- 1Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences, University “Magna Graecia” of Catanzaro, Catanzaro, Italy
- 2Respiratory Medicine Unit, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
- 3Department of Biomedical Sciences, Humanitas University, Pieve Emanuele/Milano, Italy
- 4Personalized Medicine, Asthma and Allergy, Humanitas Clinical and Research Center, IRCCS, Rozzano/Milano, Italy
- 5Department of Translational Medical Sciences, University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
- 6Center for Basic and Clinical Immunology Research (CISI), University of Naples Federico II, Naples, Italy
- 7Department of Medicine, Surgery, and Dentistry, University of Salerno, Salerno, Italy
- 8Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, University of Catania, Catania, Italy
- 9Department of Health Sciences, University “Magna Graecia” of Catanzaro, Catanzaro, Italy
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is an alarmin mainly released by airway epithelial cells injured by many environmental noxious agents such as aeroallergens, respiratory viruses, bacteria, airborne pollutants and cigarette smoking. Airway expression levels of TSLP are related to both asthma severity and the extent of bronchial obstruction occurring in asthmatic patients. The pivotal pathogenic role played by TSLP in asthma is due to its capability of acting as an upstream driver of multiple cellular and molecular proinflammatory pathways, responsible for the development and persistence of both type 2 (T2-high) and T2-low asthma. Tezepelumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody which specifically binds to TSLP, thus impeding its interaction with the TSLP receptor complex expressed by immune/inflammatory and resident cells of the airways. By virtue of this very effective mechanism of action, tezepelumab prevents disease exacerbations and improves lung function. These positive outcomes have been verified by randomized clinical trials, as well as by preliminary real-life studies. The aim of this narrative review is to provide an overview of the pathogenic involvement of TSLP in asthma, followed by an updated discussion focused on the therapeutic effects induced by tezepelumab in severe asthmatic patients.
1 Introduction
The onset and persistence of asthma arise from complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors (1). This widespread respiratory disease is characterized by chronic bronchial inflammation associated with hyperresponsiveness and structural remodeling of the airways, that are all together responsible for chest tightness, wheezing, shortness of breath, cough and worsening of lung function (2, 3). Among more than 300 million asthmatic patients scattered around the world, about 5%–10% suffer from severe asthma, featured by the failure of even high doses of standard inhaled treatments to provide an adequate therapeutic control (4, 5). In particular, recurrent exacerbations are the main clinical expressions of severe asthma (6). Intricate networks of cellular, molecular, and immunopathologic mechanisms (endotypes) lead to the manifestation of several heterogeneous asthmatic traits (phenotypes) (7, 8). The latter include either allergic or non-allergic eosinophilic inflammatory profiles, as well as neutrophilic, mixed eosinophilic/neutrophilic, and paucigranulocytic patterns (9). All the above asthmatic endotypes/phenotypes are driven, maintained and amplified by an intense biosynthetic activity of the bronchial epithelium, triggered by tissue damage induced by several noxious agents such as allergens, viruses, bacteria, fungi, cigarette smoking and airborne pollutants (10, 11). In asthmatic subjects, basal airway epithelial cells are the main source of innate cytokines known as alarmins, including interleukin-25 (IL-25), interleukin-33 (IL-33), TNF-like cytokine 1A (TL1A), high-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1), and especially thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) (12–15).
Notably, TSLP is an alarmin that plays a pivotal pathobiologic role in T2-high eosinophilic asthma, as well as in T2-low neutrophilic disease (16) (Figure 1). Indeed, TSLP promotes the production of type 2 cytokines such as interleukins 4 (IL-4), 5 (IL-5) and 13 (IL-13), involved in eosinophilic inflammation, and also stimulates the immune/inflammatory responses mediated by interleukins 1 (IL-1) and 17 (IL-17), thereby eliciting airway neutrophilic infiltration (11, 16). TSLP thus exerts potent, either direct or indirect pleiotropic effects on T and B lymphocytes, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), mast cells, basophils, macrophages, eosinophils and neutrophils (11, 16). Furthermore, TSLP contributes to bronchoconstriction and airway structural remodeling by activating the functions of resident cells like fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells (17, 18).
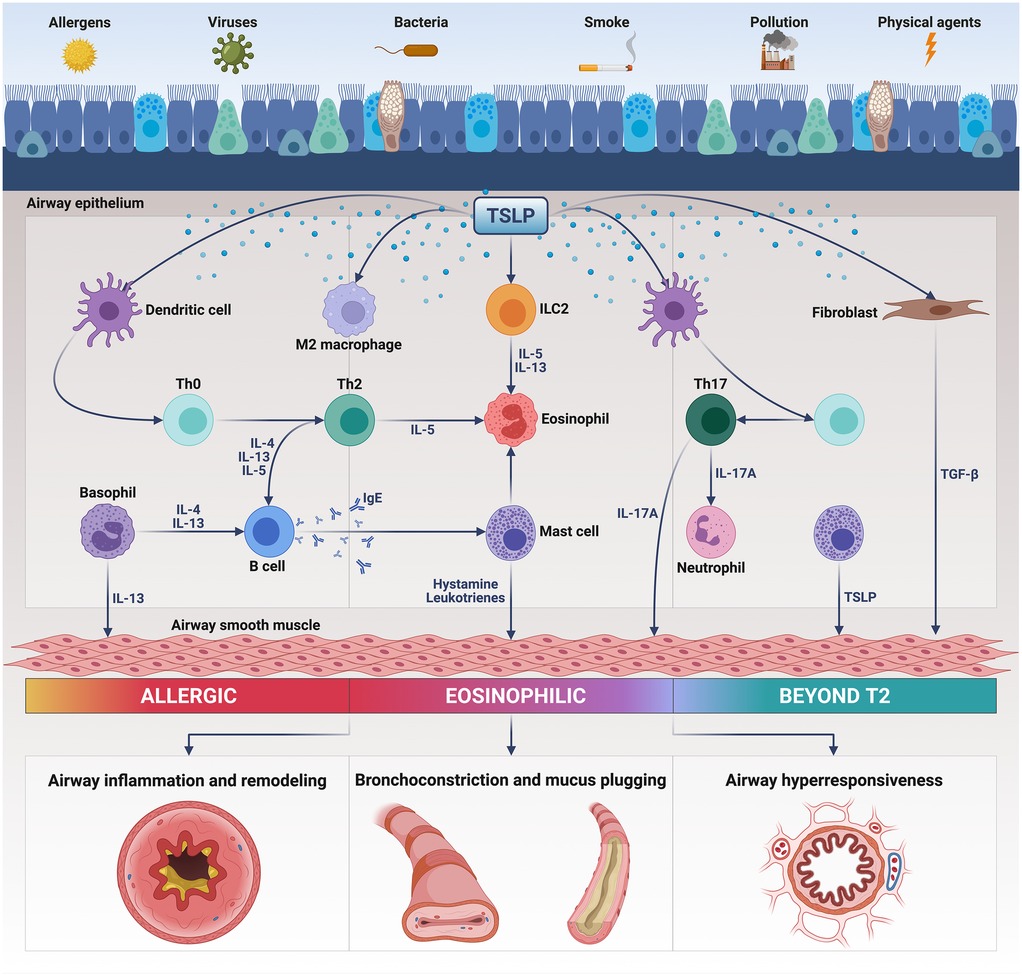
Figure 1. Pathogenic actions of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) in asthma. Released from injured bronchial epithelium, TSLP triggers the inflammatory responses underlying T2-high and T2-low asthma by activating several immune cells including dendritic cells, Th2/Th17 lymphocytes, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, and M2 macrophages. TSLP also activates airway structural cells such as fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. As a consequence of these pleiotropic actions, TSLP induces airway inflammation and remodeling, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, bronchoconstriction and mucus plugging. This original figure was created by the authors using “BioRender.com”.
Because of its relevant pathogenic features, TSLP is a very suitable molecular target for biologic treatment of severe asthma (19, 20). In this regard, the fully human anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody tezepelumab has been developed and approved as anti-asthma biologic therapy (21–23). TSLP is effectively bound and sequestered by tezepelumab, which can be usefully utilized across T2-high and T2-low asthma phenotypes/endotypes (23, 24). In fact, both randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and real-life studies have proven that tezepelumab exerts a positive therapeutic impact on both eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic severe asthma (25–35).
On the basis of the above considerations, this narrative review aims to highlight the pathogenic role of TSLP in asthma, and also to provide an updated coverage of the therapeutic use of tezepelumab as add-on biologic therapy of severe asthma.
2 Basic mechanisms of the pathogenic role of TSLP in asthma
Initially identified as a B-lymphocyte trophic factor in thymic stromal cells, TSLP belongs to the interleukin-2 (IL-2) cytokine family, and its gene originated from early chromosomal duplication of the interleukin-7 (IL-7) gene (17, 36). Notably, in severe asthmatic patients a suggestive association was found with the rs1837253 single nucleotide polymorphism present in the TSLP gene, located on chromosome 5 (37). TSLP exists as a short, non-inducible isoform (60 amino acids) characterized by homeostatic/anti-inflammatory properties, and as a longer variant (159 amino acids) whose expression can be induced by proinflammatory stimuli (38–40). The positive charges of long TSLP interact with the negative charges of a heterodimer consisting of the TSLP receptor (TSLPR) and the α subunit of IL-7 receptor (IL-7Rα/CD127) (40, 41). Specifically, TSLP binding to TSLPR induces the recruitment of IL-7Rα and the consequent assembly of the ternary complex TSLP/TSLPR/IL-7Rα (11). The latter drives the engagement of an intricate signal transduction network including several kinases and transcription factors such as Janus kinases 1 and 2 (JAK1/2), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 K), signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 and 5 (STAT3/5), and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) (41–43). In particular, TSLP triggers the activation of JAK2 pathway via TSLPR, and stimulates the functions of JAK1 signaling module through IL-7Rα (17, 44).
High TSLP levels can be detected in epithelial bronchial biopsies taken from asthmatic subjects, as well as in their bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), exhaled breath condensate, induced sputum and serum (16, 45–47). Airway TSLP expression correlates with asthma severity and bronchial obstruction (16). It is also noteworthy that genome-wide association studies have highlighted that some single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), located inside the TSLP gene, outline variable degrees of susceptibility to asthma (48–50). Moreover, TSLP mRNA is overexpressed in nasal polyps excised from patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) (51).
In asthmatic airways, bronchial epithelial cells are the main sources of TSLP, which is also produced by mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, dendritic cells, T lymphocytes, fibroblasts and airway smooth muscle cells (17, 52, 53). TSLP secretion can be elicited by a wide array of stimuli encompassing proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-13, IL-25, IL-1β and TNF-α, as well as immunoglobulins E (IgE), protease containing aeroallergens, respiratory viruses, airborne pollutants and cigarette smoking (53, 54). After being released from bronchial epithelial cells, TSLP exerts its biologic effects on many cellular targets expressing the TSLPR/IL-7Rα heterodimer.
2.1 T2-high asthma
Namely, TSLP promotes the survival of ILC2 cells and stimulates their biosynthetic activity leading to the production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13 (16, 55–57). IL-4 is essential for Th2 lymphocyte differentiation and IgE isotype switching, IL-5 is the pivotal eosinophilopoietic cytokine, IL-9 is a key mast cell growth factor, whereas IL-13 is responsible for goblet cell metaplasia, and also for bronchoconstriction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness and proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells (55, 58, 59). TSLP immunoreactivity and ILC2 share the same localization in the airways, and a close relationship has been found between TSLP amount and ILC2 counts in nasal biopsies obtained from subjects with severe asthma and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) (60, 61). Furthermore, TSLP causes ILC2 resistance to corticosteroids (62). Indeed, ex vivo studies have shown that dexamethasone is unable to inhibit cytokine production in ILC2 obtained from asthmatic patients characterized by the presence of high airway levels of TSLP (62).
Eosinophils and their progenitors also express the TSLPR/IL17-Rα receptor complex, and these cells quickly respond to TSLP that inhibits apoptosis thus lengthening cell survival, as well as elicits the release of eosinophilic pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytotoxic proteins (63, 64). All the pro-eosinophilic actions of TSLP are mediated by signal transduction pathways operated by MAPKs and NF-κB (63, 64). Interestingly, allergen challenge is followed by an overlapping localization of TSLP and eosinophilic infiltration within asthmatic airways (65). TSLP also enables eosinophils to assemble eosinophilic extracellular traps, made of complexes including cytotoxic proteins and mitochondrial DNA, which in asthmatic patients are implicated in innate immune responses and mucus hypersecretion (66). Moreover, TSLP acts on eosinophil progenitors by enhancing the expression of the α subunit of IL-5 receptor (IL-5Rα), thus contributing to stimulate IL-5-dependent maturation and differentiation of eosinophils (67). In addition to inducing eosinophilopoiesis, TSLP also facilitates the migration of eosinophil progenitors by promoting their ability to produce many chemokines such as CCL1, CCL22 and CXCL8 (16, 68).
Furthermore, TSLP affects the functions of basophils and mast cells (21). Indeed, TSLP stimulates the differentiation of basophils and their release of histamine and proinflammatory cytokines, as well as enhances the expression of CD203c, a specific marker of basophil activation (16, 69). In atopic asthmatic subjects, TSLP increases alarmin sensitivity of basophils by up-regulating their expression of ST2 and IL-17RB receptors, which are specifically activated by IL-33 and IL-25, respectively (70). TSLP is also able to empower mast cell biosynthesis of IL-5 and IL-13 (71). Additionally, by acting in conjunction with IL-33, TSLP stimulates mast cell production of prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), a pleiotropic mediator which is significantly involved in the pathophysiology of type 2 asthma (72).
TSLP plays a key role in the intercellular crosstalk occurring between the innate and adaptive immune responses underlying type 2 asthma (Figure 1). Within this pathogenic context, TSLP acts on human myeloid dendritic cells by enhancing their expression of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) antigens and co-stimulatory molecules CD40 and CD86 (73). Dendritic cells are also stimulated by TSLP to express OX40 ligand (OX40l), a powerful polarizing signal which drives the commitment of naïve CD4+ T lymphocytes towards the Th2 immunophenotype (74). Upon TSLP-induced activation, in thoracic lymph nodes OX40l + dendritic cells trigger the development of T follicular helper cells (Tfh) secreting IL-4, which is essential for the differentiation of Th2 lymphocytes and IgE isotype switching (75, 76). Moreover, TSLP stimulates dendritic cells to release the chemokines CCL17 and CCL22, which bind to the CCR4 receptor present on Th2 cells, thereby directing their migration from lung-draining lymph nodes towards the airways (16, 77). Not only dendritic cells, but also other cellular elements like CD11c+ monocytes/interstitial macrophages can convey TSLP-dependent stimulatory signals, which drive the maturation and expansion of Th2 lymphocytes (78). Anyway, in addition to its indirect actions worked out by dendritic cells and monocytes/macrophages, TSLP can also directly guide the commitment of CD4+ T cells towards the Th2 lineage (79). Another mechanism by which TSLP participates in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma is mediated by an impairment of the immuno-modulatory functions of lung T regulatory (Treg) lymphocytes (80). Specifically, TSLP inhibits Treg cellular production of interleukin-10 (IL-10), an anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory cytokine that suppresses the development of atopic immune responses (80). With regard to the pathobiology of T2-high asthma, a further contribution of TSLP refers to its property of inducing the differentiation of alternatively activated M2 macrophages, which are associated with allergic inflammation (81). Recent findings suggest that TSLP is constitutively present in the cytoplasm of human lung macrophages, where this alarmin can feed an autocrine loop leading to the release of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) from TSLP-stimulated, alternatively activated M2 cells (82, 83).
2.2 T2-low asthma
Besides being implicated in the induction and persistence of type 2 asthma, TSLP appears to be also engaged in T2-low neutrophilic bronchial inflammation, which is predominantly mediated by the pro-inflammatory pathways powered by Th17 lymphocytes (84) (Figure 1). Notably, TSLP is capable of stimulating dendritic cells to release interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-23 (IL-23), which are essential for Th17 skewing (85, 86). In turn, Th17 lymphocytes elicit the release from endothelial cells of the potent neutrophil chemoattractant CXCL8 (11). Furthermore, TSLP can also evoke a combined activation and expansion of both Th2 and Th17 immunophenotypes, featured by a concomitant biosynthesis of IL-4 and IL-17A (86).
2.3 Airway remodeling
TSLP exerts its biologic effects not only on immune/inflammatory cells, but also on airway structural cells. In particular, TSLP induces the secretion of IL-6 and CXCL8 from airway smooth muscle cells, which are prompted by adjacent mast cells to release tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and TSLP itself (87–89). TSLP is also generated by airway fibroblasts in response to a TSLP-mediated autocrine loop, leading to an increased production of α smooth muscle actin, collagen, arginase 1 and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) (90, 91). Additionally, the angiogenetic events underlying airway vascular remodeling in asthma are significantly affected by TSLP. Indeed, VEGF release from human lung macrophages can be induced by TSLP, which is overexpressed in bronchial biopsies taken from severe asthmatic patients characterized by a mixed neutrophilic/eosinophilic inflammatory pattern, coupled with excessive neo-angiogenesis (82, 92). As a consequence, these findings underscore the crucial role played by TSLP within the intercellular axis connecting airway inflammatory and structural cells, which significantly contributes to bronchial remodeling in asthma.
3 Clinical outcomes of anti-TSLP therapy with tezepelumab
The only anti-TSLP biologic drug currently available in clinical practice is tezepelumab, a fully human monoclonal IgG2λ antibody which specifically binds to TSLP and impedes its interaction with TSLPR (21, 43, 93). Tezepelumab was initially compared to placebo in subjects with mild atopic asthma, undergoing allergen challenge (94). When receiving three monthly intravenous administrations of tezepelumab (700 mg), with respect to placebo control these patients experienced a relevant protection against allergen-induced bronchoconstriction, ranging from 34.0% to 45.9% attenuation of decrease in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) at 42 and 84 days of treatment, respectively (94). Moreover, tezepelumab significantly enhanced the provocative concentration of methacholine eliciting a 20% FEV1 reduction (PC20), as well as lowered the levels of both blood/sputum eosinophils and fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) (94).
The phase 2b randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicentre PATHWAY trial was then carried out from December 2013 to March 2017 at 108 sites disseminated around 12 countries (25). All participants in this study were current non-smokers (age range: 18–75 years), suffering from uncontrolled asthma even if under treatment with an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) consisting of fluticasone propionate (250–500 μg/day or more) or other ICS at equivalent doses, plus a combined long-acting β2-adrenergic agonist (LABA). Asthma was considered to be uncontrolled when at screening the ACQ-6 (6-item Asthma Control Questionnaire) score was at least 1.5. Furthermore, during the 12 months before enrolment at least two asthma exacerbations were reported, or alternatively a single severe exacerbation requiring hospitalization had occurred. Baseline pulmonary function was featured by reversible bronchial obstruction, consisting of pre-bronchodilator FEV1 measures ranging from 40% to 80% of predicted values, which increased by at least 12% and 200 ml after a conventional pharmacodynamic bronchodilator test (inhalation of 400 μg of salbutamol). 584 selected participants were randomly assigned either to the placebo group (148 subjects) or to one of three other arms including treatments every 4 weeks with tezepelumab administered through the subcutaneous route at doses of 70 mg (145 people), 210 mg (145 patients) and 280 mg (146 participants), respectively.
The primary endpoint of the PATHWAY study referred to the effects of 52 weeks of biologic therapy with tezepelumab on the annualized asthma exacerbation rate (AAER). In comparison to placebo, tezepelumab delayed the occurrence of the next exacerbation, and significantly (p < 0.001) reduced AAER by 61%, 71%, and 66% at low, intermediate and high dosages, respectively (25). Such a noteworthy therapeutic outcome did not significantly differ among patients with various blood eosinophil counts. Moreover, a post hoc analysis of PATHWAY verified that treatment with 210 mg of tezepelumab lowered AAER in severe asthmatic patients regardless of the eventual coexistence of nasal polyposis (95). Another post hoc analysis also documented that during the PATHWAY trial, tezepelumab reduced asthma exacerbations throughout all four seasons of the year (96). In regard to the secondary outcomes of PATHWAY, after 52 weeks of add-on therapy with tezepelumab, a significant ACQ-6 score improvement was detected across all three different dosage subgroups (25). Additionally, after 52 weeks tezepelumab enhanced pre-bronchodilator FEV1 by 150 ml, 110 ml and 120 ml when used at dosages of 280 mg, 210 mg and 70 mg, respectively (25). Tezepelumab was also able to lower the levels of several biomarkers of type 2 inflammation, including serum IgE, blood eosinophils, FeNO, periostin, IL-5, IL-13, and thymus and activation-regulated chemokine (TARC) (25, 97).
Treatment with tezepelumab was safe and well tolerated, as shown by the similar numbers of adverse reactions induced by either placebo or active therapy, mainly represented by headache, nasopharyngitis and bronchitis (25). No anaphylactic reactions were reported. Anti-tezepelumab antibodies were detected in 8.8% of recipients of placebo, as well as in 0.7%, 4.9% and 2.1% of patients treated with low, medium and high drug dosages, respectively. No neutralizing antibodies were found.
The phase 3 multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled and randomized NAVIGATOR study enrolled 1,061 severe asthmatic patients (age: 12–80 years) with frequent asthma exacerbations (27). 532 participants underwent a randomized assignment to placebo, whereas 529 subjects received subcutaneous administrations of tezepelumab (210 mg) every 4 weeks for 52 weeks. Patients with either more or less than 300 eosinophils/μL blood were recruited. Referring to the primary endpoint, tezepelumab significantly decreased AAER, independently of blood eosinophil counts (27). Secondary outcomes regarded symptom control, lung function, and health-related quality of life. In comparison to placebo tezepelumab improved ACQ-6, ASD (Asthma Symptom Diary) and AQLQ (Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire) scores, as well as significantly incremented pre-bronchodilator FEV1 (27). Furthermore, tezepelumab lowered serum IgE levels, FeNO and blood eosinophil numbers. The most frequent adverse reactions similarly experienced by both placebo recipients and tezepelumab patients were upper respiratory tract infections, nasopharyngitis and headache. Local cutaneous reactions on injection sites occurred in 3.6% of subjects undergoing add-on therapy with tezepelumab, and in 2.6% of patients receiving placebo, respectively (27). Anti-tezepelumab antibodies were found in 4.9% of subjects treated with tezepelumab and 8.3% of placebo recipients, respectively. Neutralizing antibodies were detected in one patient belonging to the placebo group, as well in one subject assigned to treatment with tezepelumab (27).
SOURCE was another phase 3 randomized, 48-week, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial, which recruited 150 severe asthmatic patients, treated with medium-to-high doses of ICS/LABA combinations, associated with a further chronic OCS treatment (98). The main goal of this study was to ascertain the presumptive OCS-sparing action of tezepelumab, injected subcutaneously at the dosage of 210 mg every 4 weeks (98). The relevance of such a primary endpoint depends on the frequent OCS use occurring among people with severe asthma, who are thus subjected to the possible development of the well-known unwanted side effects of OCS, including glaucoma, cataract, hypertension, diabetes, adrenal insufficiency, hypertension, gastrointestinal diseases, infections, psychiatric disorders, osteoporosis, bone fracture, and reduced growth in children and adolescents (99). According to SOURCE, tezepelumab was not capable of significantly decreasing the daily OCS consumption (100). Nevertheless, tezepelumab reduced OCS intake in corticosteroid-dependent asthmatic patients with relatively high blood eosinophil counts (100). Moreover, the open-label WAYFINDER study [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05274815] is currently performing a more comprehensive assessment of the putative OCS sparing effect of tezepelumab.
DESTINATION was a phase 3 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, and long-term extension trial, which protracted over two years the evaluation of the therapeutic effects of tezepelumab (28). This study provided a further convincing evidence in favour of the sustained safety of tezepelumab, associated with its persistent efficacy resulting in a clinically meaningful AAER decrease (28). In addition, a further analysis of the results of both NAVIGATOR and DESTINATION trials showed that tezepelumab was able to induce on-treatment clinical remission of severe asthma, consisting of zeroing of disease exacerbations and OCS intake, unitedly with improvement of symptom control and lung function (101). In particular, asthma remission elicited by tezepelumab can be more easily achieved by patients with high levels of type 2 inflammatory biomarkers including FeNO and blood eosinophils, associated with a lower disease burden characterized by not frequent exacerbations, low OCS use, and a quite preserved pulmonary function (102).
CASCADE was a phase 2 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, which enrolled patients with moderate-to-severe asthma, receiving subcutaneous injections of tezepelumab at the dosage of 210 mg every 4 weeks for 28 weeks (103). Recruitment occurred independently of baseline blood eosinophil counts. The primary endpoint of CASCADE was to evaluate the eventual anti-inflammatory effects of tezepelumab. With this aim, bronchoscopic biopsies were performed in order to analyze the potential changes induced by tezepelumab with regard to airway infiltration by inflammatory cells (103). Furthermore, the thickness of reticular basement membrane of bronchial epithelium was measured before and after therapy with tezepelumab. This biologic drug significantly reduced eosinophil accumulation within the airway submucosal layer, whereas tezepelumab did not modify the numbers of other immune/inflammatory cells including T lymphocytes, mast cells and neutrophils (104). Moreover, tezepelumab did not change the thickness of reticular basement membrane, but improved the airway hyperresponsiveness to mannitol (104), an indirect bronhoconstrictor agent which promotes mast cell degranulation. This finding about the protective effect of tezepelumab on mannitol-induced bronchoconstriction was also confirmed by the results of the phase 2 UPSTREAM trial (105). Such observations suggest that the anti-eosinophilic effects of tezepelumab contribute to explain the partial inhibition induced by this monoclonal antibody on the inflammatory component of airway hyperresponsiveness. However, the incomplete efficacy of tezepelumab could be due to the unsuccessful action of this biologic drug on airway structural remodeling.
The initial data provided by real-life studies confirm the efficacy of tezepelumab in decreasing asthma exacerbations and OCS dependence (29, 30). Additionally, tezepelumab bettered symptom control, quality of life and lung function in severe asthmatic patients featured by either T2-high or T2-low inflammatory traits, who also experienced a dramatic reduction of their need for emergency visits (29–35). According to our recent real-world findings, tezepelumab rapidly diminished the serum levels of interleukin-2 (IL-2) and VEGF in patients with either T2-high or T2-low severe asthma (106). These results are quite interesting because can contribute to deepen the knowledge about the potential ability of tezepelumab to inhibit T lymphocyte activation and angiogenesis. Indeed, as shown by the high IL-2 levels detectable in severe asthmatic patients, this cytokine is involved in the pathophysiology of both T2-low and T2-high severe asthma by promoting the differentiation of Th1 and Th2 cells, as well as by inducing airway remodeling through up-regulation of type-1 collagen expression (107–109). Furthermore, tezepelumab could suppress TSLP-dependent macrophage release of VEGF induced by T2-high (IL-4, IL-13) and T2-low (lipopolysaccharide) proinflammatory stimuli (82, 83).
Because asthma and its frequent comorbidity nasal polyposis (NP) share common pathogenic mechanisms, it is noteworthy that tezepelumab has been recently shown to be therapeutically effective also in NP treatment (110, 111). Indeed, the WAYPOINT trial demonstrated that tezepelumab treatment decreased the size of nasal polyps and the severity of sinonasal symptoms and nasal congestion, as well as the needs for OCS therapy and surgical polypectomy (111).
Taken together, the above studies suggest that tezepelumab may be very effective in a wide subpopulation of patients with severe asthma, triggered by either multiple factors involved in T2-high disease, as well as by pathogenic mechanisms implicated in T2-low airway inflammation. However, the main limitation regarding the use of tezepelumab appears to be the lack of specific biomarkers capable of guiding the choice of asthma physicians towards this monoclonal antibody.
4 Conclusions
Several asthma triggers including aeroallergens, respiratory pathogens and airborne pollutants damage the airway epithelium and activate innate immune receptors expressed by bronchial epithelial cells, thus stimulating them to release alarmin cytokines. Among the latter, TSLP plays a key pathogenic role in the induction, persistence and amplification of both T2-high and T2-low asthma. Therefore, because of its upstream strategic position, TSLP represents a suitable molecular target for add-on treatments aimed to disrupt epithelial-driven proinflammatory pathways leading to the development of severe asthma. In fact, both randomized clinical trials and recent real-world studies emphasize the therapeutic utility of the anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody tezepelumab. This biologic drug is indeed very effective in decreasing asthma exacerbations and OCS intake, as well as in ameliorating symptom control and lung function. Hence, tezepelumab makes it possible for many patients with either type 2 or non-type 2 severe asthma to achieve the realistic goal of clinical remission, which translates into a very relevant improvement of their quality of life.
Author contributions
CP: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GP: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RP: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. CC: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AV: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GC: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. GP: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issue please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Miligkos M, Oh J, Kwon R, Konstantinou GN, Kim S, Yon DK, et al. Epidemiology of asthma across the ages. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2025) 134:376–84. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2024.12.004
2. Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, Reddel HK. Asthma. Lancet. (2018) 391:783–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33311-1
3. Porsbjerg C, Melen E, Lehtimaki L, Shaw D. Asthma. Lancet. (2023) 401:858–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02125-0
4. Stern J, Pier J, Litonjua AA. Asthma epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Immunopathol. (2020) 42:5–15. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00785-1
5. Settipane RA, Kreindler JL, Chung Y, Tkacz J. Evaluating direct costs and productivity losses of patients with asthma receiving GINA 4/5 therapy in the United States. Am Coll Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2019) 123:564–572.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.08.462
6. Castillo JR, Peters SP, Busse WW. Asthma exacerbations: pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2017) 5:918–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.05.001
7. Wenzel SE. Severe adult asthmas: integrating clinical features, biology, and therapeutics to improve outcomes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2021) 203:809–21. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202009-3631CI
8. Xie C, Yang J, Gul A, Li Y, Zhang R, Yalikun M, et al. Immunologic aspects of asthma: from molecular mechanisms to disease pathophysiology and clinical translation. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1478624. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1478624
9. Wenzel SE. Severe asthma in adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2005) 172:149–60. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200409-1181PP
10. Calven J, Ax E, Radinger M. The airway epithelium – A central player in asthma pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:8907. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238907
11. Akenroye A, Boyce JA, Kita H. Targeting alarmins in asthma: from bench to bedside. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2025) 155:1133–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.01.017
12. Yang D, Han Z, Oppenheim JJ. Alarmins and immunity. Immunol Rev. (2017) 280:41–56. doi: 10.1111/imr.12577
13. Roan F, Obata-Ninomiya K, Ziegler SF. Epithelial cell-derived cytokines: more than just signaling the alarm. J Clin Investig. (2019) 129:1441–51. doi: 10.1172/JCI124606
14. Varricchi G, Poto R, Criscuolo G, Strisciuglio C, Nair P, Marone G. TL1A, A novel alarmin in airway, intestinal, and autoimmune disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2025) 155(5):1420–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.02.018
15. Furci F, Murdaca G, Pelaia C, Imbalzano E, Pelaia G, Caminati M, et al. TSLP and HMGB1: inflammatory targets and potential biomarkers for precision medicine in asthma and COPD. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:437. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020437
16. Gauvreau GM, Sehmi R, Ambrose CS, Griffiths JM. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: its role and potential as a therapeutic target in asthma. Expert Opin Ther Targets. (2020) 24:777–92. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1783242
17. Ebina-Shibuya R, Leonard WJ. Role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergy and beyond. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:24–37. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00735-y
18. Charriot J, Ahmed E, Bourdin A. Local targeting of TSLP: feat or defeat. Eur Respir J. (2023) 61:2202389. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02389-2022
19. Pelaia C, Melhorn J, Hinks TS, Couillard S, Vatrella A, Pelaia G, et al. Type 2 severe asthma: pathophysiology and treatment with biologics. Expert Rev Respir Med. (2024) 18:485–98. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2024.2380072
20. Pastore D, Lupia C, D’Amato M, Bruni A, Garofalo E, Longhini F, et al. Emerging biological treatments for asthma. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. (2025) 30:87–97. doi: 10.1080/14728214.2025.2460529
21. Pelaia C, Pelaia G, Crimi C, Maglio A, Gallelli L, Terracciano R, et al. Tezepelumab: a potential new biologic therapy for severe refractory asthma. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4369. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094369
22. Pelaia C, Pelaia G, Longhini F, Crimi C, Calabrese C, Gallelli L, et al. Monoclonal antibodies targeting alarmins: a new perspective for biological therapies of severe asthma. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4369. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091108
23. Miralles-López JC, Antolín-Amérigo D, García-Moguel I, Domínguez-Ortega J, Delgado-Romero J, Quirce S. Positioning of tezepelumab in severe asthma. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2024) 34:1–11. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0949
24. Lindsley AW, Lugogo N, Reeh KAG, Spahn J, Parnes JR. Asthma biologics across the T2 spectrum of inflammation in severe asthma: biomarkers and mechanism of action. J Asthma Allergy. (2025) 18:33–57. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S496630
25. Corren J, Parnes JR, Wang L, Mo M, Roseti SL, Griffiths JM, et al. Tezepelumab in adults with uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:936–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1704064
26. Caminati M, Buhl R, Corren J, Hanania NA, Kim H, Korn S, et al. Tezepelumab in patients with allergic and eosinophilic asthma. Allergy. (2024) 79:1134–45. doi: 10.1111/all.15986
27. Menzies-Gow A, Corren J, Bourdin A, Chupp G, Israel E, Wechsler ME, et al. Tezepelumab in adults and adolescents with severe, uncontrolled asthma. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1800–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034975
28. Menzies-Gow A, Wechsler ME, Brightling CE, Korn S, Corren J, Israel E, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of tezepelumab in people with severe, uncontrolled asthma (DESTINATION): a randomized, placebo-controlled extension study. Lancet Respir Med. (2023) 11:425–38. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00492-1
29. Biener L, Mümmler C, Hinze CA, Suhling H, Korn S, Fisser C, et al. Real-world data on tezepelumab in patients with severe asthma in Germany. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2024) 12:2399–2407.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.05.052
30. Jiménez-Gómez M, Díaz-Campos RM, Gimeno-Díaz-De-Atauri Á, Fernández-Rodríguez C, Fernández-Crespo J, García-Moguel I. Early response to tezepelumab in type-2 severe asthma patients non-responders to other biological treatments: a real-life study. J Asthma. (2024) 61:1347–50. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2024.2349605
31. Violán VV, Cano BG, Casero MÁR, González-Mancebo E, Vicente EM, Trujillo MJT, et al. Real-life experience after 3 months with tezepelumab before marketing approval. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). (2024) 52:80–2. doi: 10.15586/aei.v52i2.1063
32. Carpagnano GE, Dragonieri S, Resta E, Lulaj E, Montagnolo F, Portacci A, et al. Short-term tezepelumab effectiveness in patients with severe asthma: a multicenter study. J Asthma. (2025) 62:456–64. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2024.2409987
33. Betancor D, Bautista S, López-Rodríguez R, Valverde-Monge M, Fernández-Nieto M, Rial MJ. Four-month real-life response to tezepelumab in patients with multi-failure to other biologics. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). (2024) 52(6):76–8. doi: 10.15586/aei.v52i6.1161
34. Miralles-López JC, Andújar-Espinosa R, Bravo-Gutierrez FJ, Cabrejos-Perotti S, Ramírez-Hernández M, Díaz-Chantar C, et al. Tezepelumab in patients with severe asthma: response at 3 months. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2025) 35:132–4. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.1041
35. Miralles-López JC, Bravo-Gutierrez FJ, Andújar-Espinosa R, Castilla-Martínez M, Díaz-Chantar C, Ramírez-Hernández M, et al. Real-life effectiveness of tezepelumab in severe asthma. J Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). (2025) 53:163–73. doi: 10.15586/aei.v53i2.1326
36. Corren J, Ziegler SF. TSLP: from allergy to cancer. Nat Immunol. (2019) 20:1603–9. doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0524-9
37. Moffatt MF, Gut IG, Demenais F, Strachan DP, Bouzigon E, Heath S, et al. A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. N Engl J Med. (2010) 363(13):1211–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0906312
38. Tsilingiri K, Fornasa G, Rescigno M. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: to cut a long story short. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 3:174–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.01.005
39. Matera MG, Rogliani P, Calzetta L, Cazzola M. TSLP inhibitors for asthma: current status and future prospects. Drugs. (2020) 80:449–58. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01273-4
40. Varricchi G, Pecoraro A, Marone G, Criscuolo G, Spadaro G, Genovese A, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin isoforms, inflammatory disorders, and cancer. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1595. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01595
41. Markovic I, Savvides SN. Modulation of signaling mediated by TSLP and IL-7 in inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1557. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01557
42. Verstraete K, van Schie L, Vyncke L, Bloch Y, Tavernier J, Pauwels E, et al. Structural basis of the proinflammatory signaling complex mediated by TSLP. Nat Struct Mol Biol. (2014) 21:375–82. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2794
43. Verstraete K, Peelman F, Braun H, Lopez J, Van Rompaey D, Dansercoer A, et al. Structure and antagonism of the receptor complex mediated by human TSLP in allergy and asthma. Nat Commun. (2017) 8:14937. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14937
44. Pandey A, Ozaki K, Baumann H, Levin SD, Puel A, Farr AG, et al. Cloning of a receptor subunit required for signaling by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Nat Immunol. (2000) 1:59–64. doi: 10.1038/76923
45. Berraïes A, Hamdi B, Ammar J, Hamzaoui K, Hamzaoui A. Increased expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in induced sputum from asthmatic children. Immunol Lett. (2016) 178:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.08.004
46. Glück J, Rymarczyk B, Kasprzak M, Rogala B. Increased levels of interleukin-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in exhaled breath condensate in chronic bronchial asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2016) 169:51–6. doi: 10.1159/000444017
47. Li Y, Wang W, Lv Z, Li Y, Chen Y, Huang K, et al. Elevated expression of IL-33 and TSLP in the airways of human asthmatics in vivo: a potential biomarker of severe refractory disease. J Immunol. (2018) 200:2253–62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701455
48. Torgerson DG, Ampleford EJ, Chiu GY, Gauderman WJ, Gignoux CR, Graves PE, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of asthma in ethnically diverse north American populations. Nat Genet. (2011) 43:887–92. doi: 10.1038/ng.888
49. Hirota T, Takahashi A, Kubo M, Tsunoda T, Tomita K, Doi S, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies three new susceptibility loci for adult asthma in the Japanese population. Nat Genet. (2011) 43:893–6. doi: 10.1038/ng.887
50. Ober C, Yao TC. The genetics of asthma and allergic disease: a 21st century perspective. Immunol Rev. (2011) 242:10–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01029.x
51. Buchheit KM, Cahill KN, Katz HR, Murphy KC, Feng C, Lee-Sarwar K, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin controls prostaglandin D2 generation in patients with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2016) 137:1566–1576.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.10.020
52. He R, Geha RS. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2010) 1183:13–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05128.x
53. Whetstone CE, Ranjbar M, Omer H, Cusack RP, Gauvreau GM. The role of airway epithelial cell alarmins in asthma. Cells. (2022) 11:1105. doi: 10.3390/cells11071105
54. Ortega H, Nickle D, Carter L. Rhinovirus and asthma: challenges and opportunities. Red Med Virol. (2021) 31:e2193. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2193
55. Lambrecht BN, Hammad H, Fahy JV. The cytokines of asthma. Immunity. (2019) 50:975–91. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.018
56. Klose CSN, Artis D. Innate lymphoid cells as regulators of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:765–74. doi: 10.1038/ni.3489
57. Camelo A, Rosignoli G, Ohne Y, Stewart RA, Overed-Sayer C, Sleeman MA, et al. IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP induce a distinct phenotypic and activation profile in human type 2 innate lymphoid cells. Blood Adv. (2017) 1:577–89. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016002352
58. Pelaia C, Paoletti G, Puggioni F, Racca F, Pelaia G, Canonica GW, et al. Interleukin-5 in the pathophysiology of severe asthma. Front Physiol. (2019) 10:1514. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01514
59. Pelaia C, Heffler E, Crimi C, Maglio A, Vatrella A, Pelaia G, et al. Interleukins 4 and 13 in asthma: key pathophysiologic cytokines and druggable molecular targets. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:851940. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.851940
60. Shikotra A, Choy DF, Ohri CM, Doran E, Butler C, Hargadon B, et al. Increased expression of immunoreactive thymic stromal lymphopoietin in patients with severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2012) 129:104–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.08.031
61. Lee TJ, Fu CH, Wang CH, Huang CC, Huang CC, Chang PH, et al. Impact of chronic rhinosinusitis on severe asthma patients. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0171047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171047
62. Liu S, Verma M, Michalec L, Liu W, Sripada A, Rollins D, et al. Steroid resistance of airway type 2 innate lymphoid cells from patients with severe asthma: the role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 141:257–68. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.032
63. Wong CK, Hu S, Cheung PF, Lam CW. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin induces chemotactic and prosurvival effects in eosinophils: implications in allergic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2010) 43:305–15. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0168OC
64. Cook EB, Stahl JL, Schwantes EA, Fox KE, Mathur SK. IL-3 and TNF-( increase thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor (TSLPR) expression on eosinophils and enhance TSLP-stimulated degranulation. Clin Mol Allergy. (2012) 10:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-7961-10-8
65. Al-Sajee D, Sehmi R, Hawke TJ, El-Gammal A, Howie KJ, Watson RM, et al. Expression of IL-33 and TSLP and their receptors in asthmatic airways after inhaled allergen challenge. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2018) 198:805–7. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2468LE
66. Morshed M, Yousefi S, Stöckle C, Simon HU, Simon D. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin stimulates the formation of eosinophil extracellular traps. Allergy. (2012) 67:1127–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2012.02868.x
67. Salter BMA, Smith SG, Mukherjee M, Plante S, Krisna S, Nusca G, et al. Human bronchial epithelial cell-derived factors from severe asthmatic subjects stimulate eosinophil differentiation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2018) 58:99–106. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0262OC
68. Smith SG, Gugilla A, Mukherjee M, Merim K, Irshad A, Tang W, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and IL-33 modulate migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells in patients with allergic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 135:1594–602. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.12.1918
69. Salter BM, Oliveria JP, Nusca G, Smith SG, Watson RM, Comeau M, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin activation of basophils in patients with allergic asthma is IL-3 dependent. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2015) 136:1636–44. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.039
70. Salter BM, Oliveria JP, Nusca G, Smith SG, Tworek D, Mitchell PD, et al. IL-25 and IL-33 induce type 2 inflammation in basophils from subjects with allergic asthma. Respir Res. (2016) 17:5. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0321-z
71. Nagarkar DR, Poposki JA, Comeau MR, Biyasheva A, Avila PC, Schleimer RP, et al. Airway epithelial cells activate Th2 cytokine production in mast cells through IL-1 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2012) 130:225–232.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.04.019
72. Pelaia C, Crimi C, Vatrella A, Busceti MT, Gaudio A, Garofalo E, et al. New treatments for asthma: from the pathogenic role of prostaglandin D2 to the therapeutic effects of fevipiprant. Pharmacol Res. (2020) 155:104490. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104490
73. Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W, Edward G, Homey B, et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell-mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. (2002) 3:673–80. doi: 10.1038/ni805
74. Ito T, Wang YH, Duramad O, Hori T, Delespesse GJ, Watanabe N, et al. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J Exp Med. (2005) 202:1213–23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051135
75. Hammad H, Lambrecht BN. The basic immunology of asthma. Cell. (2021) 184:1469–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.016
76. Pattarini L, Trichot C, Bogiatzi S, Grandclaudon M, Meller S, Keuylian Z, et al. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce human T follicular helper cell differentiation through OX40-ligand. J Exp Med. (2017) 214:1529–46. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150402
77. Barnes PJ. The cytokine network in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:3546–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI36130
78. Lai JF, Thompson LJ, Ziegler SF. TSLP Drives acute TH2-cell differentiation in lungs. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2020) 146:1406–1418.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.03.032
79. Rochman Y, Dienger-Stambaugh K, Richgels PK, Lewkowich IP, Kartashov AV, Barski A, et al. TSLP signaling in CD4(+) T cells programs a pathogenic T helper 2 cell state. Sci Signal. (2018) 11:521. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aam8858
80. Nguyen KD, Vanichsarn C, Nadeau KC. TSLP Directly impairs pulmonary treg function: association with aberrant tolerogenic immunity in asthmatic airway. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. (2010) 6:4. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-4
81. Han H, Headley MB, Xu W, Comeau MR, Zhou B, Ziegler SF. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin amplifies the differentiation of alternatively activated macrophages. J Immunol. (2013) 190:904–12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201808
82. Canè L, Poto R, Palestra F, Pirozzi M, Parashuraman S, Iacobucci I, et al. TSLP Is localized in and released from human lung macrophages activated by T2-high and T2-low stimuli: relevance in asthma and COPD. Eur J Int Med. (2024) 124:89–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2024.02.020
83. Ogulur I, Mitamura Y, Yazici D, Pat Y, Ardicli S, Li M, et al. Type 2 immunity in allergic diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. (2025) 22:211–42. doi: 10.1038/s41423-025-01261-2
84. Hinks TSC, Levine SJ, Brusselle GG. Treatment options in type-2 low asthma. Eur Respir J. (2021) 57:2000528. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00528-2020
85. Tanaka J, Watanabe N, Kido M, Saga K, Akamatsu T, Nishio A, Chiba T. Human TSLP and TLR3 ligands promote differentiation of Th17 cells with a central memory phenotype under Th2-polarizing conditions. Clin Exp Allergy. (2009) 39:89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03151.x
86. Liang Y, Yu B, Chen J, Wu H, Xu Y, Yang B, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin epigenetically upregulates fc receptor ( subunit-related receptors on antigen-presenting cells and induces TH2/TH17 polarization through dectin-2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2019) 144:1025–1035.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.06.011
87. Redhu NS, Gounni AS. Function and mechanisms of TSLP/TSLPR complex in asthma and COPD. Clin Exp Allergy. (2012) 42:994–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03919.x
88. Shan L, Redhu NS, Saleh A, Halayko AJ, Chakir J, Gounni AS. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor-mediated IL-6 and CC/CXC chemokines expression in human airway smoot muscle: role of MAPKs (ERK1/2, p38, and JNK) and STAT3 pathways. J Immunol. (2010) 184:7134–43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902515
89. Allakhverdi Z, Comeau MR, Jessup HK, Delespesse G. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a mediator of crosstalk between bronchial smooth muscles and mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2009) 123:958–960.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.01.059
90. Cao L, Liu F, Liu Y, Liu T, Wu J, Zhao J, et al. TSLP promotes asthmatic airway remodeling via p38-STAT3 signaling pathway in human lung fibroblasts. Exp Lung Res. (2018) 44:288–301. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2018.1536175
91. Wieczfinska J, Pawliczak R. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and apocynin alter the expression of airway remodeling factors in human rhinovirus-infected cells. Immunobiology. (2017) 222:892–9. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2017.05.010
92. Bertolini F, Carriero VMA, Arrigo E, Guida G, Levra S, Pizzimenti S, et al. Vascular remodeling and TSLP/angiogenin overexpression in severe mixed asthma. Respir Res. (2025) 26:78. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03133-9
93. Marone G, Spadaro G, Braile M, Poto R, Criscuolo G, Pahima H, et al. Tezepelumab: a novel biological therapy for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. (2019) 28:931–40. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1672657
94. Gauvreau GM, O’Byrne PM, Boulet LP, Wang Y, Cockcroft D, Bigler J, et al. Effects of an anti-TSLP antibody on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. N Engl J Med. (2014) 370:2102–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402895
95. Emson C, Corren J, Salapa K, Hellqvist Å, Parnes JR, Colice G. Efficacy of tezepelumab in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma with and without nasal polyposis: a post hoc analysis of the phase 2b study PATHWAY. J Asthma Allergy. (2021) 14:91–9. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S288260
96. Corren J, Karpefors M, Hellqvist Å, Parnes JR, Colice G. Tezepelumab reduces exacerbations across all seasons in patients with severe, uncontrolled asthma: a post hoc analysis of the PATHWAY phase 2b study. J Asthma Allergy. (2021) 14:1–11. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S286036
97. Dorey-Sten ZL, Shenoy KV. Tezepelumab as an emerging therapeutic option for the treatment of severe asthma: evidence to date. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2021) 15:331–8. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S250825
98. Wechsler ME, Colice G, Griffiths JM, Almqvist G, Skärby T, Piechowiak T, et al. SOURCE: a phase 3, multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tezepelumab in reducing oral corticosteroid use in adults with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Respir Res. (2020) 21:264. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01503-z
99. Canonica GW, Colombo GL, Bruno GM, Di Matteo S, Martinotti C, Blasi F, et al. Shadow cost of oral corticosteroids-related adverse events: a pharmacoeconomic evaluation applied to real-life data from the severe asthma network in Italy (SANI) registry. World Allergy Organ J. (2019) 12:100007. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2018.12.001
100. Wechsler ME, Menzies-Gow A, Brightling CE, Kuna P, Korn S, Welte T, et al. Evaluation of the oral-corticosteroid-sparing effect of tezepelumab in adults with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma (SOURCE): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Respir Med. (2022) 10:650–60. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00537-3
101. Wechsler ME, Brusselle G, Virchow JC, Bourdin A, Kostikas K, Llanos JP, et al. Clinical response and on-treatment clinical remission with tezepelumab in a broad population of patients with severe uncontrolled asthma: results over 2 years from the NAVIGATOR and DESTINATION studies. Eur Respir J. (2024) 64:2400316. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00316-2024
102. Mailhot-Larouche S, Busby J, Couillard S. Response and remission in asthma with tezepelumab: overlapping concepts informing on type-2 inflammatory-dependent treated effects. Eur Respir J. (2025) 65:2402057. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02057-2024
103. Emson C, Diver S, Chachi L, Megally A, Small C, Downie J, et al. CASCADE: a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial to evaluate the effect of tezepelumab on airway inflammation in patients with uncontrolled asthma. Respir Res. (2020) 21:265. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01513-x
104. Diver S, Khalfaoui L, Emson C, Wenzel SE, Menzies-Gow A, Wechsler ME, et al. Effect of tezepelumab on airway inflammatory cells, remodelling, and hyperresponsiveness in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma (CASCADE): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2021) 9:1299–312. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00226-5
105. Sverrild A, Hansen S, Hvidtfeldt M, Clausson CM, Cozzolino O, Cerps S, et al. The effect of tezepelumab on airway hyperresponsiveness to mannitol in asthma (UPSTREAM). Eur Respir J. (2022) 59:2101296. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01296-2021
106. Pelaia C, Greco M, Iaccino E, Crimi C, Biafora M, Dragone F, et al. Short-term therapeutic effectiveness of tezepelumab in patients with severe asthma: a real-world study. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 162:115185. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.115185
107. Leon B. Understanding the development of Th2 cell-driven allergic airway disease in early life. Front Allergy. (2023) 3:1080153. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.1080153
108. Goleij P, Rahimi M, Pourshahroudi M, Tabari MAK, Muhammad S, Suteja RC, et al. The role of IL-2 cytokine family in asthma. Cytokine. (2024) 180:156638. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156638
109. Luo W, Hu J, Xu W, Dong J. Distinct spatial and temporal roles for Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells in asthma. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:974066. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.974066
110. Pelaia C, Pelaia G, Maglio A, Tinello C, Gallelli L, Lombardo N, et al. Pathobiology of type 2 inflammation in asthma and nasal polyposis. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:3371. doi: 10.3390/jcm12103371
Keywords: severe asthma endotypes, thymic stromal lymphopoietin, alarmins, airway epithelium, innate and adaptive immune responses, tezepelumab
Citation: Pelaia C, Melhorn J, Paoletti G, Poto R, Maglio A, Crimi C, Vatrella A, Canonica GW and Pelaia G (2025) Key role of thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a molecular target for biologic treatment of severe asthma. Front. Allergy 6:1671353. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1671353
Received: 22 July 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 14 November 2025.
Edited by:
Kian Fan Chung, Imperial College London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Pankaj Kumar Bhavsar, Imperial College London, United KingdomDominick Shaw, University of Leicester, United Kingdom
Copyright: © 2025 Pelaia, Melhorn, Paoletti, Poto, Maglio, Crimi, Vatrella, Canonica and Pelaia. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Corrado Pelaia, cGVsYWlhLmNvcnJhZG9AZ21haWwuY29t
 Corrado Pelaia
Corrado Pelaia James Melhorn
James Melhorn Giovanni Paoletti
Giovanni Paoletti Remo Poto
Remo Poto Angelantonio Maglio
Angelantonio Maglio Claudia Crimi8
Claudia Crimi8 Alessandro Vatrella
Alessandro Vatrella Girolamo Pelaia
Girolamo Pelaia