- 1Shandong Hanfang Pharmaceutical Co. LTD, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Pharmacology, Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 3College of Pharmacy, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 4Biology Institute, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, China
Introduction: Bone, as both a crucial organ with mechanical support and immune regulatory functions, profoundly influencing the growth and development of fish in aquaculture systems. Deer antler and its aqueous extract Cervi Cornus Colla (CCC), are natural medicinal substances known for their bone-protective properties.
Methods: This study investigated the osteoprotective effects of CCC against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced injury to fish bones. An LPS-mediated zebrafish skeletal injury model was established and evaluated using Alcian Blue/Alizarin Red staining, fluorescence tracing, ELISA, and qPCR.
Results: The median lethal concentration (LC50) of CCC in zebrafish was 206.3 mg/mL, and staining revealed that CCC reversed LPS-induced reduction in cartilage and bone formation in a dose-dependent manner. In Tg (mpeg1: EGFP) zebrafish, CCC treatment significantly decreased macrophages-associated green fluorescence, suggesting that the extract suppressed the activation of macrophages caused by LPS. CCC also reduced the production of several inflammatory factors (IL-6, IL- 1β, and NO). Furthermore, qRT-PCR confirmed CCC restored COL2α1 and Sox9a mRNA levels. Additional studies revealed CCC inhibits LPS-induced activation of the TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that CCC can alleviate zebrafish bone injury, thereby providing an experimental basis for its application in the prevention and treatment of bone diseases in farmed fish.
1 Introduction
The skeletal system plays dual roles in fish physiology, providing structural support for the body and regulating various metabolic processes (Stundl et al., 2019; Li et al., 2021; Beriotto et al., 2023; Rees et al., 2023). Bone injuries pose significant threats to fish raised in aquaculture. In aquaculture settings, pathogens (e.g., Aeromonas hydrophila and infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus) can induce chronic cartilage inflammation and gill arch degradation, reducing feeding efficiency by 30–50% (Cavin et al., 2012; Abdelsalam et al., 2024). In wild populations, exposure to heavy metals and the resulting developmental defects may cause bone mineralization disorders, leading to otolith or spinal deformities that impair spatial navigation and escape behaviors (Wang et al., 2024). These bone-related issues have become critical challenges for fish health management and conservation, prompting the need for natural products with both anti-inflammatory and bone-protective properties.
Deer antler, a traditional Chinese medicine, contains amino acids, peptides, phospholipids, growth factors, and trace elements (e.g., Mn, Zn, and Ca) (Kim et al., 2021). Cervi Cornus Colla (CCC), an aqueous extract produced by boiling and condensing ossified antler bases from Cervus nippon or Cervus elaphus, has historically been used to “nourish essence and strengthen bones” (Hijikata et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2013). Modern studies have shown that CCC enhances chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via the BMP/Smad signaling pathway and promotes osteoblast proliferation in skull defect models (Zhang et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2016; Ren et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020). However, existing research has primarily focused on mammals, with only limited exploration of CCC’s effects on fish skeletal systems. Notably, zebrafish larvae allow direct drug absorption through their permeable skin, offering unique advantages for systemic studies. This system thus provides an opportunity to address current knowledge gaps in understanding CCC’s regulation of fish bone-immune-inflammatory networks.
In this study, we established an LPS-induced bone injury model in zebrafish to evaluate the effects of CCC on bone formation, immune-inflammatory responses, and gene regulation. We aimed to clarify CCC’s therapeutic potential for fish bone diseases and propose novel strategies for aquaculture health management.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
NaCl, KCl, CaCl2, and MgSO4 were purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai, China). Methylene blue was obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was procured from Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). Alizarin red and Alcian blue were sourced from Yuanye Bio-Technology (Shanghai, China). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and ELISA kits were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, USA). ELISA kits were acquired from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China). A BCA protein assay kit was purchased from Sevenbio (Wuhan, China). RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and qPCR kits were provided by Vazyme Biotech (Nanjing, China).
2.2 CCC preparation
Antler bases (Cervus nippon) were obtained from Jinan Dapeng Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd. Following the protocol described in the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the antler segments were boiled in distilled water (1:5 ratio) for three sequential 3-hour extractions. The combined filtrates were condensed into a paste and freeze-dried to produce CCC powder.
2.3 Experimental animals
Zebrafish were supplied by the Zebrafish Screening Platform of the Shandong Academy of Sciences. The sample size was determined by reference to the published literature (Ouyang et al., 2022; Horst et al., 2024). The fish were maintained at 28°C in temperature-controlled incubators with daily water renewal. All procedures complied with animal management regulations and the 3R (replacement, reduction, and refinement) principles (Ethics No. SWS20240407).
2.4 Safety assessment of CCC
Healthy 5-day post-fertilization (dpf) larvae were randomly divided into control and CCC groups (n = 30 per group, 10 fish/well). CCC was administered at concentrations ranging from 6.25–250 μg/mL in E3 medium (5 mM NaCl, 0.17 mM KCl, 0.33 mM CaCl2, and 0.33 mM MgSO4). The survival rates and morphological features were recorded on day 9.
2.5 Construction of a zebrafish bone injury model
Healthy 5-dpf zebrafish larvae were randomly divided into a control group (E3 medium), a model group (100 μg/mL LPS), and CCC treatment groups (100 μg/mL LPS + CCC at three concentrations determined based on safety assessments). Each group comprised three replicates, with 10 fish per well. All treatment groups were maintained at 28°C, with daily medium replacement. Zebrafish were collected at 9 dpf for subsequent experimental analyses.
2.6 Alcian Blue staining
Zebrafish were fixed in 4% PFA for 24 h and washed three times with PBS. Samples were stained overnight in 0.1% Alcian Blue, dehydrated using an ethanol gradient, and treated with 0.05% trypsin-sodium tetraborate solution for 90 min. After additional PBS washes, specimens were cleared in a 1% KOH-3% H2O2 solution (90 min) and stored in 50% glycerol. Cartilage staining in the cephalic region was imaged using a Zeiss AXIO Zoom V16 microscope. Image-Pro Plus 6.0 was used to measure the integrated optical density (IOD) in zebrafish cranial cartilaginous regions (Meckel’s cartilage, palatoquadrate, etc.), where IOD values quantitatively reflect cartilage matrix composition.
2.7 Alizarin Red staining
Zebrafish larvae (9 dpf) were collected from each group and fixed in a mixture of 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 1 hour. Samples were then transferred to 50% ethanol for 1 hour, followed by three 20-min washes with double-distilled water (ddH2O). After digestion with trypsin until skeletal structures became visible, the samples stained overnight in 0.1 g/L Alizarin Red solution. The stained specimens were stored in glycerol. For analysis, bone mineralization was imaged using a Zeiss AXIO Zoom V16 microscope. Image-Pro Plus 6.0 measured the IOD in specific skeletal regions of zebrafish, where IOD values are directly proportional to the degree of bone mineralization.
2.8 Detection of macrophage distribution and expression
The Tg (mpeg1:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish with normal development to 5 dpf after fertilization were randomly divided into a control group, a model group, and CCC treatment groups. Each group was divided into three holes, with 10 bars per hole. Macrophage fluorescence intensity was quantified at 9 dpf using microscopy (Zeiss AXIO Zoom V16). Image-Pro Plus 6.0 measured whole-body fluorescence IOD in zebrafish, with IOD values serving as a quantitative indicator of macrophage activation status.
2.9 Detection of inflammatory factors in zebrafish
Ten zebrafish larvae (9 dpf) per group were homogenized in PBS on ice and centrifuged at 3000 rpm (4°C, 20 min). The supernatants were collected for interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) quantification using ELISA kits. For nitric oxide (NO) measurement, samples were homogenized in saline (1:9 ratio), centrifuged at 3500 rpm (10 min), and analyzed using a BCA protein assay. To quantify NO levels, 0.16 mL of the supernatant was mixed with 0.08 mL of chromogenic agent and incubated for 15 min, after which the absorbance was measured at 550 nm using a BMG Labtech microplate reader.
2.10 qRT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from zebrafish using RNA isolation reagents following the manufacturer’s instructions and then reverse-transcribed into cDNA. Ribosomal protein L13a (RPL13a), which has relatively stable expression, was selected as the reference gene, and the expression levels of Collagen Type II Alpha 1 (COL2α1), SRY-box transcription factor 9a (Sox9a), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), and mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (Smad3) were quantified using the SYBR Green-based qPCR (StepOnePlus System). The genes were amplified using the following gene-specific primers: COL2α1, F:CGGACTCTCCTGCTACTTGTG, R:ATCTTGAACACAGCCGCCAA; Sox9a, F:CCTGGATGACCAAACCCCAA, R:AGGAACCGTAGCTGATGTGC; TGF-β, F:GTCCGAGATGAAGCGCAGTA, R:TGGAGACAAAGCGAGTTCCC; Smad3, F:TGTCTCCTGCCCACAACAAT, R:GAGTTGGACGGGTCTGTGAA; and Rpl13a, F:CGGTCGTCTTTCCGCTATTG, R:CTTGCGGAGGAAAGCCAAAT. The samples were analyzed using a LightCycler® 96 Instrument (Roche, Switzerland). For quantitative analysis, fold changes were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCt method.
2.11 Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analyses used IBM SPSS Statistics 25 for one-way ANOVA with the least significant difference (LSD) post-hoc tests (recommended for ≥3 experimental groups), while GraphPad Prism 10 generated graphical representations. Statistical significance was defined as P < 0.05 with multiple comparison adjustment.
3 Results
3.1 Safety evaluation of CCC
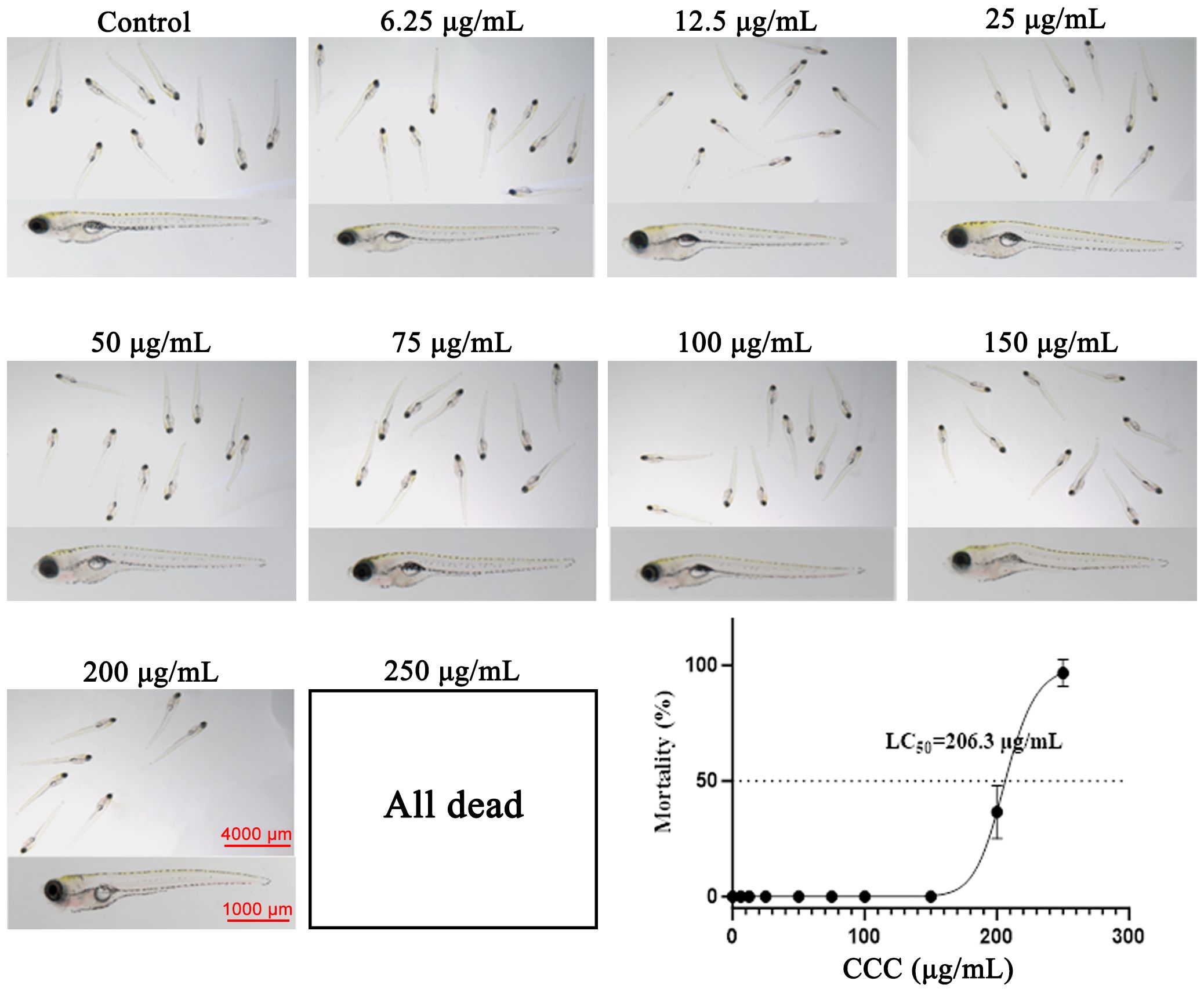
To determine the appropriate dosage of CCC, we first investigated its safety profile. As shown in Figure 1, there were no significant morphological abnormalities and no mortality in zebrafish treated with CCC at concentrations of 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 75, 100, or 150 μg/mL compared with the control group. In contrast, mortality and deformities were observed at 200 μg/mL, and the 250 μg/mL dose was lethal. The calculated half-maximal inhibitory concentration (LC50) of CCC was 206.3 μg/mL. Therefore, 50, 100, and 150 μg/mL CCC concentrations were selected for subsequent experiments.
3.2 CCC alleviates LPS-induced cartilage hypoplasia
Cartilage morphology reflects developmental processes involving cell proliferation, differentiation, and extracellular matrix synthesis. Alcian Blue staining was used to evaluate cartilage development (Figure 2). Compared with the control group, the LPS-treated group exhibited significantly reduced staining intensity in Meckel’s cartilage and palatoquadrate regions (P < 0.01), along with signs of cartilage atrophy and hypoplasia. CCC treatment restored cartilage staining intensity and structural integrity, indicating its ability to counteract LPS-induced cartilage developmental defects.
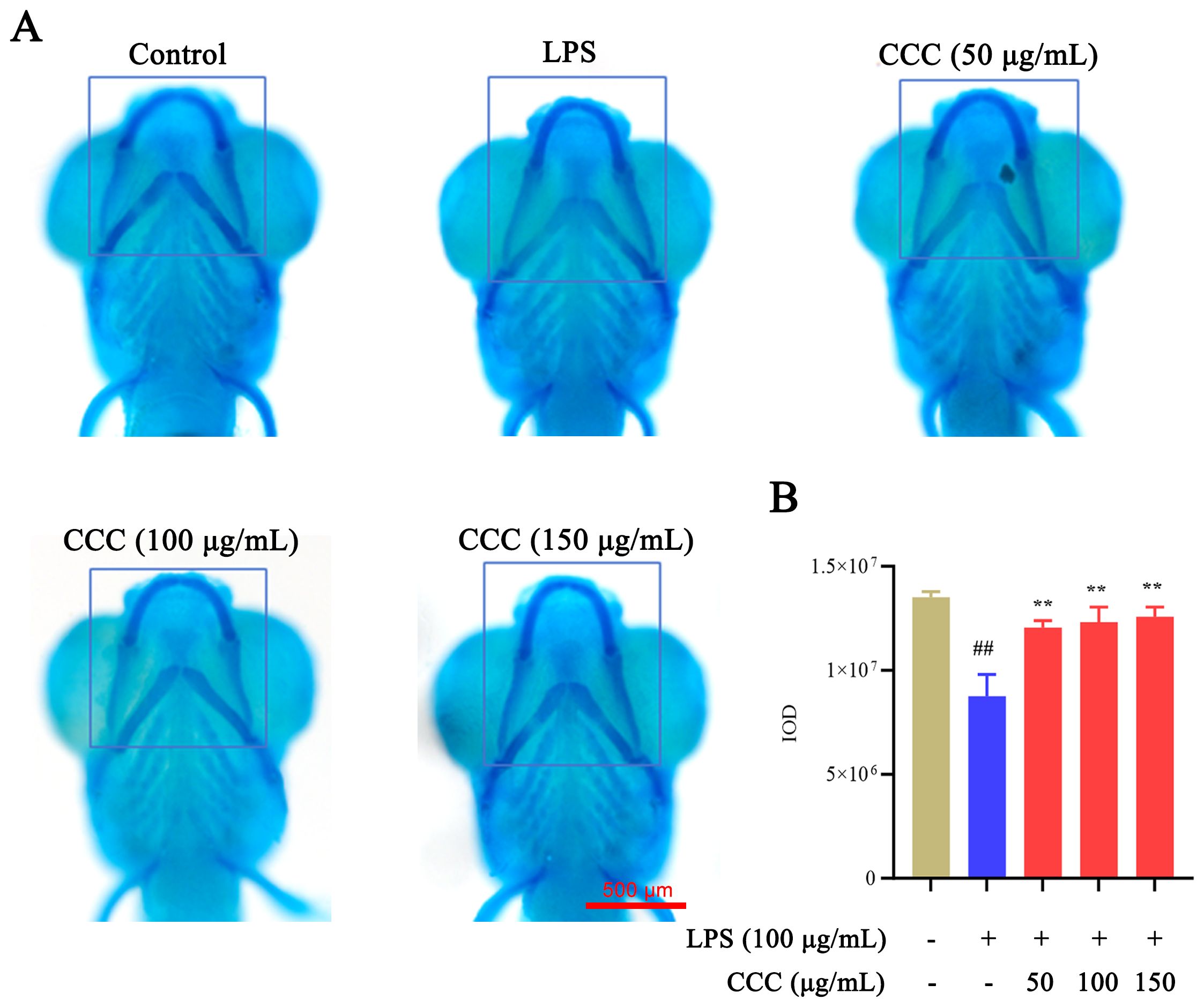
Figure 2. Effects of CCC and/or LPS on zebrafish cartilage. (A) Representative images of Alcian Blue staining. (B) Histogram of IOD values. The blue-boxed areas represent regions selected for IOD measurement. # vs. control: ## P < 0.01; * vs. LPS model: **P < 0.01.
3.3 CCC restores LPS-impaired bone mineralization
Bone formation plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and function. Alizarin Red staining was used to demonstrate the effects of CCC on bone formation (Figure 3). LPS exposure significantly reduced the intensity of bone mineralization compared with the control group (P < 0.01). CCC treatment enhanced mineralization in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.01 vs. LPS model), confirming its protective effect against the suppression of LPS-induced bone formation.
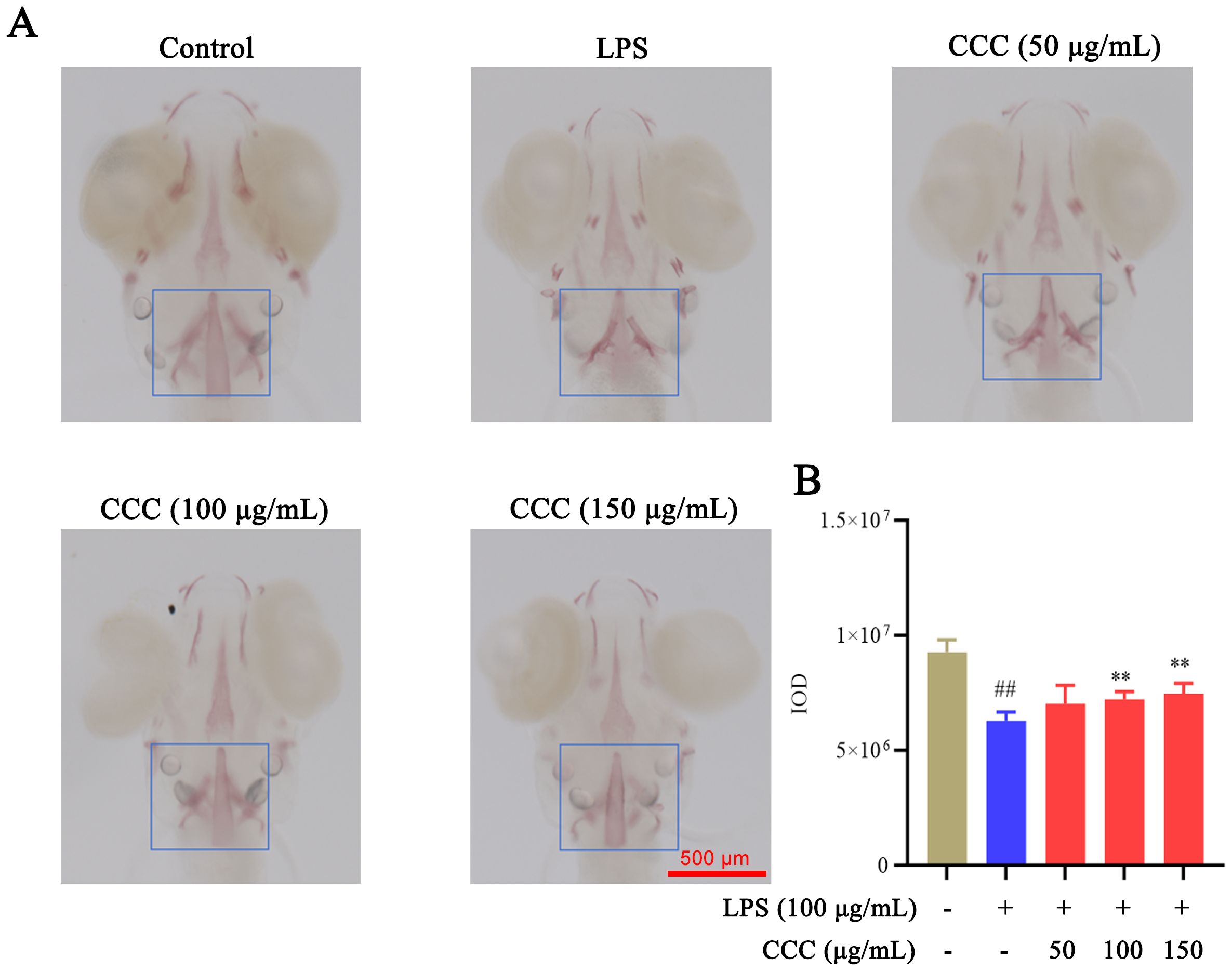
Figure 3. Effects of CCC and/or LPS on zebrafish bone formation. (A) Representative images of Alizarin Red staining. (B) Histogram of IOD values. The blue-boxed areas represent regions selected for IOD measurement. # vs. control: ## P < 0.01; * vs. LPS model: **P < 0.01.
3.4 CCC inhibits LPS-triggered activation of macrophages
Macrophage activation contributes to LPS-induced cartilage damage (Sun et al., 2022). Fluorescence imaging of Tg (mpeg1:EGFP) zebrafish revealed that LPS exposure significantly increased macrophage fluorescence intensity compared with the control group (P < 0.01; Figure 4). CCC treatment reduced macrophage activation, with the 100 and 150 μg/mL groups showing the most pronounced effects (P < 0.01). The results indicated that CCC could inhibit LPS-induced immune activation and reduce the number of macrophages in zebrafish.
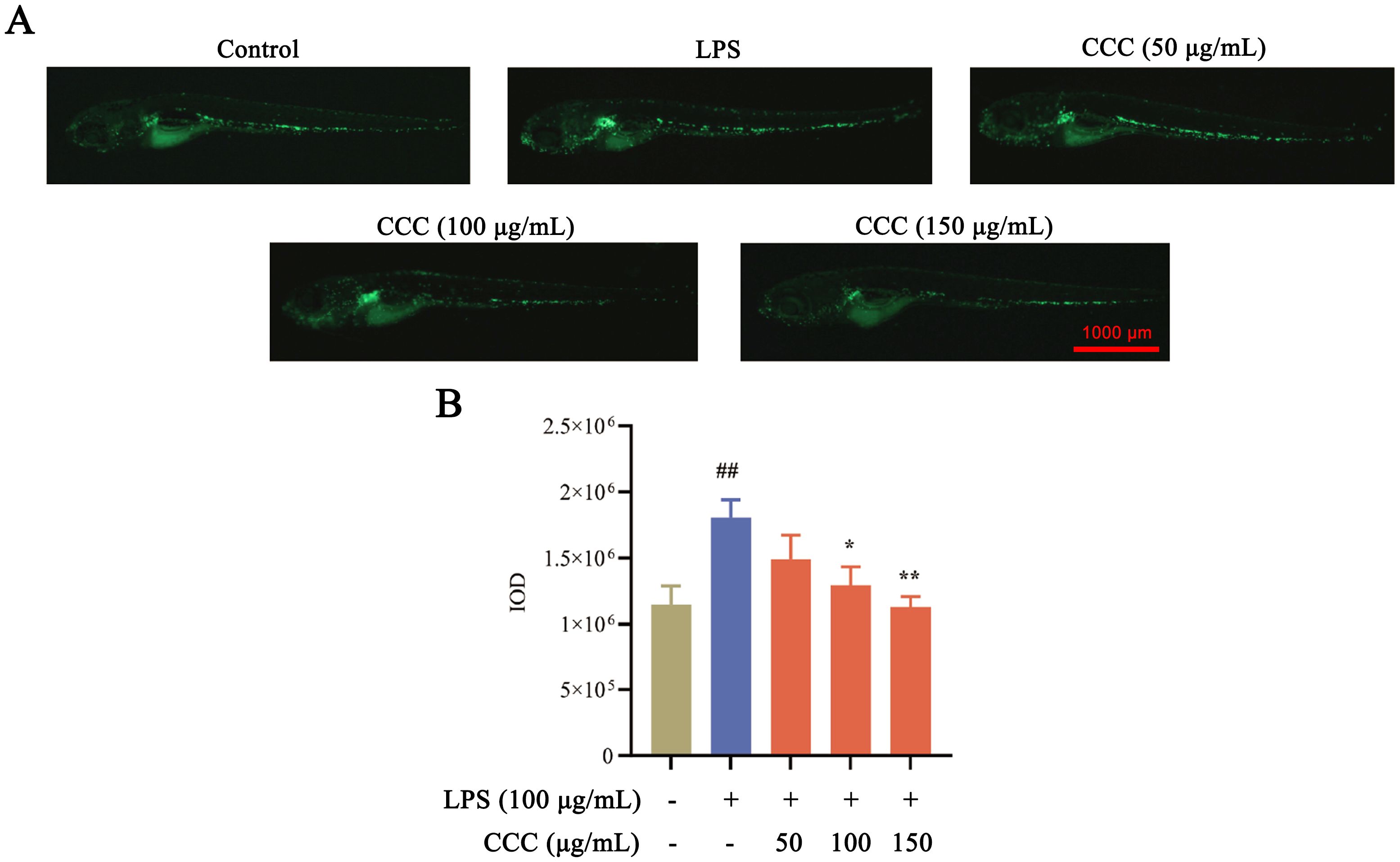
Figure 4. Effects of CCC and/or LPS on macrophage activity. (A) Representative macrophage fluorescence images. (B) Histogram of fluorescence IOD values. # vs. control: ## P < 0.01; * vs. LPS model: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
3.5 CCC reduces LPS-induced inflammatory factor expression
Inflammatory factors are important causes of bone injury as they can induce apoptosis and pyroptosis (Li et al., 2022). ELISA analysis showed that exposure to LPS significantly elevated the levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and nitric oxide (NO) compared with the controls (P < 0.01; Figure 5). CCC treatment effectively suppressed these inflammatory markers, with the most significant inhibition observed in NO levels (P < 0.01). The results indicated that CCC could inhibit LPS-induced inflammatory response by reducing the expression of the above inflammatory factors.
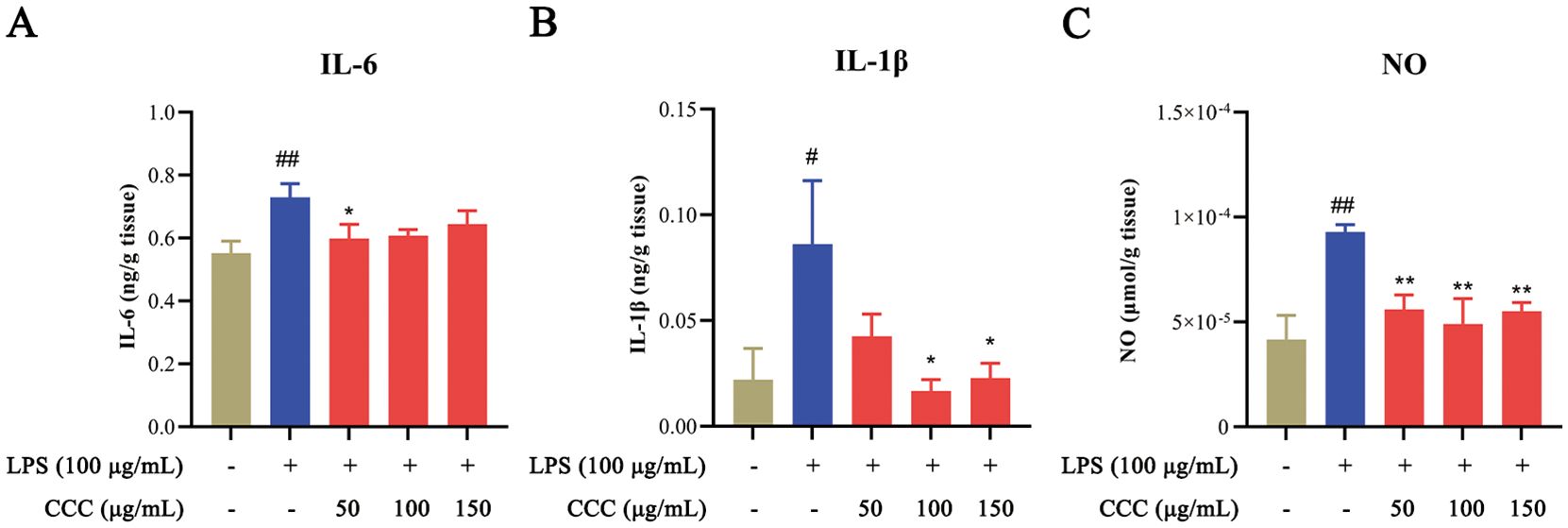
Figure 5. Effects of CCC and/or LPS on inflammatory factors. (A) IL-6 levels. (B) IL-1β levels. (C) NO levels. # vs. control: # P < 0.05 and ## P < 0.01; * vs. LPS model: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
3.6 CCC regulates bone-related gene expression
COL2α1 and Sox9a play central roles in bone development, homeostasis, and repair, with their synergistic regulation being crucial for maintaining bone structure and function (Deng et al., 2016; Song and Park, 2020). qRT-PCR analysis (Figure 6) demonstrated that exposure to LPS significantly downregulated COL2α1 and Sox9a mRNA levels compared with the controls (P < 0.01). CCC treatment restored the expression of these critical bone development genes to near normal levels (P < 0.01 vs. LPS model). The results thus demonstrated that CCC could promote bone development.
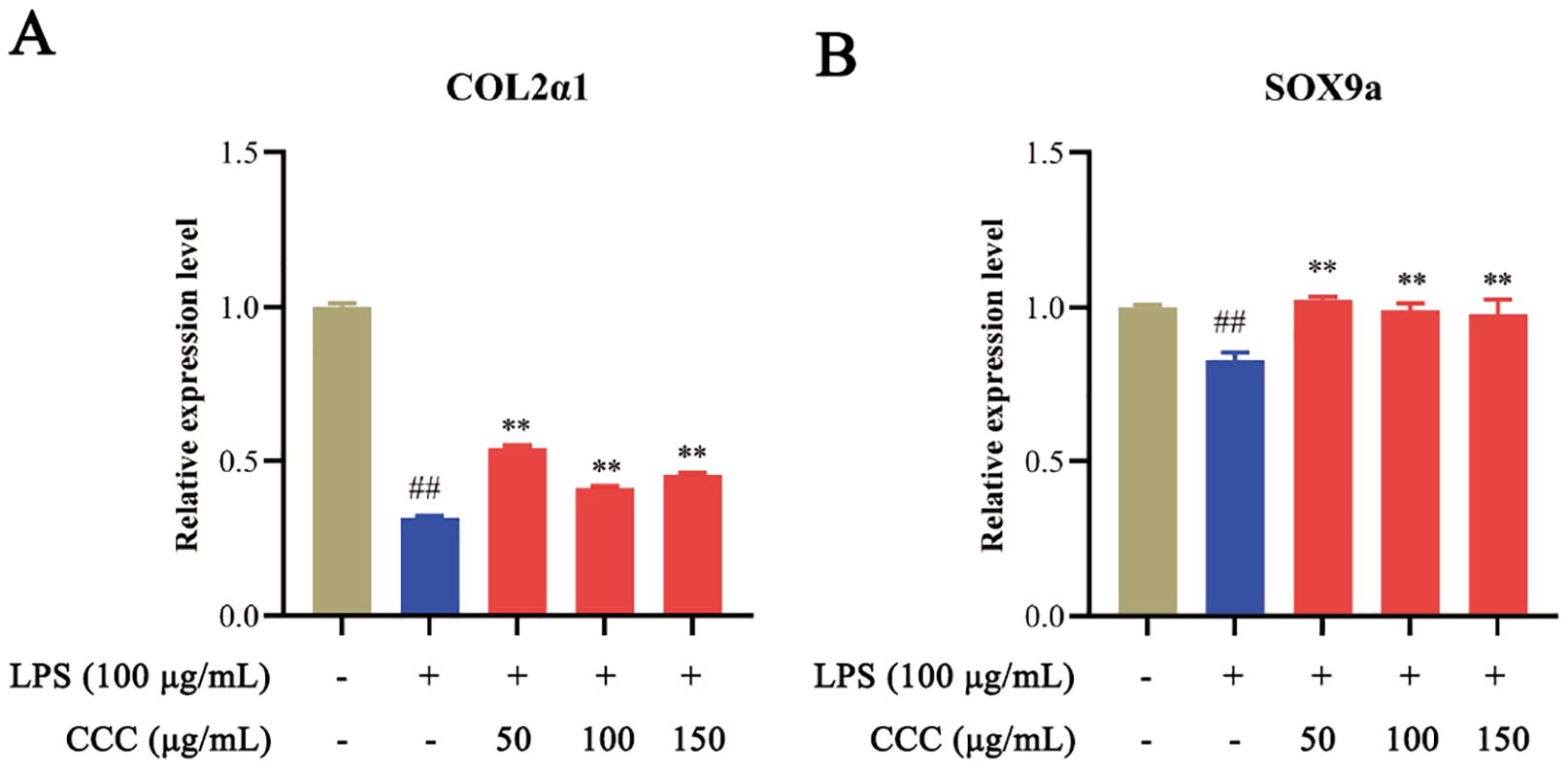
Figure 6. Effects of CCC and/or LPS on the expression of COL2α1 and Sox9a. (A) COL2α1 mRNA levels. (B) Sox9a mRNA levels. # vs. control: ## P < 0.01; * vs. LPS model: **P < 0.01.
3.7 CCC inhibits the activation of the TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway
The TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway plays a critical role in bone homeostasis, and its excessive or sustained activation contributes to the development of inflammatory bone disease (Zhen et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2021; Hu et al., 2024). The qRT-PCR analysis (Figure 7) revealed that LPS treatment significantly elevated the levels of TGF-β and Smad3 compared to the control group (P < 0.01). Notably, CCC intervention effectively suppressed the expression of these TGF-β/Smad3 pathway markers, restoring their levels to near-normal values. These findings demonstrate that CCC attenuates the activation of the TGF-β/Smad3 signaling cascade by downregulating TGF-β and Smad3 expression.
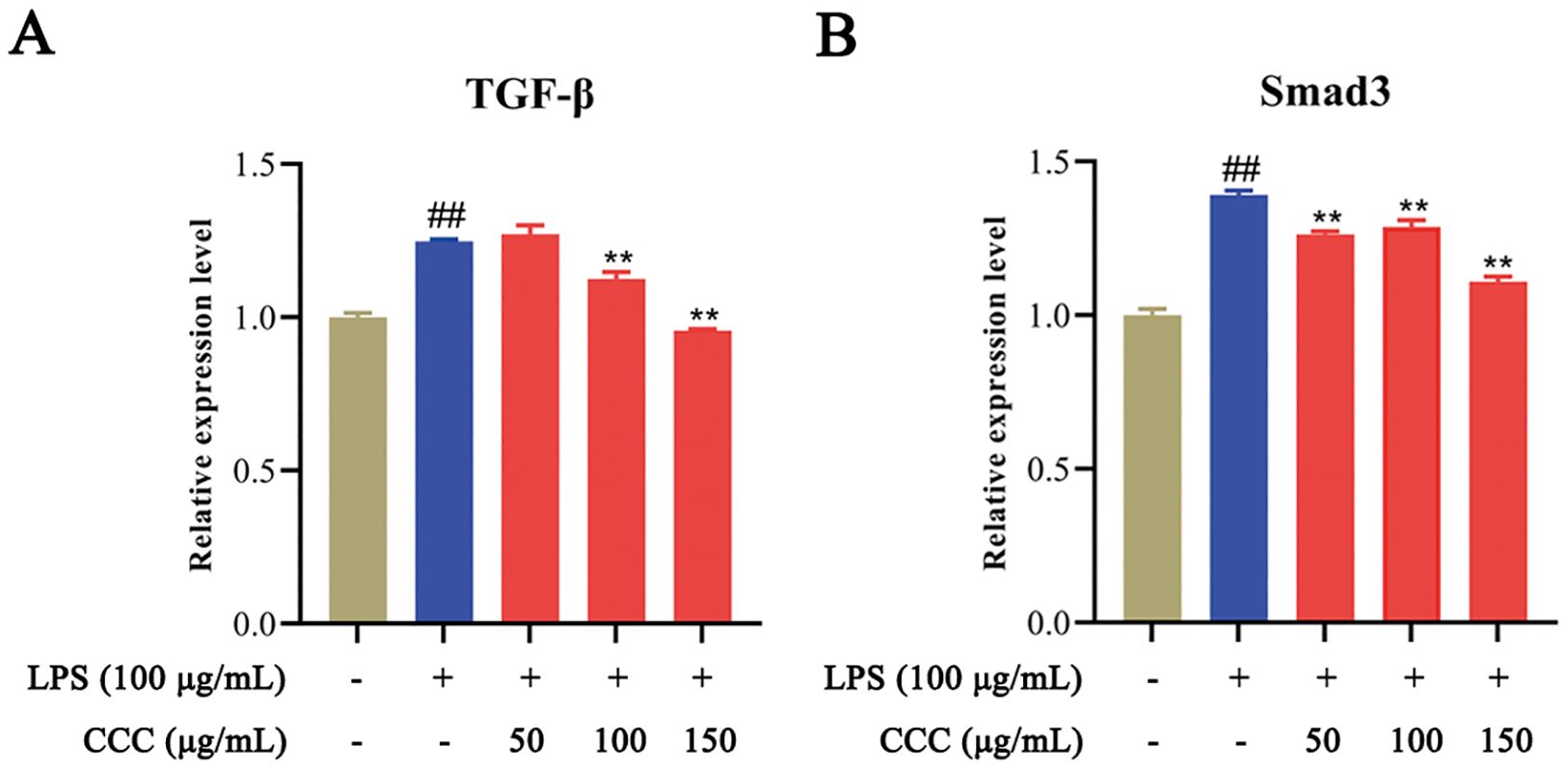
Figure 7. Effects of CCC and/or LPS on the expression of TGF-β and Smad3. (A) TGF-β mRNA levels. (B) Smad3 mRNA levels. # vs. control: ## P < 0.01; * vs. LPS model: **P < 0.01.
4 Discussion
This study investigated the therapeutic potential of CCC against LPS-induced skeletal injury in zebrafish, revealing its dual capacity to enhance bone regeneration and suppress macrophage-mediated inflammatory cascades. These findings expand the pharmacological profile of CCC and provide novel insights for alleviating piscine skeletal disorders.
Deer antler has traditionally been recognized for its kidney-tonifying and bone-strengthening properties. Ren et al. demonstrated that aqueous antler extracts promoted the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic differentiation through activation of the BMP-2/Smad1,5/Runx2 pathway, effectively counteracting ovariectomy-induced bone loss (Ren et al., 2019). Antler extracts also accelerate fracture healing through activation of BMP2-Smad-mediated osteoblasts (Gu et al., 2025). In addition, Li et al. found that antler chloroform extracts inhibited the differentiation of RANKL- and M-CSF-stimulated osteoclasts and bone resorption (Li et al., 2007). While these studies highlight the osteogenic effects of deer antler extracts in mammals, their skeletal protective effects in fish remain underexplored. Our findings confirm CCC’s bone-protective action in aquatic models, effectively ameliorating LPS-induced cartilage dysplasia and suppressing bone mineralization.
Post-injury inflammatory responses activate monocytes to differentiate into mature macrophages, particularly pro-inflammatory M1 phenotypes that secrete inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases that degrade type II collagen and proteoglycans, thereby accelerating the degeneration of articular cartilage (Wu et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2022). LPS-induced M1 polarization further exacerbates inflammation through the generation of reactive oxygen species and excessive production of NO (Yan et al., 2023; Xue et al., 2024). Previous studies have reported that antler extracts inhibit the activation of LPS-triggered macrophages and suppress NO synthesis (Widyowati et al., 2020). Kuo et al. demonstrated the suppressive effects of antler extracts on TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells (Kuo et al., 2018), while Widyowati et al. further corroborated these findings, showing that the administration of oral antler extract reduced IL-1β levels and joint swelling in osteoarthritic rats (Widyowati et al., 2023). Consistent with these findings, our results showed that CCC treatment in Tg (mpeg1:EGFP) zebrafish suppressed LPS-induced macrophage activation downregulated the levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and NO.
Bone metabolic balance is regulated by multiple genes (Parolini, 2025). COL2α1, a gene encoding type II collagen, regulates both intramembranous and endochondral ossification, with mutations in this gene causing skeletal dysplasia due to abnormal collagen structure (Viakhireva et al., 2024). Runx2, like COL2α1, is an osteogenic marker that transcriptionally regulates osteocalcin (OCN) expression and critically mediates bone matrix mineralization (Hwang et al., 2023). Notably, Runx2 overexpression in chondrocytes accelerates post-traumatic osteoarthritis progression in adult mice (Catheline et al., 2019). Sox9a serves as a master transcriptional regulator for the osteoblast differentiation and extracellular matrix synthesis, and it is being essential for the COL2α1 expression (Bell et al., 1997). During normal skeletogenesis, Sox9a directly activates COL2α1 transcription by binding its enhancer, thereby facilitating the production of type II collagen (Bell et al., 1997). Conversely, Sox9a downregulation in osteoarthritis reduces COL2α1 synthesis, thereby accelerating cartilage degradation and bone loss (Carmon et al., 2023; Horváth et al., 2023). This destructive process is further amplified by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), particularly MMP-13 which selectively degrades COL2α1 under inflammatory conditions (Malemud, 2018; Phillips, 2021). Our study demonstrated CCC’s ability to reverse LPS-induced suppression of COL2α1 and Sox9a expression, confirming its protective role against skeletal injury. However, comprehensive evaluation of CCC’s impact on the entire bone cascade requires future investigation incorporating additional bone remodeling markers such as Runx2 (osteoblast differentiation), osteocalcin (mineralization), and MMPs (matrix degradation).
The TGF-β/Smad3 signaling pathway, implicated in diverse bone pathologies through dysregulated bone remodeling and inflammation. Clinical and mechanistic studies demonstrate that TGF-β1 is a top-ranked pathway in osteoarthritis polygenic risk scores (Nielsen et al., 2024), while TGF-β3 is upregulated in human osteoarthritis tissues (Du et al., 2023). Similarly, Smad3 polymorphisms are linked to osteoarthritis susceptibility (Yang et al., 2018), and its overexpression in articular cartilage exacerbates aberrant bone remodeling (Tardif et al., 2013). Persistent TGF-β/Smad3 activation disrupts cartilage-subchondral bone crosstalk, promoting osteoarthritis progression (Yi et al., 2020). Therapeutic strategies targeting this pathway, such as engineered extracellular vesicles (Jing et al., 2024), have shown promise. Notably, pilose antler peptides (PAP)—a natural compound similar to CCC in both origin and extraction methods—ameliorate liver fibrosis by suppressing TGF-β/Smad3 signaling (Chunhua and Hongyan, 2017). Our findings align with this mechanism, as CCC similarly inhibited TGF-β/Smad3 in LPS-induced bone remodeling dysfunction, suggesting shared bioactive properties. This supports CCC’s potential as a disease-modifying agent for inflammatory bone disease by restoring TGF-β/Smad3 homeostasis.
The zebrafish larval model provided significant advantages for this foundational mechanistic study, particularly its optical transparency and conserved skeletal pathways—notably, as a prominent model organism in aquaculture research (Dahm and Geisler, 2006; López Nadal et al., 2020; Wan-Mohtar et al., 2021; Truzzi et al., 2022; Kumar et al., 2023). However, we explicitly acknowledge the inherent limitations of findings derived from this early developmental stage for direct aquaculture translation. Consequently, the observed efficacy of Cervi Cornus Colla (CCC) in mitigating LPS-induced bone injury and inflammation necessitates validation in later life stages (e.g., juvenile/adult zebrafish) that better reflect the physiology of commercially harvested fish. Furthermore, extending these protective effects to economically vital species (e.g., tilapia, salmon) requires dedicated study, as species-specific physiological and husbandry parameters may influence efficacy and optimal dosing regimens. Collectively, our findings identify CCC as a promising therapeutic candidate for ameliorating bone injury in fish, supporting its potential for future development in sustainable aquaculture practices.
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrated that CCC could alleviated LPS-induced skeletal damage in zebrafish by enhancing bone regeneration via the TGF-β/Smad3 axis and suppressing macrophage-mediated inflammation, thus providing a potential therapeutic strategy for treating aquaculture-related bone disorders. While this study establishes the protective role of CCC against LPS-induced bone injury in zebrafish larvae, future research is essential to validate these effects in later developmental stages of zebrafish and in commercially important aquaculture species.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Shandong Academy of Sciences Zebrafish Screening Platform, and all procedures complied with Animal Management Regulations and the 3R principles (Ethics No. SWS20240407). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
FX: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Validation. LD: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation. CQ: Writing – review & editing, Project administration. YR: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. LK: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Writing – review & editing, Software. HD: Writing – review & editing, Software. QX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Formal Analysis. CW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. PW: Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the 20 New Universities Funding Project of Jinan (202228121 and 202333006), the State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine -Shandong Provincial Health Commission Joint Science & Technology Project (GZY-KJS-2023-027), the Shandong Province Technology Innovation Guidance Program (YDZX2024122), and the Shandong Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science & Technology Project (Z-2023123T, Q-2023201, and M-2023291T).
Acknowledgments
We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com.cn) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Author FX, CQ, YR, LK were employed by the company Shandong Hanfang Pharmaceutical Co. LTD.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1620056/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdelsalam M., Attia M. M., Marzouk M. S., Korany R. M. S., Elgendy M. Y., Soliman A. W., et al. (2024). Investigating dynamics, etiology, pathology, and therapeutic interventions of Caligus clemensi and Vibrio alginolyticus co-infection in farmed marine fish. Sci. Rep. 14, 20704. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70528-x
Bell D. M., Leung K. K., Wheatley S. C., Ng L. J., Zhou S., Ling K. W., et al. (1997). SOX9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat. Genet. 16, 174–178. doi: 10.1038/ng0697-174
Beriotto A. C., Vissio P. G., Gisbert E., Fernández I., Álvarez González C. A., Di Yorio M. P., et al. (2023). From zero to ossified: Larval skeletal ontogeny of the Neotropical Cichlid fish Cichlasoma dimerus. J. Morphol 284, e21641. doi: 10.1002/jmor.21641
Carmon I., Zecharyahu L., Elayyan J., Meka S. R. K., Reich E., Kandel L., et al. (2023). HU308 mitigates osteoarthritis by stimulating sox9-related networks of carbohydrate metabolism. J. Bone Miner Res. 38, 154–170. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4741
Catheline S. E., Hoak D., Chang M., Ketz J. P., Hilton M. J., Zuscik M. J., et al. (2019). Chondrocyte-specific RUNX2 overexpression accelerates post-traumatic osteoarthritis progression in adult mice. J. Bone Miner Res. 34, 1676–1689. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3737
Cavin J. M., Donahoe S. L., Frasca S. Jr., Innis C. J., Kinsel M. J., Kurobe T., et al. (2012). Myxobolus albi infection in cartilage of captive lumpfish (Cyclopterus lumpus). J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 24, 516–524. doi: 10.1177/1040638712440990
Chunhua M. and Hongyan L. (2017). Protective effect of pilose antler peptide on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 99, 648–654. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.024
Dahm R. and Geisler R. (2006). Learning from small fry: the zebrafish as a genetic model organism for aquaculture fish species. Mar. Biotechnol. 8, 329–345. doi: 10.1007/s10126-006-5139-0
Deng H., Huang X., and Yuan L. (2016). Molecular genetics of the COL2A1-related disorders. Mutat. Res/Rev Mutat. Res. 768, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2016.02.003
Deng Z., Chen F., Liu Y., Wang J., Lu W., Jiang W., et al. (2021). Losartan protects against osteoarthritis by repressing the TGF-β1 signaling pathway via upregulation of PPARγ. J. Orthopaedic Translation 29, 30–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.03.005
Du X., Cai L., Xie J., and Zhou X. (2023). The role of TGF-beta3 in cartilage development and osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 11, 2. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00239-4
Gu J. H., Chae M. Y., Choi J. J., Duc T. C., Son C. G., and Lee E. J. (2025). Deer antler velvet (Cervus elaphus sibiricus) promotes fracture healing via partial BMP2-Smad mediated osteoblast differentiation. J. Orthop Surg. Res. 20, 70. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05426-z
Hijikata Y., Kano T., and Xi L. (2009). Treatment for intractable anemia with the traditional Chinese medicines Hominis Placenta and Cervi Cornus Colla (deer antler glue). Int. J. Gen. Med. 2, 83–90. doi: 10.2147/ijgm.s5253
Horst F., Bodenstein E., Brand M., Hans S., Karsch L., Lessmann E., et al. (2024). Dose and dose rate dependence of the tissue sparing effect at ultra-high dose rate studied for proton and electron beams using the zebrafish embryo model. Radiother Oncol. 194. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110197
Horváth E., Sólyom Á., Székely J., Nagy E. E., and Popoviciu H. (2023). Inflammatory and metabolic signaling interfaces of the hypertrophic and senescent chondrocyte phenotypes associated with osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216468
Hu X., Jin M., Sun K., Zhang Z., Wu Z., Shi J., et al. (2024). Type II collagen scaffolds repair critical-sized osteochondral defects under induced conditions of osteoarthritis in rat knee joints via inhibiting TGF-β-Smad1/5/8 signaling pathway. Bioact Mater 35, 416–428. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.008
Hwang Y. J., Hwang H.-J., Go H., Park N., and Hwang K.-A. (2023). Sword bean (Canavalia gladiata) pods induce differentiation in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells by activating the BMP2/SMAD/RUNX2 pathway. Nutrients 15, 4372. doi: 10.3390/nu15204372
Jing Z., Zhang G., Cai Y., Liang J., Lv L., and Dang X. (2024). Engineered extracellular vesicle-delivered TGF-β inhibitor for attenuating osteoarthritis by targeting subchondral bone. J. Tissue Eng. 15, 20417314241257781. doi: 10.1177/20417314241257781
Kim J., Jeong H. S., Li H., Baek K. J., Kwon N. S., Yun H. Y., et al. (2013). Effects of Cervi cornus Colla (deer antler glue) in the reconstruction of a skin equivalent model. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 305, 85–89. doi: 10.1007/s00403-012-1283-8
Kim Y. A., Kim S. W., Lee M. H., Lee H. K., and Hwang I. H. (2021). Comparisons of chemical composition, flavor and bioactive substances between korean and imported velvet antler extracts. Food Sci. Anim. Resour 41, 386–401. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2021.e4
Kumar N., Marée R., Geurts P., and Muller M. (2023). Recent advances in bioimage analysis methods for detecting skeletal deformities in biomedical and aquaculture fish species. Biomolecules 13, 1797. doi: 10.3390/biom13121797
Kuo C. Y., Cheng Y. T., Ho S. T., Yu C. C., and Chen M. J. (2018). Comparison of anti-inflammatory effect and protein profile between the water extracts from Formosan sambar deer and red deer. J. Food Drug Anal. 26, 1275–1282. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2018.02.005
Li Y. J., Kim T. H., Kwak H. B., Lee Z. H., Lee S. Y., and Jhon G. J. (2007). Chloroform extract of deer antler inhibits osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. J. Ethnopharmacol 113, 191–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.04.020
Li M., Yin H., Yan Z., Li H., Wu J., Wang Y., et al. (2022). The immune microenvironment in cartilage injury and repair. Acta Biomater 140, 23–42. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.12.006
Li B., Zhang Y. W., Liu X., Ma L., and Yang J. X. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of intermuscular bone development in fish: a review. Zool Res. 42, 362–376. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2021.044
López Nadal A., Ikeda-Ohtsubo W., Sipkema D., Peggs D., McGurk C., Forlenza M., et al. (2020). Feed, microbiota, and gut immunity: using the zebrafish model to understand fish health. Front. Immunol. Volume 11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00114
Nielsen R. L., Monfeuga T., Kitchen R. R., Egerod L., Leal L. G., Schreyer A. T. H., et al. (2024). Data-driven identification of predictive risk biomarkers for subgroups of osteoarthritis using interpretable machine learning. Nat. Commun. 15, 2817. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46663-4
Ouyang T., Yin H., Yang J., Liu Y., and Ma S. (2022). Tissue regeneration effect of betulin via inhibition of ROS/MAPKs/NF-ĸB axis using zebrafish model. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy 153, 113420. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113420
Parolini C. (2025). Pathophysiology of bone remodelling cycle: Role of immune system and lipids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 235, 116844. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116844
Phillips R. (2021). Targeting articular mmp13 in OA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol 17, 645. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00696-x
Rees J. M., Sleight V. A., Clark S. J., Nakamura T., and Gillis J. A. (2023). Ectodermal Wnt signaling, cell fate determination, and polarity of the skate gill arch skeleton. Elife 12. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79964
Ren C., Gong W., Li F., and Xie M. (2019). Pilose antler aqueous extract promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by stimulating the BMP-2/Smad1, 5/Runx2 signaling pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 17, 756–767. doi: 10.1016/s1875-5364(19)30092-5
Song H. and Park K. H. (2020). Regulation and function of SOX9 during cartilage development and regeneration. Semin. Cancer Biol. 67, 12–23. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.04.008
Stundl J., Pospisilova A., Jandzik D., Fabian P., Dobiasova B., Minarik M., et al. (2019). Bichir external gills arise via heterochronic shift that accelerates hyoid arch development. Elife 8. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43531
Sun Z., Liu Q., Lv Z., Li J., Xu X., Sun H., et al. (2022). Targeting macrophagic SHP2 for ameliorating osteoarthritis via TLR signaling. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 12, 3073–3084. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.02.010
Tardif G., Pelletier J.-P., Fahmi H., Hum D., Zhang Y., Kapoor M., et al. (2013). NFAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD3 regulate the expression of miR-140 in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 15, R197. doi: 10.1186/ar4387
Truzzi C., Girolametti F., Giovannini L., Olivotto I., Zarantoniello M., Scarponi G., et al. (2022). New eco-sustainable feed in aquaculture: influence of insect-based diets on the content of potentially toxic elements in the experimental model zebrafish (Danio rerio). Molecules 27, 818. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030818
Viakhireva I., Bychkov I., Markova T., Shatokhina O., Karandasheva K., Udalova V., et al. (2024). The molecular complexity of COL2A1 splicing variants and their significance in phenotype severity. Bone 181, 117013. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117013
Wang C. L., Li P., Liu B., Ma Y. Q., Feng J. X., Xu Y. N., et al. (2024). Decrypting the skeletal toxicity of vertebrates caused by environmental pollutants from an evolutionary perspective: From fish to mammals. Environ. Res. 255, 119173. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119173
Wang P., Shi B., Gao Z. H., Sun T. F., Yang W. B., Han S. F., et al. (2016). Effect of colla cornus cervi combined with LV-Mediated BMP7 transfected BMSCs on ANFH in rats. Acta Pol. Pharm. 73, 1521–1530.
Wang P., Sun T. F., Li G., Zhang H. M., Liu F. J., Gao Z. H., et al. (2020). The separation of antler polypeptide and its effects on the proliferation and osteogenetic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020, 1294151. doi: 10.1155/2020/1294151
Wan-Mohtar W.A.A.Q.I., Ilham Z., Jamaludin A. A., and Rowan N. (2021). Use of zebrafish embryo assay to evaluate toxicity and safety of bioreactor-grown exopolysaccharides and endopolysaccharides from european ganoderma applanatum mycelium for future aquaculture applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 1675. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041675
Widyowati R., Suciati S., Hariyadi D. M., Chang H. I., Ipg Suryawan N., Tarigan N., et al. (2023). The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-Iβ alteration by deer (Rusa unicolor) antler extract on osteoarthritis rat model. Saudi Pharm. J. 31, 1109–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.03.022
Widyowati R., Suciati S., Haryadi D. M., Chang H. I., Suryawan I. N., and Utama A. W. (2020). The effect of rusa unicolor antler deer extracts from east kalimantan in bone turnover cell models. Turk J. Pharm. Sci. 17, 440–445. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2019.57805
Wu C. L., Harasymowicz N. S., Klimak M. A., Collins K. H., and Guilak F. (2020). The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 28, 544–554. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2019.12.007
Xue C., Tian J., Cui Z., Liu Y., Sun D., Xiong M., et al. (2024). Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated M1 macrophage-dependent nanomedicine remodels inflammatory microenvironment for osteoarthritis recession. Bioact Mater 33, 545–561. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.10.032
Yan Y., Lu A., Dou Y., Zhang Z., Wang X. Y., Zhai L., et al. (2023). Nanomedicines reprogram synovial macrophages by scavenging nitric oxide and silencing CA9 in progressive osteoarthritis. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10, e2207490. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207490
Yang H. Y., Hu W. H., Jiang T., and Zhao H. (2018). SMAD3 gene rs12901499 polymorphism increased the risk of osteoarthritis. Biosci. Rep. 38. doi: 10.1042/bsr20180380
Yi X., Wu L., Liu J., Qin Y. X., Li B., and Zhou Q. (2020). Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound protects subchondral bone in rabbit temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by suppressing TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. J. Orthop Res. 38, 2505–2512. doi: 10.1002/jor.24628
Zhang X., Cai Q., Liu H., Heng B. C., Peng H., Song Y., et al. (2012). Osteoconductive effectiveness of bone graft derived from antler cancellous bone: an experimental study in the rabbit mandible defect model. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 41, 1330–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.05.014
Keywords: aquaculture, Cervi Cornus Colla, zebrafish, bone, immunity
Citation: Xu F, Dong L, Qin C, Ren Y, Kong L, Zhang M, Du H, Xia Q, Wang C and Wang P (2025) Therapeutic potential of Cervi Cornus Colla in zebrafish bone injury: implications for aquaculture. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1620056. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1620056
Received: 29 April 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 22 August 2025.
Edited by:
Seyyed Morteza Hoseini, Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute (IFSRI), IranReviewed by:
Doaa M. Mokhtar, Assiut University, EgyptYa-Ting Chen, National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology, Taiwan
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Dong, Qin, Ren, Kong, Zhang, Du, Xia, Wang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cheng Wang, MTgzMDYzOTAyNzVAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Ping Wang, d2FuZ3BpbmdqaW5hbkAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Fengxia Xu1†
Fengxia Xu1† Limin Dong
Limin Dong Haitao Du
Haitao Du Qing Xia
Qing Xia Cheng Wang
Cheng Wang Ping Wang
Ping Wang