Abstract
Introduction:
Marine petroleum pollution has adversely affected marine ecosystems and human living environments, while improvements in shipping efficiency offer a new avenue for mitigating such pollution.
Methods:
Based on panel data from 11 coastal regions in China spanning 2010 to 2022, this study examines the impact mechanisms of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution and further analyzes the moderating effects of port specialization and environmental regulation.
Results:
The results indicate that, overall, shipping efficiency in coastal regions has shown a steady upward trend, with an average efficiency index of 1.046 and an annual growth rate of 4.6%. However, some regions, such as Liaoning, Shandong, and Tianjin, have experienced declines in efficiency, highlighting regional disparities in development. Regression analysis reveals a significant negative relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution. The two-way fixed effects model shows that a 0.01 increase in shipping efficiency corresponds to an approximate 0.01% reduction in marine petroleum pollution, suggesting that enhanced shipping efficiency effectively contributes to improving marine environmental quality. Furthermore, the moderating effect analysis demonstrates that both port specialization and environmental regulation exert significant negative moderating effects on the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution.
Discussion:
Overall, this study enriches the theoretical understanding of the relationship between the operational efficiency of transport infrastructure and environmental pollution and provides robust empirical support for formulating green and efficient shipping policies and advancing sustainable marine environmental governance in coastal regions.
1 Introduction
Marine pollution has become one of the most significant challenges to global environmental security. By disrupting and even degrading marine ecosystems, it poses a severe threat to marine biodiversity and has profound impacts on human living environments (Bani Hani et al., 2019). According to a report by the Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection (GESAMP), more than 80% of marine pollution originates from land-based sources, with petroleum pollution being one of the most significant forms (United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), 2021). It is estimated that approximately 1.5 to 10 million tons of petroleum hydrocarbons enter the marine environment each year, primarily resulting from anthropogenic activities, including untreated wastewater discharges, municipal and industrial runoff, and offshore and onshore petrochemical operations (Varjani and Upasani, 2017; Hazaimeh and Ahmed, 2021). These pollutants, often consisting of persistent and recalcitrant compounds, alter the physical and chemical properties, including viscosity, of seawater, thereby posing a high risk to marine ecosystems (Yan et al., 2019).
The ecological impacts of petroleum pollution are highly complex, characterized by the multidimensional nature of its pollution mechanisms, the staged responses of ecosystems, and the long-term nature of ecosystem recovery processes. This implies that once ecological damage occurs, restoration often requires considerable time and incurs high ecological costs (Da Silva et al., 1997; Dey et al., 2023). Although the hazards of petroleum pollution have attracted widespread attention, existing research has predominantly focused on the following aspects: first, the sources of petroleum pollution (Latimer et al., 1990; Zhang et al., 2007; Guo et al., 2022); second, the removal and remediation of petroleum pollution (Das and Chandran, 2011; Mohammadi et al., 2020); third, the toxic effects and structural damage of petroleum pollution on ecosystems (Gao et al., 2022; Koduvayur Habeebullah et al., 2025; Mohanta et al., 2024); and fourth, the potential threats of petroleum pollution to human health (Freije, 2015; Adipah, 2019). In summary, although current research has provided substantial evidence regarding the micro-level mechanisms of petroleum pollution, the relationship between pollution sources and macro-level structural variables remains underexplored, highlighting the urgent need for further in-depth analysis of the driving factors behind marine petroleum pollution.
At present, research specifically addressing the drivers of marine petroleum pollution remains limited, with most existing studies focusing on the broader determinants of marine pollution and examining them from multiple perspectives. The literature indicates that the level of economic development and regional characteristics are important variables influencing marine pollution (Wang et al., 2020). While the growth of the marine economy has contributed positively to industrial upgrading, its impact on the discharge of marine pollutants (such as industrial wastewater) exhibits certain nonlinear characteristics (Hou and Zhan, 2023). In addition, typical marine industries such as coastal tourism, mariculture, and shipbuilding exert direct pressure on the aquatic environment and are widely recognized as key contributors to water quality degradation (Ji and Ding, 2024a; Yu et al., 2024). Trade liberalization is also viewed as an external shock variable that exacerbates pollution (Ullah et al., 2023), while seafood trade has been found to exert a dual effect—intensifying pollution pressures in the short term but promoting sustainable governance in the long term (Liu F. et al., 2022). At a deeper level, the extensive use of fossil fuels and the lag in environmental governance capacity constitute fundamental causes of the persistent nature of marine pollution (Alsaleh and Abdul-Rahim, 2024). It is worth noting that shipping, as an integral part of coastal and marine development, exerts significant direct and indirect impacts on the marine environment (McConnell, 2002; Venkatesh et al., 2017). However, current research still lacks a systematic perspective on how shipping influences marine petroleum pollution, with its theoretical mechanisms and empirical pathways remaining insufficiently explored.
Building on this foundation, this study aims to achieve the following three specific research objectives: (1) to construct an integrated analytical framework from the perspective of shipping operational efficiency, systematically examining the mechanisms through which shipping efficiency affects marine petroleum pollution, thereby addressing the lack of holistic framework-based analysis in existing research; (2) to empirically test the actual impact of shipping efficiency on land-based marine petroleum pollutant emissions using panel data from 11 coastal regions in China covering the period 2010–2022, providing quantitative evidence for pollution control; and (3) to focus on analyzing the moderating roles of port specialization and environmental regulation in the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution, identifying key external conditions that influence emission reduction effectiveness and enriching the theoretical understanding of pollution mitigation mechanisms.
2 Literature review
2.1 Related research on the impact of transportation infrastructure on environmental pollution
The relationship between transportation infrastructure and environmental pollution has been the subject of extensive academic inquiry. Makarova et al. (2020) highlight the negative environmental impacts of urban motorization, particularly noise pollution and vehicle emissions, and emphasize the critical role of transportation infrastructure and management systems in regulating traffic flow and mitigating environmental effects. Research indicates that optimizing infrastructure in key corridors can effectively enhance traffic efficiency and alleviate environmental pressure. Xie et al. (2016)demonstrate that transportation infrastructure exerts significant direct negative effects on the urban environment and generates adverse spatial spillover effects on surrounding areas. Similarly, Y. Guo et al. (2020) point out a nonlinear relationship between transportation investment and air quality, identifying vehicle density as a key moderating variable: in areas with low vehicle density, transportation investment improves air quality, whereas in high-density areas, it may lead to environmental degradation. The differentiated environmental impacts of various transportation modes have also received considerable scholarly attention. Erdogan (2020), using data from OECD countries, finds that rail investment helps mitigate environmental pollution, while investment in road and air transport significantly exacerbates carbon emissions. Liu Y. et al. (2022), in testing the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis, also concludes that rail investment suppresses environmental degradation. Likewise, Wang et al. (2023) further confirm that investments in different types of transportation infrastructure have markedly divergent environmental impacts: rail investment contributes to emissions reduction, whereas road and air investments tend to worsen pollution. Focusing on developing countries, Dzator et al. (2021) report that both air and rail infrastructure contribute to increased carbon emissions, particularly in nations where the energy structure has not yet transitioned toward greener sources; in such contexts, rail infrastructure may even intensify the relationship between per capita GDP and carbon emissions. Meanwhile, Acheampong et al. (2022), employing a system GMM approach, reveal an inverted U-shaped relationship between rail and freight infrastructure investment and carbon emissions, suggesting that moderate investment can achieve emissions reduction, whereas excessive investment may have counterproductive effects. Wang and Wang (2023) constructed a maritime supply chain model comprising ports, shipping companies, and freight forwarders under the background of green maritime transportation, focusing on the impact of green investment in transportation infrastructure and vertical alliances on the mitigation of shipping pollution. The study finds that the construction of green transportation infrastructure, when combined with coordinated governance across upstream and downstream enterprises, can significantly reduce shipping emissions. Furthermore, some studies have explored the indirect pathways through which transportation infrastructure affects the environment. For instance, Sun C. et al. (2019) show that road infrastructure can lower pollution intensity and enhance urban green development by fostering green technological innovation and promoting regional integration. Sun D. et al. (2019) find that rail transit offers a significantly greater marginal benefit for improving air quality compared to road improvements, although its construction phase may introduce short-term negative environmental impacts.
It is worth noting that Lo Storto and Evangelista (2023) is among the few studies that examine the relationship between transport infrastructure efficiency and environmental outcomes. This study employs Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) to assess the efficiency of road and rail infrastructure and constructs an environmental impact index based on greenhouse gas emissions and major air pollutants. The findings reveal that few countries can simultaneously enhance the operational efficiency of transport infrastructure while reducing its environmental impacts. Moreover, the study highlights that in most countries, policymakers often struggle to clearly distinguish between the objectives of improving efficiency and reducing pollution when formulating policies.
2.2 Related research on petroleum pollution
As one of the core variables in this study, petroleum pollution has long attracted widespread academic attention due to its significant negative environmental impacts. Current research on petroleum pollution mainly focuses on its sources, environmental impact mechanisms, and governance strategies. From the perspective of pollution sources, petroleum pollution primarily stems from human activities, with substantial leakage and discharge risks occurring during oil exploration, extraction, transportation, and refining processes (Sharma et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2019). In addition, municipal and industrial wastewater discharges, surface runoff, and petrochemical operations in coastal and inland areas are also recognized as major land-based contributors to marine petroleum pollution (Hazaimeh and Ahmed, 2021). According to the GESAMP report, over 80% of marine pollution originates from land-based sources, with petroleum pollution identified as one of the main pollutants. The Global Program of Action for the Protection of the Marine Environment from Land-based Activities (GPA) also lists petroleum hydrocarbons among the nine major categories of land-based pollutants. In terms of pollutant characteristics, petroleum pollutants are chemically complex and include substances such as crude oil, heavy fuel oils, and highly toxic light fuel oils. Their main components are hydrocarbons, which exhibit notable persistence and resistance to degradation, allowing them to remain in sediments and ecosystems for extended periods (Blumer and Sass, 1972). Furthermore, the petroleum refining and petrochemical industries are significant sources of hazardous air pollutants, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), heavy metals, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing dual threats to atmospheric quality and public health (Tavella et al., 2025). Numerous studies have further elucidated the environmental impacts of petroleum pollution from both regional and specific pollution perspectives. For example, Ejiba et al. (2016), using the Niger Delta as a case study, highlighted that oil spills and gas flaring are key drivers of local environmental degradation. Although companies often attribute spills to sabotage, aging infrastructure and management negligence are also critical contributing factors. Ekpenyong and Udofia (2015), in their assessment of water quality in oil-producing regions, found significantly elevated concentrations of heavy metals such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and nickel (Ni), with overall water quality parameters falling well below acceptable standards—indicating severe impacts on the aquatic environment. Habeebullah et al. (2025) take the northwestern Arabian Gulf as a case study and find that total petroleum hydrocarbon contamination in marine sediments is severe, with concentrations in some samples exceeding moderate pollution thresholds by several orders of magnitude, thereby significantly heightening ecological risks. The study indicates that even in designated marine protected areas, petroleum-based pollutants may continue to pose a persistent threat to ecosystem health. Petroleum pollution causes not only physical ecological damage but also profound human health effects. Nriagu et al. (2016) found that exposure to petroleum pollution induces physical health symptoms, functional impairments, and significantly increases psychological burdens, including fear, irritability, and emotional disorders. Buonocore et al. (2023), in their assessment of emissions from the U.S. oil and gas industry, emphasized that reducing such emissions can yield substantial public health benefits in addition to mitigating climate change. At the ecosystem level, petroleum pollution exerts destructive effects on both terrestrial and marine life. Ozigis et al. (2020) reported that oil spills alter the spectral reflectance of forest and grassland vegetation, leading to marked declines in vegetation health. Walker et al. (2006) found that in areas near oil and gas facilities, lichen community diversity significantly decreased, and soil concentrations of lead and nitrogen increased—early indicators of soil ecosystem disturbance due to petroleum-related activities. During transportation, petroleum spills likewise pose major environmental risks. Jha and Dahiya (2022) underscored the high toxicity and broad ecological destructiveness of petroleum spills, which can impact a wide range of species, including fish, seabirds, invertebrates, and phytoplankton. While land-based spills tend to be localized events, they can still alter microbial community structures. Marine oil spills, however, are subject to greater uncertainties due to factors such as weather and currents, making their prediction and management more challenging. Samsuria et al. (2025) comprehensively reviewed the threats posed by petroleum pollution in aquatic environments to human health, aquatic ecosystems, and economic activities, noting that under the combined effects of meteorological and hydrological factors, petroleum pollutants are more prone to dispersion, persistent retention, and enhanced toxicity—potentially resulting in long-term environmental burdens in the absence of effective monitoring and governance. Adeola et al. (2022), from the perspective of developing countries, emphasized that although petroleum development generates fiscal revenues, it also degrades land, pollutes water resources, and undermines livelihoods. In contexts of weak regulation and corporate malpractice, issues of resource misallocation and environmental degradation are particularly severe.
2.3 Research gap
The research gap in this study is mainly reflected in the following three aspects, which form the basis for the corresponding research objectives. First, although existing studies have explored the relationship between shipping activities and environmental pollution, they lack a unified analytical framework from the perspective of shipping efficiency to systematically reveal the mechanisms through which it affects marine petroleum pollution. To fill this gap, this study proposes a comprehensive theoretical framework that clarifies the pathways through which shipping efficiency influences marine pollution, providing new theoretical insights to the field. Second, the current literature primarily focuses on the impact of shipping on air pollution, while insufficient attention has been given to land-based marine petroleum pollution, a type of pollution that is more ecologically sensitive and more challenging to manage, thus limiting the applicability of related findings. To address this shortcoming, this study uses empirical data to systematically evaluate the effect of shipping efficiency on land-based marine petroleum pollutant emissions, thereby broadening the scope and depth of environmental pollution research. Finally, existing studies offer limited exploration of the transmission channels through which shipping efficiency contributes to marine petroleum emission reduction and how external conditions moderate this process. Therefore, this study identifies the key mechanisms at play and places particular emphasis on empirically examining the moderating effects of port specialization and environmental regulation, aiming to deepen the theoretical understanding of pathways for achieving pollution reduction.
3 Methodology and data
3.1 Econometric model
3.1.1 Benchmark regression model
To assess the impact of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution, this study employs models with individual fixed effects (Equation 1), time fixed effects (Equation 2), and two-way fixed effects (Equation 3). The model is specified as follows:
In this model, for coastal province or city and year , represents the level of marine petroleum pollution in the respective province or city, while denotes shipping efficiency. is a vector of control variables, including marine economic development, technological innovation, population size, and industrial structure. represents province/city fixed effects, which account for all time-invariant regional heterogeneity factors, such as natural conditions and cultural background. captures year fixed effects, controlling for the influence of unobserved time-varying factors, such as economic growth and policy adjustments. is the random error term.
3.1.2 Moderating effect model
To further examine the moderating effects of port specialization (Equation 4) and government environmental regulation (Equation 5), this study constructs the following moderating effect models:
Where, denotes the port specialization index, and is the interaction effect between shipping efficiency and the port specialization index. represents the intensity of environmental regulation, and captures the interaction effect between shipping efficiency and environmental regulation intensity. The remaining variables are consistent with those in (Equation 3).
3.2 Variable selection and data sources
3.2.1 Dependent variable
The dependent variable in this study is marine petroleum pollution. With continuous population growth, accelerating urbanization, and increasingly intensive industrial activities, estuarine regions are facing escalating challenges of water pollution (Niu et al., 2021). As critical transitional zones between land and sea, estuaries have become primary pathways through which land-based pollutants enter marine ecosystems, posing significant threats to coastal and marine environments (Li et al., 2023). In particular, the discharge of large volumes of organic pollutants into water leads to rapid depletion of dissolved oxygen during aerobic decomposition, thereby severely disrupting the habitats of aquatic organisms (Lim et al., 2006). Notably, the petrochemical industry, as a key pillar of China’s coastal economy, entails considerable risks of organic pollutant emissions throughout its production, processing, and transportation processes, with petroleum-based pollutants being the most prominent (Crain et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2020). Considering this, following Ji and Ding (2024); Liu et al. (2011) and Peng (2015), this study adopts the volume of land-based marine petroleum pollutant emissions in China’s coastal regions as the indicator for marine petroleum pollution. The data are sourced from The Bulletin of Marine Ecology and Environment Status of China.
3.2.2 Independent variable
The independent variable is shipping efficiency. Shipping efficiency refers to the ratio of inputs to outputs in waterway transportation within port cities (including ports and shipping companies), reflecting the overall level of resource allocation and utilization (Wu and Wang, 2022). In recent years, driven by national economic growth and supportive policies, China’s shipping industry has experienced rapid development. Leveraging advantages such as low cost, large transport capacity, and broad coverage, the industry now handles approximately 90% of the country’s import and export freight, playing a crucial role in supporting foreign trade and contributing to national economic and social development (Chen et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2025). However, challenges related to resource waste and insufficient output in resource allocation persist within the shipping sector (Jian et al., 2022). Analyzing and enhancing shipping efficiency is therefore essential not only for optimizing transportation resource allocation and reducing operational costs but also for strengthening China’s competitiveness and standing in global markets with respect to resource utilization. To construct a sound indicator system for measuring shipping efficiency, this study reviews relevant literature on efficiency evaluation in the port and shipping sector. Table 1 summarizes commonly used input and output variables in existing studies, providing a theoretical foundation for the analysis.
Table 1
| Papers | Year | Inputs | Outputs | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monteiro (2018) | 2018 | Land, labor, number of cranes, number of other equipment, number of berths | Volume of cargo traffic in million tons, number of vessels handled | DEA Malmquist |
| Nguyen et al. (2019) | 2019 | Berth length, number of quay cranes, container yard area, the number of industrial parks at port’s hinterland area, the population of port’s hinterland area | Container throughput, the number of vessel call | DEA Malmquist, DEA-BBC, DEA-CCR |
| Nguyen et al. (2021) | 2021 | Gross crane productivity, crane intensity, berth length, berth depth | Calls, moves, elapsed time | DEA Malmquist |
| Nikolaou and Dimitriou (2021) | 2021 | Infrastructure and equipment context of port terminals | TEUs | DEA-CCR |
| C.-N. Wang et al. (2021) | 2021 | Total assets, Owner’s equity, Liabilities, Operation expenses | Revenue, net profit | DEA Malmquist |
| Ben Mabrouk et al. (2022) | 2022 | Number of berths, the total number of gears, and the total number of workers | Cargo throughput | DEA Malmquist, DEA-BBC, DEA-CCR |
| C.-N. Wang et al. (2022) | 2022 | Terminal length, equipment, ship calls | Cargo throughput, container throughput | DEA Malmquist |
| Yu et al. (2022) | 2022 | Number of berths, length of the wharf | Cargo throughput, container throughput | DEA Malmquist, DEA-BBC |
| Nong (2023) | 2023 | Capital, operational expenses, labor, area, quay length, and depth | Sales revenue and cargo throughputs | DEA-BBC, DEA-CCR |
| Yen et al. (2023) | 2023 | Port cost | Cargo throughput | DEA-BBC, DEA-CCR |
Input and output variables used in prior research.
At present, there is limited research on the measurement of shipping efficiency. This study adopts the shipping efficiency indicators proposed by Wu and Wang (2022). According to the Solow growth model, the input factors driving economic growth include capital and labor. In addition, a review of relevant literature indicates that berth length and the number of berths is also important input variables. Therefore, this study considers input variables from three dimensions: infrastructure, capital investment, and labor. Specifically, the number of berths, berth length, fixed asset investment in waterway transportation, and the number of employees in the water transport industry are selected as input variables. For output variables, the study uses waterway cargo throughput and waterway cargo turnover. Waterway cargo throughput serves as an indicator of shipping operational capacity, production scale, and efficiency, directly reflecting the capabilities and competitiveness of the shipping industry (Ding et al., 2025). Waterway cargo turnover captures both the volume of transport and the transport distance, providing a comprehensive measure of the production outcomes of waterway transportation (Ma, 2021). All data used to calculate shipping efficiency are sourced from the China Port Yearbook.
This study employs the DEA-Malmquist index method to measure shipping efficiency across 11 coastal regions in China, including Zhejiang, Tianjin, Shanghai, Shandong, Liaoning, Jiangsu, Hebei, Hainan, Guangxi, Guangdong, and Fujian, from 2010 to 2022. The Malmquist index was originally proposed by Swedish economist and statistician Malmquist, and Caves et al. (1982) subsequently applied it to assess changes in productivity. Later (Charnes et al., 1997), integrated the index with the DEA model, leading to the development of the DEA-based Malmquist index method (Lu and Wang, 2023).
Unlike the traditional DEA model, which can only conduct static efficiency analysis, the DEA-Malmquist index method can handle datasets with multiple inputs and outputs and enables dynamic evaluation of productivity changes across different time periods, thereby offering a more comprehensive perspective for analyzing the sources of efficiency variation (Färe et al., 1997; Thrall, 2000; Nguyen et al., 2021; Zhang, 2021). The Malmquist Productivity Index (MPI) consists of two core components: “Catch-up” and “Frontier-shift”. The “Catch-up” component reflects changes in the efficiency of decision-making units (DMUs), indicating the extent to which a DMU has improved its efficiency. In contrast, the “Frontier-shift” component captures changes in the production frontier between two time periods, representing technological progress or regression in the environment (Eraqi et al., 2009; Manh, 2023; Nong and Ha, 2023).
The analytical procedure of this method is like that of the basic DEA model. However, its distinct feature lies in the need to separate data from period and period . Specifically, for each , it is necessary to consider its input-output combinations in both periods, and , where , . According to the DEA model equations, the distance function of the MPI is expressed as . Accordingly, following (Nguyen et al., 2021; Ben Mabrouk et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022), the formula for calculating the MPI of the k-th decision-making unit from to is presented in Equation 6 and its equivalent form in Equation 7:
When the MPI value equals 1, it indicates that the productivity of the DMU remains stable between the two periods. If the MPI value is greater than 1, it suggests that the DMU’s productivity has improved during this period; conversely, if it is less than 1, it indicates a decline in productivity.
3.2.3 Moderating variable
Considering the mechanisms that influence the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution, this study selects two moderating variables, port specialization and environmental regulation.
Port specialization is regarded as an effective approach to mitigating intense competition among ports, and the quantification of port specialization has become a key focus of interest and in-depth research among port geography scholars (Zhang et al., 2021). Following the approach of (Zhang et al., 2021) and (Zhou et al., 2023), this study employs the Port Specialization Index (PSI) to measure the level of specialization of ports across various provinces and municipalities in China. Given that PSI demonstrates strong applicability and explanatory power for cross-provincial comparisons of port specialization in coastal China, it is adopted in this study as a moderating variable. The calculation formulas for PSI are shown in Equations 8 and 9:
represents the port specialization index for province . denotes the share of cargo type in the total port cargo throughput of province , and refers to the total number of cargo types in province . The PSI ranges from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating a greater degree of port specialization in the province. Data on port throughput by cargo type are sourced from the China Port Statistical Yearbook.
This study also incorporates environmental regulation as a moderating variable in the model. Drawing on the approaches of Yang et al. (2021) and Zeng et al. (2019), the study uses the total investment in industrial pollution control as a proxy variable for the intensity of environmental regulation. This indicator captures capital expenditures directed toward the treatment of industrial pollutants, including wastewater, waste gas, and solid waste. Generally, larger investment amounts are associated with more advanced pollution control equipment and technologies, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of industrial pollution mitigation (Yang et al., 2021). Building on this, strengthening the intensity of environmental regulation can improve the capacity to control pollutant emissions, more effectively curtail the discharge of land-based pollutants into the marine environment, and ultimately improve environmental quality in coastal regions (Sun et al., 2023). The relevant data are sourced from the China Statistical Yearbook.
3.2.4 Control variables
This study incorporates four control variables. First, Gross Ocean Product (GOP) refers to the total final output generated by various marine economic activities in coastal regions during a given period. It is calculated as the sum of the value added by the three major categories of marine industries and provides a comprehensive reflection of regional marine economic development (Ji and Ding, 2024; Shao et al., 2021a). Following (Shao et al., 2021b), this study employs per capita GOP as an indicator of marine economic development, with data sourced from the China Marine Statistical Yearbook. Second, technological innovation is widely recognized as contributing to the mitigation of ecological pressures on the marine environment (Ren and Ji, 2021), and patents serve as an important indicator of technological innovation (Li et al., 2022). Accordingly, following (Liu et al., 2021), this study adopts the number of marine research and development institutions as the proxy variable for technological innovation, with data also obtained from the China Marine Statistical Yearbook. In addition, population size is measured by total year-end population, with data drawn from the China Statistical Yearbook. Finally, consistent with the approach of (Jiang and Li, 2021), this study uses the proportion of the secondary industry’s value added to GDP as a proxy variable for industrial structure. The sources and definitions of all variables are presented in Table 2, and Table 3 are the descriptive statistics of the variables.
Table 2
| Variable | Symbol | Specification | References | Data source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marine petroleum pollution | The logarithm of land-based marine petroleum pollution | (Ji and Ding, 2024) | China Marine Statistical Yearbook | |
| Shipping Efficiency | DEA-Malmquist index method estimation | (Wu and Wang, 2022) | China Port Statistical Yearbook | |
| Port Specialization Index | Estimation of the port specialization index | (Zhang et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2023) | China Port Statistical Yearbook | |
| Environmental Regulation | The logarithm of completed investment in industrial pollution control | (Zeng et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021) | China Statistical Yearbook | |
| Marine Economic Development | The ratio of gross ocean product to total population | (Shao et al., 2021b) | China Marine Statistical Yearbook | |
| Technological Innovation | The logarithm of the number of marine research and development institutions | (Liu et al., 2021) | China Marine Statistical Yearbook | |
| Population Size | The logarithm of the total population | (Li et al., 2019) | China Statistical Yearbook | |
| Industrial Structure | The ratio value added of the secondary industry to GDP | (Jiang and Li, 2021) | China Statistical Yearbook |
Variables and data sources.
Table 3
| Variable | Obs. | Mean | Std. dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 143 | 3.008 | 2.499 | -4.605 | 6.543 | |
| 143 | 1.083 | 0.262 | 0.310 | 2.200 | |
| 143 | 0.218 | 0.185 | 0.003 | 0.769 | |
| 143 | 12.030 | 1.247 | 6.165 | 14.164 | |
| 143 | 1.390 | 1.031 | 0.126 | 4.194 | |
| 143 | 2.536 | 0.585 | 1.099 | 3.689 | |
| 143 | 8.387 | 0.768 | 6.767 | 9.448 | |
| 143 | 0.407 | 0.084 | 0.190 | 0.528 |
Descriptive statistics of variables.
4 Empirical results and discussion
4.1 Shipping efficiency calculation results
Shipping efficiency in China’s coastal regions shows an overall upward trend, while some provinces have experienced a decline in efficiency, indicating notable regional disparities. As shown in Table 4, the average shipping efficiency index in China’s coastal regions from 2010 to 2021 was 1.046, indicating an average improvement of 4.6% in shipping efficiency during this period and demonstrating a steady upward trend. However, it is noteworthy that some provinces, such as Liaoning, Shandong, and Tianjin, experienced a decline in shipping efficiency. This phenomenon may reflect certain shortcomings in these regions regarding resource allocation, technological upgrading, or management capabilities, which have hindered their ability to adapt promptly to structural adjustments in shipping and evolving market demands. Furthermore, the industrial structure in these provinces remains heavily reliant on traditional heavy industries, with a high proportion of high-pollution enterprises, which may also constrain further improvements in shipping efficiency. Overall, although most regions have seen steady gains in shipping efficiency, regional disparities still warrant attention.
Table 4
| Region | Shipping efficiency | Ranking | Region | Shipping efficiency | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fujian | 1.129 | 2 | Liaoning | 0.856 | 11 |
| Guangdong | 1.122 | 3 | Shandong | 0.997 | 9 |
| Guangxi | 1.148 | 1 | Tianjin | 0.915 | 10 |
| Hainan | 1.077 | 6 | Zhejiang | 1.049 | 7 |
| Hebei | 1.045 | 8 | Shanghai | 1.081 | 5 |
| Jiangsu | 1.091 | 4 |
Shipping efficiency calculation results of coastal provinces and cities.
4.2 Baseline regression results
Improvements in shipping efficiency significantly reduce marine petroleum pollution, with the results from the two-way fixed effects model proving to be the most robust. Specifically, Table 5 presents the regression results on the impact of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution in coastal provinces. Column (1) reports the results controlling only for provincial fixed effects, Column (2) reports the results controlling only for time fixed effects, and Column (3) reports the results of the two-way fixed effects model controlling for both provincial and time fixed effects. The findings indicate that improvements in shipping efficiency significantly reduce marine petroleum pollution across all models. We adopt the two-way fixed effects model as the baseline model, as it effectively controls unobserved regional heterogeneity and time trends, thereby reducing omitted variable bias. The baseline regression results show that for every 0.01 increase in shipping efficiency, marine petroleum pollution decreases by approximately 0.01% on average, suggesting that improvements in shipping efficiency play a significant role in enhancing the marine environment.
Table 5
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| -0.854** (0.399) |
-1.081** (0.453) |
-1.023** (0.425) |
|
| -0.706* (0.409) |
-0.098 (0.361) |
-0.300 (0.449) |
|
| 0.777** (0.345) |
1.246*** (0.368) |
0.959** (0.380) |
|
| -4.592 (4.044) |
-0.002 (0.735) |
-1.572 (4.912) |
|
| -0.995 (3.707) |
-7.369 (5.789) |
-15.260* (8.080) |
|
| Constant | 41.860 (34.067) |
5.146 (4.849) |
22.720 (39.589) |
| Year Fixed Effect | NO | YES | YES |
| Province Fixed Effect | YES | NO | YES |
| Observations | 143 | 143 | 143 |
Baseline regression results.
The values enclosed in parentheses represent standard errors. *, **, and *** denote significance at the 10%, 5%, and 1% levels, respectively.
We argue that the improvement of shipping efficiency, as a key manifestation of the operational efficiency of transportation infrastructure, can effectively mitigate land-based marine petroleum pollution through two main channels: (1) enhancing pollution prevention and control capacity via the optimization of shipping facilities, and (2) promoting green industrial transformation by reducing transportation costs.
First, the improvement of shipping facilities significantly strengthens the system’s ability to control pollution sources, thereby reducing the risk of petroleum pollutants entering the ocean. With the continuous upgrading of waterway transportation infrastructure, the environmental performance of port operations has steadily improved (Hua et al., 2020). For instance, intelligent centralized pollutant treatment systems help reduce emissions during loading, unloading, and transportation processes; meanwhile, automated monitoring and emergency response systems enable the real-time detection of, and rapid response to, unexpected pollution incidents, thereby effectively curbing the spread of pollutants into the marine environment (Yang et al., 2018; Durán et al., 2025).
Second, the improvement of shipping efficiency helps to lower overall logistics costs and enhance the reliability of the transportation system, which is particularly important for high-end manufacturing and modern service industries that are highly sensitive to cost control. As port and shipping systems operate more efficiently, these low-pollution, high value-added industries are increasingly drawn to port cities, gradually replacing traditionally dominant, high-pollution sectors such as petroleum refining, heavy chemical industries, and coal handling (Fan et al., 2021). This industrial shift elevates the level of industrial development in port areas and promotes the green transformation of regional economies, thereby alleviating environmental pressures on coastal ecosystems (Su et al., 2024).
In summary, improvements in shipping efficiency are reflected not only in enhanced shipping facilities but also in reduced transportation costs and industrial restructuring (Psaraftis and Kontovas, 2013). The former strengthens pollution control capacity and operational cleanliness, effectively reducing pollutant emissions; the latter diminishes the dominance of high-pollution industries, thereby constraining petroleum-related pollutant emissions at the source. These two mechanisms complement each other, making the enhancement of shipping efficiency an important pathway for addressing land-based marine petroleum pollution.
4.3 Moderating effects results
Port specialization and environmental regulation both exert negative moderating effects on the role of shipping efficiency in reducing marine petroleum pollution. In other words, in regions with lower levels of port specialization or relatively lenient environmental regulation, improvements in shipping efficiency have a more pronounced effect on pollution reduction, indicating a certain degree of substitutability between the two. Specifically, as shown in Table 6, the regression results in column (2) indicate that the interaction term has a regression coefficient of 6.323, which is significantly positive at the 1% level. This suggests that port specialization exerts a significant negative moderating effect on the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution. Specifically, in coastal provinces with lower levels of port specialization, improvements in shipping efficiency have a more pronounced suppressive effect on marine petroleum pollution. This finding indicates a certain degree of “substitutability” between port specialization and shipping efficiency in the context of pollution control.
Table 6
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -0.876** (0.435) |
-2.468*** (0.525) |
-1.000** (0.426) |
-15.520*** (3.437) |
|
| 1.005 (2.960) |
-6.757** (3.295) |
|||
| 6.323*** (1.503) |
||||
| 0.152 (0.181) |
-1.269*** (0.374) |
|||
| 1.258*** (0.296) |
||||
| -0.248 (0.502) |
-0.413 (0.455) |
-0.321 (0.451) |
-0.298 (0.420) |
|
| 0.010 (0.398) |
1.466*** (0.376) |
0.987** (0.382) |
1.612*** (0.385) |
|
| 3.588 (5.107) |
-6.504 (4.750) |
-2.061 (4.953) |
-2.610 (4.621) |
|
| -13.590 (8.476) |
-10.540 (7.766) |
-13.99* (8.230) |
-15.540** (7.684) |
|
| Constant | -19.170 (40.124) |
61.610 (38.220) |
24.350 (39.687) |
44.540 (37.314) |
| Year Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province Fixed Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 143 | 143 | 143 | 143 |
Moderating effects results.
The values enclosed in parentheses represent standard errors. *, **, and *** denote significance at the 10%, 5%, and 1% levels, respectively.
Figure 1 further validates the above findings by illustrating the moderating effect of port specialization on the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution. The results show that when PSI is below approximately 0.3, the marginal effect of EFFI on PET is significantly negative, indicating that in regions with lower levels of port specialization, improvements in shipping efficiency exert a stronger suppressive effect on pollution. This suggests that in contexts where port functions are blurred and operational processes are less standardized, enhancing efficiency becomes a key means of improving environmental performance. In contrast, when PSI exceeds 0.3, the marginal effect gradually increases and becomes insignificant, implying that as port specialization intensifies, the pollution reduction effect of shipping efficiency is either substituted or diminished, thereby weakening the moderating effect.
Figure 1
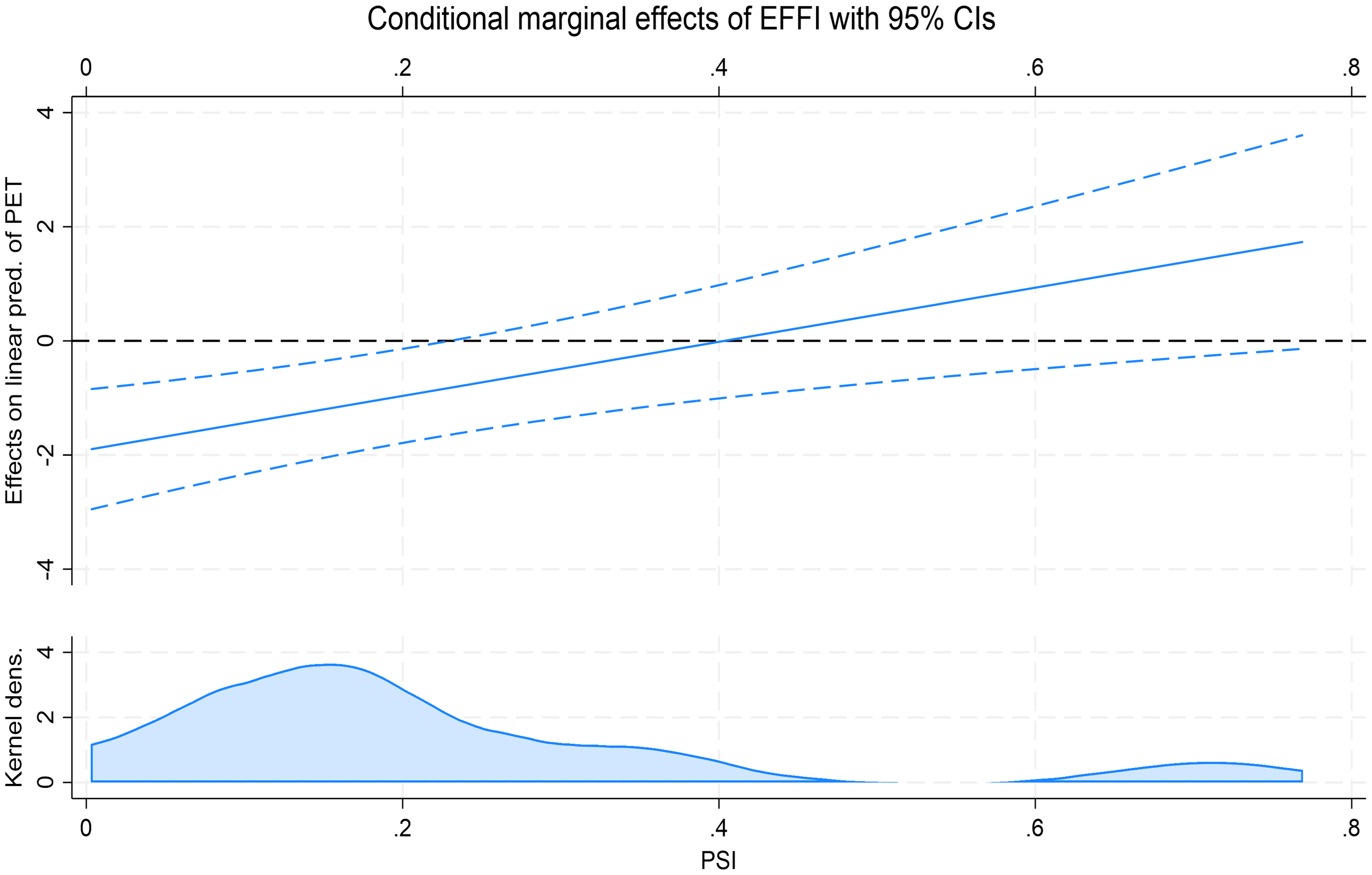
Marginal effect of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution at varying levels of port specialization.
When the degree of port specialization is low, the division of functions within the port is unclear, operational processes are not well standardized, and there is a lack of effective collaboration and pollution control mechanisms. Under such circumstances, improving shipping efficiency becomes an important means of mitigating environmental pollution, with a more pronounced emission reduction effect. In contrast, when the degree of port specialization is high, pollution sources are generally brought under initial control through rational functional division and spatial zoning, and the port itself tends to possess strong pollution treatment capabilities. In this context, the additional emission reduction benefits resulting from enhanced shipping efficiency diminish, exhibiting a trend where greater efficiency improvements yield increasingly limited pollution reduction effects. Overall, although port specialization and shipping efficiency follow different pathways in pollution control, both contribute positively to reducing marine petroleum pollution and can, to some extent, serve as substitutes for each other.
Moreover, the results in column (4) show that the regression coefficient of the interaction term is 1.258, which is also significant at the 1% level, further confirming that environmental regulation exerts a negative moderating effect on the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution. Specifically, in regions where environmental regulation is relatively weak, with insufficient emission standards, regulatory frameworks, and pollution control requirements, ports and shipping enterprises generally face limited external policy constraints. Under such conditions, their environmental performance relies more heavily on improvements in internal operational efficiency, making shipping efficiency a key mechanism for driving pollution reduction.
Figure 2 provides a visual illustration of the moderating effect. The results show that when the intensity of environmental regulation is below 12, the marginal effect of EFFI on PET is significantly negative, indicating that improvements in shipping efficiency have a stronger pollution-reducing effect in regions with weaker regulatory enforcement. In this phase, EFFI functions as a “substitute mechanism” for policy regulation, indirectly achieving pollution control objectives through enhanced operational efficiency. However, as environmental regulation strengthens (ER>12), the marginal effect gradually becomes insignificant, suggesting that in regions with stricter regulation, the independent emission-reduction effect of EFFI is weakened by policy constraints, and the moderating effect tends to diminish.
Figure 2
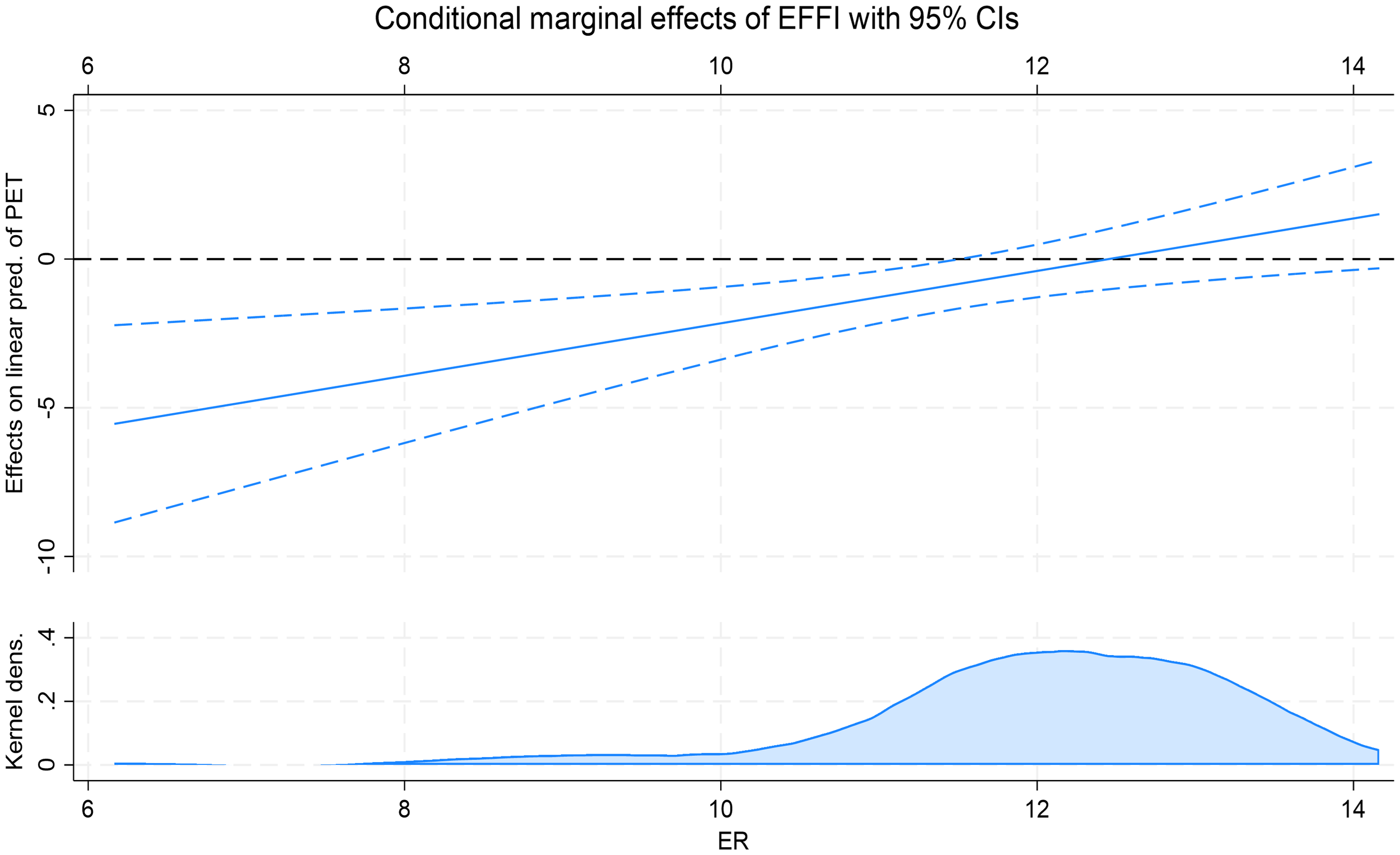
Marginal effect of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution at varying levels of environmental regulation.
Improvements in shipping efficiency are typically accompanied by cost reductions, technological upgrades, and streamlined processes. Although these changes are not primarily aimed at environmental protection, they can effectively reduce pollution in practice. In regions where external environmental policies are relatively weak, enhanced shipping efficiency can partially compensate for regulatory shortcomings and serve as an alternative means of pollution control. Therefore, in areas with less stringent environmental requirements, the pollution-reducing impact of improved shipping efficiency becomes more pronounced, demonstrating its greater environmental potential.
5 Conclusion
Based on panel data from 11 coastal regions in China spanning the period from 2010 to 2022, this study investigates the impact of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution. The main findings are as follows. First, overall, shipping efficiency in China’s coastal regions has shown a steady upward trend, although some provinces, such as Liaoning, Shandong, and Tianjin, still exhibit declines in efficiency, indicating regional disparities in development. Second, the baseline regression results reveal that shipping efficiency has a significant negative impact on marine petroleum pollution, suggesting that improvements in shipping efficiency contribute substantially to mitigating marine petroleum pollution. Third, port specialization and environmental regulation exhibit significant negative moderating effects on the relationship between shipping efficiency and marine petroleum pollution.
Based on the above findings, the following policy recommendations are proposed. First, shipping efficiency in provinces such as Liaoning, Shandong, and Tianjin remains relatively low, primarily due to a narrow industrial structure, outdated port facilities, and poor transport connectivity. It is essential to accelerate the intelligent upgrading of shipping infrastructure, promote the adoption of automated loading and unloading systems and intelligent scheduling, and enhance operational efficiency. In addition, coastal industries should be guided toward higher value-added and lower-pollution sectors to reduce dependence on traditional energy-intensive industries. Efforts should also be made to improve the intermodal transport network by promoting rail-waterway integration and developing a coordinated and efficient port logistics system. Second, given that improvements in shipping efficiency help reduce marine petroleum pollution, coastal regions should expedite the development of green shipping systems. This includes strengthening technological upgrades in port operations, introducing energy-saving equipment and intelligent management systems to reduce fuel consumption and leakage risks during operations. Furthermore, standardized environmental protection facilities, such as waste oil-water recovery systems, shore power systems, and emergency response equipment, should be installed to control pollution at its source. Third, management strategies should be tailored to different levels of port specialization. For ports with a lower degree of specialization, priority should be given to pollution control through efficiency improvements, emphasizing operational enhancements as the primary emission reduction pathway. For highly specialized ports, greater emphasis can be placed on functional division, pollutant-specific management, and supporting facilities to improve the overall level of environmental management and enhance the systematization and precision of pollution control. Fourth, the intensity of environmental regulation should be carefully calibrated to avoid unintended negative consequences. In regions with relatively weak regulatory foundations, local governments should first be encouraged to reduce emissions through efficiency improvements, and more stringent standards should be introduced gradually as their capacity increases, following an efficiency-first, policy-following approach. In regions with stronger regulatory frameworks, greater emphasis should be placed on the synergy between policy instruments and market mechanisms to prevent cost pressures from discouraging local governments from investing in environmental protection, thereby ensuring the sustainability and effectiveness of regulatory policies.
This study has certain limitations, which provide opportunities for further research. On the one hand, due to data availability constraints, the study period is limited to 2022. Future research could extend the time span as updated data become available, allowing for a more comprehensive examination of the dynamic relationship between shipping efficiency and environmental impact. On the other hand, the current analysis is based primarily on regional-level panel data and does not capture micro-level differences at the port or firm level. Future studies may incorporate more granular data (such as port-level or firm-level data) to explore the heterogeneous effects of shipping efficiency on environmental outcomes under different port types, transportation routes, and operational characteristics.
Statements
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: China Marine Statistical Yearbook; China Port Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Yearbook; The Bulletin of Marine Ecology and Environment Status of China.
Author contributions
XJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft. XD: Methodology, Validation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. WH: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft. YQ: Validation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the Universities in Guangxi Young and Middle-Aged Teachers’ Basic Ability Improvement Project “Measurement and Enhancement Path of Green Total Factor Productivity in Guangxi Beibu Gulf Ports” (2025KY0452), by the National Social Science Fund of China (21BGJ034), and by the BK21 FOUR Program through Jeonbuk National University Research Grant.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Editors and the reviewers for the useful and constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Acheampong A. O. Dzator J. Dzator M. Salim R. (2022). Unveiling the effect of transport infrastructure and technological innovation on economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Technol. Forecasting Soc. Change182, 121843. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2022.121843
2
Adeola A. O. Akingboye A. S. Ore O. T. Oluwajana O. A. Adewole A. H. Olawade D. B. et al . (2022). Crude oil exploration in Africa: socio-economic implications, environmental impacts, and mitigation strategies. Environ. Syst. Decisions42, 26–50. doi: 10.1007/s10669-021-09827-x
3
Adipah S. (2019). Introduction of petroleum hydrocarbons contaminants and its human effects. J. Environ. Sci. Public Health3, 1–9. doi: 10.26502/jesph.96120043
4
Alsaleh M. Abdul-Rahim A. S. (2024). What are the influence of fishery activities and their implication on marine water pollution? An empirical analysis. Environment Dev. Sustainability, 1–32. doi: 10.1007/s10668-024-05561-x
5
Bani Hani E. Tawalbeh M. Al-Othman A. Assad M. E. H. (2019). Rheological study on seawater contaminatedwith oil components. Polish J. Environ. Stud.28, 2585–2591. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/92121
6
Ben Mabrouk M. et al . (2022). Joined efficiency and productivity evaluation of Tunisian commercial seaports using DEA-based approaches. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.10, 626. doi: 10.3390/jmse10050626
7
Blumer M. Sass J. (1972). Oil pollution: persistence and degradation of spilled fuel oil. Science176, 1120–1122. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4039.1120
8
Buonocore J. J. Reka S. Yang D. Chang C. Roy A. Thompson T. et al . (2023). Air pollution and health impacts of oil & gas production in the United States. Environ. Res.: Health1, 021006. doi: 10.1088/2752-5309/acc886
9
Caves D. W. Christensen L. R. Diewert W. E. (1982). The economic theory of index numbers and the measurement of input, output, and productivity. Econometrica50, 1393. doi: 10.2307/1913388
10
Charnes A. Cooper W. Lewin A. Y. Seiford L. M. (1997). Data envelopment analysis theory, methodology and applications. J. Operational Res. Soc.48, 332–333. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jors.2600342
11
Chen S. Miao C. Zhang Q. (2024). Understanding the evolution of China’s green shipping policies: Evidence by social network analysis. J. Cleaner Prod.482, 144204. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.144204
12
Crain C. M. Halpern B. S. Beck M. W. Kappel C. V. (2009). Understanding and managing human threats to the coastal marine environment. Ann. New York Acad. Sci.1162, 39–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04496.x
13
Das N. Chandran (2011). Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminants: an overview. Biotechnol. Res. Int.2011, 1–13. doi: 10.4061/2011/941810
14
Da Silva E. M. Peso‐Aguiar M. C. De Fátima Teixeira Navarro M. De Barros E Azevedo Chastinet C. (1997). Impact of petroleum pollution on aquatic coastal ecosystems in Brazil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem.16, 112–118. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620160112
15
Dey S. Das A. Mallick K. Sahu A. Das A. P. (2023). “Environmental petroleum waste: pollution, toxicity, sustainable remediation,” in Impact of Petroleum Waste on Environmental Pollution and its Sustainable Management Through Circular Economy. Eds. BeheraI. D.DasA. P. (Springer Nature Switzerland (Environmental Science and Engineering, Cham), 159–175. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-48220-5_7
16
Ding X. Song J. Zhu N. Ji X. (2025). Does the digital economy reduce shipping-related pollution? Evidence from coastal port cities in China. Front. Mar. Sci.12. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1538634
17
Durán C. Fernández-Campusano C. Espinosa-Leal L. Castañeda C. Carrillo E. Bastias M. et al . (2025). Exploring boost efficiency in text analysis by using AI techniques in port companies. Appl. Sci.15, 4556. doi: 10.3390/app15084556
18
Dzator M. Acheampong A. O. Dzator J. (2021). Does transport infrastructure development contribute to carbon emissions? Evidence from developing countries. Environ. Sustainability Economy, 19–33. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-822188-4.00012-9. Elsevier.
19
Ejiba I. Onya S. Adams O. (2016). Impact of oil pollution on livelihood: evidence from the Niger delta region of Nigeria. J. Sci. Res. Rep.12, 1–12. doi: 10.9734/JSRR/2016/26633
20
Ekpenyong N. S. Udofia U. S. (2015). Oil Pollution and Its Impact on Water Quality in Ibeno Community. Studies in sociology of science, 6 (2), 8–12. (city: Umudike).
21
Eraqi A. S. A. Khader A. T. Mustafa A. (2009). DEA Malmquist index measurement in Middle East and East African containers terminals. Int. J. Shipping Transport Logistics1, 249. doi: 10.1504/IJSTL.2009.027533
22
Erdogan S. (2020). Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of disaggregated transport infrastructure investments. Sustain. Cities Soc.61, 102338. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102338
23
Fan F. Zhang X. Yang W. Liu C. (2021). Spatiotemporal evolution of China’s ports in the international container transport network under upgraded industrial structure. Transportation J.60, 43–69. doi: 10.5325/transportationj.60.1.0043
24
Färe R. Grosskopf S. Lindgren B. Poullier J. P. (1997). Productivity growth in health-care delivery. Med. Care35, 354–366. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199704000-00006
25
Freije A. M. (2015). Heavy metal, trace element and petroleum hydrocarbon pollution in the Arabian Gulf: Review. J. Assoc. Arab Universities Basic Appl. Sci.17, 90–100. doi: 10.1016/j.jaubas.2014.02.001
26
Gao H. Wu M. Liu H. Xu Y. Liu Z. (2022). Effect of petroleum hydrocarbon pollution levels on the soil microecosystem and ecological function. Environ. pollut.293, 118511. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118511
27
Guo Y. Zhang Q. Lai K. K. Zhang Y. Wang S. Zhang W. (2020). The impact of urban transportation infrastructure on air quality. Sustainability12, 5626. doi: 10.3390/su12145626
28
Guo W. Wang X. Liu S. Kong X. Wang P. Xu T. (2022). Long-term petroleum hydrocarbons pollution after a coastal oil spill. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.10, 1380. doi: 10.3390/jmse10101380
29
Habeebullah S. F.K. Al Said T. Alagarsamy S. Ahamed N. Martinez K. Abusam A. et al . (2025). Pollution dynamics in the first marine protected area of the Northwestern Arabian Gulf: Environmental assessment and management implications. Environmental Pollution, 369, 125856.
30
Hazaimeh M. D. Ahmed E. S. (2021). Bioremediation perspectives and progress in petroleum pollution in the marine environment: a review. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.28, 54238–54259. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15598-4
31
Hou G. Zhan B. (2023). Relationship among marine pollution, outdoor activities, and climate change: Fresh evidence from panel threshold regression analysis from coastal regions of China. Environ. Res.236, 116668. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116668
32
Hua C. Chen J. Wan Z. Xu L. Bai Y. Zheng T. et al . (2020). Evaluation and governance of green development practice of port: A sea port case of China. J. Cleaner Prod.249, 119434. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119434
33
Jha S. Dahiya (2022). Impact analysis of oil pollution on environment, marine, and soil communities. Adv. Oil-Water Separation, 99–113. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-89978-9.00017-3. Elsevier.
34
Ji X. Ding X. (2024). Analysis on the relationship between coastal tourism and marine pollution: an empirical analysis of China’s 11 coastal regions. Front. Mar. Sci.11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1471467
35
Jian L. Guo J. Ma H. (2022). Research on the impact of digital innovation driving the high-quality development of the shipping industry. Sustainability14, 4648. doi: 10.3390/su14084648
36
Jiang S.-S. Li J.-M. (2021). Do political promotion incentive and fiscal incentive of local governments matter for the marine environmental pollution? Evidence from China’s coastal areas. Mar. Policy128, 104505. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104505
37
Koduvayur Habeebullah S. F. Al Said T. Alagarsamy S. Ahamed N. Martinez K. Abusam A. et al . (2025). Pollution dynamics in the first marine protected area of the Northwestern Arabian Gulf: Environmental assessment and management implications. Environ. pollut.369, 125856. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2025.125856
38
Latimer J. S. Hoffman E. J. Hoffman G. Fasching J. L. Quinn J. G. et al . (1990). Sources of petroleum hydrocarbons in urban runoff. Water Air Soil pollut.52 (1), 1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00283111
39
Li Y. Lu Q. Yang J. Xing Y. Ling W. Liu K. et al . (2023). The fate of microplastic pollution in the Changjiang River estuary: A review. J. Cleaner Prod.425, 138970. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138970
40
Li K. Fang L. He L. (2019). How population and energy price affect China’s environmental pollution? Energy Policy129, 386–396. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.02.020
41
Li Y. Kong J. Ji J. (2022). Environmental regulation, technological innovation and development of marine fisheries—Evidence from ten coastal regions in China. Fishes7, 20. doi: 10.3390/fishes7010020
42
Lim H.-S. Diaz R. J. Hong J. S. Schaffner L. C. (2006). Hypoxia and benthic community recovery in Korean coastal waters. Mar. pollut. Bull.52, 1517–1526. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.05.013
43
Liu S. Lou S. Kuang C. Huang W. Chen W. Zhang J. et al . (2011). Water quality assessment by pollution-index method in the coastal waters of Hebei Province in western Bohai Sea, China. Mar. pollut. Bull.62, 2220–2229. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.06.021
44
Liu F. Huang Y. Zhang L. Li G. (2022). Marine environmental pollution, aquatic products trade and marine fishery Economy——An empirical analysis based on simultaneous equation model. Ocean Coast. Manage.222, 106096. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106096
45
Liu Y. Ali A. Chen Y. She X. (2022). The effect of transport infrastructure (road, rail, and air) investments on economic growth and environmental pollution and testing the validity of EKC in China, India, Japan, and Russia. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.30, 32585–32599. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24448-w
46
Liu P. Zhu B. Yang M. (2021). Has marine technology innovation promoted the high-quality development of the marine economy? ——Evidence from coastal regions in China. Ocean Coast. Manage.209, 105695. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2021.105695
47
Lo Storto C. Evangelista (2023). Infrastructure efficiency, logistics quality and environmental impact of land logistics systems in the EU: A DEA-based dynamic mapping. Res. Transportation Business Manage.46, 100814. doi: 10.1016/j.rtbm.2022.100814
48
Lu Z. Wang K. (2023). Research on Regional Waterway Transportation Efficiency Based on DEA and Malmquist Index Model: Taking Guangxi Beibu Gulf as an Example. Information Systems and Economics,4 (3). (city: Liuzhou).
49
Ma R. (2021). Forecast of waterway cargo turnover volume based on genetic algorithm to optimize neural network parameters. J. Physics: Conf. Ser.2083, 32010. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2083/3/032010
50
Makarova I. Mavrin V. Magdin K. Barinov A. Gusev E. (2020). “Reducing the impact of vehicles on the environment by the modernization of transport infrastructure,” in Reliability and Statistics in Transportation and Communication. Eds. KabashkinI.YatskivI.PrentkovskisO. (Springer International Publishing (Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Cham), 531–540. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-44610-9_52
51
Manh H. L. (2023). A comparative analysis on operational efficiency of container terminals by basic and malmquist DEA models: A case of haiphong port. Int. J. e-Navigation Maritime Economy21, 9–20. doi: 10.52820/j.enavi.2023.21.009
52
McConnell M. (2002). Capacity building for a sustainable shipping industry: a key ingredient in improving coastal and ocean and management. Ocean Coast. Manage.45, 617–632. doi: 10.1016/S0964-5691(02)00089-3
53
Mohammadi L. Rahdar A. Bazrafshan E. Dahmardeh H. Susan M. A.B.H. Kyzas G. Z. (2020). Petroleum hydrocarbon removal from wastewaters: A review. Processes8, 447. doi: 10.3390/pr8040447
54
Mohanta S. Pradhan B. Behera I. D. (2024). Impact and remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants on agricultural land: A review. Geomicrobiol. J.41, 345–359. doi: 10.1080/01490451.2023.2243925
55
Monteiro J. G. R. (2018). Measuring Productivity and Efficiency of Seaports in India using DEA technique. Cent. Eur. Rev. Econom. Manage.2, 153. doi: 10.29015/cerem.529
56
Nguyen T. L. H. Park S. H. Kim Y. Yeo G. T. (2021). An efficiency analysis of container terminals in Southern Vietnam using DEA dynamic efficiency evaluation. Asian J. Shipping Logistics37, 329–336. doi: 10.1016/j.ajsl.2021.09.003
57
NGUYEN D. D. Park G.-K. Choi K.-H. (2019). The performance analysis of container terminals in Vietnam using DEA-malmquist. J. Navigation Port. Res.43, 101–109. doi: 10.5394/KINPR.2019.43.2.101
58
Nikolaou Dimitriou L. (2021). Lessons to be learned from top-50 global container port terminals efficiencies: A multi-period DEA-tobit approach. Maritime Transport Res.2, 100032. doi: 10.1016/j.martra.2021.100032
59
Niu L. Cai H. Jia L. Luo X. Tao W. Dong Y. et al . (2021). Metal pollution in the Pearl River Estuary and implications for estuary management: The influence of hydrological connectivity associated with estuarine mixing. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf.225, 112747. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112747
60
Nong T. N.-M. (2023). Performance efficiency assessment of Vietnamese ports: An application of Delphi with Kamet principles and DEA model. Asian J. Shipping Logistics39, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajsl.2022.10.002
61
Nong N.-M. T. Ha D.-S. (2023). Port efficiency evaluation: an application of AHP and malmquist DEA model. J. Distribution Sci.21, 77–89. doi: 10.15722/JDS.21.11.202311.77
62
Nriagu J. Udofia E. A. Ekong I. Ebuk G. (2016). Health risks associated with oil pollution in the Niger delta, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health13, 346. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13030346
63
Ozigis M. S. Kaduk J. D. Jarvis C. H. da Conceição Bispo P. Balzter H. (2020). Detection of oil pollution impacts on vegetation using multifrequency SAR, multispectral images with fuzzy forest and random forest methods. Environ. pollut.256, 113360. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113360
64
Peng S. (2015). The nutrient, total petroleum hydrocarbon and heavy metal contents in the seawater of Bohai Bay, China: Temporal–spatial variations, sources, pollution statuses, and ecological risks. Mar. pollut. Bull.95, 445–451. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.03.032
65
Psaraftis H. N. Kontovas C. A. (2013). Speed models for energy-efficient maritime transportation: A taxonomy and survey. Transportation Res. Part C.: Emerg. Technol.26, 331–351. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2012.09.012
66
Ren W. Ji J. (2021). How do environmental regulation and technological innovation affect the sustainable development of marine economy: New evidence from China’s coastal provinces and cities. Mar. Policy128, 104468. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2021.104468
67
Samsuria N. N. C. Ismail W. Z. W. Nazli M. N. W. M. Aziz N. A. A. Ghazali A. K. (2025). Problems, effects, and methods of monitoring and sensing oil pollution in water: A review. Water17, 1252. doi: 10.3390/w17091252
68
Shao Q. Chen L. Zhong R. Weng H. (2021a). Marine economic growth, technological innovation, and industrial upgrading: A vector error correction model for China. Ocean Coast. Manage.200, 105481. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2020.105481
69
Shao Q. Guo J. Kang (2021b). Environmental response to growth in the marine economy and urbanization: A heterogeneity analysis of 11 Chinese coastal regions using a panel vector autoregressive model. Mar. Policy124, 104350. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.104350
70
Sharma K. Shah G. Singhal K. Soni V. (2024). Comprehensive insights into the impact of oil pollution on the environment. Regional Stud. Mar. Sci.74, 103516. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2024.103516
71
Su Z. Liu Y. Gao Y. Park K. S. Su M. (2024). Critical success factors for green port transformation using digital technology. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.12, 2128. doi: 10.3390/jmse12122128
72
Sun C. Zhang W. Luo Y. Xu Y. (2019). The improvement and substitution effect of transportation infrastructure on air quality: An empirical evidence from China’s rail transit construction. Energy Policy129, 949–957. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.03.005
73
Sun D. Zeng S. Lin H. Meng X. Yu B. (2019). Can transportation infrastructure pave a green way? A city-level examination in China. J. Cleaner Prod.226, 669–678. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.124
74
Sun J. Zhai N. Miao J. Mu H. Li W. (2023). How do heterogeneous environmental regulations affect the sustainable development of marine green economy? Empirical evidence from China’s coastal areas. Ocean Coast. Manage.232, 106448. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2022.106448
75
Tavella R. A. da Silva Júnior F. M.R. Santos M. A. Miraglia S. G.E.K. Pereira Filho R. D. (2025). A review of air pollution from petroleum refining and petrochemical industrial complexes: sources, key pollutants, health impacts, and challenges. ChemEngineering9, 13. doi: 10.3390/chemengineering9010013
76
Thrall R. M. (2000). Measures in DEA with an application to the malmquist index. J. Prod. Anal.13, 125–137. doi: 10.1023/A:1007800830737
77
Ullah I. Nuta F. M. Levente D. Yiyu B. Yihan Z. Yi C. et al . (2023). Nexus between trade, industrialization, and marine pollution: A quantile regression approach. Ecol. Indic.155, 110992. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110992
78
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) . (2021). Protecting the Marine Environment from Land-Based Activities. Still Only One Earth Policy Brief #9. International Institute for Sustainable Development. Retrieved from https://bit.ly/still-only-one-earth.
79
Varjani S. J. Upasani V. N. (2017). A new look on factors affecting microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. Int. Biodeterioration Biodegradation120, 71–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.02.006
80
Venkatesh V. G. Zhang A. Luthra S. Dubey R. Subramanian N. Mangla S (2017). Barriers to coastal shipping development: An Indian perspective. Transportation Res. Part D.: Transport Environ.52, 362–378. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2017.03.016
81
Walker T. R. Crittenden P. D. Young S. D. Prystina T. (2006). An assessment of pollution impacts due to the oil and gas industries in the Pechora basin, north-eastern European Russia. Ecol. Indic.6, 369–387. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2005.03.015
82
Wang C.-N. Nguyen N. A.T. Fu H. P. Hsu H. P. Dang T. T. (2021). Efficiency assessment of seaport terminal operators using DEA malmquist and epsilon-based measure models. Axioms10, 48. doi: 10.3390/axioms10020048
83
Wang C.-N. Nguyen P. H. Nguyen T. L. Nguyen T. G. Nguyen D. T. Tran T. H. et al . (2022). A two-stage DEA approach to measure operational efficiency in Vietnam’s port industry. Mathematics10, 1385. doi: 10.3390/math10091385
84
Wang W. Ali A. Wang H. Feng Y. Dai S. (2023). EKC hypothesis testing and environmental impacts of transportation infrastructure investments in China, Turkey, India, and Japan. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.30, 81600–81615. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-27580-3
85
Wang Y. Mi J. J. Chen C. Ge J. Chen Y. (2025). Evolution of China’s shipping policies and attention: Evidence from LDA analysis. Ocean Coast. Manage.267, 107746. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2025.107746
86
Wang C. Wang L. (2023). Green investment and vertical alliances in the maritime supply chain. Environment Dev. Sustainability25, 6657–6687. doi: 10.1007/s10668-022-02322-6
87
Wang Z. Zhao L. Wang Y. (2020). An empirical correlation mechanism of economic growth and marine pollution: A case study of 11 coastal provinces and cities in China. Ocean Coast. Manage.198, 105380. doi: 10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2020.105380
88
Wu L. Wang C. (2022). Evaluating shipping efficiency in chinese port cities: four-stage bootstrap DEA model. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.10, 870. doi: 10.3390/jmse10070870
89
Xie R. Fang J. Liu C. (2016). Impact and spatial spillover effect of transport infrastructure on urban environment. Energy Proc.104, 227–232. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2016.12.039
90
Yan Z. Pan J. Gao F. An Z. Liu H. Huang Y. et al . (2019). Seawater quality criteria derivation and ecological risk assessment for oil pollution in China. Mar. pollut. Bull.142, 25–30. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.02.033
91
Yang Y. Zhong M. Yao H. Yu F. Fu X. Postolache O. (2018). Internet of things for smart ports: Technologies and challenges. IEEE Instrumentation Measurement Magazine21, 34–43. doi: 10.1109/MIM.2018.8278808
92
Yang M. Yan X. Li Q. (2021). Impact of environmental regulations on the efficient control of industrial pollution in China. Chin. J. Population Resour. Environ.19, 230–236. doi: 10.1016/j.cjpre.2021.12.025
93
Yen B. T. Huang M. J. Lai H. J. Cho H. H. Huang Y. L. (2023). How smart port design influences port efficiency – A DEA-Tobit approach. Res. Transportation Business Manage.46, 100862. doi: 10.1016/j.rtbm.2022.100862
94
Yu C. Kong X. Chen X. Dou S. Zhang L. (2024). Anthropogenic impacts on the marine environment: an empirical study from China. Soc. Sci. doi: 10.20944/preprints202403.0800.v2
95
Yu S. Gong L. Qi M. (2022). Efficiency analysis of the coastal port group in the yangtze river delta. J. Mar. Sci. Eng.10, 1575. doi: 10.3390/jmse10111575
96
Zeng J. Liu T. Feiock R. Li F. (2019). The impacts of China’s provincial energy policies on major air pollutants: A spatial econometric analysis. Energy Policy132, 392–403. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.05.052
97
Zhang X. (2021). Research on evaluation of port logistics efficiency based on DEA-malmquist model. J. Physics: Conf. Ser.1971, 12071. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1971/1/012071
98
Zhang B. Matchinski E. J. Chen B. Ye X. Jing L. Lee K. (2019). Marine oil spills—Oil pollution, sources and effects. World Seas: Environ. Eval., 391–406. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-805052-1.00024-3. Elsevier.
99
Zhang L. Shi K. Yue L. (2007). Chemical characteristics and pollution sources of petroleum hydrocarbons and PAHs in sediments from the Beiluohe River, Northern China. Environ. Geol.53, 307–315. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0645-6
100
Zhang Q. Yan K. Yang D. (2021). Port system evolution in Chinese coastal regions: A provincial perspective. J. Transport Geogr.92, 103031. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2021.103031
101
Zhao Y. Song Y. Cui J. Gan S. Yang X. Wu R. et al . (2020). Assessment of water quality evolution in the pearl river estuary (South Guangzhou) from 2008 to 2017. Water12, 59. doi: 10.3390/w12010059
102
Zhou Y. Li Z. Duan W. Deng Z. (2023). The impact of provincial port integration on port efficiency: Empirical evidence from China’s Coastal Provinces. J. Transport Geogr.108, 103574. doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2023.103574
Summary
Keywords
shipping efficiency, marine petroleum pollution, fixed effect, moderating effect, coastal regions
Citation
Ji X, Ding X, Hu W and Qiu Y (2025) The effect of shipping efficiency on marine petroleum pollution: an empirical analysis of China’s 11 coastal regions. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1645175. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1645175
Received
11 June 2025
Accepted
03 September 2025
Published
17 September 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Xuemei Li, Ocean University of China, China
Reviewed by
Chuanxu Wang, Shanghai Maritime University, China
Lufeng Chen, Jianghan University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Ji, Ding, Hu and Qiu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xingong Ding, dingxingong@bbgu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.