- 1School of Ocean and Civil Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Operations and Supply Chain Management, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom
- 3State Key Laboratory of Ocean Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Inland waterway transport (IWT) plays a critical role in global logistics, offering large-capacity, long-distance transport at a lower cost. Recently, the advent of autonomous ships has promised to revolutionize efficiency and sustainability within the shipping industry. While existing research predominantly targets maritime settings, the distinct challenges of inland waterways such as fluctuating water depths, varying river currents, and confined channels demand tailored technological solutions. This study provides a thorough bibliometric analysis of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport, based on 163 publications from the Web of Science (WoS) core collection. This study identifies key technological milestones in this field and highlights the research gaps of adapting maritime autonomous ship technologies to inland waterways. The pressing need for customized solutions is also discussed. By reviewing the current landscape, this study contributes to the field as a beneficial reference for researchers, industry professionals, and policymakers, promoting the development of autonomous ship technology in inland waterways.
1 Introduction
Waterway transport, characterized by its large capacity, long distance and low cost, plays a pivotal role in the global transportation sector (Homburger et al., 2025; Li et al., 2022; Yuan et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2021a). Globally, the development level of inland waterway shipping reflects a country or region’s transport infrastructure and economic strength. For example, as of the end of 2023, China’s inland waterways had a navigable length of 128,200 kilometers. According to the China Statistical Yearbook 2024, the inland waterway freight transport turnover reached 2.07 trillion ton-kilometers in 2023, representing 8.96% of China’s total freight transport turnover. This significant development in inland shipping reduces logistics costs, promotes regional economic flow, and generates substantial economic benefits.
Nowadays, the concept of intelligence is increasingly being extended to the shipping sector. The vigorous development of autonomous shipping, particularly autonomous ships, has become a global consensus in the shipping industry (Pei et al., 2024). Although definitions of autonomous ships vary, they are generally understood as an advanced evolution of existing ship subsystems, culminating in autonomous vessels (Dijk et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2024a; van Cappelle et al., 2018). Autonomous ships can be categorized based on their level of autonomy, with the ultimate goal of achieving fully autonomous ships that operate without human intervention (Masoudi, 2019; Ranjan et al., 2025; Söffker et al., 2025). Currently, however, only certain aspects of ship intelligence have been realized, and full autonomy remains a future aspiration.
Autonomous ship technology is built upon four interconnected domains: 1) navigation, 2) guidance, 3) physical ship architecture, and 4) control systems, which collectively form the backbone of intelligent maritime applications (Alamoush and Ölçer, 2025; Dijk et al., 2018; Martelli et al., 2021; van Cappelle et al., 2018). The seamless integration of these advanced technologies enhances operational efficiency, ensures safety, and advances the autonomy of modern vessels (Shang et al., 2024).
Navigation technology relies on a variety of sensors, such as radar, LIDAR, Automatic Identification System (AIS), probes, and cameras, to gather environmental data while ships are at sea. These sensors are integral to constructing intelligent algorithms that enhance navigational accuracy and safety (Wang et al., 2024b), as they enable precise representation of both internal and external environmental conditions through advanced perception algorithms (von Brandis et al., 2025). Wang et al. (2022b) proposed a perception model to effectively address the challenges posed by the uncertainty in ship position prediction. Zhou et al. (2021b) enhanced the YOLOv5 algorithm to improve the detection and recognition of various ship types. Sonntag et al. (2025) proposes a COLREGs-compliant reinforcement learning approach for USV autonomous navigation and obstacle avoidance in a custom simulation environment. To enable fast and accurate environmental perception in adverse weather conditions, researchers have developed hybrid attention module (Zheng et al., 2025), edge reparameterization- and attention-guided neural network (Liu et al., 2024b), convolutional neural network algorithms (Guo et al., 2023), AECR-Net (Wu et al., 2021), Radar Polarization Selection and Recognition (Korban et al., 2024) and other methods to mitigate the impact of haze and other factors.
By leveraging innovations such as state-of-the-art navigation systems, guidance systems, and automated control mechanisms, autonomous ships can optimize their routes, reduce fuel consumption, and significantly lower the likelihood of accidents. In the quest to mitigate the risk of maritime collisions, machine learning (ML) has proven instrumental, offering robust solutions for autonomous navigation systems (Lazarowska, 2024). Some researchers have developed a fuzzy collision risk indicator and a fuzzy collision avoidance acting timing indicator (Chen et al., 2021b), while others have proposed T-minute prediction algorithms based on the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), Lee and Woo (2022) proposed a reactive collision avoidance algorithm that locally adjusts the trajectory while preserving the current path. Sun et al. (2022) developed a self-organizing cooperative pursuit strategy for dynamic targets, enabling pursuit USV clusters to effectively capture intelligent evaders while maintaining strong obstacle avoidance ability and flexibility. Nguyen et al. (2023) and Hagen et al. (2023) proposed fuzzy logic and formulas expressed as mathematical expressions respectively for the verification of the collision algorithm.
The intelligence of autonomous ships also extends to the design of their hulls. Given that the hull is the largest component of a vessel, optimizing its form has become a significant focus (Coppede et al., 2018; Tadros et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2024). Subdivision surface and free-form deformation techniques, as well as hydrodynamic theory and simulation-based design (SBD) technologies, are currently employed to optimize hull designs (Coppede et al., 2018; Zhu et al., 2024). In terms of propulsion and power systems, research by Koschorrek et al. (2022) proposed an optimization-based thrust allocation strategy to control an over-actuated propulsion system consisting of four cycloidal propeller. Altosole et al. (2021) proposed an innovative hybrid turbocharger producing electric power to achieve flexible and efficient power management. Ghazali et al. (2024) comprehensively analyzed the historical, current, and future aspects of USV hull design, explored its applicable scenarios and constraints, examined key design parameters, and forecasted development trends. Chen et al. (2023) has changed the traditional distributed architecture, proposing a domain controller-based electronic and electrical architecture (EEA) for inland remote control ships, achieving the information interaction requirements of the ship. Wang et al. (2024a) designed a wave - adaptive unmanned quadramaran with an independent suspension mechanism, which boasts excellent stability and safety, significantly facilitating maritime search and rescue operations.
Although interest in autonomous ships is growing, existing technological and academic efforts have largely centered on maritime environments. In contrast, inland waterway applications have received comparatively less attention. And the significant differences between inland waterways and maritime environments, such as variations in flow rates, depth fluctuations, and channel widths, imply that autonomous ship technologies developed for marine environments may not be directly applicable to inland waterways (Donandt et al., 2022). This has created both the opportunity and the necessity for a focused review that synthesizes current inland-related developments and identifies critical research gaps. However, the research on technologies specifically tailored to inland waterway conditions remains fragmented, lacking systematic synthesis of research trends, knowledge structures, and collaborative networks specific to inland waterway autonomy. This absence of a systematic literature mapping hampers the identification of emerging trends, research gaps, and potential interdisciplinary collaboration. It’s difficult for new researchers to quickly understand the disciplinary landscape or identify influential research teams for the lack of a comprehensive mapping of the field’s knowledge structure and key contributors. Similarly, the lack of collaboration network analysis hinders scholars from evaluating whether invisible barriers or regional silos constrain cross-institutional cooperation, or whether academic research is aligned with ongoing policy developments. Moreover, without a quantitative examination of the field’s historical evolution and thematic shifts, it is challenging to identify long-term, macro-level trends or anticipate potential breakthrough points. Hence, a bibliometric analysis is necessary to clarify the current state of research, highlight scholarly contributions, and provide strategic insights for future development.
Therefore, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the literature on autonomous ships in inland waterway transport, emphasizing the unique technological advancements and challenges in this field. By examining key trends, persistent challenges, and emerging opportunities, this paper seeks to shed light on the potential of autonomous ships to revolutionize inland waterway transport. Through synthesizing current works, this study offers a macro-level perspective on the development and application of autonomous ship technologies tailored to the specific demands of inland waterway transport, thereby bridging the research gap.
This paper contributes to the existing literature in three key ways:
1. This paper fills the gaps in quantitative analysis of the literature on autonomous ships for inland waterway transport, providing a comprehensive overview of the field.
2. It examines the technology application and development of autonomous ships in inland waterway, offering a holistic understanding of the state of the art in this domain.
3. It identifies key trends and technological evolution paths, highlighting current research hotspots and potential future directions in the field.
The structure of this paper is outlined as follows. Section 2 details the methodologies employed in the current research. Section 3 presents the findings, including both bibliometric and comparative analyses. Section 4 offers an in-depth discussion of the results. Section 5 concludes the paper with a summary of the key insights and contributions.
2 Methodology
The framework of this paper is illustrated in Figure 1, and the subsequent sections are organized in accordance with this structure.
This methodology section delineates the bibliometric methodology adopted to systematically map the intellectual structure of autonomous ship technologies in inland waterways. By integrating quantitative analysis of publication trends, collaboration networks, and keyword evolution, this paper aims to address the fragmentation in existing literature identified in Section 1. The methodology comprises three components: (1) a research framework of the current study; (2) the selection rationale for analytical tools; and (3) data collection and refinement protocols ensuring domain relevance.
2.1 Research framework
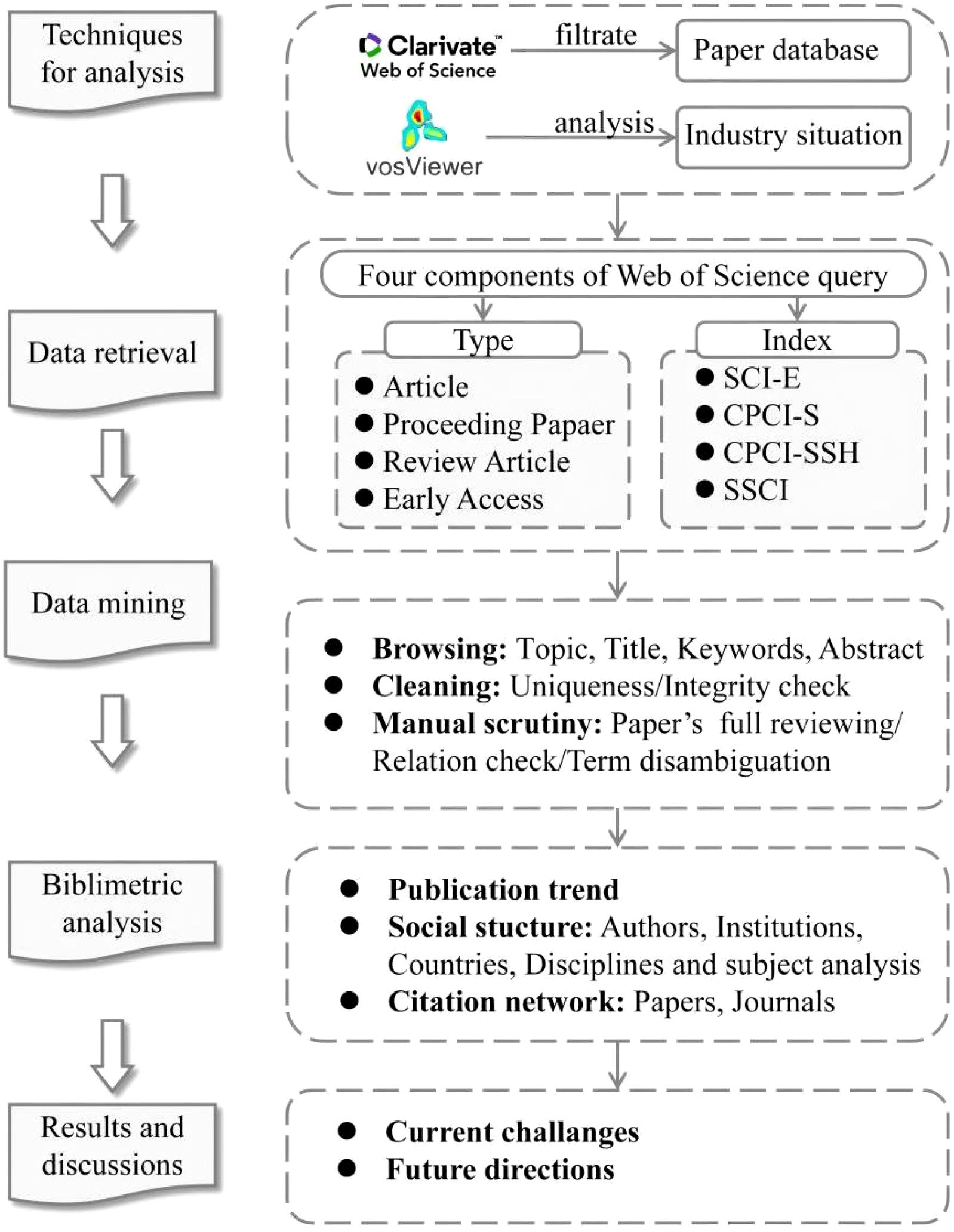
This study employs a bibliometric analysis approach to systematically explore the development of autonomous ship technologies in inland waterway transport. By analyzing articles from the Web of Science Core Collection database, including publication trends, co-authorship patterns, and keyword co-occurrence, this research aims to identify emerging themes for future exploration.
Figure 2 illustrates a structured research framework for analyzing the development of autonomous ship technologies in inland waterway transport through bibliometric analysis. The process begins with data retrieval from the Web of Science Core Collection database, focusing on various document types such as articles, proceeding papers, review articles, and early access papers, across different indexes like SCI-E, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, and SSCI. Following data retrieval, data mining involves browsing through topics, titles, keywords, and abstracts, cleaning data for uniqueness and integrity, and conducting manual scrutiny for a comprehensive review and term disambiguation. The subsequent bibliometric analysis examines publication trends, social structures including authors, institutions, countries, disciplines, and subject analysis, and citation networks involving papers and journals. The final step synthesizes the findings into results and discussions, highlighting current challenges and suggesting future directions for research in the field.
2.2 Analysis tool
Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative research method that utilizes statistical techniques to map the evolution, collaboration patterns, and knowledge structures within a scientific field. By analyzing publication metadata (e.g., authors, citations, keywords), it enables objective identification of research trends, disciplinary intersections, and emerging frontiers, overcoming the subjective limitations of traditional narrative reviews (Donthu et al., 2021; Zupic and Čater, 2015). In general, bibliometric analysis encompassed the examination of spatial and temporal dynamics, disciplinary and journal landscapes, institutional contributions, authorship profiles, citation patterns, and keyword.
This study utilizes VOSviewer to conduct bibliometric analyses of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport. VOSviewer is a freely available computer software for bibliometric mapping, first presented in 2009 (van Eck and Waltman, 2010). Scholars across various disciplines, including business economics (Jumansyah et al., 2023; MaChado et al., 2022; Nath and Chowdhury, 2021), physiology (Deng et al., 2023; Hong et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2020), geography (Chang et al., 2022; Meng et al., 2020; Petrovic and Thomas, 2024) and engineering (Song et al., 2024; Sulistiawati et al., 2023; Wang and Kim, 2023; Xiong et al., 2024), have widely adopted VOSviewer to construct and visualize bibliometric maps. Based on VOSviewer, bibliometric data can be swiftly synthesized to assess and forecast the evolution of a research field, offering a more efficient approach compared to traditional review analysis (Chen et al., 2021a; Zacarias and Sant'Ana, 2024).
2.3 Bibliometric data
The data for this study were extracted from the Web of Science (WoS) Core Collection, a widely recognized and comprehensive database encompassing peer-reviewed journals, conference proceedings, books, and other scholarly publications across various academic disciplines.
While multiple databases are available, like Scopus and CNKI, this study deliberately focused on the Web of Science Core Collection due to its standardized data format, compatibility with bibliometric software, and its long-standing adoption in bibliometric research, especially within the engineering and technology domains. The inclusion of high-quality peer-reviewed journals ensures analytical rigor and enables reliable trend analysis. Although this choice may omit some region-specific literature, it provides a robust foundation for the current investigation and aligns with prevailing methodological practices in the field.
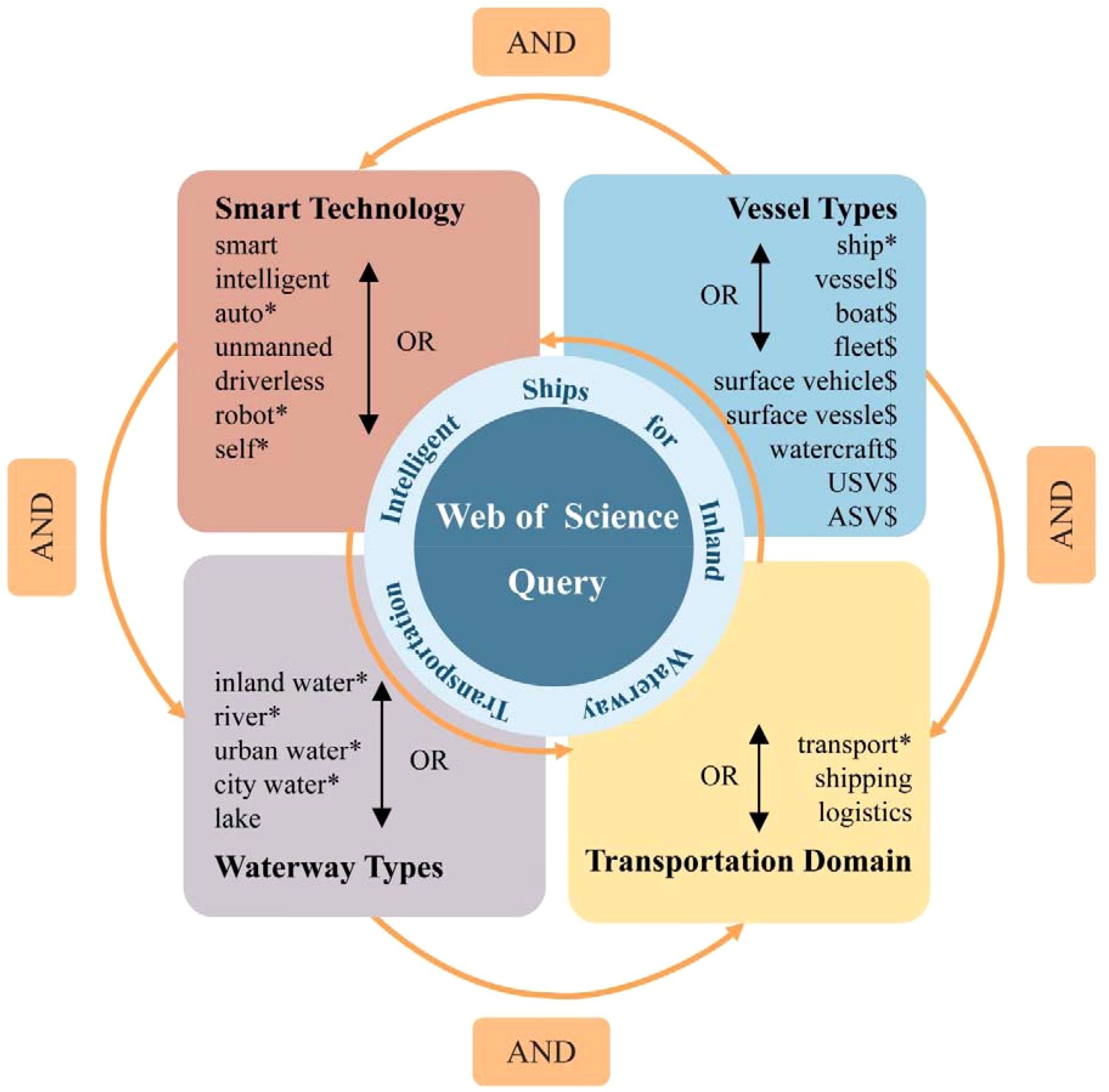
The search query was designed to capture a broad spectrum of relevant studies on autonomous ship technologies in inland waterway transport. As shown in Figure 3, the search query consisted of four key components.
1. Smart Technology: TS = (smart OR intelligent OR auto* OR unmanned OR driverless OR robot* OR self*).
2. Vessel Types: TS = (ship* OR vessel$ OR surface vehicle$ OR surface vessel$ OR boat$ OR fleet$ OR watercraft$ OR USV$ OR ASV$).
3. Waterway Types: TS = (inland water* OR river* OR urban water* OR city water* OR lake).
4. Transportation Domain: TS = (transport* OR shipping OR logistics).
This search strategy incorporated synonyms and variations of terms related to autonomous ships, their operational environments, and their role within transportation systems, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the relevant literature.
Upon conducting the search, 851 publications were initially retrieved (accessed on 12 November 2024). A preliminary screening of titles, abstracts, and keywords resulted in the identification of 191 articles deemed relevant to the focus of the current study. Subsequently, a more detailed review of the full texts allowed for further refinement of the dataset, ultimately selecting 163 articles that most directly addressed the integration and application of autonomous ship technologies in inland waterway transport.
The multi-step selection process, combining broad search terms with a careful review of content relevance, ensured that the final dataset was both comprehensive and focused, providing a solid foundation for the bibliometric analysis.
3 Results
The analysis of publication trends, social structures, citation networks, and keyword distributions is crucial for understanding the evolution and impact of research in the field of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport. By examining these aspects, this article can identify key areas of interest, influential works, and the collaborative landscape that shapes the direction of future research. It provides insights into the interdisciplinary nature of the field, the influence of various institutions and countries, and the emerging trends that are driving innovation. Additionally, it situates the research within global technological and environmental priorities, underscoring the relevance of autonomous ships in sustainable transportation. This section provides a comprehensive overview of these aspects, focusing on technical metrics and underlying reasons for observed changes.
3.1 Publication trend
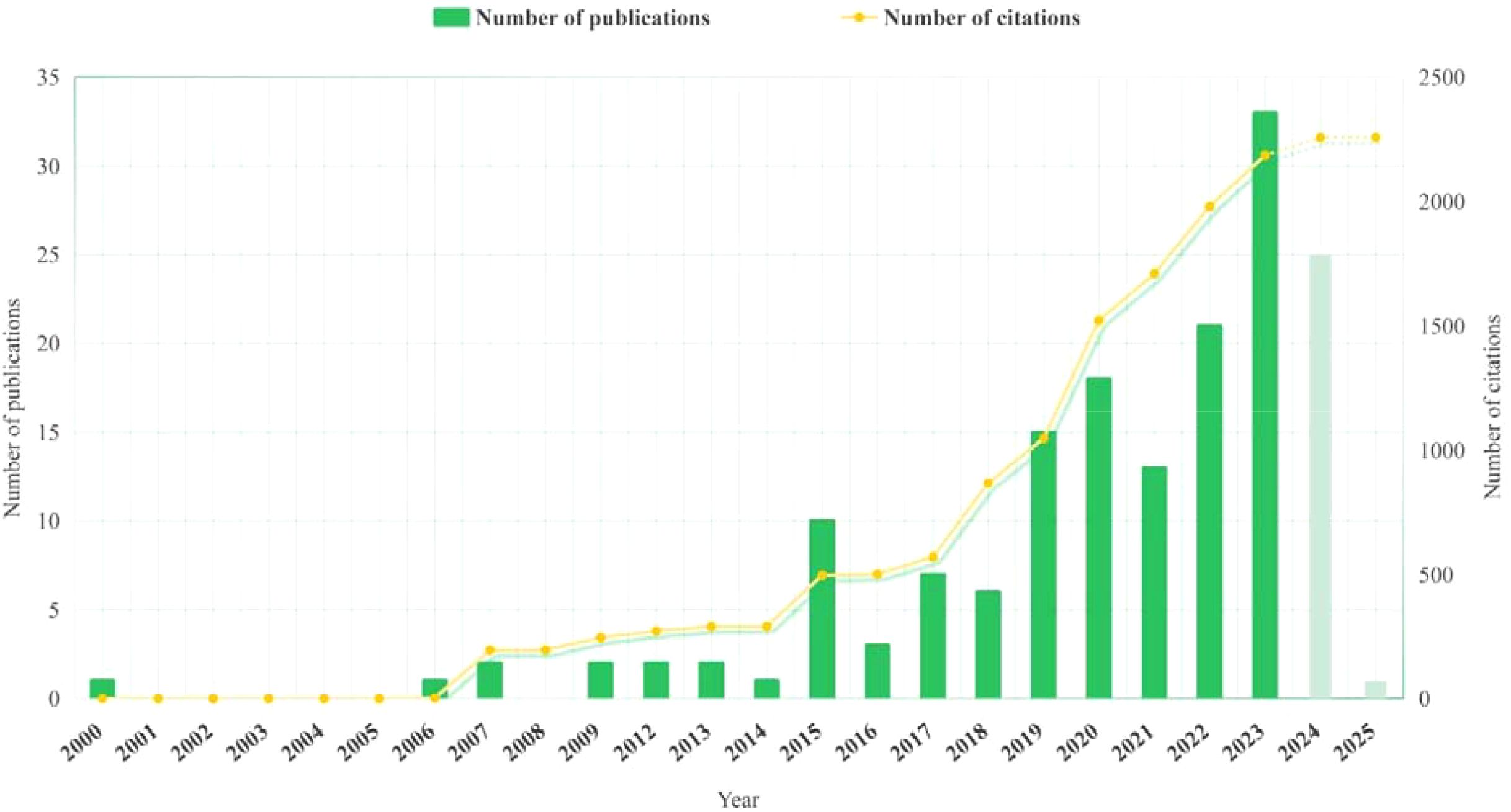
Figure 4 presents the publication trend and the corresponding citation trend for research on autonomous ship technologies in inland waterway transport from 2000 to 2025. Since the data were obtained as of November 12, 2024, the data for 2024 and 2025 are incomplete; hence, they are filled with green diagonal stripes; data for other years are filled with solid green. As shown in Figure 4, there is a growing trend in the research of autonomous ships within inland waterways. However, before 2015, only a few studies were found, with a significant increase commencing around 2015. Therefore, the whole publication trend can be divided into three phases, each characterized by underlying technological and policy-driven shifts:
1. Initial Phase (2000-2014): Both the number of publications and citations remained consistently low, with few articles being published annually. This nascent stage in the field was likely due to the slow and outdated pace of technological advancement, resulting in limited scholarly attention. For example, the limited maturity of key enabling technologies such as onboard sensing, autonomous control algorithms, and inland digital infrastructure, can result to the lack of academic momentum. At the same time, research in intelligent maritime navigation was predominantly focused on ocean-going vessels, and the specificity of inland waterway constraints—such as narrow channels, fluctuating depths, and high-density traffic—was largely overlooked. This technological and application gap resulted in minimal scholarly activity. What cannot be overlooked is that, during this stage, policies specifically related to autonomous inland ships were scarce, and the field was not prioritized as a national development focus.
2. Growing Phase (2015-2018): Interest in the field began to grow, with more than 6 articles published per year. A proliferation of studies focused on collision avoidance and trajectory prediction. Notably, 2015 marked a significant turning point, with the number of relevant publications increasing dramatically from 1 in 2014 to 10 in 2015. However, the number of publications fell back in 2016-2018, although it still maintained a moderate level. Similarly, the number of citations increased during this period, albeit at a faster pace than in the initial phase. Chinese researchers emerged as predominant contributors, with a particular focus on ship collision avoidance. The boom can be attributed to the “Made in China 2025” initiative launched by the State Council of China and the first “Smart Ship Code” launched by the China Classification Society (CCS) in 2015. Driven by national policies, an increasing number of scholars have devoted themselves to related fields for research, which has greatly promoted the publication of papers.
3. Rapid developing Phase (2019-now): Benefiting from the policy incentives and the accumulation of technological and data foundations in the previous phase, the development in this stage accelerated significantly. There was a dramatic surge in the number of publications, with annual outputs exceeding 30 articles by 2023. The average annual publications reached over 20 documents. In terms of citations, the number gradually climbed from 1,048 in 2019 to 2,258 in 2024. This indicates a growing scholarly interest in the field, with the scope of research expanding beyond ship collision avoidance to encompass areas such as AIS, control model development, and other related aspects. National-level support provided institutional momentum for research, while the technological groundwork laid in earlier phases facilitated more advanced and diversified research directions during this stage.
These trends indicate that the field of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport has evolved from a niche area of interest to a highly active domain with substantial academic and practical implications. Its expansion aligns with global trends in automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and sustainable transportation, reflecting its relevance to broader technological and environmental priorities. In the forthcoming period, substantial progress is anticipated in the domains of artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics, which are poised to significantly enhance the navigation, monitoring, and management systems of ships. Notably, these advancements are expected to be particularly transformative for inland waterway transport, where constrained waterways, frequent traffic interactions, and proximity to urban areas demand highly adaptive and intelligent control systems. Concurrently, the escalation of global and regional trade is projected to exert a substantial influence on the development trajectory of autonomous ships, as there is an increasing necessity to devise efficient and cost-effective transportation solutions to satisfy burgeoning market demands.
3.2 Social structure
To better understand the development and knowledge structure of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport, this section adopts a social structure perspective—referring to the collaborative and productive relationships among individuals, institutions, and countries that shape scientific knowledge production. Specifically, this section focus on authors, institutions, and countries, as these are commonly analyzed dimensions in bibliometric studies to assess research productivity, collaboration patterns, and geographical distribution of scholarly impact. These aspects not only reveal the key contributors and research hubs in the field (Leoni et al., 2025; Peng et al., 2025), but also help identify potential collaboration networks (Zhao et al., 2024) and regional development trends. Therefore, their analysis provides a foundation for understanding how knowledge in this field is constructed and disseminated.
3.2.1 Authors
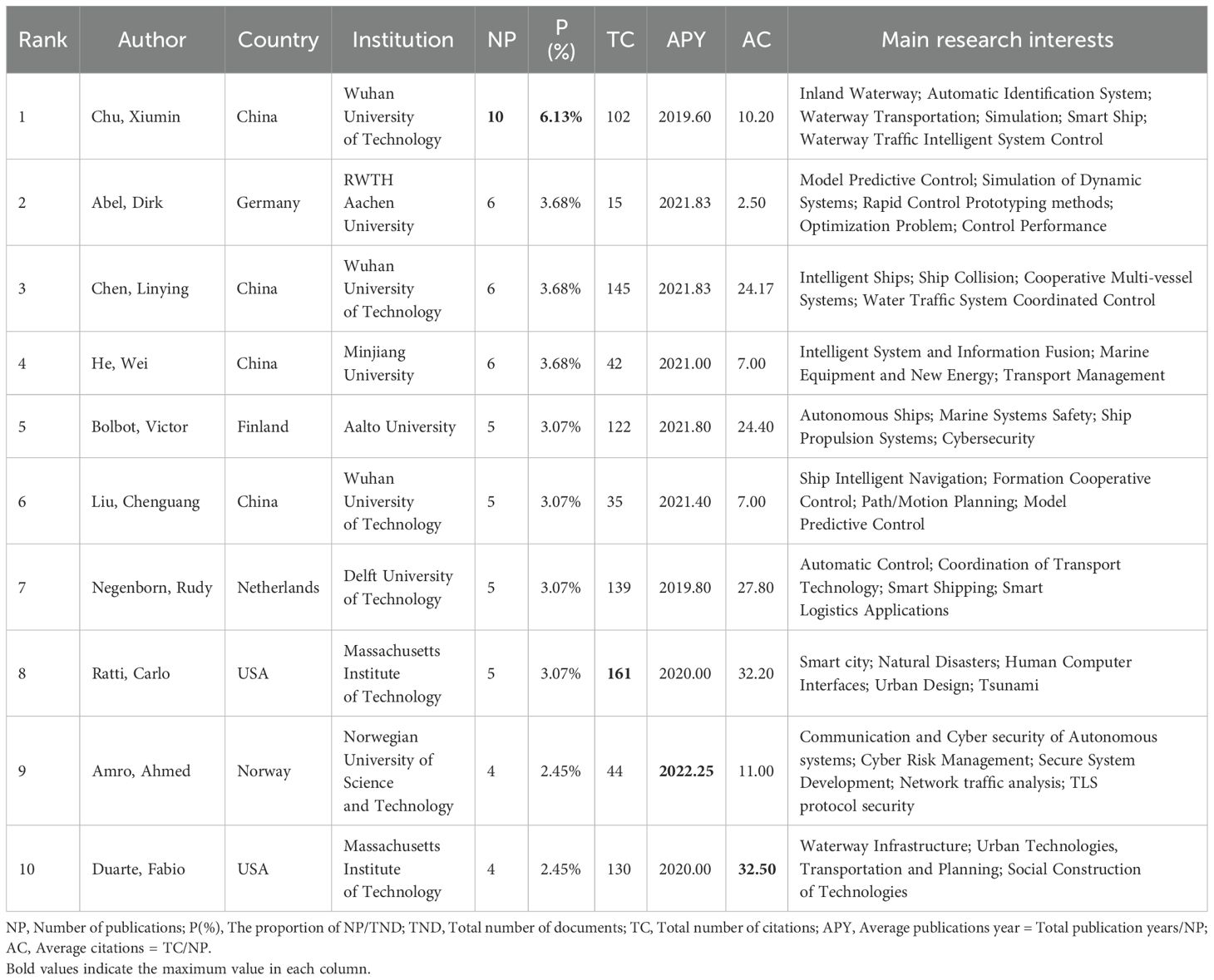
A total of 541 scholars have contributed to the field of autonomous ships in inland shipping through their publications. Notably, 82.9% of these scholars have authored only one article. Table 1 presents the top 10 most productive authors, detailing the number of publications, frequency of citations, research interests, and other relevant characteristics for each scholar.
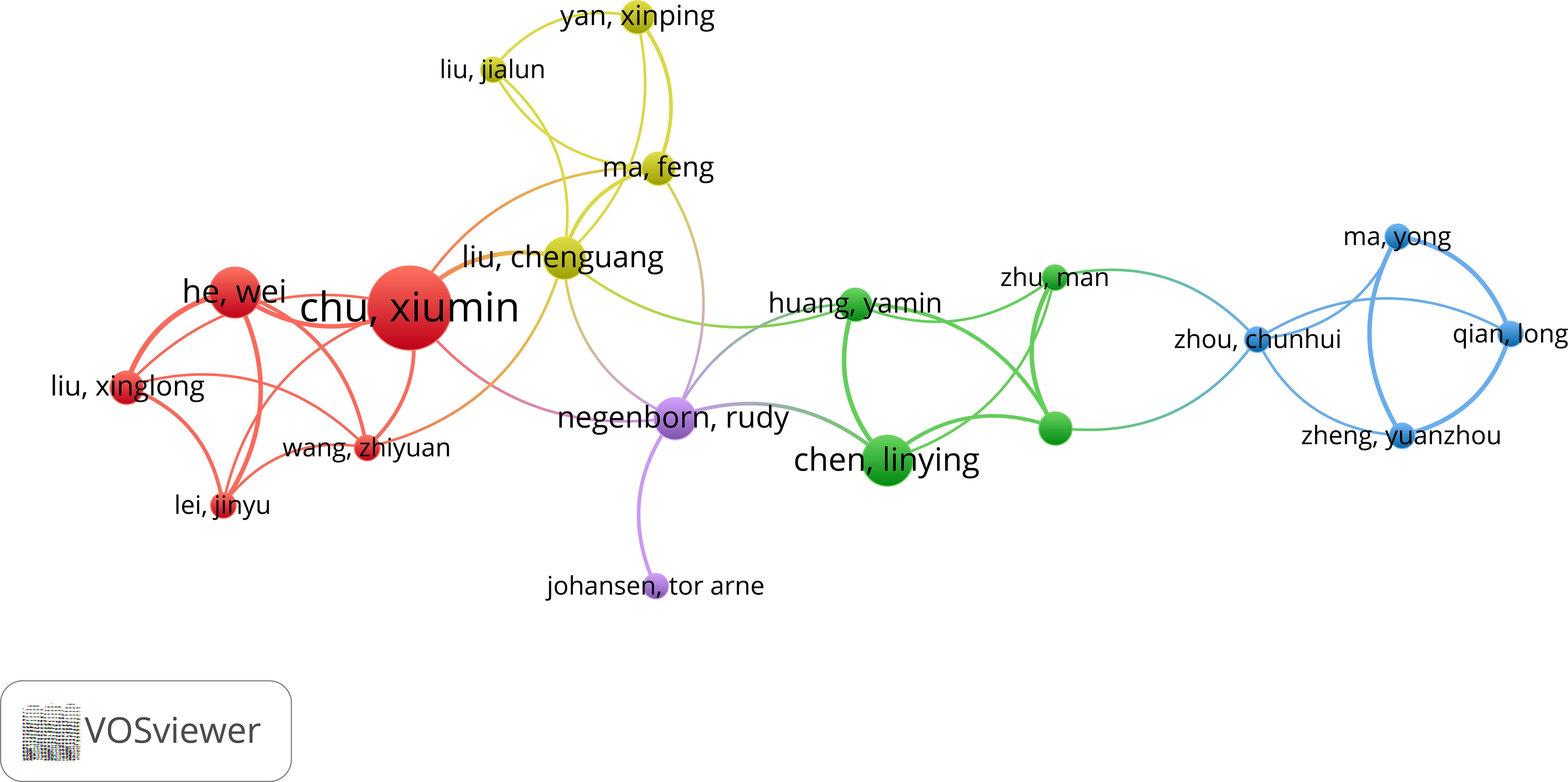
To elucidate the author collaboration network with greater clarity, Figure 5, with a threshold of at least 3 publications, presents a network diagram of scholarly collaborations. This visualization was constructed by first establishing a threshold of a minimum of 1 publications per scholar, and scholars are interrelated rather than isolated. As can be seen from Figure 5, Chu Xiuming is in a very core position. Not only is he very active in the field himself, but he also plays a bridging role and has very close cooperation with other authors. And the cooperation mainly focuses on Chinese scholars, with less international exchanges and cooperation, and Negenborn Rudy from the Nerthlands mainly connects domestic scholars.
3.2.2 Institutions
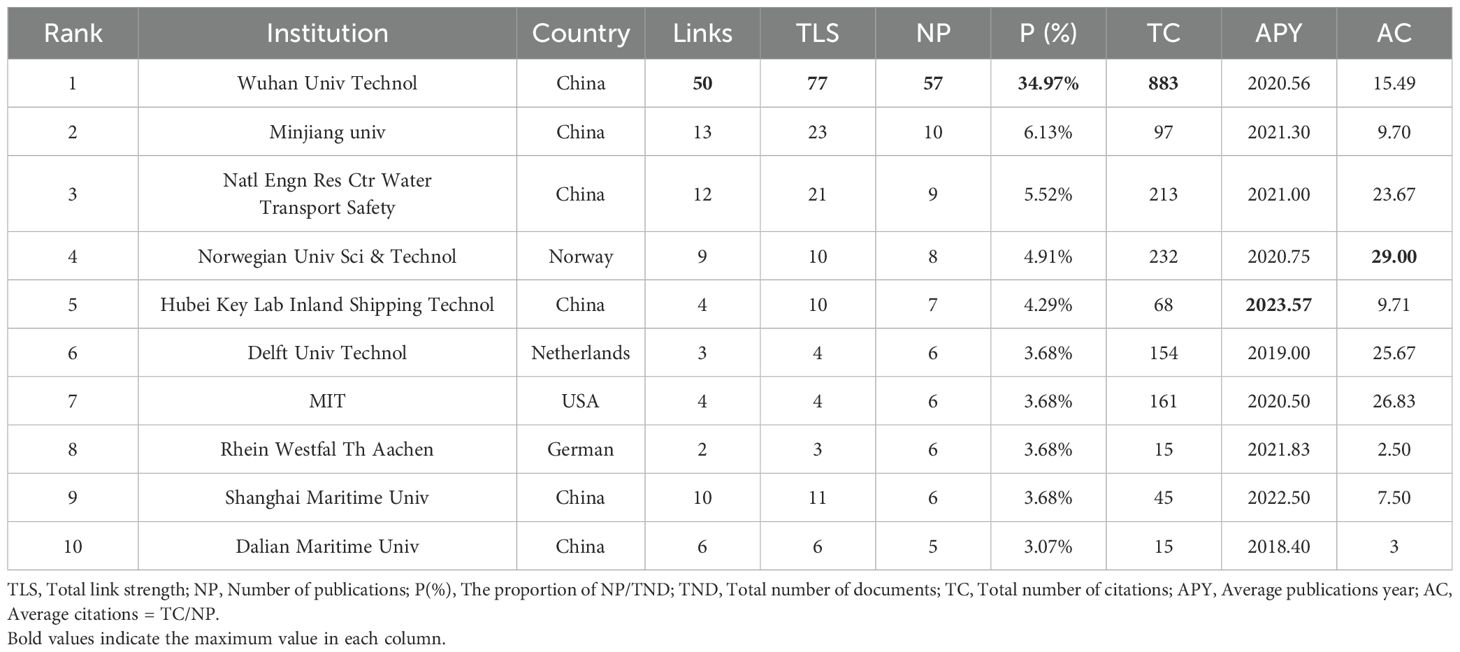
A total of 176 institutions were involved in the 163 documents analyzed in this study. Table 2 illustrates the top 10 research institutions in the explored domain based on the number of publications. Figure 6 provides a comprehensive analysis of the collaborative landscape.
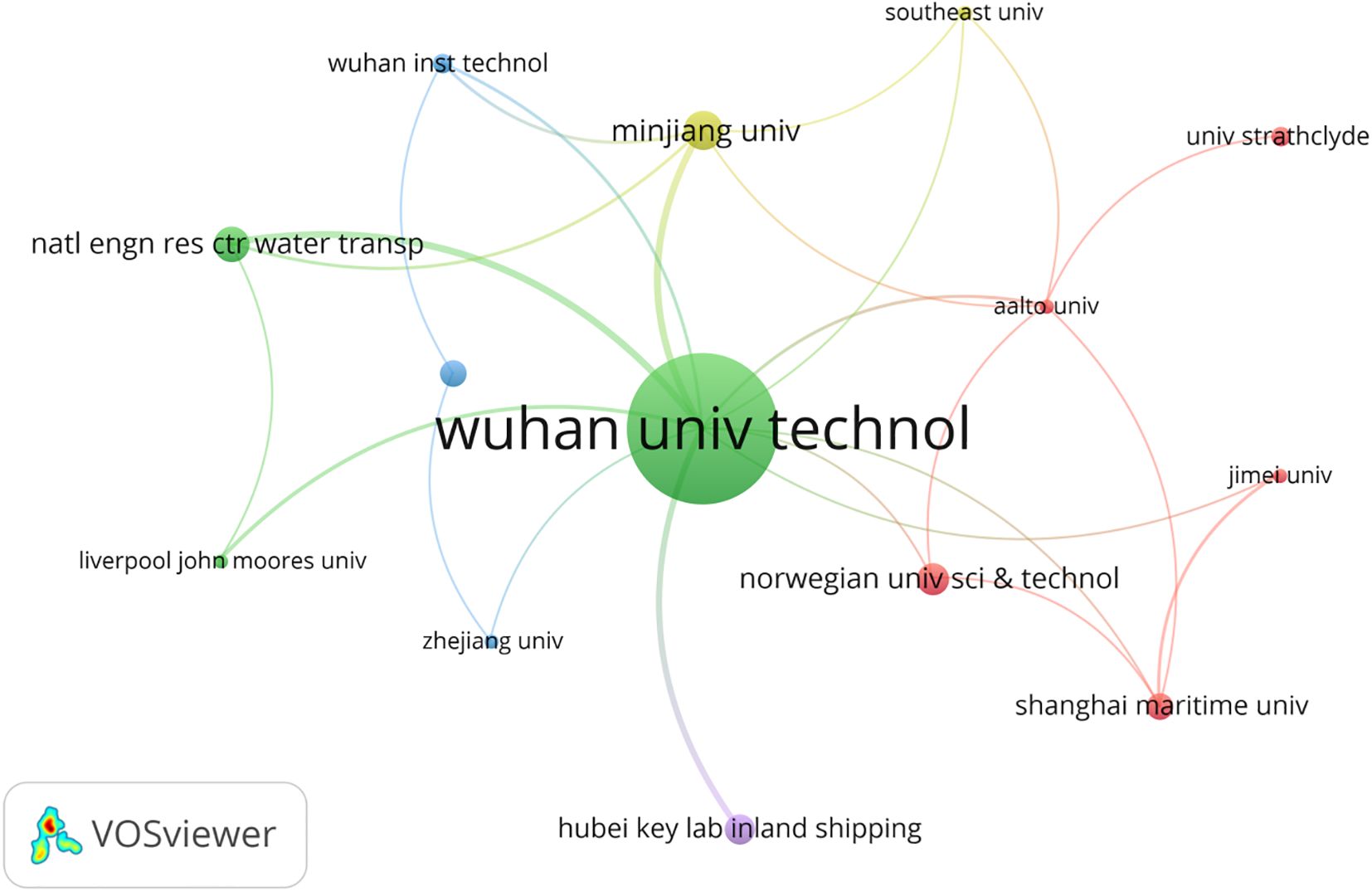
The network diagram visually represents the intricate web of connections among numerous institutions. As depicted in Figure 6, Wuhan University of Technology (Wuhan Univ Technol) is prominently positioned at the center of this network, acting as a central hub that has established extensive collaborative ties with a diverse array of both domestic and international entities. This central role is corroborated by the institution’s preeminent standing in the accompanying table, where it boasts the highest total link strength (TLS of 77), indicative of its expansive collaborative endeavors and comprehensive research network. Total link strength refers to the cumulative strength of an institution’s collaborative links with other entities, reflecting both the number and intensity of co-authored publications (Duan et al., 2020). A higher TLS value indicates stronger or more numerous collaborations, reflecting the overall extent of the institution’s research connectivity.
Wuhan University of Technology’s leadership is further accentuated by its dominance in the number of publications (NP of 57) and total citations (TC of 883), which serve as clear markers of its significant research output and profound impact on the academic community. The average publication year (APY) for most institutions is concentrated in the 2020s, indicating a notable upswing in research endeavors within the field of inland autonomous shipping during this period. This surge in activity underscores the dynamic and rapidly evolving nature of the research landscape in this domain.
Norwegian University of Science and Technology (Norwegian Univ Sci & Technol) stands out with a high average citation per publication (AC of 29), indicating a significant impact per publication despite a lower NP (8). Hubei Key Laboratory of Inland Shipping Technology (Hubei key lab inland shipping technol), despite having a lower NP (7) and TC (68), shows a recent APY (2023.57), indicating its emergence as a new yet influential contributor in the field. Both Hubei Key Laboratory of Inland Shipping Technology and the National Engineering Research Center for Water Transport Safety are based at Wuhan University of Technology, highlighting its influential role in this field. The settings of figure parameters are provided in Appendix A Table A1.
3.2.3 Countries
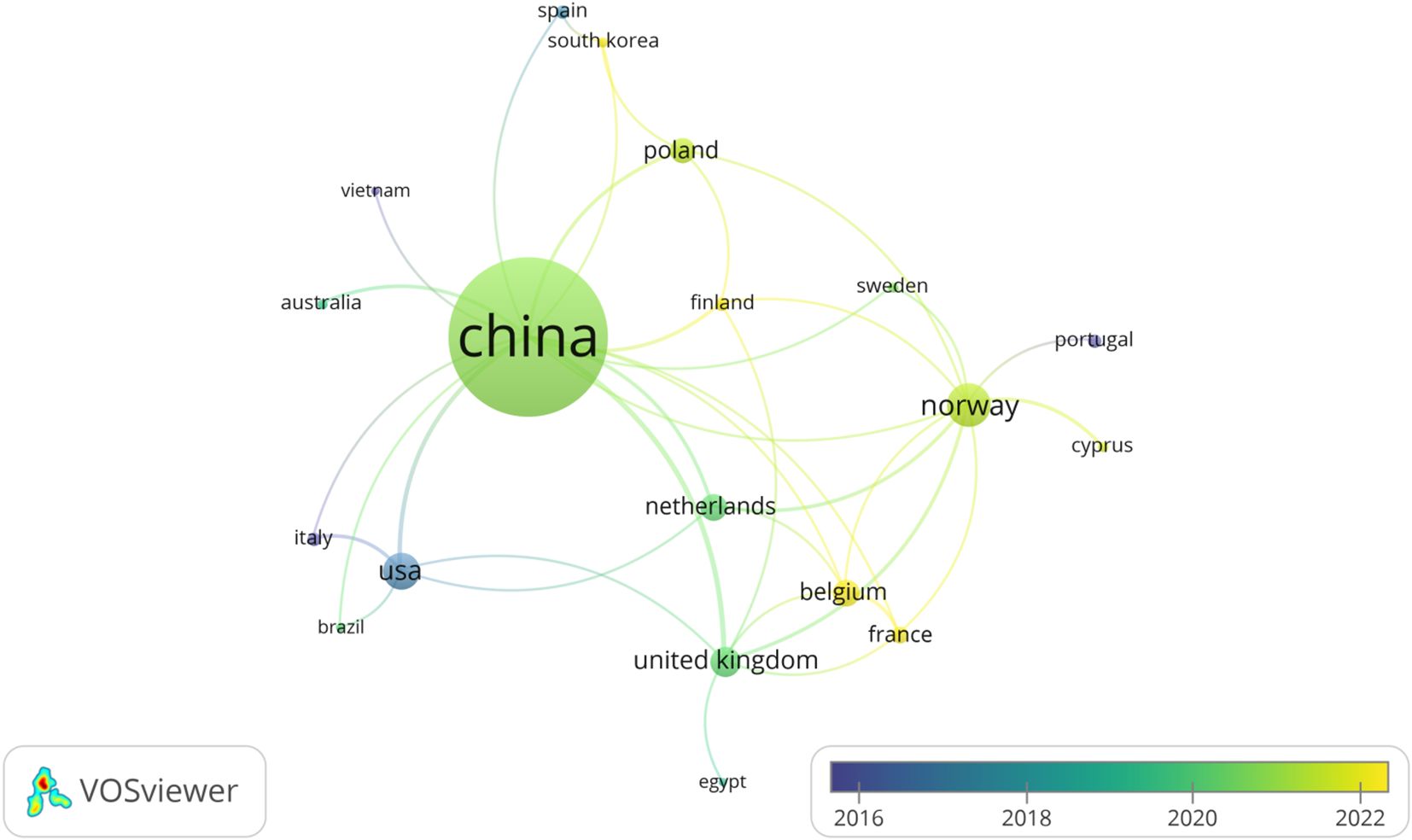
Figure 7 illustrates the cooperation relationships between China and other countries from 2016 to 2022. China is represented by the largest node, indicating its leading role in this field with a significant number of publications and collaborations. Meanwhile, countries such as Brazil, Australia, and South Korea are emerging as contributors to the field.
The color gradient from dark blue (2016) to yellow (2022) indicates the timeline of the publications and collaborations. The prominence of yellow connections, particularly those linked to China, points to a significant upswing in collaborative endeavors in recent years. Conversely, the prevalence of darker-hued connections, especially those interconnecting the UK with its European counterparts, implies the existence of enduring collaborative relationships. The settings of figure parameters are provided in Appendix A Table A1.
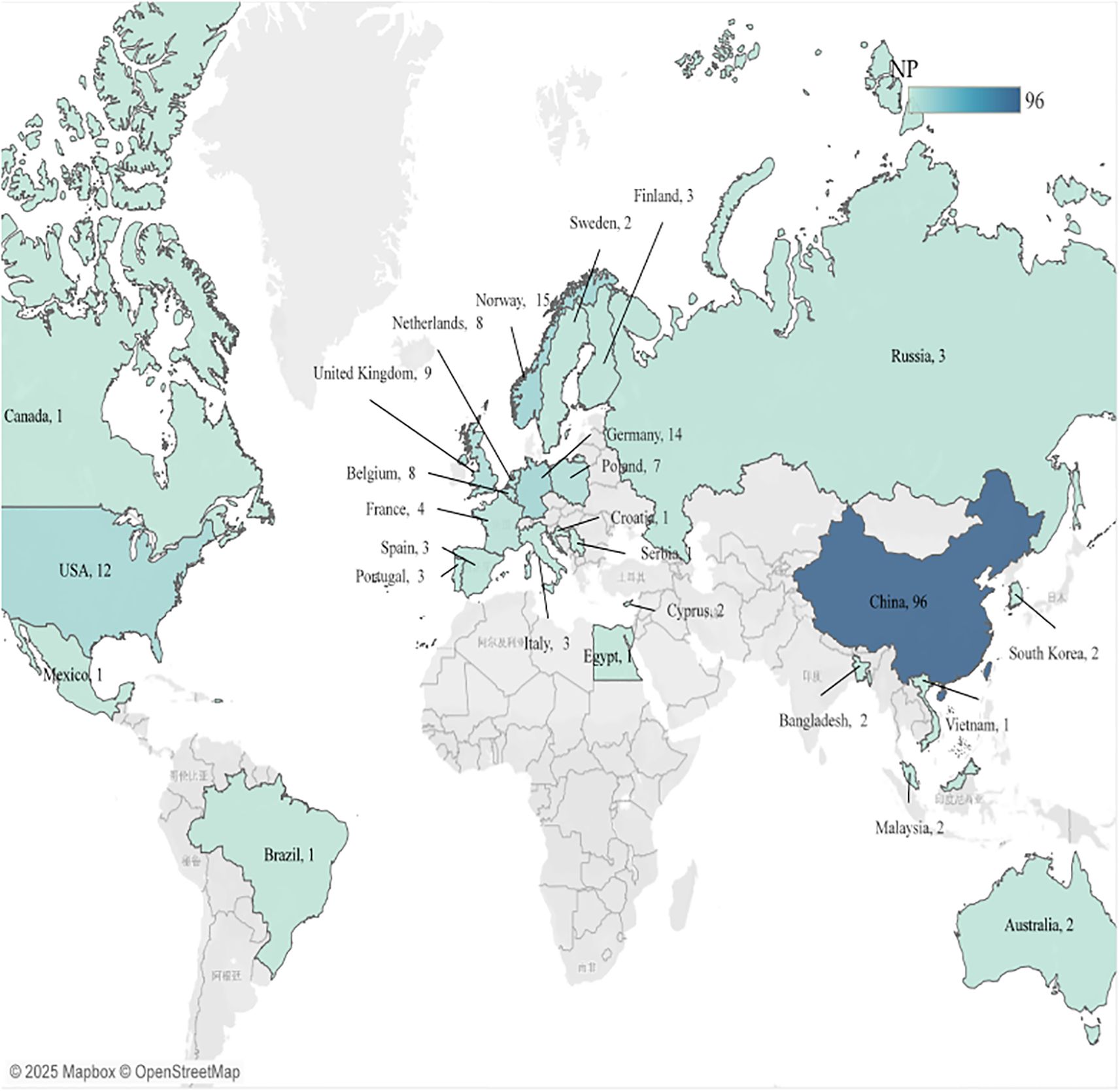
As depicted in Figure 8, academic publications exhibit a geographically diverse spread, spanning 27 countries worldwide. Notably, Europe accounts for 15 of these countries, signifying its significant contribution and strong research presence in the relevant academic fields. Asia follows with 5 countries, highlighting the region’s growing engagement and intellectual output. In North America, three countries, namely Canada, the USA, and Mexico, have made their mark, leveraging their research capabilities and resources. Additionally, one representative country, each from South America, Africa, Oceania, and Eurasia, underscores the truly global nature of the academic exploration and collaboration within the scope of these publications, with contributions from every corner of the world.
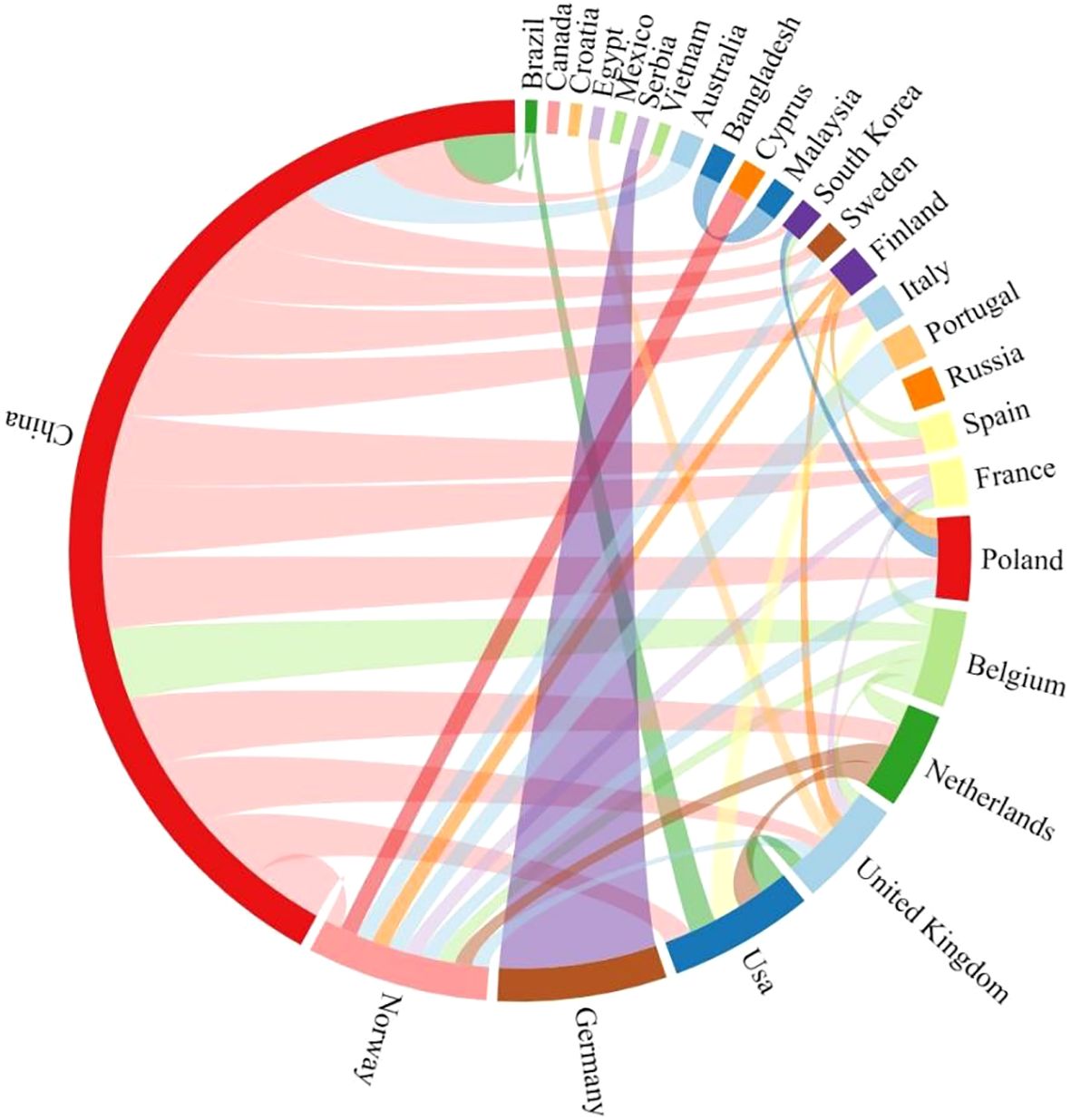
A chord diagram is defined as a group of chords whose endpoints are distinct and lie on a circle (Acan, 2017; Young, 2024). By drawing a chord map of national partnerships and numbers, it provides a visual representation of the collaborative relationships among various countries in the field of autonomous inland waterway vessels. This type of diagram is useful for illustrating the complexity and interconnectedness of international research collaborations.
As depicted in Figure 9, China, with its thick and numerous chords (15), stands out as a primary hub, indicating its extensive involvement in collaborative research within the field, consistent with the previous analysis. In addition, China plays an active role in cooperation, with 12 out of the 15 cooperation initiatives initiated by China, while only 3 were initiated by other parties with China’s participation. Regional clustering is particularly evident in Europe, signifying a concerted collaborative push within the continent. For instance, European countries such as Belgium, Germany, and the United Kingdom are interconnected, which may be due to shared geographical proximity, similar research interests, and collaborative frameworks facilitated by the European Union. The chords extending to countries like Australia, Brazil, and Mexico indicate a global reach of research efforts. Countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, which have thinner chords, represent emerging markets in the field. A few countries in the diagram are isolated, indicating potential opportunities for future collaborations. There may be untapped potential for research partnerships that could benefit from the unique perspectives and resources these countries bring to the field.
3.2.4 Disciplines and subject analysis
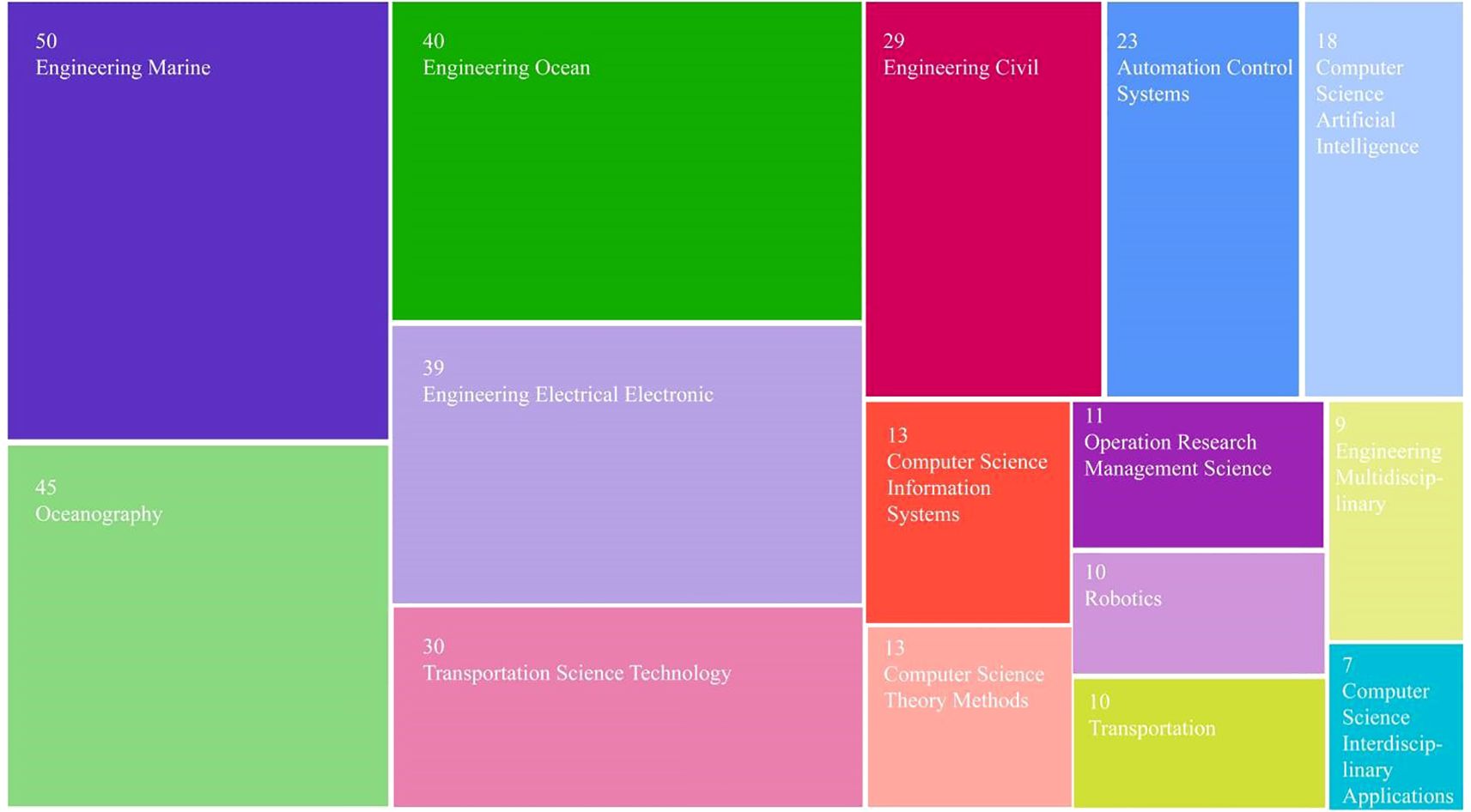
The treemap visualization provides a detailed breakdown of the academic disciplines associated with publications in the field of autonomous inland waterway vessels. The sizes of the rectangles are proportional to the number of publications, offering a clear representation of the distribution of research focus across various disciplines.
Figure 10 illustrates the disciplinary distribution of publications with more than seven articles per subject category. The research on autonomous ships in inland waterway transport spans 44 academic categories, but is clearly dominated by engineering-related disciplines. Notably, Engineering Marine, Oceanography, Engineering Electrical and Electronic, and Engineering Ocean together account for the majority of contributions, reflecting the sector’s strong technical foundation.
In parallel, the presence of subject categories such as Computer Science, Operations Research and Management Science reflects the increasing interdisciplinarity of the field. These areas bring perspectives from computer science, data-driven control, and logistics optimization, aligning with the smart and autonomous nature of next-generation inland shipping technologies.
Overall, the disciplinary structure demonstrates a shift from traditional marine engineering toward a more integrated, intelligent, and data-oriented research paradigm.
3.3 Citation network
3.3.1 Papers
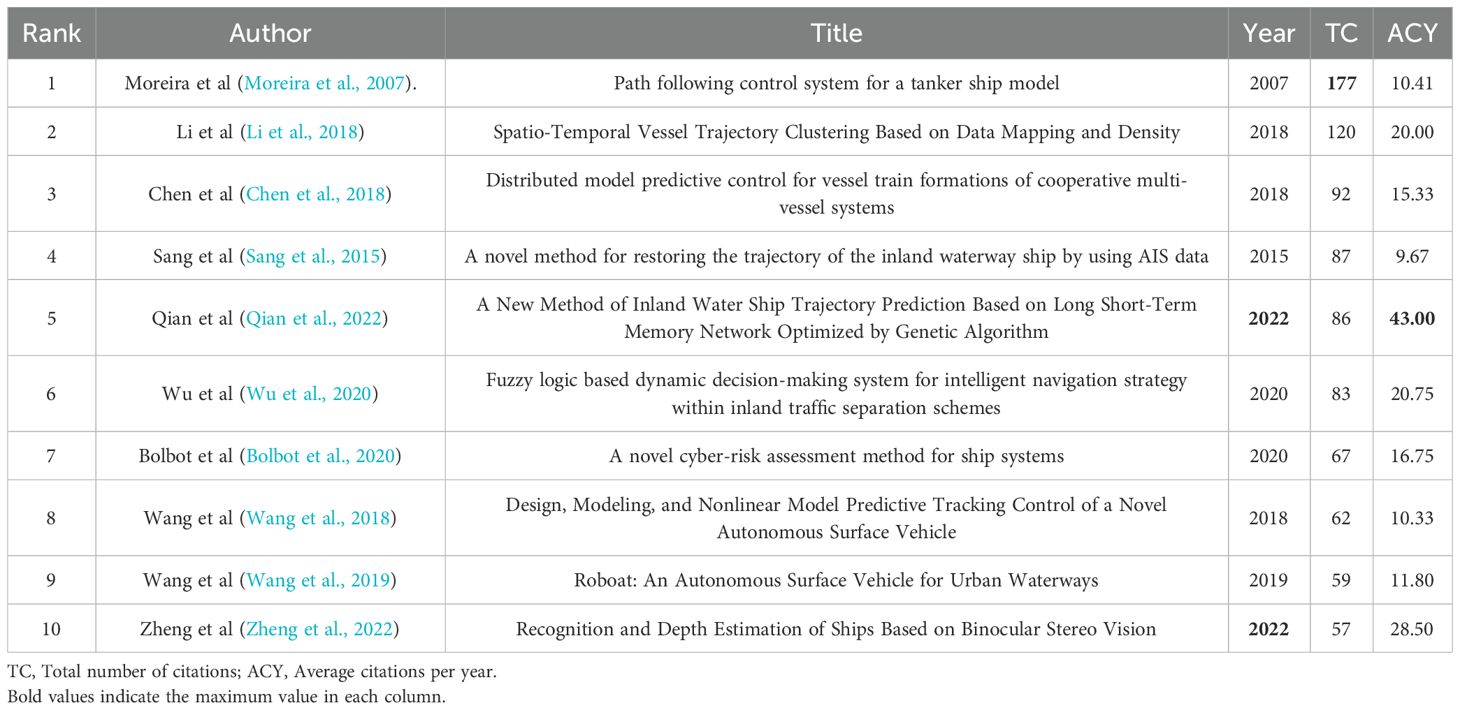
Table 3 presents the most influential papers in the field over the past 20 years, based on the measurement of the total number of citations. The analysis of the citation data reveals a rich diversity of research topics within the top 10 most influential papers. These topics range from advanced navigation and control systems to innovative ship design and autonomous operations.
Moreira et al. (2007) stands out as the most frequently cited paper, with a total of 177 citations. Despite its high citation count, the annual citation rate is moderate at 10.41 citations per year, suggesting sustained interest over time rather than a recent surge in attention. Qian et al. (2022) has the highest annual citation rate among the top 10 papers, with an average of 43 citations per year.
The disparity in citation rates between the most cited paper and the one with the highest annual citations highlights the dynamic nature of research in this field. It suggests that while some works have accumulated recognition over time, others are quickly gaining prominence due to their relevance in addressing contemporary challenges and advancements in autonomous shipping technologies. This trend underscores the rapid evolution of the field and the increasing importance of cutting-edge research in driving innovation and improving the safety and efficiency of inland shipping operations.
Furthermore, the presence of authors like Linying Chen and Bolbot Victor among the top 10 most cited papers reinforces their status as leading contributors to the field.
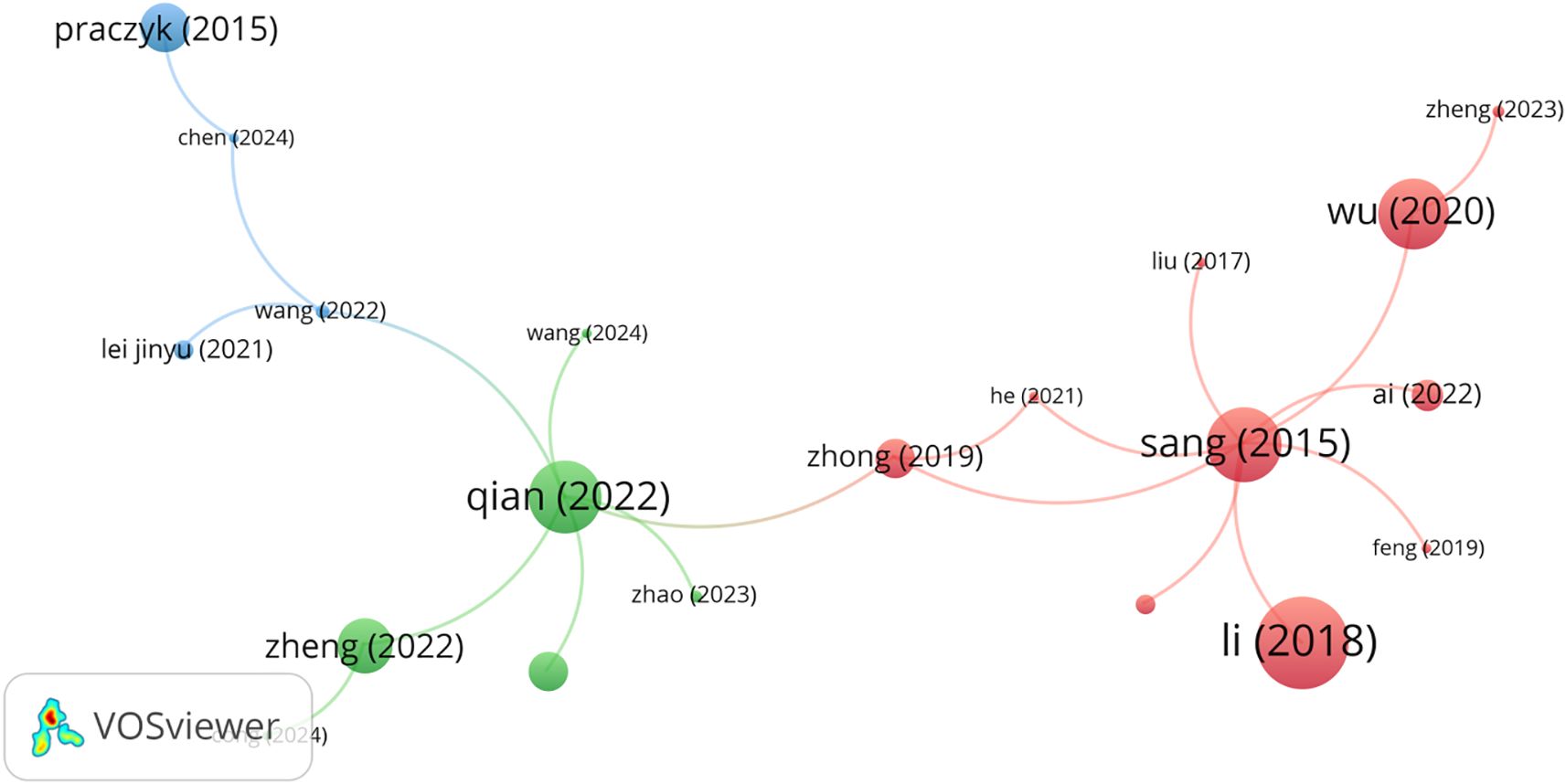
Figure 11 displays a citation network that delineates the relationships and distinctions among diverse research interests in the field of autonomous inland waterway vessels. The network is color-coded: 1) the blue cluster focuses on collision risk assessment of autonomous ships, emphasizing safety; 2) the green cluster examines trajectory prediction; 3) the red cluster examines trajectory restoration. The graphical parameters are outlined in Appendix A Table A1.
3.3.2 Journals
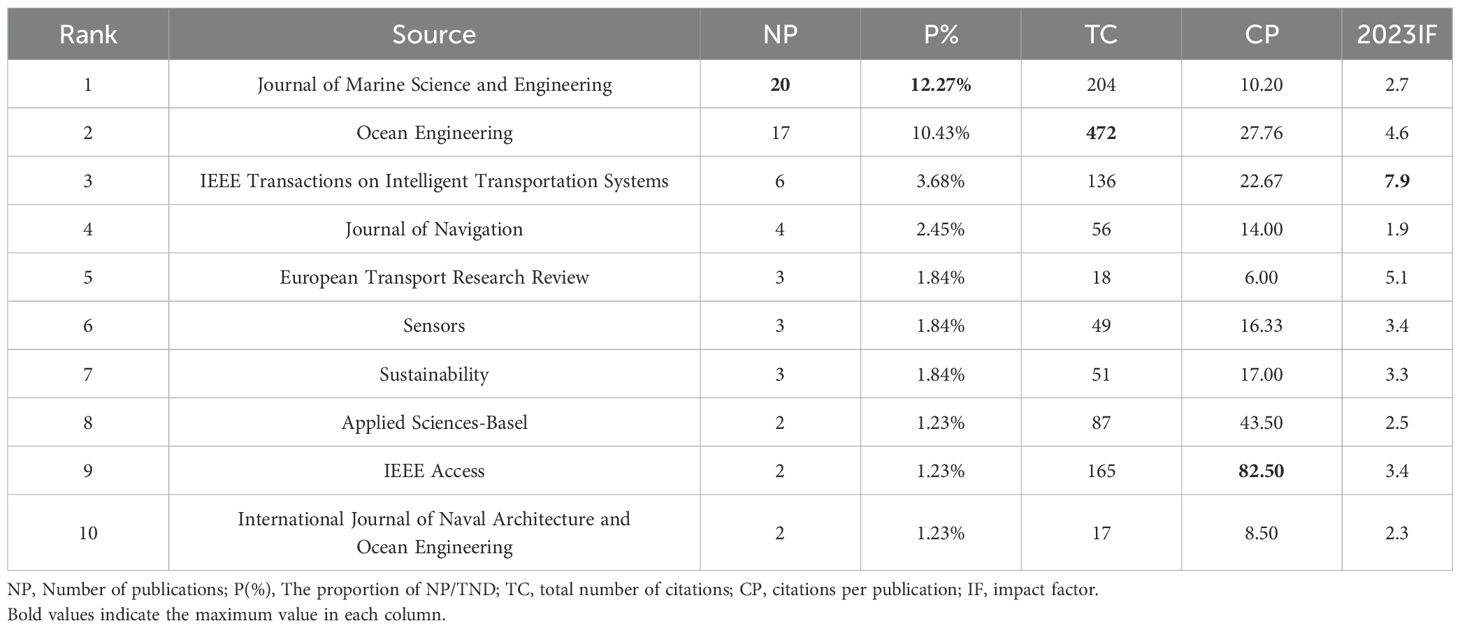
From 2000 to 2025, there were 97 publication sources in the investigated field. Table 4 list the top 10 most prolific journals with at least 2 publications. These journals include Journal of Marine Science and Engineering (20, 12.27%), Ocean Engineering (17, 10.43%), IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems (6, 3.68%), Journal of Navigation (4, 2.45%), European Transport Research Review (3, 1.84%), Sensors (3, 1.84%), Sustainability (3, 1.84%), Applied Sciences-Basel (2, 1.23%), IEEE Access (2, 1.23%), and International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering (2, 1.23%) respectively.
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering is the most prolific publisher in the field, with a total of 20 publications. However, while it leads in quantity, it does not surpass all other journals in terms of citation frequency, ranking second with a total of 204 citations. Ocean Engineering, with an impressive impact factor (IF) 4.6, boasts its substantial total of 472 citations. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems claims the title of the journal with the highest IF (7.9) on the list.
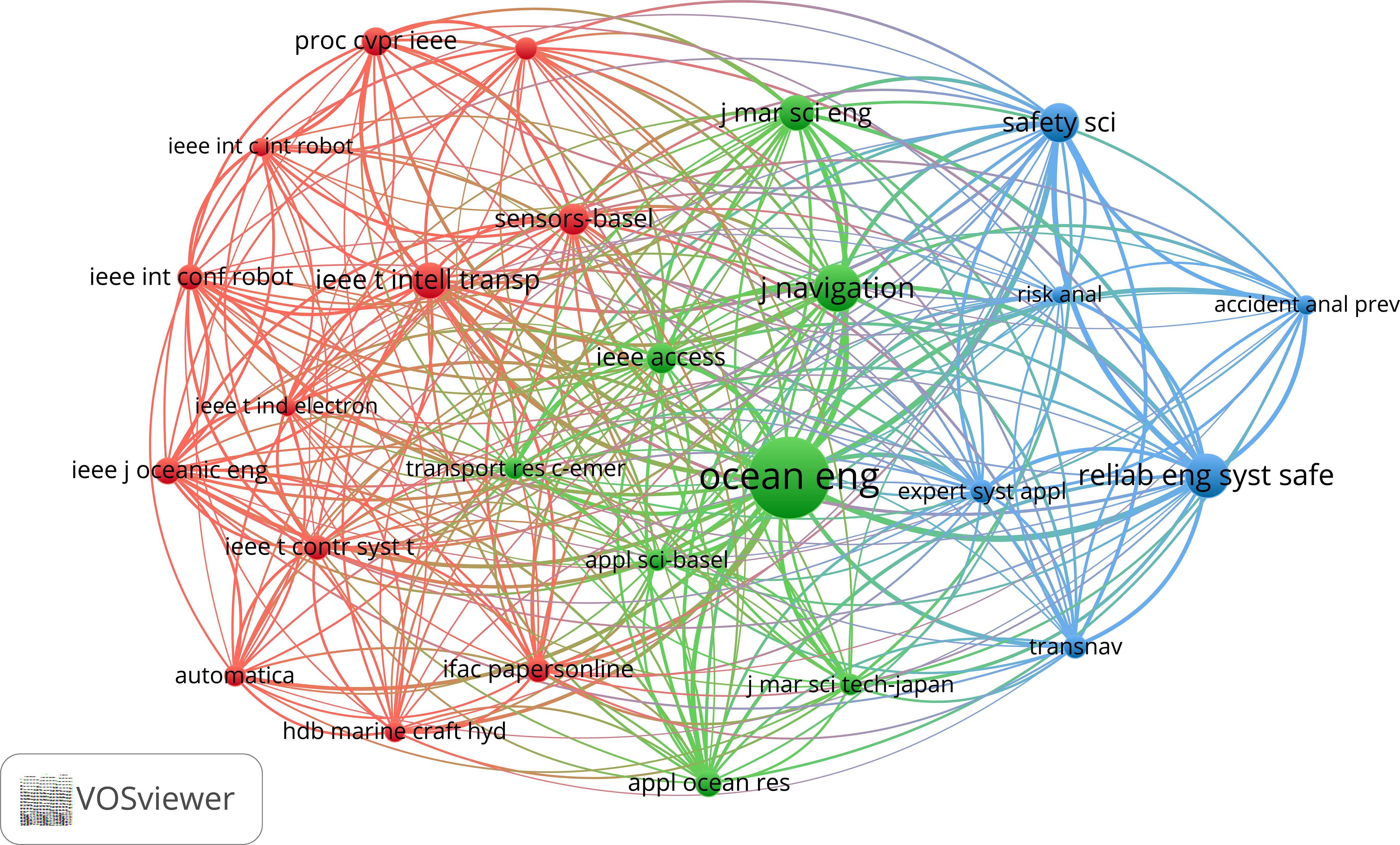
The journal co-citation network depicted in Figure 12 aligns with the findings presented in Table 4, reinforcing the significance of Ocean Engineering as the journal with the highest citation count. The network’s visualization helps to uncover the central journals that are pivotal in the discourse on autonomous ships in inland waterway transport. It also reveals the clusters of journals that are frequently cited together, suggesting shared research interests or complementary academic dialogues. The settings of figure parameters are provided in Appendix A Table A1.
3.4 Keywords
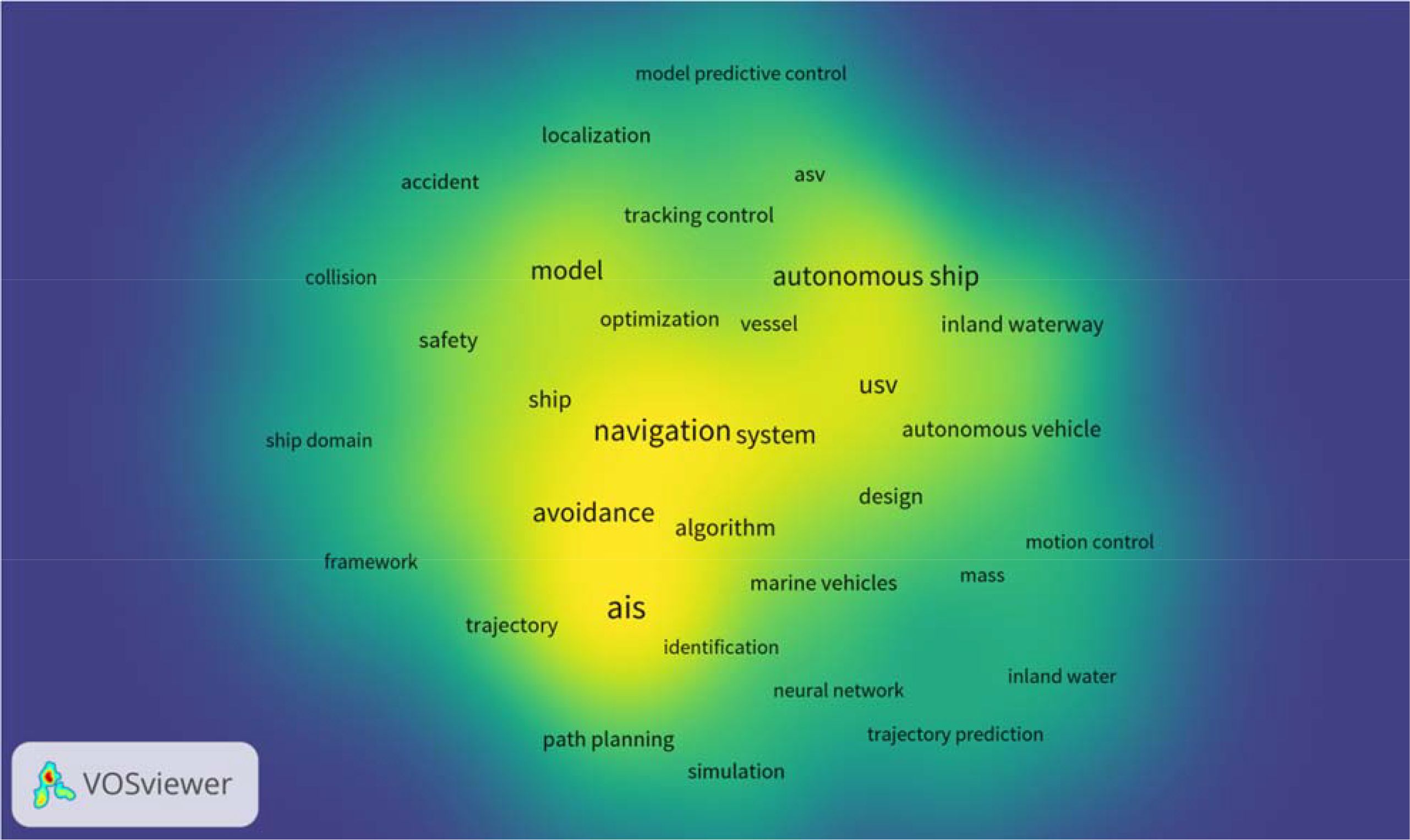
The keyword analysis conducted through VOSviewer on the 163 highly related documents has yielded a vivid heatmap (see Figure 13), revealing the intellectual landscape of the field. The more frequently keyword appears, the larger the size of the word and the brighter the color. A total of 697 keywords were identified by VOSviewer, of which 572 keyword appeared only once. The keyword set follows a marked long-tail distribution: about 82% of the terms occur only once and 94% no more than three times. This research therefore set the threshold at four occurrences, retaining the top 5% of higher-frequency keywords. This subset captures the majority of co-occurrence links and thematic clusters, sufficiently reflecting the field’s mainstream research directions while preventing node overcrowding and edge clutter, thus improving the clarity of the visualization.
As seen in Figure 13, the brightness of most keywords is relatively uniform, indicating similar frequencies of occurrence. However, keywords such as AIS, avoidance, navigation, system are relatively more prominent, revealing the core hotspots of the research field.
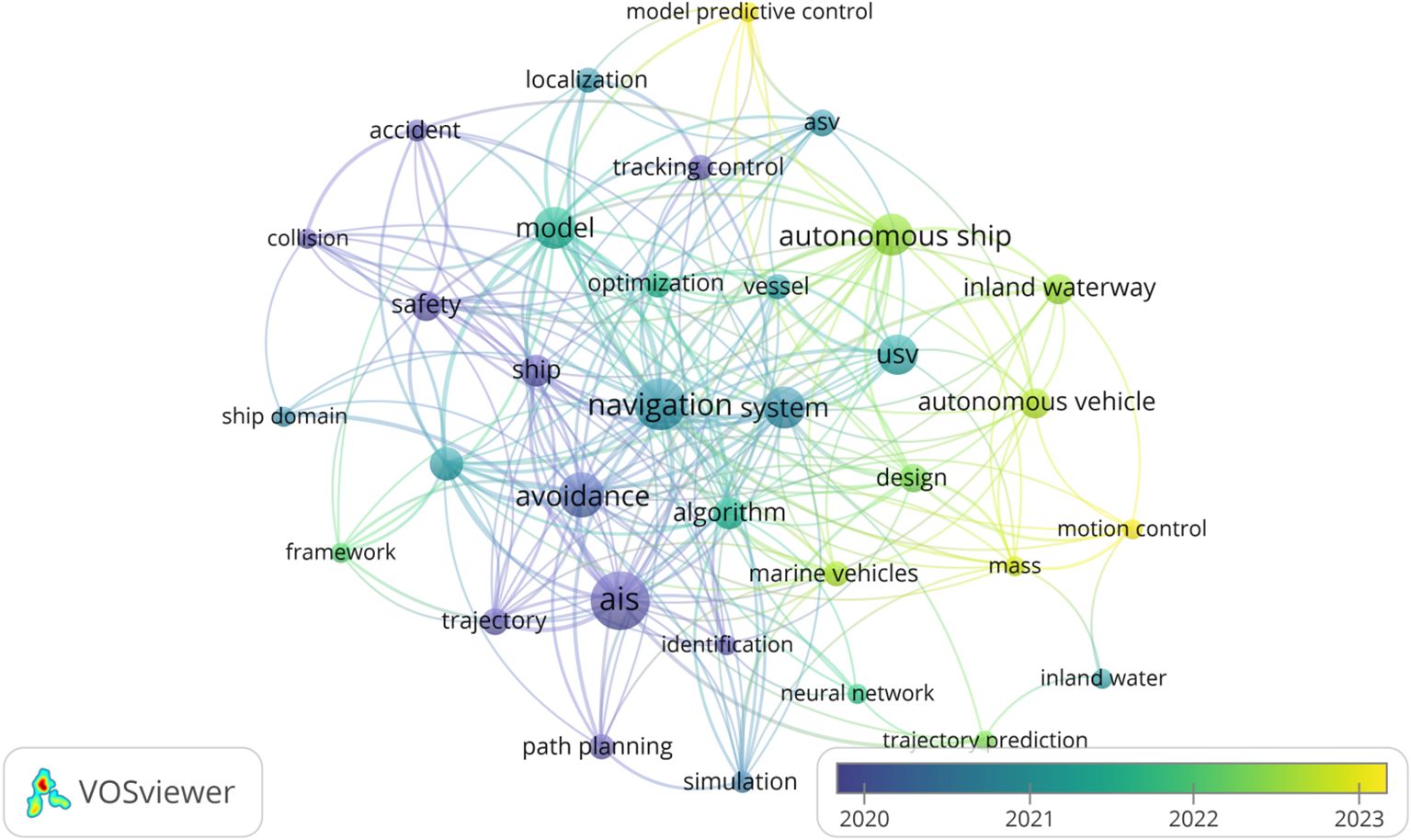
Figure 14 illustrates the temporal occurrence of the keywords. With a threshold of at least 4 occurrences, a total of 34 keywords meets this criterion. The transition from darker to lighter colors, especially around keywords such as MASS(Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships), model predictive control, and motion control suggests a recent surge in research activity. This trend reflects the growing importance of autonomous technologies in inland shipping. The larger nodes for AIS, navigation, and safety indicate a mature research area with a significant body of work. These nodes’ central position and extensive connections reflect their foundational role in the field. The settings of the figure parameters are provided in Appendix A Table A1.
4 Discussion
Autunomous ships in inland waterway transportation represent a burgeoning frontier with substantial potential for enhancing safety and efficiency in both transport and commercial sectors, garnering escalating interest from the global research community. However, this evolution is not without its challenges, and its successful implementation demands careful consideration of technological, regulatory, and operational factors. Building upon the three-phase growth trajectory and the other results in Section 3, the study next contextualize these bibliometric signals against prevailing technological, regulatory and sustainability imperatives. This section provides a detailed analysis of the challenges and the future directions for autonomous ships in inland waterway transportation.
4.1 Current challenges
4.1.1 Technology integration
Inland waterways present unique constraints—narrow channels (Yan et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2024b), fluctuating water levels, and high traffic density (Zhang et al., 2024b)—that demand extraordinary precision and adaptability from smart technologies. As evidenced by Figure 13, technical terms such as navigation, system, and avoidance are central in the existing literature, underscoring a research focus on foundational technologies. However, current technologies often struggle to meet the high standards of responsiveness and reliability required in such dynamic environments. These very capabilities depend on position data that, in inland waterways, are frequently corrupted by multipath reflections and signal shadowing from banks, bridges, and urban obstacles. Therefore, it is necessary to study autonomous ship technologies tailored to the inland waterway context.
Moreover, the heterogeneous nature of inland fleets, ranging from small barges to medium-sized cargo vessels, imposes challenges in scalability and customization. Solutions optimized for large ocean-going vessels often fail to address the specific needs of inland shipping.
Autonomous ships leverage information technology to automatically gather and analyze data related to the vessel, surrounding environment, logistics chains, and port infrastructure, thereby enabling intelligent navigation, management, maintenance, and cargo operations (Pei et al., 2024). While these systems have shown promise in open-sea contexts, their adaptation to inland waterway environments introduces a distinct layer of complexity.
In inland waterways, data sources are often fragmented, and the operational environment is highly variable—ranging from small regional ports with limited digital infrastructure to congested urban canals. This calls for more localized, fine-grained sensing and decision-making capabilities, such as ultra-precise maneuvering in narrow locks or adaptive route planning under rapidly changing hydrological conditions. The development of context-aware autonomous systems, capable of handling these dynamic, spatially constrained settings, marks a unique technological frontier in inland shipping.
At the core of this challenge lies the need to harmonize diverse systems. To achieve a higher level of intelligence, autunomous ships need to integrate a variety of technologies, such as autonomous navigation (Mei and Arshad, 2017), control (Zhang et al., 2022), and self-learning (Epikhin et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2022a), each of which brings its own set of technical demands. Yet, these technologies are often developed in isolation by different manufacturers, creating issues of compatibility that hinder seamless operation (Kim and Son, 2020; Peng, 2023).
4.1.2 Regulatory framework
As shown by the keywords “avoidance”, “accident”, and “collision risk” in Section 3.4, addressing accidents involving autonomous ships is crucial. In the inland waterway context, this issue becomes particularly complex due to the dense traffic, narrow passages, and diverse vessel types commonly encountered, all of which amplify the consequences of regulatory ambiguity.
However, the adoption of autonomous ships for inland waterways faces significant challenges, as regulation and standardization, while considered the backbone of technological innovation in transportation, also act as a bottleneck in their implementation (Orzechowski et al., 2024). The fragmented governance structure—with oversight often split between national, regional, and local authorities—makes the formulation of cohesive regulatory frameworks particularly difficult in inland settings. The international co-authorship network depicted in Figure 9, characterized by tightly knit national clusters and sparse cross-border bridges, visually mirrors this patchwork oversight and helps explain why a harmonized set of inland-navigation rules has yet to emerge, to some content. Furthermore, the rapid evolution of smart systems, with their autonomous capabilities and interconnected devices, has outpaced the regulatory frameworks designed to oversee them (Backalov, 2020; Nzengu et al., 2021; Ringbom, 2019). This mismatch is especially problematic in inland shipping, where route-specific constraints (e.g., locks, bridges) require regulatory adaptation at a much more granular level than in open-sea operations.
Unresolved legal questions around liability in collision scenarios, for example, are further compounded in inland waterways by the proximity of vessels to critical infrastructure and to each other (Carey, 2023). These ambiguities generate uncertainty for shipowners, insurers, and technology developers, thereby delaying deployment.
Cross-border inland navigation adds another layer of complexity. The lack of harmonized safety, communication, and operational standards among countries and regions along interconnected inland river systems (e.g., the Danube, Rhine, or Yangtze tributaries) often forces operators to adapt to a patchwork of local rules, driving up operational costs and reducing efficiency (Liu et al., 2024a).
To address these issues, a dynamic regulatory approach is needed—one that evolves in step with technological advancements. Collaborative efforts between industry leaders, policymakers, and international organizations can foster the development of universal standards, ensuring that innovation is not stifled by outdated frameworks.
4.1.3 Cybersecurity
Notably, although Figure 13 does not explicitly list the term cybersecurity, it nonetheless surfaces a cluster of thematically allied keywords—such as AIS, navigation, and risk assessment. It suggest that cyber-related vulnerabilities remain latent. Autonomous ships, interconnected through IoT devices, real-time communication networks, and autonomous control systems, are highly vulnerable to cyberattacks (Alsalem et al., 2023; Symes et al., 2024; Tusher et al., 2022). Threats such as ransomware, unauthorized data breaches, and targeted sabotage have the potential to disrupt navigation systems, compromise cargo security, or even endanger lives (Yousaf et al., 2024). These risks are especially acute in inland waterway contexts, where vessels operate in densely populated corridors and often in proximity to critical urban infrastructure, amplifying the potential consequences of cyber incidents.
A particularly challenging aspect of managing these risks is the integration of physical and digital components on autonomous ships. The cyber-physical nature of these systems creates numerous entry points for attackers, especially when different components are sourced from multiple vendors without standardized security protocols. Many inland waterways, especially those in remote or less-developed regions, lack robust connectivity infrastructure, further exacerbating vulnerabilities by delaying critical updates or weakening real-time monitoring capabilities.
Moreover, inland waterway operations involve frequent vessel-to-shore interactions——at locks, urban ports, or multimodal terminals——which introduce additional security risks through shore-based access points (Stepien, 2025). In highly-traffic areas, cyberattacks targeting one vessel’s control systems could potentially cascade into broader network failures, given the close operational proximity of multiple autonomous ships.
Mitigating these risks requires a proactive, multi-layered defense strategy. Encryption, regular software updates, real-time threat detection systems, and secure communication channels are just the beginning. It also necessitates investment in cybersecurity training for operators and technicians, ensuring that human error does not become a weak link in the whole system (Martínez et al., 2024).
4.1.4 Environmental and sustainability considerations
As Figure 10 reveals, environmental-science–related categories are entirely absent from the top-ten disciplinary clusters, indicating that scholarly attention to decarbonization and sustainability remains markedly lower than that devoted to technological and engineering themes. This evidentiary gap is especially consequential because environmental and sustainability considerations already represent a significant challenge for the development of autonomous ships in inland waterway transportation (Pei et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2025). While autonomous ships promise to reduce emissions and improve energy efficiency through optimized navigation and alternative propulsion systems (Ren et al., 2022), such as electric or hydrogen engines, these benefits must be evaluated within the specific environmental and operational contexts of inland waterways. Inland autonomous ships operating on inland routes typically navigate shorter distances with frequent stops, often within urban or ecologically sensitive areas, such as wetlands, lakes, or densely populated riverbanks. These characteristics amplify the environmental stakes: for example, emissions from conventional engines have a direct and localized impact on air quality, making zero-emission solutions not just desirable but often mandatory. Yet the deployment of green propulsion technologies on smaller inland vessels is far from straightforward. The storage and application of hydrogen (Van Hoecke et al., 2021) and battery (Zou et al., 2022) in maritime affairs still face many challenges at present.
The production of advanced components, such as sensors and batteries, requires rare materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, which contribute to the overall environmental footprint. These impacts are particularly pronounced in inland shipping, where the fleet is highly fragmented, and retrofitting existing vessels can be more resource-intensive than building new ones. Additionally, questions about the lifecycle sustainability of these technologies remain important—particularly in terms of recycling, waste management, and the disposal of decommissioned systems (ElMenshawy et al., 2024). To ensure that the environmental benefits of inland autonomous shipping are fully realized, future technological developments must prioritize not only clean propulsion and efficient navigation but also modular, recyclable, and space-adaptive designs tailored to the inland context. Policies and industry standards should likewise reflect the unique environmental conditions and infrastructure limitations of inland waterway systems.
4.1.5 Infrastructure adaptation
Current ports, waterways, and related facilities are largely designed for conventional vessels and often fall short of meeting the technological demands of autonomous ships. For instance, autonomous navigation systems rely on detailed and continuously updated digital maps, along with robust data feeds from shore-based monitoring systems. However, many inland waterway networks lack these critical digital enhancements, creating gaps that limit the effectiveness of smart technologies. Also, port facilities must evolve to support the needs of advanced vessels. The current intelligent maritime transportation is entering a critical window period of deep integration between Internet technology and automated port infrastructure (Zou et al., 2025). IoT, charging infrastructure (Gabbar, 2022) for electric propulsion, and high-speed data communication networks (Jo and Shim, 2019; Wei et al., 2021) are essential, yet such features remain rare in many inland regions. These gaps not only limit the deployment of autonomous technologies but also deepen the urban-rural divide in maritime digitalization, making it more difficult to realize the full benefits of autonomous inland shipping. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated modernization strategy that aligns technology development with infrastructure upgrades, tailored specifically to the scale, density, and geographic diversity of inland waterway networks.
4.1.6 Challenge interactions
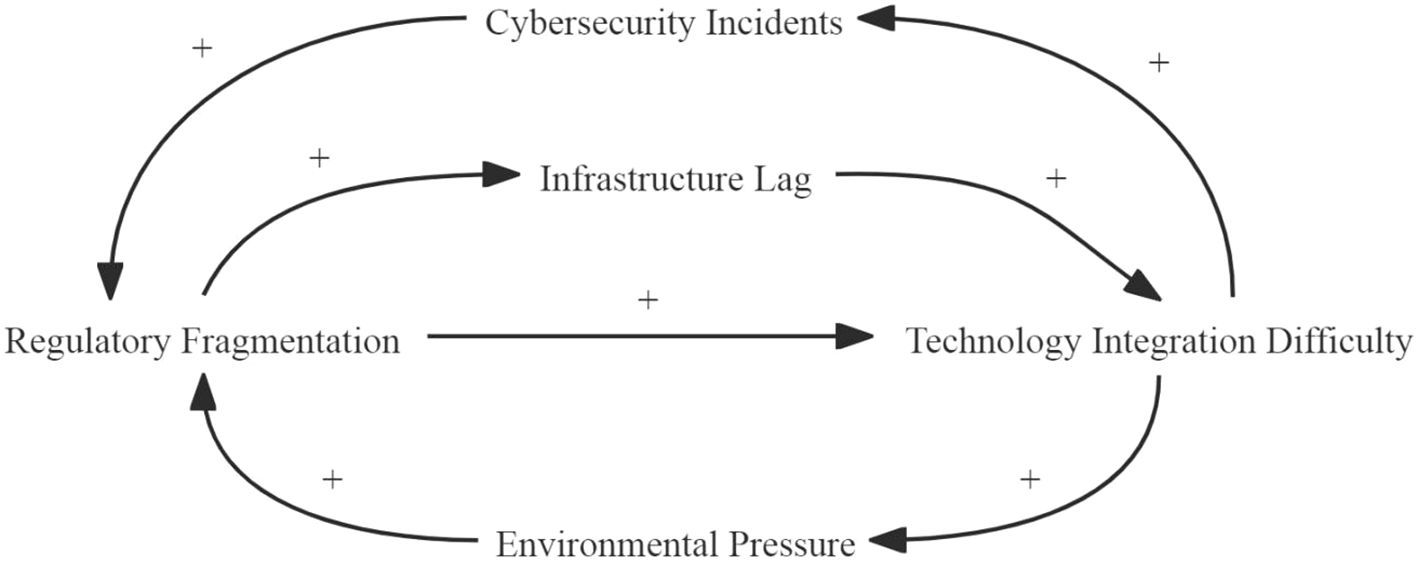
The above five challenges form a coupled system rather than a collection of separable issues. Measures aimed at a single challenge can propagate through this system and inadvertently intensify others. Therefore, understanding these interdependencies is therefore essential for formulating effective, durable interventions.
System-dynamics modelling applies feedback-based theory and simulation to analyze how complex systems evolve over time (Kanellos et al., 2024), it represents feedback loops, time lags, and non-linear interactions explicitly. A causal-loop diagram (CLD) provides the necessary visual framework, helping to reveal leverage points for policy.
As shown in Figure 15, this study plots causal loop diagrams for the five major challenges and derives three mutually reinforcing key feedback loop loops.
1. Loop R1 (Regulation–Infrastructure–Technology–Cyber). Regulatory fragmentation slows infrastructure modernization; outdated physical and digital assets exacerbate technology-integration difficulty; integration gaps enlarge the cyber-attack surface, leading to high-profile incidents; each incident precipitates additional ad-hoc rules, which further fragment regulation and restart the cycle.
2. Loop R2 (Technology–Environment–Regulation). Integration difficulty delays the roll-out of clean propulsion and energy-management systems, amplifying environmental pressure. Heightened public and political concern then triggers a surge of uncoordinated environmental mandates, thereby adding new layers of fragmented regulation that discourage coherent infrastructure investment and, in turn, entrench integration barriers.
3. Loop R3 (Regulation–Technology–Cyber). Fragmented rules inflate compliance costs and technical complexity, which again widens the attack surface; subsequent cybersecurity incidents invite yet more patchwork regulation, accelerating the fragmentation process.
These mutually reinforcing loops indicate that isolated remedies are unlikely to succeed. Progress depends on coordinated action that aligns regulatory harmonization, infrastructure modernization, and cybersecurity management and others so as to weaken the amplifying feedbacks identified above.
4.2 Future directions
4.2.1 Coordinated fleet operations
The improvement of shipping efficiency is currently limited by individual ship operations, as each vessel typically operates in isolation, unable to fully optimize its movements in relation to others (Peng et al., 2021). In the coming years, vessels will no longer operate in isolation but will be part of interconnected fleets capable of coordinating their movements autonomously across entire waterways (Osorio et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2013).
Through the optimization of multiple unmanned vessel paths (Ning et al., 2020; Ren et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2023) and the distribution of multiple tasks (Jin et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2024a), this coordinated approach will reduce congestion, and improve the efficiency of cargo transport, allowing for seamless operation of fleets without the need for constant human intervention. Unlike in ocean shipping, where vessels often navigate vast, open waters with fewer constraints, inland waterways require precision coordination, as each vessel’s movement must align with the navigational limits of a shared, confined space.
The integration of autonomous fleets in inland waterway transport will not only enhance the overall efficiency and flexibility of the system but will also address the specific challenges posed by navigation. Future inland waterways could operate as unified systems, where fleet coordination is continuously adjusted to account for variable traffic conditions, lock schedules, and local weather patterns. This transition will reshape the logistics landscape, enabling autonomous fleets to seamlessly operate across multiple river segments, without the need for constant human intervention or manual scheduling, and drastically reduce operational bottlenecks in high-traffic regions.
4.2.2 Data-driven decision making
As intelligent technology progresses, autonomous ships are increasingly leveraging big data to improve decision-making. By tapping into real-time and historical data from sensors, weather systems, and traffic platforms, future vessels can operate autonomously, optimizing route planning, fuel consumption, and maintenance (Hu et al., 2022; Shi and Liu, 2020).
Standardized communication protocols and AI advancements are crucial for unlocking predictive insights, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and boosting safety. This data-centric method will streamline operations and enable proactive management. For inland waterways, this means not only improving data communication between ships but also ensuring effective interaction with port and infrastructure systems. This data-centric approach will streamline operations, reduce congestion, and enable proactive management of river traffic, especially in areas with frequent bottlenecks. In terms of data privacy protection, Federated Learning (FL) is highly suitable for scenarios where multiple enterprises participate and need to protect their respective private data (Liu et al., 2022). Through federated learning, each participant can train their own data locally and only upload model parameters (such as weights or gradients) to the platform instead of the original data, thereby effectively avoiding the risk of data leakage.
With large-scale data, autonomous ships in inland waterways can anticipate maintenance, avoid hazards, and adapt operations in real-time. Ultimately, big data integration will revolutionize inland maritime operations, driving efficiency, sustainability, and safety towards autonomous decision-making (An, 2024).
4.2.3 Green and sustainability
As global pressure to reduce environmental impact increases, the future of autonomous ships will be shaped by sustainability (Lee et al., 2013; Tang et al., 2018; Yigit and Acarkan, 2018). For inland waterways, where traffic density is high and the environmental footprint of operations can be more significant due to limited space and frequent stop-and-go movements, the need for eco-friendly solutions is even more critical. Vessels will be designed to operate with minimal environmental footprints, adopting eco-friendly propulsion systems (Guo et al., 2024; Litwin et al., 2019) and energy-efficient designs (Luo et al., 2024; Niu et al., 2018; Zeng et al., 2024). In addition to reducing emissions, autonomous ships will focus on optimizing energy consumption, minimizing waste, and enhancing operational efficiency. These innovations will ensure that inland waterway transport remains a competitive, eco-friendly mode of shipping, aligning with global sustainability goals while improving performance and reducing environmental impact.
To transform sustainability rhetoric into verifiable knowledge, forthcoming studies should deliver a rigorous life-cycle comparison of GHG, heavy-metal, and particulate emissions of battery-electric versus hydrogen–battery hybrid barges, integrate techno-economic models that weigh battery-swap against high-rate shore-charging infrastructure on metrics of turnaround, grid resilience and levelized cost, and identify the recycling or second-life pathways that minimize the total environmental burden of retired maritime lithium-ion packs across alternative policy regimes; the quantitative insights obtained will directly inform the smart-infrastructure blueprint in Section 4.2.4 and the governance instruments discussed in Section 4.2.5.
4.2.4 Smart infrastructure and logistics networks
The future of inland waterway transport will depend on the seamless integration of autonomous ships with advanced port infrastructures. Currently, the lack of real-time coordination between ships, ports, and logistics systems limits the full potential of autonomous ships. As these vessels become more autonomous, ports must automate cargo handling, enhance real-time waterway monitoring, and improve communication networks. This will enable dynamic coordination, allowing vessels to adjust schedules, routes, and docking plans based on live data, thereby optimizing efficiency and minimizing downtime. Additionally, integrating autonomous ships with broader transportation networks—such as rail and road—will streamline the supply chain, facilitating smoother intermodal transfers and reducing wait times (Abu Aisha et al., 2024). A fully integrated, data-driven ecosystem will make inland waterway transport more efficient, sustainable, and competitive within the global logistics network.
To translate this vision into practice, stakeholders should move toward a shared digital infrastructure that continuously captures hydrological, traffic, energy and terminal-operation data, delivered through reliable, low-latency communication channels and coupled to adaptive control algorithms. Such an architecture allows autonomous vessels and port assets to negotiate dynamic schedules, insure safe passage through locks, and synchronise with rail-and-road timetables without manual intervention. When anchored in common data standards, robust cybersecurity rules and harmonised carbon-accounting methods, these capabilities create a self-adjusting logistics ecosystem that shortens dwell times, lowers emissions and strengthens the overall resilience of inland trade corridors.
4.2.5 Regulatory and governance
Ship accidents are frequent at sea, and while substantial research has focused on collision avoidance (Fan et al., 2023; Gao and Shi, 2020; Zhai et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2022), a comprehensive global regulatory and governance framework for autonomous ships remains absent. As the technology behind autonomous vessels continues to advance, regulatory frameworks must evolve to ensure their safe, equitable, and sustainable operation. Future efforts will likely prioritize the harmonization of international standards for autonomous inland shipping, facilitating seamless integration between ships, ports, and regulatory authorities within a unified legal structure. This will involve developing global guidelines that address a wide range of issues, including liability, data security, environmental protection, cybersecurity, and operational standards. By establishing these frameworks, the full potential of autonomous ships can be realized, ensuring that technological advancements are implemented in a safe, standardized, and environmentally responsible manner.
A regionally adaptive, multi-level governance approach is essential for inland autonomous shipping. Establishing sandbox zones in key river basins would allow governments to test new operational, liability, and certification frameworks. Digital tools like real-time digital twins and AI-driven risk-based permitting could enhance regulatory capacity despite institutional fragmentation.
4.3 Limitations
While this study provides valuable insights into the current state and trends in autonomous ships in inland waterway transport, several limitations should still be considered when interpreting the findings. The analysis relies solely on literature from the Web of Science (WoS) core collection, which may not capture the full range of the field. WoS tends to prioritize well-established journals, potentially underrepresenting studies from other databases like Scopus or Google Scholar. Additionally, WoS may have a bias toward English-language publications, overlooking valuable research in other languages, such as Chinese or Russian, that could offer unique insights into inland waterway shipping. Moreover, keyword selection and literature screening are crucial to the analysis. Any subjectivity or inconsistency in these processes can affect the comprehensiveness of the results. While the impact of subjectivity can be minimized, it cannot be entirely eliminated in the current study.
5 Conclusions
This study presents a meticulous bibliometric analysis of 163 publications from the Web of Science core collection, providing a quantitative overview of research on autonomous ships in inland waterway transport. By systematically examining 163 publications, this study precisely dissected publication trends, influential scholars, organizations, and countries and prominent journals. This analysis not only charts the historical growth trajectory of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport, but also pinpoints emerging research hotspots, challenges, and opportunities in the field.
Utilizing bibliographic mapping tools such as VOSviewer, the study has meticulously delineated the collaborative networks within the research community, offering a clear insights into scholarly and institutional interactions. The identification of research clusters has further elucidates dominant narrative patterns in the field, revealing areas of concentrated interest like autonomous navigation. The quantitative analysis establishes a robust framework for understanding the current state of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport, serving both a concise snapshot of existing research and a strategic roadmap for future investigations. Autonomous inland shipping faces core bottlenecks in technological adaptability, regulatory lag, cybersecurity, sustainability, and infrastructure readiness. Against this backdrop, the findings of this study highlight critical areas that warrant deeper exploration for researchers, and identify key gaps that must be addressed by industry stakeholders to drive technological and operational advancements.
The study contributes significantly to the field by systematically consolidating past progress and offering actionable insights that inform the future development and application of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport. Looking ahead, five strategic directions—fleet coordination, data-driven decision-making, green technologies, smart logistics infrastructure, and adaptive regulation—should guide the development of intelligent autonomous inland waterway ships. These findings offer a reference for researchers and policymakers aiming to align technological advancement with practical deployment and governance.
Author contributions
JX: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Validation, Methodology, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. QL: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Software, Visualization. YS: Writing – original draft, Resources, Writing – review & editing. PY: Writing – original draft, Software. YF: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HH: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52201413, the Natural Science Foundation of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, grant number 23ZR1434400, the Soft Science Research Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, grant number 24692105500, the Opening Foundation of Key Laboratory of Safety and Risk Management on Transport Infrastructures for the Ministry of Transport, grant number 2023KFKT015, the Research Seed Fund between UoL and SJTU, grant number WH410260402, the Oceanic Interdisciplinary Program of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, grant number SL2022PT107, and the Startup Fund for Young Faculty at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, grant number 22X010503469. The APC was funded by Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abu Aisha T., Audy J.-F., and Ouhimmou M. (2024). Toward an efficient sea-rail intermodal transportation system: a systematic literature review. J. Shipping Trade 9, 1–27. doi: 10.1186/s41072-024-00182-z
Acan H. (2017). On a uniformly random chord diagram and its intersection graph. Discrete Math. 340, 1967–1985. doi: 10.1016/j.disc.2016.11.004
Alamoush A. S. and Ölçer A. I. (2025). Maritime autonomous surface ships: architecture for autonomous navigation systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 13, 29. doi: 10.3390/jmse13010122
Alsalem T. S., Almaiah M. A., Lutfi A., and Shin S. (2023). Cybersecurity risk analysis in the ioT: A systematic review. Electronics 12, 3958. doi: 10.3390/electronics12183958
Altosole M., Balsamo F., Campora U., and Mocerino L. (2021). Marine dual-fuel engines power smart management by hybrid turbocharging systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9, 663. doi: 10.3390/jmse9060663
An J. (2024). Maritime logistics and digital transformation with big data: review and research trend. Maritime Business Rev. 9, 229–242. doi: 10.1108/MABR-10-2023-0069
Backalov I. (2020). Safety of autonomous inland vessels: An analysis of regulatory barriers in the present technical standards in Europe. Saf. Sci. 128, 104763. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104763
Bolbot V., Theotokatos G., Boulougouris E., and Vassalos D. (2020). A novel cyber-risk assessment method for ship systems. Saf. Sci. 131, 14. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2020.104908
Carey L. (2023). Contractual and tortious maritime liability regimes and the introduction of autonomous vessels. SSRN Electronic J. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4403620
Chang L., Watanabe T., Xu H., and Han J. (2022). Knowledge mapping on Nepal's protected areas using citeSpace and VOSviewer. Land 11, 1109. doi: 10.3390/land11071109
Chen H. L., Wen Y. Q., Zhu M., Huang Y. M., Xiong W. T., Xiao C. S., et al. (2023). A function-oriented electronic and electrical architecture of remote control ship on inland river: design, verification, and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 9, 1641–1652. doi: 10.1109/tte.2022.3178138
Chen L. Y., Hopman H., and Negenborn R. R. (2018). Distributed model predictive control for vessel train formations of cooperative multi-vessel systems. Transportation Res. Part C-Emerging Technol. 92, 101–118. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.04.013
Chen W. H., Ahmed M. M., Sofiah W. I., Isa N. A. M., Ebrahim N. A., and Hai T. (2021a). A bibliometric statistical analysis of the fuzzy inference system-based classifiers. IEEE Access 9, 77811–77829. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3082908
Chen Y.-Y., Ellis-Tiew M.-Z., Chen W.-C., and Wang C.-Z. (2021b). Fuzzy risk evaluation and collision avoidance control of unmanned surface vessels. Appl. Sciences-Basel 11, 6338. doi: 10.3390/app11146338
Coppede A., Vernengo G., and Villa D. (2018). A combined approach based on Subdivision Surface and Free Form Deformation for smart ship hull form design and variation. Ships Offshore Structures 13, 769–778. doi: 10.1080/17445302.2018.1457235
Deng H. M., Wei J., Min K. T., Yang H., Wang S., Xiao Z. R., et al. (2023). Research trends in ferroptosis since the origin of the concept: A bibliometric analysis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 50, 149–157. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13732
Dijk T., Dorsser H., Berg R., Moonen H., and Negenborn R. R. (2018). Smart ships and the changing maritime ecosystem. Montréal, Canada: CGI Inc.
Donandt K., Boettger K., and Soeffker D. (2022). “Short-term inland vessel trajectory prediction with encoder-decoder models,” in Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE).
Donthu N., Kumar S., Mukherjee D., Pandey N., and Lim W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Business Res. 133, 285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Duan P. L., Wang Y. Q., and Yin P. (2020). Remote sensing applications in monitoring of protected areas: A bibliometric analysis. Remote Sens. 12, 772. doi: 10.3390/rs12050772
ElMenshawy O. M., Ulku M. A., and Hsuan J. (2024). Navigating green ship recycling: A systematic review and implications for circularity and sustainable development. Sustainability 16, 7407. doi: 10.3390/su16177407
Epikhin A. I., Khekert E. V., Toriya T. G., and Modina M. A. (2023). Development of a self-learning system for intelligent control agents of a ship's engine. Mar. Intellectual Technol. 60, 85–91. doi: 10.37220/mit.2023.60.2.010
Fan Y. S., Sun Z., and Wang G. F. (2023). A novel intelligent collision avoidance algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning approach for USV. Ocean Eng. 287, 115649. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115649
Gabbar H. A. (2022). “Fast Charging for Marine Transportation,” in Fast Charging and Resilient Transportation Infrastructures in Smart Cities. Ed. Gabbar H. A. (Springer International Publishing, Cham), 147–163.
Gao M. and Shi G.-Y. (2020). Ship-collision avoidance decision-making learning of unmanned surface vehicles with automatic identification system data based on encoder-decoder automatic-response neural networks. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 8, 754. doi: 10.3390/jmse8100754
Ghazali M. H. M., Satar M. H. A., and Rahiman W. (2024). Unmanned surface vehicles: From a hull design perspective. Ocean Eng. 312, 118977. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118977
Guo J. D., Feng H., Xu H. X., Yu W. Z., and Ge S. S. (2023). D3-Net: Integrated multi-task convolutional neural network for water surface deblurring, dehazing and object detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 117, 105558. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105558
Guo X. D., Lang X., Yuan Y. P., Tong L., Shen B. Y., Long T., et al. (2024). Energy management system for hybrid ship: Status and perspectives. Ocean Eng. 310, 118638. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118638
Hagen I. B., Vassbotn O., Skogvold M., Johansen T. A., and Brekke E. F. (2023). Safety and COLREG evaluation for marine collision avoidance algorithms. Ocean Eng. 288, 13. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115991
Homburger H., Wirtensohn S., Hoher P., Baur T., Griesser D., Diehl M., et al. (2025). Solgenia-A test vessel toward energy-efficient autonomous water taxi applications. Ocean Eng. 328, 19. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.121011
Hong Y.-K., Wang Z.-Y., and Cho J. Y. (2022). Global research trends on smart homes for older adults: bibliometric and scientometric analyses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19, 14821. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214821
Hu Z. H., Zhou T. R., Zhen R., Jin Y. X., Li X. H., and Osman M. T. (2022). A two-step strategy for fuel consumption prediction and optimization of ocean-going ships. Ocean Eng. 249, 110904. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.110904
Huang X., Liu X., Shang Y. L., Qiao F., and Chen G. (2020). Current trends in research on bone regeneration: A bibliometric analysis. BioMed. Res. Int. 2020, 1–12. doi: 10.1155/2020/8787394
Jin X. Z., Zhang G. X., Yang M., Peng X. C., and Shi B. H. (2022). Cooperative multi-task traversing with complex marine environment for multiple unmanned surface vehicles inspired by membrane computing. Ocean Eng. 266, 112586. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112586
Jo S. W. and Shim W. S. (2019). LTE-maritime: high-speed maritime wireless communication based on LTE technology. IEEE Access 7, 53172–53181. doi: 10.1109/access.2019.2912392
Jumansyah R., Dewi N. P., Soegoto E. S., Luckyardi S., and Alshiqi S. (2023). Modeling islamic marketing research using vosviewer application A bibliometric analysis. J. Eastern Eur. Cent. Asian Res. 10, 31–45. doi: 10.15549/jeecar.v10i1.1090
Kanellos N., Katsianis D., and Varoutas D. (2024). A system dynamics modeling framework for forecasting the diffusion of ioT-enabling technologies. IEEE Commun. Mag. 62, 60–67. doi: 10.1109/mcom.002.2400115
Kim J. and Son J. (2020). An implementation of standardization for telecom systems on ships and offshore plants based on the TMS. Telecommunication Syst. 74, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s11235-019-00619-y
Korban D., Melnyk O., Onishchenko O., Kurdiuk S., Shevchenko V., and Obniavko T. (2024). Radar-based detection and recognition methodology of autonomous surface vehicles in challenging marine environment. Sci. J. Sil. Univ. Technol.-Ser. Transp. 122, 111–127. doi: 10.20858/sjsutst.2024.122.7
Koschorrek P., Kosch M., Nitsch M., Abel D., and Jürgens D. (2022). Towards semi-autonomous operation of an over-actuated river ferry. AT-Autom. 70, 433–443. doi: 10.1515/auto-2021-0152
Lazarowska A. (2024). A comparative analysis of computational intelligence methods for autonomous navigation of smart ships. Electronics 13, 1370. doi: 10.3390/electronics13071370
Lee D. and Woo J. (2022). Reactive collision avoidance of an unmanned surface vehicle through gaussian mixture model-based online mapping. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10, 472. doi: 10.3390/jmse10040472
Lee K. J., Shin D., Yoo D. W., Choi H. K., and Kim H. J. (2013). Hybrid photovoltaic/diesel green ship operating in standalone and grid-connected mode - Experimental investigation. Energy 49, 475–483. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2012.11.004
Leoni M. L. G., Mercieri M., Viswanath O., Cascella M., Rekatsina M., Pasqualucci A., et al. (2025). Neuropathic pain: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of research trends, contributions, and future directions. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 29, 73. doi: 10.1007/s11916-025-01384-1
Li H. H., Liu J. X., Wu K. F., Yang Z. L., Liu R. W., and Xiong N. X. (2018). Spatio-temporal vessel trajectory clustering based on data mapping and density. IEEE Access 6, 58939–58954. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2866364
Li S. J., Xu C. Q., and Liu J. L. (2022). Data-driven model predictive control of underactuated ships with unknown dynamics in confined waterways. J. Navig. 75, 1389–1409. doi: 10.1017/s0373463322000522
Litwin W., Lesniewski W., Piatek D., and Niklas K. (2019). Experimental research on the energy efficiency of a parallel hybrid drive for an inland ship. Energies 12, 1675. doi: 10.3390/en12091675
Liu J., Huang J. Z., Zhou Y., Li X. H., Ji S. L., Xiong H. Y., et al. (2022). From distributed machine learning to federated learning: a survey. Knowledge Inf. Syst. 64, 885–917. doi: 10.1007/s10115-022-01664-x
Liu R. W., Lu Y., Gao Y., Guo Y., Ren W. Q., Zhu F. H., et al. (2024b). Real-time multi-scene visibility enhancement for promoting navigational safety of vessels under complex weather conditions. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 25, 19979–19994. doi: 10.1109/tits.2024.3454597
Liu Y. C., Song R., Bucknall R., and Zhang X. Y. (2019). Intelligent multi-task allocation and planning for multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) using self-organising maps and fast marching method. Inf. Sci. 496, 180–197. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.05.029
Liu J. L., Yang F., Li S. J., Lv Y. Q., and Hu X. J. (2024a). Testing and evaluation for intelligent navigation of ships: Current status, possible solutions, and challenges. Ocean Eng. 295, 116969. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.116969
Luo J., Zhuang J. Y., Jin M. J., Xu F., and Su Y. M. (2024). An energy-efficient path planning method for unmanned surface vehicle in a time-variant maritime environment. Ocean Eng. 301, 117544. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117544
MaChado F., Duarte N., Amaral A., and Araujo M. (2022). “Digital transformation in manufacturing smes: A bibliometric analysis using vosviewer,” in 12th International Scientific Conference on Business and Management (Vilnius, Lithuania: Vilnius Gediminas Technical University (VILNIUS TECH)), Vilnius, Lithuania, 12–13 May 2022.
Martelli M., Virdis A., Gotta A., Cassarà P., and di Summa M. (2021). An outlook on the future marine traffic management system for autonomous ships. IEEE Access 9, 157316–157328. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3130741
Martínez F., Sànchez L. E., Santos-Olmo A., Rosado D. G., and Fernàndez-Medina E. (2024). Maritime cybersecurity: protecting digital seas. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 23, 1429–1457. doi: 10.1007/s10207-023-00800-0
Masoudi N. S. (2019). Smart shipping - seizing opportunities while controlling risks. Mar. Eng. 54, 236–238. doi: 10.5988/jime.54.236
Mei J. H. and Arshad M. R. (2017). A smart navigation and collision avoidance approach for Autonomous Surface Vehicle. Indian J. Geo-Marine Sci. 46, 2415–2421.
Meng L. C., Wen K.-H., Brewin R., and Wu Q. (2020). Knowledge atlas on the relationship between urban street space and residents' Health-A bibliometric analysis based on VOSviewer and citeSpace. Sustainability 12, 2384. doi: 10.3390/su12062384
Moreira L., Fossen T. I., and Soares C. G. (2007). Path following control system for a tanker ship model. Ocean Eng. 34, 2074–2085. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2007.02.005
Nath R. D. and Chowdhury M. A. F. (2021). Shadow banking: a bibliometric and content analysis. Financial Innovation 7, 68–68. doi: 10.1186/s40854-021-00286-6
Nguyen D. T., Trodahl M., Pedersen T. A., and Bakdi A. (2023). Verification of collision avoidance algorithms in open sea and full visibility using fuzzy logic. Ocean Eng. 280, 20. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114455
Ning J., Chen H. M., Li T. S., Li W., and Li C. Z. (2020). COLREGs-compliant unmanned surface vehicles collision avoidance based on multi-objective genetic algorithm. IEEE Access 8, 190367–190377. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3030262
Niu H. L., Lu Y., Savvaris A., and Tsourdos A. (2018). An energy-efficient path planning algorithm for unmanned surface vehicles. Ocean Eng. 161, 308–321. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.01.025
Nzengu W., Faivre J. M., Pauwelyn A. S., Bolbot V., Wennersberg L. A. L., and Theotokatos G. (2021). Regulatory framework analysis for the unmanned inland waterway vessel. Wmu J. Maritime Affairs 20, 357–376. doi: 10.1007/s13437-021-00237-z
Orzechowski S. C., Verheyen W., and Sys C. (2024). A systematic literature review of factors influencing the regulation of autonomous inland shipping in Europe. Eur. Transport Res. Rev. 16, 54. doi: 10.1186/s12544-024-00678-6
Osorio M. G., Ierardi C., Flores I. J., Martín M. P., and Gata P. M. (2024). Coordinated control of multiple autonomous surface vehicles: Challenges and advances - A systematic review. Ocean Eng. 312, 119160. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119160
Pei Z. Y., Kang Y. H., and Long F. (2024). Research and development of inland green and smart ship technologies in China. Appl. Sciences-Basel 14, 2316. doi: 10.3390/app14062316
Peng Y. (2023). COLREGs experience-based real-time route planning of intelligent ship. IEEE Access 11, 31924–31930. doi: 10.1109/access.2023.3260650
Peng Z. H., Wang D., Chen Z. Y., Hu X. J., and Lan W. Y. (2013). Adaptive dynamic surface control for formations of autonomous surface vehicles with uncertain dynamics. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 21, 513–520. doi: 10.1109/tcst.2011.2181513
Peng Z. H., Wang J., Wang D., and Han Q. L. (2021). An overview of recent advances in coordinated control of multiple autonomous surface vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 17, 732–745. doi: 10.1109/tii.2020.3004343
Peng X. R., Zhang L., Lee S., Song W. H., and Shou K. (2025). Navigating hospitality innovation, (1995-2023): a bibliometric review and forward outlook. J. Hospitality Tourism Technol. 16, 91–123. doi: 10.1108/jhtt-03-2023-0070
Petrovic E. K. and Thomas C. A. (2024). Global patterns in construction and demolition waste (C&DW) research: A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer. Sustainability 16, 1561. doi: 10.3390/su16041561
Qian L., Zheng Y. Z., Li L., Ma Y., Zhou C. H., and Zhang D. F. (2022). A new method of inland water ship trajectory prediction based on long short-term memory network optimized by genetic algorithm. Appl. Sciences-Basel 12, 16. doi: 10.3390/app12084073
Ranjan R., Kulkarni K., and Musharraf M. (2025). Potential of explanations in enhancing trust - What can we learn from autonomous vehicles to foster the development of trustworthy autonomous vessels? Ocean Eng. 325, 11. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2025.120753
Ren J., Zhang J., and Cui Y. N. (2021). Autonomous obstacle avoidance algorithm for unmanned surface vehicles based on an improved velocity obstacle method. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 10, 618. doi: 10.3390/ijgi10090618
Ren Y. J., Zhang L. Y., Shi P., and Zhang Z. Q. (2022). Research on multi-energy integrated ship energy management system based on hierarchical control collaborative optimization strategy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10, 1556. doi: 10.3390/jmse10101556
Ringbom H. (2019). Regulating autonomous ships-concepts, challenges and precedents. Ocean Dev. Int. Law 50, 141–169. doi: 10.1080/00908320.2019.1582593
Sang L. Z., Wall A., Mao Z., Yan X. P., and Wang J. (2015). A novel method for restoring the trajectory of the inland waterway ship by using AIS data. Ocean Eng. 110, 183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.10.021
Shang X. Y., Zhang G. Q., Lyu H. G., and Tan G. F. (2024). Research on intelligent navigation technology: intelligent guidance and path-following control of USVs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 12, 1548. doi: 10.3390/jmse12091548
Shi J. H. and Liu Z. J. (2020). Deep learning in unmanned surface vehicles collision-avoidance pattern based on AIS big data with double GRU-RNN. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 8, 682. doi: 10.3390/jmse8090682
Söffker D., Boschmann W., and Shyshova O. (2025). Progress towards multidimensionally scalable assisted and/or automated ship navigation and control - part I: reliable and autonomous guidance - a contradiction? J. Mar. Eng. Technol., 1–10. doi: 10.1080/20464177.2025.2476862
Song L., Lu C. G., Li C., Xu Y. J., Liu L., and Wang X. B. (2024). Progress of photovoltaic DC fault arc detection based on VOSviewer bibliometric analysis. Energies 17, 2540. doi: 10.3390/en17112450
Sonntag V., Perrusquía A., Tsourdos A., and Guo W. S. (2025). A COLREGs compliance reinforcement learning approach for USV manoeuvring in track-following and collision avoidance problems. Ocean Eng. 316, 13. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.119907
Stepien B. (2025). “Defending the Fleet: Cybersecurity and Autonomous Ships,” in 40 Years of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (Abingdon, UK; New York, NY, USA: Routledge), 1 edition, 334–344.
Sulistiawati J. A., Kusumah Y. S., Dahlan J. A., Juandi D., and Arifin S. (2023). The trends of studies in technology-Assisted inquiry-Based learning: the perspective of bibliometric analySIS. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 18, 69–80.
Sun Z. Y., Sun H. B., Li P., and Zou J. (2022). Cooperative strategy for pursuit-evasion problem with collision avoidance. Ocean Eng. 266, 112742. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112742
Symes S., Blanco-Davis E., Graham T., Wang J., and Shaw E. (2024). Cyberattacks on the maritime sector: A literature review. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 23, 689–706. doi: 10.1007/s11804-024-00443-0
Tadros M., Ventura M., and Soares C. G. (2023). Review of the decision support methods used in optimizing ship hulls towards improving energy efficiency. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 11, 17. doi: 10.3390/jmse11040835
Tang R. L., Li X., and Lai J. G. (2018). A novel optimal energy-management strategy for a maritime hybrid energy system based on large-scale global optimization. Appl. Energy 228, 254–264. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.06.092
Tusher H. M., Munim Z. H., Notteboom T. E., Kim T. E., and Nazir S. (2022). Cyber security risk assessment in autonomous shipping. Maritime Economics Logistics 24, 208–227. doi: 10.1057/s41278-022-00214-0
van Cappelle L. E., Chen L. Y., and Negenborn R. R. (2018). “Survey on short-term technology developments and readiness levels for autonomous shipping,” in 9th International Conference on Computational Logistics (ICCL) (Cham, Switzerland: Springer Cham), Vietri sul Mare, ITALY, 01–03 Oct 2018.
van Eck N. J. and Waltman L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84, 523–538. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Van Hoecke L., Laffineur L., Campe R., Perreault P., Verbruggen S. W., and Lenaerts S. (2021). Challenges in the use of hydrogen for maritime applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 815–843. doi: 10.1039/d0ee01545h
von Brandis A., Menges D., and Rasheed A. (2025). Multi-target tracking for autonomous surface vessels using liDAR and AIS data integration. Appl. Ocean Res. 154, 19. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2024.104348
Wang Y. Q., Chen X. Q., Wu Y. Z., Zhao J. S., Postolache O., and Liu S. H. (2024b). Visual navigation systems for maritime smart ships: A survey. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 12, 1781. doi: 10.3390/jmse12101781
Wang N., Gao Y., Liu Y. J., and Li K. (2022a). Self-learning-based optimal tracking control of an unmanned surface vehicle with pose and velocity constraints. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 32, 2950–2968. doi: 10.1002/rnc.5978
Wang W., Gheneti B., Mateos L. A., Duarte F., Ratti C., Rus D., et al. (2019). “Roboat: an autonomous surface vehicle for urban waterways,” in IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), New York, 04–08 Nov.
Wang J. and Kim H.-S. (2023). Visualizing the landscape of home ioT research: A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer. Sensors 23, 3086. doi: 10.3390/s23063086
Wang W., Mateos L. A., Park S., Leoni P., Gheneti B., Duarte F., et al. (2018). “Design, modeling, and nonlinear model predictive tracking control of a novel autonomous surface vehicle,” in IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May.
Wang N., Song J., and Dong Q. (2024a). Structural design of a wave-adaptive unmanned quadramaran with independent suspension. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 25, 12395–12406. doi: 10.1109/tits.2024.3375278
Wang S. B., Zhang Y. J., Huo R., and Mao W. G. (2022b). A real-time ship collision risk perception model derived from domain-based approach parameters. Ocean Eng. 265, 112554. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112554
Wei T., Feng W., Chen Y. F., Wang C. X., Ge N., and Lu J. H. (2021). Hybrid satellite-terrestrial communication networks for the maritime internet of things: key technologies, opportunities, and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 8, 8910–8934. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2021.3056091
Wu B., Cheng T. T., Yip T. L., and Wang Y. (2020). Fuzzy logic based dynamic decision-making system for intelligent navigation strategy within inland traffic separation schemes. Ocean Eng. 197, 15. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106909
Wu H. Y., Qu Y. Y., Lin S. H., Zhou J., Qiao R. Z., Zhang Z. Z., et al. (2021). “Contrastive learning for compact single image dehazing,” in IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE), 19–25 Jun 2021.
Xiong H., Chen X., Feng J., Zhang F., Qiu M., Zhang Q., et al. (2024). Bibliometric and visual analysis of studies on ceramic membranes: A review. Membranes 14, 144. doi: 10.3390/membranes14070144
Xu L., Wu J. Y., Yan R., and Chen J. H. (2025). Is international shipping in right direction towards carbon emissions control? Transp. Policy 166, 189–201. doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2025.03.009
Yan X. T., He J., Ren Q. Q., Bai C. G., Zhang C. J., and Wang C. W. (2022). Research on extraction method of multiple narrow channel vessel trajectory feature in yangtze river based on VITS data. J. Advanced Transportation 2022, 1–17. doi: 10.1155/2022/6533223
Yigit K. and Acarkan B. (2018). A new electrical energy management approach for ships using mixed energy sources to ensure sustainable port cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 40, 126–135. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2018.04.004
Young D. (2024). Counting bubbles in linear chord diagrams. J. Integer Sequences 27, 2442. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2311.01569
Yousaf A., Amro A., Kwa P. T. H., Li M. X., and Zhou J. Y. (2024). Cyber risk assessment of cyber-enabled autonomous cargo vessel. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 46, 100695. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcip.2024.100695
Yuan X. Y., Wang J. W., Zhao G., and Wang H. B. (2024). Comprehensive study on optimizing inland waterway vessel routes using AIS data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 12, 28. doi: 10.3390/jmse12101775
Zacarias T. G. and Sant'Ana W. C. (2024). A bibliometric and comprehensive review on condition monitoring of metal oxide surge arresters. Sensors 24, 235. doi: 10.3390/s24010235
Zeng H., Su Z., Xu Q. C., Li R. D., Wang Y. T., Dai M. H., et al. (2024). USV fleet-assisted collaborative computation offloading for smart maritime services: an energy-efficient design. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 73, 14718–14733. doi: 10.1109/tvt.2024.3359310
Zhai P. Y., Zhang Y. J., and Wang S. B. (2022). Intelligent ship collision avoidance algorithm based on DDQN with prioritized experience replay under COLREGs. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10, 585. doi: 10.3390/jmse10050585
Zhang G. Q., Han J., Li J. Q., and Zhang X. K. (2022). APF-based intelligent navigation approach for USV in presence of mixed potential directions: Guidance and control design. Ocean Eng. 260, 111972. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111972
Zhang J., Ren J., Cui Y. N., Fu D. L., and Cong J. Y. (2024a). Multi-USV task planning method based on improved deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 11, 18549–18567. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2024.3363044
Zhang L., Zhu Y. X., Banda O. A. V., Du L., Gan L. X., and Li X. B. (2024b). Navigational risk assessment of inland waters based on bi-directional PSO-LSTM algorithm and ship maneuvering characteristics. Ocean Eng. 310, 118628. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.118628
Zhao X. Y., He Y. X., Huang L. W., Mou J. M., Zhang K., and Liu X. (2022). Intelligent collision avoidance method for ships based on COLRGEs and improved velocity obstacle algorithm. Appl. Sciences-Basel 12, 8926. doi: 10.3390/app12188926
Zhao X. Y., Zhang S. N., Nan D. Y., Han J. L., and Kim J. H. (2024). Human-computer interaction in healthcare: A bibliometric analysis with citeSpace. Healthcare 12, 2467. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12232467
Zhao Z. Y., Zhu B., Zhou Y., Yao P., and Yu J. B. (2023). Cooperative path planning of multiple unmanned surface vehicles for search and coverage task. Drones 7, 21. doi: 10.3390/drones7010021
Zheng Y. Z., Liu P., Qian L., Qin S. Q., Liu X. Y., Ma Y., et al. (2022). Recognition and depth estimation of ships based on binocular stereo vision. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10, 22. doi: 10.3390/jmse10081153
Zheng Y. Z., Qian L., Zhang Y. F., Cao J. X., Liu X. Y., and Ma Y. (2025). A novel image dehazing algorithm for complex natural environments. Pattern Recognition 157, 110865. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110865
Zhou D., Huang F., Wang Q., and Liu X. (2021a). The role of structure change in driving CO2 emissions from China's waterway transport sector. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 171, 105627. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105627
Zhou J. C., Jiang P., Zou A. R., Chen X. L., and Hu W. W. (2021b). Ship target detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv5. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9, 908. doi: 10.3390/jmse9080908
Zhu S. W., Sun N., Lv S. Y., Chen K. F., Fang W., and Cao L. L. (2024). Research progress on intelligent optimization techniques for energy-efficient design of ship hull forms. J. Membr. Comput. 6, 318–334. doi: 10.1007/s41965-024-00169-6
Zou Y. J., Sun M., Xu W. P., Zhao X., Du T. L., Sun P. T., et al. (2022). Advances in marine self-powered vibration sensor based on triboelectric nanogenerator. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 10, 1348. doi: 10.3390/jmse10101348
Zou Y. Q., Xiao G. N., Li Q. J., and Biancardo S. A. (2025). Intelligent maritime shipping: A bibliometric analysis of internet technologies and automated port infrastructure applications. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 13, 26. doi: 10.3390/jmse13050979
Zupic I. and Čater T. (2015). Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organizational Res. Methods 18, 429–472. doi: 10.1177/1094428114562629
Appendix A
Explanation of Visualization Parameters:
Threshold: The minimum number of occurrences (e.g., publications, co-authorships, citations) required for an item (author, institution, country, keyword, etc.) to be included in the map. For example, a threshold of 3 in an author collaboration network means only authors with at least 3 documents are displayed.
Attr. (Attraction): A layout parameter that controls the strength of the attractive forces between related nodes. Higher attraction values pull related nodes closer together, emphasizing cluster cohesion.
Repul. (Repulsion): Short for Repulsion, this layout parameter determines how strongly nodes repel each other. A higher repulsion value spreads the nodes farther apart, helping to prevent overlap and improve readability.
Type: The visualization type used, including:
1) Network: Displays relationships (e.g., co-authorships, co-citations) as a graph of nodes and links.
2) Overlay: Adds additional attributes (e.g., average publication year, citation impact) as color overlays on a network map.
3) Density: Shows the concentration or frequency of items (e.g., keywords) using heatmap-style coloring to indicate areas of higher intensity.
Table A1 Parameter setting for bibliographic mapping.
Keywords: autonomous ship, inland waterway transport, bibliometric analysis, VOSviewer, evolutionary trends
Citation: Xue J, Li Q, Song Y, Yang P, Feng Y and Hu H (2025) A bibliometric analysis of the development of autonomous ships in inland waterway transport. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1624596. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1624596
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 23 July 2025.
Edited by:
Lang Xu, Shanghai Maritime University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qiang Mei, Shanghai Maritime University, ChinaGuangnian Xiao, Shanghai Maritime University, China
Copyright © 2025 Xue, Li, Song, Yang, Feng and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jie Xue, ai54dWVAc2p0dS5lZHUuY24=
 Jie Xue
Jie Xue Qianbing Li1
Qianbing Li1 Peijie Yang
Peijie Yang