Abstract
Intensive aquaculture of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus spp.) is often constrained by inefficient feed conversion and recurrent outbreaks of vibriosis. This study investigated the individual and combined effects of dietary polypeptin and bioture on growth performance, physiological status, and disease resistance in juvenile hybrid grouper. A 3 × 3 factorial design was employed to formulate nine iso-nitrogenous and iso-lipidic diets (i.e., P0B0, P2B0, P4B0, P0B2, P2B2, P4B2, P0B4, P2B4, and P4B4), incorporating polypeptin and bioture at 0%, 0.2%, and 0.4% inclusion levels. Fish were fed experimental diets for 56 days, followed by a 144 h challenge with Vibrio harveyi. The results showed that co-supplementation significantly improved multiple performance indicators, exhibiting notable synergistic effects: final body weight, weight gain, and specific growth rate increased, while feed conversion ratio and hepatosomatic index decreased. Digestive enzyme activities, particularly pepsin and trypsin, were markedly elevated, indicating improved digestive efficiency. Furthermore, antioxidant capacity was significantly enhanced in co-supplemented groups, as evidenced by increased T-AOC, SOD, and CAT, coupled with reduced MDA contents. Serum biochemical parameters related to stress and hepatic function, including AST, ALT, LDH, TG, T-CHO, and cortisol, were significantly lower in supplemented groups. The levels of LZM, ACP, AKP, and IgM were significantly upregulated both at baseline and post-challenge, indicating enhanced humoral immunity. During the V. harveyi challenge, the highest survival rates were observed in P4B4, demonstrating delayed onset and reduced cumulative mortality relative to the control. In conclusion, dietary co-administration of polypeptin and bioture, particularly in the P4B4 group, elicited synergistic benefits across multiple physiological and immunological parameters, significantly enhancing growth performance, digestive function, oxidative balance, and disease resistance in juvenile hybrid grouper. These findings support the potential of precision-nutrition strategies incorporating functional feed additives for sustainable and health-optimized grouper aquaculture.
1 Introduction
Aquaculture has emerged as the fastest-growing source of animal protein globally. However, the intensification of production systems subjects cultured fish to various nutritional, environmental, and pathogenic stressors, ultimately compromising growth performance and increasing susceptibility to disease. The hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × E. lanceolatus♂) is a high-value marine carnivore known for its rapid growth and desirable flesh quality. Nevertheless, its industry expansion is constrained by inefficient feed conversion and recurrent outbreaks of vibriosis, predominantly caused by Vibrio harveyi, which result in substantial economic losses (Deng et al., 2020; Mohd Yazid et al., 2021). These limitations underscore the urgent need for nutrition-based strategies that simultaneously enhance growth efficiency and disease resistance (Xin et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2023). Within this context, precision immunonutrition—defined as the strategic combination of digestibility enhancers and evidence-based immunomodulators—presents a promising approach to bolster host resilience while reducing dependence on antibiotics (Hossain et al., 2020).
Peptide hydrolysates play a central role in targeted nutritional strategies aimed at enhancing immune resilience in aquatic species (Ospina-Salazar et al., 2016). Compared with intact proteins, hydrolysates composed of short peptides and oligopeptides are rapidly absorbed, stimulate digestive secretions, and modulate enterocyte function, thereby enhancing enzyme activity and nutrient assimilation (Ospina-Salazar et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2020). Across multiple species, dietary supplementation with fish protein hydrolysates has been shown to improve growth performance and protein utilization. Specifically, in hybrid grouper, partial substitution of fishmeal with hydrolyzed protein has promoted intestinal development and elevated digestive enzyme activities (Hlordzi et al., 2022; Refstie et al., 2004). Additionally, bioactive peptides exhibit intrinsic antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties, further supporting host physiological status (Chen et al., 2018; Sheng et al., 2023). In this study, polypeptin is a peptide-rich hydrolysate predominantly consisting of short peptides and oligopeptides, with minor proportions of free amino acids and nucleotides, which was paired with bioture—a yeast-derived compound enriched with β-glucans, mannan-oligosaccharides (MOS), nucleotides, small peptides, and vitamins. This pairing was designed to integrate digestive enhancement with immunological stimulation.
The immunonutrient functions of bioture are grounded in well-characterized biological pathways. β-Glucans are recognized by C-type lectin-like receptors on phagocytes, activating antimicrobial responses and improving disease resistance (Petit et al., 2019a). In addition to their role in acute immune activation, β-glucans have been shown to induce trained innate immunity, which involves the functional reprogramming of innate immune cells to enhance subsequent immune responses. This phenomenon has been increasingly reported in teleost fish (Petit et al., 2019b; Waikhom et al., 2022; You et al., 2024). MOS complement these effects by inhibiting pathogen adhesion, modulating gut microbiota composition, and reinforcing epithelial barrier integrity (Ding et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2022; Torrecillas et al., 2015). Furthermore, dietary nucleotides have been shown to support leukocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis, thereby enhancing both growth performance and disease resistance in fish (Burrells et al., 2001a, b; Li and Gatlin, 2006; Pelusio et al., 2023). Collectively, these compounds contribute to the maintenance of redox homeostasis, thus preserving mucosal health under intensive aquaculture conditions (Li et al., 2023; Xin et al., 2022).
Despite the well-documented benefits of peptide hydrolysates and yeast-derived immunonutrients when applied individually, their combined use in marine carnivorous species remains largely underexplored (Hossain et al., 2020; Rimoldi et al., 2020). Furthermore, studies employing factorial designs to assess potential synergistic interactions between these additives are notably scarce. In hybrid grouper, previous research has shown that dietary prebiotics and phytogenics can enhance growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and nonspecific immune responses (Xin et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023). However, a systematic evaluation of peptide hydrolysate supplementation in combination with a β-glucan/MOS/nucleotide complex has not yet been conducted. Given the mechanistic complementarity—where peptide hydrolysates enhance digestive capacity and nutrient utilization while yeast-based components modulate immune responsiveness and epithelial integrity (Ospina-Salazar et al., 2016; Petit et al., 2019a)—we hypothesized that co-supplementation would yield additive or synergistic effects across multiple physiological domains, including growth performance, feed efficiency, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant status, humoral immune indices, and resistance to V. harveyi.
To test this hypothesis, a multifactorial feeding trial was conducted to assess the main and interactive effects of dietary polypeptin and bioture in juvenile hybrid grouper. By integrating metrics related to growth, physiology, and pathogen resistance, this study aimed to provide both mechanistic insights and practical guidance for the development of precision aquafeeds that support sustainable grouper aquaculture.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental design and diet preparation
A 3 × 3 factorial arrangement was implemented to evaluate both the individual (main) and combined (interactive) effects of dietary polypeptin (P: 0, 0.2, and 0.4 %) and bioture (B: 0, 0.2, and 0.4 %) on juvenile hybrid grouper. Nine iso-nitrogenous and iso-lipidic diets were prepared accordingly, denoted as P0B0, P2B0, P4B0, P0B2, P2B2, P4B2, P0B4, P2B4, and P4B4 (Gokulakrishnan et al., 2022; Konstantinidis et al., 2022). Key ingredients included fish meal, fermented soybean meal, casein, gelatin, corn starch, fish oil, and soybean lecithin. Proximate analyses verified that all diets contained approximately 51 % crude protein and 10 % crude lipid (see Table 1).
Table 1
| Ingredients | Diet treatments | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0B0 | P2B0 | P4B0 | P0B2 | P2B2 | P4B2 | P0B4 | P2B4 | P4B4 | |
| Fish meal | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 | 32.00 |
| Fermented soybean meal | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 | 18.00 |
| Corn Starch | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 | 16.00 |
| Casein | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 | 14.00 |
| Gelatin | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Fish oil | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| Soybean lecithin | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.50 |
| Choline chloride | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Compound premix1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Polypeptin | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.40 |
| Bioture | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Microcrystalline cellulose | 7.50 | 7.30 | 7.10 | 7.30 | 7.10 | 6.90 | 7.10 | 6.90 | 6.70 |
| Proximate analysis | |||||||||
| Crude protein | 51.02 | 50.29 | 51.33 | 50.24 | 50.89 | 52.10 | 51.64 | 52.27 | 51.86 |
| Crude lipid | 10.20 | 9.56 | 10.32 | 10.08 | 10.47 | 9.79 | 10.22 | 10.50 | 10.34 |
| Ash | 9.66 | 9.65 | 8.99 | 9.35 | 9.55 | 9.68 | 9.90 | 9.32 | 9.40 |
| Moisture | 7.30 | 7.35 | 7.55 | 7.37 | 7.50 | 7.05 | 7.21 | 7.02 | 7.19 |
Formulation and proximate composition of the experimental diets (dry matter, %).
1One kilogram of compound premix contained: VA700,000 IU, VD3 200,000 IU, VB1 0.9 g, VB2 1.5g, VB5 4.5 g, VB6 1.0 g, VC 10.0 g, VE 8.0 g, VH 0.1 g, VK3 1.2g, folic acid 0.5 g, nicotinamide 8.0 g, inositol 10.0 g, Fe 20.0 g, Zn 9.0 g, Mn 5.5 g, Cu 1.0 g, Co 0.1 g, Se 0.05 g.
Polypeptin is a peptide-based functional additive produced by Shandong Deep-Sea Biotechnology Co., Ltd. through enzymatic hydrolysis. It consists primarily of short peptides and oligopeptides, along with small amounts of free amino acids and nucleotides. Similarly, bioture—a yeast-derived functional additive enriched in β-glucans, mannan-oligosaccharides (MOS), nucleotides, small peptides, and vitamins—was obtained from the same source. All dry feed ingredients were thoroughly blended, extruded into pellets (2 mm diameter) using a screw extruder, and subsequently dried by forced-air convection at 45–50 °C for 24 h until constant weight was achieved. Final feed pellets were stored in airtight containers at 4°C, shielded from light until use.
Juvenile hybrid grouper (initial body weight 25.20 ± 1.10 g) were procured from a hatchery in Haiyang, Shandong Province, China, and acclimated for three weeks under controlled conditions. Following acclimation, fish were randomly allocated to nine treatment groups, each with three replicate tanks (30 fish per replicate). Individuals were reared for 56 days in 500 L cylindrical fiberglass-reinforced plastic tanks linked to a recirculating aquaculture system. Key water quality parameters were maintained as follows: dissolved oxygen > 6 mg L-¹, total ammonia−nitrogen < 0.03 mg L-¹, salinity 28–32 ‰, pH 7.8–8.2, and temperature 26–30 °C. Fish were hand-fed twice daily (at 08:00 and 16:00) to satiation equivalent to ~3% of their body weight per day (Zhu et al., 2023). Uneaten feed was collected after each meal to accurately measure feed intake per tank.
2.2 Sample collection and determination
To standardize gut contents, feed was withheld for 24 h prior to final sampling. For each tank, total biomass and fish count were recorded. Individual fish were measured for total length and body weight. Prior to tissue collection and blood sampling, fish were anesthetized in an aqueous bath of eugenol (100 mg/L; Sigma-Aldrich, USA) until loss of equilibrium and cessation of opercular movement were observed. For euthanasia, overdosing with eugenol solution (200 mg/L) was applied, followed by severance of the spinal cord to ensure death before dissection. All procedures involving fish handling, anesthesia, and euthanasia were conducted in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals of Qingdao Agricultural University.
From each tank, five fish were randomly selected and dissected to determine viscera and liver weights. Growth performance was calculated using the following equations (Tacon and Metian, 2008):
Immediately after viscera removal, intestines were excised on ice, gently flushed with prechilled saline to eliminate contents, and homogenized in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.4) containing 0.1 % Triton X−100 at a 1:9 (w/v) ratio. Homogenates were centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the resulting supernatants were collected for enzyme activity assays.
Digestive enzyme activities—including pepsin, trypsin, amylase, and lipase—were determined using commercial assay kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China) and measured with a Multiskan Spectrum microplate reader (Thermo Scientific, USA) according to the manufacturers’ protocols (Hlordzi et al., 2022). Pepsin activity was assessed using a casein substrate under acidic conditions, with absorbance read at 280 nm; one unit of pepsin activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to release 1 μg of tyrosine equivalents per minute. Trypsin activity was measured using Nα-Benzoyl-DL-arginine p-nitroanilide as substrate at 37 °C, with absorbance at 410 nm; one unit was defined as the amount of enzyme producing 1 μmol of p-nitroaniline per minute. Amylase activity was determined using soluble starch as substrate, incubated at 37 °C for 30 min; the resulting reducing sugars were quantified via the dinitrosalicylic acid method at 540 nm, with one unit defined as the amount of enzyme hydrolyzing 10 mg of starch in 30 min. Lipase activity was measured using p-nitrophenyl palmitate as substrate at 37°C, with absorbance at 405 nm; one unit was defined as the amount of enzyme releasing 1 μmol of p-nitrophenol per minute. Total protein concentration in tissue homogenates was determined using the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) method, and all enzyme activities were normalized and expressed as units per milligram of protein (U mg-¹ prot-¹).
Total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were analyzed in liver and intestinal tissues using commercial kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China) (Xin et al., 2022). T-AOC was measured by the ferric-reducing antioxidant power method at 593 nm, while SOD activity was determined via the xanthine oxidase method at 550 nm, with one unit defined as the amount of enzyme causing 50% inhibition of the reaction rate. CAT activity was assessed using the Aebi method with hydrogen peroxide as substrate, and absorbance was read at 240 nm. MDA levels were quantified by the thiobarbituric acid reaction method at 532 nm. All assays were conducted in triplicate for each sample. Results were normalized to tissue protein content determined by the BCA method using bovine serum albumin as the standard and expressed as units per milligram of protein (U mg-¹ prot-¹), except for MDA, which was expressed as nmol mg-¹ prot-¹.
Blood samples were collected from the caudal vein without anticoagulant prior to euthanasia, allowed to clot at room temperature, and then centrifuged at 3,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C to obtain serum. The resulting serum was aliquoted and stored at –80°C until biochemical analysis, which was conducted within two weeks. Serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were determined using kinetic assays based on the reaction of transaminase-generated oxaloacetate and pyruvate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, with absorbance read at 510 nm and results expressed in U L-¹. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity was measured at 340 nm by monitoring NADH consumption and similarly expressed as U L-¹. Triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (T-CHO) concentrations were determined through enzymatic colorimetric assays at 510 nm and reported in mmol L-¹. Cortisol levels were quantified using a commercial ELISA kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China; sensitivity 0.5 ng/mL, assay range 2–200 ng/mL, intra-assay CV<8%, inter-assay CV<10%), with concentrations calculated from a standard curve and expressed as ng mL-¹.
2.3 Pathogen challenge test
Upon completing the 56-day feeding trial, fish from each dietary treatment group were randomly selected in equal numbers for a V. harveyi challenge. The target pathogen was originally isolated from diseased hybrid grouper and authenticated by morphological profiling, biochemical tests, and 16S rRNA sequencing, then laboratory-propagated under standardized conditions to preserve virulence. A single colony from LB agar was inoculated into LB broth and cultured at 28°C, 180 rpm until reaching mid-logarithmic phase (OD600 ≈ 0.8), as measured using a UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800, Japan). The bacterial concentration was calibrated by plating serial dilutions on LB agar followed by colony enumeration. Cells were harvested, washed twice in sterile PBS, and resuspended to the desired median lethal dose (LD50). The challenge dose was established through preliminary trials in which healthy juvenile groupers (n = 20 per group) were intraperitoneally injected with serial dilutions of the bacterial suspension (104–108 CFU mL-¹). Mortality was recorded 96 h post-injection, and probit analysis was used to calculate the LD50, which was determined to be approximately 1.1 × 107 CFU mL-¹.
Randomly selected fish were lightly anesthetized with 100 mg L-¹ eugenol and intraperitoneally injected with 0.20 mL of the V. harveyi suspension. Control fish received 0.20 mL of sterile PBS. Fish were subsequently recovered in aerated seawater, returned to separate tanks within the same recirculating system, and monitored unfed for 144 h. Mortality and time of death were recorded continuously; dead or moribund fish were sampled from the liver, kidney, and spleen to re-isolate the pathogen and confirm cause of death.
To assess nonspecific immune responses, blood samples were collected from subsampled fish at 0, 12, and 24 h following the bacterial challenge (Shi et al., 2022; Zanuzzo et al., 2020). Lysozyme (LZM) activity was evaluated in serum using the turbidimetric method with Micrococcus lysodeikticus as the substrate, and absorbance was measured at 530 nm, with results expressed in U mL-¹. Acid phosphatase (ACP) and alkaline phosphatase (AKP) activities were determined using p-nitrophenyl phosphate as the substrate at 37°C, and absorbance was recorded at 405 nm; enzyme activities were calculated from standard curves and reported in U L-¹. Serum immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels were measured using an ELISA kit, with absorbance read at 450 nm and concentrations expressed in μg mL-¹, based on calibration against a standard curve.
2.4 Statistical analysis
All data were first tested for normality (Shapiro–Wilk test) and homogeneity of variances (Levene’s test). Survival data were arcsine square-root transformed prior to analysis. For variables such as growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, serum biochemistry, antioxidant parameters, and disease-resistance indices, one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test (P<0.05) was used when comparing dietary groups. To assess the individual and interactive effects of polypeptin and bioture, a two-way ANOVA was performed; significant interaction terms were further explored via simple main-effects analysis. For nonspecific immune parameters measured at multiple time points before and after the challenge, paired-sample t tests were employed for pairwise comparisons. All results are presented as mean ± SD. Scatter plots and other visualizations were generated using the CNSknowall platform (https://cnsknowall.com), a web-based data analysis and visualization service.
3 Results
3.1 Growth performance and feed utilization
Throughout the 56-day feeding trial, survival rates did not differ significantly among the dietary treatments, ranging from 92.22 ± 1.92% to 97.78 ± 1.92% (P > 0.05; Table 2). In contrast, final body weight, weight gain, and SGR demonstrated progressive improvements with increasing levels of polypeptin and bioture supplementation. The P4B4 group exhibited the highest values for final body weight (140.98 ± 6.19 g), weight gain (463.93 ± 24.75%), and SGR (3.09 ± 0.08% day-¹), all of which were significantly greater than those observed in the control group (P0B0: 123.99 ± 1.53 g, 395.96 ± 6.11%, and 2.86 ± 0.02% day-¹, respectively; P<0.05). Intermediate performance metrics were observed in groups receiving moderate supplementation, such as P4B0, P2B2, and P0B4. FCR decreased correspondingly with supplementation level, reaching the lowest value in the P4B4 group (0.67 ± 0.04), which was significantly lower than that of the control group (0.78 ± 0.02; P<0.05). No significant differences were observed in VSI or CF across treatments (P > 0.05). However, HSI declined significantly with increasing supplementation, with the lowest value recorded in the P4B4 group (2.59 ± 0.08%), compared with 3.09 ± 1.21% in the control (P<0.05). Two-way ANOVA revealed significant main effects of polypeptin on final body weight, weight gain, SGR, FCR, and HSI (P<0.05 to P<0.001), and of bioture on final body weight, weight gain, SGR, FCR, and HSI (P <0.01 to P <0.001). Furthermore, significant interaction effects between polypeptin and bioture were observed for FCR and HSI (P<0.05 to P<0.01), suggesting a synergistic influence of the combined supplementation on feed efficiency and liver condition.
Table 2
| Dietary treatments | Survival (%) | Final weight (g) | Weight gain (%) | SGR (% day-1) | FCR | VSI (%) | HSI (%) | CF (g cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0B0 | 93.00 ± 3.33 | 123.99 ± 1.53a | 395.96 ± 6.11a | 2.86 ± 0.02a | 0.78 ± 0.02a | 10.92 ± 0.68 | 3.09 ± 1.21a | 3.00 ± 0.19 |
| P2B0 | 92.22 ± 1.92 | 123.70 ± 4.55a | 394.81 ± 18.19a | 2.85 ± 0.07a | 0.79 ± 0.04a | 10.98 ± 0.40 | 3.07 ± 0.22a | 2.87 ± 0.29 |
| P4B0 | 95.55 ± 3.85 | 132.86 ± 2.78bc | 431.43 ± 21.17bc | 2.98 ± 0.04bc | 0.72 ± 0.02bc | 11.01 ± 0.55 | 2.85 ± 0.23ab | 2.91 ± 0.19 |
| P0B2 | 93.22 ± 1.92 | 126.43 ± 3.37ab | 405.71 ± 13.48ab | 2.90 ± 0.05ab | 0.76 ± 0.02ab | 11.16 ± 0.56 | 2.92 ± 0.16ab | 3.02 ± 0.12 |
| P2B2 | 94.44 ± 1.93 | 132.81 ± 5.73bc | 431.23 ± 22.90bc | 2.98 ± 0.08bc | 0.72 ± 0.04bc | 10.91 ± 0.32 | 2.77 ± 0.10ab | 2.96 ± 0.23 |
| P4B2 | 96.67 ± 3.34 | 134.54 ± 4.43bc | 438.16 ± 17.72bc | 3.01 ± 0.06bc | 0.71 ± 0.03bc | 10.42 ± 0.26 | 2.66 ± 0.15b | 2.84 ± 0.14 |
| P0B4 | 97.78 ± 1.92 | 132.47 ± 3.94b | 429.88 ± 15.74b | 2.98 ± 0.06bc | 0.72 ± 0.03bc | 10.77 ± 0.36 | 2.85 ± 0.27ab | 3.05 ± 0.38 |
| P2B4 | 96.67 ± 3.34 | 134.14 ± 5.24bc | 436.57 ± 20.97bc | 3.00 ± 0.07bc | 0.71 ± 0.04bc | 10.68 ± 0.75 | 2.65 ± 0.16b | 2.99 ± 0.14 |
| P4B4 | 97.78 ± 1.92 | 140.98 ± 6.19c | 463.93 ± 24.75c | 3.09 ± 0.08c | 0.67 ± 0.04c | 10.32 ± 0.24 | 2.59 ± 0.08b | 2.86 ± 0.16 |
| Two-way ANOVA2 | ||||||||
| Polypeptin | ns | ** | ** | ** | *** | ns | * | ns |
| Bioture | ns | ** | ** | ** | *** | ns | ** | ns |
| Interaction | ns | ns | ns | ns | ** | ns | * | ns |
Growth performance and feed utilization of juvenile hybrid grouper under different dietary treatments.1.
1Data are present as mean ± SD. The superscripted lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the dietary treatments (P<0.05).
2*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns, non-significant.
3.2 Digestive enzyme activities
Activities of key digestive enzymes in the intestine, including pepsin, trypsin, amylase, and lipase, were significantly improved by dietary polypeptin and bioture supplementation (Figure 1). Pepsin activity increased markedly from 8.79 ± 1.13 U mg-¹ prot-¹ in the control group (P0B0) to a peak value of 20.43 ± 0.62 U mg-¹ prot-¹ in the P4B4 group (P<0.05). Trypsin activity exhibited a similar upward trend, with the highest level observed in P4B4 (242.82 ± 15.37 U mg-¹ prot-¹), significantly higher than in P0B0 (170.90 ± 12.32 U mg-¹ prot-¹; P<0.05). Amylase and lipase activities also increased in response to supplementation, reaching maximum values in groups receiving both additives. Amylase activity rose from 0.61 ± 0.07 U/mg protein in P0B0 to 0.87 ± 0.05 U mg-¹ prot-¹ in P4B4, while lipase activity increased from 18.17 ± 1.99 U g-¹ prot-¹ to 19.81 ± 1.82 U g-¹ prot-¹ (P <0.05 for both). Two-way ANOVA revealed significant main effects of both polypeptin and bioture on the activities of all measured enzymes (P<0.001), except for the effect of polypeptin on lipase activity. Significant interaction effects were also detected for pepsin, trypsin, and amylase (P<0.01 to P<0.001), indicating a synergistic enhancement of enzymatic activity through combined supplementation.
Figure 1
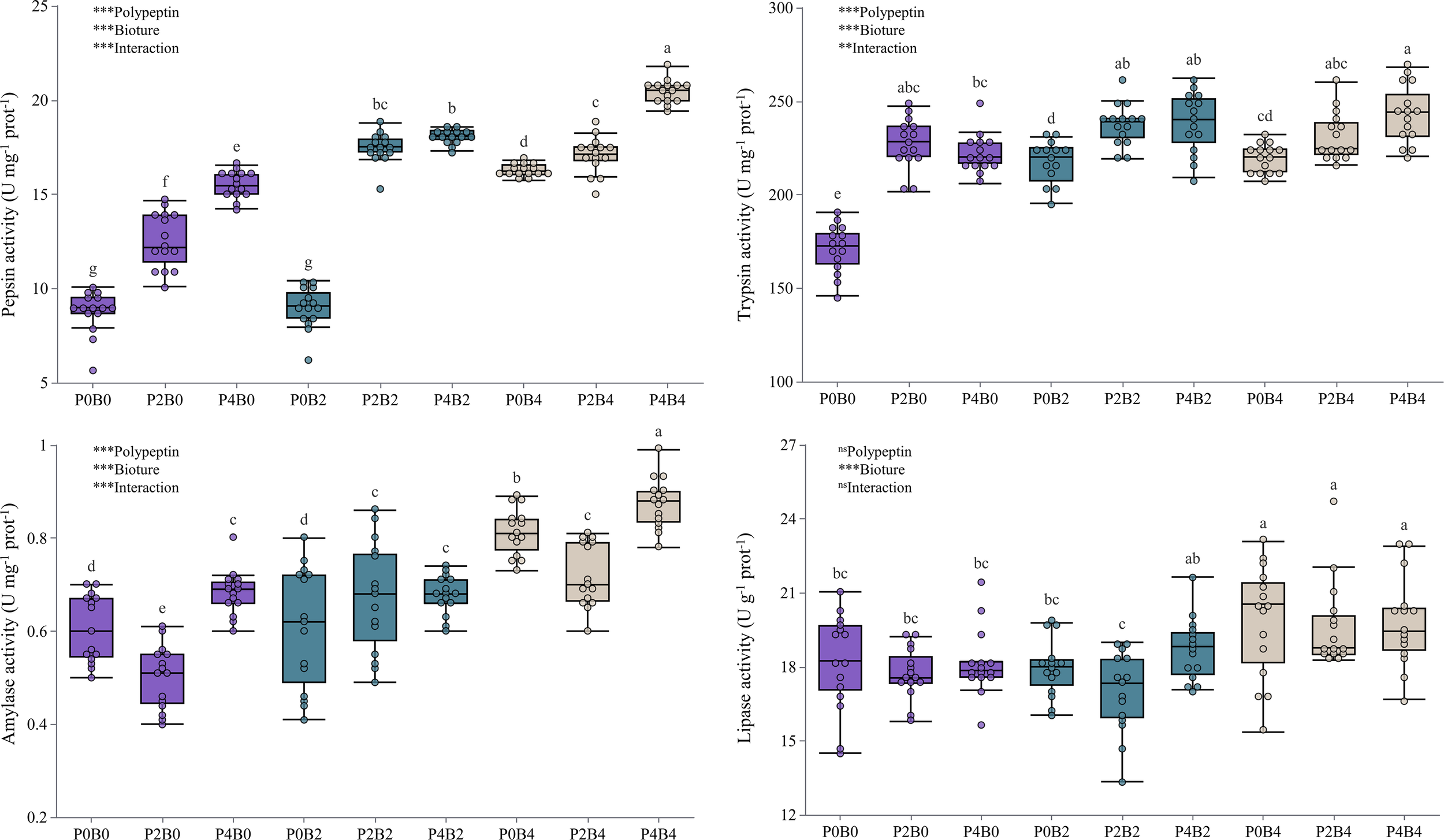
Digestive enzyme activities of juvenile hybrid grouper under different dietary treatments. The superscripted lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the dietary treatments (P<0.05). Two-way ANOVA: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns: non-significant.
3.3 Serum physio-biochemical indices
Serum concentrations of AST, ALT, LDH, TG, T-CHO, and cortisol exhibited a significant decline with increasing levels of polypeptin and bioture supplementation (Table 3). AST activity was highest in the control group (P0B0: 32.10 ± 1.90 U L-¹) and lowest in the P4B4 group (21.32 ± 1.06 U L-¹; P<0.05). A similar trend was observed for ALT, decreasing from 328.62 ± 17.23 U L-¹ in P0B0 to 276.27 ± 14.06 U L-¹ in P4B4 (P<0.05). LDH levels also declined significantly in the higher supplementation groups, with the lowest value recorded in P2B4 (14.54 ± 2.00 U L-¹), which was significantly lower than in P0B2 (18.02 ± 0.79 U L-¹; P<0.05). TG and T-CHO contents decreased progressively across treatment groups, with the lowest levels observed in P4B4 (TG: 0.72 ± 0.07 mmol L-¹; T-CHO: 1.84 ± 0.10 mmol L-¹; P<0.05 vs. control). Cortisol levels showed a marked reduction from 17.42 ± 0.83 ng mL-¹ in P0B0 to 10.92 ± 0.94 ng mL-¹ in P2B4 (P<0.05). Two-way ANOVA revealed significant main effects of polypeptin on AST, ALT, TG, T-CHO, and cortisol (P <0.01 to P<0.001), and of bioture on all measured indices (P<0.01 to P<0.001). Furthermore, significant interaction effects between polypeptin and bioture were observed for AST, ALT, TG, T-CHO, and cortisol (P<0.05 to P<0.01), indicating that the combined supplementation exerted a synergistic influence on these biochemical parameters.
Table 3
| Dietary treatments | AST (U L-1) | ALT (U L-1) | LDH (U L-1) | TG (mmol L-1) | T-CHO (mmol L-1) | Cortisol (ng mL-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0B0 | 32.10 ± 1.90a | 328.62 ± 17.23a | 17.26 ± 1.44ab | 1.21 ± 0.13a | 2.58 ± 0.21a | 17.42 ± 0.83a |
| P2B0 | 31.37 ± 2.56a | 310.83 ± 6.81ab | 17.43 ± 1.37ab | 1.00 ± 0.07b | 2.39 ± 0.10ab | 15.61 ± 0.52b |
| P4B0 | 28.12 ± 1.83b | 294.48 ± 7.77bc | 16.17 ± 0.78abc | 0.93 ± 0.04b | 2.24 ± 0.06bc | 12.71 ± 0.73cd |
| P0B2 | 29.47 ± 0.80ab | 328.20 ± 14.91a | 18.02 ± 0.79a | 1.25 ± 0.13a | 2.51 ± 0.11a | 15.70 ± 0.71b |
| P2B2 | 26.58 ± 1.28b | 292.20 ± 21.91bc | 16.33 ± 0.83abc | 0.91 ± 0.07b | 2.11 ± 0.09cd | 13.22 ± 1.13c |
| P4B2 | 21.74 ± 1.60c | 277.52 ± 15.59c | 16.29 ± 1.14abc | 0.87 ± 0.08bc | 2.01 ± 0.07de | 11.50 ± 0.54de |
| P0B4 | 27.66 ± 1.53b | 286.96 ± 14.42bc | 15.91 ± 0.94abc | 1.03 ± 0.11b | 2.44 ± 0.10a | 14.57 ± 0.92b |
| P2B4 | 22.57 ± 1.08c | 276.39 ± 14.78c | 14.54 ± 2.00c | 0.88 ± 0.10c | 2.19 ± 0.05cd | 10.92 ± 0.94e |
| P4B4 | 21.32 ± 1.06c | 276.27 ± 14.06c | 15.18 ± 0.59bc | 0.72 ± 0.07c | 1.84 ± 0.10e | 11.12 ± 1.08e |
| Two-way ANOVA2 | ||||||
| Polypeptin | *** | ** | ns | ** | *** | *** |
| Bioture | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | ** |
| Interaction | ** | * | ns | * | ** | * |
Serum physio-biochemical indices of juvenile hybrid grouper under different dietary treatments.1.
1Data are present as mean ± SD. Superscripted lowercase letters indicate significant differences among dietary treatments (P<0.05).
2*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns: non-significant.
3.4 Antioxidant capacity
Dietary supplementation with polypeptin and bioture significantly enhanced antioxidant capacity in both the liver and intestine (Figure 2). Liver T-AOC increased from 0.89 ± 0.19 mmol g-¹ prot-¹ in the control group (P0B0) to 1.52 ± 0.05 mmol g-¹ prot-¹ in P4B4, with a comparable rise observed in the intestine (0.19 ± 0.05 to 0.45 ± 0.09 mmol g-¹ prot-¹; both P<0.05). SOD and CAT activities were consistently elevated across treatments, with maximum activities detected in P4B4 (liver SOD: 33.95 ± 1.71 vs. 27.70 ± 1.72 U mg-¹ prot-¹ in P0B0; liver CAT: 23.71 ± 1.10 vs. 18.94 ± 1.63 U mg-¹ prot-¹; intestinal SOD: 30.51 ± 2.09 vs. 25.79 ± 2.31 U mg-¹ prot-¹; intestinal CAT: 22.10 ± 1.94 vs. 20.36 ± 0.82 U mg-¹ prot-¹; all P <0.05). In contrast, MDA concentrations declined significantly, with the lowest levels observed in the P4B4 group (liver: 6.97 ± 0.72 vs. 8.33 ± 0.82 nmol mg-¹ prot-¹ in P0B0; intestine: 5.22 ± 1.46 vs. 6.19 ± 0.90 nmol mg-¹ prot-¹; P <0.05).
Figure 2
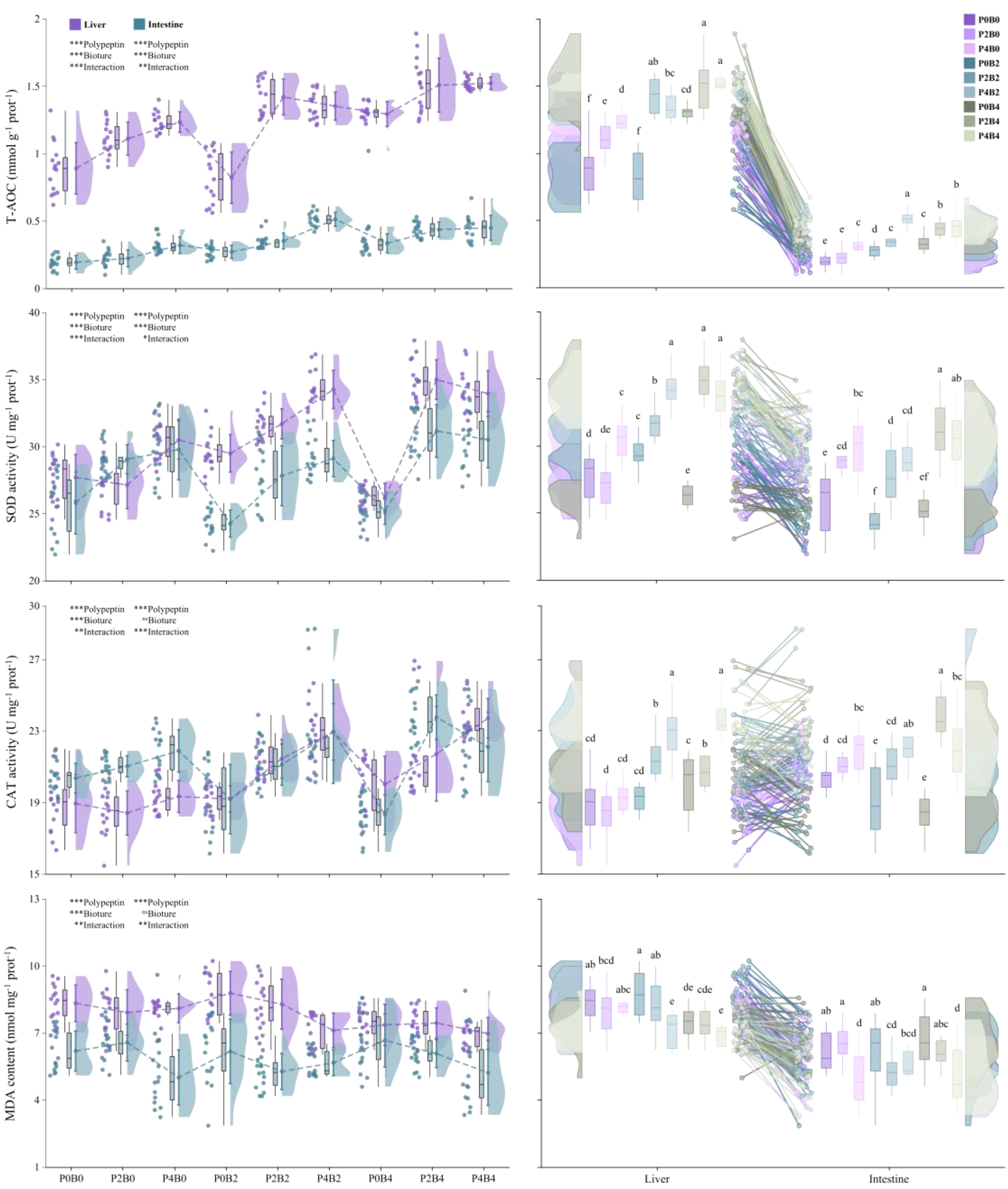
Effects of dietary polypeptin and bioture on the antioxidant status of juvenile hybrid grouper. The superscripted lowercase letters indicate significant differences among dietary treatments (P<0.05). Two-way ANOVA: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns: non-significant.
Two-way ANOVA indicated significant main effects of both polypeptin and bioture on all antioxidant indices (P <0.001), except for the effect of bioture on liver CAT activity and MDA content. Significant interaction effects were also detected in both liver and intestine (P<0.05 to P<0.001), highlighting synergistic improvements in antioxidant status under combined supplementation.
3.5 Non-specific immune responses
Prior to the V. harveyi challenge, serum nonspecific immune parameters—including LZM, ACP, AKP, and IgM—were significantly elevated in groups receiving polypeptin and bioture supplementation compared with the control, with the highest values generally observed in the co-supplemented groups, particularly P4B4 (Figure 3; P<0.05). Following the bacterial challenge, all groups exhibited time-dependent increases in these parameters at 12 and 24 h; however, the increases were more pronounced in supplemented groups, with peak responses recorded in high-dose co-supplementation treatments (P<0.05). Independent-samples t tests confirmed significant post-challenge increases within each treatment group (P <0.05 to P<0.001). Two-way ANOVA further demonstrated significant main effects of polypeptin and bioture, as well as their interaction, on all immune parameters across time points (P<0.01 to P<0.001), with the exception of bioture on ACP activity at 24 h.
Figure 3
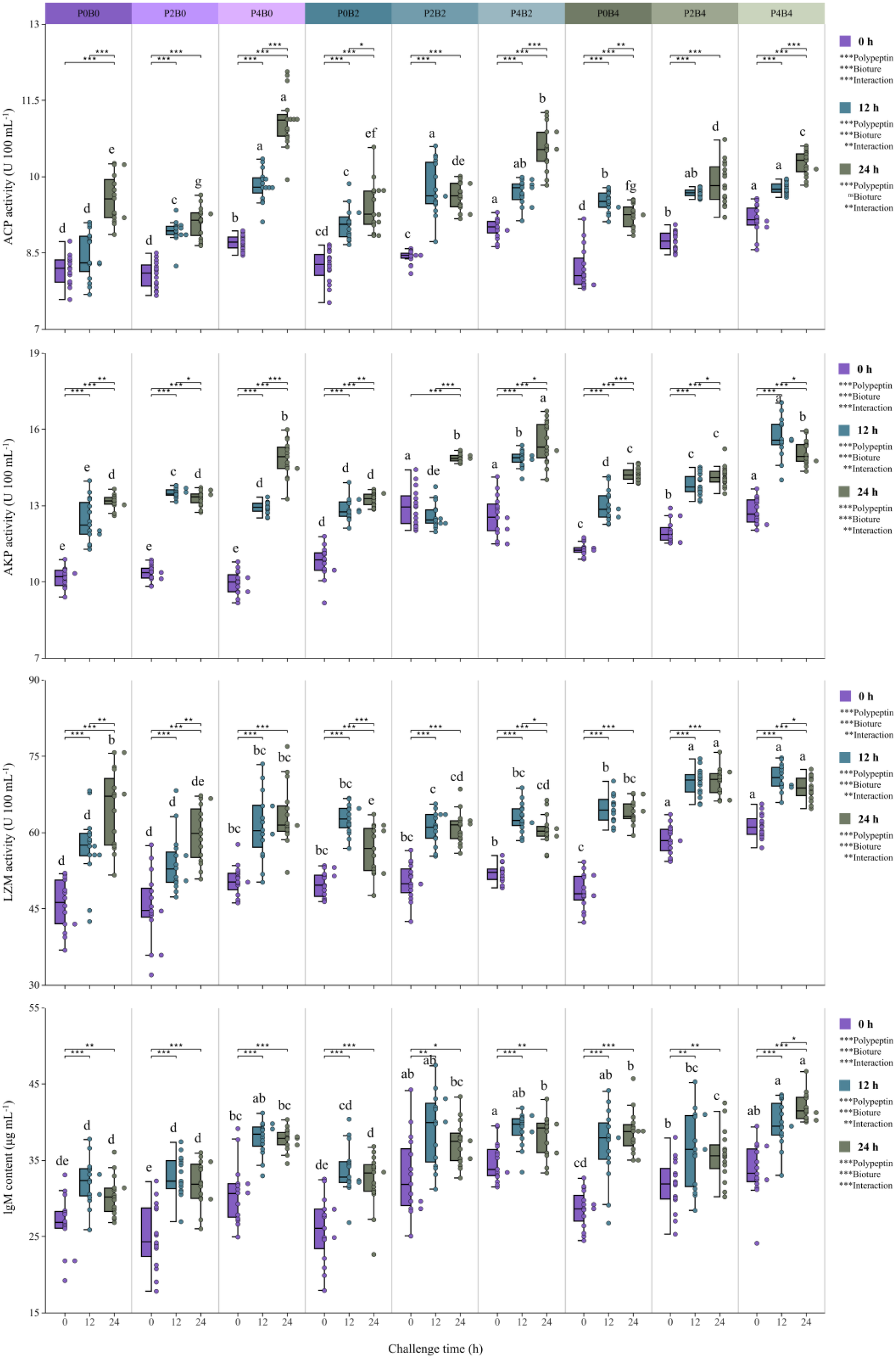
Non-specific immune responses in juvenile hybrid grouper before and after a 24 h challenge test. The superscripted lowercase letters indicate significant differences among dietary treatments (P<0.05). Paired t test and two-way ANOVA: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns, non-significant.
3.6 Disease resistance
During the 144 h pathogen challenge, cumulative survival rates were significantly enhanced by dietary supplementation with polypeptin and bioture (Figure 4). The control group (P0B0) exhibited the lowest survival, whereas the P4B4 group achieved the highest, with intermediate survival rates observed in singly or moderately supplemented groups (P <0.05). Mortality onset was delayed, and overall mortality was reduced in supplemented groups, most notably between 48 and 96 h post-challenge. Two-way ANOVA confirmed significant main effects of both polypeptin and bioture on survival rates (P<0.01 to P<0.001), as well as a significant interaction effect (P<0.05), indicating synergistic protection conferred by combined supplementation.
Figure 4
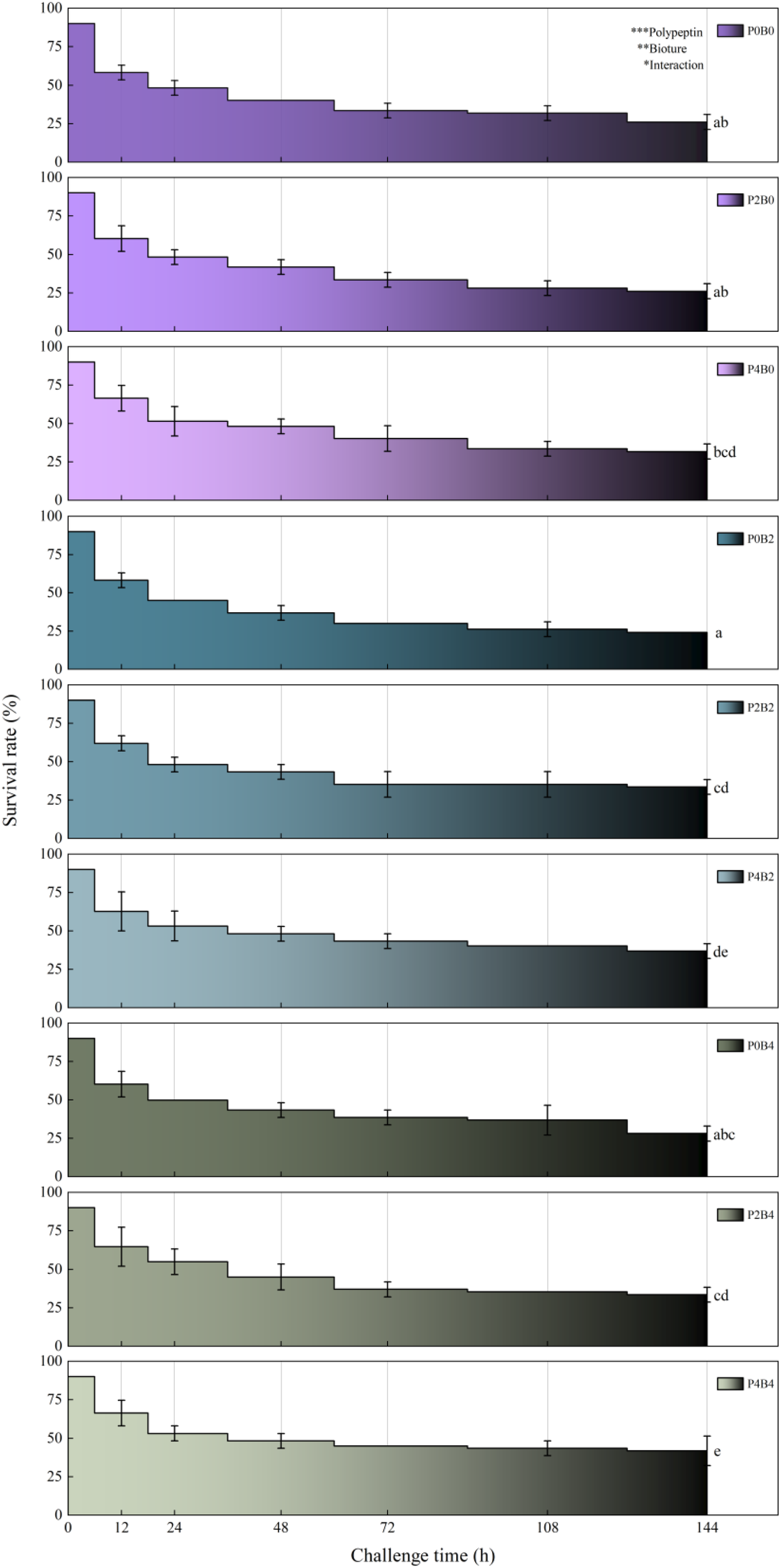
Survival rates of juvenile hybrid grouper under different treatments during a 144 h challenge test. The superscripted lowercase letters indicate significant differences among dietary treatments (P<0.05). Two-way ANOVA: *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns: non-significant.
4 Discussion
The present study demonstrates that dietary supplementation with a peptide-rich hydrolysate (polypeptin) and a yeast-derived complex (bioture) exerts both individual and synergistic benefits on growth, physiological health, and pathogen resistance in juvenile hybrid grouper. The factorial design enabled the separation of main and interaction effects, revealing that co-supplementation improved multiple physiological parameters—including digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant defense, humoral immunity, and survival—beyond the additive contributions of the single additives. These findings complement and extend earlier research on hydrolyzed proteins and immunonutrients in marine finfish (Hlordzi et al., 2022; Xin et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023), providing mechanistic insights into how metabolic and immune pathways converge to enhance resilience in intensive aquaculture systems.
Polypeptin supplementation markedly enhanced intestinal pepsin and trypsin activities, particularly when co-administered with bioture, suggesting increased proteolytic capacity and more efficient protein assimilation. These outcomes are consistent with the established roles of peptide hydrolysates: small peptides and free amino acids are rapidly absorbed, stimulate digestive secretions, and modulate enterocyte differentiation and transporter expression (Ospina-Salazar et al., 2016). In hybrid grouper, hydrolyzed protein sources have previously been shown to promote intestinal development and enzyme activity under low-fishmeal diets (Hlordzi et al., 2022), and similar effects have been reported in barramundi and turbot (Ospina-Salazar et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2020).
The observed reductions in HSI and serum lipid levels in supplemented groups suggest a shift in nutrient allocation from hepatic storage toward somatic growth. This pattern, previously linked to improved nutrient utilization from hydrolysates and other gut-active additives (Hlordzi et al., 2022), reflects both enhanced digestion and metabolic reprogramming at the whole-organism level. From an applied perspective, lower HSI values may indicate alleviation of hepatic lipid accumulation, a common issue in aquaculture species fed high-energy or plant-based diets. By improving proteolytic efficiency and redirecting nutrients toward growth, polypeptin contributes to more sustainable feed utilization and growth optimization.
In parallel, bioture supplementation provided immunological benefits that complemented the digestive enhancements of polypeptin. β-Glucans, as canonical immunomodulators, engage C-type lectin-like receptors on macrophages and neutrophils, priming innate immune responses and enhancing downstream humoral effector production (Petit et al., 2019a; Hadjiamam et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022). MOS prevent pathogen adhesion, modulate intestinal microbiota, and strengthen epithelial tight junctions (Torrecillas et al., 2015; Ding et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2022). Nucleotides further support leukocyte proliferation, antibody synthesis, and mucosal repair (Burrells et al., 2001a, b; Pelusio et al., 2023).
The factorial analysis revealed significant main and interaction effects for immune indices such as lysozyme, ACP, AKP, and IgM, both under baseline conditions and post-challenge. These results suggest that polypeptin provides metabolic substrates to fuel energy-intensive immune processes, whereas bioture primes sentinel immune functions. Together, they establish a state of immune readiness, allowing faster and more effective responses to bacterial invasion. This dual-pathway mechanism—integrating metabolic support with immune priming—represents a key innovation of our approach, contrasting with previous studies that evaluated single agents in isolation (Xin et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023). Similar synergistic strategies have shown stable improvements in immune and growth performance when combining β-glucans with phytogenics or probiotics (Zhu et al., 2023). Our results extend this concept by quantitatively demonstrating synergistic interactions between hydrolyzed peptides and yeast-derived complexes.
Another important outcome was the marked enhancement of systemic antioxidant capacity. Fish receiving co-supplementation exhibited elevated T-AOC, SOD, and CAT activities, together with lower MDA concentrations, indicating stronger protection against reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxidation. These results agree with previous findings that dietary additives such as oregano oil, prebiotics, and organic acids enhance antioxidant defense and mucosal integrity (Sun et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2024). Although gene expression was not evaluated here, the antioxidant patterns observed are consistent with activation of the KEAP1–NRF2 pathway, which orchestrates oxidative stress responses in fish (Li et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2022). Bioactive peptides from hydrolysates may directly scavenge radicals and chelate metals, while β-glucans and MOS likely act indirectly by strengthening epithelial barriers and reducing inflammation (Hadiuzzaman et al., 2022; Lu et al., 2022). Therefore, co-supplementation not only supports digestion and immunity but also provides systemic protection against oxidative damage.
The protective efficacy of these dietary treatments was most evident during the Vibrio harveyi challenge. Co-supplemented fish achieved the highest survival rates and exhibited delayed onset of mortality, especially during the critical 48–96 h postinfection window dominated by innate immune responses. These findings align with recent evidence that certain feed components can induce “trained immunity” in teleosts, whereby innate cells undergo functional reprogramming to mount stronger responses upon re-exposure (Petit et al., 2019b; You et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). The elevated baseline levels of humoral factors (LZM, ACP, AKP, and IgM) observed before infection, combined with rapid postchallenge increases, suggest that bioture components act as training stimuli, while polypeptin provides metabolic reinforcement. In groupers, vibriosis caused by V. harveyi remains a major production constraint (Deng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2024), and previous studies have shown that immunostimulants can mitigate mortality (Zeng et al., 2024). Our results advance this field by demonstrating that a defined peptide–yeast combination provides stronger and more consistent protection than single agents, likely through metabolic–immune crosstalk.
Unlike most previous work that tested hydrolysates, β-glucans, or MOS in isolation (Sun et al., 2021; Hlordzi et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023), our factorial design revealed genuine synergistic interactions across digestive, antioxidant, and immune domains. This provides robust evidence for a mechanism-informed, combinatorial approach to aquafeed design. Practically, the identified biomarkers could serve as useful endpoints for optimizing feed formulations and monitoring fish health in farm environments. Such integrative nutritional strategies are particularly timely as the aquaculture industry seeks to reduce antibiotic use. Nutritional interventions that enhance host resilience represent sustainable alternatives (Hossain et al., 2020). Furthermore, the ubiquity of Vibrio species in marine ecosystems underscores the importance of prophylactic approaches that prime rapid innate defenses, thereby minimizing dependence on therapeutic treatments and reducing economic losses (Mohd Yazid et al., 2021; Zeng et al., 2024).
Despite these promising findings, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, while the three inclusion levels (0, 0.2%, and 0.4%) demonstrated clear synergy, broader dose–response studies are needed to refine optimal inclusion rates under varying dietary and environmental conditions. Second, this study focused on juveniles; extending experiments to other life stages, including broodstock and grow-out fish, would improve generalizability. Third, the intraperitoneal challenge model bypasses mucosal immunity, whereas cohabitation or bath challenges with mixed pathogens would better simulate field conditions (Deng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). Fourth, mechanistic resolution remains incomplete, and future research should include histological analyses, microbiome profiling (16S rRNA and metagenomics), and molecular assays targeting PRR signaling, cytokine networks, and KEAP1–NRF2 pathway activation (Li et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2022). Finally, given the ongoing shift toward fishmeal-free formulations, our results are particularly relevant. Plant-based proteins often exhibit poor digestibility and limited immunological functionality; however, the peptide hydrolysates and yeast-derived compounds examined here may offset these deficiencies. Their synergistic effects on growth, digestion, and immunity suggest that they could become key ingredients in next-generation, sustainable aquafeeds that balance performance with resilience.
5 Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that dietary supplementation with polypeptin and bioture exerts synergistic effects on juvenile hybrid grouper, significantly enhancing growth performance, feed utilization, digestive enzyme activities, antioxidant capacity, humoral immune responses, and resistance to V. harveyi infection. A factorial experimental design revealed significant interaction effects between the two additives, highlighting the complementary roles of polypeptin in promoting nutrient assimilation and bioture in modulating immune function. Co-supplementation yielded superior outcomes compared with individual administration, supporting the efficacy of an integrated precision-nutrition strategy that combines digestive optimization with immunological enhancement. These findings provide robust evidence for the inclusion of polypeptin and bioture in grouper diets to foster sustainable aquaculture practices. Further research is warranted to determine optimal dosing strategies and to elucidate underlying microbiome dynamics and molecular mechanisms.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the ethics committee of Qingdao Agricultural University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
FJ: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XY: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YR: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YH: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. QZ: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. BX: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. PL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32573482), the Modern Agriculture Industry System of Shandong Province (SDAIT-12-16) and the First Class Fishery Discipline Program in Shandong Province, China.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the CNSknowall platform (https://cnsknowall.com) for providing data analysis services.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmars.2025.1700264/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Burrells C. Williams P. D. Forno P. F. (2001b). Dietary nucleotides: a novel supplement in fish feeds. 2. Effects on vaccination, saltwater transfer, growth and physiology of Atlantic salmon. Aquaculture199, 171–184. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00578-6
2
Burrells C. Williams P. D. Southgate P. J. Wadsworth S. L. (2001a). Dietary nucleotides: a novel supplement in fish feeds. 1. Effects on vaccination and protection against disease in salmonids (Oncorhynchus mykiss and Salmo salar). Aquaculture199, 149–161. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00576-2
3
Chen J. Ren Y. Wang G. Zhang L. Zhao H. Sun J. et al . (2018). Dietary supplementation of biofloc influences growth performance, physiological stress, antioxidant status and immune response of juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). Fish Shellfish Immun.72, 143–152. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.10.061
4
Deng Y. Zhang Y. Chen H. Li J. Wang Y. Xu Z. et al . (2020). Gut-liver immune response and gut microbiota profiling reveal the pathogenic mechanisms of Vibrio harveyi in pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus × E. fuscoguttatus). Front. Immunol.11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.607754
5
Ding Z. Liu Y. Xu J. Li X. Wang L. Zhang R. et al . (2022). Dietary mannan oligosaccharides modulate innate immunity, gut microbial and health status of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) juveniles reared in outdoor pond condition. Front. Immunol.13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.904435
6
Gokulakrishnan M. Kumar R. Pillai B. R. Singh S. Thomas J. Anand A. et al . (2022). Dietary brewer’s spent yeast enhances growth, hematological parameters, and innate immune responses at reducing dietary fishmeal level in climbing perch, Anabas testudineus fingerlings. Front. Nutr.9. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.982572
7
Hadjiamam M. Moniruzzaman M. Shahjahan M. Rahman M. M. Akter S. Alam M. J. et al . (2022). β-Glucan: mode of action and its uses in fish immunomodulation. Front. Mar. Sci.9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.905986
8
Hlordzi V. Wang J. Li T. Chen S. Zhang Y. Liu H. et al . (2022). Effects of lower fishmeal with hydrolyzed fish protein powder on the growth performance and intestinal development of juvenile pearl gentian grouper. Front. Mar. Sci.9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.830038
9
Hossain M. S. Koshio S. Kestemont P. (2020). Recent advances of nucleotide nutrition research in aquaculture: a review. Rev. Aquac.12, 1028–1053. doi: 10.1111/raq.12370
10
Konstantinidis I. Firmino J. P. Ruiz A. Fernandez-Alacid L. Navarro A. Esteban M. A. et al . (2022). Brewer’s spent dry yeast modulates immunity in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Front. Mar. Sci.9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.857592
11
Li P. Gatlin D. M. III (2006). Nucleotide nutrition in fish: current knowledge and future applications. Aquaculture251, 141–152. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.01.009
12
Li Y. Chen Z. Wang X. Zhao Q. Sun L. Liu J. et al . (2023). The KEAP1-NRF2 pathway regulates oxidative stress and inflammation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) during bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol.133, 108595. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108595
13
Lu Y. Feng L. Jiang W. D. Wu P. Liu Y. Kuang S. Y. et al . (2022). Dietary mannan oligosaccharides strengthen intestinal immune barrier function via multipath cooperation during Aeromonas hydrophila infection in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Front. Immunol.13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1010221
14
Mohd Yazid S. H. Mohd Daud H. Amal Azmai M. N. Ibrahim T. Ismail N. Sahimi M. B. et al . (2021). Estimating the economic loss due to vibriosis in net-cage cultured Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer): Evidence from the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Front. Vet. Sci.8. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.644009
15
Ospina-Salazar G. H. Partridge G. J. Hauler R. C. (2016). Fish hydrolysate improves growth performance and intestinal health of barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Anim. Nutr.2, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2016.03.001
16
Pelusio N. F. Parma L. Volpe E. Cocci P. Giorgini E. Faccenda F. et al . (2023). Yeast extracted nucleotides and nucleic acids as promising feed additives for European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Front. Mar. Sci.10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1145660
17
Petit J. Bailey E. C. Wheeler R. T. de Bruijn I. Forlenza M. Wiegertjes G. F. et al . (2019a). Studies into β-glucan recognition in fish suggest a key role for the C-type lectin pathway. Front. Immunol.10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00280
18
Petit J. Embregts C. W. E. Forlenza M. Wiegertjes G. F. (2019b). Evidence of trained immunity in a fish: conserved features in carp macrophages. J. Immunol.203, 216–224. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900137
19
Refstie S. Olli J. J. Standal H. (2004). Feed intake, growth, and protein utilization by post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in response to graded levels of fish protein hydrolysate in the diet. Aquaculture232, 105–117. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00510-5
20
Rimoldi S. Gini E. Koch J. F. A. Iannini F. Brambilla F. Terova G. et al . (2020). Effects of hydrolyzed fish protein and autolyzed yeast as substitutes of fishmeal in the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) diet, on fish intestinal microbiome. BMC Vet. Res.16, 118. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02335-1
21
Sheng Z. Huang L. Wu K. (2023). Protein hydrolysate from high lipid microalga boosts larval performance and gut development in snakehead (Channa striata) larvae. Aquaculture563, 738896. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738896
22
Shi X. Chi H. Sun Y. Li Q. Wang H. Zhao X. et al . (2022). The early peritoneal cavity immune response to Vibrio Anguillarum infection and to inactivated bacterium in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Microorganisms10, 2175. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10112175
23
Sun Y. Xiao S. He Q. Zhou W. Li H. Zhang X. et al . (2021). A mixture of Chinese herbs and a commercial probiotic Bacillus species improves hemato-immunological status and reduces mortality of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) following challenge with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquacult. Rep.20, 100651. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100651
24
Tacon A. G. J. Metian M. (2008). Global overview on the use of fish meal and fish oil in industrially compounded aquafeeds: Trends and future prospects. Aquaculture285, 146–158. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.08.015
25
Torrecillas S. Montero D. Caballero M. J. Robaina L. Izquierdo M. S. Zamorano M. J. et al . (2015). Dietary mannan oligosaccharides: counteracting the side effects of soybean meal oil inclusion on European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) gut health and skin mucosa mucus production? Front. Immunol.6. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00397
26
Waikhom D. Das S. Sahoo P. K. (2022). β-Glucan stimulation induces trained-immunity markers in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol.124, 423–432. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.03.027
27
Wang Z. Li Q. Chen Y. (2024). Mannan-oligosaccharide induces trained immunity and protects turbot from acute liver injury. Aquaculture579, 739658. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2024.739658
28
Wu P. Zhang L. Hou Y. Zhang L. (2020). Fish protein hydrolysate affects amino acid absorption and metabolism in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus). Anim. Nutr.6, 389–398. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.03.004
29
Wu P. Zhang L. Jiang W. Liu Y. Zhou X. Feng L. et al . (2022). Dietary vitamin A improved the flesh quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) in relation to the enhanced antioxidant capacity through Nrf2/Keep 1a signaling pathway. Antioxidants11, 148. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010148
30
Xin Y. Liu H. Yan X. Chen Y. Zhao H. Wang J. et al . (2022). Effect of dietary oregano oil on growth performance, disease resistance, intestinal morphology, immunity, and microbiome of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × E. lanceolatus). Front. Mar. Sci.9. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.1038394
31
Xu P. Zhang L. Jiang W. Liu Y. Zhou X. Feng L. et al . (2022). Dietary vitamin A improved the flesh quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) in relation to the enhanced antioxidant capacity through Nrf2/Keap1a signaling pathway. Antioxidants11, 148. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010148
32
You X. Yang J. Wang Z. Zhao Y. Huang L. Zhang Q. et al . (2024). Progress and perspective of trained immunity in teleost fish. Rev. Aquac.16, 732–740. doi: 10.1111/raq.12863
33
Zanuzzo F. S. Beemelmanns A. Hall J. R. Rise M. L. Gamperl A. K . (2020). The innate immune response of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) is not negatively affected by high temperature and moderate hypoxia. Front. Immunol.11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01009
34
Zeng Y. H. Liu F. Zhou X. (2024). Progress and perspective of trained immunity in teleost fish. Rev. Aquac.16, e12863. doi: 10.1111/raq.12863
35
Zhang Y. Guo M. Li N. Chen H. Wang Y. Xu Z. et al . (2022). New insights into β-glucan-enhanced immunity in large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea by transcriptome and intestinal microbial composition. Front. Immunol.13. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1068103
36
Zhang Y. Guo M. Li N. Zhao H. Wang Y. Xu Z. et al . (2024). Dual RNA-seq reveals early virulence programs of Vibrio harveyi in hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × E. lanceolatus). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.14. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1445678
37
Zhang Y. Li X. Chen H. (2021). Chitosan oligosaccharide enhances resistance to Vibrio harveyi in pearl gentian grouper. Aquacult. Res.52, 6354–6365. doi: 10.1111/are.14912
38
Zhu L. Wang S. Cai Y. Liu H. Zhang R. Chen Y. et al . (2023). Effects of five prebiotics on growth, antioxidant capacity, non-specific immunity, stress resistance, and disease resistance of juvenile hybrid grouper. Animals13, 754. doi: 10.3390/ani13040754
Summary
Keywords
hybrid grouper, polypeptin, bioture, immunonutrition, Vibrio harveyi resistance
Citation
Jing F, Yin X, Ren Y, Han Y, Zhou Q, Xia B, Li Q and Liu P (2025) Dietary supplementation with polypeptin and bioture improves growth, feed utilization, antioxidant capacity, and disease resistance in juvenile hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × E. lanceolatus♂). Front. Mar. Sci. 12:1700264. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2025.1700264
Received
06 September 2025
Accepted
13 October 2025
Published
29 October 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Amit Ranjan, Tamil Nadu Fisheries University, India
Reviewed by
Mingqing Zhang, Guangzhou University, China; Ahmed Elsebaey, Mansoura University, Egypt; Julieta Sánchez, Universidad Autonoma de Queretaro Facultad de Ingenieria, Mexico
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Jing, Yin, Ren, Han, Zhou, Xia, Li and Liu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Xia, ac_xbin@126.com; Peng Liu, liupeng_ocean@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.