- 1Department of Horticulture, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, United States
- 2Alabama Cooperative Extension Service, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, United States
- 3Department of Mechanical Engineering, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, United States
- 4College of Agriculture, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, United States
Legislative measures and societal pressures are reshaping the landscape maintenance industry by imposing restrictions on gas-powered outdoor power equipment. These regulations are driving a significant shift toward the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives in landscape maintenance practices. To gain insights into the perceptions, benefits, and challenges of adopting battery-powered outdoor power equipment, a survey was conducted among landscape maintenance operators in the USA. Professional landscape companies prioritize operation efficiency factors such as “Reliability” (score of 4.6 out of 5), “Work Capacity” (score of 4.5 out of 5), and equipment “Availability” (score of 4.3 out of 5) rather than the environmental factors such as “Air Pollution” (score of 3.1 out of 5) and “Noise Pollution” (score of 3.2 out of 5) emphasized in recent legislative measures. Of the participants surveyed, 52% said they have integrated battery-powered equipment into their landscape maintenance operations in some capacity. “Noise Pollution” (score of 3.9 out of 5) and “Air Pollution” (score of 3.7 out of 5) were identified as the main drivers behind the integration of battery-powered equipment. “Competitive Advantage” (score of 3.0 out of 5) and “Cost” (score of 2.7 out of 5) were the least motivating factors for battery-powered equipment adoption, suggesting that economic concerns pose a significant barrier to adoption. However, for traditional equipment operators, addressing concerns related to the “Work Capacity, “Power,” and “Quality” of battery-powered equipment could be pivotal in overcoming skepticism. Of traditional gas-powered equipment users, 70% indicated they would consider adopting battery-powered equipment if their concerns were alleviated. Based on these results, future research should aim to fill the existing knowledge gap regarding the long-term operational costs and benefits of battery-powered equipment and gas-powered equipment.
1 Introduction
Urbanization has steadily risen at an unprecedented rate over the last few decades. In 2020, 80% of the USA population lived in urban areas with a projected increase to 89% by 2050 (Ritchie and Rodés-Guirao, 2024). Worldwide, more than half the global population lives in urban areas (Ritchie and Rodés-Guirao, 2024; Zhang et al., 2022). As urbanization continues, it is vital to understand the importance of green spaces and their ecosystem services (Ugolini et al., 2020; Venter et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2023). Green landscapes, including parks, gardens, and lawns have been shown to provide numerous benefits to urban communities, such as improving air quality (Diener and Mudu, 2021; Hewitt et al., 2020; Száraz, 2014), reducing urban heat island effects (Aram et al., 2019; Turner-Skoff and Cavender, 2022; Yu et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2022), and promoting physical and mental well-being (Hedblom et al., 2019; Slater et al., 2020; Labib et al., 2020). Given the numerous benefits of urban landscapes, preserving the value derived from these urban landscapes is paramount.
The landscape services industry, commonly referred to as the “Green Industry,” is closely associated with the production and retail of horticultural live goods and is the largest sector within the US environmental horticulture industry. In 2018, the landscape services industry had an estimated market capitalization of $160 billion and an economic influence of $348 billion (Hall et al., 2020). Among its diverse segments, landscape maintenance emerges as the largest segment within the Green Industry, generating approximately 40% of total revenue or ~$60 billion (Stucke and Horn, 2022). Employing over a million US residents, this industry plays a vital role in the US economy (Hall et al., 2020).
To provide these landscape services, conventional gas-powered outdoor equipment (GPE), such as mowers and leaf blowers, are used in maintenance activities. In 2015, the USA had an estimated 121 million pieces of GPE deployed (Banks and McConnell, 2015). The Environmental Protection Agency projections suggest that gas-powered OPE contributes significantly to air pollution, noise pollution, and carbon emissions (Banks and McConnell, 2015). Specifically, GPE is estimated to contribute nearly 4% of all volatile organic compound emissions and 12% of carbon monoxide (CO) emissions (Banks and McConnell, 2015). Discerning the precise percentage of emission produced by commercial and residential equipment remains challenging. Commercial-grade outdoor power equipment typically operates for more extended hours annually and boasts larger engine displacements, attributing to a potentially greater environmental impact. The environmental footprint of GPE has triggered legislative measures aimed at reducing their usage.
The state of California’s recently enacted Bill AB 1346 (October 2021), prohibiting sales of small combustion engines starting in January 2024, marks a significant step in the regulation of landscape equipment usage in the USA (AB1346, 2021). California’s bill seemingly spurred similar legislative action across various governance levels nationwide. Although initiated by the California Air Resources Board, most ordinances targeting equipment regulation across the USA focus on noise pollution and gas-powered leaf blowers (AB A2133, 2023; HB 1853, 2022; Illinois State General Assembly, 2020). Presently, over 200 municipalities spanning 15 states have implemented diverse bans on GPE. These types of bans include hourly or seasonal bans depending on where their usage occurs. As of January 1, 2024, around 16.7% of the USA populace will be subjected to landscape equipment usage restrictions (Bartley et al., unpublished data).
The COVID-19 pandemic drastically increased the percentage of workers transitioning from working in an office to working from home. Between 2019 and 2021, the percentage of at home workers tripled from 5.7% (9 million) to 17.9% (27.6 million) of the USA workforce (U.S. Census Bureau, 2022). In 2023, 35% of employed people worked a portion or all their hours at home, an 11% increase from 2019 (Bureau of Labor Statistics U.S., 2024). With people spending most of their work and leisure time at home, they became more aware of landscape maintenance operations. While it is difficult to attribute the pandemic directly to legislative measures, it did shift how Americans view the work-from-home lifestyle. This shift possibly contributed to an increased interest in sustainability and environmentally friendly practices (Fratello et al., 2021; Bulgari et al., 2021; Tansil et al., 2022). As society returns to pre-pandemic norms, the trend of preserving outdoor spaces has become a long-term goal (Herman and Drozda, 2021; Tansil et al., 2022).
These legislative measures and societal pressures significantly impact the Green Industry, notably altering the landscape maintenance industry. The stringent restrictions on GPE reshape the industry’s operational norms and equipment utilization practices. With a substantial number of municipalities enforcing bans or limitations, this industry faces a pivotal shift toward adopting alternative, eco-friendly equipment. This transformation not only challenges the existing landscape maintenance practices but also necessitates investment in and adaptation to newer, greener technologies within the sector. To glean insights into the perceptions, benefits, and obstacles associated with adopting battery-powered outdoor power equipment (BPE), a survey was distributed to landscape maintenance operators in the USA. This nationwide survey, sponsored by the National Association of Landscape Professionals, assisted in procuring this key information.
2 Materials and methods
The survey was developed and implemented to gain insights into the perceptions, barriers, and the current adoption rate of BPE among professional landscape companies (PLCs). Input for the survey was gathered from professional landscapers utilizing both gas-powered equipment (GPE) or BPE, as well as equipment manufacturers and industry experts. The survey was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB). The generation and administration of the survey was conducted online using Qualtrics (Seattle, Washington). The distribution of the survey began in July of 2022 and ended Dec of 2022. Survey flyers and links were distributed via email occurred through monthly newsletters sent by a variety of industry-lead organizations, including state associations like the Alabama Nursery & Landscape Association and national associations such as the National Association of Landscape Professionals. To protect the privacy of survey participants, all responses were collected anonymously.
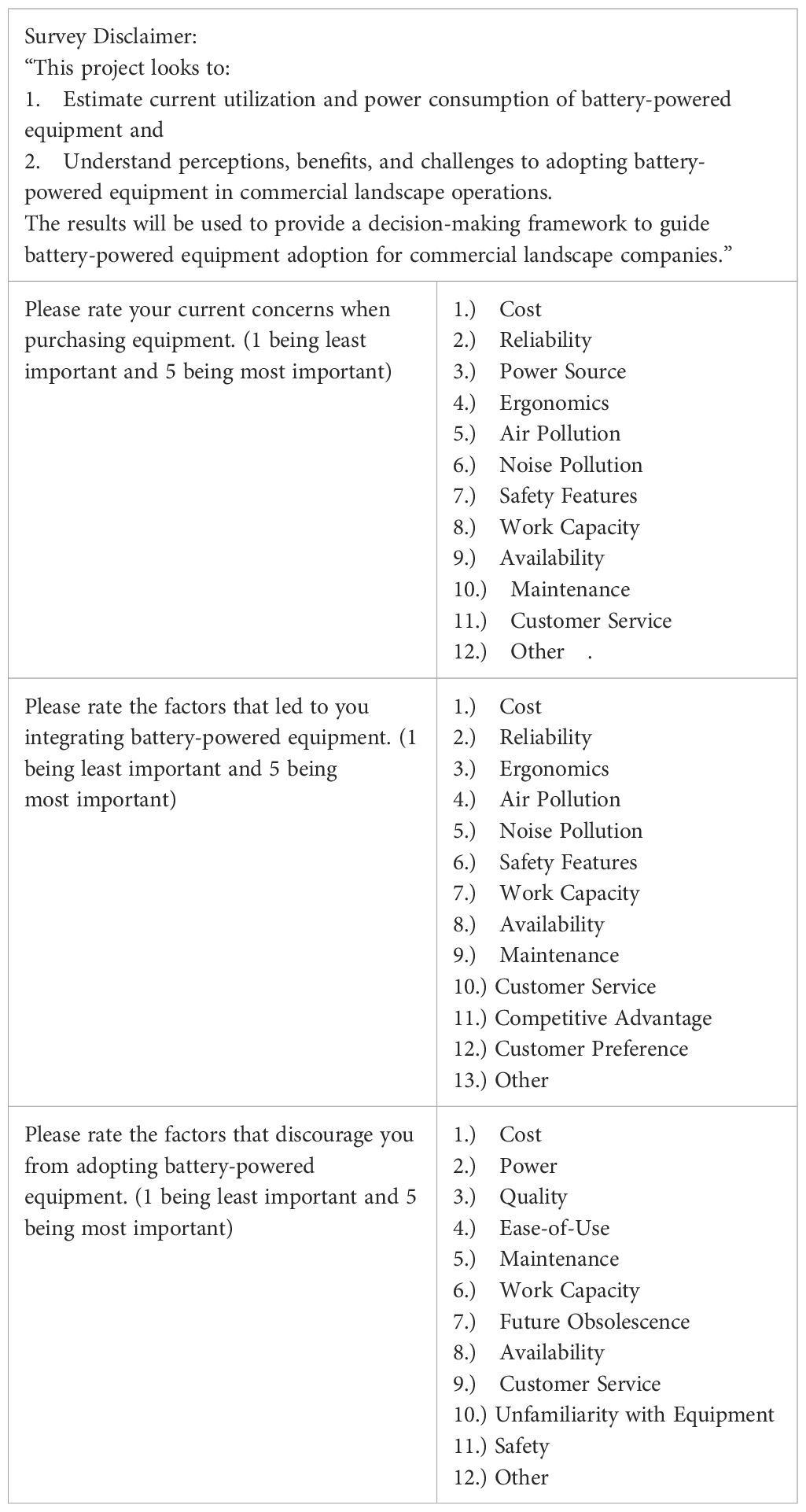
To ensure the validity of responses, two qualifying questions were presented at the beginning of the survey. These questions confirmed that participants held an administrative position within their respective company, had the authority to make equipment purchasing decisions, and possessed knowledge of the company’s demographics. Participants who answered “No” to either question were thanked for their willingness to participate but were not allowed to proceed with the survey. Those who answered “Yes” moved on to the questions regarding company demographics. A flow diagram outlining the survey format can is provided in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Flow diagram of the survey demonstrating how survey participants were directed into two paths, gas-powered and battery-powered equipment users.
The final sample size comprised of 108 participants who completed the survey, selected through a completely random sampling design. Initially, all qualifying participants were asked about their general views on purchasing equipment, irrespective of their preferred power source. Based on their response to whether they use BPE or not, they were directed to a specific set of questions. Participants who use GPE exclusively were asked about the concerns that prevent them from adopting BPE, while BPE users were asked about the factors that led them to integrate BPE in their maintenance operations. The concerns and factors explored aspects such as work capacity, reliability, cost, maintenance, and others (Table 1). Participants were asked to rate each factor on a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 representing “Least Concerning” and 5 representing “Most Concerning.”
To analyze the survey responses, SAS Studio (version 3.81; SAS Inc., Cary, NC) was used to perform principal component analysis (PCA) resulting from the PROC PRINQUAL procedure. A PCA was used to identify correlations among the various factors rated by participants, revealing underlying patterns in the data by reducing its dimensionality. Subsequently, a cluster analysis was performed using PROC CLUSTER to group participants based on their similar response patterns. By clustering participants, distinct groups with shared concerns were identified, allowing for a more detailed understanding of the different perspectives within the landscape maintenance industry. The analyses provided a comprehensive overview of how factors were perceived and the extent to which they influence equipment purchasing decisions.
3 Results
The most recent survey of landscape professional operations shows 341,782 landscape businesses in the USA (Hall et al., 2020). This number reflects all aspects of professional landscaping and may not represent the number of businesses performing landscape maintenance. The total number of responses collected between July 2022 and Dec 2022 was 210, with 108 participants completing all questions. Survey participants with missing responses were not considered usable observations.
Responses were collected in all USA geographical regions except New England (Figure 2). The majority of responses (34) were received in the West South Central region comprised of LA, TX, AR, and OK. Twenty-six (26) landscape maintenance professionals submitted complete surveys from the South Atlantic region, comprised of DE, MD, WV, VA, NC, SC, GA, and FL. The Middle Atlantic, East North Central, and East South Central regions contributed 17, 14, and 11 completed surveys, respectively. Only four (4) completed surveys were received from states located in the Mountain (2) and Pacific (2) regions. The distribution of the professional landscape industry closely mirrors the population distributions across the USA. CA, FL, and TX employ the most full-time and part-time landscape professionals (Hall et al., 2018). The states of TX and FL were represented in the West South Central and South Atlantic Regions, respectively, where many survey participants were located. The Western USA, particularly CA, was underrepresented in this survey.
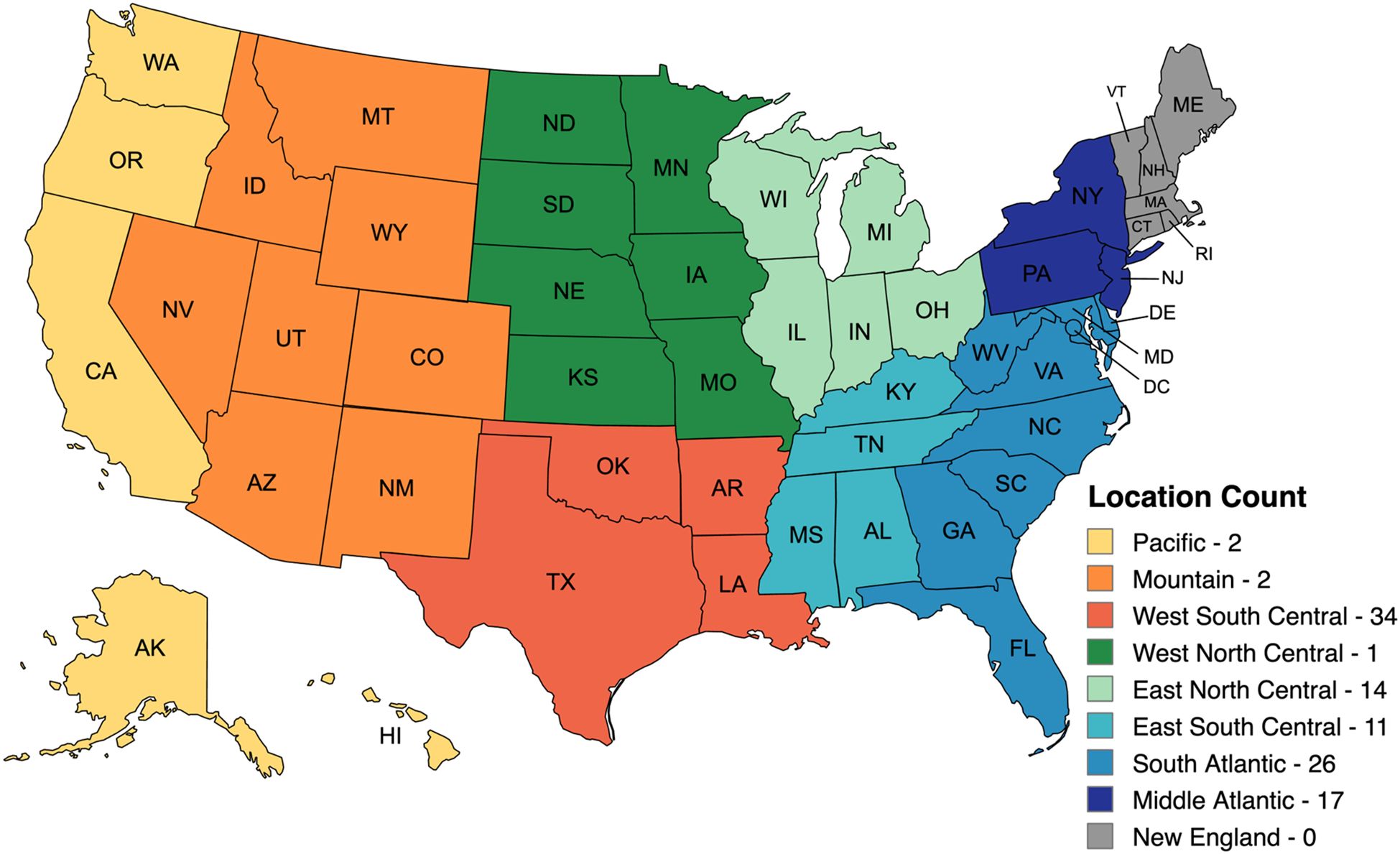
Figure 2. Geographic distribution of survey participants from an online national survey of landscape maintenance professionals. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
The survey participants employed an average of 77 full-time or part-time workers, but most employed only two (2) full-time or part-time workers (Table 2). Companies were classified into the following size categories: X-Large (≥101 employees), Large (51-100 employees), Medium (26-50 employees), Small (6-25 employees), X-Small (≤5 employees). Thirty-eight (38) participants represented X-Small companies, followed by Small companies with 32 participants. Medium and Large companies were represented by 18 and 11 participants, respectively. Seven (7) participants represented X-Large companies with one (1) having more than 1,000 employees. The average duration of operation was 26 years, with a range spanning from 2 to 102 years. The proportion of gross sales from landscape maintenance averaged 40%, with six participants reporting that 100% of their gross sales came from landscape maintenance. The average hectares under management was 1,505, with a range spanning from 2 to 101,171 hectares. Participants reported and average of 500 man-hours per week dedicated to landscape maintenance. The average workforce experience among employees was 10 years.
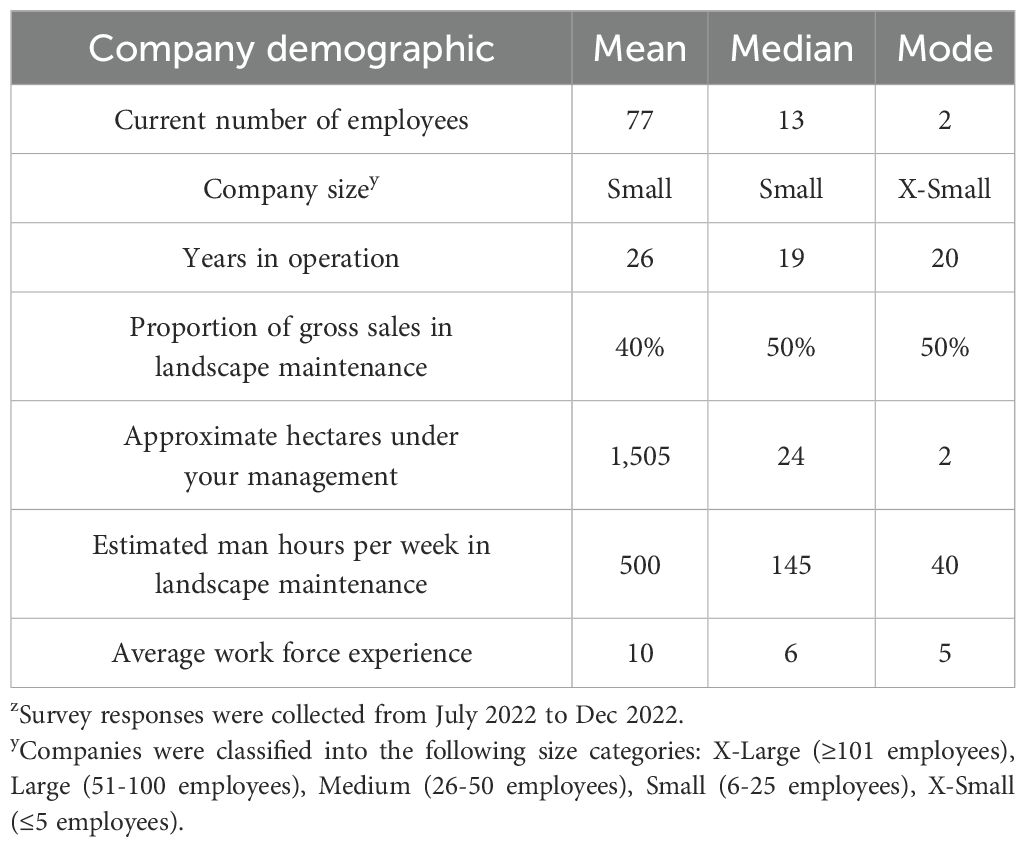
Table 2. Descriptive statistics of participants from an online national survey of landscape maintenance professionalsz.
Qualifying questions selected for business owners or those responsible for purchasing equipment. Responses were limited to one submission per IP (internet protocol) address. The age distribution of survey participants was concentrated between the ages of 35 and 74 (Figure 3). Less than 2% of survey participants were 18 to 24 years of age. The gender distribution was predominantly male, with less than 12% of responses being female. The ethnicity distribution contained 92.55% white/Caucasian. Six percent of the survey participants were black/African American, Hispanic/Latino, or more than one race.
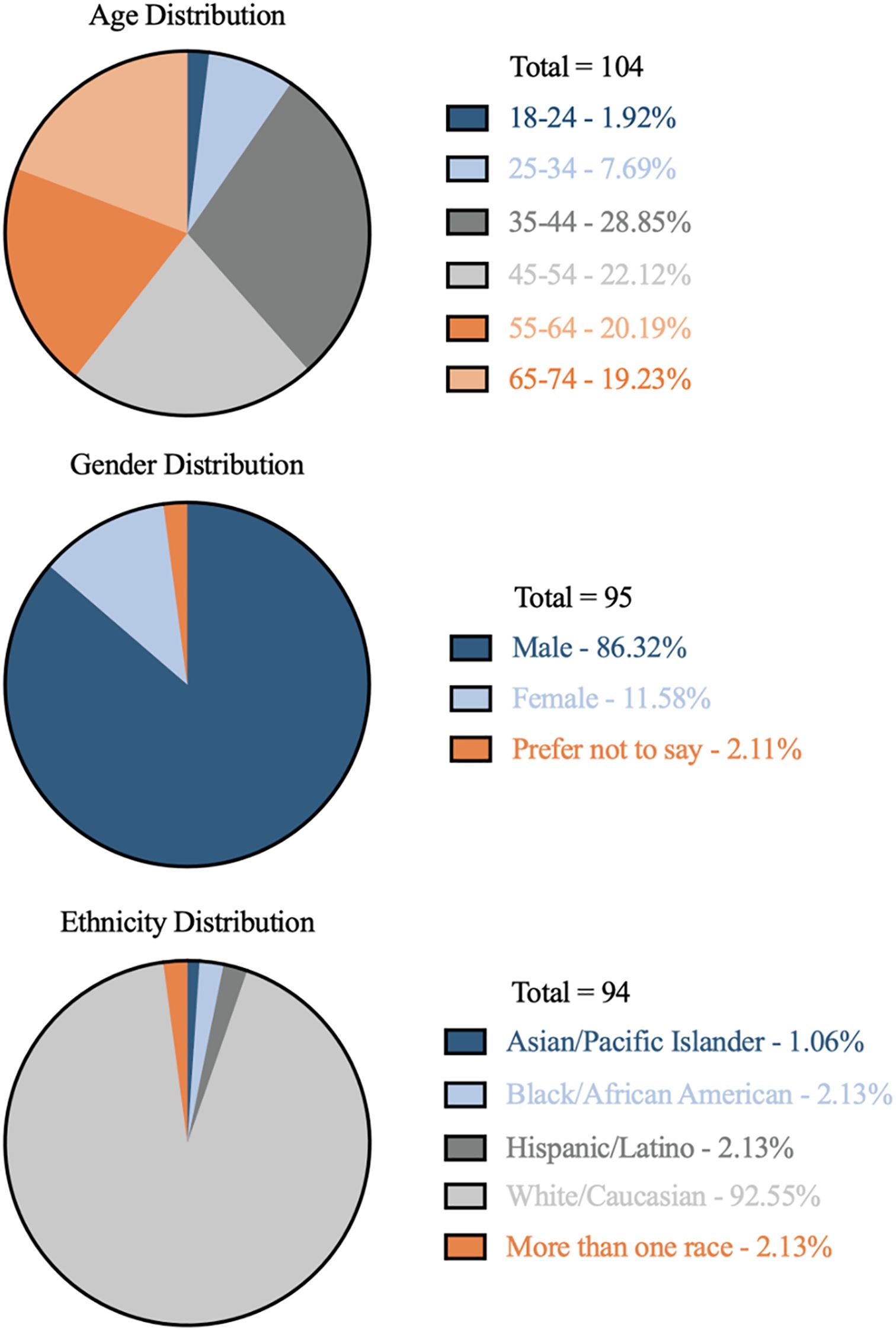
Figure 3. Personal demographics of participants from an online national survey of landscape maintenance professionals. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
3.1 Industry concerns when purchasing equipment
Respondents were most concerned with operational efficiencies when making equipment purchasing decisions. Characteristics such as “Reliability,” “Work Capacity,” and “Maintenance” of landscape equipment averaged 4.6, 4.5, and 4.2, respectively, with “5” representing “Most Concerning” and “1” representing “Least Concerning” (Figure 4). When asked to select the single most influential factor in their purchasing decisions, 48% of participants selected “Reliability.” No other factor was selected by more than 12% of participants. During the survey period, geopolitical disturbances combined with a surge in demand following the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in supply constraints and limited equipment availability. These factors likely contributed to landscape professionals ranking “Availability” as their third most important factor, with an average score of 4.3. Landscape professionals perceive “Safety Features” and “Customer Service” as important factors when purchasing equipment, averaging 4.0 and 3.9, respectively. “Ergonomics,” “Cost,” and “Power Source” were viewed indifferently. The least concerning factors for landscape professionals when purchasing equipment were “Noise Pollution” and “Air Pollution.” “Other” concerns when purchasing equipment were “quality warranty,” “dealership network,” “their crew’s preference,” “ease of operation,” and “build quality.” Several survey participants were additionally concerned with the availability of replacement parts and repair costs.
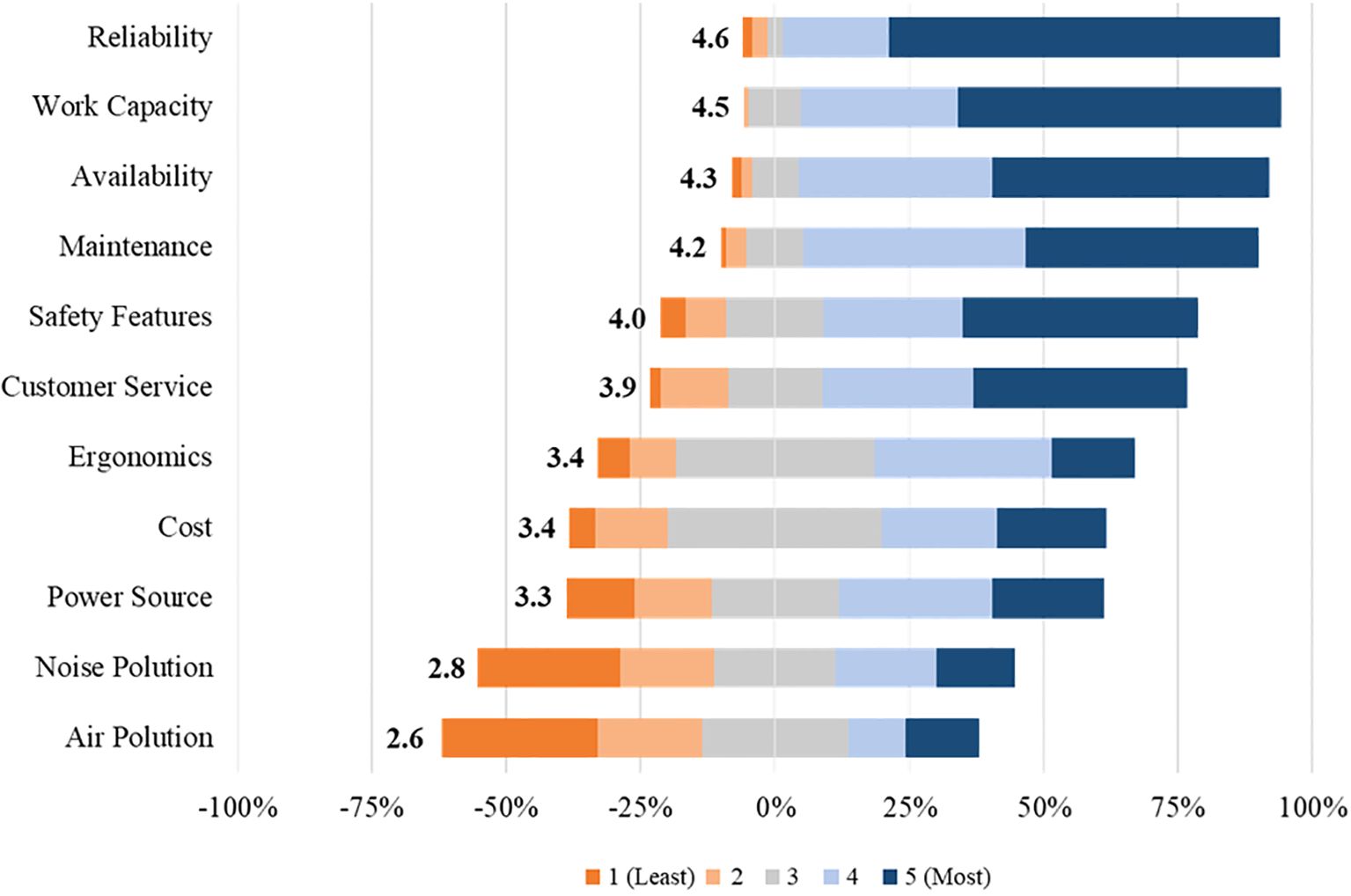
Figure 4. Participant responses to the prompt, “Please rate your concerns when purchasing equipment,” from an online survey of 108 landscape maintenance professionals with equipment purchasing power in the USA. The stacked bars represent the distribution of responses across a 5-point Likert scale, where “1” indicates “Least concerned” and “5” the “Most concerned.” A response of “3” was considered neutral, contributing equally to both positive (0% to 100%) and negative (-100% to 0%) sentiment. The average response score is displayed to the left of each stacked bar. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
The association between factors to the prompt, “Please rate your current concerns when purchasing equipment,” was explored using PCA, which transformed responses and projected them onto a two-dimensional plane (Figure 5). The first two components, PC1 (28.97%) and PC2 (24.35%), accounted for 53.32% of the total variance in the dataset. The direction and magnitude of the vectors for each factor (i.e., Availability, Work Capacity, Power Source) represent their correlation and relevance to the component (i.e., acute angles denote positive associations and obtuse angles denote negative associations). Operational efficiency factors like “Work Capacity,” “Availability,” “Customer Service,” “Maintenance,” and “Reliability” were positively correlated. Environmental factors such as “Noise Pollution,” “Air Pollution,” and “Power Source” were not correlated to operational efficiency factors but were positively correlated to one another. “Ergonomics,” “Safety Features,” and “Cost” were not strongly correlated to operational efficiency factors or environmental factors. “Cost” and “Power Source” were least relevant to the components analyzed, possibly indicative of participants’ indifference to these factors if the equipment meets or exceeds performance expectations. The observations or participants were concentrated at the axis of each component. However, some dispersion occurred to the PCA’s lower left quadrant. Observations 59, 76, 29, and 61 responded with low values (less than the mean) of the scale for the many variables “Cost,” “Reliability,” “Ergonomics,” “Safety Features,” and “Customer Service.”
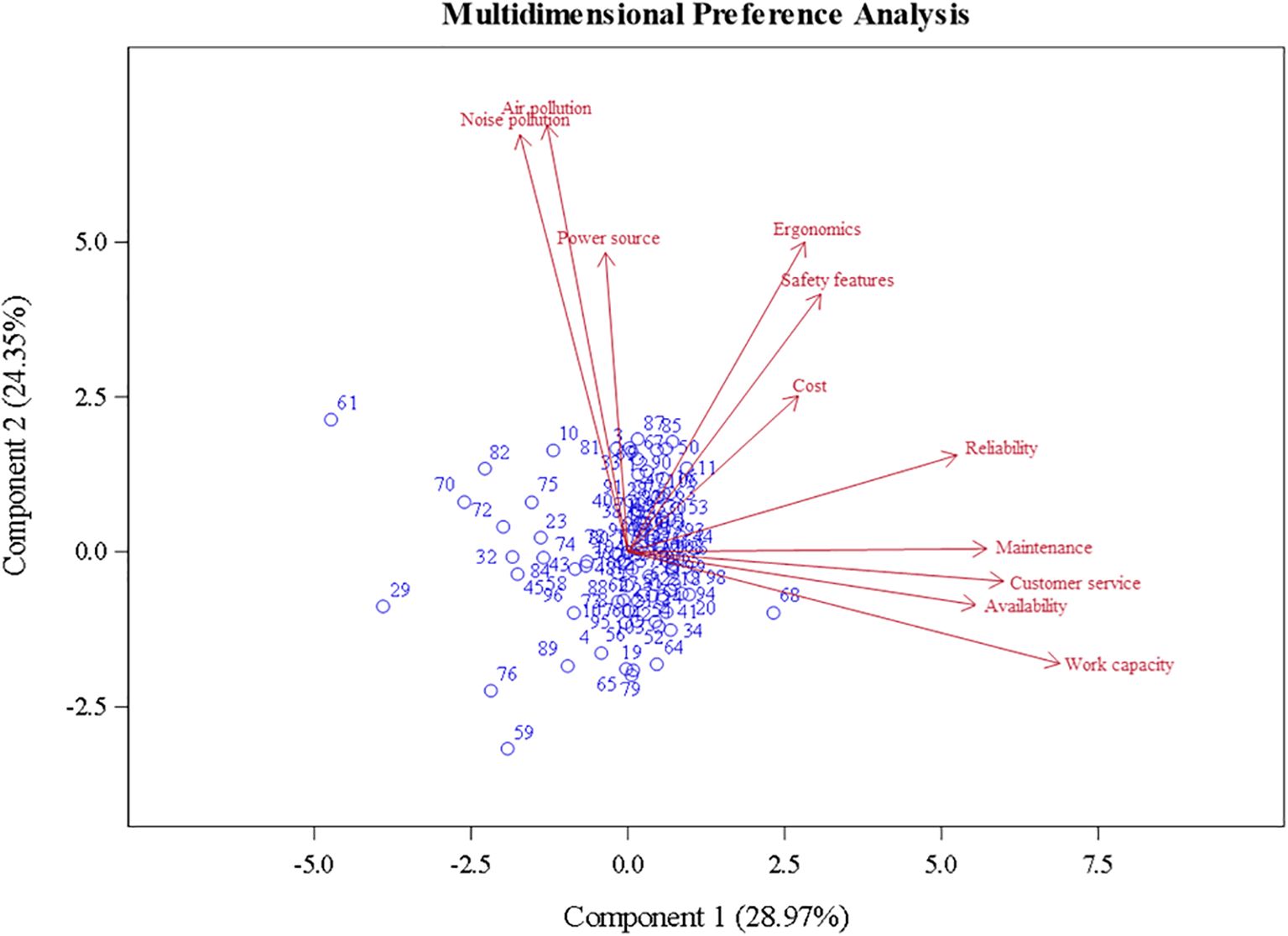
Figure 5. Results of the principal component analysis: projection of landscape maintenance professional concerns when purchasing equipment.
To identify groups with disparate values of the factors analyzed, a cluster analysis was conducted, resulting in the identification of six clusters (Figure 6). The demographics of companies identified within each cluster were averaged to determine if patterns, such as company size or years in operation, could be used to interpret the factors by which they were most or least concerned. Due to the broad range of companies represented in this survey, deviations around many averages were substantial. These broad deviations are also indicative of shared perceptions across demographic groups, suggesting that, while there are common concerns related to operational efficiency and equipment performance, individual company characteristics may still significantly influence specific attitudes towards maintenance equipment. Cluster 1 was predominately categorized as Small in company size but managed a considerably large area of 397 ± 1,282 hectares. Consequently, they were most concerned with factors related to operation efficiency. Participants in Cluster 1 had not integrated BPE into their maintenance practices and were least concerned by “Noise Pollution” and “Air Pollution.” Participants in Cluster 2 managed Medium-sized companies, managed considerable acreage, and devoted the most man-hours (935 ± 1,996) per week to landscape maintenance. Cluster 2 participants had not yet integrated BPE but were more conscientious of “Noise Pollution” and “Air Pollution” than participants in Cluster 1. Cluster 3, though predominately comprised of Small-sized companies, maintained the largest area (6,772 ± 26,115 hectares). Some of the largest companies participating in this survey were associated with Cluster 3. Participants in Cluster 3 valued most factors highly. “Cost” and “Ergonomics” were the only factors given a value less than “4.” Participants in Cluster 3 had integrated BPE into their maintenance operations. Cluster 4 was similar to Cluster 2 but emphasized “Cost” and “Power Source” when purchasing equipment. Participants in Cluster 4 managed Small companies with the most years of operation. Cluster 5 had the fewest number of participants (6) and was primarily concerned with “Work Capacity” and “Availability.” They valued factors such as “Safety Features,” “Noise Pollution,” “Air Pollution,” and “Power Source” lower than other participants. On average, the proportion of gross sales from landscape maintenance was lowest in Cluster 5. Participants in Cluster 6 managed Small-sized companies that intensively managed their properties (man-hours per week: hectares under management). They did not value any factors considerably important but had integrated BPE into the maintenance operations.
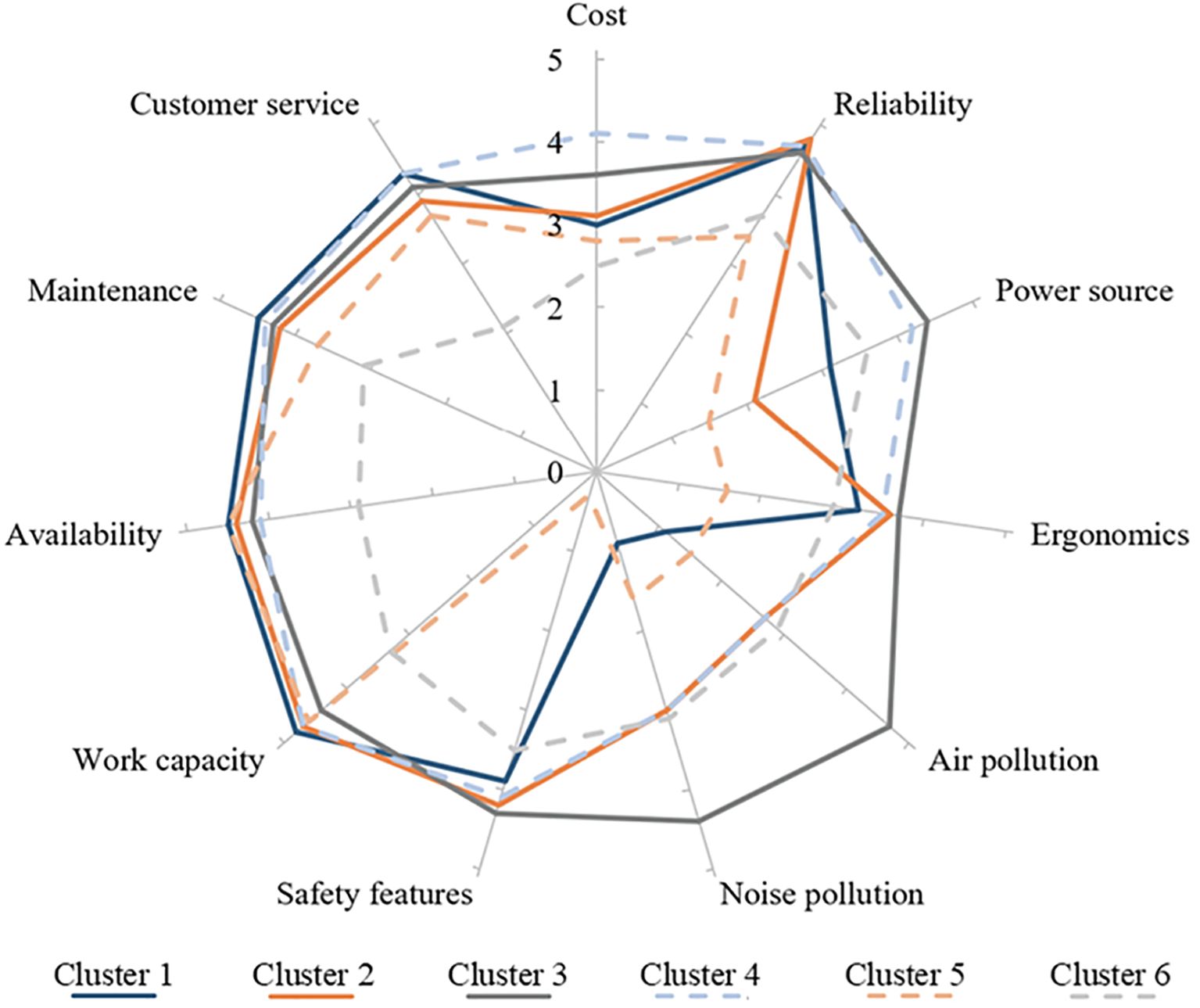
Figure 6. Radar diagram illustrating cluster analysis groupings and cluster characteristics of participants responding to the prompt, “Please rate your concerns when purchasing equipment,” from an online survey of 108 landscape maintenance professionals with equipment purchasing power in the US. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
3.2 Battery adoption and perception
Of the survey respondents, 52% said they have integrated BPE into their landscape maintenance operations. Based on anecdotal evidence and communications with landscape equipment manufacturers, the adoption rate was expected to be between 10% and 30% for landscape maintenance professionals. The high BPE adoption rate recorded in this survey could have resulted from our dissemination method. Members of professional organizations, such as the National Association of Landscape Professionals and state nursery and landscape associations, are more likely tech-savvy innovators and early adopters within the Green Industry. Of those who have integrated BPE, it is unclear what percentage of their equipment is battery-powered or its utilization rate.
Among those who have integrated BPE, the types of equipment varied significantly. When asked, “Which battery-powered landscape equipment do you use?” the most commonly used tools were blowers, with 75% of respondents reporting their use. This was followed by hedge trimmers (61.5%), string trimmers (55.8%), and chainsaws (48.1%). Mowers and edgers were less prevalent, used by 40.4% and 38.5% of BPE adopters, respectively. Seventeen percent (17%) of respondents indicated they use “Other” BPE like hand tools (i.e., drills and grinders) and sprayers. These results suggest that while the adoption of specific BPE varies, adoption is likely influenced by the specific advantages BPE offers, like the reduced noise pollution of battery-powered leaf blowers.
Battery-powered equipment integrators cited “Noise Pollution” as the top factor leading them to adopt BPE, with an average rating of 3.9 (Figure 7). Although its average rating was slightly lower at 3.7, “Air Pollution” was selected as the most influential factor leading to BPE integration by 24% of respondents. Noise and air pollution have been regularly cited in legislation as justification for restricting GPE usage. These factors were expected to be the primary factors leading to BPE integration. This alignment with legislative measures underscores the industry’s shift towards environmentally friendly equipment and practices.
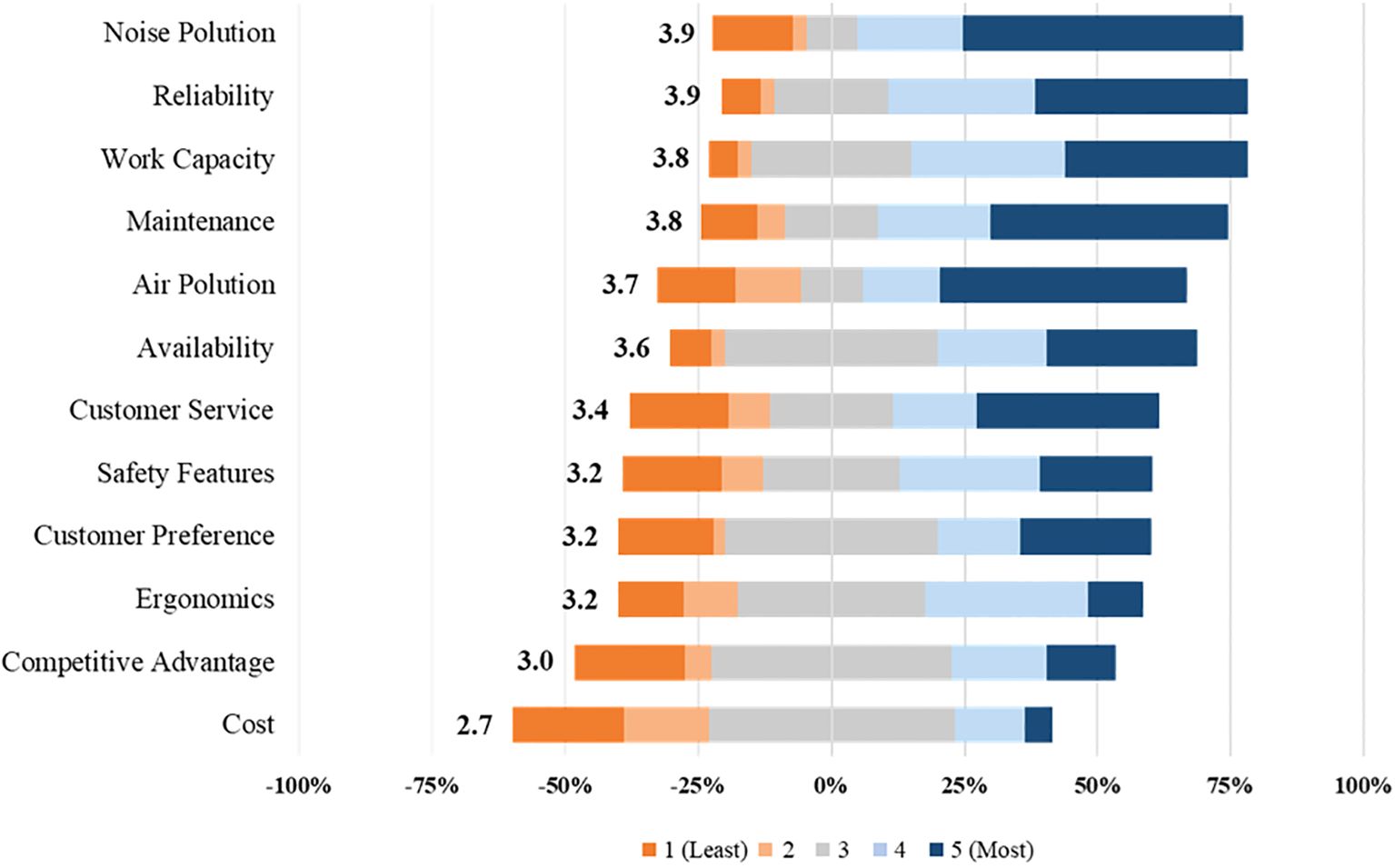
Figure 7. Participant responses to the prompt, “Please rate the factors that lead to battery-powered equipment adoption,” from an online survey of 108 landscape maintenance professionals with equipment purchasing power in the USA. The stacked bars represent the distribution of responses across a 5-point Likert scale, where “1” indicates “Least influential” and “5” the “Most influential.” A response of “3” was considered neutral, contributing equally to both positive (0% to 100%) and negative (-100% to 0%) sentiment. The average response score is displayed to the left of each stacked bar. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
The second most influential factor leading to BPE adoption was “Reliability,” with an average rating of 3.9. “Reliability” was selected by 18% of respondents as the most important factor in their adoption of BPE. No other factors received 12% or more of the votes from participants. “Work Capacity” and “Maintenance” had an average rating of 3.8, indicating that BPE users perceive the equipment as capable as their counterparts while requiring less maintenance. “Availability” and “Customer Service” were rated 3.6 and 3.4, respectively. “Safety Features,” “Customer Preference,” and “Ergonomics” each received a rating of 3.2, indicating that these factors neither significantly influenced nor deterred BPE users from adoption.
“Competitive Advantage” and “Cost” were the least encouraging factors for BPE adoption, receiving ratings of 3.0 and 2.7, respectively. Battery-powered equipment is estimated to cost three to five times the capital expense compared to GPE (Odom, 2023). In a highly competitive and margin-suppressed market, professional landscape operators perceived that investing in BPE and offering zero-emission landscape maintenance services did not significantly improve their ability to attract new clients. The high initial costs and the perception that customers do not prioritize eco-friendly services as a key differentiator likely contributed to the lower emphasis on these factors. This suggests that, while environmental considerations are gaining attention, economic factors remain a critical barrier to widespread BPE adoption in the industry. “Other” factors offered by survey respondents that encouraged their adoption of BPE were “government mandates,” “equal or better performance,” “fuel cost savings,” “ease-of-use,” and “(maintenance of) educational facilities.”
The association between factors to the prompt, “Please rate the factors that lead to BPE adoption,” was analyzed using PCA (Figure 8). The first two components, PC1 (52.99%) and PC2 (16.5%), accounted for 69.49% of the total variance in the dataset. The factors “Customer Preference,” “Noise Pollution,” and “Air Pollution” were positively correlated. Operational efficiency factors such as “Work Capacity,” “Availability,” and “Reliability” were positively correlated but not with the environmental factors. “Cost” showed a correlation to “Work Capacity,” “Availability,” and “Reliability,” but it was the least relevant factor analyzed, possibly because it had minimal influence on users’ decision to adopt BPE. The factors “Competitive Advantage,” “Maintenance,” “Ergonomics,” and “Customer Service” were positively correlated to one another and the operational efficiency factors but were less correlated with “Customer Preference,” “Noise Pollution,” and “Air pollution.” “Safety Features” showed a moderate correlation with both groups of factors. Most observations, or participant responses, were concentrated around the axis of each component. However, some dispersion was observed in the PCA’s lower left quadrant. Observations 22, 42, 44, and 62 had lower-than-average scores for “Customer Preference,” “Noise Pollution,” “Air Pollution,” and “Safety Features.” These findings suggest a divergence in priorities between environmental and operational efficiency factors, with cost consideration potentially playing a more complex role in the decision-making process.
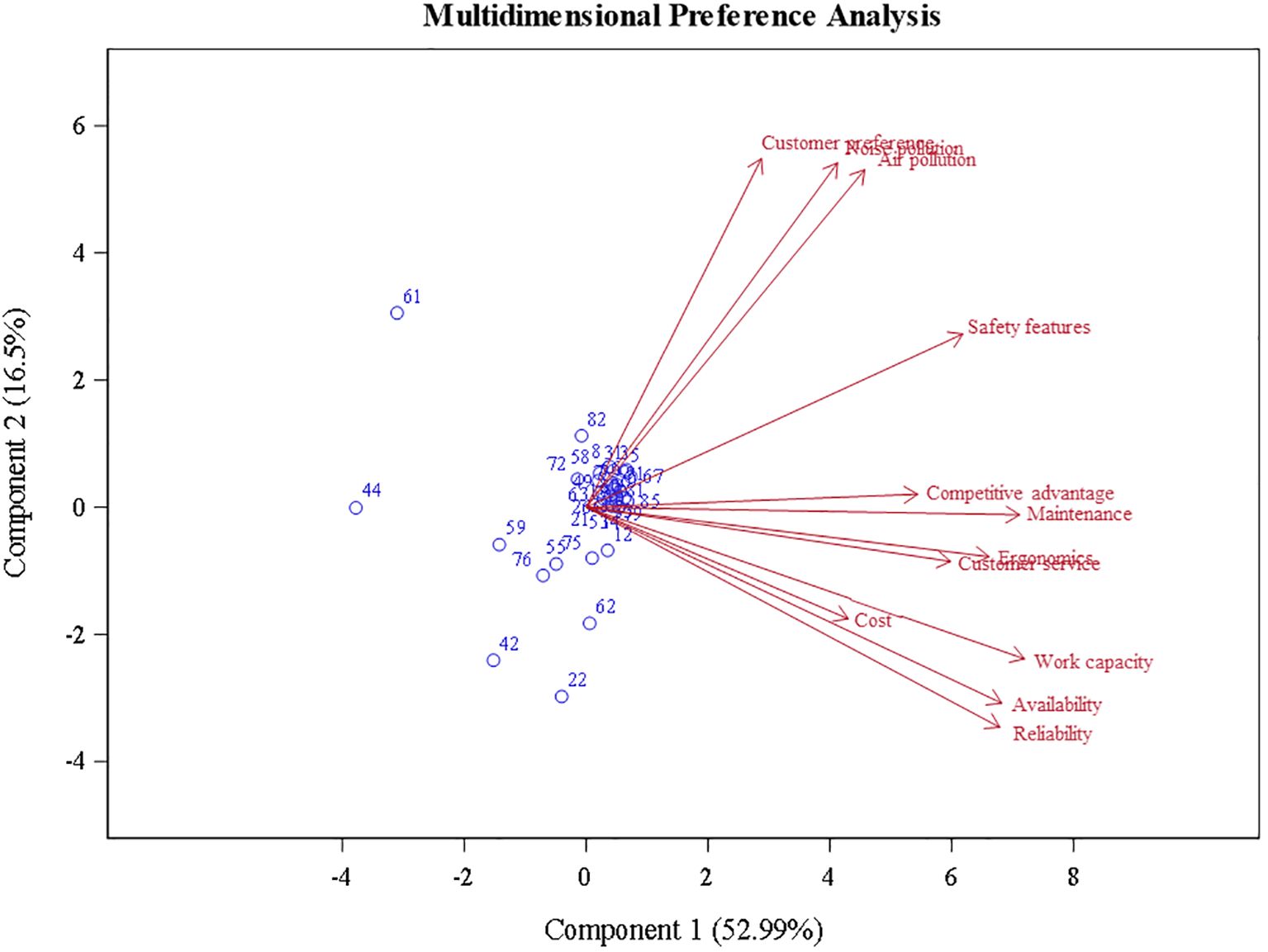
Figure 8. Results of the principal component analysis: projection of landscape maintenance professional factors which led to battery-powered equipment adoption.
To identify groups with distinct values for the analyzed factors, a cluster analysis was conducted, revealing three (3) clusters with similar influences on the decision to adopt BPE (Figure 9). Cluster 1, comprised of 29 respondents, consisted of companies that were Small to Medium in size. They were responsible for maintaining an average of 486 ± 2,023 hectares. These participants earned, on average, 40% ± 20% of the gross sales from maintenance, dedicating 752 ± 1,873 man-hours per week to landscape maintenance activities. While they were moderately encouraged by most of the factors considered, “Cost,” “Competitive Advantage,” and “Customer Preference” were the least influential. The significant cost disparity between equipment types was not advantageous for these PLCs to adopt BPE. However, “Noise Pollution” most influenced them, suggesting a close alignment with recently passed legislation. Operational efficiency factors such as “Reliability” and “Work Capacity” also played a role in their adoption decisions. Unlike Cluster 1, participants in Cluster 2 were least influenced by “Noise Pollution,” “Air Pollution,” or “Safety Features.” Instead, they rated factors such as “Reliability,” “Work Capacity,” and “Availability” favorably. The last group, Cluster 3, contained just two participants, each responsible for maintaining 14 hectares. Despite the modest acreage, they generated 650 ± 778 man-hours per week in maintenance. Cluster 3 did not seem influenced by many factors, with scores ranging from 0.9 to 2.9. While “Noise Pollution” was the most influential to them, “Customer Preference” and “Air Pollution” were also notable. Cluster 3 may represent PLCs with a customer base that favored BPE, but perceived the equipment as ineffective in most categories.
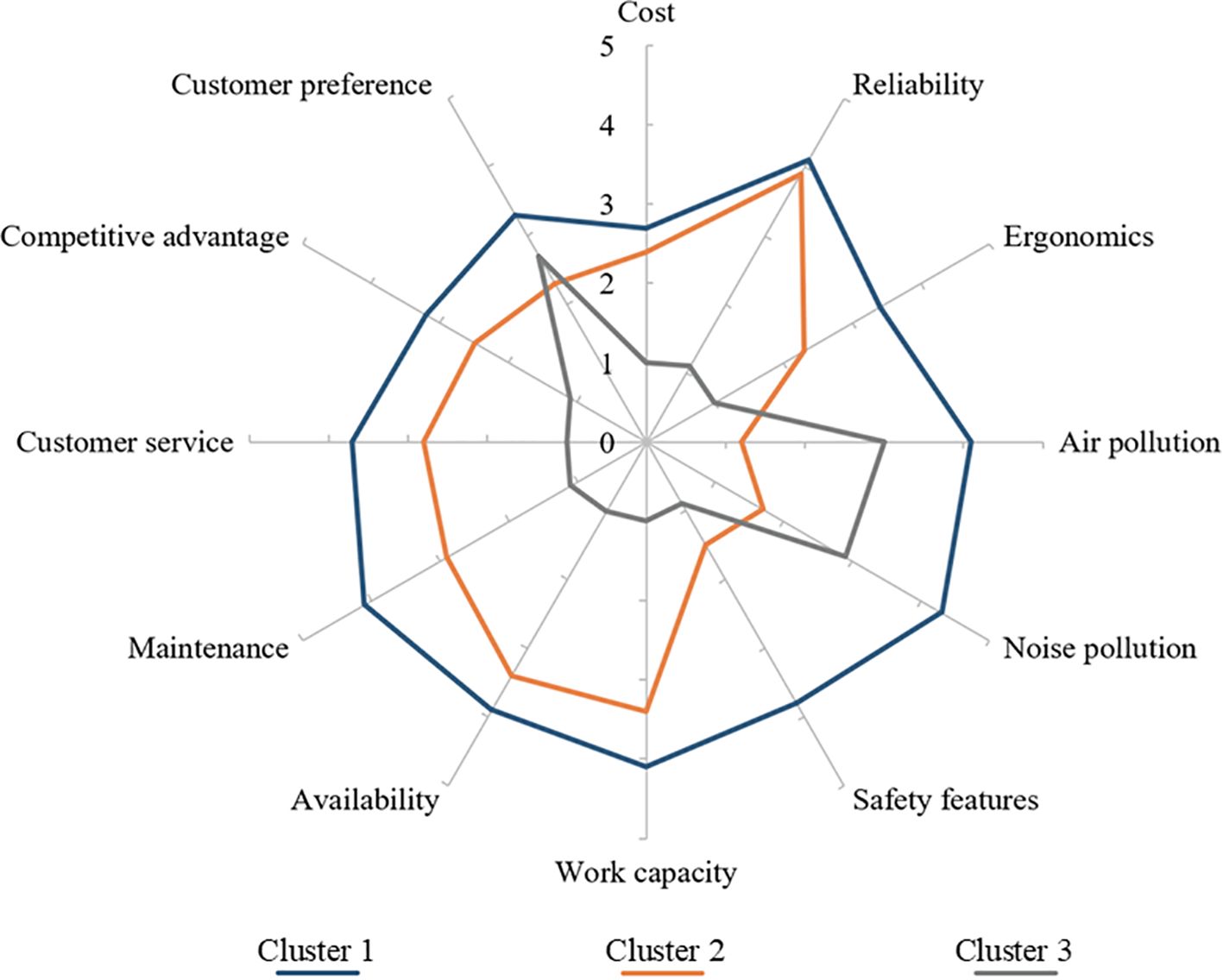
Figure 9. Radar diagram illustrating cluster analysis groupings and cluster characteristics of participants responding to the prompt, “Please rate the factors that lead to battery-powered equipment adoption,” from an online survey of 108 landscape maintenance professionals with equipment purchasing power in the US. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
3.3 Barriers to battery adoption
Of the participants, 48% use GPE exclusively for landscape management operations. When prompted to “rate the factors that discourage you from adopting BPE,” these respondents expressed significant concerns about the “Work Capacity” of BPE, rating it 4.9 (Figure 10). Additionally, 48% identified “Work Capacity” as the primary factor discouraging them from making the switch to BPE. The perceived “Power” and “Quality” of BPE were also significant deterrents for GPE users, each receiving a rating of 4.3. “Maintenance” and “Availability” received ratings of 3.6 and 3.4, respectively. Surprisingly, “Cost” and “Future Obsolescence” did not significantly influence respondents’ decisions regarding BPE adoption, with “Cost” being the least influential factor for BPE users at the time of adoption. The factors “Customer Service,” “Ease-of-Use,” and “Safety” do not discourage PLCs towards adoption. “Unfamiliarity with Equipment” received the lowest rating of 2.6. The relatively low concerned for factors such as “Ease-of-Use” and “Unfamiliarity with Equipment” suggests that operational and technical aspects of BPE are not significant barriers to adoption for PLCs. “Other” factors that deter BPE adoption included concerns about the “viability of charging in the field,” “battery life,” “battery charge time,” “reliability in different climates,” and “the rate of advancing technology.”
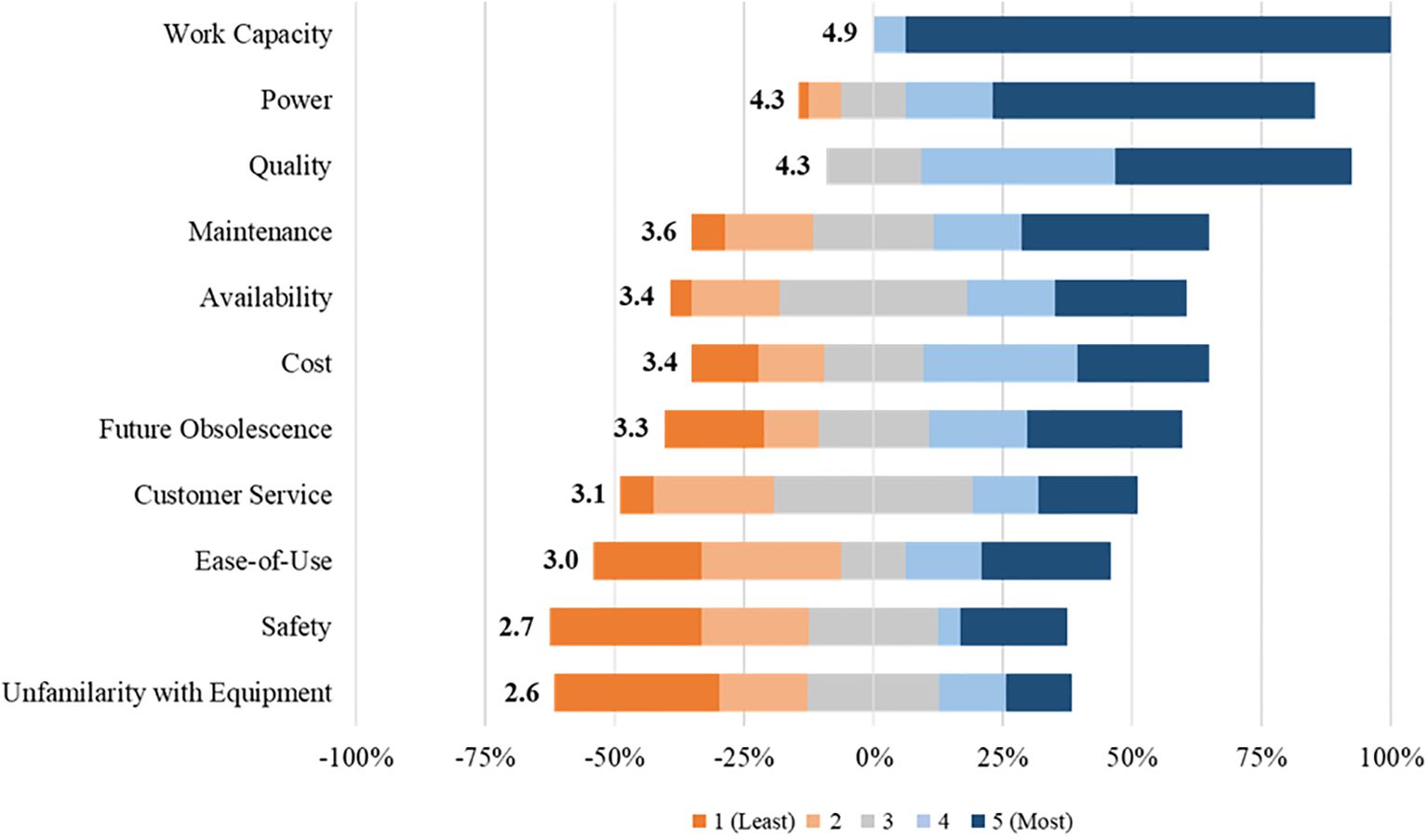
Figure 10. Participant responses to the prompt, “Please rate the factors that discourage you from adopting battery-powered equipment,” from an online survey of 108 landscape maintenance professionals with equipment purchasing power in the USA. The stacked bars represent the distribution of responses across a 5-point Likert scale, where “1” indicates “Least discouraging” and “5” the “Most discouraging.” A response of “3” was considered neutral, contributing equally to both positive (0% to 100%) and negative (-100% to 0%) sentiment. The average response score is displayed to the left of each stacked bar. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
The association between factors to the prompt, “Please rate the factors that discourage you from adopting battery-powered equipment,” was analyzed using PCA (Figure 11). The first two components, PC1 (37.95%) and PC2 (16.8%), accounted for 54.75% of the total variance in the dataset. The factors “Customer Service,” “Unfamiliarity,” “Availability,” “Safety,” and “Future obsolescence” were all positively correlated, indicating that respondents who rated one of these factors highly were likely to rate the others similarly. Operational efficiency factors “Ease-of-use,” “Maintenance,” “Quality,” “Power,” and “Work Capacity” were also all positively correlated but showed less correlation to the first group of factors. This distinct grouping of operational efficiency factors further enforces their importance in the decision-making process. “Cost” did not show a significantly correlation with “Ease-of-use,” “Maintenance,” “Quality,” “Power,” and “Work Capacity.” This lack of correlation suggests that while operational concerns are critical, cost considerations may not play as central a role in discouraging BPE adoption as expected.
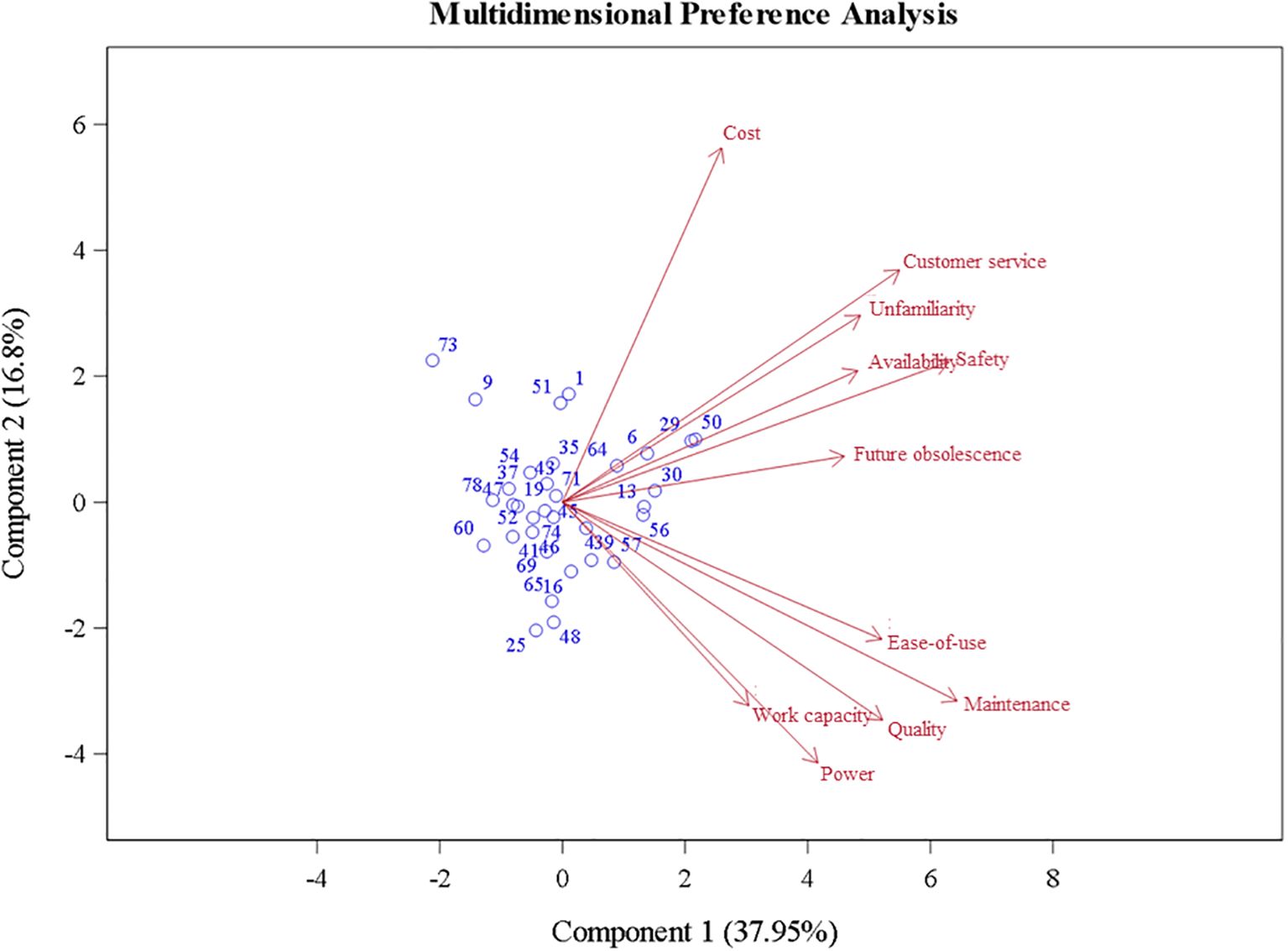
Figure 11. Results of the principal component analysis: projection of landscape maintenance professional factors which discourage battery-powered equipment adoption.
The cluster analysis conducted for this prompt identified five clusters for further evaluation (Figure 12). Among these, “Work Capacity” emerged as the leading factor discouraging the adoption of BPE across all clusters. Similarly, all clusters were discouraged by operational efficiency factors such as “Power” and “Quality.” Clusters 1 and 2 were primarily composed of medium-sized companies. Cluster 1 managed 198 ± 267 hectares and had been in operation for an average of 25 ± 24 years, reporting a high proportion of gross sales from landscape maintenance (60% ± 20%). Cluster 2, which managed 214 ± 340 hectares, had the highest average workforce experience and rated most factors higher than the other clusters, indicating a broader range of concerns. Companies grouped into Cluster 2 had the greatest concern about the “Cost” of BPE. Cluster 4, also managing significant acreage, had been in operation the longest, averaging 37 ± 31 years. Cluster 4 companies considered factors such as “Maintenance” and “Ease-of-Use” to be significant barriers to the adoption of BPE. Clusters 3 and 5 consisted of X-Small to Small companies that maintained significantly less acreage. For these clusters, “Work Capacity,” “Power,” and “Quality” remained the top factors discouraging BPE adoption. However, the least discouraging factors differed: Cluster 3 rated “Safety” as the least concerning, while Cluster 5 rated “Ease-of-Use” lowest.
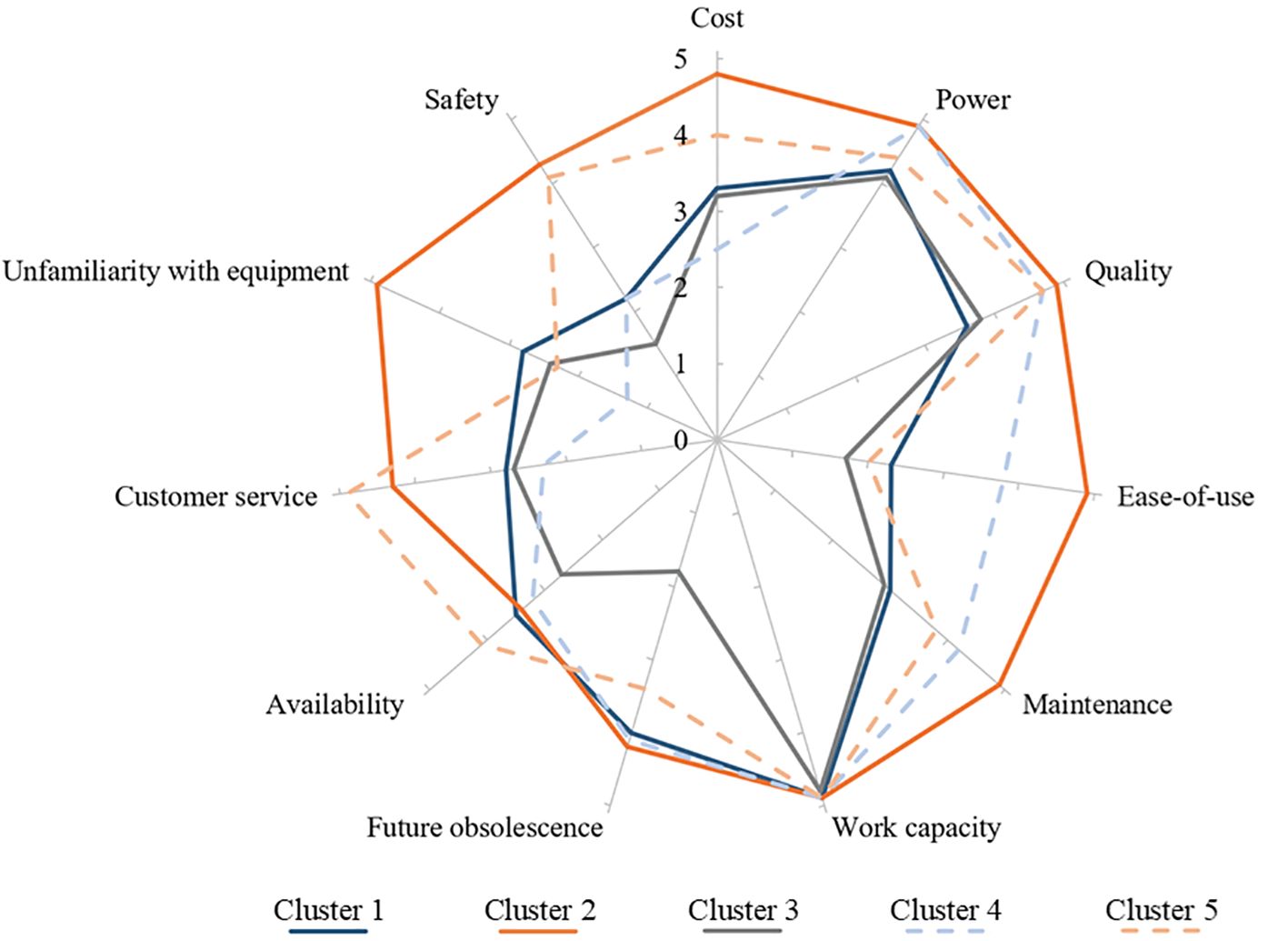
Figure 12. Radar diagram illustrating cluster analysis groupings and cluster characteristics of participants responding to the prompt, “Please rate the factors that discourage you from adopting battery-powered equipment,” from an online survey of 108 landscape maintenance professionals with equipment purchasing power in the US. Survey responses were collected from July 2022 to Dec 2022.
Overall, companies using GPE perceive BPE as having lower operational efficiency compared to traditional equipment. Concerns regarding BPE’s “Power” and “Quality” may have been influenced by the experiences of early beta testers. Following the prompt to rate discouraging factors, traditional equipment users were asked, “If your concerns were addressed, would you consider adopting battery-powered equipment?” Interestingly, a significant majority, 70%, responded affirmatively, indicating they would consider adopting BPE if their concerns were alleviated. The remaining 30% were evenly split, with 15% responding “Maybe” and 15% responding “No.” This data suggests that addressing key issues such as power and quality could substantially increase the adoption of BPE among traditional equipment users.
4 Discussion
Effective and sustainable landscape maintenance practices are essential to preserving the benefits provided by urban green spaces. Traditional methods, which rely heavily on GPE, present significant challenges to these goals. These tools contribute to air and noise pollution (Banks and McConnell, 2015; Volckens et al., 2007) and carbon emissions. The findings from this nationwide survey reveal that PLCs prioritize operational efficiency and the availability of equipment above all other concerns when selecting equipment. This emphasis on the equipment’s ability to complete tasks effectively reflects a pragmatic sentiment, prioritizing productivity and dependability, which reveals a clear industry bias toward performance and practicality, often driven by productivity pressures in a highly competitive market. Environmental factors such as air pollution and noise pollution ranked last among PLC’s concerns, highlighting a discrepancy between industry priorities and the environmental considerations driving recent legislative measures. This misalignment suggests that the industry’s perspective on GPE does not fully align with the environmental objectives being pursued by policymakers.
Despite the industry’s skepticism of BPE, more than half of survey respondents have integrated BPE. The decision to adopt BPE is primarily driven by environmental concerns such as noise and air pollution. However, financial considerations, such as the initial cost of BPE and the perceived lack of competitive advantage, remain significant barriers. For example, commercial battery-powered zero-turn mowers start at $18,999, while their gas-powered counterparts are priced around $5,000. Similar cost disparities can be observed across various equipment categories. Although the cost difference is more pronounced for commercial-grade equipment, the disparity is less significant for residential-grade tools, making BPE more feasible for do-it-yourself homeowners (Saidani and Kim, 2021; Dutzik et al., 2023). While these economic concerns are significant, they may not be the primary barrier to adoption. Instead, addressing PLCs’ concerns related to the perceived reliability and usability of BPE could play a more crucial role in encouraging its adoption. Improving the operational efficiency of BPE alongside better research and education could help overcome the skepticism associated with its performance capabilities.
Despite the valuable insights provided by the survey, several limitations must be acknowledged. First, the survey sample was not fully representative of the entire USA landscape maintenance industry. While this survey received participants from a higher concentration of professional landscapers, areas such as New England and the Pacific were underrepresented. Landscape professionals in these underrepresented regions are heavily pressured by state and smaller governing bodies legislation. The regional imbalance and limited number of participants in this survey may constrain the broader applicability of these conclusions. However, the sample size and representation in terms of the number of employees are still substantial, lending credibility to the findings within the represented regions. Secondly, the survey did not capture the extent of BPE usage within companies, leaving uncertainty about whether respondents using BPE are early adopters, integrating a small amount of BPE, or represent broader adopters of BPE across the majority of their operations.
Facing increasing pressure to dramatically change operational norms, the landscape maintenance industry has received little academic support to guide this transition. While there is a substantial body of work referencing landscape sustainability, only a fraction of publications specifically address equipment and maintenance practices. Much of the existing research focuses on small autonomous mowers for turf quality rather than broader landscape operations (Boeri et al., 2023; Luglio et al., 2023). The landscape maintenance industry lacks comprehensive data on the cost, productivity, and effectiveness of technological innovations in outdoor power equipment. Aside from the broader use of equipment and its environmental impacts, understanding the impact of landscape equipment on worker health and safety, especially regarding noise exposure, is another critical research gap. This area is underexplored in the landscape maintenance sector compared industries like construction and forestry.
To address these gaps, future work should focus on bridging the knowledge gap in the landscape maintenance industry regarding the operational efficiency and cost comparisons between GPE and BPE. There is a notable absence of comprehensive data on the long-term operational costs and benefits of BPE versus GPE, including maintenance, energy consumption, and environmental impact. Expanding the survey’s demographic scope to include a more diverse range of companies, including smaller, less commercialized business, and regions like New England and Pacific, would provide a more comprehensive understanding of the industry’s perceptions. Establishing a new demographic group based on the percentage of BPE versus GPE usage could also yield valuable insights into the adoption patterns and challenges of companies utilizing both power sources. This broader perspective is essential for developing targeted strategies that support the industry’s understanding of maintenance equipment and address its diverse operational needs and preferences. Bridging these research gaps will help guide the industry toward more informed, sustainable decisions while balancing environmental goals with economic feasibility.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Auburn University Human Research Protection Program. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because the survey was granted exemption status upon review of the materials and methods for data collection.
Author contributions
KK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MH: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BC-C: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Association of Landscape Professionals, The Alabama Agriculture Experiment Station Agricultural Research Enhancement, Exploration, and Development Program, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
- ^ Nomenclature: PLC, professional landscape company; BPE, battery-powered equipment; GPE, gas-powered equipment; PCA, principal component analysis.
References
AB 1346 (2021). “Air pollution: small off-road engines,” in The california state senate 2021-2022 legislative session. Available at: https://leginfo.legislature.ca.gov/faces/billNavClient.xhtml?bill_id=202120220AB1346 (Accessed June 6, 2024).
AB A2133 (2023). “Prohibiting the use of gas-powered leaf and lawn blowers,” in NY state 2023-2024 legislative session. Available at: https://www.nysenate.gov/legislation/bills/2023/A2133 (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Aram F., Garcia E. H., Solgi E., and Mansournia S. (2019). Urban green space cooling effect in cities. Heliyon 5, e01339. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01339
Banks J. L. and McConnell R. (2015). National emissions from lawn and garden equipment. Available online at: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/banks.pdf (Accessed October 19, 2023).
Boeri P. A., Lindsey A. J., and Unruh J. B. (2023). Autonomous compared with conventional mower use on st. augustinegrass lawn quality. HortTechnology 33, 377–380. doi: 10.21273/HORTTECH05206-23
Bulgari R., Petrini A., Cocetta G., Nicoletto C., Ertani A., Sambo P., et al. (2021). The impact of COVID-19 on horticulture: critical issues and opportunities derived from an unexpected occurrence. Horticulturae 7, 124. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7060124
Bureau of Labor Statistics U.S. Department of Labor (2024). American time use survey – 2023 results. Available online at: https://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/atus.pdf (Accessed June 4, 2024).
Diener A. and Mudu P. (2021). How can vegetation protect us from air pollution? A critical review on green spaces’ mitigation abilities for air-borne particles from a public health perspective - with implications for urban planning. Sci. Total Environ. 796, 148605. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148605
Dutzik T., Sokolow L., Metzger L., and Schatz K. (2023). Lawn care goes electric. Available online at: https://publicinterestnetwork.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Lawn_Care_Goes_Electric_Oct23.pdf (Accessed Aug 19, 2024).
Fratello D. S., Campbell B. L., Secor W. G., and Campbell J. H. (2021). Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on gardening in the United States: postpandemic expectations. HortTechnology 32, 32–38. doi: 10.21273/HORTTECH04911-21
Hall C. R., Hodges A. W., Khachatryan H., and Palma M. A. (2020). Economic contributions of the green industry in the United States in 2018. J. Environ. Horticulture 38, 73–79. doi: 10.24266/0738-2898-38.3.73
HB 1853 Gasoline-Powered Leaf Blowers (2022). The hawaii state senate thirty-first legislature 2022. Available online at: https://www.capitol.hawaii.gov/sessions/session2022/bills/HB1853_.HTM. (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Hedblom M., Gunnarsson B., Iravani B., Knex I., Schaefer M., Thorsson P., et al. (2019). Reduction of physiological stress by urban green space in a multisensory virtual experiment. Sci. Rep. 9, 10113. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46099-7
Herman K. and Drozda Ł. (2021). Green infrastructure in the time of social distancing: urban policy and the tactical pandemic urbanism. Sustainability 13, 1632. doi: 10.3390/su13041632
Hewitt C. N., Ashworth K., and MacKenzie A. R. (2020). Using green infrastructure to improve urban air quality (GI4AQ). Ambio 49, 62–73. doi: 10.1007/s13280-019-01164-3
Illinois State General Assembly (2020). SB 3313 EPA-Gas leaf blower ban – Bill Status for SB 3313. 2020-2021 Illinois 101st General Assembly. Available online at: https://www.ilga.gove/legislation/BillStatus.asp?GA=101&DocTypeID=SB&DocNum=3313&GAID=15&SessionID=108&LegID=124890 (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Labib S. M., Lindley S., and Huck J. J. (2020). Spatial dimensions of the influence of urban green-blue spaces on human health: A systematic review. Environ. Res. 180, 108869. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108869
Liu W., Li H., Xu H., Zhang X., and Xie Y. (2023). Spatiotemporal distribution and driving factors of regional green spaces during rapid urbanization in Nanjing metropolitan area, China. Ecol. Indic. 148, 110058. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110058
Luglio S. M., Sportelli M., Frasconi C., Raffaelli M., Gagliardi L., Peruzzi A., et al. (2023). Monitoring autonomous mowers operative parameters on low-maintenance warm-season turfgrass. Appl. Sci. 13, 7852. doi: 10.3390/app13137852
Odom J. (2023). “The shift from battery to gas,” in The edge magazine. Available at: https://blog.landscapeprofessionals.org/the-shift-from-gas-to-battery/.
Ritchie H. and Rodés-Guirao L. (2024). Peak global population and other key findings from the 2024 UN World Population Prospects. Available online at: https://ourworldindata.org/un-population-2024-revision (Accessed Aug 20, 2024).
Saidani M. and Kim H. (2021). Quantification of the environmental and economic benefits of the electrification of lawn mowers on the US residential market. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 26, 1267–1284. doi: 10.1007/s11367-021-01917-x
Slater S. J., Christiana R. W., and Gustat J. (2020). Recommendations for keeping parks and green space accessible for mental and physical health during COVID-19 and other pandemics. Preventing Chronic Dis. 17, E59. doi: 10.5888/pcd17.200204
Stucke T. and Horn B. (2022). “State of the industry report,” in Lawn & Landscape magazine, S1-S24. Valley View, OH, USA: GIE Media Inc. Available at: https://cdn.gie.net/fileuploads/document/2022/11/14/soi%20lawn_full%20report_new_rfs.pdf (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Száraz L. R. (2014). The impact of urban green spaces on climate and air quality in cities. Geographical Locality Stud. 2, 326–354. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176770
Tansil D., Plecak C., Taczanowska K., and Jiricka- Pürrer A. (2022). Experience them, love them, protect them—Has the COVID-19 pandemic changed people’s perception of urban and suburban green spaces and their conservation targets? Environ. Manage. 70, 1004–1022. doi: 10.1007/s00267-022-01721-9
Turner-Skoff J. B. and Cavender N. (2022). The benefits of trees for livable and sustainable communities. Plants People Planet 1, 323–335. doi: 10.1002/ppp3.39
Ugolini F., Massetti L., Calaza-Martínez P., Cariñanos P., Dobbs C., and Ostoić S. K. (2020). Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the use and perceptions of urban green space: An international exploratory study. Urban Forestry Urban Greening 56, 126888. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126888
United State Census Bureau (2022). The number of people primarily working from home tripled between 2019 and 2021. Available online at: https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2022/people-working-from-home.html:~:text=SEPT.,by%20the%20U.S.%20Census%20Bureau (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Venter Z. S., Barton D. N., Gundersen V., Figari H., and Nowell M. (2020). Urban nature in a time of crisis: recreational use of green space increases during the covid-19 outbreak in Norway. Environ. Res. Lett. 15, 104075. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abb396
Volckens J., Braddock J., Snow R. F., and Crews W. (2007). Emissions profile from new and in-use handheld, 2-stroke engines. Atmospheric Environ. 41, 640–649. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.08.033
Wang C., Ren Z., Dong Y., Zhang P., Guo Y., Wang W., et al. (2022). Efficient cooling of cities at global scale using urban green space to mitigate urban heat island effects in different climatic regions. Urban Forestry Urban Greening 74, 127635. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2022.127635
Yu Z., Yang G., Zuo S., Jørgensen G., Koga M., and Vejre H. (2020). Critical review on the cooling effect of urban blue-green space: A threshold-size perspective. Urban Forestry Urban Greening 49, 126630. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126630
Keywords: battery-powered, gas-powered, zero-emission, sustainability, environmental impact, landscape maintenance, green industry, horticultural services
Citation: Kent K, Brodbeck A, Hoffman M, Chaves-Cordoba B and Bartley PC III (2025) Perceptions, barriers, and challenges of adopting battery-powered landscape equipment in professional maintenance. Front. Hortic. 4:1490879. doi: 10.3389/fhort.2025.1490879
Received: 03 September 2024; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 03 July 2025.
Edited by:
Francesco Ferrini, University of Florence, ItalyReviewed by:
Daniela Romano, University of Catania, ItalyBarbara De Lucia, University of Bari Aldo Moro, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Kent, Brodbeck, Hoffman, Chaves-Cordoba and Bartley. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Paul C. Bartley III, cGF1bC5iYXJ0bGV5QGF1YnVybi5lZHU=
 Kati Kent
Kati Kent Arnold Brodbeck2
Arnold Brodbeck2 Mark Hoffman
Mark Hoffman Paul C. Bartley III
Paul C. Bartley III