- 1Research Center for Agricultural Information Technology, National Agricultural and Food Research Organization (NARO), Tokyo, Japan
- 2Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, NARO, Tsukuba, Japan
- 3Institute of Crop Science, NARO, Tsukuba, Japan
A Correction on
Phenology analysis for trait prediction using UAVs in a MAGIC rice population with different transplanting protocols
by Taniguchi, S., Sakamoto, T., Nakamura, H., Nonoue, Y., Guan, D., Fukuda, A., Fukuda, H., Wada, K. C., Ishii, T., Yonemaru, J.-I., and Ogawa, D. (2025). Front. Artif. Intell. 7:1477637. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1477637
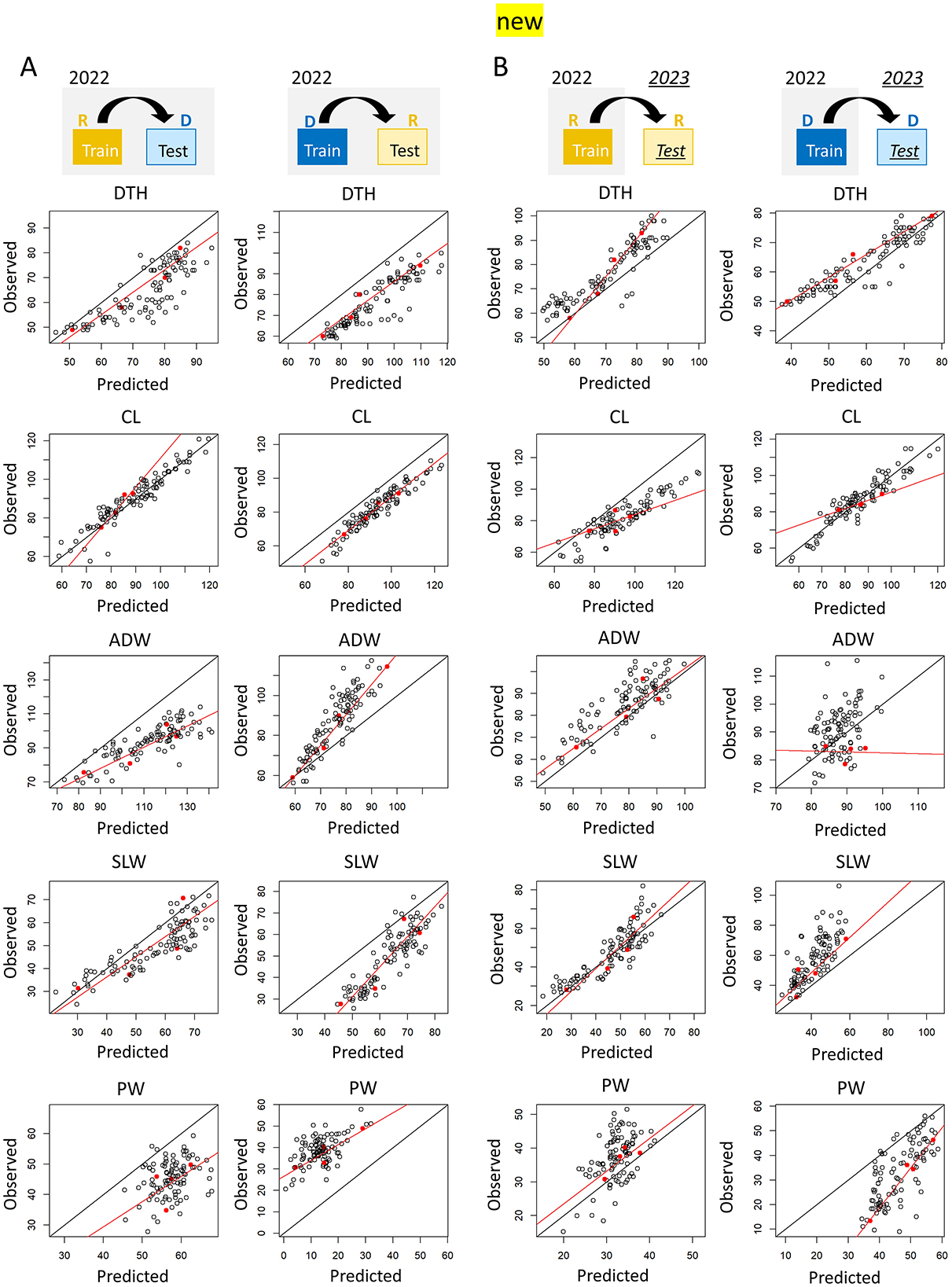
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 9B and Figure 10B as published. The CH and CIg parameter data for the 2023 dataset were incorrectly labeled: the transplanting protocols Regular (R) and Delayed (D) were mistakenly swapped. The corrected Figure 9B and Figure 10B appear below.
In the published article, there was an error in Supplementary Table 13, Table 15, which is in Supplementary Table 1. The CH and CIg parameter data for the 2023 dataset were incorrectly labeled: the transplanting protocols Regular (R) and Delayed (D) were mistakenly swapped. The correct material statement appears in the updated Supplementary Table 1.
In the published article, there was an error in Supplementary Figure 8. The CH and CIg parameter data for the 2023 dataset were incorrectly labeled; the transplanting protocols Regular (R) and Delayed (D) were mistakenly swapped. Supplementary Presentation 1 has been updated.
In the published article, there was an error in Supplementary Data Sheet 1. The CH and CIg parameter labels for the 2023 dataset have been revised. This dataset was used for reanalysis and supports the updated results presented in the corrected figures, tables and text. The correct material statement appears in the updated Supplementary Data Sheet 1.
In the published article, there was an error. The CH and CIg parameter data for the 2023 dataset were incorrectly labeled: the transplanting protocols Regular (R) and Delayed (D) were mistakenly swapped.
A correction has been made to Results, 3.5 Calibration of training and test data obtained under different protocols, Paragraph 1. This text previously stated:
“The calibration also reduced the RMSE values for the prediction of ADW, SLW, and PW (Supplementary Table 14). In terms of type-2 model robustness, calibration reduced the RMSE values for CL, ADW, PW, and DTH (Supplementary Table 15). There were, however, two cases where calibration resulted in a larger RMSE: the prediction of CL under the delayed transplanting protocol (type-1 model robustness) and the prediction of SLW of the delayed protocol in 2023 (type-2 model robustness). In these two cases, the phenotypic data of the four parental cultivars did not cover the full range of phenotypic variance of the JAM2 lines.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The calibration also reduced the RMSE values for the prediction of ADW, SLW, and PW (Supplementary Table 14). There was one case where calibration resulted in a larger RMSE: the prediction of CL under the delayed transplanting protocol. In terms of type-2 model robustness, calibration reduced the RMSE values for PW (Supplementary Table 15), but the calibration did not always work well for CL, ADW, DTH and SLW. In these cases, the phenotypic data of the four parental cultivars did not cover the full range of phenotypic variance of the JAM2 lines.”
A correction has been made to Discussion, Paragraph 6. The sentence previously stated:
“Only in the two cases did the calibration not work well. This may be because the phenotypic data …”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The calibration did not work well for some cases. This may be because the phenotypic data …”
The original article has been updated.
Generative AI statement
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: rice, phenology, time-series analysis, MAGIC, UAV, remote sensing, transplanting protocol
Citation: Taniguchi S, Sakamoto T, Nakamura H, Nonoue Y, Guan D, Fukuda A, Fukuda H, Wada KC, Ishii T, Yonemaru J-I and Ogawa D (2025) Correction: Phenology analysis for trait prediction using UAVs in a MAGIC rice population with different transplanting protocols. Front. Artif. Intell. 8:1725594. doi: 10.3389/frai.2025.1725594
Received: 15 October 2025; Accepted: 31 October 2025;
Published: 25 November 2025.
Edited and reviewed by: Sapna Langyan, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), India
Copyright © 2025 Taniguchi, Sakamoto, Nakamura, Nonoue, Guan, Fukuda, Fukuda, Wada, Ishii, Yonemaru and Ogawa. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shoji Taniguchi, dGFuaWd1Y2hpczUzMkBhZmZyYy5nby5qcA==; Daisuke Ogawa, RGFpc3VrZS5PZ2F3YUBhZmZyYy5nby5qcA==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Shoji Taniguchi
Shoji Taniguchi Toshihiro Sakamoto2†
Toshihiro Sakamoto2† Di Guan
Di Guan