Abstract
Based on panel data on Land-Based Marine Pollution from 11 coastal provinces in China spanning 2012 to 2023, this study employs Fixed-Effects, Threshold Regression, and Mediation Models to investigate the impact of Environmental Regulation on Land-Based Marine Pollution. The results show that: (1) there exists an inverted U-shaped relationship between Environmental Regulation and Land-Based Marine Pollution, where regulation beyond a certain threshold continuously reduces pollution levels; (2) threshold regression analysis reveals a single threshold effect in the negative impact of Environmental Regulation on the management of Land-Based Marine Pollution; (3) mediation analysis indicates that Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure play a mediating role between Environmental Regulation and pollution management. Specifically, Environmental Regulation reduces Land-Based Marine Pollution by promoting Green Innovation in enterprises and facilitating Industrial upgrading. To improve the management of Land-Based Marine Pollution in China, it is recommended to appropriately strengthen Environmental Regulation intensity and encourage enterprises to engage in Green Technological Innovation and Industrial restructuring, thus balancing environmental management with economic development and providing a scientific basis for pollution control.
1 Introduction
China, as a major maritime nation, has over 18,000 kilometers of mainland coastline, more than 14,000 kilometers of island coastline, and jurisdiction over approximately 3 million square kilometers of sea. To achieve sustainable development of the marine ecosystem and promote harmonious human–sea coexistence, China’s coastal provinces play a crucial role in addressing Land-Based Marine Pollution. Land-Based Marine Pollution significantly degrades nearshore seawater quality and poses serious challenges to the marine environment. According to statistics, about 80% of global marine pollution originates from Land-Based sources (Alam et al., 2021). According to Article 2 of the Regulations of the People’s Republic of China on the Administration of Prevention and Control of Pollution and Damage to the Marine Environment by Land-Based Pollutants, Land-Based Pollution is defined as the discharge of pollutants from land into the sea, which causes or is likely to cause pollution and damage to the marine environment through various sites and facilities. In this study, Land-Based Pollution refers specifically to the harm caused to the marine environment by such discharges, i.e., Land-Based Marine Pollution (hereinafter referred to as LBMP) (Ring, 1997). LBMP seriously degrades nearshore seawater quality and poses significant challenges to the marine environment. With the rapid urbanization and industrialization, pollutants generated by human activities enter the oceans through multiple pathways, including the atmosphere, sewage systems, rivers, and groundwater (Dahms, 2014). To achieve sustainable development of the marine ecosystem and promote harmonious human–sea coexistence, China’s coastal provinces have taken on a crucial role in managing LBMP. In recent years, the Chinese government has implemented a series of measures to curb LBMP. After sustained efforts, significant progress has been made, and the water quality of nearshore waters has improved notably. Nevertheless, the 2023 Bulletin on the State of China’s Marine Ecological Environment indicates that although the overall water quality within China’s jurisdictional waters is steadily improving, nearshore areas such as Liaodong Bay, the Yangtze River Estuary, Hangzhou Bay, and the Pearl River Estuary remain dominated by seawater classified as poor (Class IV). Environmental Regulation, as a key tool for local governments to intervene in environmental governance, plays a crucial role in addressing LBMP and achieving sustainable development of the marine environment (Yu et al., 2017; Tapver, 2019). The existing literature on the relationship between Environmental Regulation and environmental pollution is extensive but inconclusive (Dasgupta et al., 2001). Current research mainly presents three perspectives. (1) Environmental Regulation can effectively reduce environmental pollution. This view is further divided into the “innovation compensation theory” and the “mandatory emission reduction theory.” The “innovation compensation theory” is primarily based on Porter’s hypothesis, which suggests that appropriate Environmental Regulation can generate a compensatory innovation effect (Porter, 1996). Long-term reasonable regulation can thus effectively reduce pollution (Porter and van der Linde, 1995; Neves et al., 2020), and empirical studies have confirmed Porter’s hypothesis in the marine context (Ye et al., 2022). The “mandatory emission reduction theory” argues that governments can enforce Environmental Regulation by imposing sewage charges on polluters, increasing firms’ environmental costs, thereby reducing pollution emissions (Liu et al., 2020; Farouq et al., 2021). (2) Environmental Regulation may exacerbate environmental pollution. This perspective includes the “cost compliance theory” and the “green paradox.” The cost compliance theory posits that Environmental Regulation increases firms’ cost burdens, which not only fails to incentivize technological innovation but also drives firms to increase pollution emissions in pursuit of profit maximization (Greenstone, 2002). Proponents of the green paradox argue that stricter environmental regulation accelerates energy extraction, as firms rush to sell energy assets before new standards take effect, leading to a surge in pollution (Sinn, 2008). (3) There exists a nonlinear relationship between Environmental Regulation and environmental pollution. For example, Wang found an inverted U-shaped relationship: at low levels of regulation, firms tend to evade compliance, rendering environmental regulation ineffective in reducing pollution; only when regulation intensity reaches a certain threshold does it contribute to pollution reduction (Wang et al., 2021). Similarly, Ye demonstrated an inverted U-shaped nonlinear relationship between environmental regulation and the marine environment (Ye et al., 2022).
In summary, the relationship between Environmental Regulation and environmental pollution has been extensively studied in the academic community. However, most research focuses on general environmental pollution, with relatively few studies addressing LBMP. Since Land-Based pollution is the root cause of marine environmental issues, it is a critical aspect of marine environmental protection and sustainable development. This paper specifically examines the impact of Environmental Regulation on LBMP.
In recent years, green technological innovation and industrial structure have gained increasing attention as key mechanisms for promoting pollution control. These factors not only reflect enterprises’ responses to environmental regulation but also reduce pollution emissions at the source by driving technological advancement and industrial transformation. Numerous studies have shown that environmental regulation can indirectly enhance governance effectiveness by incentivizing firms to improve production processes through green technological innovation (Cai et al., 2020; Zhang and Li, 2020; Zhou et al., 2023). The relationship between industrial structure and pollution has also been extensively explored (Hao et al., 2020; Xi and Zhai, 2023). However, empirical research on the mediating roles of Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure in managing LBMP remains scarce. Therefore, this study introduces Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure as mediating variables to examine their effects between Environmental Regulation and LBMP, aiming to provide empirical support for improving coordinated management of LBMP.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
2.1 The direct impact of environmental regulation on LBMP
Due to the public goods nature of the ocean, the negative externalities affecting the marine environment require government intervention through the formulation of relevant Environmental Regulations (Zheng et al., 2023). Governments commonly employ Environmental Regulation tools such as sewage charges and environmental taxes to increase enterprises’ pollution control costs, thereby reducing energy consumption and curbing environmental pollution (Gao et al., 2017). Some scholars argue that imposing environmental taxes and establishing emissions trading systems effectively raise production and pollution control costs for firms, leading to pollution reduction (Pei et al., 2019). However, this view has also been questioned (Sinn, 2008). Regarding the relationship between Environmental Regulation and environmental pollution, some studies suggest a U-shaped relationship (Liu et al., 2019; Li et al., 2023), while others support an inverted U-shaped curve (Mazhar and Elgin, 2013; Wang and Shen, 2016; Ouyang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021; He et al., 2022). In terms of regulatory effectiveness across pollution levels, certain scholars find that Environmental Regulation plays a more significant role in heavily polluted areas (Li and Wang, 2025), whereas others contend it is more effective in less polluted regions (Zou and Zhang, 2022). Furthermore, the impact of Environmental Regulation on land-based pollution varies regionally (Zhang et al., 2019).
Accordingly, this study proposes Hypothesis 1: there is an inverted U-shaped relationship between environmental regulation and Land-Based Marine Pollution.
2.2 Indirect effects of environmental regulation on LBMP
Human activities are the primary drivers exacerbating LBMP, and regulating such behaviors is crucial for the sustainable development of the marine environment. Some scholars have identified Industrial Restructuring and Green Technological Innovation as key factors influencing environmental pollution (Yan and Zhu, 2023; Zheng, 2025). Building on previous research and considering the roles of Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure, this study posits that Environmental Regulation affects LBMP not only directly but also indirectly by influencing Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure.
2.2.1 Environmental regulation reduces LBMP by influencing green technological innovation
Green Technological Innovation improves environmental quality through advances in production and pollution control technologies (Li and Zhao, 2011). Environmental Regulation serves as a government tool to correct market failures and coordinate economic development with environmental protection, reflecting a balance between the positive “innovation compensation effect” and the negative “cost of compliance effect” (Xiao et al., 2024). The innovation compensation effect suggests that Environmental Regulation compels firms to engage in Green Technological Innovation by increasing pollution control costs and encouraging investment in pollution control research and development (Yuan and Chen, 2019). Conversely, the cost of compliance effect indicates that higher production and pollution control costs may constrain firms’ available funds, thereby reducing R&D investment and hindering technological innovation (Albrizio et al., 2017).
Based on this, Hypothesis 2 is proposed: Environmental Regulation can positively and indirectly reduce LBMP through the innovation compensation effect of Green Technological Innovation.
2.2.2 Environmental regulation reduces LBMP by influencing industrial restructuring
The relationship between Environmental Regulation and Industrial Structure remains inconclusive. The “pollution haven” hypothesis suggests that variations in national or regional Environmental Regulation strength may lead highly polluting industries to relocate to areas with weaker regulations to evade stricter controls (Liu and Li, 2021). In contrast, Porter’s hypothesis posits that moderate Environmental Regulation can stimulate technological improvements in firms, thereby driving industrial upgrading (Zheng and Li, 2021). Industrial Restructuring can reduce pollution emissions while achieving both economic growth and environmental benefits.
Based on this, Hypothesis 3 is proposed: environmental regulation can indirectly reduce LBMP by promoting Industrial Structure upgrading.
3 Model design and data description
3.1 Model design
The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis suggests an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic performance and environmental degradation; specifically, pollution levels increase with economic growth up to a certain turning point, after which they decline (Wang et al., 2019). This hypothesis has been observed in many countries and regions (Wang et al., 2019). Accordingly, this study employs the EKC framework to model the relationship between economic development and environmental pollution, with the benchmark model specified as follows:
Where denotes the pollution level in region i at year t; X represents control variables; is the constant term; is the random error term; are the coefficients of the linear and quadratic terms, respectively. and 2 represent the natural logarithm of per capita GDP and its squared term. Based on the EKC framework, as shown in Equation 1, the following model is constructed according to the approach of Song et al. (2020).
In the formula, denotes the level of LBMP in region i at year t; represents the per capita GDP level in region i at year t; indicates the intensity of Environmental Regulation in region i at year t; and represents other control variables in region i at year t. denotes individual fixed effects, and is the error term.
To test Hypotheses 2 and 3, this study adopts Baron and Kenny’s (1986) three-step approach to examine the mediating effects of environmental regulation on LBMP (Baron and Kenny, 1986). The procedure includes: (a) assessing the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable; (b) evaluating the effect of the independent variable on the mediator; and (c) examining the effect of the mediator on the dependent variable while controlling for the independent variable. A fixed effects model (FE) is employed to sequentially estimate these steps. To capture potential nonlinear effects, the squared term of the independent variable is included in the model. The mediating roles of Green Technological Innovation (GTI) and Industrial Structure (lnIS) in coastal provinces are tested according to Equations 3–5, where GTI and IS represent the levels of Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure, respectively, modeled as follows:
According to the above model, the effect of environmental regulation on marine land-based pollution in this paper is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
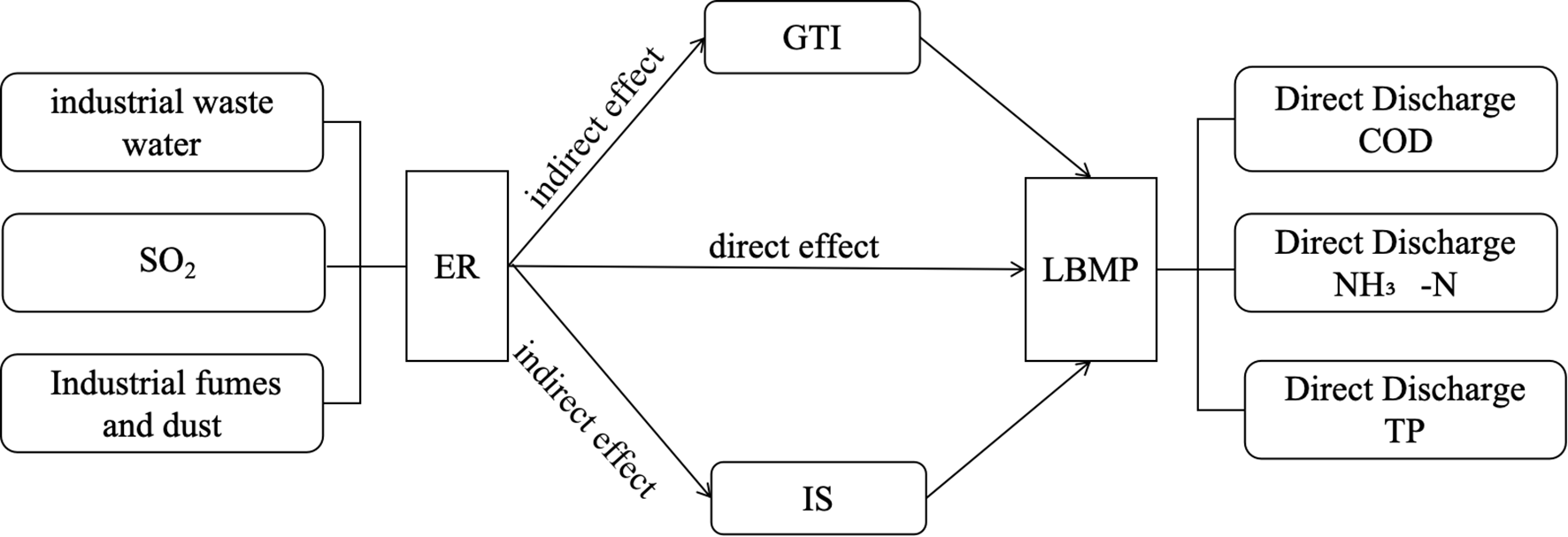
Effect diagram of environmental regulation on LBMP.
3.2 Selection of variables
3.2.1 Explained variable
The explained variable in this study is LBMP. Currently, there is no unified standard for measuring LBMP. Some scholars use single indicators such as industrial wastewater emissions (He and Chen, 2018) or seawater quality area (Zhang et al., 2020) to represent nearshore marine pollution levels. Others employ composite indicators, for example, combining pollutant data from industrial wastewater with the entropy weighting method to construct a comprehensive pollution index for nearshore waters (Ma et al., 2022). Although studies indicate that approximately 80% of nearshore marine pollution originates from Land-Based Sources, relying solely on industrial wastewater or seawater quality data is too general and insufficiently specific to LBMP. Therefore, this study utilizes pollutant discharge data directly into the sea, as published in the Bulletin of Ecological Condition of the Marine Environment of China. The main pollutants identified are Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), NH3-N, and Total Phosphorus (TP). Since the bulletin provides data only at the provincial level, to ensure data completeness and empirical rigor, this study employs the entropy weighting method to calculate a comprehensive LBMP index based on these three pollutants.
3.2.2 Explanatory variables
Environmental Regulation intensity, as the core explanatory variable in this study, lacks a unified quantitative standard. Existing methods to measure environmental regulation strength mainly include single-indicator and composite-indicator approaches (Ouyang et al., 2019). Single indicators commonly used include investment in pollution control (Lan et al., 2012), operating costs of polluting equipment (Yuan et al., 2017), the ratio of pollution control investment to GDP or industrial output (Jiang et al., 2018), environmental protection taxes (Li et al., 2018), and sewage charges (Ye et al., 2022). Composite indicators often combine industrial wastewater emissions, industrial SO2 emissions, and industrial fumes and dust emissions to construct an Environmental Regulation index (Zhao and Sun, 2016). Given the multidimensional nature of Environmental Regulation and potential errors from relying on a single indicator, this study follows Ma’s method (Ma et al., 2022), constructing a composite environmental regulation index based on the three industrial emission indicators: wastewater, SO2, and industrial fumes and dust. These emissions are used as inverse proxies for regulation intensity, consistent with the mechanism “strict regulation → emission reduction pressure → emissions decline.”
3.2.3 Control variables
3.2.3.1 Level of economic development
This study uses the logarithm of GDP per capita to measure economic development. Existing studies indicate that the relationship between economic growth and environmental pollution varies by region, supporting different EKC hypotheses (Bibi and Jamil, 2021). Some scholars observe an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic growth and pollution, confirming the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis (Unruh and Moomaw, 1998; Diao et al., 2009), while others report a U-shaped relationship using GDP per capita and its square (Park and Lee, 2011; Shao et al., 2011). To test the EKC hypothesis, lnGDP and lnGDP2 are included in the model; if the EKC holds, the coefficient of lnGDP should be positive and that of lnGDP2 negative.
3.2.3.2 Urbanization process
Rapid urbanization intensifies pollution discharges, with regional variations. Generally, higher urbanization levels correlate with more severe Land-Based Marine Pollution due to expanded infrastructure, industrial scale, and domestic sewage discharge. Urbanization is measured by the ratio of urban population to total resident population at year-end.
3.2.3.3 Population scale
The balance between population growth and environmental carrying capacity is a key concern in population-resource-environment studies (Ultsch, 1973). While common sense suggests “more people produce more pollution,” research generally finds a negative correlation between population size and environmental pollution (Lamsal et al., 2013). Population size (PS) is measured as the logarithm of total resident population in each province at year-end.
3.2.3.4 Green technological innovation
Green Technological Innovation(GTI) is vital for pollution management through industrial transformation and upgrading. It enhances enterprise value by improving product quality and services (Kogan et al., 2017), reduces energy intensity, and improves environmental quality. Patent counts per capita have been used to measure technological progress (Rahko, 2015). Considering data availability, this study uses the logarithm of enterprise patent applications in China’s coastal provinces as a proxy for green technological innovation.
3.2.3.5 Industrial structure
Upgrading Industrial Structure (IS) is crucial for environmental quality improvement (Oosterhaven and Broersma, 2007). The rapid growth of the tertiary sector reflects China’s shift toward a greener Industrial Structure, significant for sustainable economic development (Wang et al., 2018). This study measures industrial upgrading by the ratio of tertiary to secondary industry value added; a higher ratio indicates a transition from traditional industry to a service-oriented economy.
3.3 Data description
This study uses data from 11 coastal provinces in China spanning 2012 to 2023, including Liaoning, Hebei, Tianjin, Shandong, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan due to data availability). The raw data were sourced from the China Research Data Service Platform (CNRDS), China Marine Ecological and Environmental Status Bulletin, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Yearbook, and China Urban Statistical Yearbook. To address heteroskedasticity and scale inconsistencies, all variables were log-transformed. Table 1 presents descriptive statistics for the variables used in this study.
Table 1
| Variable | Obs | Mean | Std.dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnLBMP | 132 | -2.430672 | 1.441938 | -7.407238 | -0.0378759 |
| lnER | 132 | -0.2870057 | 0.2667125 | -1.189958 | -0.002032 |
| lnER2 | 132 | 0.1529689 | 0.2690733 | 4.13E-06 | 1.416001 |
| lnGDP | 132 | 11.202 | 0.4269014 | 10.23824 | 12.15647 |
| lnGDP2 | 132 | 125.6656 | 9.560625 | 104.8216 | 147.7797 |
| lnUL | 132 | 4.180867 | 0.183005 | 3.770888 | 4.544907 |
| lnPS | 132 | 8.398782 | 0.7680976 | 6.813445 | 9.44983 |
| lnGTI | 132 | 10.15952 | 1.557827 | 6.089045 | 12.81289 |
| lnIS | 132 | 0.26459 | 0.3801304 | -0.4002231 | 1.167631 |
Descriptive analysis of variables of LBMP.
4 Empirical results and analysis
4.1 Panel regression results
4.1.1 Panel unit root test
This study uses STATA/SE 17.0 software for empirical research. In order to avoid pseudo-regression, we need to conduct smoothness tests on all variables to obtain reliable regression results. The test used in this paper is Levine-Lin-Chu method (LLC test) to determine whether the variables are smooth or not. When the P-value is less than 5%, the variables are considered smooth, otherwise the variables are non-smooth. The results of the test are shown in
As can be seen in Table 2, most of the variables passed the test of smoothness at the 1% level and all the variables passed the test at the 5% level of significance. Therefore it can be concluded that the variables in this paper are smooth.
Table 2
| LLC | LnLBMP | lnER | lnGDP | lnUL | lnPS | lnGTI | lnIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | -6.312*** | -10.059*** | -1.953** | -4.345*** | -1.993** | -4.717*** | -1.909** |
| P-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.023 | 0.000 | 0.028 |
Panel data LLC test.
* p < 0.1, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01.
4.1.2 Panel cointegration test
Based on the previously mentioned stationarity tests, this study applies the Pedroni panel cointegration test to examine whether a cointegration relationship exists among the variables, indicating a long-term stable equilibrium. All variables are included in the Pedroni test, with results presented in Table 3. The Pedroni statistic rejects the null hypoth4.4esis of no cointegration at the 1% significance level, demonstrating a long-term stable cointegration relationship among the variables.
Table 3
| Test Method | Statistic | P -value | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Phillips–Perron t | 5.3575*** | 0.0000 | yes |
| Phillips–Perron t | -23.9943*** | 0.0000 | yes |
| Augmented Dickey–Fuller t | -14.4150*** | 0.0000 | yes |
Panel cointegration test.
4.1.3 Benchmark regression results
This study quantitatively assesses the relationship between Environmental Regulation and LBMP using the benchmark model, Equation 2. To examine this relationship, Ordinary Least Squares (OLS), fixed-effects(FE), and random-effects models(RE) were employed. Based on the BP and Hausman tests, the FE model was deemed most appropriate for this study. empirical estimates in Table 4 and test results are presented in Table 5.
Table 4
| VARIABLES | lnLBMP | lnLBMP | lnLBMP |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnER | -9.343*** | -5.295*** | -6.629*** |
| (1.977) | (1.307) | (1.521) | |
| lnER2 | -7.135*** | -4.362*** | -5.219*** |
| (1.557) | (0.984) | (1.167) | |
| lnGDP | 10.743 | -17.88* | 0.0640 |
| (13.610) | (9.877) | (11.32) | |
| lnGDP2 | -0.498 | 0.715* | 0.0160 |
| (0.593) | (0.427) | (0.493) | |
| lnUL | -3.900*** | -0.767 | 1.743 |
| (1.381) | (2.018) | (1.970) | |
| lnPS | -1.245** | 24.08*** | 0.973 |
| (0.582) | (3.469) | (0.764) | |
| lnGTI | 0.442 | -0.784** | -0.842** |
| (0.352) | (0.395) | (0.391) | |
| lnIS | 0.442* | -1.017** | -0.954* |
| (0.352) | (0.474) | (0.526) | |
| Constant | -39.74 | -83.58 | -12.91 |
| (77.30) | (54.06) | (62.56) | |
| Model | OLS | FE | RE |
| Observations | 132 | 132 | 132 |
| Number of PROVINCE | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| R-squared | 0.290 | 0.596 | 0.4348 |
Benchmark regression results.
Standard errors in parentheses *p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
Table 5
| Test method | P -value | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| BP | 0.0000 | Reject OLS |
| Hausman | 0.0012 | FE |
Level-by-level regression results.
The results indicate that the linear and quadratic terms of Environmental Regulation are statistically significant at the 1% level across all models. The coefficients of these terms confirm an inverted U-shaped nonlinear relationship between environmental regulation and LBMP (Figure 2). The turning point of the curve occurs at a logarithmic Environmental Regulation value of -0.607 (corresponding to a regulation intensity of 0.544). Beyond this threshold, the marginal effect of regulation is negative and increasing in magnitude, indicating an accelerated pollution reduction effect. This suggests that stricter regulation forces firms to adopt cleaner technologies or exit the market, reflecting a “survival of the fittest” mechanism. When the logarithmic value of Environmental Regulation is below -0.607 (i.e., regulation intensity below 0.544), the marginal effect is positive, implying that weak regulation may exacerbate pollution due to high compliance costs or technological lag, such as firms resorting to emission evasion. However, few observations fall within this range, limiting its representativeness. This issue will be further explored using a threshold regression model. These benchmark regression results support Hypothesis 1. Therefore, in the short term, over-reliance on low-intensity environmental regulation should be avoided, and technology subsidies or tax incentives should be provided to lower transition costs. In the long term, regulation intensity should exceed 0.544 (log value above -0.607) to achieve accelerated emission reductions.
Figure 2
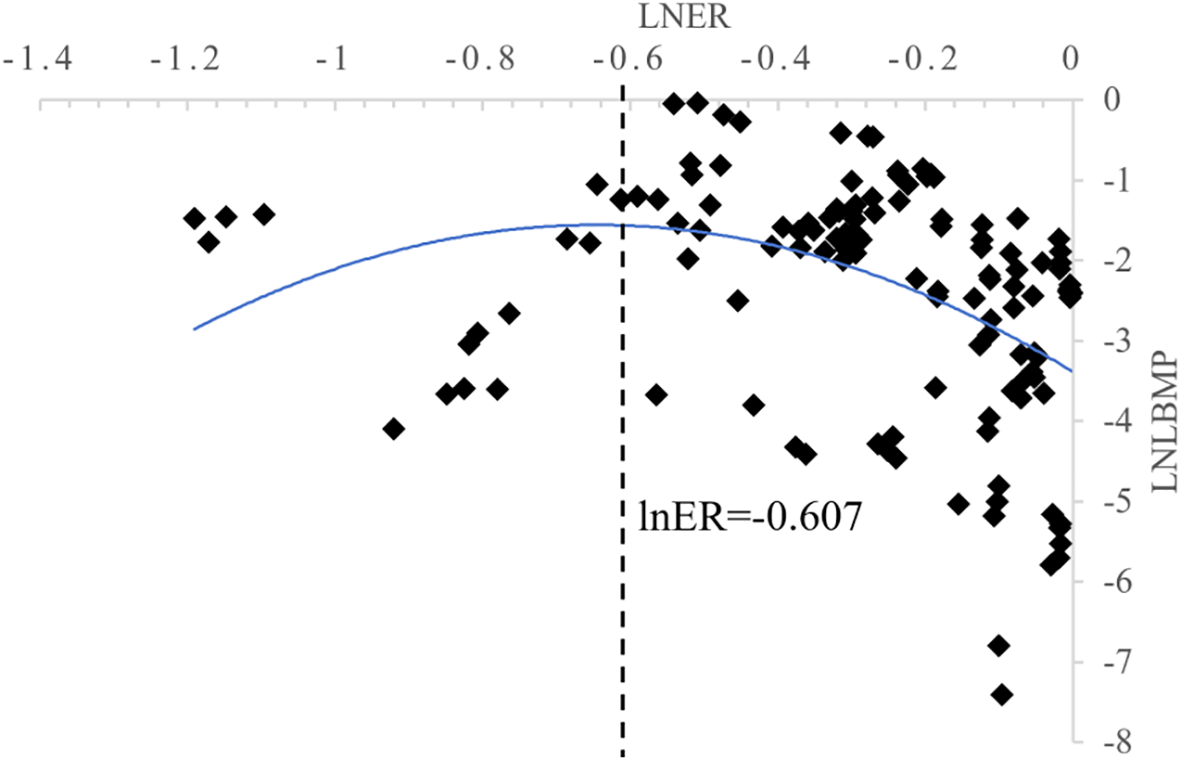
Inverted “U”-shaped relationship between Environmental Regulation and LBMP.
There is a significant inverted U-shaped relationship between the intensity of Environmental Regulation and LBMP. This pattern arises from nonlinear changes in firms’ cost-benefit analyses and behavioral responses under dynamic regulatory pressures, amplified by the unique characteristics of marine pollution. In the initial stage of low regulatory intensity, strengthening regulation often fails to curb pollution effectively and may even exacerbate emissions in the short term. This is primarily due to low compliance costs (e.g., pollution fees and fines) that do not offset pollution control investments. Consequently, firms may evade supervision through illegal discharge or data falsification or resort to symbolic, inefficient end-of-pipe measures. Weak law enforcement further diminishes the deterrent effect, lowering firms’ perceived risk of violation. Under such conditions, stricter regulation can prompt more covert evasion or costly yet ineffective technological upgrades, creating a “cost squeeze effect,” resulting in slow pollution decline or even increases. However, once regulatory intensity surpasses a critical threshold (the turning point of the inverted U), the system enters a high-intensity stage (the descending right side of the curve), fundamentally altering regulatory effectiveness. At this stage, stringent emission standards, substantially increased violation costs (e.g., heavy fines, shutdown risks), and robust enforcement raise firms’ expected violation costs above compliance costs for meaningful emission reductions (e.g., adoption of efficient end-of-pipe technologies or cleaner production methods). This shift triggers the “innovation compensation effect” as described by Porter’s hypothesis. Firms are incentivized to invest in clean technology and process improvements, reducing pollution at the source, which not only lowers long-term compliance costs but may enhance competitiveness. Simultaneously, intense regulation accelerates the exit of high-polluting, low-efficiency firms and promotes Green Industrial transformation.
Therefore, the inverted U-shaped relationship reveals a dynamic regulatory threshold: only when regulatory intensity and enforcement capacity surpass this critical value in a coordinated manner can the system transition from a cost squeeze to an innovation-driven regime, achieving effective reductions in LBMP.
4.2 Robustness analysis
To ensure that the regression results accurately reflect the impact of Environmental Regulation on LBMP, this study conducts robustness tests using four approaches. The results are presented in Table 6 and Table 7.
Table 6
| VARIABLES | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnER | -9.515*** | -8.550*** | -8.529*** | -6.983*** | -6.425*** | -5.295*** |
| (1.246) | (1.328) | (1.388) | (1.188) | (1.215) | (1.307) | |
| lnER2 | -6.827*** | -6.337*** | -6.330*** | -5.369*** | -5.030*** | -4.362*** |
| (1.072) | (1.094) | (1.105) | (0.939) | (0.948) | (0.984) | |
| lnGDP | -7.058 | -6.782 | -22.36** | -21.33** | -17.88* | |
| (10.33) | (11.57) | (9.982) | (9.897) | (9.877) | ||
| lnGDP2 | 0.280 | 0.269 | 0.869** | 0.851** | 0.715* | |
| (0.457) | (0.505) | (0.433) | (0.429) | (0.427) | ||
| lnUL | -0.108 | -3.476* | -1.672 | -0.767 | ||
| (2.017) | (1.763) | (2.004) | (2.018) | |||
| lnPS | 24.85*** | 24.66*** | 24.08*** | |||
| (3.547) | (3.513) | (3.469) | ||||
| lnGTI | -0.733* | -0.784** | ||||
| (0.401) | (0.395) | |||||
| lnIS | -1.017** | |||||
| (0.474) | ||||||
| Constant | -4.117*** | 39.96 | 38.76 | -56.55 | -64.16 | -83.58 |
| (0.220) | (58.37) | (62.79) | (54.52) | (54.13) | (54.06) |
Level-by-level regression results.
Standard errors in parentheses *p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
Table 7
| VARIABLES | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnER | -4.594*** | -6.374*** | |
| (0.487) | (1.284) | ||
| lnER2 | -2.743*** | -4.918*** | |
| (0.366) | (0.951) | ||
| lnER(t-1) | -7.982*** | ||
| (1.487) | |||
| lnER(t-1)2 | -5.810*** | ||
| (0.366) | (1.128) | ||
| lnGDP | -19.49*** | -5.339 | -16.02 |
| (3.677) | (12.47) | (11.44) | |
| lnGDP2 | 0.813*** | 0.257 | 0.585 |
| (0.159) | (0.542) | (0.506) | |
| lnUL | -0.404 | 3.073 | 0.894 |
| (0.751) | (2.054) | (2.343) | |
| lnPS | 1.619 | 1.028 | 22.07*** |
| (1.291) | (0.865) | (3.729) | |
| lnGTI | 1.000*** | -0.913** | -0.624 |
| (0.147) | (0.423) | (0.393) | |
| lnIS | -0.395** | -1.116** | -0.233 |
| (0.177) | (0.545) | (0.659) | |
| Constant | 104.3*** | 11.69 | -84.60 |
| (20.12) | (69.53) | (70.62) |
Robustness test results.
Standard errors in parentheses *p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
4.2.1 Stepwise inclusion of control variables
Table 6 shows the regression results: column (1) reports results without control variables, while columns (2) to (6) sequentially add control variables. In column (1), both the linear and quadratic coefficients of the core variable, Environmental Regulation, are negative and significant at the 1% level. After adding control variables, the results remain consistent and significant at the 1% level, confirming an inverted U-shaped relationship between environmental regulation and LBMP and supporting the robustness of these findings.
4.2.2 Alternative dependent variable
Due to the lack of a unified standard for measuring LBMP, this test follows He (2018) (He and Chen, 2018) by using industrial wastewater discharge as an alternative indicator. The regression results Table 7 [column (1)] exhibit similar significance levels for all variables, further confirming robustness.
4.2.3 Lagged core explanatory variable
Considering the lagged effects of environmental regulation, the core explanatory variable is lagged by one period. The results Table 7 [column (2)] still indicate an inverted U-shaped relationship, supporting the robustness of the main findings.
4.2.4 Excluding municipalities
Given that Shanghai and Tianjin are municipalities, this test excludes these two regions to avoid administrative bias. The robustness results Table 7 [column (3)] remain generally consistent with the full-sample two-way fixed effects results, confirming the robustness of the full-sample estimations.
4.3 Endogeneity test
There may be a bidirectional causal relationship between environmental regulation and LBMP, leading to potential endogeneity issues that can bias regression results. To ensure the reliability of the baseline estimates, this study follows Ma (2022) (Ma et al., 2022) by using lagged Environmental Regulation variables (lagged by one and two periods) as instrumental variables. The endogeneity test is conducted using instrumental variable regression, with results presented in Table 8. The findings show that the coefficients of the linear and quadratic terms of Environmental Regulation remain significantly negative at the 5% significance level, confirming an inverted U-shaped relationship between environmental regulation and LBMP and verifying the robustness of the results.
Table 8
| lnY | Coefficient | std. | z | P>|z| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnER | -11.55334*** | 4.272818 | -2.88 | 0.010 |
| lnER2 | -10.26434** | 3.574479 | -2.85 | 0.013 |
| lnGDP | 5.703101 | 22.37007 | 1.23 | 0.218 |
| lnGDP2 | -0.2659579 | 0.9567177 | -1.17 | 0.243 |
| lnUL | -4.349091** | 2.247815 | -1.77 | 0.050 |
| lnPS | -1.350569 | 0.8858378 | 0.88 | 0.251 |
| lnGTI | 0.452703 | 0.5831602 | -2.08 | 0.541 |
| lnIS | 1.074722 | 2.304375 | 2.1 | 0.229 |
| _cons | -10.12245 | 134.9011 | -1.11 | 0.931 |
Endogeneity test.
* p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
4.4 Threshold effect test
The baseline regression results confirm an inverted U-shaped relationship between Environmental Regulation and LBMP. Specifically, low levels of Environmental Regulation fail to reduce LBMP, whereas high levels significantly mitigate it, suggesting the existence of a threshold effect. To further verify this, this study employs a threshold regression model.
Following Hansen’s (1999) methodology (Hansen, 1999), the threshold effect is tested using Environmental Regulation as the threshold variable. The model is estimated under the null hypotheses of one, two, and three thresholds, with F-statistics and p-values obtained via bootstrap sampling. Results, shown in Table 9, indicate a significant single threshold effect at the 5% level, while double and triple thresholds are not statistically significant. Consequently, subsequent analyses focus on the single threshold model.
Table 9
| Model | F-Statisic | P-Value | 1% | 5% | 10% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Threshold | 31.62** | 0.0267 | 21.2035 | 25.6699 | 35.2850 |
| Double Threshold | 11.25 | 0.4367 | 25.5919 | 32.5634 | 44.1350 |
| Triple Threshold | 8.20 | 0.5800 | 23.7930 | 29.7806 | 43.6402 |
Threshold effect test results.
* p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
The estimation results of the panel threshold regression model are presented in Table 10. When the logarithm of Environmental Regulation is below -0.7636 (corresponding to an actual regulation intensity of 0.466), the coefficient is -0.460 but statistically insignificant, indicating that Environmental Regulation has no effect on LBMP in this range. When the logarithm exceeds -0.7636, the coefficient is -3.082 and significant at the 1% level, suggesting that Environmental Regulation effectively reduces pollution beyond this threshold, thereby reinforcing the baseline regression findings.
Table 10
| lnLBMP | Coefficient | std. | err. | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lnGDP | -22.64058** | 9.77313 | -2.32 | 0.022 |
| lnGDP2 | 0.8723255** | 0.4197262 | 2.08 | 0.040 |
| lnPS | 27.15818*** | 3.211867 | 8.46 | 0.000 |
| lnUL | -3.907865** | 1.937888 | -2.02 | 0.046 |
| lnGTI | -0.185632 | 0.474312 | -0.39 | 0.696 |
| lnIS | -0.1791819 | 0.3765747 | -0.48 | 0.635 |
| lnER<-0.7636 | -0.4595759 | 0.4646224 | -1.08 | 0.281 |
| lnER≥-0.7636 | -3.082159*** | 0.737019 | -4.67 | 0.000 |
| _cons | -69.29317 | 54.10743 | -1.28 | 0.203 |
Regression results of the single-threshold effects model.
* p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
After completing the threshold regression analysis on panel data, the estimated threshold value must be tested for statistical significance. Figure 3 displays the Likelihood Ratio (LR) distribution curve, where the vertical axis represents the LR test statistic and the horizontal axis corresponds to the threshold variable. According to Hansen’s criteria, if the minimum point of the LR curve (at the estimated threshold value of -0.7636) lies below the critical significance level, the threshold effect is considered statistically significant. In this study, the LR statistic at -0.7636 is significantly below the 5% significance level, confirming the presence of a structural break in the model parameters. This test effectively rules out the possibility of a spurious threshold effect and provides a robust econometric foundation for the preceding economic interpretation.
Figure 3
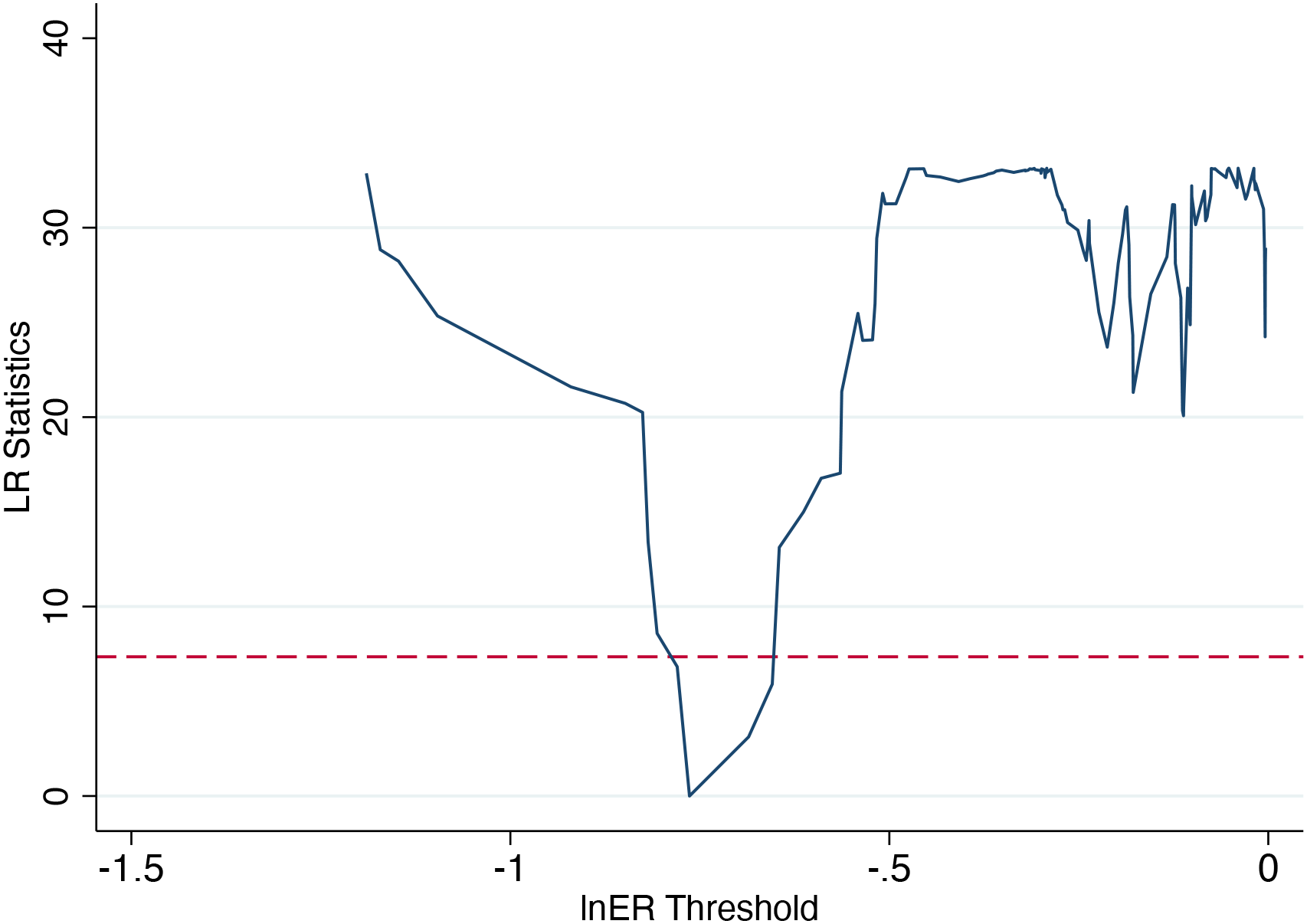
Threshold estimates and confidence intervals.
4.5 Mechanism analysis
To test Hypotheses 2 and 3, this study employs the three-step mediation analysis method proposed by Baron and Kenny (1986), following formulas (3), (4), and (5). The empirical results are presented in Table 11 and Table 12
Table 11
| VARIABLES | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnLBMP | lnGTI | lnLBMP | |
| lnGTI | -0.784** | ||
| (0.395) | |||
| lnER | -5.953*** | 0.840*** | -5.295*** |
| (1.281) | (0.300) | (1.307) | |
| lnER2 | -4.761*** | 0.508** | -4.362*** |
| (0.976) | (0.228) | (0.984) | |
| Constant | -74.37 | -11.75 | -83.58 |
| (54.55) | (12.77) | (54.06) | |
| Control | yes | yes | yes |
| Observations | 132 | 132 | 132 |
| Number of PROVINCE | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| R-squared | 0.581 | 0.855 | 0.596 |
Green Technology Innovation indirectly affects regression results.
Standard errors in parentheses *p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
Table 12
| VARIABLES | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| lnLBMP | lnIS | lnLBMP | |
| lnIS | -1.017** | ||
| (0.474) | |||
| lnER | -6.425*** | 1.112*** | -5.295*** |
| (1.215) | (0.236) | (1.307) | |
| lnER2 | -5.030*** | 0.657*** | -4.362*** |
| (0.948) | (0.184) | (0.984) | |
| Constant | -64.16 | -19.10* | -83.58 |
| (54.13) | (10.52) | (54.06) | |
| Control | yes | yes | |
| Observations | 132 | 132 | 132 |
| Number of PROVINCE | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| R-squared | 0.579 | 0.654 | 0.596 |
Industrial Structure indirectly affects regression results.
Standard errors in parentheses*p < 0.1, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
Table 11 examines the mediating effect of Green Technological Innovation on the relationship between Environmental Regulation and LBMP (Hypothesis 2). In Model (1), without including the mediator, the linear and quadratic terms of Environmental Regulation significantly and negatively affect LBMP, indicating that Environmental Regulation effectively reduces pollution emissions. In Model (2), with Green Technological Innovation (GTI) as the dependent variable, both terms of Environmental Regulation are positively significant at the 1% level, suggesting that regulation motivates firms to engage in Green Technological Innovation. After adding the mediator in Model (3), the coefficient of Green Technological Innovation is -0.784, significantly reducing LBMP. Meanwhile, the Environmental Regulation terms remain significant at the 1% level, indicating a partial mediating effect of Green Technological Innovation.
Table 12 assesses the mediating role of Industrial Structure (Hypothesis 3). In Model (1), without the mediator, Environmental Regulation’s linear and quadratic terms significantly and negatively influence LBMP, confirming a significant total effect. In Model (2), Environmental Regulation positively and significantly affects the mediator (IS), indicating it promotes industrial restructuring. Finally, in Model (3), including the mediator, the coefficient of Industrial Structure is -1.017 and significant at the 5% level, showing a significant inhibitory effect on pollution. The regulation terms remain significant at the 1% level, suggesting industrial structure partially mediates the effect of environmental regulation on LBMP.
Overall, Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure play partial mediating roles in the relationship between environmental regulation and LBMP. Environmental Regulation not only directly reduces LBMP but also indirectly enhances environmental governance effectiveness by stimulating Green Technological Innovation and promoting Industrial Structural adjustment.
5 Conclusion and policy recommendations
This study employs panel data from 11 coastal provinces in China between 2012 and 2023 to investigate the impact of Environmental Regulation on LBMP. It further explores the threshold effect of Environmental Regulation using Environmental Regulation intensity as the threshold variable, and examines the mediating roles of Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure adjustment. The main findings are summarized as follows:
First, there exists a significant inverted U-shaped relationship between Environmental Regulation and LBMP. Baseline regression results show that both the linear and quadratic terms of Environmental Regulation are significantly negative at the 1% level, confirming this nonlinear relationship. Specifically, at low regulatory intensity, pollution control effects are limited and may even provoke evasive behaviors by firms, temporarily increasing pollution. However, once regulation intensity surpasses the critical threshold (-0.7636), its pollution reduction capacity strengthens, validating the “cost squeeze–innovation compensation” mechanism consistent with Porter’s hypothesis.
Second, a significant single threshold effect is identified. Threshold regression results indicate that Environmental Regulation only significantly reduces pollution once the intensity crosses the estimated threshold. Below this threshold, regulation has limited or no effect on pollution reduction, highlighting the necessity of achieving sufficient regulatory strength.
Third, Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Structure partially mediate the effect of Environmental Regulation on LBMP. Mediation analysis demonstrates that Environmental Regulation not only directly curbs pollution but also indirectly enhances governance effectiveness by promoting Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Restructuring.
Based on these conclusions, the following policy recommendations are proposed:
5.1 Increase environmental regulation intensity beyond the critical threshold
Local governments should dynamically adjust the intensity and mode of Environmental Regulation in accordance with local pollution levels, economic conditions, and enforcement capacities. Special attention should be paid to regions currently under weak regulation, enabling them to surpass the critical threshold and thus improve pollution governance.
5.2 Promote green technological innovation and industrial upgrading
Given the significant indirect effects, Green Technological Innovation and Industrial Restructuring should be integrated into marine pollution control strategies. Policy measures could include establishing green innovation funds, providing green credit and tax incentives, and lowering barriers for enterprises to adopt clean technologies. Concurrently, fiscal guidance and local assessment reforms should encourage the phased exit of high-pollution industries, fostering a clean, low-carbon, and sustainable industrial system.
5.3 Strengthen regional collaboration and cross-jurisdictional pollution control
Due to disparities in Industrial Structure, innovation capacity, economic development, and population across coastal provinces, uniform regulation standards may be ineffective. Pollution emission standards should be tailored based on regional heterogeneity, with graded controls reflecting local conditions. Furthermore, given the transboundary nature of marine pollution and administrative fragmentation, coordinated regional legislation and governance targets are essential. The Marine Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China explicitly encourages inter-provincial monitoring cooperation. The Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Regulations give operational effect to these broad statutory provisions by establishing detailed monitoring protocols, standardized methodologies, and mechanisms for integrated, collaborative surveillance. These instruments will further promote reciprocal information-sharing arrangements among provinces. China is currently developing the Ecological Protection Section of the Ecological Environment Code, which is intended to provide unified legislative guidance across environmental domains. Building upon this emerging framework,Enhancing inter-regional cooperation and developing institutional frameworks for the exchange of monitoring information and mutual recognition of data establishing cross-jurisdictional pollution control mechanisms will prevent pollution transfer and improve overall marine environmental management.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
HW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. YC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YW: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was not received for this work and/or its publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Alam M. W. Xiangmin X. Ahamed R. (2021). Protecting the marine and coastal water from land-based sources of pollution in the northern Bay of Bengal: A legal analysis for implementing a national comprehensive act. Environ. Challenges4, 100154. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2021.100154
2
Albrizio S. Kozluk T. Zipperer V. (2017). Environmental policies and productivity growth: Evidence across industries and firms. J. Environ. Economics Manage.81, 209–226. doi: 10.1016/j.jeem.2016.06.002
3
Baron R. M. Kenny D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol.51, 1173. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173
4
Bibi F. Jamil M. (2021). Testing environment Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis in different regions. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.28, 13581–13594. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11516-2
5
Cai X. Zhu B. Zhang H. Li L. Xie M. (2020). Can direct environmental regulation promote green technology innovation in heavily polluting industries? Evidence from Chinese listed companies. Sci. Total Environ.746, 140810. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140810
6
Dahms H. U. (2014). The grand challenges in marine pollution research. Front. Mar. Sci.1, 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2014.00009
7
Dasgupta S. Laplante B. Mamingi N. Wang H. (2001). Inspections, pollution prices, and environmental performance: evidence from China. Ecol. Economics36, 487–498. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(00)00249-4
8
Diao X. Zeng S. Tam C. M. Tam V. W. (2009). EKC analysis for studying economic growth and environmental quality: a case study in China. J. Cleaner Production17, 541–548. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.09.007
9
Farouq I. S. Sambo N. U. Ahmad A. U. Jakada A. H. Danmaraya I. A. (2021). Does financial globalization uncertainty affect CO2 emissions? Empirical evidence from some selected SSA countries. Quant. Financ. Econ5, 247–263. doi: 10.3934/QFE.2021011
10
Gao J. Woodward A. Vardoulakis S. Kovats S. Wilkinson P. Li L. et al . (2017). Haze, public health and mitigation measures in China: A review of the current evidence for further policy response. Sci. Total Environ.578, 148–157. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.231
11
Greenstone M. (2002). The impacts of environmental regulations on industrial activity: evidence from the 1970 and 1977 clean air act amendments and the census of manufactures. J. Political Economy110, 1175–1219. doi: 10.1086/342808
12
Hansen B. (1999). Testing for linearity. J. Economic Surveys13, 551–576. doi: 10.1111/1467-6419.00098
13
Hao Y. Zheng S. Zhao M. Wu H. Guo Y. Li Y. (2020). Reexamining the relationships among urbanization, industrial structure, and environmental pollution in China—New evidence using the dynamic threshold panel model. Energy Rep.6, 28–39. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2019.11.029
14
He L. Chen X. (2018). Empirical research on the effect of marine environmental pollution to marine economic development based on the panel data. Ocean Dev. Manage35, 17–21.
15
He Z. X. Cao C. S. Wang J.-M. (2022). Spatial impact of industrial agglomeration and environmental regulation on environmental pollution—Evidence from pollution-intensive industries in China. Appl. Spatial Anal.15, 1525–1555. doi: 10.1007/s12061-022-09470-2
16
Jiang Z. Wang Z. Li Z. (2018). The effect of mandatory environmental regulation on innovation performance: Evidence from China. J. cleaner production203, 482–491. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.078
17
Kogan L. Papanikolaou D. Seru A. Stoffman N. (2017). Technological innovation, resource allocation, and growth. Q. J. economics132, 665–712. doi: 10.1093/qje/qjw040
18
Lamsal L. N. Martin R. V. Parrish D. D. Krotkov N. A. (2013). Scaling relationship for NO2 pollution and urban population size: A satellite perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol.47, 7855–7861. doi: 10.1021/es400744g
19
Lan J. Kakinaka M. Huang X. (2012). Foreign direct investment, human capital and environmental pollution in China. Environ. Resource Econ51, 255–275. doi: 10.1007/s10640-011-9498-2
20
Li W. Gu Y. Liu F. Li C. (2018). The effect of command-and-control regulation on environmental technological innovation in China: a spatial econometric approach. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.26 (34), 34789–34800. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3678-3
21
Li J. Wang X. (2025). Towards high-quality development: The complex role of environmental regulation. PloS One20, e0312816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312816
22
Li B. Zhao X. (2011). Economic structure, technological progress and environmental pollution: an analysis based on data from China’s industrial sector. Financial Res.37, 112–122. doi: 10.16538/j.cnki.jfe.2011.04.002
23
Li M. Zou S. Jing P. (2023). Spatial spillover effect of water environment pollution control in basins—based on environmental regulations. Water15, 3745. doi: 10.3390/w15213745
24
Liu Z. Cai Y. Hao X. (2020). The agglomeration of manufacturing industry, innovation and haze pollution in China: Theory and evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health17, 1670. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051670
25
Liu Y. Li L. (2021). The mechanism of vertical environmental regulation on the transfer of polluting industries–an analysis based on the perspective of local government competition. Ecol. Economy37, 206–210 + 219.
26
Liu Y. Luo N. Wu S. (2019). Nonlinear effects of environmental regulation on environmental pollution. Discrete Dynamics Nat. Soc.2019, 1–10. doi: 10.1155/2019/6065396
27
Ma J. Hu Q. Wei X. (2022). Impact of environmental regulation on coastal marine pollution—a case of coastal prefecture-level cities in China. Front. Mar. Sci.9, 882010. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.882010
28
Mazhar U. Elgin C. (2013). Environmental regulation, pollution and the informal economy. SBP Res. Bull.9, 62–81.
29
Neves S. A. Marques A. C. Patrício M. (2020). Determinants of CO2 emissions in European Union countries: does environmental regulation reduce environmental pollution? Economic Anal. Policy68, 114–125. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2020.09.005
30
Oosterhaven J. Broersma L. (2007). Sector structure and cluster economies: A decomposition of regional labour productivity. Regional Stud.41, 639–659. doi: 10.1080/00343400601120320
31
Ouyang X. Shao Q. Zhu X. He Q. Xiang C. Wei G. (2019). Environmental regulation, economic growth and air pollution: Panel threshold analysis for OECD countries. Sci. total Environ.657, 234–241. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.056
32
Park S. Lee Y. (2011). Regional model of EKC for air pollution: Evidence from the Republic of Korea. Energy Policy39, 5840–5849. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2011.06.028
33
Pei Y. Zhu Y. Liu S. Wang X. Cao J. (2019). Environmental regulation and carbon emission: The mediation effect of technical efficiency. J. Cleaner Production236, 117599. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.07.074
34
Porter M. E. (1996). “ America’s green strategy,” in Business and the Environment–A Reader. Eds. WelfordR.StarkleyR. (United States: Taylor&Francis).
35
Porter M. E. van der Linde C. (1995). Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J. economic Perspect.9, 97–118. doi: 10.1257/jep.9.4.97
36
Rahko J. (2015). Internationalization of corporate R&D activities and innovation performance. Ind. Corporate Change25, dtw012. doi: 10.1093/icc/dtw012
37
Ring D. A. (1997). Sustainability dynamics: land-based marine pollution and development priorities in the island states of the commonwealth Caribbean. Colum. J. Envtl. L.22, 65.
38
Shao S. Yang L. Yu M. Yu M. (2011). Estimation, characteristics, and determinants of energy-related industrial CO2 emissions in Shanghai (China), 1994–2009. Energy Policy39, 6476–6494. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2011.07.049
39
Sinn H.-W. (2008). Public policies against global warming: a supply side approach. Int. Tax Public Finance15, 360–394. doi: 10.1007/s10797-008-9082-z
40
Song Y. Yang T. Li Z. Zhang X. Zhang M. (2020). Research on the direct and indirect effects of environmental regulation on environmental pollution: Empirical evidence from 253 prefecture-level cities in China. J. Cleaner Production269, 122425. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122425
41
Tapver T. (2019). CSR reporting in banks: does the composition of the board of directors matter. Quantitative Finance Economics3, 286–314. doi: 10.3934/QFE.2019.2.286
42
Ultsch G. R. (1973). Man in balance with the environment: pollution and the optimal population size. BioScience23, 642–643. doi: 10.2307/1296776
43
Unruh G. C. Moomaw W. R. (1998). An alternative analysis of apparent EKC-type transitions. Ecol. Economics25, 221–229. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(97)00182-1
44
Wang Z. Jia H. Xu T. Xu C. (2018). Manufacturing industrial structure and pollutant emission: An empirical study of China. J. Cleaner Production197, 462–471. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.092
45
Wang M. Liao G. Li Y. (2021). The relationship between environmental regulation, pollution and corporate environmental responsibility. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health18, 8018. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18158018
46
Wang H. Lu X. Deng Y. Sun Y. Nielsen C. P. Liu Y. et al . (2019). China’s CO2 peak before 2030 implied from characteristics and growth of cities. Nat. Sustainability2, 748–754. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0339-6
47
Wang Y. Shen N. (2016). Environmental regulation and environmental productivity: The case of China. Renewable Sustain. Energy Rev.62, 758–766. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.05.048
48
Xi B. Zhai P. (2023). Economic growth, industrial structure upgrading and environmental pollution: Evidence from China. Kybernetes52, 518–553. doi: 10.1108/K-02-2022-0279
49
Xiao F. Zhang B. Liao S. (2024). A study of the impact of environmental regulation on green technology innovation - A moderating analysis of staged digital transformation. Res. Manage.45, 99–108. doi: 10.19571/j.cnki.1000-2995.2024.11.010
50
Yan T. Zhu M. (2023). Impact of technological innovation and industrial structure upgrading on environmental pollution. J. Chongqing Univ. (Social Sci. Edition)29, 70–84.
51
Ye F. He Y. Yi Y. Quan Y. Deng Y. (2022). Promotion of environmental regulation on the decoupling of marine economic growth from marine environmental pollution—based on interprovincial data in China. J. Environ. Plann. Manage.65, 1456–1482. doi: 10.1080/09640568.2021.1932771
52
Yu W. Ramanathan R. Nath P. (2017). Environmental pressures and performance: An analysis of the roles of environmental innovation strategy and marketing capability. Technological Forecasting Soc. Change117, 160–169.
53
Yuan Y. Chen Z. (2019). Environmental regulation, green technology innovation and the transformation and upgrading of China’s manufacturing industry. Res. Sci.37, 1902–1911. doi: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2019.10.020
54
Yuan B. Ren S. Chen X. (2017). Can environmental regulation promote the coordinated development of economy and environment in China’s manufacturing industry?–A panel data analysis of 28 sub-sectors. J. cleaner production149, 11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.065
55
Zhang W. Li G. (2020). Environmental decentralization, environmental protection investment, and green technology innovation | Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.1–16, 12740–12755.
56
Zhang H. Liu M. Zhang C. Wang K. (2020). Study on the dynamic impact of land-based industrial structure evolution on the marine environment: A case study of the Yangtze River Basin and East China Sea coastal area. Yangtze River Basin Resour. Environ.29, 1586–1596.
57
Zhang K. Xu D. Li S. (2019). The impact of environmental regulation on environmental pollution in China: an empirical study based on the synergistic effect of industrial agglomeration. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.26, 25775–25788. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05854-z
58
Zhao X. Sun B. (2016). The influence of Chinese environmental regulation on corporation innovation and competitiveness. J. cleaner production112, 1528–1536. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.029
59
Zheng W. (2025). The role mechanism and threshold effect of digital finance enabling green technology innovation–based on the dual perspective of green finance and institutional environment. J. Guizhou Normal Univ. (Social Sci. Edition)2, 84–97. doi: 10.16614/j.gznuj.skb.2025.02.009
60
Zheng J. Gao C. Zhu C. (2023). Environmental decentralization, marine environmental regulation and marine environmental pollution. Stat Decision Making39, 75–80. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2023.05.014
61
Zheng F. Li J. (2021). Scientific and technological environmental regulation forcing industrial transformation and upgrading in resource-oriented cities-theoretical model and double effect analysis. Soft Sci.35, 22–28. doi: 10.13956/j.ss.1001-8409.2021.12.04
62
Zhou J. Zhou Y. Bai X. (2023). Can green-technology innovation reduce atmospheric environmental pollution? Toxics11, 403. doi: 10.3390/toxics11050403
63
Zou H. Zhang Y. (2022). Does environmental regulatory system drive the green development of China’s pollution-intensive industries? J. Cleaner Production330, 129832. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129832
Summary
Keywords
environmental regulation, land-based marine pollution, marine environmental protection, synergistic governance, green technology innovation, industrial structure
Citation
Wu H, Cao Y and Wang Y (2026) A study of the impact of environmental regulation on land-based marine pollution—evidence from 11 coastal provinces in China. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1610100. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1610100
Received
11 April 2025
Accepted
07 July 2025
Published
13 January 2026
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Leonardo Rörig, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Brazil
Reviewed by
Vasilii Erokhin, Harbin Engineering University, China
Ini-Ibehe Nabuk Etim, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Wu, Cao and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yilin Cao, gracesufelaw@stu.sufe.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.