Abstract
Middle Eastern (ME) mangroves, spatially restricted and fragmented at the arid limit of the biome, underpin shoreline protection, fisheries, and blue-carbon initiatives along rapidly urbanizing coasts. However, global generalisations tend to overestimate their functional capacity, risking context mismatched restoration and overestimated offset potential. We conducted a comprehensive multi-method review across the Red Sea, Arabian/Persian Gulf, and adjoining shores. From peer-reviewed and agency sources, the literature was synthesized across four domains: eco-biophysical dynamics, socio-economics, climate-risk pathways, and governance. The review demonstrated that four primary controls govern distribution and function: freshwater inputs, hypersalinity, heat, and sheltering geomorphology. Avicennia marina dominates as dwarf, slow-growing stands of ~2–4 m, allocating resources below ground on carbonate and nutrient-poor substrates. Vertical accretion is modest ~1–3 mm yr-¹, organic carbon burial is low ~10–15 g C m-² yr-¹, and soil stocks are small ~43 ± 5 Mg C ha-¹ relative to the humid tropics. A wave-energy threshold and micro- to mesotidal ranges constrain the flushing. Sea-level rise (SLR) of 2.92 mm yr-¹, with a projected increase of 39.1 cm by 2100, combined with thermal and salinity extremes, dust burial, and oiling, raises the risk. However, undisturbed soils confer high carbon permanence. Socio-economic benefits, such as nursery support, shoreline defense, and cultural amenities, are large, but enforcement, monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV), and co-management remain uneven. A region-specific framework is most essential. Priorities are to safeguard groundwater-fed refugia, secure retreat corridors, reduce local stressors, and implement stress-matched restoration that replicates resilient features, such as space, sediment, seepage, and shelter, while grounding mitigation in arid-zone MRV and avoided-loss accounting. This study provides a resilience–threat typology and integrated governance framework linking legal protection, climate-linked restoration, regional coordination, and inclusive co-management.
1 Introduction
The Middle East has mangroves that fringe the Arabian/Persian Gulf and Red Sea, which are small in area but ecologically significant nodes in one of the driest seascapes on the planet (Su et al., 2021). They stabilize coastlines, provide food through fisheries, and sequester blue carbon; however, they are susceptible to extreme temperatures, hypersalinity, and low levels of freshwater input (Krauss et al., 2022). National commitments, such as the United Arab Emirates (UAE) vow to grow mangroves by 2030 and extensive nurseries along the Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia, have accelerated these systems into regional policy discussions on climate change and coastal-risk avoidance and mitigation (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021; Saudi Green Initiative, 2025). Meanwhile, high coastal development and historical pollution in the Gulf increases their vulnerability (Al-Nadabi and Sulaiman, 2021; Al-Tarshi et al., 2024), which is why a synthesis that models these complexities beyond global generalizations is required.
Although several reviews and technical assessments exist, such as the regional organization for the conservation of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden (PERSGA) Red Sea guidance (PERSGA/GEF, 2004), country-focused appraisals, and systematic reviews, coverage remains fragmented across subregions and disciplines. Earlier reviews typically emphasize ecology or distribution, with limited integration of arid-zone biogeochemistry, groundwater–sediment controls, livelihoods, governance performance, and emerging blue-carbon finance. The lack of attention to the dimensions of equity and livelihood is noted in the most recent Western Asia literature review by Yap and Al-Mutairi (2025), even though these are salient dimensions of policies. These gaps are addressed in our review , in which we integrate an eco-biophysical perspective with governance and socioeconomic dimensions in the specific context of the predominantly desert dominated regions we examine.
The fundamental issue addressed in this in-depth review is the comparative mismatch existing between the global mangrove assumptions and the Middle Eastern counterparts. The arid climate has made mangroves in this region nutrient-limited and of dwarf stature (Naidoo, 2006); sediment budgets are dominated by carbonate (Saderne et al., 2018), and carbon burial rates are an order of magnitude lower than those of humid-tropical references (Breithaupt et al., 2012). These facts are highly relevant to realistic blue-carbon accounting for site-appropriate restoration. Further, global averages are overemphasized, which is accompanied by the risk of exaggerated carbon claims and irrelevant plantation objectives. Simultaneously, the rate of development, temperature rise, and rise in sea levels create pressure by reducing the available populations to settle with limited opportunities to migrate landward (Spencer et al., 2016; Saintilan et al., 2020). Thus, a compelling, locally specific evidence base is needed to refocus expectations, target pristine freshwater-mediated refugia, and match restoration to hydro-geomorphic boundary conditions.
In this backdrop, we have synthesized a comprehensive review that integrates peer-reviewed publications with official data repositories, regional agencies, and national climate reports to assemble eco-biophysical characteristics, sedimentology and hydrology, biogeochemistry, socio-economic values, climate-risk pathways, and governance tools across key ME nations where mangroves can be found, including Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen. This integration will result in the generation of restoration, protection, and MRV of blue carbon efforts in arid environments to create decision-relevant baselines and thresholds.
This review article aims to (i) synthesize and critically evaluate available eco-biophysical and biogeochemical data on ME mangroves against a backdrop of heat and salinity stress; (ii) quantify what can or cannot be paralleled between global mangrove paradigms and arid coasts and, correspondingly, the implications on blue-carbon accounts; (iii) map a region-specific agenda on adaptation, restoration, and monitoring against national climate commitments and without falling into easy-one size fits all variance; and (iv) integrate socio-economic benefits and equity considerations with governance performance to identify actionable solutions.
2 Materials and methods
We used a multi-method evidence-based comprehensive review methodology to support four review objectives relevant to ME arid-zone mangrove systems (Taherdoost, 2022), that included (i) to compress and evaluate eco-biophysical and biogeochemical evidence on heat-salinity stress; (ii) to test what remains and does not transfer between the global mangrove paradigm and arid coasts; (iii) to plot a region-specific adaptation, restoration, and monitoring agenda in step with national climate commitments; and (iv) to reconcile socio-economic and equity dimensions with high performance of governance. We targeted the geography of Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen. The results are presented in five sections of the paper: (3.1) eco-biophysical systems, (3.2) socio-economics, (3.3) climate change impacts and adaptation, (3.4) governance/policy, and (3.5) limitations and future scope. Figure 1 shows the ME countries where this review was conducted. Figure 2 shows the overall methodology used in this study.
Figure 1
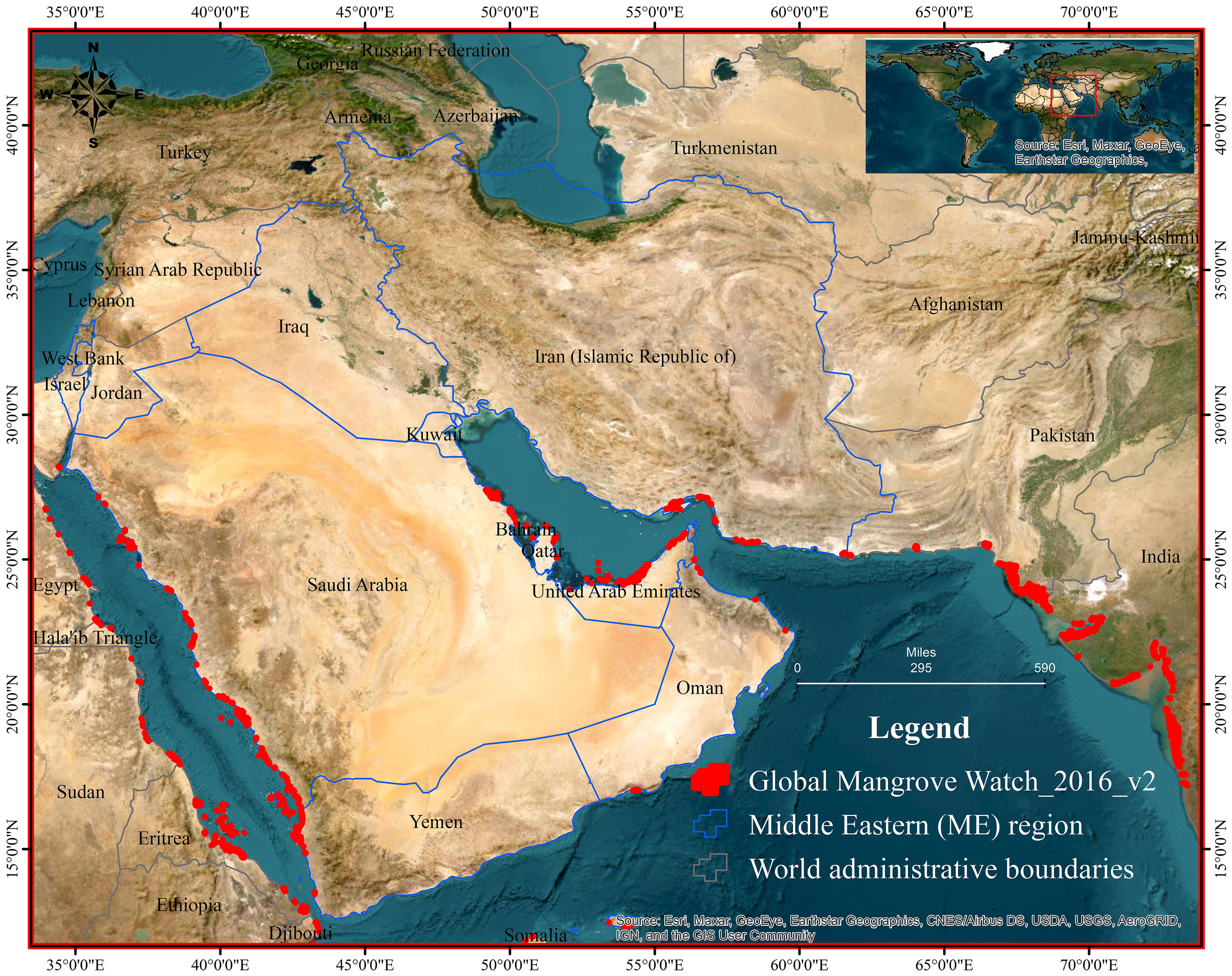
Study region across the Middle East with national boundaries shown as blue outlines. Red polygons depict mangrove distribution from the Global Mangrove Watch (GMW) 2016 v2 dataset; polygon outlines are intentionally exaggerated for legibility and are not to scale. The upper-right inset situates the study area in the global context. Graticule coordinates are standard geographic (WGS84). Basemap credits: Esri and partners; administrative boundaries: Natural Earth.
Figure 2
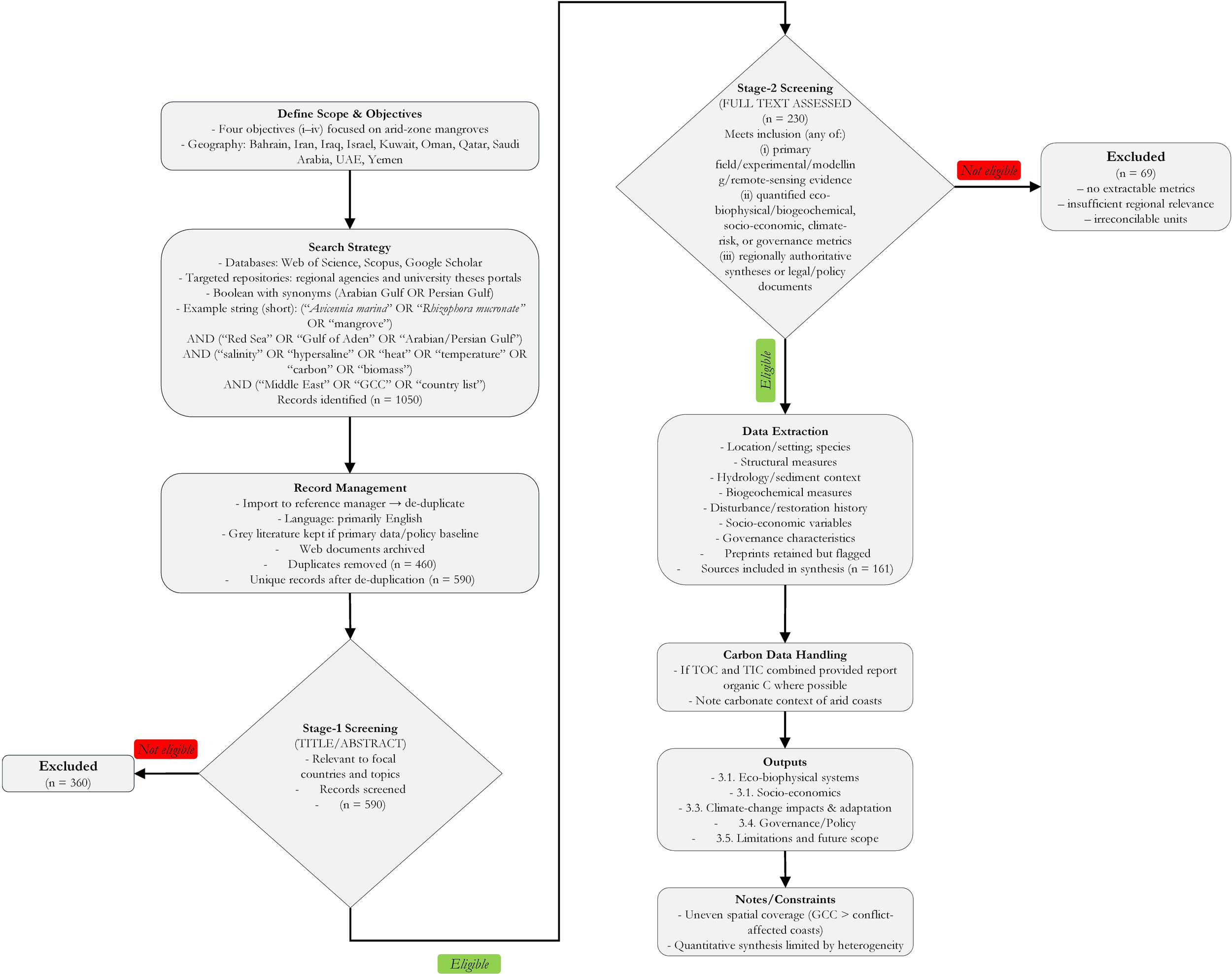
Methodology flowchart used in this comprehensive review.
Iterative searches were conducted in Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar, complemented by targeted queries of regional agency repositories and university theses portals, with no restriction on search date. We applied no publication‐year restrictions to avoid excluding foundational arid-zone studies and evolving grey literature (policies, agency reports). Boolean strings combined taxonomy, locality, and process terms, with regional synonyms (e.g., “Arabian Gulf” OR “Persian Gulf”). For example, (“Avicennia marina” OR “Rhizophora mucronata” OR mangrove) AND (“Red Sea” OR “Gulf of Aden” OR “Arabian Gulf” OR “Persian Gulf”) AND (salinity OR hypersaline OR heat OR temperature OR carbon OR biomass) AND (“Middle East” OR “Gulf Council Cooperation” OR “GCC” OR “Bahrain” OR “Iran” OR “Iraq” OR “Israel” OR “Kuwait” OR “Oman” OR “Qatar” OR “Saudi Arabia” OR “United Arab Emirates” OR “UAE” OR “Yemen”). Near-duplicate items were consolidated for counts.
Grey literature has explicitly been incorporated where it forms primary data and policy baselines. We restricted the corpus to English to a large extent. A reference manager was used to eliminate duplicate files; web documents were placed in storage. This two-stage screening retained records that either: (i) documented primary field, experimental, modelling, or remote-sensing evidence pertinent to our focal countries; (ii) quantified biophysical or biogeochemical parameters, socio-economic outcomes, measures of climatic risks, or governance instruments; or (iii) contained regionally authoritative syntheses or legal/policy documents. Articles that were not relevant to the topic in a significant way, which had no methods identified, and which were beyond the area of geographical scope were avoided. Preprints that have transparent methods with obvious regional relevance were not discarded but marked, as part of the appraisal process. We sampled location and setting, species, structural measures, hydrology/sediment context, biogeochemical measures, history of disturbance, restoration success, socio-economic variables, and governance characteristics, and only those records were sampled that were eligible. Where organic and inorganic fractions of carbon were combined, we presented organic carbon alone where it was possible to do so and indicated the carbonate context of arid coasts. Given methodological heterogeneity across the ME studies, we conducted a structured narrative synthesis rather than a meta-analysis.
In total, about 1050 records were retrieved. After de-duplication (460), 590 unique records proceeded to title/abstract screening; 360 were excluded as out of scope for focal countries, which were basically not about mangroves, and or lacking identifiable methods, leaving 230 for full-text assessment. A further 69 full texts were excluded for not meeting inclusion criteria, which were no extractable eco-biophysical/biogeochemical or governance metrics, insufficient regional relevance, or irreconcilable reporting units, that finally resulted in 161 sources included in the synthesis, which included 145 scholarly articles and 16 web/agency/portal items cited as numbered footnotes. Coverage was skewed toward GCC states with comparatively fewer studies from conflict-affected coasts; this asymmetry is noted in the limitations.
Legal protection, management instruments, restoration/offset commitments, and multi-level/transboundary mechanisms were some of the policy documents. Spatial coverage of the evidence is uneven between countries and sub-basins, with more concentrated coverage in GCC states. Quantitative synthesis was restricted by the heterogeneity of methods and reporting units. In the region, sources of a policy are new or developing, and enforcement decisions are still partly a matter of judgment. We thus laid greater stress on decision-relevant ranges, empirically restricted thresholds, and transparently identified uncertainties as compared to sole value generalizations. Here, we also note that despite comprehensive, multi-database searches with documented criteria, dynamic indexing and grey-literature volatility mean that inadvertent omissions may occur, and the number of searchable publications may vary over time.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Eco-biophysical mangrove systems in the Middle East
Mangrove ecosystems in the ME are unique outposts of tropical biodiversity in an otherwise arid region. Understanding their eco-biophysical dynamics is crucial because these mangroves provide valuable services, such as coastal protection, carbon sequestration, and nursery habitat, which are under extreme environmental stress. ME mangrove forests, found in Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen, occur at the harsh limits of mangrove tolerance, characterized by high salinity, high temperatures, and minimal freshwater input (Friis and Killilea, 2024). Consequently, they are often stunted dwarf forests with patchy distributions and low standing biomass (Waleed et al., 2025). Nonetheless, they represent important natural capital in the region’s coastal zones and form natural laboratories for studying mangrove adaptations to extreme conditions. In the context of climate change and regional coastal development, there is growing interest in mangroves as nature-based solutions for carbon storage and shoreline stabilization (Ahmed et al., 2022). In this section, we highlight the key findings from peer-reviewed studies and technical reports and identify knowledge gaps and future research needs.
3.1.1 Species distribution and biogeography
It is estimated that the total Gulf mangrove area is ~165 km² (Almahasheer, 2018). Approximately half of this occurs in the UAE, especially in Abu Dhabi, which alone now supports about 55–60 km², and about 40% in Iran, mainly in Hormozgan Province. Qatar supports ~ 10 km² of mangroves, chiefly at Al Khor and Al Dhakhira in the northeast. Bahrain’s mangroves are the smallest by country, covering only ~0.6 km² in Tubli Bay in Ras Sanad, a relictual population at the extreme environmental limit. Saudi Arabia retains ~10 km² of fragmented stands, primarily around Tarut Bay, while Kuwait and Iraq still have no self-sustaining native mangrove populations. Earlier afforestation attempts in Kuwait during the 1960s–70s failed, but post-1990 plantings in protected embayments such as Sulaibikhat Bay have survived, with A. marina reaching ~2.5 m height after seven years (AboEl-Nil, 2001). Iraq historically lacked mangroves, though a small pilot planting in the Shatt al-Arab delta began in the 2020s1. Throughout the Gulf, A. marina typically grows as isolated, low thickets or dwarf trees lining muddy lagoons and estuaries, reflecting the region’s extreme heat and hypersalinity.
Mangroves in the Red Sea–Gulf of Aden have reached their most significant ME development. A. marina dominates the Saudi and Yemeni coasts, forming extensive forests of about 200 km², forests along the Saudi Red Sea shores (Almahasheer, 2018; Shaltout et al., 2021), whereas R. mucronata appears only in well-flushed southern lagoons of Yemen and Djibouti and sparsely on the Farasan Islands (PERSGA/GEF, 2004; Alharbi, 2019). Yemen’s Tihama plain and Adenic lagoons also hold sizeable, although poorly quantified, stands (USAID, 2013). Poleward limits persist as relictual A. marina patches at Sinai and a tiny spring-fed colony near Eilat (28° 10N) (Por et al., 1977), highlighting the hydrographic controls on distribution.
South of Hormuz, Indian Ocean mangroves persist as scattered A. marina enclaves nourished by runoff and summer monsoons. On Iran’s Baluchestan coast, A. marina lines estuaries such as Govatr Bay, with R. mucronata recorded only at Sirik (Zahed et al., 2010). The only extensive forest is the 823.60 km² Hara Biosphere Reserve on Qeshm Island (Zahed et al., 2010). Oman contains approximately 11 km² split among Batinah, Muscat, the central Arabian Sea, and monsoon-fed Dhofar khawrs (Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), 2004). All stands occupy low-energy bays and estuaries that receive periodic freshwater input.
Only two true mangrove tree species are found in the Middle East: the grey mangrove A. marina, dominant throughout the region, and the red mangrove R. mucronata, restricted to a few locales (Waleed et al., 2025). A. marina has an extensive but discontinuous distribution along the Middle Eastern coasts, which reflects its high tolerance for the region’s hyper-saline and hot environments (Haseeba et al., 2025a). In contrast, R. mucronata reached its northern limits here and survived only in more sheltered or southern sites with slightly moderated conditions (Ahmed and Abdel-Hamid, 2007). Overall, mangrove cover in this region is modest, at approximately 0.19% of the global mangrove area (Bunting et al., 2022). However, spatial patterns vary among sub-regions due to differences in climate and coastal geomorphology.
Several environmental factors govern the biogeography of mangroves in the Middle East. The foremost of these is freshwater availability. Studies have consistently shown that proximity to freshwater inputs, such as river outflows, groundwater springs, or rainfall, has a strong influence on mangrove presence and growth in this desert region. For instance, in Qatar and the UAE, mangroves thrive best at inlets receiving intermittent wadi flow or subsurface fresh groundwater, whereas purely marine locations with no freshwater tend to have sparser, more stunted mangroves or none at all (Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 2008; Friis and Killilea, 2024). Al-Khayat and Balakrishnan (2014) documented that Qatar’s dense mangrove stands occur near the outfalls of ancient river systems in the northeast, highlighting the role of past freshwater delivery. Likewise, A. marina stands in Iran’s Hara-forest, gets benefit from dilution of salinity by riverine inflow from the Mehran River, thereby contributing to its relatively luxuriant condition with trees reaching approximately 5 to 6 m tall (Ghasemi et al., 2013; Karimi et al., 2025). In contrast, sites with no freshwater runoff, such as Bahrain’s Tubli Bay and some UAE lagoons, exhibit hypersaline waters that have constrained the size and coverage of mangroves in the region (Aljenaid et al., 2022; Mateos-Molina et al., 2024).
Extreme salinity and temperature are the overriding climatic constraints on mangrove biogeography. The Arabian Gulf, in particular, is a hostile setting, wherein salinities in shallow lagoons routinely exceed 45 practical salinity units (PSU) and can reach more than 70 PSU in enclosed sabkha creeks during the dry season (Rivers et al., 2020). Summer sea temperatures climb to ~35°C, while winter air temperatures in the northern Gulf can dip near freezing, a combination outside the tolerance of most mangrove species. A. marina is the only species resilient enough to tolerate these extremes, making it the sole naturally occurring mangrove in the Gulf (Haseeba et al., 2025a; Lachkar et al., 2025). Even Avicennia grows only in the warmer lower Gulf and not in the far north; 30°N is approximately the latitudinal limit, beyond which winter cold kills propagules, such as earlier attempts to naturalize A. marina in Iraq and Kuwait largely failed due to winter stress (Haseeba et al., 2025a). R. mucronata, being more thermophilic and less salt-tolerant than A. marina, is confined to the frost-free coasts of the Red Sea and the Sea of Oman, where average sea surface salinities remain moderate, typically between 36 and 40 PSU (Sofianos and Johns, 2007; Waleed et al., 2025). These environmental conditions contrast with the more hypersaline and temperature-variable settings of the Arabian Gulf, where R. mucronata is absent. Even there, Rhizophora only establishes in particularly sheltered, warm pockets, illustrating that ME conditions push this species to its ecological margin.
Coastal geomorphology and hydrodynamics shape mangrove distribution. Exposure to high wave action, such as open sea fronts, generally prevents mangrove growth in these areas. Indeed, Martínez-Díaz and Reef (2023) have noted that A. marina does not persist where the mean significant wave height exceeds 1.4 m. Hence, mangroves in this region preferentially colonize low-energy environments, such as the leeward sides of islands, inner reaches of bays, deltaic channels, and behind coral reef flats. Further, the ME coastline, with its many sheltered khors, such as the creeks along the Oman-UAE coast and the Red Sea mersas, provides niches where wave stress is reduced and fine sediment accumulates, providing a base for mangrove rooting. The tidal regime is micro- to meso-tidal: the Red Sea experiences a microtidal range with 0.6 m in the north, increasing to 0.9–1.0 m in the southern reaches, while the Persian Gulf features a mixed semi-diurnal tide with average tidal ranges of 1–2 m (Hoseini and Soltanpour, 2021; Guo et al., 2024). These relatively small tides indicate that tidal flushing is limited in some interior lagoons, contributing to hypersalinity. However, tidal exchange is vital for seed dispersal and nutrient import; mangroves are often found fringing tidal channels where daily flushing mitigates salt buildup. These landform–hydrodynamic controls, and the key thresholds for wave energy and tidal range, are summarized in Figure 3.
Figure 3
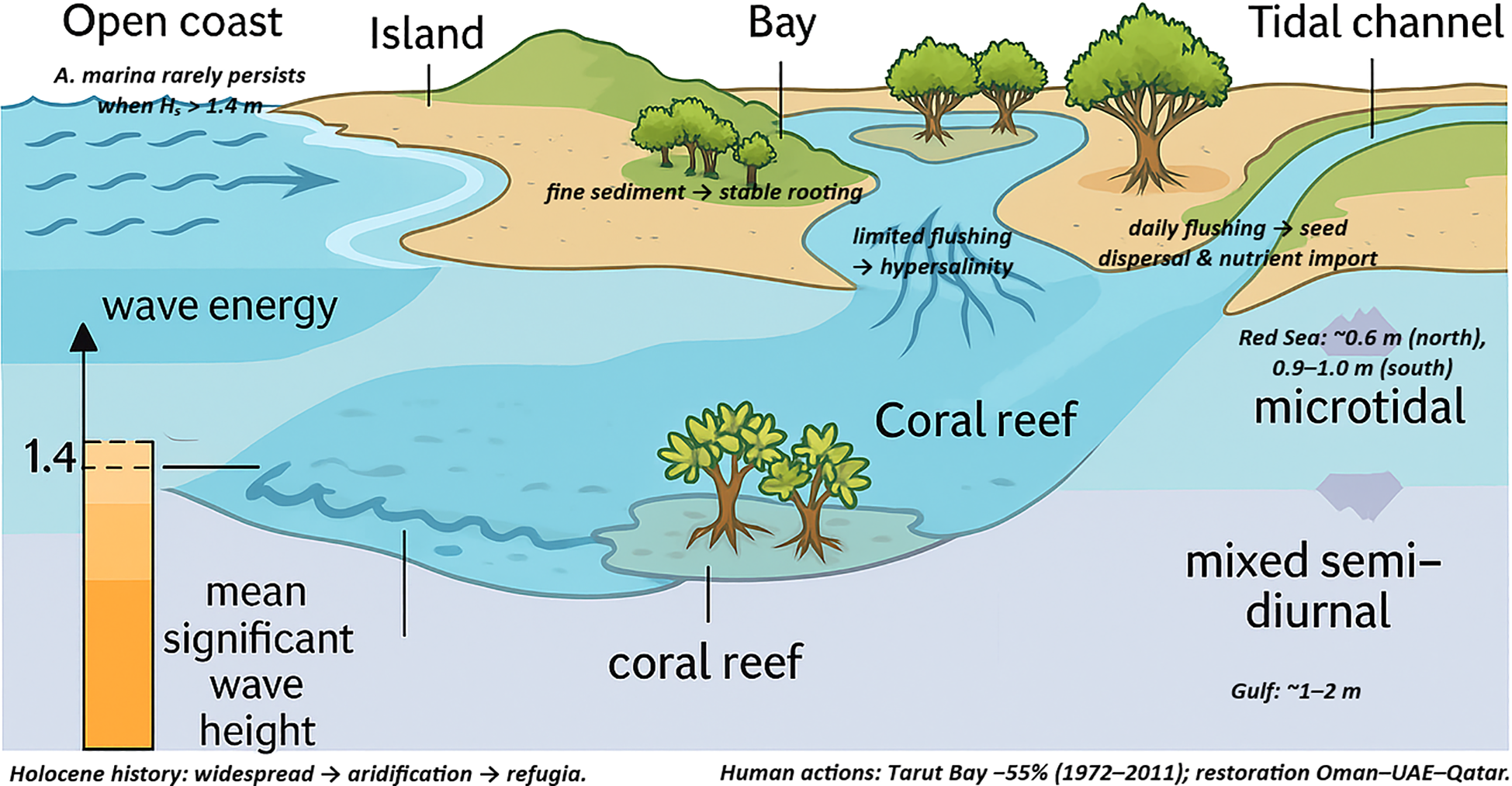
Conceptual controls on ME mangroves: sheltering landforms and reef flats reduce wave energy and trap fine sediment, enabling establishment; A. marina is generally absent on open coasts where Hs > 1.4 m. Small tidal ranges (Red Sea ~0.6–1.0 m; Gulf ~1–2 m) limit flushing in interior lagoons (causing hypersalinity) but daily exchange along channels disperses propagules and imports nutrients.
Historical biogeography also plays an important role. Paleoecological evidence suggests that mangroves were more widespread in the Middle East during the mid-Holocene climatic optimum, as sea levels and humidity were higher; however, many stands collapsed as conditions became more arid in the late Holocene (Rossignol-Strick, 2002; Decker et al., 2021). This history means that today’s mangrove populations are remnants of refugial sites. Genetic studies, for example, on A. marina populations, indicate low diversity and possible local adaptation to extreme conditions (Malekmohammadi et al., 2023). For example, Avicennia in the Gulf may have shorter dispersal ranges and distinct phenotypes, such as dwarfism and high salt excretion capacity, than their conspecifics elsewhere (Naidoo, 2006). These biogeographical characteristics highlight the isolation and uniqueness of each pocket of ME mangroves, meriting country-specific conservation efforts.
Finally, human actions have also impacted mangrove distribution, for instance, coastal land reclamation has also destroyed some stands for example, Saudi Arabia’s Gulf mangroves were reported to have declined by 55% from 1972 to 2011 due to urban-industrial development around Tarut Bay (Almahasheer et al., 2013), while restoration planting has added new stands in parts of Oman, UAE, and Qatar in recent decades. Overall, however, ME mangroves remain relatively few and far between, living on the edge of what mangrove species can withstand environmental stressors. The four dominant abiotic controls, freshwater availability, salinity, temperature extremes, and coastal geomorphology, are summarized in Figure 4.
Figure 4
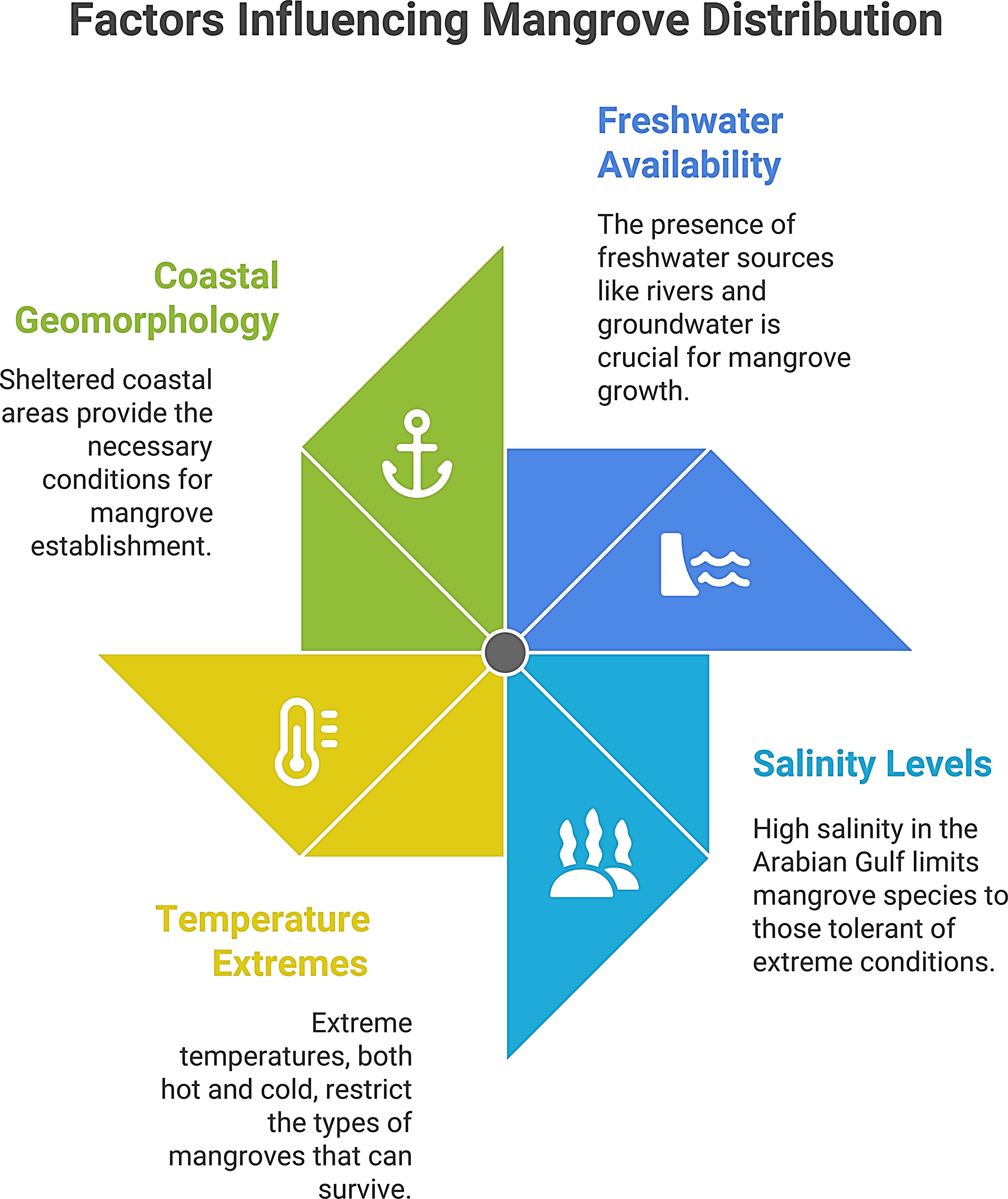
Dominant abiotic controls on ME mangrove distribution and performance. Schematic highlighting (i) freshwater availability (rivers/groundwater seepage), (ii) salinity levels (hypersaline Gulf conditions), (iii) temperature extremes (summer heat and winter cold limits), and (iv) coastal geomorphology (sheltered leeward settings).
3.1.2 Structural and functional traits
ME mangroves exhibit distinctive structural and functional traits as adaptations to extreme environments. One conspicuous trait is that of dwarfism. Across the region, mangrove trees are typically short in stature, often only 2–4 m tall at maturity, in stark contrast to the 10–30 m heights recorded in more humid tropical mangroves. Surveys confirm that Gulf mangroves are especially stunted; for example, A. marina along the Gulf coast of the UAE and Qatar seldom exceeds 3 m in height, with many stands resembling that of shrublands (Al-Khayat and Balakrishnan, 2014).
Nutrient and freshwater limitations, coupled with high salinity and heat stress, are thought to constrain the vertical growth of mangroves, resulting in their dwarf forms. In the Red Sea, where conditions are slightly less harsh, A. marina can grow taller, reaching 8–10 m in the best sites, such as in parts of Sudan or near freshwater seepage zones; however, even there, the average tree height (5–6 m) is modest by global standards (PERSGA/GEF, 2004; Waleed et al., 2025). These trees also have relatively slender trunks and limited canopy spread. Field measurements in Qatar found that over half of adult A marina were only 3–5 years old, with few trees living beyond 30 years, suggesting high population turnover, and diameter at breast height (DBH) seldom exceeded 10–15 cm (Hegazy, 1998). These metrics reflect the diminutive nature of mangroves in arid regions.
Despite their small stature, productivity and growth are ongoing, albeit at a slow pace. Recent studies using tree-ring and node analyses have quantified their growth rates. Almahasheer (2021) measured branch extension in Saudi Gulf mangroves through internode counts and found that A. marina produces, on average, approximately 6–9 nodes per year, corresponding to a linear growth of approximately 20–25 cm in shoot length per year. These growth rates are notably lower than those recorded in more favorable, wetter tropical regions, where annual shoot elongation can exceed 50 cm/year, for example, Rhizophora apiculata in Thailand and A. marina in the Central Red Sea. This comparison suggests that Arabian Gulf A. marina populations are only modestly productive in terms of wood increment due to environmental stress such as hypersalinity, heat extremes, and pollution. Similarly, litterfall production, a proxy for net primary productivity, is on the lower end of the global mangrove values. Hegazy (1998) conducted a field study in Qatar, wherein A. marina litterfall was observed to be seasonal and bimodal, totaling approximately 17 tons/ha/year, with leaves comprising about 34% of the total mass. These values are relatively modest compared to some Indo-Pacific mangroves. However, these productivity levels are remarkable given the stress conditions and are sufficient to sustain detrital food webs locally. The trees compensate for slower growth by year-round activity; Avicennia in this region is evergreen and retains some leaves throughout all seasons, continuing photosynthesis whenever moisture and temperature are within tolerable ranges.
Regarding the leaf traits and water-use efficiency, ME Avicennia leaves are small, thick, and succulent, classic xeromorphic structures that store water and limit transpiration. Their midday orientation, which is <180°from the horizontal, reduces incident radiation and leaf temperature (Naskar and Palit, 2015). Salt-secreting glands expel excess ions, and field observations note that Gulf leaves glisten with crystallized salt; periodic shedding of these salt-laden leaves further relieves the ionic load. Collectively, succulence, salt glands, and sacrificial leaf drop allow A. marina to persist in waters 2–3 times seawater salinity (Waisel et al., 1986). R. mucronata, which lacks such glands and relies on root exclusion and internal tolerance (Naidoo and Naidoo, 2017), is consequently scarce under hypersaline conditions, thereby highlighting the regional dominance of Avicennia.
It is worth noting that the root architecture mirrors these extreme edaphic pressures. A. marina develops extensive shallow laterals studded with dense, stubby pneumatophores, up to approximately 10000 within 2.5 m of a single trunk (Cabahug et al., 2006). Prolonged aerial exposure due to brief tidal inundation enhances gas exchange in anoxic sediments; however, high pore-water salinity restricts nutrient uptake and seedling establishment (Ocean, 2023). Therefore, trees concentrate their roots in slightly fresher surface layers generated by rain or groundwater seepage. Where present, R. mucronata compensates with stilt roots arching 1–2 m above the substrate; studies indicate that up to 25% of its biomass resides in aerial roots, emphasizing investment in support and aeration in the Red Sea’s soft, saline muds (Sulochanan, 2013). Such architectures optimize oxygen acquisition and stability under combined anoxia and salinity stress.
Furthermore, physiological performance further confirms life at the tolerance limits. Yasseen and Abu-Al-Basal (2008) reported lower chlorophyll concentrations and photosynthetic rates than those in humid-tropical mangroves, attributing the declines to chronic salt and heat stress. They also observed that A. marina maintains high water-use efficiency by partial stomatal closure at peak stress while accumulating osmolytes, such as proline, to balance external salinity. Reproductive metrics mirror these constraints, as demonstrated by Hegazy (1998), who recorded only approximately 13% propagule maturation in Qatar, suggesting resource-driven abortion. Phenological timing appears adaptive; flowering in April–May and fruiting in June–August exploit warm, calmer seas for dispersal, whereas vegetative flushing peaks in late winter–spring and nearly ceases during the cooler, saline mid-winter. These seasonal rhythms tightly couple productivity to temperature and salinity.
With regard to structural biomass and allometry, studies reveal the cumulative outcomes of these stress-adapted strategies. In Abu Dhabi, A. marina stands exhibit relatively modest structural attributes compared to Southeast Asian mangroves. Average above-ground biomass typically ranges between 200–300 t ha-¹, with mean trunk diameters of approximately 10 cm and estimated stand ages under 50 years, which reflects their adaptation to arid conditions and environmental constraints in the Arabian Gulf region (Alsumaiti, 2014; Alsumaiti et al., 2019).
A. S. Al-Nadabi and Sulaiman (2021) observed in their study on an Omani mangrove stand, northern Arabian Sea coast, that A. marina exhibited root-to-shoot biomass ratios ranging from 1.0 to 2.1, indicating elevated below-ground allocation under arid stress (Komiyama et al., 2008). likewise reported ratios of 0.9–2.8 for A. marina, with the highest values common in Gulf/Red Sea populations. In contrast, tropical Southeast Asian mangrove systems typically display more balanced root-to-shoot ratios of approximately 1:1 (Donato et al., 2011). Such allocation maximizes water and nutrient uptake and anchors trees in shifting substrates. However, it limits woody carbon storage, confirming that survival, not growth, governs mangrove functioning at the desert sea margin.
To conclude this section, we come to the fact that the structural and functional profiles of ME mangroves are characterized by miniaturization and resilience. Diminutive, slow-growing trees with thick salt-managing leaves and extensive aerial roots perform the key functions of mangroves, such as primary production, litter turnover, and habitat provision, albeit at a reduced pace. These traits allow them to persist where few other woody plants can survive, essentially pushing the limits of the mangrove life-form. However, it also means that these populations are vulnerable; any additional stress, for example, heightened salinity or temperature from climate change, can easily reduce their growth or reproductive capacity further. Thus, understanding these functional traits is not only scientifically interesting but also critical for informing management, for example, knowing that freshwater supplementation or nutrient addition could substantially improve growth in restoration projects. Table 1 below provides key quantitative indicators of structural and functional adaptation in ME A marina.
Table 1
| Structural and functional traits | Metrics* | Why they matter | Source (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure (stature and form) |
Height: Middle East typical 2–4 m; Gulf (UAE–Qatar) seldom > 3 m; Red Sea avg 5–6 m (best 8–10 m). DBH: 10–15 cm. | Regional dwarfism; slender stems vs humid tropics (10–30 m). | (Al-Khayat and Balakrishnan, 2014; PERSGA/GEF, 2004; Waleed et al., 2025; Hegazy, 1998) |
| Growth and productivity | Shoot elongation: 6–9 nodes yr-¹ ~ 20–25 cm yr-¹. Litterfall: ~ 17 t ha-¹ yr-¹ (leaves ~ 34%). | Slow wood increment; modest but sustaining detrital NPP. | (Hegazy, 1998; Almahasheer, 2021) |
| Demography and reproduction | Age: > 50% adults 3–5 yr; few > 30 yr. Propagule maturation: ~ 13%. | High turnover; low reproductive success under stress. | (Hegazy, 1998) |
| Physiology and tolerance (leaves) | Operates at 2–3× seawater salinity (through salt glands, succulence). | Explains Avicennia dominance under hypersalinity. | (Waisel et al., 1986) |
| Roots, allocation and stocks | Pneumatophores: up to ~10,000 within 2.5 m radius. Root:shoot: 1.0–2.1 (regional range 0.9–2.8). AGB (Abu Dhabi): 200–300 t ha-¹. | Heavy below-ground investment; modest above-ground carbon. | (Cabahug et al., 2006; Al-Nadabi and Sulaiman, 2021; Komiyama et al., 2008; Alsumaiti, 2014; Alsumaiti et al., 2019) |
Key quantitative indicators of structural and functional adaptation in ME A marina.
*All values refer to A. marina unless noted.
3.1.3 Sedimentology, hydrology, and geomorphology
The eco-physical setting of ME mangroves is defined by extreme hydrological conditions and distinctive sedimentary environments. Hydrology, i.e., salinity and freshwater flux, governs the region’s mangroves, which inhabit one of the most water-stressed marine environments on the planet. Rainfall is extremely low, which is generally <100 mm/year along the Arabian Gulf shores and only slightly higher on the Red Sea coast (Barth and Khan, 2008; Al-Ansari et al., 2022). In contrast, evaporation is intense, on the order of 1.5–2 m/year in the Gulf (Barth and Khan, 2008), causing net water loss and salinity concentration in coastal embayments. As a result, the ambient water in mangrove habitats is usually hypersaline. The average sea salinity in the Gulf range is ~39–42 PSU, which is already above normal oceanic salinity (Al-Ansari et al., 2022), and enclosed mangrove creeks regularly measure far higher. In the Red Sea, salinity is also elevated, which is approximately 30–60 PSU in the central/southern Red Sea, owing to high evaporation and low influx (Mezger et al., 2016). These background conditions thus indicate that even minor hydrological fluctuations have a significant effect on mangroves. Therefore, freshwater inputs are considered as a critical modulator, as episodic rain or flood events can temporarily reduce salinity in lagoons, providing mangroves some reprieve from salt stress.
Groundwater also influences the salinity. It has been reported that limited groundwater seepage creates pockets of lower salinity around spring outlets in, for example, southern Oman, such as Dhofar, where limestone mountains provide freshwater springs that flow into coastal khawrs, resulting in brackish conditions in which Avicennia flourish at sites such as Khawr Rawri and Khawr Baleed (Hoorn and Cremaschi, 2004). A similar groundwater influence has also been reported in parts of the Red Sea coast of Yemen, where subsurface freshwater maintains mudflat moisture during droughts (PERSGA/GEF, 2004). Studies have found that mangrove stand conditions correlate with proximity to freshwater, and stands receiving measurable groundwater or runoff tend to have taller trees and denser canopies (Haseeba et al., 2025b). Conversely, mangroves in purely marine-fed lagoons often show signs of water stress characterized by leaf succulence, salt encrustation, and seasonal leaf drop.
Tidal exchange, although micro to mesotidal, remains the cornerstone of hydrological functioning in ME mangroves. Tidal ranges are typically < 1 m in the Red Sea and 1–3 m in the Gulf, giving roots only brief immersion in each cycle. Limited flooding concentrates salts through evaporation, whereas daily inundation can flush salts and replenish oxygen. Crucially, flood tides carry carbonate-rich sand and silt from neighboring reefs or shoals; Indeed, Almahasheer et al. (2017), found that Central Red Sea mangrove soils are composed mainly of minerogenic material (sand and carbonate silt), and vertical accretion rates were on the order of a few millimeters per year, comparable to global mangrove accretion rates. In contrast, Gulf forests rely on sparse carbonate, relictual terrigenous silt, and benthic algal matting, producing calcareous, low-organic substrates (Haseeba et al., 2025a). Therefore, tidal action simultaneously mitigates salinity and sustains soil building, yet its brevity accentuates edaphic stress.
ME mangroves generally root in carbonate or evaporitic sand rather than deltaic clay. In the UAE’s Khor al Beida, for instance, sand and shell fragments dominate, with organic carbon only a few percent (Samara et al., 2020). Such a high permeability accelerates drainage and drying between tides, and at the same time carbonate matrices precipitate phosphate, thereby reinforcing nutrient scarcity. Further, many forests have been found to occupy slight depressions along the Pleistocene sabkha, where pneumatophores trap particles and gradually raise the surface (Alsharhan and Kendall, 2019). However, once the elevation exceeds the tidal reach, hypersaline flats form landward, thereby limiting further expansion. This sediment–vegetation feedback confines mangroves to narrow coastal fringes that are sensitive to seaward or landward changes.
Coastal geomorphology also features sharms, khors, and mersas, sheltered inlets that serve as nurseries for mangroves along the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, and Oman coast. Yemen’s forests cluster at wadi mouths, such as Khor Kathib, while Oman’s extensive Mahout Island stands in a barrier-protected lagoon. Conversely, surf-dominated open coasts lack suitable depositional settings and thus host virtually no mangroves (Zerboni et al., 2020). Field experiments have shown that once mangroves disappear, whether through die-back or cutting, sediment stability collapses. Al-Hurban (2014) and Khalil (2015) have demonstrated how rapid erosion of exposed mudflats in Kuwait due to anthropogenic activities caused similar outcomes as observed in the southern Red Sea. Therefore, root networks play a decisive role in shoreline retention.
Groundwater interactions with the ocean waters, introduce a vertical salinity gradient that further structures the mangrove rooting depth. Hypersaline groundwater can infiltrate from adjacent salt flats, compelling mangroves to concentrate fine roots within the top layer, where occasional rain or tides dilute salts. Salinity profiles from Abu Dhabi have revealed that pore-water salinity rises sharply with depth (Moore et al., 2015). In contrast, Omani springs deliver subsurface freshwater that permits deeper rooting (Fouda and AI-Muharrami, 1996). It can be concluded that by partitioning the soil column, trees balance osmotic stress against water acquisition; however, their dependence on shallow layers heightens their vulnerability to surface salinity spikes.
As far as coastal processes and landform dynamics are concerned, the region is cyclone-free, mainly. However, episodic Arabian Sea storms, such as Cyclone Gonu (2007), can impose acute disturbances (Blount et al., 2008). In Oman, extreme waves uprooted trees and scoured substrata. However, post-event monitoring revealed a rapid recovery fueled by freshwater and sediment pulses (Rahdarian and Niksokhan, 2017; Najah et al., 2025). Elsewhere, sedimentary evolution is governed by slower tides, residual currents, and wind-borne dust. Water residence times are long, 2–5 years in the Gulf and decades in the Red Sea, allowing fine sediments and contaminants to gradually accumulate in mangrove creeks (Hughes and Hunter, 1979; Hunter, 1983). Over geological timescales, such steady processes, rather than episodic storms, have shaped most of the regional depositional profiles.
Overall, ME mangroves persist through a finely balanced interplay between hydrological scarcity and excess salinity. Autochthonous carbonate sands with limited nutrients compel tight internal cycling, whereas geomorphic barriers restrict upslope migration. Accretion rates of ~1–3 mm yr-¹ documented in the Red Sea have thus far tracked twentieth-century SLR (Almahasheer et al., 2017). However, accelerated rise, tectonic subsidence, and intensive coastal development increasingly threaten a coastal squeeze, especially for Gulf stands having limited sediment supply. Studies highlight critical data gaps on groundwater influence and sediment budgets on mangrove ecosystems (Macklin et al., 2021; Tomer et al., 2025), and filling these gaps will refine projections of mangrove resilience and inform better-targeted restoration. Hydrologic scarcity, elevated salinity, small tidal ranges, carbonate-dominated substrates, and long residence times define the regional setting as summarized in Table 2.
Table 2
| Sedimentology, hydrology and geomorphology | Metrics* | Why they matter | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrologic balance | Rainfall < 100 mm yr-¹ (Arabian Gulf shores); Red Sea “slightly higher”. Evaporation 1.5–2 m yr-¹ (Gulf). | Extreme evaporative deficit causes chronic hypersalinity risk in embayments. | (Barth and Khan, 2008; Al-Ansari et al., 2022) |
| Ambient salinity | Gulf seawater ~39–42 PSU (creeks often higher). Red Sea ~30–60 PSU (central/southern). | Background waters are already hypersaline; small freshwater pulses have outsized effects. | (Al-Ansari et al., 2022; Mezger et al., 2016) |
| Tidal regime / immersion | Red Sea < 1 m (microtidal). Gulf 1–3 m (micro–mesotidal). | Brief inundation each cycle causes limited flushing, salt concentration, and short aeration windows. | (Barth and Khan, 2008; Al-Ansari et al., 2022) |
| Sediment supply and vertical accretion | Accretion ~1–3 mm yr-¹ (Red Sea); soils largely sand + carbonate silt (minerogenic). | Capacity to (so far) track 20th-century SLR; carbonate-dominated substrates. | (Almahasheer et al., 2017) |
| Substrate composition | Organic carbon only “a few %” (Khor al Beida, UAE); sand and shell fragments dominate. | Calcareous, low-OC, high-permeability soils cause rapid drainage and nutrient limitation. | (Samara et al., 2020) |
| Water residence time | Gulf: 2–5 years; Red Sea: decades. | Long residence enhances the accumulation of fines and contaminants in mangrove creeks. | (Hughes and Hunter, 1979; Hunter, 1983) |
Eco-physical setting of ME mangroves.
*Freshwater springs (e.g., Dhofar khawrs) create localized brackish pockets that improve condition, but are site-specific and not quantified in the text; cyclone impacts are episodic (e.g., Gonu 2007) and qualitative here.
3.1.4 Biogeochemical cycling
Mangrove ecosystems are renowned for their role in the biogeochemical cycling of carbon, nutrients, and metals. In the Middle East, mangroves function as blue carbon sinks and nutrient transformers, but the oligotrophic conditions of the region modulate their biogeochemical performance. Here, mangroves sequester carbon in both biomass and sediment, although generally at lower rates and quantities than wetter mangrove forests. Almahasheer et al. (2017) conducted a detailed study of Saudi Arabian Red Sea mangroves and found that soil organic carbon stocks in these arid mangroves are among the lowest reported globally. This study measured an average of only ~43 ± 5 Mg C/ha stored in the top 1 m of mangrove soil in the central Red Sea, which is roughly 25–30% of the typical values (>150 Mg/ha) recorded in Indo-Pacific mangroves.
Several factors explain this low carbon storage, such as (1) low productivity yields relatively small carbon inputs, such as leaf litter, root turnover, to the soil; (2) high temperatures and dry aerated conditions between tides can enhance decomposition, releasing much of the carbon as CO2 rather than accumulating in peat; and (3) limited allochthonous input – unlike riverine mangroves that receive external organic matter, these stands rely primarily on what they themselves produce. Correspondingly, carbon sequestration, i.e., the rate of carbon burial, in Red Sea mangrove sediments was estimated at only ~15 g C/m²/yr in recent decades, and ~3 g C/m²/yr over millennial timescales, which is an order of magnitude lower than the global mangrove average, and this low carbon sink capacity is attributed to the extreme environmental conditions of the Red Sea (Van Der Werf et al., 2009). This implies a very low nutrient supply and high evaporation limits mangrove growth and increases soil respiration rates. Essentially, any organic material that enters the soil is decomposed relatively efficiently, given warmth and periodic oxygenation, leaving little to be buried long-term.
Nevertheless, ME mangroves still play a non-trivial role in carbon cycling at the local scale. They fix CO2 through primary production and contribute detritus to the coastal food webs. The total ecosystem carbon stocks, including biomass, were modest but not negligible. For example, a multi-habitat carbon stock inventory across UAE coastal lagoons found mangroves had the highest carbon storage per hectare (~94.3 ± 19.6 t C ha-¹) among all coastal ecosystems. About 51% of this carbon is in living biomass, and the rest is in soils. Soil stocks in the top 50 cm averaged 53.9 t C ha-¹ (Carpenter et al., 2023; Dhawi, 2025). Region-wide, the total mangrove carbon pool is significant when considering large extents, such as the ~355 km² in Saudi Arabia2.
Thus, these mangroves represent vital carbon sinks in countries that otherwise have carbon-poor desert landscapes. Governments in the region have recognized this and started including mangroves in their Blue Carbon and climate mitigation strategies, such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia, which have initiatives to plant millions of mangrove trees to enhance carbon sequestration (Waleed et al., 2025). However, it must be kept in mind that environmental constraints limit per-tree or per-hectare carbon uptake. Any projections of carbon offset from ME mangroves must use region-specific low sequestration rates rather than global averages to be realistic.
Furthermore, greenhouse gas exchange in arid mangroves deviates from humid-tropical norms. High salinity and well-aerated substrates suppress methanogenesis, yielding minimal CH4 fluxes reported for the Red Sea by Breavington et al. (2025) and earlier studies. Breavington et al. (2025) demonstrated that summer heat accelerates heterotrophic respiration, driving substantial CO2 efflux, such that combined CO2 + CH4 emissions can approach burial rates. Therefore, resolving the true sink capacity depends on year-round flux data. Nutrient cycling is also constrained. With negligible river input, new nitrogen and phosphorus arrive chiefly through oligotrophic seawater or aeolian dust, which imposes chronic limitations (Anton et al., 2020). Chlorotic foliage, high C:N ratios, and slow growth reflect N scarcity, whereas A. marina recruits cyanobacterial mats (Fatimahsari et al., 2014) and diazotrophic endophytes (Inoue et al., 2024) to fix atmospheric nitrogen. Furthermore, phosphorus binds to carbonate sands, and in the case of studies conducted in the UAE, mangrove leaves contain only 0.05–0.1% phosphorus (Almahasheer et al., 2017), whereas litter decays slowly under hot, nutrient-poor conditions (Hegazy, 1998). Tight internal recycling creates limited outflow, as shown by the high 69–72 % resorption efficiencies in Red Sea stands (Almahasheer et al., 2018). Although it was shown that fertilization plots briefly boosted production, management favors safeguarding natural particulate inflows. Such conservation and opportunistic fixation sustain productivity despite the desert austerity.
Furthermore, trace metal dynamics reveal a filtering yet finite capacity. Surveys of Tarut Bay in Saudi Arabia and Tubli Bay in Bahrain recorded arsenic, chromium, copper, nickel, and vanadium much higher than international permissible limits (Almahasheer, 2019; Samara et al., 2020), surpassing the other global baselines reported for mangrove sediments (MacFarlane and Burchett, 2000). In fact, A. marina sequesters part of this load, and studies in Hormozgan, Iran, have shown that the accumulation of lead and zinc illustrates its phytoremediation potential (Ghasemi et al., 2018). However, ecological functions deteriorate once thresholds are exceeded. Protected Khor al Beida, UAE, in contrast, remains primarily within safe ranges, aside from slight Zn and Ni enrichment (Samara et al., 2020), highlighting the value of proactive pollution control.
Concerning hydrocarbon and plastic contaminants, they further add emerging pressures on mangroves. Even moderate oiling can leave persistent residues on A. marina tissues and adjacent sediments, with recovery often taking years (Burns et al., 1993). Although in the typically anaerobic mangrove sediments, mixed microbial consortia can biodegrade hydrocarbons, though attenuation is generally slow (Fakhrzadegan et al., 2019). Microplastics have recently been detected in Omani sediments and mollusks (Al-Tarshi et al., 2024), confirming mangrove creeks as depositional traps. Nevertheless, healthy stands improve neighboring habitats. In Bahrain’s Tubli Bay, they have been shown to attenuate nutrient-metal runoff, thereby benefiting seagrass beds (Saavedra-Hortua et al., 2023). Alongside organic burial, arid soils store significant inorganic carbon in biogenic carbonates (Saderne et al., 2018), which is an under-recognized pathway.
Collectively, ME mangroves operate as multifaceted biogeochemical filters, the efficiency of which is modulated by salinity, heat, and anthropogenic inputs. Restricted mainly to A. marina, they endure as scattered refugia where sheltered carbonate shores coincide with brief tidal exchanges. Dwarf canopies, salt-excreting leaves, and oxygenating roots sustain growth on sabkha soils nourished by rare freshwater pulses. Although their blue carbon, nutrient, and pollutant sinks are modest, these forests still stabilize coasts and underpin regional biodiversity. However, critical knowledge gaps cloud future projections. Hydrological minima, thermal and salinity thresholds, and long-term trends in growth, recruitment, and sediment accretion remain largely undocumented for most stands. Targeted work on local genotypes, soil microbiomes, and trophic links, especially mangrove support of oligotrophic fisheries, would clarify adaptive capacity and ecosystem connectivity. Closing these gaps is essential for robust climate forecasts.
Management assessments have warned of an approaching tipping point. SLR without compensatory sediment, further warming of Gulf waters, and relentless coastal development could exceed physiological tolerances. Therefore, protecting groundwater discharge oases, curbing reclamation, and aligning restoration with site hydrogeology are priority actions. Regional planting campaigns succeed best when sites offer slight freshwater seepage and employ locally stress-hardened propagules. Hence, these modest forests deliver disproportionate benefits while illustrating life at environmental extremes. Integrated monitoring that couples hydrology, soils, and vegetation must be launched urgently. Without it, escalating climatic and anthropogenic pressures may outpace intervention. Safeguarding ME mangroves will conserve ecological heritage and provide a living model for adaptation under intensifying stress. These relationships are synthesized in Figure 5, which links drivers, traits, and biogeochemical processes to services, threats, management levers, and knowledge gaps in the literature.
Figure 5
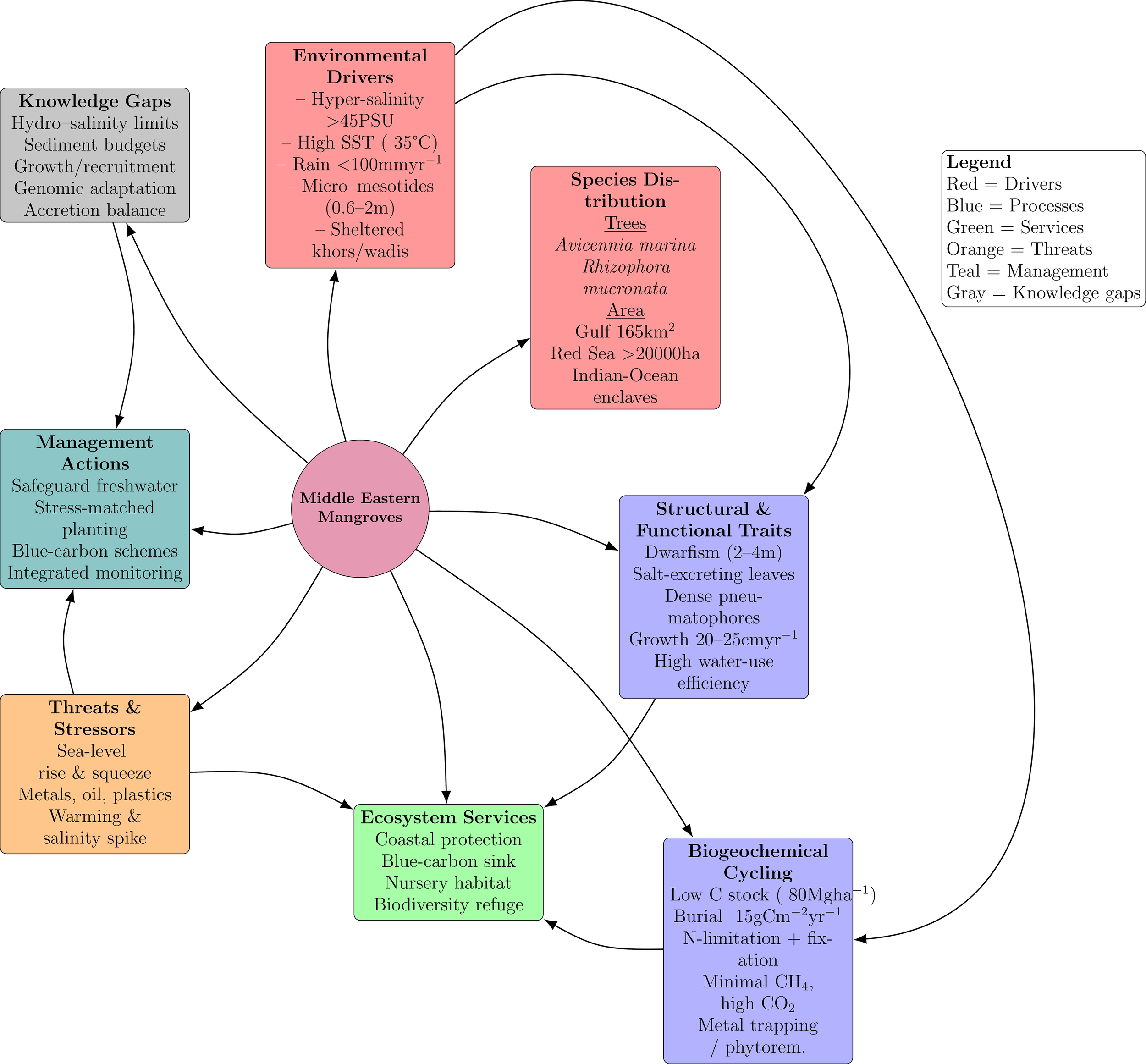
Conceptual map of the mangrove ecobiophysical system in the Middle East. Eight color-coded modules radiate from the central Middle Eastern mangrove node. Environmental drivers (red), species distribution (red), structural and functional traits (blue), biogeochemical cycling (blue), ecosystem services (green), threats and stressors (orange), management actions (teal), and knowledge gaps (grey). Curved radial arrows denote direct influences on the mangrove system, while secondary curved arrows trace the dominant causal pathways among modules, for example, hyper-salinity regulates physiological traits, which in turn modulate service provision. Box positions convey thematic relationships rather than geography. The diagram synthesizes peer-reviewed evidence to show how extreme salinity, heat, and limited freshwater create dwarf, Avicennia-dominated stands with low carbon stocks, and it pinpoints priority interventions, maintaining freshwater inputs, applying stress-matched restoration, and instituting integrated monitoring, to safeguard these desert-edge forests under rising sea levels and expanding coastal development.
3.2 Socio-economic dimensions of ME mangroves
Although the Middle East’s mangrove ecosystems are limited in extent compared to tropical regions, they provide critical socio-economic benefits in an arid context. These salt-tolerant A. marina stands are the only evergreen forests in these regions that act as natural buffers and resource repositories along desert coasts. Regional mangroves span from substantial forests in Saudi Arabia’s Red Sea and Gulf shores to small patches in Bahrain. Some countries, such as Iraq and Israel, have negligible mangrove cover. Understanding their socio-economic aspect is vital because rapid coastal development, climate stress, and resource pressure threaten these fragile ecosystems. Recent research has begun to highlight how ME mangroves support fisheries, protect shorelines, store blue carbon, and enrich local culture and livelihoods. We organized the discussion into three domains, i.e., provisioning and regulating services, cultural and recreational values, and livelihood and equity analyses, and shed light on why socioeconomic insights into ME mangroves are important for conservation and sustainable development.
3.2.1 Provisioning and regulating services
ME mangroves underpin coastal fisheries by functioning as nurseries for commercially valuable juveniles. In Qatar, they shelter blue swimming crabs and myriad fish. Al-Khayat and Jones (1999) and Al-Maslamani et al. (2012) reported dense juvenile assemblages along the nation’s east coast. Restoration in Oman restored more productive fishing grounds, with molluscs, crabs, and fish crowding replanted creeks3. Even modest stands host remarkable diversity, with 177 fish species catalogued in an Omani mangrove lagoon (Al Jufaili et al., 2021). Although studies have found limited evidence that mangroves subsidise offshore fisheries, these forests sustain prey and ecosystem engineers that are critical for higher trophic levels (Al-Khayat and Giraldes, 2020), thereby reinforcing regional food security.
Coastal defense services are equally consequential. PERSGA/GEF (2004) has documented that Red Sea mangroves stabilize sediments, curb erosion, and arrest dune migration, the benefits judged far more valuable than wood harvest. In Oman, decades of planting have created the lungs of Muscat, a living barrier that filters water and absorbs cyclonic surges (Al-Afifi, 2018). Such extensive Arabian Gulf plantations are expected to enhance protection from rising seas and extreme tides (Erftemeijer et al., 2020). Thus, even dwarf stands will act as natural breakwaters, safeguarding rapidly urbanizing shorelines.
Blue carbon sequestration adds climate mitigation value. Despite physiological stress, Gulf mangroves rank among the largest carbon sinks, regionally (SChile et al., 2017). Bahrain’s remnant forests store approximately 200 Mg C ha-¹ (Naser, 2023), and natural UAE stands reach ~156 Mg C ha-¹ (SChile et al., 2017). Although Oman’s stocks are lower (around 60–133 Mg C ha-¹), these densities approach humid-tropical benchmarks (Al-Nadabi and Sulaiman, 2018). Recognizing this asset, Bahrain aims to quadruple its mangrove area by 2035 to meet net-zero pledges (Naser, 2023), while Saudi Arabia and the UAE have embedded restoration within their Vision 2030/2050 strategies4. Although carbon monetization is still nascent, the inclusion of mangroves in national greenhouse-gas inventories signals rising economic valuation.
Traditional provisioning persists, where alternatives lag. On Iran’s Qeshm Island, mangrove branches supply forage, fuel, and boat timber, and blossoms sustain apiculture. Similar subsistence use is observed in Yemeni and Iranian villages, but unregulated cutting and grazing have accelerated the decline (Zahed et al., 2010). Wartime fuel shortages have intensified wood harvesting in Yemen5. However, global synthesis shows that indirect benefits, such as fisheries enhancement, shoreline stability, and carbon storage, vastly outweigh the market value of wood or fodder (Su et al., 2021). Therefore, balancing subsistence use with conservation is pivotal for retaining the full socio-economic portfolio of ME mangroves.
3.2.2 Cultural and recreational services
Even in desert societies, mangrove ecosystems have notable cultural significance and recreational value. Al-Afifi et al. (2024) demonstrated that Omani coastal residents highly value mangrove services, even associating them with Arabic and Islamic stewardship. In their study, they showed that the respondents emphasized the intrinsic, instrumental, and relational values of mangroves are embodied in their vernacular term, called al qurm. Historical practices where livestock rest beneath mangrove canopies or even use its bark as traditional medicine are very common examples. In Qatar, school children and university volunteers now plant mangroves as green oases along a barren coast6. These patterns confirm that mangroves anchor the regional identity and heritage.
Eco-tourism has translated this cultural attachment into economic value. The UAE’s Eastern Mangrove Lagoon, threaded with boardwalks and kayaking routes, provides urban green space and birdwatching opportunities for the region. Emirates Nature–WWF has placed a high monetary value on such amenities, highlighting ecotourism as a pillar of the UAE’s blue-economy vision7. Further, UN Environment (2018) has called the Qurm Ramsar reserve Muscat’s green lung, where charismatic fauna heighten the aesthetic experience8. Carefully managed access thus integrates conservation and livelihood benefits in these areas.
Soheili village on Qeshm Island exemplifies community-led models. Adjacent to the UNESCO-listed Hara forest, residents have created dolphin-watching tours, homestays, and mangrove-themed handicrafts that immerse tourists in local folklore. Women operate more than 30 craft shops and many guesthouses, preserving cultural skills while diversifying income9. Therefore, the valorization of the ecosystem has reinforced social cohesion and pride in Persian Gulf coastal culture.
Beyond formal tourism, newly planted stands in Bahrain and Kuwait serve as outdoor classrooms and family picnic spots, illustrating the everyday value of amenities. Education programs employ nurseries and reserves to instill conservation ethics, cultural services with long-term societal returns. Qualitative surveys in Oman, visitor counts in UAE parks, and community narratives in Iran converge on a single takeaway. Although spatially limited, ME mangroves wield a disproportionate influence as symbols of resilience, loci of recreation and eco-spiritual connection, and catalysts for heritage-based development in rapidly modernizing nations (Moussa et al., 2024).
3.2.3 Livelihood and equity analyses
Socioeconomic dependence on mangroves varies markedly across the Middle East. In wealthy Gulf states, mangroves underpin public goods, fisheries recruitment, and coastal protection, without direct household extraction. In contrast, coastal communities in Yemen, Oman, and remote Iranian and Saudi districts still harvest fuelwood and fodder, especially where conflict or poverty constrain the alternatives. Yemen’s sixth national biodiversity report notes that the war−related fuel crisis has again accelerated the use of fuel−wood for cooking, intensifying mangrove cutting (Republic of Yemen, Ministry of Water and Environment, Environment Protection Authority, 2019). Because most Yemeni and Djiboutian stands remain government land with de-facto open access, villagers gain short-term relief, but it risks long-term degradation. Therefore, policies that replace biomass energy or institute regulated community forestry are essential to reconcile subsistence needs with conservation.
Where co-management has been adopted, the livelihood outcomes differ sharply. On Qeshm Island, the village of Soheili has transformed the UNESCO-listed Hara forest into a community-run ecotourism hub. Residents operate boat tours, homestays, and handicraft enterprises through their councils, achieving full employment and gender-balanced participation. Women now lead more than 30 craft shops and guide visitors, overturning the historic male monopoly on mangrove labor. This empowerment shows that involving local actors, especially women and youth, can align equity with ecosystem stewardship.
In high-income settings, restoration initiatives are essentially state- or corporation-driven. Qatar’s coastal planting projects and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 campaigns deliver climate mitigation and urban amenities. However, their chief beneficiaries are distant publics rather than traditional users10. Yap and Al-Mutairi (2025), in their regional governance review, highlighted fragmented authority and limited community inclusion, calling for participatory approaches. Oman’s JICA-supported programs now engage villagers in monitoring and replanting, cultivating shared ownership (Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), 2004). Thus, channeling investment toward subsistence fishers and herders is pivotal for distributive justice.
Despite these advances, socioeconomic inquiry remains limited. Yap and Al-Mutairi (2025) also found that only 21 of the 168 Western−Asian mangrove studies examined livelihoods or economic valuation. Systematic data on gender roles, benefit distribution, and the efficacy of restoration for well-being are largely absent, constraining evidence-based policymaking. Figure 6 summarizes a simple theory-of-change for the region demonstrating participatory co-management at the core, enabled by (i) replacing biomass dependence and (ii) channeling investment to local users, shifting systems from limited to expanded mangrove benefits. This implies that as the governance moves from top-down projects toward co-management and targeted support for local users, benefits expand, such as nursery support, shoreline protection, and cultural amenities.
Figure 6
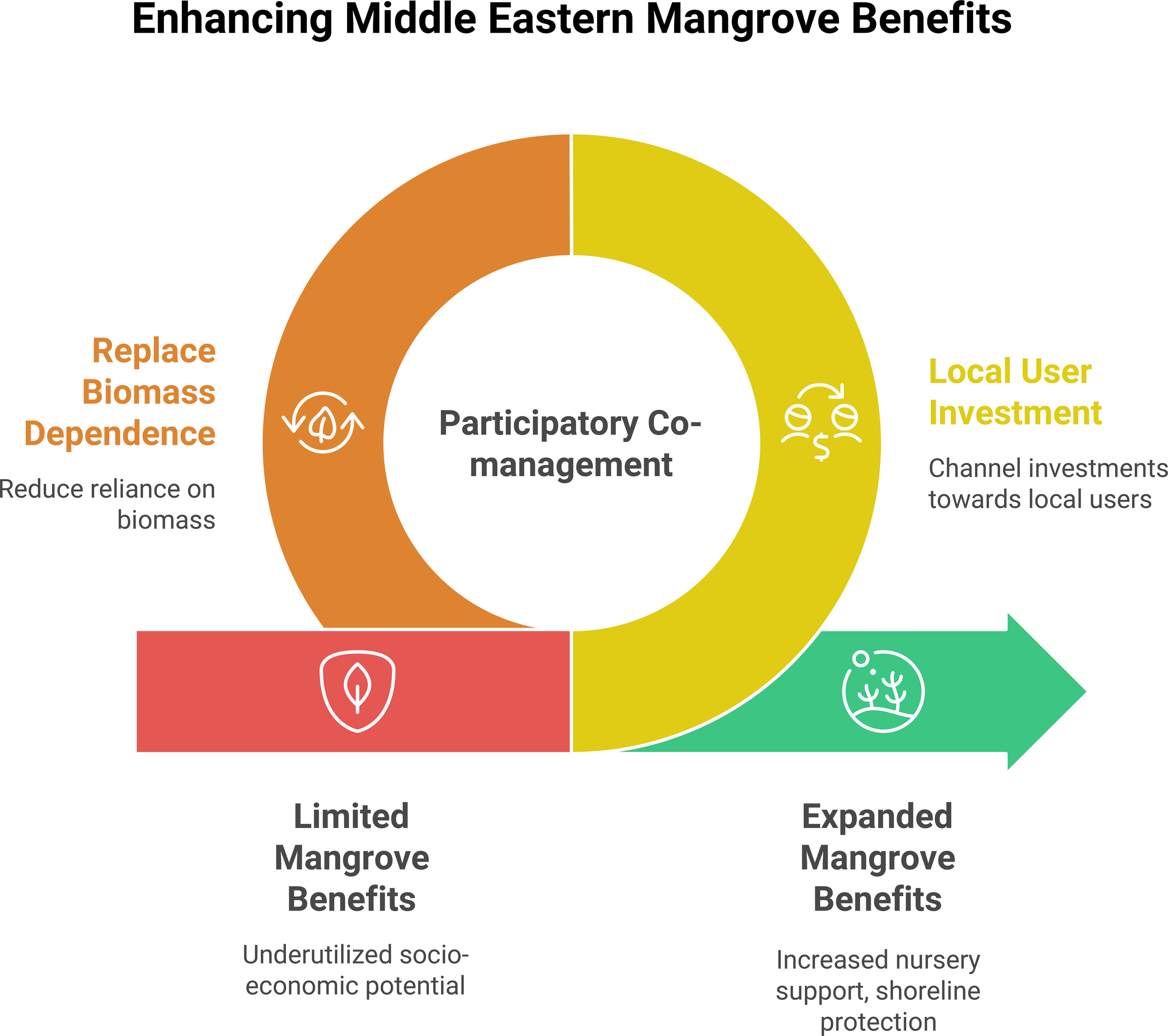
Enhancing ME mangrove benefits, policy pathway schematic. Central ring: participatory co-management. Left lever: replace biomass dependence (alternatives to fuelwood; regulated community forestry). Right lever: local user investment (directing funds and decision-making to fishers, herders, and community groups). The pathway arrow depicts a transition from limited benefits (underutilized socio-economic potential) to expanded benefits (increased nursery support, shoreline protection, and cultural–livelihood gains).
Collectively, the literature reveals that even modest ME mangrove tracts furnish essential livelihoods, risk reduction, and cultural identity, and where inclusive governance is embraced, these benefits expand while pressure on resources declines. Filling the current research gaps and embedding local voices in management will therefore be pivotal in securing both ecological integrity and equitable development along the region’s rapidly changing coasts. Key socio-economic metrics and policy anchors are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3
| Socio-Economic metrics | Metrics (values/claims) | Why they matter | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning / Nursery | Dense juvenile fish and blue swimming crabs in Qatar (east coast); dense juvenile assemblages along the east coast | Direct nursery function supporting local fisheries | (Al-Khayat and Jones, 1999; Al-Maslamani et al., 2012) |
| Restoration in Oman causes more productive fishing in replanted creeks | Restoration converts habitat to near-term livelihood gains | Footnote 3 | |
| 177 fish species recorded in an Omani mangrove lagoon | High biodiversity in modest stands; prey base for higher trophic levels | (Al Jufaili et al., 2021) | |
| Coastal defense | Stabilize sediments, curb erosion, arrest dune migration; dwarf stands act as natural breakwaters; buffer cyclonic surges (Oman) | Shoreline risk reduction for urbanizing coasts | (PERSGA/GEF, 2004; Al-Afifi, 2018; Erftemeijer et al., 2020) |
| Blue carbon and climate policy | Bahrain ~200 Mg C ha-¹; UAE ~156 Mg C ha-¹; Oman ~60–133 Mg C ha-¹ | Significant carbon stocks despite aridity | (SChile et al., 2017; Naser, 2023; Al-Nadabi and Sulaiman, 2018) |
| Bahrain: 4× mangrove area by 2035 | National mitigation commitment tied to mangroves | (Naser, 2023) | |
| Included in national greenhouse gas (GHG) inventories | Formal recognition causes rising economic valuation | Footnote 4 | |
| Restoration embedded in Vision 2030/2050 (KSA/UAE) | Long-horizon policy backing for expansion | Footnote 4 | |
| Cultural and recreation | Stewardship values (Al Qurm); boardwalks/kayaking/birding (UAE); Muscat’s green lung; school and volunteer planting | Cultural identity and urban amenity benefits | (Al-Afifi et al., 2024); Footnote 6 |
| Livelihood and equity | Fuelwood/fodder where alternatives are limited (Yemen, parts of Iran/Oman); Soheili, Qeshm: community ecotourism; >30 women-led craft shops | Equity, women’s participation, and diversified local income | (Republic of Yemen, Ministry of Water and Environment, Environment Protection Authority, 2019); Footnote 9 (Soheili case) |
| Evidence base/gaps | Only 21 of 168 West-Asian studies assessed livelihoods and valuation. | Sparse socio-economic evidence limits policy design | (Yap and Al-Mutairi, 2025) |
Consolidated socio-economic anchors for ME mangroves.
3.3 Climate-change impacts and adaptation in ME mangrove ecosystems
Mangrove forests in the Middle East exist at the threshold of environmental tolerance, making their resilience to climate change a critical issue. These arid-region mangroves, primarily A. marina, endure extreme heat, hypersalinity, and minimal freshwater input, yet they provide outsized ecosystem services in otherwise desert coastlines. In recent years, there has been growing interest in their fate under climate change, as nations such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia have invested in mangrove restoration for coastal protection and carbon mitigation. This section synthesizes the current knowledge on climate change impacts and adaptive responses in ME mangroves, spanning Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen. Key themes covered in this section include SLR and coastal squeeze, thermal and salinity extremes, acute disturbance events, and blue carbon sequestration potential. Understanding these factors is vital for safeguarding the region’s mangroves as climate-resilient green infrastructure.
3.3.1 Sea-level rise and coastal squeeze
Relative SLR is a major climate threat to mangroves globally, especially in the low-lying arid coasts of the Middle East. Tide-gauge records indicate that the Arabian Gulf has experienced, on average, 2.92 mm/year of SLR in recent decades (Al-Subhi and Abdulla, 2021), a rate exceeding the global 20th-century average of 1.7 mm/year (Church and White, 2011). Regional modelling projects that Gulf sea levels could rise 39.1 cm by 2100 under the high-emissions RCP8.5 scenario, outpacing typical vertical accretion rates in local mangroves (Al-Subhi and Abdulla, 2021). Sediment cores and surface elevation surveys suggest that Persian/Arabian Gulf mangroves have low sediment supply and accumulation rates, often <3 mm/year, reflecting the region’s paucity of riverine input.
In Saudi Arabia’s coastal lagoons, for example, accretion rates of only 2–4 mm/year have been recorded, with up to half of the sediment mass contributed by carbonate deposits rather than terrigenous mud. Such slow vertical growth raises concerns that ME mangroves will be unable to keep pace with the accelerating SLR beyond the mid-century (Saderne et al., 2018). Saintilan et al. (2020) estimated that at a sustained SLR >7 mm/year, mangrove sediment accretion will lag, leading to the drowning of mangrove roots and peat collapse. Where inland migration is blocked by urban development or topographic barriers, called coastal squeeze, the outlook is particularly dire. One study has warned that up to 90% of the coastal wetland area in the Middle East could be lost by 2100 if high-end SLR scenarios unfold without room for landward shifts (Spencer et al., 2016).
Despite these threats, geological and modern evidence suggest that mangroves can survive moderate SLR if accommodation space and sediment exist. Mangroves have historically migrated landward during Holocene SLR, as evidenced by paleo-mangrove peat deposits found inland. However, in the Middle East, such opportunities are limited by steep desert hinterlands and extensive coastal development. Decker et al. (2021) observed that paleoecological records from Oman illustrate the potential and limits of mangrove resilience. During the mid-Holocene, i.e., 6000 years before present, the Omani coast supported extensive mangrove swamps, but these ecosystems abruptly collapsed within decades owing to environmental change. Interestingly, this collapse was not driven by a sea-level highstand, as sediment archives show no evidence of a significant mid-Holocene SLR peak in Oman, but rather by increasing aridity and salinity as monsoonal rainfall waned. The resulting lack of freshwater and silting up of lagoons by wind-blown sand led to hypersaline soils that mangroves cannot tolerate, causing a rapid die-off. This paleoepisode highlights that mangrove retreat can occur from climate-driven coastal desiccation as much as from coastal inundation. In the current context, the landward migration of ME mangroves is only feasible in undeveloped areas, such as some sabkha plains. Remote-sensing studies have shown that in parts of the Gulf of Oman and the southern Gulf, mangrove cover has expanded in recent decades (Rondon et al., 2023), possibly aided by conservation planting and slight SLR inundating previously barren salt flats. However, such gains are localized. Overall, without proactive planning for mangrove retreat pathways, rising seas will likely squeeze many regional mangroves against seawalls and arid uplands, resulting in net habitat loss.
3.3.2 Thermal and salinity extremes
ME mangroves endure some of the harshest temperature and salinity conditions of any mangrove biome. Summer air temperatures regularly exceed 45°C and sea surface temperatures surpass 35°C in shallow Gulf lagoons (Paparella et al., 2019), pushing A. marina near its physiological limits. Field observations have indicated that mangrove productivity peaks only up to an upper thermal threshold of approximately 38–40°C, beyond which heat stress impairs photosynthesis and growth (Ward et al., 2016). Extreme heat can induce midday stomatal closure and leaf thermal damage. For instance, Persian Gulf mangroves exist in climates with mean annual temperatures >30°C and very high solar radiation, resulting in chronic heat and evaporative stress (Naderi Beni et al., 2021). However, intriguingly, the absence of winter frosts at these latitudes has allowed A. marina to extend further north than in other regions, and studies have demonstrated that recent warming of minimum winter temperatures has facilitated mangrove range expansion into previously cooler zones (Cavanaugh et al., 2014). Thus, ME mangroves are simultaneously benefiting from milder winters while suffering from more frequent summer heat extremes as the climate warms.
Hypersalinity is another formidable stressor. Mangroves in the Arabian/Persian Gulf routinely experience pore-water salinities above 40 PSU, far above the optimal range for most mangrove species (Moore et al., 2015). In hyper-arid Qatar, soil salinities in the intertidal zone can seasonally reach 50–60 PSU because of high evaporation and negligible rainfall (Rivers et al., 2020). A. marina exhibits remarkable salt tolerance. It is facultatively halophytic, meaning it can grow in fresh water but performs best in moderately saline conditions. Recent greenhouse experiments with Gulf mangrove seedlings found that medium salinity, for example, ~50% seawater, ~17 PSU, produced the highest growth rates, whereas both freshwater and full-strength seawater stunted growth and increased leaf shedding (Moslehi et al., 2025).
In the hyper-saline Arabian Gulf, surface waters routinely exceed 39 PSU (Sheppard et al., 2010), imposing intense osmotic stress on A. marina populations. Leaf-level work from the Qatari coast shows that these trees divert a large share of photosynthate to salt-gland secretion and other osmoregulatory pathways, confirming a high metabolic cost of life at such salinities (Yasseen and Abu-Al-Basal, 2008). The growth penalty is evident in the field. Monospecific A. marina thickets in Tarut Bay and adjacent sites rarely exceed 2 m in stature, with canopy dwarfism linked to prolonged hypersalinity and associated nutrient stress (Saderne et al., 2020). Globally, the same species can reach 14 m in lower-salinity settings, such as eastern Australia, highlighting the dwarfing effect of hypersalinity (Sadeer and Mahomoodally, 2022).
Low freshwater inflow also means that nutrients are scarce, compounding stress, and nitrogen limitation is particularly acute in these oligotrophic saline soils. As salinity and heat rise beyond thresholds, mangroves face an increased risk of hydraulic failure, i.e., inability to take up water, and metabolic disruption. Episodes of mass mangrove mortality in other regions have been linked to extreme heatwaves and droughts that elevate salinity, a combination that could threaten ME mangroves during severe climatic events. The tolerance limits of Gulf mangroves are still being investigated. However, available evidence shows that prolonged pore-water salinity above approximately 60 ppt and sustained air/leaf temperatures exceeding approximately 49°C can trigger canopy die-back and reproductive failure in A. marina (Gauthey et al., 2022; Naseef et al., 2024; Dhawi, 2025). Continued research is currently quantifying these thresholds using remote sensing of canopy health and in situ physiological measurements to predict how intensifying summer heat and evaporation may tip mangroves from resilience to collapse.
3.3.3 Extreme events and disturbance regimes
In addition to gradual climate shifts, ME mangroves are periodically affected by acute disturbances that can result in rapid degradation. Tropical cyclones, although relatively infrequent in this region, pose a significant episodic threat, especially along the Arabian Sea coasts of Oman and Yemen. Cyclones bring powerful winds, storm surges, and torrential rains that can uproot mangroves, erode sediment, and alter coastal geomorphology. In June 2007, Cyclone Gonu, the strongest cyclone on record in the Arabian Sea, struck Oman with >250 km/h winds and a 5 m storm surge (Blount et al., 2008). Mangrove stands in low-lying estuaries are inundated by saline floodwaters and buried under storm-driven sediment; post-storm assessments have noted extensive defoliation and tree mortality in affected lagoons (Banan-Dallalian et al., 2021). However, cyclonic events can have complex effects. While they can defoliate and damage trees, they also deposit new sediment that, in some cases, raises soil elevation and can help mangroves keep pace with SLR (Krauss and Osland, 2019). Following Cyclone Gonu, Omani authorities accelerated mangrove replanting programs, recognizing that storm-disturbed areas could be recolonized to serve as natural coastal buffers (Al-Afifi, 2018). More recently, Cyclone Mekunu (2018) hit the Yemen/Oman border region, causing flash floods in wadi deltas with mangroves, and field observations documented siltation around mangrove roots and increased seedling recruitment in the storm’s aftermath (Mansour, 2019). Thus, while severe storms can decimate individual mangrove stands, they may also create new sedimentary niches for mangroves to expand if post-disturbance conditions are favorable for their growth. We have demonstrated these disturbance patterns in site-level decisions using a simple resilience–threat framework, as shown in Figure 7 below.
Figure 7
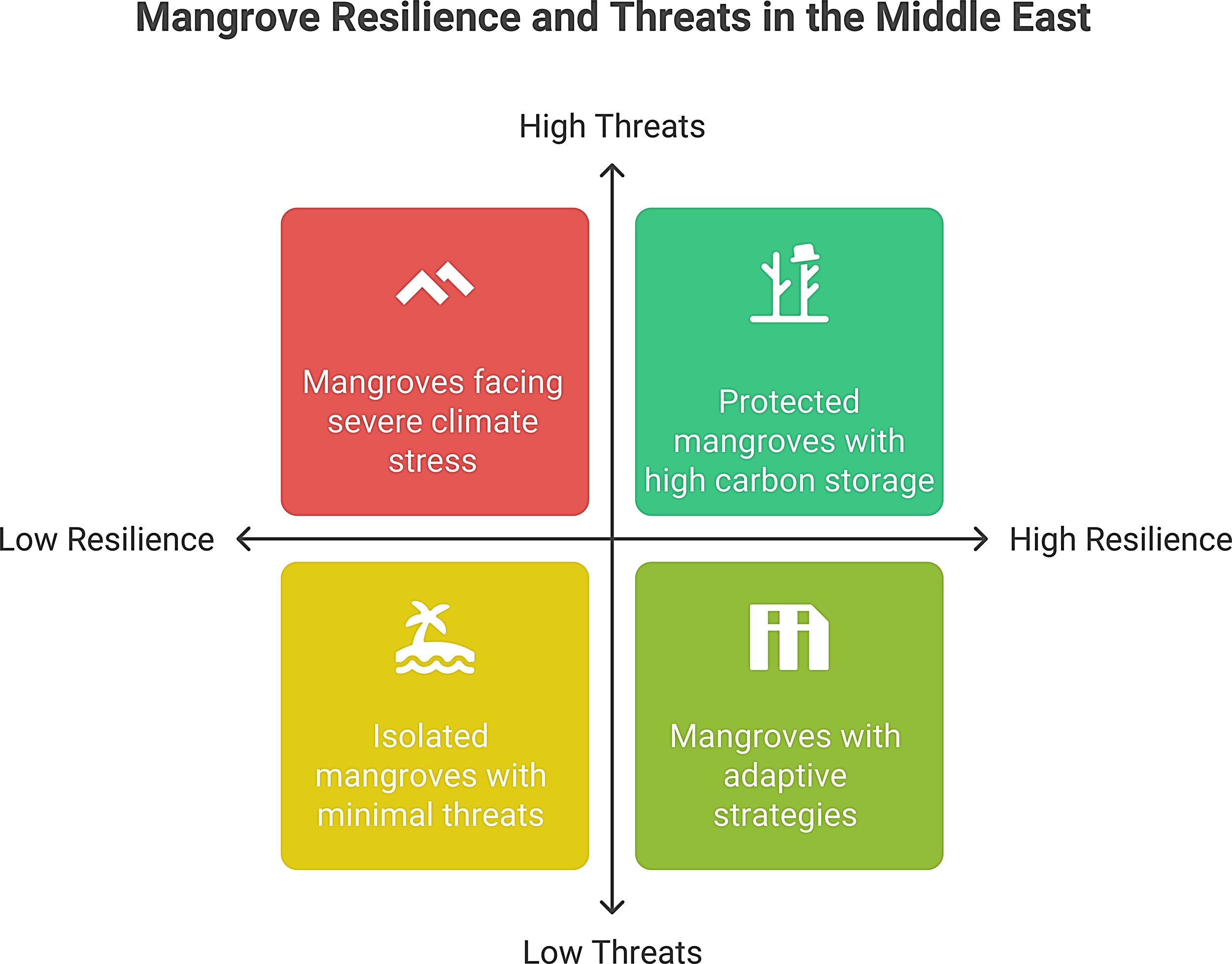
Resilience–threat typology and management pathways for ME mangroves.
Dust storms and sand dune migration represent insidious disturbance regimes. In hyper-arid landscapes, such as the southern Gulf coast, high winds frequently mobilize sand and fine dust from inland deserts, which can be deposited onto mangrove zones. Large dust storms referred to as shamal events reduce sunlight and can coat mangrove leaves with dust, impairing photosynthesis in the short term. More critically, wind-blown sand can infill tidal creeks and smother pneumatophores, effectively suffocating the mangrove roots. The paleoclimate record from Oman demonstrated that increased aeolian sand deposition was a key factor in ancient mangrove collapse, as intensifying drought led to dune encroachment on coastal lagoons (Decker et al., 2021). In modern times, sand encroachment is evident in some UAE lagoons where mangroves border active dune fields. Managers have observed that without intervention, sand burial can kill fringe mangroves and prevent propagule establishment (Al-Afifi, 2018). Climate change may exacerbate the impact of dust if higher temperatures and drought frequency increase the region’s dust storm activity, further challenging mangrove survival.
Among anthropogenic disasters, oil spills have been particularly devastating to ME mangroves. The region’s history includes the world’s largest oil spill, for example, during the 1991 Gulf War, an estimated 1.0–1.5 million tons of crude oil were released into the northern Gulf. Thick oil slicks blanketed the coastlines of Kuwait and Saudi Arabia, inundating mudflats and mangrove swamps. In Saudi Arabia’s Abu Ali Bay and Tarut Bay, home to the Gulf’s most extensive mangrove forests, oil-coated pneumatophores and sediment caused a massive mangrove die-off. Surveys after the war found almost 100% mortality of mangroves in the worst-hit intertidal zones, with black oil residue persisting in the substrate for years. By one estimate, approximately one-third of Saudi mangroves were destroyed or severely degraded by the 1991 spill alone, and recovery has been protracted (Issa and Vempatti, 2018).
Mangroves are particularly sensitive to oil. Even light oiling of roots and leaves can block gas exchange and poison tissues, leading to defoliation and tree death. Chronic oil pollution is also a concern in the Gulf, given the intensive petroleum shipping. Low-level spills and industrial effluents cause sublethal stress that reduces mangrove growth and reproduction (Duke, 2016). For example, in Bahrain and Iran, mangroves fringing busy tanker routes show stunted growth and elevated sediment hydrocarbon concentrations. The long-term ecological effects of oil contamination include reduced seedling recruitment, due to seed toxicity and substrate fouling, and altered faunal communities. Crab and mollusk populations have often crashed following oil exposure, disrupting the benthic food webs (Hassanshahian et al., 2020). Restoration of oiled mangroves can take decades, as natural regeneration is slow, and aggressive clean-up can sometimes do more harm than good by removing substrate along with oil. Hence, preventing spills and improving emergency responses are paramount for mangrove conservation in this region.
Other acute disturbances impacting ME mangroves include coastal urbanization and dredging, which, although human-driven, often occur suddenly on an ecosystem scale. Large-scale land reclamation, for example, artificial islands and ports, has directly cleared mangroves in parts of the UAE, Iran, and Bahrain, and altered the hydrology of the remaining stands. Sudden changes in tidal flow or sediment supply can trigger erosion or waterlogging stress in adjacent mangroves (Almahasheer et al., 2017). Additionally, dust deposition from regional sandstorms, extremely high-temperature events, and potential pest outbreaks, such as wood-boring insects that might proliferate under warmer conditions, are emerging disturbance factors under climate change. Overall, the disturbance regime of ME mangroves is shifting.
Historically, overexploitation and coastal development were the primary threats. However, climate-driven extremes, such as storms, heatwaves, droughts, and pollution incidents, now constitute an increasingly significant part of the risk profile. Building resilience will require strategies such as creating mangrove shelterbelts to buffer wind and dust, spill contingency planning around oil infrastructure, and rehabilitating degraded sites to jump-start natural recovery after extreme events. To operationalize these dynamics for management, we position sites along two axes: external threats, such as cyclones, heatwaves/drought, dust burial, oiling, reclamation, and intrinsic resilience, such as accretion capacity, flushing, groundwater influence, and genetic/structural robustness. This yields four practical management classes that tie observed disturbance regimes to triage, protection, and replication decisions (Figure 7).
Using the resilience–threat framework in Figure 7, we can map site conditions to distinct management pathways, from triage and retreat corridors in high-stress settings to protection and replication of resilient features in low-threat, high-capacity systems. Table 4 operationalizes each quadrant with diagnostic indicators and priority interventions, describing the critical information with Figure 7.
Table 4
| Threat-resilience profile | Conditions (diagnostic indicators) | Priority actions |
|---|---|---|
| I – High threats / Low resilience | Hypersaline, sediment-starved, hemmed in by infrastructure; disturbance and pollution can trigger a rapid decline. | Secure retreat corridors; consider elevation gain where feasible; reduce local stressors (e.g., spill prevention, water-quality controls); triage for assisted regeneration. |
| II – High threats / High resilience | Inside reserves or actively managed; adequate sediment or room to migrate; still exposed to extremes. | Maintain protection; strengthen monitoring/MRV; prevent new barriers to landward migration; avoid disturbances that could unlock stored carbon. |
| III – Low threats / Low resilience | Small, fragmented patches; limited genetic exchange and/ or freshwater inputs; quiet now but intrinsically fragile. | Improve connectivity; safeguard freshwater seeps; establish early-warning monitoring. |
| IV – Low threats / High resilience | Accommodation space, periodic flushing, and/ or groundwater influence buffer stress. | Use as reference sites for restoration designs; replicate resilient features (space, sediment, seepage, shelter); embed co-management to keep pressures low. |
Management pathways by resilience–threat quadrant, listing diagnostic indicators and corresponding interventions.
The above typology highlights the choice of instruments described in section 3.4 and the MRV priorities for mitigation discussed in 3.3.4.
3.3.4 Blue-carbon mitigation potential
Despite their modest extent, ME mangroves are gaining recognition for their blue carbon value, the ability to sequester and store carbon in biomass and waterlogged soils as a climate mitigation service. The carbon sequestration rates in these arid mangroves tend to be lower than those in wetter tropical mangroves owing to slow tree growth and limited sediment trapping. For instance, Saudi Arabian Red Sea mangroves have sequestered only approximately 10–15 g of organic carbon per square meter per year in recent decades, roughly 0.1–0.2 t C/ha/yr as demonstrated by Almahasheer et al. (2017). They also reported that over millennial timescales, the long-term burial rate is even lower (~3 g C/m²/yr), indicating that the extreme environment curtails net carbon accumulation. These values are 2–5 times lower than the global mangrove average (~50–100 g C/m²/yr in many Indo-Pacific forests) (Breithaupt et al., 2012). The reasons are multifold, such as arid mangroves have lower plant productivity due to heat/salinity stress and nutrient scarcity. Further, high soil respiration rates in hot conditions can remineralize a greater fraction of organic matter before it is buried, as described by Almahasheer et al. (2017).
Additionally, the sediment in ME mangroves often contains a high proportion of inorganic carbon, constituting calcium carbonate from shells and coral debris, which does not contribute to long-term organic carbon storage. Indeed, the soil carbon density in Red Sea mangroves is among the lowest reported globally, only ~43 Mg C/ha in the top meter of sediment, compared to hundreds of Mg/ha typical in Southeast Asian mangroves. These findings temper expectations for massive carbon offsets from arid mangrove preservation alone.
However, while per-hectare carbon sequestration is low, carbon permanence in these systems can be quite high if left undisturbed. The hypersaline, anoxic muds beneath ME mangroves can preserve buried organic carbon for millennia. Cores in UAE and Saudi mangroves reveal peat layers dating back ~6000 years, indicating the long-term stability of sequestered carbon during the Holocene (Ghandour et al., 2021). However, disturbance, either human clearing or climate-driven erosion, can rapidly oxidize these stores. Mangrove deforestation or die-back exposes rich organic soils to air, releasing CO2 back into the atmosphere. Thus, avoiding mangrove loss is crucial for maintaining the existing carbon sink.
Model projections suggest that continued warming and SLR, if unchecked, could further diminish soil carbon sequestration rates in arid mangroves (Chatting et al., 2022). Under high-emission scenarios, increased temperature stress may stunt mangrove growth, lowering carbon input to soils, and accelerated SLR without space for migration could convert mangroves to mudflats, resulting in net carbon emissions (Lovelock et al., 2015). However, climate change could also enhance blue carbon uptake in some areas if higher CO2 fertilization and rainfall, in currently ultra-dry sites, boost mangrove productivity (Lovelock and Reef, 2020). Globally, a 7% increase in mangrove carbon stocks by 2100 is projected under moderate climate change; however, this is highly regional and assumes that mangroves migrate landward rather than drown (Chatting et al., 2022). For the Middle East, with its tight geographic constraints, the net carbon balance will depend on effective conservation, enabling mangroves to persist in the landscape.
The past decade has seen significant advances in the MRV of mangrove carbon in the region, laying the groundwork for blue-carbon initiatives. The Abu Dhabi Blue Carbon Demonstration Project (2013) was a pioneering effort that quantified UAE mangrove carbon stocks both above and below ground, finding over 40 million tons of CO2 equivalent stored in Abu Dhabi’s coastal ecosystems (Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative (AGEDI), 2013). This project and subsequent national inventories, for example, in Qatar and Bahrain, have developed standardized protocols for field carbon measurements for biomass and soil carbon, aligned with the IPCC guidelines. Concurrently, remote sensing technologies have improved the mapping of mangrove extent and even the estimation of biomass carbon via radar and optical imagery (Hu et al., 2020). For example, high-resolution satellite data combined with field plots have enabled the creation of carbon stock maps of Saudi Arabia’s mangroves, informing their inclusion in the country’s climate strategies (Shaltout et al., 2021).
MRV systems now utilize satellite monitoring of mangrove area changes to detect any loss or gain, and periodic field sampling of carbon density, ensuring that carbon offset projects are rigorously audited. Several ME nations have integrated mangroves into their Nationally Determined Contributions. The UAE has pledged to plant 100 million mangroves by 2030, partly for carbon sequestration, and Saudi Arabia’s Green Initiative, similarly, emphasizes mangrove restoration as a nature-based climate solution (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021; Red Sea Global, 2023). The verification of carbon credits from these efforts will rely on robust MRV. For instance, digital platforms can track the growth of planted mangroves and model their carbon accumulation, while soil cores provide ground-truth data on sequestration rates. Although arid mangroves sequester carbon slowly, the avoidance of emissions by protecting existing carbon pools is significant in mitigating climate change. Preventing one hectare of Gulf mangrove from degradation avoids the release of up to ~300 t CO2 that would be emitted if its soil carbon were oxidized, an important contribution given the relatively small size of these forests (Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative (AGEDI), 2014). As summarized in Figure 8, arid mangroves sequester carbon more slowly than humid systems yet can preserve it for millennia; thus, protection, robust MRV, and restoration under national pledges deliver the main near-term mitigation gains.
Figure 8
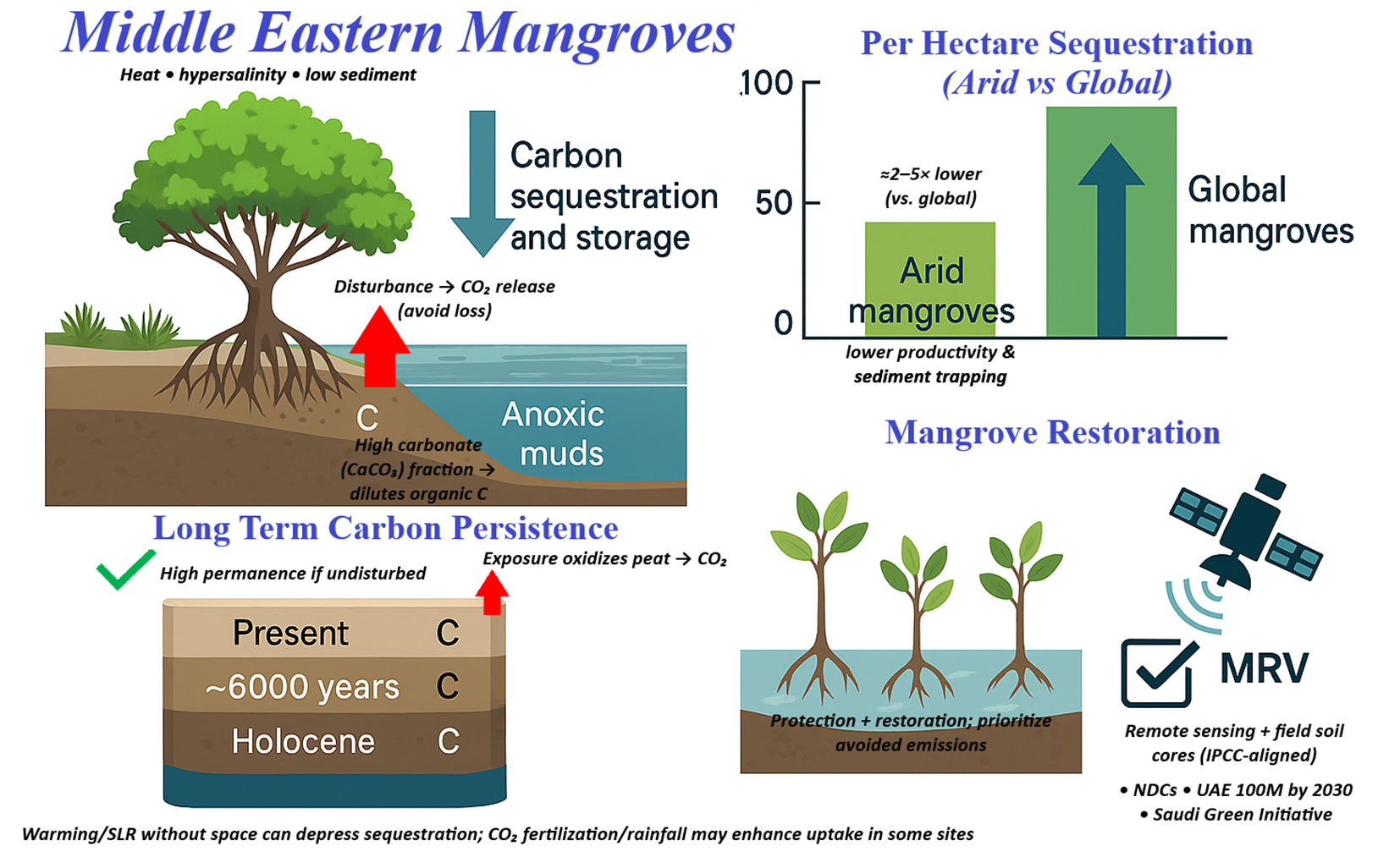
Blue-carbon mitigation potential of ME mangroves. Left panel: arid A. marina stands store carbon in anoxic, often carbonate-rich soils; disturbance exposes peat and releases CO2 (so avoiding loss is a major benefit). Top-right: per-hectare sequestration is ~2–5 times lower than global mangroves due to lower productivity and sediment trapping. Bottom-left: buried organic carbon can persist for millennia if undisturbed, but oxidizes when exposed. Bottom-right: restoration and MRV underpin crediting and national pledges.
Hence, ME mangroves are being recognized not only for their adaptation value, such as coastal defense and fish habitat, but also for their modest mitigation potential within emerging blue-carbon markets. Continued refinements in MRV, such as drone-based biomass surveys and region-specific carbon accounting models, will enhance the credibility and financial viability of mangrove carbon offset projects in this region in the future. Key climate-risk thresholds, disturbance anchors, and blue-carbon metrics are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5
| Climate-change impacts and adaptation indicator | Core metrics (values) | Why they matter | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLR vs. vertical accretion | Gulf SLR 2.92 mm yr-¹ (recent); global 20th-c. avg 1.7 mm yr-¹ | Regional rise is already faster than the historic global mean | (Al-Subhi and Abdulla, 2021; Church and White, 2011) |
| Projection +39.1 cm by 2100 (RCP8.5, Gulf) | Likely outpaces many local sediment gains | (Al-Subhi and Abdulla, 2021) | |
| Typical accretion <3 mm yr-¹; Saudi lagoons 2–4 mm yr-¹ | Low sediment supply limits vertical tracking | (Saderne et al., 2018) | |
| Functional threshold: SLR >7 mm yr-¹ causes accretion lags, root/peat drowning | Tipping point for persistence | (Saintilan et al., 2020) | |
| Potential wetland loss up to 90% by 2100, without room to migrate | Coastal squeeze risk under high SLR | (Spencer et al., 2016) | |
| Thermal limits | Summer air >45°C; SST >35°C (shallow Gulf) | Ambient extremes near physiological limits | (Paparella et al., 2019) |
| Productivity upper threshold ~38–40°C | Above this, photosynthesis/growth decline | (Ward et al., 2016) | |
| Die-back trigger ~49°C (sustained air/leaf temps) | Heat threshold for canopy/reproduction failure | (Gauthey et al., 2022; Naseef et al., 2024; Dhawi, 2025) | |
| Salinity limits | Pore-water commonly >40 PSU; Qatar soils 50–60 PSU seasonally | Chronic hypersalinity | (Moore et al., 2015; Rivers et al., 2020) |
| Seedling growth optimum ~17 PSU (~50% seawater) | Performance peak vs. fresh or full seawater | (Moslehi et al., 2025) | |
| Surface waters >39 PSU routine (Gulf) | High osmotic stress baseline | (Sheppard et al., 2010) | |
| Die-back trigger >~60 ppt pore-water | Salinity threshold for collapse risk | (Gauthey et al., 2022; Naseef et al., 2024) | |
| Disturbance metrics | Cyclone Gonu: winds >250 km h-¹, storm surge ~5 m | Episodic extreme forcing | (Blount et al., 2008) |
| 1991 Gulf War spill 1.0–1.5 Mt oil; worst-hit zones ~100% mangrove mortality; ~⅓ of Saudi mangroves destroyed/degraded | Acute pollution impacts, protracted recovery | (Issa and Vempatti, 2018) | |
| Blue-carbon rates and stocks | Red Sea sequestration ~10–15 g C m-² yr-¹ (0.1–0.2 t C ha-¹ yr-¹); millennial burial ~3 g C m-² yr-¹ | Low per-hectare fluxes in arid settings | (Almahasheer et al., 2017) |
| Global comparator ~50–100 g C m-² yr-¹ | Shows regional shortfall vs humid tropics | (Breithaupt et al., 2012) | |
| Soil organic C density (Red Sea) ~43 Mg C ha-¹ (top 1 m) | Among the lowest reported globally | (Almahasheer et al., 2017) | |
| Abu Dhabi coastal ecosystems store >40 Mt CO2e | Regional stock magnitude supporting policy | (Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative (AGEDI), 2013) | |
| Avoided-loss benefit: preventing 0.1 km2 degradation avoids ~300 t CO2 emissions | High permanence; protection value | (Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative (AGEDI), 2014) | |
| Policy and adaptation signals | UAE to plant 100 million mangroves by 2030; Saudi Green Initiative emphasizes restoration | NDC-linked expansion/mitigation pathway | (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021; Red Sea Global, 2023) |
| Post-cyclone replanting (Oman); remote sensing shows localized expansion (southern Gulf, Gulf of Oman) | Opportunities where accommodation space exists | (Al-Afifi, 2018; Rondon et al., 2023) |
Climate-change metrics and thresholds for ME mangroves.
Further, we translate these risk pathways into actionable management and policy steps in 3.5.1, wherein we prioritize freshwater/space/flushing filters, and retreat corridors where SLR outpaces accretion, for an efficient stress-matched restoration framework.
3.4 Governance, management, and policy of mangrove ecosystems in the Middle East
Mangrove ecosystems in the ME are limited in extent but are critically important for coastal resilience. Found in arid Gulf and Red Sea shorelines, A. marina forests provide nurseries for fisheries, stabilize shorelines, and sequester significant carbon despite harsh conditions. In recent years, regional governments have begun to recognize that robust governance and policy frameworks are essential to safeguard these benefits against intensifying threats, such as coastal development, pollution, and climate change. Ineffective management and fragmented policies have historically contributed to mangrove decline, whereas strengthened laws, protected areas, and cooperative initiatives are now seen as pivotal for mangrove conservation and restoration. This section reviews how ME countries govern their mangrove ecosystems. It examines national legislation and protected area coverage, restoration and offset programs, and emerging multilevel and transboundary governance efforts that shape mangrove resilience in the region. Key governance instruments, restoration commitments, finance mechanisms, regional bodies, and participation pathways are summarized in Table 6. We organize the governance architecture into four different themes: national legal protection, climate-linked restoration and finance, regional coordination, and community co-management, converging on effective mangrove management (Figure 9).
Table 6
| Mangrove governance, management, and policy | Values/claims | Why they matter | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| National legislation and protection | Iran has protected mangroves since 1972; Hara forests ~270 km² (UNESCO Biosphere Reserve; Ramsar). UAE Federal Law 24 (1999) bans clearance; it underpins Eastern Mangrove NP and emirate reserves. Saudi Arabia reform 2020: mangroves classed as high-importance habitats with management plans. Saudi Vision 2030 targets 30% protected-area coverage. Bahrain: Tubli Bay Ramsar reserve (SCE). Kuwait/Qatar/Oman: comparable statutes enabling reserves/replanting. | Establishes legal basis and protected coverage across most stands. | (UNESCO, 2024; United Arab Emirates, 1999; Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture [MEWA], 2020; Saudi Green Initiative, 2025; Supreme Council for Environment [SCE], 2024; Loughland et al., 2020) |
| Enforcement and governance gaps | Fragmented mandates (environment, municipalities, fisheries, ports); weak EIA compliance; encroachment and pollution persist (e.g., roads within Iran’s Dayyer wetland). Conflict hinders implementation in Yemen. | Law–practice gap; risks from reclamation, discharge, and under-enforcement. | (Yap and Al-Mutairi, 2025; Savari et al., 2022; Conflict and Environment Observatory [CEOBS], 2021) |
| Restoration scale-up (GCC and neighbors) | Oman: 10 Million Trees (1.5 M planted); Oman Blue Carbon pledges 100 M more (projected 14 Mt CO2; US$150 M credits). Saudi Arabia: gov and Aramco >2 M seedlings; Red Sea Global pledge 50 M by 2030. UAE: 100 M by 2030; drone dispersal; existing stock captures about 115 kt CO2 yr-¹. Qatar: 1 M by 2022, 10 M by 2030. Iran: ~0.86 km² new mudflat planted (Hormozgan). Iraq: 4 M seedlings for Basra. | Demonstrates a shift from ad-hoc plantings to national programs tied to mitigation and coastal defense. | (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021; Red Sea Global, 2023; Ataullah, 2024) |
| Finance and market instruments | Gulf Blue Carbon Network mobilizes US$300 M (regional restoration/MRV). Bahrain to 4 times coverage to 3.6 M trees by 2035 within the 2060 net-zero pathway. Saudi voluntary GHG Credit and Offsetting Scheme targets mangrove projects. UAE Blue Carbon Demonstration underpins Mangrove Breakthrough; Oman program structured around credit revenue. | Aligns restoration with carbon finance; enables verified credits and long-term funding. | (Abdelraouf and Al Majed, 2025; Naser, 2023; Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021) |
| Regional and transboundary bodies | ROPME (Kuwait Convention 1978) and PERSGA (Jeddah Convention 1982) list mangroves as critical habitat but have weak enforcement; Green Gulf Pact 2025 lacks compliance teeth; tensions (e.g., Strait of Hormuz, southern Red Sea) impede data sharing. | Need stronger regional coordination and compliance to manage shared forests. | (ROPME, 2013; PERSGA/GEF, 2004; Abdelraouf and Al Majed, 2025; Aman, 2021) |
| Participation and co-management | Iranian community phenology monitoring; Saudi/UAE youth mass plantings (episodic); Bahrain UN-Habitat–HSBC urban rehabilitation (boardwalks/centers); Oman FAO projects engage fisherfolk. Reviews warn that co-management is underdeveloped; low post-planting survival when projects end. | Inclusive governance links ecological gains to durable stewardship and survival. | (Yap and Al-Mutairi, 2025, 2025; Haddad, 2024) |
Governance, management, and policy anchors for ME mangroves.
Figure 9
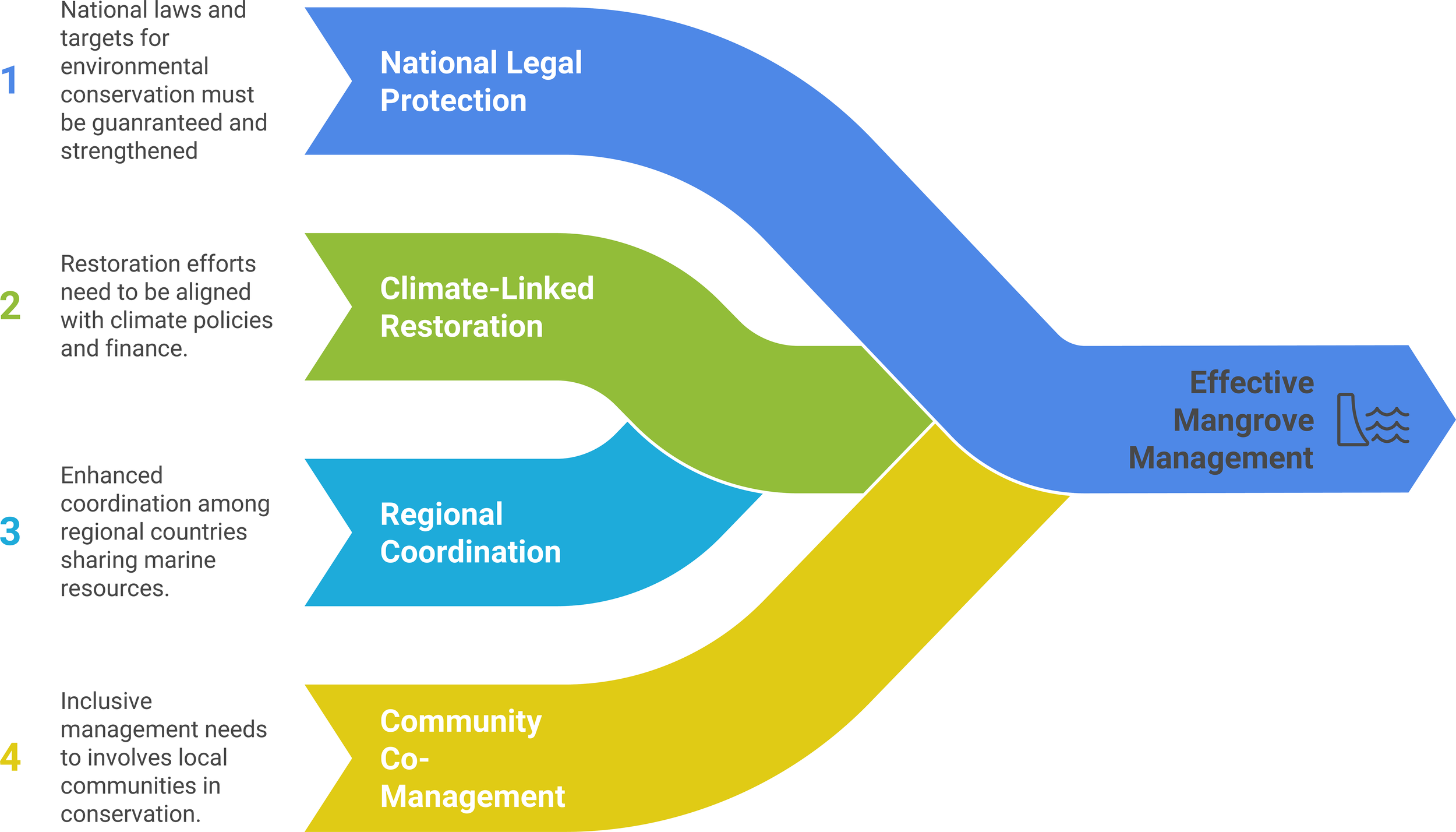
Governance levers converging on effective mangrove management in the Middle East. Braided schematic showing four strands: (1) National legal protection (statutes, protected areas, environmental impact assessment (EIA) enforcement); (2) Climate-linked restoration (targets aligned with NDCs, MRV, carbon finance); (3) Regional coordination (ROPME/PERSGA standards, data-sharing, compliance); and (4) Community co-management (local participation, livelihood alignment). Concurrent progress on all four strengthens outcomes; strands map to section 3.4.1–3.4.3 and the instruments summarized in Table 6.
3.4.1 National legislation and protected-area coverage
Across the Middle East, statutory instruments now encompass nearly all mangrove stands. Iran pioneered protection in 1972, later designating the ~270 km² Hara forests on Qeshm Island as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve and Ramsar Wetland (UNESCO, 2024). Bahrain followed with decrees that converted Tubli Bay’s last mangroves into a Ramsar reserve overseen by the Supreme Council for Environment (Supreme Council for Environment [SCE], 2024). UAE Federal Law 24 (1999) bans clearance, while emirate-level rules mandate mitigation, underpinning Abu Dhabi’s Eastern Mangrove National Park and sister reserves in Sharjah and Umm al-Quwain (United Arab Emirates, 1999). Saudi Arabia’s 2020 reforms classify mangroves as habitats of high environmental importance, obliging dedicated management plans under the regulation for the sustainable management of the marine and coastal environment (Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture [MEWA], 2020). Oman, Qatar, and Kuwait invoke comparable statutes and biodiversity plans, facilitating reserves and pilot replanting along Kuwait Bay (Loughland et al., 2020). Collectively, these laws confirm that mangroves are treated as critical natural capital.
Most Gulf states have embedded mangrove targets into their climate and biodiversity strategies. Bahrain’s plan links planting to ecotourism11; Saudi Vision 2030 pledges 30% protected-area coverage, including extensive groves (Saudi Green Initiative, 2025), and the UAE’s 2021 pledge elevates blue-carbon habitats within its mitigation portfolio (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021). Oman’s JICA-supported programs and Qatar’s biodiversity strategy demonstrate these ambitions, although conflict hampers implementation in Yemen (Conflict and Environment Observatory [CEOBS], 2021). Such policies crystallize a regional consensus that mangroves simultaneously advance carbon commitment and coastal resilience.
However, enforcement remains uneven. Governance is split among environment ministries, municipalities, fisheries bodies, and port authorities, producing gaps documented as by Yap and Al-Mutairi (2025). Coastal development still encroaches on protected forests in Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Iran, often without adequate environmental safeguards. Weak EIA compliance, scant public data, and rarely applied penalties permit sewage discharge, land reclamation, and even road construction within reserves such as Iran’s Dayyer wetland12 (Kabiri and Abedi, 2025). Savari et al. (2022) concluded that in Iran, although every state now possesses a legal foundation for mangrove conservation, but effectiveness still hinges on political will, inter-agency coordination, and credible monitoring, without which the discord between law and practice will persist.
3.4.2 Restoration and offset programs
Heightened recognition of mangroves as keystones for climate mitigation and coastal defense has precipitated a wave of large-scale restoration across the Gulf, transforming once sporadic planting into nationally branded programs tied to carbon targets (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021).
Oman exemplifies this new ambition, where the 10 million trees initiative has already placed 1.5 million seedlings on former tidal flats13. In comparison, the Oman blue carbon project pledges 100 million additional trees, projected to sequester 14 Mt CO2 and yield US$150 million in credits14. Saudi Arabia embeds mangroves within its Saudi Green Initiative, wherein government and Saudi Aramco plantings have exceeded 2 million seedlings and restored creek hydrology from Yanbu to Tarut Bay, complemented by a Red Sea Global pledge of 50 million by 2030 (Red Sea Global, 2023). The UAE, building on five decades of afforestation, committed at COP26 to plant 100 million new trees by 2030, wherein drone dispersal over Al Dhafra has accelerated delivery, bolstering a stock already capturing approximately 115 kt CO2 yr-¹ (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021).
Smaller states are following this trend. Qatar has integrated goals of planting 1 million seedlings by 2022 and 10 million by 2030 into its climate plans, with school and corporate volunteers expanding cover along the northeastern coast (Ataullah, 2024). Kuwait’s Environment Public Authority has trialed A. marina plantings under new protective regulations (Loughland et al., 2020), whereas Iran has extended mangroves across ~0.86 km² of new mudflat in Hormozgan. Even Iraq, which is historically mangrove-free, is cultivating four million seedlings for Basra’s tidal flats to counter salinity intrusion without freshwater irrigation15. Regional coordination is emerging through the Gulf Blue Carbon Network, which has attracted US$300 million for joint restoration and sequestration projects (Abdelraouf and Al Majed, 2025).
These programs are increasingly monetized through blue carbon finance. Bahrain plans to quadruple its coverage to 3.6 million trees by 2035, positioning the credits within its 2060 net-zero pathway16. Saudi Arabia’s voluntary GHG credit and offsetting scheme similarly targets mangrove projects as dual suppliers and purchasers of credits. The UAE’s pioneering blue carbon demonstration project underpinned its mangrove breakthrough agenda for COP28, while Oman’s initiative is explicitly structured around credit revenue (Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE], 2021).
However, experts caution that offsets must complement, not replace, the protection of old-growth stands whose carbon debt is irreplaceable (Pendleton et al., 2012). Early evidence of stabilizing or expanding cover in the UAE and Qatar is encouraging (Rondon et al., 2023). Nevertheless, long-term success hinges on rigorous site selection, survival monitoring, and transparent verification of carbon gains. Collectively, these initiatives mark a decisive regional shift from 20th-century neglect to 21st-century strategic investment, positioning mangroves as an indispensable natural infrastructure for a warming, urbanizing Middle East.
3.4.3 Multi-level and transboundary governance
The governance of ME mangroves increasingly hinges on collaboration that transcends administrative boundaries; however, existing regional mechanisms remain embryonic. ROPME, created under the 1978 Kuwait Convention, assembles all eight Gulf states to harmonize coastal zone standards and lists mangroves as critical habitat (ROPME, 2013). PERSGA, formed by the 1982 Jeddah Convention, fulfils a parallel role for the Red Sea–Gulf of Aden, issuing technical guidelines and status reports on sustainable mangrove management (PERSGA/GEF, 2004). However, recent assessments condemn the weak regulatory and enforcement capacities of these bodies; the voluntary Green Gulf Pact 2025 likewise lacks compliance teeth (Abdelraouf and Al Majed, 2025). Geopolitical tensions around the Strait of Hormuz and the southern Red Sea further stall data exchange and joint monitoring, leaving ecologically contiguous forests without robust supranational oversight (Aman, 2021).
Recognizing these deficits, scholars and policymakers now advocate purpose-built networks that insulate science from politics and pool resources for restoration (Yap and Al-Mutairi, 2025). The Gulf Blue Carbon Network, launched by Qatar and the UAE in 2024, mobilizes US$300 million for regional research, finance, and restoration, while GCC environment ministers increasingly align national visions, such as Saudi Vision 2030, the UAE Green Agenda, and Qatar’s Climate Action Plan, under shared objectives (Abdelraouf and Al Majed, 2025). Such initiatives could standardize methodologies, reduce duplication, and forge a unified response to transboundary threats.
Vertical integration is also critical. Historically, top-down mangrove policy only recently began incorporating local knowledge: Iranian pilots engage coastal villagers in phenological monitoring, and youth groups in Saudi Arabia and the UAE join mass plantings, though mainly episodically. Reviews warn that community co-management remains underdeveloped across the region, contributing to low post-planting survival once project funding ends (Yap and Al-Mutairi, 2025). Encouraging counterexamples have emerged. In Bahrain, the UN-Habitat–HSBC rehabilitation of Manama’s coast embeds boardwalks and visitor centers to cultivate urban stewardship (Al-Shaeel, 2023), whereas Oman’s FAO-supported programs enlist fisherfolk so that restoration aligns with nursery-ground protection of the target species (Haddad, 2024). These cases illustrate that inclusive governance can couple ecological gains with durable stewardship.
Hence, ME mangrove governance is shifting from isolated national mandates toward multi-layered cooperation, although the scaffolding of a cohesive regime is still under construction. Consolidating transboundary agreements, bolstering ROPME and PERSGA enforcement, and institutionalizing community-state co-management are imperative to bridge lingering policy gaps and secure mangroves that buffer coasts, sequester carbon, and underpin regional socio-ecological resilience.
3.5 Implications, limitations, and future scope
3.5.1 Implications for policy, management, and accounting
Taken together, the evidence assembled in this review requires a recalibration of expectations about what arid-zone mangroves can deliver and how they should be governed. Per-hectare carbon burial, standing biomass, and wood increment are consistently lower than in humid tropical analogues, yet the permanence of stored carbon is high where disturbance is avoided. Mitigation strategies should therefore be framed around the primacy of avoided loss of existing stocks and the use of region-specific emission factors and sequestration rates in MRV protocols that clearly separate organic from inorganic carbonate pools. Planting pledges, while politically salient, are most credible when cast as adaptation-led projects whose climate benefits accrue slowly and are measured conservatively.
Management triage should be guided by three first-order filters that recur throughout the record: freshwater availability, including groundwater seepage, accommodation space for landward migration, and tidal flushing. Sites with one or more of these attributes consistently sustain taller canopies, higher recruitment, and greater functional capacity. Conversely, exposed open coasts with a mean significant wave height above ~1.4 m, enclosed sabkhas lacking seepage, or shorelines pinned by infrastructure should not be prioritized for afforestation; in such settings, retreat corridors and risk-reduction measures are more appropriate than tree-planting targets. Where restoration is justified, designs must follow the hydro-geomorphic template: stress-matched local propagules, sheltered leeward micro-basins and channel margins, and, where supported by diagnostics, sediment augmentation, micro-topographic contouring, or flushing improvements. Temporary establishment irrigation can be considered in strictly controlled pilots that safeguard water quality. Rhizophora plantings should be confined to verified, well-flushed southern pockets; elsewhere A. marina remains the only viable tree.
Institutional implications are equally clear. Most states have enacted protective statutes, but the binding constraint is uneven enforcement and coordination. Routine EIA compliance for reclamation and dredging must be tightened; oil-spill contingency planning requires creek-specific protocols and exercises; dust and sand encroachment demand physical management where mangroves abut active dune fields; and early-warning indicators, pore-water salinity, surface-elevation change, and canopy temperature, should be embedded in management plans with pre-agreed response thresholds.
Regionally, the roles of organizations such as ROPME and PERSGA should move from guidance to standard-setting with compliance audits, supported by a shared data infrastructure insulated, as far as possible, from geopolitical volatility. Durable ecological outcomes will also depend on co-management. Channeling finance and decision rights to local custodians, such as fishers, women’s groups, herders, pairing urban amenities with stewardship obligations, and making substantive participation a condition for public and private investment. Finally, in carbon accounting and markets, the arid-zone profile, lower fluxes but high permanence, argues for conservative baselines, explicit uncertainty bounds, and long-horizon verification. Where credits are issued, a material share should be ring-fenced for operation and maintenance, spill readiness, and community participation rather than seedling counts alone.
3.5.2 Limitations
The synthesis is constrained by several limitations that qualify inference and generalization. First, evidence heterogeneity is substantial. Methods, reporting units, and spatial scales vary across studies, precluding a formal meta-analysis and requiring narrative synthesis. Second, sampling and language biases persist; the corpus is densest for GCC states and thinnest for conflict-affected coasts, and most non-English sources could not be systematically incorporated. Third, several claims in the governance and MRV domains in our review draw on grey literature and program documents whose implementation and performance remain in flux. Fourth, attribution of process, particularly for thresholds linking accretion to SLR, or heat and salinity to die-back, remains site-contingent in the absence of long-term monitoring. Finally, the conceptual figures advanced here are synthesis frameworks, not mechanistic models. They have been deliberately simplified to demonstrate the spatial heterogeneity and must not substitute for site-level diagnostics. While we conducted comprehensive, multi-database searches with documented criteria, the dynamic indexing of databases and grey-literature discoverability means inadvertent omissions are possible, a limitation we acknowledge and for which we welcome pointers to pertinent sources for future updates. These constraints highlight the need for standardized monitoring, open data, and cross-country comparability before region-wide generalizations can be considered predictive.
3.5.3 Future research and implementation agenda
A forward program emerges directly from these gaps, as discussed below.
First, the region would benefit from a sentinel observatory network spanning the Gulf, Red Sea, and Oman Sea, with harmonized protocols for surface-elevation table–marker horizon measurements, continuous water-level and pore-water salinity logging, groundwater tracers, and wave-energy sensors. Coupling these with eddy-covariance for year-round CO2 and CH4 fluxes would close the greenhouse-gas balance and sharpen arid-zone MRV. Parallel work should quantify sediment budgets, including carbonate versus terrigenous fractions, dust deposition, and lagoon residence times, all of which condition accretion potential.
Second, experimental research should resolve collapse thresholds and recovery windows through salinity–temperature mesocosms and in situ warming manipulations using local A. marina lineages. Genomic and common-garden studies are needed to distinguish local adaptation from plasticity, to evaluate the feasibility and risks of assisted gene flow, and to clarify the functional role of microbiomes, such as diazotrophs, halotolerant consortia, in nutrient acquisition. Managed aquifer recharge, freshwater pulse supplementation, and flushing or channel restoration should be tested in carefully designed pilots to quantify ecological gains and side effects.
Third, restoration science should move beyond seedling counts to comparative trials of sediment augmentation, reef-flat conservation, and living breakwaters, and micro-topographic designs suited to micro- to meso-tidal regimes. At the same time, the region requires comprehensive oil-spill vulnerability mapping of mangrove creeks and low-impact response protocols that are exercised regularly. Decision tools that operationalize the resilience–threat typology by linking measurable indicators to triage, protection, or replication actions would translate science into planning practice.
Fourth, socio-economic research remains underdeveloped. Systematic valuation and distributional analyses, including gender-disaggregated outcomes and the livelihood effects of restoration, are necessary to align equity with ecological goals. Co-management experiments with clear property or usage rights, shared revenue from tourism or carbon credits, and participatory MRV should be rigorously evaluated. These efforts would be accelerated by a regional open-data commons, curated by organizations such as ROPME and PERSGA with academic partners, hosting maps, monitoring streams, and restoration performance, and by an annual state-of-mangroves report with transparent compliance scoring.
Finally, accounting and markets should develop arid-zone emission factors and uncertainty frameworks for IPCC-compliant inventories that explicitly separate organic carbon from inorganic carbon, incorporate disturbance emissions, and quantify permanence risk. Results-based finance that pays for verified survival and function, elevation gain, salinity moderation, nursery use, rather than inputs alone, would better align incentives with long-term ecosystem performance.
Drawing these strands together, we propose a five-pillar, action-oriented agenda, regional satellite-based monitoring, experimental research, stress-matched restoration science, socio-economic and equity research, and MRV-linked carbon accounting, that is specific to arid ME coasts as shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10
The research and practice agenda to realize the mangrove resilience in the Middle East. This five-pillar approach entails a monitoring network across a region; experiments measuring survival thresholds to thermal/salinity stress; restoration science restoring natural refugia (space, sediment, seepage) with effective survival monitoring; socioeconomic studies on co-management and livelihoods outcomes; MRV-linked carbon accounting and carbon markets supported with region-specific parameters and nested in national climate-change commitments.
Hence, ME mangroves are small, stressed, and disproportionately valuable. Treating them as desert-edge laboratories rather than tropical archetypes changes the management calculus, which can be summed up as, protect freshwater-mediated refugia, create room to move, engineer within geomorphic limits, finance stewardship, not only seedlings, and measure what matters over decades. With that reframing, and with a shared, regionally grounded evidence base, the region can secure these forests for adaptation first, while realizing credible, mitigation co-benefits.
4 Conclusions
ME mangroves are biological anomalies that are causing a recalibration of world assumptions. Combining eco-biophysical data with socio-economic and governance models across the Gulf to Red Sea and adjacent coasts, we demonstrate that such systems will continue to operate within the fringe of mangrove tolerance and hence may need regionally distinct performance, risk, and management expectations.
First, abiotic controls range together to limit distribution and structure in four aspects: freshwater supply, hypersalinity, extreme temperature, and protective geomorphology. Where osmotic and wave stress are reduced by freshwater seepage, tidal channels, or reef-sheltered bays, stands endure; where mean significant wave height and micro/mesotidal flushing are adverse, stands are deprived or severely stunted. In line with this, ME A. marina occurs as typified by being dwarf, slow-growing, and strongly underground-biased in its allocation. Nutrient-poor, carbonate-dominated substrates and short inundation periods constrain productivity and encourage tight internal cycling. Biogeochemically, stocks and burial rates of organic carbon are far below humid-tropical standards, and methane fluxes remain low; hot soils driven to bursts of aeration drive efflux of CO2. Such characteristics validate survival in chronic stress and not most biomass accumulation.
Second, climate risks operate through the SLR exceeding normal rates of accretion offset, a paucity of accommodation space leading to coastal squeeze, and increasing extreme events of heat and salinity stress approaching physiological limits. The sets of disturbances are still mixed: infrequent cyclones, dust burial causes damage to existing colonization; oiling and chronic pollution are long-term losses. Many Gulf stands are not likely to track the 21st-century change without proactive corridors of landward migration and conservation of groundwater-fed refugia.
Third, even when of small extent, these forests provide disproportionate returns of socio-economic benefits, such as nursery habitat, shoreline stabilization, blue-carbon stability in soils untouched by human interference, and cultural facilities in treeless coasts. There is more governance (legal security, national goals, rehabilitation commitments, new carbon finance), but implementation and coordination are variable, and the role of communities is unresolved. The implication of applying global averages to blue-carbon accounting, in this case, is the risk of over-claiming; avoidance of losses of existing blue-carbon stocks is likely to be a key credible mitigation factor, but arid zone factors will need to be applied.
Fourth, there is a synthesis of management doctrine. A resilience-threat typology should guide site-specific approach which includes (i) protect and replicate characteristics of naturally resilient sites (migration space, sufficient sediment, periodic flushing, freshwater influence), (ii) mitigate local stressors and ensure retreat corridors where threats are most severe, (iii) construct stress-matched restoration that is derived from refugia, such as sediment, seepage, and shelter, not generic planting, and (iv) incorporate MRV that is resilient such that mitigation approaches are arguably defensible and compared across jurisdiction.
In practical terms, for Middle Eastern ministries, we recommend prioritizing sites that meet at least one of three criteria: freshwater/groundwater influence, accommodation space for landward retreat, and tidal flushing, while avoiding open coasts where mean Hs ≳ 1.4 m. Restoration should default to locally sourced A. marina (with Rhizophora mucronata limited to verified, well-flushed southern pockets), be designed with micro-topographic contouring and sediment augmentation where diagnostics support it, and be governed by tightened EIA enforcement, creek-level spill preparedness, and arid-zone MRV that separates OC from IC and emphasizes avoided loss, coordinated through strengthened ROPME/PERSGA mechanisms and inclusive co-management.
Beyond these immediate policy steps, several evidence gaps and coordination needs remain that require a regional research and monitoring agenda. Observations of groundwater salinity dynamics, sediment budgets, vertical land motion, whole-system carbon fluxes, and demographic processes, made locally and over long timescales, are rare. There are few assessments of socio-economic conditions or equity outcomes. A pragmatic research and practice agenda would thus include a regional satellite-based monitoring network; experimental research to establish thermal/salinity thresholds and genotype performance; restoration science to test refugia-mimicking designs using survival and growth benchmarks; rigorous MRV-linked carbon accounting calibrated to arid environments; and ongoing community co-management whereby ecological gains are coupled with livelihoods. Enhanced cross-boundary collaboration (ROPME/PERSGA and consortium networks) will be needed to harmonize approaches, exchange information, and coordinate investments.
To conclude, the mangroves situated in the Middle East are tiny, stressed, and dispersed, but of strategic value. Setting the expectations to align with their realities in the environment, modifying the expectations to align and protect their freshwater oases, creating breathing space, minimizing local demands, and investing in stress-tolerant, verified forms of restoration is the best way forward to keep them at perceived coast and climate, even in a world of accelerating change.
Statements
Author contributions
GM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MYA: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. TA: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AM: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SS: Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SK: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. MA: Writing – review & editing. MB: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work in this paper was supported by the Open Access Program from the American University of Sharjah. This paper represents the opinions of the author(s) and does not mean to represent the position or opinions of the American University of Sharjah. Additionally, the work in this paper was supported by the Postdoctoral Fellowship Award (PDFA25-S57) grant from the American University of Sharjah.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the two reviewers and the editorial team for their thoughtful comments and suggestions, which have significantly improved the manuscript. We are also grateful to all researchers whose work is cited here. Their datasets, case studies, and conceptual advances provide the basis for this comprehensive review. Every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the many numerical values, figures, and technical details reported. However, any remaining inaccuracies or omissions are entirely unintentional, and all specific data and interpretations should be checked against the original sources before being used to inform policy, management decisions, or operational applications. The authors would welcome being informed of any corrections so that they can be addressed in future work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. During the preparation of this work the author used AI service (PaperPal) only in order to correct grammar and expression errors. After using this service, the author reviewed and edited the content as needed and takes full responsibility for content of the publication.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1.^https://www.reuters.com/business/environment/iraq-plants-mangrove-forest-fight-climate-disaster-2023-06-29/
2.^https://www.fao.org/neareast/news/blog/blog-details/greening-agriculture--water-scarcity-and-climate-action/2024/07/25/leading-the-way--gulf-countries'-efforts-in-mangrove-restoration/
3.^https://gefblueforests.org/2018/01/19/mangrove-restoration-paying-dividends-in-oman
4.^https://www.fao.org/neareast/news/blog/blog-details/greening-agriculture--water-scarcity-and-climate-action/2024/07/25/leading-the-way--gulf-countries%27-efforts-in-mangrove-restoration/en
5.^https://www.reuters.com/business/environment/wider-image-with-fuel-scarce-yemens-forests-are-next-casualty-war-2021-08-11/
6.^https://thepeninsulaqatar.com/article/06/01/2025/moecc-educates-students-on-importance-of-mangrove-trees
7.^https://www.emiratesnaturewwf.ae/en/blogs/14-unveiling-the-economic-value-of-ecosystem-services-in-the-uaes-coastal-lagoons-a-focus-on-ecotourism
8.^https://gefblueforests.org/2018/01/19/mangrove-restoration-paying-dividends-in-oman
9.^https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/513935/Soheili-village-a-model-of-sustainable-tourism-in-southern-Iran
10.^https://www.gulf-times.com/article/702542/qatar/mangrove-planting-on-qetaifan-island-north
11.^https://www.bna.bh/en/news?cms=q8FmFJgiscL2fwIzON1%2BDiNgl4a6IJjroX8TzgLSze0%3D
12.^https://www.tehrantimes.com/news/499412/Mangrove-the-wonder-of-marine-habitats
13.^https://www.muscatdaily.com/2022/07/24/ea-to-plant-1-5mn-mangrove-seeds-in-al-wusta/
14.^https://carboncredits.com/omans-mangrove-restoration-could-generate-150-million-in-carbon-credits/
15.^https://www.middleeastmonitor.com/20230629-iraq-plants-mangrove-forest-to-fight-climate-disaster/
16.^https://www.newsofbahrain.com/bahrain/116265.html
References
1
Abdelraouf M. Al Majed Y. (2025). Recent GCC joint environmental initiatives. GRC Commentary & Analysis ( Gulf Research Center). Available online at: https://www.grc.net/documents/681ca6efe596dRecentGCCJointEnvironmentalInitiatives.pdf (Accessed June 25, 2025).
2
AboEl-Nil M. M. (2001). Growth and establishment of mangrove (Avicennia marina) on the coastlines of Kuwait. Wetl. Ecol. Manage.9, 421–428. doi: 10.1023/A:1012098525918
3
Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative (AGEDI) (2013). Blue Carbon in Abu Dhabi – Protecting our Coastal Heritage: The Abu Dhabi Blue Carbon Demonstration Project. Available online at: https://gridarendal-website-live.s3.amazonaws.com/production/documents/:s_document/43/original/BC_Demo_Final_Report_RB_Final_Web_17.04.14.pdf?1483646352 (Accessed May 15, 2025).
4
Abu Dhabi Global Environmental Data Initiative (AGEDI) (2014). Baseline assessment report: Coastal ecosystem carbon stocks (Abu Dhabi Blue Carbon Demonstration Project) ( AGEDI). Available online at: https://gefblueforests.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/AD-BC-Final-Baseline-Carbon-Assessment-Report-2014-External-2-FD.pdf (Accessed May 20, 2025).
5
Ahmed E.-K. A. Abdel-Hamid A. (2007). Zonation Pattern of Avicennia marina and Rhizophora mucronata along the Red Sea Coast, Egypt. World Applied Sciences Journal2 (4), 283-288.
6
Ahmed S. Kamruzzaman Rahman S. Sakib N. Azad S. Dey T. (2022). Stand structure and carbon storage of a young mangrove plantation forest in coastal area of Bangladesh: The promise of a natural solution. Nat.-Based Solut.2, 100025. doi: 10.1016/j.nbsj.2022.100025
7
Al-Afifi Z. M. M. (2018). The conservation, sustainable use and management of mangrove habitats in Oman ( University of York). Available online at: https://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/id/eprint/23437/ (Accessed July 21, 2025).
8
Al-Afifi Z. Raffaelli D. Stewart B. (2024). Public perception of the benefits of mangroves in qurayyat, Oman: implications for their sustainable utilisation and management. Adv. Ecol. Environ. Res.9, 33–52. https://www.ss-pub.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/AEER2024032501.pdf.
9
Al-Ansari E. M. A. S. Husrevoglu Y. S. Yigiterhan O. Youssef N. Al-Maslamani I. A. Abdel-Moati M. A. et al . (2022). Seasonal variability of hydrography off the east coast of Qatar, central Arabian Gulf. Arab. J. Geosci.15, 1659. doi: 10.1007/s12517-022-10927-4
10
Alharbi T. (2019). A phylogenetic assessment of the affinities of the farasan islands flora. Available online at: https://centaur.reading.ac.uk/93923/1/22826085_Alharbi_Thesis.pdf (Accessed July 24, 2025).
11
Al-Hurban A. E. (2014). Effects of recent anthropogenic activities on the surface deposits of Kuwait. Arab. J. Geosci.7, 665–691. doi: 10.1007/s12517-013-0866-9
12
Aljenaid S. Abido M. Redha G. K. AlKhuzaei M. Marsan Y. Khamis A. Q. et al . (2022). Assessing the spatiotemporal changes, associated carbon stock, and potential emissions of mangroves in Bahrain using GIS and remote sensing data. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci.52, 102282. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2022.102282
13
Al Jufaili S. M. Jawad L. A. Park J. M. Al Sariri T. S. Al Balushi B. Y. (2021). Fish diversity of mangrove ecosystems in Sultanate of Oman. Cah. Biol. Mar. (2021) 62, 235–249. doi: 10.21411/CBM.A.BEB6B7E7
14
Al-Khayat J. Balakrishnan P. (2014). Avicennia marina around Qatar: tree, seedling and pneumatophore densities in natural and planted mangroves using remote sensing. Int. J. Sci.3, 18–27. Available online at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2573637.
15
Al-Khayat J. A. Giraldes B. W. (2020). Burrowing crabs in arid mangrove forests on the southwestern Arabian Gulf: Ecological and biogeographical considerations. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci.39, 101416. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101416
16
Al-Khayat J. A. Jones D. A. (1999). A comparison of the macrofauna of natural and replanted mangroves in Qatar. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci.49, 55–63. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(99)80009-2
17
Almahasheer H. (2018). Spatial coverage of mangrove communities in the Arabian Gulf. Environ. Monit. Assess.190, 85. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6472-2
18
Almahasheer H. (2019). High levels of heavy metals in Western Arabian Gulf mangrove soils. Mol. Biol. Rep.46, 1585–1592. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-04603-2
19
Almahasheer H. (2021). Internodal analysis of avicennia marina in the western arabian gulf. Front. Mar. Sci.8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.698596
20
Almahasheer H. Al-Taisan W. Mohamed M. K. (2013). Mangrove deterioration in Tarut Bay on the eastern province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Pakhtunkhwa J. Life Sci.1, 49–59. http://www.awkum.edu.pk/PJLS/Downloads/01-Volume-2013/02-Issue-2013/01-PJLS%20001_0213_0513%20Hanan%20et%20al.pdf.
21
Almahasheer H. Duarte C. M. Irigoien X. (2018). Leaf nutrient resorption and export fluxes of avicennia marina in the central red sea area. Front. Mar. Sci.5. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00204
22
Almahasheer H. Serrano O. Duarte C. M. Arias-Ortiz A. Masque P. Irigoien X. (2017). Low Carbon sink capacity of Red Sea mangroves. Sci. Rep.7, 9700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10424-9
23
Al-Maslamani I. Walton M. E. M. Kennedy H. Le Vay L. (2012). Sources of primary production supporting food webs in an arid coastal embayment. Mar. Biol.159, 1753–1762. doi: 10.1007/s00227-012-1963-0
24
Al-Nadabi A. Sulaiman H. (2018). Carbon sink potential of avicennia marina in the al-qurm nature reserve, muscat, Oman. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci.151, 12003. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/151/1/012003
25
Al-Nadabi A. S. Sulaiman H. (2021). Carbon sequestration service of a ramsar site: A conservation-role model for defying developmental pressure in the middle of a rapidly expanding city. Open J. For.11, 381–397. doi: 10.4236/ojf.2021.114023
26
Al-Shaeel F. (2023). ( UNESCO). Available online at: https://en.unesco.org/silkroad/silk-road-themes/biosphere-reserve/hara (Accessed June 30, 2025).
27
Alsharhan A. S. Kendall C. G. (2019). “ Interpretations of holocene carbonate-evaporites of coastal and inland sabkhas of abu dhabi (United arab emirates) from landsat satellite images and field survey,” in Sabkha ecosystems. Eds. GulB.BöerB.KhanM. A.Clüsener-GodtM.HameedA. ( Springer International Publishing, Cham), 151–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-04417-6_11
28
Al-Subhi A. M. Abdulla C. P. (2021). Sea-level variability in the arabian gulf in comparison with global oceans. Remote Sens.13, 4524. doi: 10.3390/rs13224524
29
Alsumaiti T. (2014). Structure, Aboveground Biomass, and Soil Characterization of Avicennia marina in Eastern Mangrove Lagoon National Park, Abu Dhabi (Fayetteville: University of Arkansas). Available online at: https://scholarworks.uark.edu/etd/2120 (Accessed June 25, 2025).
30
Alsumaiti T. S. Tullis J. A. Xue B. (2019). LIDAR-derived biomass and height inventory of avicennia marina in eastern mangrove lagoon national park, Abu Dhabi. Int. J. Bus Appl. Soc. Sci.5, 137–152. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tareefa-Alsumaiti/publication/365161411_LIDAR-derived_Biomass_and_Height_Inventory_of_Avicennia_Marina_in_Eastern_Mangrove_Lagoon_National_Park_Abu_Dhabi/links/636789742f4bca7fd0399905/LIDAR-derived-Biomass-and-Height-Inventory-of-Avicennia-Marina-in-Eastern-Mangrove-Lagoon-National-Park-Abu-Dhabi.pdf .
31
Al-Tarshi M. Dobretsov S. Gallardo W. (2024). Marine litter and microplastic pollution in mangrove sediments in the Sea of Oman. Mar. pollut. Bull.201, 116132. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116132
32
Aman F. (2021). Finding common ground: Fostering environmental cooperation in the Persian Gulf ( Middle East Institute). Available online at: https://www.mei.edu/publications/finding-common-ground-fostering-environmental-cooperation-persian-gulf (Accessed July 31, 2025).
33
Anton A. Almahasheer H. Delgado A. Garcias-Bonet N. Carrillo-de-Albornoz P. Marbà N. et al . (2020). Stunted mangrove trees in the oligotrophic central red sea relate to nitrogen limitation. Front. Mar. Sci.7. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00597
34
Ataullah S. (2024). Mangrove green belt project enhances Plant Ten Million Tree initiative: MoECC official ( The Peninsula Qatar). Available online at: https://thepeninsulaQatar.com/article/01/07/2024/mangrove (Accessed July 31, 2025).
35
Banan-Dallalian M. Shokatian-Beiragh M. Golshani A. Mojtahedi A. Lotfollahi-Yaghin M. A. Akib S. (2021). Study of the effect of an environmentally friendly flood risk reduction approach on the Oman coastlines during the gonu tropical cyclone (Case study: the coastline of sur). Eng2, 141–155. doi: 10.3390/eng2020010
36
Barth H.-J. Khan N. Y. (2008). “ Biogeophysical setting of the gulf,” in Protecting the gulf’s marine ecosystems from pollution. Eds. AbuzinadaA. H.BarthH.-J.KruppF.BöerB.Al AbdessalaamT. Z. ( Birkhäuser Basel, Basel), 1–21. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7643-7947-6_1
37
Blount C. Fritz H. M. Albusaidi F. B. Al-Harthy A. H. (2008). Storm surge hazard in Oman based on cyclone gonu and historic events. Available online at: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2008AGUFM.A53E0327B (Accessed August 13, 2025).
38
Breavington J. Steckbauer A. Fu C. Ennasri M. Duarte C. M. (2025). Dynamics of CO2 and CH4 fluxes in Red Sea mangrove soils. Biogeosciences22, 117–134. doi: 10.5194/bg-22-117-2025
39
Breithaupt J. L. Smoak J. M. Smith T. J. Sanders C. J. Hoare A. (2012). Organic carbon burial rates in mangrove sediments: Strengthening the global budget. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles26, 2012GB004375. doi: 10.1029/2012GB004375
40
Bunting P. Rosenqvist A. Hilarides L. Lucas R. M. Thomas N. (2022). Global mangrove watch: updated 2010 mangrove forest extent (v2.5). Remote Sens.14, 1034. doi: 10.3390/rs14041034
41
Burns K. A. Garrity S. D. Levings S. C. (1993). How many years until mangrove ecosystems recover from catastrophic oil spills? Mar. pollut. Bull.26, 239–248. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(93)90062-O
42
Cabahug D. M. Bansal A. K. Gogate M. G. (2006). Technical manual for restoration of mangroves-OFSDS ( Orissa Forestry Sector Development Society). Available online at: http://ofsds.in/Publication/TechnicalManualMangrove.pdf (Accessed May 25, 2025).
43
Carpenter S. Evans C. Pittman S. J. Antonopoulou M. Bejarano I. Das H. S. et al . (2023). Multi-habitat carbon stock assessments to inform nature-based solutions for coastal seascapes in arid regions. Front. Mar. Sci.10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1239904
44
Cavanaugh K. C. Kellner J. R. Forde A. J. Gruner D. S. Parker J. D. Rodriguez W. et al . (2014). Poleward expansion of mangroves is a threshold response to decreased frequency of extreme cold events. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.111, 723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315800111
45
Chatting M. Al-Maslamani I. Walton M. Skov M. W. Kennedy H. Husrevoglu Y. S. et al . (2022). Future mangrove carbon storage under climate change and deforestation. Front. Mar. Sci.9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.781876
46
Church J. A. White N. J. (2011). Sea-level rise from the late 19th to the early 21st century. Surv. Geophys.32, 585–602. doi: 10.1007/s10712-011-9119-1
47
Conflict and Environment Observatory [CEOBS] (2021). Protected area conservation in Yemen’s conflict ( Conflict and Environmental Observatory). Available online at: https://ceobs.org/protected-area-conservation-in-yemens-conflict/ (Accessed May 25, 2025).
48
Decker V. Falkenroth M. Lindauer S. Landgraf J. Al-Lawati Z. Al-Rahbi H. et al . (2021). Collapse of Holocene mangrove ecosystems along the coastline of Oman. Quat. Res.100, 52–76. doi: 10.1017/qua.2020.96
49
Dhawi F. (2025). Mastering resilience: Avicennia marina’s survival in hypersaline arid zones. Front. Sustain. Food Syst.9. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1598548
50
Donato D. C. Kauffman J. B. Murdiyarso D. Kurnianto S. Stidham M. Kanninen M. (2011). Mangroves among the most carbon-rich forests in the tropics. Nat. Geosci.4, 293–297. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1123
51
Duke N. C. (2016). Oil spill impacts on mangroves: Recommendations for operational planning and action based on a global review. Mar. pollut. Bull.109, 700–715. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.082
52
Erftemeijer P. L. A. Agastian T. Yamamoto H. Cambridge M. L. Hoekstra R. Toms G. et al . (2020). Mangrove planting on dredged material: three decades of nature-based coastal defence along a causeway in the Arabian Gulf. Mar. Freshw. Res.71, 1062. doi: 10.1071/MF19289
53
Fakhrzadegan I. Hassanshahian M. Askari Hesni M. Saadatfar A. (2019). A study of crude oil-degrading bacteria from mangrove forests in the Persian Gulf. Mar. Ecol.40, e12544. doi: 10.1111/maec.12544
54
Fatimahsari T. K. Fitri S. G. S. Khastini R. O. (2014). “ Epiphytic cyanobacteria on Avicennia marina pneumatophore in mangrove ecosystem of Cagar Alam Pulau Dua (CAPD) Serang, Banten,” in International conference on research, implementation and education of mathematics and sciences (Depok, Indonesia: Yogyakarta State University). Available online at: https://www.academia.edu/download/103259350/B24-Tika_20Khusnul.pdf (Accessed May 18-20, 2014).
55
Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (2008). Irrigation in the middle east in figures: AQUASTAT survey 2008 (Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization). Available online at: https://www.fao.org/4/i0936e/i0936e02.pdf (Accessed April 25, 2025).
56
Fouda M. M. AI-Muharrami M. A. (1996). Significance of mangroves in the arid environment of the sultanate of Oman. J. Agric. Mar. Sci. JAMS1, 41. doi: 10.24200/jams.vol1iss0pp41-49
57
Friis G. Killilea M. E. (2024). “ Mangrove ecosystems of the United Arab Emirates,” in A natural history of the emirates. Ed. BurtJ. A. ( Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham), 217–240. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-37397-8_7
58
Gauthey A. Backes D. Balland J. Alam I. Maher D. T. Cernusak L. A. et al . (2022). The role of hydraulic failure in a massive mangrove die-off event. Front. Plant Sci.13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.822136
59
Ghandour I. M. Al-Zubieri A. G. Basaham A. S. Mannaa A. A. Al-Dubai T. A. Jones B. G. (2021). Mid-late holocene paleoenvironmental and sea level reconstruction on the al lith red sea coast, Saudi Arabia. Front. Mar. Sci.8. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.677010
60
Ghasemi S. Mola N. Zakaria M. (2013). Aboveground biomass, litterfall, and forest structure in the mangroves of hormozgan province, Iran. Nat. Areas J.33, 339–343. doi: 10.3375/043.033.0312
61
Ghasemi S. Siavash Moghaddam S. Rahimi A. Damalas C. A. Naji A. (2018). Phytomanagement of trace metals in mangrove sediments of Hormozgan, Iran, using gray mangrove (Avicennia marina). Environ. Sci. pollut. Res.25, 28195–28205. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2684-9
62
Guo D. Zhan P. Ma J. Vasou P. Krokos G. Alghamdi H. et al . (2024). Seasonal variation and fundamental characteristics of baroclinic tides in the Arabian Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci.11. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2024.1475593
63
Haddad F. (2024). Leading the way: Gulf countries’ efforts in mangrove restoration ( Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Regional Office for Near East and North Africa). Available online at: https://www.fao.org/neareast/news/blog/blog-details/greening-agriculture–water-scarcity-and-climate-action/2024/07/25/leading-the-way–gulf-countries’-efforts-in-mangrove-restoration/en (Accessed July 31, 2025).
64
Haseeba K. P. Aboobacker V. M. Vethamony P. Al-Khayat J. A. (2025a). Significance of avicennia marina in the arabian gulf environment: A review. Wetlands45, 16. doi: 10.1007/s13157-025-01899-8
65
Haseeba K. P. Aboobacker V. M. Vethamony P. Al-Khayat J. A. (2025b). Water and sediment characteristics in the Avicennia marina environment of the Arabian Gulf: A review. Mar. pollut. Bull.216, 117963. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2025.117963
66
Hassanshahian M. Amirinejad N. Askarinejad Behzadi M. (2020). Crude oil pollution and biodegradation at the Persian Gulf: A comprehensive and review study. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng.18, 1415–1435. doi: 10.1007/s40201-020-00557-x
67
Hegazy A. K. (1998). Perspectives on survival, phenology, litter fall and decomposition, and caloric content ofAvicennia marinain the Arabian Gulf region. J. Arid Environ.40, 417–429. doi: 10.1006/jare.1998.0457
68
Hoorn C. Cremaschi M. (2004). Late Holocene palaeoenvironmental history of Khawr Rawri and Khawr Al Balid (Dhofar, Sultanate of Oman). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol.213, 1–36. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2004.03.014
69
Hoseini S. M. Soltanpour M. (2021). Tide characteristics and tidal wave propagation in the Persian Gulf. Ocean Sci. Discuss. [preprint]. doi: 10.5194/os-2021-98
70
Hu T. Zhang Y. Su Y. Zheng Y. Lin G. Guo Q. (2020). Mapping the global mangrove forest aboveground biomass using multisource remote sensing data. Remote Sens.12, 1690. doi: 10.3390/rs12101690
71
Hughes P. Hunter J. R. (1979). A proposal for a physical oceanography program and numerical modeling of the KAP region (Paris: UNESCO).
72
Hunter J. R. (1983). “ Aspects of the dynamics of the residual circulation of the arabian gulf,” in Coastal oceanography. Eds. GadeH. G.EdwardsA.SvendsenH. ( Springer US, Boston, MA), 31–42. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-6648-9_3
73
Inoue T. Kohzu A. Akaji Y. Miura S. Baba S. (2024). Diazotrophic nitrogen fixation through aerial roots occurs in Avicennia marina : implications for adaptation of mangrove plant growth to low-nitrogen tidal flats. New Phytol.241, 1464–1475. doi: 10.1111/nph.19442
74
Issa N. Vempatti S. (2018). Oil spills in the Arabian Gulf: A case study and environmental review. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res.8, 144–153. doi: 10.5539/enrr.v8n2p144
75
Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) (2004). Mangrove master plan study on restoration, conservation, and multipurpose use in the sultanate of Oman (Draft final report) (Oman: Oman Ministry of Regional Municipalities, Environment and Water Resources). Available online at: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/11780624_01.pdf (Accessed May 20, 2025).
76
Kabiri K. Abedi E. (2025). Rapid mangrove dieback in the northern Persian Gulf driven by anthropogenic activities and environmental stressors. Discover Environ.3, 22. doi: 10.1007/s44274-025-00207-9
77
Karimi A. Abtahi B. Kabiri K. (2025). Mapping and estimating blue carbon in mangrove forests using drone and field-based tree height data: A cost-effective tool for conservation and management. Forests16, 1196. doi: 10.3390/f16071196
78
Khalil A. S. M. (2015). “ Mangroves of the red sea,” in The red sea. Eds. RasulN. M. A.StewartI. C. F. ( Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg), 585–597. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-45201-1_33
79
Komiyama A. Ong J. E. Poungparn S. (2008). Allometry, biomass, and productivity of mangrove forests: A review. Aquat. Bot.89, 128–137. doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.12.006
80
Krauss K. W. Lovelock C. E. Chen L. Berger U. Ball M. C. Reef R. et al . (2022). Mangroves provide blue carbon ecological value at a low freshwater cost. Sci. Rep.12, 17636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21514-8
81
Krauss K. W. Osland M. J. (2019). Tropical cyclones and the organization of mangrove forests: a review. Ann. Bot.125 (2), 213–234. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcz161
82
Lachkar Z. Pauluis O. Paparella F. Khan B. Burt J. A. (2025). Local and remote climatic drivers of extreme summer temperatures in the Arabian Gulf. EGUsphere [preprint], doi: 10.5194/egusphere-2025-2948
83
Loughland R. Butt S. J. Nithyanandan M. (2020). Establishment of mangrove ecosystems on man-made islands in Kuwait: Sustainable outcomes in a challenging and changing environment. Aquat. Bot.167, 103273. doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2020.103273
84
Lovelock C. E. Cahoon D. R. Friess D. A. Guntenspergen G. R. Krauss K. W. Reef R. et al . (2015). The vulnerability of Indo-Pacific mangrove forests to sea-level rise. Nature526, 559–563. doi: 10.1038/nature15538
85
Lovelock C. E. Reef R. (2020). Variable impacts of climate change on blue carbon. One Earth3, 195–211. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2020.07.010
86
MacFarlane G. R. Burchett M. D. (2000). Cellular distribution of copper, lead and zinc in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Aquat. Bot.68, 45–59. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3770(00)00105-4
87
Macklin P. Rosentreter J. Arifanti V. B. Suryaputra I. G. N. A. (2021). “ Groundwater research in mangrove coastal ecosystems—new prospects,” in Dynamic sedimentary environments of mangrove coasts ( Elsevier), 67–81. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-816437-2.00010-0
88
Malekmohammadi L. Sheidai M. Ghahremaninejad F. Danehkar A. Koohdar F. (2023). Studies on genetic diversity, gene flow and landscape genetic in Avicennia marina: Spatial PCA, Random Forest, and phylogeography approaches. BMC Plant Biol.23, 459. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04475-6
89
Mansour S. (2019). Geospatial modelling of tropical cyclone risks to the southern Oman coasts. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct.40, 101151. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101151
90
Martínez-Díaz M. G. Reef R. (2023). A biogeographical approach to characterizing the climatic, physical and geomorphic niche of the most widely distributed mangrove species, Avicennia marina. Divers. Distrib.29, 89–108. doi: 10.1111/ddi.13643
91
Mateos-Molina D. Pittman S. J. Antonopoulou M. Carpenter S. Möller M. Muzaffar S. B. et al . (2024). “ Coastal lagoons (Khors) of the emirates,” in A natural history of the emirates. Ed. BurtJ. A. ( Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham), 241–265. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-37397-8_8
92
Mezger E. M. De Nooijer L. J. Boer W. Brummer G. J. A. Reichart G. J. (2016). Salinity controls on Na incorporation in Red Sea planktonic foraminifera. Paleoceanography31, 1562–1582. doi: 10.1002/2016PA003052
93
Ministry of Climate Change and Environment [MOCCAE] (2021). UAE announces enhanced target to plant 100 million mangroves by 2030 at COP26. Available online at: https://www.moccae.gov.ae/en/media-center/news/9/11/2021/uae-announces-enhanced-target-to-plant-100-million-mangroves-by-2030-at-cop26.aspx (Accessed May 25, 2025).
94
Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture [MEWA] (2020). Executive regulation for the sustainable management of the marine and coastal environment. Available online at: https://www.mewa.gov.sa/en/InformationCenter/DocsCenter/RulesLibrary/Docs/Executive%20Regulation%20for%20Sustainable%20Management%20of%20the%20Marine%20and%20Coastal%20Environment.pdf (Accessed April 5, 2025).
95
Moore G. E. Grizzle R. E. Ward K. M. Alshihi R. M. (2015). Distribution, pore-water chemistry, and stand characteristics of the mangroves of the United Arab Emirates. J. Coast. Res.314, 957–963. doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-14-00142.1
96
Moslehi M. Ahmadi A. Pypker T. Dehghani Ghanatghestani M. Hassani M. Zarafshar M. (2025). Halophyte adaptations in gray mangrove seedlings to salinity on the Persian Gulf coastline. Front. For. Glob. Change8. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2025.1523229
97
Moussa L. G. Mohan M. Burmeister N. King S. A. L. Burt J. A. Rog S. M. et al . (2024). Mangrove ecotourism along the coasts of the gulf cooperation council countries: A systematic review. Land13, 1351. doi: 10.3390/land13091351
98
Naderi Beni A. Marriner N. Sharifi A. Azizpour J. Kabiri K. Djamali M. et al . (2021). Climate change: A driver of future conflicts in the Persian Gulf Region? Heliyon7, e06288. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06288
99
Naidoo G. (2006). Factors contributing to dwarfing in the mangrove avicennia marina. Ann. Bot.97, 1095–1101. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl064
100
Naidoo G. Naidoo K. (2017). Ultrastructural effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the mangroves Avicennia marina and Rhizophora mucronata. Flora235, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.flora.2017.08.006
101
Najah A. Merwe R. V. D. Al Shehhi M. R. (2025). Review of tropical cyclones impacting the Western Arabian Sea and Oman. J. Oper. Oceanogr.18, 21–39. doi: 10.1080/1755876X.2024.2444753
102
Naseef A. Javad A. Kausal A. K. Barua D. Ashtamoorthy S. K. (2024). High heat tolerance and thermal safety margins in mangroves from the southwestern coast of India. Sci. Total Environ.954, 176366. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176366
103
Naser H. A. (2023). Sediment carbon stock in natural and transplanted mangroves in Bahrain, arabian gulf. Land12, 2055. doi: 10.3390/land12112055
104
Naskar S. Palit P. K. (2015). Anatomical and physiological adaptations of mangroves. Wetl. Ecol. Manage.23, 357–370. doi: 10.1007/s11273-014-9385-z
105
Ocean S. (2023). Mangroves ( Smithsonian Museum of Natural History). Available online at: https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/plants-algae/mangroves (Accessed May 25, 2025).
106
Paparella F. Xu C. Vaughan G. O. Burt J. A. (2019). Coral bleaching in the persian/arabian gulf is modulated by summer winds. Front. Mar. Sci.6. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00205
107
Pendleton L. Donato D. C. Murray B. C. Crooks S. Jenkins W. A. Sifleet S. et al . (2012). Estimating global “Blue carbon” Emissions from conversion and degradation of vegetated coastal ecosystems. PloS One7, e43542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043542
108
PERSGA/GEF (2004). Status of mangroves in the red sea and gulf of aden (Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: Regional Organization for the Conservation of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden). Available online at: https://www.cbd.int/doc/meetings/mar/ebsaws-2015-02/other/ebsaws-2015-02-persga-submission3-en.pdf (Accessed May 15, 2025).
109
Por F. D. Dor I. Amir A. (1977). The mangal of Sinai: Limits of an ecosystem. Helgoländer Wiss. Meeresunters.30, 295–314. doi: 10.1007/BF02207843
110
Rahdarian A. Niksokhan M. H. (2017). Numerical modeling of storm surge attenuation by mangroves in protected area of mangroves of Qheshm Island. Ocean Eng.145, 304–315. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.09.026
111
Red Sea Global (2023). Red Sea Global on track to plant 50 million mangrove trees by 2030 with launch of dedicated nursery. Available online at: https://www.redseaglobal.com/en/w/media-center/red-sea-global-on-track-to-plant-50-million-mangrove-trees-by-2030-with-launch-of-dedicated-nursery/ (Accessed June 24, 2025).
112
Republic of Yemen, Ministry of Water and Environment, Environment Protection Authority (2019). (Yemen, Aden: Environment Protection Authority). Available online at: https://www.cbd.int/doc/nr/nr-06/ye-nr-06-en.pdf (Accessed February 2, 2025).
113
Rivers J. M. Dalrymple R. W. Yousif R. Al-Shaikh I. Butler J. D. Warren C. et al . (2020). Mixed siliciclastic-carbonate-evaporite sedimentation in an arid eolian landscape: The Khor Al Adaid tide-dominated coastal embayment, Qatar. Sediment. Geol.408, 105730. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2020.105730
114
Rondon M. Ewane E. B. Abdullah M. M. Watt M. S. Blanton A. Abulibdeh A. et al . (2023). Remote sensing-based assessment of mangrove ecosystems in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries: a systematic review. Front. Mar. Sci.10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1241928
115
ROPME (2013). State of the marine environment report-2013 (Kuwait: Regional Organization for the Protection of the Marine Environment, Kuwait (ROPME). Available online at: https://ropme.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/SOMER_2013_full.pdf (Accessed May 15, 2025).
116
Rossignol-Strick M. (2002). “ Holocene climatic changes in the Eastern Mediterranean and the spread of food production from Southwest Asia to Egypt,” in Droughts, food and culture: Ecological change and food security in Africa’s later prehistory ( Springer US, Boston, MA), 157–169.
117
Saavedra-Hortua D. Nagelkerken I. Estupinan-Suarez L. M. Gillis L. G. (2023). Effects of connectivity on carbon and nitrogen stocks in mangrove and seagrass ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ.896, 164829. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164829
118
Sadeer N. B. Mahomoodally M. F. (2022). “ Avicennia marina (Forssk.) vierh,” in Mangroves with therapeutic potential for human health ( Elsevier), 187–199. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-99332-6.00023-0
119
Saderne V. Cusack M. Almahasheer H. Serrano O. Masqué P. Arias-Ortiz A. et al . (2018). Accumulation of carbonates contributes to coastal vegetated ecosystems keeping pace with sea level rise in an arid region (Arabian peninsula). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences123, 1498–1510. doi: 10.1029/2017JG004288
120
Saderne V. Cusack M. Serrano O. Almahasheer H. Krishnakumar P. K. Rabaoui L. et al . (2020). Role of vegetated coastal ecosystems as nitrogen and phosphorous filters and sinks in the coasts of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Res. Lett.15, 034058. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab76da
121
Saintilan N. Khan N. S. Ashe E. Kelleway J. J. Rogers K. Woodroffe C. D. et al . (2020). Thresholds of mangrove survival under rapid sea level rise. Science368, 1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.aba2656
122
Samara F. Solovieva N. Ghalayini T. Nasrallah Z. A. Saburova M. (2020). Assessment of the environmental status of the mangrove ecosystem in the United Arab Emirates. Water12, 1623. doi: 10.3390/w12061623
123
Saudi Green Initiative (2025). Protecting 30 % of Saudi Arabia’s land and sea by 2030. Available online at: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/en/explore/projects/saudi-green-initiative (Accessed July 23, 2025).
124
Savari M. Damaneh H. E. Damaneh H. E. (2022). Factors involved in the degradation of mangrove forests in Iran: A mixed study for the management of this ecosystem. J. Nat. Conserv.66, 126153. doi: 10.1016/j.jnc.2022.126153
125
SChile L. M. Kauffman J. B. Crooks S. Fourqurean J. W. Glavan J. Megonigal J. P. (2017). Limits on carbon sequestration in arid blue carbon ecosystems. Ecol. Appl.27, 859–874. doi: 10.1002/eap.1489
126
Shaltout K. H. Ahmed M. T. Alrumman S. A. Ahmed D. A. Eid E. M. (2021). Standing Crop Biomass and Carbon Content of Mangrove Avicennia marina (Forssk.) Vierh. along the Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability13, 13996. doi: 10.3390/su132413996
127
Sheppard C. Al-Husiani M. Al-Jamali F. Al-Yamani F. Baldwin R. Bishop J. et al . (2010). The Gulf: A young sea in decline. Mar. pollut. Bull.60, 13–38. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.10.017
128
Sofianos S. S. Johns W. E. (2007). Observations of the summer Red Sea circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans112, 2006JC003886. doi: 10.1029/2006JC003886
129
Spencer T. Schuerch M. Nicholls R. J. Hinkel J. Lincke D. Vafeidis A. T. et al . (2016). Global coastal wetland change under sea-level rise and related stresses: The DIVA Wetland Change Model. Glob. Planet. Change139, 15–30. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.12.018
130
Su J. Friess D. A. Gasparatos A. (2021). A meta-analysis of the ecological and economic outcomes of mangrove restoration. Nat. Commun.12, 5050. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25349-1
131
Sulochanan B. (2013). Mangrove ecosystem and its impact on fisheries. Cent. Mar. Fish. Res. Inst., 57–62. [Preprint; http://eprints.cmfri.org.in/9873/1/Bindu_10.pdf].
132
Supreme Council for Environment [SCE] (2024). Tubli bay reserve. Available online at: https://www.sce.gov.bh/en/TubliBayReserve?cms=iQRpheuphYtJ6pyXUGiNqnbUuLMcjfdP (Accessed May 15, 2025).
133
Taherdoost H. (2022). What are different research approaches? Comprehensive review of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method research, their applications, types, and limitations. J. Manage. Sci. Eng. Res.5, 53–63. doi: 10.30564/jmser.v5i1.4538
134
Tomer A. S. McKenzie T. Majtényi-Hill C. Cabral A. Yau Y. Y. Y. Call M. et al . (2025). Groundwater releases CO2 to diverse global coastal ecosystems. Sci. Adv.11, eadr3240. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr3240
135
UNESCO (2024). Hara ( UNESCO). Available online at: https://en.unesco.org/silkroad/silk-road-themes/biosphere-reserve/hara (Accessed May 5, 2025).
136
United Arab Emirates (1999). Federal Law No. 24 of 1999 concerning the protection and development of the environment. Available online at: https://uaelegislation.gov.ae/en/legislations/1146/download.
137
USAID (2013). Yemen biodiversity and tropical forest assessment ( United States Agency for International Development). Available online at: https://ye.chm-cbd.net/sites/ye/files/2022-09/Yemen2013.pdf (Accessed February 5, 2025).
138
Van Der Werf G. R. Morton D. C. DeFries R. S. Olivier J. G. J. Kasibhatla P. S. Jackson R. B. et al . (2009). CO2 emissions from forest loss. Nat. Geosci.2, 737–738. doi: 10.1038/ngeo671
139
Waisel Y. Eshel A. Agami M. (1986). Salt balance of leaves of the mangrove Avicennia marina. Physiol. Plant67, 67–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1986.tb01264.x
140
Waleed T. A. Abdel-Maksoud Y. K. Kanwar R. S. Sewilam H. (2025). Mangroves in Egypt and the Middle East: current status, threats, and opportunities. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol.22, 1225–1262. doi: 10.1007/s13762-024-05788-1
141
Ward R. D. Friess D. A. Day R. H. Mackenzie R. A. (2016). Impacts of climate change on mangrove ecosystems: a region by region overview. Ecosyst. Health Sustain.2, e01211. doi: 10.1002/ehs2.1211
142
Yap C. K. Al-Mutairi K. A. (2025). Mangrove ecosystems in Western Asia: a literature review of trends, conservation gaps, and sustainable management strategies. Front. For. Glob. Change8. doi: 10.3389/ffgc.2025.1556158
143
Yasseen B. T. Abu-Al-Basal M. A. (2008). Ecophysiology of Limonium axillare and Avicennia marina from the coastline of Arabian Gulf-Qatar. J. Coast. Conserv.12, 35–42. doi: 10.1007/s11852-008-0021-z
144
Zahed M. A. Rouhani F. Mohajeri S. Bateni F. Mohajeri L. (2010). An overview of Iranian mangrove ecosystems, northern part of the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea. Acta Ecol. Sin.30, 240–244. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2010.03.013
145
Zerboni A. Perego A. Mariani G. S. Brandolini F. Al Kindi M. Regattieri E. et al . (2020). Geomorphology of the Jebel Qara and coastal plain of Salalah (Dhofar, southern Sultanate of Oman). J. Maps16, 187–198. doi: 10.1080/17445647.2019.1708488
Summary
Keywords
arid-zone mangroves, Avicennia marina , blue-carbon MRV, hypersalinity, heat stress, sea-level rise, mangrove governance, Red Sea
Citation
Meraj G, Abouleish MY, Ali T, Hashimoto S, Marazi A, Chakrabortty R, Singh SK, Kanga S, Almazroui M and Bhuyan MS (2025) Middle Eastern mangroves at the arid limit (Red Sea and Arabian/Persian Gulf): eco-biophysical dynamics, blue-carbon MRV, climate-risk pathways, and governance for resilient restoration - a comprehensive review. Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1695426. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1695426
Received
29 August 2025
Accepted
31 October 2025
Published
01 December 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Francesco Paparella, New York University Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Reviewed by
Keivan Kabiri, Iranian National Institute for Oceanography and Atmospheric Science, Iran
Nicholas Culligan, Florida Gulf Coast University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Meraj, Abouleish, Ali, Hashimoto, Marazi, Chakrabortty, Singh, Kanga, Almazroui and Bhuyan.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gowhar Meraj, gowharmeraj@gmail.com; gmeraj@aus.edu; Mohamed Yehia Abouleish, mabouleish@aus.edu
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.