- 1Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Cancer Institute (Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Intervention, China National Ministry of Education), Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 3Department of Human Genetics, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Institute of Genetics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression features of discordant inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) twin pairs to identify novel molecular features and markers. We collected an expression dataset of discordant twin pairs with ulcerative colitis and performed integrative analysis to identify the genetic-independent expression features. Through deconvolution of the immune cell populations and tissue expression specificity, we refined the candidate genes for susceptibility to ulcerative colitis. We found that dysregulated immune systems and NOD-related pathways were enriched in the expression network of the discordant IBD twin pairs. Among the identified factors were significantly increased proportions of immune cells, including megakaryocytes, neutrophils, natural killer T cells, and lymphatic endothelial cells. The differentially expressed genes were significantly enriched in a gene set associated with cortical and medullary thymocytes. Finally, by combining these expression features with genetic resources, we identified some candidate genes with potential to serve as novel markers of ulcerative colitis, such as CYP2C18. Ulcerative colitis is a subtype of inflammatory bowel disease and a polygenic disorder. Through integrative analysis, we identified some genes, such as CYP2C18, that are involved in the pathogenesis of IBD as well as some candidate therapeutic targets, such as LOXL2.
Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a multifactorial disorder that includes three main subtypes, Crohn’s disease (CD), Ulcerative Colitis (UC), and IBD unclassified (IBDU) (Uhlig and Muise, 2017). The phenotypes of these disorders are usually caused by defects in the epithelial barrier and dysregulation in the innate and adaptive immune responses. The pathogenic pathways of IBDs overlap with those of other disorders, such as psoriasis (Parkes et al., 2013). Therefore, the underlying genetic or epigenetic factors likely have pleiotropy phenotype which further complicates the identification of the molecular etiology of IBDs.
Familial aggregation and twin-paired studies have provided evidence that genetic factors contribute to the pathogenesis of IBDs. For instance, concordance in the diagnosis of UC (15.3 vs. 3%) and CD (51.6 vs. 5.1%) is higher in monozygotic twins than dizygotic twins (Annese, 2020). The heritability of IBDs varies across subtypes, as has been observed in twin studies of UC and CD. Rare variants in IL10 and IL10RB have been shown to be highly penetrant for intestinal inflammation (Uhlig and Schwerd, 2016). However, the penetrance of some variants might be variable, and researches on rare variants in IBDs is limited. Complex phenotypes are observed in IBDs, and the genetic results support this complexity. Thus far, more than 240 genes or loci have been linked to the IBDs (Annese, 2020), which indicates that these disorders are polygenic. Genome-wide association studies have refined the candidate genes involved in the pathogenesis of IBDs and have identified candidates in the NOD2-related microbe sensing pathway (Jostins et al., 2012), IL-23 driven T-helper cell response (Liu et al., 2015), and autophagy (Schwerd et al., 2017).
IBDs are multifactorial disorders. Research on discordant twin pairs with IBDs has indicated some genetic-independent factors underlying the pathogenesis. For instance, differences were observed in the gut microbiome of the inflamed and non-inflamed segments of the gut in both CD and UC (Ryan et al., 2020). However, a recent report showed that the gut microbiome of the healthy cotwins from discordant IBD twin pairs displays IBD-like signatures, indicating that the discordant monozygotic twins with IBD not only share the same genetic background but also the same gut microbiome (Brand et al., 2021). Thus, the causative role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis of IBDs requires longitudinal follow-up to confirm. Based on these findings, we supposed that the differential expression patterns between the affected and unaffected discordant twins could provide clues to the mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of IBD. In this study, we identified dysregulation of seven immune cell subpopulations as factors that might contribute to IBD, especially those related to the cortical and medullary thymocyte. In addition, we identified some candidate makers and therapeutic targets for UC.
Materials and Methods
Microarray Dataset
We download a transcriptome dataset from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database that included 10 paired discordant monozygotic twins for UC (GSE22619). We also collected expression data from 20 paired unrelated healthy twins (GSE7821).
Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
We performed rma normalization of the gene array dataset of twin pairs and identified the Differential Express Genes (DEGs) using the oligo (Carvalho and Irizarry, 2010) and limma R packages (Ritchie et al., 2015). The cutoff for DEGs was a log fold change (| logFC|) > 2 and a p-value less than 0.01.
Principal Component Analysis and Sample Similarity Analysis
We performed principal component analysis (PCA) on the expression dataset using the R package FactoMineR (Lê et al., 2008) and factoextra1.
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
We performed a Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment using the R package clusterProfiler (Yu et al., 2012) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) to evaluate the underlying expression spectrum of UC using the R package GSEABase (Morgan et al., 2020).
Deciphering the Immune Cell Populations Using the Expression Dataset
We applied the expression matrix to xCell (Aran et al., 2017) to decipher the immune cell proportion with the parameters set as default and applied paired Wilcoxon.test to evaluate the differential cell populations.
Deconvolution of the Tissue Expression Specificity of the DEGs
We downloaded the normalized RNA-seq dataset from Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Portal and tissue origin annotation information and used the t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) approach to investigate the tissue expression specificity of the identified DEGs and normalized the mean expression for each type of tissues. To keep the consistency of the gene names, the gene symbols were converted to Ensembl gene id by gprofiler (Reimand et al., 2007), and the genes unmatched were ruled out in the downstream analysis.
Cell Culture and Treatments
The human colon cancer cell lines HCT116 and HT29 were used in this study Cell lines were cultured at 37°C under 5% CO2 in McCoy’s 5A (Gibco) supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco) and penicillin G (100 U/ml, Gibco) and streptomycin (100 μg/ml, Gibco). To induce the inflammation status, the cell lines were stimulated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. And the control group, the cell lines were treated with DMSO. All the experiments were repeated three times.
Determine the Expression of CYP2C18
The expression level of CYP2C18 was determined in cell lines, HCT116, HT29, and the control cell line. Cells were washed with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), harvested with a cell scraper (Corning), centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C, and resuspend with RIPA buffer supplemented with PMSF (Sigma), protease inhibitor (Roche). Lysates were subjected to sonication and spun at 13,300 rpm at 4°C. The supernatant was transferred into new tubes. Protein concentrations were qualified with the BCA reagent (Thermo Scientific). Protein lysates were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels, and protein of interest was detected with one of the following antibodies: CYP2C18 (PA5-112394, Invitrogen), β-actin (ab8226, Abcam). Paraffin section from 7 unrelated UC affected cases and 5 normal controls were applied to immunohistochemistry, which was performed as recommended with the antibody CYP2C18 (PA5-112394, Invitrogen).
Curation the Association of Variants in Given Candidate Genes With Risk of IBDs
The rare non-silent variants in the identified genes were further inspected based on the IBD Exome Browser2 following the guidelines as described before (Richards et al., 2015; Yin et al., 2019).
Results
Revisiting the Potential Causative Genetic Factors of IBDs
To evaluate the genetic architecture underlying IBDs, we retrieved candidate genes by text mining and estimate their prevalence and penetrance using the IBD exome browser. Second, we focused on high confidence variants likely to be disease causative based on the results of a previous fine-mapping study (Huang et al., 2017). Of the fine-mapped genes with at least one variant located in the coding region, six genes, NOD2 (n = 7), IL23R (n = 3), CCDC71 (n = 2), BANK1 (n = 2), MST1 (n = 2), and FUT2 (n = 2) had recurring non-silent variants. We evaluated the potential phenotypes of IBD associated with these fine-mapped candidate genes, and we found that the terms abnormal immunological process, colitis, and inflammation of gastrointestinal or intestinal recurred in the top 10 human phenotypes (Supplementary Table 1). To validate this result, we evaluated the enriched non-silent variants in these candidate genes using the IBD exome browser (IBD Exomes Portal, 2021), and only NOD2 was highly enriched with potential disease-causing variants (Data not shown). Although Mendelian IBD has been reported, the underlying genetic factors interact with other non-genetic factors to determine the final phenotype. Therefore, it might be difficult to identify all the penetrant variants for IBDs and combine multiple sources of dataset, including gene mutation burden test results, gene tissue expression specificity and differential expression genes between affected cases and control could refine the candidate genes (Supplementary Figure 1).
Expression Features Identified in the Discordant Twin Pairs
To identify the most informative gene for distinguishing the affected twins from the unaffected twins, we retrieved the expression profile of discordant twin pairs (monozygotic) for IBDs (n = 10). We also included healthy twin pairs (n = 20) for quality control (Supplementary Figure 2). We first performed PCA on the healthy twin pairs cohort, and little distinction was observed among the individuals from each twin pairs (Supplementary Figure 2). In the discordant twin pairs for IBDs, the affected twins could be distinguished from the unaffected twins; however, in four twin pairs (ID: 03, 04, 07, and 12), there was little difference between the affected and unaffected twins (Figure 1A). We also performed a pairwise correlation using the expression dataset and obtained results similar to the PCA (Figure 1B). Although heterogeneity exists among different twin pairs, the distinction between the discordant pairs could provide specific information regarding the pathogenesis of IBD.
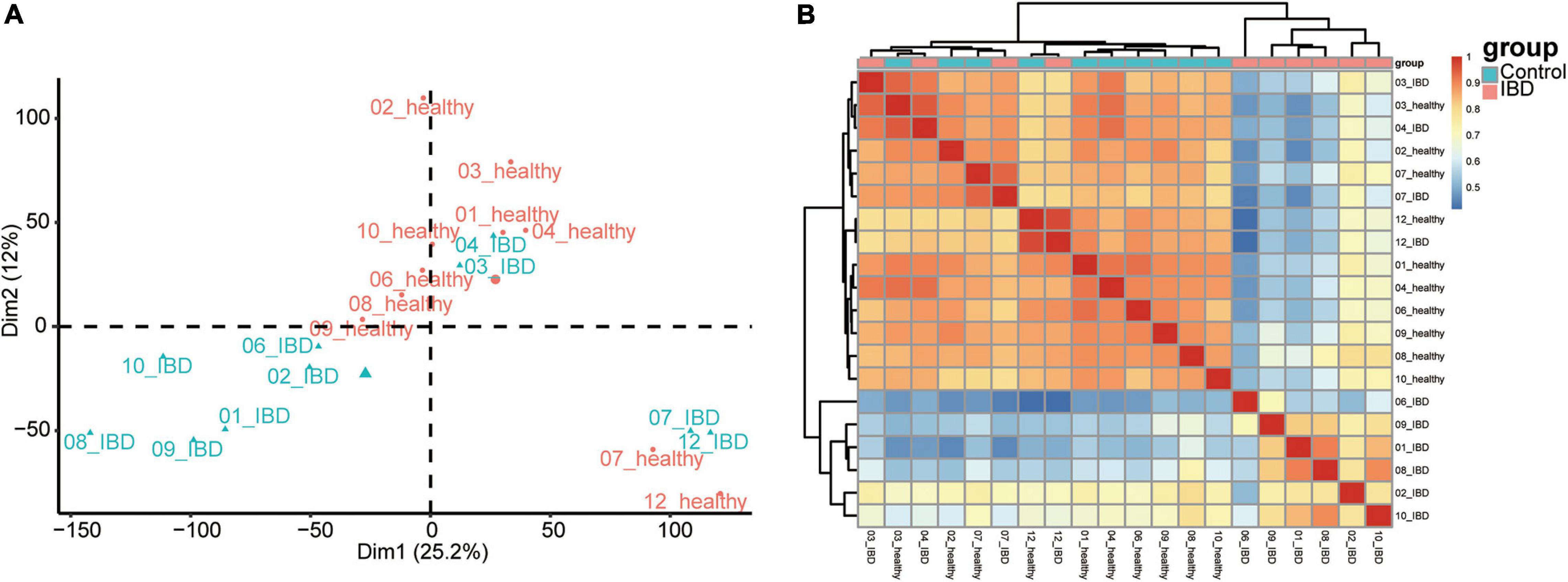
Figure 1. Sample inherent similarity based on principle component analysis (PCA) and pairwise correlation analysis. (A) Scatter plot of the top two components from the PCA. (B) Sample similarity derived from the pairwise correlation analysis. Pearson’s correlation results were shown in the heatmap.
To evaluate the expression dataset for possible noise, we first identify the DEGs among the healthy twin pair, and we did not identify any genes with significant differences (Supplementary Figure 3). Second, we examined the expression datasets from discordant IBD twin pairs. In total, we identified 118 genes that tended to be differentially expressed between the affected and unaffected twins (P < 0.01 and | log2FC| > 1; Figure 2A and Supplementary Table 2). A comparison to genes reported to be related to IBDs based on GWAS and DiseaseNet identified four genes, CDH3, CXCL8, IL1R2, and NXPE1, that were differentially expressed between the discordant twin pairs (Supplementary Figure 4 and Supplementary Table 3). Among the top up-regulated DEGs, OLFM4, MMP1, CYP2C18, COL12A1, and LOXL2, gene OLFM4 encodes Olfactomedin4, which is a stem cell marker for small intestinal. The expression of OLFM4 was highly upregulated in inflamed colonic epithelium, especially in UC (Gersemann et al., 2012; Suzuki et al., 2018). Furthermore, the relationships between IBD and some of the top DEGs (Figure 2B), such as MMP1 (Wang and Qiu, 2010) and COL12A1 (Ji et al., 2020), have also been reported. Interestingly, the serum levels of LOXL2 are significantly higher in primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) (Pollheimer et al., 2018), which is closely associated with IBD, and LOXL2 targeting in IBD has been evaluated in PSC (Lynch et al., 2019). Meanwhile, among the top down-regulated DEGs, such as BRINP3, CKB, CP, CLDN8 and DPP10-AS1, down regulation of BRINP3 (Smith et al., 2014), CLDN8 (Wang et al., 2016), has been reported in UC. CLDN8 has been identified as a novel target of IL23 signaling and inhibition of CLDN8 could destroy the intestinal barrier function (Wang et al., 2016; Li et al., 2020). However, the roles of CYP2C18, DPP10-AS1, CKB, and CP involved in the IBD associated syndrome has not been reported. Therefore, the top DEGs identified in this study, especially those had not been reported, were deemed to be worthy of further investigation.
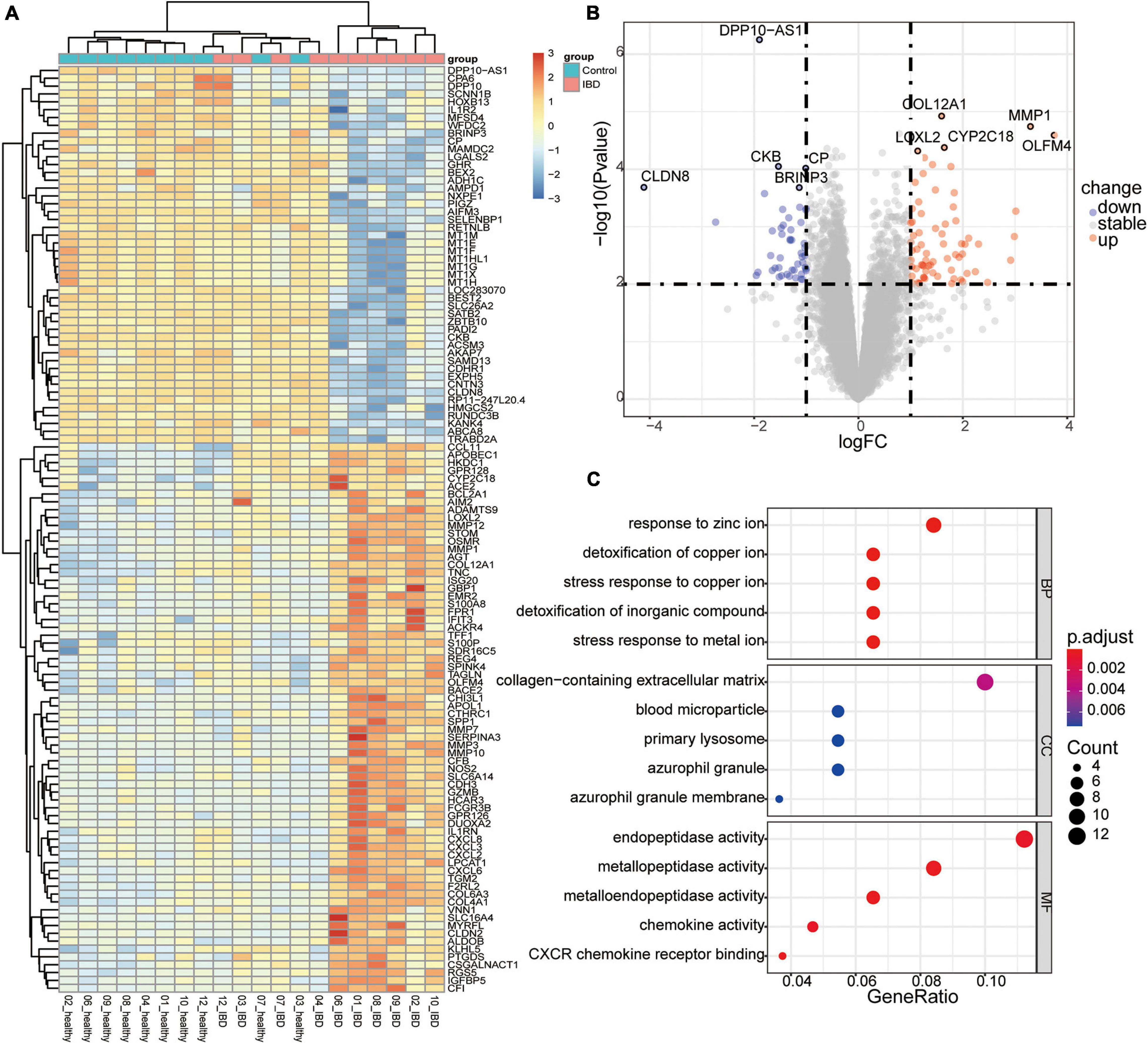
Figure 2. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the discordant inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) twin pairs. (A) Heatmap of the scaled expression values of DEGs. (B) Volcano plot of the DEGs, with the top five upregulated and downregulated genes labeled. (C) Enriched components containing the DEGs.
Gene Set Enrichment of the Differentially Expressed Genes and Immune Signatures Associated With UC
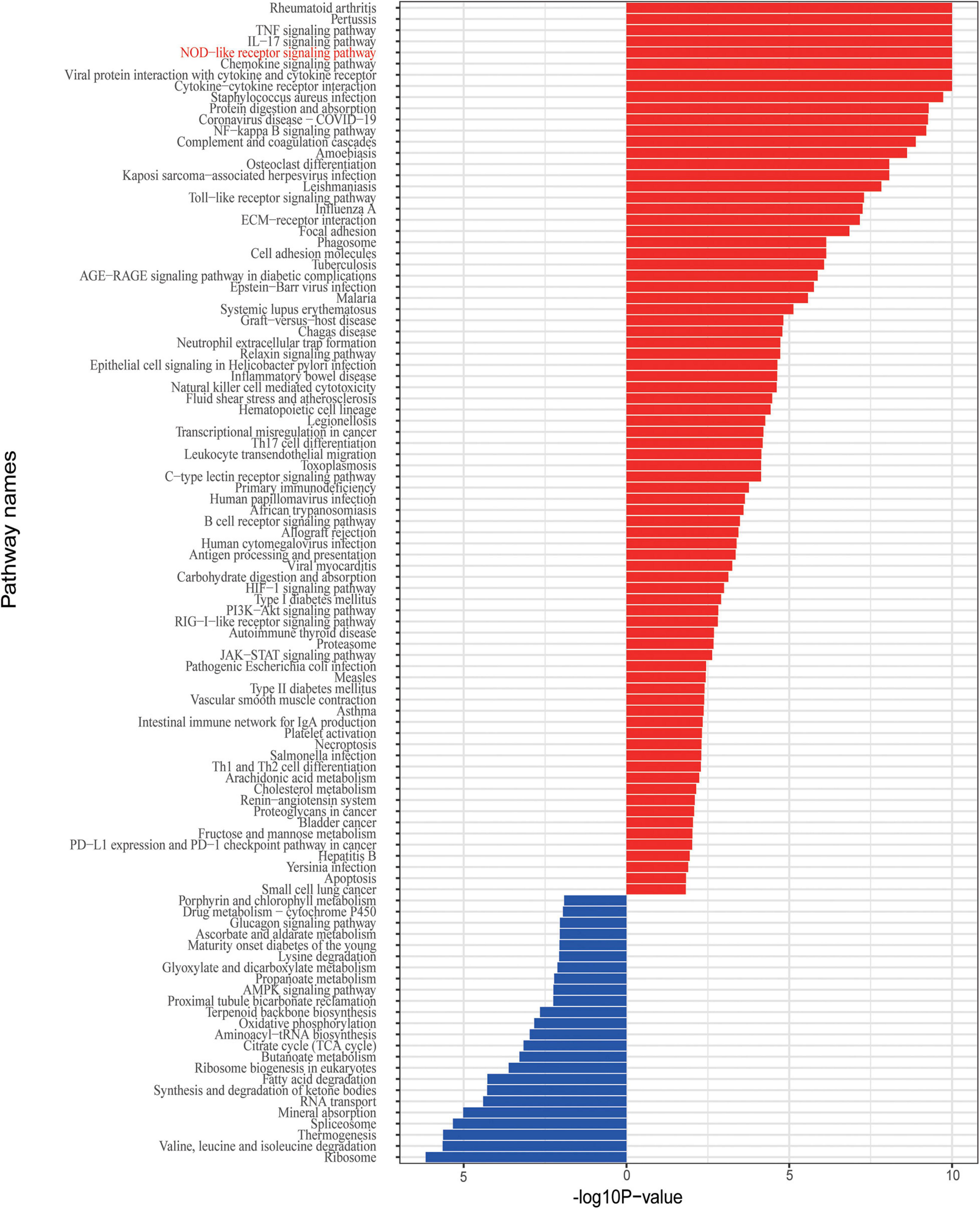
Given that the IBD and related disorders are characterized by the dysregulated immune system, quality control based on gene set enrichment and pathway analysis were performed to check the confidence of the informative markers identified via DEG analysis. To estimate the underlying functional components, we performed gene set enrichment analysis and we found that the DEGs were significantly related to functions, such as ion response and chemokine activity (Figure 2C). To further investigate the dysfunction network underlying the pathogenesis of IBD, we performed functional pathway enrichment analysis. In our analysis, the top five enriched pathways were rheumatoid arthritis, pertussis, TNF signaling pathway, IL-17 pathway, and NOD-like receptor signaling pathway (Figure 3), which is consistent with the observation the NOD2-related pathways were involved in the pathogenesis mechanism underlying IBD. Generally, immune system dysregulation was highly enriched in the related functional pathways, and pathways related to virus infection recurred (Figure 3). Interestingly, we also found that the DEGs were also enriched in the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) associated pathway, which was consistent with some recent publications (Allocca et al., 2020). Apart from the immune-related disorders, dysregulated expression of the identified DEGs might also be involved in other disorders, such as cancer. For instance, the PD1/PD-L1 checkpoint pathway was highly regulated among the affected twins (Figure 3). Therefore, individuals with IBDs may have a high predisposition to other disorders and might benefit from the immune checkpoint inhibitors treatment.
Given that abnormal immune responses were highly enriched in the IBDs, we further evaluated the dysregulated immune cell subpopulations. We applied xCell to estimate the immune cell subpopulation and we found seven immune cell subpopulations that were distinct between the affected and unaffected twins (Figure 4A). For instance, the proportion of megakaryocytes, neutrophils, natural killer T (NKT), and endothelial cells was highly increased in the UC affected twins; and the proportion of CD4+ T cell, CLP, and MEP subpopulations was significantly decreased in the UC affected twins (Figure 4B). Furthermore, we performed a GSEA of the immune-related gene sets, we found that the DEGs were enriched in cortical and medullary thymocyte gene sets (P = 0.0016; q < 0.05), and the genes with the greatest contribution were VNN1, CHI3L1, APOBEC1, CXCL2, CXCL6, IL1RN, CXCL3, and IFIT3. Therefore, the genetic-independent pathways involved in the pathogenesis of discordant twin pairs of IBDs were similar to the dysfunction of genetic components, such as NOD2.
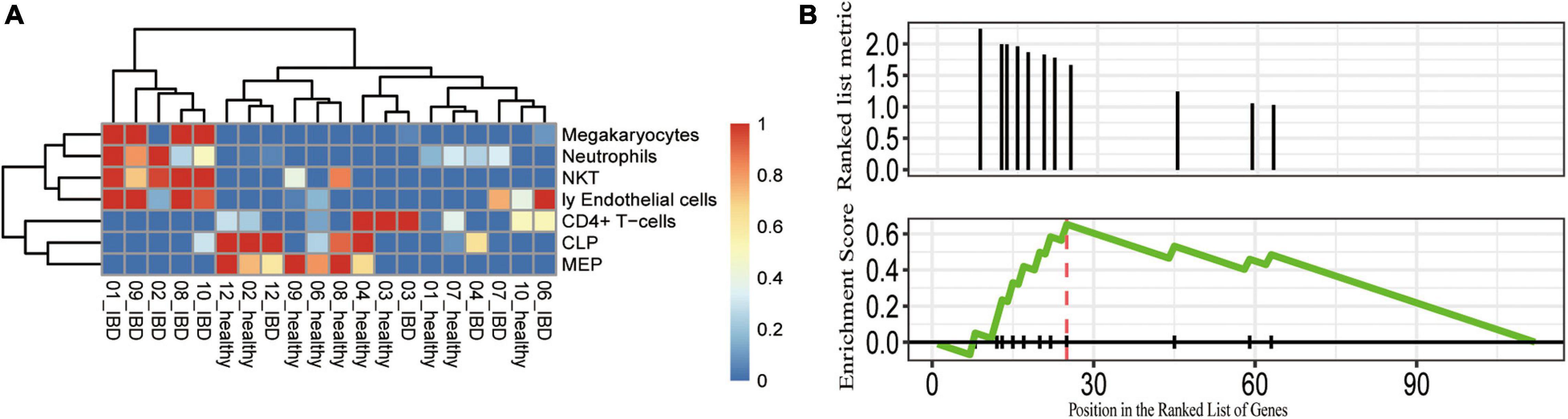
Figure 4. Potentially dysregulated immune cell subpopulations and pathways identified in the discordant IBD twin pairs. (A) The cell subpopulations that differ between the healthy and control. The scaled cell proportions were shown in the heatmap. (B) GSEA showing that the DEGs enriched in the gene set were upregulated in cortical and medullary thymocytes. CLP, common lymphoid progenitor; MEP, megakaryocytic-erythroid progenitors; Ly endothelial cells, lymphatic endothelial cells; NKT, natural killer T cells.
Deconvolution of the Tissue Specificity of the DEGs and Refinement of Candidate Genes
To refine the candidate genes involved in IBD, we deconvolve the tissue expression specificity of the DEGs that do not have disease-causative supporting evidence in either GWAS FineMapping or DiseaseNet curation by t-SNE based approach. Due to RP11-247L20.4, LOC283070, EMR2, GPR126, MFSD4, and GPR128 have unmatched gene id in the GTEx dataset, we rule them out from the downstream analysis. Based on the GTEx dataset, we found that those DEGs showed wide tissue specificity (Figure 5). After normalized the expression level, we found two clusters of genes, including OLFM4, NXPE1, APOBEC1, CYP2C18 that were specifically expressed in either the colon or small intestine (Figure 6). Given that the role of the gene CYP2C18 in the pathogenesis of IBDs has not been investigated, we mainly focused on determining the functional role of CYP2C18. Interestingly, we found multiple, rare, non-silent variants in CYP2C18 (e.g., Tyr68Ter, Cys279Arg, and Thr243Met) that were enriched in IBD using the IBD exome browser (Supplementary Table 4). We performed functional assay to validate the results we observed. After inducing the inflammation signaling by TNF-α, the expression of CYP2C18 was significantly increased in the HCT116 and HT29 cell lines (Figure 7A). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis showed that the expression of CYP2C18 was highly increased in the UC-affected cases in comparison with the normal individuals (Figure 7B). Therefore, CYP2C18 is a good candidate susceptible gene for IBDs and valuable for further investigation.
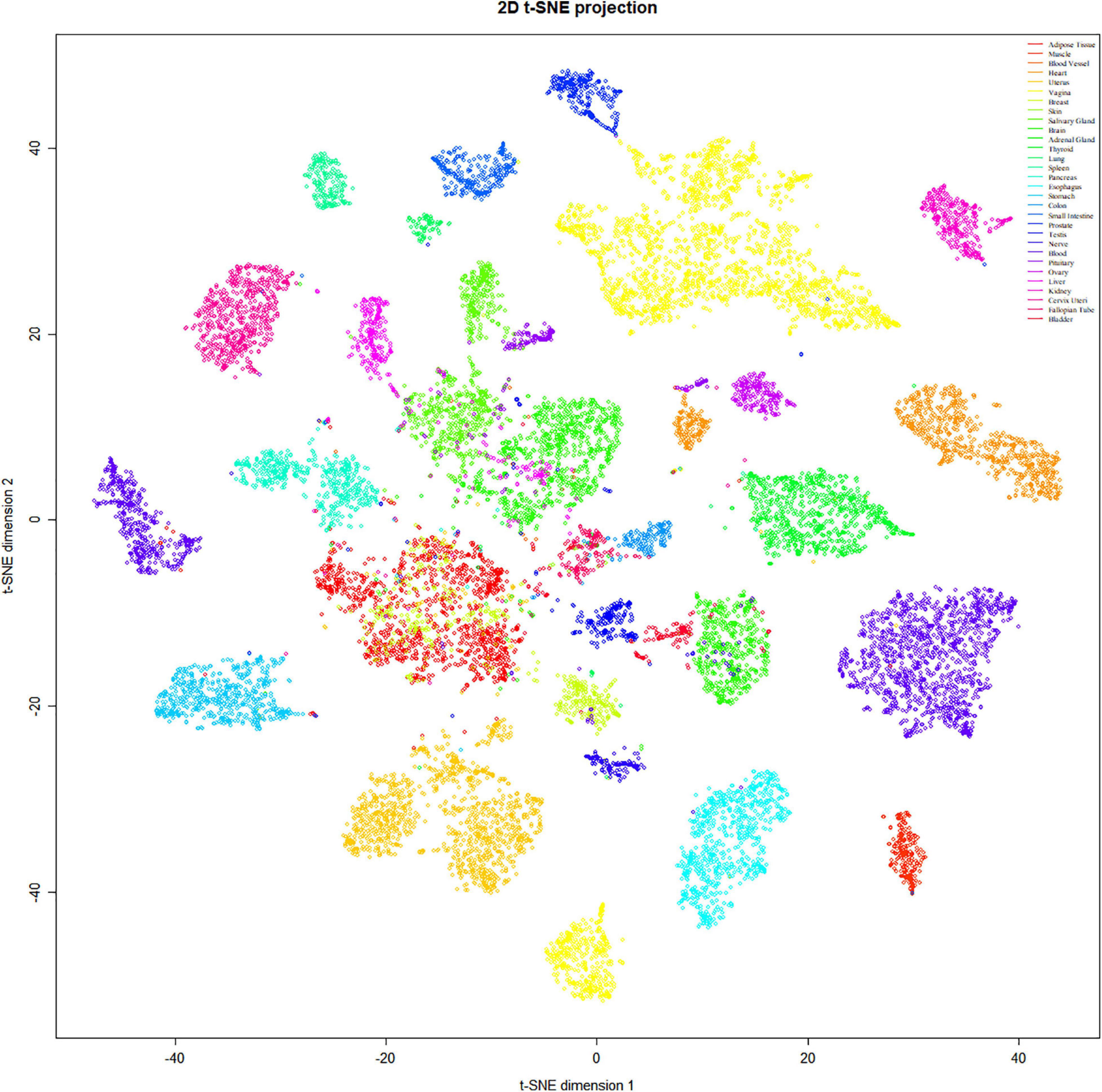
Figure 5. Tissue specificity of the DEGs was identified in the discordant IBD twin pairs. The expression spectrum across 30 different tissue types indicates a variable spectrum of the identified DEGs.
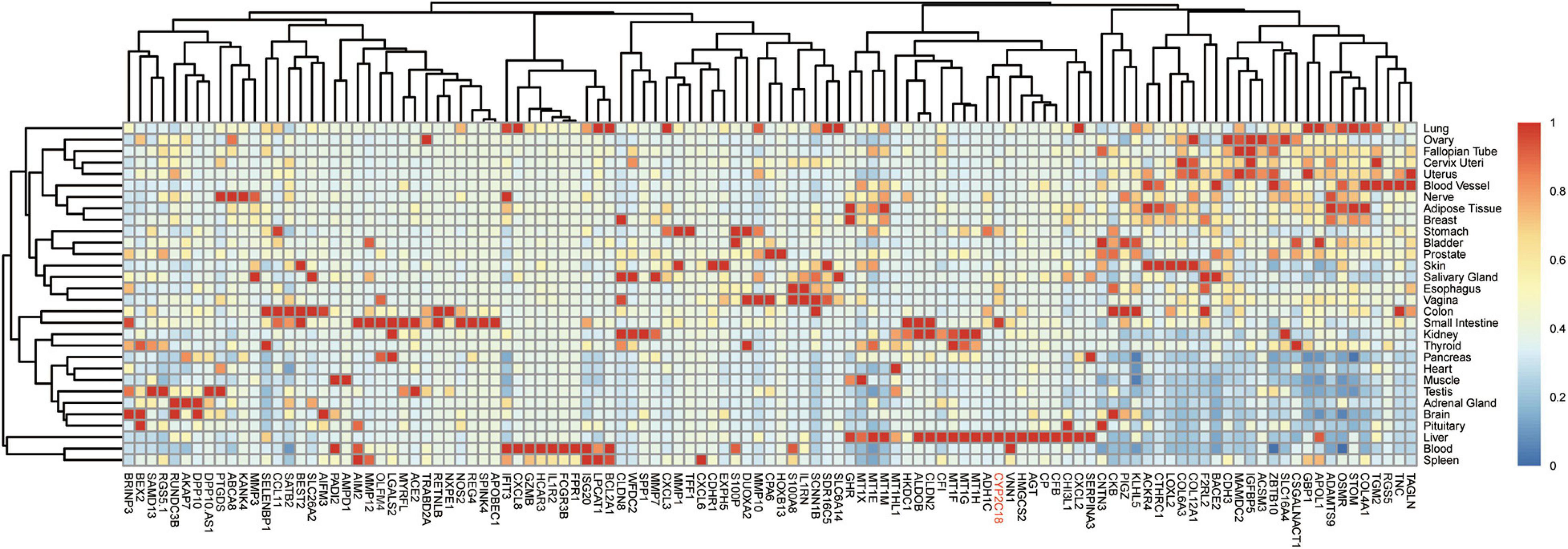
Figure 6. Expression spectrum of the DEGs across different tissues. Normalized expression values across the tissues were shown in the heatmap. Among the identified candidate genes for the pathogenesis of IBD, gene CYP2C18 could be a novel marker for IBD, especially UC and CYP2C18 was labeled in red.
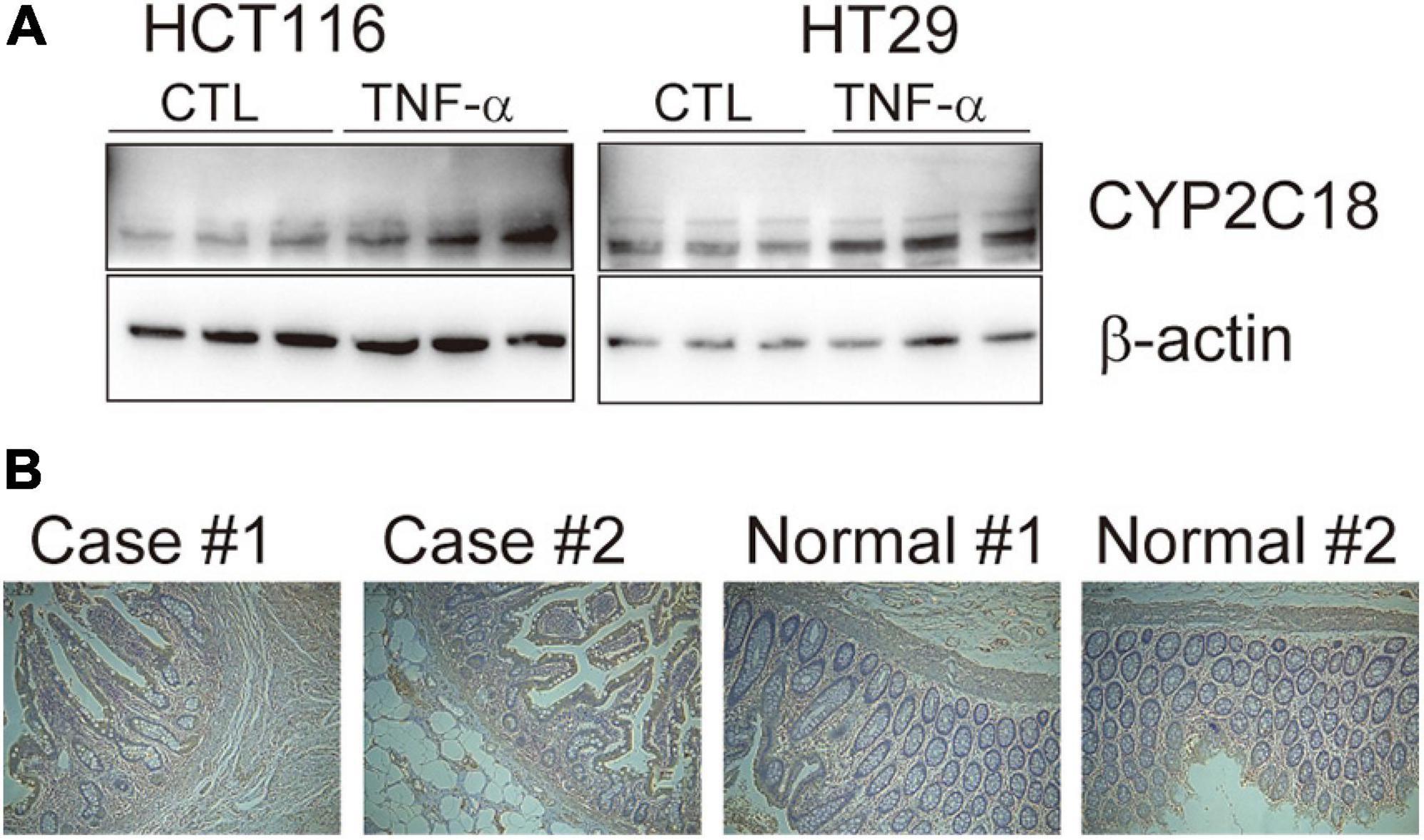
Figure 7. The expression level of CYP2C18 was upregulated in colorectal cancer cell lines and UC-affected cases. (A) The expression level of CYP2C18 was highly increased after TNF-α stimulation. (B) Representative images of immunohistochemistry staining of CYP2C18 in UC affected cases and normal individuals. Scale bar: 100 μm.
Discussion
Shared etiological factors owing to both clinical and immunological characteristics among immune-mediated diseases (IMDs) have long been suspected (Parkes et al., 2013). Individuals who are affected by one type of IMD could have higher susceptibility to other IMDs. There are two main types of IMDs, seropositive autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and seronegative auto-inflammatory disorders, such as CD and psoriasis (Parkes et al., 2013). In our studies, we found that genes upregulated in UC are also enriched in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Therefore, IMDs could have some shared susceptibility loci and similar underlying genetic etiologies.
Consistent with the phenotypes observed in IBD, the DEGs identified in the discordant twin pairs were significantly enriched in the immune-related pathways and components. In our analysis, we found that the proportions of four immune-related cell subpopulations were increased in UCs. The proportion of megakaryocytes was significantly increased in the UC-affected twins, but the proportion of megakaryocytic-erythroid progenitor cells was decreased in the UC-affected twins. Megakaryocytes are derived from hematopoietic stem cell precursor cells in the bone marrow and produce platelets. Inflammation and coagulation are involved in the pathogenesis and clinical manifestation of IBDs (Voudoukis et al., 2014), and the increased influx of progenitor cells in the megakaryocyte cell compartment in IBD would alter the platelet count (Voudoukis et al., 2014). Interestingly, infliximab treatment significantly rescued pro-platelet formation by megakaryocytes from IBD patients but not by megakaryocytes from healthy controls (Di Sabatino et al., 2016), which confirms the specific role of megakaryocytes in the pathogenesis of IBDs.
Neutrophils have a dual role in intestinal inflammation, and overactivated neutrophils cause chronic inflammation in IBDs (Fournier and Parkos, 2012). NKT cells are involved in both the innate and adaptive immune responses and recognize CD1−restricted microbial and self-lipids, which participate in the development of IBD by regulating intestinal homeostasis (Lai et al., 2019; Brailey et al., 2020). In addition, during inflammation, the lymphatic system undergoes intense expansion through lymphangiogenesis, and aberrant increases in the lymphatic vasculature have been reported in patients with CD and UC (Danese, 2011). Therefore, the distinct proportions of immune cell subpopulations in UC-affected and unaffected twins explain, in part, the underlying pathogenesis of IBD.
By combining the expression features identified in our analysis with the rare variants enriched in IBD-affected twins, we identified some candidate makers for IBDs. Although we excluded random expression noise by including unrelated healthy twin pairs in our analysis, the sample size was quite small. In our analysis, the role of the top DEGs, such as OLFM4, LOXL2, COL12A1, MMP1, and CLDN8, involved in the pathogenesis of IBD has recently been identified. Gene OLFM4 acts as a stem cell marker of the small intestine and is overexpressed in the inflamed colonic epithelium, especially in UC-affected cases. And we also identified some novel candidates which might have disease contributing roles. For instance, we observed that the expression of CYP2C18 is highly upregulated in IBD-affected twins, and multiple rare non-silent variants in CYP2C18 are enriched in IBDs. So far, the roles of CYP2C18 in the pathogenesis of IBDs have not been elucidated. Therefore, we focused on validating the association between CYP2C18 and UC.
CYP2C18 encodes a member of cytochrome P450 (CYPs) superfamily of enzyme, which catalyze the metabolism of endogenous and exogenous substances, and extrahepatic and extrarenal CYP enzymes play critical roles in the development of UC (Sen and Stark, 2019). In vitro, the expression of CYP2C18 was significantly upregulated in TNF-α induced inflammation status (Figure 7A). And the expression of CYP2C18 was also increased in the UC-affected case (Figure 7B). Based on the mouse model, various components such as P450 substrates and P450 metabolites in the blood may change with the UC-specific pattern (Yamamoto et al., 2018). The secretion of CYP2C18 in serum and varied expression of CYP2C18 between UC affected cases and UC unaffected cases, provide the possibility to evaluate UC using P450 enzyme through non-invasive method. However, the sample size was limited in our analysis, further investigation is needed to confirm our results and determine the detailed mechanism by which the identified genes contribute to the pathogenesis of IBDs.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics Statement
The colon tissues were collected with informed consent from UC affected cases and controls who had undergone surgery resection at the First Affiliated hospital of Zhejiang University, School of Medicine. Researches were performed under a protocol approved by Clinical Research Committee of the First Affiliated Hospitical, Zhejiang University School of Medicine (2020-593).
Author Contributions
JD and JZ: conception and design. JD: administrative support. JD, JY, HD, and JZ: provision of study materials or patients. JY, HD, and JZ: collection and assembly of data. JD and JY: data analysis and interpretation. All authors wrote and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Projects of National Natural Science Foundations of China (82000489), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Y19H030059).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank editage (www.editage.cn) for english language editing of this manuscript.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2021.680125/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Outlines of the analysis approaches involved in this study.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Principle component analysis of healthy twin pairs. a and b indicate the matched individuals in each twin pairs.
Supplementary Figure 3 | Volcano plot of the differentially expressed genes in the healthy twin pairs. All the genes show stable expression spectrum between the healthy twin pairs.
Supplementary Figure 4 | Venn diagram of the candidate disease-causative genes with evidence from GWAS-FineMapped, DiseaseNet and the DEGs.
Supplementary Table 1 | The enriched human phenotypes and disorders related to the fine-mapped genes.
Supplementary Table 2 | Differentially expressed genes identified in the discordant IBD twin pairs. The adjusted p-value was computed by Benjamini-Hochberg correction.
Supplementary Table 3 | The intersection of the genes across FineMapped, DiseaseNet, and DEGs.
Supplementary Table 4 | The non-silent variants of CYP2C18 that were enriched in IBDs.
Footnotes
References
Allocca, M., Fiorino, G., Zallot, C., Furfaro, F., Gilardi, D., Radice, S., et al. (2020). Incidence and Patterns of COVID-19 Among Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients From the Nancy and Milan Cohorts. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 2134–2135. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.071
Annese, V. (2020). Genetics and epigenetics of IBD. Pharmacol. Res. 159:104892. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104892
Aran, D., Hu, Z., and Butte, A. J. (2017). xCell: digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 18:220.
Brailey, P. M., Lebrusant-Fernandez, M., and Barral, P. (2020). NKT cells and the regulation of intestinal immunity: a two-way street. FEBS J. 287, 1686–1699. doi: 10.1111/febs.15238
Brand, E. C., Klaassen, M. A. Y., Gacesa, R., Vila, A. V., Ghosh, H., De Zoete, M. R., et al. (2021). Healthy cotwins share gut microbiome signatures with their inflammatory bowel disease twins and unrelated patients. Gastroenterology 160, 1970–1985.
Carvalho, B. S., and Irizarry, R. A. (2010). A framework for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics 26, 2363–2367. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq431
Danese, S. (2011). Role of the vascular and lymphatic endothelium in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: ‘brothers in arms’. Gut 60, 998–1008. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.207480
Di Sabatino, A., Santilli, F., Guerci, M., Simeone, P., Ardizzone, S., Massari, A., et al. (2016). Oxidative stress and thromboxane-dependent platelet activation in inflammatory bowel disease: effects of anti-TNF-α treatment. Thromb. Haemost. 116, 486–495. doi: 10.1160/th16-02-0167
Fournier, B. M., and Parkos, C. A. (2012). The role of neutrophils during intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 5, 354–366. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.24
Gersemann, M., Becker, S., Nuding, S., Antoni, L., Ott, G., Fritz, P., et al. (2012). Olfactomedin-4 is a glycoprotein secreted into mucus in active IBD. J. Crohns Colitis 6, 425–434. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2011.09.013
Huang, H., Fang, M., Jostins, L., Umićević Mirkov, M., Boucher, G., Anderson, C. A., et al. (2017). Fine-mapping inflammatory bowel disease loci to single-variant resolution. Nature 547, 173–178.
IBD Exomes Portal (2021). Cambridge, MA. Available online at: http://ibd.broadinstitute.org
Ji, E., Wang, T., Xu, J., Fan, J., Zhang, Y., Guan, Y., et al. (2020). Systematic Investigation of the Efficacy of Sinitang Decoction Against Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Pharmacol. 11:1337. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01337
Jostins, L., Ripke, S., Weersma, R. K., Duerr, R. H., Mcgovern, D. P., Hui, K. Y., et al. (2012). Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 491, 119–124.
Lai, L. J., Shen, J., and Ran, Z. H. (2019). Natural killer T cells and ulcerative colitis. Cell Immunol. 335, 1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.08.010
Lê, S., Josse, J., and Husson, F. (2008). FactoMineR: an R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 25:18.
Li, M., Zhao, J., Cao, M., Liu, R., Chen, G., Li, S., et al. (2020). Mast cells-derived MiR-223 destroys intestinal barrier function by inhibition of CLDN8 expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Biol. Res. 53:12.
Liu, J. Z., Van Sommeren, S., Huang, H., Ng, S. C., Alberts, R., Takahashi, A., et al. (2015). Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat. Genet. 47, 979–986. doi: 10.1038/ng.3359
Lynch, K. D., Keshav, S., and Chapman, R. W. (2019). The Use of Biologics in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 18, 115–126. doi: 10.1007/s11901-019-00456-2
Morgan, M., Falcon, S., and Gentleman, R. (2020). GSEABase: Gene Set Enrichment Data Structures and Methods. R package version 1.52.1.
Parkes, M., Cortes, A., Van Heel, D. A., and Brown, M. A. (2013). Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 14, 661–673. doi: 10.1038/nrg3502
Pollheimer, M. J., Racedo, S., Mikels-Vigdal, A., Marshall, D., Bowlus, C., Lackner, C., et al. (2018). Lysyl oxidase-like protein 2 (LOXL2) modulates barrier function in cholangiocytes in cholestasis. J. Hepatol. 69, 368–377. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.04.009
Reimand, J., Kull, M., Peterson, H., Hansen, J., and Vilo, J. (2007). g:Profiler–a web-based toolset for functional profiling of gene lists from large-scale experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W193–W200.
Richards, S., Aziz, N., Bale, S., Bick, D., Das, S., Gastier-Foster, J., et al. (2015). Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 17, 405–424. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30
Ritchie, M. E., Phipson, B., Wu, D., Hu, Y., Law, C. W., Shi, W., et al. (2015). limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:e47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007
Ryan, F. J., Ahern, A. M., Fitzgerald, R. S., Laserna-Mendieta, E. J., Power, E. M., Clooney, A. G., et al. (2020). Colonic microbiota is associated with inflammation and host epigenomic alterations in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Commun. 11:1512.
Schwerd, T., Pandey, S., Yang, H. T., Bagola, K., Jameson, E., Jung, J., et al. (2017). Impaired antibacterial autophagy links granulomatous intestinal inflammation in Niemann-Pick disease type C1 and XIAP deficiency with NOD2 variants in Crohn’s disease. Gut 66, 1060–1073. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310382
Sen, A., and Stark, H. (2019). Role of cytochrome P450 polymorphisms and functions in development of ulcerative colitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 25, 2846–2862. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i23.2846
Smith, P. J., Levine, A. P., Dunne, J., Guilhamon, P., Turmaine, M., Sewell, G. W., et al. (2014). Mucosal transcriptomics implicates under expression of BRINP3 in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 20, 1802–1812. doi: 10.1097/mib.0000000000000169
Suzuki, K., Murano, T., Shimizu, H., Ito, G., Nakata, T., Fujii, S., et al. (2018). Single cell analysis of Crohn’s disease patient-derived small intestinal organoids reveals disease activity-dependent modification of stem cell properties. J. Gastroenterol. 53, 1035–1047. doi: 10.1007/s00535-018-1437-3
Uhlig, H. H., and Muise, A. M. (2017). Clinical Genomics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Trends Genet. 33, 629–641.
Uhlig, H. H., and Schwerd, T. (2016). From Genes to Mechanisms: the Expanding Spectrum of Monogenic Disorders Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 22, 202–212. doi: 10.1097/mib.0000000000000614
Voudoukis, E., Karmiris, K., and Koutroubakis, I. E. (2014). Multipotent role of platelets in inflammatory bowel diseases: a clinical approach. World J. Gastroenterol. 20, 3180–3190. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3180
Wang, H., Chao, K., Ng, S. C., Bai, A. H., Yu, Q., Yu, J., et al. (2016). Pro-inflammatory miR-223 mediates the cross-talk between the IL23 pathway and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Biol. 17:58.
Wang, Z. Y., and Qiu, B. F. (2010). Increased Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 and 3 in Remission Patients of Steroid-Dependent Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterol. Res. 3, 120–124.
Yamamoto, R., Muroi, K., and Imaishi, H. (2018). Serum derived from ulcerative colitis mouse changes the metabolism of the fluorescent substrate by P450 depending on the degree of disease progression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 290, 88–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.05.012
Yin, J., Wu, K., Ma, Q., Dong, H., Zhu, Y., Hu, L., et al. (2019). Revisiting Non-BRCA1/2 Familial Whole Exome Sequencing Datasets Implicates NCK1 as a Cancer Gene. Front. Genet. 10:527. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00527
Keywords: inflammatory bowel diseases, ulcerative colitis, novel marker, CYP2C18, LOXL2
Citation: Du J, Yin J, Du H and Zhang J (2021) Revisiting an Expression Dataset of Discordant Inflammatory Bowel Disease Twin Pairs Using a Mutation Burden Test Reveals CYP2C18 as a Novel Marker. Front. Genet. 12:680125. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.680125
Received: 13 March 2021; Accepted: 24 May 2021;
Published: 15 June 2021.
Edited by:
Gurmeet Kaur, National Center for Biotechnology Information (NLM), United StatesReviewed by:
Soumitra Pal, National Center for Biotechnology Information (NLM), United StatesHaoyun Lei, Carnegie Mellon University, United States
Copyright © 2021 Du, Yin, Du and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Du, ZHVqdWFuQHpqdS5lZHUuY24=; Jiawei Zhang, and6aGFuZ0B6anUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Juan Du1*†
Juan Du1*† Jie Yin
Jie Yin Jiawei Zhang
Jiawei Zhang