Abstract
Coral reefs around the world are affected by numerous disturbances, such as high-intensity cyclones and severe thermal anomalies, which are occurring with increasing frequency and intensity. In 2019, our study site Pulau Bidong near Terengganu, Peninsular Malaysia, was affected by the passage of tropical storm Pabuk over this region, followed by a localized bleaching event later in the year. This study investigated the changes in reef cover and composition over a 5-year period between 2017 and 2021, before and after these successive natural disturbances. At the beginning of our study, live coral cover was 46.11 ± 7.56% and the reef was in a “fair” condition. However, after the multiple disturbances in 2019, the live coral cover decreased by 68% to 14.63 ± 4.35%, mainly due to the decline of the dominant genera Fungia sp. and Acropora sp. The coral bleaching triggered by the local heat stress event mainly affected the massive Fungia sp., as the branching Acropora sp. were severely affected by the previous storm event due to their mechanical vulnerability. After the successive disturbances, SIMPER showed that the community composition in Pulau Bidong had changed. After the disturbance, ‘dead corals covered with algae’ (DCA) now dominated the reef benthos, whereas previously live corals (Fungia sp.) dominated the reef picture. The nMDS plot showed a clear clustering of the benthic community composition between years, with the disturbance survey transects clustered separately from the years without disturbance. The β-diversity box plot showed that the reef community was rather monotonous before the disturbances, but after the consecutive disturbances in 2019, there was a higher variation in coral diversity. Although Pulau Bidong experienced multiple disturbances, the community structure recovered somewhat to pre-disturbance levels towards the end of our study in 2021.
1 Introduction
Coral reefs, sometimes referred to as “rainforests of the sea”, are among the most productive and diverse marine ecosystems in the world: they occupy less than 0.17% of the global ocean area (Spalding et al., 2001), but harbor over 33% of all marine species (Fisher et al., 2015) and provide ecological goods and services worth approximately US$30 billion annually (Moberg and Folke, 1999; Cesar et al., 2003). The Indo-Pacific region, which comprises the ‘Coral Triangle’, is home to 76% of the world’s reef-building corals and is recognized as a global center of coral biodiversity (Veron et al., 2009). Malaysia, which lies on the edge of the Coral Triangle, harbors a reef area of ~4,000 km2 consisting mainly of fringing reefs along the mainland (Burke et al., 2002). Peninsular Malaysia harbors a total of 323 species of hard corals (Harborne et al., 2000), while West Malaysia harbors 398 species of hard corals (Huang et al., 2015).
Coral reef ecosystems are increasingly threatened by natural (rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification and intense tropical cyclones) and anthropogenic (overfishing, sedimentation and nutrient pollution) disturbances (Wilkinson and Souter, 2008). Tropical storms (i.e. cyclones, typhoons and hurricanes) cause severe disturbance to coral reef ecosystems (Scoffin, 1993; Harmelin-Vivien, 1994), ranging from removal of reef matrix, fragmentation and detachment of coral colonies, to scouring by sandblasting and burial of reef organisms (Done, 1992a; Fabricius et al., 2008). When tropical storms make landfall, they have further effects near the coast: decreases in salinity due to rainfall and flooding (leading to coral bleaching) and changes in turbidity (due to sand drift and sediment resuspension) (Sully and van Woesik, 2019). Cyclones play a major role in the redistribution of reef material and are important drivers in shaping geomorphology and restoring reef habitats (Fabricius et al., 2008; De’Ath et al., 2012). The damage caused by tropical storms varies greatly and is determined by the intensity and duration of the storm (Done, 1992a; Fabricius et al., 2008). On the reef side, vulnerability to storms depends on the following factors: Location (windward front reef vs. leeward back reef) (Perry and Smithers, 2006), community type (branching vs. massive) (Fabricius et al., 2008) and stage of coral development (newly settled young colonies vs. mature undisturbed assemblages) (Madin and Connolly, 2006).
Coral bleaching, which is caused by extreme temperature anomalies due to rising sea surface temperatures, leads to the loss of intracellular symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007; Hughes et al., 2017) and - after prolonged disruption of the symbiosis - eventually to the death of the coral itself (Glynn, 1993; Berkelmans et al., 2004). Coral species differ in their susceptibility to bleaching and subsequent death (Marshall and Baird, 2000; McClanahan et al., 2004). This differential response to thermal stress and the associated differences in mortality rates ultimately lead to a change in coral community composition and diversity (Marshall and Baird, 2000; McClanahan et al., 2007). Differences in the severity of bleaching among coral taxa are dependent on numerous factors, including: coral morphology (branching vs. massive corals) (van Woesik et al., 2011; Swain et al., 2016), depth (shallow reefs vs. deeper reefs) (Grimsdich et al., 2010), light intensity (local irradiance and surface reflectance) (Dunne and Brown, 2001), water flow (lagoon reefs vs. open ocean reefs) (Nakamura and van Woesik, 2001; McClanahan et al., 2007), turbidity (Williams et al., 2010; Sully and van Woesik, 2019), coral colony size (smaller/juvenile colony vs. larger/mature colony) (Pratchett et al., 2013; Wagner et al., 2010), symbiont type (Clade C vs. Clade D) (Sampayo et al., 2008; Howells et al., 2013), topographic complexity (elevated, open, crevice, overhang) (Lundgren and Hillis-Starr, 2008; Gorospe and Karl, 2011), temperature history (high temperature fluctuations vs. stable temperature regimes) (Schoepf et al., 2015, 2019; Barshis et al., 2018), and bleaching history (acclimatization vs. adaptation) (Bay and Palumbi, 2015; Matz et al., 2018).
Malaysia rarely experiences severe tropical storms due to its proximity to the equator, as the weak Coriolis forces prevent the formation of strong storms in this region (Chang et al., 2003; Zuki and Lupo, 2008). Nonetheless, a number of storms have passed through this area - Tropical Storm Greg in December 1996, Typhoon Vamei in December 2001 and more recently, Tropical Storm Pabuk in January 2019. As for coral bleaching in Malaysia, it has been estimated that up to 40% of corals on the reefs of Peninsular Malaysia died after the first global bleaching event, while between 5-6% of Malaysian corals may have died during the second global mass bleaching event (Reef Check Malaysia, 2011). Finally, after the 3rd global mass bleaching event, there was a 5.6% decline in live corals between 2014 and 2017 (Reef Check Malaysia, 2020).
Numerous studies have been published on the effects of tropical storms and coral bleaching as individual disturbances on coral reef ecosystems (Goreau et al., 2000, Fabricius et al., 2008; Guest et al., 2012; Beeden et al., 2015; Hughes et al., 2017; Baird et al., 2018; Burt et al., 2019; Eakin et al., 2019; Harrison et al., 2019). However, there is very little research on the effects of storms and bleaching (as multiple disturbances) on coral reef ecosystems (Madin et al., 2018; Ribas-Deulofeu et al., 2021). In January 2019, Cyclone Pabuk, originating from the South China Sea and travelling in a northwesterly direction, passed through the waters off the coast of Peninsular Malaysia before moving into the Gulf of Thailand. Between April and August of the same year, during the bleaching season, a localized bleaching event occurred on Pulau Bidong. Our study aims to address this research gap by investigating the impacts of tropical storms and bleaching (as successive disturbances) over a 5-year period, between 2017 and 2021, in Pulau Bidong. Thereby, our research will investigate the temporal changes in coral cover and benthic composition due to consecutive disturbances (i.e. Cyclone Pabuk and a localized bleaching event) in 2019– analyzing both the pre-disturbance (2017 and 2018) and post-disturbance (2020 and 2021) periods; at a shallow, remote reef in Pulau Bidong on the edge of the South China Sea.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study site
The study site, Pulau Bidong (5°37'7.60"N latitude and 103°3'47.84"E longitude) (Figure 1), is an archipelago consisting of six well-vegetated, low-lying islands located 15 kilometers off the coast of Terengganu. Until the end of 1991, the island was a former Vietnamese refugee settlement. Today it is uninhabited and hosts a UMT research station on its northwestern coast (Roslan et al., 2017). Pulau Bidong has a good population of live corals (46.67%)- and the health of the reef is rated as fair (Reef Check Malaysia, 2020). It is the only island in Terengganu that is not designated as a marine park by the Department of Fisheries.
Figure 1
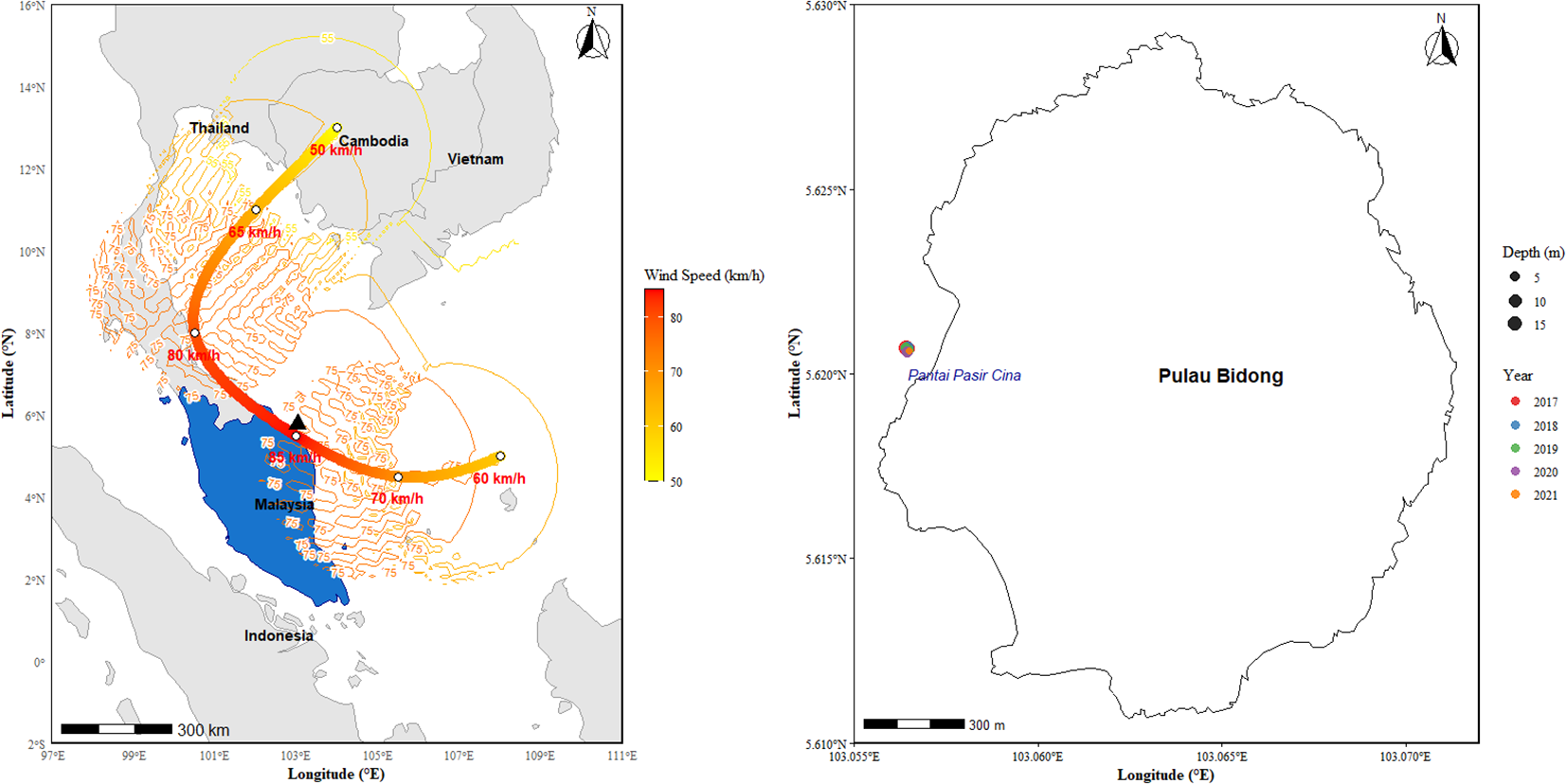
Map showing the passage of Cyclone Pabuk (1–5 January 2019) over Peninsular Malaysia (left) and the study area (Pantai Pasir Cina) in Pulau Bidong, Terengganu (right). The study area is marked by the black triangle.
Sampling was conducted over 5 years (2017-2021) at Pantai Pasir Cina, Pulau Bidong. Repeated benthic surveys were performed at adjacent transects to evaluate changes in coral community structure in response to successive disturbances. Additionally, in-situ sea-water temperature HOBO loggers were deployed in the sampling site to monitor and record seawater temperatures throughout the study period.
2.2 Benthic survey methodology
The quantification of changes in the benthic community of the reef were carried out using the Coral Video Transect (CVT) technique, which was optimized by Safuan et al. (2015). An underwater camera (Panasonic LUMIX DMC-FT4) with an underwater housing (LUMIX 40 m Marine Case) was used to record 1080p high definition (HD) videos of the reef corals and benthic substrate along a 100 m transect tape. The transect belt was divided into 4 sub-transects, each 20 m long, with a 5 m gap between them. In this way, each transect had 4 sub-transects as repeats.
The 100 m long transect tape was laid along the reef bottom, following the reef contour and running parallel to the coastline. The video recordings were made with the camera pointing vertically downwards onto the reef substrate, at a distance of 50 cm (± 10 cm) above the substrate. To minimize parallax error and keep the camera at a fixed distance perpendicular to the substrate, a 50 cm long reference rod was attached to the camera housing. The diver swam at a speed of 4 meters/min so that the camera had enough time to focus on the substrate and avoid image blurring. In addition, a dive computer (Mares Puck Pro) was used to record dive depth and track dive times.
Between 2017 and 2019, 3 transects were recorded each year during the same period (August of each year). However, in 2020 and 2021, due to COVID lockdown restrictions, only a single transect was recorded each year (April 2020 and March 2021). As the transects towards the end of our study could not be replicated due to the COVID lockdown, we therefore had to consider all the transects in our study as independent transects.
A total of 50 non-overlapping frames were automatically extracted from the video of each sub-transect (50 frames per 20 m replicate), with 50 points overlaid on each frame and analyzed using the software ‘Coral Point Count with Excel Extension’ (CPCe) version 4.0 (Kohler and Gill, 2006). A total of 38 video recordings were analyzed in our study, resulting in 1,900 images and 95,000 points. Five types of main benthic categories were used in our study - corals (C), bleached corals (BC), algae (ALG), other invertebrates (OT) and dead corals (DC). Percent cover for the coral (C) category was based on 79 genera identified by Affendi and Faedzul (2011) based on Scleractinus species found in Peninsular Malaysia, as well as data from Veron (2000) and Kelly (2016). The percentage cover of bleached corals (BC) included the above 79 living coral genera in bleached form. Percent cover of algae (ALG) was based on 6 algal species. The category Other (OT) included all living organisms, such as anemones, sponges, sea urchins, etc. The percentage of dead corals (DC) were recorded as either dead coral, recently dead coral, dead coral with algae, debris and diseased corals. The substrate was identified as sand, rock or silt. This percentage of coral taxa (genera) was used to determine the changes in coral community structure in our study area.
2.3 Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis of the data in our study was performed using the software Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research (PRIMER) Ver. 7.0 (Clarke and Gorley, 2006) and R 4.0.3 (R Core Team, 2020). Prior to statistical analysis, the data set was square root transformed. A one-way similarity analysis (ANOSIM) was performed to test for significant differences in benthic community composition between years. A percent similarity analysis (SIMPER) was conducted to determine the percent similarity of the benthic categories that contributed most to the observed differences between years.
A non-metric multidimensional scaling test (nMDS) was used to visualize the differences in community composition across years. To show which coral genera and benthic categories were responsible for these differences, significant correlation vectors (‘envfit’ in vegan) were superimposed on the nMDS plot. Hierarchical agglomerative clustering (CLUSTER analysis) based on the similarity profile test (SIMPROF) (‘simprof’ function in the clustsig package) was used to generate the concentration ellipses in the nMDS diagram based on posterior grouping of years. In addition, we also estimated β-diversity dispersion by estimating the distance to the group centroid for each year (‘betadisper’ in vegan). Differences in β-diversity dispersion between years were tested using PERMANOVA. Finally, we used the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-test for our univariate statistical analysis- to test for significant differences in the temporal distribution of our study and to determine differences between groups of benthic cover.
The Degree Heating Weeks (DHW) metric was used to measure the thermal stress on coral reefs caused by prolonged periods of elevated sea surface temperatures. Using in-situ HOBO-logger seawater temperatures from our study site, we used the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) coral bleaching methodology to calculate DHWs and also to categorize bleaching thresholds. At 4 °C-weeks- corals experience moderate heat stress and may start to show signs of bleaching; while at 8 °C-weeks- corals experience high thermal stress and are at significant risk of widespread coral bleaching.
3 Results
The percentage of live corals at the beginning of our study was 46.11 ± 7.56% in 2017 and the health of the reef was classified as ‘fair condition’ according to Chou et al. (2002) (Figure 2a). After successive disturbances in 2019, the live coral population decreased by 68% to 14.63 ± 4.35% (‘poor condition’). By the end of our study in 2021, coral cover had returned to pre-disturbance levels. The two dominant genera (Fungia sp. and Acropora sp.) accounted for 83.01% of living corals in our study. Fungia sp., the most abundant taxa, recorded an 84.62% decrease in genera coverage from 26.40 ± 8.77% in 2018 to 4.06 ± 3.05% in 2019 after the successive disturbances (Mann-Whitney U-test, Z = 3.534, p < 0.001) (Figure 2b). The second most abundant genera, Acropora sp. recorded a 65.44% decrease in genera after successive disturbances from 19.13 ± 10.22% in 2018 to 6.61 ± 5.35% in 2019 (Mann-Whitney U-test, Z = 2.555, p = 0.011) (Figure 2b). Towards the end of our study, both genera returned to near their pre-disturbance abundances.
Figure 2
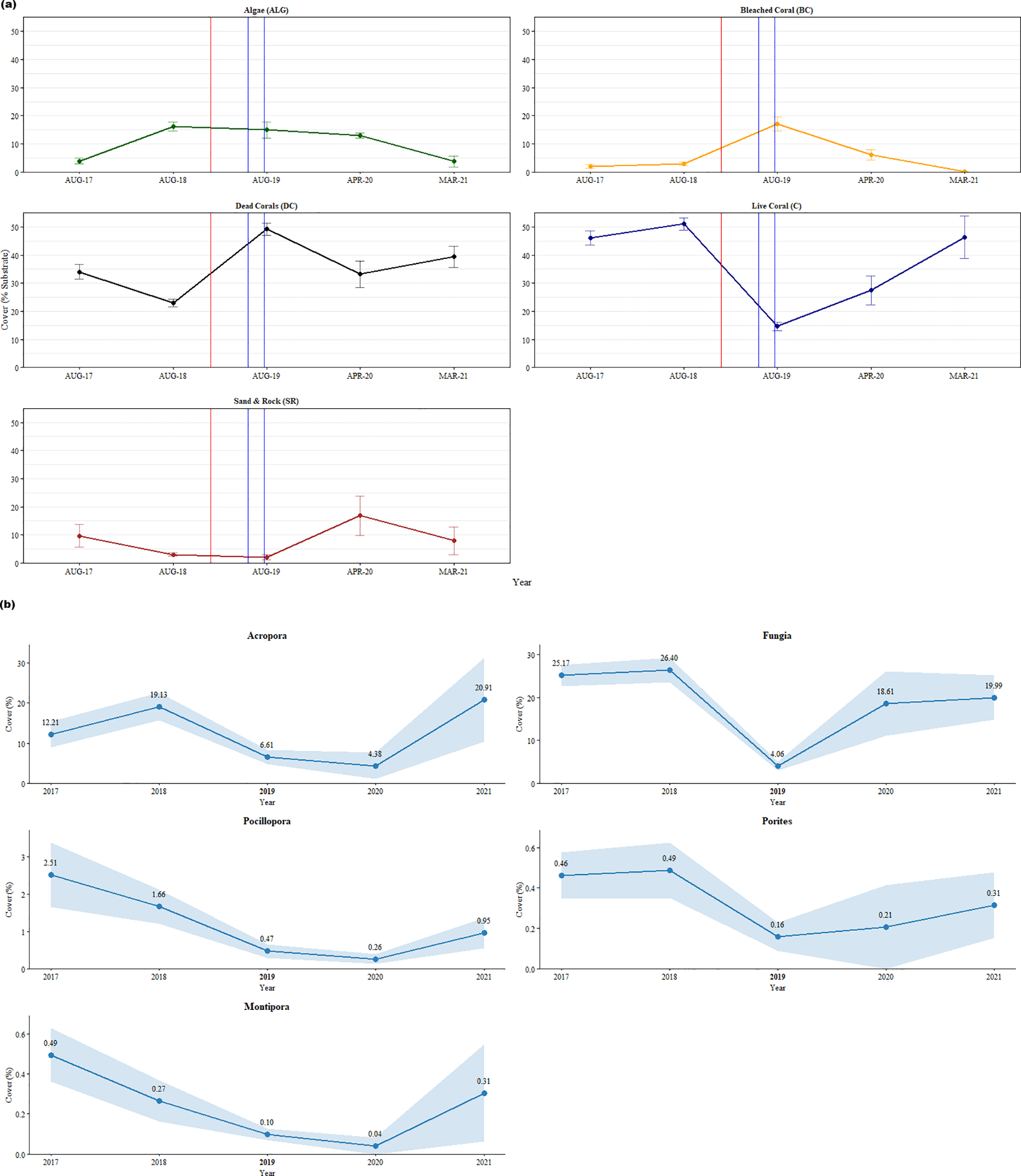
(a) Graphs showing the percentage benthic cover in Pantai Pasir Cina over 5 years (2017-2021) (% Cover ± Standard Error). The vertical lines represent the dual disturbance events in 2019- with the red vertical line denoting the storm disturbance, while the two blue vertical lines denote the thermal stress event period (April-August 2019). The values for the points in the graph can be found in the Supplementary Table 1. (b) Graphs illustrating the percentage cover of the dominant major live coral taxa cover in Pantai Pasir Cina across the 5-years (2017-2021) study period. Values represent Mean % Cover ± Standard Error bands. 2019 (in bold) is the disturbance year.
The proportion of dead corals at the beginning of our study was 34.04 ± 7.68% in 2017, while they dominated half of the reef benthos (49.24 ± 6.58%) after successive disturbances in 2019 (Figure 2a). After disturbance, the proportion of dead corals remained high and was dominated by both ‘dead corals with algae’ (DCA) and ‘coral rubble’ (R). The percentage of algae in the benthos was low (~4%) at the beginning of our study (Figure 2a). However, in 2018, there was a sudden increase in algal cover by 312% to 16.18 ± 4.66%. After the subsequent disturbances in 2019, the percentage benthic algal cover was ~15%. The abiotic substrate of the reef showed a decrease in percentage cover after the disturbances (9.71 ± 11.79% in 2017 to only 2% in 2019) (Figure 2a). However, immediately in the following year (2020) - sand contributed to an eightfold increase in abiotic benthic cover to 16.86 ± 12.04% (Mann-Whitney U-test, Z = -1.852, p = 0.064). All above values of percentage cover throughout our study can be found in Supplementary Table 1.
Coral bleaching was minimal on the reefs in Pantai Pasir Cina. The only bleaching observed in our study was during the local bleaching season (April-October 2019) (Figure 3), where a maximum of 17.03 ± 7.55% of corals were bleached, compared to only ~2-3% in other years (Figure 2a). Bleaching was mainly observed in Fungia sp. Pulau Bidong experienced 0 °C-weeks (Degree Heating Weeks) throughout the whole study period, except for a few months between February 2020 and June 2020 (local bleaching season) - when a few hot-spots were detected by our in-situ temperature hobo loggers (Figure 3). Nonetheless, temperatures never crossed the 4 °C-weeks temperature thresholds required when bleaching is likely to be observed, according to NOAA Coral Reef Watch bleaching methodology. A one-tailed ANOSIM test showed a significant difference in benthic reef community composition across years (GLOBAL R = 0.339, p < 0.001) (Supplementary Table 2). Pairwise ANOSIM tests between years showed that all were significant, except for the pairs ‘2017 and 2021’ and ‘2020 and 2021’. SIMPER analysis revealed that prior to the successive disturbances, live corals comprised almost half of the reef’s benthos (Fungia sp. and Acropora sp.) (Figure 4). However, after the 2019 disturbance, ‘dead corals with algae’ (DCA) dominated the reef and accounted for 49.52% of the reef benthos, followed by bleached Fungia sp. (13.98%) and coral rubble (9.20%). Towards the end of our study- ‘dead corals with algae’ (DCA) remained high (31.77%) and also remained the dominant category. While the genus Fungia sp. (23.38%) and Acropora sp. (13.96%)- both showed slight recovery, nevertheless, coral rubble cover was consistently high (18.60%).
Figure 3
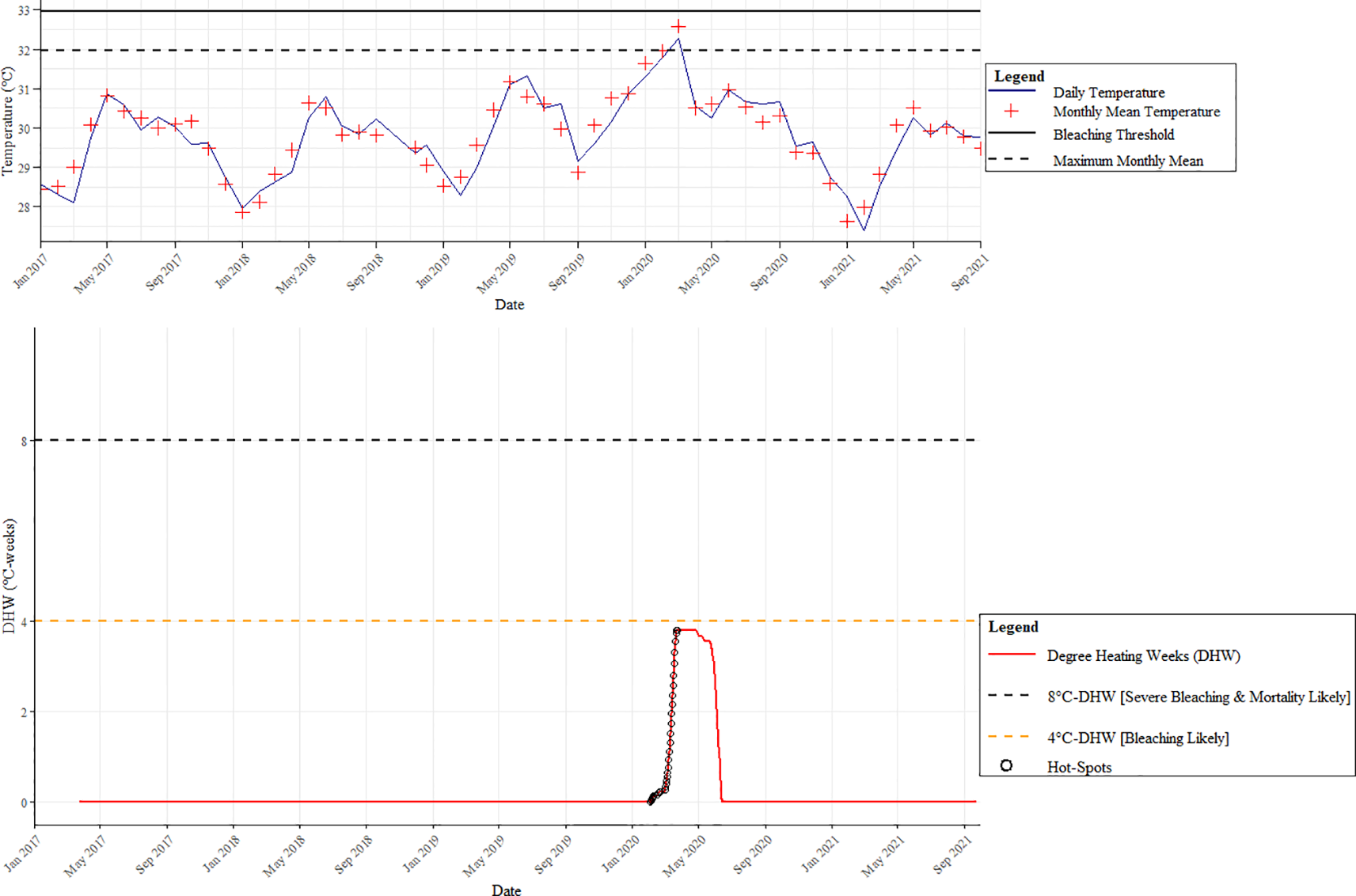
Pulau Bidong in-situ HOBO-logger seawater temperatures (January 2017 – September 2021) (Top). NOAA Coral Reef Watch Degree Heating Weeks (DHW) based on in-situ HOBO-logger seawater temperatures for Pulau Bidong (January 2017 – September 2021) (Bottom).
Figure 4
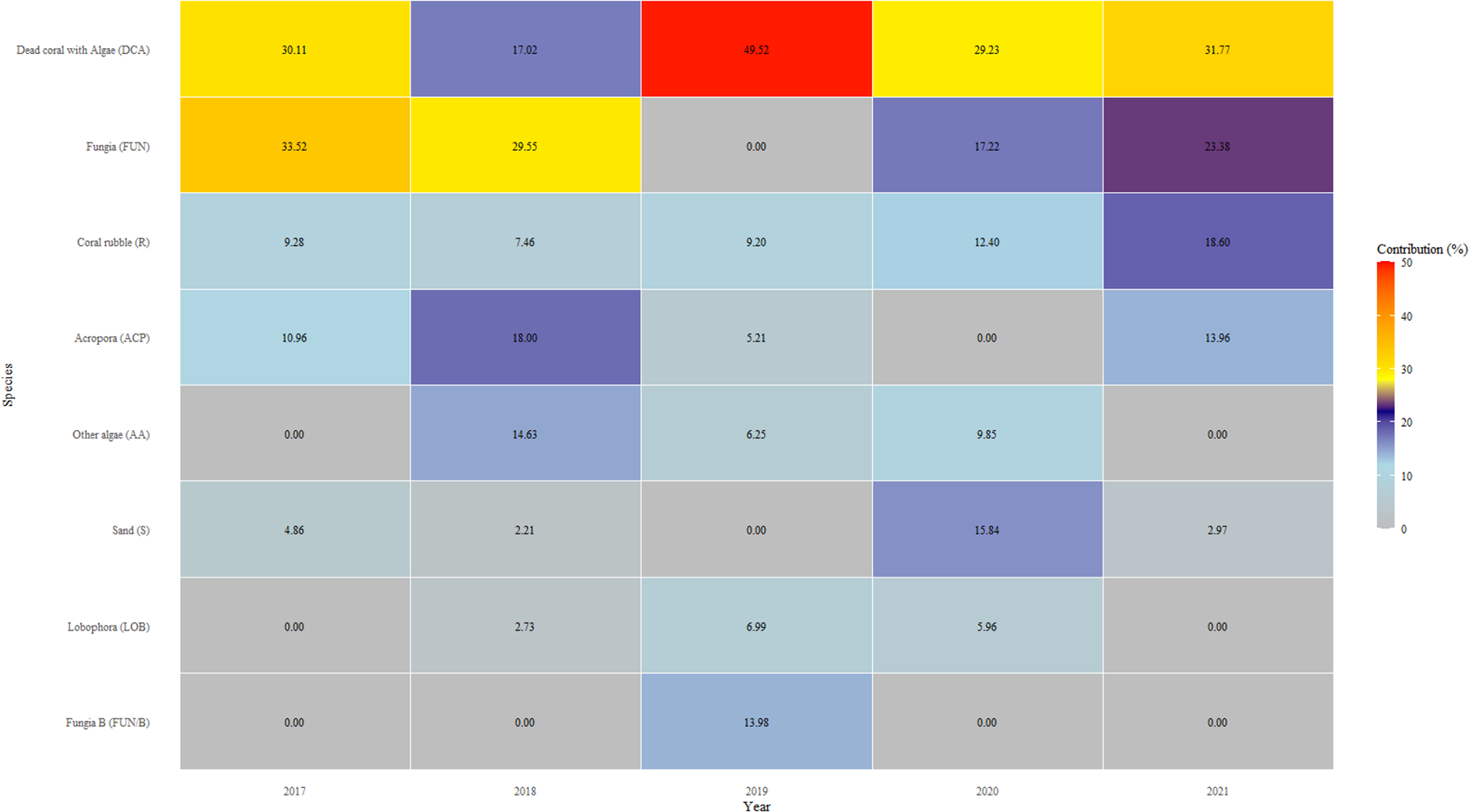
Similarity Percentage (SIMPER) analysis of benthic cover in Pantai Pasir Cina between 2017 and 2021. Cumulative percentage contribution cut-off: 90%.
The nMDS plot (Figure 5) shows that the composition of the benthos in Pantai Pasir Cina formed distinct groups based on the SIMPROF analysis (Supplementary Figure 1), with the resulting posteriori clusters grouped according to the different years. Before the successive disturbances in 2019, the differences in community composition were mainly determined by live corals (Fungia sp., Acropora sp., Porites sp., and Montipora sp.), dead corals (DC) and rocks (RCK).However, in 2019, following the sequential disturbances, the community formed a clear cluster on the right hand side of the nMDS plot and was dominated by bleached corals (Fungia/B sp., Acropora/B sp., Porites/B sp., Pavona/B sp., Symphyllia/B sp., Pocillopora/B sp.), ‘dead corals with algae’ (DCA), ‘other algae’ (OA) and Lobophora sp. (LOB) (Figure 5). Towards the end of our study in 2021, the nMDS cluster showed a curved return with ‘coral rubble’ (R) determining the benthic community composition. The CLUSTER/SIMPROF Dendrogram corroborated the findings of the above nMDS results with the two main branches separating into disturbance year (left) and non-disturbance years (right) (Supplementary Figure 1).
Figure 5
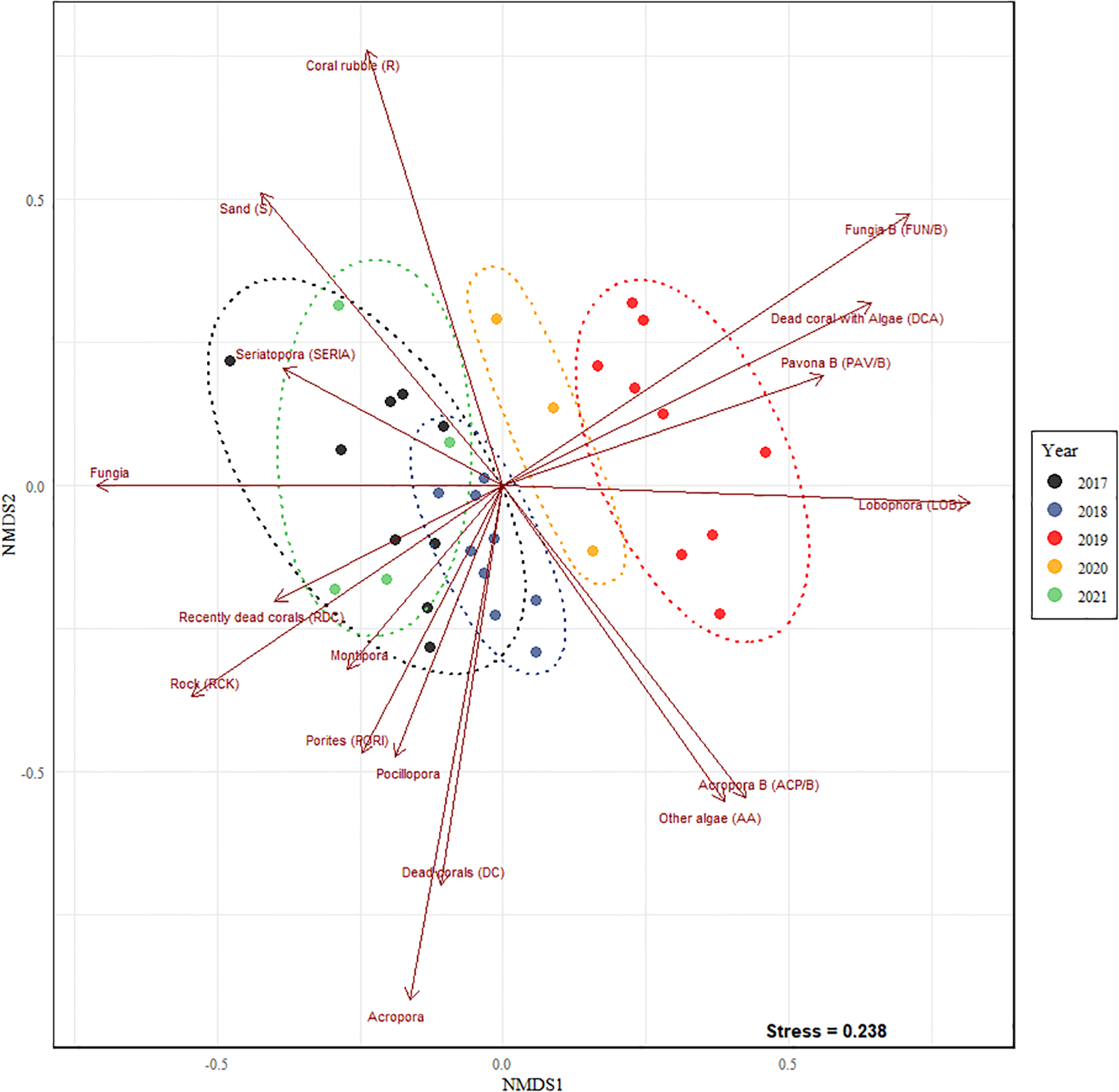
Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling (nMDS, stress: 0.238) plot illustrating changes in community composition across the years. Ellipses are based on posteriori SIMPROF analysis, coinciding with year grouping. Displayed vectors significantly drive the differences across the years (p < 0.05).
The box plots of β-diversity showed that the reef community in Pulau Bidong was stable, with a varied coral and benthic cover in 2017 (β-dispersion: ~ 0.25) (Figure 6). Between 2018 and 2019, the community experienced rising β-dispersion; with 2018 (β-dispersion: ~ 0.35) indicating community disruption and 2019 (β-dispersion: ~ 0.45) signaling both ecosystem wide-disruption and chaotic re-organization. Following the successive disturbances, in 2020- there was a decline in β-dispersion to ~ 0.30 indicating a stable community state forming. Finally in 2021, β-dispersion value (~ 0.28) was similar to 2017, but nonetheless, the community composition was different (Figure 4).
Figure 6
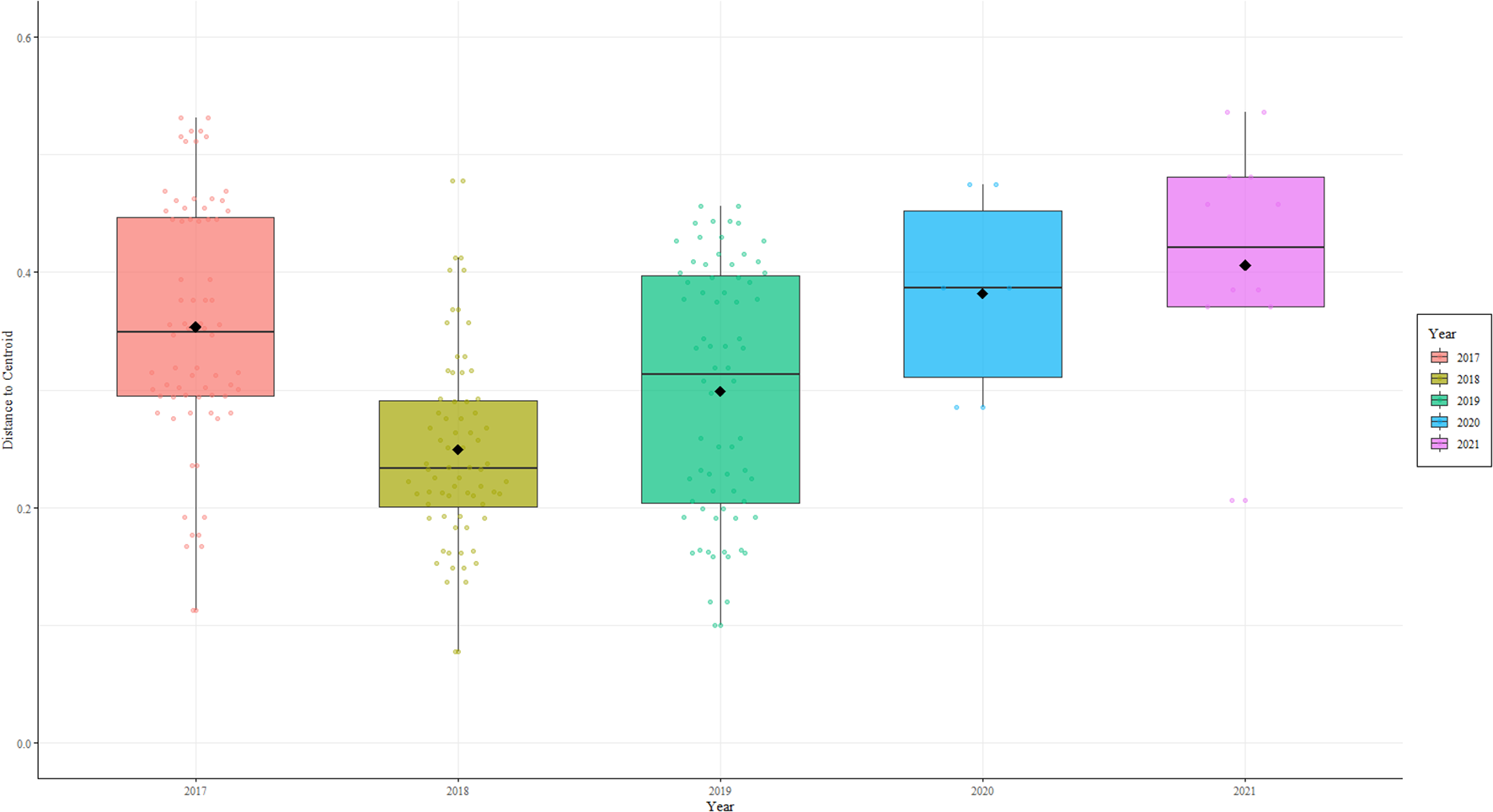
The dispersion of β-diversity shown as the distance to centroid for the benthic communities across the years.
4 Discussion
The reef landscape in Pantai Pasir Cina underwent a significant change in the composition of the benthic community due to the consecutive disturbances during our study. Before the double disturbance by storm and bleaching events, the reef was dominated by living scleractinian corals (especially Fungia sp. and Acropora sp.) at the beginning of our study. After the disturbances, there was a shift in the main components of the benthic composition - live corals decreased significantly while dead corals increased, so that the post-disturbance community was dominated by ‘dead corals covered with algae’ (DCA). These changes in the composition of the living assemblage immediately after the multiple disturbances could be due to the differential susceptibility of different taxa to disturbance by cyclones and bleaching (Aronson and Precht, 1995; Baird et al., 2018).
After the storm disturbance, the percentage of living taxa of Acropora sp. decreased by half compared to the beginning of our study. Branching taxa colonies are most susceptible to storm waves due to the mechanical vulnerability of their morphology, causing them to break and fragment easily (Loya et al., 2001; Baird and Marshall, 2002). In 2020, the year after the storm event, the population of the genus Acropora sp. continued to decline. The die-off of Acropora sp. may have continued after the 2019 disturbances in several ways: Firstly – following the storm event, Acropora sp. were forced to divert their energy to repair and regeneration. This reduced their energy reserves (lipid stores) which are also critical for surviving thermal stress, as corals rely on these reserves to sustain themselves while their symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) are lost. Hence, following the heat stress event (April – August 2019)– corals began to bleach even at minimal thermal stress levels and were less likely to survive prolonged bleaching, due to their already depleted energy reserves (Nyström et al., 2000; Berkelmans et al., 2004; Graham et al., 2015; Heron et al., 2016; Hughes et al., 2017; Madin et al., 2018). Additionally, the minor subsequent heat stress (even 0 °C-weeks) triggered bleaching due to these corals’ baseline stress levels already being high (i.e. lowered stress threshold). Therefore, the compounding effect of the thermal stress following the physical disturbance lead to the sustained mortality of the genus (Thompson and van Woesik, 2009; Heron et al., 2010; Guest et al., 2012; Carrigan and Puotinen, 2014; Liu et al., 2014; Eakin et al., 2019; Barott et al., 2021). Secondly, torrential rains following the storm may have resulted in runoff of nutrients and sediments from the surrounding island of Pantai Pasir Cina, leading to algal takeover or smothering of the already stressed Acropora sp. This double occurrence of disturbance events may have ultimately led to a persistent and further mortality of the genus (Dollar and Tribble, 1993; Guillemot et al., 2010).
Towards the end of our study, the branching Acropora sp. were able to recover quite quickly, and the taxa were similarly represented as at the beginning of our study. Although mechanically susceptible morphologies such as Acropora sp. can suffer severe to sometimes catastrophic damage following major disturbance, they are simultaneously opportunistic and grow rapidly, dominating reefs following disturbances (van Woesik et al., 1991; Osborne et al., 2011). Conversely, faster-growing Acropora sp. corals, which are responsible for the structural complexity of reefs, are sometimes severely affected by storm disturbances and, depending on the intensity and frequency, sometimes cannot recover, leading to shifts in reef assemblage composition towards simpler, massive morphologies (Cheal et al., 2017; Madin et al., 2018; Torda et al., 2018; Ribas-Deulofeu et al., 2021). However, in our study- Tropical Storm Pabuk resulted in sustained winds below 100 km/h – which are known to cause only localized moderate damage, including the breakage of branching corals and limited structural reef damage, compared to stronger cyclones that can flatten reefs (Harmelin-Vivien, 1994; Fabricius et al., 2008; Baird et al., 2018). Furthermore, weaker cyclones generate less destructive waves which aren’t strong enough to topple larger colonies or de-stabilize reef frameworks, leading to patchy recoverable damage (Madin and Connolly, 2006; Puotinen et al., 2020). Hence, it is plausible that Tropical Strom Pabuk only caused minor damage to branching Acropora sp. corals and didn’t cause significant structural damage, leading to their quick recovery post-disturbance. Although the abundance of massive Fungia sp. decreased significantly (~84%) after the subsequent storm and local bleaching, the abundance immediately increased back to pre-disturbance levels towards the end of our study. Massive morphologies are more resilient to storm damage and suffer minimal scour from impact injury and are generally only toppled, dislodged or uprooted (Hughes and Jackson, 1985; Harmelin-Vivien, 1994; Madin and Connolly, 2006). In addition, massive, slow-growing corals are not only less affected by physical disturbance from storm events, but are also more resistant to bleaching induced by thermal stress; they are known to dominate assemblages following disturbance (Madin and Connolly, 2006; Fabricius et al., 2008).
The only significant bleaching observed in Pantai Pasir Cina during the local heat stress event involved Fungia sp. while the other dominant living taxa (Acropora sp.) bleached only slightly. Although bleaching of Fungia sp. increased sevenfold during the bleaching period compared to previous years, the effects of this thermal anomaly were short-lived as the cover of living taxa recovered the following year. As previously stated, following the initial storm disturbance, damaged coral tissues diverted their energy from growth and reproduction to repair and maintenance. This depleted their lipid and carbohydrate reserves, which would otherwise have been used for surviving thermal stress events. Hence, even modest temperature increases triggered bleaching in already weakened corals (Nyström et al., 2000; Berkelmans et al., 2004; Graham et al., 2015; Heron et al., 2016; Hughes et al., 2017; Madin et al., 2018). For example, following Cyclone Yasi in the Great Barrier Reef in 2011 – a subsequent bleaching event resulted in 70-90% coral mortality in damaged reefs, compared to just 30-50% in un-disturbed reefs (Hughes et al., 2017). Furthermore, storms and cyclones break branching corals, flattening reefs and thereby reducing shading. This results in a destruction of microhabitat conditions whereby it alters local hydrodynamics, reducing water flow and increasing heat retention around corals (i.e. creating hot-spots). Therefore, localized bleaching in damaged reefs is triggered earlier, than would otherwise have happened in non-disturbed reefs (Berkelmans et al., 2004; Madin et al., 2018). Additionally, massive corals are less susceptible to bleaching due to their thick tissue, as they contain a higher density of fluorescent tissue pigments that protect them from UV radiation. The expansion and contraction of these thick tissues provides pathways to regulate the radiant heat reaching the zooxanthellae, while the retraction of these tissues provides self-shading for the symbiotic algae (Salih et al., 2000; Dove et al., 2001; Loya et al., 2001; Hoogenboom et al., 2017). Conversely, only insignificant bleaching was observed in Acropora sp. as the population in our study area was decimated by the initial storm damage and was mostly dead and covered with algae or fragmented into debris.
The percentage of dead corals fluctuated during our study period and consisted mainly of ‘coral rubble’ (R) and ‘dead corals covered with algae’ (DCA). After the numerous disturbances (especially the storm), the reef benthos was dominated by ‘dead coral covered with algae’ (DCA), which was attributed to the algal proliferation of the reef benthos after the storm event (Fabricius et al., 2008; Guillemot et al., 2010; Chong-Seng et al., 2014; Harii et al., 2014). Similarly, ‘coral rubble’ (R) accounted for ~17% of the reef benthos after the storm disturbance and determined the composition of the benthos towards the end of our study. Coral rubble composition was mainly determined by the break-up and fragmentation of branching Acropora sp. following the storm disturbance (van Woesik et al., 1995; Fabricius et al., 2008; Madin et al., 2014; Beeden et al., 2015; Baird et al., 2018).
In terms of algae cover, there was an anomalous increase in algae cover in 2018. Between 2017 and 2018, the algae cover in the study area increased fourfold, which could be due to possible nutrient loading from the nearby UMT marine research station (Littler et al., 2006; Fong and Paul, 2011). After the passage of Cyclone Pabuk in this region, ‘dead coral with algae’ (DCA) dominated the reef benthos in Pantai Pasir Cina, demonstrating the typical pattern of algal dominance/take-over following coral mortality after a disturbance event. Numerous studies have shown that after the passage of a storm, the loss of living corals leads to an immediate opening of space for recolonization in an otherwise spatially restricted environment. This leads to competition between coral larvae and algae and can result in algae overgrowth of the reef benthos, preventing coral recruitment, inhibiting regrowth of surviving coral fragments and regeneration of partially damaged colonies, and ultimately delaying reef recovery (Emslie et al., 2008; Guillemot et al., 2010; Harii et al., 2014; Gouezo et al., 2015; Torda et al., 2018; Ribas-Deulofeu et al., 2021). In addition, typhoon rainfall leads to nutrient runoff, which can also promote algal proliferation (Blanco et al., 2008; Fabricius et al., 2008; Chong-Seng et al., 2014).
Sand, rock and silt cover in Pantai Pasir Cina was relatively low throughout our study period, with the exception of 2020. In the year following the multiple disturbances, cover increased eightfold, which was entirely due to sand. Following the passage of Tropical Cyclone Pabuk in 2019, the reef benthos at Pantai Pasir Cina was immediately dominated by dead corals and algae-covered rubble fragments covering the now empty substrate below. However, in the following year, 2020, the bare substrate of the reef was revealed as the coral debris was removed from the reef area by water currents. Cyclonic disturbances cause catastrophic damage to the reef substrate, from breaking and detachment of corals to tearing and removal of the reef matrix (Done et al., 1992b; Scoffin and Walton-Smith, 1993; Harmelin-Vivien, 1994). After storms, land or river runoff leads to the removal of coral rubble and the opening of reef spaces for recolonization (Emslie et al., 2008; Chumkiew et al., 2016).The reefs at Pantai Pasir Cina and Pulau Bidong as a whole were able to withstand the successive disturbances they were exposed to in a relatively short-time period. The reef went through five phases: a pre-disturbance phase (2017), stress accumulation phase (2018), disturbance events’ phase (2019), community re-organization phase (2020) and finally reaching a state of novel equilibrium in (2021). At the end of our study period the Live Coral (LC) cover was some-what similar to our pre-disturbance (2107) era. This recovery could be attributed mostly to the recovery mechanisms of the fast-growing genus (Acropora sp.) and the resilience of the massive morphologies (Fungia sp.); as the storm event resulted in patchy moderate damage (i.e. mainly to Acropora sp.) and the subsequent heat stress event caused bleaching (i.e. mainly to Fungia sp.) - as these corals were already at their stress threshold limits. Following the storm disturbance event, broken Acropora sp. fragments re-attached themselves to suitable substrates (Lirman, 2000; Cetz-Navarro et al., 2016) and survivorship usually depends on fragment size (> 5cm) - having higher success rates as they have greater energy reserves and being less susceptible to predation (Bruckner and Bruckner, 2001).
Conversely, Fungia sp. are shown to regenerate from partial mortality with as little as 20% remaining tissue (Kramarsky-Winter and Loya, 1996) and have been observed to have > 80% survivability post-storm owing to their sturdy form (Gilmour, 2004). Furthermore, Fungia sp. corals demonstrated their resilience to thermal stress, even when they were already at their stress threshold levels from the initial disturbance, through numerous mechanisms. Firstly, the expansion and contraction of their thick tissues provide pathways to regulate the radiant heat reaching their zooxanthellae, in addition to these thick tissues containing higher density of fluorescent tissue pigments that protect them from UV radiation (Salih et al., 2000; Loya et al., 2001; Hoogenboom et al., 2017). Secondly, Fungia sp. produce anti-oxidants (e.g. superoxide dismutase) that mitigate oxidative stress from high light/heat (Dove et al., 2008). Thirdly, they host thermally tolerant Symbiodiniaceae (e.g. Cladocopium or Durusdinium spp.) which are more resistant to heat stress, and can modulate symbiont density seasonally; reducing susceptibility to bleaching (Fitt et al., 2000; Yamashita et al., 2014). Lastly, unlike colonial corals, Fungia sp. free-living form allows it to reposition itself to avoid excessive light or sediment stress (Hoogenboom et al., 2012).
Storm disturbances can reset a reef’s topography, creating available substrate for coral larval recruitment. While larval dispersal can replenish planulae in storm-damaged areas (Hughes et al., 2019), the remoteness of our study site may result in limited larval input (Graham et al., 2015); and it isn’t thought that this is one of the forms of recovery of the reefs in Pantai Pasir Cina.
Although the reefs in Pantai Pasir Cina were able to recover relatively quickly following these consecutive disturbances, owing to the fact that the storm damage was moderate and the minimal thermal stress inducing bleaching due to the corals already being at peak stress levels (from the initial disturbance); nonetheless, the increasing intensity and magnitude of the storms and thermal anomalies calls into question the recovery potential of the reefs in this region in the future. The incomplete recovery of coral communities due to shorter recovery times means that communities are constantly in a state of primary succession, transitioning to simpler morphologies, creating novel reef ecosystems dominated by opportunistic species, and in extreme cases leading to ‘dead aquatic habitats’.
Our study was limited in scope as sampling was carried out at a single sampling site. Comparing our study site with a control (i.e. undisturbed near-by reference site) would provide a comparative assessment of how these disturbance events influenced reefs in this region. Additionally, 2-years following the disturbance events didn’t provide adequate data to understand the reef’s recovery trajectory, as it was in the very early stages of recovery. Future research prospects should take the above limitations into consideration.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author contributions
SS: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CT: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. NM: Writing – review & editing. ZB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia, Fundamental Research Grant (FRGS) and the Institute of Oceanography and Environment (INOS) -Universiti Malaysia Terengganu.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the collaborative support provided by the Institute of Oceanography and Environment (INOS), Universiti Malaysia Terengganu. The principal author would like to thank Dr. Hin Boo Wee at the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia for his statistical analytical input for this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1552229/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Affendi Y. A. Faedzul R. R. (2011). Current Knowledge on Coral Diversity of Peninsular Malaysia. Malaysia Marine Biodiversity: Inventory and Current Status (Putrajaya, Malaysia: Department of Marine Park), 21–31pp.
2
Aronson R. B. Precht W. F. (1995). Landscape patterns of reef coral diversity: A test of the intermediate disturbance hypothesis. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.192, 1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(95)00052-S
3
Baird A. H. Madin J. S. Álvarez-Noriega M. Fontoura L. Kerry J. T. Kuo C. Y. et al . (2018). A decline in bleaching suggests that depth can provide a refuge from global warming in most coral taxa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.603, 257–264. doi: 10.3354/meps12732
4
Baird A. H. Marshall P. A. (2002). Mortality, growth and reproduction in scleractinian corals following bleaching on the great barrier reef. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.237, 133–141. doi: 10.3354/meps237133
5
Barott K. L. Huffmyer A. S. Davidson J. M. Lenz E. A. Matsuda S. B. Hancock J. R. et al . (2021). Coral bleaching response is unaltered following acclimatization to reefs with distinct environmental conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America118, e2025435118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2025435118
6
Barshis D. J. Birkeland C. Toonen R. J. Gates R. D. Stillman J. H. (2018). High-Frequency Temperature Variability Mirrors fixed Differences in Thermal Limits of the Massive Coral Porites lobata. J. Exp. Biol.221, 24. doi: 10.1242/jeb.188581
7
Bay R. A. Palumbi S. R. (2015). Rapid acclimation ability mediated by transcriptome changes in reef-building corals. Genome Biol. Evol.7, 1602–1612. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv085
8
Beeden R. Maynard J. Puotinen M. Marshall P. Dryden J. Goldberg J. et al . (2015). Impacts and recovery from severe tropical cyclone yasi on the great barrier reef. PloS One10. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121272
9
Berkelmans R. De’ath G. Kininmonth S. Skirving W. J. (2004). A comparison of the 1998 and 2002 coral bleaching events on the great barrier reef: spatial correlation, patterns, and predictions. Coral Reefs23, 74–83. doi: 10.1007/s00338-003-0353-y
10
Blanco A. C. Nadaoka K. Yamamoto T. (2008). Planktonic and benthic microalgal community composition as indicators of terrestrial influence on a fringing reef in Ishigaki Island, Southwest Japan. Mar. Environ. Res.66, 520–535. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2008.08.005
11
Bruckner A, and Bruckner, R . (2001). Condition of restored Acropora palmata fragments off Mona Island, Puerto Rico, 2 years after the Fortuna Reefer ship grounding. Coral Reefs, 20(3), 235–243. doi: 10.1007/s003380100164
12
Burke L. Selig E. Spalding M. (2002). Reefs at Risk in Southeast Asia (Washington DC: World Resources Institute).
13
Burt J. A. Paparella F. Al-Mansoori N. Al-Mansoori A. Al-Jailani H. (2019). Causes and consequences of the 2017 coral bleaching event in the southern Persian/Arabian Gulf. Coral Reefs38, 567–589. doi: 10.1007/s00338-019-01767-y
14
Carrigan A. D. Puotinen M. (2014). Tropical cyclone cooling combats region-wide coral bleaching. Global Change Biol.20, 1604–1613. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12541
15
Cesar H. Burke L. Pet-Soede L. (2003). The Economics of Worldwide Coral Reef Degradation (Arnhem, The Netherlands: International Coral Reef Action Network).
16
Cetz-Navarro N. P. Espinoza-Avalos J. Vega-Zepeda A. Cerón-Flores A. I. Raigoza-Figueras R. E. de J. (2016). Reclutamiento del coral Acropora palmata sobre sustratos de dos materiales. Rev. Biol. Marina y Oceanografia51, 643–653. doi: 10.4067/S0718-19572016000300015
17
Chang C. P. Liu C. H. Kuo H. C. (2003). Typhoon Vamei: an equatorial tropical cyclone formation. Geophys. Res. Lett.30, 1150. doi: 10.1029/2002GL016365
18
Cheal A. J. MacNeil M. A. Emslie M. J. Sweatman H. (2017). The Threat to Coral Reefs from more Intense Cyclones under Climate Change. Global Change Biol.23, 1511–1524. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13593
19
Chong-Seng K. M. Graham N. A. J. Pratchett M. S. (2014). Bottlenecks to coral recovery in the Seychelles. Coral Reefs33, 449–461. doi: 10.1007/s00338-014-1137-2
20
Chou L. M. Tuan V. S. Yeemin T. Cabanban A. Kessna S. Kessna I. (2002). “Status of Southeast Asia coral reefs,” in Status of Coral Reefs of the World (Townsville, Australia: Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network), 123–152.
21
Chumkiew S. Jaroensutasinee M. Jaroensutasinee K. (2016). Monitoring the impact of tropical cyclone on coral reef community and its recovery using landscape mosaic technique at Racha Yai Island, Phuket. J. Fisheries Environ.40, 93–101.
22
Clarke K. R. Gorley R. N. (2006). PRIMERv6: user manual/tutorial (Plymouth: PRIMER-e).
23
De’Ath G. Fabricius K. E. Sweatman H. Puotinen M. (2012). The 27–year decline of coral cover on the great barrier reef and its causes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.109, 17995–17999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1208909109
24
Dollar S. J. Tribble G. W. (1993). Recurrent storm disturbance and recovery: A long-term study of coral communities in Hawaii. Coral Reefs12, 223–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00334481
25
Done T. J. (1992a). Effects of tropical cyclone waves on ecological and geomorphological structures on the great barrier reef. Continent. Shelf Res.12, 859–872. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(92)90048-O
26
Done T. J. (1992b). Phase shifts in coral reef communities and their ecological significance. Hydrobiologia247, 121–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00008211
27
Dove S. G. Hoegh-Guldberg O. Ranganathan S. (2001). Major colour patterns of reef-building corals are due to a family of GFP-like proteins. Coral Reefs19, 197–204. doi: 10.1007/PL00006956
28
Dove S. G. Lovell C. Fine M. Deckenback J. Hoegh-Guldberg O. Iglesias-Prieto R. et al . (2008). Host pigments: potential facilitators of photosynthesis in coral symbioses. Plant Cell Environ.31 (11), 1523–1533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01852.x
29
Dunne R. Brown B. (2001). The influence of solar radiation on bleaching of shallow water reef corals in the Andaman Sea 1993–1998. Coral Reefs20, 201–210. doi: 10.1007/s003380100160
30
Eakin C. M. Sweatman H. Brainard R. E. (2019). The 2014–2017 global-scale coral bleaching event: insights and impacts. Coral Reefs38, 539–545. doi: 10.1007/s00338-019-01844-2
31
Emslie M. J. Cheal A. J. Sweatman H. Delean S. (2008). Recovery from disturbance of coral and reef fish communities on the great barrier reef, Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.371, 177–190. doi: 10.3354/meps07657
32
Fabricius K. E. De’Ath G. Puotinen M. L. Done T. Cooper T. F. Burgess S. C. (2008). Disturbance Gradients on Inshore and Off-Shore Coral reefs caused by a Severe Tropical Cyclone. Limnol. Oceanogr.53, 690–704. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.2.0690
33
Fisher R. O’Leary R. A. Low-Choy S. Mengersen K. Knowlton N. Brainard R. E. et al . (2015). Species richness on coral reefs and the pursuit of convergent global estimates. Curr. Biol.25, 500–505. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.12.022
34
Fitt W. K. McFarland F. K. Warner M. E. Chilcoat G. C. (2000). Seasonal patterns of tissue biomass and densities of symbiotic dinoflagellates in reef corals and relation to coral bleaching. Limnol. Oceanogr.45, 677–685. doi: 10.4319/lo.2000.45.3.0677
35
Fong P. Paul V. J. (2011). Coral Reef Algae. In Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition (Dordrecht: Springer), 241–272.
36
Gilmour J. (2004). Size-structures of populations of the mushroom coral Fungia fungites: The role of disturbance. Coral Reefs23, 493–504. doi: 10.1007/s00338-004-0427-5
37
Glynn P. W. (1993). Coral reef bleaching: ecological perspectives. Coral Reefs12, 1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00303779
38
Goreau T. McClanahan T. Hayes R. Strong A. L. (2000). Conservation of coral reefs after the 1998 global bleaching event. Conserv. Biol.14, 5–15. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.00011.x
39
Gorospe K. D. Karl S. A. (2011). Small-scale spatial analysis of in-situ sea temperature throughout a single coral patch reef. J. Mar. Biol. 2011, 1–12. 10.1155/2011/719580
40
Gouezo M. Golbuu Y. Van Woesik R. Rehm L. Koshiba S. Doropoulos C. (2015). Impact of two sequential super typhoons on coral reef communities in Palau. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.540, 73–85. doi: 10.3354/meps11518
41
Graham N. A. J. Jennings S. MacNeil M. A. Mouillot D. Wilson S. K. (2015). Predicting climate-driven regime shifts versus rebound potential in coral reefs. Nature518, 94–97. doi: 10.1038/nature14140
42
Grimsdich G. Mwaura J. M. Kilonzo J. Amiyo N. (2010). The effects of habitat on coral bleaching responses in Kenya. Ambio39, 295–304. doi: 10.1007/s13280-010-0052-1
43
Guest J. R. Baird A. H. Maynard J. A. Muttaqin E. Edwards A. J. Campbell S. J. et al . (2012). Contrasting patterns of coral bleaching susceptibility in 2010 suggest an adaptive response to thermal stress. PloS One7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033353
44
Guillemot N. Chabanet P. Le Pape O. (2010). Cyclone effects on coral reef habitats in New Caledonia (South Pacific). Coral Reefs29, 445–453. doi: 10.1007/s00338-010-0587-4
45
Harborne A. Fenner D. Barnes A. Beger M. Harding S. Roxburgh T. (2000). Status Report on the Coral Reefs of the East Coast of Peninsula Malaysia Vol. 88 (Malaysia: Department of Fisheries Malaysia).
46
Harii S. Hongo C. Ishihara M. Ide Y. Kayanne H. (2014). Impacts of multiple disturbances on coral communities at Ishigaki Island, Okinawa, Japan, during a 15 year survey. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.509, 171–180. doi: 10.3354/meps10890
47
Harmelin-Vivien M. L. (1994). The effects of storms and cyclones on coral reefs. A review. J. Coast. Res.12, 211–231.
48
Harrison H. B. Alvarez-Noriega M. Baird A. H. Heron S. F. MacDonald C. Hughes T. P. (2019). Back-to-back coral bleaching on isolated atolls in the coral sea. Coral Reefs38, 713–719. doi: 10.1007/s00338-018-01749-6
49
Heron S. F. Maynard J. A. van Hooidonk R. Eakin C. M. (2016). Warming trends and bleaching stress of the world’s coral reefs 1985-2012. Sci. Rep.6, 38402. doi: 10.1038/srep38402
50
Heron S. F. Willis B. L. Skirving W. J. Eakin C. M. Page C. A. Miller I. R. (2010). Summer hot snaps and winter conditions: Modelling white syndrome outbreaks on Great Barrier Reef corals. PloS One5, e12210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012210
51
Hoegh-Guldberg O. Mumby P. J. Hooten A. J. Steneck R. S. Greenfield P. Gomez E. et al . (2007). Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science318, 1737–1742. doi: 10.1126/science.1152509
52
Hoogenboom M. O. Frank G. E. Chase T. J. Jurriaans S. Álvarez-Noriega M. Peterson K. et al . (2012). Survival costs of growth in a variable environment: The case of a scleractinian coral. Oecologia169, 661–670.
53
Hoogenboom M. O. Frank G. E. Chase T. J. Jurriaans S. Álvarez-Noriega M. Peterson K. et al . (2017). Environmental drivers of variation in bleaching severity of acropora species during an extreme thermal anomaly. Front. Mar. Sci.4. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2017.00376
54
Howells E. J. Berkelmans R. Van Oppen M. J. H. Willis B. L. Bay L. K. (2013). Historical thermal regimes define limits to coral acclimatization. Ecology94, 1078–1088. doi: 10.1890/12-1257.1
55
Huang D. Licuanan W. Y. Hoeksema B. W. Chen C. A. Ang P. O. Huang H. et al . (2015). Extraordinary diversity of reef corals in South China Sea. Mar. Biodivers.45, 157–168. doi: 10.1007/s12526-014-0236-1
56
Hughes T. P. Jackson J. B. (1985). Population dynamics and life histories of foliaceous corals. Ecol. Monogr.55, 142–166. doi: 10.2307/1942555
57
Hughes T. P. Kerry J. T. Álvarez-Noriega M. Álvarez-Romero J. G. Anderson K. D. Baird A. H. et al . (2017). Global warming and recurrent mass bleaching of corals. Nature543, 373–377. doi: 10.1038/nature21707
58
Hughes T. P. Kerry J. T. Baird A. H. Connolly S. R. Chase T. J. Dietzel A. et al . (2019). Global warming impairs stock-recruitment dynamics of corals. Nature568, 387–390. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1081-y
59
Kelly R. (2016). Coral Finder, 3.0, Indo-Pacific (Townsville, Australia: Russell Kelly), 34.
60
Kohler K. E. Gill S. M. (2006). Coral point count with excel extension (CPCe): A visual basic program for the determination of coral and substrate coverage using random point count methodology. Comput. Geol.32, 1259–1269. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2005.11.009
61
Kramarsky-Winter E. Loya Y. (1996). Regeneration versus budding in fungiid corals: A trade-off. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.134, 179–185. doi: 10.3354/meps134179
62
Lirman D. (2000). Fragmentation in the branching coral Acropora palmata (Lamarck): Growth, survivorship, and reproduction of colonies and fragments. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol.251, 41–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-0981(00)00205-7
63
Littler M. M. Littler D. S. Brooks B. L. (2006). Harmful algae on tropical coral reefs: bottom-up eutrophication and top-down herbivory. Harmful Algae5, 565–585. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2005.11.003
64
Liu G. Heron S. Eakin C. Muller-Karger F. Vega-Rodriguez M. Guild L. et al . (2014). Reef-scale thermal stress monitoring of coral ecosystems: New 5-km global products from NOAA Coral Reef Watch. Remote Sens.6, 11579–11606. doi: 10.3390/rs61111579
65
Loya Y. Sakai K. Yamazato K. Nakano Y. Sambali H. van Woesik R. (2001). Coral bleaching: the winners and the losers. Ecol. Lett.4, 122–131. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2001.00203.x
66
Lundgren I. Hillis-Starr Z. (2008). Variation in Acropora palmata Bleaching Across Benthic Zones at Buck Island Reef National Monument (St. Croix, USVI) During the 2005 Thermal Stress Event. Bull. Mar. Sci.83, 441–451.
67
Madin J. S. Baird A. H. Bridge T. C. Connolly S. R. Zawada K. J. Dornelas M. (2018). Cumulative effects of cyclones and bleaching on coral cover and species richness at lizard island. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.604, 263–268. doi: 10.3354/meps12735
68
Madin J. S. Baird A. H. Dornelas M. Connolly S. R. (2014). Mechanical vulnerability explains size-dependent mortality of reef corals. Ecol. Lett.17, 1008–1015. doi: 10.1111/ele.12306
69
Madin J. S. Connolly S. R. (2006). Ecological consequences of major hydrodynamic disturbances on coral reefs. Nature444, 477–480. doi: 10.1038/nature05328
70
Marshall P. A. Baird A. H. (2000). Bleaching of corals on the great barrier reef: differential susceptibilities among taxa. Coral Reefs19, 155–163. doi: 10.1007/s003380000086
71
Matz M. V. Treml E. A. Aglyamova G. V. Bay L. K. (2018). Potential and limits for rapid genetic adaptation to warming in a great barrier reef coral. PloS Genet.14(4). doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007220
72
McClanahan T. R. Ateweberhan M. Graham N. A. J. Wilson S. K. Ruiz Sebastian C. Guillaume M. M. M. et al . (2007). Western Indian Ocean coral communities: bleaching responses and susceptibility to extinction. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.337, 1–13. doi: 10.3354/meps337001
73
McClanahan T. R. Baird A. H. Marshall P. A. Toscano M. A. (2004). Comparing bleaching and mortality responses of hard corals between Southern Kenya and the great barrier reef, Australia. Mar. pollut. Bull.48, 327–335. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.08.024
74
Moberg F. Folke C. (1999). Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems. Ecol. Econ.29, 215–233. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(99)00009-9
75
Nakamura T. van Woesik R. (2001). Differential survival of corals during the 1998 bleaching event is partially explained by water-flow rates and passive diffusion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.212, 435–496. doi: 10.3354/meps212301
76
Nyström M. Folke C. Moberg F. (2000). Coral reef disturbance and resilience in a human-dominated environment. Trends Ecol. Evol.15, 413–417. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(00)01948-0
77
Osborne K. Dolman A. M. Burgess S. C. Johns K. A. (2011). Disturbance and the dynamics of coral cover on the great barrier reef, (1995–2009). PloS One6, 17516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017516
78
Perry C. T. Smithers S. G. (2006). Taphonomic signatures of turbid-zone reef development: examples from paluma shoals and lugger shoal, inshore central great barrier reef, Australia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol.242, 1–20. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.05.006
79
Pratchett M. S. McCowan D. Maynard J. A. Heron S. F. (2013). Changes in bleaching susceptibility among corals subject to ocean warming and recurrent bleaching in Moorea, French Polynesia. PloS One8, 70443. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070443
80
Puotinen M. Drost E. Lowe R. Depczynski M. Radford B. Heyward A. et al . (2020). Towards modelling the future risk of cyclone wave damage to the world’s coral reefs. Global Change Biol.26, 4302–4315. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15136
81
R Core Team (2020). R: A language and environment for statistical computing (Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
82
Reef Check Malaysia (2011). Status of Coral Reefs in Malaysia 2011 (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: Reef Check Malaysia).
83
Reef Check Malaysia (2020). Status of Coral Reefs in Malaysia 2020 (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: Reef Check Malaysia).
84
Ribas-Deulofeu L. Denis V. Château P. A. Chen C. A. (2021). Impacts of heat stress and storm events on the benthic communities of kenting national park (Taiwan). PeerJ9, 11744. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11744
85
Roslan A. David G. Pesiu E. Zahidin M. A. Rosmidi F. H. Izzati N. I. et al . (2017). “Promoting wildlife tourism as a conservation effort of the island flying fox in Pulau Bidong, Terengganu,” in Ecotourism Potentials in Malaysia. (Selangor, Malaysia: Universiti Putra Malaysia.)
86
Safuan M. Boo W. H. Siang H. Y. Chark L. H. Bachok Z. (2015). Optimization of coral video transect technique for coral reef survey: comparison with intercept transect technique. OJMS5, 379–397. doi: 10.4236/ojms.2015.54031
87
Salih A. Larkum A. Cox G. Kühl M. Hoegh-Guldberg O. (2000). Fluorescent pigments in corals are photoprotective. Nature408, 850–853. doi: 10.1038/35048564
88
Sampayo E. M. Ridgway T. Bongaerts P. Hoegh-Guldberg O. (2008). Bleaching susceptibility and mortality of corals are determined by fine-scale differences in symbiont type. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.105, 10444–10449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708049105
89
Schoepf V. Carrion S. A. Pfeifer S. M. Naugle M. Dugal L. Bruyn J. et al . (2019). Stress-Resistant Corals may not Acclimatize to Ocean Warming but Maintain Heat Tolerance Under Cooler Temperatures. Nat. Commun.10, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12065-0
90
Schoepf V. Stat M. Falter J. L. McCulloch M. T. (2015). Limits to the thermal tolerance of corals adapted to a highly fluctuating, naturally extreme temperature environment. Sci. Rep.5, 1–14. doi: 10.1038/srep17639
91
Scoffin T. P. (1993). The geological effects of hurricanes on coral reefs and the interpretation of storm deposits. Coral Reefs12, 203–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00334480
92
Scoffin T. P. Walton-Smith F. G. (1993). History of a Fringing Reef on the West Coast of Barbados 1974–1992. Global Aspects of Coral Reefs: Health, Hazards and History (Miami, Florida: Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science).
93
Spalding M. Spalding M. D. Ravilious C. Green E. P. (2001). World Atlas of Coral Reefs (Berkeley, USA: University of California Press).
94
Sully S. van Woesik R. (2019). Turbid reefs moderate coral bleaching under climate-related temperature stress. Global Change Biol.26, 1367–1373. doi: 10.1111/gcb.14948
95
Swain T. D. Vega-Perkins J. B. Oestreich W. K. Triebold C. DuBois E. Henss J. et al . (2016). Coral bleaching response index: A new tool to standardize and compare susceptibility to thermal bleaching. Global Change Biol.22, 2475–2488. doi: 10.1111/gcb.13276
96
Thompson D. M. van Woesik R. (2009). Corals escape bleaching in regions that recently and historically experienced frequent thermal stress. Proc. Biol. Sci.276, 2893–2901. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.0591
97
Torda G. Sambrook K. Cross P. Sato Y. Bourne D. G. Lukoschek V. et al . (2018). Decadal erosion of coral assemblages by multiple disturbances in the palm islands, central great barrier reef. Sci. Rep.8, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29608-y
98
van Woesik R. Ayling A. M. Mapstone B. (1991). Impact of tropical cyclone ‘Ivor’ on the great barrier reef, Australia. J. Coast. Res.7, 551–557.
99
van Woesik R. De Vantier L. M. Glazebrook J. S. (1995). Effects of cyclone ‘Joy’on nearshore coral communities of the great barrier reef. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.128, 261–270. doi: 10.3354/meps128261
100
van Woesik R. Sakai K. Ganase A. Loya Y. (2011). Revisiting the winners and the losers a decade after coral bleaching. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.434, 67–76. doi: 10.3354/meps09203
101
Veron J. E. (2000). Corals of the World Vol. Volume 1-3 (Townville, Australia: Australian Institute of Marine Science), 1382 p.
102
Veron J. E. Devantier L. M. Turak E. Green A. L. Kininmonth S. Stafford-Smith M. et al . (2009). Delineating the coral triangle. Galaxea J. Coral Reef Stud.11, 91–100. doi: 10.3755/galaxea.11.91
103
Wagner D. E. Kramer P. Van Woesik R. (2010). Species composition, habitat, and water quality influence coral bleaching in Southern Florida. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.408, 65–78. doi: 10.3354/meps08584
104
Wilkinson C. R. Souter D. (2008). Status of Caribbean coral reefs after bleaching and hurricanes in 2005. in Status of Coral Reefs of the World.
105
Williams R. Paul V. Arnold S. Steneck R. (2010). Larval Settlement Preferences and Post-Settlement Survival of the Threatened Caribbean Corals Acropora palmata and A. cervicornis. Coral Reefs29, 71–81. doi: 10.1007/s00338-009-0555-z
106
Yamashita H. Suzuki G. Kai S. Hayashibara T. Koike K . (2014). Establishment of coral-algal symbiosis requires attraction and selection. PloS One9(5), e97003. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097003
107
Zuki Z. M. Lupo A. R. (2008). Interannual variability of tropical cyclone activity in the Southern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos.113.
Summary
Keywords
tropical storm, coral bleaching, multiple disturbance, cyclone pabuk, South China Sea
Citation
Sumayed SM, Tan CH, Mokhtar NAH and Bachok Z (2025) Impact of multiple disturbances on coral communities at a remote shallow reef in the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1552229. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1552229
Received
27 December 2024
Accepted
01 July 2025
Published
29 July 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Wei Jiang, Guangxi University, China
Reviewed by
Yi Guan, Guangdong Ocean University, China
Aarón Israel Muñiz-Castillo, Healthy Reefs Initiative, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Sumayed, Tan, Mokhtar and Bachok.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Syed Muhammed Sumayed, sumayed_syed@hotmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.