- 1Research and Development, Department, APC LLC, Ankeny, IA, United States
- 2Department of Animal Science, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, United States
- 3Department of Animal Science, University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana, IL, United States
Three experiments evaluated the effects of a novel milk ingredient blend (FXP) in phase 1 and 2 nursery pig diets on growth performance, diarrhea score, and survival. In Experiment 1, pigs were fed a 3-phase nursery regimen, with phases 1, 2, and 3 lasting 10, 11, and 6 days, respectively. Treatments included a control diet in each phase (CONTROL), 4% spray-dried plasma (SDP) in phase 1 followed by the CONTROL diet in phases 2 and 3 (SDP), and 0.5% FXP in phases 1 and 2, followed by the CONTROL diet in phase 3 (FXP). There were 8, 9, and 10 pens assigned to the CONTROL, SDP, and FXP treatments, respectively. Pigs fed SDP during phase 1 had greater (P < 0.05) average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and average body weight (BW) on day 10 than pigs fed the CONTROL or FXP treatments, and a greater (P < 0.05) gain-to-feed ratio (G:F) than pigs fed the FXP diet. In Experiment 2, the 3-phase nursery feed regimen consisted of diets fed for 11, 10, and 21 days in phases 1 to 3, respectively, using the same treatments as in Experiment 1: CONTROL, 4% SDP in phase 1 only, and 1% FXP in phases 1 and 2. Each treatment included 12 pens. Pigs fed SDP in phase 1 had significantly greater (P < 0.05) ADG, ADFI, and BW on day 11 than those fed CONTROL or FXP diets. Cumulative mortality by day 21 was higher (P < 0.05) for pigs fed FXP compared with CONTROL and SDP, and fecal score was lower (P < 0.05) for SDP compared with CONTROL. In Experiment 3, pigs were assigned to either a CONTROL or FXP group, with 0.5% FXP included only in phases 1 and 2. Phases 1 to 3 lasted 11, 12, and 19 days, respectively. Each treatment was assigned to 64 pens of 25–26 pigs per pen. Pigs fed FXP had a higher (P < 0.05) removal rate during phase 3 than the CONTROL. Overall, there were no benefits from feeding 0.5% to 1% FXP on pig growth performance, diarrhea incidence, or survival based on the results from these experiments.
Introduction
There are no regulatory restrictions on the use of feed ingredients derived from animal proteins in swine diets in the USA. Animal protein ingredients such as spray-dried plasma (SDP) are frequently used in nursery pig diets as highly digestible and functional protein sources to support growth, feed intake, and feed efficiency during the critical post-weaning stress period (Torrallardona, 2010; Balan et al., 2021). However, some pork production systems that cater to consumer markets requiring pigs never to be fed antibiotics may also prohibit the use of animal-origin ingredients (except for bovine milk ingredients) in the feed for pigs they produce. A novel product described as a blend of bioactive milk-based ingredients (FXP) is commercially available for use in swine diets within “never-fed-antibiotics” systems or other swine producers who prefer to exclude non-milk animal proteins from feed. The product label for FXP listed dried whey product, dried buttermilk, dried whey protein concentrate, dried skim milk, and casein as ingredients, with a minimum guarantee of 47% crude protein and 10% crude fat in the blend, and a recommended inclusion rate of up to 0.5% in diets. Public information on this novel milk product is limited to three abstracts published in conference proceedings (Cemin et al., 2020; Horn et al., 2022; Spencer et al., 2025), which indicate that as little as 0.3% to 0.6% of this product in nursery pig diets during the initial 3 weeks after weaning can increase growth performance, reduce diarrhea incidence, and improve survival. In the abstract by Horn et al. (2022), FXP was not explicitly named but was described as a novel whey protein concentrate containing bioactive proteins similar to those found in colostrum. However, the supplier of the whey protein concentrate was a co-author on all three abstracts. No peer-reviewed manuscripts have yet been published on the effects of this novel milk ingredient blend on nursery pig growth performance and survival. Therefore, the objectives of the present experiments were to test the hypothesis that inclusion of the novel milk ingredient blend (FXP) in diets for newly weaned pigs, would support growth performance, fecal scores, and pig survival to the same extent as SDP.
Materials and methods
Three sequential nursery experiments were conducted. The novel milk ingredient blend (FXP, Ani-Tek, LLC, Social Circle, GA, USA) was used in all three experiments, but the experiments were conducted at different institutions. The experimental protocols for Experiments 1 and 2 were reviewed and approved by an Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee before the animal phase was initiated. The institutional approval numbers were 22–438 and 21245, respectively, for Experiments 1 and 2. The institution that conducted Experiment 3 did not provide an institutional approval number; however, this institution conducts private contract research that is supervised by professional animal scientists and veterinarians who adhere to standard operating protocols for animal care and use.
Chemical analysis: FXP samples were analyzed at the APC LLC laboratory (Ankeny, IA, USA) for dry matter (method 930.15; AOAC, 2019), dry ash (method 942.05; AOAC, 2019), and nitrogen content using the combustion method (method 990.03; AOAC, 2019). Crude protein was calculated as analyzed nitrogen × 6.25. A 10% solution of FXP was mixed until fully dissolved, and its pH was measured using a calibrated pH meter following routine procedures at the APC LLC laboratory. Bovine IgG concentration was performed using radial immunodiffusion (RID) on agar plates containing anti-bovine IgG at standard concentrations, following the supplier’s instructions (JJJ Diagnostics, Bellington, WA, USA). Additional FXP samples were analyzed at the APC LLC laboratory using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits produced specifically for quantifying bovine IgA (detection range: 1.37–1,000– ng/mL) and bovine lactoferrin (detection range: 0.69–500 ng/mL), according to procedures described by the manufacturer (Bethyl Laboratories, Inc., Montgomery, TX, USA).
Two additional FXP samples were submitted to Midwest Laboratories (Omaha, NE, USA). One was analyzed for nitrogen as described above; the other was analyzed for amino acids. Most amino acids were analyzed after acid hydrolysis (method 994.12; AOAC, 2019). Methionine and cysteine were converted to methionine sulfone and cysteic acid, respectively, using performic acid oxidation prior to hydrolysis. Tryptophan was analyzed by alkaline hydrolysis (method 988.15; AOAC, 2019). The other sample was used for macro- and micro-mineral analysis via wet digestion and inductively coupled atomic plasma spectrometry (method 985.01; AOAC, 2019). An additional FXP sample was sent to Silliker Laboratories (Minnetonka, MN, USA) for crude fat analysis using an acid hydrolysis method (method 948.15; AOAC, 2019). The analyzed composition of FXP is presented in Table 1.
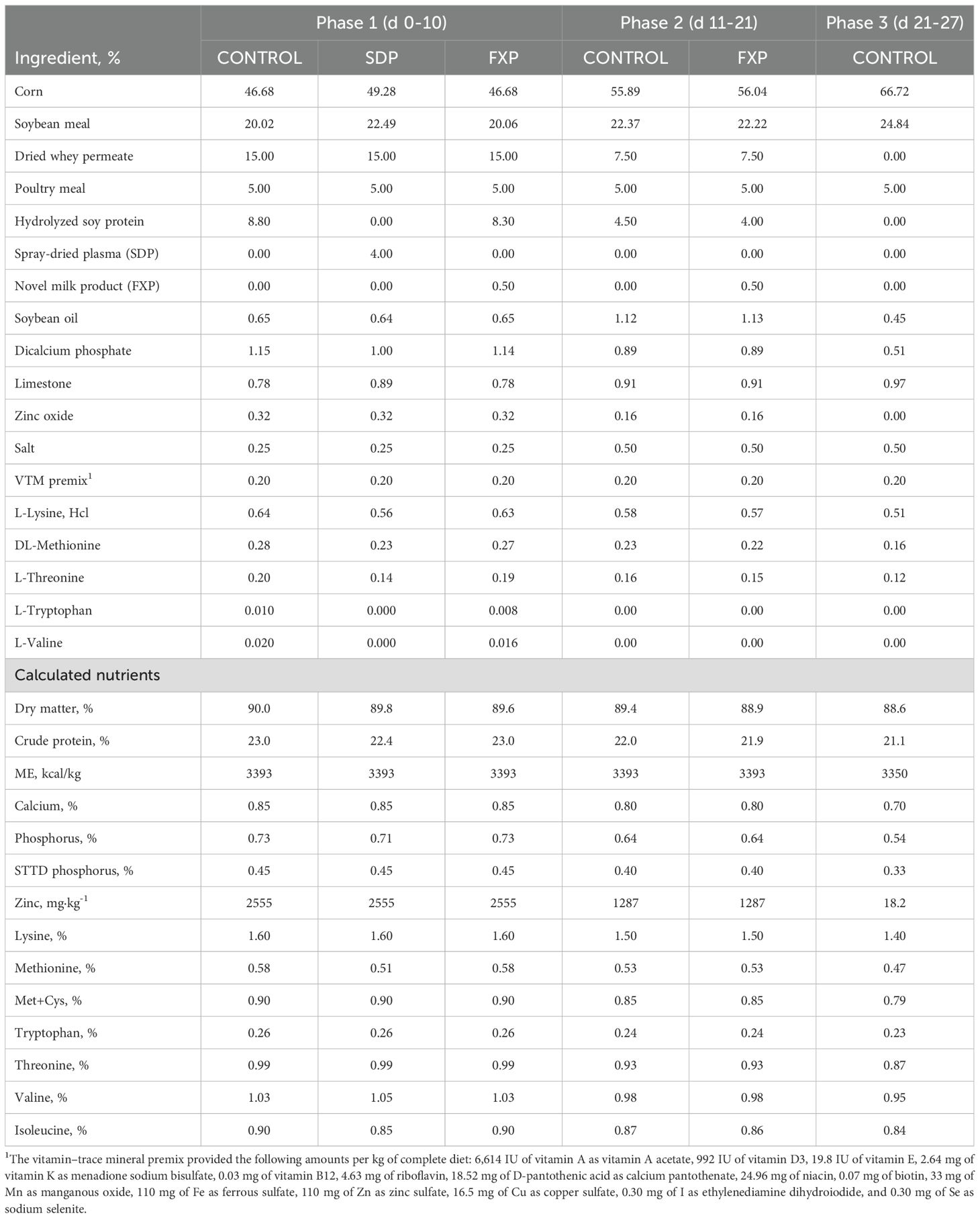
Experiment 1 was conducted at the North Carolina State University Swine Education Unit in Raleigh, NC, USA, as an initial nursery study to determine dietary effects on pig growth performance using a 3-phase feeding regimen with three treatments. The CONTROL treatment consisted of diets without SDP or FXP included in any phase. The SDP treatment included 4% porcine SDP in the phase 1 diet, followed by the CONTROL diets in phases 2 and 3. The FXP treatment included 0.5% FXP in the phase 1 and 2 diets, followed by the CONTROL diet in phase 3. Phase 1 diets were provided for the initial 10 days after weaning (d 0–10), phase 2 diets for the following 11 days (d 10–21), and the phase 3 diet for an additional 6 days (d 21–27). The duration of phase 3 was limited to 6 days because pigs were needed for a different project. All diets (Table 2) were mixed at the university feed mill and provided in mash form, with feed and water provided ad libitum throughout all phases. The phase 1 SDP diet contained 4% porcine SDP, replacing the enzyme-treated soybean meal (HP300, Hamlet Protein, Findlay, OH, USA) used in the CONTROL phase 1 diet. The FXP phase 1 and 2 diets included 0.5% FXP, partially replacing 0.5% of the enzyme-treated soybean meal used in the CONTROL diets for phases 1 and 2. Dietary treatments within each phase were formulated to provide equivalent amounts of metabolizable energy (ME), total lysine, and standardized total tract digestible (STTD) phosphorus. All phase 1 and 2 diets contained equal amounts of lactose and pharmaceutical levels of zinc oxide.
The facility used in Experiment 1 was an environmentally controlled nursery room with 48 pens designed to house 3 pigs per pen. Crossbred sows (Yorkshire × Large White × Landrace) mated with pooled semen from crossbred boars (Duroc × Spotted × Hampshire) were used to produce the pigs at the Swine Education Unit. Pigs were weaned as a group at 21 days of age and transported to the nursery. Upon arrival, pigs were individually weighed and allotted to pens by sex (males and females) and two body weight (BW) blocks—light BW (6.03 ± 0.35 kg) and heavy BW (7.30 ± 0.43 kg) across the 48 pens. Only 28 of the 48 pens in the nursery were used for the 3 treatment groups (CONTROL, SDP, FXP) in this experiment. Overall, 8 pens were randomly assigned within BW blocks and sex to the CONTROL treatment, and 10 pens were assigned to each of the SDP and FXP treatments, for a total of 84 pigs. Pigs were weighed at the start and on the last day of each phase (day 10, 21 and 27) to calculate average body weight (BW) and average daily gain (ADG) per pen. Feed additions were recorded, and remaining feed in feeders was weighed on day 10, 21, and 27 to calculate average daily feed intake (ADFI). If a pig died or was removed from the pen for animal welfare reasons, the date and BW of removal were recorded to adjust ADG and ADFI based on pig-days per pen. Pen feed efficiency, or gain to feed ratio (G:F), was calculated using the adjusted ADG and ADFI data in the event of pig removals.
Data were analyzed as a randomized complete block design with unequal replication by treatment and sex. Growth performance data by single and cumulative phases, using pen average values as the experimental unit, were analyzed using a mixed model to test the fixed effects of dietary treatment and sex, with BW block as the random effect (PROC MIXED; SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA; SAS Proprietary Software 9.4). No treatment-by-sex interactions (P > 0.10) were detected for any performance variables; therefore, sex was removed from the final model. All data from one pen provided the SDP treatment were deleted as an outlier due to an apparent discrepancy in the feed records. Two pens fed FXP had negative ADG during phase 1, resulting in negative G:F values; therefore, phase 1 performance data from these pens were excluded as outliers. Results are reported as least squares means with the pooled SEM from 8, 9, and 10 pens for the CONTROL, SDP, and FXP treatments, respectively (Table 3). Statistical significance for treatment differences was set at P < 0.05, and trends with P-values between 0.05 and 0.10 are discussed. Significant treatment differences were assessed by pairwise comparisons using Tukey–Kramer-adjusted P-values.
Experiment 2 was conducted at the University of Illinois Swine Research Center (Champaign, IL, USA) following Experiment 1 to test the null hypothesis that growth performance and fecal scores were not affected by the three dietary treatments. A 3-phase nursery feeding regimen was used, consisting of phase 1 diets fed during the initial 10 days (d 0–10), phase 2 diets fed for 11 days (d 10–21), and the phase 3 CONTROL diet fed to all treatments during the final 21 days (d 21–42). The CONTROL treatment used diets that did not contain SDP or FXP during any phase. The SDP treatment included a phase 1 diet with 4% bovine SDP, followed by the CONTROL phase 2 and 3 diets. The FXP treatment included 1% FXP in the phase 1 and 2 diets, followed by the CONTROL diet in phase 3 (Table 4). The soy protein concentrate (Soycomil-P, ADM Animal Nutrition, Decatur, IL, USA) used in CONTROL phase 1 and 2 diets was partially replaced by 4% bovine SDP in the phase 1 diet or 1% FXP in the phase 1 and 2 diets for the respective SDP and FXP treatments. The reason for using 1% FXP in the diets was to determine if a greater inclusion rate than used in Experiment 1 would affect growth performance because results from Experiment 1 showed no differences in pig performance comparing the CONTROL treatment with the FXP treatment using the supplier recommended 0.5% FXP in phase 1 and 2 diets. All diets were mixed at the University of Illinois Feed Technology Center (Urbana, IL, USA) and were fed in mash form. Diets within each phase were formulated to provide equal ME, lysine, and STTD phosphorus. All phase 1 and 2 diets contained equal amounts of lactose and pharmaceutical-grade zinc oxide. Feed and water were provided on an ad libitum basis in all phases.
Crossbred pigs, the offspring of Line 800 boars mated to Camborough sows (PIC, Hendersonville, TN, USA), were weaned from the University of Illinois Swine Research sow farm at 19 to 21 days of age as two separate groups weaned over a 2-week interval. Each weaned pig group was placed in a different environmentally controlled nursery room using 18 pens per room with 5 pigs per pen. The first weaned pig group was individually weighed and allotted based on 6 initial BW blocks, with the lightest BW block averaging 4.82 ± .0 kg BW and the heaviest BW pens averaging 6.34 ± 0.01 kg BW, to provide a total of 6 pens for each of the three dietary treatments. The second weaned pig group followed the same allotment procedure, with the lightest BW pens averaging 4.71 ± 0.04 kg BW and the heaviest BW pens averaging 6.88 ± 0.02 kg BW, again providing 6 BW blocks of pens for each treatment. For both weaned pig groups, there was an equal ratio of male to female pigs per pen within BW block. Treatments were equally assigned within the BW blocks of each weaning group to provide a total of 12 pens per treatment for the experiment. Pigs, daily feed provisions, and remaining feed in the feeders were weighed on the last day of each phase (day 10, 21, and 42). Pen feeder weight and any dead or removed pigs were recorded, and pig days per pen were used to adjust ADG and ADFI calculations per pen. The G:F was calculated from adjusted ADG and ADFI values in the event of any pig removals.
Fecal scores per pen were recorded on days 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, and 20 of the experiment. Fecal scores ranged from 1 to 5, with 1 indicating normal feces, 2 moist feces, 3 mild diarrhea, 4 severe diarrhea, and 5 watery diarrhea (Bailey et al., 2024).
The experiment was analyzed as a randomized complete block design with equal replication. Growth performance data by single and cumulative phases, using pen average values as the experimental unit, were analyzed using a mixed model to test the fixed effects of dietary treatment, with weaning group (block) and replication as random effects (PROC MIXED; SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA; SAS Proprietary Software 9.4). Fecal score data within phase were analyzed using a mixed model to test the effects of treatment, day, and the interaction of treatment and day, with day as the repeated measure and block and replication as random effects (PROC MIXED; SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA; SAS Proprietary Software 9.4). There were no significant treatment-by-day interactions (P > 0.10) for fecal score variables. Performance and fecal score results are reported as least squares means with the pooled SEM from 12 pens per treatment group (Table 5). Statistical significance for treatment differences was set at P < 0.05, and trends with P-values between 0.05 and 0.10 are discussed. Significant treatment differences of the least squares means were assessed by pairwise comparisons using Tukey–Kramer-adjusted P-values. Probability values of the F-test were reported for growth performance variables, while chi-square P-values were reported for percentage variables such as pig removals or diarrhea incidence.

Table 5. Experiment 2 performance and fecal score results by treatment for single or cumulative phases.
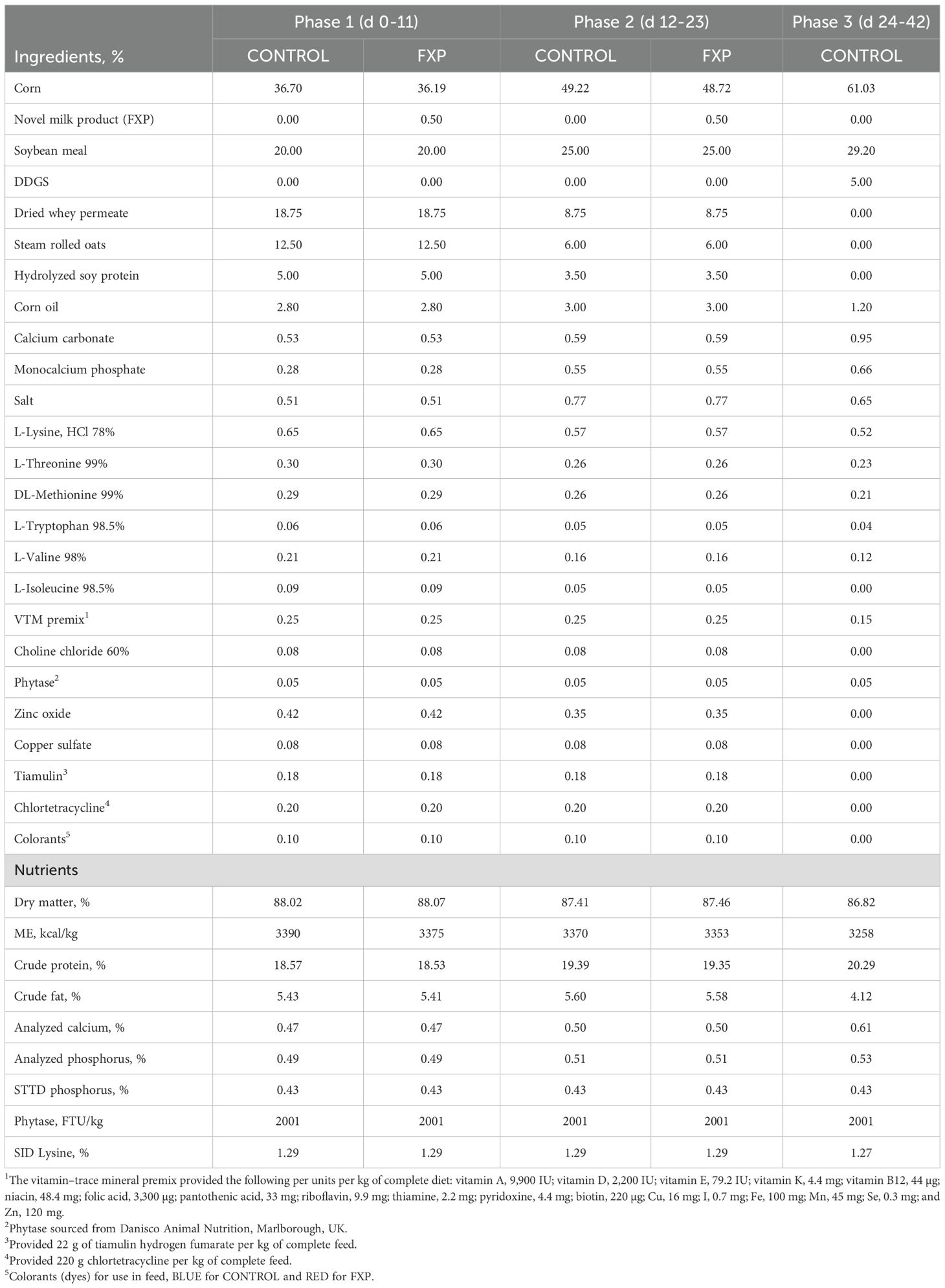
Experiment 3 was conducted at a private commercial research nursery facility in the USA under the supervision of professional nutritionists and veterinarians. The objectives were to determine whether phase 1 and 2 diets containing 0.5% FXP resulted in any differences compared with a CONTROL treatment in terms of growth performance, fecal scores, or pig removals under commercial production conditions. This large-scale experiment included a high number of replications, with 24–26 pigs assigned per pen, to primarily assess the impact of FXP on pig removals.
Two treatment groups were used in a 3-phase nursery feed regimen consisting of diets without FXP fed during phases 1, 2, and 3 (CONTROL) or a treatment (FXP) with 0.5% FXP included in the phase 1 and 2 diets, followed by the CONTROL diet used in phase 3. Phase 1 diets were provided for 11 days (d 0–11), phase 2 diets for 12 days (d 11–23), and the common phase 3 CONTROL diet was provided for 19 days (d 23–42). All diets were prepared at a third-party feed mill and contained different micro-tracer colorants to distinguish feed color differences between the two treatment groups (Table 6). Both phase 1 and 2 diets contained corn, soybean meal, whey permeate, steam-rolled oats, and enzyme-treated soybean meal (HP300, Hamlet Protein, Findlay, OH, USA), with equal amounts of phytase, synthetic amino acids, pharmaceutical-grade zinc oxide, copper sulfate, tiamulin, and chlortetracycline within phase. The 0.5% FXP replaced 0.5% of the corn used in the phase 1 and 2 CONTROL diets. Diets contained identical levels of ME, standardized ileal digestible lysine, and STTD phosphorus.
Four groups of crossbred pigs from a commercial sow farm were weaned at 19–21 days of age and placed in 32 pens in 4 separate but identically designed nursery rooms over 2- or 3-day consecutive intervals. Within each room, pigs were weighed, separated by sex, and allotted to 16 replications of 2 pens per sex, with 24–26 pigs per pen, such that within each replication of 2 pens, the initial average BW was identical. The 2 treatments were randomly assigned within each replication in the 4 rooms using a randomized complete block design. Overall, there were four rooms with 32 pens (16 barrow pens and 16 gilt pens) per room, for a total of 128 pens (64 pens per treatment) using 3,263 pigs. Pigs, feed provisions, and remaining feed in the feeders were weighed on the last day of each phase. Pen feeder weight and dead or removed pigs were recorded, and pig days per pen were used to adjust ADG, ADFI, and G:F calculations per pen. Pig removals included the number of dead pigs or pigs removed due to failure to thrive or other welfare reasons such as lameness and are reported as a percentage of pigs removed per the original number of pigs placed per pen.
All pens were visually assessed and given a fecal score every day of the experiment. Fecal consistency was recorded by trained technicians using the 5-score system described in Experiment 2. The sum of the daily fecal score per pen was divided by the number of phase days to calculate an average fecal score per treatment. The frequency of diarrhea within phase was calculated per pen as the percentage of the pen days with a fecal score > 2. The number of individual pig medications was also recorded per pen and summed to calculate an average number of medications administered per treatment over the entire study.
Growth performance data by single and cumulative phases, using pen average values as the experimental unit, were analyzed using a mixed model to test the fixed effects of dietary treatment, sex, and their interaction, with block (defined by room) as a random effect (PROC MIXED; SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA; SAS Proprietary Software 9.4). There were no significant treatment-by-sex interactions (P > 0.10) for performance data; therefore, the interaction of treatment and sex was removed from the final model. Fecal score data within phase were analyzed using a mixed model to test the effects of treatment, day, and the interaction of treatment and day, with day as the repeated measure and block and replication as random effects (PROC MIXED; SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA; SAS Proprietary Software 9.4). There were no significant (P > 0.10) treatment-by-day interactions for fecal score variables. Results for growth performance, fecal score variables, and mortality/removal rate (Table 7) are reported as least squares means with the pooled SEM from 64 pens per treatment. Treatment differences were assessed using Tukey–Kramer-adjusted P-values. Statistical significance for treatments was set at P < 0.05, and trends with P-values between 0.05 and 0.10 are discussed. Probability values from the F-test were reported for growth performance data, while chi-square probability values were reported for percentage variables such as pig removal or diarrhea incidence.
Results and discussion
FXP analyzed composition: The FXP product contained 57.60% crude protein, 18.95% crude fat, 2.79% ash, and had a pH of 6.36, indicating that the blended product was primarily based on whey protein. The ash content of FXP was similar to that of whey protein concentrate (Stein, 2025), and the amino acid profile of FXP was more consistent with that of whey protein relative to dried skim milk and casein. Whey protein has a greater concentration of threonine, isoleucine, and aspartic acid but contains less glutamic acid as a percentage of the crude protein than dried skim milk and casein (INRAE-CIRAD-AFZ, 2025; Stein, 2025). The bovine IgG (2.46%) results indicate that the FXP blended product is derived primarily from mature milk ingredients because colostrum contains much more IgG than mature milk (Hurley and Theil, 2011). The bovine IgA (1.83%) and lactoferrin (0.43%) results were within the range expected for mature milk and/or whey protein (Gapper et al., 2007; Cheng et al., 2008; Le et al., 2010).
Experiment 1:
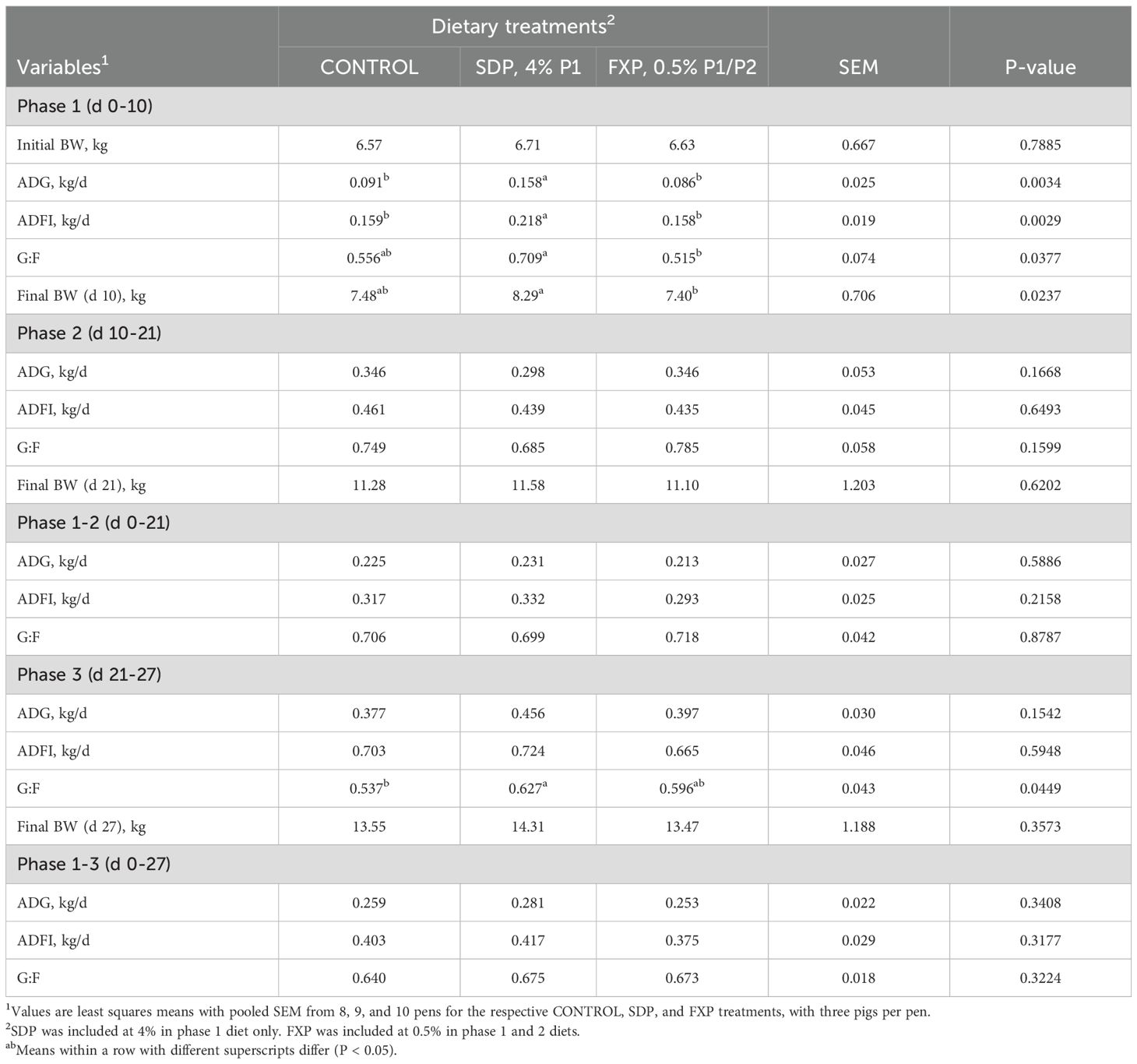
Results: During phase 1 (d 0–10), pigs fed phase 1 diets with SDP had greater ADG and ADFI compared with pigs fed CONTROL or FXP phase 1 diets (P < 0.05). The G:F and BW at day 10 were greater (P < 0.05) for pigs fed SDP versus FXP. There were no differences in growth performance variables between CONTROL and FXP treatments during phase 1.
After SDP was no longer included in the feed during phase 2 (d 10–21), and for the cumulative performance of phases 1 and 2 (d 0–21), there were no differences among treatments for growth performance variables.
During phase 3 (d 21–27), pigs previously fed SDP had greater (P < 0.05) G:F than pigs fed the CONTROL diets. The phase 3 G:F for pigs previously fed FXP did not differ from CONTROL or SDP treatments. Overall cumulative results of phases 1–3 (d 0–27) did not indicate differences in performance among treatments.
Discussion: Experiment 1 was an initial study to determine the effects of FXP on pig growth performance relative to a CONTROL feeding regimen without or with 4.0% SDP in the phase 1 diet as a functional protein source. FXP was included at 0.5% in the phase 1 and 2 diets, following supplier recommendations. The phase 1 results were as expected for the SDP treatment, as two separate reviews of multiple published studies consistently show that weaned pigs fed diets with SDP, compared to other specialty protein sources (including milk-based ingredients), have greater ADG and ADFI during the post-weaning phase (Torrallardona, 2010; Balan et al., 2021). The improvement in growth performance for pigs fed diets with SDP is associated with the inherent functional protein composition in SDP, which includes immunoglobulins, transferrin, albumen, bioactive peptides, complementary proteins, and others that can support improved digestive and immune functions during periods of stress (Weaver et al., 2014; Pérez-Bosque et al., 2016; Kazimierska and Biel, 2023). Bovine whey protein from either colostrum or mature milk has 293 proteins, with 217 proteins common to both, whereas colostrum and mature milk have 36 and 40 unique proteins, respectively (Le et al., 2010). Although the performance of pigs fed diets with 0.5% FXP did not differ from the CONTROL, this product contained functional milk proteins, including IgG, IgA, and lactoferrin. The lack of a performance response to 0.5% FXP in Experiment 1 compared with the CONTROL diet contrasts with the reported improved performance of pigs fed diets with 0.3% FXP (Cemin et al., 2020), 0.5% novel whey protein concentrate (Horn et al., 2022), or 0.6% FXP (Spencer et al., 2025). In the experiment by Cemin et al. (2020), 0.3% FXP was included in corn, soybean meal, and whey permeate-based diets with 3,000 mg·kg-1 added zinc and fed for 23 days, resulting in improved ADG and ADFI that was maintained after feeding a common corn–soybean meal-based phase 3 diet to the end of the 48-day experiment. In Experiment 1, there was a numerical improvement in G:F during phase 3 for the FXP versus the CONTROL treatment, indicating a potential feed efficiency benefit from using 0.5% FXP in the phase 1 and 2 diets. However, pigs were available for only 6 days during phase 3, so a longer phase 3 duration may be needed to confirm these results. Overall, including 0.5% FXP in the phase 1 and 2 diets did not benefit pig growth performance to the extent of 4% SDP used in the phase 1 diet and did not differ from the CONTROL treatment.
Experiment 2:
Results: During phase 1 (d 0–11), ADG, ADFI, and BW at day 11 were greater (P < 0.01) for pigs fed the SDP phase 1 diet compared with the CONTROL or FXP groups. The G:F tended (P = 0.0527) to be greater for pigs fed the phase 1 SDP diet compared with the FXP treatment. There were no significant differences in growth performance between the CONTROL and FXP groups.
Average fecal score and incidence of mild diarrhea (days with a fecal score of 3) did not differ among treatments. No pens received a fecal score > 3 on any day fecal scores were recorded during the study.
In phase 2 (d 11–21), after SDP was no longer included in the diet, there was a tendency (P = 0.0851) for pigs fed SDP during phase 1 to have lower G:F compared with pigs fed FXP. Other growth performance variables, mortality, and fecal score variables did not differ among treatments.
For the cumulative results through the end of phase 2 (d 0–21), the percentage of mortality was greater (P < 0.05) for the FXP treatment compared with the CONTROL and SDP treatments. The ADFI for pigs fed diets with SDP during phase 1 tended (P = 0.0806) to be greater compared with the CONTROL group, but there were no differences in ADFI between FXP and the other treatments. The average fecal score was lower (P < 0.05) for pigs fed SDP than for CONTROL, whereas the average fecal score of pigs fed the FXP diet was not different from the other treatments. Diarrhea incidence was not different among treatments.
During phase 3 (d 21–42), when all pigs were fed the CONTROL phase 3 diet, pigs fed SDP had reduced (P < 0.05) G:F compared with pigs fed the CONTROL diet in phase 1, whereas the G:F for pigs fed FXP was not different from the other treatments.
For the cumulative results (d 0–42), G:F tended (P = 0.0549) to be greater for the CONTROL than for the SDP treatment, whereas FXP was not different from the other treatments. Percentage mortality tended (P = 0.0703) to be greater for FXP compared with CONTROL, whereas mortality for pigs fed SDP was not different from the other treatments.
Discussion: The improved growth and feed intake for pigs fed the phase 1 SDP diet agree with other studies comparing SDP to soy protein-based ingredients (Torrallardona, 2010; Deng et al., 2023; Bailey et al., 2024), or to other specialty soy products or low inclusion dietary levels of activated porcine plasma or hyperimmunized egg products (Crenshaw et al., 2017). Results from Experiments 1 and 2 did not confirm the improvements in growth performance, reduced diarrhea incidence, or improved survival reported by others using 0.3% to 0.6% FXP in nursery diets (Cemin et al., 2020; Horn et al., 2022; Spencer et al., 2025).
In the experiment by Horn et al. (2022), pigs were fed diets without or with 0.5% novel whey protein concentrate product (assumed to be FXP) and were subjected to a 24-h deprivation of feed and water on day 3 postweaning to induce intestinal stress. The authors reported a tendency for improved ADG and a significant reduction in diarrhea, along with an increased villus height-to-crypt depth ratio, for pigs fed 0.5% novel whey protein concentrate for 21 days.
Specifically related to common whey protein concentrates, overall growth performance of weaned pigs fed diets with whey protein concentrate (73% crude protein) replacing 2.5 or 5.0% SDP in diets on an equal protein basis—or at variable replacement ratios of whey protein concentrate to SDP—was similar, although pigs fed SDP had improved growth performance, particularly during week 1 of the experiment (Grinstead et al., 2000). However, Gottlob et al. (2007) reported that weaned pigs fed diets with 5% whey protein concentrate (80% crude protein) sourced from 5 different suppliers varied in growth performance relative to SDP, with some whey protein concentrate sources having similar or reduced growth performance compared with pigs fed a diet containing 5% SDP.
Assuming that FXP is primarily derived from whey protein concentrate, greater inclusion levels of FXP should be used to potentially provide similar performance to that of pigs fed diets with SDP.
Results from Experiments 1 and 2 did not support the hypothesis that inclusion of 0.5% or 1.0% FXP in phase 1 and 2 diets would impact growth performance or diarrhea scores.
Experiment 3:
Results: There were no treatment effects on growth performance or fecal score variables during any phase of Experiment 3. The percentage of pig removals was greater (P = 0.0187) for the FXP treatment during phase 3 than for the CONTROL treatment.
Discussion: Spencer et al. (2025) reported increased BW and reduced mortality in pigs fed a diet with 0.6% FXP during a natural outbreak of severe diarrhea associated with rotavirus A, F18 E. coli, S. enterica, and S. suis. The authors had originally designed a controlled F-18 E. coli challenge experiment with 8 pens of 4 pigs per pen, each fed either a control diet or a 0.6% FXP diet, with all pigs housed in the same room on raised decks. However, due to a natural outbreak of rotavirus on day 5 after weaning, the original F18 E. coli challenge was canceled, but the authors continued the experiment and collected blood and fecal swab samples and recorded mortality and body weights of pigs to day 23 of the experiment. Pigs fed FXP had greater BW throughout the experiment and reduced mortality until day 14 (4% versus 38%, P = 0.07), but by day 23, mortality was not different between treatments (43% versus 50%, P = 0.11). Serum haptoglobin and total coliforms from fecal swabs collected on days 14 and 23 were lower or tended to be lower for pigs fed FXP, and the villus height-to-crypt depth ratio tended to be greater on day 23 for pigs fed FXP. The authors suggested that 0.6% FXP in diets reduced the severity of a complex disease event by improving survivability, growth performance, and gut health.
Under controlled experimental conditions evaluating SDP functionality, Corl et al. (2007) conducted an intragastric rotavirus challenge on day 5 of age in neonatal pigs fed liquid diets without or with 15% SDP replacing soy protein isolate. Control pigs from both treatments were given an intragastric dose of saline on day 5 of age. On day 3 post-infection, infected pigs fed SDP had no diarrhea and ADG that was not different from non-infected pigs, whereas infected pigs fed soy protein isolate had reduced ADG and severe diarrhea, although fecal swab excretion of rotavirus was not different between challenged treatments through day 13 post-infection. The authors concluded that dietary SDP had the potential to improve the health of diarrheic neonates. More recently, Yan et al. (2024) conducted a rotavirus challenge experiment using weaned pigs fed diets with either 6% soy protein isolate or 6% SDP for 14 days. Pigs were then challenged with rotavirus on day 15, while one group of pigs fed soy protein isolate was not challenged, to evaluate the protection conferred by SDP against gastroenteritis during the progression of rotavirus infection. This included the manifestation stage (days 15–18) and the convalescence stage (days 19–21). Before infection on day 15 (normal stage), pigs fed SDP had greater ADG, more M1 macrophages, and increased CD4+ T cells in blood and different organs (intestinal mucosa, Peyer’s patches, spleen) without increases in proinflammatory serum or mucosal cytokines. During the manifestation stage on day 18, infected pigs fed SDP had enhanced mucosal immunity with increased M1 macrophages, M1/M2 ratio and mucosa cytokines with greater intraepithelial CD8+ T cells for rotavirus clearance. During the convalescence stage on day 21, M2 macrophage polarization with reduced proinflammatory cytokines was promoted in the SDP group to facilitate tissue repair and reduce chronic inflammation. Results from these rotavirus challenge experiments using neonatal or weaned pigs indicate that dietary SDP has potential as a therapeutic approach for infectious gastroenteritis by enhancing mucosal immunity that promotes viral clearance while maintaining immune homeostasis to prevent chronic inflammation.
Although the other studies using 0.3% to 0.6% FXP in experimental diets reported some performance and intestinal health benefits, details about the nutrient composition and bioactive properties of FXP and the complete ingredient and nutrient composition of experimental diets were not provided. Horn et al. (2022) noted that the novel whey protein concentrate product had high concentrations of dairy-derived bioactive proteins, like those commonly found in colostrum. Our analysis of FXP showed relatively low percentages of IgG (2.46%), IgA (1.83%), and lactoferrin (0.43%); however, we did not analyze FXP for any other bioactive milk proteins. Our experiments used diets with pharmaceutical levels of zinc, and Experiment 3 diets also included antibiotics, yet there were no performance benefits from using 0.5% to 1% FXP in the diets. Cemin et al. (2020) mentioned that the diets used in their experiment contained corn, soybean meal, and whey permeate with added pharmaceutical levels of zinc, and they reported benefits on growth performance with 0.3% FXP in the diet. There may be other factors affecting the discrepancy between our results and those of others, including differences in the use of feed additives or antimicrobials in diets, pig disease status, environmental stressors, and pig genetics, but such details from the other studies were not provided. Therefore, the reasons for the conflicting results of our studies with FXP in phase 1 and 2 diets, compared with results from others, remain unknown. Based on the results reported by Spencer et al. (2025), future studies using higher doses or longer feeding durations of FXP—compared to SDP or in combination with SDP—under controlled conditions of experimental pathogen challenge may be warranted to develop nutritional strategies that support animal health while reducing reliance on the use of antibiotics and pharmaceutical levels of zinc.
Conclusions: Under the experimental conditions of these three experiments, there were no beneficial effects of using 0.5% or 1.0% FXP in phase 1 or 2 diets on pig growth performance, diarrhea incidence, or survival. In Experiments 1 and 2, using 4% SDP in Phase 1 diets improved pig growth performance during the early phases of the post-weaning period, while FXP did not elicit a similar response.
Data availability statement
Data from these experiments were funded by APC LLC a private company and are not available for general public use. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to am9lLmNyZW5zaGF3QGFwY3Byb3RlaW5zLmNvbQ==.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by University of Illinois Animal Care and Use Committee and North Carolina State University Animal Care and Use Committee. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. APC LLC, Ankeny, IA, USA provided funds to Institutions that conducted the experiments and paid the publishing fee for the manuscript. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication.
Conflict of interest
Authors YS, JP and JC are employees of the Research and Development Department at APC LLC, Ankeny, IA, USA.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
AOAC (2019). Official methods of AOAC International: 21st edition 2019 (Rockville, MD, USA: AOAC Int.).
Bailey H. M., Fanelli N. S., Campbell J. M., and Stein H. H. (2024). Addition of spray-dried plasma in phase 2 diets for weanling pigs improves growth performance, reduces diarrhea incidence, and decreases mucosal pro-inflammatory cytokines. Animals 14, 2210. doi: 10.3390/ani14152210
Balan P., Staincliffe M., and Moughan P. J. (2021). Effects of spray-dried animal plasma on the growth performance of weaned piglets-A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 105, 699–714. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13435
Cemin H. S., Swalla L. A., Pietig J. L., Hansen S. A., Hansen E. L., Ratliff B. W., et al. (2020). Effects of a functional protein on growth performance of nursery pigs.” Abstract (PSIV-16) in. J. Anim. Sci. 98 (Supp1. 3), 178–179. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa054.316
Cheng J. B., Wang J. Q., Bu D. P., Liu G. L., Zhang C. G., Wei H. Y., et al. (2008). Factors affecting the lactoferrin concentration in bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 91, 970–976. doi: 10.3168/jds.2007-0689
Corl B. A., Harrell R. J., Moon H. K., Phillips O., Weaver E. M., Campbell J. M., et al. (2007). Effect of animal plasma proteins on intestinal damage and recovery of neonatal pigs infected with rotavirus. J. Nutr. Biochem. 18, 778–784. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2006.12.011
Crenshaw J. D., Campbell J. M., Polo J., and Stein H. H. (2017). Effects of specialty proteins as alternatives to bovine or porcine spray-dried plasma in non-medicated diets fed to weaned pigs housed in an unsanitary environment. Transl. Anim. Sci. 1, 333–342. doi: 10.2527/tas2017.0040
Deng Z., Duarte M. E., Kim S. Y., Hwang Y., and Kim S. W. (2023). Comparative effects of soy protein concentrate, enzyme-treated soybean meal, and fermented soybean meal replacing animal protein supplements in feeds on growth performance and intestinal health of nursery pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotech. 14, 89. doi: 10.1186/s40104-023-00888-3
Gapper L. W., Copestake D. E. J., Otter D. E., and Indyk D. E. (2007). Analysis of bovine immunoglobulin G in milk, colostrum and dietary supplements: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 389, 93–109. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1391-z
Gottlob R. O., DeRouchey J. M., Tokach M. D., Nelssen J. L., Goodband R. D., and Dritz S. S. (2007). Comparison of whey protein concentrate and spray-dried plasma protein in diets for weanling pigs. Prof. Anim. Scientist. 23, 116–122. Available online at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1080744615309517 (Accessed May 5, 2025).
Grinstead G. S., Goodband R. D., Dritz S. S., Tokach M. D., Nelssen J. L., Woodworth J. C., et al. (2000). Effects of a whey protein product and spray-dried animal plasma on growth performance of weanling pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 78, 647–657. doi: 10.2527/2000.783647x
Horn N., Ajuwon K., Li E., Gaines A., and Goodwin J. (2022). “Novel whey protein concentrate improves nursery pig growth and intestinal morphology,” in Proceedings of 2022 Digestive Physiology of Pigs Conference. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, Vol. 13. 167. Available online at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/animal-science-proceedings/vol/13/issue/2 (Accessed May 12, 2025).
Hurley W. L. and Theil P. K. (2011). Review: Perspectives on immunoglobulins in colostrum and milk. Nutrients 3, 422–474. doi: 10.3390/nu3040442.
INRAE-CIRAD-AFZ (2025). Feed Tables. Available online at: https://www.feedtables.com/ (Accessed April 2, 2025).
Kazimierska K. and Biel W. (2023). Chemical composition and functional properties of spray-dried animal plasma and its contributions to livestock and pet health: A review. Animals 13, 2484. doi: 10.3390/ani13152484
Le A., Barton D., Sanders J. T., and Zhang Q. (2010). Exploration of bovine milk proteome in colostral and mature whey using an ion-exchange approach. J. Proteome Res. 10, 692–704. doi: 10.1021/pr100884z
Pérez-Bosque A., Polo J., and Torrallardona D. (2016). Spray dried plasma as an alternative to antibiotic in piglet feeds, mode of action and biosafety. Porcine Health Manag. 2, 16. doi: 10.1186/s40813-016-0034-1
Spencer J. D., Puls C. L., McCallum M., Gaines A., and Horn N. (2025). “A milk-based bioactive (FXP®) mitigates a severe and natural enteric disease challenge,” in Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the American Association of Swine Veterinarians, March 1-4, (Perry, Iowa, USA, San Francisco, CA: American Association of Swine Veterinarian), 320–321. Poster 68. doi: 10.54846/am2025/142
Stein H. H. (2025). Feed Ingredient Database (Champaign-Urbana, IL: Animal Science Department, University of Illinois). Available online at: https://nutrition.ansci.illinois.edu/static/feed_database.html.
Torrallardona D. (2010). Spray dried animal plasma as an alternative to antibiotics in weanling pigs – A review. Asian Aust. J. Anim. Sci. 23, 131–148. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2010.70630
Weaver A. C., Campbell J. M., Crenshaw J. D., Polo J., and Kim S. W. (2014). Efficacy of dietary spray dried plasma protein to mitigate the negative effects on performance of pigs fed diets with corn naturally contaminated with multiple mycotoxins. J. Anim. Sci. 92, 3878–3886. doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-6939
Keywords: weaned pigs, milk protein, spray-dried plasma, diarrhea score, pig survival
Citation: Shen Y, Kim SW, Stein HH, Polo J and Crenshaw J (2025) Novel milk ingredient blend in nursery pig diets did not improve growth performance and survival compared to control diets without or with spray-dried plasma. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1648283. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1648283
Received: 17 June 2025; Accepted: 17 July 2025;
Published: 18 August 2025.
Edited by:
Anusorn Cherdthong, Khon Kaen University, ThailandReviewed by:
Ravikanthreddy Poonooru, University of Missouri, United StatesGabriela Miotto Galli, Federal University of Rio Grande, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Kim, Stein, Polo and Crenshaw. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Joe Crenshaw, am9lLmNyZW5zaGF3QGFwY3Byb3RlaW5zLmNvbQ==
 Yanbin Shen
Yanbin Shen Sung Woo Kim
Sung Woo Kim Hans H. Stein
Hans H. Stein Javier Polo
Javier Polo Joe Crenshaw
Joe Crenshaw