Abstract
The eastern coastal area of Jiangsu, China, is characterized by a silty and muddy coast, exhibiting substantial seasonal variations in suspended sediment transport within the sea area. This study draws from the quasi-synchronous hydrological and sediment observation data from various stations in the eastern Jiangsu coast during the spring tide cycle in the summer of 2006 and the winter of 2007. Then, the study analyzes the seasonal variation characteristics and mechanisms of the plane and vertical distribution of sediment transport and further examines their correlations with tidal current, wave, and seawater temperature. The findings reveal an “M-shape” distribution pattern in the plane of sediment concentration both in summer and winter, with two pronounced peaks in the Binhaigang and Jianggang sea areas in the coastal direction and a gradual decline in the offshore direction. Meanwhile, the vertical distribution of sediment concentration exhibited greater uniformity in profile during winter than during summer. Under mild sea conditions in the Jiangsu coast, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the plane distribution of sediment concentration are in the following order: tidal current > wave > seawater temperature. From Lianyungang to Sheyanggang, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the seasonal variation of plane distribution of sediment concentration are as follows: tidal current > wave > seawater temperature; from Sheyanggang to Lvsigang, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the seasonal variation of plane distribution of sediment concentration are wave in the following order: wave > tidal current > seawater temperature. Meanwhile, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the seasonal variation of sediment concentration profile area are as follows: seawater temperature > wave > tidal current. These results differ from the previous understanding about seasonal variation of sediment transport in silty and muddy coasts, which shows that waves play a dominant role in influencing the seasonal change of sediment transport in coastal waters.
1 Introduction
The eastern coastal sea area of Jiangsu Province in China (Figure 1) is affected by the rotating tide in the northern sea waters and the advancing tide in the southern waters. As a result, its hydrodynamic forces are extremely complex, leading to significant regional differences in sediment transport characteristics (Huang and Wang, 2020). Moreover, the Jiangsu coast is characterized by its silty and muddy coastline, with suspended sediment particle sizes ranging from 0.006 to 0.022 mm. Moreover, it is also famous for its wide tidal flat, accounting for a quarter of the tidal flat resources of China.
Figure 1
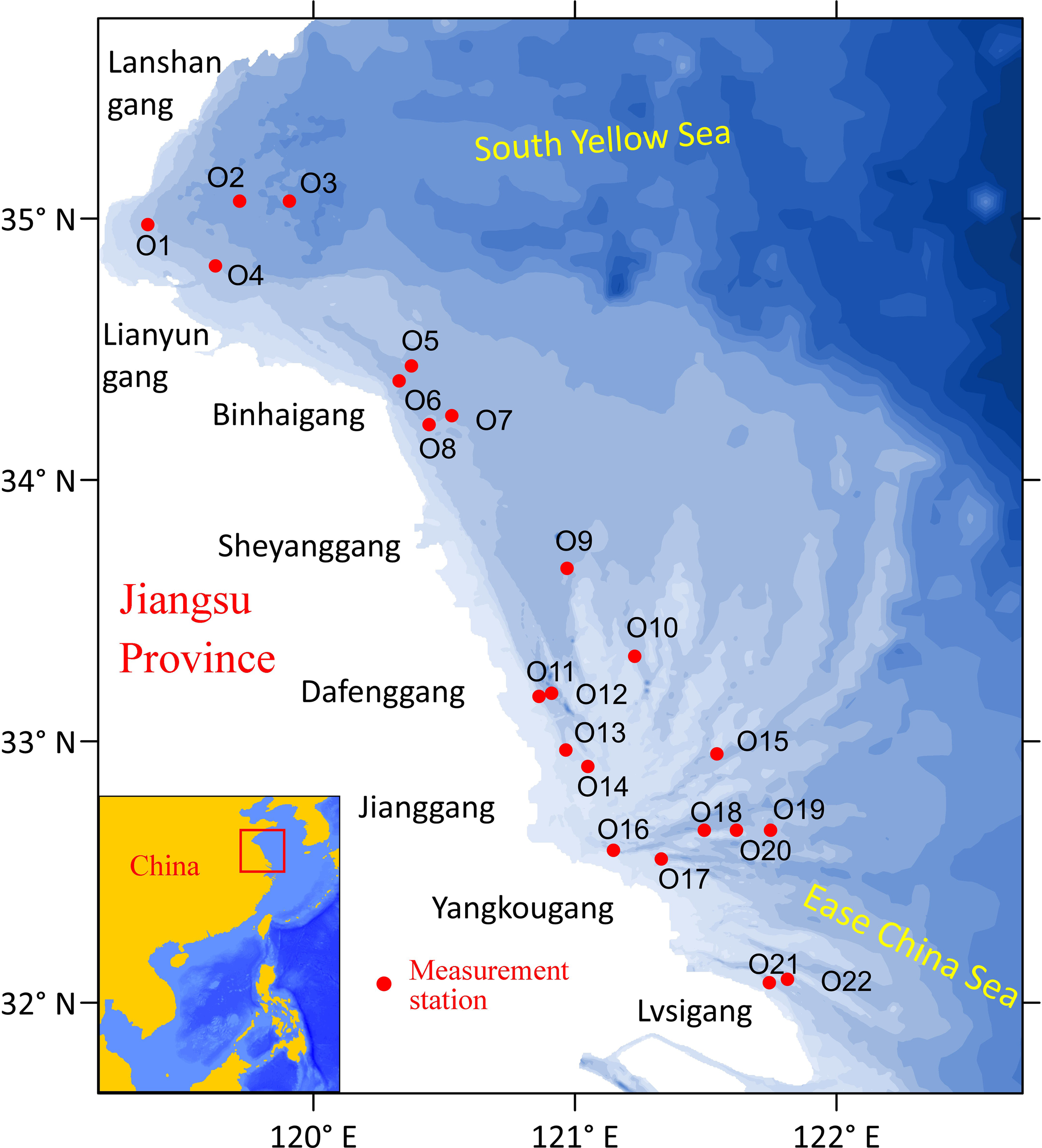
Schematic diagram of coastal waters and measurement station locations (red points) in the eastern Jiangsu Province.
Due to remarkable ocean dynamic effects and complex sediment characteristics, the sediment transport in the Jiangsu coastal waters also exhibits characteristics of high sediment concentration and large sediment transport rate (Wang, 2014). Especially in the sea area of the central Jiangsu coast, as the convergence point of double tidal waves, the hydrodynamics are controlled by strong tides with the measured maximum tidal range reaching 9.39 m in history (Kang et al., 2015) and present obvious regional changes in the southern and northern sides of Jianggang. As a result, it further leads to intense sediment transport and exchange in this area and frequent underwater topography evolution (Ren et al., 1986). At the same time, the eastern part of the sea area is wide and open and lacks island barriers; consequently, the nearshore shoal area is easily affected by the direct incident wave from the outside sea and, thus, presents a sediment transport pattern of “wave lifting sediment and tidal current transporting sediment” (Yang and Ren, 2002).
In addition, under the control of the subtropical monsoon climate, the hydrodynamic and meteorological factors in the Jiangsu coast present obvious seasonal changes, with the sediment movement showing obvious seasonal differences (Huang et al., 2013).
Therefore, the complex sediment transport laws in the Jiangsu coastal sea waters have attracted attention in the past decades. Since the first investigation of coastal resources in the early 1980s, many scholars have conducted extensive and in-depth research on the sediment transport characteristics and internal action mechanisms of the eastern coast of Jiangsu for four decades. These studies mainly involve the following four aspects:
1.1 Hydrodynamics vs. sediment transport
The strong hydrodynamic environment in the Jiangsu coast shapes the complicated underwater topography with intertwined shoals and channels by strengthening sediment transport, and then the change of underwater topography in turn adjusts the hydrodynamic environment (Xing et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2017). This interaction is particularly obvious in the large-scale radial sand ridges in the central part of the Jiangsu coast. The radial tidal current field shapes the radial tidal channel–sand ridge landform pattern of the radial sand ridges, which also in turn strengthens the radial hydrodynamic environment with Jianggang as its convergence point (Zhang et al., 1999, 2020; Tao et al., 2019). Meanwhile, wave action promotes the resuspension and lateral transport of sediments by increasing the bottom shear stress (Liu, 2019; Gao et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2021; Gao et al., 2023; Gao et al., 2024).
1.2 Topography evolution vs. sediment transport
The mutual feedback adaptability between topography and sediment transport is significant in the Jiangsu coast. The large-scale tidal flat on the eastern coast of Jiangsu is famous for its intricate tidal flat and tidal channel system. While the sediment transport changes topography, the topography in turn affects the intensity and direction of sediment transport (Yao and Tao, 2018; Su et al., 2017). In general terms, the change of sediment transport flux in tidal channels reflects the growth and development state of sand ridges. Meanwhile, the variation of sand ridges also in turn indicates the evolution of sediment transport state (Zhang et al., 2013; Cheng et al., 2020).
1.3 Deposit composition and its geochemical characteristics vs. sediment transport
The composition and geochemical change of bed deposits are the inevitable result of sediment transport, so the analysis of deposit composition and its geochemical characteristics is also an important means to reflect the source and path of sediment transport (Liu et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2021). Typically, the characteristics of deposit composition and geochemistry in the sea area of the radial sand ridges not only reveal that the material source of the radial sand ridges is mainly derived from fine sand in the old Yangtze River system but also show that fine clay and silt are replenished by the abandoned Yellow River in the north and the modern Yangtze River in the south (Wang et al., 1998; Rao et al., 2017; Su et al., 2018; He et al., 2022).
1.4 Climate change vs. sediment transport
Climate change in coastal waters often directly leads to the evolution of the coastal dynamic environment and then consequently leads to the adjustment of sediment transport laws (Song et al., 2018). Commonly, the obvious seasonal climate changes often make the waves in the sea area tend to be stronger in winter than in summer, which consequently leads to the seasonal variation of sediment transport intensity (Wang et al., 2023). At the same time, extreme meteorological conditions, such as typhoons and cold waves, often bring about short-term, rapid, and significant changes in a hydrodynamic environment, which further cause rapid and intense changes in sediment transport in a very short period (Qi et al., 2019).
Over the years, several studies have been conducted on sediment transport around the Jiangsu coast, and limited studies have also discussed the seasonal variation of sediment transport in the context of wave disturbance. However, due to the lack of large-scale seasonal observed data around the Jiangsu coast, these studies were always confined to a small sea area or a limited coastal region. As a result, they almost ignored the role of seasonal variation of meteorological factors, which have characteristics of large-scale and significant change. Moreover, former studies on seasonal changes of sediment transport often focused on depth-averaged sediment concentration but paid less attention to the profile variation of sediment transport. Thus, the deep-seated hydrodynamic and meteorological reasons for the seasonal changes in sediment transport across the whole Jiangsu coast still need to be further unraveled at present.
Therefore, based on the large-scale quasi-synchronous measurement data of hydrodynamics, sediment, and seawater temperature during the spring tide cycle in the summer of 2006 and winter of 2007 around the Jiangsu coastal areas, this paper provides a comprehensive analysis and discussion on the laws and internal mechanisms of seasonal variation of suspended sediment transport in Jiangsu coastal waters.
2 Data and method
2.1 Data collection
In order to capture the seasonal variation characteristics of large-scale water and sediment transport in the coastal waters of eastern Jiangsu, quasi-synchronous hydrological, sediment, and water temperature data of 22 measurement stations in the spring tide during August to September of 2006 (as the summer period) and December of 2006 to January of 2007 (as the winter period) were compiled here, including hourly water depth, stratified tidal current, stratified sediment concentration, and surface seawater temperature. The specific locations of the measurement stations are shown in Figure 1. The region with observed data covers the sea waters of Lianyungang, Binhaigang, Dafenggang, Jianggang, Yangkougang, Lvsigang, and other important sea areas along the eastern coast of Jiangsu. According to the definition in the Marine Observation Standard (National Technical Committee on Marine Standardization, 2022), waves with a significant wave height of 2.5 m or higher are classified as heavy waves. The wave data obtained in this study show that the maximum significant wave heights in summer and winter are 0.933 and 1.412 m, respectively, both below the heavy wave threshold defined by the standard. Based on this, this study defines wave conditions with significant wave heights below 2.5 m as mild sea conditions.
The field water depths and current profiles were monitored by the ADCP, the suspended sediment concentrations were measured using the baking method on field water samples collected by horizontal samplers, and the field water temperature was measured by the convenient water temperature monitors.
Furthermore, waves are one of the important factors affecting sediment transport. However, there were no relevant wave observations conducted at the stations; thus, here, the ECMWF hindcast database (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/) during the same measurement period was used to complement the wave data at each measurement station (Reikard et al., 2011). However, due to the grid resolution of this database being relatively coarse in the coastal waters of eastern Jiangsu, the ECMWF hindcast wave data during the same observation period were interpolated to each measurement station by the linear interpolation method to supplement the wave data of the stations.
The spatial resolution of the ECMWF reanalysis wave data along the eastern coast of Jiangsu Province is relatively coarse. Therefore, to verify the applicability of ECMWF reanalysis wave data along the eastern coast of Jiangsu Province, this study also collected buoy wave measurement data from the eastern waters of Dafeng Port during the winter and summer periods of 2020. Subsequently, ECMWF reanalysis wave data from the same period were interpolated to the buoy locations for comparison with the measured values. The results indicate that during 2020, the ECMWF reanalysis wave data at the eastern buoys of Dafeng Port showed strong consistency with the measured wave height data (see Figure 2). The mean measured wave heights for winter and summer were 0.755 and 0.665 m, respectively. In contrast, the mean ECMWF reanalysis wave heights were 0.817 and 0.760 m, respectively. The values were closely aligned, thereby confirming the applicability of ECMWF reanalysis wave data along the eastern coast of Jiangsu Province.
Figure 2
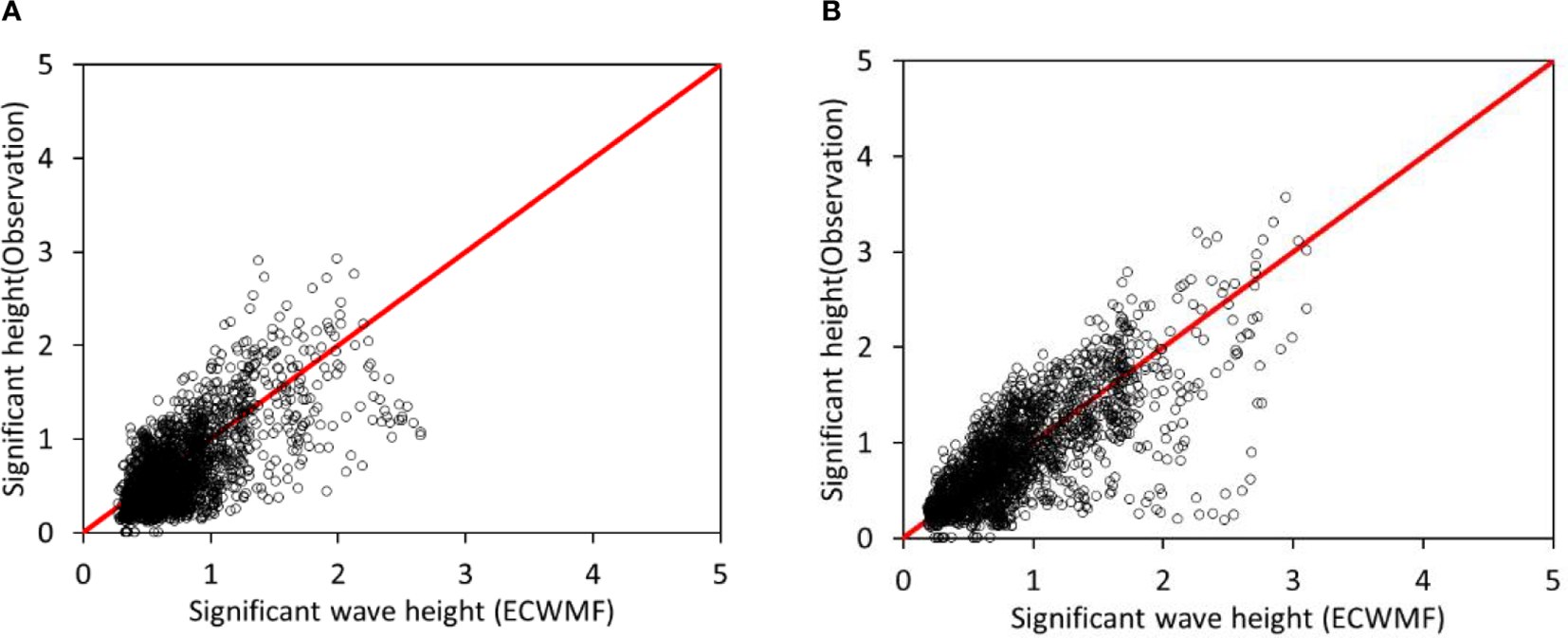
Comparison of observed wave data and ECMWF reanalysis wave data at Dafenggang in the summer (A) and winter (B) of 2020.
2.2 Study method
This paper mainly focuses on seasonal sediment transport characteristics and mechanisms in the plane and vertical directions. Therefore, firstly, the kriging interpolation method was employed to generate the plane fields of tidal average depth-averaged sediment concentration during summer and winter from the observed data sets of 22 stations. Then, the plane fields were drawn in contour maps to present their distribution characteristics, and the correlation analysis methods of Pearson, Spearman, and Kendal (Liu, 2019; Van den Heuvel and Zhan, 2022; De Winter et al., 2016; Altman and Krzywinski, 2015) were further used to examine the relationships among sediment concentration, hydrodynamics including tidal currents and waves, and water temperature in different seasons. Moreover, according to the interaction strengths of these relationships, seasonal variation mechanisms of sediment transport in the plane direction were further discussed and revealed.
Secondly, the profile of the relative value of tide-averaged sediment concentration and the uniformity coefficient of sediment concentration profile were respectively defined and calculated to examine the vertical distribution characteristics of sediment concentration in different seasons. Then, the Pearson, Spearman, and Kendal correlation analysis methods (Liu, 2019; Van den Heuvel and Zhan, 2022; De Winter et al., 2016; Altman and Krzywinski, 2015) were also employed here to examine the relationships among hydrological, meteorological, and sedimentary elements. Then, their action weights were further assessed by the correlation coefficient values. In addition, due to widely distributed measurement stations, the average water depths of these stations also varied widely from 5.0 to 30.0 m. Thus, in order to avoid the impact of widely varied water depths that may confuse research results, the analyses on vertical characteristics of sediment transport were all carried out in relative water depth.
The hydrodynamics in the Jiangsu coastal waters were often dominated by tidal currents and waves, which were closely related to sediment concentration. Thus, the sediment transport in coastal waters often had the characteristics of “wave lifting sediment and tidal current transporting sediment” (Yang and Ren, 2002; Liu, 2019). Then, the commonly used sediment carrying capacity formula along the eastern coast of China was adopted here to examine the influence of tidal currents and waves on the plane distribution of depth-averaged sediment concentration.The specific sediment carrying capacity formula is as follows (see Equation 1) (JTS 145-2015, 2022; Yang and Ren, 2002):
Where, S is the sediment carrying capacity, representing the capacity of transporting sediment of the tidal currents and waves in the entire water column; is the density of sediment particles; is the acceleration of gravity; d is the water depth; is the tidal current velocity; is the current velocity caused by waves, wherein ; H is the wave height; and c is the wave velocity.
To calculate the settling velocity () of suspended sediment, the study adopted the exponential vertical distribution formula of sediment concentration proposed by Huang et al. (2010), which was derived from the diffusion theory and is suitable for estuarine and coastal waters. The specific equations can be found in Equations 2–4:
Where, is the sediment concentration at height , is the reference concentration near the bed (at ), is the von Kármán constant (typically 0.4), is the ratio of sediment turbulent diffusion coefficient to momentum exchange coefficient (often assumed as 1), is the shear velocity, is the normalized vertical coordinate, L is the dimensionless surface mixing length, z is the vertical height measured from the riverbed bottom, and H is the total water depth.
The settling velocity, denoted by , was determined through the application of formula (2) to measure vertical sediment concentration profiles, employing the least squares method for data fitting.
3 Results
3.1 Seasonal difference in the plane distribution of sediment concentration
Figure 3 shows the plane distribution characteristics of tidal average depth-averaged sediment concentration in the coastal areas of Jiangsu during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 and winter of 2007.
Figure 3
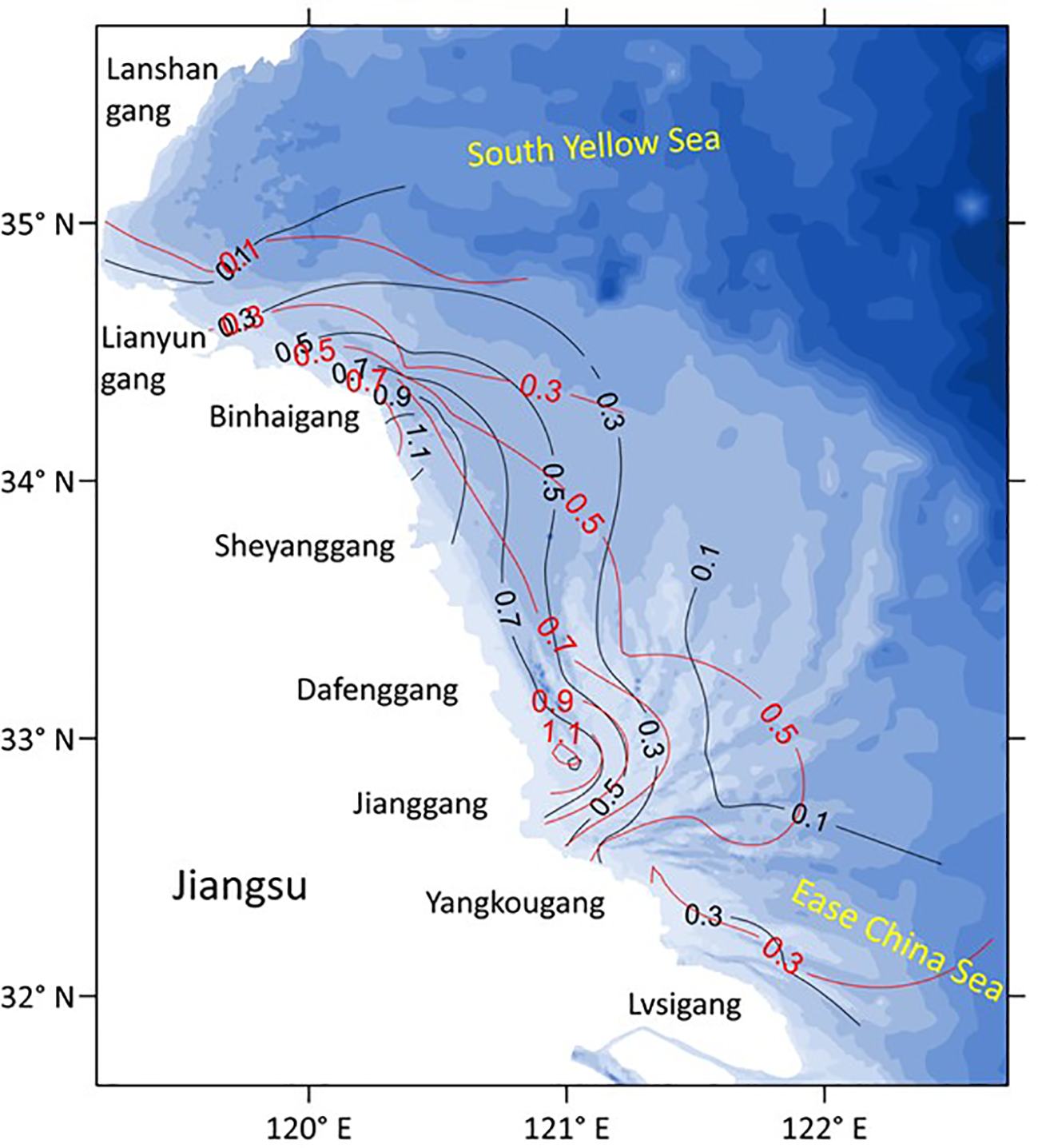
Plane distribution characteristics of tidal average depth-averaged sediment concentration (kg/m3) during a typical spring tidal cycle in the coastal waters of eastern Jiangsu in the winter of 2007 (red line) and the summer of 2006 (black line).
As shown by the figure, the plane distribution trends of depth-averaged sediment concentration in different seasons are similar. From north to south along the Jiangsu coast, the sediment concentrations in different seasons all showed an “M-shape” trend, with the peak values located around the coastal waters of Binhaigang and Jianggang, respectively. Meanwhile, in the offshore direction, the sediment concentrations all showed a significant decreasing trend in different seasons. Their specific variations are as follows:
3.1.1 Variation in coastal direction
-
In the north of Lianyungang, the sediment concentration was close and relatively low in winter and summer, and the values were basically below 0.1 kg/m3.
-
From Lianyungang to Sheyanggang, the sediment concentration in summer was relatively higher than that in winter, but the peak values all appeared near Binhaigang, reaching above 1.1 kg/m3 in summer and 0.7 kg/m3 in winter.
-
In the sea area from Sheyanggang to Yangkougang, the sediment concentration in winter was relatively higher than that in summer, and the peak values were all located near Jianggang, reaching above 1.1 kg/m3 in winter and 0.9 kg/m3 in summer.
-
In the southern waters of Yangkougang, the sediment concentrations obviously decreased below 0.3 kg/m3, and the values in winter were basically higher than those in summer.
3.1.2 Variation in offshore direction
-
In winter and summer, the sediment concentrations all showed an obvious trend that high values occurred near the shore and rapidly decreased in the offshore direction.
-
In summer, the area with sediment concentration greater than 0.5 kg/m3 could be as far as 58 km offshore. In winter, the area could even reach 91 km offshore as far as possible.
-
In different seasons, near the sea area of Jianggang, where the sediment concentration was the highest in the Jiangsu coast, the area of high sediment concentration with value >0.9 kg/m3 could even approach to 33 km offshore; meanwhile, near the sea area of Binhaigang, where the sediment concentration was the second highest, the relevant area could approach to approximately 24 km offshore.
By comparison, the plane distribution trends of sediment concentration in summer and winter were all similar to those in the 1980s (Ren et al., 1986). It indicated that the seasonal plane variation pattern of sediment concentration had maintained a certain stability in the recent four decades. However, it should be noted that the plane distribution of sediment concentration did not show the obvious characteristic that the sediment concentration in winter was always higher than that in summer. It showed regional differences with Sheyanggang as the dividing line. In the south of Sheyanggang, the sediment concentration in winter was higher than that in summer, but it was opposite in the north of Sheyanggang, especially around Binhaigang. This phenomenon was partly different from previous research, which generally showed that the sediment concentration in winter was always higher than that in summer (Yang and Ren, 2002; Liu, 2019).
Actually, according to the measurement data of hydrodynamics, in the south of Sheyanggang, the average tidal current speed in winter was approximately 0.72 m/s, which is a little lower than that in summer with an average value of approximately 0.83 m/s, but the average significant wave height in winter was approximately 1.12 m, which is obviously bigger than that in summer with an average value of approximately 0.52 m. Then, under the combined action of tidal currents and waves, the sediment concentration in winter became higher than that in summer in the south of Sheyanggang. Actually, this also confirmed the importance of the wave acting on sediment transport. Moreover, this was also consistent with the previous understanding that the sediment concentration in winter was higher than that in summer and generally caused by higher waves in winter than in summer.
However, in the north of Sheyanggang and around Binhaigang, the significant wave heights in different seasons were close and all below 0.4 m, limiting their action on sediment transport. Meanwhile, the average tidal current speed during the measurement period in summer was approximately 1.03 m/s, obviously exceeding that in winter with an average value of approximately 0.66 m/s. Then, it subsequently caused a stronger sediment carrying capacity and a higher sediment concentration around Binhaigang in summer than in winter. This seemed to further indicate that not only the wave but also the tidal current could significantly impact the seasonal change in sediment concentration along the Jiangsu coast. Moreover, this was also the point of the Jiangsu coast that differed from other coastal areas.
3.2 Seasonal variation of sediment concentration profile
In order to illustrate the difference in sediment concentration profile along the eastern coast of Jiangsu in different seasons, Figure 4 shows the vertical distribution characteristics of the relative value of tide-averaged sediment concentration during the typical spring tide of each station in the winter of 2007 and the summer of 2006.
Figure 4
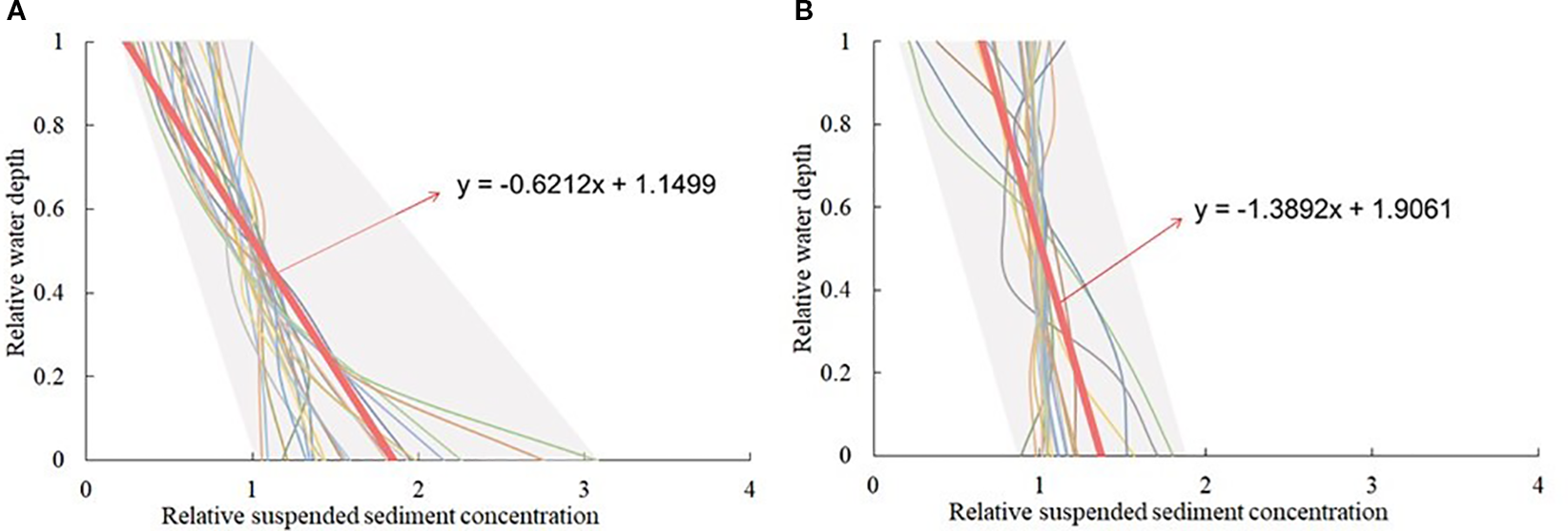
Vertical distribution characteristics of relative values of the tide-averaged sediment concentration during the typical spring tide at the measurement stations in the summer of 2006 (A) and the winter of 2007 (B) around the Jiangsu coastal waters.
Among them, the relative value of the tide-averaged sediment concentration was calculated by the Equation 5:
Where, is the relative value of the tide-averaged sediment concentration at water column height ; is the tide-averaged sediment concentration at water column height ; and is the tide-averaged value of the depth-averaged sediment concentration.
It can be seen that the vertical distributions of the relative value of the tide-averaged sediment concentration presented obvious seasonal changes, as follows:
3.2.1 Seasonal variation of sediment concentration profile
-
In winter and summer, the relative values of the tide-averaged sediment concentration in the surface layer of the water column basically ranged from 0.2 to 1.2. Furthermore, the relative values of the surface layer in winter were closer to 1.0, while those in summer were basically less than 1.0.
-
In different seasons, the relative values of the tide-averaged sediment concentration in the middle layer of the water column were all concentrated to approximately 1.0.
-
In winter, the relative values of the tide-averaged sediment concentration at the bottom layer of the water column basically ranged from 0.8 to 1.8; correspondingly, in summer, the relative values of the tide-averaged sediment concentration at the bottom layer of the water column varied widely, ranging from 1.0 to 3.1.
3.2.2 Seasonal difference in the uniformity of the sediment concentration profile
-
In winter, the vertical distribution of sediment concentration was more uniform; in summer, it was obviously non-uniform in profile.
-
In winter, the vertical maximum values of sediment concentration occurred basically from the middle to the bottom layer of the water column. In summer, the positions with the vertical maximum sediment concentration were basically in the bottom layer.
-
During winter, the average slope of the relative value profile of tide-averaged sediment concentration in all measurement stations was approximately −1.39, but during summer, it was approximately −0.62, which is nearly half of the slope in winter.
In sum, the vertical distributions of sediment concentration were obviously uneven in summer and uniform in winter. In winter, the sediment concentrations at the bottom layer of the water column were relatively close to those in other water layers, while the sediment concentrations at the surface layer were slightly less than the depth-averaged sediment concentrations. Furthermore, the vertical maximum values of the sediment concentration did not necessarily appear in the bottom layer.
At the same time, in summer, the vertical distributions of sediment concentration were characterized by smaller values at the surface layer and larger values at the bottom layer. According to previous understanding, a preliminary analysis of the reason might be that the vertical exchange of suspended sediment in the water column was more strongly disturbed by hydrodynamics in winter than in summer, due to stronger waves in winter and weaker waves in summer.
4 Discussion
4.1 Data representativeness study
Based on historical observed data and recent research findings, a comparative analysis of tidal current characteristics in the study area was conducted. The observed data from 2006 to 2007 indicate that the average tidal current velocity in the study area during summer was 0.80 m/s and 0.64 m/s during winter. Recent studies indicate that the annual average current velocity in this region ranges between 0.40 and 0.80 m/s, which is in good agreement with historical observational data. The tidal current velocity characteristics of the study area exhibit a strong stability over time, with the velocity variation range remaining relatively stable over a span exceeding a decade. This provides a reliable foundation for subsequent related research.
Concerning suspended sediment content, the observed data from the study area during 2006–2007 demonstrated that the average depth-averaged suspended sediment concentration during the summer spring tide was 0.42 kg/m3, and the average depth-averaged suspended sediment concentration during the winter spring tide was 0.53 kg/m3. Subsequent observations (Su et al., 2020) demonstrated that in 2018, the depth-averaged suspended sediment concentration in the Sheyanggang to Dafenggang sea area was 0.20–0.87 kg/m3 during the summer and 0.18–0.56 kg/m3 during the winter. This finding served to substantiate the relevance of the study of sediment concentration.
A comparison of water temperature data from 2006 to 2007 with recent observations from 2019 to 2023 (National Marine Data Center, National Science & Technology Resource Sharing Service Platform of China, 2023 [https://mds.nmdis.org.cn/]) reveals the presence of consistent seasonal patterns in surface water temperature in Jiangsu’s coastal waters. From 2006 to 2007, the surface water temperature in the study area ranged from 23.4 °C to 29.2°C during the summer months and 7.1 °C to 10.8 °C during the winter months. At Lianyungang, the average surface water temperature from August to September of 2022 was 26.5°C. At Lvsigang, the average surface water temperature from August to September of 2019 was 26.9°C, and from December 2019 to January 2020, it was 8.8°C. These findings demonstrate a notable degree of consistency. These findings confirm the validity of the temperature ranges from 2006 to 2007 for studying seasonal variations in the region.
Comparative analysis reveals that the observed data from 2006 to 2007 are highly consistent with the 2018 observations and recent numerical simulation results in terms of flow velocity magnitude, spatial distribution of sediment content, and surface water temperature. These findings underscore the data’s climate representativeness and scientific applicability.
4.2 Influence of tidal currents and waves on the seasonal change of the plane distribution of sediment concentration
Figure 5 shows the plane distribution characteristics of tide-averaged sediment carrying capacity under the combined action of tidal currents and waves in the Jiangsu coastal waters during the spring tide of winter of 2007 and summer of 2006.
Figure 5
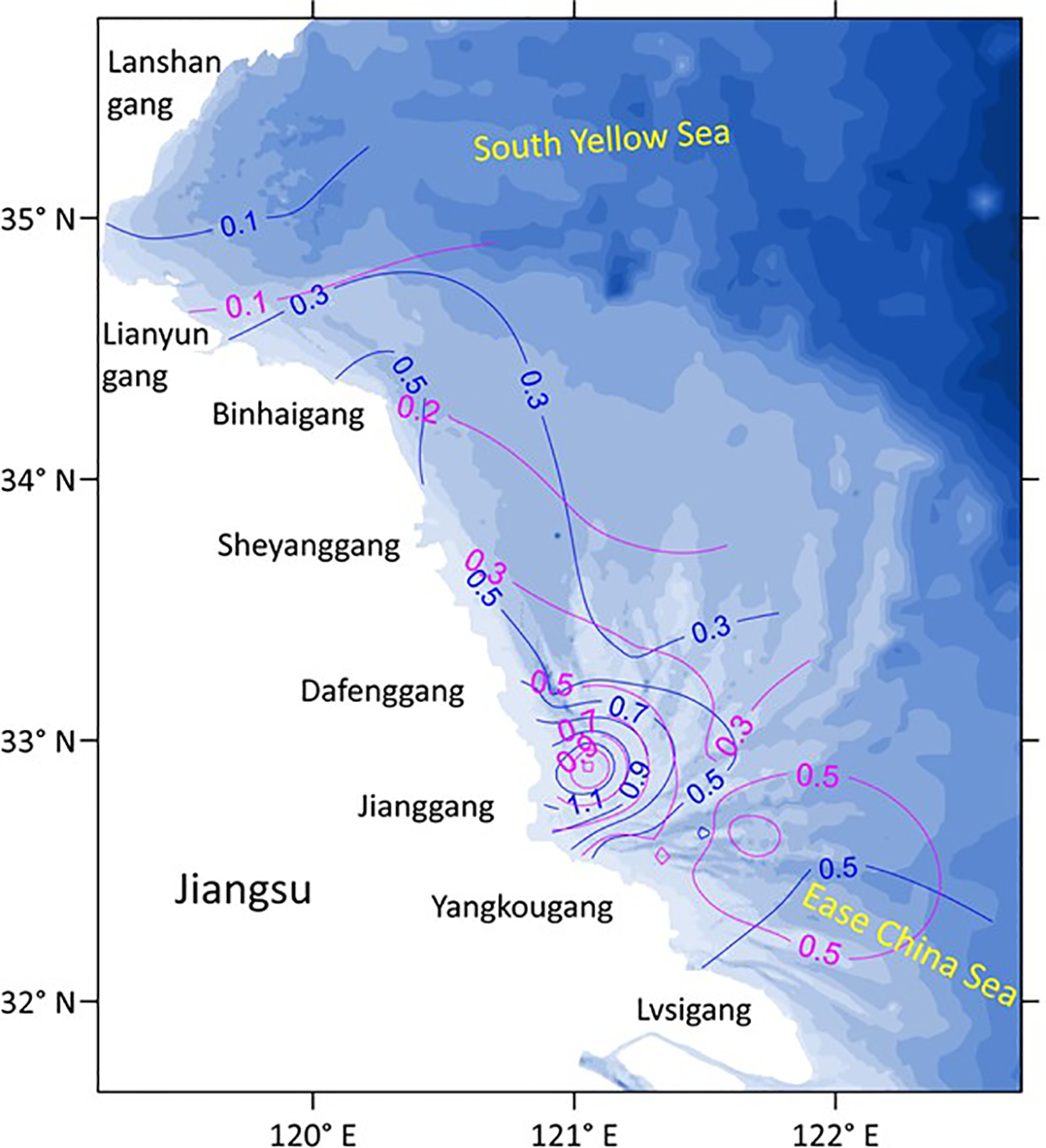
Plane distribution characteristics of tidal average sediment carrying capacity (kg/m3) during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 (blue line) and the winter of 2007 (pink line) under the combined action of tidal currents and waves in the eastern coast of Jiangsu Province.
It can be found that being similar to the seasonal plane distribution characteristics of measured depth-averaged sediment concentration along the eastern Jiangsu coast, the plane distribution of tidal average sediment carrying capacity in winter and summer also all show an “M-shape” variation trend with peak values at the sea areas of Binhaigang and Jianggang in the coastal direction. Moreover, this distribution pattern is also relatively more significant in summer. This confirms the former understanding that the suspended sediment transport in the coastal waters of eastern Jiangsu Province is mainly driven by the tidal currents and waves.
Thus, by adopting the Pearson, Spearman, and Kendal correlation analysis methods, Figure 6 further shows the correlation between the measured tidal average suspended sediment concentration (SSC) at the measurement stations and the relevant sediment carrying capacity with the combined action of tidal current and wave (SCW), single action of tidal current (SC), and single action of wave (SW), which present the action weights of different hydrodynamics on suspended sediment transport.
Figure 6
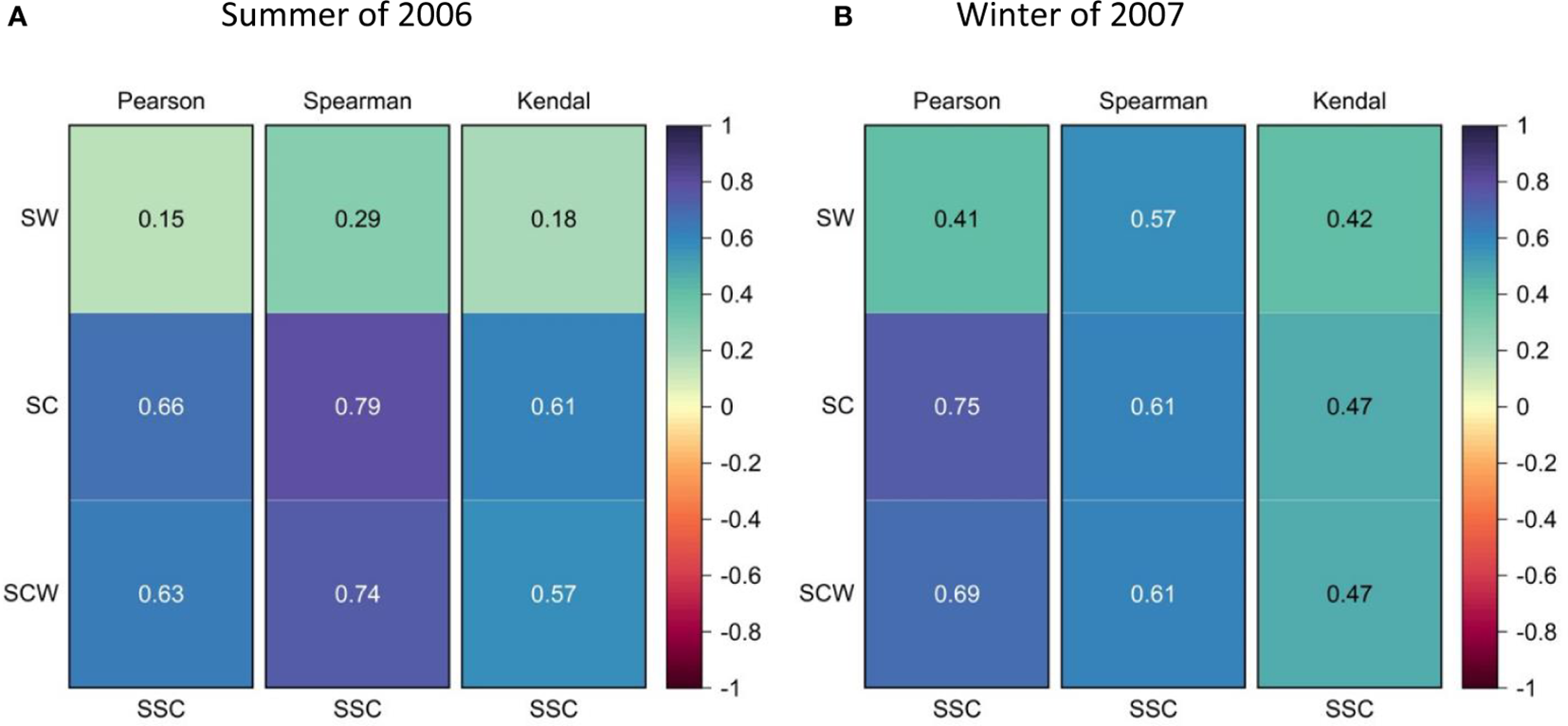
Correlations between tidal average sediment concentration measured at the stations and relevant sediment carrying capacity in the summer of 2006 (A) and the winter of 2007 (B), under the combined action of waves and currents, single action of tidal currents, and single action of waves.
It can be found that the tidal average sediment carrying capacities under the combined action of waves and tidal currents at the measurement stations have good relationships with the measured sediment concentrations in winter and summer, and their correlation coefficients are all more than 0.47, wherein the correlation coefficients of Pearson and Spearman even reach above 0.61 in different seasons. Meanwhile, the correlations between the measured sediment concentration and sediment carrying capacity with the single action of tidal current in different seasons are also good and even a bit better than in the combined action of currents and waves. Thus, it can be concluded that tidal currents are the main factor influencing the planar distribution of suspended sediment concentration.
Nevertheless, the correlations between measured sediment concentration and sediment carrying capacity with the single action of waves in different seasons significantly decrease with values even decreasing to below 0.20 in summer. Meanwhile, the correlation coefficients also present obvious seasonal changes, even reaching approximately 0.57 in winter, but obviously higher in summer, with the smallest value of only 0.15. Through analysis, this is mainly due to relatively stronger waves in winter than in summer; consequently, it causes stronger sediment transport and then promotes higher correlation with SSC in winter. On the contrary, the weaker wave in summer limits its action on sediment transport and then causes the lower correlation with SSC in summer.
Tidal currents and waves both influence the spatial distribution of sediment by increasing bottom shear stress. When the bottom shear stress generated by tidal currents and sediment exceeds the sediment’s incipient shear stress, the sediment begins to move. As tidal currents and waves continue to intensify, the sediment becomes suspended in the water and is transported by tidal currents and waves. When the flow velocity decreases below the critical velocity for deposition, the sediment begins to settle.
At the same time, it should be noted that the controlling factors for the seasonal variation in the planar distribution of sediment concentration cannot be determined from Figure 6. From Lianyungang to Sheyanggang, the sediment concentration in summer is relatively higher than that in winter, consistent with the seasonal variation in sediment transport capacity shown in Figure 5. Therefore, tidal currents are the dominant factor influencing the seasonal variation in the spatial distribution of sediment concentration in this region. This result is inconsistent with the general understanding that waves dominate the seasonal variation in sediment concentration (Yang and Ren, 2002; Liu, 2019). From Sheyanggang to Lvsigang, sediment concentration in winter is relatively higher than in summer, which is inconsistent with the seasonal variation of the sediment carrying capacity shown in Figure 5. This is because the relative wave height in winter is larger than that in summer, and waves have a stronger influence on the seasonal variation of sediment concentration distribution. Therefore, waves are the dominant factor influencing the seasonal variation of sediment concentration distribution in this region.
4.3 Influence of seawater temperature on the seasonal change of the plane distribution of sediment concentration
Due to the control of subtropical monsoon climate, meteorological factors around the Jiangsu coast have obvious seasonal variation characteristics, such as the wind and temperature. Thus, their effects on suspended sediment transport in coastal waters also show seasonal variation laws. However, their influences are often indirect. For the two most important meteorological factors, i.e., the wind and air temperature, the wind generally forms waves and then acts on suspended sediment transport, and the air temperature always affects seawater temperature and then acts on the settlement of suspended sediment in the water column (Camenen, 2007; Ren, 2024). The wind action on sediment transport is actually included in the wave action that has been analyzed above. Thus, in fact, seawater temperature is the real subject that needs to be discussed.
For this, also by adopting the Pearson, Spearman, and Kendal correlation analysis methods, Figure 7 shows the correlation between the tidal average seawater temperature in the surface water layer (ST) and tidal average depth-averaged suspended sediment concentration during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 and the winter of 2007 at various measurement stations.
Figure 7
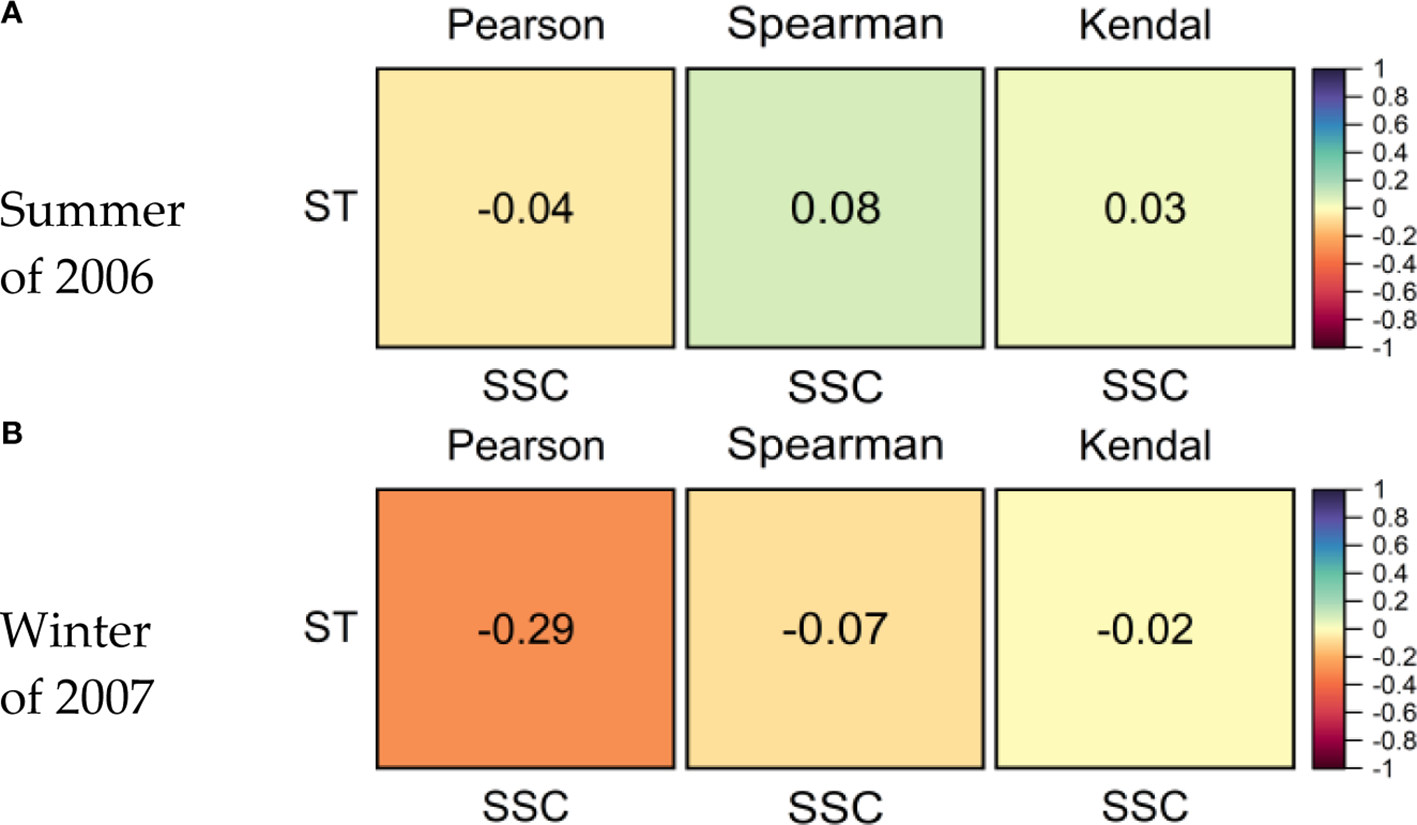
Correlations between the tide-averaged surface seawater temperature and relevant value of depth-averaged sediment concentration, measured in the spring tide cycle during the summer of 2006 (A) and the winter of 2007 (B) at various stations.
According to measurement data, seawater temperatures in the surface layer are between 23.4°C and 29.2°C in the summer and 7.1 °C and 10.8°C in the winter, showing obvious seasonal variation characteristics. However, the relationships between the surface seawater temperature and the measured depth-averaged sediment concentration show an obvious weak correlation, with correlation coefficients basically below 0.10 in different seasons. This indicates that the significant seasonal variation of seawater temperature has no significant effect on the seasonal change of depth-averaged sediment concentration in coastal water.
Then, comparing the seasonal variation of correlation coefficients between actions of tidal current, wave, seawater temperature, and depth-averaged sediment concentration, it can be found that the action weights of factors affecting the seasonal variation of the plane distribution of sediment concentration are in the following order: tidal current > wave > seawater temperature. This conclusion is a bit different from the general understanding about sediment transport in coastal waters, postulating that the wave is the dominant factor in the seasonal variation of sediment transport (Yang and Ren, 2002; Liu, 2019).
Through analysis, there may be several reasons leading to this result. Firstly, to ensure the implementation of measurement and safety of instruments and operators, these two field measurement periods are all in mild sea conditions with weak waves; as a result, the ratios of significant wave height to water depth are basically below 0.19 in winter and 0.10 in summer, which are insufficient to significantly drive the sediment transport. Secondly, the seasonal variation of seawater temperature is often insufficient to obviously change bed shear stress and then drive a large amount of sediment to resuspend from the seabed. Thirdly, the Jiangsu coastal waters have strong tidal zones with the biggest tidal range approaching above 9.0 m (Kang et al., 2015), leading to strong tidal current speeds around the coastal waters. Actually, during these two measurement periods, the average tidal current speed of the various stations is more than 0.60 m/s in winter and 0.80 m/s in summer. Thus, the strong tidal current has a stronger action on sediment transport than that of the wave and seawater temperature in the Jiangsu coast. Thus, this is why the eastern Jiangsu coast differs from other common sea areas.
4.4 Influence of tidal current and wave on the seasonal change of sediment concentration profile
As shown by the above analysis, tidal currents and waves are the two primary driving forces for the plane distribution of sediment concentration. So, is this still true for the seasonal change in the vertical distribution of sediment concentration?
Figure 8 provides the profile characteristics of the tide-averaged relative value of tidal current during the spring tide in the winter of 2007 and the summer of 2006 at each measurement station. Among them, the relative value of tidal current of each water layer in the water column is calculated by the Equation 6:
Figure 8
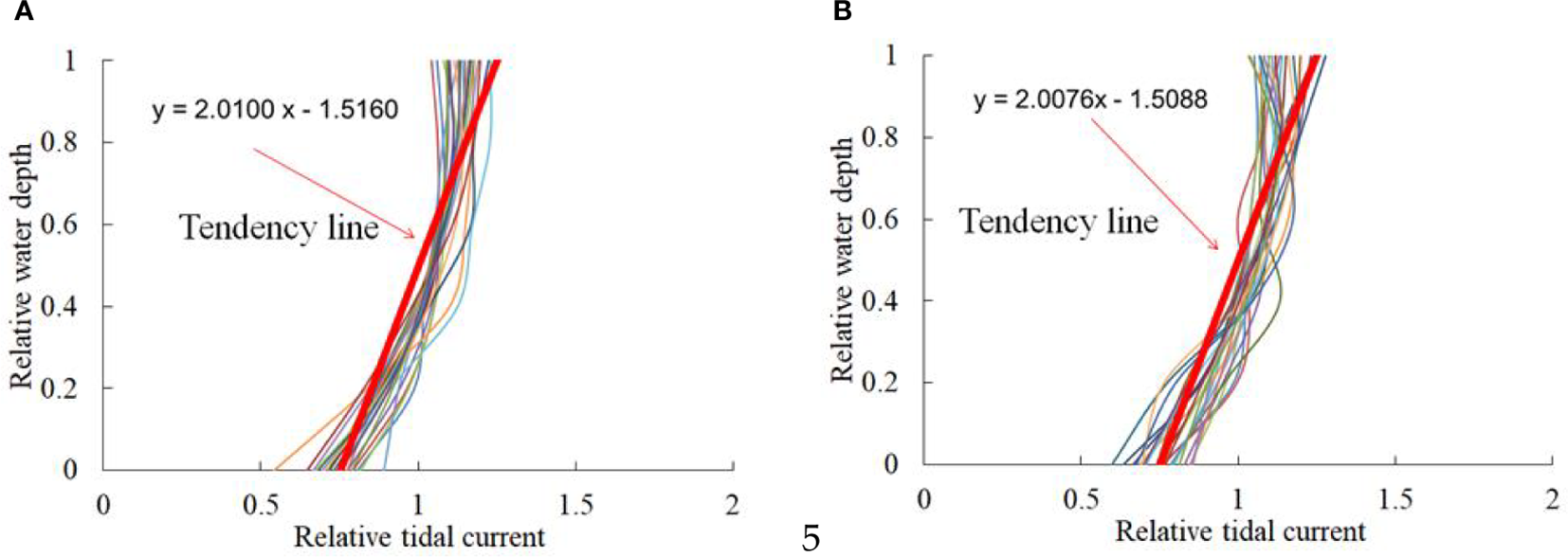
Vertical distribution characteristics of tide-averaged relative value of tidal current speed during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 (A) and the winter of 2007 (B) at the measurement stations.
Where, is the relative value of the tidal current speed at the water column height z; is the tidal current speed at height z; and is the depth-averaged value of the tidal current speed.
As shown in Figure 8, the profile characteristics of the tide-averaged value of the relative tidal current speed in summer and winter are very similar, and the profile shapes of the relative current speed all show an obvious decreasing trend from the surface to the bottom of the water column. Meanwhile, the slopes and intercepts of the trend lines of the relative current speed profiles in different seasons are also very close to each other, approaching 2.01 and −1.51, respectively. This indicates that the vertical distribution pattern of tidal current speed in the Jiangsu coast does not show significant seasonal differences during winter and summer; thus, it is difficult for tidal currents to be the fundamental reason for the significant seasonal differences in sediment concentration profile.
Based on this, through using the Pearson, Spearman, and Kendal correlation analysis methods, Figure 9 also further shows the correlations between the tide-averaged uniformity coefficient of sediment concentration profile (UCS) and the corresponding relative wave height (RW) and uniformity coefficient of tidal current speed profile (UCC), during the spring tide in summer and winter at the measurement stations. The RW is defined as the ratio of significant wave height to water depth, and the uniformity coefficients of sediment concentration profile and tidal current profile are defined by the Equation 7:
Figure 9
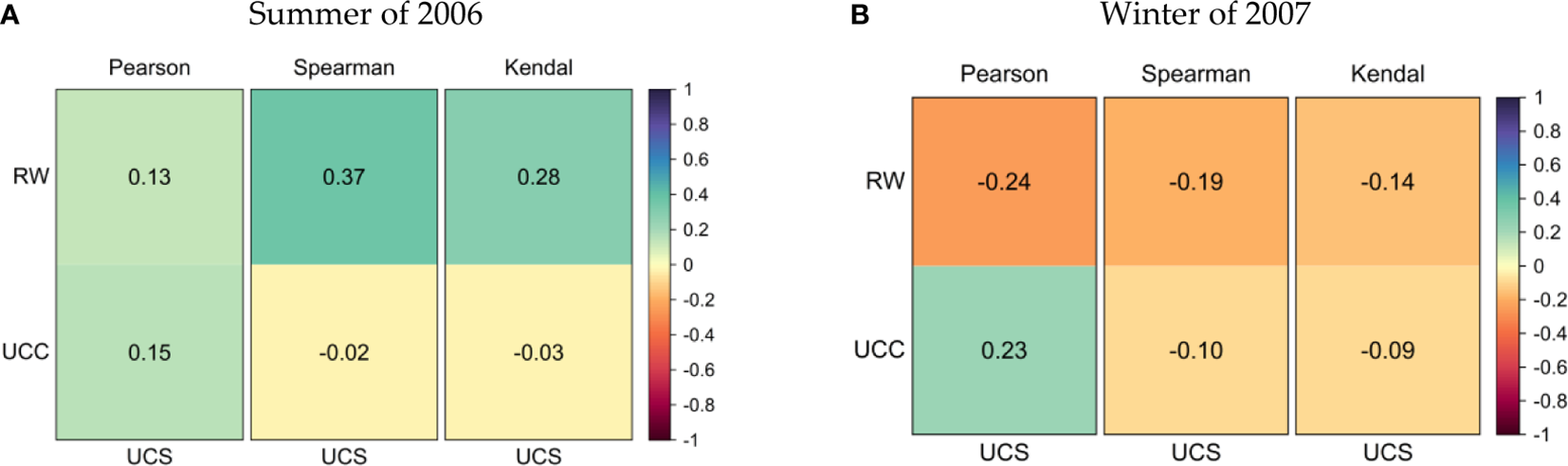
The correlations between the tide-averaged uniformity coefficient of sediment concentration profile and the relative wave height and the uniformity coefficient of tidal current speed profile during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 (A) and the winter of 2007 (B) at the measurement stations.
Where, UCS is the uniformity coefficient of sediment concentration profile; is the sediment concentration at the water column height z; and is the depth-averaged sediment concentration. Similarly, UCC is the uniformity coefficient of the tidal current speed profile; is the tidal current speed at the water column height z; and is the depth-averaged tidal current speed. N is the number of vertical sediment layers or water layers.
In general, the closer the uniformity coefficient is to 0, the stronger the uniformity of sediment concentration or tidal current speed profile is; on the contrary, the farther the uniformity coefficient is from 0, the weaker the uniformity of sediment concentration or tidal current speed profile is.
As shown by the figure, the correlation coefficients of the tidal current profile with the sediment concentration profile are all small in different seasons; only the values of Pearson are slightly bigger, but still below 0.23. This indicates that the tidal current profile is in weak correlation with the sediment profile, which is consistent with the former inference deduced from Figure 8.
Meanwhile, the correlation coefficients of wave action with uniformity of sediment profile are basically bigger than those of tidal current action, with values basically smaller than 0.37. This shows to some extent that the wave action on seasonal changes of sediment concentration profile is relatively stronger than that of the tidal current. In summer, the vertical distribution of sediments is more non-uniform, and wave disturbance easily causes sediment resuspension and enhances vertical mixing. In contrast, the vertical distribution of sediments is relatively more uniform in winter, and wave action has less noticeable effects on vertical sediment mixing. However, it should also be noted that the correlation coefficients of waves with the sediment profile in different seasons are still insignificant. Through analysis, during the measurement period, this may be due to the fact that wave height is always limited; thus, the disturbance effect of waves on the vertical mixing of suspended sediment is also limited. Consequently, the waves cannot dominate the sediment concentration profile in normal sea conditions. This is the key point that many previous studies have not clarified.
4.5 Influence of seawater temperature on the seasonal change of sediment concentration profile
As an important meteorological factor, seawater temperature in the coastal waters also shows significant variation characteristics, with lower values in winter and higher values in summer. Therefore, in order to observe the influence of seawater temperature on the seasonal change of sediment concentration profile, Figure 10 shows the correlations of Pearson, Spearman, and Kendal between the tide-averaged uniformity coefficient of the sediment concentration profile and the corresponding seawater temperature in the surface layer of the water column during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 and the winter of 2007.
Figure 10
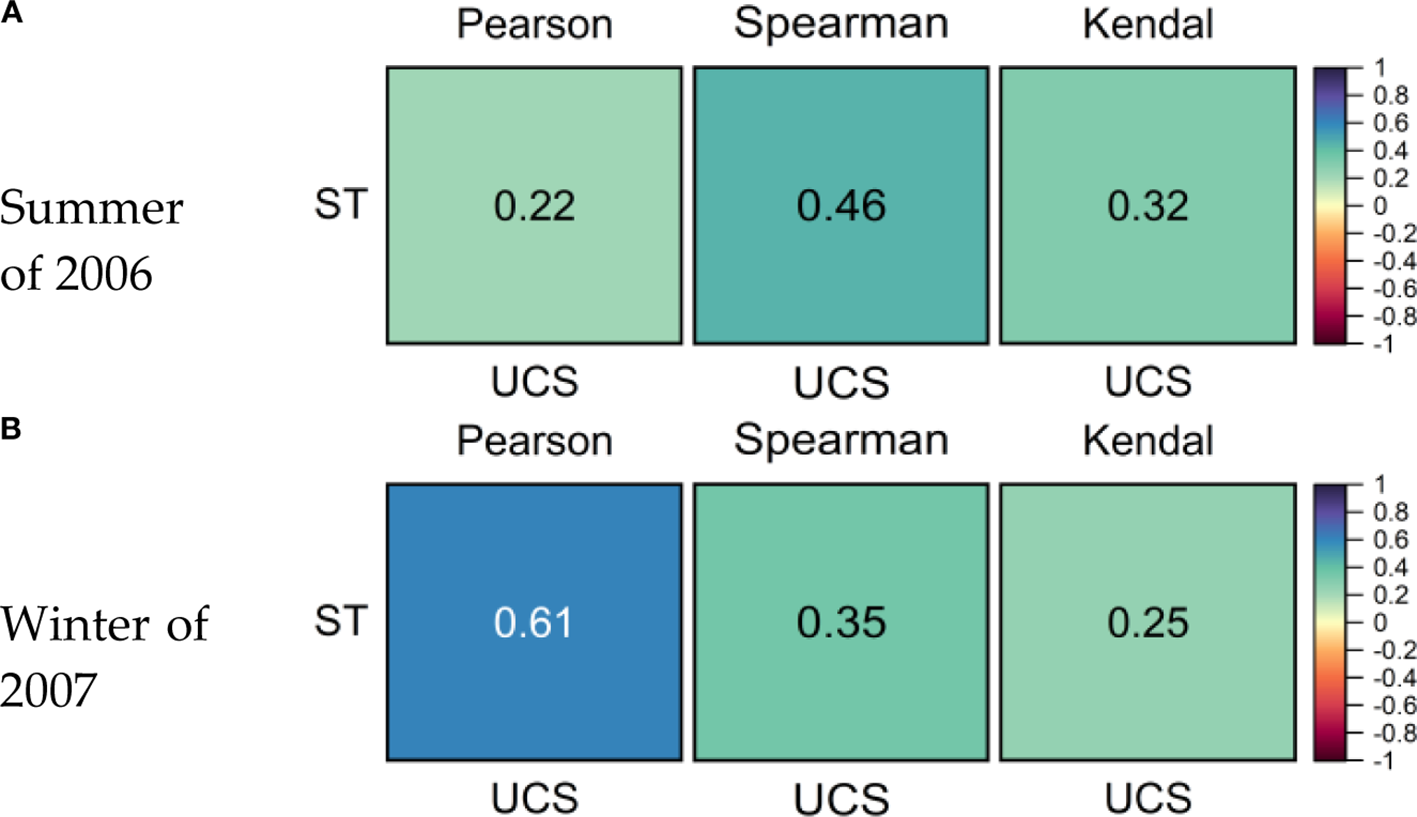
The correlations between the tide-averaged uniformity coefficient of sediment concentration profile and surface water temperature during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 (A) and the winter of 2007 (B).
It can be found that there are close relationships between the uniformity coefficient of sediment concentration profile and the surface seawater temperature in different seasons, with the biggest correlation coefficient even reaching approximately 0.61. At the same time, comparing the results in Figure 9, it can be further found that seawater temperature has a stronger influence on the uniformity of the sediment concentration profile than that of waves and tidal currents.
Therefore, in order to further detect the reason for the influence of seawater temperature change on the seasonal variation of sediment concentration profile, the vertical distribution profiles of sediment concentration in the measurement stations are respectively fitted by the vertical distribution formula of sediment concentration put forward by Huang et al. (2010), which is suitable for estuarine and coastal areas. Then, the tide-averaged effective settling velocities of suspended sediment during the spring tide cycle in the summer of 2006 and the winter of 2007 can be further obtained using the method of Huang et al. (2010). The results are shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11
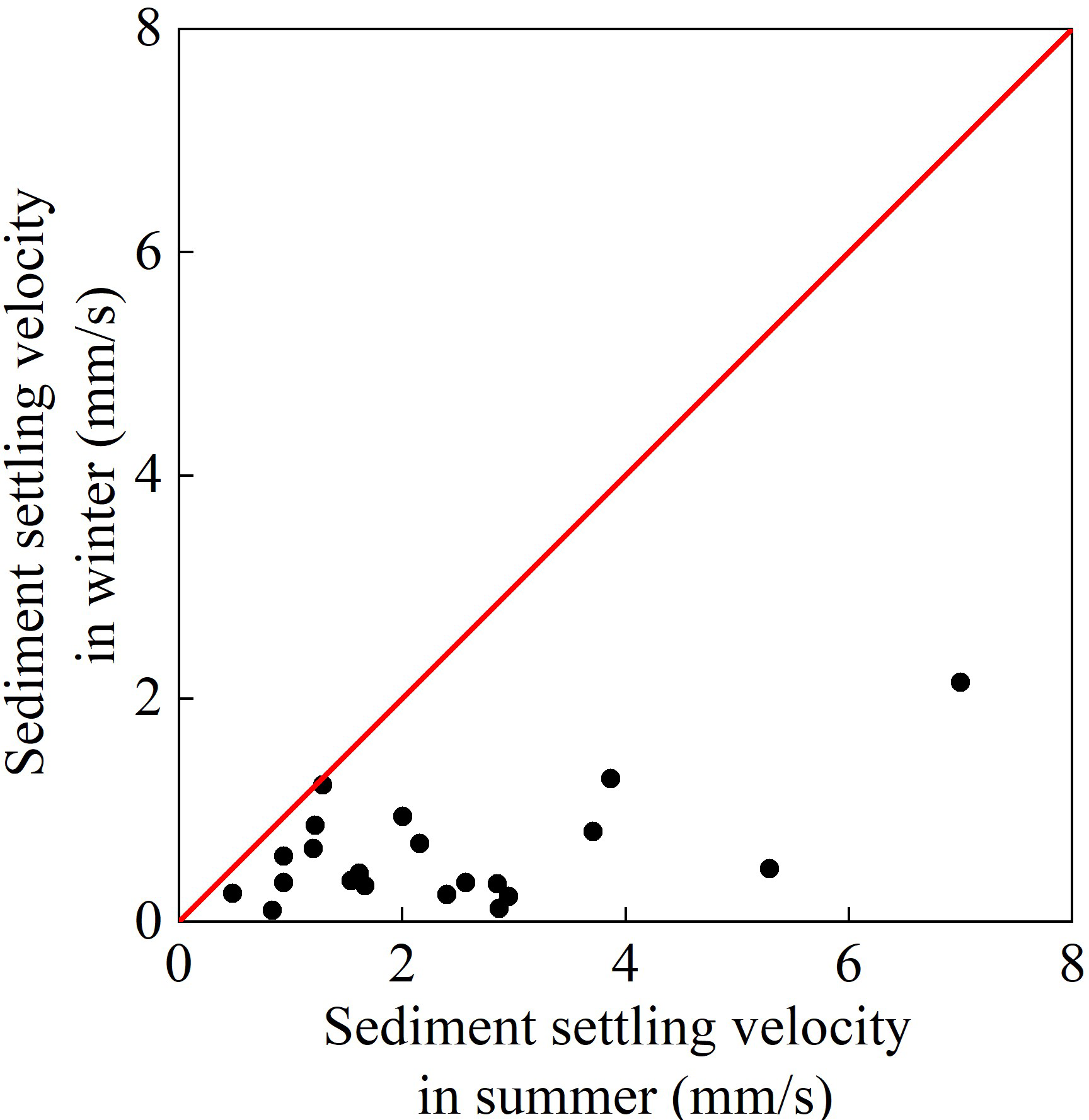
Difference of tide-averaged effective settling velocity of suspended sediment during the spring tide in the summer of 2006 and the winter of 2007.
As shown in Figure 11, the scatter points in the figure are all below the red line, indicating that the effective settling velocities of suspended sediment in summer are obviously greater than those in winter, with the biggest multiples even approaching 26. This is consistent with the previous understanding that sediment settling velocity increases with the increase of temperature (Camenen, 2007; The Sediment Professional Committee of the Chinese Water Conservancy Society, 1989).
Based on the aforementioned results, it is possible to deduce the mechanism by which temperature exerts its influence on the vertical distribution of suspended sediment. In summer, the surface seawater temperature rises, which increases the settling velocity of sediment (Qiao et al., 2019). This results in a concentration of sediment near the bottom layer, thereby affecting the uniformity of the sediment concentration profile. In winter, the surface seawater temperature decreases, and the settling velocity of sediment decreases significantly compared to summer. This results in a more uniform sediment concentration profile. This mechanism elucidates the observed seasonal variations in the vertical distribution of suspended sediment. This mechanism elucidates the observed seasonal variations in the vertical distribution of suspended sediment.
In addition, according to the correlations between tidal current, wave, seawater temperature, and the vertical distribution pattern of sediment concentration, it can be further deduced that the action weights of factors affecting the seasonal variation of sediment concentration profile are in the following order: seawater temperature > wave > tidal current in the measurement period with mild sea conditions. This is partly different from the previous understanding that wave disturbance is the main reason for the seasonal change of sediment transport (Yang and Ren, 2002; Liu, 2019).
Through analysis, this may be due to the fact that, in the normal weather period of summer and winter around the Jiangsu coast, the similarly strong tidal current profiles cause similar sediment concentration profiles. Meanwhile, a relatively weak wave is not sufficient to induce intense vertical sediment mixing in the water column, and then obviously change sediment concentration profiles. Thus, the action of seasonal variation of sediment settling velocity caused by seasonal variation of water temperature on sediment concentration profiles starts to play a more important role and further results in obvious seasonal variation of sediment concentration profiles.
Actually, according to the classical Rouse formula, the action of sediment settling velocity on the sediment concentration profile can also be directly deduced. Based on the Rouse formula, the suspension index determines the sediment concentration profile, and as decreases, the sediment concentration profile tends to be uniform in the vertical direction. Here, is the settling velocity of the sediment, k is the Karman constant, and is the friction velocity. Thus, it can be assumed that while the are unchanged in winter and summer, due to smaller sediment settling velocity in winter than that in summer, in winter will be also smaller than that in summer; as a result, the sediment concentration profile will be more uniform in winter than in summer.
Furthermore, it should also be noted that this scenario mainly applies to the sediment concentration profile in mild sea conditions. Meanwhile, in non-normal weather conditions, such as during typhoons and cold waves, following the significant strengthening of sea conditions, the disturbance action of waves will also significantly increase and then play a dominant role in sediment transport (Liu, 2009). Subsequently, it will inevitably cause the action of seawater temperature on the sediment transport profile to decrease gradually.
4.6 Practical implications for coastal engineering
The temperature-dependent sediment settling phenomenon demonstrated in Figure 11 has direct operational implications for dredging activities. Analysis reveals significantly faster sediment settling velocities during summer, which promotes rapid redeposition of suspended sediment. This accelerated settling process substantially reduces the effective duration of dredging benefits, requiring more frequent maintenance interventions.
Conversely, winter conditions exhibit slower settling velocities due to lower water temperatures, resulting in prolonged sediment suspension. These conditions lead to a reduction of immediate redeposition near dredged channels and, consequently, longer-lasting dredging effects.
These findings suggest that scheduling major dredging projects during winter would optimize operational efficiency by extending maintenance intervals.
5 Conclusions
Based on the observation data of various stations during the typical spring tide in the coastal waters of eastern Jiangsu in the winter of 2007 and the summer of 2006, this paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the variation laws of the plane and vertical distribution of sediment concentration in the Jiangsu coast in the context of seasonal changes. Then, it reveals that two peak values of depth-averaged sediment concentration are located near the waters of Binhaigang and Jianggang in different seasons, and also further points out the basic characteristics where the sediment concentration profile is more uniform in winter than in summer.
Then, through correlation analysis, this paper subsequently reveals that under mild sea conditions in the Jiangsu coast, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the plane distribution of sediment concentration are in the following order: tidal current > wave > seawater temperature. From Lianyungang to Sheyanggang, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the seasonal variation of plane distribution of sediment concentration are as follows: tidal current > wave > seawater temperature; from Sheyanggang to Lvsigang, the action weights of the influencing factors affecting the seasonal variation of plane distribution of sediment concentration are in the following order: wave > tidal current > seawater temperature. Meanwhile, the paper also further puts forward a new finding that the action weights on seasonal change of sediment profile are seawater temperature > wave > tidal current under mild sea conditions in the Jiangsu coast. These results differ from the former understanding that waves are the fundamental reason for the seasonal change of sediment transport in common seawaters.
Therefore, the research results of the Jiangsu coast that differ from other common coasts are helpful to improve the study depth on the mutual feedback laws of hydrodynamics and sediment transport, and also to promote the breadth of the study on the law of hydrodynamics and sediment movement in estuaries and coasts.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
HH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SW: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2022YFC3106100); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51979096); Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Coast and Island Management Technology Study (No. FJCIMTS2022-03); Joint Fund of the Ministry of Education for Equipment Pre-research (No. 8091B022123); the Key Laboratory of Coastal Disasters and Defense, Ministry of Education, Hohai University Program (The influence of the Deepwater Channel Regulation Project on saltwater intrusion in the Changjiang River Estuary); and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Public Welfare Research Institutes, Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute Welfare Research Institutes, Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute (No. YN912001). This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52201321).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Altman N. Krzywinski M. (2015). Points of significance: association, correlation and causation. Nat. Methods12, 899–900. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3587
2
Camenen B. (2007). Simple and general formula for the settling velocity of particles. J. Hydraul. Eng.133, 229–233. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2007)133:2(229)
3
Chen K. F. Zheng J. H. Zhang C. Wang N. R. Zhou C. Y. (2017). The evolution characteristics of main waterways and their control mechanism in the radial sand ridges of the southern Yellow Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin.36, 91–98. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1042-y
4
Cheng G. L. Wang Y. P. Voulgaris G. Du J. B. Sheng J. Y. Xiong J. L. et al . (2020). Sediment exchange between channel and sand ridges in the southern Yellow Sea: The importance of tidal asymmetries. Cont. Shelf Res.205, 104169. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2020.104169
5
De Winter J. C. F. Gosling S. D. Potter J . (2016). Comparing the pearson and spearman correlation coefficients across distributions and sample sizes: A tutorial using simulations and empirical data. Psychol. Methods21, 273–290. doi: 10.1037/met0000079
6
Gao J. Hou L. Liu Y. Shi H. (2024). Influences of Bragg reflection on harbor resonance triggered by irregular wave groups. Ocean Eng.05, 117941. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117941
7
Gao J. Ma X. Chen H. Zang J. Dong G. (2021). On hydrodynamic characteristics of transient harbor resonance excited by double solitary waves. Ocean Eng.219, 108345. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108345
8
Gao J. Ma X. Zang J. Dong G. Ma X. Zhu Y. et al . (2020). Numerical investigation of harbor oscillations induced by focused transient wave groups. Coast. Eng.158, 103670. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2020.103670
9
Gao J. Shi H. Zang J. Liu Y . (2023). Mechanism analysis on the mitigation of harbor resonance by periodic undulating topography. Ocean Engineering, 281, 114923. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114923
10
He L. Ye S. Xue C. Zhao G. Yang S. Amorosi A. et al . (2022). Sedimentology and evolution of the Holocene radial tidal sand ridge in the south Yellow Sea, China. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 1107495. doi: 10.3389/feart.2022.1107495
11
Huang H. M. Wang Y. G. (2020). Hydrodynamic sedimentary environment and tidal flat reclamation in the radial sand ridges of the south Yellow Sea (Nanjing: Hohai University Press).
12
Huang H. M. Wang Y. G. Chen C. Sun J. B. Yuan C. G. (2013). Distribution patterns of suspended sediment in radial sand ridges area, South Yellow Sea, China. Appl. Mech. Mater.368-370, 1640–1643. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM
13
Huang H. M. Wang Y. G. Wen Y. C. Zhu H. M. (2010). Vertical distribution of momentum exchange coefficient and sediment concentration in estuarine and coastal waters. China Ocean Eng.24, 677–692.
14
JTS 145-2015 (2022). Hydrological specifications for ports and waterways (Beijing: China Communication Press).
15
Kang Y. Y. Ding X. R. Zhang C. K. (2015). Maximum tidal range analysis of radial sand ridges in the southern Yellow Sea. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci.44, 971–976.
16
Liu J. J. (2009). Research and application of coastal sediment movement (Beijing: China Ocean Press).
17
Liu X. S. (2019). A probabilistic explanation of pearson's correlation. Teach. Stat.41, 115–117. doi: 10.1111/test.12204
18
Liu T. Shi X. F. Li C. X. Yang G. (2012). The reverse sediment transport trend between abandoned Huanghe River (Yellow River) Delta and radial sand ridges along Jiangsu coastline of China-an evidence from grain size analysis. Acta Oceanol. Sin.31, 83–91. doi: 10.1007/s13131-012-0255-3
19
National Marine Data Center, National Science & Technology Resource Sharing Service Platform of China (2023). Marine data service. Available online at: https://mds.nmdis.org.cn/ (Accessed August 10, 2025).
20
National Technical Committee on Marine Standardization (2022). GB/T 42176-2022, Specification for oceanographic observation—Observations at coastal stations and by volunteer ships (Beijing: Standards Press of China).
21
Qi Q. H. Zhu Z. X. Zhang R. Liu L. L. (2019). Application of coupled mathematical model of wave and tidal current in strong wind on muddy coast of Lianyungang, China. J. Coast. Res.93), 220–231. doi: 10.2112/SI93-030.1
22
Qiao G. Q. Zhang J. F. Zhang Q. H. Feng X. Lu Y. C. Feng W. B. (2019). The influence of temperature on the bulk settling of cohesive sediment in still water with the lattice boltzmann method. Water11, 945. doi: 10.3390/w11050945
23
Rao W. B. Mao C. P. Wang Y. G. Huang H. M. Ji J. F. (2017). Using Nd-Sr isotopes and rare earth elements to study sediment provenance of the modern radial sand ridges in the southwestern Yellow Sea. Appl. Geochem.81, 23–35. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.03.011
24
Reikard G. Pinson P. Bidlot J. R. (2011). Forecasting ocean wave energy: The ECMWF wave model and time series methods. Ocean Eng.38, 1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2011.04.009
25
Ren J. (2024). Research on spatial distribution characteristics of seasonal hydrodynamics and suspended sediment concentration in the Radiation Sandbank Sea Area (Nanjing: Hohai University).
26
Ren M. E. Xu Y. G. Zhu J. W. Chen B. B. (1986). Investigation of Jiangsu coastal zone and tidal flat resources (Beijing: Ocean Press).
27
Song Z. Li J. Meng F. Tang W. Yuan X. (2018). Seasonal distribution of suspended particulate matter off China's Subei coast. Pol. J. Environ. Stud.27, 845–852. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/75826
28
Su J. Rao W. Wang Y. G. Mao C. P. (2018). Detrital zircon geochronology of the radial sand ridge system of Jiangsu coast, east China: implication for sediment provenance. J. Earth Sci.29, 144–154. doi: 10.1007/s12583-017-0769-x
29
Su M. Yao P. Wang Z. B. Zhang C. K. Stive M. J. F. (2017). Exploratory morphodynamic modeling of the evolution of the Jiangsu coast, China, since 1855: Contributions of old Yellow River-derived sediment. Mar. Geol.390, 306–320. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.10.013
30
Su D. P. Ye S. Y. Wang Y. Wang Y. H. Yuan H. M. (2020). Hydrodynamic characteristic of Yancheng area in Jiangsu Province. Mar. Geology Front.36, 1–10.
31
Tao J. F. Wang Z. B. Zhou Z. Xu F. Zhang C. K. (2019). A morphodynamic modeling study on the formation of the large-scale radial sand ridges in the Southern Yellow Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf.124, 1742–1761. doi: 10.1029/2018JF004866
32
The Sediment Professional Committee of the Chinese Water Conservancy Society (1989). Sediment handbook (Beijing: China Environmental Press).
33
Van den Heuvel E. Zhan Z. (2022). Myths about linear and monotonic associations: pearson's r, spearman's ρ, and kendall's τ. Am. Stat.76, 44–52. doi: 10.1080/00031305.2021.2004922
34
Wang Y. (2014). Environment and resources of the radial sand ridges in the South Yellow Sea (Beijing: China Ocean Press).
35
Wang N. R. Chen K. F. Wang Y. H. Zeng C. J. Lu P. D. (2023). Seasonal variations in suspended sediment concentration and its drivers in the radial sand ridges of China's Jiangsu coast. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci.283, 108275. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2023.108275
36
Wang R. R. Zhu Y. W. Hu F. F. Xu X. Y. Sun Z. Y. Liu Z. Y. (2021). Distribution and source identification of Pu in the tidal flat wetlands of northern Jiangsu Province and radial sand ridge of southern Yellow Sea-An explanation of "land-sea interaction. Catena206, 105506. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105506
37
Wang Y. Zhu D. K. Zhou L. F. Wang X. Y. Jiang S. L. Li H. Y. et al . (1998). Depositional features and its evolution of the radial sand ridges in southern Yellow Sea. Sci. China Ser. D28, 385–393.
38
Xing F. Wang Y. P. Wang H. V. (2012). Tidal hydrodynamics and fine-grained sediment transport on the radial sand ridge system in the southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol.291-294, 192–210. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.006
39
Yang K. Ren Q. X. (2002). Coastal engineering (Beijing: China Ocean Press).
40
Yao J. Tao J. F. (2018). An Investigation of the mixing and exchange characteristics in tidal channels of radial sand ridges in the South Yellow Sea, China. J. Coast. Res.85, 136–140. doi: 10.2112/SI85-028.1
41
Zhang C. K. Yang Y. Z. Tao J. F. Chen Y. P. Yao P. Su M. (2013). Suspended sediment fluxes in the radial sand ridge field of South Yellow Sea. J. Coast. Res.65, 624–629. doi: 10.2112/SI65-106.1
42
Zhang W. N. Zhang X. H. Huang H. M. Wang Y. G. Fagherazzi S. (2020). On the morphology of radial sand ridges. Earth Surf. Process. Landf.45, 2613–2630. doi: 10.1002/esp.v45.11
43
Zhang C. K. Zhang D. S. Zhang J. L. Wang Z. (1999). Tidal current-induced formation-storm-induced change-tidal current-induced recovery-interpretation of depositional dynamics of formation and evolution of radial sand ridges on the Yellow Sea seafloor. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci.42, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF02878492
Summary
Keywords
silty and muddy coast, suspended sediment concentration, plane distribution, vertical distribution, seasonal change, tidal current, wave, water temperature
Citation
Huang H, Wang S, Lan Y and Zhang Y (2025) Significant seasonal evolution of sediment transport with mild sea conditions in the eastern Jiangsu coast of China. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1662069. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1662069
Received
08 July 2025
Accepted
22 August 2025
Published
12 September 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Dongfeng Xie, Zhejiang Institute of Hydraulics & Estuary, China
Reviewed by
Junliang Gao, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, China
Wen Wei, Sun Yat-sen University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Huang, Wang, Lan and Zhang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng Wang, sheng.wang@hhu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.