- 1Environment and Life Sciences Research Centre, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Safat, Kuwait
- 2Department of Animal Production, College of Agriculture, Al-Muthanna University, Al-Muthanna, Iraq
- 3Department of Animal Production, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Anbar, Anbar, Iraq
- 4Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Suez Canal University, Ismailia, Egypt
- 5Animal Production Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Al-Azhar University, Assiut Branch, Assiut, Egypt
Introduction: Due to the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties of betaine, it may serve as a beneficial feed supplement for laying hens. This research aimed to evaluate whether betaine enhances the productive, reproductive, and intestinal health of layer hens.
Methods: A total of 240 laying hens, aged 60 weeks, were divided into four treatment groups, each consisting of 60 hens. Each group was further divided into four replicates of 15 hens each. The first group, designated as the control (CTRL), received only the basal diet. The other treatment groups received the basal diet supplemented with betaine at levels of 0.3, 0.6, and 1.2 g/kg. The experiment was conducted over 24 weeks.
Results: The results indicated that the addition of betaine improved the growth performance traits of Fayoumi laying hens. Specifically, the inclusion of 0.6 g of betaine per kilogram of feed led to increased fertility (p ≤ 0.05) and hatchability rates. In addition, betaine treatment significantly enhanced (p ≤ 0.05) both the absolute and relative carcass weights while reducing abdominal fat. Moreover, a betaine level of 1.2 g/kg improved the lipid profile by lowering the serum levels of total lipids, cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL). This level also significantly (p ≤ 0.05) increased the counts of beneficial bacteria, including the total bacterial count (TBC) and Lactobacillus, in the cecum while reducing the count of pathogenic bacteria.
Discussion: Overall, dietary treatments with betaine, particularly at levels of 0.6 and 1.2 g/kg, could enhance the performance, carcass traits, blood indices, and cecal bacterial populations of Fayoumi laying hens.
1 Introduction
Feed additives are essential for the poultry sector, providing a significant amount of animal protein. Feeding constitutes roughly 60%–70% of the expenses associated with poultry rearing. Therefore, effective feed usage is critical (Elsherbeni et al., 2024a; Elsherbeni et al., 2024b; Kamal et al., 2025; Saeed et al., 2025). In addition, antibiotics are no longer permitted as growth enhancers in poultry production due to their long-term use resulting in the emergence of bacterial resistance and the buildup of antibiotic residues in poultry products such as eggs and meat (Al-Khalaifa et al., 2019; Al-Khalaifah et al., 2020; Abd El-Hack et al., 2023). To improve the immunity and productivity of birds and farm animals, organic nutritional supplements have recently supplanted synthetic growth enhancers and antibiotics to augment the growth efficiency and enhance the carcass characteristics (Kamal et al., 2023; El-Ratel et al., 2024; Ali et al., 2025).
Betaine (Bet), a trimethylglycine derivative, is vital in the diet of birds and is used by plants and animals for the production of methionine, carnitine, and creatine (Arif et al., 2022; Elmahdy et al., 2025). Bet is associated with several biological processes, including immunology, fat distribution, methionine and choline sparing, and osmo-protection (Attia et al., 2019; Arumugam et al., 2021). It is a safe and effective feed additive commonly used in poultry as it promotes growth, reduces inflammation, and protects against oxidative stress (Shakeri et al., 2018). It is an important component of improving performance and stress tolerance (Yang et al., 2025). Bet is crucial for improving poultry performance by protecting the intestinal cell proteins and enzymes, preventing dehydration, promoting water retention, and lowering the body temperature in heat-stressed hens (Lan and Kim, 2018; Al-Qaisi et al., 2023). In addition, Liu et al (2019) found that the addition of Bet at levels of 0.50, 1.0, and 2.0 g/kg into broiler diet reduced the negative impact of heat stress on the feed intake and body weight. Bet has been shown to reduce fat; moreover, it has antioxidants, anti-coccidiosis, and anti-stress properties (Ahmed et al., 2018; Abd El-Ghany and Babazadeh, 2022). Moreover, it enhances the carcass yields and muscle protein deposition in broilers (Chen et al., 2022). The addition of Bet into the feed led to increased weight gain (WG), final body weight (FBW), and feed intake (FI) (Al-Sagan et al., 2021; De Prekel et al., 2024). According to Park and Kim (2019), the addition of Bet into diets with enough methyl group donors increased the feed efficiency and WG by approximately 3%–15%.
Dual-purpose hens (both meat and egg production) raised under prolonged heat stress and supplemented with 200 mg vitamin C and 1,000 mg Bet/kg diet showed improved egg-laying rates, albumen weight, yolk weight, and Haugh unit (HU), and this supplementation also helped birds tolerate heat stress (Attia et al., 2016). Hao et al (2017) reported that the health, laying performance, and egg production of layer chickens under heat stress improved after the addition of 400 mg Bet/kg diet. In quail, Ratriyanto et al (2017) suggested that the addition of Bet (at levels of 0.06%–0.12%) into quail layer diets increased the egg weight and egg yolk weight in birds raised in tropical environments. A previous study by Zaki et al (2023) found that Bet supplementation positively impacted the immune response, egg quality assessment, and productive performance of Bovans Brown laying hens. Beneficial bacteria in poultry improve the health of host birds by competing with pathogenic bacteria and fostering the gut microbiota. Bet, despite its insufficient direct antibacterial impact, may prevent intestinal rupture, diarrhea, and dehydration; improve gut health; and enhance poultry resistance to Clostridium infections (Mohamed et al., 2024).
The growth-promoting and stress-relieving properties of Bet have been extensively studied, especially in broilers; however, its effects on laying hens—particularly during the later stages of production, when the physiological functions and egg quality regularly deteriorate—are not well understood. The late-laying stage is characterized by a reduced feed efficiency, a worse reproductive performance, and a compromised intestinal integrity. After 60 weeks of age, the laying rate and egg quality traits of laying hens—particularly the eggshell quality—decline (Molnár et al., 2016; Alfonso-Carrillo et al., 2021). Therefore, maintaining economic efficiency in egg production relies on identifying effective nutritional strategies to sustain the productivity and health at this stage. Due to the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties of Bet, it might represent a useful feed supplement for old-age layers. Further research is needed to fully comprehend the influence of Bet on the late-laying egg production period and egg quality (Guo et al., 2023). Thus, our study hypothesizes that Bet can serve as an effective dietary additive, promoting growth and health outcomes. Thus, the goal of this research was to determine whether this natural additive can enhance the productive, reproductive, and intestinal health of old-age layer hens.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Ethical approval
The present investigation was conducted on an Alnajem Poultry Farm, located at 28°36′57.3′′ N, 48°05′26.1′′ E, Al Wafra City, Kuwait, under the supervision of the Environment and Life Sciences Research Center, Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, Kuwait. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research Ethics Committee assessed and approved all experimental protocols at the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research. The approvals ensured that all research activities complied with ethical standards for the treatment and utilization of animals in studies.
2.2 Birds and management
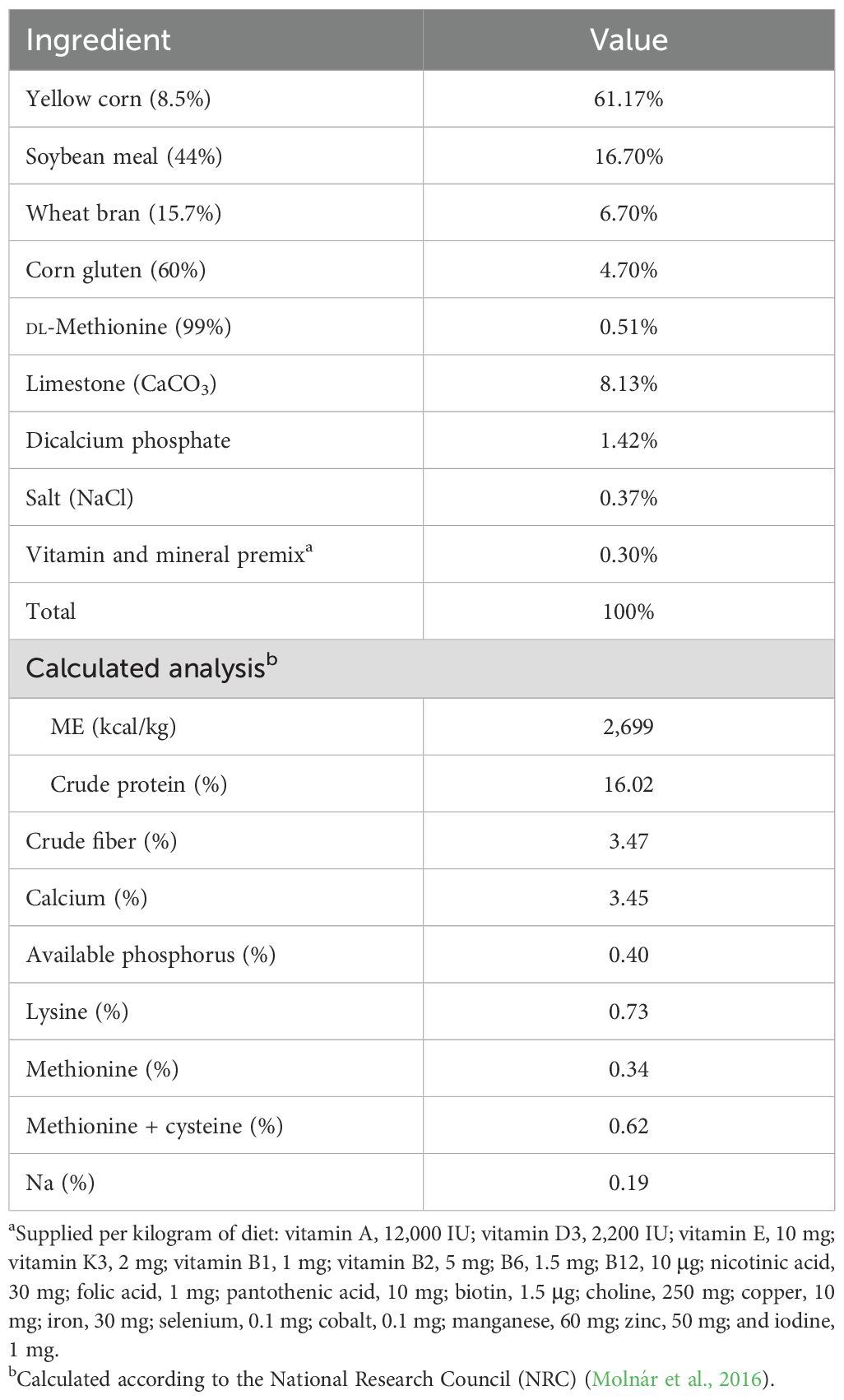
A total of 240 laying hens, aged 60 weeks, were divided into four treatment groups, each consisting of 60 hens. Each group was further divided into four replicates of 15 hens each in a completely random design. The average body weight and daily egg production of each group were approximately similar. The birds were housed in identical controlled sanitary and climatic conditions and were provided unlimited access to a basal layer diet (Table 1), which was created based on the suggested requirements of the National Research Council (NRC) (National Research Council, 1994). The duration of daylight during the trial period was set to 16 h each day. All birds were housed in floor-laying shelters measuring 3 m × 2 m. The experiment was conducted from 60 to 84 weeks, encompassing 24 weeks of egg production.
2.3 Experimental design
The Bet (synthetic betaine hydrochloride) used in the current study was obtained from Shandong Ruihong Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Dezhou, China) and contains ≥98% Bet. To guarantee homogeneity, Bet (in a powder form) was completely premixed with a small amount of the basal diet (in a mashed form) and then blended into the full feed batch for 30 min using a mechanical mixer. An experiment was conducted utilizing four different dietary Bet concentrations (0, 0.3, 0.6, and 1.2 g/kg diet). The first group (control, CTRL) consumed only the basal diet. The remaining three experimental groups consumed the basal diet with the addition of Bet at a concentration of 0.3, 0.6, or 1.2 g/kg.
2.4 Productive performance
We weighed each hen to the nearest gram at the start of the trial and monthly thereafter. Furthermore, the diet of each experimental replicate was weighed daily, and then the average FI/hen was determined by collecting and weighing the leftover diet. The FI was recorded. Moreover, the feed conversion ratio (FCR) was calculated according to the following equation:
2.5 Laying performance
For each replicate, the eggs were physically retrieved twice a day during the study period. The number of eggs (EN) and the weight of the eggs (EW) were both noted down to the nearest gram. To determine the egg mass (EM) for each replicate in each experimental group, we multiplied the total EN laid by the average EW during the experiment. We also used the following formula to calculate the monthly laying rate (LR) for each replicate:
Monthly, a total number of 20 fresh eggs were taken from each replicate (80 eggs/treatment) over three consecutive days for incubation. Before incubation, each egg was labeled and kept at 18°C with 70% relative humidity. The eggs were automatically rotated every 2 h during incubation at the standard settings of 37.8°C and 55%–60% relative humidity. The eggs were candled on day 7 of incubation to detect infertile eggs, which were then noted and removed. At the end of the incubation period, the total number of hatched chicks was recorded. The methods outlined by Attia et al (2019) and El-Ratel et al (2024) were employed for the incubation process, as well as the fertility (in percent) and hatchability (in percent) calculations. The fertility and hatchability were calculated as follows:
2.6 Egg quality traits
For each month of the experiment, eight fresh eggs per treatment were randomly chosen, weighed to the nearest gram, and separated. A digital caliper was used to measure the length, width, yolk height, diameter, and albumen height of the egg. The weights of the yolk and the shell were measured using a highly precise scale with a sensitivity of 0.01 g. The thickness of the shell, including the membranes, was measured using a micrometer to the nearest 0.01 mm. The egg shape index was determined by dividing the width of the egg by its length (Anderson et al., 2004). In addition, the yolk index was calculated by division of the yolk height by the diameter multiplied by 100 (Kondaiah et al., 1983). The egg HU was determined using the formula proposed by Moula et al (Moula et al., 2013).
2.7 Carcass and blood biochemical parameters
At the end of the experiment (84 weeks), two chickens from each treatment group were randomly selected to measure the carcass traits. Hens were weighed separately, kept without food overnight (but with free access to water), and then slaughtered by hand to determine how much the carcass and edible components weighed. Blood samples were taken from two hens per replication (the same birds used to examine the carcass traits) and were placed into tubes that did not have heparin. Subsequently, at 4°C and 5,000 rpm, the samples were spun in a centrifuge to obtain the serum. This was maintained at −20°C until analysis. The serum was assessed utilizing commercially available assays. The alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activities were measured, along with the total protein (TP), albumin (Alb), globulin (gl), total lipid (TL), cholesterol (Cho), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels.
2.8 Microbiological analysis
After carcass evaluation, 10 g of each bird’s cecum was collected, mixed with sterilized peptone water (90 ml), and then stirred for 30 min. The supernatant was taken, and serial dilutions up to 10−7 were set, as suggested by Abd El-Hack et al (Abd El-Hack et al., 2025). “The TBC, Lactobacilli, E. coli, coliforms, and Salmonella spp.” were counted on the growth media, as described by Abd El-Hack et al (Anderson et al., 2004). Bacterial counts were transformed to logarithm of colony-forming units per gram (log CFU/g) (Sheiha et al., 2020).
2.9 Statistical analysis
Statistical data analysis in the SAS application utilized the general linear model (GLM) technique (SAS Institute, 2004). Duncan’s multiple range test was used to assess distinct differences among the means of several treatments (Duncan, 1995). The study employed the following statistical model:
where Yij is the value of the corresponding variable, μ is the overall mean of the corresponding variable, and Ti is the effect caused by the ith Bet concentration, where i = 1, 2, 3, and 4 (1 = 0, 2 = 0.3, 3 = 0.6, and 4 = 1.2 g Bet/kg diet). ϵij is a random error related to the ijth observation and is presumed to be independently and normally distributed. Significant difference was considered at p ≤ 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Growth efficiency
Table 2 illustrates the impact of Bet supplementation on the live body weight (LBW), FI, and FCR of Fayoumi hens throughout the experimental period. There was a significant (p ≤ 0.05) influence of Bet levels on the FBW and FI only. Bet addition increased the layers’ FBW, especially at the level of 0.6 g/kg diet, followed by 0.3 and 1.2 g/kg diets. Moreover, the FI decreased gradually with increasing Bet levels. Noticeably, the lowest FI values were obtained from layers fed 1.2, 0.6, and 0.3 g Bet/kg diet. Although the FCR was not significantly affected by Bet treatment, the lowest FCRs were obtained from layers fed 0.6 g Bet/kg diet, followed by 1.2 and 0.3 g Bet/kg diets, in comparison to the CTRL group. According to these findings, enhanced growth performance was up to the level of 0.6 g/kg, after which the impact plateaued.
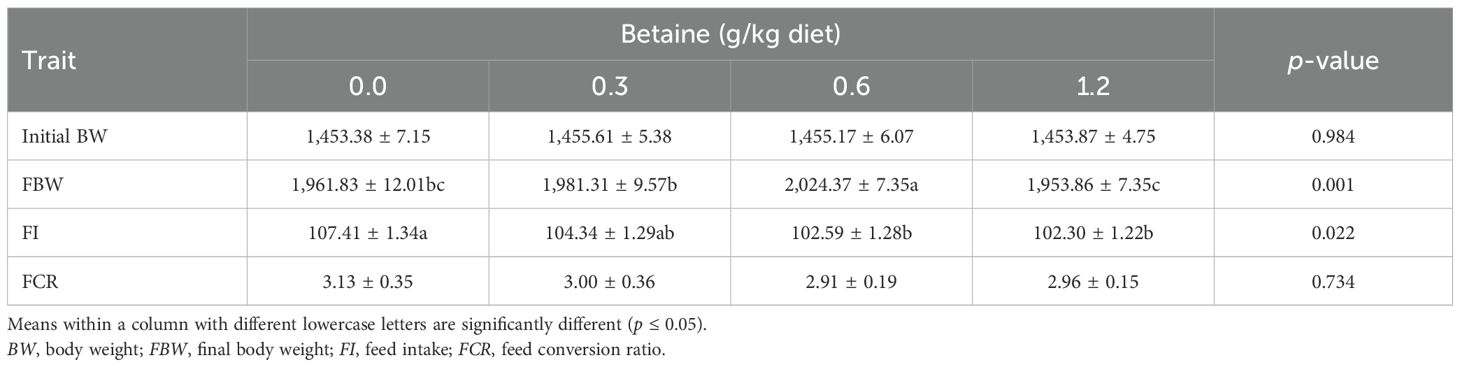
Table 2. Growth performance of Fayoumi laying hens as affected by the addition of different levels of betaine (Bet) (mean ± SE).
3.2 Laying production
The data illustrated in Table 3 display the impact of Bet on the egg production and reproduction parameters. It was apparent that dietary supplementation with Bet meaningfully (p ≤ 0.05) improved the LR, EM, and fertility (in percent), with an insignificant increase in EW and hatchability (in percent). Layers receiving 0.6 g Bet/kg diet achieved the highest rates of these parameters compared with those on other Bet levels and those in the CTRL group. The addition of Bet had no noticeable impact on hatchability or EW. This suggests that, for productive and reproductive efficiency, a modest supplementation level (0.6 g/kg) is ideal.
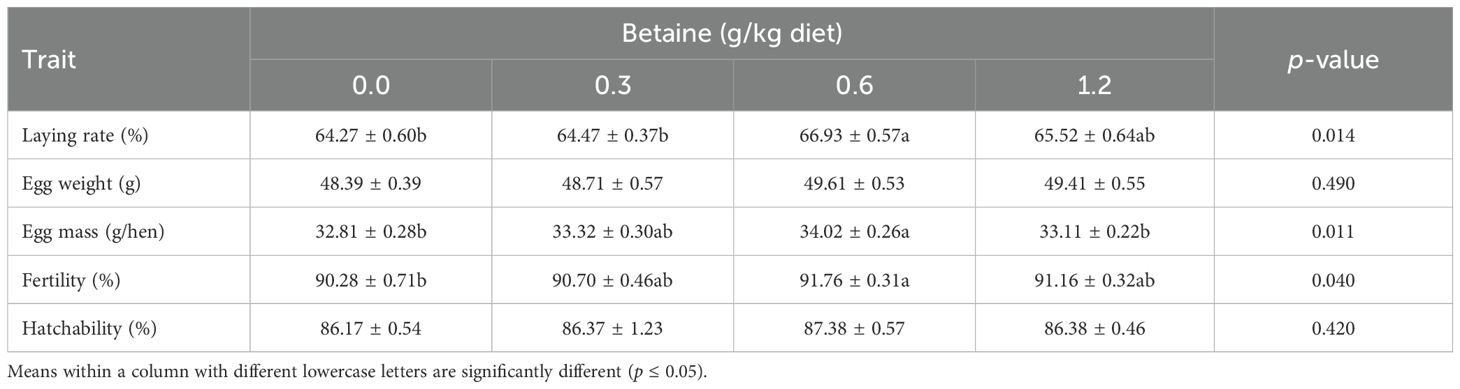
Table 3. Egg production and reproduction parameters of Fayoumi laying hens affected by the addition of different levels of betaine (Bet) (mean ± SE).
3.3 Egg quality
Table 4 shows the influence of Bet addition at different levels into Fayoumi layers’ diet on their egg quality characteristics. There was a substantial increase (p ≤ 0.05) in each egg yolk index and eggshell thickness due to Bet treatment. Compared with the different treatments and the CTRL group, Bet at 0.6 g/kg diet exhibited the highest values for all egg quality traits. The other egg quality traits (e.g., albumen index, shape index, and HU) were not significantly affected by the Bet levels.
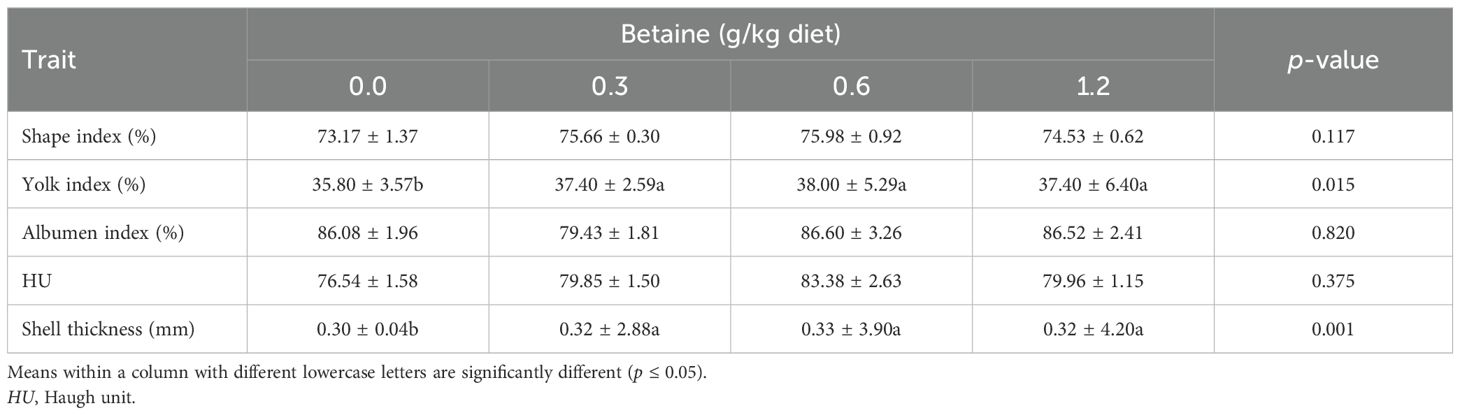
Table 4. Egg quality traits of Fayoumi laying hens affected by the addition of different levels of betaine (Bet) (mean ± SE).
3.4 Carcass traits
The impact of the different Bet levels on the carcass traits of Fayoumi layers is summarized in Table 5. All carcass traits were affected (p ≤ 0.05) by the addition of Bet, except for the absolute and relative weights of giblets. The addition of 0.6 g Bet/kg diet improved all carcass traits when compared with the other Bet levels and the untreated group. Moreover, both the absolute and relative abdominal fat weights were meaningfully (p ≤ 0.05) diminished due to the addition of different levels of Bet, especially at 0.6 g.
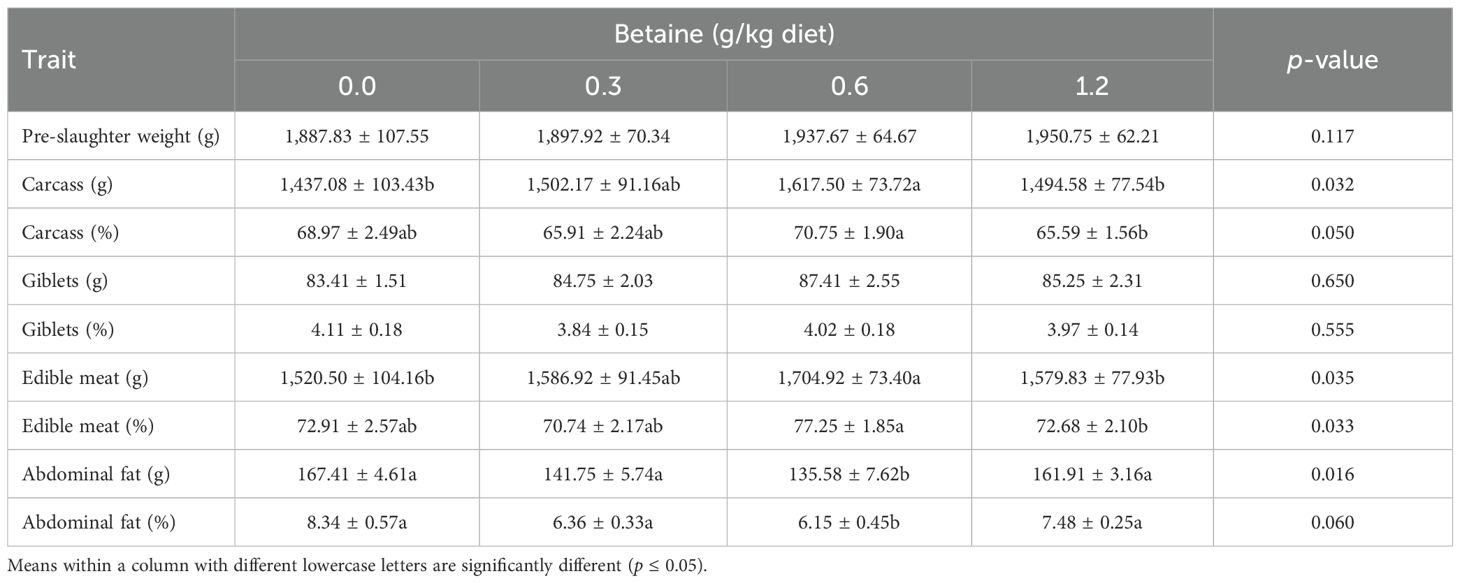
Table 5. Carcass traits of Fayoumi laying hens affected by the addition of different levels of betaine (Bet) (mean ± SE).
3.5 Blood parameters
The blood biochemical indices, as well as the antioxidant enzyme activity, represent the general health and nutritional status of poultry. The data presented in Table 6 indicate the effects of Bet treatment on the different blood indices. Notably, Bet significantly (p ≤ 0.05) affected the LDL and AST levels only. Compared with the other levels of Bet added, 1.2 g/kg exhibited the lowest levels of TLs, Cho, and LDL, while the highest level of HDL was obtained from the addition of 0.3 g/kg Bet. Regarding the liver enzymes, the addition of 0.6 and 1.2 g/kg Bet showed the highest levels of AST and ALT, respectively. The highest values of TP, Alb, gl, as well as the albumin-to-globulin (A/G) ratio, were obtained from the addition of 0.3 g/kg Bet compared with other treatments.
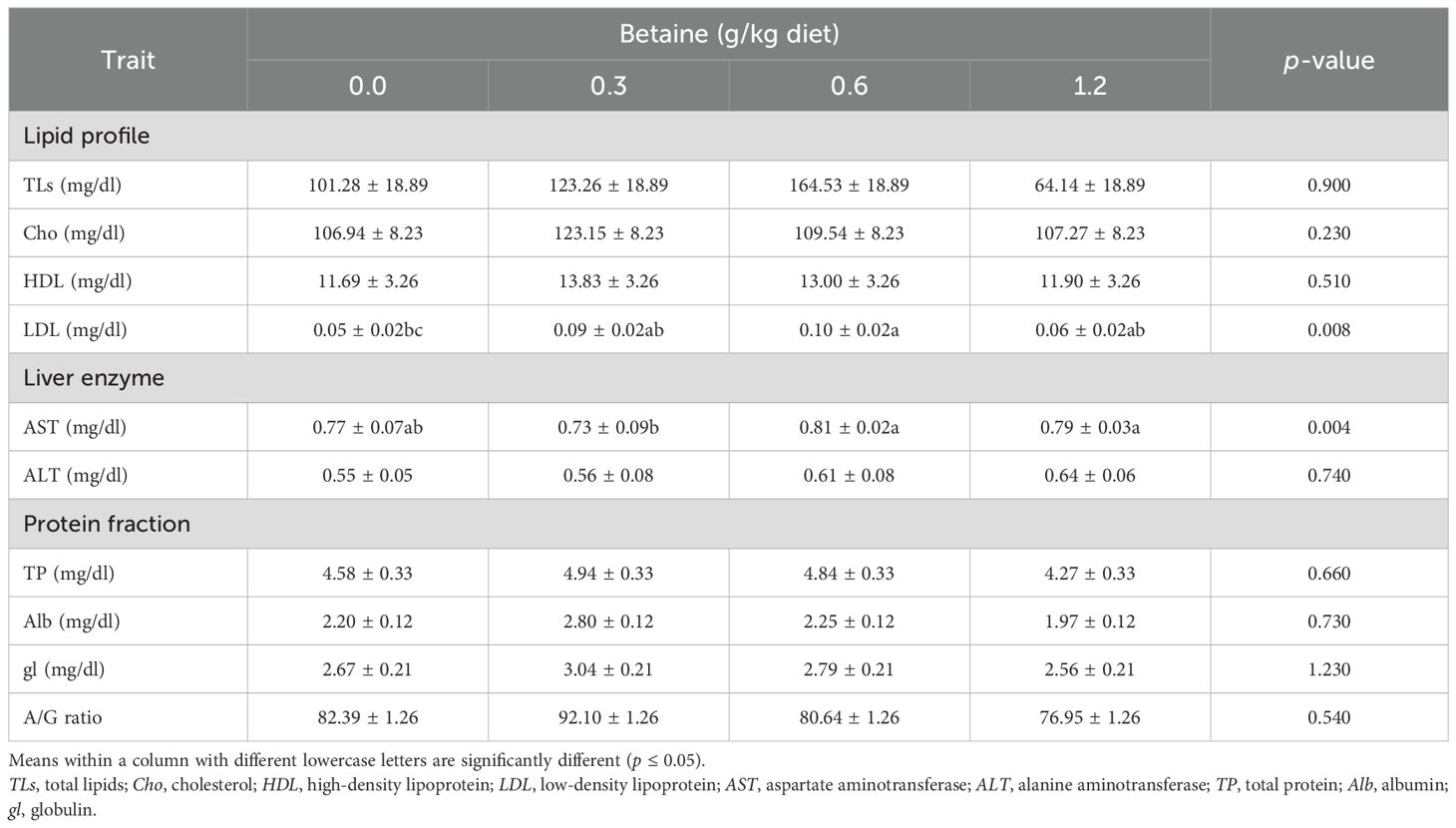
Table 6. Blood parameters of Fayoumi laying hens affected by the addition of different levels of betaine (Bet) (mean ± SE).
3.6 Microbiological analysis
The types of bacterial cultures and specific phytochemicals in the intestines of poultry were found to be significantly correlated, resulting in improved productive performance. The results presented in Figure 1 indicate a significant (p ≤ 0.05) modification of the total bacterial count (TBC) and cecal microflora due to dietary supplementation with different levels of Bet. From the outcomes obtained, it is evident that Bet addition at levels of 0.6 and 1.2 g/kg produced the maximum TBC and Lactobacillus counts. Similarly, the same levels exhibited the lowest count of pathogenic bacteria (coliform, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Clostridium) compared with the other Bet levels and the CTRL group.
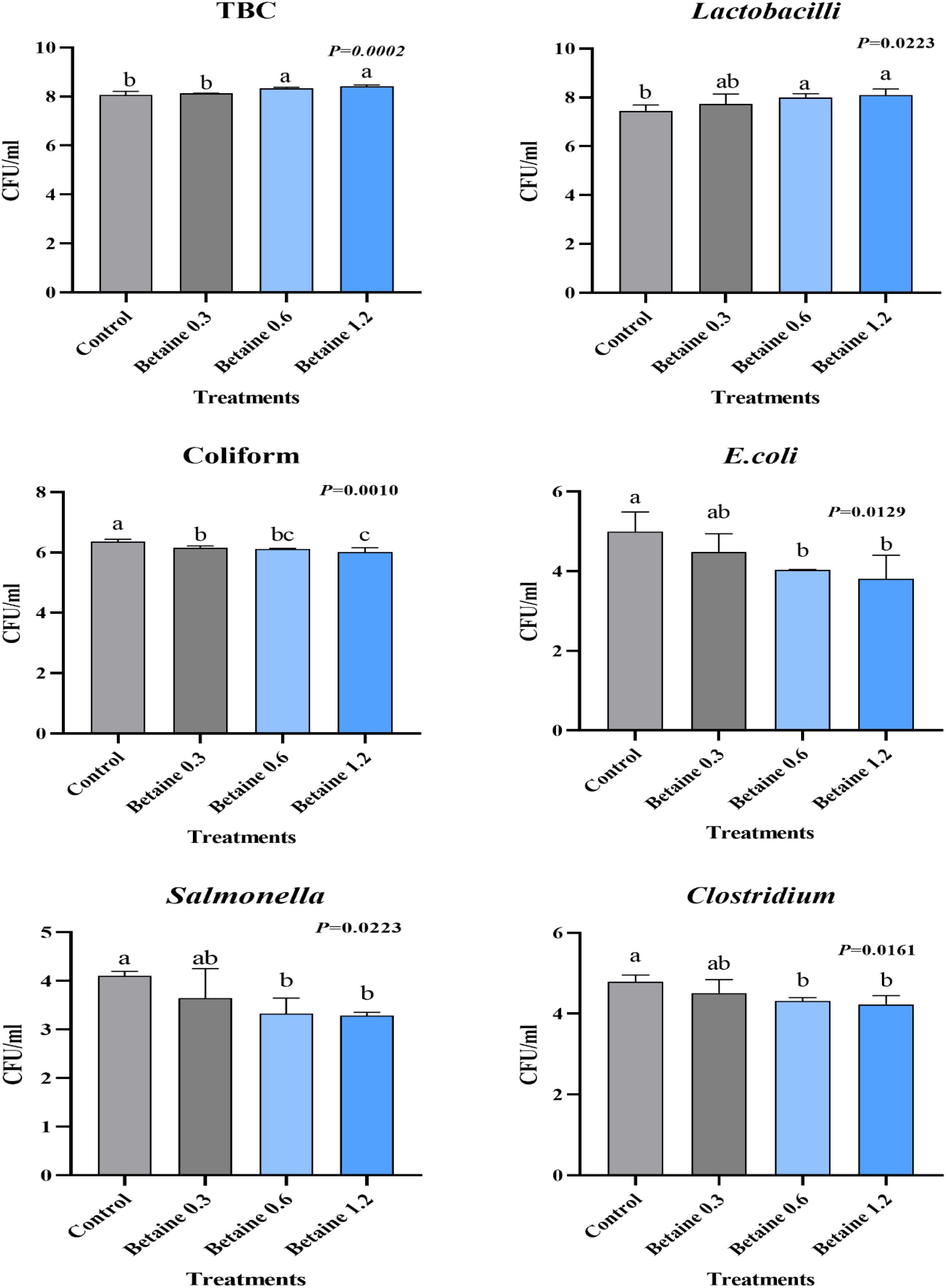
Figure 1. Cecal microbial counts [in colony-forming units (CFU) per milliliter] in Fayoumi laying hens affected by the addition of different levels of betaine (Bet). a, b, and c above the columns, with different superscripts, are significantly different (P≤0.05).
4 Discussion
Phytogenic additives have continuously shown success in improving a range of poultry performance traits in recent years (Al-Ardhi et al., 2020; Almrsomi et al., 2021). Bet is a safe and effective feed supplement that promotes growth and lipotropic activity. As a result, it is widely utilized as a nutritional supplement for many poultry species. Furthermore, it has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. According to the results obtained in the current trial, the addition of different levels of Bet improved the FBW, FI, and FCR. Our results are in the same line as those of Rao et al (Rao et al., 2011), who found that supplementing broiler diet with 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 g Bet/kg resulted in significant increases in FI and LBW, as well as an improvement in FCR. Similarly, several researchers indicated that Bet improves the growth performance, FCR, and carcass breast yield (Dos Santos et al., 2019).
Furthermore, Savaram et al (2021) and Elmahdy et al (2025) found that the body weight gain (BWG) and FI were meaningfully augmented when broilers were fed diets with different levels of Bet in comparison to broilers fed a free-methionine basal diet. Furthermore, both the body weight and BWG, as well as the FI, increased when 25-week-old Lohmann Brown laying hens were fed diets containing 0.35% methionine and 0.75 g Bet/kg feed for 15 weeks (Omara et al., 2023). Bet supplementation may improve the digestibility of crude fiber, dry matter, and protein and promote mucosal expansion in the intestines, resulting in improved growth performance (El-Husseiny et al., 2007; Gonzalez-Rivas et al., 2020). Bet supplementation in birds enhances nutrient utilization, leading to the greater availability of sulfur-containing amino acids such as methionine and cysteine for muscle protein deposition and reducing the requirement for metabolizable energy (Awad et al., 2022). Conversely, Park and Ryu (2011) noted that the FI and FCR were not significantly affected when laying hens were fed a diet with 0.60 g/kg Bet.
In this work, it was revealed that there is a greater need for research on the impacts of Bet on the egg production, egg quality, fertility, and hatchability of laying hen strains. Although Bet addition did not significantly affect the EW and hatchability (in percent), it improved all of the egg production and reproduction traits, particularly when added at 0.6 g. A similar study by Guo et al (2023) and Xing and Jiang (2012) found that supplementing laying hen diets with Bet increased the egg production percentage. Gudev et al (2011) also noted that the egg production rate was significantly improved in laying hens fed diets added with 0.7 and 1.5 g Bet/kg, with an insignificant enhancement in the EW and EM. In addition, incorporating Bet into the diet at a dose of 1 g/kg enhanced the FI, oviduct index, LR, and EM in laying hens (Attia et al., 2016; Hao et al., 2017). Bet appears to reduce the requirement for additional CH3 donors, such as choline and methionine, while enhancing the ability of the liver to synthesize proteins and fatty acids, ultimately resulting in improved egg production rates (Zaki et al., 2023). Bet enhances the egg production rates likely by promoting ovarian health and improving the key antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and catalase (CAT), thereby exhibiting antioxidant properties in the intestinal tract and ovary of older laying hens (Du et al., 2025).
In the current study, as the dietary Bet levels increased up to 0.6 g/kg diet, there was a noticeable improvement in both egg production and reproductive performance; thereafter, the response either plateaued or slightly declined. This indicates that, to maximize reproductive efficiency, the ideal level for Fayoumi laying hens at the late phase of production is 0.6 g/kg. The following decline after this point could be caused by an osmotic imbalance at greater Bet concentrations or the saturation of CH3 group consumption. Similar dose-dependent effects were observed by Gudev et al (2011) and Guo et al (Guo et al., 2023), suggesting that while excessive amounts of Bet may not provide further benefits, moderate levels promote the physiological processes supporting reproduction and egg formation. The biological function of Bet as a CH3 donor supporting hormone production, follicular development, and embryo viability is highlighted by the observed improvements in fertility (in percent) and hatchability (in percent) at 0.6 g/kg.
In this study, increasing the dietary Bet levels to 0.6 g/kg significantly enhanced the egg production and reproductive performance of Fayoumi laying hens. However, beyond this level, these improvements plateaued or slightly decreased, suggesting that 0.6 g/kg is optimal for maximizing the reproductive efficiency in the late production phase. The decline past this point may have resulted from osmotic imbalance or CH3 group consumption saturation. The similar dose-dependent effects noted by Gudev et al (2011) suggest that while excessive Bet supplementation may be unproductive, moderate levels enhance the reproductive processes and egg formation. Bet serves as a CH3 donor, aiding in hormone production, follicular development, and embryo viability, which was reflected in the improved fertility and hatchability at 0.6 g/kg (Guo et al., 2023). In addition, the administration of Bet improved the fertility and hatchability of Fayoumi laying hens in comparison to the CTRL group. A prior investigation demonstrated that injecting doses of Bet (5, 10, and 15 mg) into fertile incubated eggs from meat breeder hens significantly improved hatchability, likely due to its role in methylation processes essential for gluconeogenesis during hatching (Tanimowo et al., 2024). However, high doses of Bet (0.10 g/egg) administered in ovo were found to significantly reduce hatchability (Kadam et al., 2013).
Gholami et al (2015) found no significant effects of Bet at levels of 0.250 and 0.50 mg/egg on hatchability. However, improvements in the fertility rates may be linked to hormones such as lutein, triiodothyronine, estradiol, thyroxine, follicle-stimulating hormone, and progesterone, which increase with dietary Bet (Zou XiaoTing et al., 1998). Specifically, Bet addition at 0.6 g improved the egg quality traits of Fayoumi hens, notably the egg yolk index and the eggshell thickness (Attia et al., 2016). Ryu et al (2002) also reported that 0.2% Bet in the diet can enhance the egg production and eggshell quality under heat stress conditions. In addition, in quails, the egg yolk and eggshell weights were meaningfully improved, while the Alb weight decreased due to the addition of 0.6 and 1.2 g Bet/kg, but did not significantly enhance the shell thickness (Abobaker et al., 2017; Ratriyanto et al., 2017). Adding 0.5% Bet to layer hens’ diet at 65 weeks of production significantly increased the eggshell thickness. The thickness varies by breed, laying season, and diet, with Bet affecting the initial phase of eggshell formation rather than the final stage (Molnár et al., 2016). The EW, yolk color, and Alb width increased with the addition of Bet (0.125, 0.250, and 0.500 g/kg) in the diet of 57-week-old laying hens, with the highest values observed at 0.500 g. Bet also elevated the serum estrogen and melatonin levels, contributing to increased EM and production (Zaki et al., 2023).
The results from our study are in contrast to those of Gudev et al (Gudev et al., 2011), who reported no significant changes in the shell weight, egg Alb weight, egg yolk weight, and the HU scores with 0.7 and 1.5 g Bet/kg diet, although the shell thickness increased. Furthermore, the yolk%, albumen%, and eggshell% exhibited no significant alterations due to Bet at concentrations of 0, 0.70, 1.40, and 2.10 g/kg diet (Ratriyanto et al., 2018). The eggshell thickness significantly decreased with the addition of Bet at 1.5 g/kg in low-methionine diets. There were no significant differences in the egg Alb weight, yolk weight, or HU among the various levels of Bet added. In addition, the shell quality declined due to the increase in EW, meaning that a constant shell is distributed across a larger egg (Omara et al., 2023).
The investigation indicates that the addition of varying doses of Bet, particularly at 0.6 g, enhances numerous carcass traits in Fayoumi layer hens. These results align with previous research showing increases in the carcass weight, the dressing percentage, and the giblet, thigh, and breast weights, alongside a significant reduction in the abdominal fat weight (Saeed et al., 2017; Abd El-Ghany and Babazadeh, 2022). There were clear differences in the weights of the different parts of broiler meat (i.e., drumstick, breast, shank, head, gizzard, liver, spleen, heart, and intestines) when different amounts of Bet were added into the diet. This may be related to the osmotic role of Bet in promoting water retention (Yeasmin T Jaman et al., 2023; Elmahdy et al., 2025). Moreover, the improvements in the carcass traits could be attributed to the function of Bet as a methyl group donor, enhancing the availability of essential amino acids (methionine and cysteine) crucial for protein synthesis (McDevitt et al., 2000; Neto et al., 2000). Previous studies have indicated that the effects of Bet supplementation on the carcass traits may be dependent on the methodology, animal species, and stress conditions (Sakomura et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2022; Kirrella et al., 2023).
In this study, the inclusion of 1.2 g Bet into the diet of Fayoumi laying hens improved their lipid profile by lowering the serum levels of TLs, Cho, and LDL, while all Bet doses increased HDL compared with the CTRL group. Similar findings were observed in broilers, where natural feed additives, including Bet, led to reduced blood lipid profiles and abdominal fat (Gholami et al., 2015; Xie et al., 2024). The role of the liver in converting fatty acids into triacylglycerols for transportation as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) was highlighted, and previous research confirmed that Bet decreased the triglyceride (TG) levels in both broilers and laying hens (Aljumaily et al., 2019; Hu et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2022). Bet can induce glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene production in poultry, which is involved in regulating processes of TG homeostasis and lipid metabolism (Wang et al., 2012; Omer et al., 2018). In addition, Bet prevents the accumulation of hepatic fat and boosts the mitochondrial activity and content. This evidence implies that Bet regulates fat metabolism (Zhang et al., 2019). The increased egg quality and TP and gl levels, along with the decreased Cho and LDL, may lead to an improved blood profile.
Wu et al (2024) demonstrated that Bet administration reduced the hepatic cholesterol buildup in corticosterone-induced laying hens by increasing the CYP7A1 and decreasing the HMGCR expression. In addition, the effect of Bet on lowering the blood lipids may have stemmed from the reduced hormone-sensitive lipase activity and the increased concentration of the methyl groups, promoting the formation of methylated compounds that enhance fat transport in the body, underscoring the importance of Bet in lipid metabolism (Zhan et al., 2006; He et al., 2015). Bet impacts the expression of the genes related to lipid transport, affecting TG regulation and VLDL secretion (VerHague et al., 2013; Guo et al., 2020). In Cobb 500 broilers, the addition of Bet at 0.03%–0.12% into the drinking water increased HDL and decreased LDL and Cho, likely due to its antioxidant properties (Yeasmin T Jaman et al., 2023). Conversely, some studies reported higher Cho levels in broilers given 0.8 g/kg Bet without alterations in the TG levels (Rao et al., 2011).
The TP content in serum is crucial for the assessment of bird immunity, performance, and organ function. A study by Park and Kim (2019) identified that broilers on 1.2 g Bet/kg diet had higher total serum Alb levels. This decrease was attributed to the ability of Bet to contribute CH3 in protein metabolism and to reduce protein loss by enhancing the intestinal integrity. Furthermore, Bet at 0.1 and 0.2%/kg diet diminished the ALT levels in broiler serum (Konca et al., 2008). Similarly, Mohamed et al (2022) found that the addition of 1 ml/L Bet into the drinking water lowered the Alb, gl, and TP levels while increasing ALT and AST. In contrast, Awad et al (2014) reported that incorporating 0.1 and 1.5 g Bet/kg in the diet of ducklings significantly lowered the ALT and AST activity. In contrast, adding Bet at levels of 0.125, 0.250, and 0.500 g/kg into the diet of laying hens at 57 weeks did not affect the plasma levels of AST, ALT, TP, Cho, gl, LDL, HDL, and TGs (Zaki et al., 2023; Elmahdy et al., 2025).
Poultry gut function is influenced by region, age, and production status. The small intestine is responsible for nutrient digestion and absorption, while the intestinal mucosal barrier protects against microbial threats (Peterson and Artis, 2014). The gut microbiota is essential for preserving intestinal health and enhancing immune function (Qi et al., 2021). In addition, when ducks underwent heat stress and were supplemented with 0.07%–0.13% Bet, they demonstrated an increase in microbial fermentation products and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (Park and Kim, 2017). Bet exhibits antibacterial properties and enhances the antioxidant capacity, protecting gut cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, suggesting that it may also shield the intestinal microbiota from osmotic stress (Ratriyanto et al., 2009; Blagodatskikh et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021). Our findings corroborate those of Pradista et al (Pradista et al., 2022), indicating that Bet, used as a feed additive at 0.12%/kg for ducks under heat stress, when supplemented at 0.07%–0.13%, resulted in an increased production of Clostridiaceae UCG-002 while decreasing Olsenella. Furthermore, Bet treatment significantly lowered the Clostridium perfringens counts in vivo, potentially due to improved cellular immunity characterized by leukocytosis, monocytosis, increased lymphocytosis, and enhanced phagocytic activity (Mohamed et al., 2022). Supplementing Lohmann laying pullets with Bet at 1.2 g/kg diet significantly increased the levels of various Lactobacillus species, as shown by Al Wahid et al (Al Wahid et al., 2024). This enhancement in beneficial bacteria may be attributed to the osmoprotective property of Bet, which promotes cell–bacteria concordance in the intestinal tract, and its ability to enhance the microbial fermentation of dietary fibers, resulting in improved fiber digestibility and increased production of SCFAs.
5 Conclusions
The addition of Bet, especially at the level of 0.6 g/kg diet, improved the growth performance, egg production, and quality. Moreover, it enhanced the fertility and hatchability rates and the blood indices in such a late period of production. The addition of high levels of Bet improved the cecal microbiota by increasing the beneficial bacteria and decreasing the pathogenic species. Henceforward, safe, healthy, and economical egg production could be achieved by utilizing Bet as a diet additive to layer hens at the late periods of production.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research Ethics Committee assessed and approved all experimental protocols at the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
HA-k: Investigation, Visualization, Funding acquisition, Validation, Supervision, Project administration, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. SA-A: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Validation. HN: Validation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. AA-N: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Resources, Data curation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Software. HK: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MS: Resources, Investigation, Writing – original draft. HA: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to the management of the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research (KISR) for funding this research under the project encoded FA004O.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank every member who helped during the experiment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd El-Ghany W. A. and Babazadeh D. (2022). Betaine: A potential nutritional metabolite in the poultry industry. Animals 12, 2624. doi: 10.3390/ani12192624
Abd El-Hack M. E., Abdelnour S. A., Kamal M., Khafaga A. F., Shakoori A. M., Bagadood R. M., et al. (2023). Lactoferrin: Antimicrobial impacts, genomic guardian, therapeutic uses and clinical significance for humans and animals. BioMed. Pharmaco 164, 114967. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114967
Abd El-Hack M. E., Aldhalmi A. K., Ashour E. A., Kamal M., Khan M. M., and Swelum A. A. (2025). The effects of formic acid or herbal mixture on growth performance, carcass quality, blood chemistry, and gut microbial load in broiler chickens: Formic Acid & Herbal Mixture in broiler diets. Poult Sci. 104, 105085. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105085
Abobaker H., Hu Y., Hou Z., Sun Q., Idriss A. A., Omer N. A., et al. (2017). Dietary betaine supplementation increases adrenal expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and yolk deposition of corticosterone in laying hens. Poult Sci. 96, 4389–4398. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex241
Ahmed M., Ismail Z., and Abdel-Wareth A. (2018). Application of betaine as feed additives in poultry nutrition–a review. J. Exp. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2, 266–272. doi: 10.20454/jeaas.2018.1428
Al-Ardhi S. A., Areaaer A. H., and Hamead M. H. (2020). Effect of cumin and black seed oil on productive and physiological traits of Japanese quail. Indian J. Ecol. 12, 302–305.
Alfonso-Carrillo C., Benavides-Reyes C., de Los Mozos J., Dominguez-Gasca N., Sanchez-Rodríguez E., Garcia-Ruiz A. I., et al. (2021). Relationship between bone quality, egg production and eggshell quality in laying hens at the end of an extended production cycle (105 weeks). Animals 11, 623. doi: 10.3390/ani11030623
Ali I. M., Nafea H. H., and Ilbas A. I. (2025). Aqueous and alcoholic parsley (petroselinum crispum) extracts supplemented into drink-ing water and stocking density affect productive performance and antioxidant status of broilers. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 35, 174–185. doi: 10.36899/japs.2025.1.0013
Aljumaily T. K. H., Kamil Y. M., and Taha A. T. (2019). Effect of the addition amla (Phyllanthus emblica) and vitamin C powder on some physiological and production performance of broiler. Plant Arch. 19, 1117–1120.
Al-Khalaifa H., Al-Nasser A., Al-Surayee T., Al-Kandari S., Al-Enzi N., Al-Sharrah T., et al. (2019). Effect of dietary probiotics and prebiotics on the performance of broiler chickens. Poult Sci. 98, 4465–4479. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez282
Al-Khalaifah H., Al-Nasser A., Givens D. I., Rymer C., and Yaqoob P. (2020). Comparison of different dietary sources of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on immune response in broiler chickens. Heliyon 6. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03326
Almrsomi T. S., Areaaer A. H., and Mohammad M. S. (2021). Influence of addition different levels of ginger powder in diet on productive performance of broiler Ross 308. J. Kerbala Univ 13, 50–54.
Al-Qaisi M., Abdelqader A., Abuajamieh M., Abedal-Majed M. A., and Al-Fataftah A. R. (2023). Impacts of dietary betaine on rectal temperature, laying performance, metabolism, intestinal morphology, and follicular development in heat-exposed laying hens. J. Therm Biol. 117, 103714. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2023.103714
Al-Sagan A. A., Al-Abdullatif A., Hussein E. O., Saadeldin I. M., Al-Mufarrej S. I., Qaid M., et al. (2021). Effects of betaine supplementation on live performance, selected blood parameters, and expression of water channel and stress-related mRNA transcripts of delayed placement broiler chicks. Front. Vet. Sci. 7, 632101. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.632101
Al Wahid Z., Pradista L. A., Prastowo S., and Ratriyanto A. (2024). Betaine Alter SCFA-producing Bacteria population in laying pullet reared in tropical climate. In IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 1341, 012060. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1341/1/012060
Anderson K. E., Tharrington J. B., Curtis P. A., and Jones F. T. (2004). Shell characteristics of eggs from historic strains of single-comb white leghorn chickens and the relationship of egg shape to shell strength. Int. J. Poult Sci. 3, 17–19. doi: 10.3923/ijps.2004.17.19
Arif M., Baty R. S., Althubaiti E. H., Ijaz M. T., Fayyaz M., Shafi M. E., et al. (2022). The impact of betaine supplementation in quail diet on growth performance, blood chemistry, and carcass traits. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 29, 1604–1610. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.002
Arumugam M. K., Paal M. C., Donohue T. M., Ganesan M., Osna N. A., and Kharbanda K. K. (2021). Beneficial effects of betaine: a comprehensive review. Biology 10, 456. doi: 10.3390/biology10060456
Attia Y. A., Abd El-Hamid A. E. H. E., Abedalla A. A., Berika M. A., Al-Harthi M. A., Kucuk O., et al. (2016). Lay-ing performance, digestibility and plasma hormones in laying hens exposed to chronic heat stress as affected by betaine, vitamin C, and/or vitamin E supplementation. Springer Plus 5, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-3304-0
Attia Y. A., El-Naggar A. S., Abou-Shehema B. M., and Abdella A. A. (2019). Effect of supplementation with trimethylglycine (betaine) and/or vitamins on semen quality, fertility, antioxidant status, DNA repair and welfare of roosters exposed to chronic heat stress. Animals 9, 547. doi: 10.3390/ani9080547
Awad A. L., Ibrahim A. F., Fahim H. N., and Beshara M. M. (2014). Effect of dietary betaine supplementation on growth performance and carcass traits of Domyati ducklings under summer conditions. Egypt Poult Sci. J. 34.
Awad W. A., Ruhnau D., Gavrău A., Dublecz K., and Hess M. (2022). Comparing effects of natural betaine and betaine hydrochloride on gut physiology in broiler chickens. Poult Sci. 101, 102173. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102173
Blagodatskikh I. V., Vyshivannaya O. V., Alexandrova A. V., Bezrodnykh E. A., Zelenikhin P. V., Kulikov S. N., et al. (2018). Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of betainated oligochitosane derivatives. Microbiol 87, 725–731. doi: 10.1134/S0026261718050041
Chen R., Song Y., Yang M., Wen C., Liu Q., Zhuang S., et al. (2022). Effect of dietary betaine on muscle protein deposition, nucleic acid and amino acid contents, and proteomes of broilers. Animals 12, 736. doi: 10.3390/ani12060736
De Prekel L., Maes D., Van den Broeke Ampe B., and Aluwé M. (2024). Effect of simultaneous dietary supplementation of betaine, selenomethionine, and vitamins E and C under summer conditions in growing–finishing pigs. Vet. Sci. 11, 110. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11030110
Dos Santos T. T., Baal S. C. S., Lee S. A., E Silva F. R. O., Scheraiber M., and Da Silva A. V. F. (2019). Influence of dietary fibre and betaine on mucus production and digesta and plasma osmolality of broiler chicks from hatch to 14 days of ag. Livest Sci. 220, 67–73. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2018.12.005
Du X., Pian H., Zhao D., Zhang Y., Wu X., He J., et al. (2025). Enhancing gut-ovary health in aged laying hens: the impact of dietary betaine supplementation. Poult Sci. 104, 104894. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104894
Duncan D. B. (1995). The multiple range and multiple F-tests. Biometrics 11, 1–42. doi: 10.2307/3001478
El-Husseiny O. M., Abo-El-Ella M. A., Abd-Elsamee M. O., and Abd-Elfattah M. M. (2007). Response of broiler performance to dietary betaine and folic acid at different methionine levels. Int. J. Poult Sci. 6, 515–523. doi: 10.3923/ijps.2007.515.523
Elmahdy M. I., El-Kholy M. S., Bassiony S. S., Abolmaaty S. M., Azzam M. M., El-Kassas S., et al. (2025). Effect of dietary betaine (CH3) 3N+ CH2CO− 2) fortifications on growth performance, carcass traits, and blood biochemistry of broilers under heat stress condition. Res. Chem. 15, 102178. doi: 10.1016/j.rechem.2025.102178
El-Ratel I. T., Amara M. M., Beshara M. M., El Basuini M. F., Fouda S. F., El-Kholy K. H., et al. (2024). Effects of supplemental vitamin A on reproduction and antioxidative status of aged laying hens, and growth, blood indices and immunity of their offspring. Poult Sci. 103, 103453. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103453
Elsherbeni A. I., Youssef I. M., Hamouda R. E., Kamal M., El-Gendi G. M., El-Garhi O. H., et al. (2024a). Performance and economic efficiency of laying hens in response to adding zeo-lite to feed and litter. Poult Sci. 103, 103799. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103799
Elsherbeni A. I., Youssef I. M., Kamal M., Youssif M. A., El-Gendi G. M., El-Garhi O. H., et al. (2024b). Impact of adding zeolite to broilers' diet and litter on growth, blood parameters, immunity, and ammonia emission. Poult Sci. 103, 103981. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103981
Gholami J., Qotbi A. A., Seidavi A., Meluzzi A., Tavaniello S., and Maiorano G. (2015). Effects of in ovo administration of betaine and choline on hatchability results, growth and carcass characteristics and immune response of broiler chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 14, 3694. doi: 10.4081/ijas.2015.3694
Gonzalez-Rivas P. A., Chauhan S. S., Ha M., Fegan N., Dunshea F. R., and Warner R. D. (2020). Effects of heat stress on animal physiology, metabolism, and meat quality: A review. Meat Sci. 162, 108025. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.108025
Gudev D., Popova-Ralcheva S. Yanchev I., Moneva P., Petkov E., and Ignatova M. (2011). Effect of betaine on egg performance and some blood constituents in laying hens reared indoor under natural summer temperatures and varying levels of air ammonia. Bulgar J. Agric. Sci. 17, 859–866. doi: 10.2298/bah1103687g
Guo F., Jing M., Zhang A., Yi J., and Zhang Y. (2023). Effects of dietary betaine on the laying performance, antioxidant capacity, and uterus and ovary function of laying hens at the late stage of production. Animals 13, 3283. doi: 10.3390/ani13203283
Guo M., Xu Y., Dong Z., Zhou Z., Cong N., Gao M., et al. (2020). Inactivation of ApoC3 by CRISPR/Cas9 protects against atherosclerosis in hamsters. Circulat Res. 127, 456–1458. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317686
Hao S., Liu L., Wang G., Gu X., and Pan F. (2017). Effects of dietary betaine on performance, egg quality and serum biochemical parameters of laying hens under heat stress condition. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 29, 184–192.
He S., Zhao S., Dai S., Liu D., and Bokhari S. G. (2015). Effects of dietary betaine on growth performance, fat deposition and serum lipids in broilers subjected to chronic heat stress. Anim. Sci. J. 8, 897–903. doi: 10.1111/asj.12372
Hu Y., Feng Y., Ding Z., Lv L., Sui Y., Sun Q., et al. (2020). Maternal betaine supplementation decreases hepatic cholesterol deposition in chicken offspring with epigenetic modulation of SREBP2 and CYP7A1 genes. Poult Sci. 99, 3111–3120. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.12.058
Kadam M. M., Bhuiyan M. M., Islam F., and Iji P. A. (2013). Evaluation of betaine as an in ovo feeding nutrient for broiler chickens. Proc. 24th Aust. Poult Sci. Sympos 17, 158. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6301
Kamal M., Aldhalmi A. K., Abd El-Hack M. E., Elsherbeni A. I., Youssef I. M., Hussein S., et al. (2025). Enhancing the feed efficiency of crop residues in ruminants–A comprehensive review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 25 (2), 529–545. doi: 10.2478/aoas-2024-0081
Kamal M., Kishk W. H., Khalil H. A., Abdel-Khalek A. M., Ayoub M. A., Swelum A. A., et al. (2023). Effect of dietary chitosan supplementation on productive and physiological performance parameters of growing New Zealand white rabbits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 230, 123166. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123166
Kirrella A. A., El-Kassas S., El-Naggar K., Galosi L., Biagini L., Rossi G., et al. (2023). Growing and laying performance of two different-plumage color Japanese quail varieties supplemented with corn silk in their diet. Poult Sci. 102, 102360. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102360
Konca Y., Kirkpinar F., Mert S., and Yaylak E. (2008). Effects of betaine on performance, carcass, bone and blood characteristics of broilers during natural summer temperatures. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 7, 930–937. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2008.70399
Kondaiah N., Panda B., and Singhal R. A. (1983). Internal egg-quality measure for quail eggs. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 53, 1261–1264.
Lan R. and Kim I. (2018). Effects of feeding diets containing essential oils and betaine to heat-stressed growing-finishing pigs. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 72, 368–378. doi: 10.1080/1745039X.2018.1492806
Liu W., Yuan Y., Sun C., Balasubramanian B., Zhao Z., and An L. (2019). Effects of dietary betaine on growth performance, digestive function, carcass traits, and meat quality in indigenous yellow-feathered broilers under long-term heat stress. Animals 9, 506. doi: 10.3390/ani9080506
McDevitt R. M., Mack S., and Wallis I. R. (2000). Can betaine partially replace or enhance the effect of methionine by improving broiler growth and carcass characteristics? Br. Poult Sci. 41, 473–480. doi: 10.1080/713654957
Mohamed G. A. E., Ali N. M., and Amen O. A. (2022). The effect of betaine on broilers infected experimentally with Clostridium perfringens. SVU-IJVS 5, 174–192. doi: 10.21608/svu.2022.165000.1229
Mohamed L. A., Dosoky W. M., Kamal M., Alshehry G., Algarni E. H., Aldekhail N. M., et al. (2024). Growth performance, carcass traits and meat physical characteristics of growing Japanese quail fed ginger powder and frankincense oil as feed additives. Poult Sci. 103, 103771. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103771
Molnár A., Maertens L., Ampe B., Buyse J., Kempen I., Zoons J., et al. (2016). Changes in egg quality traits during the last phase of production: is there potential for an extended laying cycle? Br. Poult Sci. 57, 842–847. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2016.1209738
Moula N., Ait-Kaki A., and Leroy P. (2013). Antoine-Moussiaux N. Quality assessment of marketed eggs in Bassekabylie (Algeria). Braz. J. Poult Sci. 15, 395–399. doi: 10.1590/S1516-635X2013000400015
National Research Council (1994). Nutrient requirements of poultry. 9th rev. ed (Washington, DC: Natl Acad Press).
Neto M. G., Pesti G. M., and Bakalli R. I. (2000). Influence of dietary protein level on the broiler chicken's response to methionine and betaine supplements. Poult Sci. 79, 1478–1484. doi: 10.1093/ps/79.10.1478
Omara I. I., Suliman M. A. E., and Eltanani R. R. (2023). Spacing effect of betaine supplementation in low methionine laying hen diets on productive performance and egg quality. Egypt Poult Sci. J. 43, 141–155. doi: 10.21608/epsj.2023.291446
Omer N. A., Hu Y., Hu Y., Idriss A. A., Abobaker H., Hou Z., et al. (2018). Dietary betaine activates hepatic VTGII expression in laying hens associated with hypomethylation of GR gene promoter and enhanced GR expression. J. Anim. Sci. Biotech. 9, 2. doi: 10.1186/s40104-017-0218-9
Park S. O. and Kim W. K. (2017). Effects of betaine on biological functions in meat-type ducks exposed to heat stress. Poult Sci. 96, 1212–1218. doi: 10.3382/ps/pew359
Park J. H. and Kim I. H. (2019). The effects of betaine supplementation in diets containing different levels of crude protein and methionine on the growth performance, blood components, total tract nutrient digestibility, excreta noxious gas emission, and meat quality of the broiler chickens. Poult Sci. 98, 6808–6815. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez412
Park J. H. and Ryu K. S. (2011). Relationship between dietary protein levels and betaine supplementation in laying hens. J. Poult Sci. 48, 217–222. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.010101
Peterson L. W. and Artis D. (2014). Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 14, 141–153. doi: 10.1038/nri3608
Pradista L. A., Prastowo S., Widyas N., and Ratriyanto A. (2022). Metagenomic analysis of non-pathogenic and pathogenic cecal bac-teria profiles in quail supplemented with betaine. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 1114, 012008. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/1114/1/012008
Qi X., Yun C., Pang Y., and Qiao J. (2021). The impact of the gut microbiota on the reproductive and metabolic endocrine system. Gut Microb. 13, 1894070. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1894070
Rao S. V., Raju M. V. L. N., Panda A. K., Saharia P., and Sunder G. S. (2011). Effect of supplementing betaine on performance, carcass traits and immune responses in broiler chicken fed diets containing different concentrations of methionine. Asian-Aust J. Anim. Sci. 24, 662–669. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2011.10286
Ratriyanto A., Indreswari R., Dewanti R., and Wahyuningsih S. (2018). Egg quality of quails fed low methionine diet supplemented with betaine. In IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 142, 012002. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/142/1/012002
Ratriyanto A., Indreswari R., and Nuhriawangsa A. M. P. (2017). Effects of dietary protein level and Betaine supplementation on nu-trient digestibility and performance of Japanese quails. Rev. Brasil Cien Avi 19, 445–454. doi: 10.1590/1806-9061-2016-0442
Ratriyanto A., Mosenthin R., Bauer E., and Eklund M. (2009). Metabolic, osmoregulatory and nutritional functions of betaine in mo-nogastric animals. Asian-Aust J. Anim. Sci. 22, 1461–1476. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2009.80659
Ryu M. S., Cho K. H., Shin W. J., and Ryu K. S. (2002). Influence of dietary supplemental betaine on performance and egg quality of laying hens during the heat stress. Kor J. Poult Sci. 29, 117–123.
Saeed M., Babazadeh D., Naveed M., Arain M. A., Hassan F. U., and Chao S. (2017). Reconsidering betaine as a natural anti-heat stress agent in the poultry industry: a review. Trop. Anim. Health Prod 49, 1329–1338. doi: 10.1007/s11250-017-1355-z
Saeed M., Hassan F. U., Al-Khalaifah H., Islam R., Kamboh A. A., and Liu G. (2025). Fermented banana feed and nanoparticles: a new eco-friendly, cost-effective potential green approach for poultry industry. Poult Sci., 105171. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105171
Sakomura N. K., Barbosa N. A., Silva E. D., Longo F. A., Kawauchi I. M., and Fernandes J. B. (2013). Effect of betaine supplementation in diets for broiler chickens on thermoneutral environment. Rev. Bras. Ciênc Agrár 8, 336–341. doi: 10.1590/s1516-635x2013000200005
Savaram V. R., Mantena V. L. N. R., Bhukya P., Paul S. S., and Devanaboyina N. (2021). Effect of methyl donors supplementation on performance, immune responses and antioxidant variables in broiler chicken fed diet without supplemental methionine. Anim. Biosci. 35, 475. doi: 10.5713/ab.20.0812
Shakeri M., Cottrell J. J., Wilkinson S., Ringuet M., Furness J. B., and Dunshea F. R. (2018). Betaine and antioxidants improve growth performance and breast muscle development and ameliorate thermoregulatory responses to cyclic heat exposure in broiler chickens. Animals 8, 162. doi: 10.3390/ani8100162
Sheiha A. M., Abdelnour S. A., Abd El-Hack M. E., Khafaga A. F., Metwally K. A., Ajarem J. S., et al. (2020). Effects of dietary biological or chemical-synthesized nano-selenium supplementation on growing rabbits exposed to thermal stress. Animals 10, 430. doi: 10.3390/ani10030430
Tanimowo D. A., Ewuola E. O., and Longe O. G. (2024). Effect of in ovo betaine-hydrochloride supplementation on hatchability, chick quality and organ weights of broiler chicks. Trop. Agric. 101, 29–38.
VerHague M. A., Cheng D., Weinberg R. B., Shelness G. S., and Apolipoprotein A.-I. V. (2013). expression in mouse liver enhances tri-glyceride secretion and reduces hepatic lipid content by promoting very low density lipoprotein particle expansion. ATVB 33, 2501–2508. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301948
Wang J. C., Gray N. E., Kuo T., and Harris C. A. (2012). Regulation of triglyceride metabolism by glucocorticoid receptor. Cell Biosci. 2, 19. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-19
Wang C., Ma C., Gong L., Dai S., and Li Y. (2021). Preventive and therapeutic role of betaine in liver disease: A review on molecular mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 912, 174604. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174604
Wu Y., Zhang M., Meng F., Ren K., Li D., Luo X., et al. (2024). Betaine supplementation alleviates corticosterone-induced hepatic cholesterol accumulation through epigenetic modulation of HMGCR and CYP7A1 genes in laying hens. Poult Sci. 103, 103435. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103435
Xie S., Li Y., Suo Y., Wang Z., Zhang B., Li J., et al. (2024). Effect of organic, nano, and inorganic zinc sources on growth performance, antioxidant function, and intestinal health of young broilers. Biol. Trace Elem Res. 203 (5), 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04341-y
Xing J. and Jiang Y. (2012). Effect of dietary betaine supplementation on mRNA level of lipogenesis genes and on promoter CpG methylation of fatty acid synthase (FAS) gene in laying hens. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 11, 6633–6640. doi: 10.5897/ajb11.3197
Yang M., Chen R., Song Y. D., Zhou Y. M., Liu Q., and Zhuang S. (2022). Effects of dietary betaine supplementation on growth performance, meat quality, muscle fatty acid composition and antioxidant ability in slow-growing broiler chickens. Br. Poult Sci. 63, 351–359. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2021.2008313
Yang Z., Shao Y., Yang J., Xing X., Yang H., and Wang Z. (2025). Betaine enhances hepatic antioxidant activity and thymus-associated immunity in lipopolysaccharide-challenged goslings. BMC Vet. Res. 21, 77. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04527-z
Yeasmin T Jaman M. A., Uzzal H., and Gausur M. R. (2023). Impact of betaine on the performance and specific haemato-biochemical parameters in heat-stress exposed broiler chickens. J. Istanbul Vet. Sci. 7, 154–162. doi: 10.30704/http-www-jivs-net.1346643
Zaki A., Jiang S., Zaghloul S., El-Rayes T. K., Saleh A. A., Azzam M. M., et al. (2023). Betaine as an alternative feed additive to choline and its effect on performance, blood parameters, and egg quality in laying hens rations. Poult Sci. 102, 102710. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102710
Zhan X. A., Li J. X., Xu Z. R., and Zhao R. Q. (2006). Effects of methionine and betaine supplementation on growth performance, carcase composition and metabolism of lipids in male broilers. Br. Poult Sci. 47, 576–580. doi: 10.1080/00071660600963438
Zhang L., Qi Y., ALuo Z., Liu S., Zhang Z., and Zhou L. (2019). Betaine increases mitochondrial content and improves hepatic lipid metabolism. Food Func 10, 216–223. doi: 10.1039/C8FO02004C
Zhao B. C., Tang Y. X., Qiu B. H., Xu H. L., Wang T. H., Elsherbeni A. I. A., et al. (2022). Astragalus polysaccharide mitigates transport stress-induced hepatic metabolic stress via improving hepatic glucolipid metabolism in chicks. J. Anim. Sci. 100, skac244. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac244
Keywords: Fayoumi layer hens, reproductive performance, blood indicators, carcass traits, intestinal microbiota
Citation: Al-khalaifah HS, Al-Ardhi SA, Nafea HH, Al-Nasser A, Khalil HA, Hassan MIS and Ahmed HA (2025) Impact of betaine on laying hens’ productive and physiological reactions at the late stage of production. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1708362. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1708362
Received: 18 September 2025; Accepted: 07 November 2025; Revised: 06 November 2025;
Published: 26 November 2025.
Edited by:
Esin Ebru Onbasilar, Ankara University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Cemil Tölü, Faculty of Agriculture, Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University, TürkiyeMohmmad Al-Qaisi, The University of Jordan, Jordan
Copyright © 2025 Al-khalaifah, Al-Ardhi, Nafea, Al-Nasser, Khalil, Hassan and Ahmed. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hanan S. Al-khalaifah, aGtoYWxpZmFAa2lzci5lZHUua3c=; aGtoYWxpZmEyMDI1QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Hanan S. Al-khalaifah
Hanan S. Al-khalaifah Saad Attallah Al-Ardhi2
Saad Attallah Al-Ardhi2 Mahmoud I. S. Hassan
Mahmoud I. S. Hassan