- 1College of Animal Science, Anhui Science and Technology University, Chuzhou, China
- 2Anhui Province Key Laboratory of Animal Nutritional Regulation and Health, Chuzhou, China
- 3Anhui Engineering Technology Research Center of Pork Quality Control and Enhance, Chuzhou, China
- 4Anhui Haoxiang Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Co., Ltd., Lixin, China
- 5College of Animal Science and Technology, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China
- 6Anhui Anye Agricultural Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Luan, China
- 7National Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
- 8Desert Research Center, Cairo, Egypt
Intramuscular fat (IMF) deposition is a key determinant of meat quality, and microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important regulators of this process. However, studies investigating how miRNAs influence IMF deposition and muscle growth in the longissimus dorsi (LD) tissues of Chinese and Western pig breeds remain limited. In this study, we analyzed the LD tissues of Huoshou black (HS) pigs and Yorkshire (YY) pigs using transcriptome sequencing, identifying 2,833 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 51 differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs). Functional enrichment analysis demonstrated that the DEGs were significantly associated with metabolic pathways related to IMF deposition and fatty acid synthesis, including the MAPK and AMPK signaling pathways and the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway. Target genes of the DEMs were enriched in metabolic pathways such as PI3K–Akt signaling, apelin signaling, and the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids. Four randomly selected DEGs and four DEMs were validated using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), confirming the reliability of the sequencing data. Furthermore, candidate miRNAs associated with muscle growth and IMF deposition (miR-10a-5p, miR-29b, miR-29a-3p, miR-122-5p, miR-194a-5p, miR-221-3p, miR-31, miR-127, and miR-205) were identified through the construction of an miRNA–mRNA interaction network. The interaction between MYH7B and miR-205 was further validated using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Overall, this study provides novel insights into miRNA-mediated regulation of IMF in LD muscle between Chinese and Western pig breeds, offering a theoretical foundation for future strategies to improve pork quality.
1 Introduction
Pork plays a pivotal role in China’s meat consumption, serving as the primary source of animal protein. Consequently, pork quality is an important economic trait that strongly influences consumer preferences (Khan et al., 2015). Intramuscular fat (IMF) content is a critical biomarker of pork quality and is widely used as a key indicator for meat quality evaluation (Dodson et al., 2015).
The Huoshou black (HS) pig, a local breed from Anhui Province, is a fat-type pig known for its tolerance to roughage and strong disease resistance. It is characterized by high IMF content and good meat quality but has a relatively slow growth rate and low slaughter yield (Zhang et al., 2022). In contrast, the Yorkshire (YY) pig, an introduced lean-type breed, exhibits high production efficiency, rapid growth, and a high proportion of lean meat but generally has low IMF content (Liu et al., 2018). These contrasting characteristics make HS and YY pigs ideal comparative models for studying IMF deposition and provide a solid basis for elucidating the molecular regulatory mechanisms of lipid metabolism in porcine adipose tissue.
With continuous advancements in high-throughput transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) technology, increasing evidence indicates that microRNAs (miRNAs) play crucial roles in regulating IMF deposition, as well as muscle growth and development. MiRNAs are endogenous, small noncoding RNAs that act as post-transcriptional regulators by binding to the 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) of target mRNAs, leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression (Lu and Rothenberg, 2018; Mohr and Mott, 2015). For example, Shen et al (2016) reported that miR-23a regulates meat quality by targeting and downregulating MEF2C. Similarly, Li et al. (2016) found that miR-29a modulates type III collagen biosynthesis in Laiwu pork by inhibiting COL3A1 expression, thereby affecting meat quality. Moreover, Sun et al. (2017) demonstrated that miR-34a significantly modulates IMF deposition during porcine intramuscular preadipocyte differentiation by targeting forkhead box protein O1 (FoxO1) expression and regulating the Erk signaling pathway. Collectively, these studies highlight the essential roles of miRNAs in porcine IMF deposition and fatty acid biosynthesis.
However, the molecular mechanisms by which miRNAs regulate IMF deposition and muscle development in the longissimus dorsi (LD) muscle of Chinese and Western pig breeds remain poorly understood. To address this gap, the present study investigated the role of miRNAs in IMF deposition in the LD muscle of HS and YY pigs. Using transcriptome sequencing, we profiled miRNA and mRNA expression, identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs), and constructed an miRNA–mRNA interaction network to elucidate regulatory mechanisms underlying IMF differences between Chinese and Western pig breeds. The identified DEGs and DEMs provide valuable molecular markers and theoretical insights for future improvements in pork quality.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Collection of experimental animals and test samples
Three castrated adult male HS pigs and three castrated adults male YY pigs were randomly selected as experimental subjects. All pigs were maintained under identical housing and feeding conditions, with ad libitum access to feed and water, and remained healthy throughout the trial. After fasting for approximately 12 h, pigs were humanely euthanized by electrical stunning (1.5A, 5s) followed by exsanguination. Exsanguination was performed by severing the carotid arteries and jugular veins, and death was confirmed by the absence of heartbeat and respiration. LD tissues from the third to the fourth intercostal spaces were collected immediately after euthanasia. Portions of tissue were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen for transcriptome sequencing, while others were rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for histological analysis. Samples from HS pigs were labeled HS1–HS3, and those from YY pigs were labeled YY1–YY3.
2.2 Histological analysis of LD muscle
The morphology of LD muscle in HS and YY pigs was compared and analyzed using hematoxylin–eosin (H&E) staining. After fixation in 4% PFA, approximately 1 cm³ of muscle tissue was processed for dehydration, clearing, embedding, sectioning, and staining with hematoxylin and eosin. Tissue sections were observed under a light microscope equipped with a digital imaging system.
2.3 Total RNA Extraction and transcriptome sequencing
Total RNA was extracted from LD muscle tissue using TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA). RNA purity and concentration were determined with a NanoDrop ND-2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA), and RNA integrity was assessed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. High-quality RNA samples were submitted to Shanghai Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) for library construction and sequencing.
Raw sequencing data were initially assessed with FastQC (version: 0.20.1) (Chen et al., 2018). Low-quality reads and adapter sequences were removed using Seqtk trimfq. Clean reads were then aligned to the pig reference genome (Sscrofa 11.1) using Hisat2 (version: 2.0.4) software (Kim et al., 2015). Transcripts assembly was performed with StringTie (v1.3.5) (Kovaka et al., 2019). DEGs were identified using DESeq2 (Love et al., 2014) with thresholds of |Log2FC| ≥ 0.58 and a Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate (FDR)-adjusted P < 0.05.
2.4 miRNA sequencing and analysis
miRNA analysis was performed using miRDeep2 (Friedlander et al., 2012), including identification of known miRNAs, prediction of novel miRNAs, and quantification of expression levels. Expression abundance was normalized to transcripts per million (TPM), and fold change (FC) values were derived from the expression matrix (Zhao et al., 2020). Differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) were identified using DESeq2 with thresholds of |Log2FC| ≥ 0.58 and FDR-adjusted P < 0.05 (Love et al., 2014). Target genes of DEMs were predicted using miRanda (v3.3a) with default parameters (John et al., 2004).
2.5 Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis
Gene Ontology (GO) provides a framework for annotating genes and classifying biological functions in transcriptome and other high-throughput data. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database is widely used to investigate biological pathways, genomes, chemical substances, diseases, and drugs. Functional enrichment analyses of DEGs and predicted target genes of DEMs were conducted using ClusterProfiler (v4.0)(Wu et al., 2021a). GO terms and metabolic pathway enrichment were considered significant at P < 0.05 and highly significant at P < 0.01. For DEG analysis, the background gene set included all expressed genes (TPM > 1 in at least one sample). For DEM target analysis, all detected miRNAs (read count ≥ 10 in ≥ 2 samples) were used as the background.
2.6 Construction of the mRNA-miRNA network
To explore potential interactions between DEGs and DEMs, predicted miRNA target genes were intersected with DEGs. Target gene prediction was performed using the miRanda online database (http://www.miranda.org) and the R package multiMiR. Perl scripts were then used to identify overlapping genes, yielding 170 differentially expressed target genes (DETGs). Based on the principle of miRNA-mediated negative regulation, interaction pairs were identified and visualized using Cytoscape (v3.8.0) (Shannon et al., 2003).
2.7 Validation of DEGs and DEMs by quantitative real-time PCR
To validate the sequencing data, four DEGs and four DEMs were randomly selected for qRT-PCR analysis. Primer sequences were designed using Oligo 7 and miRNA Design software (listed in Supplementary Table S1). GAPDH and U6 small nuclear RNA were used as internal reference genes. Relative expression levels of DEGs and DEMs were calculated using the 2^-ΔΔCT method (Bustin et al., 2009).
2.8 Dual-luciferase reporter assay
The interaction between miR-205 and MYH7B, predicted in the miRNA–mRNA network, was validated using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. The 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) of MYH7B (wild type, WT; mutant, MUT) was cloned into the psiCHECK2 vector. HEK293T cells were seeded in 24-well plates and transfected at 70%–80% confluence with 1 μg of recombinant plasmid (WT or MUT) and 15 pmol of miR-205 mimic using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Negative controls included empty vectors and scrambled miRNA. After 48 h, cells were lysed and supernatants collected by centrifugation (12,000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C). Firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured, and the Renilla/Firefly ratio was used for normalization. Statistical differences between groups were assessed using two-tailed Student’s t-tests, with significance set at P < 0.01.
2.9 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0. qRT-PCR data were analyzed with Student’s t-tests. Graphs were generated with GraphPad Prism (v8.2.1). A P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Morphological structure of LD muscle tissue
H&E staining revealed distinct morphological differences in LD muscle between HS and YY pigs (Figure 1). In HS pigs, muscle fibers appeared oval shaped, relatively small, and separated by wider inter-fiber gaps. In contrast, YY pigs exhibited irregularly square-shaped muscle fibers that were larger and more closely packed. Quantitative analysis showed that the mean fiber diameter in HS pigs was significantly smaller than that in YY pigs (P < 0.05) (Figure 1E).
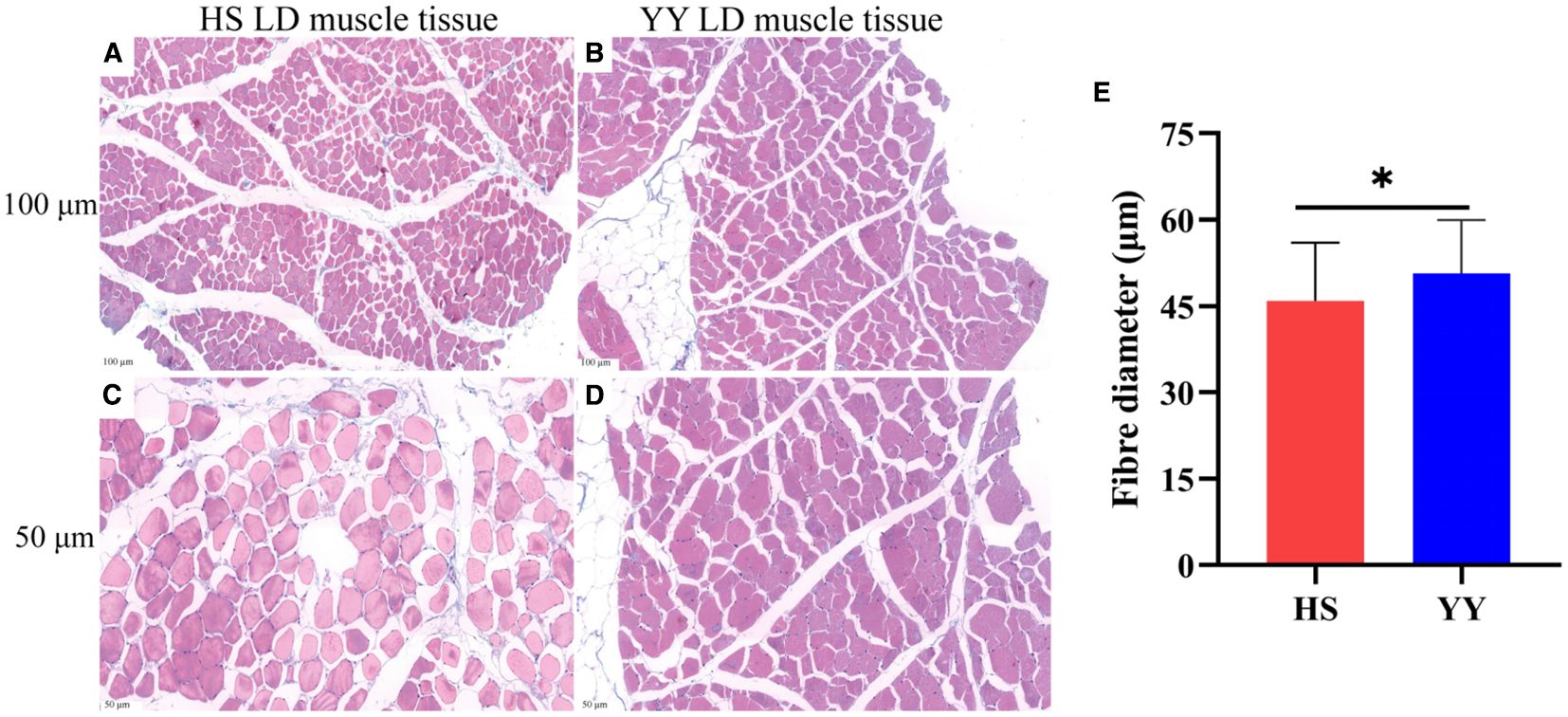
Figure 1. H&E staining of LD muscle tissue. (A) HS pig (100 μm); (B) YY pig (100 μm); (C) HS pig (50 μm); (D) YY pig (50 μm); (E) Fibre diameter of HS and YY pigs. *, P<0.05.
3.2 Quality control of raw sequencing data
From the six LD muscle samples, 338,715,774 raw reads were obtained from the mRNA libraries and 159,376,543 reads from the miRNA libraries (Supplementary Tables S2, S3). After alignment with the pig reference genome, 313,740,633 mRNA reads were successfully mapped, with alignment rates ranging from 94.5% to 97.1% (Supplementary Table S2). Pearson correlation analysis confirmed strong biological repeatability, with R² values exceeding 0.99 for mRNA libraries and 0.80 for miRNA libraries (Supplementary Figure S1). These results indicate that the libraries were of high quality and suitable for subsequent analyses.
3.3 Identification of DEGs and DEMs
Differential expression analysis identified 2,833 DEGs (1,559 upregulated and 1,274 downregulated) and 51 DEMs (14 upregulated and 37 downregulated) between HS and YY pigs (Figures 2A, B; Supplementary Figure S2; Supplementary Tables S6, S7).
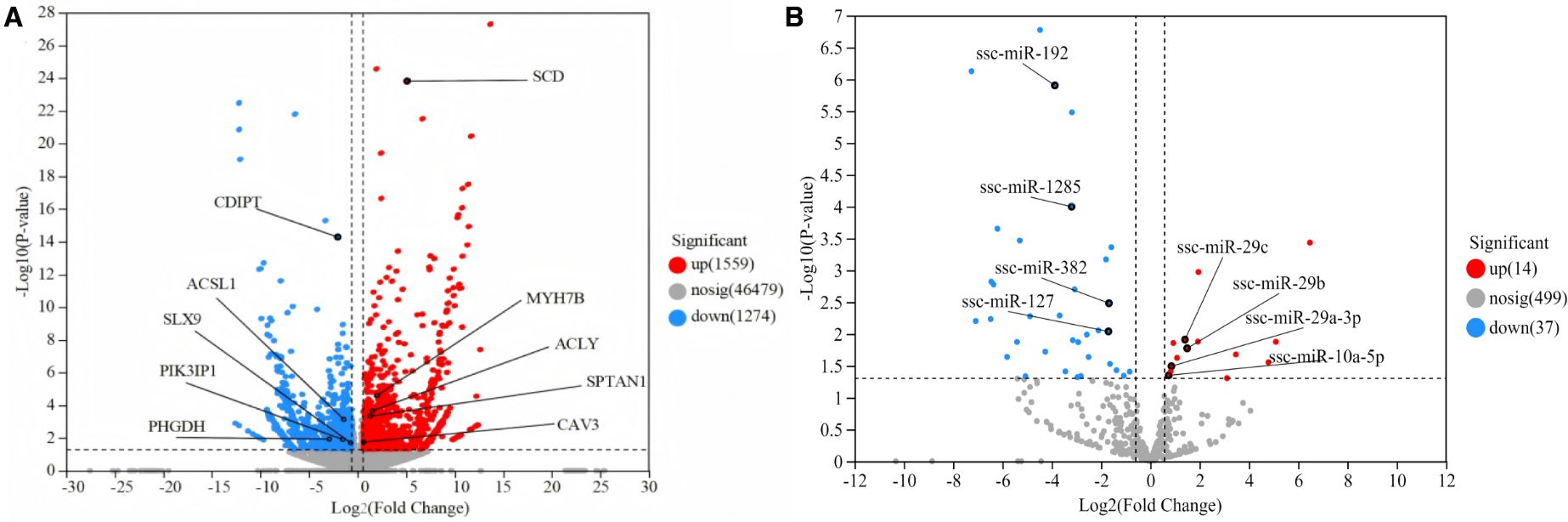
Figure 2. Differential expression analysis of LD muscle between HS and YY pigs. (A) Volcano plot of DEGs; (B) Volcano plot of DEMs.
3.4 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of DEGs
GO enrichment analysis categorized DEGs into biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions (Figure 3A; Supplementary Table S8). Among biological processes, 1,066 significantly enriched terms (70.3%) were identified, mainly related to lipid metabolism, lipid biosynthesis, and lipid homeostasis (P < 0.05). For cellular components, 135 enriched terms (8.9%) were detected, including the collagen-containing extracellular matrix, Golgi apparatus, and synaptic cleft extracellular matrix (P < 0.05). In molecular functions, 316 enriched terms (20.8%) were identified, such as ubiquitin protein ligase binding, protein kinase regulator activity, and protein binding (P < 0.05).
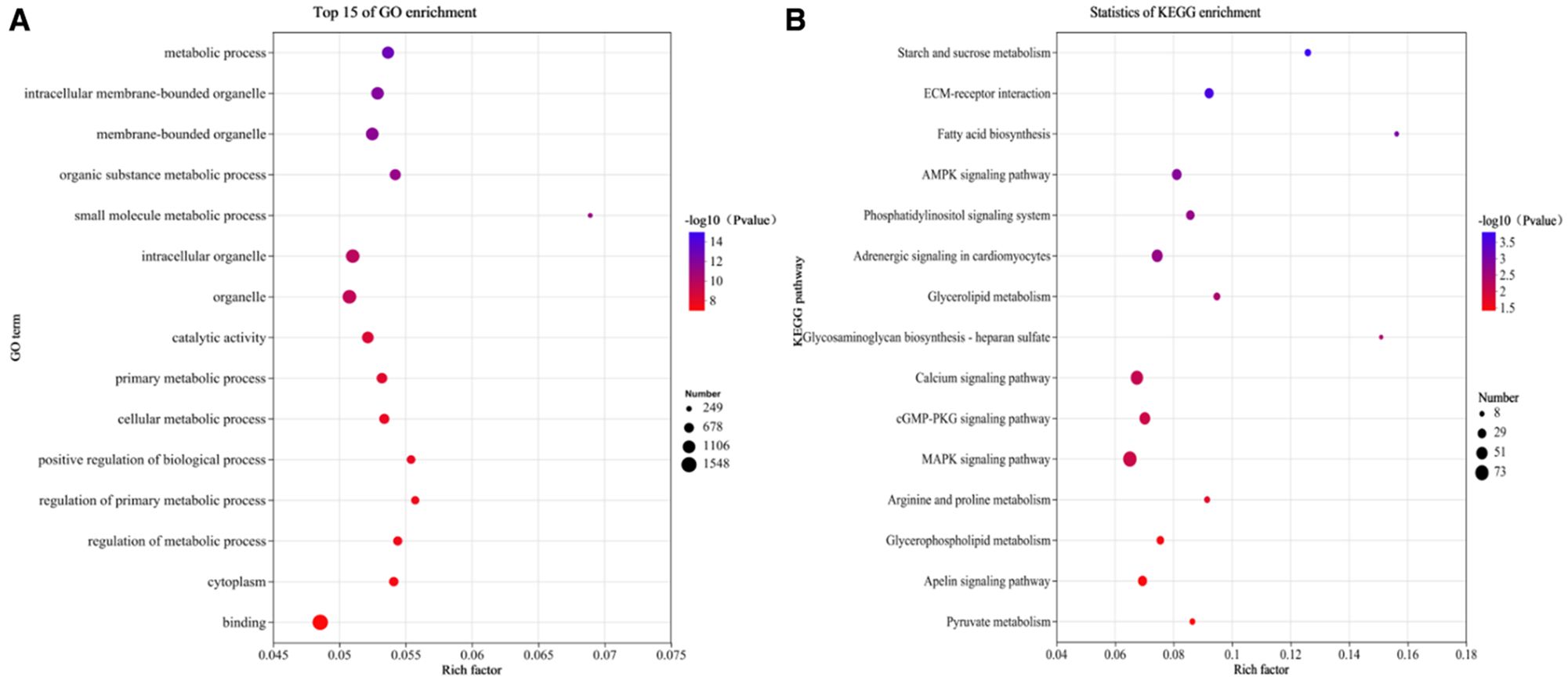
Figure 3. Enrichment analysis of DEGs. (A) Top 15 GO terms; (B) Top 15 metabolic pathways enrichment.
Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis revealed significant enrichment of DEGs in 70 pathways, including fatty acid biosynthesis, MAPK signaling, and AMPK signaling pathways (P < 0.05; Figure 3B; Supplementary Table S9).
3.5 Prediction and enrichment analysis of DEM target genes
A total of 1,205 target genes were predicted for 51 DEMs, forming 2,045 interaction pairs. GO analysis revealed 936 enriched terms, including 597 biological processes (63.8%), 100 cellular components (10.7%), and 239 molecular functions (25.5%) (Figure 4A; Supplementary Table S10). The target genes were significantly enriched in lipid metabolism, lipid homeostasis, and fatty acid metabolism.
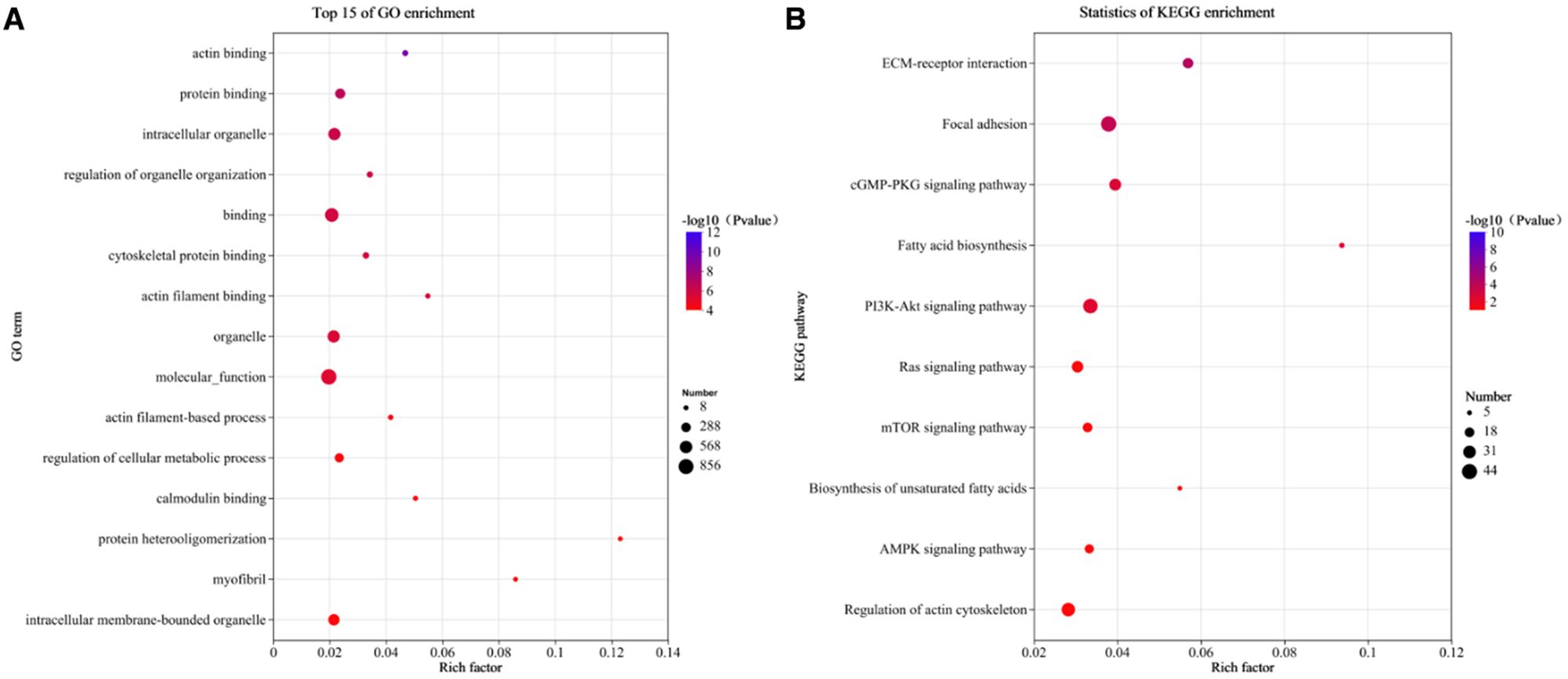
Figure 4. Enrichment analysis of DEM target genes. (A) Top 15 GO terms; (B) Top 10 enriched metabolic pathways.
Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis identified 41 significantly enriched pathways (P < 0.05), including the biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, PI3K-Akt signaling, and Ras signaling pathways (Figure 4B, Supplementary Table S11).
3.6 Validation of sequencing data by qRT-PCR
Four genes and four miRNAs were randomly selected for qRT-PCR validation. Their expression patterns were consistent with the RNA-seq and small RNA-seq results, confirming the reliability of the sequencing data (Figure 5; Supplementary Table S4).
3.7 Construction of the mRNA–miRNA interaction network
A total of 208 predicted target genes overlapped with 2,129 DEGs, resulting in 170 DEGs for network construction. The final interaction network contained 194 nodes and 173 edges, including 170 mRNAs and 23 miRNAs (Figure 6A).
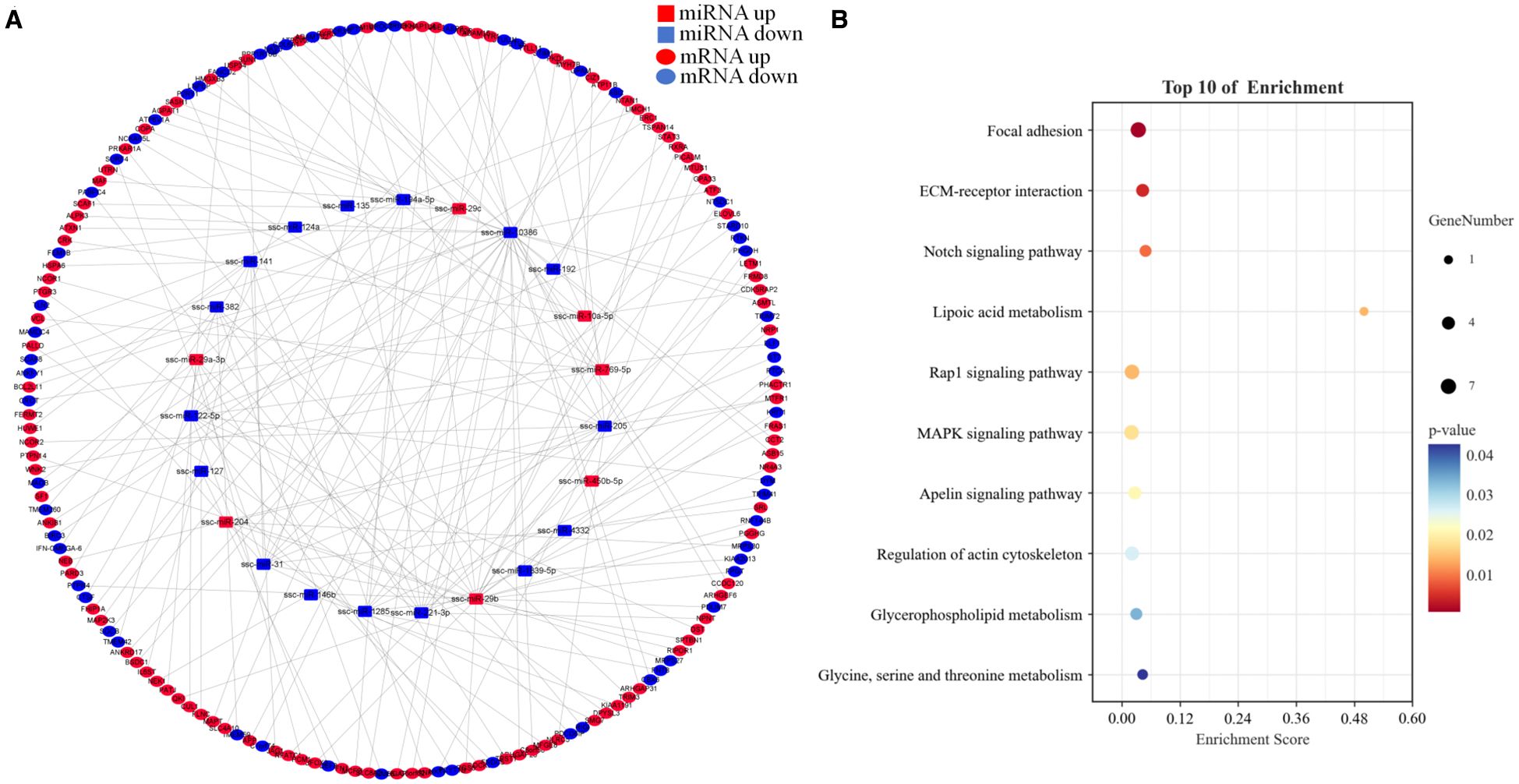
Figure 6. miRNA-mRNA interaction network and metabolic pathway enrichment analyses. (A) Interaction network (red squares = upregulated miRNAs; blue squares = downregulated miRNAs; red ellipses = upregulated mRNAs; blue ellipses = downregulated mRNAs). (B) Metabolic pathway enrichment analyses of DEM target genes.
Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis revealed that target genes were significantly enriched in ECM–receptor interaction, apelin signaling, and MAPK signaling pathways (P < 0.05) (Figure 6B).
3.8 Dual-luciferase reporter assay
miR-205 was significantly downregulated, while MYH7B was upregulated in HS pigs. Bioinformatic predictions (RNAhybrid, miRanda, and TargetScan) indicated that MYH7B is a direct target of miR-205. To validate this, a mutant vector was constructed. As shown in Figure 7 (Supplementary Table S4), the dual-luciferase activity of the miR-205 + MYH7B-3′UTR-WT group was significantly reduced compared with the control (P < 0.01), whereas no significant difference was observed in the miR-205 + MYH7B-3′UTR-MUT group. These results confirm the direct targeting relationship between miR-205 and MYH7B.
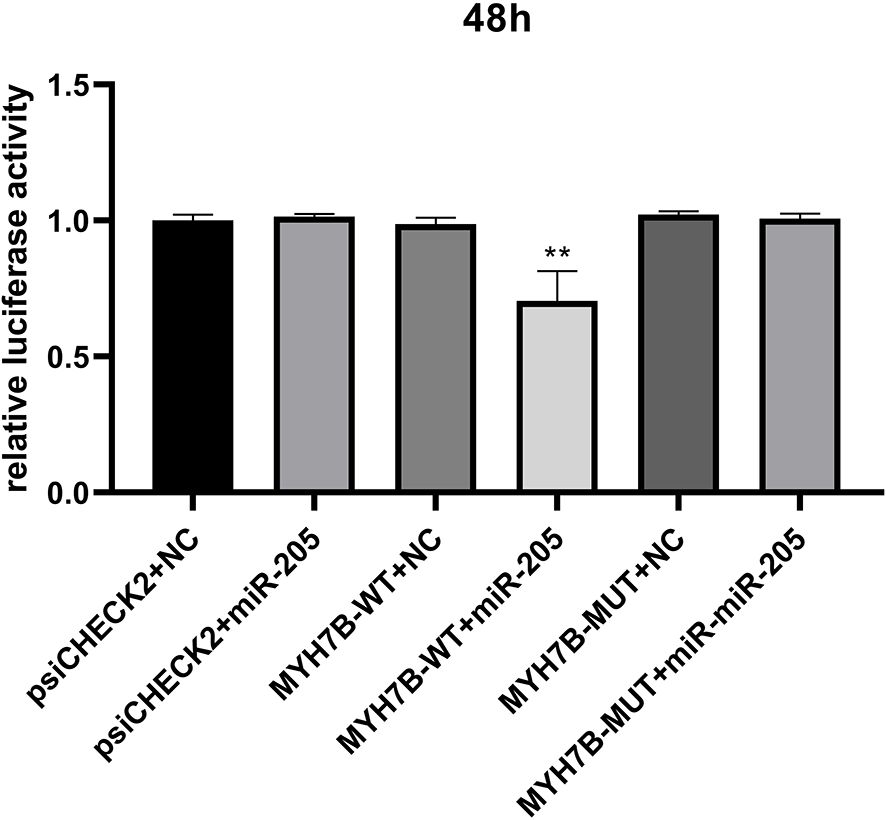
Figure 7. Verification of miR-205 targeting MYH7B using the dual-luciferase reporter assay. **P < 0.01.
4 Discussion
Pork quality is a key economic trait that strongly influences consumer preferences, with IMF being a crucial characteristic and primary indicator of meat quality. Previous research has demonstrated a close relationship between muscle fiber diameter and pork quality (Zhang et al., 2020). In this study, the morphological structure of LD muscle in HS and YY pigs was analyzed. HS pigs exhibited wider gaps and smaller muscle fiber diameters compared with YY pigs, consistent with their higher IMF content.
In recent years, miRNAs have garnered increasing attention for their regulatory roles in IMF deposition and muscle development (Ballarino et al., 2016). Although miRNAs have been shown to be essential in these processes, the mechanisms by which they regulate IMF deposition and muscle growth in the LD muscle of Chinese versus Western breeds remain poorly understood. To address this, we used HS and YY pigs as models, performing transcriptome sequencing to characterize the expression profiles of miRNAs and mRNAs, identify DEGs and DEMs, and construct miRNA–mRNA interaction networks to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying IMF differences between breeds.
Comparative transcriptome profiling identified 3,025 DEGs between HS and YY pigs. GO enrichment highlighted significant biological processes related to lipid regulation, including lipid metabolism, biosynthesis, and homeostasis. Metabolic pathway enrichment analysis further revealed that DEGs were enriched in pathways relevant to IMF deposition, such as fatty acid biosynthesis, MAPK signaling, and AMPK signaling (Figure 3B).
The MAPK signaling pathway mediates intracellular signaling and plays key roles in adipocyte differentiation and skeletal muscle growth (Ambele et al., 2020; Arriojas et al., 2023). In this study, 77 DEGs were significantly enriched in the MAPK signaling pathway. For example, MAPK14 promotes adipogenesis and myogenesis (Keren et al., 2006). MAPKAPK2, a downstream protein kinase within the p38 MAPK signaling pathway, supports skeletal muscle development when activated (Scharf et al., 2013). Previous studies reported higher MAPK14 expression in Chinese Debao pigs compared with Landrace pigs (Huang et al., 2018) and lower MAPKAPK2 expression in Laiwu pigs compared with Yorkshire pigs (Chen et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2018). The AMPK pathway, which restores energy balance by regulating lipid and protein biosynthesis and fatty acid oxidation (Xiao et al., 2007), was also enriched. Among the genes involved, ADIPOR2 and LEP were notable. ADIPOR2,a primary receptor for adiponectin, mediates the regulation of fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake through activation of the AMPK signaling pathway (Yamauchi et al., 2002), LEP, an adipocyte-secreted protein hormone, regulates muscle fatty acid oxidation via the AMPK signaling pathway (Minokoshi et al., 2002). Previous studies reported significantly higher expression of ADIPOR2 in the LD muscle of Yorkshire pigs compared with Northeast Min pigs (Yao et al., 2019), and higher expression of LEP in Dahe pigs (Yi et al., 2024). Fatty acid biosynthesis, which synthesizes aliphatic acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA through fatty acid synthase, is essential for fat deposition and muscle growth (Heil et al., 2019). In this study, 10 DEGs were significantly enriched in this pathway, including FASN and ACSL1. FASN promotes fat deposition and fatty acid synthesis (Sakai et al., 2020; Solsona et al., 2021), while ACSL1 activates fatty acids to form acyl-CoA, thereby regulating lipid synthesis (Li et al., 2020). Previous findings showed higher expression of FASN and ACSL1 in the LD muscle of Wannanhua and Laiwu pigs compared with Yorkshire pigs (Chen et al., 2017; Li et al., 2016). In our study, MAPK14, MAPKAPK2, LEP, and FASN were expressed at significantly higher levels in HS pigs compared with YY pigs, while ADIPOR2 and ACSL1 were expressed at significantly lower levels. These findings suggest that differences in IMF content between HS and YY pigs may be mediated by differential regulation of the MAPK, AMPK, and fatty acid biosynthesis pathways.
Differential miRNA expression profiling identified 51 DEMs. Subsequent target prediction analysis revealed that these DEMs potentially regulate 1,549 target genes, forming 2,580 miRNA–mRNA regulatory pairs. Enrichment analysis of the predicted target genes revealed significant associations with lipid homeostasis and fatty acid metabolism. Metabolic pathway enrichment further indicated strong links to IMF deposition and lipid metabolism, including biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids, PI3K–Akt signaling, and Rap1 signaling (Figure 6B). The biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids regulates muscle cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation, thereby promoting fat deposition and muscle development (Lipina and Hundal, 2017). The PI3K–Akt signaling pathway serves as a central regulator of cellular growth, differentiation, and lipid metabolism (Savova et al., 2023), while the Ras signaling pathway is critical for adipocyte differentiation (Mitin et al., 2001). From these pathways, seven DEMs associated with fat deposition and muscle growth were identified: miR-10a-5p, miR-29b, miR-29a-3p, miR-122-5p, miR-194a-5p, miR-221-3p, and miR-31. For example, miR-10a-5p promotes adipogenesis by suppressing KLF11 (Zhang et al., 2024). MiR-29b enhances intramuscular adipocyte proliferation but inhibits differentiation by targeting CTRP6 (Wu et al., 2021b). miR-29a-3p, a member of the miR-29 family, regulates adipogenesis and adipocyte differentiation by inhibiting SPARC expression (Song et al., 2018), miR-122-5p modulates lipid and cholesterol metabolism by directly targeting FABP5 and HMGCS2 (Zhai et al., 2023), miR-194a-5p regulates lipid and cholesterol metabolism via Apoa5 and Hmgcs2 (Nie et al., 2017; Torres et al., 2019), miR-221-3p influences adipocyte differentiation and metabolism by directly regulating ANGPTL8 (Mysore et al., 2017), and miR-31 regulates adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis via PIK3C2A and C/EBPa (Tang et al., 2009). Our results showed that miR-10a-5p, miR-29b, and miR-29a-3p were more highly expressed in HS pigs, while miR-122-5p, miR-194a-5p, miR-221-3p, and miR-31 were expressed at lower levels in HS pigs compared with YY pigs. These differences suggest that DEMs contribute to breed-specific variations in IMF deposition.
Furthermore, this study identified four miRNAs (miR-10a-5p, miR-122-5p, miR-127, and miR-205) associated with IMF deposition and muscle growth in the miRNA–mRNA network. miR-10a-5p targets COL6A1 and CROT, both negatively correlated with its expression. COL6A1 enhances adipogenic differentiation and IMF deposition (Zhang et al., 2020), while CROT regulates fatty acid oxidation and lipid metabolism (Wanders et al., 2010). Lower expression of these genes in HS pigs compared with YY pigs suggests that miR-10a-5p may promote fat deposition by suppressing them (Figure 6A). miR-122-5p targets ELOVL6, a fatty acid elongase involved in adipocyte proliferation and differentiation (Du et al., 2018). Higher ELOVL6 expression in HS pigs suggests that miR-122-5p may enhance fat deposition by promoting its expression (Figure 6A). miR-127, a negative regulator of fat deposition, targets FN1, which promotes adipogenic differentiation and lipid droplet accumulation (Gao et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019). HS pigs exhibited lower expression of miR-127 but higher expression of FN1, suggesting a regulatory role in IMF deposition (Figure 6A). Finally, miR-205 targets MYH7B, a myosin heavy chain protein essential for sarcomere structure, muscle growth, and contraction (Yu et al., 2014). In this study, miR-205 was expressed at lower levels in HS pigs, while MYH7B was expressed at higher levels. Dual-luciferase reporter assays confirmed the targeting relationship, indicating that miR-205 may regulate lipid biosynthesis by modulating MYH7B expression.
In summary, these identified DEMs and their target genes play key roles in regulating muscle fat deposition and growth, providing promising molecular targets for future studies to improve pork quality.
5 Conclusion
This study employed transcriptome sequencing to investigate mRNA and miRNA expression in the LD muscle of Chinese (HS) and Western (YY) pig breeds. Numerous DEGs and DEMs associated with IMF deposition and muscle growth were identified. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that DEM target genes were significantly enriched in lipid metabolism–related pathways, including MAPK signaling, AMPK signaling, and fatty acid biosynthesis.
Within the miRNA–mRNA interaction network, nine candidate miRNAs (miR-10a-5p, miR-29b, miR-29a-3p, miR-122-5p, miR-194a-5p, miR-221-3p, miR-31, miR-127, and miR-205) were identified. Notably, the interaction between miR-205 and MYH7B was experimentally validated using a dual-luciferase reporter assay. These findings indicate that the identified miRNAs regulate IMF deposition and muscle development by modulating key target genes.
Overall, this study provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying fat deposition and myogenesis in pigs, offering a theoretical framework for improving pork quality through molecular breeding strategies.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, PRJNA1210103.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Anhui Science and Technology University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XL: Methodology, Data curation, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Project administration. FX: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Data curation. CJ: Writing – review & editing. MJ: Writing – review & editing. WZ: Writing – review & editing. AG: Writing – review & editing. MR: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. SL: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YG: Project administration, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Provincial financial Agricultural Germplasm Resources Protection and Utilization project “Anhui Provenance Pig Genetic Evaluation Center Special Project (2023)” and the talent introduction project of Anhui Science and Technology University (DKYJ202105), Postdoctoral Research Project of Anhui Province (2023B693), The University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (GXXT-2022-076).
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to the staff of the experimental farm and slaughterhouse. We appreciate the technical support we received for the bioinformatics analysis from Shanghai Meiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).
Conflict of interest
Authors XL and YG were employed by the company Anhui Haoxiang Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Co., Ltd. Author WZ was employed by the company Anhui Anye Agricultural Science and Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fanim.2025.1630616/full#supplementary-material
References
Ambele M. A., Dhanraj P., Giles R., and Pepper M. S. (2020). Adipogenesis: a complex interplay of multiple molecular determinants and pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 4283. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124283
Arriojas A., Patalano S., Macoska J., and Zarringhalam K. (2023). A Bayesian noisy logic model for inference of transcription factor activity from single cell and bulk transcriptomic data. NAR Genom Bioinform. 5, 106. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqad106
Ballarino M., Morlando M., Fatica A., and Bozzoni I. (2016). Non-coding RNAs in muscle differentiation and musculoskeletal disease. J. Clin. Invest. 126, 2021–2030. doi: 10.1172/JCI84419
Bustin S. A., Benes V., Garson J. A., Hellemans J., Huggett J., Kubista M., et al. (2009). The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 55, 611–622. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Chen C., Zeng S., Ma Y., Zheng J., Li X., Xiong C., et al. (2022). Screening candidate genes related to psoas muscle traits in Debao and Landrace pigs based on transcriptome analysis. J. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 5, 1000218. doi: 10.1101/2022.04.04.487004
Chen S., Zhou Y., Chen Y., and Gu J. (2018). Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, 884–890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Chen W., Fang G., Wang S., Wang H., and Zeng Y. (2017). Longissimus lumborum muscle transcriptome analysis of Laiwu and Yorkshire pigs differing in intramuscular fat content. Genes Genomics 39, 759–766. doi: 10.1007/s13258-017-0540-9
Dodson M. V., Allen R. E., Du M., Bergen W. G., Velleman S. G., Poulos S. P., et al. (2015). INVITED REVIEW: Evolution of meat animal growth research during the past 50 years: Adipose and muscle stem cells. J. Anim. Sci. 93, 457–481. doi: 10.2527/jas.2014-8221
Du J., Xu Y., Zhang P., Zhao X., Gan M., Li Q., et al. (2018). MicroRNA-125a-5p affects adipocytes proliferation, differentiation and fatty acid composition of porcine intramuscular fat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 501. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020501
Friedlander M. R., Mackowiak S. D., Li N., Chen W., and Rajewsky N. (2012). MiRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 37–52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr688
Gao Y., Wang Y., Chen X., Peng Y., Chen F., He Y., et al. (2019). MiR-127 attenuates adipogenesis by targeting MAPK4 and HOXC6 in porcine adipocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 21838–21850. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28660
Heil C. S., Wehrheim S. S., Paithankar K. S., and Grininger M. (2019). Fatty acid biosynthesis: chain-length regulation and control. Chembiochem 20, 2298–2321. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201800809
Huang W., Zhang X., Li A., Xie L., and Miao X. (2018). Genome-Wide Analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs of Intramuscular Fat Related to Lipid Metabolism in Two Pig Breeds. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 50, 2406–2422. doi: 10.1159/000495101
John B., Enright A. J., Aravin A., Tuschl T., Sander C., and Marks D. S. (2004). Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2, e363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020363
Keren A., Tamir Y., and Bengal E. (2006). The p38 MAPK signaling pathway: a major regulator of skeletal muscle development. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 252, 224–230. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2006.03.017
Khan M. I., Jo C., and Tariq M. R. (2015). Meat flavor precursors and factors influencing flavor precursors—a systematic review. Meat Sci. 110, 278–284. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.08.002
Kim D., Langmead B., and Salzberg S. L. (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–360. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317
Kovaka S., Zimin A. V., Pertea G. M., Razaghi R., Salzberg S. L., and Pertea M. (2019). Transcriptome assembly from long-read RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 20, 278. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1910-1
Li C., Chen W., Hu J., Wang Y., Wang S., Zeng Y., et al. (2016a). MiRNA-29a targets COL3a1 to regulate the level of type III collagen in pig. Gene 592, 140–147. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.07.068
Li T., Li X., Meng H., Chen L., and Meng F. (2020). ACSL1 affects Triglyceride Levels through the PPARgamma Pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 17, 720–727. doi: 10.7150/ijms.42248
Li X., Zhou J., Liu L., Qian K., and Wang C. (2016b). Identification of genes in longissimus dorsi muscle differentially expressed between Wannanhua and Yorkshire pigs using RNA-sequencing. Anim. Genet. 47, 324–333. doi: 10.1111/age.12421
Lipina C. and Hundal H. S. (2017). Lipid modulation of skeletal muscle mass and function. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 8, 190–201. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12144
Liu H., Xi Y., Liu G., Zhao Y., Li J., and Lei M. (2018). Comparative transcriptomic analysis of skeletal muscle tissue during prenatal stages in Tongcheng and Yorkshire pig using RNA-seq. Funct. Integr. Genomics 18, 195–209. doi: 10.1007/s10142-017-0584-6
Love M. I., Huber W., and Anders S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Lu T. X. and Rothenberg M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 141, 1202–1207. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Minokoshi Y., Kim Y., Peroni O. D., Fryer L. G. D., Muller C., Carling D., et al. (2002). Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 415, 339–343. doi: 10.1038/415339a
Mitin N., Kudla A. J., Konieczny S. F., and Taparowsky E. J. (2001). Differential effects of Ras signaling through NFkappaB on skeletal myogenesis. Oncogene 20, 1276–1286. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204223
Mohr A. M. and Mott J. L. (2015). Overview of microRNA biology. Semin. Liver Dis. 35, 3–11. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1397344
Mysore R., Ortega F. J., Latorre J., Ahonen M., Savolainen-Peltonen H., Fischer-Posovszky P., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-221-3p regulates angiopoietin-like 8 (ANGPTL8) expression in adipocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 102, 4001–4012. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00453
Nie H., Song C., Wang D., Cui S., Ren T., Cao Z., et al. (2017). MicroRNA-194 inhibition improves dietary-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through targeting on FXR. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1863, 3087–3094. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.09.020
Sakai H., Murakami C., Usuki T., Lu Q., Matsumoto K., Urano T., et al. (2020). Diacylglycerol kinase eta regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation through the mTOR signaling pathway. Biochimie 177, 13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2020.07.018
Savova M. S., Mihaylova L. V., Tews D., Wabitsch M., and Georgiev M. I. (2023). Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in obesity. BioMed. Pharmacother. 159, 114244. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114244
Scharf M., Neef S., Freund R., Geers-Knorr C., Franz-Wachtel M., Brandis A., et al. (2013). Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinases 2 and 3 regulate SERCA2a expression and fiber type composition to modulate skeletal muscle and cardiomyocyte function. Mol. Cell Biol. 33, 2586–2602. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01692-12
Shannon P., Markiel A., Ozier O., Baliga N. S., Wang J. T., Ramage D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13, 2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303
Shen L., Chen L., Zhang S., Zhang Y., Wang J., and Zhu L. (2016). MicroRNA-23a reduces slow myosin heavy chain isoforms composition through myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C) and potentially influences meat quality. Meat Sci. 116, 201–206. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.02.023
Solsona R., Pavlin L., Bernardi H., and Sanchez A. M. (2021). Molecular regulation of skeletal muscle growth and organelle biosynthesis: practical recommendations for exercise training. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 2741. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052741
Song H., Ding L., Zhang S., and Wang W. (2018). MiR-29 family members interact with SPARC to regulate glucose metabolism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 497, 667–674. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.129
Sun Y., Qin J., Liu S., Cai R., Chen X., Wang X., et al. (2017). PDGFRalpha Regulated by miR-34a and FoxO1 Promotes Adipogenesis in Porcine Intramuscular Preadipocytes through Erk Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 2424. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112424
Tang Y., Zhang Y., Li X., Li C., Tian W., and Liu L. (2009). Expression of miR-31, miR-125b-5p, and miR-326 in the adipogenic differentiation process of adipose-derived stem cells. Omics 13, 331–336. doi: 10.1089/omi.2009.0017
Torres L. F., Cogliati B., and Otton R. (2019). Green Tea Prevents NAFLD by Modulation of miR-34a and miR-194 Expression in a High-Fat Diet Mouse Model. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2019, 1–18. doi: 10.1155/2019/4168380
Wanders R. J. A., Ferdinandusse S., Brites P., and Kemp S. (2010). Peroxisomes, lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1801, 272–280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.01.001
Wang Y., Fu Y., Yan Z., Zhang X., and Pei M. (2019). Impact of fibronectin knockout on proliferation and differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad-derived stem cells. Front. Bioeng Biotechnol. 7. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00321
Wu T., Hu E., Xu S., Chen M., Guo P., Dai Z., et al. (2021a). ClusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation (Camb) 2, 100141. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100141
Wu W., Xu K., Li M., Zhang J., and Wang Y. (2021b). MicroRNA-29b/29c targeting CTRP6 influences porcine adipogenesis via the AKT/PKA/MAPK Signalling pathway. Adipocyte 10, 264–274. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2021.1917811
Xiao B., Heath R., Saiu P., Leiper F. C., Leone P., Jing C., et al. (2007). Structural basis for AMP binding to mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 449, 496–500. doi: 10.1038/nature06161
Yamauchi T., Kamon J., Minokoshi Y., Ito Y., Waki H., Uchida S., et al. (2002). Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 8, 1288–1295. doi: 10.1038/nm788
Yao C., Pang D., Lu C., Xu A., Huang P., Ouyang H., et al. (2019). Data mining and validation of AMPK pathway as a novel candidate role affecting intramuscular fat content in pigs. Anim. (Basel) 9, 137. doi: 10.3390/ani9040137
Yi L., Li Q., Zhu J., Cheng W., Xie Y., Huang Y., et al. (2024). Single-nucleus RNA sequencing and lipidomics reveal characteristics of transcriptional and lipid composition in porcine longissimus dorsi muscle. BMC Genomics 25, 622. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10488-8
Yu J., Chen Y., Qin L., Cheng L., Ren G., Cong P., et al. (2014). Effect of miR-205 on 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation through targeting to glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta. Biotechnol. Lett. 36, 1233–1243. doi: 10.1007/s10529-014-1491-8
Zhai B., Li H., Li S., Gu J., Zhang H., Zhang Y., et al. (2023). Transcriptome analysis reveals FABP5 as a key player in the development of chicken abdominal fat, regulated by miR-122-5p targeting. BMC Genomics 24, 386. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09476-1
Zhang L., Guo Y., Wang L., Liu X., Yan H., Gao H., et al. (2020). Genomic variants associated with the number and diameter of muscle fibers in pigs as revealed by a genome-wide association study. Animal 14, 475–481. doi: 10.1017/S1751731119002374
Zhang M., Li D., Zhai Y., Wang Z., Ma X., Zhang D., et al. (2020). The landscape of DNA methylation associated with the transcriptomic network of intramuscular adipocytes generates insight into intramuscular fat deposition in chicken. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00206
Zhang W., Li X., Jiang Y., Zhou M., Liu L., Su S., et al. (2022). Genetic architecture and selection of Anhui autochthonous pig population revealed by whole genome resequencing. Front. Genet. 13. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1022261
Zhang W., Zhao T., Gao X., Ma S., Gong T., Yang Y., et al. (2024). MiR-10a-5p regulates the proliferation and differentiation of porcine preadipocytes targeting the KLF11 gene. Anim. (Basel) 14, 337. doi: 10.3390/ani14020337
Keywords: Huoshou black pig, Yorkshire pig, longissimus dorsi muscle, IMF, miRNA
Citation: Li X, Xie F, Jiang C, Jin M, Zhao W, Ghonaim AH, Ren M, Li S, Gao Y and Yin Z (2025) miRNA-mRNA crosstalk in porcine longissimus dorsi muscle: multi-omics identification of breed-specific regulatory networks and functional verification. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1630616. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1630616
Received: 18 May 2025; Accepted: 25 September 2025;
Published: 17 October 2025.
Edited by:
Angela Cánovas, University of Guelph, CanadaReviewed by:
Jinlong Huo, Yunnan Agricultural University, ChinaYe Tian, Hebei North University, China
Copyright © 2025 Li, Xie, Jiang, Jin, Zhao, Ghonaim, Ren, Li, Gao and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yafei Gao, Z2FveWFmbGluZ0AxNjMuY29t; Zongjun Yin, eWluem9uZ2p1bkBhaGF1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Xiaojin Li1,2,3,4,5†
Xiaojin Li1,2,3,4,5† Fei Xie
Fei Xie Ahmed H. Ghonaim
Ahmed H. Ghonaim Shenghe Li
Shenghe Li