- 1Institute for Marine Biological Resources and Biotechnology (IRBIM), National Research Council (CNR), Ancona, Italy
- 2Institute of Polar Sciences (ISP), National Research Council (CNR), Bologna, Italy
We addressed the impact of angling in two Mediterranean inshore sites by conducting a tag-recapture study on caught-and-released black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus) and giant goby (Gobius cobitis). We assessed the relationship between the fish vitality at release and the main factors affecting it, i.e. air exposure time, water temperature, fish length and handling. Then, we used conventional fish tags to study fish survivability to catch and release, growth rates, behaviour and site fidelity. Overall, 17 species (mainly gobids and sparids) were caught, with differences in species composition and abundance between the two sites, probably related to their different depth range. A total of 136 individuals of S. porcus and 38 of G. cobitis were caught, tagged and released. S. porcus had a better vitality than G. cobitis once released, which was negatively associated with an increase in air exposure time, although not significant. We recorded 34 recapture events, with a resulting recapture rate of 19.9% for S. porcus (without considering multiple recaptures) and 5.3% for G. cobitis. The length-weight relationship revealed an isometric growth in both species. The von Bertalanffy growth parameters (± standard error) estimated for S. porcus were L∞ = 26 cm ± 5.25 and k = 0.21 ± 0.09, with no significant differences detected in growth rate between immature and mature individuals. The species’ high site fidelity and resilience to catch-and-release indicate its potential susceptibility to repeated angling in confined coastal habitats. These results highlight the need to account for the cumulative ecological impacts of recreational fisheries in the management of coastal fish populations.
1 Introduction
Recreational fishing in both marine and freshwater ecosystems worldwide is an important activity in socio-economic terms (Morales-Nin et al., 2005; Hyder et al., 2018) and in number of participants (Arlinghaus and Cooke, 2009; Iborra et al., 2024). Recreational fisheries can have a significant impact on aquatic ecosystems, especially due to the removal of fish biomass of several species that are also of commercial importance (Coleman et al., 2004; Erbay et al., 2024). Most of these catches are currently not included in official statistics and thus excluded from the assessments of the status of commercial stocks (Bolognini et al., 2022). The recreational fishing impact is increasingly being recognized and evaluated by the scientific community in recent years (Brownscombe et al., 2019; ICES, 2024), yet information is still scarce for several fisheries concerning reliable catch and mortality estimates and socio-economic aspects (Grati et al., 2021). The insufficient data availability hinders a proper consideration of this sector in policymaking and thus the sustainable management of fish stocks (Hyder et al., 2014).
In the Mediterranean, people involved in angling i.e. fishing conducted using rod, reel and hook, represent one of the largest fractions of marine recreational fishers (Giovos et al., 2018). Marine coastal areas are the most frequently exploited, due to their ease accessibility for a wide variety of anglers; therefore, fishing from the shoreline (beaches, rocky areas and harbours) accounts for the highest participation rates (Bolognini et al., 2022). A portion of the fish caught by anglers is released back into the water, usually alive and immediately after catch, in what is referred as “catch-and-release” practice (C&R, hereafter). C&R can be mandatory e.g. for individuals under the minimum landing size or exceeding the allowed quota (depending on regulations) or voluntary (Arlinghaus et al., 2007). The voluntary C&R practices are growing in the latest years, since they are considered as a conservation practice to prevent overfishing and help the sustainable management of fish stocks (Cooke and Schramm, 2007; Ferter et al., 2013). The few estimates available for the Mediterranean suggest that at least half of the fish caught by anglers are released (Font and Lloret, 2014; Papadopoulos et al., 2022). However, there is a fishing mortality associated to caught-and-released fish, which is usually species-specific (NSW-DPI, 2013). Also, the survivability, fitness and behaviour of a fish post-release vary depending on i) fishing-related stressors, as hooking, handling, exhaustive physical exercise, air exposure; ii) environmental factors, as air or water temperature, catch depth; iii) life and reproductive stage of the individual (NSW-DPI, 2013; Depasquale et al., 2023).
Sedentary species such as scorpionfish (Scorpaena spp.) are amongst the most valuable captures for small-scale fisheries in coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea (Battaglia et al., 2010; Sureda et al., 2020). Annual landings of scorpionfish can range from tens to several hundreds of tons, depending on geographical area; for instance, in 2021, landings in Italy ranged from 41.2 tons in the Adriatic Sea to 446.6 tons in the Ionian Sea (FAO, 2023), while in the early 2000s, total catches of black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus) in the eastern basin reached 240 tons (Bilgin and Çelik, 2009). Recreational fisheries can contribute to the fishing mortality for these species, which can be caught accidentally when targeting other species, but also voluntarily through specific fishing techniques (Tiralongo, 2024). One of such techniques is the light rock fishing (LRF), which employs single silicon lures and light sinkers to target inshore rockfish species and has become a recent trend among Mediterranean and Black Sea anglers (Peksu et al., 2020). Other rockfish commonly targeted by this technique belong to the Gobiidae family; some species can have also a local commercial interest (e.g. grass goby, Zosterisessor ophiocephalus and black goby, Gobius niger; Hajji et al., 2013; Virgili et al., 2024), while the giant goby (Gobius cobitis) is considered as key species in intertidal rocky shores (Faria and Almada, 2006). There is some degree of C&R by anglers towards rockfish species, especially for smaller individuals, but its effects on survivability and sub-lethal effects is still not known.
In this study, we addressed the impact of recreational fishing towards two inshore fish species i.e. black scorpionfish (S. porcus) and giant goby (G. cobitis) by conducting a tag-and-recapture experiment on specimens caught-and-released by anglers from shore using LRF technique. We used conventional fish tagging as it is one of the most useful approaches to study C&R effects, besides providing some additional biological data (e.g., growth and spatial movements; Gillanders et al., 2001). Specifically, we aimed at:
i. Assessing the post-release vitality of caught-and-released individuals of S. porcus and G. cobitis using hook and line (LRF technique) and estimate the main factors (environmental, handling-related, individual-related) affecting it;
ii. ii) Estimating survivability, growth rates, behaviour and site fidelity of S. porcus and G. cobitis by tag-recapture data.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Target species
In the present study, we focused on two inshore rockfish species. S. porcus and G. cobitis are predators mainly inhabiting rocky substrates of coastal waters (Harmelin-Vivien et al., 1989; Faria and Almada, 2006, 2009; Compaire et al., 2018).
Along with other scorpionfish species, the black scorpionfish is regarded as a key predator crucial to the proper functioning of rocky-reef ecosystems (D’Iglio et al., 2024). It is one of the main species, in terms of abundance and biomass, in the catches of several Mediterranean artisanal fisheries in Spain (Forcada et al., 2009), Italy (La Mesa et al., 2010), Turkije (Bilgin and Çelik, 2009) and Croatia (Stagličić et al., 2011), thus representing a large source of income as it is considered a valuable species for fish soup. It is mostly caught by means of passive set nets and the fishing effort towards this species has increased in some areas, with consequent reduction in stocks (Ferri et al., 2012; D’Iglio et al., 2024). S. porcus is a target species also for some recreational fishing activities e.g. spearfishing (Tiralongo, 2024) and LRF technique (Peksu et al., 2020).
The giant goby inhabits intertidal zones of rocky shores and acts as an indicator of the health of these ecosystems, which are facing several threats, as habitat degradation due to coastal development and pollution, and climate change (Claudet and Fraschetti, 2010; Sarà et al., 2014). G. cobitis is locally protected in the United Kingdom (Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981; Tillin and Riley, 2017), which represents the northernmost area of its distribution, expanding to the Atlantic coasts down to Morocco and including the Mediterranean. Although it is not targeted by commercial fisheries, the giant goby represents a gamefish for LRF anglers (Froese and Pauly, 2010).
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed S. porcus and G. cobitis as Least Concern in the Mediterranean Sea, although information on abundances and population trends of both species is currently scarce.
2.2 Study area and data collection
Two study areas were selected for the tagging programme (Figure 1). Both are inshore locations within two Italian harbours of the north-western Adriatic Sea, i.e. Numana (Site 1; small touristic harbour) and Ancona (Site 2; large commercial harbour), consisting in semi-enclosed areas connected to the open sea through the main entrance of the harbours. The grounds of both sites are characterized by artificial blocks below the docks, surrounded by sandy bottom. Each site, measured in dock length, was divided into sub-areas (10 meters long) to take into account the exact place where the fish were caught, released and eventually recaptured. The main features of the study areas are listed in Table 1.
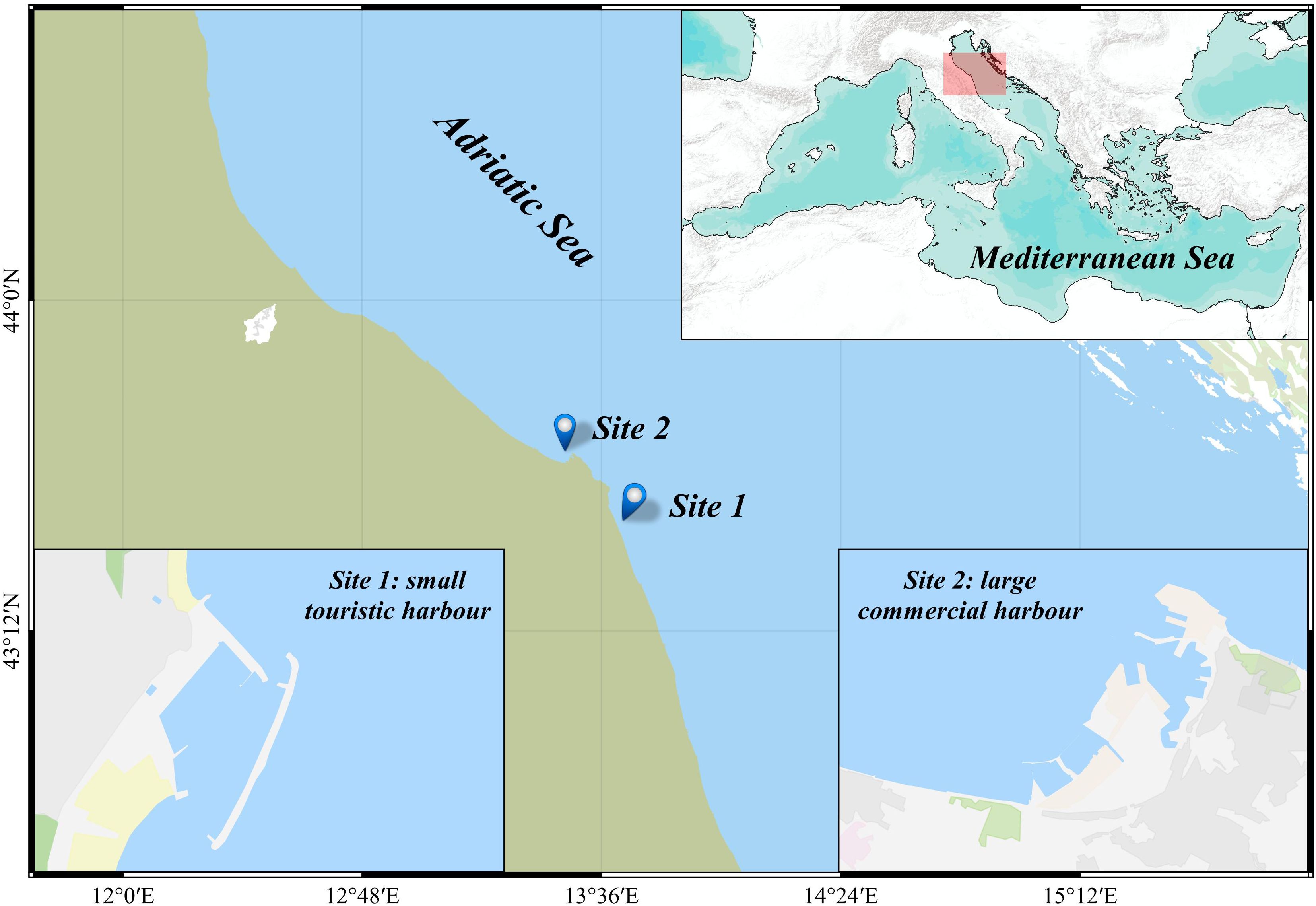
Figure 1. Map of the study area (north-western Adriatic Sea), where both Site 1 (small touristic harbour) and Site 2 (large commercial harbour) are located.
A total of 88 fishing sessions were conducted from January 2024 to January 2025, covering all four seasons (31 in winter, 24 in spring, 21 in autumn, 12 in summer). Total fishing time amounted to 91.5 hours at Site 1 and 48 hours at Site 2, irrespective of the number of anglers. In each site and session, fishing operations were performed from the dock using the LRF technique by 1 to 5 experienced anglers, while one researcher witnessed as onsite observer. The fishing rods were 1.8-2.1 m long with casting weight of 0.5-15 gr, associated with 1000–2500 spinning reels spooled with 0.06-0.10 mm braided line and 0.20-0.28 mm fluorocarbon leader. The jig-heads used had hook size ranging from 2 to 8, and lead weight from 0.9 to 5 gr. The lures on the hook were largely the same across the entire study period: i) 4-7 cm long silicon shads and crabs as artificial bait; ii) pieces of deep-water rose shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) as natural bait. Additional baits (i.e. bread and anchovy, Engraulis encrasicolus) were used by interviewed anglers who recaptured tagged fish outside the monitored fishing operations. Each fishing session consisted in one or more anglers covering all the sub-areas and deploying the jig-head within the rocks below the docks. In sessions with multiple baits (artificial and natural), one angler used artificial bait and the other angler used natural bait. The jig-head was maintained in constant movement as typical in LRF and spinning techniques.
Targeted species caught (S. porcus and G. cobitis) were individually measured (total length, L, to the nearest 0.1 mm below), weighted (total body weight, W, to the nearest 0.1 g below), tagged by the researcher and released in the exact location where hooked. A T-bar anchor tag (Hallprint Fish Tags, Hindmarsh Valley, Australia) labelled with a unique five-digit identification number and a telephone number was placed below the dorsal fin of each fish. The air exposure time, which depended on unhooking, measuring and tagging procedures and/or photos before release was recorded. The fish handling process i.e. the retrieval, unhooking and tagging phases prior to release, was recorded as a two-category handling: i) good, if the fish did not fell to the ground or did not show any bleeding or evident damage; ii) poor, if the fish fell to the ground, showed bleeding or evident damage. Also, information on the fish vitality at release was recorded as a two-category instant vitality, based on visual inspection from both observer and fisher(s): i) good, i.e. the fish quickly swam away as soon as touching the water, with vigorous body movement; ii) poor, i.e. the fish rested for some second in the water with no reflexes and/or swam away in a slow manner with weak body movement or unbalanced. For all the other species caught in the sessions, only the individual weight was recorded.
For each fishing session, data on both air and water temperature was recorded. Information on recaptured fish (date, code, length, weight, location, bait type) was provided by researchers during fishing sessions (direct observation) or by fishers through the phone number printed on the tag (interview).
2.3 Data analysis
All analyses described below were performed within the R statistical environment (R Core Team, 2025).
2.3.1 Fishing effort
To allow for comparisons, catch data was standardized by calculating the Catch Per Unit Effort (CPUE) for both the total catch and the two target species. CPUE was expressed both in terms of biomass (CPUEw) and number of individuals (CPUEn) caught per angler per hour of fishing in each session, including those with zero catch. The Kruskal–Wallis H test (χ2) was applied to assess differences in CPUE between bait types (artificial or natural), and across target species and sites. To quantitatively describe the distribution of CPUEw and CPUEn of target species across sites, we further applied descriptive statistics, including mean, standard deviation, and percentage.
2.3.2 Length-weight relationship
Being one of the most used in any analysis of fishery data, the Le Cren formula W = a*Lb allows to estimate W from L for individuals and viceversa (Le Cren, 1951; Froese, 2006; Petetta et al., 2019). We calculated the length-weight relationship for both S. porcus and G. cobitis, to obtain information on their growth (Petetta et al., 2019). The parameter a is the intercept, representing the initial growth coefficient. The exponent b is the slope and represents the relative growth rates of the variables, with b = 3, the growth is isometric, while with b statistically different from 3, the growth is allometric (positive if b > 3, negative if b < 3).
We estimated both a and b parameters by linear regression analyses using log-transformed data, and assessed the degree of interdependence between them by the Pearson correlation coefficient (r). Then, we applied a t-test (ts=(b-3)/sb) with a confidential level of 95%, to determine the significance of morphometric relationships through the allometry coefficient b (=, < or > 3) (Huxley and Teissier, 1936; Sokal and Rohlf, 1987).
2.3.3 Vitality after release
We applied generalized linear models (GLMs) with a binomial error distribution and a logit link function to investigate the relationship between post-release vitality (response variable; good/poor) and a set of explanatory variables. All plausible covariates were initially considered, including fish total length (cm), water temperature at capture (°C), air exposure time (minutes), species (G. cobitis/S. porcus), handling (good/poor), and site (1/2), as well as all two‐way interactions with species. We assessed multicollinearity among covariates using pairwise Pearson correlation coefficients, considering values above 0.8 as indicative of potential collinearity issues.
The selection of the best model was guided by the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC), using a bidirectional stepwise selection procedure to identify the most parsimonious combination of predictors. Model adequacy was then evaluated by visually inspecting residual plots for violations of model assumptions or indications of poor fit, following the approach by Zuur et al. (2009). The effect of the covariates on the response variable in the final model was assessed using a p-value threshold of 0.05 (significant effect with p-value < 0.05).
2.3.4 Growth modelling
Sufficient tag-recapture data were obtained only for S. porcus, allowing us to estimate, for its sampled population, the von Bertalanffy growth parameters L∞ and k, i.e. the asymptotic maximum length and the Brody growth coefficient, respectively, by applying the formula Lt - Lm = (L∞ - Lm) (1- e-kΔt). Lm is the fish length at the time of tagging, Lt is the length of the fish at the time of recapture, and Δt is the time at liberty, i.e. the number of days between the release and subsequent recapture (Fabens, 1965). Growth parameters are estimated by minimizing the sum of squared residuals. The individual growth rate was derived from the increment size during the time at liberty and expressed as daily percentage change in body size (G = (100 x (Lr - Lm) Δt-1) Lt-1) to be able to compare growth in specimens of different size. Considering a threshold length of 17 cm, which represents the size at sexual maturity of S. porcus in the north-western Adriatic (La Mesa et al., 2010), tag-recaptured fish were divided into two groups, i.e. immature and mature individuals. A linear regression analysis was performed to model fish size increment against the time at liberty for each group, and one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was applied to test for equal means and homogeneity of slopes between them, again by using a p-value threshold of 0.05 to detect significant differences.
2.4 Ethical statement
Specific authorization was required for the fishing activities inside the two sampling sites, from both the Italian Coast Guard (Site 1) and private authority (Site 2). Protected species have not been involved in any part of the field studies. Ethical review and approval were not required because fish were sampled during recreational angling activities and were not subject to any experimental manipulation, in line with the Explanatory Note of the Italian Ministry of Health’s Directorate- General for Animal Health and Veterinary Medicinal Products (DGSAF) of July 26, 2017. Animal manipulation complied with the guidelines of the European Union Directive (2010/63/EU) and the Italian Legislative Decree 26 of March 4, 2014 “Attuazione della Direttiva 2010/63/UE sulla protezione degli animali utilizzati a fini scientifici”.
3 Results
3.1 Catch and tagging overview
Overall, 17 species (16 fish species and 1 cephalopod species) were caught, respectively 15 in Site 1 and 9 in Site 2 (Supplementary Table S1). Each LRF session monitored often resulted in more than 4 species caught. Most of the catches consisted of small fish belonging to the Gobiidae (4 species), Sparidae (3 species) and Blennidae (2 species) families. In Site 1, the catch was dominated by S. porcus, in both number of individuals and weight, followed by rock goby (Gobius paganellus); all the other species were caught in small amounts (less than 10 individuals). In Site 2, G. paganellus was the most abundant catch in both number of individuals and weight, followed, in number of individuals, by black goby (Gobius niger), G. cobitis and S. porcus. We decided not to tag individuals of G. paganellus or G. niger since: i) they are not considered target species of LRF technique; ii) the majority of them were too small to be tagged with T-bar anchor tag (dimensions: 2.5 cm in length, 0.1 g in weight). Further species were caught, in small amounts, only in Site 1 (n = 8) while fewer species were caught only in Site 2 (n = 2). Full species lists for both sites are provided in Supplementary Table S1. Considering the total catch, the mean (± standard error) CPUEw was 61.7 g ± 6.01 with artificial bait and 39.3 ± 5.97 with natural bait, with no significant differences detected (χ² = 1.34; p value = 0.25).
A total of 149 S. porcus (129 in Site 1; 20 in Site 2) and 38 G. cobitis (6 in Site 1; 32 in Site 2) were captured during the fishing sessions (Supplementary Table S1). All the individuals were tagged, except for recaptured individuals (which were already tagged), resulting in 136 S. porcus and 38 G. cobitis. The length range was 9.0-27.4 cm for S. porcus and 10.2-26.9 cm for G. cobitis. The length-frequency distributions are represented in Figure 2. Regarding S. porcus, in both sites, we observed the highest frequencies for individuals of 11-12 cm and 14-15 cm length ranges. By contrast, the largest individuals (above 19 cm) were caught only in Site 1. Regarding G. cobitis, all the individuals caught in Site 1 were above 15 cm, while in Site 2 we observed the highest frequencies for both smaller individuals (11-13 cm length range) and for individuals of 17-18 cm length range (Figure 2).
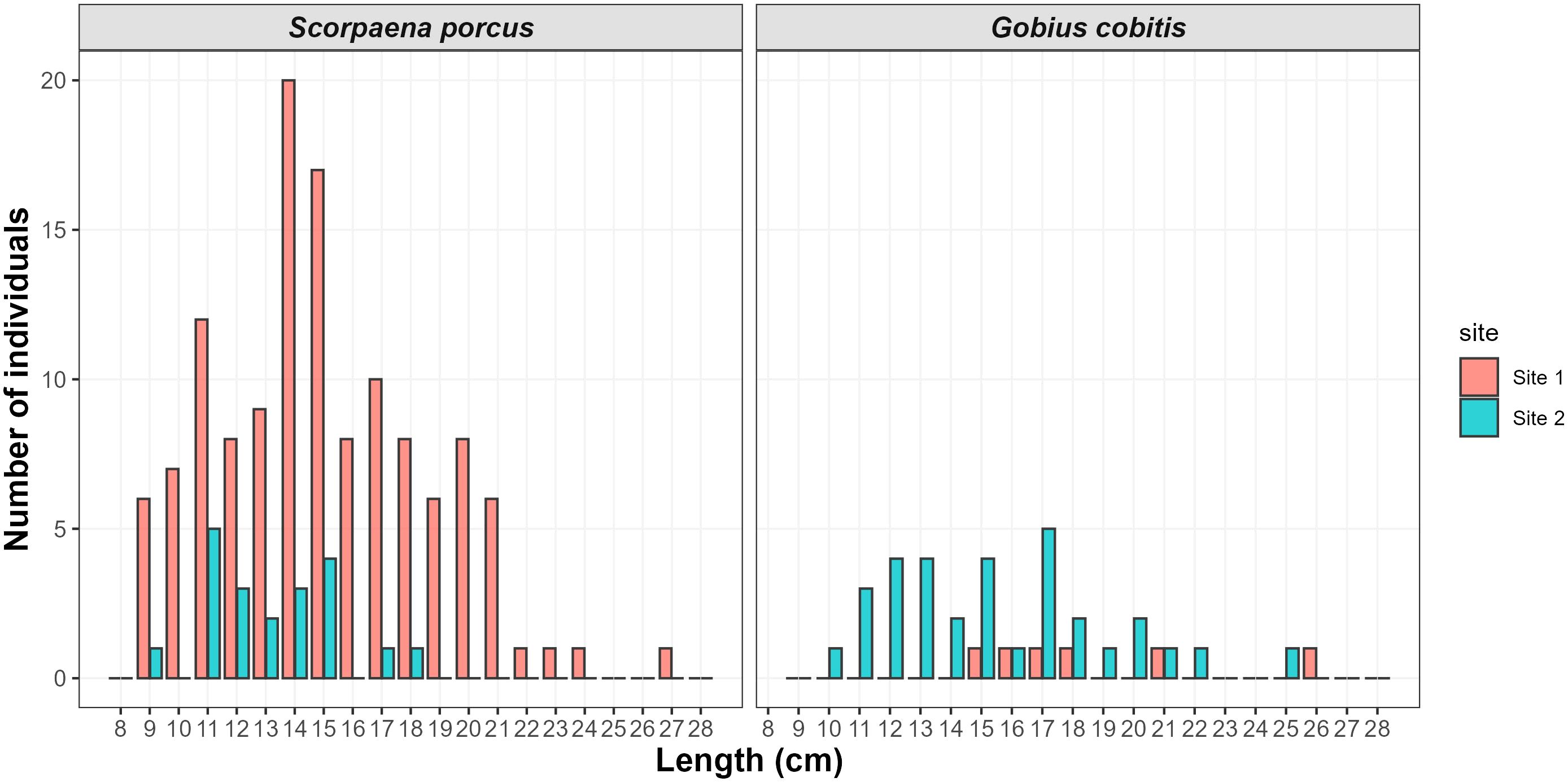
Figure 2. Length frequency distribution of black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus) and giant goby (Gobius cobitis) in Sites 1 (pink) and 2 (green).
We observed a significant difference between the CPUE of S. porcus and G. cobitis within the two Sites (Figure 3 and Supplementary Table S2). The mean (± standard error) CPUE of S. porcus was significantly higher in Site 1 (CPUEw 106.51 g ± 18.16 and CPUEn 1.11 ± 0.17) than in Site 2 (CPUEw 31.12 g ± 8.54 and CPUEn 0.51 ± 0.14). By contrast, a significantly higher CPUE for G. cobitis was observed in Site 2 (CPUEw 39.91 g ± 10.00 and CPUEn 0.69 ± 0.12), when compared to Site 1 (CPUEw 7.50 g ± 4.23 and CPUEn 0.07 ± 0.04; Figure 3 and Supplementary Table S2).
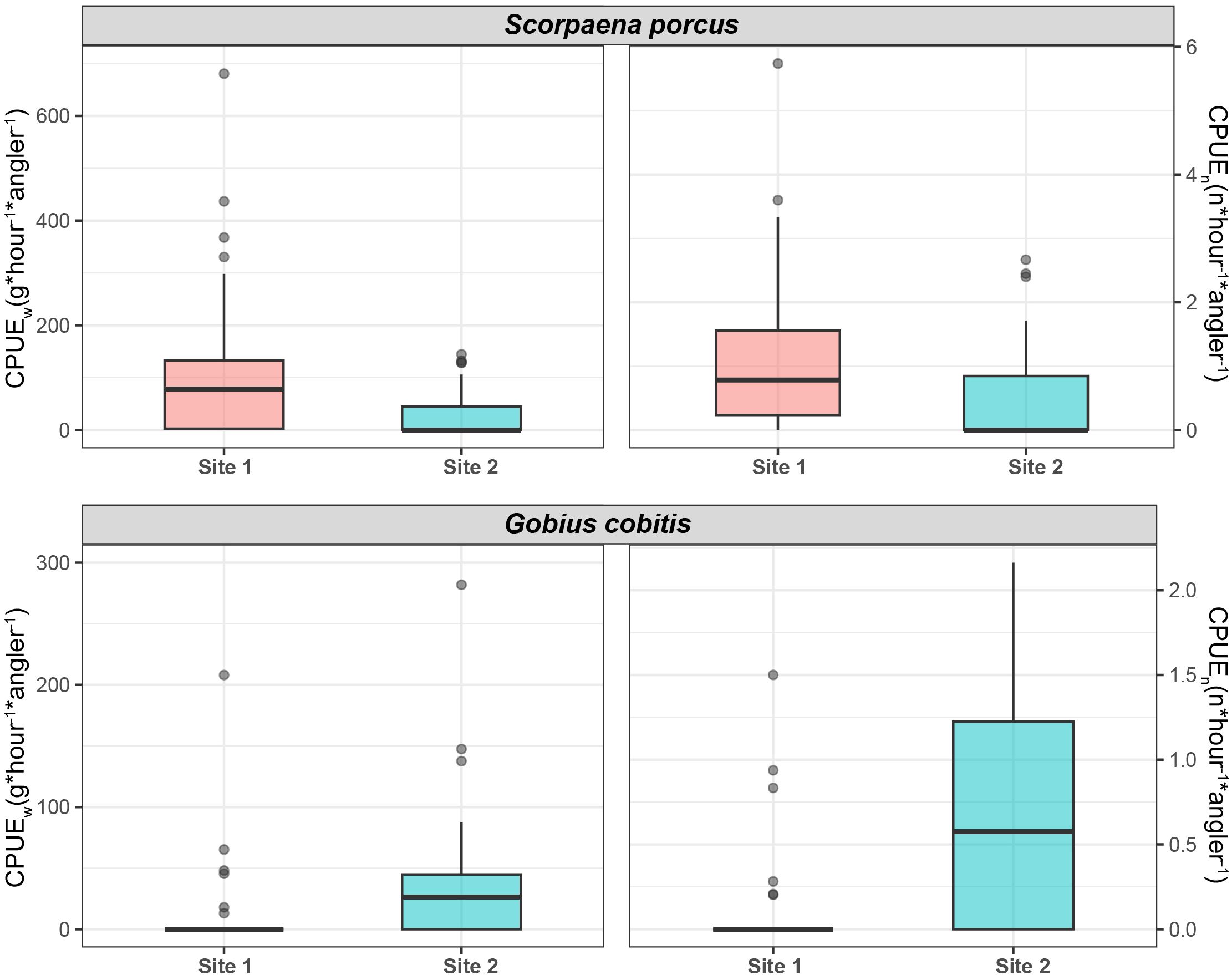
Figure 3. Catch per Unit Effort (CPUE; in both g/hour/angler and n/hour/angler) observed for both black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus) and giant goby (Gobius cobitis) in Sites 1 and 2. In each boxplot, the bold horizontal line indicates the median, the upper and lower hinges correspond to the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively, whiskers extend to the largest or smallest values within 1.5× the interquartile range, and individual points beyond the whiskers are plotted as outliers.
3.2 Length-weight relationship
Length-weight relationships of both S. porcus and G. cobitis are presented in Supplementary Figure S1. Both species displayed isometric growth (S. porcus: b = 3.04, a = 0.02; G. cobitis: b = 3.01, a = 0.01), indicating that individuals generally maintain their shape and proportions as they increase in size. In both species, the model well fitted the data (S. porcus: R2 = 0.98; G. cobitis: R2 = 0.97).
3.3 C&R effects on vitality
Each angling event i.e. from hookset to fish landing, lasted from 0 to 5 seconds, mainly depending on the fish size. Since the anglers immediately hooked the fish after feeling the bite on the jig-head, very few individuals ingested the hook (3 individuals of S. porcus and 1 individual of G. cobitis).
The air exposure time ranged from 1 to 15 minutes (mean 3.1 ± 0.11) and varied according to different unhooking and handling times. The handling of the fish was good in 71.8% of the cases for S. porcus and 76.3% of the cases for G. cobitis (Supplementary Table S3). The instant vitality of released fish was higher in S. porcus (96.0%) than in G. cobitis (76.3%; Supplementary Table S3). The tagging process did not produce any mortality event before release and did not apparently affect the vitality of tagged fish.
No concerning multicollinearity was detected, as the highest pairwise Pearson correlation coefficient among predictors was 0.25 (between fish length and air exposure). The final model, selected by bidirectional stepwise AIC, retained air exposure time, species and their interaction as predictors (Supplementary Table S4). This model, having the lowest AIC (93.37; Supplementary Table S4), showed that individuals of S. porcus had a significantly higher probability of good vitality once released compared to G. cobitis (p value < 0.001), indicating a species-specific difference in resilience to capture. Although the air exposure time did not reach statistical significance (p value = 0.25 regardless of the species), it showed a negative association with vitality in S. porcus (p value = 0.07), indicating a decline in vitality with increased air exposure time (Table 2).
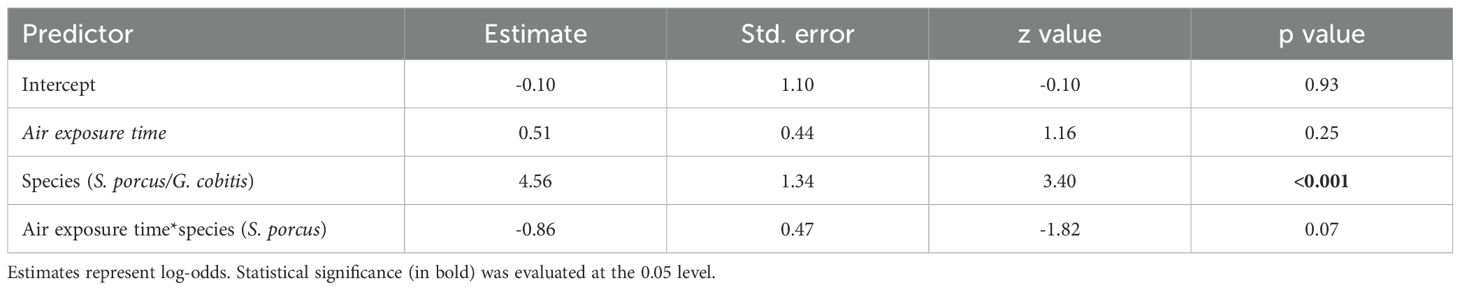
Table 2. Results of the selected model from generalized linear model (GLM) with binomial error distribution and logit link function, assessing the effects of air exposure time, species and their interaction on post-release fish vitality.
3.4 Tag-recapture data
Table 3 reports the number of recapture events out of the total tagged fish, while Table 4 lists each recapture event recorded for both species, with information on dates, handling, vitality and eventual lure (or gear) switching, sub-area change, length range and increment in total length. The tag-recapture data was obtained both during the fishing sessions (observer modality) and through fishers’ interview until 30th April 2025. Figure 4 illustrates the capture and recapture timelines for all individuals recaptured during the study.
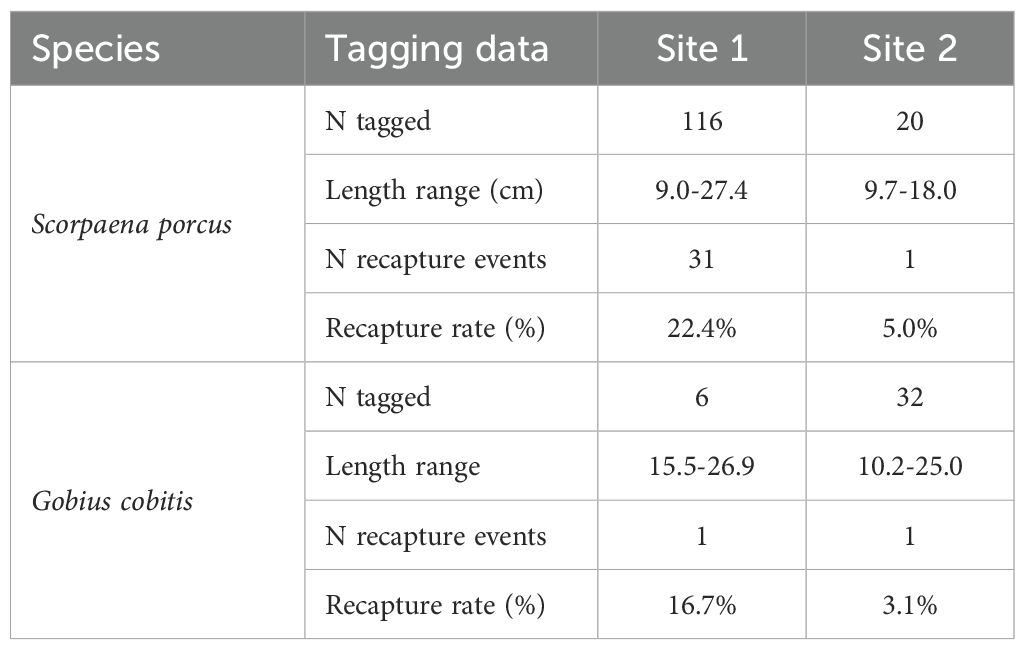
Table 3. Summary of tagged and recaptured individuals of black scorpionfish (S. porcus) and giant goby (G. cobitis), with relative recapture rates in both sites 1 and 2.
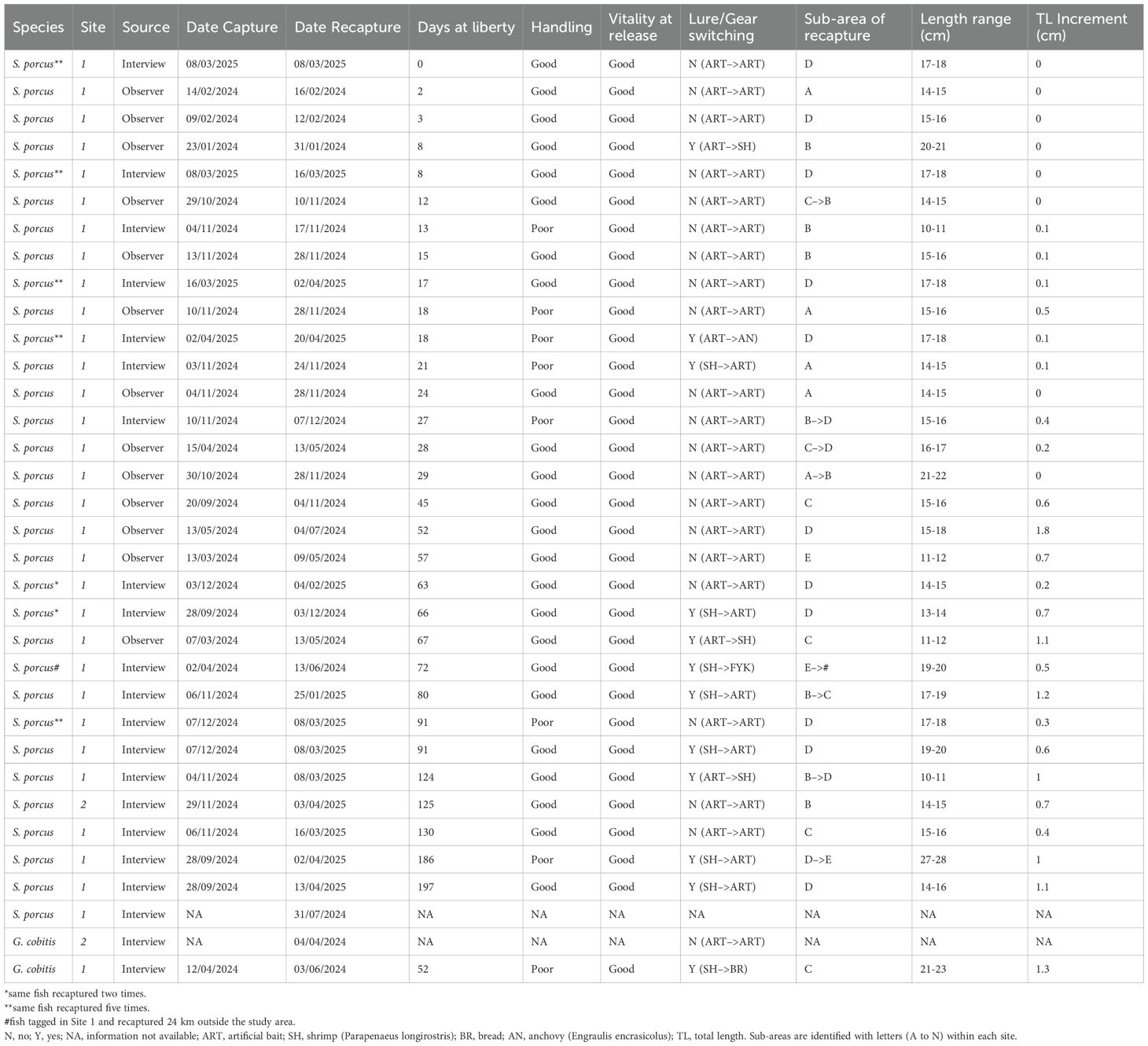
Table 4. Recapture events of black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus) and giant goby (Gobius cobitis), ordered by increasing days at liberty.
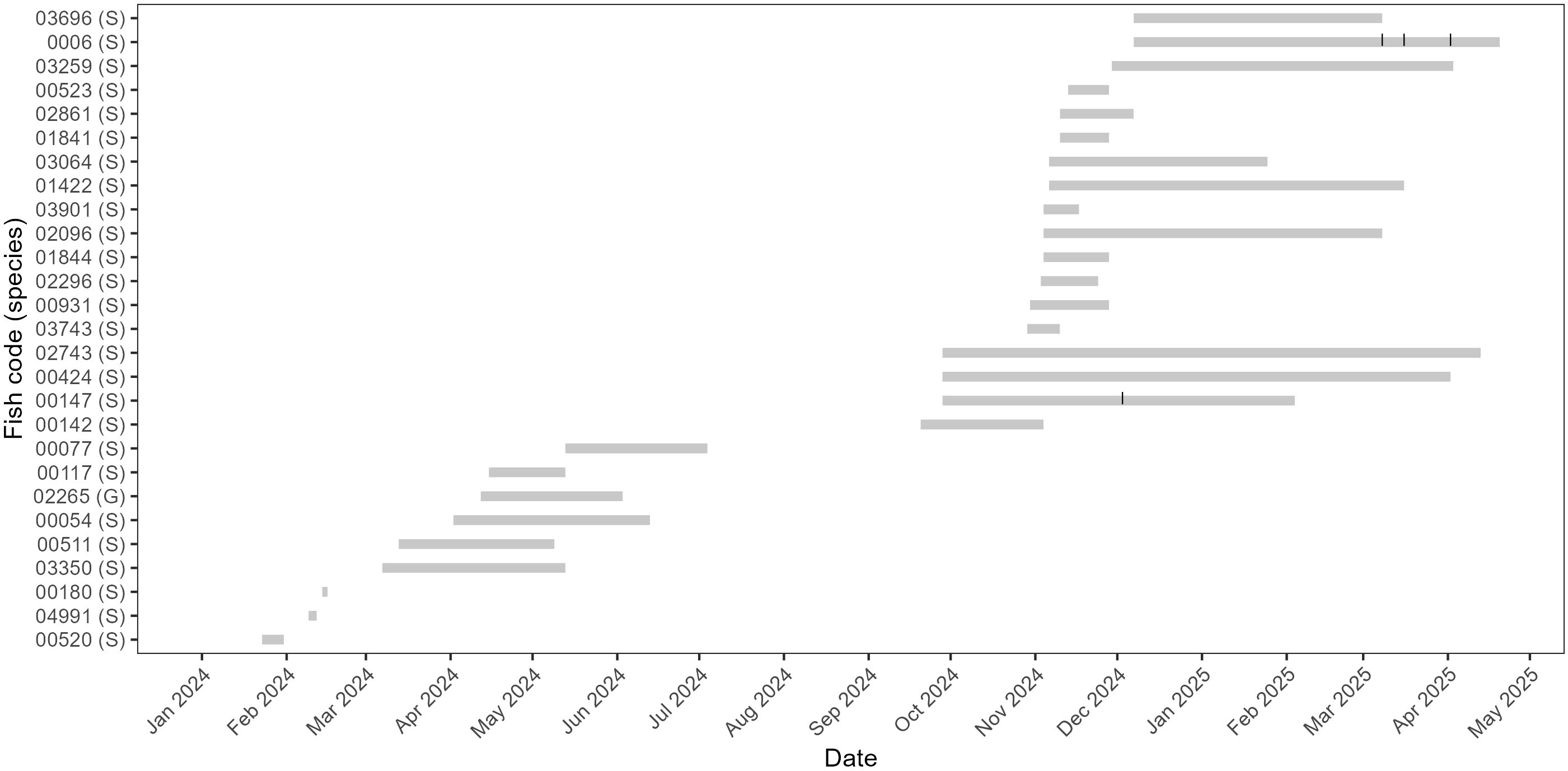
Figure 4. Histories of recaptured individuals over the entire study period. Each horizontal bar represents the time at liberty between initial capture and recapture for a single individual. Fish codes are reported on the y-axis, followed by species identifier (S = Scorpaena porcus; G = Gobius cobitis). Vertical ticks along bars indicate multiple recapture events.
A total of 34 recapture events were recorded (Table 4). Regarding S. porcus, 32 recapture events were recorded (31 in Site 1 and 1 in Site 2). During the fishing sessions, 13 recapture events were observed. Further 19 recapture events were recorded thanks to fishers that contacted the authors through the phone number printed on the tag: 17 of them were caught using rod and reel, mainly through LRF technique, while 1 was caught in a fyke net commonly employed in artisanal fishery of the area (Petetta et al., 2020). Two S. porcus specimens were recaptured multiple times: one was caught five times and another was caught two times (Table 4). Without considering the multiple recapture events for the same individuals, the tag-recapture rate was 19.9% (27 distinct individuals out of 136 tagged) regardless of the site; however, we observed a marked difference between Site 1, with a tag-recapture rate of 22.4% (26 out of 116 tagged), and Site 2, where 1 fish was recaptured out of 20 tagged (5.0%; Table 3). Recapture events of S. porcus were recorded throughout the study period, with highest frequencies in autumn 2024, spring 2024 and winter 2025, respectively (Table 4; Figure 4).
Regarding G. cobitis, only 2 individuals were recaptured (1 in Site 1 and 1 in Site 2), both thanks to anglers that were interviewed. The resulting tag-recapture rate was 5.3% (2 out of 38 tagged) but again with a marked difference between Site 1 (16.7%; 1 out of 6 tagged) and Site 2 (3.1%; 1 out of 32 tagged; Table 3).
We failed to identify 2 recaptured individuals (1 S. porcus and 1 G. cobitis), since the interviewed anglers did not record the unique code printed on the T-bar tag (Table 4). Regardless of the species, the days at liberty ranged from 0 to 197 days (mean 55.6 ± 9.4 err. std.).
3.4.1 Survivability insights
The recapture events confirmed the survivability of those 29 caught-and-released individuals, which had at least a second chance to bite the lure/bait again. Regardless of the species, 75% of recaptured fish had experienced a good handling during the first C&R process, while 100% of recaptured fish had shown a good vitality at first release (Table 4).
3.4.2 Growth modelling, behaviour and site fidelity
Fish growth at liberty of the recaptured specimens was expressed in absolute terms (Figure 5), as well as daily growth as a function of fish size (Figure 6). Most recaptured fish were immature (19 out of 27 distinct recaptured individuals, 70.4%); considering all the 30 recapture events for which we had length information and with more than 0 days at liberty, 19 and 11 concerned immature and mature individuals, respectively (Figure 5). The growth rate of S. porcus was, on average, 1 cm every 185 days for immature and every 172 days for mature individuals (Figure 5), corresponding to an annual growth rate of 2.0 and 2.1 cm, respectively. However, no significant differences were detected between the growth trend of the two size groups (test for equal means: F (1, 26) = 0.228, p = 0.637; homogeneity of slopes: F = 0.022, p = 0.883). Despite this, we observed that the daily growth (expressed as percentage of body size) generally decreases in larger fish (Figure 6). The von Bertalanffy growth parameters (± standard error) estimated for S. porcus are the following: L∞ = 26 cm ± 5.25 and k = 0.21 ± 0.09.
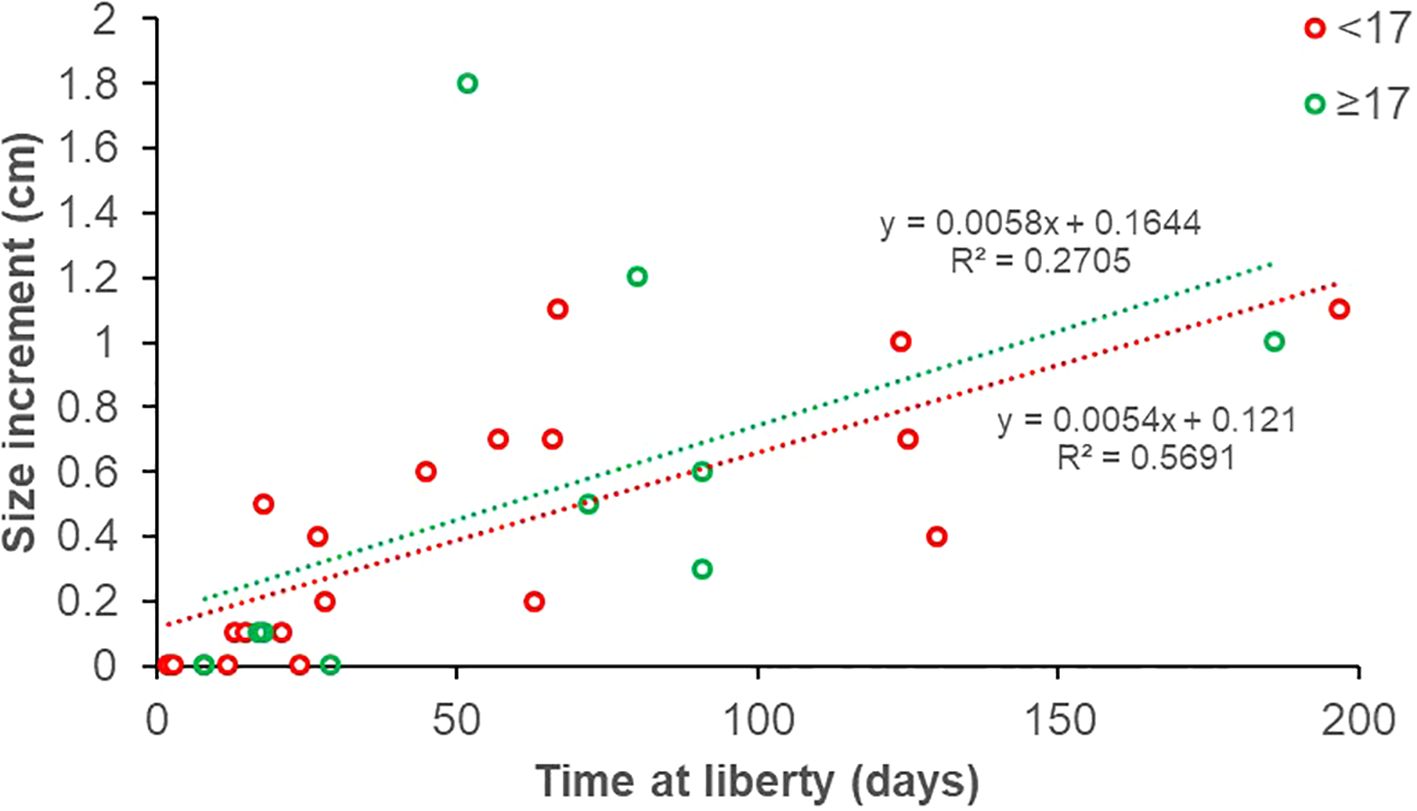
Figure 5. Size increment plotted against time at liberty of recaptured black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus). The individuals are grouped into two length ranges: < 17 cm (immature; red dots and line); ≥ 17 cm (mature; green dots and line).
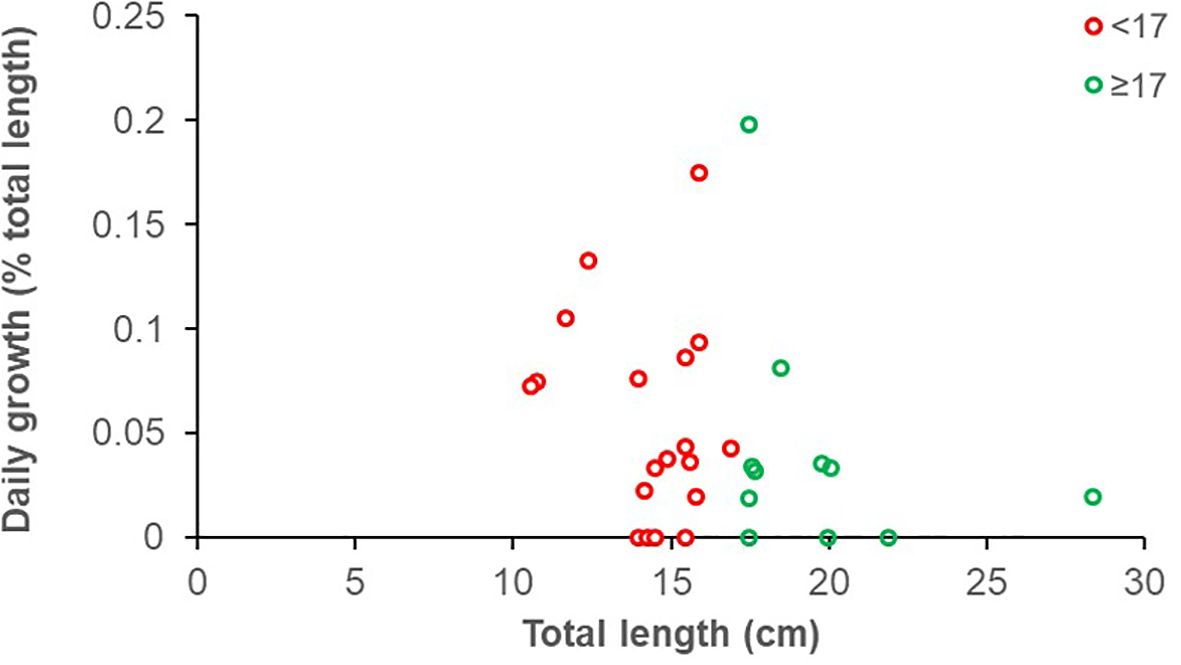
Figure 6. Daily growth, expressed as percentage of size increment per day to the total fish length, plotted against fish total length of recaptured black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus). The individuals are grouped into two length ranges: < 17 cm (immature; red dots and line); ≥ 17 cm (mature; green dots and line).
Most of the recaptured black scorpionfish (n = 20) showed no lure switching between the first and second capture events. By contrast, six of them switched from natural (mainly shrimp) to artificial bait and four from artificial to natural bait; one individual was caught with a different gear (from rod and reel to fyke net). Concerning G. cobitis, one individual did not show lure switching, while another was caught with shrimp bait the first time, and with bread the second time (Table 4).
The majority of black scorpionfish (23 individuals, 74.2%) were recaptured in the same sub-area where they were caught the first time, often in the same hole between the rocks. Further 7 individuals where recaptured in the same site but in another sub-area, which was often adjacent to the first one. Only 1 individual of S. porcus was caught 24 km away from the first capture site, in a shallow rocky area around 0.2 nautical miles from the shoreline. The only individual of G. cobitis for which we had information on the position in the first and second capture events did not show a sub-area change (Table 4).
4 Discussion
4.1 Multispecies angling in coastal marine habitats
We addressed the effort and impact of recreational fishing in coastal marine habitats, through the LRF technique. LRF can be included in what is called “micro fishing”, a term increasingly used to describe recreational angling that targets small-bodied fish, including species that remain small as adults or the early-life stages of larger species. This concept was originally popularized within angler communities and has recently been introduced into the scientific literature to describe emerging recreational fishing behaviours, particularly those that differ from traditional trophy-oriented angling (Cooke et al., 2020). One goal of this activity is to encounter as many species as possible, often with C&R practices, and sometimes creating a so-called “life-list” of the species caught (Cooke et al., 2020). LRF is becoming more and more widespread among Mediterranean and Black Sea anglers due to the practicality of the gear, which only requires silicon lures and light sinkers (Peksu et al., 2020).
In the present study, we often observed many species caught in each monitored LRF session, with a total of 17 different species. The difference observed in species composition between the two coastal sites, despite being spatially close (around 20 km distance between them) might be related to a slightly different habitat. Both are similar semi-enclosed areas within harbours, and the main difference is related to depth, with Site 1 having deeper habitats (1 to 5 m) than Site 2 (0 to 2 m), which might attract more species (15 vs 9 species; Table 1). Greater depth, even on a small scale, can provide a wider range of microhabitats and environmental gradients (e.g. light, temperature, shelter), potentially supporting higher species richness (Gratwicke and Speight, 2005; Ellis et al., 2012). The higher anthropogenic impact of Site 2, inserted in a large commercial harbour, could also prevent the presence of some species that were instead caught in Site 1, which belongs to a significantly smaller touristic harbour. We also observed significant differences in the catches of the two target species (black scorpionfish and giant goby), highlighting a clear habitat separation between them. The shallower grounds of Site 2 seemed to be suitable only for immature individuals of S. porcus, while Site 1 was frequented by all the sizes of the species. The preference of younger and smaller individuals for shallower habitats is consistent with ontogenetic niche shifts aimed at reducing predation or competition pressure (Werner and Gilliam, 1984). By contrast, the significantly higher amounts of G. cobitis caught in Site 2 compared to Site 1 confirm the tendency of the species of inhabiting the upper sheltered shores of the intertidal zone (Wheeler, 1993; Compaire et al., 2022), while only few large individuals were caught in the deeper grounds of Site 1.
Here, we applied conventional tags and gathered data from recapture events to gain insights on the fate of released fish and to derive some useful biological data in terms of growth and spatial movements. Overall, the frequent recapture events observed for S. porcus highlights the vulnerability of this species to recreational fisheries, especially in semi-enclosed areas such as harbours or docks. The high recapture rate observed for this species is in accordance with what found in literature, where scorpionfish usually have the highest recapture rates, when compared to other species (Hanan and Curry, 2012). We also observed an intra-specific variability, since two S. porcus specimens were recaptured multiple times, many others one time, while the majority was never recaptured. Interestingly, there was a marked difference between the two sites, with Site 1 including almost all the recapture events for both species. This may be due to the wider area of Site 2, which could have hampered detailed research of the fish within the rocks as it happened in Site 1. Recapture events were more frequent in seasons where a higher fishing effort was exerted.
4.2 C&R effects and consequences
C&R in angling can be compared to discarding in commercial fisheries, even if fish caught and released by anglers usually experience better conditions and less damage than those caught by most commercial fishing gears (Cooke and Wilde, 2007). Nevertheless, no form of angling is entirely risk-free for fish, and understanding survival/mortality rates of released individuals remains central to C&R scientific studies.
In the present work, we estimated the effects and consequences of C&R on S. porcus and G. cobitis, two species characterized by slow growth rates and relatively short lifespans (maximum lifespan of around 10 years for both species; La Mesa et al., 2010; Tillin and Riley, 2017). Both species can be caught as target or bycatch through all inshore angling techniques employing sinker and bait in rocky shallow waters or through spearfishing (Tiralongo, 2024). S. porcus is also a shared resource between Mediterranean recreational and artisanal fisheries, being an important catch and source of income in the coastal passive set nets and traps (Ferri et al., 2012; Özgül et al., 2019). For this species, a general decline in catches and average size has been observed in different areas due to fishing activities (D’Iglio et al., 2024; Tiralongo, 2024), and thus a closure of fisheries during the spawning season and the establishment of a minimum landing size have been suggested (Bilgin and Çelik, 2009). Therefore, assessing the impact of C&R practices in angling towards these species contribute to understand the potential threats of the fisheries sector to marine resources.
We correlated the instant vitality of released fish with some of the factors that are known to most affect survivability and post-release effects (Bartholomew and Bohnsack, 2005). These were water temperature, which is the most important environmental parameter; fish length, which reflects different life stages (e.g. immature and mature) and angler behaviour, categorized into air exposure time and handling of the fish. We did not consider the barotrauma effects, due to the shallow depths (less than 5 meters), the hooking location, since the fish is usually not given time to ingest the hook with LRF technique, or the eventual predation after release, since the study areas rarely host larger predators in shallow rocky bottoms, and no predation events were observed. Although the air exposure time did not significantly affect post-release vitality in our model, it showed a negative trend for S. porcus, consistent with the hypothesis that prolonged air exposure may reduce the chances of recovery after release. It is in fact known that fish exposed to air suffer from cardiac disturbances and physiological homeostasis disruptions (Bartholomew and Bohnsack, 2005; Cooke et al., 2013) which can cause lethal and sub-lethal effects, especially with longer durations (Cooke and Suski, 2005; Cook et al., 2015). Air exposure was shown to affect mortality, recovery times, stress, swimming performances, reproductive fitness of several saltwater and freshwater fish species (Schisler and Bergersen, 1996; Richard et al., 2013; Blyth and Bower, 2022; Butler et al., 2022). While the association with vitality was not statistically conclusive in our dataset, its direction and ecological plausibility support further investigation, especially in studies with larger sample sizes or higher variation in exposure times.
Usually, a good instant vitality is not directly linked to survivability in the longer term (Petetta et al., 2025); however, the frequent recapture events observed for scorpionfish, with all recaptured individuals showing a good vitality at first release, are a definitive proof of their survivability. The less percentage of G. cobitis specimens showing good vitality after release (76.3% vs 96% of S. porcus), which was not significantly related with increasing air exposure time, poor handling, water temperature or fish length, may derive from a stress of the capture event itself. This is observed also in the lower recapture rates compared to scorpionfish, which may indicate a higher mortality or other C&R effects (modified behaviour after release, better memory of the capture event etc.). More detailed information and observations, especially on the sub lethal physiological and behavioural consequences of C&R, can be obtained by further studies using biotelemetry technology (Donaldson et al., 2008). For smaller specimens, which are frequently caught in coastal habitats (e.g. the individuals of G. paganellus of the present study), alternative tagging techniques such as visible implant elastomer tagging could be considered (Roma et al., 2018; Compaire et al., 2022).
4.3 Growth rates, behaviour and spatial movements
The isometric growth, estimated for S. porcus by length-weight relationship, is in accordance with what observed by La Mesa et al. (2010) in the same area and differs from results obtained in Aegean Sea (negative allometric growth; Moutopoulos and Stergiou, 2002; Karakulak et al., 2006) and Black Sea (positive allometric growth; Bilgin and Çelik, 2009; Demirhan and Can, 2009). Some authors suggested the presence of a distinct population of S. porcus in the Adriatic Sea (Ferri et al., 2010; D’Iglio et al., 2024), with a weak east/west genetic differentiation observed within this basin (Boissin et al., 2016).
The estimated values of asymptotic size and body growth rate for S. porcus, although with relatively wide confidence limits (L∞= 26 cm ± 5.25 and k = 0.21 ± 0.09), were similar to those calculated in the same area by La Mesa et al. (2010) from natural reefs (L∞ = 22.3 cm and k = 0.23). Similarly, the mean annual growth rate calculated for our specimens was between 2.0-2.1 cm/year (corresponding approximately to a modal size of 14-16 cm), closely resembled that reported from natural reef for fish between 14.1 and 16.6 cm (La Mesa et al., 2010, Table 3). The observed decrease in daily growth rate with increasing body size aligns with the well-documented pattern of growth deceleration as individuals approach their asymptotic size (Pauly, 1981). It is worth to note the high variability in individual growth rates observed in the field due to relatively large size range of fish sampled and, possibly, to the different seasons of the catch/recapture events.
The information of conventional tagging employed in this study is limited to the date and position at release and at recapture; however, we could derive some patterns in the site fidelity of the recaptured fish. The high tag-recapture rate observed for S. porcus in the same site, and often in the same sub-area, highlights its sedentary lifestyle or at least its high site fidelity. These results are in line with what observed for the same species by Özgül et al. (2019) by using acoustic telemetry on adult individuals in artificial reefs. We instead observed that the majority of recaptured S. porcus were juveniles, suggesting that shallow rocky areas within harbours may have a key role as nursery area for this species, as observed in rocky intertidal pools (Compaire et al., 2022). By contrast, mature individuals (i.e. above the length at first maturity of 17 cm; La Mesa et al., 2010) could use them only as temporary sites for feeding or for reproduction purposes. In fact, the few recapture events of these larger individuals in the same site after more than 10 days may be a sign that they leave the site, and the individual recaptured at 24 km distance from the first catch may support this hypothesis. As observed by La Mesa et al. (2010) in the same study area, adult populations of S. porcus may find the ideal habitat in offshore artificial reefs with deeper waters (10-40 m), which are not frequented by juveniles. From a management perspective, the observed site fidelity of S. porcus, particularly in juveniles, suggests that area-based conservation measures, such as spatial closures or the designation of nursery habitats within harbours, could be effective in protecting early life stages (Cooke and Cowx, 2006). These localized management strategies could help reducing the catch of immature and undersized individuals of several species which are known to inhabit shallow waters and to be frequently caught by shore recreational fisheries (Erbay et al., 2024; Iborra et al., 2024).
Very few studies estimated growth rates for G. cobitis (Koutrakis and Tsikliras, 2003; Compaire et al., 2020); the observed isometric growth is in accordance to what found in Aegean Sea (Koutrakis and Tsikliras, 2003). This species is known to be a sedentary species, often inhabiting intertidal rock pools with high site fidelity (Compaire et al., 2022) but with microhabitat shifts following tide changes (i.e. moving to deeper channels during low-tides; Faria and Almada, 2009). No sufficient data was available on G. cobitis to determine a growth rate trend. The only individual of G. cobitis for which we had length information was within the 21-23 cm length range, i.e. above the length at first maturity observed for the species (12-13 cm; Tillin and Riley, 2017). Our relatively low tag-recapture rate for this species contrasts with what found by Compaire et al. (2022) (mean recapture rate of 38.9% by using anaesthetic and hand nets on rock pools) and therefore might be related to the angling process that may have influenced survivability and behaviour, as stated above. In fact, G. cobitis is considered highly resilient and able to migrate in and out of an area impacted by pollution or habitat alteration (Tillin and Riley, 2017), and thus it may escape from an area or hide to avoid angling. External tags may have further affected G. cobitis, which relies on moving through narrow crevices, potentially altering its natural behaviour more than in S. porcus, which tend to remain more exposed on the substrate.
5 Conclusion
The frequent recapture events observed for S. porcus underline its high site fidelity and strong resilience to C&R practices, but also its high sensitivity to inshore angling techniques in shallow waters, particularly for smaller individuals. Despite the high vitality observed at release, these fish may be subjected to repeated angling events and experience sub-lethal effects, which could ultimately impair the recruitment of new individuals into the stock. Being also one of the main target species of Mediterranean artisanal fisheries, the impact of recreational fishing towards S. porcus should be included in its stock assessment and management. To further preserve the fish stocks of S. porcus, we suggest C&R especially towards immature individuals < 17 cm, and the adoption of good practices, such as a reduced air exposure time. Localized management strategies as spatial closures of nursery habitats within harbours, could also be effective in protecting these early life stages. Further studies should be conducted on both S. porcus and G. cobitis and other coastal fish species to better understand the lethal and sub-lethal effects of C&R.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Specific authorization was required for the fishing activities inside the two sampling sites, from both the Italian Coast Guard (Site 1) and private authority (Site 2). Threatened or protected species have not been involved in any part of the field studies. Ethical review and approval were not required because fish were sampled during recreational angling activities and were not subject to any experimental manipulation, in line with the Explanatory Note of the Italian Ministry of Health’s Directorate- General for Animal Health and Veterinary Medicinal Products (DGSAF) of July 26, 2017. Animal manipulation complied with the guidelines of the European Union Directive (2010/63/EU) and the Italian Legislative Decree 26 of March 4, 2014 “Attuazione della Direttiva 2010/63/UE sulla protezione degli animali utilizzati a fini scientifici”. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
AP: Data curation, Visualization, Conceptualization, Validation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Software. DLV: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Software. MLM: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. FG: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Project funded under the National Recovery and Resilience Plan (NRRP), Mission 4 Component 2 Investment 1.4 - Call for tender No. 3138 of 16 December 2021, rectified by Decree n.3175 of 18 December 2021 of Italian Ministry of University and Research funded by the European Union – NextGenerationEU.
Acknowledgments
We express our utmost gratitude to all the anglers that helped carrying out the research, in particular Francesco Marchetti, Xavier Paulo Jacovella, Marco Acciarri and Mattia Massimi. We are also indebted to Margherita Carrino and Martina Ettorre for their valuable assistance in the field work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1638216/full#supplementary-material
References
Arlinghaus R. and Cooke S. J. (2009). Recreational fisheries: socioeconomic importance, conservation issues and management challenges. Recreat hunting Conserv. Rural livelihoods Sci. Pract., 39–58. doi: 10.1002/9781444303179.fmatter
Arlinghaus R., Cooke S. J., Lyman J., Policansky D., Schwab A., Suski C., et al. (2007). Understanding the complexity of catch-and-release in recreational fishing: An integrative synthesis of global knowledge from historical, ethical, social, and biological perspectives. Rev. Fish Sci. 15, 75–167. doi: 10.1080/10641260601149432
Bartholomew A. and Bohnsack J. A. (2005). A review of catch-and-release angling mortality with implications for no-take reserves. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish 15, 129–154. doi: 10.1007/s11160-005-2175-1
Battaglia P., Romeo T., Consoli P., Scotti G., and Andaloro F. (2010). Characterization of the artisanal fishery and its socio-economic aspects in the central Mediterranean Sea (Aeolian Islands, Italy). Fish Res. 102, 87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2009.10.013
Bilgin S. and Çelik E.Ş. (2009). Age, growth and reproduction of the black scorpionfish, Scorpaena porcus (Pisces, Scorpaenidae), on the Black Sea coast of Turkey. J. Appl. Ichthyol 25, 55–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2008.01157.x
Blyth S. A. and Bower S. D. (2022). After the spawn and on the hook: Sea trout Salmo trutta biophysical responses to different components of catch and release in a coastal fishery. J. Fish Biol. 101, 464–477. doi: 10.1111/jfb.15108
Boissin E., Micu D., Janczyszyn-Le Goff M., Neglia V., Bat L., Todorova V., et al. (2016). Contemporary genetic structure and postglacial demographic history of the black scorpionfish, Scorpaena porcus, in the Mediterranean and the Black Seas. Mol. Ecol. 25, 2195–2209. doi: 10.1111/mec.13616
Bolognini L., Cevenini F., Franza V., Guicciardi S., Petetta A., Santangelo L., et al. (2022). Preliminary estimation of marine recreational fisheries (MRF) in the time of COVID-19 pandemic: the marche region case study (Adriatic sea, Italy). Front. Mar. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.823086
Brownscombe J. W., Hyder K., Potts W., Wilson K. L., Pope K. L., Danylchuk A. J., et al. (2019). The future of recreational fisheries: Advances in science, monitoring, management, and practice. Fish Res. 211, 247–255. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2018.10.019
Butler E. C., Arkert N. K., Childs A. R., Pringle B. A., Skeeles M. R., Foster R. M., et al. (2022). Incorporating estuarine-angler behaviour and delayed blood sampling into the rapid assessment of catch-and release angling on the iconic dusky kob Argyrosomus japonicus. Fish Res. 253, 106364. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2022.106364
Claudet J. and Fraschetti S. (2010). Human-driven impacts on marine habitats: A regional meta-analysis in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Conserv. 143, 2195–2206. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2010.06.004
Coleman F. C., Figueira W. F., Ueland J. S., and Crowder L. B. (2004). The impact of United States recreational fisheries on marine fish populations. Sci. (80-.) 305, 1958–1960. doi: 10.1126/science.1100397
Compaire J. C., Casademont P., Cabrera R., Gómez-Cama C., and Soriguer M. C. (2018). Feeding of Scorpaena porcus (Scorpaenidae) in intertidal rock pools in the Gulf of Cadiz (NE Atlantic). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingdom 98, 845–853. doi: 10.1017/S0025315417000030
Compaire J. C., Montes J., Gonçalves J. M. S., Soriguer M. C., and Erzini K. (2022). Site fidelity of fish on a rocky intertidal in the south of Portugal. J. Sea Res. 183, 102202. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2022.102202
Compaire J. C., Soriguer M. C., and De Ciencias F. (2020). Length-weight relationships of seven fish species from tidepools of an intertidal rocky shore in the Gulf of Cadiz, Spain (NE Atlantic). J. Appl. Ichthyol 1–3, 1–2. doi: 10.1111/jai.14087
Cook K. V., Lennox R. J., Hinch S. G., and Cooke S. J. (2015). FISH out of WATER: how much air is too much? Fisheries 40, 452–461. doi: 10.1080/03632415.2015.1074570
Cooke S. J. and Cowx I. G. (2006). Contrasting recreational and commercial fishing: searching for common issues to promote unified conservation of fisheries resources and aquatic environments. Biol. Conserv. 128, 93–108. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2005.09.019
Cooke S. J., Donaldson M. R., O’connor C. M., Raby G. D., Arlinghaus R., Danylchuk A. J., et al. (2013). The physiological consequences of catch-and-release angling: Perspectives on experimental design, interpretation, extrapolation and relevance to stakeholders. Fish Manage. Ecol. 20, 268–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2400.2012.00867.x
Cooke S. J., Lennox R. J., Cantrell B., and Danylchuk A. J. (2020). Micro-fishing as an emerging form of recreational angling: research gaps and policy considerations. Fisheries 45, 517–521. doi: 10.1002/fsh.10487
Cooke S. J. and Schramm H. L. (2007). Catch-and-release science and its application to conservation and management of recreational fisheries. Fish Manage. Ecol. 14, 73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2400.2007.00527.x
Cooke S. J. and Suski C. D. (2005). Do we need species-specific guidelines for catch-and-release recreational angling to effectively conserve diverse fishery resources? Biodivers. Conserv. 14, 1195–1209. doi: 10.1007/s10531-004-7845-0
Cooke S. J. and Wilde G. R. (2007). “The fate of fish released by recreational anglers,” in By-catch reduction in the world’s fisheries (Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer), 181–234.
Demirhan S. A. and Can M. F. (2009). Age, growth and food composition of Scorpaena porcus (Linnaeus 1758) in the southeastern black sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol 25, 215–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2009.01217.x
Depasquale S. W., Howell B. E., Navarroli G., Jeffries K. M., Cooke S. J., Wijenayake S., et al. (2023). Are the effects of catch-and-release angling evident in changes to mRNA abundances related to metabolism, acid-base regulation and stress in lake trout (Salvelinus namaycush) gills? Conserv. Physiol. 11, 1–10. doi: 10.1093/conphys/coad065
D’Iglio C., Famulari S., Ferri J., Albano M., Spanò N., Capillo G., et al. (2024). Ecomorphological adaptation of Scorpaena porcus (Linnaeus 1758): evidence from two different environments revealed by sagittae features and somatic growth rates. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1347897
Donaldson M. R., Arlinghaus R., Hanson K. C., and Cooke S. J. (2008). Enhancing catch-and-release science with biotelemetry. Fish Fish 9, 79–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2979.2007.00265.x
Ellis J. R., Milligan S. P., Readdy L., Taylor N., and Brown M. J. (2012). Spawning and nursery grounds of selected fish species in UK waters: Science series technical report no. 147. (Lowestoft, England: Cefas).
Erbay M., Carlson A., and Grati F. (2024). Evaluating the unexplored recreational fishing in the Turkish Black Sea: socio-economic significance and environmental impact. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1386911
Fabens A. J. (1965). Properties and fitting of the von Bertalanffy growth curve. Growth 29, 265–289.
FAO (2023). FishStatJ—Software for fishery and aquaculture statistical time series (Rome, Italy: FAO Fish. Aquac. Rep). Available online at: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/topic/166235?lang=en.
Faria C. and Almada V. C. (2006). Patterns of spatial distribution and behaviour of fish on a rocky intertidal platform at high tide. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 316, 155–164. doi: 10.3354/meps316155
Faria C. and Almada V. C. (2009). Tidal shifts in microhabitat use by Gobius cobitis: An adaptation to its feeding strategy? J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingdom 89, 641–643. doi: 10.1017/S0025315408002191
Ferri J., Petrić M., and Matić-Skoko S. (2010). Biometry analysis of the black scorpionfish, Scorpaena porcus (Linnaeus 1758) from the eastern adriatic sea. Acta Adriat 51, 45–53.
Ferri J., Stagličić N., and Matić-Skoko S. (2012). The black scorpionfish, Scorpaena porcus (Scorpaenidae): Could it serve as reliable indicator of Mediterranean coastal communities’ health? Ecol. Indic 18, 25–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.11.004
Ferter K., Weltersbach M. S., Strehlow H. V., Vølstad J. H., Alo J., Arlinghaus R., et al. (2013). Unexpectedly high catch-and-release rates in European marine recreational fisheries: implications for science and management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 70, 1319–1329. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fst104
Font T. and Lloret J. (2014). Biological and ecological impacts derived from recreational fishing in Mediterranean coastal areas. Rev. Fish Sci. Aquac 22, 73–85. doi: 10.1080/10641262.2013.823907
Forcada A., Valle C., Bonhomme P., Criquet G., Cadiou G., Lenfant P., et al. (2009). Effects of habitat on spillover from marine protected areas to artisanal fisheries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 379, 197–211. doi: 10.3354/meps07892
Froese R. (2006). Cube law, condition factor and weight–length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol 22, 241–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00805.x
Gillanders B. M., Ferrell D. J., and Andrew N. L. (2001). Estimates of movement and life-history parameters of yellowtail kingfish (Seriola lalandi): how useful are data from a cooperative tagging programme? Mar. Freshw. Res. 52, 179–192. doi: 10.1071/MF99153
Giovos I., Keramidas I., Antoniou C., Deidun A., Font T., Kleitou P., et al. (2018). Identifying recreational fisheries in the Mediterranean Sea through social media. Fish Manage. Ecol. 25, 287–295. doi: 10.1111/fme.12293
Grati F., Carlson A., Carpentieri P., and Cerri J. (2021). Handbook for data collection on recreational fisheries in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper (Rome (Italy: FAO: Food & Agriculture Org).
Gratwicke B. and Speight M. R. (2005). The relationship between fish species richness, abundance and habitat complexity in a range of shallow tropical marine habitats. J. Fish Biol. 66, 650–667. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-1112.2005.00629.x
Hajji F., Ouannes-Ghorbel A., Ghorbel M., and Jarboui O. (2013). Age and growth of the grass goby Zosterisessor ophiocephalus Pallas 1811 in the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia, Central Mediterranean). Acta Adriat 54, 27–40.
Hanan D. A. and Curry B. E. (2012). Long-term movement patterns and habitat use of nearshore groundfish: tag-recapture in central and southern california waters. Open Fish Sci. J. 5, 30–43. doi: 10.2174/1874401x01205010030
Harmelin-Vivien M. L., Kaim-Malka R. A., Ledoyer M., and Jacob-Abraham S. S. (1989). Food partitioning among scorpaenid fishes in Mediterranean seagrass beds. J. Fish Biol. 34, 715–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1989.tb03352.x
Huxley J. S. and Teissier G. (1936). Terminology of relative growth. Nature 137, 780–781. doi: 10.1038/137780b0
Hyder K., Armstrong M., Ferter K., and Strehlow H. V. (2014). Recreational sea fishing–the high value forgotten catch. ICES Insight 51, 8–15.
Hyder K., Weltersbach M. S., Armstrong M., Ferter K., Townhill B., Ahvonen A., et al. (2018). Recreational sea fishing in Europe in a global context—Participation rates, fishing effort, expenditure, and implications for monitoring and assessment. Fish Fish 19, 225–243. doi: 10.1111/faf.12251
Iborra L., Lejeune P., Marengo M., Valleteau C., Gobert S., and Cuny P. (2024). A multimethod approach to assess marine recreational fishing activity in a Mediterranean area: A case study of the Balagne region (Corsica, France). Marine and Coastal Fisheries: Dynamics, Management, and Ecosystem Science. 1–22. doi: 10.1002/mcf2.10313
ICES (2024). Working Group on Recreational Fisheries Surveys (WGRFS; outputs from 2023 meeting). ICES Scientific Reports. Copenhagen, Denmark: International Council for the Exploration of the Sea. doi: 10.17895/ices.pub.25067702.v1
Karakulak F. S., Erk H., and Bilgin B. (2006). Length–weight relationships for 47 coastal fish species from the northern Aegean Sea, Turkey. J. Appl. Ichthyol 22, 274–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00736.x
Koutrakis B. E. T. and Tsikliras A. C. (2003). Short Communication Length – weight relationships of fishes from three northern Aegean estuarine systems. J. Appl. Ichthyol 19, 258–260. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0426.2003.00456.x
La Mesa M., Scarcella G., Grati F., and Fabi G. (2010). Age and growth of the black scorpionfish, Scorpaena porcus (Pisces: Scorpaenidae) from artificial structures and natural reefs in the Adriatic Sea. Sci. Mar. 74, 677–685. doi: 10.3989/scimar.2010.74n4677
Le Cren E. D. (1951). The length-weight relationship and seasonal cycle in gonad weight and condition in the perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Anim Ecol. 20, 201–219. doi: 10.2307/1540
Morales-Nin B., Moranta J., García C., Tugores M. P., Grau A. M., Riera F., et al. (2005). The recreational fishery off Majorca Island (western Mediterranean): Some implications for coastal resource management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 62, 727–739. doi: 10.1016/j.icesjms.2005.01.022
Moutopoulos D. K. and Stergiou K. I. (2002). Length-weight and length-length relationships of fish species from the Aegean Sea (Greece). J. Appl. Ichthyol 18, 200–203. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0426.2002.00281.x
NSW-DPI (2013). NSW recreational fishing catch and release handbook (New South Wales, Coffs Harbour.: NSW DPI, Coffs Harbour). Available online at: https://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/:data/assets/pdf_file/0009/478053/nsw-recreational-fishingcatch-and-release-handbook.Pdf (Accessed February 12, 2025).
Özgül A., Lök A., Tansel Tanrıkul T., and Alós J. (2019). Home range and residency of Scorpaena porcus and Scorpaena scrofa in artificial reefs revealed by fine-scale acoustic tracking. Fish Res. 210, 22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2018.10.008
Papadopoulos A., Touloumis K., Tziolas E., Boulamatsis D., and Koutrakis E. (2022). Evaluation of marine recreational fisheries and their relation to sustainability of fisheries resources in Greece. Sustainability 14, 3824. doi: 10.3390/su14073824
Pauly D. (1981). The relationship between gill surface area and growth performance in fish: a generalization of von Bertalanffy’s theory of growth. Meeresforsch 28, 251–282.
Peksu M., Uzer U., Yildiz T., Ayaz A., and Karakulak F. S. (2020). Hook selectivity and catch efficiency in two sport fishing sectors in the Strait of Istanbul, Turkey: Classic handline fishing and Light Rock Fishing (LRF). J. Appl. Ichthyol 36, 893–900. doi: 10.1111/jai.14140
Petetta A., Bargione G., Vasapollo C., Virgili M., and Lucchetti A. (2019). Length–weight relationships of bivalve species in Italian razor clam Ensis minor (Chenu 1843) (Mollusca: bivalvia) fishery. Eur. Zool. J. 86, 363–369. doi: 10.1080/24750263.2019.1668066
Petetta A., Herrmann B., Li Veli D., Canduci G., Tatone I., Bonanomi S., et al. (2025). Vitality insights of fish escaping from a sorting grid installed on a bottom trawl net. Sci. Rep. 15, 1–21. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84364-6
Petetta A., Vasapollo C., Virgili M., Bargione G., and Lucchetti A. (2020). Pots vs trammel nets: A catch comparison study in a Mediterranean small-scale fishery. PeerJ 8, e9287. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9287
Richard A., Dionne M., Wang J., and Bernatchez L. (2013). Does catch and release affect the mating system and individual reproductive success of wild A tlantic salmon (S almo salar L.)? Mol. Ecol. 22, 187–200. doi: 10.1111/mec.12102
Roma J., Dias M., Vinagre C., and Silva A. C. F. (2018). Site fidelity of intertidal fish to rockpools. J. Appl. Ichthyol 34, 535–541. doi: 10.1111/jai.13553
Sarà G., Milanese M., Prusina I., Sarà A., Angel D. L., Glamuzina B., et al. (2014). The impact of climate change on mediterranean intertidal communities: Losses in coastal ecosystem integrity and services. Reg Environ. Change 14, 5–17. doi: 10.1007/s10113-012-0360-z
Schisler G. J. and Bergersen E. P. (1996). Postrelease hooking mortality of rainbow trout caught on scented artificial baits. North Am. J. Fish Manage. 16, 570–578. doi: 10.1577/1548-8675(1996)016<0570:PHMORT>2.3.CO;2
Stagličić N., Matić-Skoko S., Pallaoro A., Grgičević R., Kraljević M., Tutman P., et al. (2011). Long-term trends in the structure of eastern Adriatic littoral fish assemblages: Consequences for fisheries management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 94, 263–271. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.07.005
Sureda A., Barceló C., Tejada S., Montero I., Langley E., and Box A. (2020). Physiological and survival effects of capture of red scorpion fish Scorpaena scrofa (Osteichthyes: Scorpaenidae) by different fishing gears in the Balearic Islands (Western Mediterranean). Fish Res. 229, 105616. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105616
Team R. C. (2025). R: a language and environment for statistical computing (Vienna: The R Foundation for Statistical Computing). Available online at: http://www.R-project.org (Accessed April 20, 2025).
Tillin H. M. and Riley K. (2017). “Gobius cobitis. Giant goby,” in MARLIN (Marine information network) (Plymouth, UK: Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom), 20.
Tiralongo F. (2024). Unraveling the story of the black scorpionfish (Scorpaena porcus linnaeus 1758): exploring local ecological knowledge and the exploitative history of a marine species. Fishes 9, 1–11. doi: 10.3390/fishes9010031
Virgili M., Petetta A., Herrmann B., Cerbule K., Guicciardi S., Li Veli D., et al. (2024). Efficient and sustainable: innovative pot design for a Mediterranean small-scale fishery. Front. Mar. Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1408036
Werner E. E. and Gilliam J. F. (1984). The ontogenetic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 15, 393–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.15.110184.002141
Wheeler A. (1993). The distribution of Gobius cobitis in the British Isles. J. Fish Biol. 43, 652–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1993.tb00450.x
Keywords: marine recreational fishing, Scorpaena porcus, Gobius cobitis, catch & release, tag-recapture, growth rates, fish vitality, Mediterranean sea
Citation: Petetta A, Li Veli D, La Mesa M, Grati F and Bolognini L (2025) Catch, release and second chances: exploring the impact of angling on two coastal fish species. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1638216. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1638216
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 17 July 2025;
Published: 04 August 2025.
Edited by:
Tomaso Fortibuoni, Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (ISPRA), ItalyReviewed by:
Jesus C. Compaire, CONICET Centro de Estudios de Sistemas Marinos (CESIMAR), ArgentinaLantun Paradhita Dewanti, Padjadjaran University, Indonesia
Samuel Blyth, Uppsala University, Sweden
Copyright © 2025 Petetta, Li Veli, La Mesa, Grati and Bolognini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Andrea Petetta, YW5kcmVhLnBldGV0dGFAY25yLml0
 Andrea Petetta
Andrea Petetta Daniel Li Veli
Daniel Li Veli Mario La Mesa2
Mario La Mesa2 Fabio Grati
Fabio Grati Luca Bolognini
Luca Bolognini