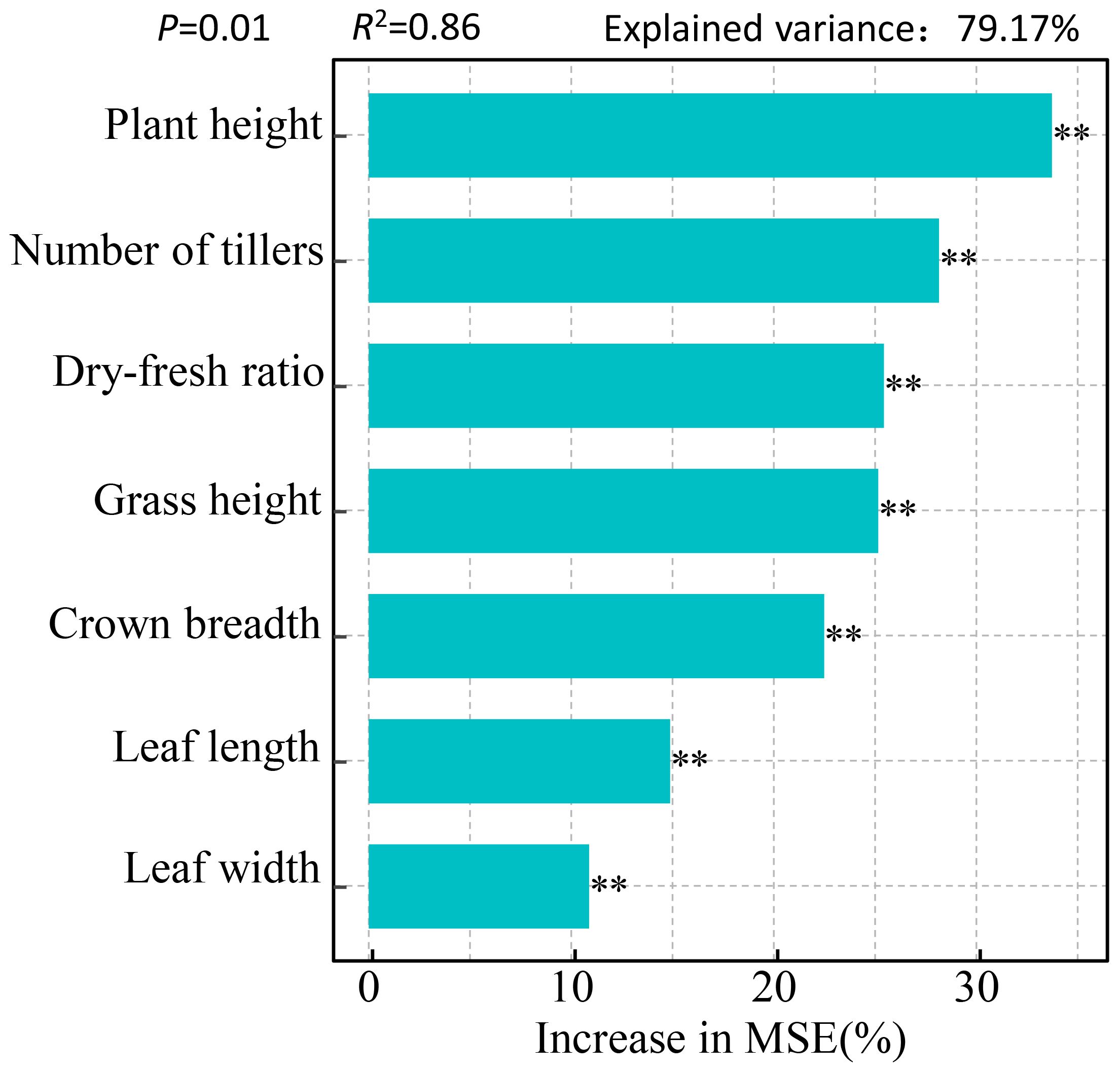
Figure 4. The importance ranking of variable factors in forage performance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns: No significant difference.
3.4 Analysis of influencing factors and pathways on production performance
Based on the results of the Random Forest model analysis, factors that significantly influenced the forage production performance of Elymus nutans were selected to construct a piecewise structural equation model (Figure 5). This model was used to explore the processes and pathways through which year, variety, and their interactions affect the forage production performance of Elymus nutans. The results showed that the piecewise structural equation model had a good fit (P = 0.974, Fisher’s C = 0.051). Year indirectly affected the dry grass yield per plant through its effects on plant height, crown breadth, grass height, and dry-fresh ratio. Variety indirectly affected the dry grass yield per plant through its effects on grass height and dry-fresh ratio. Plant height, crown breadth, grass height, and dry-fresh ratio all had significant positive effects on the dry grass yield per plant, with path coefficients of 0.257, 0.782, 1.285, and 0.433, respectively (Figure 5A).
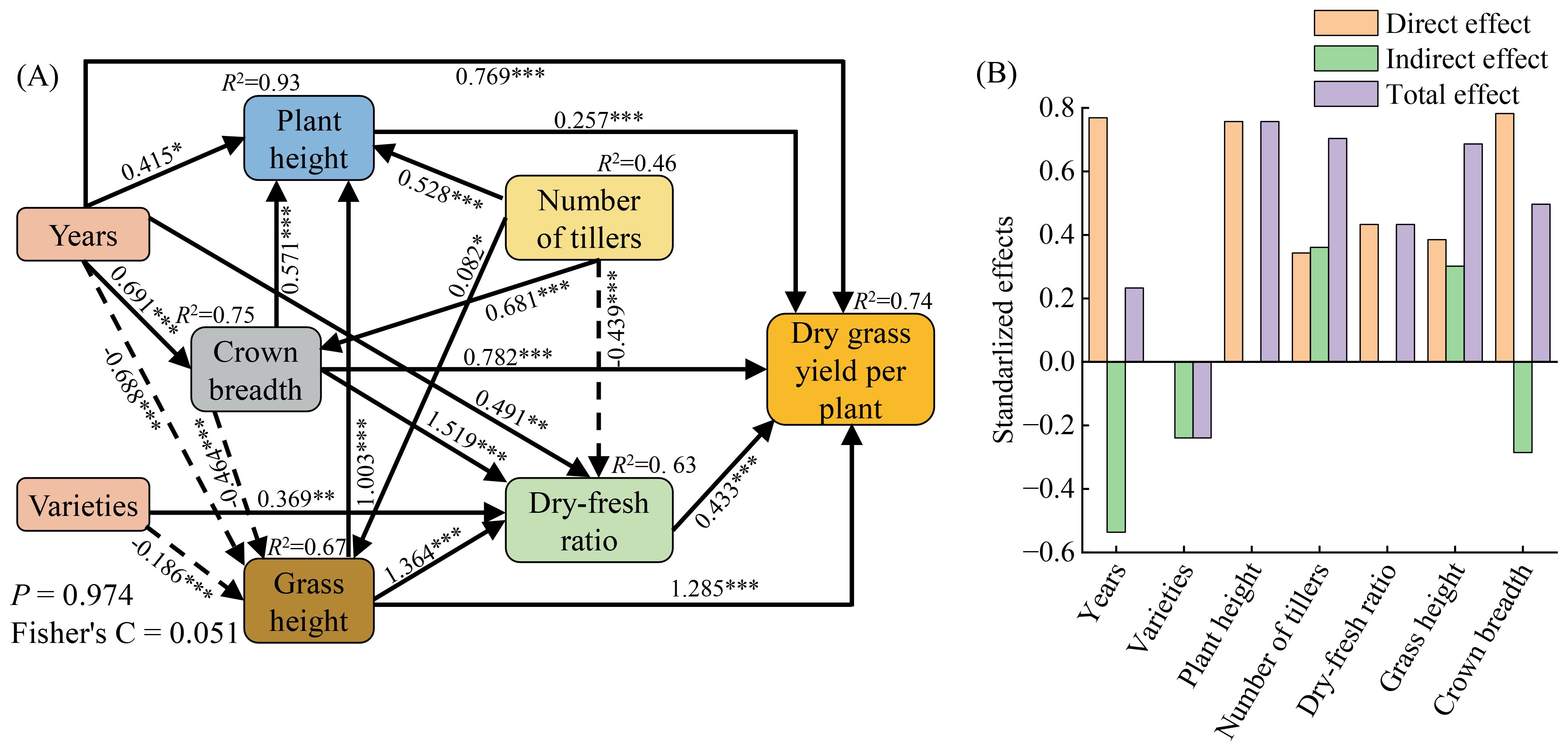
Figure 5. Structural equation model analyzed the influence paths of years and varieties on forage yield per plant (A) and the standardized effect values of each factor (B). Figures A and B show the structural equation model for individual grass yield, the standardized effect of each factor on grass yield, respectively. Solid and dashed arrows represent significantly positive and negative effects at the 0.05 level, respectively. The significant standard path coefficients are shown by arrows. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
The direct, indirect, and total effects of each factor were calculated based on the standardized path coefficients in the piecewise structural equation model (Figure 5B). The results showed that for the dry grass yield per plant of Elymus nutans resources, plant height, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio had the highest total effect values, at 0.757, 0.703, and 0.686, respectively. Therefore, year and variety mainly affected the forage yield of Elymus nutans through their effects on plant height, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio.
4 Discussion
Agronomic traits, as important indicators for evaluating forage production performance, are jointly influenced by the genetic characteristics of plants themselves and external environmental factors (Habib et al., 2024; Tefera et al., 2024). In this study, among the second to the fourth year Elymus nutans resources, 18–023 had a higher plant height and grass height, more tillers, and larger leaves. 15–010 had relatively high plant height and large crown breadth, with the second-highest number of tillers after 18-023; 17–213 had a higher dry-fresh ratio; 17–067 had a smaller crown breadth and lower dry-fresh ratio. The differences in the experimental materials may be due to varying adaptabilities of germplasm resources to ecological environments, or influenced by their inherent genetic characteristics (Barrett-Lennard et al., 2013; Barrio and Rapini, 2023; Chen et al., 2024). 18–023 was collected from the lower sunny slope position of a natural pasture in Guide County, Qinghai Province, where the native habitat features abundant sunlight, suitable temperatures, fertile soil, and higher soil moisture content. In contrast, the cultivation site is relatively dry, colder, and has poorer soil. Despite these differences, 18–023 maintained good growth at the cultivation site, indicating a broad ecological amplitude and strong drought, cold, and infertile tolerance. Therefore, 18–023 can be considered a suitable grass species for the ecological restoration of degraded grasslands. 15–010 was collected from the banks of a stream in Datong County, Qinghai Province, where the native habitat is moist and well-watered, providing favorable conditions for plant growth and development. Although the cultivation site is relatively dry, 15–010 still maintained good growth, demonstrating a broad ecological amplitude and strong adaptability to variable habitats, as well as good drought resistance. Thus, 15–010 can adapt to the variable growth environments of the alpine regions of the Tibetan Plateau and can be used as high-quality material for breeding new variety. 17–213 was collected from a gravel pile by the roadside in Guide County, Qinghai Province, where the native habitat is dry and water deficient. The cultivation site provided more favorable growth conditions compared to its native habitat. Therefore, 17–213 was more fresh, tender and juicy than other resources, making it suitable for use as a forage species in artificial pastures intended for grazing. 17–067 was collected from a fenced and protected pasture in Guide County, Qinghai Province, where the native habitat receives higher rainfall and has more fertile soil. However, its growth was poor at the cultivation site, showing no significant advantages. This indicates that 17–067 has relatively poor adaptability to growth environments and does not meet the breeding concept of strong adaptability and comprehensive performance. Additionally, in this study, the agronomic traits (plant height, grass height, leaf length, leaf width, number of tillers, and crown breadth) of the second to fourth year Elymus nutans materials were best in the third year, followed by the second year, and poorest in the fourth year. This is mainly determined by the growth habits and genetic characteristics of Elymus nutans (Weiss et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2025b). As a perennial sparse-tufted plant, the biomass and cover of Elymus nutans increase with the extension of cultivation years. The traits reached their peak in the third year. Subsequently, the central part of the tussock gradually years, and the tillering capacity of the underground parts decreases, leading to weaker tussocks. Moreover, long-term cultivation of Elymus nutans may also lead to soil nutrient depletion in the cultivation area, further exacerbating the degradation of Elymus nutans plants (Bin et al., 2015; Luo et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2019).
Forage yield is an important indicator of forage production performance and economic value of cultivated plants. It is an intuitive manifestation of the ecological adaptability of plant germplasm resources in a particular region and is a key factor to consider when determining whether a plant germplasm resource can be widely cultivated in that area (Wang et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2024). In this study, significant differences in forage yield and agronomic traits of Elymus nutans resources were observed among different years. This finding is similar to the results reported by Zhang et al (Zhang et al., 2022), Zhou et al (Zhou et al., 2000), (Wang et al., 2024), and Wang et al (Wang et al., 2025). in their studies on the perennial forage grass Elymus sibiricus. These differences are primarily attributed to the combined effects of precipitation, temperature, and genetic characteristics of Elymus nutans (Heinze et al., 2017; Stephenson et al., 2019; Habib et al., 2024). Precipitation and temperature mainly influence plant biomass accumulation by affecting physiological activities such as photosynthesis, respiration, and nutrient uptake (Skarpaas et al., 2016; Yao et al., 2022). In contrast, genetic characteristics are important factors that regulate plant growth and development (Demura and Ye, 2010). During the cultivation period in this study, higher precipitation and suitable temperatures from June to August (Figure 1) met the water and temperature requirements for the heading to maturity stages of Elymus nutans. The forage yield was the highest in the third year, followed by the second year, and the lowest in the fourth year. This pattern is mainly determined by the growth habits and genetic characteristics of Elymus nutans (Habib et al., 2024). During the cultivation period, plant biomass increased annually from 0 to the third year, reaching its highest level in the third year. In the fourth year, the yield of Elymus nutans decreased. This is mainly because Elymus nutans is a loose-tufted, top-growth dominant grass. As cultivation years increase, the plant gradually degenerates from the center of the tuft. Therefore, as cultivation years increased, the plant gradually degenerated from the center of the tuft, resulting in a progressive reduction in forage yield with extended cultivation (Bin et al., 2015; Luo et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2019). The piecewise structural equation model analysis in this study indicated that plant height, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio were key factors influencing the forage yield of Elymus nutans. This finding was consistent with the results reported by Yuan et al (Yuan et al., 2023). and Wang et al (Wang et al., 2025). This is because taller plants with stronger tillering capacity have higher utilization efficiency of ecological factors such as soil moisture, soil nutrients, and light. This, in turn, promotes the effective accumulation of organic matter within the plant, thereby increasing forage yield (Fernandez et al., 2009; Kariali et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2022).
In this study, the TOPSIS model was employed to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the agronomic traits and dry grass yield per plant of the experimental materials. The results indicated that 18–023 and 15–010 exhibited the best overall performance during the experimental period, with superior forage production capacity. These materials are considered more ideal materials for cultivation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone. This was attributed to the fact that both 18–023 and 15–010 originated from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone and maintained high ecological memory and genetic advantages in the experimental site, demonstrating superior growth, development, and effective accumulation of organic matter (Ma et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2019). The collection and screening of wild, high-quality forage resources are crucial for breeding new forage varieties and enriching the germplasm resource gene bank. It is recommended that future breeding efforts involving wild germplasm resources conduct multi-year comprehensive evaluation trials across multiple ecological regions to identify wild, high-quality resources with strong adaptability and good production performance. These resources can serve as parental materials for new variety breeding, laying the foundation for the development of forage species that are both ecologically adapted and suitable for forage production.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we conducted a systematic investigation of the agronomic traits and forage yield of 10 Elymus nutans resources over three consecutive years in Xihai Town. We also explored how years, varieties, and their interactions affect forage yield through their influence on agronomic traits using structural equation modeling. The following conclusions were drawn:
1. All 10 Elymus nutans resources were able to grow and develop normally in the experimental site. However, for each resource, both agronomic traits and dry grass per plant were highest in the third year, followed by the second year, and lowest in the fourth year during the experimental period, Thus, in the second year and the third year were mainly used for germplasm propagation, with the fourth year onwards used for grazing.
2. During the experimental period, 18–023 exhibited higher plant height, dry grass yield per plant, and grass height, as well as more tiller and larger leaves compared to other varieties. Thus, making it suitable for forage production or pasture establishment for grazing.
3. The comprehensive evaluation using the TOPSIS model indicated that 18–023 and 15–010 had the best overall production performance. They are ideal materials for degraded grassland ecological restoration and parental materials for high - yield and stable - yield variety breeding.
4. Structural equation model analysis revealed that plant height, number of tillers, and dry-fresh ratio were key factors influencing the forage yield of Elymus nutans.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
WW: Writing – original draft. WL: Writing – review & editing. KL: Writing – review & editing. WL: Writing – review & editing. XC: Writing – review & editing. GL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Qinghai innovation platform construction project (2025) and the 483 China Agriculture Research System (CARS-34).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the Qinghai Innovation Platform Construction Project (2025) and the 483 China Agriculture Research System (CARS-34) for our support. We also thank the Academy of Animal and Veterinary Sciences at Qinghai University for providing experimental materials and the research platform. Additionally, we are grateful to all the authors for their technical support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Barrett-Lennard E. G., Bennett S. J., and Altman M. (2013). Survival and growth of perennial halophytes on saltland in a Mediterranean environment is affected by depth to watertable in summer as well as subsoil salinity. Crop Pasture Sci. 64, 123–136. doi: 10.1071/CP12416
Barrio I. C. and Rapini A. (2023). Plants under pressure: the impact of environmental change on plant ecology and evolution. BMC Ecol. Evol. 23, 13. doi: 10.1186/s12862-023-02115-z
Bin Z., Zhang R., Zhang W., and Xu D. (2015). Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon addition on leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus concentration of Elymus nutans of alpine meadow on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Acta Ecologica Sin. 35, 4699–4706. doi: 10.5846/stxb201311142729
Chen D., Jia C., Zhao X. H., Yuan Z., Luo X. P., Bao J. L., et al. (2025a). Local adaptation is highly dependent on common garden conditions where seeds were propagated: Evidence from a 7romen study on a dominant alpine meadow species. J. Ecol. 113, 689–700. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.14491
Chen D., Jia C., Zhao X. H., Yuan Z., Luo X. P., Bao J. L., et al. (2025b). Local adaptation is highly dependent on common garden conditions where seeds were propagated: Evidence from a 7romen study on a dominant alpine meadow species. J. Ecol. 113, 689–700. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.14491
Chen J., Xu D. L., Xiao Q. C., Zheng Y. X., Liu H. J., Li X. Y., et al. (2024). Responses of soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality to environments changes in volcanic ecosystems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12, 113334. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.113334
Demura T. and Ye Z. H. (2010). Regulation of plant biomass production. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 13, 298–303. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2010.03.002
Edgington E. S. (1965). The assumption of homogeneity of variance for the t test and nonparametric tests. J. Psychol. 59, 177–179. doi: 10.1080/00223980.1965.9916790
Fernandez M., Becraft P., Yin Y. H., and Lübberstedt T. (2009). From dwarves to giants? Plant height manipulation for biomass yield. Trends Plant Sci. 14, 454–461. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2009.06.005
Ferrigno M. (2015). Perspectives from the roof of the world: tibetan nomadic perspectives on climate change (Prescott College: World Development Perspectives). 40, 100742. doi: 10.1016/j.wdp.2025.100742
Habib Z., Ijaz S., Haq I. U., Hashem A., Avila-Quezada G. D., Abd_Allah E. F., et al. (2024). Empirical phenotyping and genome-wide association study reveal the association of panicle architecture with yield in Chenopodium quinoa. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1349239. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1349239
He F., Li Q., Chen D. D., Zhao X. Q., Luo C. Y., Xu Q., et al. (2019). Variation characteristics of CO2 fluxes of elymus nutans artificial grassland for A planting cycle in agro-pastoral transition area of sanjiangyuan. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 28, 918–929. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2019.05.008
Heinze J., Gensch S., Weber E., and Joshi J. (2017). Soil temperature modifies effects of soil biota on plant growth. J. Plant Ecol. 10, 808–821. doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtw097
Hou C., Wei X., Zhou L., Ma J. H., Ren X., Wang Y. Y., et al. (2023). Dynamics of soil nematode community in perennial gramineae artificial grasslands in Northwest Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sin. 43, 10104–10118. doi: 10.20103/j.stxb.202307121501
Johnson L. C., Galliart M. B., Alsdurf J. D., Maricle B. R., Baer S. G., Bello N. M., et al. (2022). Reciprocal transplant gardens as gold standard to detect local adaptation in grassland species: New opportunities moving into the 21st century. J. Ecol. 110, 1054–1071. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.13695
Kariali E., Sarangi S., Panigrahi R., Panda B. B., and Mohapatra P. K. (2012). Variation in senescence pattern of different classes of rice tillers and its effect on panicle biomass growth and grain yield. Am. J. Plant Sci. 3, 1047–1057. doi: 10.4236/ajps.2012.38125
Li H., Gao J., Hu Q., Li Y., Tian J., Liao C., et al. (2019). Assessing revegetation effectiveness on an extremely degraded grassland, southern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, using terrestrial LiDAR and field data. Agriculture Ecosyst. Environ. 282, 13–22. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2019.05.013
Li X., Li X., Shi Y., Zhao S. J., Liu J. L., Lin Y. Y., et al. (2024). Effects of microtopography on soil microbial communities in alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Catena 239, 107945. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2024.107945
Liu X., Song S., and Yue M. (2019). Plant memory research in ecology. Acta Ecologica Sin. 39, 9387–9395. doi: 10.5846/stxb201809121959
Luo W. R., Li W. H., Ganjurjav H., Yan Y. L., Li Y., Cao X. J., et al. (2018). Effects of nitrogen on leaf functional traits and population characteristics of the artificial grassland Elymus nutans in Northern Tibet. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 27, 51–60. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2017266
Ma D. T., Guo Y. X., Hou F. J., Zhai X. Y., Wang W., Tian M., et al. (2014). Plant genetic diversity and grazing management on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A case study of a dominant native wheatgrass (Elymus nutans). Biochem. Systematics Ecol. 56, 16–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2014.04.014
Ren W., Lin C., Zhang Z., and Shen Y. (2025). Square-sowing patterns enhance mixed grass/legume communities of Elymus nutans and Onobrychis viciifolia production in the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Ind. Crops Products 223, 120159. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.120159
Ringselle B., Bergkvist G., Aronsson H., and Andersson L. (2016). Importance of timing and repetition of stubble cultivation for postivatione control of Elymus repens. Weed Res. 56, 41–49. doi: 10.1111/wre.12183
Shi Z. H., Liang G. L., Li S. D., and Liu W. H. (2024). Adequate water supply enhances seedling growth and metabolism in Festuca kryloviana: insights from physiological and transcriptomic analys. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 714. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05353-5
Skarpaas O., Meineri E., Bargmann T., Pötsch C., Töpper J., Vandvik V., et al. (2016). Biomass partitioning in grassland plants along independent gradients in temperature and precipitation. Perspect. Plant Ecology Evol. Systematics 19, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ppees.2016.01.006
Song J. C., Yang H., Yu X. J., Chen Y. Z., Yang C. Y., He Y. L., et al. (2025). Effects of combined application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers on seed yield, seed quality and economic returns of Elymus nutans in alpine region. BMC Plant Biol. 25, 130. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06126-4
Stephenson M. B., Volesky J. D., Schacht W. H., Lawrence N. C., Soper J., and Milby J. (2019). Influence of precipitation on plant production at different topographic positions in the Nebraska Sandhills. Rangeland Ecol. Manage. 72, 103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.rama.2018.09.001
Sun W., Zhang E., Liu Y., and Shen J. (2025). The black carbon record of mid-to late-holocene environmental changes and its links to climate change and anthropogenic activity on the northwest Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 965, 178659. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2025.178659
Tefera A. T., O’Leary G. J., Rao S., Shunmugam A. S., Silva-Perez V., Brand J., et al. (2024). Identification of agro-phenological traits of lentil that optimise temperature and water limited flowering time and seed yield. Eur. J. Agron. 155, 127138. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2024.127138
Wang J. L., Li W., Cao W. X., and Wang S. L. (2022). Effects of different intensities of long-term grazing on plant diversity, biomass and carbon stock in alpine shrubland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ 10, e12771. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12771
Wang B., Li J., and Song G. (2014). Biophysical regulation of the net ecosystem CO2 exchange over an Elymus nutans artificial pasture in the Three-River Source Region of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Japanese Soc. Grassland Sci. 43, 1820–1831.
Wang W., Liang G., Liu W., and Wang F. Y. (2025). Comprehensive evaluation of agronomic traits and yield of eight Elymus sibiricus varieties in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 34, 123–132. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2024118
Wang L., Lou Y., and Shao S. (2022). Effects of planting density on the growth and quality of Eremopyrum orientale. Pratacultural Sci. 39, 503–510. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2021-0543
Wang Z., Wang C., Tan X., Gao G., El-Badri A. M., Batool M., et al. (2024). Diversified spatial configuration of rapeseed-vetch intercropping benefits soil quality, radiation utilization, and forage production in the Yangtze River Basin. Field Crops Res. 318, 109587. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2024.109587
Weiss T., Crisp P. A., Rai K. M., Song M., Springer N. M., and Zhang F. (2022). Epigenetic features drastically impact CRISPR–Cas9 efficacy in plants. Plant Physiol. 190, 1153–1164. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac285
Wu G. L., Liu Z. H., Zhang L., Hu T. M., and Chen J. M. (2010). Effects of artificial grassland establishment on soil nutrients and carbon properties in a black-soil-type degraded grassland. Plant Soil 333, 469–479. doi: 10.1007/s11104-010-0363-9
Wu S. N., Zhang X., Gao X. X., Xu D. Y., Wu X. H., Shan X. K., et al. (2019). Succession dynamics of a plant community of degraded alpine meadow during the human-induced restoration process in the Three Rivers Source region. Acta Ecologica Sin. 39, 2444–2453. doi: 10.5846/stxb201804070783
Yao Z., Xin Y., Yang L., Zhao L., and Ali A. (2022). Precipitation and temperature regulate species diversity, plant coverage and aboveground biomass through opposing mechanisms in large-scale grasslands. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 999636. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.999636
Yuan Y., Chen D. M., Liu W., Huyan M. J., Lv A., and Wang D. G. (2023). Correlation analysis and comprehensive evaluation of production and reproductive of forage oat in northwest Sichuan plateau. J. Sichuan Agric. Univ. 41 , 1116–1123. doi: 10.16036/j.issn.1000-2650.202304271
Zhang Q., Ma L., Zhang Z. H., Xu W. H., Zhou B. R., Song M. H., et al. (2019). Ecological restoration of degraded grassland in Qinghai-Tibet alpine region: degradation status, restoration measures, effects and prospects. Acta Ecologica Sin. 39, 7441–7451. doi: 10.5846/stxb201908301803
Zhang Y. C., Wei X. X., Liang G. L., Qin Y., Liu W. H., Jia Z. F., et al. (2022). Phenotype changes during ageing over six years of Elymus sibiricus stands and the effects of nutrient addition. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 31, 101–111. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2021103
Zhou J., Li Y., Wang X., Liu Y., David-Schwartz R., Weissberg M., et al. (2022). Analysis of Elymus nutans seed coat development elucidates the genetic basis of metabolome and transcriptome underlying seed coat permeability characteristics. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 970957. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.970957
Zhou H., Yang B., and Han J. G. (2000). Studies some structure characteristics of community of grassland of Elymus sibiricus planted in different years. Acta Agrestia Sin. 04), 245–252. doi: cdxu.0.2000-04-001
Keywords: Elymus nutans, agronomic traits, forage, model, comprehensive evaluation
Citation: Wang W, Liu W, Liu K, Li W, Chen X and Liang G (2025) Comprehensive evaluation of the agronomic traits and forage production performance of Elymus nutans in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau zone. Front. Agron. 7:1659855. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1659855
Received: 04 July 2025; Accepted: 14 October 2025;
Published: 27 November 2025.
Edited by:
Nasim Ahmad Yasin, University of the Punjab, PakistanReviewed by:
Xiaobin Wang, Zhejiang University, ChinaRuijuan Liu, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Alireza Pourmohammad, University of Maragheh, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Liu, Liu, Li, Chen and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoling Liang, cWhsaWFuZ2d1b2xpbmdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Kaiqiang Liu, orcid.org/0000-0001-7020-2896
Wen Li, orcid.org/0009-0005-9383-3136
Xin Chen, orcid.org/0009-0009-9914-3012
Guoling Liang, orcid.org/0000-0002-5516-012X
 Wenhu Wang
Wenhu Wang Wenhui Liu
Wenhui Liu Kaiqiang Liu1,2†
Kaiqiang Liu1,2†