- 1Department of Chemical Engineering, College of Engineering and Petroleum, Kuwait University, Kuwait City, Kuwait
- 2Petroleum Refining and Petrochemical Research Center, College of Engineering and Petroleum, Kuwait University, Kuwait City, Kuwait
PEGylation is widely used in biopharmaceuticals to enhance protein stability and half-life, but the resulting mixtures typically contain multiple PEGylated derivatives alongside unmodified proteins, complicating purification. In this study, we developed a novel aqueous two-phase separation (ATPS) strategy for selectively purifying mono-PEGylated human serum albumin (HSA). HSA was PEGylated using polyethylene glycol (PEG) reagents of different molecular weights (20 kDa and 40 kDa) and subsequently purified using ATPS. Our results demonstrated that ATPS effectively isolated PEGylated HSA with purity >99% and extremely high selectivity in the top phase. Tie-line length (TLL) significantly influenced yield and purity, whereas the volume ratio (Vr) had a minimal effect. Optimal conditions for the separation of 20 kDa PEGylated HSA were identified at a TLL of 29% (w/w) and a Vr of 2.5, achieving a yield of 50% and an equilibrium constant of 1.6. Under identical conditions, the yield and equilibrium constants for 40 kDa PEGylated HSA increased to 58% and 18, respectively, attributed to enhanced hydrophobic interactions from the larger PEG reagent. Furthermore, ATPS reached equilibrium rapidly within 30 min, resulting in high productivity levels of 1.3 and 1.5 g/L/h for 20 and 40 kDa PEGylated HSA, respectively. These findings illustrate the high efficiency and industrial potential of ATPS as an effective purification strategy for PEGylated therapeutic proteins.
1 Introduction
The introduction of therapeutic proteins and peptides as biotherapeutics marked a significant advancement in the healthcare industry during the 20th century. Since the early 1980s, progress in recombinant protein biomanufacturing has laid the foundation for treating various diseases, including cancer (Tripathi and Shrivastava, 2019). These advancements have driven the global market to a value of $333.1 billion in 2022, with projections estimating growth to $856.1 billion by 2030 (BioSpace, 2022). However, the rapid clearance of recombinant proteins from circulation, remains a significant challenge in protein therapeutics, necessitating frequent dosing, increased production demands, and escalating manufacturing expenses (Zaman et al., 2019). This challenge has led to ongoing efforts aimed at extending the circulation half-life of protein-based therapeutics.
Covalent conjugation of polyethylene glycol (PEG) polymers to amino acid residues, known as PEGylation, is widely employed to prolong the half-life of proteins. To date, over 25 PEGylated therapeutic proteins have been approved by the FDA (Holz et al., 2023). Although random PEGylation is commonly used to produce PEGylated protein therapeutics, it often produces a heterogeneous mixture of PEGylated species (PEGmers). These undesired variants can alter pharmacokinetics, reduce efficacy, or cause undesirable toxicological and immunological responses (Mao et al., 2022). Consequently, site-specific PEGylation is preferred to minimize heterogeneity and improve product consistency (Belén et al., 2019).
Targeting cysteine residues presents a promising approach for site-specific PEGylation, especially when free thiol groups are present. Although cysteines constitute only about 1% of amino acid residues in proteins, their selective reactivity with maleimide-functionalized PEG reagents enables efficient and specific conjugation with minimal side reactions (Nair et al., 2014; Dozier and Distefano, 2015; Wall et al., 2020). Notable examples of cysteine site-specific PEGylation include modification of human serum albumin (HSA) (Zhao et al., 2012; Mehtala et al., 2015), alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) (Liu et al., 2022a; Liu et al., 2022b), and antibodies or their derivatives targeting cancer-associated antigens (Alric et al., 2016; Kholodenko et al., 2019; Kalinovsky et al., 2023a; Kalinovsky et al., 2023b). Owing to the specificity of thiol-maleimide bioconjugation, its applications extend beyond site-specific PEGylation to the development of next-generation immunotherapies, such as antibody-drug conjugates (Benjamin et al., 2019; Jendryczko et al., 2022; Osgood et al., 2024).
PEGylation alters protein properties, influencing the selection of an appropriate chromatographic technique (Ramos-de-la-Peña and Aguilar, 2020). Therefore, various chromatographic techniques have been employed to separate unmodified proteins from PEGylated protein derivatives. Ion-exchange chromatography, for instance, differentiates proteins and their PEGylated derivatives based on net surface charge (Moosmann et al., 2010; Morgenstern et al., 2017; Sánchez-Trasviña et al., 2021). However, the separation of large biomolecules is primarily governed by diffusion within the pores of the stationary phase, which prolongs separation time and reduces productivity (Schultze-Jena et al., 2020). Consequently, chromatographic operations often fail to reach equilibrium binding, typically described by the batch Langmuir isotherm uptake model (Ghose et al., 2004). Traditional protein chromatography entails a tradeoff between resolution and productivity (Bigelow et al., 2021). As a result, productivity is constrained in large-scale protein processing due to the need for multiple chromatography cycles.
Aqueous two-phase separation (ATPS) is a liquid-liquid extraction technique in which two distinct phases formed at a critical concentration of two mutually incompatible solutes (Roque et al., 2020). ATPS systems consist of either polymer-polymer or polymer-salt combinations. Protein partitioning between phases depends on both protein properties and system characteristics (Azevedo et al., 2008). For example, Rosa et al. demonstrated that an ATPS comprising PEG 3350, phosphate, and NaCl could extract immunoglobulin G (IgG) from a model protein mixture containing IgG, HSA and myoglobin, achieving yield and purity of 97% and 99%, respectively (Rosa et al., 2007). Similarly, Azevedo et al. employed an ATPS consisting of PEG 3350, citrate buffer, and NaCl, which effectively recovered IgG from a hybridoma cell culture supernatant into the top phase with a yield of 99% and purity of 44% (Azevedo et al., 2009a). ATPS has been used as a harvest step in downstream processing of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell culture supernatants (Azevedo et al., 2008; Azevedo et al., 2009b). Furthermore, ATPS has been applied to the fractionation and purification of PEGylated proteins from PEGylation reaction mixtures (González-Valdez et al., 2011; Santos et al., 2017). Moreover, ATPS has been integrated into PEGylation process merging reaction/fractionation steps (Mejía-Manzano et al., 2017; Santos et al., 2019; Campos-García et al., 2021).
In this study, HSA was selected as a model protein for site-specific PEGylation, and ATPS was evaluated as an extraction and purification method for PEGylated proteins. To the best of our knowledge, no prior studies have investigated ATPS as a purification platform for site-specific PEGylated proteins. Reactive cysteine PEGylation reagents (methoxy PEG maleimide) of two molecular weights (20 and 40 kDa) were reacted with HSA, and molar conversion was monitored over time using electrophoresis and ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC). The ATPS model system consisted of PEG 3350 and citrate buffer (pH 6). The separation performance of ATPS for 20 kDa and 40 kDa PEGylated HSA was evaluated in terms of yield and equilibrium constant (Kp). Additionally, the effects of key operational parameters, including tie-line length (TLL), volume ratio (Vr), and the presence of NaCl, were investigated.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
HSA (part number A9731), PEG (molecular weight: 3350 g/mol), citric acid, trisodium citrate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), monobasic sodium phosphate, dibasic sodium phosphate, cysteine, sodium chloride, trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), and acetonitrile were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Methoxy PEG maleimides (20 kDa and 40 kDa) were obtained from JenKem Technology. The Bio-Rad protein assay dye reagent concentrate, Bio-Safe Coomassie stain, and Precision Plus Protein™ All Blue Standards were procured from Bio-Rad.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 PEGylation reaction
HSA was PEGylated following a procedure similar to that reported by Mehtala et al. (2015) and Liu et al. (2022a). Briefly, HSA was dissolved in 10 mL reaction buffer (50 mM phosphate buffer with 10 mM EDTA, pH 6.5) at a concentration of 10 mg/mL (0.15 mM) in a 15 mL falcon tube. Methoxy PEG maleimide (mPEG-MAL; 20 or 40 kDa) was added at a 5:1 ratio relative to HSA, and the reaction was allowed to proceed for 3 h at 37 °C. Aliquots (0.2 mL) were withdrawn periodically and mixed with 10 µL of 20 mg/mL cysteine solution to quench the reaction. The samples were stored at −20°C for further assays/ATPS.
2.2.2 Bradford total protein assay
The total protein concentration was determined using the Bradford assay (Bradford, 1976). A standard calibration curve was prepared using HSA standards in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) within the concentration range of 0.50–0.05 mg/mL. Unknown samples were diluted in the same buffer. The Protein Assay Dye Reagent Concentrate was diluted five-fold in double-distilled water (DD-H2O). HSA standards and unknown samples (20 µL) were mixed with 1 mL of the diluted dye reagent, and absorbance were measured at 595 nm using a Perkin Elmer Lambda 25 spectrophtometer.
2.2.3 SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE was performed using 4–20% Tris-HCl precast gradient gels (Bio-Rad) in a Mini-PROTEAN® II cell (Bio-Rad), following a procedure similar to that described by Alkanaimsh et al. (2019). Briefly, samples were mixed with 4× Laemmli buffer and heated at 95°C for 5 min. Precision Plus Protein ™ All Blue Pertained Protein Standards and samples were loaded into the gels and electrophoresis was run at 200 V for 35 min. The gels were washed thrice with double-distilled H2O (DD-H2O), and then stained with Bio-safe Coomassie Blue G-250 Stain for 1 h. The gels were then incubated overnight with double-distilled H2O for destaining.
2.2.4 ATPS extraction studies
ATPS was performed by mixing appropriate amounts of 50% (w/w) PEG 3350 stock solution, 40% (w/w) citrate buffer stock, protein solution, NaCl, and DD-H2O. The PEG 3350 stock solution was prepared by dissolving 50 g of PEG 3350 in 50 mL of DD-H2O. The citrate buffer stock solution was prepared by mixing 40% (w/w) citric acid and 40% (w/w) trisodium citrate to reach a pH of 6. The densities of both stock solutions were measured and used to determine the volumes required for ATPS formation. The protein solution from the PEGylation reaction was diluted in 0.1 M phosphate buffer at a concentration of 5 mg/mL (pH 7) and used as a stock. For each extraction, 0.3 g of this solution was transferred to a 2.0 mL Eppendorf microcentrifuge tube along with the appropriate volumes of 50% PEG 3350 stock and 40% citrate buffer stock (pH 6). DD-H2O was added until the system reached a total mass of 1.5 g. The final weight percentages of PEG 3350 and citrate in the ATPS were determined based on binodal curves established by Azevedo et al. (2009a). NaCl was added in powder form to adjust the system to the required final weight percentage. All system components were mixed thoroughly using a vortex and phase separation was allowed to proceed under gravity force at room temperature. Volume of each phase was recorded. Aliquots from each phase was taken for analysis. ATPS performance was evaluated by calculating the recovery percentage (yield %) of PEGylated HSA, the equilibrium constant (Kp), and selectivity. These parameters were calculated according to Equations 1-3 shown below.
2.2.5 Analytical procedure
Reaction aliquots and ATPS phase fractions (10 µL) were analyzed by reverse-phase UPLC (RP-UPLC) using an ACQUITY UPLC Protein BEH C4 column (300 Å, 1.7 µm, 2.1 mm × 50 mm; Waters Corporation). Gradient elution was performed at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min, according to the manufacturer instructions. It was established using solvent A (0.1% (v/v) TFA in DD-H2O) and solvent B (71.4% acetonitrile and 28.6% DD-H2O containing 0.075% (v/v) TFA). The gradient profile was as follows: 0 min (A%: 72, B%: 28), 25 min (A%: 0, B%: 100), 27 min (A%: 0, B%: 100), and 45 min (A%: 72, B%: 28). Absorbance was measured at 280 nm using a diode array detector (DAD). The composition of each protein species was calculated as the ratio of the area under the curve (AUC) of each protein peak to the total AUC of all protein peaks. Based on the gradient elution conditions, the retention times (Rt) of HSA, 20 kDa PEG-HSA, and 40 kDa PEG-HSA were 10.5, 12.3, and 13.7 min, respectively.
2.2.6 Statistical analysis
All aqueous two-phase separation conditions were performed in duplicate, and samples from each replicate were analyzed in triplicate. For each sample replicate, a mean was calculated, and the data represents the mean of both sample replicates. Error bars indicate standard deviation calculated using GraphPad Prism 10.5.0.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 HSA site-specific PEGylation
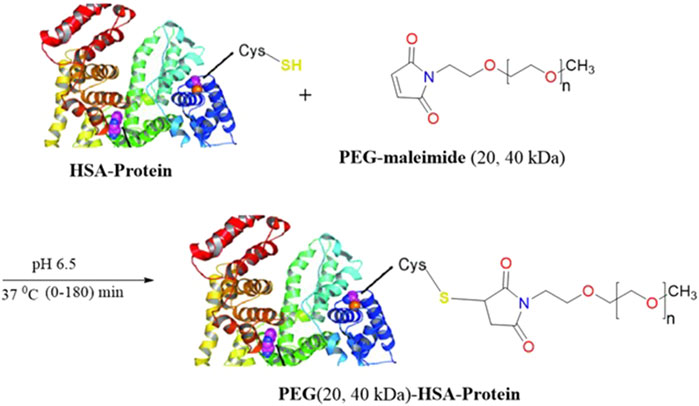
Methoxy PEG maleimide reagents of two molecular weights (20 and 40 kDa) were employed for site-specific HSA PEGylation (Figure 1). In both cases, the starting HSA solution (10 mg/mL) in reaction buffer was mixed with a five-fold molar excess of the PEG reagent. Samples were collected at multiple time points (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, and 180 min), and the progression of PEGylated HSA formation was monitored by RP-UPLC (Supplementary Figures S1 and S2). The PEG polymer increases the hydrophobicity of the PEGylated species, thereby increasing their Rt compared to unmodified HSA (Cisneros-Ruiz et al., 2014). Accordingly, the greater the molecular weight of the PEG reagent, the more PEGylated protein derivative is retained. This explains the observed Rt values of 10.5, 12.3, and 13.7 min for unmodified HSA, the 20 kDa PEG-HSA derivative, and the 40 kDa PEG-HSA derivative, respectively. The identity of these peaks in each sample aliquot was confirmed by SDS-PAGE (Figure 2), which demonstrated successful conjugation of PEG to HSA.
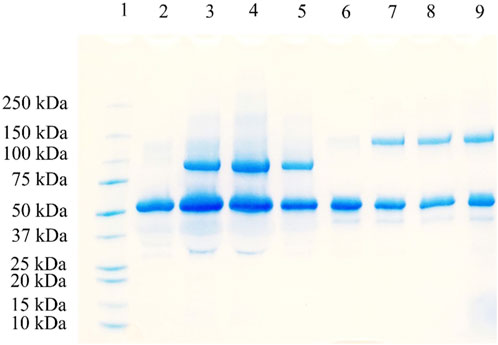
Figure 2. SDS-PAGE analysis of HSA PEGylation using 20 and 40 kDa methoxy PEG maleimide reagents. Lane 1: protein marker; Lane 2: 20 kDa PEGylation reaction at 0 min; Lane 3: 20 kDa PEGylation reaction at 30 min; Lane 4: 20 kDa PEGylation reaction at 60 min; Lane 5: 20 kDa PEGylation reaction at 120 min; Lane 6: 40 kDa PEGylation reaction at 0 min; Lane 7: 40 kDa PEGylation reaction at 30 min; Lane 8: 40 kDa PEGylation reaction at 60 min; and Lane 9: 40 kDa PEGylation reaction at 120 min.
The concentrations of both native and PEGylated protein derivatives were calculated by determining the individual AUC for each RP-UPLC peak relative to the total protein concentration obtained from the Bradford assay. Figure 3 compares the concentration profiles of unmodified HSA and 20 kDa and 40 kDa PEGylated HSA. The figure illustrates that comparable conversions were achieved by the end of the 3-h reaction: 23% ± 0.1% for the 20 kDa PEG reagent and 22% ± 0.1% for the 40 kDa PEG reagent. The initial reaction rates were determined by analyzing the linear portion of the HSA concentration curves within the first 15 min of the reactions. The initial rates were calculated as 1.5 ± 0.1 μM/min and 1.8 ± 0.2 μM/min for the 20 and 40 kDa PEGylation reactions, respectively. PEGylated HSA formation rates decreased after 15 min and reached a plateau by 45 min. The increase in conversion was <5% from 45 to 180 min for both reactions.
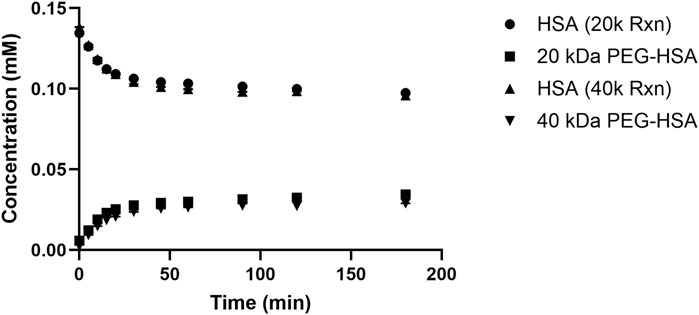
Figure 3. HSA and 20 kDa and 40 kDa PEGylated HSA protein concentration profiles during the conjugation reactions.
The observed decrease in reaction rate can be attributed to the susceptibility of PEG maleimide reagents to hydrolysis in aqueous buffers (Martínez-Jothar et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019). For example, Wang et al. demonstrated that 40 kDa Y-shaped methoxy PEG maleimide deactivates in aqueous buffers following first-order kinetics, with a deactivation constant of 0.03 min-1 at 37°C, extrapolated from values obtained at 20°C and 30°C (Wang et al., 2018). Based on these data, it is anticipated that the deactivation constant in this study is similarly high, as a value of 0.03 min-1 corresponds to approximately 80% deactivation after a 45-min reaction. To evaluate the effect of protein concentration on PEGylation efficiency, the initial HSA concentration was varied between 2 and 20 mg/mL, while maintaining a fixed five-fold molar excess of the 20 kDa methoxy PEG maleimide reagent. Although previous studies have reported a positive correlation between increased initial protein concentration and higher conversion in thiol PEGylation of HSA and AAT (Mehtala et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2022a), no significant differences in conversion were observed under the conditions used in this study. These findings support the hypothesis that hydrolytic degradation of the PEG maleimide reagent significantly limits the PEGylated yield. Nonetheless, site-specific PEGylation of HSA was successfully achieved using the proposed protocol and served as the starting material for ATPS optimization studies.
3.2 ATPS of PEGylated HSA protein derivates
3.2.1 Establishment of high selectivity ATPS for purification of PEGylated HSA at shorter TTL
ATPS is considered one of the non-traditional protein purification techniques (Shukla et al., 2017; Phong et al., 2018; Almeida et al., 2023; Singla and Sit, 2023; Segaran and Chua, 2024), and has been used to extract/purify relevant biopharmaceutical protein like IgG (Ramalho et al., 2018; Capela et al., 2019; Capela et al., 2023) and others (Castro et al., 2020; Magri et al., 2020). ATPS performance was assessed based on PEGylated protein yield, selectivity, and the equilibrium partition coefficient, as calculated by Equations 1-3. Selectivity refers to the degree of effective separation, where target molecules preferentially migrate to one phase, while impurities are directed into the other. Figure 4 shows chromatographs of the loaded feed material and the resulting PEG-rich top and salt-rich bottom phases following ATPS. The feed material exhibited two peaks corresponding to unmodified HSA and its 20 kDa PEGylated derivative. In contrast, the PEG-rich top and salt-rich bottom phase chromatograms revealed predominantly single peaks: unmodified HSA partitioned into the salt-rich bottom phase, while the PEGylated HSA partitioned into the PEG-rich top phase. For ATPS systems with TLLs of 29% and 35% (w/w), the top phases were free of unmodified HSA, and the bottom phases contained HSA with a mass fraction ≥0.9. This demonstrates that PEG-based ATPS can efficiently separate PEGylated HSA from unmodified HSA with extremely high selectivity, calculated by Equation 3.
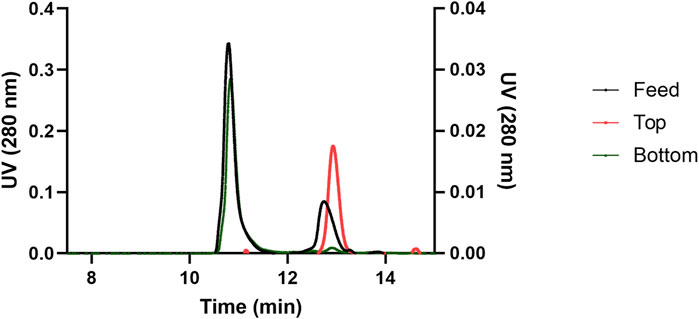
Figure 4. Comparison of the chromatographs of the reaction mixture, top phase, and bottom phase after performing ATPS at a TLL of 29 (w/w) % and Vr of 1. The primary y-axis (left) represent the UV absorbance of the feed and the bottom phase, and the secondary y-axis (right) represents the UV absorbance of the top phase.
Protein separation in ATPS is primarily influenced by several factors, including hydrophobicity, electrochemistry/ionizability, and biospecific affinity (Asenjo and Andrews, 2011). Various mechanisms govern the differential partitioning of HSA and its PEGylated derivatives into the bottom and top phases, respectively. HSA is a highly hydrophilic protein that preferentially partitions into the salt-rich bottom phase. This behavior can be attributed to the higher water activity in the bottom phase, which facilitates interactions with the charged groups of proteins and promotes the formation of hydration shells, thereby stabilizing protein structure, a phenomenon well recognized in aqueous environments (Morón, 2021). Großmann et al. showed that glycine, a hydrophilic amino acid, partitions into the bottom phase, further supporting the role of water-mediated stabilization (Großmann et al., 1995). Moreover, at higher ionic strengths, charge shielding occurs, which reduces electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged albumin and citrate ions, thereby enhancing albumin partitioning into the bottom phase (Haynes et al., 1989). In contrast, the PEG-rich top phase does not support favorable conditions for HSA partitioning. PEG molecules in the top phase impose steric hindrance on large proteins (e.g., HSA), effectively excluding them from this crowded environment (Liu et al., 2016). Moreover, the top phase is known to be more hydrophobic than the salt-rich bottom phase, making it unsuitable for accommodating highly hydrophilic proteins such as HSA (Asenjo and Andrews, 2011).
In contrast to native HSA, PEGylated proteins exhibit altered physiochemical properties that influence their partitioning. The increased hydrophobicity of PEGylated proteins drives their migration into the more hydrophobic top phase rather than the salt-enriched bottom phase (Dreyer et al., 2009). The hydrophilic properties of HSA decrease upon PEGylation, as evidenced by the increased retention times during hydrophobic interaction chromatography (Ghosh, 2005; Shang et al., 2013; Retnaningtyas et al., 2016). Enhanced partitioning of PEGylated proteins into the PEG-rich top phase, due to this increased hydrophobicity, has been consistently reported (González-Valdez et al., 2011; Mejía-Manzano et al., 2017; Campos-García et al., 2021). Furthermore, the salting-out effect reduces the solubility of hydrophobic proteins in salt-rich environments, such as the bottom phase of PEG-salt ATPS. Hachem et al. (1996) demonstrated that protein hydrophobicity strongly correlates with preferential partitioning into the PEG-rich top phase in PEG/phosphate systems (Hachem et al., 1996). This finding supports the hypothesis that PEGylated proteins, due to their reduced solubility in ionic environments, are excluded from the salt-rich bottom phase and preferentially recovered in the PEG-rich top phase. Supporting this, Azevedo et al. (2007), Azevedo et al. (2009a) showed that increasing NaCl content to 15% (w/w) facilitated the partitioning of IgG into the top phase of a PEG/salt system, whereas it was retained in the bottom phase under NaCl-free ATPS (Azevedo et al., 2007; Azevedo et al., 2009a). This can be extended to PEGylated proteins, which are more susceptible to salting out due to their increased hydrophobicity and thus favor partitioning into the top phase. Furthermore, PEGylated proteins may exhibit affinity-like behaviors due to the presence of PEG chains, which can interact with PEG-rich environments. Jorge et al. (2024) demonstrated that PEG-PEG self-interactions occur, as indicated by lateral packing between PEG chains, which may contribute to enhanced recovery of PEGylated proteins in the top phase (Jorge et al., 2024).
In contrast to the high selectivity observed at shorter TLL values (i.e., 29% and 35% w/w), operating at longer TLL (43% w/w) resulted in decreased selectivity, as HSA partitioned into both phases. As shown in Supplementary Figure S3, the top phase contained both proteins, with an HSA mass fraction of 0.31. In contrast, the bottom phase contained a minor amount of PEGylated protein, and the HSA mass fraction was 0.94. At high TLL, both PEG and citrate concentrations increase, leading to reduced water activity in both phases. Consequently, the bottom phase becomes more salt-rich and water-deprived, resulting in the loss of hydration shells that normally stabilize proteins. This phenomenon, known as salting-out, can explain the redistribution of HSA into both phases under longer TLL conditions (Huddleston et al., 1996). Moreover, the increased citrate ion concentration in the bottom phase may contribute to electrostatic repulsion with the negatively charged HSA at pH 6, further impacting protein partitioning. Our results are in agreement with Santos et al. who showed decrease in recovery of target protein with increasing TLL in ATPS and migration of contaminates hydrophilic proteins due to salting-out effects (Santos et al., 2018). To confirm that salting-out was the primary driving force for the migration of HSA into the top phase, ATPS was operated at 29% (w/w) TLL with the addition of 15% (w/w) NaCl. As shown in Supplementary Figure S4, the top phase contained both HSA and its PEGylated derivative, but the HSA mass fraction increased to 0.42. It is well established that NaCl induces salting-out, promoting the transfer of proteins from the salt-rich bottom phase into the PEG-rich top phase in PEG/salt systems (Azevedo et al., 2007; Azevedo et al., 2009a). These findings confirm that salting-out was the primary mechanism responsible for HSA migration into the top phase in both systems, with a greater salting-out effect induced by NaCl presence. At higher TLL, this effect was accompanied by the additional presence of concentrated citrate ions in the bottom phase. In such conditions, electrostatic repulsion serves as a secondary mechanism that further promotes protein migration. In contrast, in the high-ionic-strength system (15% w/w NaCl), minimal electrostatic repulsion occurs due to chloride ions, leaving salting-out as the dominant driving force.
3.2.2 Impact of TLL and volume ratio on output parameters for PEGylated HSA purification by ATPS
While selectivity refers to the extent of separation between target molecules and impurities across two phases, protein yield refers to the percentage recovery of the target protein in a single phase relative to its total amount in the system. In this context, yield is defined as the mass of PEGylated HSA recovered in the top phase relative to the total PEGylated HSA mass in the ATPS feed (Equation 1). The equilibrium constant reflects the distribution of PEGylated HSA between the top and bottom phases (Equation 2). Figure 5 shows the yield and equilibrium constant for 20 kDa PEGylated HSA as a function of TLL at a fixed volume ratio (Vr = 1). Operation the ATPS at a lower TTL (i.e., 29% w/w) resulted in a higher PEGylated HSA yield but a lower equilibrium constant. Specifically, the yields of PEGylated HSA in the top phase were 42.6% ± 0.5%, 31.6% ± 0.8%, and 29.7% for TLLs of 29, 35, and 43% (w/w), respectively. In contrast, the corresponding equilibrium constants were 1.60 ± 0.1, 2.13 ± 0.1, and 2.15, respectively. The effect of Vr was further examined at 29% (w/w) TLL, with Vr ranging from 1.0 to 2.5. The recovery yield of PEGylated has increased with increasing Vr. For instance, yields were 42.6% ± 0.5% and 49.8% ± 0.6% at Vr values of 1.0 and 2.5, respectively (Figure 6). Conversely, the equilibrium constant decreased with increasing Vr from 1.60 ± 0.1 to 1.36 ± 0.1 (Figure 6).
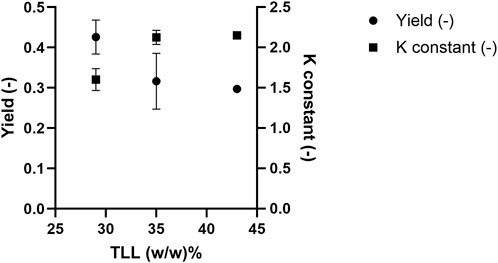
Figure 5. 20 kDa PEGylated-HSA yield in the top phase and equilibrium constant after ATPS fractionation.
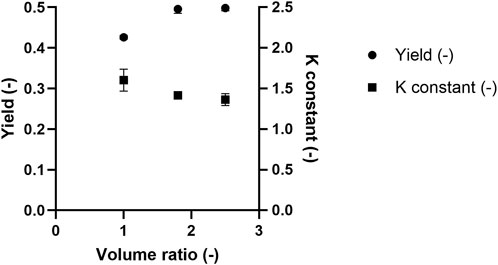
Figure 6. The effect of Vr on 20 kDa PEGylated-HSA yield in the top phase and equilibrium constant after ATPS fractionation.
The enhancement of the equilibrium constant of PEGylated HSA with increasing TLL can be attributed to the increasing concentrations of PEG and citrate concentrations in the top and bottom phases, respectively. Higher concentrations of the phase-forming agents increase the hydrophobicity contrast between the two phases, favoring the partitioning of PEGylated HSA into the more hydrophobic top phase. Moreover, increased PEG concentration in the top phase enhances PEG-PEG affinity interactions, further promoting PEGylated HSA partitioning into this phase and resulting in a higher equilibrium constant. A minor contributing mechanism may be electrostatic repulsion between PEGylated HSA and citrate ions in the bottom phase. Because PEGylation shields surface charges on the protein, PEGylated HSA is less responsive to electrostatic interactions compared to native HSA. Therefore, a higher citrate concentration is required to induce repulsion, which may contribute to the exclusion of PEGylated HSA from the bottom phase.
However, the lower yield observed at higher TLL values can be explained by the loss of PEGylated protein at the phase interface. To account for the total protein mass, a mass balance was performed by summing the protein present in the top and bottom phases and at the interface. Interfacial tension increases with rising TLL due to greater compositional differences between the two phases (Wu and Zhu, 1999; Asenjo et al., 2002). This results in increased protein accumulation at the interface. Azevedo et al. (2009a) reported similar findings, where protein losses at the interface grew with increasing TLL (Azevedo et al., 2009a). Likewise, Nisslein et al. (2021) observed significant antibody loss at the interface when using longer TLLs in ATPS systems, attributing this to increased interfacial tension that causes target molecules to become trapped at the phase boundary (Nisslein et al., 2021). Consequently, the combined effects of interfacial trapping and bottom-phase partitioning of PEGylated HSA at higher TLLs led to reduced yields in the top phase (Figure 5). Our results are in agreement with Santos et al. who showed a decrease in recovery of target PEGylated cytochrome c protein with increasing TLL in ATPS (Santos et al., 2017). This was explained by decreasing in water content in top-phase leading to excluding the PEGylated protein derivate with intermediate hydrophobicity.
The findings of this study are consistent with those reported by González-Valdez et al. (2011), who attributed enhanced recovery of PEGylated derivatives in the top phase to increased free volume availability (González-Valdez et al., 2011). This aligns with other studies demonstrating that a reduced Vr increases the equilibrium constant, and that changes in equilibrium constants are smaller at shorter TLLs (Marcos et al., 1998; Nisslein et al., 2021). In our study, increasing the volume ratio resulted in a larger top phase volume, which diluted the concentration of PEGylated HSA. Although the PEG-concentration remained fixed at a given TLL, the dilution effect led to a reduced PEGylated protein mass per unit volume. This in turn weakened PEG-PEG affinity interactions, resulting in a decreased equilibrium constant at higher volume ratios (Figure 6). However, the lower concentration of PEGylated HSA in the top phase also reduced the chemical potential, thereby promoting additional protein transfer into the top phase. This is supported by Johansson et al. (1998), who demonstrated that partitioning in ATPS is entropy driven toward phases with a higher density of phase-forming agents relative to solute molecules (Johansson et al., 1998). As a result, despite a reduction in the equilibrium constant, increased volume ratios yielded higher PEGylated HSA recovery in the top phase.
3.2.3 Impact of mPEG-MAL size on the output parameters of PEGylated HSA purification by ATPS
We investigated the influence of PEG molecular weight on ATPS performance in separating PEGylated HSA derivatives. In our previous experiments, 20 kDa mPEG-MAL was conjugated to HSA, and the resulting mixture was subjected to ATPS for purification. Subsequently, ATPS was applied to purify the reaction mixture resulting from 40 kDa mPEG-MAL conjugation to HSA. As shown in Figures 2, 3, the reaction yields for both PEG sizes were similar, indicating that the conclusions drawn from ATPS performance reflect differences in PEG size rather than initial conjugation efficiency.
The yields and equilibrium constants for 20 and 40 kDa PEGylated HSA were compared under ATPS conditions of 29% (w/w) TLL and a Vr of 2.5 (Figure 7). Application of ATPS to the 40 kDa PEGylated HSA derivate resulted in improved separation performance. Specifically, the 20 kDa PEGylated HSA yielded49.8% ± 0.6% with an equilibrium constant of 1.36 ± 0.1, whereas the 40 kDa PEGylated HSA achieved a higher yield of 58.2% ± 0.9% and a significantly greater equilibrium constant of 18 ± 2, respectively. These results are consistent with the findings of Santos et al. who showed enhanced yield and equilibrium constants upon increasing reactive PEG conjugation polymer size (Santos et al., 2019). This improvement in both yield and equilibrium constant can be attributed to the increased hydrophobicity of the 40 kDa PEGylated HSA compared with its 20 kDa counterpart. A similar effect has been reported with increasing PEGylation degree (tri- > di- > mono-PEGylated forms), which results enhanced partitioning into the top phase (Mejía-Manzano et al., 2017). The enhancement in yield and equilibrium constant upon increasing the PEG conjugation size can be attributed to increased PEG-PEG affinity forces, leading to greater partitioning of the greater molecular weight PEGylated derivative HSA into the top phase. Moreover, due to its more hydrophobic nature, the greater molecular weight PEGylated is more susceptible to salting-out, resulting in reduced concentration in the salt-rich bottom phase and further improving separation efficiency.
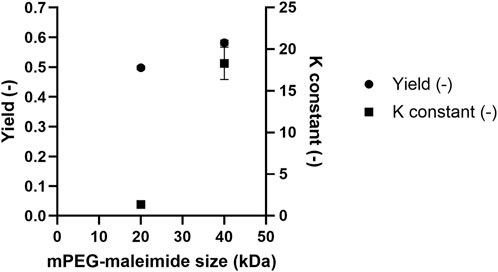
Figure 7. Comparison of the PEGylated HSA yield and equilibrium constant after ATPS fractionation as a function of methoxy PEG maleimide reagent size.
SDS-PAGE was performed for the 20 and 40 kDa PEGylation reaction mixtures after ATPS purification (Figure 8). In both cases, the top phase samples (lanes 4 and 7) exhibited nearly pure PEGylated HSA, whereas the bottom phase samples (lanes 3 and 6) contained only unmodified HSA.
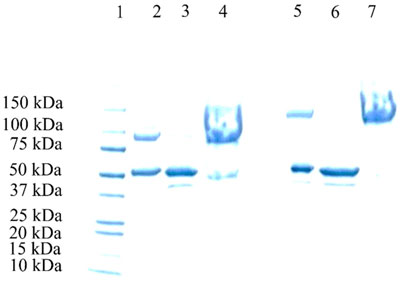
Figure 8. SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of the ATPS of various HSA-PEGylation reaction mixtures. Lane 1: protein marker; Lane 2: 20 kDa HSA-PEGylation reaction mixture; Lane 3: bottom phase of the 20 kDa HAS-PEGylation reaction mixture after ATPS fractionation; Lane 4: top phase of the 20 kDa HSA- PEGylation reaction mixture after ATPS fractionation; Lane 5: 40 kDa HSA- PEGylation reaction mixture after ATPS fractionation; Lane 6: bottom phase of the 40 kDa HSA-PEGylation reaction mixture after ATPS fractionation; and Lane 7: top phase of the 40 kDa HSA-PEGylation reaction mixture after ATPS fractionation.
3.3 Establishment of ATPS as an effective separation technique relative to traditional protein chromatography
After establishing an effective ATPS-based protocol for PEGylated HSA separation, we evaluated its performance relative to traditional chromatography by comparing key downstream bioprocessing metrics. In addition to protein yield, productivity is an essential metric for assessing the robustness of a separation strategy. While productivity in chromatography is typically defined as the mass of target protein recovered per unit volume of resin per operation time, here we are going to describe the productivity as the mass concentration of the target protein per unit time to compare chromatographic and non-chromatographic purification techniques.
Although protein chromatography is a powerful tool for protein purification due to its high resolution and selectivity (Sánchez-Trasviña et al., 2021), it is limited by factors such as resin underutilization and mass transfer resistance. These limitations are especially pronounced in large-scale columns with high process loads, resulting in reduced productivity (Behere and Yoon, 2020).
In our study, ATPS was applied to both 20 and 40 kDa PEGylation HSA reaction mixtures using a TLL of 29% (w/w) and a Vr of 2.5. Under these conditions, phase separation was completed within 30 min. Inferred from the results, the productivity for 20 and 40 kDa PEG-HSA was calculated to be 1.3 and 1.5 g/L/h, respectively. This high productivity is largely attributed to the significantly shorter processing time of ATPS. In comparison, chromatography typically requires multiple steps and extended processing times. For example, assuming a 10 mL reaction mixture loaded at a residence time of 5 min using a 1 mL resin column, and an additional five column volumes (CV) each for equilibration, washing, and elution, the total processing time would be approximately 125 min. This time-intensive cyclic process (i.e., equilibration, loading, washing, and elution) contributes to lower throughput compared to ATPS. By contrast, ATPS enables rapid, selective recovery of PEGylated HSA in a high-purity form with superior productivity. These results confirm that ATPS offers a robust and efficient alternative to traditional chromatography-based purification.
Previous reports have shown that batch chromatography imposes limitations on process productivities (Kim et al., 2022). Thus, ATPS serves as a viable alternative for purification of PEGylated proteins. Moreover, this study highlights the cost-effectiveness of ATPS-based separation over conventional chromatography for a wide range of recombinant proteins, including monoclonal antibodies and industrial enzymes (Aguilar et al., 2006; Naganagouda and Mulimani, 2008; Rosa et al., 2011; Bhavsar et al., 2012; Torres-Acosta et al., 2016).
Although selectivity and equilibrium constant observed in our studies were efficient for PEGylated HSA, the observed yield (∼60%) suggests losses at the phase interface. Reducing PEG molecular weight may decrease interfacial tension and minimize losses as higher molecular weight leads to greater interfacial tension (Giraldo-Zuniga et al., 2006; Hyde et al., 2017). Moreover, using sulfate (stronger salting-out agent (Jimenez et al., 2022)) as salt instead of citrate might improve PEGylated HSA yield by excluding PEGylated HSA into top phase.
4 Conclusion
This study demonstrates that ATPS offers a simple and effective purification strategy for the fractionation of PEGylated HSA derivatives. Different parameters, such as TLL, Vr, and NaCl content, were investigated for their impact on separation efficiency. Shorter TLL led HSA and PEGylated HSA to migrate into the bottom phase and top phase, respectively, establishing a selective purification scheme. Longer TLLs led to the migration of native HSA into the top phase, primarily due to salting-out and electrostatic repulsion, resulting in reduced selectivity and lower PEGylated HSA purity in the top phase. In contrast, increasing Vr enhanced the volume of the top phase and improved the recovery percentage of PEGylated HSA. A comparison of PEGylated HSA prepared with 20 and 40 kDa mPEG-MAL revealed that larger PEG conjugate achieved a higher equilibrium constant and a 36% greater yield in the top phase under the same ATPS conditions. These results were attributed to enhanced PEG–PEG interactions and increased salting-out sensitivity due to the greater hydrophobicity of the 40 kDa conjugate. Furthermore, the rapid equilibrium and shorter processing times of ATPS systems compared to traditional chromatographic methods result in significantly improved purification productivity. Thus, ATPS presents a promising alternative for the efficient recovery of PEGylated HSA. This study has several important implications. Firstly, it provides a robust, rapid, and scalable alternative to conventional chromatography for purifying PEGylated therapeutic proteins, potentially reducing production time and costs. Secondly, by explicitly evaluating and optimizing key ATPS parameters, the findings offer practical guidance for developing commercial-scale purification processes. Future research could explore strategies to enhance PEGylation reagent stability and ATPS yield, thus further increasing reaction yield and efficiency. Investigations into the scalability and economic feasibility of ATPS purification for diverse biotherapeutics beyond HSA would also be valuable, expanding the utility of ATPS as a mainstream downstream bioprocessing tool.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation. Inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author (cy5hbGthbmFpbXNoQGt1LmVkdS5rdw==).
Author contributions
SA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. OA-R: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MS: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported and funded by a grant from Kuwait University Research (Grant No. EC01/23), Kuwait.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Dr. Hussain Magar, and the General Facility Labs (GE03/08), College of Engineering and Petroleum, Kuwait University for the use of the UV spectrophotometer and Waters UPLC analytical instruments. We also thank Dr. Mohammed Samir, and the General Facility Labs (Project-GS01/03), College of Science, Kuwait University, for the use of the HPLC-Shimadzu analytical instrument.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fceng.2025.1609277/full#supplementary-material
References
Aguilar, O., Albiter, V., Serrano-Carreón, L., and Rito-Palomares, M. (2006). Direct comparison between ion-exchange chromatography and aqueous two-phase processes for the partial purification of penicillin acylase produced by E. coli. J. Chromatogr. B 835 (1), 77–83. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.03.016
Alkanaimsh, S., Corbin, J. M., Kailemia, M. J., Karuppanan, K., Rodriguez, R. L., Lebrilla, C. B., et al. (2019). Purification and site-specific N-glycosylation analysis of human recombinant butyrylcholinesterase from Nicotiana benthamiana. Biochem. Eng. J. 142, 58–67. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2018.11.004
Almeida, C., Pedro, A. Q., Tavares, A. P. M., Neves, M. C., and Freire, M. G. (2023). Ionic-liquid-based approaches to improve biopharmaceuticals downstream processing and formulation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1037436. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1037436
Alric, C., Aubrey, N., Allard-Vannier, É., di Tommaso, A., Blondy, T., Dimier-Poisson, I., et al. (2016). Covalent conjugation of cysteine-engineered scFv to PEGylated magnetic nanoprobes for immunotargeting of breast cancer cells. RSC Adv. 6 (43), 37099–37109. doi:10.1039/C6RA06076E
Asenjo, J. A., and Andrews, B. A. (2011). Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: a perspective. J. Chromatogr. A 1218 (49), 8826–8835. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.051
Asenjo, J. A., Mistry, S. L., Andrews, B. A., and Merchuk, J. C. (2002). Phase separation rates of aqueous two-phase systems: correlation with system properties. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 79 (2), 217–223. doi:10.1002/bit.10273
Azevedo, A. M., Gomes, A. G., Rosa, P. A. J., Ferreira, I. F., Pisco, A. M. M. O., and Aires-Barros, M. R. (2009a). Partitioning of human antibodies in polyethylene glycol–sodium citrate aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 65 (1), 14–21. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2007.12.010
Azevedo, A. M., Rosa, P. A., Ferreira, I. F., and Aires-Barros, M. R. (2008). Integrated process for the purification of antibodies combining aqueous two-phase extraction, hydrophobic interaction chromatography and size-exclusion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1213 (2), 154–161. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.09.115
Azevedo, A. M., Rosa, P. A., Ferreira, I. F., de Vries, J., Visser, T. J., and Aires-Barros, M. R. (2009b). Downstream processing of human antibodies integrating an extraction capture step and cation exchange chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 877 (1-2), 50–58. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.11.014
Azevedo, A. M., Rosa, P. A. J., Ferreira, I. F., and Aires-Barros, M. R. (2007). Optimisation of aqueous two-phase extraction of human antibodies. J. Biotechnol. 132 (2), 209–217. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.04.002
Behere, K., and Yoon, S. (2020). Chromatography bioseparation technologies and in-silico modelings for continuous production of biotherapeutics. J. Chromatogr. A 1627, 461376. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461376
Belén, L. H., Rangel-Yagui, C. d.O., Beltrán Lissabet, J. F., Effer, B., Lee-Estevez, M., Pessoa, A., et al. (2019). From synthesis to characterization of site-selective PEGylated proteins. Front. Pharmacol. 10 (1450), 1450. doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01450
Benjamin, S. R., Jackson, C. P., Fang, S., Carlson, D. P., Guo, Z., and Tumey, L. N. (2019). Thiolation of Q295: site-specific conjugation of hydrophobic payloads without the need for genetic engineering. Mol. Pharm. 16 (6), 2795–2807. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00323
Bhavsar, K., Ravi Kumar, V., and Khire, J. M. (2012). Downstream processing of extracellular phytase from aspergillus Niger: chromatography process vs. aqueous two phase extraction for its simultaneous partitioning and purification. Process Biochem. 47 (7), 1066–1072. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2012.03.012
Bigelow, E., Song, Y., Chen, J., Holstein, M., Huang, Y., Duhamel, L., et al. (2021). Using continuous chromatography methodology to achieve high-productivity and high-purity enrichment of charge variants for analytical characterization. J. Chromatogr. A 1643, 462008. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462008
BioSpace (2022). Biopharmaceuticals market size to hold USD 856. Available online at: https://www.biospace.com/biopharmaceuticals-market-size-to-hold-usd-856-1-bn-by-2030#:∼:text=The%20global%20biopharmaceuticals%20market%20size,12.5%25%20from%202022%20to%202030.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72 (1), 248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Campos-García, V. R., Benavides, J., and González-Valdez, J. (2021). Reactive aqueous two-phase systems for the production and purification of PEGylated proteins. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 54, 60–68. doi:10.1016/j.ejbt.2021.09.003
Capela, E. V., Magnis, I., Rufino, A. F. C. S., Torres-Acosta, M. A., Aires-Barros, M. R., Coutinho, J. A. P., et al. (2023). Using three-phase partitioning for the purification and recovery of antibodies from biological media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 316, 123823. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123823
Capela, E. V., Santiago, A. E., Rufino, A. F. C. S., Tavares, A. P. M., Pereira, M. M., Mohamadou, A., et al. (2019). Sustainable strategies based on glycine–betaine analogue ionic liquids for the recovery of monoclonal antibodies from cell culture supernatants. Green Chem. 21 (20), 5671–5682. doi:10.1039/C9GC02733E
Castro, L. S., Pereira, P., Passarinha, L. A., Freire, M. G., and Pedro, A. Q. (2020). Enhanced performance of polymer-polymer aqueous two-phase systems using ionic liquids as adjuvants towards the purification of recombinant proteins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 248, 117051. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117051
Cisneros-Ruiz, M., Mayolo-Deloisa, K., Rito-Palomares, M., and Przybycien, T. M. (2014). Separation of PEGylated variants of ribonuclease A and apo-α-lactalbumin via reversed phase chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1360, 209–216. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.085
Dozier, J. K., and Distefano, M. D. (2015). Site-specific PEGylation of therapeutic proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 (10), 25831–25864. doi:10.3390/ijms161025831
Dreyer, S., Salim, P., and Kragl, U. (2009). Driving forces of protein partitioning in an ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase system. Biochem. Eng. J. 46 (2), 176–185. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2009.05.005
Giraldo-Zuniga, A. D., dos Reis Coimbra, J. S., Arquete, D. A., Minim, L. A., Mendes da Silva, L. H., and Maffia, M. C. (2006). Interfacial tension and viscosity for poly(ethylene glycol) + maltodextrin aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chem. and Eng. Data 51 (3), 1144–1147. doi:10.1021/je0600348
Ghose, S., Nagrath, D., Hubbard, B., Brooks, C., and Cramer, S. M. (2004). Use and optimization of a dual-flowrate loading strategy to maximize throughput in protein-a affinity chromatography. Biotechnol. Prog. 20 (3), 830–840. doi:10.1021/bp0342654
Ghosh, R. (2005). Fractionation of human plasma proteins by hydrophobic interaction membrane chromatography. J. Membr. Sci. 260 (1), 112–118. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2005.03.024
González-Valdez, J., Cueto, L. F., Benavides, J., and Rito-Palomares, M. (2011). Potential application of aqueous two-phase systems for the fractionation of RNase A and α-Lactalbumin from their PEGylated conjugates. J. Chem. Technol. and Biotechnol. 86 (1), 26–33. doi:10.1002/jctb.2507
Großmann, C., Tintinger, R., Zhu, J., and Maurer, G. (1995). Aqueous two-phase systems of poly(ethylene glycol) and Di-Potassium hydrogen phosphate with and without partitioning biomolecules – experimental results and modeling of thermodynamic properties. Berichte Bunsenges. für Phys. Chem. 99 (5), 700–712. doi:10.1002/bbpc.19950990503
Hachem, F., Andrews, B. A., and Asenjo, J. A. (1996). Hydrophobic partitioning of proteins in aqueous two-phase systems. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 19 (7), 507–517. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(96)80002-D
Haynes, C. A., Blanch, H. W., and Prausnitz, J. M. (1989). Separation of protein mixtures by extraction: thermodynamic properties of aqueous two-phase polymer systems containing salts and proteins. Fluid Phase Equilibria 53, 463–474. doi:10.1016/0378-3812(89)80112-8
Holz, E., Darwish, M., Tesar, D. B., and Shatz-Binder, W. (2023). A review of Protein- and peptide-based chemical conjugates: past, present, and future. Pharmaceutics 15 (2), 600. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15020600
Huddleston, J., Abelaira, J. C., Wang, R., and Lyddiatt, A. (1996). Protein partition between the different phases comprising poly(ethylene glycol)-salt aqueous two-phase systems, hydrophobic interaction chromatography and precipitation: a generic description in terms of salting-out effects. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 680 (1), 31–41. doi:10.1016/0378-4347(95)00448-3
Hyde, A. M., Zultanski, S. L., Waldman, J. H., Zhong, Y.-L., Shevlin, M., and Peng, F. (2017). General principles and strategies for salting-out informed by the hofmeister series. Org. Process Res. and Dev. 21 (9), 1355–1370. doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00197
Jendryczko, K., Rzeszotko, J., Krzyscik, M. A., Kocyła, A., Szymczyk, J., Otlewski, J., et al. (2022). Drug conjugation via maleimide–thiol chemistry does not affect targeting properties of cysteine-containing Anti-FGFR1 peptibodies. Mol. Pharm. 19 (5), 1422–1433. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00946
Jimenez, O. A. Q., Costa, J. M., de Souza, B. R., Medeiros, A. C., Monteiro-Junior, E. G., and Basso, R. C. (2022). Effect of sulfate, citrate, and tartrate anions on the liquid-liquid equilibrium behavior of water + surfactant. Processes 10 (10), 2023. doi:10.3390/pr10102023
Johansson, H.-O., Karlström, G., Tjerneld, F., and Haynes, C. A. (1998). Driving forces for phase separation and partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 711 (1), 3–17. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00585-9
Jorge, A. M. S., Silva, G. M. C., Coutinho, J. A. P., and Pereira, J. F. B. (2024). Unravelling the molecular interactions behind the formation of PEG/PPG aqueous two-phase systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 26 (9), 7308–7317. doi:10.1039/D3CP05539F
Kalinovsky, D. V., Kholodenko, I. V., Kibardin, A. V., Doronin, I. I., Svirshchevskaya, E. V., Ryazantsev, D. Y., et al. (2023a). Minibody-based and scFv-Based antibody fragment-drug conjugates selectively eliminate GD2-Positive tumor cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (2), 1239. doi:10.3390/ijms24021239
Kalinovsky, D. V., Kholodenko, I. V., Svirshchevskaya, E. V., Kibardin, A. V., Ryazantsev, D. Y., Rozov, F. N., et al. (2023b). Targeting GD2-Positive tumor cells by pegylated scFv fragment–drug conjugates carrying maytansinoids DM1 and DM4. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45 (10), 8112–8125. doi:10.3390/cimb45100512
Kholodenko, I. V., Kalinovsky, D. V., Svirshchevskaya, E. V., Doronin, I. I., Konovalova, M. V., Kibardin, A. V., et al. (2019). Multimerization through pegylation improves pharmacokinetic properties of scFv fragments of GD2-Specific antibodies. Molecules 24 (21), 3835. doi:10.3390/molecules24213835
Kim, T. K., Sechi, B., Romero Conde, J. J., Angelo, J., Xu, X., Ghose, S., et al. (2022). Design and economic investigation of a multicolumn countercurrent solvent gradient purification unit for the separation of an industrially relevant PEGylated protein. J. Chromatogr. A 1681, 463487. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463487
Liu, X., Kouassi, K. G. W., Vanbever, R., and Dumoulin, M. (2022a). Impact of the PEG length and PEGylation site on the structural, thermodynamic, thermal, and proteolytic stability of mono-PEGylated alpha-1 antitrypsin. Protein Sci. 31 (9), e4392. doi:10.1002/pro.4392
Liu, X., Vanvarenberg, K., Kouassi, K. G. W., Mahri, S., and Vanbever, R. (2022b). Production and characterization of mono-PEGylated alpha-1 antitrypsin for augmentation therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 612, 121355. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121355
Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Wu, X., and Yan, X. (2016). Effect of excluded-volume and hydrophobic interactions on the partition of proteins in aqueous micellar two-phase systems composed of polymer and nonionic surfactant. Fluid Phase Equilibria 429, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.fluid.2016.08.026
Magri, A., Pimenta, M. V., Santos, J. H., Coutinho, J. A., Ventura, S. P., Monteiro, G., et al. (2020). Controlling the l-asparaginase extraction and purification by the appropriate selection of polymer/salt-based aqueous biphasic systems. J. Chem. Technol. and Biotechnol. 95 (4), 1016–1027. doi:10.1002/jctb.6281
Mao, L., Russell, A. J., and Carmali, S. (2022). Moving protein PEGylation from an art to a data science. Bioconjugate Chem. 33 (9), 1643–1653. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00262
Marcos, J. C., Fonseca, L. P., Ramalho, M. T., and Cabral, J. M. S. (1998). Variation of penicillin acylase partition coefficient with phase volume ratio in poly(ethylene glycol)–sodium citrate aqueous two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 711 (1), 295–299. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00633-6
Martínez-Jothar, L., Doulkeridou, S., Schiffelers, R. M., Sastre Torano, J., Oliveira, S., van Nostrum, C. F., et al. (2018). Insights into maleimide-thiol conjugation chemistry: conditions for efficient surface functionalization of nanoparticles for receptor targeting. J. Control. Release 282, 101–109. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.03.002
Mehtala, J. G., Kulczar, C., Lavan, M., Knipp, G., and Wei, A. (2015). Cys34-PEGylated human serum albumin for drug binding and delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 26 (5), 941–949. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00143
Mejía-Manzano, L. A., Mayolo-Deloisa, K., Sánchez-Trasviña, C., González-Valdez, J., González-González, M., and Rito-Palomares, M. (2017). Recovery of PEGylated and native lysozyme using an in situ aqueous two-phase system directly from the PEGylation reaction. J. Chem. Technol. and Biotechnol. 92 (10), 2519–2526. doi:10.1002/jctb.5307
Moosmann, A., Christel, J., Boettinger, H., and Mueller, E. (2010). Analytical and preparative separation of PEGylated lysozyme for the characterization of chromatography media. J. Chromatogr. A 1217 (2), 209–215. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.11.031
Morgenstern, J., Wang, G., Baumann, P., and Hubbuch, J. (2017). Model-based investigation on the mass transfer and adsorption mechanisms of mono-pegylated lysozyme in ion-exchange chromatography. Biotechnol. J. 12 (9), 1700255. doi:10.1002/biot.201700255
Morón, M. C. (2021). Protein hydration shell formation: dynamics of water in biological systems exhibiting nanoscopic cavities. J. Mol. Liq. 337, 116584. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116584
Naganagouda, K., and Mulimani, V. H. (2008). Aqueous two-phase extraction (ATPE): an attractive and economically viable technology for downstream processing of Aspergillus oryzae α-galactosidase. Process Biochem. 43 (11), 1293–1299. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2008.07.016
Nair, D. P., Podgórski, M., Chatani, S., Gong, T., Xi, W., Fenoli, C. R., et al. (2014). The thiol-michael addition click reaction: a powerful and widely used tool in materials chemistry. Chem. Mater. 26 (1), 724–744. doi:10.1021/cm402180t
Nisslein, M., González-González, M., and Rito-Palomares, M. (2021). Influence of tie line length and volume ratio on the partition behavior of peripheral blood and conjugated CD34 antibody in polymer-polymer aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 257, 117830. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117830
Osgood, A. O., Roy, S. J. S., Koo, D., Gu, R., and Chatterjee, A. (2024). A genetically encoded photocaged cysteine for facile site-specific introduction of conjugation-ready thiol residues in antibodies. Bioconjugate Chem. 35 (4), 457–464. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00513
Phong, W. N., Show, P. L., Chow, Y. H., and Ling, T. C. (2018). Recovery of biotechnological products using aqueous two phase systems. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 126 (3), 273–281. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.03.005
Ramalho, C. C., Neves, C. M., Quental, M. V., Coutinho, J. A., and Freire, M. G. (2018). Separation of immunoglobulin G using aqueous biphasic systems composed of cholinium-based ionic liquids and poly(propylene glycol). J. Chem. Technol. and Biotechnol. 93 (7), 1931–1939. doi:10.1002/jctb.5594
Ramos-de-la-Peña, A. M., and Aguilar, O. (2020). Progress and challenges in PEGylated proteins downstream processing: a review of the last 8 years. Int. J. Peptide Res. Ther. 26 (1), 333–348. doi:10.1007/s10989-019-09840-4
Retnaningtyas, E., Sumitro, S., Soeatmadji, D. W., and Widjayanto, E. (2016). Molecular dynamics simulation for revealing the role of water molecules on conformational change of human serum albumin, 8, 158–161.
Roque, A. C. A., Pina, A. S., Azevedo, A. M., Aires-Barros, R., Jungbauer, A., Di Profio, G., et al. (2020). Anything but conventional chromatography approaches in bioseparation. Biotechnol. J. 15 (8), 1900274. doi:10.1002/biot.201900274
Rosa, P., Azevedo, A., Sommerfeld, S., Bäcker, W., and Aires-Barros, M. (2011). Aqueous two-phase extraction as a platform in the biomanufacturing industry: economical and environmental sustainability. Biotechnol. Adv. 29, 559–567. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.03.006
Rosa, P. A., Azevedo, A. M., and Aires-Barros, M. R. (2007). Application of central composite design to the optimisation of aqueous two-phase extraction of human antibodies. J. Chromatogr. A 1141 (1), 50–60. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.11.075
Sánchez-Trasviña, C., Flores-Gatica, M., Enriquez-Ochoa, D., Rito-Palomares, M., and Mayolo-Deloisa, K. (2021). Purification of modified therapeutic proteins available on the market: an analysis of chromatography-based strategies. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 717326. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.717326
Santos, J. H., Flores-Santos, J. C., Meneguetti, G. P., Rangel-Yagui, C. O., Coutinho, J. A., Vitolo, M., et al. (2018). In situ purification of periplasmatic L-asparaginase by aqueous two phase systems with ionic liquids (ILs) as adjuvants. J. Chem. Technol. and Biotechnol. 93 (7), 1871–1880. doi:10.1002/jctb.5455
Santos, J. H. P. M., Carretero, G., Coutinho, J. A. P., Rangel-Yagui, C. O., and Ventura, S. P. M. (2017). Multistep purification of cytochrome c PEGylated forms using polymer-based aqueous biphasic systems. Green Chem. 19 (24), 5800–5808. doi:10.1039/C7GC02600E
Santos, J. H. P. M., Mendonça, C. M. N., Silva, A. R. P., Oliveira, R. P. S., Pessoa, A., Coutinho, J. A. P., et al. (2019). An integrated process combining the reaction and purification of PEGylated proteins. Green Chem. 21 (23), 6407–6418. doi:10.1039/C9GC01459D
Schultze-Jena, A., Boon, M. A., de Winter, D. A. M., Bussmann, P. J. T., Janssen, A. E. M., and van der Padt, A. (2020). Predicting intraparticle diffusivity as function of stationary phase characteristics in preparative chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1613, 460688. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460688
Segaran, A., and Chua, L. S. (2024). Review of recent applications and modifications of aqueous two-phase system for the separation of biomolecules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 276, 133856. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133856
Shang, X., Wittbold, W., and Ghosh, R. (2013). Purification and analysis of mono-PEGylated HSA by hydrophobic interaction membrane chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 36 (23), 3673–3681. doi:10.1002/jssc.201300511
Shukla, A. A., Wolfe, L. S., Mostafa, S. S., and Norman, C. (2017). Evolving trends in mAb production processes. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2 (1), 58–69. doi:10.1002/btm2.10061
Singla, M., and Sit, N. (2023). Theoretical aspects and applications of aqueous two-phase systems. ChemBioEng Rev. 10 (1), 65–80. doi:10.1002/cben.202200026
Torres-Acosta, M. A., Aguilar-Yáñez, J. M., Rito-Palomares, M., and Titchener-Hooker, N. J. (2016). Economic analysis of uricase production under uncertainty: contrast of chromatographic purification and aqueous two-phase extraction (with and without PEG recycle). Biotechnol. Prog. 32 (1), 126–133. doi:10.1002/btpr.2200
Tripathi, N. K., and Shrivastava, A. (2019). Recent developments in bioprocessing of recombinant proteins: expression hosts and process development. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7, 420. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2019.00420
Wall, A., Wills, A. G., Forte, N., Bahou, C., Bonin, L., Nicholls, K., et al. (2020). One-pot thiol–amine bioconjugation to maleimides: simultaneous stabilisation and dual functionalisation. Chem. Sci. 11 (42), 11455–11460. doi:10.1039/D0SC05128D
Wang, J., Yang, S., and Zhang, K. (2019). Multi-arm PEG-Maleimide conjugation intermediate characterization and hydrolysis study by a selective HPLC method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 164, 452–459. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.11.009
Wang, X.-D., Wei, N.-N., Wang, S.-C., Yuan, H.-L., Zhang, F.-Y., and Xiu, Z.-L. (2018). Kinetic optimization and Scale-Up of site-specific Thiol-PEGylation of loxenatide from laboratory to pilot scale. Industrial and Eng. Chem. Res. 57 (44), 14915–14925. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.8b02613
Wu, Y.-T., and Zhu, Z.-Q. (1999). Modeling of interfacial tension of aqueous two-phase systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 54 (4), 433–440. doi:10.1016/S0009-2509(98)00255-3
Zaman, R., Islam, R. A., Ibnat, N., Othman, I., Zaini, A., Lee, C. Y., et al. (2019). Current strategies in extending half-lives of therapeutic proteins. J. Control. Release 301, 176–189. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.02.016
Keywords: protein PEGylation, human serum albumin, aqueous two-phase separation, protein purification, downstream bioprocessing
Citation: Alkanaimsh S, Al-Rashed OA and Shaaban M (2025) Aqueous two-phase separation enables selective purification of mono-PEGylated human serum albumin: influence of process parameters and reagent size. Front. Chem. Eng. 7:1609277. doi: 10.3389/fceng.2025.1609277
Received: 10 April 2025; Accepted: 15 July 2025;
Published: 06 August 2025.
Edited by:
Byung Hoon Jo, Gyeongsang National University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Viviana Monje, University at Buffalo, United StatesQiang WU, Weifang People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Alkanaimsh, Al-Rashed and Shaaban. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Salem Alkanaimsh, cy5hbGthbmFpbXNoQGVkdS5rdw==
†ORCID: Salem Alkanaimsh, orcid.org/0000-0001-6266-4863; Mohamed Shaaban, 0000-0001-9281-2505
 Salem Alkanaimsh
Salem Alkanaimsh Osama A. Al-Rashed1
Osama A. Al-Rashed1 Mohamed Shaaban
Mohamed Shaaban