Abstract
The northern Gulf of Mexico (NGOM) coastal shelf adjacent to the Mississippi and Atchafalaya rivers system experiences strong seasonal hypoxia in the late summer and coupled physical-biological models suggest that hypoxia formation in the NGOM is sensitive to benthic biogeochemical processes. However, the processes driving sediment oxygen consumption and their relationship to bottom oxygen concentration remain enigmatic. This study for the first time concurrently measured in situ total oxygen uptake (TOU) and diffusive oxygen uptake (DOU) during two different hypoxia seasons. The relatively large DOU: TOU ratio of 0.33 ± 0.07 observed during this study suggests more significant benthic infauna community activity driving oxygen fluxes than previously thought. Future hypoxia models for this region should consider the role of infaunal-mediated oxygen consumption in biogeochemical variables.
1 Introduction
Marine sediments play a key role in the global carbon cycle. The remineralization of organic matter in sediments involves several biogeochemical processes mediated by a variety of microorganisms and electron acceptors (Froelich et al., 1979; Canfield, 1993). Since aerobic respiration is considered the dominant pathway for organic matter remineralization in sediments due to its favorable energy yield, total oxygen utilization (TOU) in sediment is commonly used as a proxy for the total benthic organic carbon mineralization in marine sediments. TOU integrates degradation through aerobic activity, autotrophic and heterotrophic nitrification, re-oxidation of reduced inorganic compounds, and oxygen uptake related to meio- and macrofauna-mediated processes like bioirrigation and faunal respiration (Froelich et al., 1979; Seiter et al., 2005; Glud, 2008). A fraction of TOU is driven by diffusive processes related to the difference in dissolved oxygen (DO2) concentration between the sediment and the overlying water, which is referred to as diffusive oxygen uptake (DOU). DOU is generally considered to represent the microbial component of TOU since microbial oxygen consumption is a main driver of oxygen depletion within the sediment (Cai and Sayles, 1996), and it can also include oxygen utilized in the re-oxidation of reduced chemical species such as iron and manganese that are trapped in the sediment as well as oxygen produced by microphytobenthos.
Continental shelf sediments are a key region for biogeochemical cycling as they account for 87% of carbon burial in the global seafloor despite representing only 8% of the seafloor area (Laruelle et al., 2013). Deltaic shelf sediments alone account for 41% of carbon burial on continental margins (Smith and Hollibaugh, 1993; Smith et al., 2015). Continental margins around the globe are undergoing rapid transformations due to anthropogenic factors including ocean warming and subsequent increased stratification. This will likely lead to declines in DO2 in the ocean interior with implications for ocean productivity, nutrient cycling, carbon cycling, and marine habitat. Ocean models predict declines of 1-7% in the global ocean oxygen inventory over the next century. Such decline in DO2 is more pronounced in coastal water where both direct anthropogenic modifications to landscape and discharge and climate change contribute to aggravating hypoxia issues (Diaz and Rosenberg, 2008; Rabalais et al., 2010; Breitburg et al., 2018; Fennel and Testa, 2019; Wang et al., 2020), where hypoxia is defined as DO2 below 2 mg/l or 63 µM, which is the threshold where pelagic fauna begin to move away from affected waters (Rabalais et al., 2010).
The Mississippi River, the seventh largest river in the world in terms of both water and sediment discharge (Milliman and Meade, 1983), leads to one such river-dominated coastal system that experiences seasonal eutrophication and subsequent hypoxia: the northern Gulf of Mexico (NGOM) continental shelf along the coast of Louisiana. Here, seasonal hypoxia averages an areal extent of 13,500 km2 [1985-2009] (Rabalais et al., 2010). The NGOM hypoxic zone persists even after high spring river discharge returns to normal, until the storm season in early fall promotes mixing on the shelf. The persistence of the hypoxic zone could be related to positive feedback mechanisms within the sediment with delayed respiration of accumulated organic matter. TOU has been identified as an important driver of hypoxia in the NGOM, and various estimates suggest that TOU could be responsible for 22-60% of the oxygen consumption below the pycnocline (Rowe et al., 2002; Murrell and Lehrter, 2011; Fennel et al., 2013). Physical-biogeochemical model simulations for the NGOM shelf also indicate the size of the NGOM hypoxic zone to be highly sensitive to the sediment sink of oxygen (Fennel et al., 2013, 2016), which in turn depends on parameterization of sediment oxygen utilization rates. This makes it critical to understand the underlying mechanisms that can influence the current understanding of TOU on the NGOM shelf.
Previous sediment oxygen studies in this region have used only ex situ sediment core incubations (Murrell and Lehrter, 2011; Lehrter et al., 2012; McCarthy et al., 2013; Nunnally et al., 2013, 2014; Wang et al., 2020), models based on ex situ incubations (Fennel et al., 2013; Fennel et al., 2016; Morse and Eldridge, 2007; Sunda and Cai, 2012; Laurent et al., 2016), in situ sediment incubations (Rowe et al., 2002; Berelson et al., 2019), or sediment microprofiles (Rabouille et al., 2021) but did not combine multiple methodologies to identify the relative contribution of DOU and benthic fauna to TOU. The major objective of this work is to utilize in situ sediment incubations and DO2 microprofiles collected simultaneously to investigate the components of sediment oxygen consumption in the NGOM hypoxic zone.
2 Methodology
2.1 Sampling plan
Field samples were collected on two research cruises on the Louisiana continental shelf (Figure 1). The cruises were conducted on board the R/V Pelican during the predicted seasonal hypoxia in late summer: August 2018 and July 2019. The station locations for the current study were chosen to reflect a range of hypoxic conditions based on annual hypoxia frequency from 1985 to 2016 (Smith and Rabalais, 2022). These four stations—B5 (17 m), C6 (19 m), D3 (17 m), and D5 (32 m)—are the focus of this study where observations were conducted for a period of 24 hours during both cruises. Water column characteristics including salinity (PSU), temperature (°C), DO2 (µM), fluorescence (µg/l), and PAR throughout the area of river influence were collected with CTD casts. The data are available in a publicly-accessible repository (Beck, 2024).
Figure 1
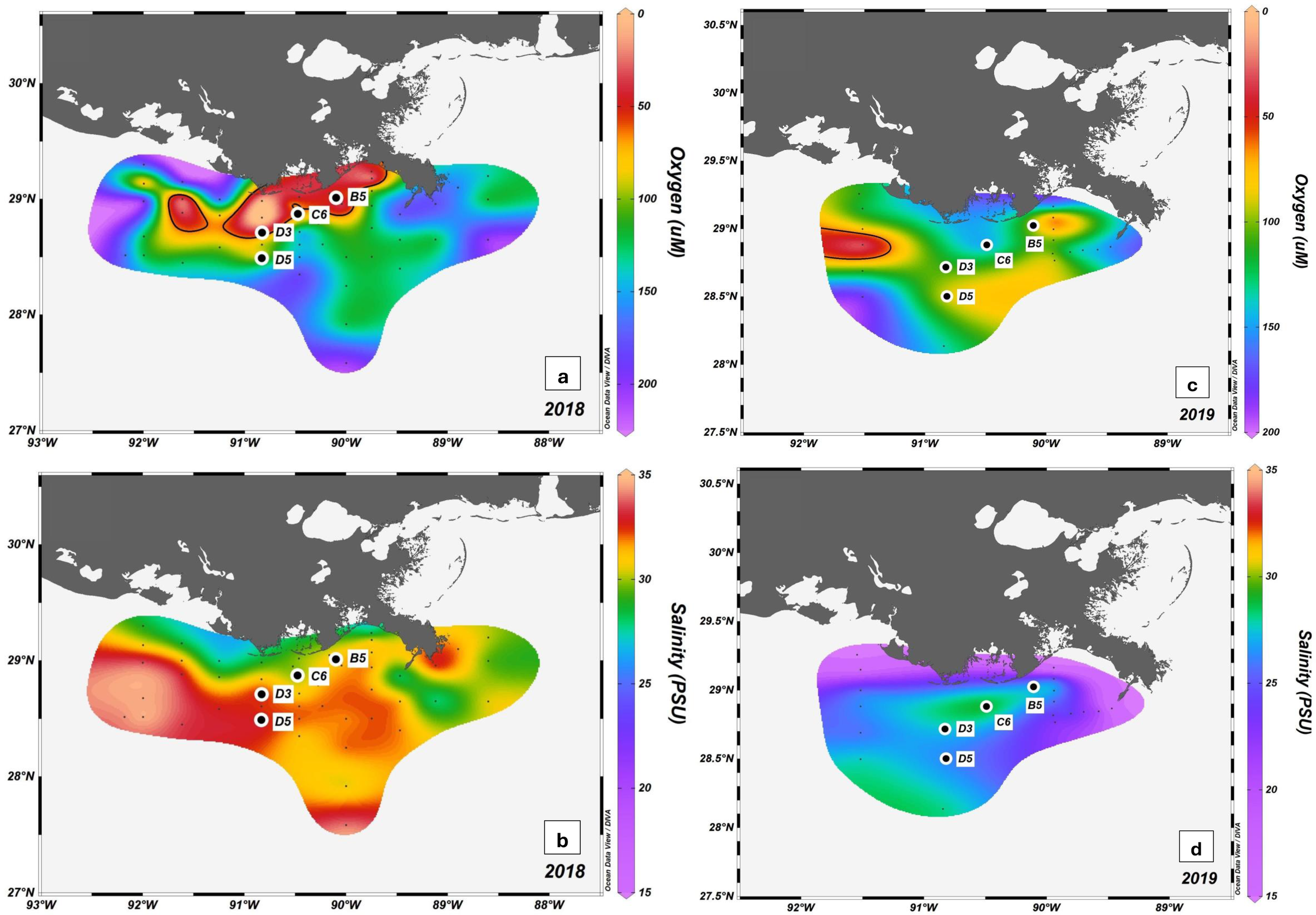
Study area oxygen (µM O2) and salinity (PSU) during sampling. Grey dots represent CTD cast locations and black dots with white outline indicate flux experiments and sediment collection in addition to a CTD cast. Those locations are also labeled with their station name. (a, c) show bottom water oxygen concentration in August 2018 and July 2019 respectively, where the contour line shows 63 µM O2; (b, d) show salinity in PSU at 3 meters depth in August 2018 and July 2019 respectively.
2.2 Total and diffusive oxygen utilization
A benthic lander was deployed with minimum sediment disturbance at each of the stations to carry out in situ flux measurements for TOU. The lander system was equipped with chambers that each seal a sediment surface area of 840 cm2 and a volume of approximately 16 L of overlying bottom water. Each chamber included a magnetically coupled stirrer that mixed the water within the chamber uniformly in about 20 minutes at 12-16 rpm and produced a 300-400 µm diffusive boundary layer. It has been shown that within the chambers of a benthic lander, a diffusive boundary layer between 120-550 µm did not produce any noticeable influence on the measured oxygen and nutrient fluxes (Tengberg et al., 2004). Leakage was calculated from the loss of a CsBr tracer from samples taken from each chamber every 4 hours. Chamber data were not utilized when CsBr loss was greater than 20%. Such a leak was observed for D3 in 2018, when two chambers began leaking after 700 mins. Thus, TOU for that station was estimated from the first 10 hours of (600min) deployment. Three of the benthic chambers were fitted with Seaguard DO2 optode sensors that measured DO2 every 15 minutes with an error of <4 µM. These data were then corrected for sample volume replacement and plotted against time elapsed to produce the rate of TOU (Supplementary Figure S1). In 2018, the bottom water dissolved oxygen concentration inside the chamber dropped below 32 µM during the incubation period. Previous studies have shown that sediment oxygen consumption rates become non-liner around this concentration (Ghaisas et al., 2019), so TOU was only estimated from the region of the curve where DO2 was greater than 32 µM (Supplementary Figure S1).
Sediment oxygen profiles were measured with a Unisense in situ microprofiler system, which was equipped with two oxygen sensors (250 µm) and a resistivity sensor. The resistivity data was not found to be reliable in identifying the sediment-water interface (SWI) due to the presence of a thick benthic boundary layer at the seafloor, leading to a gradual rather than a sharp change in resistivity. The position of the SWI relative to the profiles was thus determined from the DO2 slope, which consists in assigning the interface position to a break in the oxygen concentration gradient and if the slope break was not clearly visible, the position of maximum gradient was assigned the sediment – water interface (Revsbech, 1989; Sweerts et al., 1989; Rabouille et al., 2003). Oxygen penetration depth (OPD) was determined by using the depth where the DO2 dropped below 1 µM. The profiler system was programmed to record ten measurements at 250 µm depth intervals and the data presented is the average of the ten measurements at each depth (Supplementary Figure S2). DOU was calculated with an adaptation of Fick’s law of diffusion using the oxygen gradient in coastal sediments (Rassmann et al., 2016):
where φ is the sediment porosity; is the apparent diffusion coefficient in porous environments, which is calculated using DO2 = D/(1 + 3(1- φ)) where D is the O2 diffusion coefficient in water (Broecker and Peng, 1974); and dO2/dz at z=0 represents the oxygen gradient at the sediment-water interface. NGOM sediment is generally muddy with low permeability, averaging about 75% silt and clay, so diffusion is the dominant process of benthic-pelagic exchange (Murrell and Lehrter, 2011) Porosity was calculated using the top 1 cm slice of sediment from each station in 2018 and the same values were used for 2019. Due to multicorer malfunction, no sediment core was collected from B5 in 2018, so the porosity value for C6 was used. No data could be collected from station B5 in 2019 because the lander and the profiler sank too much into the sediment. The profile at D5 in 2019 was carried out on a sediment core after it was collected and allowed to equilibrate onboard for 3 hours. Due to reduced resolution for this measurement, DOU was calculated using the OPD method (Cai and Sayles, 1996). Despite this effort, the profile may be slightly disturbed and thus DOU calculated from this station should be regarded with caution.
3 Results
3.1 Hydrography
The hydrographic conditions were notably different between the two years when samples were collected (Figures 1, 2). In 2018, sampling occurred during a period of extended stratification and all four stations exhibited hypoxia (< 63 µM O2) at least once during the 24 hours of observation when repeat CTD casts were carried out. In 2019, sampling occurred only 3-10 days after the passage of Hurricane Barry, which re-oxygenated a large portion of the usual hypoxic zone through mixing of the water column. The hurricane also delivered large amounts of fresh water to the NGOM in the form of direct rain and coastal rain runoff. However, despite these disturbances, stratified hypoxic conditions returned relatively quickly to some areas of the shelf. This hurricane made landfall as a mild category 1 storm about 120 km west of C6 and may have had limited impact on this study’s sediments. There was a clear pycnocline at D3, and B5 and D5 both experienced strict hypoxia at least once during the 24 hours of observation in 2019.
Figure 2
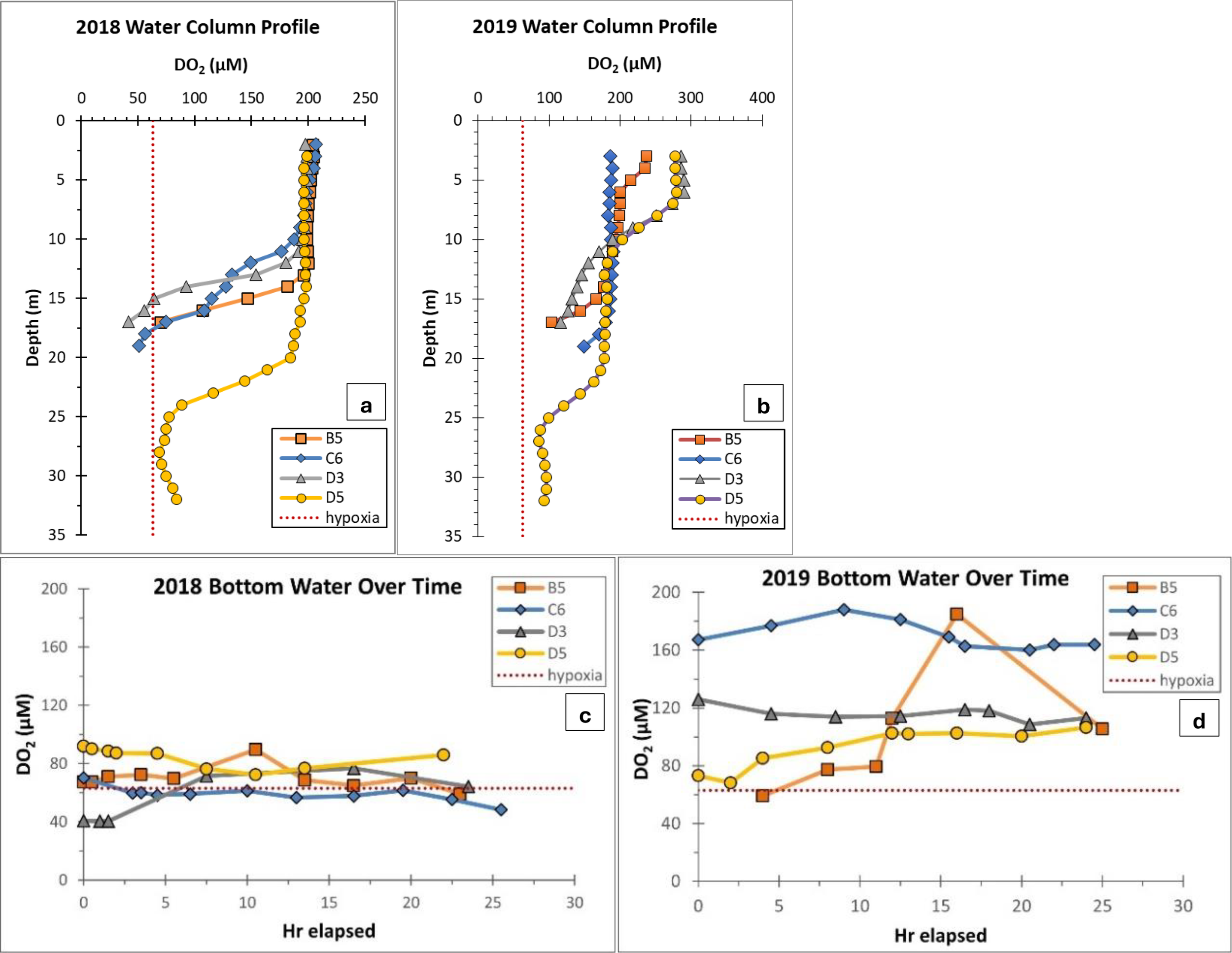
(a, b) Water column dissolved oxygen profiles from 2018 and 2019. Each value represents the average DO2 in µM for that depth across the 20-30 hours that the station was monitored. All bottom depth values are within one meter of the sea floor. (c, d) Average DO2 concentration over 24 hours for the bottom meter at each station as collected by multiple CTD casts during TOU measurements. The dotted red line represents the threshold of strict hypoxia, 63 µM DO2.
3.2 Sediment oxygen uptake
Total oxygen uptake was calculated from the slope of the linear regression of DO2 plotted against time elapsed. In 2018, TOU ranged from 13.8 – 21.9 mmol/m2/d and averaged 19.2 ± 3.2 mmol/m2/d. In 2019, TOU ranged from 16.4 – 35.1 mmol/m2/d and averaged 25.5 ± 7.6 mmol/m2/d. Other studies in this region have reported in situ TOU averaging 15.9 ± 14.1 mmol/m2/d (Rowe et al., 2002; Berelson et al., 2019), which covers the range observed in this study.
Dissolved oxygen within the sediment decreased rapidly with depth even when the overlying water was not hypoxic. Sediment OPD in 2018 ranged from 1.5-6.9 mm and averaged 3.2 mm. In 2019, it ranged from 2.8-7.0 mm and averaged 3.8 mm. DOU ranged from 1.9 – 11.7 mmol/m2/d, with an average of 6.2 ± 3.3 mmol/m2/d (Figure 3). Another study in this region has reported DOU ranging from 4.8-15.1 mmol/m2/d, which is similar to the range observed in this study (Rabouille et al., 2021).
Figure 3
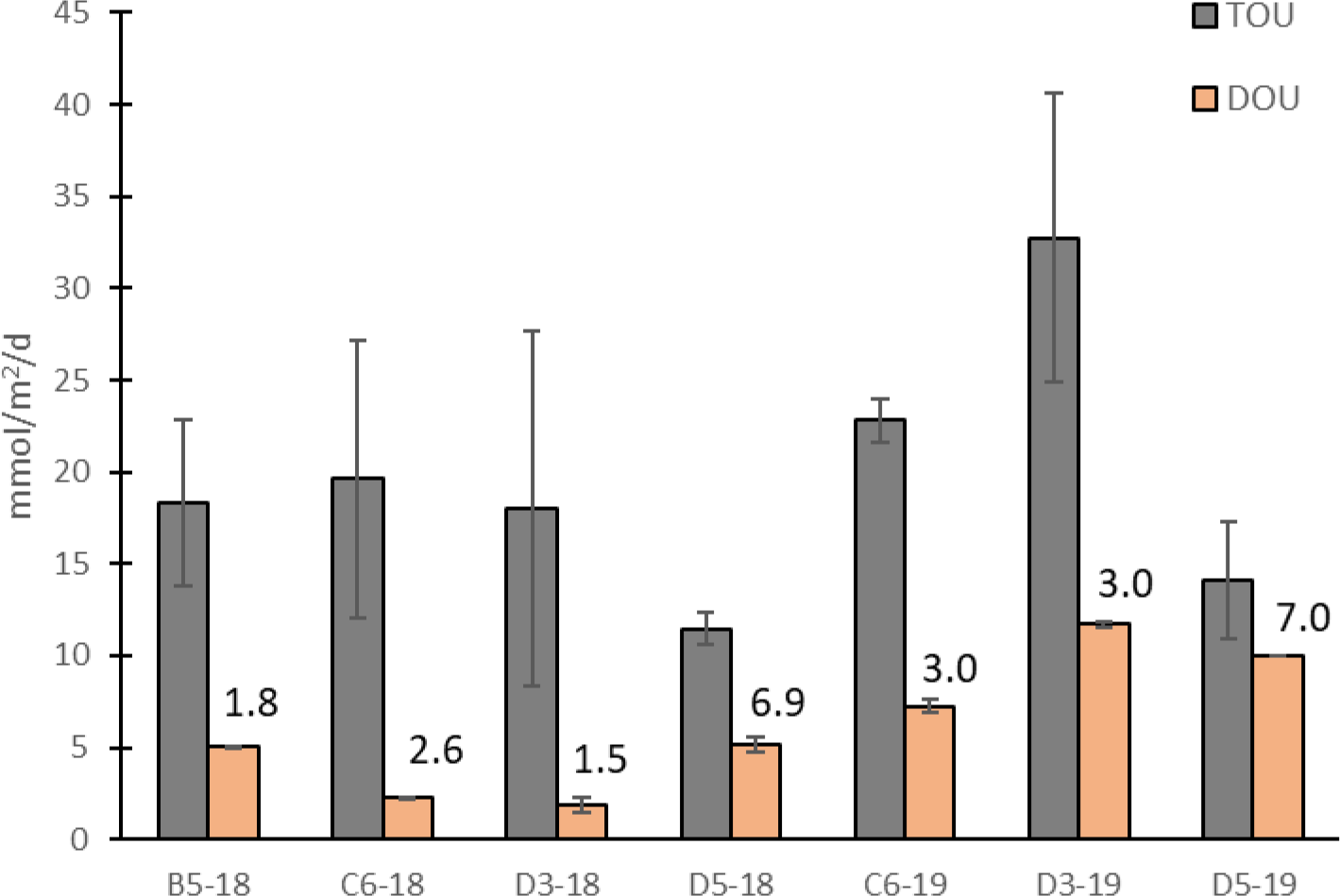
Total oxygen uptake minus water column respiration and diffusive oxygen uptake in mmol/m2/d for all stations both years. The numbers above the DOU bars represent the average sediment oxygen penetration depth in mm.
4 Discussion
4.1 Sediment oxygen utilization and component processes
According to existing literature, oxygen flux due to fauna-mediated processes is unlikely a significant factor of TOU in the NGOM hypoxic zone since the presence of large fauna is rare during these conditions (Rabalais et al., 2001; Rowe et al., 2002; Middelburg and Levin, 2009; Rabalais and Baustian, 2020). Macrobenthos in this area during hypoxia are greatly decreased and the species distribution is dominated by polychaetes that, when stressed in low oxygen conditions, live and feed at the surface of the sediment and do not burrow (Baustian and Rabalais, 2009; Shivarudrappa and Briggs, 2017; Rabalais and Baustian, 2020). Polychaete density was estimated to be about 350 individuals per m2 in August 2004 (Baustian and Rabalais, 2009). During hypoxia in the NGOM, it has been observed that bioactivity is sparse or absent as a factor in sediment dynamics (Briggs et al., 2015; Rabouille et al., 2021), where macrofaunal communities are dominated by polychaetes (>50%) that are typically surface feeders. However, there have been observations that polychaete density in the surface layer of the sediment actually increases at bottom water DO2 minima as a result of the redox interface moving upward (Baustian and Rabalais, 2009). The large difference between TOU and DOU in this study—DOU being only 10-71% the magnitude of TOU, averaging 33%—suggests that fauna may indeed be present and turbating in this system, or at least extant and respiring.
Before such a conclusion can be drawn, another sink of DO2 that can impact TOU needs to be considered: oxygen consumption in the water column itself. Within each chamber, there was approximately 16 L of seawater overlying the sediment surface and microbial respiration within this water can contribute to oxygen uptake measured in TOU. To represent the true TOU of sediment, this water column respiration must be subtracted. Therefore, all TOU values presented in this manuscript have been corrected as such for subsequent TOU and DOU comparison and DOU: TOU ratios. The lander was outfitted with a Niskin bottle with an oxygen optode sensor installed inside, but unfortunately the mechanism to properly seal the Niskin bottle at the seafloor failed. Thus, we must rely on previous work to make such an estimate of near-sediment water column respiration. To our knowledge, the most applicable data available for this correction was collected in August 2007 at C2 and C6, which estimated that near-sediment water column respiration was 10.8 mmol/m3/d (Murrell and Lehrter, 2011). This value becomes about 2.3 mmol/m2/d when adjusted for the specifications of our lander chambers. Subtracting 2.3 mmol/m2/d from our preliminary TOU “gap”—that is, the difference between TOU and DOU—yields a final TOU gap that is best explained by macrofaunal factors. This is surprising given that hypoxia is generally considered to decrease faunal activity and lends support to previous observations of increased polychaete density in surface sediments during low oxygen periods (Baustian and Rabalais, 2009; Middelburg and Levin, 2009).
DOU: TOU ratio, which is frequently used to represent faunal activity where a low ratio indicates higher faunal activity, was variable between the two years with lower values observed in 2018 (0.24 ± 0.06) compared to 2019 (0.46 ± 0.09). This suggests more active faunal behavior closer to the hypoxia threshold in 2018. A previous study has concluded that in the coastal ocean (< 100m), DOU represents about 43% of TOU in non-photic cohesive sediments (Glud, 2008). Similarly, another global review of DOU: TOU concludes that fauna-mediated oxygen uptake in coastal regions accounts for about half of TOU (Jørgensen et al., 2022). Both conclusions translate to a DOU: TOU ratio of about 0.5. This is similar to the DOU: TOU ratios observed in our study for 2019 but much higher than those observed in 2018. It must be noted that the above two literature reviews exclude measurements from hypoxic regions. During our study, bottom water was significantly more oxic in 2019 due to storm-related mixing, whereas in 2018 the bottom water conditions more closely represent classic hypoxic conditions. The lower DOU: TOU ratios observed in 2018 are primarily driven by the lower values at stations C6 and D3, where we observed the lowest dissolved oxygen concentrations (58.5 and 32.0 µM respectively) for this study. These two stations are also where hypoxia is reported most frequently. Thus, it appears that the lower DOU: TOU ratios observed in this study, which are driven by estimates from stations C6-2018 and D3-2018, is related to bottom water hypoxia. Hence, a positive relationship (R2 = 0.77; p< 0.005) between bottom DO2 and DOU: TOU is observed in our study (Figure 4a), as well as an inverse relationship between historical hypoxia frequency and DOU: TOU (Figure 4b), which aligns with our above conclusion that low bottom water DO2 can cause fauna present in the sediments to migrate to the sediment surface and thereby contribute to the observed increase in fauna-mediated oxygen consumption with decreasing bottom water DO2.
Figure 4
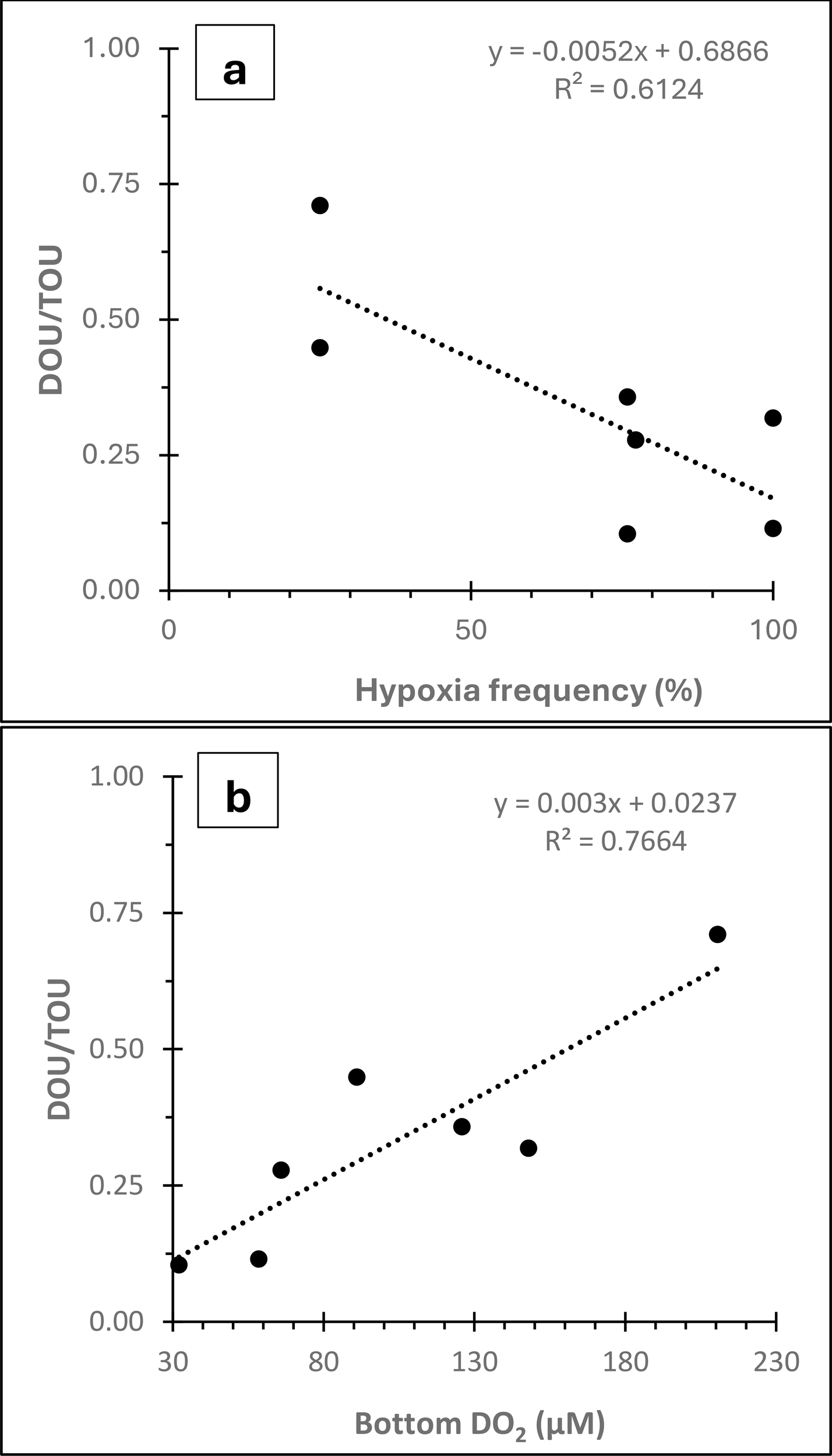
(a) DOU: TOU vs historical hypoxia frequency. (b) DOU: TOU vs observed bottom water DO2.
It could be that the variable DO2 conditions of the NGOM contribute to a stress response in the fauna that leads to a short burst of movement—and therefore irrigation—as bottom water transitions from oxic to hypoxic. It has been observed that infaunal density increases toward the sediment surface as bottom water conditions become hypoxic due to upward migration of the oxic-anoxic interface (Baustian and Rabalais, 2009; Middelburg and Levin, 2009). This means that both fauna-mediated activities like bioirrigation as well as respiration performed by the fauna itself would increase oxygen flux across the sediment-water interface with decreasing bottom water DO2, potentially producing low DOU: TOU values like the values observed in 2018 for this study. This could even potentially be an extended behavior with long-lasting effects on TOU if DO2 fluctuates back and forth over the threshold between normal infaunal behavior and hypoxic behavior. Since normoxic infaunal behavior includes being burrowed in the sediment and hypoxic dormancy behavior involves burrowing in the shallow sediment or lying on top of the sediment, transitioning between the two states would include moving into and out of sediment burrows, which could cause a lower-than-expected DOU: TOU. In this study, bottom water DO2 crossed back and forth over the hypoxia threshold more in 2018 than in 2019, despite overall conditions being more variable in 2019 (Figure 2), which supports the hypothesis that bottom water DO2 conditions near the hypoxia threshold may actually increase faunal behavior and therefore decrease DOU: TOU.
4.2 The northern Gulf of Mexico
There are many studies investigating the relationship between bottom water DO2 and sediment TOU in the NGOM hypoxic zone, as well as models based on them (Hetland and DiMarco, 2008; Fennel et al., 2016; Laurent et al., 2016), but the majority of these studies trace back to only three ex situ sediment core incubations (Murrell and Lehrter, 2011; McCarthy et al., 2013; Nunnally et al., 2013). While sediment core incubations can be a robust and cost-effective method for studying coastal sediment processes, ex situ measurement methods may not be ideal for studying hypoxic environments (Miller-Way et al., 1994). Three studies in the northern Gulf of Mexico relate TOU with bottom water DO2 using in situ TOU measurements (Rowe et al., 2002; Berelson et al., 2019) or DOU measurements (Rabouille et al., 2021), but not both. All three of these studies found a positive correlation between TOU and bottom water DO2, though the strength of the correlation varies between studies and methods. It should be noted that in the above-mentioned studies, TOU ranged 0-55 mmol/m2/d in hypoxic waters and 3-40 mmol/m2/d in oxic waters. The fact that these ranges are so large and overlap almost completely means that further investigation into this system is necessary. Previous studies using benthic lander systems (Rowe et al., 2002; Berelson et al., 2019) reported weak positive correlations (r2 = 0.09 and 0.52 respectively) between TOU and bottom DO2. However, in both of these studies TOU was found to drop significantly when bottom DO2 concentrations were less than 30 µM. In our current study, we did not observe bottom DO2 less than 48 µM which could be a reason for the weak positive relationship between TOU and DO2 (r2 = 0.22).
Up until now, there is no comparison of in situ TOU and DOU within the same study for the NGOM hypoxic zone. It is worth noting that both of the in situ TOU studies mentioned above are based on observations that are 10-30 years old—Berelson et al. performed their measurements in 2011 and Rowe et al. performed their measurements in 1991-1994. The NGOM hypoxic zone is a highly dynamic system that is growing and changing annually in response to climate change, Louisiana coastal land loss, and upstream land management practices (Rabalais et al., 1994, 2010), so data that is decades old may no longer be an accurate representation of current processes.
In our study, hypoxia conditions varied between years, among stations, and even from hour to hour. CTD casts taken at each station while the TOU flux experiments were conducted showed variable bottom water DO2 on both spatial and temporal scales (Figures 1, 2). The data taken in 2019 are more variable than the data taken in 2018 due to Hurricane Barry, but they should not be discounted as outliers as hurricanes are a regular part of the NGOM ecosystem. It can be expected that in response to such dynamic changes in bottom water DO2 conditions that sediment oxygen processes will also vary. However, even though sampling took place after Hurricane Barry, the yearly difference between TOU gaps is not statistically significant, suggesting that this gap could be attributable to enduring local processes rather than transient weather events. This is likely because this hurricane made landfall as a mild category 1 storm about 120 km west of station C6 and may have had a limited impact on sediments at our sampling stations. Our study also indicates that bottom water can transition from oxygenated after storm mixing back to hypoxic conditions in a short period of time, which agrees with modeling results and unpublished bottom water DO2 time series data from this region.
5 Conclusions
Coastal margins are robust, dynamic systems that play a major role in the ocean’s biogeochemical cycling. River-dominated coastal margins that are rich in organic matter tend to support active benthic infaunal communities, but the relationship between coastal eutrophication-driven hypoxia and fauna-mediated sediment processes has yet to be fully explored. The northern Gulf of Mexico seasonal hypoxia zone has previously been considered an area of minimal fauna activity, but our concurrent in situ observations of TOU and DOU demonstrate otherwise. The large difference between TOU and DOU in this study—DOU accounting for 10-71% of TOU, averaging 33%—suggests that benthic infauna in this area may have a much larger impact on sediment oxygen dynamics than previously thought. Thus, further study is needed to clarify the fauna-mediated DO2 consumption in this region to better understand NGOM sediment oxygen dynamics and how they might change in the future. Such fauna mediated DO2 consumption, if found to be significant, should be incorporated into coupled sediment-water biogeochemical models that are utilized for hypoxia predication and analysis.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.12536642.
Author contributions
HB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Investigation. KM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Project administration, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Funding provided by NSF Chemical Oceanography program, Award Number OCE- 1756788.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend special thanks to the crew of the R/V Pelican for field support, and collaborators Courtney Harris, Linlin Cui, and Dongxiao Yin. We would also like to thank the reviewers, especially CR, for their comments and advice which significantly improved this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1532999/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Baustian M. Rabalais N. (2009). Seasonal composition of benthic macroinfauna exposed to hypoxia in the northern gulf of Mexico. Estuaries. Coasts.32, 975–983. doi: 10.1007/s12237-009-9187-3
2
Beck H. (2024). Sediment O2 Dynamics in NGOM hypoxia (version 1) (CERN, Switzerland: Zenodo). doi: 10.5281/zenodo.12536641
3
Berelson W. McManus J. Severmann S. Rollins N. (2019). Benthic fluxes from hypoxia-influenced Gulf of Mexico sediments: Impact on bottom water acidification. Mar. Chem.209, 94–106. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2019.01.004
4
Breitburg D. Levin L. Oschlies A. Grégoire M. Chavez F. Conley D. et al . (2018). Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science359, eaam7240. doi: 10.1126/science.aam7240
5
Briggs K. Cartwright G. Friedrichs C. Shivarudrappa S. (2015). Biogenic effects on cohesive sediment erodibility resulting from recurring seasonal hypoxia on the Louisiana shelf. Continent. Shelf. Res.93, 17–26. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.11.005
6
Broecker W. S. Peng T.-H. (1974). Gas exchange rates between air and sea1. Tellus. A.: Dynamic. Meteorol. Oceanogr.26, 21. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v26i1-2.9733
7
Cai W.-J. Sayles F. (1996). Oxygen penetration depths and fluxes in marine sediments. Mar. Chem.52, 123–131. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00081-X
8
Canfield D. E. (1993). “Organic matter oxidation in marine sediments,” in Interactions of C, N, P and S biogeochemical Cycles and Global Change. Eds. WollastR.MackenzieF. T.ChouL. (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg), 333–363. NATO ASI Series. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76064-8_14
9
Diaz R. Rosenberg R. (2008). Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science321, 926–929. doi: 10.1126/science.1156401
10
Fennel K. Hu J. Laurent A. Marta-Almeida M. Hetland R. (2013). Sensitivity of hypoxia predictions for the northern Gulf of Mexico to sediment oxygen consumption and model nesting. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans.118, 990–1002. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20077
11
Fennel K. Laurent A. Hetland R. Justić D. Ko D. Lehrter J. et al . (2016). Effects of model physics on hypoxia simulations for the northern Gulf of Mexico: A model intercomparison. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans.121, 5731–5750. doi: 10.1002/2015JC011577
12
Fennel K. Testa J. (2019). Biogeochemical controls on coastal hypoxia. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci.11, 105–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010318-095138
13
Froelich P. Klinkhammer G. Bender M. Luedtke N. Heath G. Cullen D. et al . (1979). Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta43, 1075–1090. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90095-4
14
Ghaisas N. Maiti K. White J. (2019). Coupled iron and phosphorus release from seasonally hypoxic Louisiana shelf sediment. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf. Sci.219, 81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2019.01.019
15
Glud R. (2008). Oxygen dynamics of marine sediments. Mar. Biol. Res.4, 243–289. doi: 10.1080/17451000801888726
16
Hetland R. DiMarco S. (2008). How does the character of oxygen demand control the structure of hypoxia on the Texas–Louisiana continental shelf? J. Mar. Syst.70, 49–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2007.03.002
17
Jørgensen B. Wenzhöfer F. Egger M. Glud R. (2022). Sediment oxygen consumption: Role in the global marine carbon cycle. Earth-Science Reviews228, 103987. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103987
18
Laruelle G. G. Dürr H. H. Lauerwald R. Hartmann J. Slomp C. P. Goossens N. et al . (2013). Global multi-scale segmentation of continental and coastal waters from the watersheds to the continental margins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci.17, 2029–2051. doi: 10.5194/hess-17-2029-2013
19
Laurent A. Fennel K. Wilson R. Lehrter J. Devereux R. (2016). Parameterization of biogeochemical sediment–water fluxes using in situ measurements and a diagenetic model. Biogeosciences13, 77–94. doi: 10.5194/bg-13-77-2016
20
Lehrter J. Beddick D. Devereux R. Yates D. Murrell M. (2012). Sediment-water fluxes of dissolved inorganic carbon, O2, nutrients, and N2 from the hypoxic region of the Louisiana continental shelf. Biogeochemistry109, 233–252. doi: 10.1007/s10533-011-9623-x
21
McCarthy M. Carini S. Liu Z. Ostrom N. Gardner W. (2013). Oxygen consumption in the water column and sediments of the northern Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone. Estuarine. Coast. Shelf. Sci.123, 46–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.02.019
22
Middelburg J. Levin L. (2009). Coastal hypoxia and sediment biogeochemistry. Biogeosciences6, 1273–1293. doi: 10.5194/bg-6-1273-2009
23
Miller-Way T. Boland G. Rowe G. Twilley R. (1994). Sediment oxygen consumption and benthic nutrient fluxes on the Louisiana continental shelf: A methodological comparison. Estuaries17, 809–815. doi: 10.2307/1352749
24
Milliman J. Meade R. (1983). World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans. J. Geol.91, 1–21. doi: 10.1086/628741
25
Morse J. Eldridge P. (2007). A non-steady state diagenetic model for changes in sediment biogeochemistry in response to seasonally hypoxic/anoxic conditions in the “dead zone” of the Louisiana shelf. Mar. Chem.106, 239–255. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2006.02.003
26
Murrell M. Lehrter J. (2011). Sediment and lower water column oxygen consumption in the seasonally hypoxic region of the louisiana continental shelf. Estuaries. Coasts.34, 912–924. doi: 10.1007/s12237-010-9351-9
27
Nunnally C. Quigg A. DiMarco S. Chapman P. Rowe G. (2014). Benthic–pelagic coupling in the Gulf of Mexico hypoxic area: Sedimentary enhancement of hypoxic conditions and near bottom primary production. Continent. Shelf. Res.85, 143–152. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.06.006
28
Nunnally C. Rowe G. Thornton D. Quigg A. (2013). Sedimentary oxygen consumption and nutrient regeneration in the northern gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone. J. Coast. Res.63, 84–96. doi: 10.2112/SI63-008.1
29
Rabalais N. Baustian M. (2020). Historical shifts in benthic infaunal diversity in the northern gulf of Mexico since the appearance of seasonally severe hypoxia. Diversity12, 49. doi: 10.3390/d12020049
30
Rabalais N. Díaz R. Levin L. Turner R. E. Gilbert D. Zhang J. (2010). Dynamics and distribution of natural and human-caused hypoxia. Biogeosciences7, 585–619. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-585-2010
31
Rabalais N. Smith L. Harper D. Jr. Justić D. (2001). “Effects of seasonal hypoxia on continental shelf benthos,” in Coastal Hypoxia: Consequences for Living Resources and Ecosystems (Washington D.C., USA: American Geophysical Union (AGU), 211–240. doi: 10.1029/CE058p0211
32
Rabalais N. Wiseman W. Turner E. (1994). Comparison of continuous records of near-bottom dissolved oxygen from the hypoxia zone along the Louisiana coast. Estuaries17, 850–861. doi: 10.2307/1352753
33
Rabouille C. Denis L. Dedieu K. Stora G. Lansard B. Grenz C. (2003). Oxygen demand in coastal marine sediments: comparing in situ microelectrodes and laboratory core incubations. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 285–286, 49–69. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00519-1
34
Rabouille C. Lansard B. Owings S. Rabalais N. Bombled B. Metzger E. et al . (2021). Early diagenesis in the hypoxic and acidified zone of the northern gulf of Mexico: is organic matter recycling in sediments disconnected from the water column? Front. Mar. Sci.8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.604330
35
Rassmann J. Lansard B. Pozzato L. Rabouille C. (2016). Carbonate chemistry in sediment porewaters of the Rhône River deltadriven by early diagenesis (northwestern Mediterranean). Biogeosciences13, 5379–5394. doi: 10.5194/bg-13-5379-2016
36
Revsbech N. (1989). An oxygen microsensor with a guard cathode. Limnol. Oceanogr.34, 474–478. doi: 10.4319/lo.1989.34.2.0474
37
Rowe G. Kaegi M. E. C. Morse J. Boland G. Escobar Briones E. (2002). Sediment community metabolism associated with continental shelf hypoxia, Northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries25, 1097–1106. doi: 10.1007/BF02692207
38
Seiter K. Hensen C. Zabel M. (2005). Benthic carbon mineralization on a global scale. Global Biogeochem. Cycles.19. doi: 10.1029/2004GB002225
39
Shivarudrappa S. Briggs K. (2017). Macrobenthos community succession in the northern Gulf of Mexico hypoxic regions: testing the Pearson-Rosenberg model. J. Mar. Res.75, 18–46. doi: 10.1357/002224017821219036
40
Smith R. W. Bianchi T. S. Allison M. Savage C. Galy V. (2015). High rates of organic carbon burial in fjord sediments globally. Nat. Geosci.8, 450–453. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2421
41
Smith S. V. Hollibaugh J. T. (1993). Coastal metabolism and the oceanic organic carbon balance. Rev. Geophys.31, 75–89. doi: 10.1029/92RG02584
42
Smith L. Rabalais N. (2022). Frequency of hypoxia. Gulf. Hypoxia.
43
Sunda W. Cai W.-J. (2012). Eutrophication induced CO2-acidification of subsurface coastal waters: interactive effects of temperature, salinity, and atmospheric PCO2. Environ. Sci. Technol.46, 10651–10659. doi: 10.1021/es300626f
44
Sweerts J.-P. St Louis V. Cappenberg T. (1989). Oxygen concentration profiles and exchange in sediment cores with circulated overlying water. Freshw. Biol.21, 401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2427.1989.tb01372.x
45
Tengberg A. Stahl H. Gust G. Müller V. Arning U. Andersson H. et al . (2004). Intercalibration of benthic flux chambers I. Accuracy of flux measurements and influence of chamber hydrodynamics. Prog. Oceanogr.60, 1–28. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2003.12.001
46
Wang H. Lehrter J. Maiti K. Fennel K. Laurent A. Rabalais N. et al . (2020). Benthic respiration in hypoxic waters enhances bottom water acidification in the northern gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans.125, e2020JC016152. doi: 10.1029/2020JC016152
Summary
Keywords
Gulf of Mexico, hypoxia, sediment, oxygen, biogeochemistry, benthic infauna
Citation
Beck H and Maiti K (2025) The importance of fauna-mediated sediment O2 consumption in the NGOM hypoxic zone. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1532999. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1532999
Received
22 November 2024
Accepted
25 June 2025
Published
01 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Carlos Rosas, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Reviewed by
Christophe Rabouille, UMR8212 Laboratoire des Sciences du Climat et de l’Environnement (LSCE), France
Qicheng Meng, Ministry of Natural Resources, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Beck and Maiti.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kanchan Maiti, kmaiti@lsu.edu
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.