- 1Crop Production Division, Mbalmayo Agricultural Research Centre, Institute of Agricultural Research for Development, Yaoundé, Cameroon
- 2Centre de Recherche et d’Accompagnement des Producteurs Agro-pastoraux du Cameroun, Yaoundé, Cameroon
- 3National School of Computer Science and Systems Analysis, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco
Introduction: The cochineal scale insect scientifically known as Dactylopius opuntia was first introduced as biological control methods in regions where cactus was considered an invasive weed. Today, D. opuntiae insects is seen as one of the most important limitations to edible cactus production. In the present study, a meta-analysis was performed to assess the effectiveness of various control methods against D. opuntiae and the associated key factors.
Methods: The Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based tools were employed to screen scientific production reporting the effectiveness of the fight against D. opuntiae, while robust variance estimation (RVE) and proportional meta-regressions were applied to deal with the abundance of effect sizes within a single study and perform subgroup meta-analysis respectively.
Results: The effect sizes were pooled to 4.19 ± 0.08, I2 = 99.99%, for the nymphs and to 3.99 ± 3 0.09 I2 = 99.99%, for the adult insects. The proportional meta-analysis pooled the proportion of nymph’s mortality by 63%, I2 = 99.1%, and adult mortality by 74%, I2 = 98.6%. In subgroup analysis, a significant difference (p < 0.001) was observed among study locations (countries) and trial durations (times), suggesting that these factors can influence the effectiveness of the fight against Dactylopius pest. Importantly, non-chemical control means yielded higher proportion of adult cochineal mortality compared to chemical method.
Discussion: Finally, the scientific information obtained in the present study provides valuable insight for decision-makers towards effective, and sustainable control of white cochineal pest. Therefore, consideration of environmental influence (location) and the duration of treatments in this control is recommended.
Introduction
Approximately 60% of food production comes from dryland rain-fed farming systems, and the sustainability of irrigation in agriculture is questionable regarding the risk of water depletion (Acharya et al., 2019). Climate change observed on the Earth planet for decades has led to harmful consequences in the agricultural sector. These changes increase the appearance of abiotic and biotic constraints in crop production, threatening food security in many regions worldwide (Von Cossel et al., 2025). Many crops of important food value have seen their production decline, resulting in a situation where the population continues to grow while agricultural production declines. With approximately 300 species, Opuntia is the largest genus within the Cactaceae family, among which 10 to 12 species including Opuntia ficus-indica are commonly grown for forage and fruit production (Yahia and Sáenz, 2011). Its Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) allows the species to absorb CO2 at night time, facilitating its rapid adaptation and propagation in arid and Mediterranean basin (El Finti et al., 2013). The cactus species (Opuntia spp.) originated from Mexico and were introduced in North and South Africa and in the Mediterranean basin in the 16th century (Taoufik et al., 2015).
Opuntia is a crop of great importance in arid and semi-arid regions, providing incomes to farmers and contributing to food security for human beings and livestock. The cactus pear fruit is rich in micronutrients, the fruit pulp sugar content ranges from 70% to 80% with low acidity (0.18% citric acid), the pH varies from 5.3 to 7.1, and the vitamin content value is approximately 25 to 30 mg/100 g (Shongwe et al., 2010). Due to this importance, the interest of cacti has increased (Lopes et al., 2018; Méndez-Gallegos and Bravo-Vinaja, 2022; Marhri et al., 2023). Brazil, Morocco, Tunisia, Mexico, Algeria, Italy, and South Africa are the highest-producing countries of Opuntia spp. in the global production that occupy about 2.6 M ha (Neupane et al., 2021). In Morocco, the cactus was introduced in 1779, coming from South Africa Republic (Aalaoui et al., 2020). The plant contributes to food security for many people and to the economy of the country due to the increased demand of the European and the United States markets. The Green Morocco Plan and National Plan to Combat Desertification have contributed to the promotion of prickly pear cactus in the country (Ramdani et al., 2021).
Despite the importance of cactus, the white cochineal Dactylopius opuntiae (Cockerell), since its appearance, has rapidly spread throughout many countries, threatening wild species reported to be resilient in stress environments (Marhri et al., 2023). Dactylopius opuntiae is considered as the most destructive among the 11 species of Dactylopius genus. There are more than 167 arthropods associated with prickly pear cactus, but the most damaging in Mexico, Brazil, Spain, and, recently, Morocco is D. opuntiae, and severe infestations, with a rate of about 75%, can result in the death of the plant (Aalaoui et al., 2020). The insect was first used as a biological control where cactus was considered an weed invasive weed crop, but now the white cochineal represents a pest (Flores et al., 2013). Its expansion and damages on cactus and the associated economic impact have generated great scientific interest worldwide (Méndez-Gallegos and Bravo-Vinaja, 2022). Therefore, an integrated pest management (IPM) approach is necessary to control the pest (Ramdani et al., 2021).
Some widely used white cochineal control methods include biological control (Flores et al., 2013; Aalaoui et al., 2020), genetic control (Akroud et al., 2022; Akroud et al., 2021), chemical control (El-Aalaoui and Sbaghi, 2023), and in vitro culture (Akroud et al., 2022; Lahbouki et al., 2023; Marhri et al., 2023). In plant breeding, researchers have always used the creation of resistant varieties as the most efficient approach to control biotic and abiotic stresses. Genetic resistance is sought after by breeders because it can provide effective protection without requiring additional costs. It is also environmentally friendly and safe for the producer (Gómez et al., 2009). The resistance to D. opuntiae was already reported to be significant among Opuntia spp. genotypes (Ezzahraa, 2022). The impact of the D. opuntiae pest on some traits of interest, such as fruit yield and fruit quality, was reported to be influenced by genetic diversity (Sedki et al., 2010). Organic control likewise uses products derived from animals or plants. Their ease of decomposition in nature makes them an ecological means that preserves the environment. Organic products are also used as fertilizers and are reported to be promising for the regulation of nitrogen availability and soil fertility (Breza and Grandy, 2025). However, in conventional agriculture, these products often struggle to meet the quantitative demand for large areas, and the lack of information on dosage often leads to hazardous use and product losses. On the other side, biological control follows the same objective as the organic method in that it uses natural methods to control plant diseases and pests. However, this approach can be problematic in some cases. The Dactylopius opuntiae pest is often considered as the result of biological control of the invasive cactus by the white cochineal insect. On the other hand, chemical control, which uses synthetic pesticides, is the most widespread in intensive agriculture. Chemical products are accessible, and their effectiveness is easily measurable. Chemical pesticides have contributed to the green revolution in several countries. However, their excessive use represents a danger for the environment, the producer, and the consumer. Today, agroecology, which aims to promote agriculture that protects the environment, recommends the rational use of chemicals or simply their exclusion in agricultural practices. Finally, it is common to combine more than one control method in certain situations. This mixing approach has the advantage of optimizing control by filling the limitations of one approach with another and vice versa. However, some products can have antagonistic effects. Therefore, any mixed control method must be applied with caution.
The population that derives its profit from the cactus needs efficient methods to control this constraint. Despite the increasing scientific production on D. opuntiae pests and the associated control means, few studies have paid attention to certain factors that influence the effectiveness of these solutions. Almost all works reported do not take into account the nature of the control method used, the duration of the experiment, the location, and the experimental conditions. Then, the implementation of the control methods against D. opuntiae raises two essential questions about their effectiveness and impact. Is the control method used to eradicate D. opuntiae the only element that determines the effectiveness of the control? Alongside this method, what is the contribution of other factors involved in the experiments that may influence the success of the fight? The answers to these questions will undoubtedly be a great asset toward the sustainable and broad-spectrum management of white cochineal in the regions subject to this constraint. In the present study, we assume that the control method used is the only factor that determines the effectiveness of the fight against D. opuntiae. Using a meta-analysis supported by artificial intelligence tools, this study aimed to converge the control means against D. opuntiae with the possible factors involved in this pest management.
Methods
The meta-analysis was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (https://www.prisma-statement.org/) process (Page et al., 2021a, 2021b). The following sections were then the subject of the methodology: eligibility criteria, information sources, search strategy, selection process, data collection process, study risk of bias assessment, effect measure, meta-regression, and subgroup analysis.
Study selection criteria
The article was considered relevant for the meta-analysis study if it met the following inclusion criteria:
● The article language is English or French or it has the translated version in any of these languages;
● The full text is available;
● The article reports the control of Dactilopius opuntiae;
● The data or any information allowing to extract them were available (percentage of mortality, the size of the population, and the standard deviation);
● The study subject was Cactus (Opuntia spp.) species;
● The study location was indicated in the article;
● The experimentation duration was indicated; and
● We were able to identify the nature of the control method
Information sources and search strategy
The information sources are websites gathering research papers in agriculture, ecology, and related fields. The above-mentioned sources included Web of knowledge, Google Scholar, Scopus, IEEExpore, and the website Zenodo. We searched on these sources to find primarily relevant articles. Books, book chapters, review papers, and notes were not considered in the primary selection. We subscribed to publication notifications in Google Scholar and Academia to receive continuous updates about the articles on the topic of interest. The terms related to the topic were then introduced in the above-mentioned websites as follows: For Cactus, (prickly pear cactus OR Cactus OR Opuntia spp OR Figue de barbarie) AND for the pest (Dactylopius opuntiae OR prickly pear cochineal OR Cactus white cochineal) AND for the control, (management OR control OR eradication). Based on the results from the search, a separate dataset was built from each source prior to analysis with artificial intelligence tools.
Selection process using machine learning
The selection process of relevant articles to be included in the meta-analysis was performed in the ASReview software (Van De Schoot et al., 2021) tool after charging its library through python 3.13.2 version. After removing duplicates, a single file combining data from different sources was uploaded in ASReview for machine learning screening. A total of 2,049 articles were processed in the oracle mode. The following keywords were used as prior knowledge: “Dactylopius opuntiae, Cochineal, Control, Prickly pear cactus, Opuntia spp, Resistance”. We carefully checked titles and abstracts and set the training model with 61 papers identified as relevant and 60 as irrelevant labeled records. The active learning model (computer programs that help in the identification of eligible studies) was the TfidfVectorizer (TF-IDF) algorithm, which calculates the product of Term Frequency and Inverse Document Frequency (Lazuardi et al., 2023), while the machine learning model used as a classifier to compute relevant scores was naive Bayes. The screening was stopped after 162 continuous irrelevant papers out of 810 screened (Figure 1).
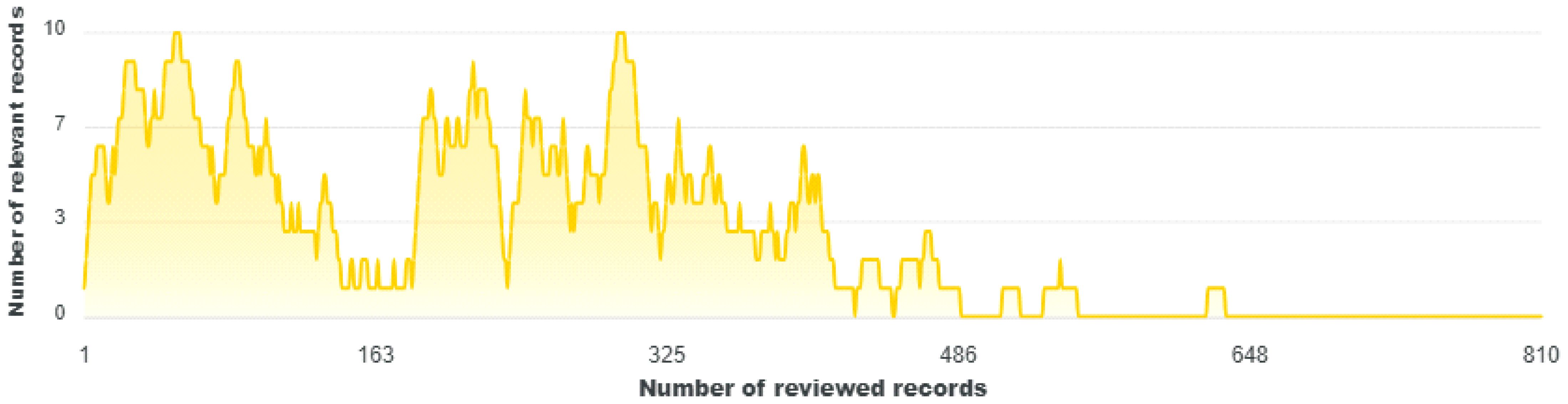
Figure 1. Screening evolution of papers in the open source ASReview artificial intelligence algorithms.
Data collection procedure
Once the papers were selected as relevant for the study, the following key information was extracted and arranged in an Excel file: author name, date of publication, the duration of the experimentation, the study location and country, and the control mean used against D. opuntiae. All control means used were classified into four categories, including chemical, biological, genetic, and organic. The data were likewise collected both for nymphs and female adult insects. If the author tested the control method at different levels of insect attacks, the result for the high level was calculated.
Meta-analysis
Effect size estimation
The individual effect size (practical significance of a research outcome) of each study was calculated as the log-transformed mean of the percentage of insects killed after application of the control method. The effect size was estimated using the percentage of insect killed, the size of the population and the standard deviation with metafor package and the function escalc in R software (Viechtbauer, 2010). However, many studies did not report the standard deviation. Over 15 alternative approaches were reported to be efficient in collecting missing information for the estimation of risk ratio (Weir et al., 2018). Depending on data availability, the standard deviation was estimated using one of the Equations 1–3 (of which the descriptions are reported in Table 1):
SDest is the standard deviation estimated, SE the standard error, n is the sample size or population of D. opuntiae evaluated, and R is the range of the percentage of mortality reported. The tabulated conversion factor (f) value based on the sample size was described in Walter and Yao (2007). After a sample size of 20, the f value is provided by class, and some sample sizes do not have an exact value of f. To overcome this situation, a linear interpolation was provided in the paper (Walter and Yao, 2007). The control of D. opuntia in most of the studies was evaluated as the percentage of dead nymphs or adults (mostly female) after application of the control method. Accordingly, this percentage was considered as the mean transformed in the effect size calculation.
Meta regression model
To deal with the multiple treatments reported in a single study, the meta regression (combined statistical analysis of study results) was performed using the robust variance estimation (REV) approach (Scammacca et al., 2014; Pustejovsky and Tipton, 2022). In standard meta-analysis, the average effect can first be calculated without including the covariates (potential moderators) in the model. In this first step, the pooled effect (average effect size) was estimated using the correlated effects model with small-sample correction. The between-study variance (τ²) was calculated using the method-of-moments estimator provided in Hedges et al. (2010), while the total heterogeneity I2 (variation between the studies’ results) was estimated as the amount of variability in effect size estimates due to effect size heterogeneity. The value of I2 above 75% indicates substantial heterogeneity, and this is the advised indicator to investigate further the heterogeneity contribution of covariates through subgroup analysis (Hak et al., 2018; Gibson and Nguyen, 2021). These analyses were followed by the sensitivity test in order to determine the effect of τ² on p-value.
Subgroup analyses
The subgroup meta-analysis of single proportion was performed using the random effects model at a 95% confidence interval. To remain focused on the research hypothesis, the effect sizes collected from a large diversity of control methods were organized into four groups plus one, according to these later control means (organic, biological, chemical, genetic, and mixture). Accordingly, the subgroup analysis and further analysis focused on these groups. In short, subgroup analysis was performed to explain the statistical heterogeneity, considering the nature of control methods as main groups, and the analysis was performed both for nymphs and adult insects. In addition, the subgroup analysis also considered the experimentation medium, location, and duration of experimentation as possible moderators. Finally, because of too many observations for the duration of the experimentation variable, we classified this covariate into classes consisting of day (≤24 h), days (experimentation conducted during many days), week (experimentation conducted during 1 week), weeks (experimentation conducted during many weeks), month (experimentation conducted during 1 month), and months (experimentation conducted during many months).
Publication bias
The publication bias was qualitatively screened through the funnel plot, a funnel plot of effect sizes plotted against the weight of each. The publication bias was next evaluated through the Egger’s regression test for funnel plot asymmetry using the weighted regression model “lm” (Egger et al., 1997). This was followed by the Duval and Tweedie trim-and-fill method to correct possible bias.
Results and discussion
Study selection and machine learning screening
The systematic review yielded 2,638 publications related to the control of D. opuntiae in cactus production. After removing duplicates, 2,049 were selected for quality check in ASReview. The Web of Knowledge produced the highest number of publications (n = 879), followed by Google Scholar (n = 649), Scopus (n = 269), Zenodo (n = 235), and IEEExplore (n = 17). The screening process in the ASReview platform with machine learning algorithms identified 131 relevant publications to be considered for further selection analysis. After a deep check, 54 publications and seven from citations and the website Zenodo fall into the eligibility criteria for a total of 61 papers selected to conduct the meta-analysis. The PRISMA flow diagram delineating the selection process is shown in Figure 2.
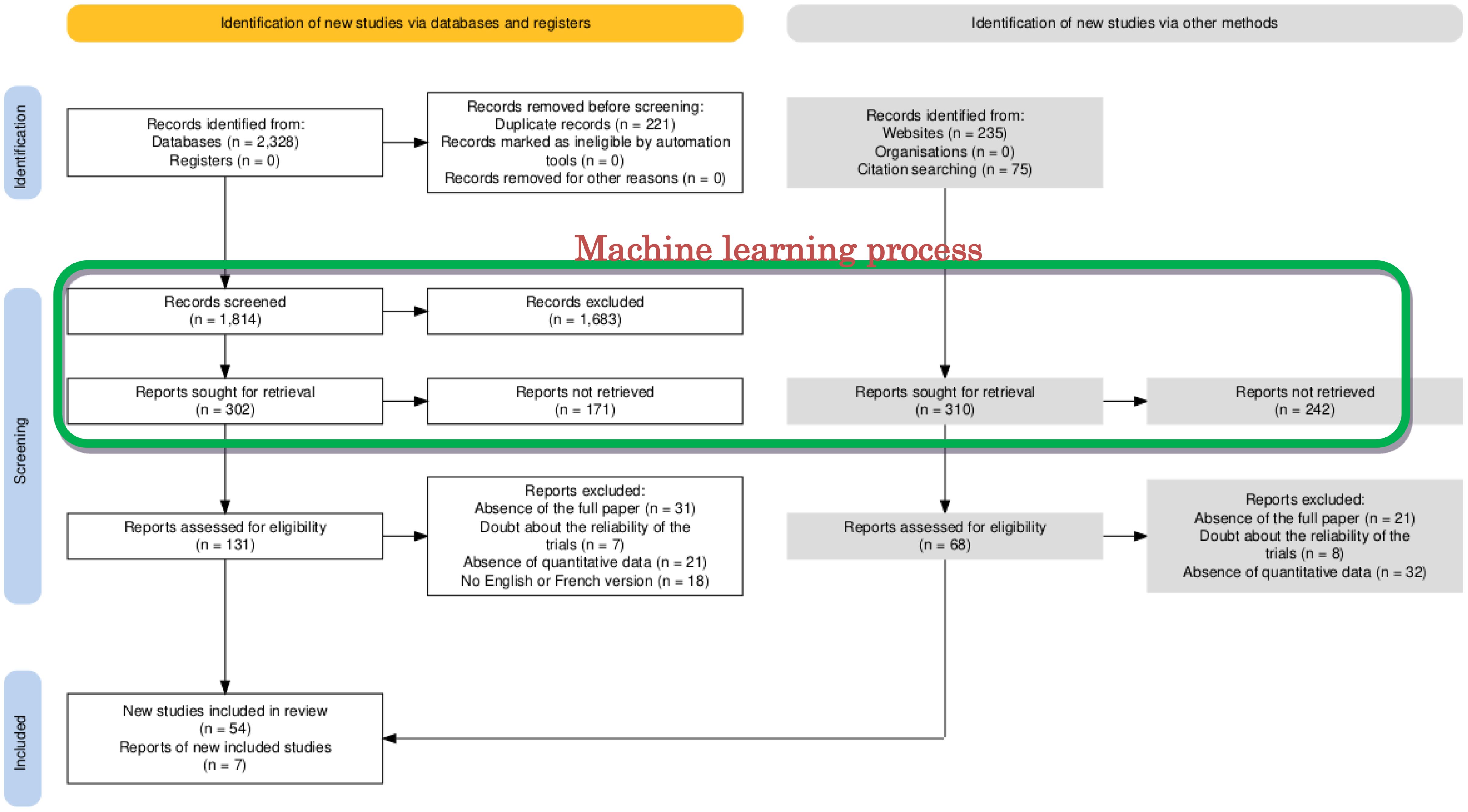
Figure 2. PRISMA flowchart detailing the selection of papers included in the meta-analysis for the control of Dactylopius opuntiae.
Study characteristics and effects size extraction
The metafor library yielded 221 effect sizes from 43 publications on nymphs and 192 effect sizes from 38 publications on adult insects. The number of effects sizes per paper ranged from one to 20 on nymphs and one to 17 on adult insects. Organic products were the most common control method used, and a large number of these methods were evaluated in laboratory conditions for many days (Figure 3). Regarding the field location, trials were recorded in arid and semi-arid regions (Figure 4), and most of the tests were conducted in Morocco (202) and in Brazil (96).
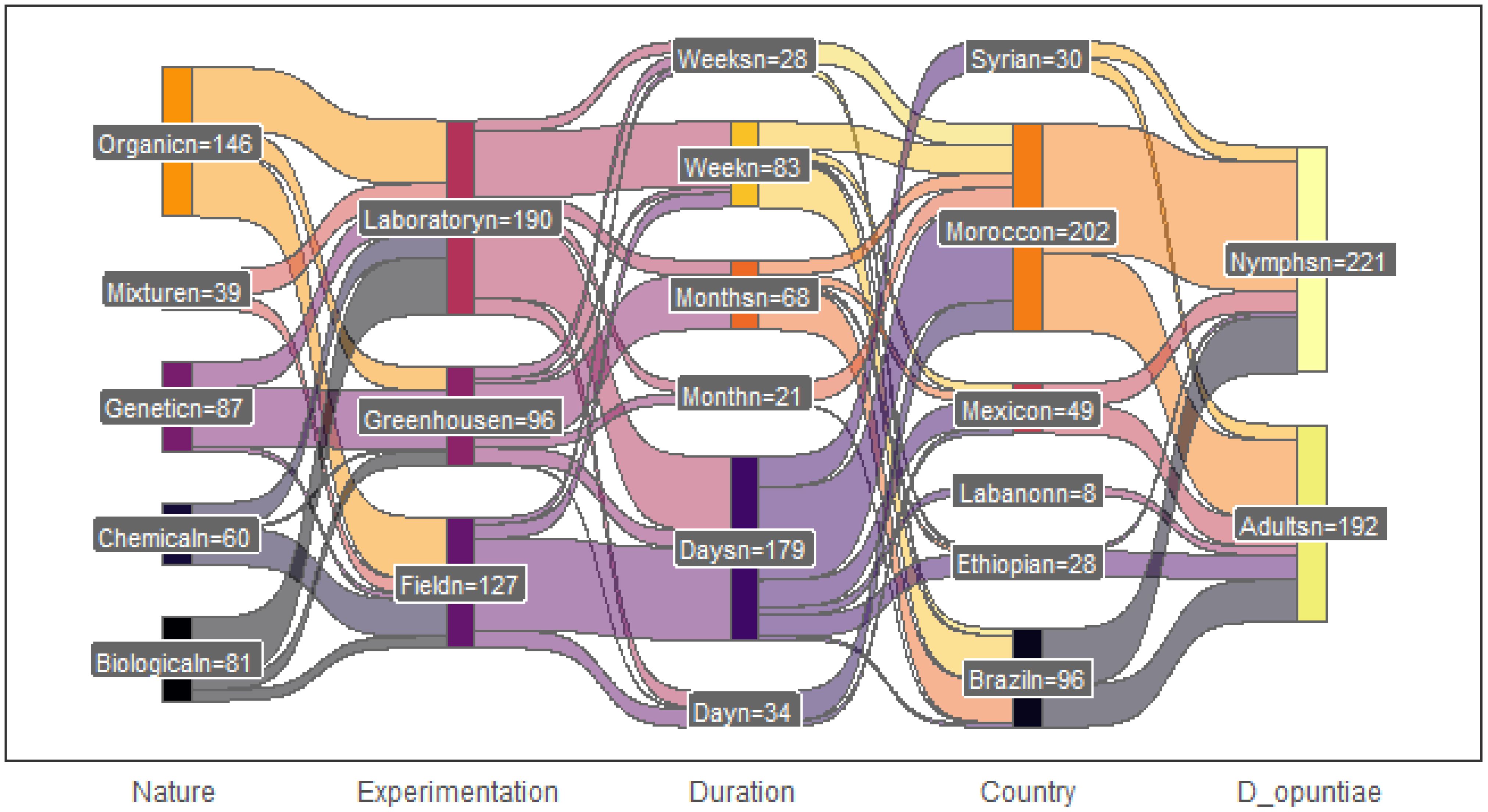
Figure 3. David Sjoberg’s ggsankey output showing the interaction flow observed between factors involved in the evaluation of the efficacy of some products to control the white cochineal Dactylopius opuntiae attacking cactus. The number n indicates how many trials were conducted for each factor.
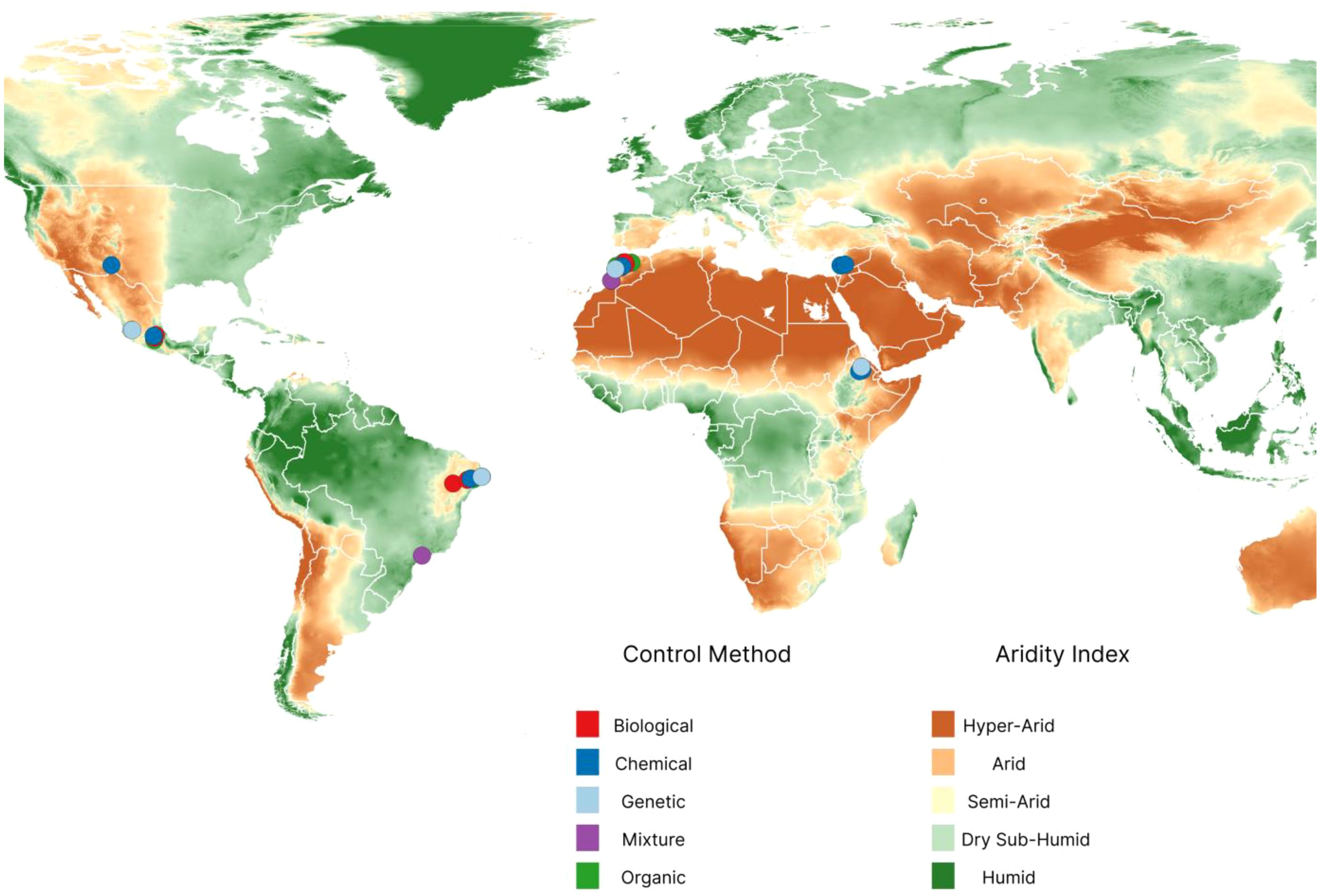
Figure 4. Geographical distribution of Dactylopius opuntiae control tests among arid and semi-arid regions. Dots indicate each control method used, and colors differentiate its nature (biological, chemical, genetic, mixture, and organic). A single point can be the overlap of several tests carried out on the same place.
Cumulative mortality of Dactylopius opuntiae
The meta-regression with the robust variance estimation of the log-transformed D. opuntia mortality yielded an estimate of 4.19 ± 0.08 (95% CI: 4.03–4.35) and 3.99 ± 0.09 (95% CI: 3.81–4.18) for the nymphs and for the adult insects, respectively. The meta-regression robustness was confirmed in sensitivity analysis in both D. opuntiae development stages, where the estimate and resulting standard error were insensitive to different values of the correlation (Figure 5). A high heterogeneity among nymphs (I2 = 99.99%, τ² = 0.09) and among adult insects (I2 = 99.99%, τ² = 0.05) was observed. Obviously, the two groups of insects were considered in subgroup proportional meta-analysis. Supplementary Tables S1, S2 report the statistics of the RVE with correlated models on nymphs and adult insects, respectively.
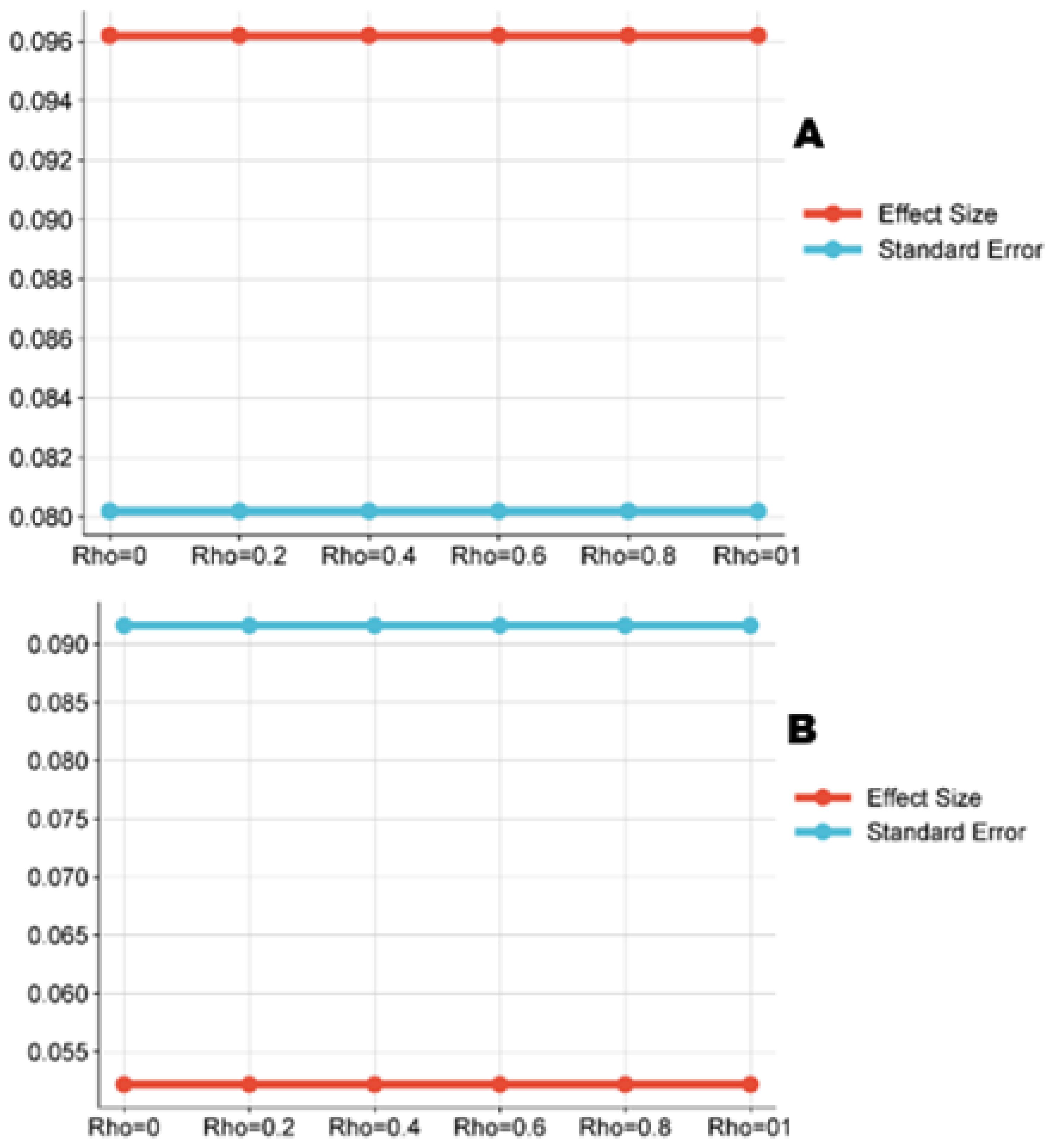
Figure 5. Line charts showing how insensitive were the estimates and the associated standard deviations to different correlation values (Rho) in nymphs (A) and adult (B).
Subgroup analysis
The mortality percentage of nymphs pooled in proportional meta-analysis yielded 0.74 (95% CI: 0.71–0.78, p < 0.001) for nymphs and 0.63 (95% CI: 0.6013–0.6739, p < 0.0001) for adult insects. The high heterogeneity was confirmed in nymphs (I2 = 98.6%, τ² = 0.06, H = 8.43) and for adult insects (I2 = 99.1%, τ² = 0.06, H = 10.74). Organic products showed the most efficient control on nymphs (0.79 ± 0.03), while the genetic approach was the most efficient on adult insects (0.91 ± 0.07). The meta-proportion of the nymph and adult insect mortality variation are reported in Figures 6 and 7, respectively. Between-groups tests for difference showed significance only on adult insects (Q = 18.31, df = 4, p < 0.001). Figures 8 and 9 show how the experiment conditions affect the proportion of nymphs and adult mortality, respectively. Studies conducted in field conditions yielded the highest proportions in both development stages of Dactylopius (0.79 ± 0.03 for nymphs and 0.65 ± 0.03 for adults), but no significant difference was observed among experimental conditions. The trials conducted in Morocco obtained the highest result (0.83 ± 0.02) on nymphs compared to other countries (Figure 10), while trials conducted in Lebanon exhibited the highest proportion on adults (0.84 ± 0.04), as reported in Figure 11. Finally, the longer the test lasted, the greater the proportion of mortality. Evaluation conducted at least during a month yielded the highest proportion of nymphs (0.96 ± 0.02) and adults (0.93 ± 0.03) killed, as displayed in Figures 12, 13. Interestingly, among countries that hosted the experimentation (Q = 35.06, df = 4, p < 0.0001 for nymphs; Q = 31.16, df = 5, p < 0.0001 for adults) and among the durations of these trials (Q = 116.07, df = 5, p < 0.0001 for nymphs; Q = 61.78, df = 5, p < 0.0001 for adults), a significant difference was observed. Accordingly, the experimentation condition was not included in moderator analysis due to the homogeneity observed both in nymphs and adults. Combined effect of moderators yielded significant variation of mortality for nymphs’ mortality (estimate = 3.70 ± 0.43, 95% CI: 2.83–4.58, p < 0.0001). The interaction between nature, country, and the duration of experimentation likewise showed significant variation for adult mortality (estimate = 3.84 ± 0.26, 95% CI: 3.29–4.39, p < 0.0001).
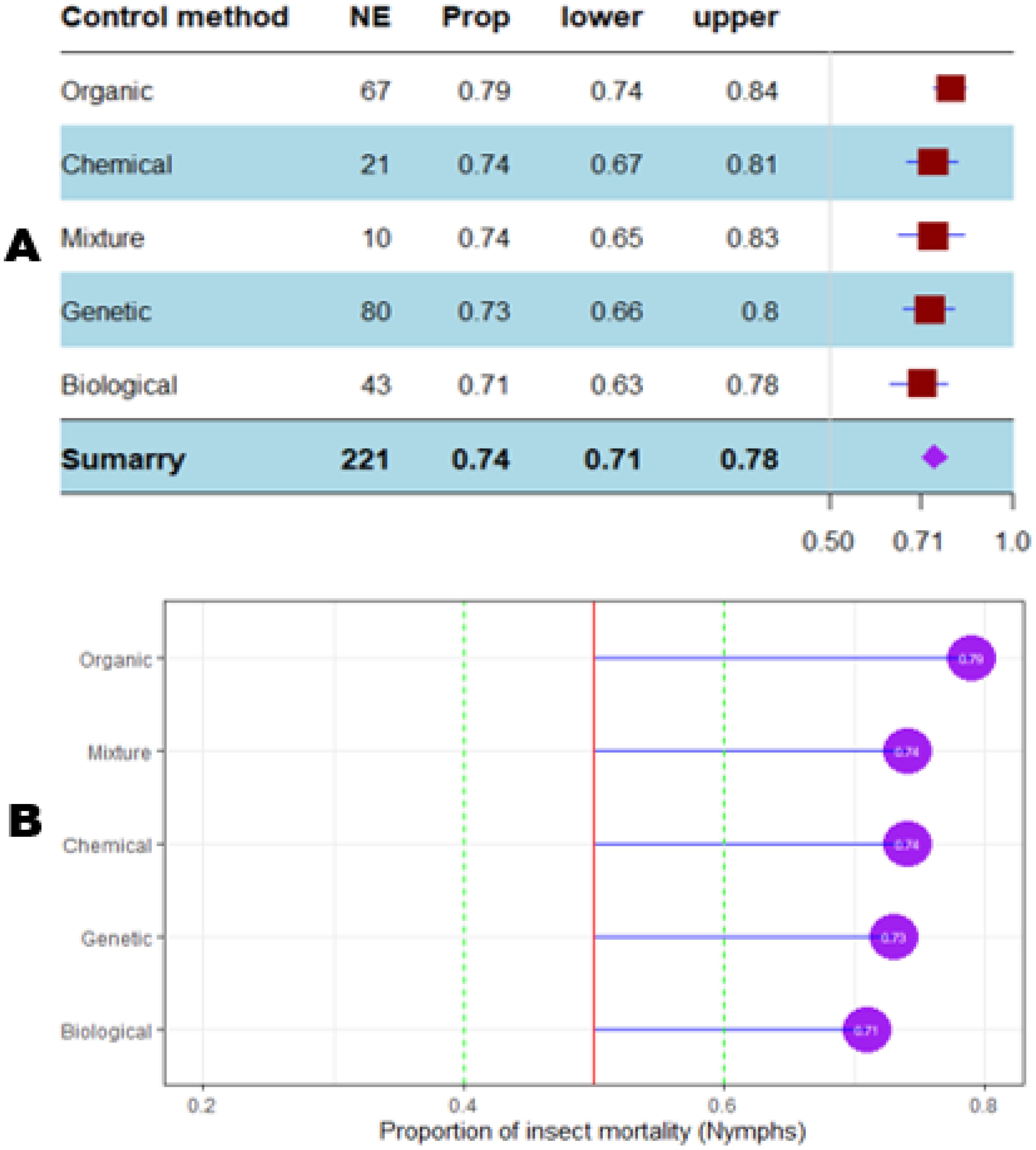
Figure 6. Meta proportion plots showing how the control of D. opuntiae nymphs is influenced by the nature of the control method used. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes for the control method. The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
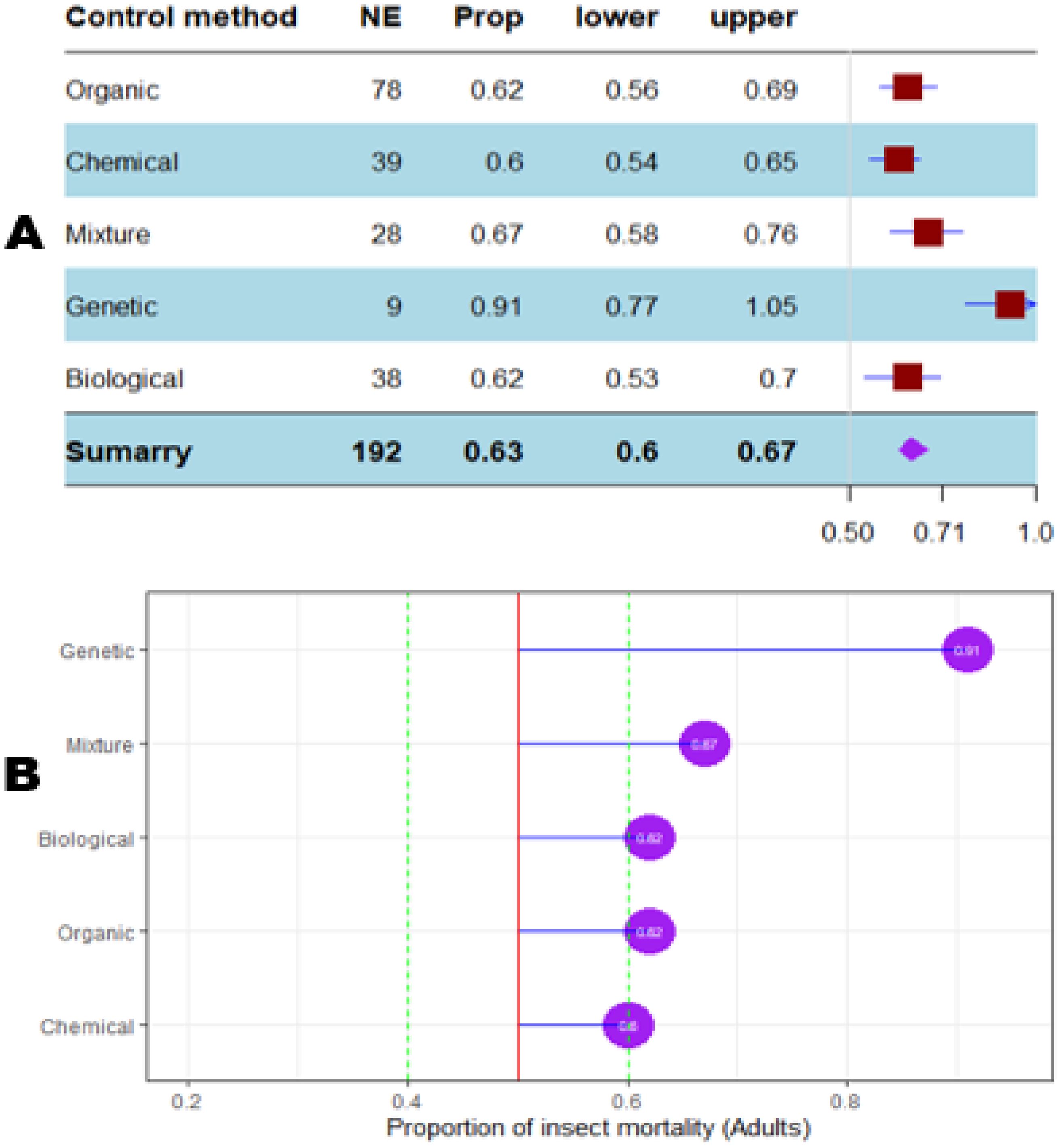
Figure 7. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae adult insects is influenced by the nature of the control method. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes for the control method. The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
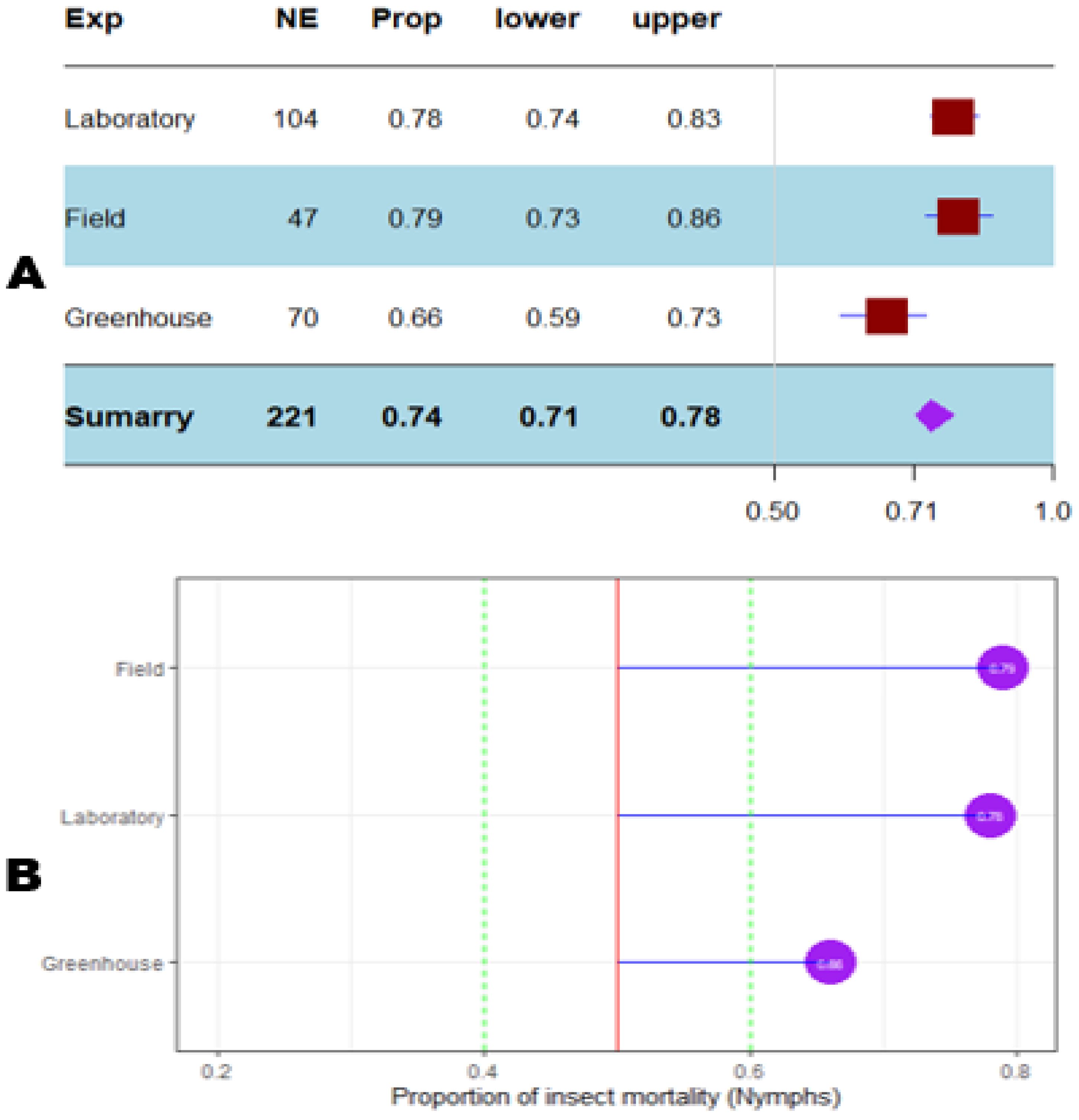
Figure 8. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae nymphs is influenced by the experimentation conditions. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes for the experimentation. The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
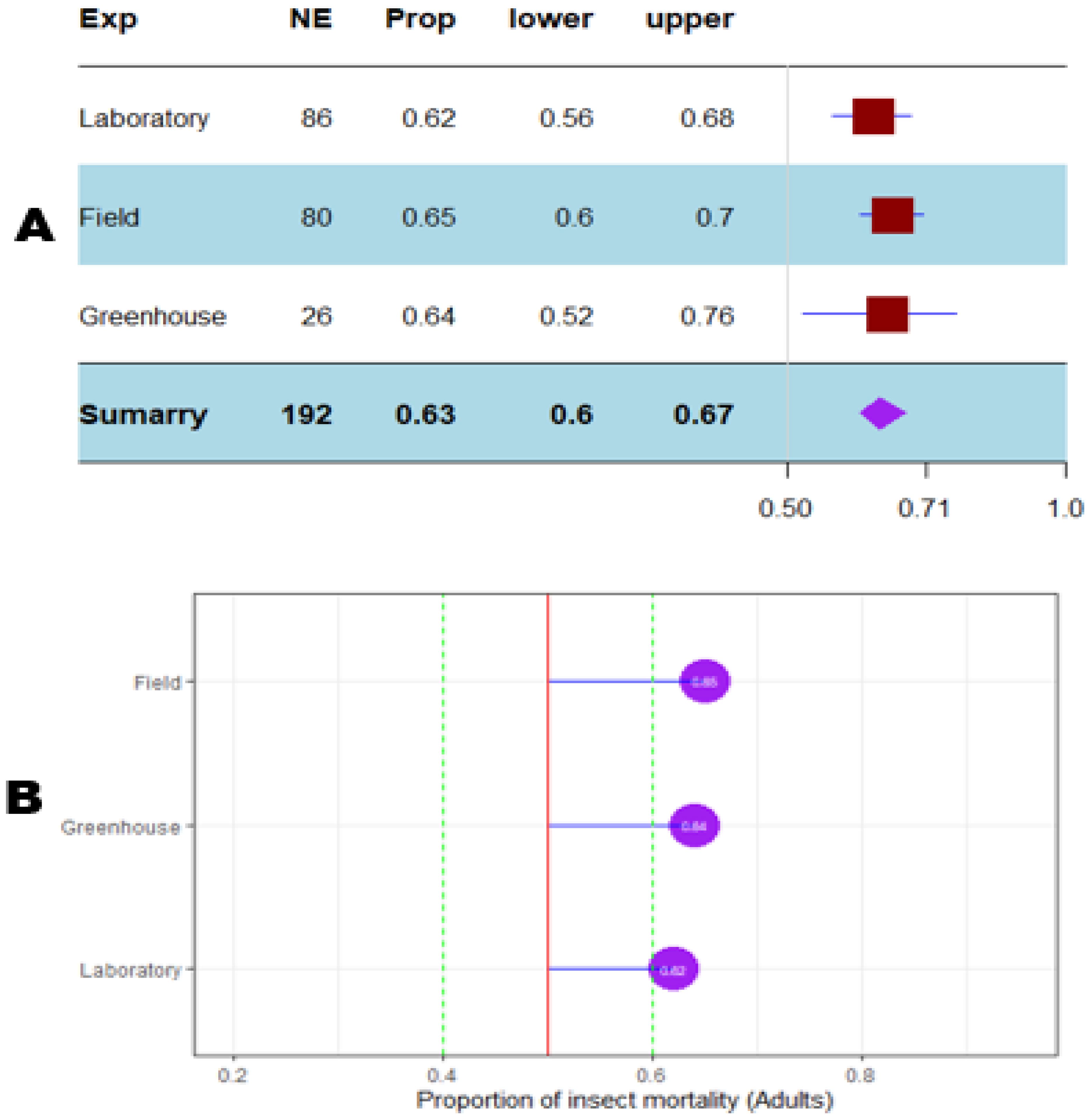
Figure 9. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae adult insects is influenced by the experimentation conditions. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes for the experimentation. The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
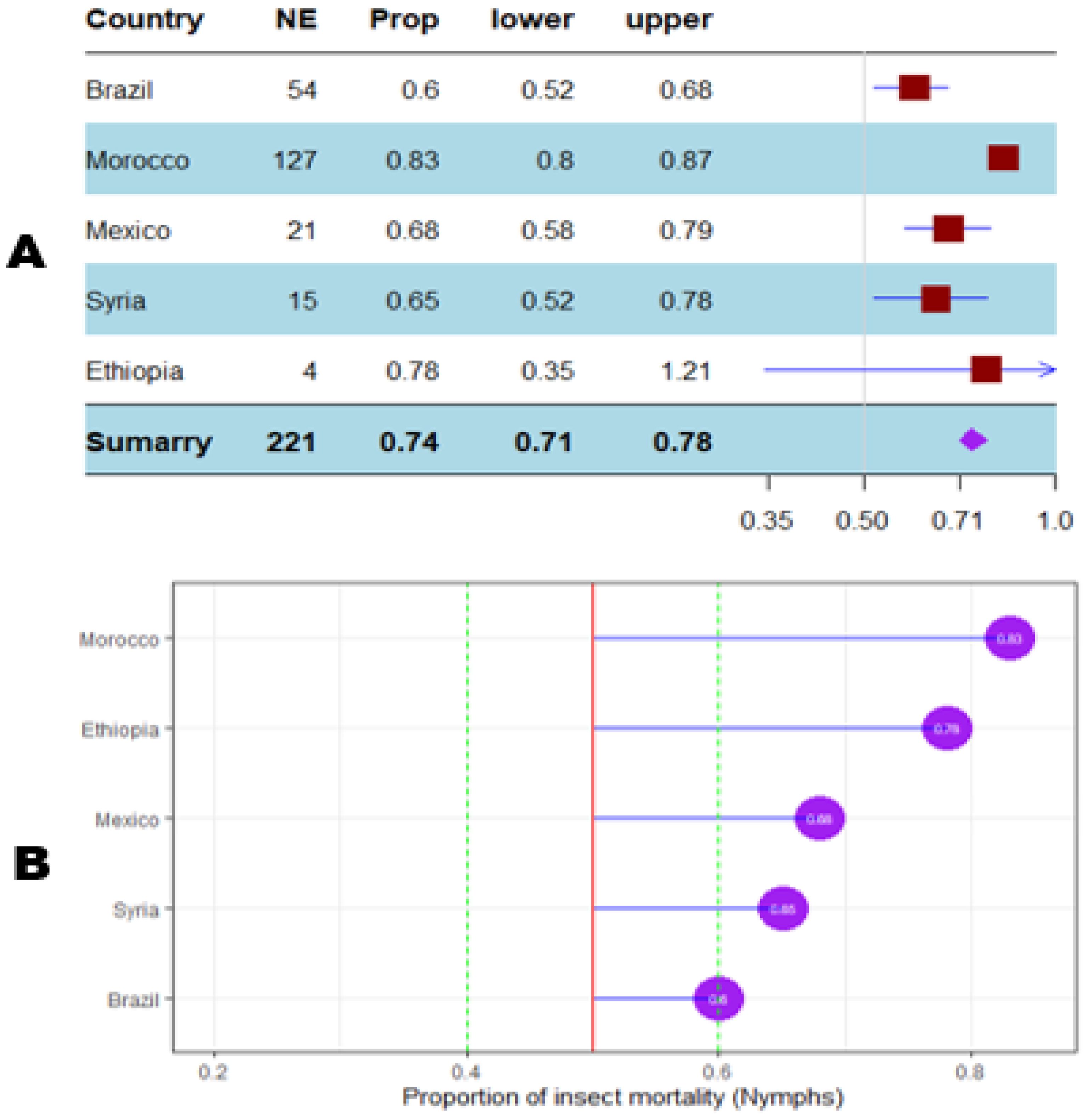
Figure 10. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae nymphs is influenced by the experimentation location. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes observed in the location (country). The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
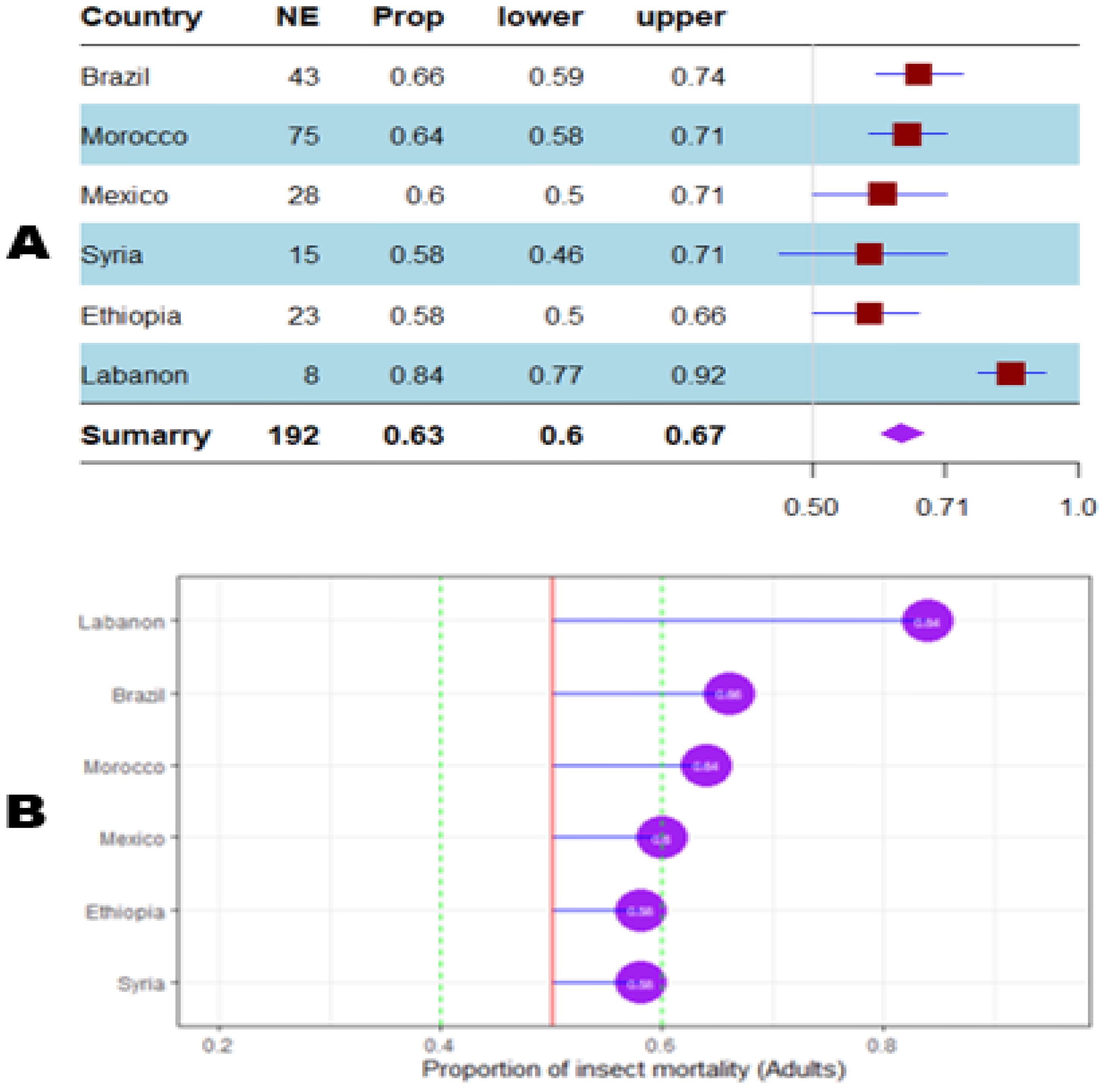
Figure 11. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae adult insects is influenced by the experimentation location. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes observed in the location (country). The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
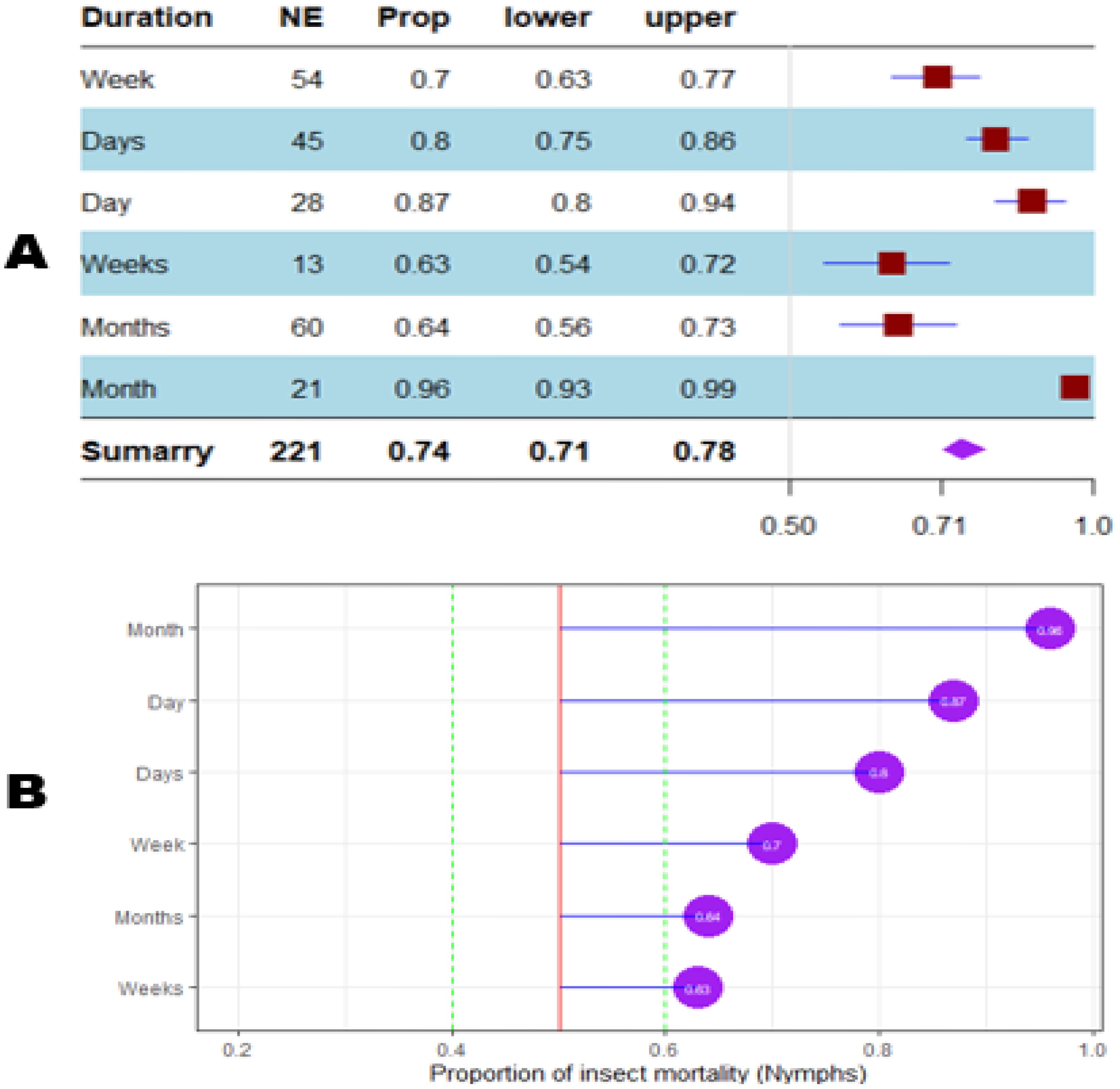
Figure 12. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae nymphs is influenced by the duration of the experimentation. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes observed for the duration of the trial. The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
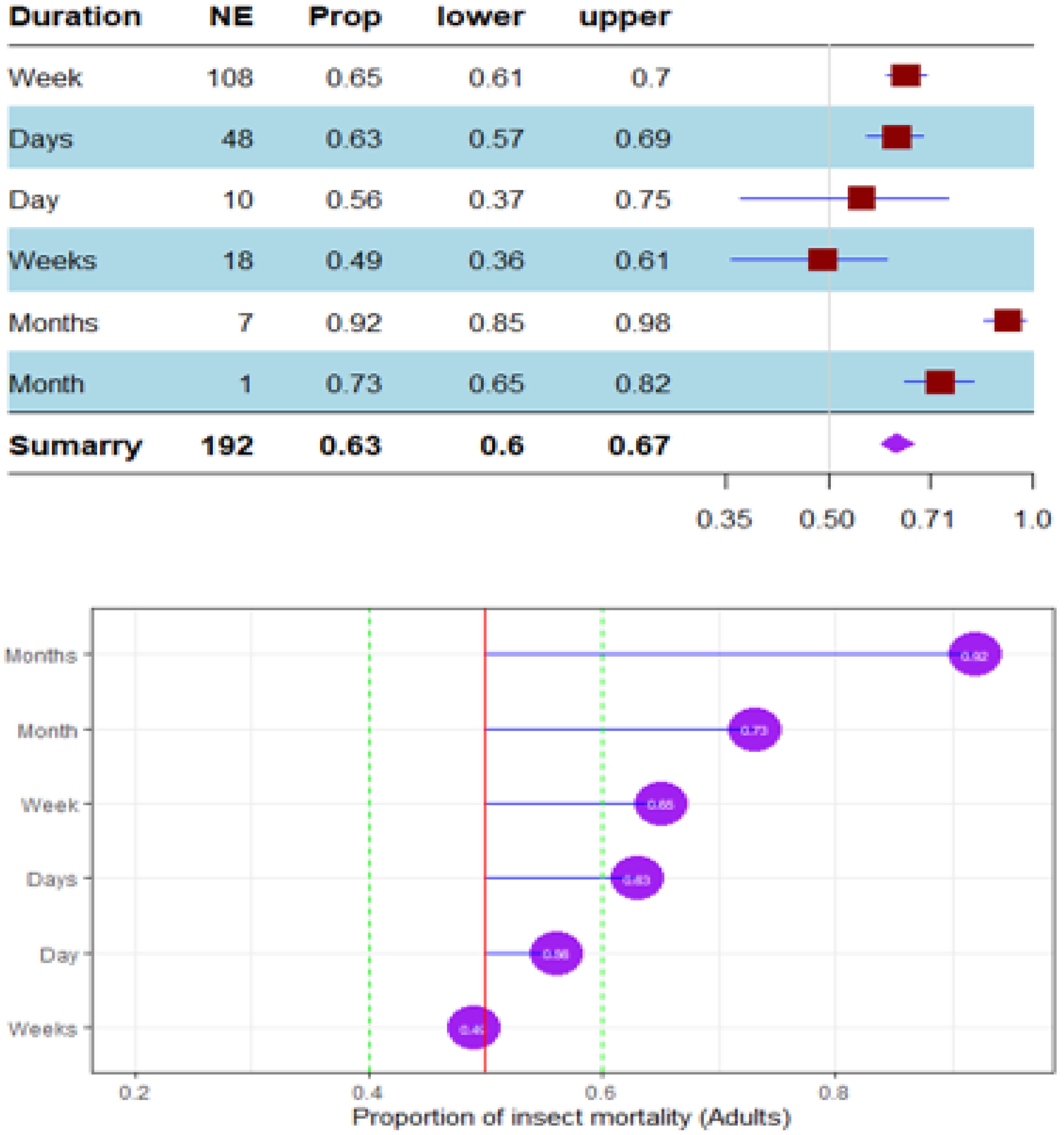
Figure 13. Meta proportion plot showing how the control of D. opuntiae adult insects is influenced by the duration of the experimentation. (A) Proportional statistics. NE is the number of effect sizes observed for the duration of the trial. The horizontal red squares with blue bars indicate the projected values and standard deviation associated. The purple square is the pooled proportion. (B) Lollipop plot. The purple dots at the right of the red line indicate proportions of insects killed greater than 50%.
Publication bias information
The symmetry of the funnel plot indicates less publication bias, although many publications did not fall into the funnel triangle (Supplementary Figures S1, S2). The regression test for the funnel plot asymmetry result proved the absence of significant bias in the publication included to evaluate the efficacy of the control method against D. opuntiae nymphs (t = -1.8082, df = 219, p = 0.0720) and adult insects (t = -0.6857, df = 190, p = 0.4938). This result was confirmed by the trim-and-fill analysis using restricted (or maximum likelihood (REML) estimator, which showed that zero (0) additional articles were necessary to validate the mortality of nymphs and adults used in the meta-analysis.
Discussion
The pooled effect size of the log-transformed mean on the mortality of D. opuntiae nymphs and adults was different from the effect size obtained in the pairwise meta-regression that included other factors, suggesting the influence of multiple factors on the control of this pest. In addition, the subgroup proportional meta-analysis showed high heterogeneity and significant difference among some groups (nature, country, and duration). Considering this, the hypothesis is rejected obviously, and scientists should consider including interactions between all factors surrounding the evaluation of a control method against the Dactylopius pest.
Systematic review
After machine learning screening and identification of new studies via other methods, 199 articles passed the eligibility criteria (Figure 2). Most of these studies assessed diverse control methods against the pest, with 221 and 192 results reporting the mortality of D. opuntiae nymphs and adults, respectively. Despite the few single studies gathering many factors studied in this work, a large diversity of control measures against D. opuntiae was demonstrated in the present work. Trends in publication on D. opuntiae were also observed in a previous report, which concluded that this can help to build a collaboration network between scientists and contribute to the development of an efficient control of the threat (Méndez-Gallegos and Bravo-Vinaja, 2022). In this research, Brazil, Morocco, and Mexico are countries with the highest number of research activities on D. opuntiae control, while organic methods are the most commonly used against the pest.
Factors influencing Dactylopius pest control
The trend in publication reported that most of the studies are conducted in laboratory conditions, converging with similar observations on other insect families (Bernardes et al., 2022). Nevertheless, field trials yielded the highest D. opuntiae mortality compared to laboratory and greenhouse tests, bringing a promising route to control the pest under real conditions. More interestingly, non-chemical products performed well in both nymphs and adults, assuming a sustainable management of the pest. In fact, much attention has been given to biological and organic control approaches (Vigueras et al., 2007; Flores et al., 2013; Lopes et al., 2018; Idris et al., 2021). The proportional mortality of D. opuntiae showed a significant difference among location and trial duration, where Morocco (0.83 ± 0.02) and Lebanon (0.84 ± 0.04) exhibited the highest performances on nymphs and adults, respectively. The importance of location while choosing a niche for cactus cultivation was demonstrated by Acharya et al. (2019). Many factors, including climate and edaphic components, were identified as key components that can affect cactus growth. When considering that these components considerably vary throughout the environment, the present study result shows the evidence of location influence on the efficacy of pest management, including D. opuntiae control. About 15 species were found associated with D. opuntiae as natural enemies in two different zones of Morocco (El Aalaoui et al., 2019a). This shows that this latter pest does not act alone and should be managed based on the location. Despite the lack of a significant difference among experimental conditions, the proportion of insects killed in field conditions surpassed that observed in a greenhouse. The controlled conditions do not represent the real environment (Cornell et al., 2021), and the conditions in the laboratory and greenhouse may be favorable to the pest against the control method. In addition, the ecosystem type was reported as an important moderator in meta-analyses including environmental conditions in trials (Breza and Grandy, 2025).
Insecticidal effect of control products
In D. opuntiae female insects, the insecticidal effect leads to the destruction of the barrier. However, very few articles included in this work have reported the biological mechanisms specifically attributed to each method used to control the pest. The use of insecticides in general has a toxic effect on insect pests. This toxicity not only reduces reproduction in female insects but can also affect their nervous system and growth. Some organic products, such as vegetable oils, have ovicidal activity and can thus prevent pest oviposition. According to El Aalaoui et al. (2019b), mineral oils reduce the number of eggs as well as the survival rate in Choristoneura rosaceana. Genetic control can likewise promote the development of defense mechanisms in the resistant variety. These mechanisms include the production of biochemical compounds that can hinder the reproduction, development, and survival of the insect on the plant. Work conducted with resistant varieties of Dactylopius coccus concluded that the maintenance of insects in the stage nymph I on the plant was probably due to the production of phyto-ecdysones (terpenoids) by the plant, which hindered molting in the larva (Berhe et al., 2022).
Reliability of meta-analysis
The pooled effect size in meta-analysis is a convincing result, as it contributes to solving the contradiction observed between studies and to confirming or not an assumption in a specific situation based on relevant studies and not on a single research work (Hak et al., 2018). Accordingly, this study found that efforts to control the cochineal insect population of cactus are promising, in general, when we see the robustness of the meta-regression in the present study. Although meta-analysis has become an important source of information for decision-makers, one observed the increase of contradiction in many publications due to the locating, selecting, and combining of studies (Egger et al., 1997b). To keep the reliability of insights provided by meta-analysis, the identification of the risk of bias in included studies is now mandatory in PRISMA and other scientific consortiums (Page et al., 2021a, 2021b). The biases in publications that were included in the present study were not significant, as confirmed by the regression and adjusted test, showing that insights provided in this work are useful for any stakeholder engaged in the control of the D. opuntiae pests. Relative asymmetry observed in this case may be due to many other reasons, and the output from the bias test must be interpreted with some caution as advised by Viechtbauer (2010). Interestingly, the adjusted mortality of nymphs (4.2205 ± 0.03, p < 0.001, 95% CI: 4.15–4.28) and adult insects (4.0337 ± 0.04, p < 0.001, 95% CI: 3.95–4.11) was very close to the estimated ones.
Toward a sustainable management of Dactylopius opuntiae
Many studies reported a large range of time to evaluate the efficacy of the product. The highest mortality reported after 1 month may suggest that farmers should apply products for this period instead the single or punctual applications that are usually observed. The proportional meta-regression revealed that, although it was showing that all groups of control methods yielded a good mortality of D. opuntiae (proportion > 0.5), the highest proportions observed for organic methods on nymphs (0.79 ± 0.03) and genetic method on adult insects (0.91 ± 0.07) are promising for the control of this pest without chemical products. This also confirms the importance of promoting resistant material as a sustainable option, as proven in many studies (Vasconcelos et al., 2009; Borges et al., 2013; Falcão et al., 2013).
The control of pests and diseases in conventional agriculture uses chemical products with harmful effects on the environment and biodiversity (Nicolopoulou-Stamati et al., 2016; Von Cossel et al., 2025). Many reports show the alarming situation led by the use of chemical products and the presence of contaminants such as arsenic (As), cadmium, fluorine, and lead reduce the biodiversity (Zhang et al., 2018). In the US, 97% of stream water samples contain pesticides, according to a survey of 51 major rivers (Zhang et al., 2018). The reduction of biodiversity due to chemical products affects the equilibrium created by this biodiversity, which allows crops to be resilient in the face of biotic and abiotic constraints (El Ouali, 2021). The integrated approaches promote the use of environmentally friendly products for the eradication of plant biotic constraints while conserving the equilibrium of the ecosystems. In the present study, proportional subgroup analysis has shown how non-chemical control means, such as organic, genetic, and biological, have demonstrated a strong efficacy against Dactylopius in field conditions across many regions (Vigueras et al., 2007; Flores et al., 2013; Idris et al., 2021; El Aalaoui et al., 2022; Naboulsi et al., 2022). This result is a good signal toward the adoption of these methods, which remain marginal in both conventional and peasant agricultures. Most of the authors reporting these products suggest biological and organic controls as alternatives to chemical products in management programs of D. opuntiae (Gonçalves Diniz et al., 2020; El Finti et al., 2022; Abadi et al., 2024). In addition, cultivars that demonstrated resistance against the pest could be used in breeding programs as parents to introduce other agronomic traits if absent or directly shared with farmers for direct use.
Conclusion
The machine learning classifier was able to gather a large number of control methods reported in the literature to eradicate Dactylopius insects. Organic products are the most utilized control methods and seem to be most efficient on nymphs, while the genetic control of adult insects yields the best performances. This is promising for a sustainable control of the pest. Although most of the evaluations are conducted in the laboratory, field trials present the highest efficacy, suggesting the implementation of control approaches in real conditions. Interestingly, subgroup analyses showed a significant difference in the mortality rate of D. opuntiae among countries and experimental durations. This result thus rejects our research hypothesis, indicating that the nature of the control method is not the only factor influencing the effectiveness of pest control. Therefore, the management of D. opuntiae must consider the effect of location and the duration of control methods.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AE: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was conducted as part of the IsDB Merit Scholarship Program for Member Countries under Postdoctoral Program, funded by the Islamic Development Bank.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the ENSIAS school which offered a good work environment wherein to conduct this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fagro.2025.1664240/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Funnel plot of the bias among the publications reporting the control of Dactylopius opuntiae Nymphs.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Funnel plot of the bias among the publications reporting the control of Dactylopius opuntiae adult insects.
Supplementary Table 1 | Robust Variance Estimation meta-regression result on Dactylopius opuntiae nymphs on 43 studies included in the analysis.
Supplementary Table 2 | Robust Variance Estimation meta-regression result on Dactylopius opuntia Adult insects on 38 studies included in the analysis.
References
Aalaoui M., Bouharroud R., Sbaghi M., Bouhssini M., and Hilali L. (2020). Functional response and predation potential of Hyperaspis campestris (Herbst 1783) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on Opuntiae Cochineal Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae) in Morocco. Test Eng. Manage. 82, 5976–5985. doi: 10.5373/JARDCS/V12SP1/20201047
Abadi A., Brhane T., and Shelema A. (2024). Efficacy of Botanical Insecticides for Controlling Cochineal Scale (Dactylopius opuntiae) Insect on Cactus (Dactylcompound sopius opuntiae) Plant at Southern Tigray. Asian J. Res. Agric. Forestry 10, 80–87. doi: 10.9734/ajraf/2024/v10i4318
Acharya P., Biradar C., Louhaichi M., Ghosh S., Hassan S., Moyo H., et al. (2019). Finding a suitable niche for cultivating cactus pear (Opuntia ficus-indica) as an integrated crop in resilient dryland agroecosystems of India. Sustainability 11, 5897. doi: 10.3390/su11215897
Akroud H., El-Bouhssini M., Bouharroud R., Udupa S., Henkrar F., Boujghagh M., et al. (2022). Genetic relations among Moroccan Opuntia genotypes with different degrees of resistance to Dactylopius opuntiae. J. Prof. Assoc. Cactus Dev. 24, 159–171. doi: 10.56890/jpacd.v24i.480
Akroud H., Sbaghi M., Bouharroud R., Koussa T., Boujghagh M., and El Bouhssini M. (2021). Antibioisis and antixenosis resistance to Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae) in Moroccan cactus germplasm. Phytoparasitica 49, 623–631. doi: 10.1007/s12600-021-00897-w
Berhe Y. K., Portillo L., and Vigueras A. L. (2022). Resistance of Opuntia ficus-indica cv ‘Rojo Pelon’to Dactylopius coccus (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae) under greenhouse condition. J. Prof. Assoc. Cactus Dev. 24, 293–309. doi: 10.56890/jpacd.v24i.509
Bernardes R. C., Botina L. L., Araujo R., dos S., Guedes R. N. C., Martins G. F., et al. (2022). Artificial intelligence-aided meta-analysis of toxicological assessment of agrochemicals in bees. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10, 845608. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.845608
Borges L., Santos D., Cavalcanti V., Gomes E., Falcão H., and da Silva D. (2013). Selection of cactus pear clones regarding resistance to carmine cochineal Dactylopius opuntiae (Dactylopiidae). Acta Hortic. 995, 359–365. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2013.995.47
Bouraïma M. B., Bielders C. L., Sikirou R., Ezin V. A., Ahohuendo B. C., and Achigan-Dako E. G. (2025). Do agroecological practices control Ralstonia solanacearum wilt on solanaceous crops? A meta-analysis. Plant Pathol. 74, 3–17. doi: 10.1111/ppa.14000
Breza L. C. and Grandy A. S. (2025). Organic amendments tighten nitrogen cycling in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis on gross nitrogen flux. Front. Agron. 7, 1472749. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1472749
Cornell C., Kokkoris V., Richards A., Horst C., Rosa D., Bennett J. A., et al. (2021). Do bioinoculants affect resident microbial communities? A meta-analysis. Front. Agron. 3, 753474. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2021.753474
Egger M., Smith G. D., Schneider M., and Minder C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. bmj 315, 629–634. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629, PMID: 9310563
El Aalaoui M., Bouharroud R., Sbaghi M., El Bouhssini M., Hilai L., and DariI N. (2019a). Natural enemies associated with Dactylopius opuntiae (Cockerell)(Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae) in Morocco and their population fluctuations. Rev. Marocaine Sci. Agron. Vét 7, 391–396.
El Aalaoui M., Bouharroud R., Sbaghi M., El Bouhssini M., Hilali L., and Dari K. (2019b). Comparative toxicity of different chemical and biological insecticides against the scale insect Dactylopius opuntiae and their side effects on the predator Cryptolaemus montrouzieri. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 52, 155–169. doi: 10.1080/03235408.2019.1589909
El Aalaoui M., Mokrini F., Dababat A. A., Lahlali R., and Sbaghi M. (2022). Moroccan entomopathogenic nematodes as potential biocontrol agents against Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae). Sci. Rep. 12, 7590. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11709-4, PMID: 35534607
El-Aalaoui M. and Sbaghi M. (2023). Efficacy of some biorational insecticides against the cactus scale pest Diaspis echinocacti (Bouché, 1833) (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) in Morocco. Afr. Mediterr. Agric. J.-Al Awamia 139, 21–36. doi: 10.34874/IMIST.PRSM/afrimed-i139.41149
El Finti A., El Boullani R., Fallah M., Msanda F., and El Mousadik A. (2013). Assessment of some agro-technological parameters of cactus pear fruit (Opuntia ficus-indica Mill.) in Morocco cultivars. J. Med. Plants Res. 7, 2574–2583. doi: 10.5897/JMPR12.1236
El Finti A., El Boullani R., Zahidi A., and El Mousadik A. (2022). Management of the Prickly Pear Mealy Bug, Dactylopius opuntiae using bio-insecticide in Morocco. Adv. Entomol. 10, 267–274. doi: 10.4236/ae.2022.104019
El Ouali H. (2021). Permaculture, a way to improve small family farmers livelihood in rural areas? (Tartu: Eesti Maaülikool), 74.
Ezzahraa E. M. F. (2022). Evaluation du pouvoir insecticide et fongicide des souches bactériennes isolées des racines du cactus vis-à-vis de la cochenille du cactus (Dactylopius opuntiae) et de champignons phytopathogènes. (Béni Mellal: Université Sultan Moulay Slimane).
Falcão H. M., Oliveira M. T., Mergulhão A. C., Silva M. V., and Santos M. G. (2013). Ecophysiological performance of three Opuntia ficus-indica cultivars exposed to carmine cochineal under field conditions. Sci. Hortic. 150, 419–424. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.11.021
Flores A., Olvera H., Rodríguez S., and Barranco J. (2013). Predation Potential of Chilocorus cacti (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to the Prickly Pear Cacti Pest Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae). Neotrop. Entomol. 42, 407–411. doi: 10.1007/s13744-013-0139-z, PMID: 23949861
Gibson A. K. and Nguyen A. E. (2021). Does genetic diversity protect host populations from parasites? A meta-analysis across natural and agricultural systems. Evol. Lett. 5, 16–32. doi: 10.1002/evl3.206, PMID: 33552533
Gómez P., Rodríguez-Hernández A. M., Moury B., and Aranda M. A. (2009). Genetic resistance for the sustainable control of plant virus diseases: breeding, mechanisms and durability. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 125, 1–22. doi: 10.1007/s10658-009-9468-5
Gonçalves Diniz A., Barbosa L. F. S., Santos A. C. D. S., Oliveira N. T. D., Costa A. F. D., Carneiro-Leão M. P., et al. (2020). Bio-insecticide effect of isolates of Fusarium caatingaense (Sordariomycetes: Hypocreales) combined to botanical extracts against Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 30, 384–395. doi: 10.1080/09583157.2020.1720601
Hak T., van Rhee H., and Suurmond R. (2018). How to interpret results of meta-analysis (Version 1.3) (Erasmus Research Institute of Management (ERIM). Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/1765/80102.22 (Accessed April 23, 2025).
Hedges L. V., Tipton E., and Johnson M. C. (2010). Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Res. Synth. Methods 1, 39–65. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.5, PMID: 26056092
Hozo S. P., Djulbegovic B., and Hozo I. (2005). Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 5, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13, PMID: 15840177
Idris I., Tayoub G., and Bakri Y. (2021). Effectiveness of some plant extracts against the different stages of the cochineal insect Dactylopius opuntiae on prickly pear in Syria. J. Agroaliment. Process. Technol 27, 94–99.
Lahbouki S., Fernando A. L., Rodrigues C., Ben-Laouane R., Ait-El-Mokhtar M., Outzourhit A., et al. (2023). Effects of humic substances and Mycorrhizal fungi on drought-stressed cactus: focus on growth, physiology, and biochemistry. Plants 12, 4156. doi: 10.3390/plants12244156, PMID: 38140483
Lazuardi M. F., Hiunarto R., Ramadhani K. F., Noviandi N., Widayanti R., and Arfian M. H. (2023). Hoax news detection using passive aggressive classifier and TfidfVectorizer. J. Tek. Inform. 16, 185–193. doi: 10.15408/jti.v16i2.34084
Lopes R. S., Oliveira L. G., Costa A. F., Correia M. T., Lima E. A. L.-A., and Lima V. L. (2018). Efficacy of Libidibia ferrea var. ferrea and Agave sisalana extracts against Dactylopius opuntiae (Hemiptera: Coccoidea). J. Agric. Sci. 10, 255–267. doi: 10.5539/jas.v10n4p255
Marhri A., Tikent A., Garros L., Merah O., Elamrani A., Hano C., et al. (2023). Rapid and Efficient In vitro propagation protocol of endangered wild prickly pear growing in Eastern Morocco. Horticulturae 9, 491. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae9040491
Méndez-Gallegos S. D. J. and Bravo-Vinaja A. B. (2022). Dactylopius opuntiae Cockrell (Hemiptera: Dactylopiidae), an emerging threat for Opuntia spp: a bibliometric analysis. J. Prof. Assoc. Cactus Dev. 24, 111–138. doi: 10.56890/jpacd.v24i.487
Naboulsi I., El Fakhouri K., Lamzira R., Ramdani C., Bitchagno G. T. M., Boulamtat R., et al. (2022). Insecticidal Activities of Atriplex halimus L., Salvia rosmarinus Spenn. and Cuminum cyminum L. against Dactylopius opuntiae (Cockerell) under Laboratory and Greenhouse Conditions. Insects 13, 930. doi: 10.3390/insects13100930, PMID: 36292878
Neupane D., Mayer J. A., Niechayev N. A., Bishop C. D., and Cushman J. C. (2021). Five-year field trial of the biomass productivity and water input response of cactus pear (Opuntia spp.) as a bioenergy feedstock for arid lands. GCB Bioenergy 13, 719–741. doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12805
Nicolopoulou-Stamati P., Maipas S., Kotampasi C., Stamatis P., and Hens L. (2016). Chemical pesticides and human health: the urgent need for a new concept in agriculture. Front. Public Health 4, 148. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2016.00148, PMID: 27486573
Page M. J., McKenzie J. E., Bossuyt P. M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T. C., Mulrow C. D., et al. (2021a). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Systematic Rev. 10, 89. doi: 10.31222/osf.io/v7gm2
Page M. J., Moher D., Bossuyt P. M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T. C., Mulrow C. D., et al. (2021b). PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and examples for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 372, 36. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n160, PMID: 33781993
Pustejovsky J. E. and Tipton E. (2022). Meta-analysis with robust variance estimation: Expanding the range of working models. Prev. Sci. 23, 425–438. doi: 10.1007/s11121-021-01246-3, PMID: 33961175
Ramdani C., Bouharroud R., Sbaghi M., Mesfioui A., and El Bouhssini M. (2021). Field and laboratory evaluations of different botanical insecticides for the control of Dactylopius opuntiae (Cockerell) on cactus pear in Morocco. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 41, 1623–1632. doi: 10.1007/s42690-020-00363-w
Scammacca N., Roberts G., and Stuebing K. K. (2014). Meta-analysis with complex research designs: Dealing with dependence from multiple measures and multiple group comparisons. Rev. Educ. Res. 84, 328–364. doi: 10.3102/0034654313500826, PMID: 25309002
Sedki M., Taoufiq A., Haddouche M., El Mousadik A., Barkaoui M., and El Mzouri E. (2013). Biophysical and biochemical characterization of cactus pear Fruit (Opuntia spp.) cultivars originating from south-west Morocco. Acta Hortic. 995, 83–91. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2013.995.10
Shongwe N., De Wit M., Osthoff G., Nel P., and Labuschagne M. (2013). The influence of location, Cultivar and season on cactus pear fruit quality. Acta Hortic. 995, 165–179. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2013.995.20
Taoufik F., Zine S., El Hadek M., Idrissi Hassani L. M., Gharby S., Harhar H., et al. (2015). Oil content and main constituents of cactus seed oils Opuntia Ficus Indica of different origin in Morocco. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 8, 85–92. doi: 10.3233/MNM-150036
Van De Schoot R., De Bruin J., Schram R., Zahedi P., De Boer J., Weijdema F., et al. (2021). An open source machine learning framework for efficient and transparent systematic reviews. Nat. Mach. Intell. 3, 125–133. doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-00287-7
Vasconcelos A. G. V. D., Lira M. D. A., Cavalcanti V. L. B., Santos M. V. F. D., and Willadino L. (2009). Selection of prickly-pear clones resistant to carmine cochineal Dactylopius sp. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 38, 827–831. doi: 10.1590/S1516-35982009000500007
Viechtbauer W. (2010). Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Software 36, 1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v036.i03
Vigueras A. L., Cibrían-Tovar J., and Pelayo-Ortiz C. (2009). Use of botanicals extracts to control wild cochineal (Dactylopius opuntiae cockerell) on cactus pear. Acta Hortic. 811, 229–234. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2009.811.28
Von Cossel M., Scordia D., Altieri M., and Gresta F. (2025). Spotlight on agroecological cropping practices to improve the resilience of farming systems: a qualitative review of meta-analytic studies. Front. Agron. 7, 1495846. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1495846
Walter S. D. and Yao X. (2007). Effect sizes can be calculated for studies reporting ranges for outcome variables in systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 60, 849–852. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.11.003, PMID: 17606182
Weir C. J., Butcher I., Assi V., Lewis S. C., Murray G. D., Langhorne P., et al. (2018). Dealing with missing standard deviation and mean values in meta-analysis of continuous outcomes: a systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 18, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0483-0, PMID: 29514597
Yahia E. M. and Sáenz C. (2011). “Cactus pear (Opuntia species),” in Postharvest biology and technology of tropical and subtropical fruits (Cambridge (UK): Elsevier), 290–331e.
Keywords: Opuntia spp., Dactylopius opuntiae, pest, control, artificial intelligence, meta-regression
Citation: Mbo Nkoulou LF and Elhassouny A (2025) Factors affecting the control of Dactylopius, an invasive pest of cactus crop: artificial intelligence-based meta-analysis. Front. Agron. 7:1664240. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1664240
Received: 11 July 2025; Accepted: 05 November 2025; Revised: 25 October 2025;
Published: 28 November 2025.
Edited by:
Rachid Bouharroud, National Institute of Agronomic Research, MoroccoReviewed by:
Mebrahtom Gebrelibanos Hiben, Mekelle University, EthiopiaEder Ramos Hernandez, Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agricolas Y Pecuarias, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Mbo Nkoulou and Elhassouny. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Luther Fort Mbo Nkoulou, am9hY2hpbW5rb3Vsb3U3LmpuQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Azeddine Elhassouny, orcid.org/0000-0002-3683-9575
 Luther Fort Mbo Nkoulou
Luther Fort Mbo Nkoulou Azeddine Elhassouny3†
Azeddine Elhassouny3†