- 1Department of Animal and Food Sciences, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, United States
- 2Livestock Issues Research Unit, United States Department of Agriculture- Agricultural Research Service (USDA-ARS), Lubbock, TX, United States
- 3Elanco Animal Health, Greenfield, IN, United States
To evaluate the acute physiological and immunological responses to Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines, weaned heifers (n = 32; body weight [BW] = 296 ± 6.4 kg) were used in a completely randomized design. Heifers were balanced by BW and randomly assigned to one of three vaccine treatments: Nuplura PH (Elanco, Greenfield, IN; NP), OneShot (Zoetis, Parsippany, NJ; OS), or Presponse SQ (Boehringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO; PS). Serial blood samples were collected for 7 d following vaccine administration to quantify multiple serum biomarkers and complete blood cell counts. Heifers were fitted with indwelling vaginal temperature recording devices for the duration of the study. No differences were noted in most CBC variables (P ≥ 0.27) except for PS heifers having greater lymphocytes (P = 0.02) and eosinophils (P < 0.01) than NP and OS heifers. Cortisol remained at or below basal concentrations for the duration of the study (P = 0.23). Glucose concentrations were greater for NP than OS, with PS being intermediate (P = 0.05). There was a tendency (P = 0.08) for a treatment × time interaction for circulating haptoglobin concentrations as NP heifers had a spike of greater magnitude but decreased duration. Likewise, a tendency (P = 0.07) was detected for decreased ceruloplasmin concentrations in PS heifers. The concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6) was lesser in OS heifers than PS and NP heifers (P = 0.02), but PS heifers had decreased IL-4 concentrations (P < 0.01). No differences were observed in circulating interferon-gamma concentrations among treatments (P = 0.20). Overall, each vaccine treatment elicited similar physiological and inflammatory immune responses despite differences in vaccine composition. Although select immunological markers differed relative to vaccine treatment, it is unlikely these differences resulted in biologically relevant differences.
1 Introduction
Mannheimia haemolytica (Mh) is an etiologic agent of bacterial pneumonic mannheimiosis, and one of the predominant bacteria responsible for the bovine respiratory disease (BRD) complex (Rice et al., 2007; Azhar et al., 2021). A Gram-negative bacterium, Mh is commensal in the nasopharynx region of cattle (Frank et al., 1989); however, this bacteria can become pathogenic, most frequently causing clinical disease during periods of stress post weaning (e.g., when cattle arrive at the feedlot; Mosier et al., 1989). While many Gram-negative vaccines exist in livestock production to protect against Mh, there is concern for adverse reactions (Ellis and Yong, 1997). Endotoxins are a major component of the Gram-negative bacteria cell wall (Woltmann et al., 1998). During bacterial cell death, induced immune activity, or inflammatory reactions, endotoxins are released (Rosenfeld and Shai, 2006; Chung et al., 2019), with beef cattle being particularly sensitive to endotoxin (Carroll et al., 2009; Smock et al., 2023).
The possible detrimental effects and adverse reactions associated with Mh vaccines has been questioned for nearly 90 years (Farley, 1932; Wilkie et al., 1980; Rice et al., 2007). The administration of multiple Gram-negative vaccines during a single processing event may lead to adverse physiological reactions because of endotoxin stacking. This problem could be exacerbated if one or more of these vaccines are mishandled, resulting in an increase in free endotoxin (Richeson et al., 2019).
Endotoxin exposure in cattle results in a conserved immunological and physiological response commonly referred to as the acute phase response. This acute phase response is partially propagated and mediated by the production and release of cytokines, resulting in the release of acute-phase proteins by hepatocytes (Baumann and Gauldie, 1994; Gulati et al., 2016). This reaction often causes behavioral changes accompanied by fever and an increase in circulating leukocytes.
Endotoxins from different Gram-negative bacteria have differing antigenicity, and this phenomenon even extends to different serovars of bacteria within the same species (van der Woude and Bäumler, 2004). Currently, legal limits for the quantity of free endotoxins in vaccines has not been established despite free endotoxin being undesirable. Although concentrations are generally low in vaccines, mishandling can increase the killing or lysis of the modified live and inactivated bacteria, thereby increasing endotoxin release and antigenicity of the vaccine (Richeson et al., 2019). We hypothesize that Mh vaccine formulation will differentially influence the metabolic and inflammatory responses following vaccine administration in feedlot cattle. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine differences in the physiological responses of cattle given differing M. haemolytica vaccines.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental design
All experimental procedures complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Agricultural Animals in Research and Teaching and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol #1809F) of the Livestock Issues Research Unit. The study was conducted in November 2018.
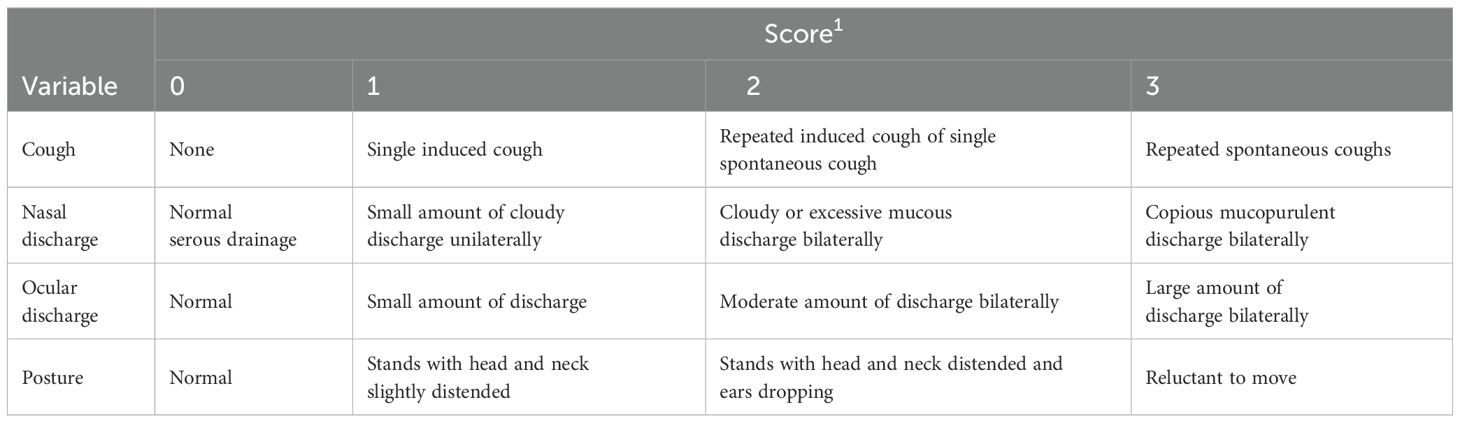
Forty heifers (296 ± 6.4 kg) obtained from a commercial feedlot in the Texas panhandle were used in a completely randomized design. Heifers were transported approximately 128 km to the Livestock Issues Research Unit Bovine Immunology Research and Development facility near Lubbock, TX on d -7. At arrival, heifers were individually weighed (3000S Paul Scale; W.W. Livestock Systems, Duncan, OK; readability ± 0.45 kg; scale calibrated with 300 kg of certified weights before use) and allotted into covered outdoor dirt holding pens (7.6 × 18.3 m; n = 10 heifers/pen) where they remained from d -7 to d -1 with ad libitum access to fresh feed and water. Heifers were fed a commercially available complete-feed starter diet comprised primarily of wet corn gluten feed (RAMP; Cargill, Minnetonka, MN) from d -7 to 7. Each morning before feeding, health scores were assigned to each heifer based on an adaptation of the system developed by McGuirk and Peek (2014). Briefly, heifers were visually observed for clinical signs of illness, including cough, nasal discharge, ocular discharge, and posture, using a 0 to 3 scoring system (Appendix A). The personnel performing health observations throughout the duration of the study were blinded to vaccine treatment.
On d -1 before feeding, heifers were weighed individually. Study candidates (n = 32) selected for enrollment displayed acceptable temperament by visual appraisal, were free of disease or injury, and possessed a uniform BW. From d -1 to 7, no heifers selected for study enrollment were removed. Indwelling jugular vein catheters (Tygon ND 100–80 micro-bore tubing; U.S. Plastics, Lima, OH, USA; Carroll et al., 2009) and vaginal thermometers that recorded temperature in 5-min intervals from d -1 to d 7 (study end) were placed into the heifers selected for enrollment. Vaginal temperature thermometers were custom-made and inserted as described by Burdick et al., 2012, where a temperature logger (DST-micro-T; Star Oddi, Iceland) was secured in a blank CIDR device prior to insertion. Heifers were subsequently moved into individual stanchions (2.28 m × 0.76 m × 1.67 m). On d 0, heifers were randomly assigned to receive 1 of 3 vaccine treatments (10 to 11 heifers/treatment) at 0 h on d 0: Nuplura PH (NP; 2 mL subcutaneous [SQ]; Elanco, Greenfield, IN), OneShot (OS; 2 mL SQ; Zoetis, Parsippany, NJ), or Presponse SQ (PS; 2 mL SQ; Boehringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO). Vaccine treatments were administered SQ in the neck of the heifer in accordance with product label and Beef Quality Assurance guidelines. Following the final blood collection at 168 h (d 7), heifers were removed from their individual stanchions, final BW was collected, and the jugular catheter and vaginal thermometer were removed.
2.2 Vaccine endotoxin analysis
Three bottles of each vaccine from the same manufacturing lot as the vaccine administered in this study were submitted to a commercial laboratory (Associates of Cape Cod Inc.; East Falmouth, MA) for analysis of endotoxin concentration determination with an endotoxin-specific gel-clot assay. Briefly, 100 µL of vaccine was mixed with 100 µL of limulus amebocyte lysate reconstituted with a buffer formulated to render the reagent insensitive to (1-3)-β-D-glucan interference. Tubes were then shaken vigorously for 30 sec before incubation at 37°C for 60 min. Endotoxin concentrations were determined via visual evaluation of a series of vaccine dilutions and a positive test was indicated by gel formation that did not collapse when the tube was inverted. The final amount of endotoxin in each vaccine was then calculated by multiplying the sensitivity of the limulus amebocyte lysate regent (0.03 endotoxin units [EU]/mL) by the dilution factor at the endpoint and expressed as EU/mL of the vaccine.
2.3 Sample collection and analysis
The diet was provided ab libitum from d -1 to 7, targeting approximately 10% daily orts. Feed disappearance was monitored daily, and if disappearance was 100% from the previous day, delivery was increased up to 0.45 kg/heifer daily. While housed in stanchions, water intake was measured via individual paddle-type waterers (Suevia Cup; QC Supply Inc., Schuyler, NE) that were connected to a custom-built water intake monitoring system.
Blood samples were collected serially via a jugular vein catheter and extension set at differing intervals between d -1 to 7. After blood collection, the catheter and extension set were flushed with 10 mL of saline to replenish fluid loss, followed by a 2.5 mL injection of heparinized saline (10 USP/mL heparin) to maintain catheter patency. Ten mL of blood was collected into vacuum tubes containing no additive (#368045, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ) at -2, -1, and 0 h before vaccination on d 0. Serum tubes were allowed to clot at room temperature for at least 30 min before centrifugation at 1,300 × g for 20 min at 4°C. Serum supernatant was then divided into triplicate aliquots into microcentrifuge tubes (Cat. No. 05-408-129; Fisherbrand, Pittsburgh, PA) for storage at -80°C until assay analysis. Additionally, 4 mL of whole blood was collected into vacuum tubes (potassium EDTA, #366643, Becton Dickinson) at -2 and 0 h on d 0 to determine baseline hematological profiles.
After the vaccines were administered at 0 h, serum and hematological blood samples were collected at 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 120, and 168 h relative to vaccination. Hematological blood counts were analyzed using a ProCyte DX Hematology Analyzer (Idexx Laboratories, Inc., Westbrook, ME) using bovine-specific algorithms. Isolated serum was used to quantify the following: cytokines (pg/mL), haptoglobin (mg/mL), ceruloplasmin (mU/mL), cortisol (ng/mL), and glucose (mg/dL). Serum cytokine concentrations were determined using a bovine-specific custom multiplex chemiluminescence ELISA kit specific for bovine interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ; Quanterix, Lexington, MA; intra-assay CV = 5.9%; inter-assay CV = 9.0%). Commercially available kits were used for analysis of serum haptoglobin (Immunology Consultants Laboratories, Inc., Cat # E-10HPT; intra-assay CV = 8.6%; inter-assay CV = 9.1%), ceruloplasmin (Arbor Assays, Ann Arbor, MI, Cat #K035-H1; intra-assay CV = 3.3%; inter-assay CV = 13.3%), and cortisol (Arbor Assays, Cat # K003-H5; intra-assay CV = 6.7%; inter-assay CV = 12.4%) concentrations. Serum glucose concentrations were determined via modification of the enzymatic Autokit Glucose (Fujifilm Wako, Richmond, VA, USA, Cat # 997-03001; intra-assay CV = 6.6%; inter-assay CV = 13.7%) to fit a 96-well format. Briefly, 300 µL of prepared working solution was added to 2 µL of serum or prepared standards in a 96-well plate. Plates were incubated at 37°C for 5 min and absorption was recorded at 505 nm. All assay plates absorbances were read using a BioTek Powerwave 340 (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA). All serum analyses were compared to standard curves for each respective sample.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Heifer was used as the experimental unit in the completely randomized design. To determine which vaccine treatment heifers were administered, a random number generator (Microsoft Excel) was used. Before statistical analysis, vaginal temperature collected at 5-min intervals was averaged into 1-h intervals. The MIXED procedure of SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) specific for repeated measures was used for all statistical analysis. The model included fixed effects of treatment, time, and the interaction of treatment × time. Heifer within treatment was the subject of the repeated measures, and the autoregressive(1) covariance structure was used. Mean separation was accomplished via LSMEANS with the Tukey option. Significance was declared at P ≤ 0.05 and tendencies were discussed at 0.05 < P ≤ 0.10.
3 Results
3.1 Endotoxin concentration
The PS vaccine contained nearly 8-times more endotoxin (42,000 EU/mL) than OS (6,300 EU/mL), and OS contained >2-times more endotoxin than NP (2,700 EU/mL). These values are descriptive by design without the intent to replicate.
3.2 Body weight and health
There was an increase in BW from d -7 to d -1 during the acclimation phase (P < 0.01; Table 1) when heifers were group housed. Conversely, from d -1 to d 7 following vaccination, heifers lost 3.7 kg on average (P = 0.05), with no difference in BW between treatments (P = 0.88). Feed disappearance did not differ between treatments (P = 0.11) from d 0 to 6; however, feed consumption decreased regardless of treatment (P < 0.01) from d 2 to 6. No treatment × time interaction was detected for water intake (P = 0.82).
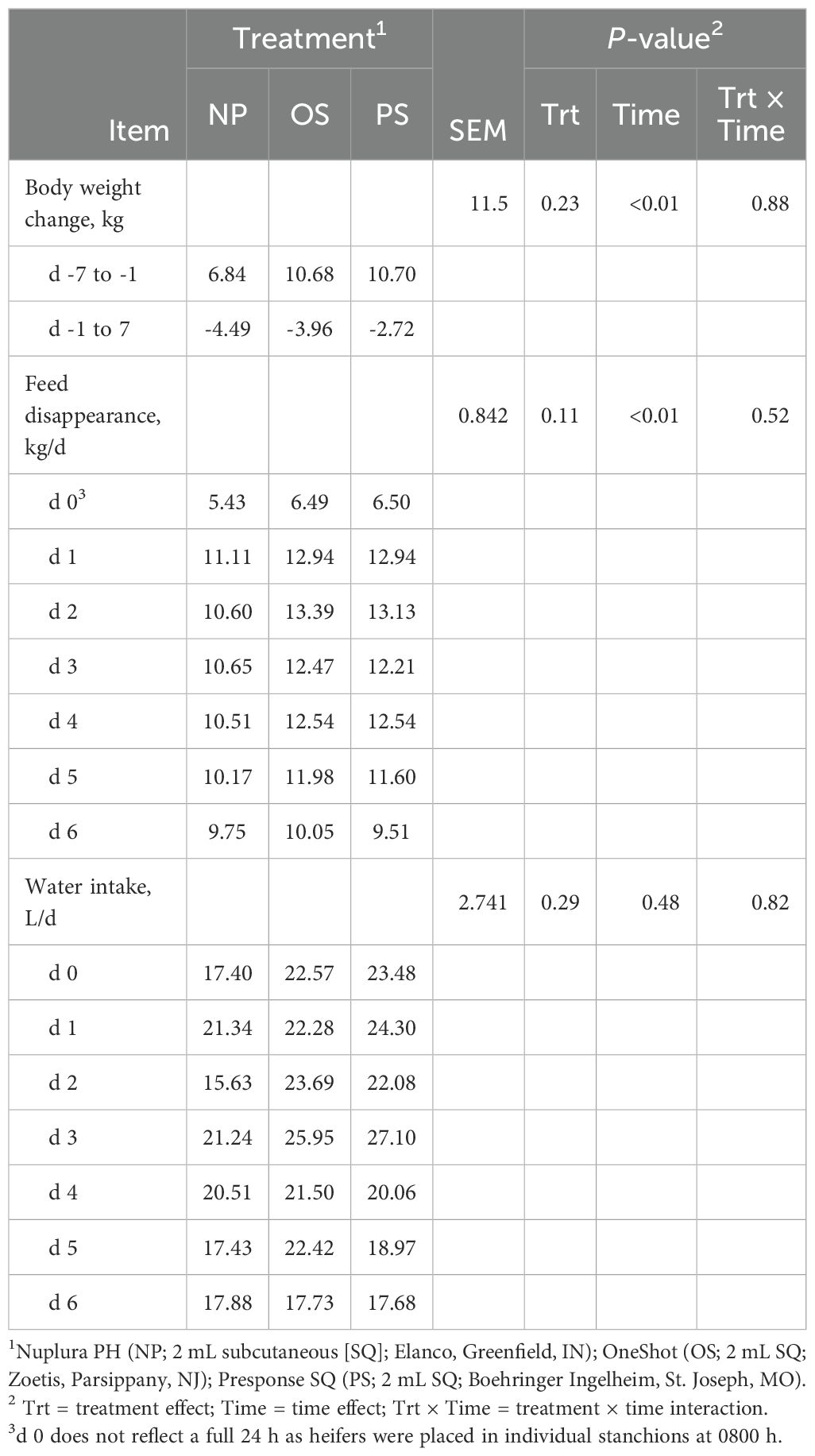
Table 1. Influence of 3 commercial Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines on heifer body weight, feed disappearance, and water intake.
There were no differences among treatments in health score with mean scores < 2 (P = 0.20; data not presented). No treatment × time interaction (P = 0.41) nor differences among treatment were observed for vaginal temperature (P = 0.68; Figure 1); however, vaginal temperature increased among treatments by 168 h relative to treatment administration (P < 0.01).
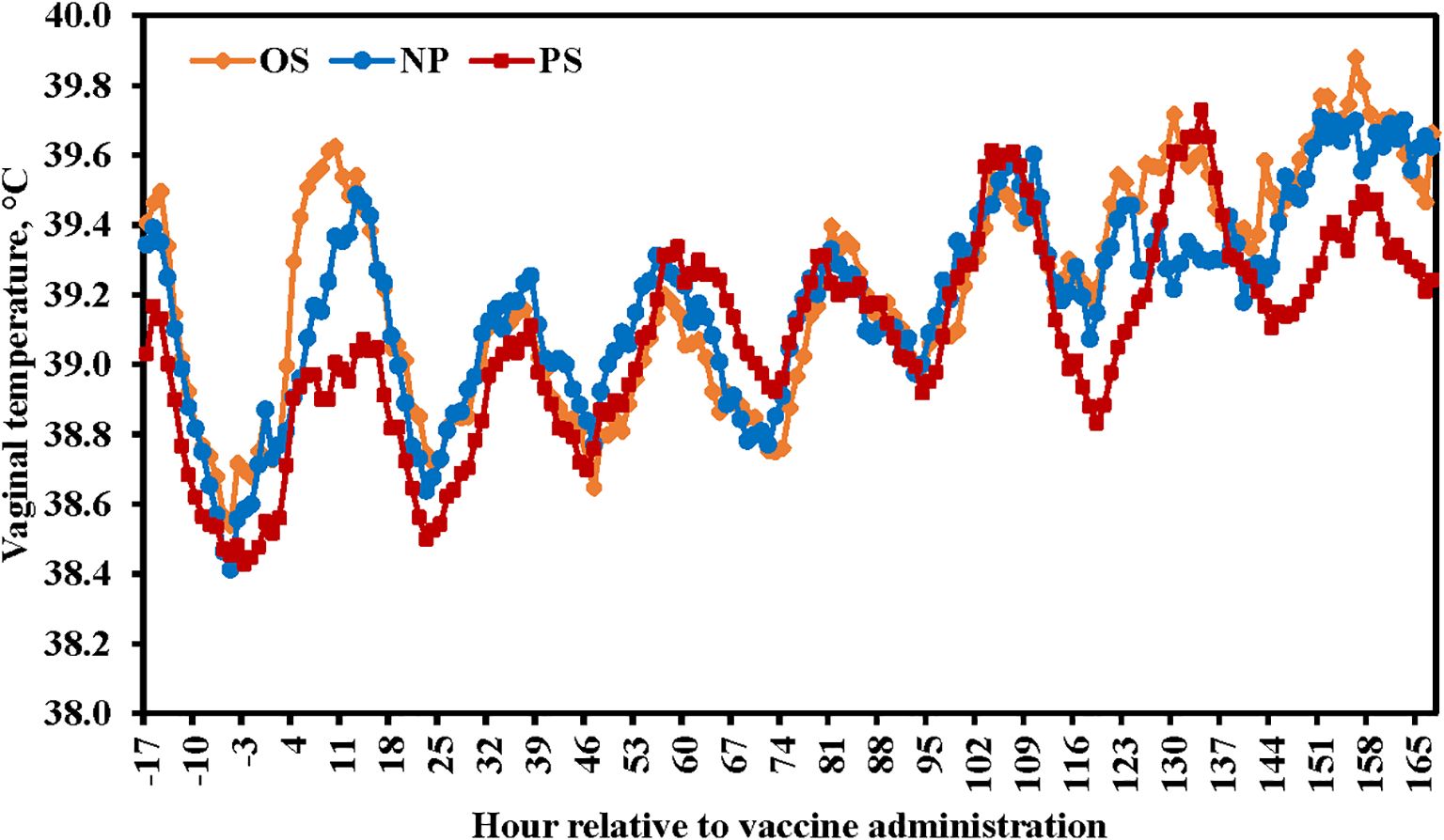
Figure 1. Influence of 3 commercial Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines on beef heifer vaginal temperature. Vaccine treatments included: Nuplura PH (NP; 2 mL subcutaneous [SQ]; Elanco, Greenfield, IN), OneShot (OS; 2 mL SQ; Zoetis, Parsippany, NJ), or Presponse SQ (PS; 2 mL SQ; Boehringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO). Heifers were sorted into treatments and fitted with vaginal thermometers on d -1, with vaginal temperatures being recorded from -17 to 168 h relative to vaccine administration.
3.3 Hematology
There was no difference in red blood cells (P = 0.77), hemoglobin (P = 0.63), nor platelets (P = 0.64) among treatments (Table 2). However, there was a treatment x time interaction for hematocrit % as PS was less (P < 0.01) than OS at 168 h. Similarly, no differences among treatments were observed in total white blood cell (P = 0.54) nor neutrophil count (P = 0.34). Lymphocyte count was greater in PS heifers than NP and OS heifers (P = 0.02). Lymphocyte baseline concentrations were greater in PS heifers (P = 0.02); therefore, the change in lymphocytes relative to baseline (-2 and 0 h) was evaluated. No differences in the change in lymphocyte count was detected (P = 0.16). Likewise, no differences among treatments were noted in neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio for the duration of the study (P = 0.44). However, there was a tendency for a treatment × time interaction in which an increase in neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio in OS heifers occurred from 4 to 8 h (P = 0.08). Circulating monocytes did not differ among treatments (P = 0.27), whereas basophils were greater in PS heifers than OS heifers (P = 0.02) with NP heifers not differing from either. Baseline basophil concentrations were greater in PS heifers (P < 0.01), with no difference in basophil change over time (P = 0.22). Eosinophil concentrations were greater in PS and NP heifers than OS heifers (P < 0.01), with no difference in baseline circulating concentrations (P = 0.12).
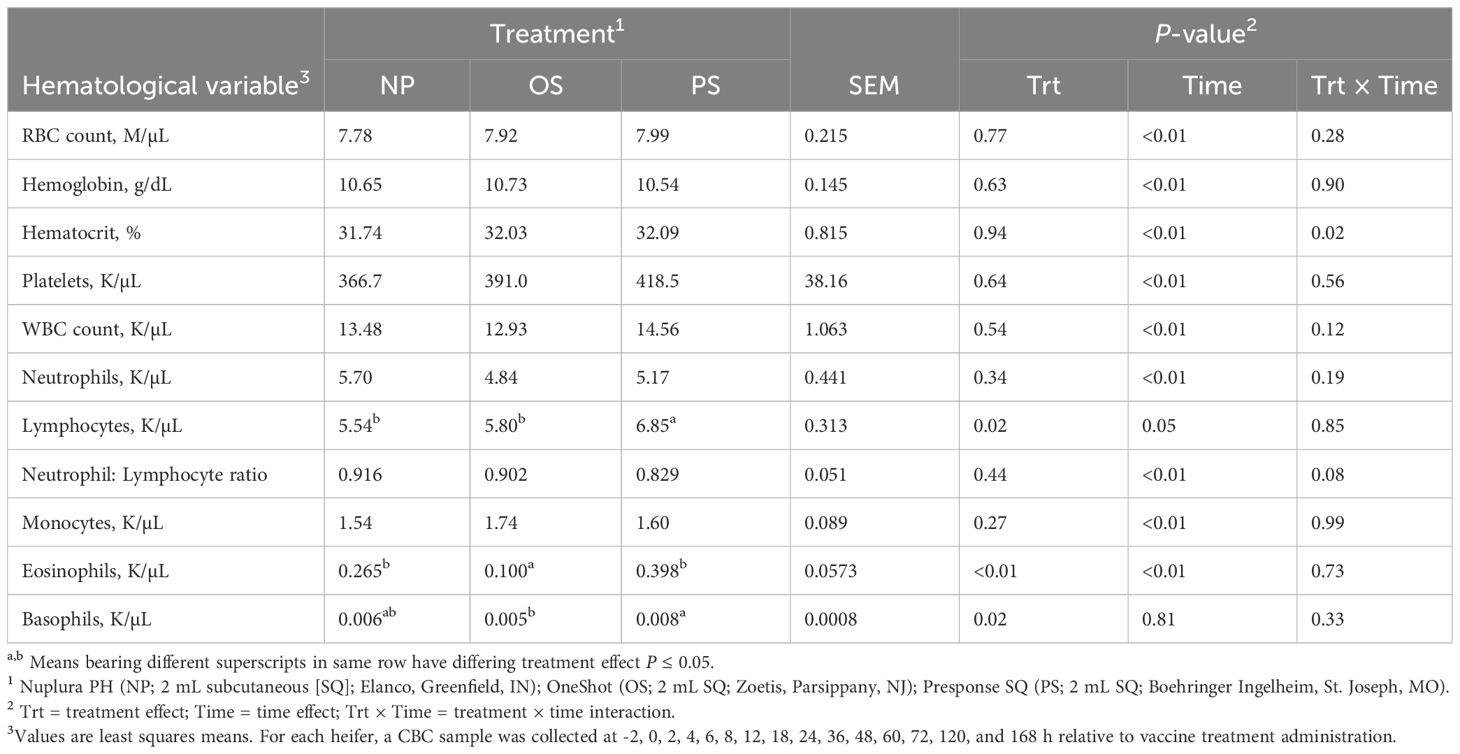
Table 2. Influence of 3 commercial Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines on the complete blood counts (CBC) from d 0 to 7 in beef heifers.
3.4 Cytokines
No treatment × time interactions were observed for cytokines (P ≥ 0.96). Circulating IL-4 concentration was lesser for PS heifers than for OS and NP heifers (P < 0.01; Figure 2A; NP: 12.52 pg/mL; OS: 10.08 pg/mL; PS: 4.76 pg/mL). All treatments displayed a spike in circulating IL-4 concentrations beginning at 48 h; however, the spike in PS heifers was of lesser magnitude than OS and NP heifers. For all heifers, IL-4 concentrations returned to baseline by 168 h. There was a difference in circulating IL-6 concentrations among treatments (P = 0.02; Figure 2B; NP: 129.86 pg/mL; OS: 94.16 pg/mL; PS: 117.63 pg/mL). Heifers given NP and PS had greater IL-6 concentrations than heifers given OS (P < 0.01), but concentrations did not differ from PS heifers (P = 0.56). Like IL-4, there was a spike in IL-6 concentrations at 48 h post-vaccination. No differences were observed in circulating IFN-γ concentrations among treatments (P = 0.20; Figure 2C; NP: 6.41 pg/mL; OS: 4.95 pg/mL; PS: 5.31 pg/mL). Circulating IFN-γ spiked in all treatments from 48 to 72 h, like the other cytokine responses, and returned to near baseline concentrations by 120 h (P < 0.01).
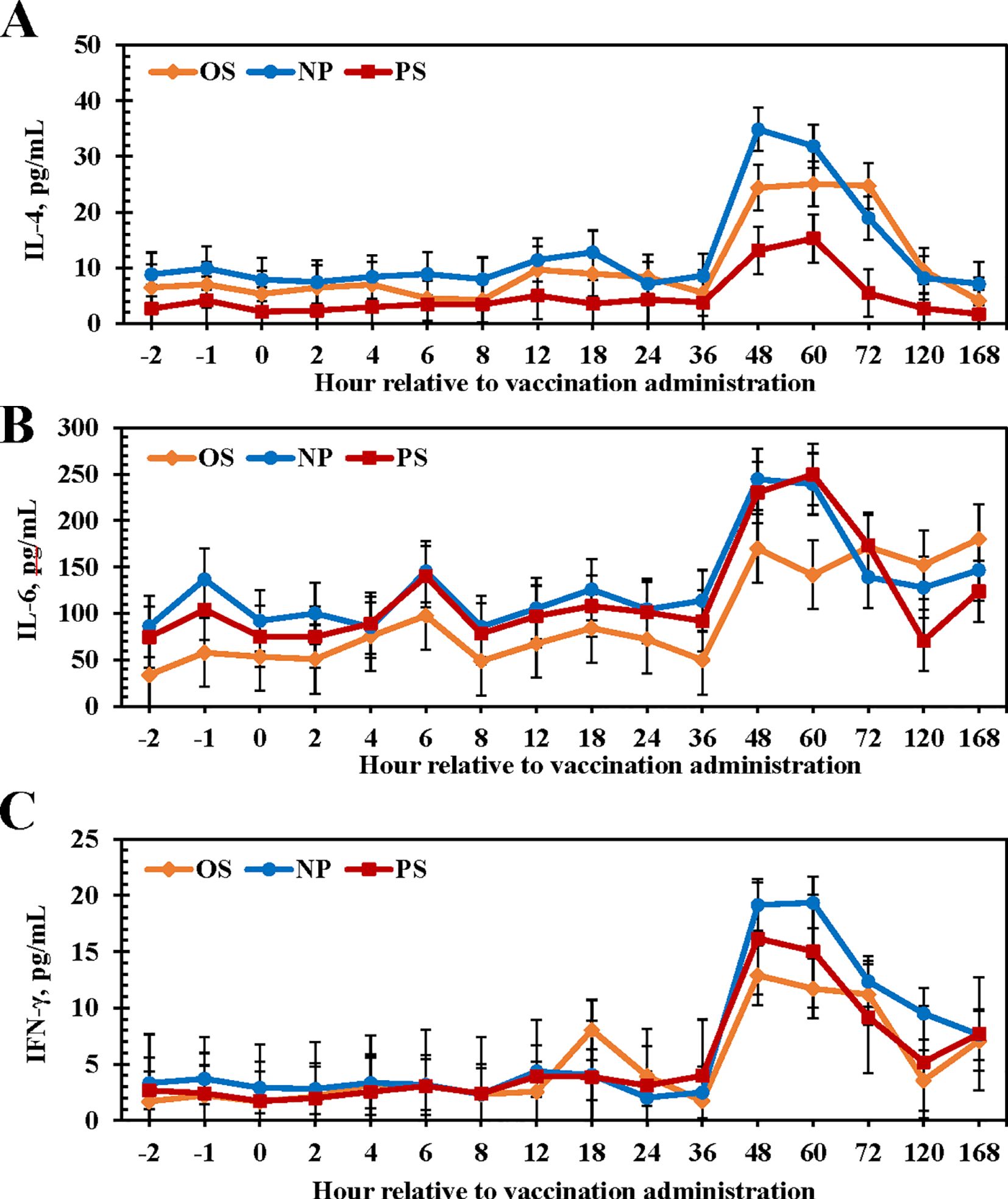
Figure 2. Influence of 3 commercial Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines on serum interleukin-4 [IL-4; (A)], interleukin-6 [IL-6; (B)], and interferon-gamma [IFN-γ; (C)] from d 0 to 7. Vaccine treatments included: Nuplura PH (NP; 2 mL subcutaneous [SQ]; Elanco, Greenfield, IN), OneShot (OS; 2 mL SQ; Zoetis, Parsippany, NJ), or Presponse SQ (PS; 2 mL SQ; Boehringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO). Vaccine treatments were administered at h 0.
3.5 Acute phase proteins
There were no differences among treatments for circulating haptoglobin concentrations (P = 0.14; Figure 3A; NP: 11.8 mg/mL; OS: 10.4 mg/mL; PS: 6.7 mg/mL); however, there was a tendency for a treatment × time interaction (P = 0.08). Haptoglobin remained near baseline for the first 8 h following vaccination but began to increase at 12-h post-vaccination. Between 48 to 72 h post-vaccination, NP heifers had greater haptoglobin concentrations than PS and OS heifers (P < 0.01), although haptoglobin concentrations began to decline at 120 and 168 h in the NP heifers. In contrast, circulating haptoglobin concentrations in PS and OS heifers displayed a gradual increase at 24 h that continued for the duration of the study. Circulating ceruloplasmin concentrations tended to be elevated in NP heifers compared with those given PS (P = 0.07; Figure 3B; NP: 28526 mU/mL; OS: 27171 mU/mL; PS: 23902 mU/mL); however, a treatment × time interaction was not observed (P = 0.57). This response was primarily driven by a decrease in circulating ceruloplasmin from 24 to 48 h post-vaccination for heifers given PS.
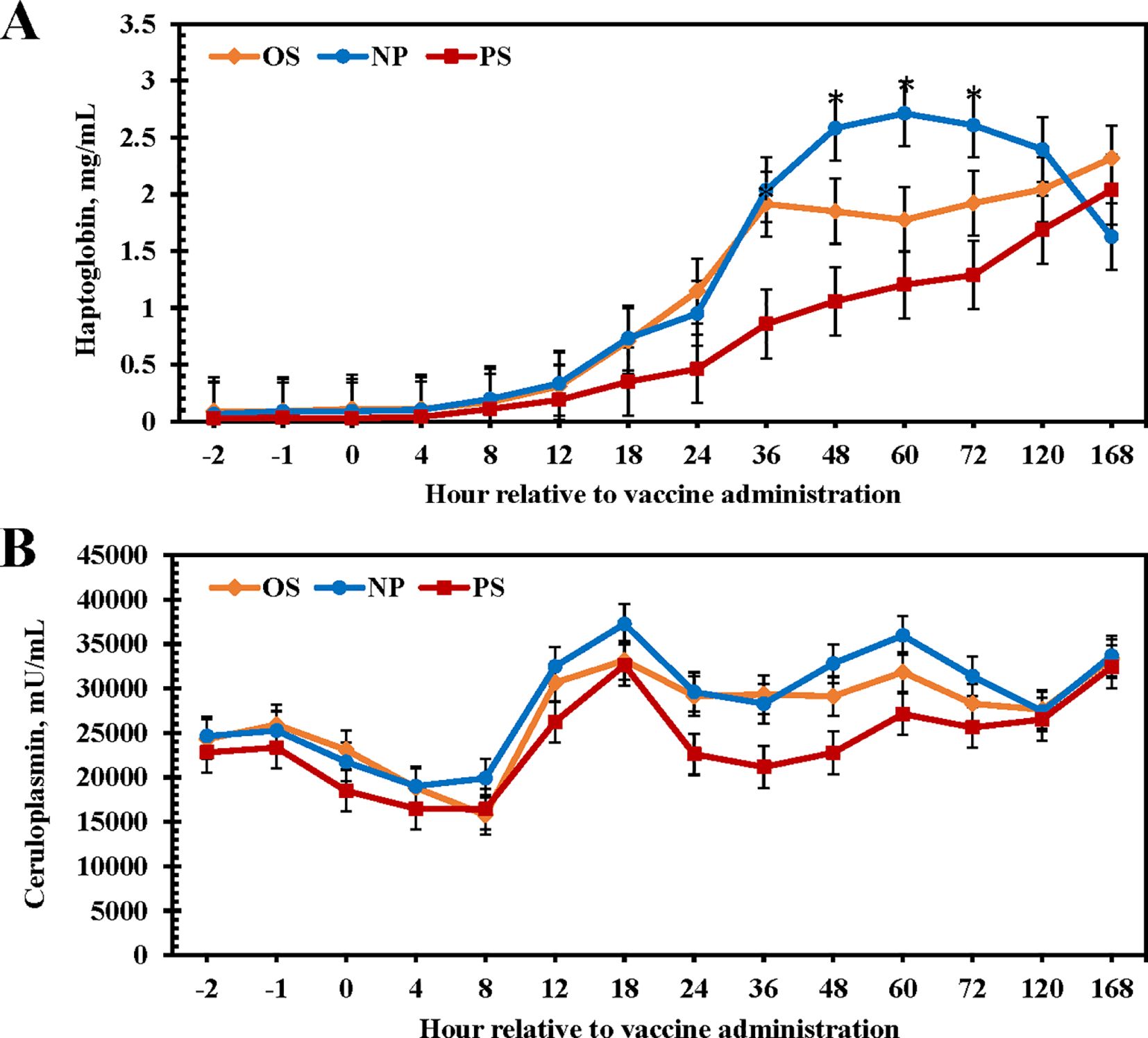
Figure 3. Influence of 3 commercial Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines on serum haptoglobin (A) and ceruloplasmin (B) concentrations from d 0 to 7. Vaccine treatments included: Nuplura PH (NP; 2 mL subcutaneous [SQ]; Elanco, Greenfield, IN), OneShot (OS; 2 mL SQ; Zoetis, Parsippany, NJ), or Presponse SQ (PS; 2 mL SQ; Boehringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO). Vaccine treatments were administered at h 0. If a treatment × time tendency was observed, the pairwise differences were sliced by day and indicated by * when 0.05 < P ≤ 0.10.
3.6 Serum metabolites
No differences among treatments were observed in circulating cortisol concentrations throughout the study, with overall cortisol concentrations remaining at or near baseline values (P = 0.23; Figure 4A; NP: 18.7 ng/mL; OS: 23.0 ng/mL; PS: 18.6 ng/mL). No treatment × time interaction was observed for glucose concentrations (P = 0.16). Glucose concentrations were greater for NP heifers than OS heifers with PS heifers being intermediate (P = 0.05; Figure 4B; NP: 77.2 mg/mL; OS: 72.6 mg/mL; PS: 74.7 mg/mL).
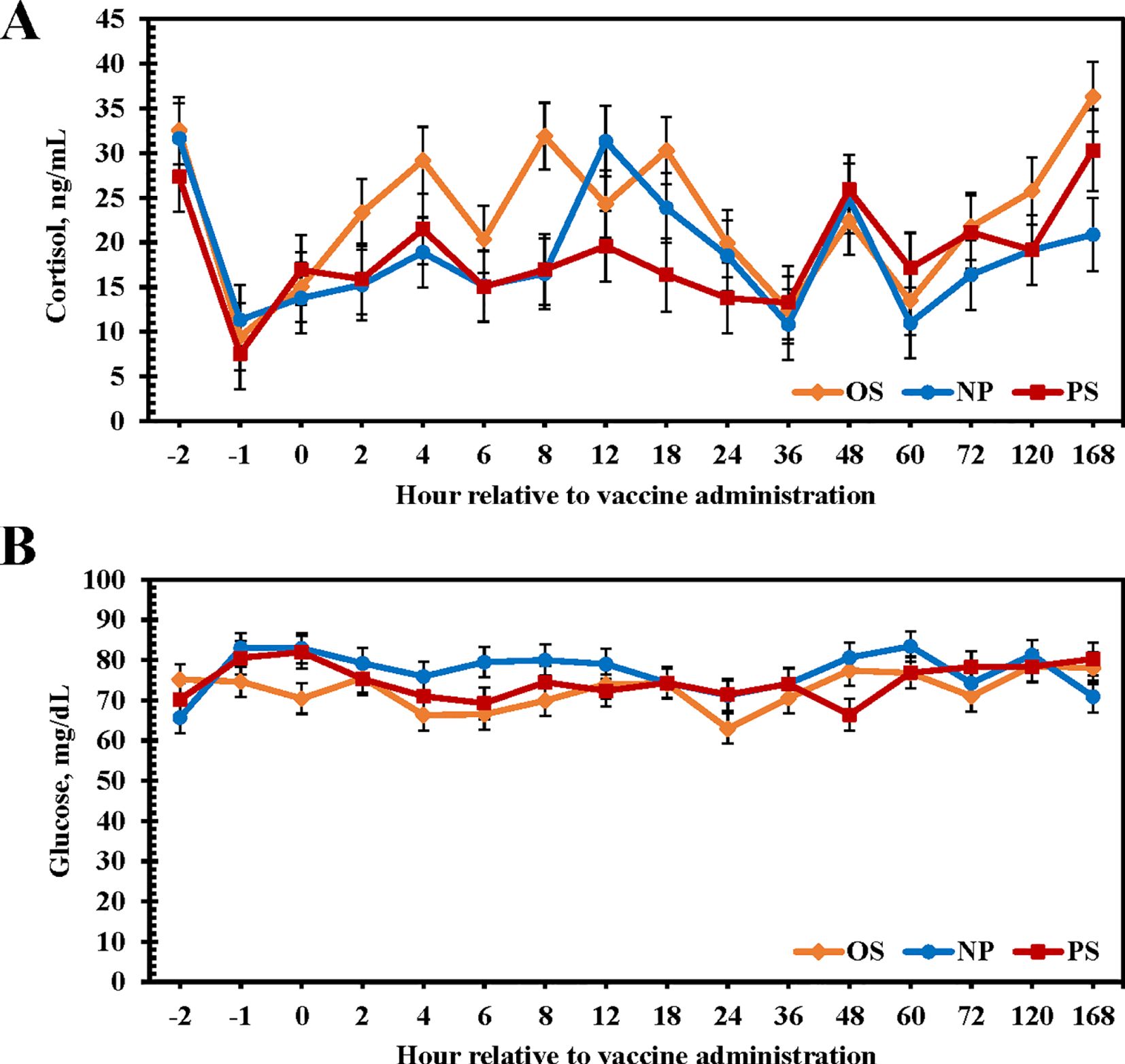
Figure 4. Influence of 3 commercial Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines on serum cortisol (A) and glucose (B) concentrations from d 0 to 7. Vaccine treatments included: Nuplura PH (NP; 2 mL subcutaneous [SQ]; Elanco, Greenfield, IN), OneShot (OS; 2 mL SQ; Zoetis, Parsippany, NJ), or Presponse SQ (PS; 2 mL SQ; Boehringer Ingelheim, St. Joseph, MO). Vaccine treatments were administered at h 0.
4 Discussion
4.1 Endotoxin concentration
Three types of Mh vaccines were evaluated in the current study. The NP vaccine is a recombinant leukotoxin vaccine containing extracted outer membrane proteins, such as 45-kDa outer-membrane protein lipoprotein, and the adjuvant dimethyldioctadecyl ammonium bromide. A whole-cell, bacterin-toxoid vaccine, OS contains a combination of cultured supernatants and killed Mh type A1. Bacteria-free, PS is a toxoid vaccine containing leukotoxin-rich cultured supernatant from the log phase growth of Mh (Srinand et al., 1996). Both PS and OS vaccines contain proprietary adjuvant formulations that are not publicly available.
Vaccine formulation can influence the concentration of vaccine-derived endotoxins like lipopolysaccharide, lipoproteins, and peptidoglycans, each of which are membrane components of the Gram-negative bacterial cell wall (Woltmann et al., 1998). The effects of lipopolysaccharide are primarily mediated by the lipid A component of the endotoxin, damaging bovine endothelial cells (Paulsen et al., 1989) while inducing proinflammatory cytokine gene expression (Lafleur et al., 1998). Although poorly understood, endotoxin stacking in cattle at feedlot arrival is common. Endotoxin from multiple bacterial sources can cause a greater physiological and immunological response with the potential for mortality (Alexander and Rietschel, 2001). Therefore, a better understanding of endotoxicity risks when designing vaccination protocols is warranted.
4.2 Performance and health
The aim of Mh vaccines is to stimulate an efficacious immune response that increases host defense mechanisms while decreasing the severity or incidence of pneumonia (Confer and Ayalew, 2018). Vaccine-induced immune stimulation has been reported to decrease feed intake (Stokka et al., 1994; Allen, 2000; Rodrigues et al., 2015). From d 2 to 6 in the current study, a 6.4% decrease in feed disappearance was observed among treatments. This decrease in feed disappearance, coupled with the transition to individual housing in a novel environment, likely contributed to the decrease in BW from d -1 to 7. Changes in BW were not observed from d -1 or 7 among treatments; however, the short duration of the study limits long-term interpretation of the effects of vaccine administration on BW change, and, therefore, should be interpreted with caution. Still, previous studies of similar length have reported no difference in BW when cattle received a Mh vaccine (Arthington et al., 2013; Rodrigues et al., 2015), further suggesting that Mh vaccines have a minimal direct effect on short-term BW changes.
From d -1 to 3, water consumption increased 32% among treatments; however, from d 3 to 6, water intake decreased 28% from the quantity consumed on d 3. This decrease in water intake could be attributable to the increase of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cattle exhibiting BRD have been reported to increase water intake relative to healthy cattle (Buhman et al., 2000; Word et al., 2020). Postpartum dairy cows receiving 1.5 or 3 µg/kg of recombinant bovine tumor necrosis factor-alpha had a 10% to 17% decrease in water intake, respectively, when compared with control cows (Yuan et al., 2013) as ill cattle are less inclined to seek out water (Hart, 1987). Current NASEM (2016) recommendations suggest a growing heifer weighing 273 kg should consume 29.5 L/d when the ambient temperature is 21.1°C. Heifers in the current study consumed an average of 20.7 L/d from d -1 to 6, although hematocrit evaluation does not indicate heifers were dehydrated. Housing heifers in a temperature-controlled facility under thermoneutral conditions likely influenced water intake behaviors (Banerjee and Ashutosh, 2011).
Little intensive data has been collected regarding the physiological responses to Mh vaccines in cattle; however, Tesfaw et al. (2014) reported slight to no change in body temperature in sheep when evaluating multiple Mh serotype vaccinations. Following Mh vaccination in the present experiment, vaginal temperature slightly increased for 24 h. Transient increases in rectal temperature lasting less than 48 h following Mh vaccine administration have previously been reported in beef calves (Confer et al., 2009a; Engelken et al., 2016).
A rectal temperature of 40°C is considered the threshold for BRD diagnosis (Perino and Apley, 1999; Duff and Galyean, 2007), with vaginal and rectal temperature being positively correlated (Abell et al., 2015). Nonetheless, no heifers in the current study had a vaginal temperature that exceeded the proposed BRD diagnosis threshold. Over the 7-d experimental period, diurnal fluctuations in vaginal temperatures among treatments gradually increased, peaking at approximately 39.5°C. The greater numerical increase in PS heifer vaginal temperature from d 3 to 5 could be associated with greater proportions of pro-inflammatory cytokines relative to anti-inflammatory cytokine and acute phase protein concentrations when compared with NS or OS heifers. Endotoxin concentrations were greatest in the PS vaccine and could have contributed to the phenomenon known as vaccine sweats (Hagenmaier et al., 2018), which is linked to the increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Johnson, 1997). Although IL-6 is involved in increasing body temperature after pathogen exposure (Bluthe et al., 2000; Harden et al., 2006), the relationship between IL-6 concentrations and vaginal temperature was not analyzed in current study.
4.3 Hematology
Red blood cell, hemoglobin, and platelet counts did not differ among vaccines used in the current study and were within clinical reference ranges (Hanzlicek et al., 2010). Although the role of these variables during an inflammatory cascade is not fully understood, previous research has reported decreased red blood cells, decreased hemoglobin, and increased platelet concentrations in calves diagnosed with BRD (Hanedan et al., 2015; Cuevas-Gómez et al., 2020). Platelet concentrations increase in calves with BRD because of the release of platelet activating factor from neutrophils (Whiteley et al., 1992). Although neutrophil and white blood cell counts did not differ among treatments in the current study, neutrophil concentrations increased following vaccine administration, returning to baseline by 36 h, on average, before continuing to decrease through 120 h. Similar responses have been observed in calves challenged with Mh (Sharon et al., 2019; Burdick Sanchez et al., 2022). These observations are understandable, as neutrophils release cytokines and chemokines that aid in acute phase protein production (Malech et al., 2014). Despite increased lymphocyte concentrations in PS heifers than NP and OS heifers throughout the study, there was no difference in lymphocyte change among treatments. Like the current study, previous Mh challenge models have not reported a change in lymphocyte concentrations following Mh inoculation (Hanzlicek et al., 2010; Word et al., 2020; Cuevas-Gómez et al., 2020), although Burdick Sanchez et al. (2022) noted that sex can alter the lymphocyte response to a Mh challenge. There was a tendency for a treatment × time interaction in neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio primarily caused by a neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio spike greater than 1 in OS heifers from 4 to 8 h and NS heifers from 12 to 36 h. A neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio greater than 1 is generally indicative of greater tissue inflammation and has been observed in calves diagnosed with BRD (Cuevas-Gómez et al., 2020; Smock et al., 2023).
When challenged with endotoxin, cattle have been documented to experience leukopenia, lymphopenia, and neutropenia (Burdick Sanchez et al., 2020; Smock et al., 2023). This is because endotoxin stimulates circulating immune cells to translocate from circulation into tissue, thereby increasing neutrophil apoptosis while decreasing lymphocyte proliferation in favor of macrophage responses (Smock et al., 2023). These observations contrast with the current study for two reasons. First, endotoxin challenges commonly rely on intravenous infusions or intratracheal inoculations of endotoxin whereas vaccines are administered intramuscularly or SQ. Secondly, vaccines like those evaluated in the current study contain lesser amounts of endotoxin relative to the LPS doses administered in challenge models (Richeson et al., 2019). Therefore, results of the current study more accurately reflect immunomodulation, not immunosuppression observed in endotoxin challenges. Ergo, interpretation of the current results with those from endotoxin challenges should be interpreted with caution.
At 168 h post-vaccination, PS heifers had a decreased hematocrit percentage when compared with NP or OS heifers. Although this led to a treatment × time interaction, all hematocrit values were within the clinical reference range for the duration of the study (Hanzlicek et al., 2010). Increased monocyte concentrations represent activation of the adaptive immune system as activated monocytes (i.e., macrophages) are responsible for activating effector functions of lymphocytes (Burdick Sanchez et al., 2022). Although monocyte concentrations were not affected by treatment in the current study, monocyte concentrations were greater for 72 h following vaccine administration relative to baseline values. Corrigan et al. (2007) reported a similar elevation for 72 h following a Mh challenge. Basophils are effector cells involved in the innate immune response (Voehringer, 2017). Even though basophil concentrations were less in NP heifers, no clear patterns of change were observed following treatment administration. Basophil responses to a Mh challenge have yielded variable results (Corrigan et al., 2007; Burciaga-Robles et al., 2010; Carlos-Valdez et al., 2016), with multivariate analyses suggesting that basophil concentrations do not aid in the prediction of BRD in calves (Richeson et al., 2013). In the current study, basophil concentrations were within clinical references ranges (Hanzlicek et al., 2010). Conversely, low eosinophil concentrations have been implicated in the identification of calves at high risk for developing BRD (Richeson et al., 2013). Baseline eosinophil concentrations in OS heifers were less than NP and PS heifers. This could partially explain the attenuated lymphocyte response and elevated neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio observed shortly after vaccine administration. Eosinophil concentrations in heifers are likely correlated to similar responses in lymphocyte concentrations (Kita, 2011; Leach et al., 2013), which were observed for both OS and PS heifers. Still, eosinophil concentrations were within clinical reference ranges and greater than the minimal threshold established for BRD risk (Richeson et al., 2013). Overall, the lack of differences in white blood cell counts among treatments suggests the inflammatory response to each vaccine did not differ.
4.4 Cytokines
Cytokines are protein-based, intracellular messengers produced by immune and endothelial cells (Gulati et al., 2016). Classified as either pro-inflammatory (IL-6 and IFN-γ) or anti-inflammatory (IL-4), cytokines maintain tissue homeostasis (Zhang and An, 2007). In the current study, cytokine concentrations spiked at 48 h post-vaccination and remained elevated through 72 h before returning to baseline values by 168 h. This observation supports previous findings demonstrating a Mh challenge or vaccination elicits an increased inflammatory response (Burciaga-Robles et al., 2010; Word et al., 2020; Burdick Sanchez et al., 2022). Greater IL-6 concentrations from 36 to 72 h likely explains the increase in haptoglobin concentrations around the same timeframe, as IL-6 is a haptoglobin stimuli (Quaye, 2008). In cattle, IFN-γ and IL-4 work antagonistically, with IFN-γ eliciting a type 1 cytokine response while IL-4 initiates a type 2 response (Brown et al., 1996; Jungi et al., 1997). A type 1 response promotes macrophage activation and inflammation, whereas the type 2 response promotes antibody production and alternative immunological macrophage activation via pro-inflammatory cytokine downregulation (Adams and Hamilton, 1984; Bogdan and Nathan, 1993). This antagonism explains the similar cytokine responses observed for IFN-γ and IL-4. While there was a lack of treatment × time interactions observed for cytokines, it is important to note that each treatment not only stimulated an immune response but activated cytokine production within a similar timeframe. Even though the NP treatment contained the least amount of endotoxin, NP heifers had the greatest cytokine response to vaccination. Although not analyzed in the current study, this observation could be attributable to a greater leukotoxin potency within the NP vaccine than the PS or OS vaccines. Another possible explanation is the adjuvant formulation in the differing vaccines. Endotoxin concentrations, adjuvants, and antigen interference could also explain the differences in inflammatory responses among vaccines; however, further research is warranted to better understand the effects of Mh vaccine composition on cytokine production.
4.5 Acute phase proteins
Haptoglobin is an acute phase protein that decreases iron availability to bacteria via hemoglobin sequestration (Huzzey et al., 2009), thereby decreasing the potential for infection. Previous research has reported haptoglobin concentrations peak at approximately d 1 to 3 following a Mh challenge (Wottlin et al., 2021; Burdick Sanchez et al., 2022) or Mh vaccination (Arthington et al., 2013; Rodrigues et al., 2015). In the current study, no differences in overall response were observed in NP heifers, in which haptoglobin concentrations peaked at 60 h post-vaccination followed by a decline at 120 and 168 h. Conversely, haptoglobin concentrations in PS and OS heifers displayed a gradual increase at 24 h that continued through 168 h. This response could be attributable to differences in vaccine formulation and adjuvant type used. Previous studies reported the NP vaccine to enhance vaccine efficacy, humoral immune stimulation, and resistance to Mh challenges (Hilgers and Snippe, 1992; Confer et al., 2003, 2006, 2009a, b, c). Haptoglobin is involved in the proliferation, activation, and functional differentiation of B- and T-cells during the humoral immune response to antigen stimulation (Heegard et al., 2000; Huntoon et al., 2008; Cao et al., 2020). Therefore, greater NP heifer haptoglobin concentrations suggest that the NP vaccine potentially elicited a more rapid innate immune response even when having a lesser endotoxin concentration than OS or PS; however, further research is warranted to understand this variation.
Like haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin decreases iron availability for bacterial metabolism and propagation (Weinberg, 1984). Additionally, ceruloplasmin increases antioxidant enzyme (cytochrome C oxidase and Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase) activity via copper transportation, increasing immune cell phagocytosis (Cerone et al., 2000). Among vaccine treatments, ceruloplasmin concentrations in the current study increased 8 h following vaccination and remained elevated above the baseline through the end of the study. A similar response was observed by Arthington et al. (2013) following vaccination with OS. In the present experiment, the NP heifers tended to have greater ceruloplasmin concentration than PS heifers from 24 to 60 h with OS heifers being intermediate. When microglial cells are activated by a pro-inflammatory stimulus like endotoxin, ceruloplasmin potentiates the production of IL-6 (Lazzaro et al., 2014), as reported in which overall IL-6 concentrations were greatest in NP heifers.
4.6 Serum metabolites
Novel environments, handling, and vaccine administration are potential psychological stressors that, when prolonged, activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal complex and initiate release of the glucocorticoid cortisol (Grossman et al., 1982; Knowles et al., 2014). Throughout the current study, cortisol concentrations remained at or near baseline, suggesting that neither the vaccine treatment, human interaction, or serial blood collections elicited a stress response. Cortisol is an important effector molecule of the acute phase response (Werling et al., 1996; Carroll et al., 2009) and has been reported to inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production (Dong et al., 2018). Intravenous endotoxin administration has been shown to rapidly activate the sympathetic nervous system and acute cortisol production (Smock et al., 2023). As vaccines were administered SQ in the current study, it is not surprising that a lesser cortisol response was observed in comparison to endotoxin challenges. Additionally, the short half-life of blood cortisol (70 to 130 min; Tunn et al., 1992), and negative feedback system of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal complex (Reader et al., 1982), suggests that blood cortisol may not be the best indicator of long-term stress.
Stimuli such as hormones (i.e., glucocorticoids), cytokines, and physiological state (i.e., a diseased state) stimulate hepatic gluconeogenesis, thereby increasing circulating serum glucose concentrations (McDowell, 1983; Williams et al., 2006). Previous studies have identified elevated blood glucose concentrations as a potential biomarker for BRD (Basoglu et al., 2016; Maurer et al., 2018; Blakebrough-Hall et al., 2020). Challenges with Mh have yielded variable results, with no difference (Word et al., 2020) and increased (Wottlin et al., 2021) blood glucose concentrations being reported. In the current study, NP heifers tended to have elevated glucose concentrations. Among treatments, mean serum glucose concentrations were 74.8 mg/dL and further suggest metabolic stress from a lack of feed disappearance was minimal.
5 Conclusion
These data suggest that each commercial Mh vaccine elicited a similar inflammatory immune response. Vaccine administration stimulated an inflammatory cascade, with neutrophil, haptoglobin, pro-inflammatory cytokine, and anti-inflammatory cytokine concentrations becoming elevated. It is important to note that similar physiological responses were observed despite large difference in vaccine endotoxin concentrations. Although select immunological markers differed relative to vaccine treatment, it is unlikely these differences resulted in biologically relevant differences. Additionally, it cannot be inferred if these differences were a product of endotoxin concentration alone, or rather an artifact of adjuvant composition. Future research should further investigate the short- and long-term metabolic consequences of vaccination on nutrient metabolism and animal performance. Such metabolic analyses could provide insights into potential trade-offs between immune activation and energy allocation following vaccination. Additionally, research is warranted to determine how the effects of vaccine mishandling may alter endotoxin release and contribute to exaggerated inflammatory responses. Moreover, exploring the interaction between endotoxin concentration and adjuvant composition could also clarify their individual and combined roles in shaping immune and physiological responses to vaccination.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol #1809F) of the USDA-ARS Livestock Issues Research Unit. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
CD: Writing – original draft. NB: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JH: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. MB: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. JC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KH: Writing – review & editing. PB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by Elanco Animal Health.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jeff W. Dailey and Jessica R. Carroll for technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
MB and JH were employed by Elanco Animal Health at the time of this study, the company that provided the funding for this experiment. MB and JH were involved in the initial study design and assisted with sample collection but were not involved in data analysis or interpretation of the results.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Author disclaimer
Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, and where applicable, sex, marital status, familial status, parental status, religion, sexual orientation, genetic information, political beliefs, reprisal, or because all or part of an individual’s income is derived from any public assistance program. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Persons with disabilities who require alternative means for communication of program information (Braille, large print, audiotape, etc.) should contact USDA’s TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TDD). To file a complaint of discrimination, write to USDA, Director, Office of Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, S.W., Washington, D.C. 20250-9410, or call (800) 795-3272 (voice) or (202) 720-6382 (TDD). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
References
Abell K. M., Theurer M. E., Larson R. L., and Mosier D. A. (2015). Effect of vaginal temperature on behavior patterns of Mannheimia haemolytica challenged beef heifer calves. AABP Proc. 48, 204. doi: 10.21423/aabppro20153577
Adams D. O. and Hamilton T. A. (1984). The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2, 283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435
Alexander C. and Rietschel E. T. (2001). Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity. J. Endotoxin Res. 7, 167–202. doi: 10.1179/096805101101532675
Allen M. S. (2000). Effects of diet on short-term regulation of feed intake by lactating dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 83, 1598–1624. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)75030-2
Arthington J. D., Cooke R. F., Maddock T. D., Araujo D. B., Moriel P., DiLorenzo N., et al. (2013). Effects of vaccination on the acute-phase protein response and measures of performance in growing beef calves. J. Anim. Sci. 91, 1831–1837. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5724
Azhar N. A., Paul B. T., Jesse F. F. A., Chung E. L. T., Isa K. M., Lila M. A. M., et al. (2021). Responses of testosterone hormone and important inflammatory cytokines in bucks after challenge with Mannheimia haemolytica A2 and its LPS endotoxin. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 53, 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02683-6
Banerjee D. and Ashutosh (2011). Effect of thermal exposure on diurnal rhythms of physiological parameters and feed, water intake in Tharparkar and Karan Fries heifers. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 42, 39–51. doi: 10.1080/09291011003726490
Basoglu A., Baspinar N., Tenori L., Vignoli A., and Yildiz R. (2016). Plasma metabolomics in calves with acute bronchopneumonia. J. Metabolomics. 12, 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11306-016-1074-x
Baumann H. and Gauldie J. (1994). The acute phase response. Immunol. Today 15, 74–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90005
Blakebrough-Hall C., Dona A., D’occhio M. J., McMeniman J., and González L. A. (2020). Diagnosis of bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle using blood 1H NMR metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 10, 115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56809-w
Bluthe R. M., Michaud B., Poli V., and Dantzer R. (2000). Role of IL-6 in cytokine-induced sickness behavior: A study with IL-6 deficient mice. Physiol. Behav. 70, 367–373. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(00)00269-9
Bogdan C. and Nathan C. (1993). Modulation of macrophage function by transforming growth factor beta, interleukin-4, and interleukin-10. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 685, 713–739. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35934.x
Brown W. C., Davis W. C., and Tuo W. (1996). Human interleukin-12 upregulates proliferation and interferon-gamma production by parasite antigenstimulated Th cell clones and gamma/delta T cells of cattle. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 795, 321–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb52682.x
Buhman M. J., Perino L. J., Galyean M. L., Wittum T. E., Montgomery T. H., and Swingle R. S. (2000). Association between changes in eating and drinking behaviors and respiratory tract disease in newly arrived calves at a feedlot. Am. J. Vet. Res. 61, 1163–1168. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.2000.61.1163
Burciaga-Robles L. O., Step D. L., Krehbiel C. R., Holland B. P., Richards C. J., Montelongo M. A., et al. (2010). Effects of exposure to calves persistently infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus type 1b and subsequent infection with Mannheimia haemolytica effects on clinical signs and immune variables: Model for bovine respiratory disease via viral and bacterial interaction. J. Anim. Sci. 88, 2166–2178. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-2005
Burdick N. C., Carroll J. A., Dailey J. W., Randel R. D., Falkenberg S. M., and Schmidt T. B. (2012). Development of a self-contained, indwelling vaginal temperature probe for use in cattle research. J. Therm. Biol. 37, 339–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2011.10.007
Burdick Sanchez N. C., Broadway P. R., and Carroll J. A. (2022). Sexual dimorphic innate immune response to a viral-bacterial respiratory disease challenge in beef calves. Vet. Sci. 9, 696. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9120696
Burdick Sanchez N. C., Carroll J. A., Broadway P. R., Edrington T. S., Yoon I., and Belknap C. R. (2020). Some aspects of the acute phase immune response to a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge are mitigated by supplementation with a Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product in weaned beef calves. Transl. Anim. Sci. 4, txaa156. doi: 10.1093/tas/txaa156
Cao J., Chen C., Liu L., Zhang Y., Zhou H., Xiao J., et al. (2020). Identification of an activation-related protein in B cells in the ABO incompatible condition. Exp. Ther. Med. 19, 741–747. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8234
Carlos-Valdez L., Wilson B. K., Burciaga-Robles L. O., Step D. L., Holland B. P., Richards C. J., et al. (2016). Effect of timing of Mannheimia haemolytica challenge following short-term natural exposure to bovine viral diarrhea virus type 1b on animal performance and immune response in beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 94, 4799–4808. doi: 10.2527/jas.2016-0712
Carroll J. A., Reuter R. R., Chase J. C. C., Coleman S. W., Riley D. G., Spiers D. E., et al. (2009). Profile of the bovine acute-phase response following an intravenous lipopolysaccharide challenge. Innate Immun. 15, 81–89. doi: 10.1177/1753425908099170
Cerone S. I., Sansinanea A. S., Streitenberger S. A., Garcia M. C., and Auza N. J. (2000). Cytochrome c oxidase, Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase, and ceruloplasmin activities in copper-deficient bovines. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 73, 269–278. doi: 10.1385/BTER:73:3:269
Chung E. L. T., Jesse F. F. A., Marza A. D., Ibrahim H. H., Abba Y., Zamri-Saad M., et al. (2019). Responses of pro-inflammatory cytokines, acute phase proteins and cytological analysis in serum and cerebrospinal fluid during hemorrhagic septicemia infection in buffaloes. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 51, 1773–1782. doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-01870-w
Confer A. W. and Ayalew S. (2018). Mannheimia haemolytica in bovine respiratory disease: immunogens, potential immunogens, and vaccines. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 19, 79–99. doi: 10.1017/S1466252318000142
Confer A. W., Ayalew S., Montelongo M., Step D. L., Wray J. H., Hansen R. D., et al. (2009a). Immunity of cattle following vaccination with a Mannheimia haemolytica chimeric PlpE-LKT (SAC89) protein. Vaccine 27, 1771–1776. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.028
Confer A. W., Ayalew S., Montelongo M., Step D. L., Wray J. H., Hansen R. D., et al. (2009c). Immunity of cattle following vaccination with a Mannheimia haemolytica chimeric PlpE–LKT (SAC89) protein. Vaccine 27, 1771–1776. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.028
Confer A. W., Ayalew S., Panciera R. J., Montelongo M., Whitworth L. C., and Hammer J. D. (2003). Immunogenicity of recombinant Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane protein PlpE and augmentation of a commercial vaccine. Vaccine 21, 2821–2829. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(03)00213-5
Confer A. W., Ayalew S., Panciera R. J., Montelongo M., and Wray J. H. (2006). Recombinant Mannheimia haemolytica serotype 1 outer membrane protein PlpE enhances commercial M. haemolytica vaccine-induced resistance against serotype 6 challenge. Vaccine 24, 2248–2255. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.11.036
Confer A. W., Ayalew S., Step D. L., Trojan B., and Montelongo M. (2009b). Intranasal vaccination of young Holstein calves with Mannheimia haemolytica chimeric protein PlpE-LKT (SAC89) and cholera toxin. Vet 132, 232–236. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2009.04.018
Corrigan M. E., Drouillard J. S., Spire M. F., Mosier D. A., Minton J. E., Higgins J. J., et al. (2007). Effects of melengestrol acetate on the inflammatory response in heifers challenged with Mannheimia haemolytica. J. Anim. Sci. 85, 1770–1779. doi: 10.2527/jas.2006-396
Cuevas-Gómez I., McGee M., McCabe M., Cormican P., O’Riordan E., McDaneld T., et al. (2020). Growth performance and hematological changes of weaned beef calves diagnosed with respiratory disease using respiratory scoring and thoracic ultrasonography. J. Anim. Sci. 98, skaa345. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa345
Dong J., Li J., Cui L., Wang Y., Lin J., Qu Y., et al. (2018). Cortisol modulates inflammatory responses in LPS stimulated RAW264.7 cells via the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. BMC Vet. Res. 14, 30. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1360-0
Duff G. C. and Galyean M. L. (2007). Board Invited Review: Recent advances in management of highly stressed, newly received feedlot cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 85, 823–840. doi: 10.2527/jas.2006-501
Ellis J. A. and Yong C. (1997). Systemic adverse reactions in young Simmental calves following administration of a combination vaccine. Can. Vet. J. 38, 45–47.
Engelken T. J., Roth J. A., Kimura K., Renter D. G., Meyer B. D., Burdett W. W., et al. (2016). The effect of respiratory vaccine components and route of delivery on weight gain and inflammatory response in suckling beef calves. Bov. Pract. 50, 165–172. doi: 10.21423/bovine-vol50no2p165-174
Farley H. (1932). An epizoological study of shipping fever in Kansas. J. Am. Vet. Med. Ass. 52, 165–172.
Frank G., Adlam C., and J. Rutter J. M. (1989). “Pasteurella and pasteurellosis,” in Pasteurellosis of Cattle. Eds. Adlam C. and Rutter J. M. (Academic Press Limited, London), 197–222.
Grossman A., Gaillard R. C., McCartney P., Rees L. H., and Besser G. M. (1982). Opiate modulation of the pituitary-adrenal axis: Effects of stress and circadian rhythm. Clin. Endocrinol. 17, 279–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1982.tb01590.x
Gulati K., Guhathakurta S., Joshi J., Rai N., and Ray A. (2016). Cytokines and their role in health and disease: a brief overview. MOJ Immunol. 4, 121. doi: 10.15406/moji.2016.04.00121
Hagenmaier J. A., Terhaar B. L., Blue K., Hoffman B. W., Fox J. T., and Theurer M. E. (2018). A comparison of three vaccine programs on the health, growth performance, and carcass characteristics of highrisk feedlot heifers procured from auction-market. Bov. Pract. 52, 120–130. doi: 10.21423/bovine-vol52no2p120-130
Hanedan B., Kirbas A., Dorman E., Timurkan Mehmet O., Kandemir M., and Alkan O. (2015). Cardiac troponin-I concentration in weaned calves with bovine respiratory disease. Acta Vet. 65, 454–462. doi: 10.1515/acve-2015-0038
Hanzlicek G. A., White B. J., Mosier D., Renter D. G., and Anderson D. E. (2010). Serial evaluation of physiologic, pathologic, and behavioral changes related to disease progression of experimentally induced Mannheimia haemolytica pneumonia in post weaned calves. Am. J. Vet. Res. 71, 359–369. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.71.3.359
Harden L. M., du Plessis I., Poole S., and Laburn H. P. (2006). Interleukin-6 and leptin mediate lipopolysaccharide-induced fever and sickness behavior. Physiol. Behav. 89, 146–155. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.05.016
Hart B. L. (1987). Behavior of sick animals. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 3, 383–391. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0720(15)31159-2
Heegaard P. M., Godson D. L., Toussaint M. J., Tjornejoj K., Larsen L. E., Viuff B., et al. (2000). The acute phase response of haptoglobin and serum amyloid a (SAA) in cattle undergoing experimental infection with bovine respiratory syncytial virus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 77, 151–159. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2427(00)00226-9
Hilgers L. A. and Snippe H. (1992). DDA as an immunological adjuvant. Res. 143, 494–503. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(92)80060-x
Huntoon K. M., Wang Y., Eppolito C. A., Barbour K. W., Berger F. G., Shrikant P. A., et al. (2008). The acute phase protein haptoglobin regulates host immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 84, 170–181. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0208100
Huzzey J. M., Duffield T. F., LeBlanc S. J., Veira D. M., Weary D. M., and von Keyserlingk M. A. G. (2009). Short communication: haptoglobin as an early indicator of metritis. J. Dairy Sci. 92, 621–625. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1526
Johnson R. W. (1997). Inhibition of growth by pro-inflammatory cytokines: an integrated view. J. Anim. Sci. 75, 1244–1255. doi: 10.2527/1997.7551244x
Jungi T. W., Brcic M., Sager H., Dobbelaere D. A., Furger A., and Roditi I. (1997). Antagonistic effects of IL-4 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) on inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in bovine macrophages exposed to gram-positive bacteria. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 109, 431–438. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1997.4891384.x
Kita H. (2011). Eosinophils: Multifaceted biological properties and roles in health and disease. Immunol. Rev. 242, 161–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01026.x
Knowles T. G., Warriss P. D., and Vogel K. (2014). “Stress physiology of animals during transport,” in Livestock Handling and Transport, 4th ed. Ed. Grandin T. (CABI, Oxfordshire, UK.), 399–420.
Lafleur R. L., Abrahamsen M. S., and Maheswaran S. K. (1998). The biphasic mRNA expression pattern of bovine interleukin-8 in Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide-stimulated alveolar macrophages is primarily due to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Infect. Immun. 66, 4087–4092. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4087-4092.1998
Lazzaro M., Bettegazzi B., Barbariga M., Codazzi F., Zacchetti D., and Alessio M. (2014). Ceruloplasmin potentiates nitric oxide synthase activity and cytokine secretion in activated microglia. J. Neuroinflammation. 11, 164. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0164-9
Leach R. J., Chitko-McKown C. G., Bennet G. L., Jones S. A., Kachman S. D., Keele J. W., et al. (2013). The change in differing leukocyte populations during vaccination to bovine respiratory disease and their correlations with lung scores, health records, and average daily gain. J. Anim. Sci. 91, 3564–3573. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5911
Malech H. L., Deleo F. R., and Quinn M. T. (2014). The role of neutrophils in the immune system: an overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 1124, 3–10. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-845-4_1
Maurer D., Koziel J., Engelken T., Cooper V., and Funk J. (2018). Detection of volatile compounds emitted from nasal secretions and serum: towards non-invasive identification of diseased cattle biomarkers. J. Sep. Sci. 5, 18. doi: 10.3390/separations5010018
McDowell G. H. (1983). Hormonal control of glucose homoeostasis in ruminants. Proc. Nutr. Soc 42, 149–167. doi: 10.1079/pns19830021
McGuirk S. M. and Peek S. F. (2014). Timely diagnosis of dairy calf respiratory disease using a standardized scoring system. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 15, 145–147. doi: 10.1017/S1466252314000267
Mosier D. A., Confer A. W., and Panciera R. J. (1989). The evolution of vaccines for bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Res. Vet. Sci. 47, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(18)31223-2
NASEM (2016). Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle. 8th Revised edition (Washington, DC: National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Natl. Acad. Press).
Paulsen D. B., Mosier D. A., Clinkenbeard K. D., and Confer A. W. (1989). Direct effects of Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide on bovine pulmonary endothelial cells in vitro. Am. J. Vet. Res. 50, 1633–1637. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.1989.50.09.1633
Perino L. J. and Apley M. (1999). “Bovine respiratory disease,” in Current veterinary therapy: food animal practice 4. Eds. Howard J. L. and Smith R. A. (WB Saunders Co, Philadelphia), 446–455.
Quaye I. K. (2008). Haptoglobin, inflammation and disease. Trans. R. Soc Trop. Med. Hyg. 102, 735–742. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2008.04.010
Reader S. C. J., Alaghband-Zadeh J., Daly J. R., and Robertson W. R. (1982). Negative, rate-sensitive feedback effects on adrenocorticotrophin secretion by cortisol in normal subjects. J. Endocrinol. 92, 443–448. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0920443
Rice J. A., Carrasco-Medina L., Hodgins D. C., and Shewen P. E. (2007). Mannheimia haemolytica and bovine respiratory disease. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 8, 117–128. doi: 10.1017/S1466252307001375
Richeson J. T., Hughes H. D., Broadway P. R., and Carroll J. A. (2019). Vaccination management of beef cattle: delayed vaccination and endotoxin stacking. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 35, 575–592. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2019.07.003
Richeson J. T., Pinedo P. J., Kegley E. B., Powell J. G., Gadberry M. S., Beck P. A., et al. (2013). Association of hematologic variables and castration status at the time of arrival at a research facility with the risk of bovine respiratory disease in beef calves. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 243, 1035–1041. doi: 10.2460/javma.243.7.1035
Rodrigues M. C., Cooke R. F., Marques R. S., Cappellozza B. I., Arispe S. A., Keisler D. H., et al. (2015). Effects of vaccination against respiratory pathogens on feed intake, metabolic, and inflammatory responses in beef heifers. J. Anim. Sci. 93, 4443–4452. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9277
Rosenfeld Y. and Shai Y. (2006). Lipopolysaccharide (Endotoxin)-host defense antibacterial peptides interactions: Role in bacterial resistance and prevention of sepsis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1758, 1513–1522. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.05.017
Sharon K. P., Liang Y., Sanchez N. C. B., Carroll J. A., Broadway P. R., Davis E. M., et al. (2019). Pre-weaning plane of nutrition and Mannheimia haemolytica dose influence inflammatory responses to a bovine herpesvirus-1 and Mannheimia haemolytica challenge in post-weaning Holstein calves. J. Dairy Sci. 102, 9082–9096. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15997
Smock T. M., Broadway P. R., Burdick Sanchez N. C., Carroll J. A., Theurer M. E., and Hales K. E. (2023). An updated profile of the bovine acute phase response following an intravenous lipopolysaccharide challenge. J. Anim. Sci. 101, skad133. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad133
Srinand S., Maheswaran S. K., Ames T. R., Werdin R. E., and Hsuan S. (1996). Evaluation of efficacy of three commercial vaccines against experimental pneumonic pasteurellosis. Vet. Microbiol. 52, 81–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(96)00055-7
Stokka G. L., Edwards A. J., Spire M. F., Brandt R. T., and Smith J. E. (1994). Inflammatory response to clostridial vaccines in feedlot cattle. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 204, 415–419. doi: 10.2460/javma.1994.204.03.415
Tesfaw L., Jenberie S., Sori H., Sisay T., and Negussie H. (2014). Efficacy of Mannheimia haemolytica A2, A7, and A2 and A7 combined expressing iron regulated outer membrane protein as a vaccine against intratracheal challenge exposure in sheep. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 8, 1237–1244. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2013.6371
Tunn S., Möllmann H., Barth J., Derendorf H., and Krieg M. (1992). Simultaneous measurement of cortisol in serum and saliva after different forms of cortisol administration. Clin. Chem. 38, 1491–1494. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/38.8.1491
van der Woude M. W. and Bäumler A. J. (2004). Phase and antigenic variation in bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 17, 581–611. doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.3.581-611.2004
Voehringer D. (2017). Recent advances in understanding basophil functions in vivo. F1000Res 6, 1464. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11697.1
Weinberg E. D. (1984). Iron withholding: a defense against infection and neoplasia. Physiol. Rev. 64, 65–102. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.65
Werling D., Sutter F., Arnold M., Kun G., Tooten P., Gruys E., et al. (1996). Characterisation of the acute phase response of heifers to a prolonged low dose infusion of lipopolysaccharide. Res. Vet. Sci. 61, 252–257. doi: 10.1016/s0034-5288(96)90073-9
Whiteley L. O., Maheswaran S. K., Weiss D. J., Ames T. R., and Kannan M. S. (1992). Pasteurella haemolytica A1 and bovine respiratory disease: pathogenesis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 6, 11–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.1992.tb00980.x
Wilkie B., Markham R., and Shewen P. (1980). Response of calves to lung challenge exposure with Pasteurella haemolytica after parenteral or pulmonary immunization. Am. J. Vet. Res. 41, 1773–1778. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.1980.41.11.1773
Williams E. L., Rodriguez S. M., Beitz D. C., and Donkin S. S. (2006). Effects of short-term glucagon administration on gluconeogenic enzymes in the liver of midlactation dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 89, 693–703. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72132-4
Woltmann A., Hamann L., Ulmer A., Gerdes J., Bruch H. P., and Rietschel E. (1998). Molecular mechanisms of sepsis. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 383, 2–10. doi: 10.1007/s004230050085
Word A. B., Broadway P. R., Burdick Sanchez N. C., Hutcheson J. P., Ellis G. B., Holland B. P., et al. (2020). Acute immunologic and metabolic responses of beef heifers following topical administration of flunixin meglumine at various times relative to bovine herpesvirus 1 and Mannheimia haemolytica challenges. Am. J. Vet. Res. 81, 243–253. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.81.3.243
Wottlin L. R., Carstens G. E., Kayser W. C., Pinchak W. E., Thomson J. M., Copie V., et al. (2021). Differential haptoglobin responsiveness to a Mannheimia haemolytica challenge altered immunologic, physiologic, and behavior responses in beef steers. J. Anim. Sci. 99, skaa404. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa404
Yuan K., Farney J. K., Mamedova L. K., Sordillo L. M., and Bradford B. J. (2013). TNFa altered inflammatory responses, impaired health and productivity, but did not affect glucose or lipid metabolism in early-lactation dairy cows. PLoS One 8, e80316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080316
Zhang J. M. and An J. (2007). Cytokines, inflammation, and pain. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 45, 27–37. doi: 10.1097/AIA.0b013e318034194e
Appendix
Keywords: Mannheimia haemolytica, vaccine, metabolism, immune response, endotoxin, beef cattle
Citation: Dornbach CW, Burdick Sanchez NC, Hagenmaier J, Brown MS, Carroll JA, Hales KE and Broadway PR (2025) Characterization of metabolic and inflammatory responses following administration of three commercially available Mannheimia haemolytica vaccines to beef heifers. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1560110. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1560110
Received: 13 January 2025; Accepted: 29 April 2025;
Published: 21 May 2025.
Edited by:
Gianmarco Ferrara, University of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
Consiglia Longobardi, University of Naples Federico II, ItalySahar Saad Eldin Ahmed, National Research Centre, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Dornbach, Burdick Sanchez, Hagenmaier, Brown, Carroll, Hales and Broadway. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Paul R. Broadway, cmFuZC5icm9hZHdheUB1c2RhLmdvdg==
 Colten W. Dornbach
Colten W. Dornbach Nicole C. Burdick Sanchez
Nicole C. Burdick Sanchez Jacob Hagenmaier3
Jacob Hagenmaier3 Kristin E. Hales
Kristin E. Hales Paul R. Broadway
Paul R. Broadway