Abstract
Introduction:
The aims of this study is to analyze the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in patients with psoriasis treated with secukinumab and ixekizumab.
Methodology:
We systematically identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that focused on the treatment of psoriasis with secukinumab and ixekizumab by conducting computerized searches of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library databases, spanning from their inception to October 31st, 2022. The search terms used included psoriasis, secukinumab, ixekizumab, and randomized controlled trial. Two independent evaluators conducted literature screening, data extraction, and assessed the quality of included studies based on predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The gather data was subjected to meta-analysis using the statistical software RevMan 5.4.
Results:
A total of 20 articles, encompassing 23 randomized controlled trials involving 10,746 psoriasis patients were included in the analysis. During the double-blind treatment period, the meta-analysis results indicated the following: There was no significant difference in the incidence of MACEs between the secukinumab and placebo groups [RR = 0.61, 95% CI (0.26, 1.44), p = 0.26]. Similarly, there was no significant difference in the incidence of MACEs with ixekizumab compared to the placebo group [RR = 0.47, 95% CI (0.15, 1.47), p = 0.20]. Furthermore, no significant difference in the incidence of MACEs was observed between secukinumab 300 mg and secukinumab 150 mg treatment groups [RR = 1.00, 95% CI (0.23, 4.35), p = 1.00]. Likewise, there was no significant difference in the incidence of MACEs between the ixekizumab Q4W (every 4 weeks) and ixekizumab Q2W (every 2 weeks) administration groups [RR = 4.01, 95% CI (0.45, 35.89), p = 0.21].
Conclusion:
The findings of this study suggest that neither secukinumab nor ixekizumab is significantly associated with the risk of MACEs in patients with psoriasis during double-blind treatment.
Systematic review registration: Unique Identifier: CRD42022373756 https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/.
1 Introduction
Psoriasis is a systemic inflammatory disease with diverse clinical manifestations and comorbidities that significantly impact the quality of life for affected individuals (1). Unlike the general population, individuals with psoriasis experience effects on almost every system in the body. Among the various conditions associated with psoriasis, cardiovascular (CV) disease stands out as a major concern due to its common occurrence and immediate implications for morbidity and mortality (2). The connection between cardiovascular disease, as one of these comorbidities, and medications used in the treatment of psoriasis has become a subject of discussion as attention on psoriasis-related comorbidities increase. Research indicates a consistent association between severe psoriasis and an elevated risk of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACEs), with medications employed in psoriasis treatment also exhibiting a connection to the development of cardiovascular disease (3, 4).
Pooled data analysis reveals that biologic treatments contribute to a reduction in CV events, coronary inflammation, and the presence of high-risk coronary plaques. In particular, anti-interleukin (IL)-17 therapy has shown positive effects on systemic inflammation and coronary plaque in patients with psoriasis (5). The introduction of biologics, specifically those inhibiting IL-17, has provided new options for the maintenance therapy of various autoimmune diseases. Currently approved in China, IL-17A inhibitors such as secukinumab and ixekizumab are human monoclonal antibodies that directly targeting interleukin-17A (IL-17A) (6). Studies conducted on the Chinese population have demonstrated that subcutaneous injections of secukinumab and ixekizumab are highly effective, provide rapid relief of symptoms, and have fewer adverse reactions (7, 8).
Hence, the purpose of this study is to systematically review the published randomized controlled trials involving secukinumab and ixekizumab in the treatment of psoriasis. The objective is to evaluate the risk of MACEs and provide recommendations for cautions clinical utilization.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and selection
A comprehensive literature search method was utilized to systemic examine all relevant literature from the inception of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases up to October 2022, without any language restrictions. This study included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving secukinumab and ixekizumab in the treatment of psoriasis. The search employed specific terms such as “secukinumab,” “ixekizumab,” “psoriasis,” “randomized controlled trial,” and others, combining subject headings and free-text terms. A detailed overview of the retrieval strategy is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1

PRISMA flow diagram.
2.2 Population of interest
The study specifically focused on adult patients aged 18 years or older who had been diagnosed with psoriasis for a duration of at least 6 months, regardless of gender. Psoriasis diagnoses were confirmed by dermatologists through examination and biopsy, while diagnoses of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) were made by rheumatologists following the CASPAR diagnostic criteria.
Exclusion criteria included patients below the age of 18, individuals unwilling to discontinue their current treatment regimen, participation in other clinical trials within the last 3 months, non-randomized controlled studies, reviews, animal studies, conference abstracts, and cases where the full text was inaccessible or data extraction was incomplete.
2.3 Interventions and comparators
In the experimental group, subcutaneous administrations of secukinumab or ixekizumab were given. The dosage of secukinumab was set at 300 mg and 150 mg, respectively, while the dosage of ixekizumab varied in frequency, either once every 2 weeks or once every 4 weeks. The control group received subcutaneous placebos, encompassing both no treatment and treatment-as-usual.
2.4 Outcomes measure
This meta-analysis aimed to examine the impact of IL-17A inhibitors on MACEs in patients with psoriasis. The analysis focused on four key aspects:
-
The incidence of MACEs in patients with psoriasis who treated with secukinumab;
-
The evaluation of the incidence of MACEs with secukinumab at 300 mg and 150 mg;
-
The assessment of MACEs incidence in patients with psoriasis treated with ixekizumab;
-
Comparative analysis of the incidence of MACEs with different frequencies of ixekizumab administration.
2.5 Data extraction
Using the Endnote X9 literature management software, two researchers conducted a thorough screening of the literature, strictly adhering to pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. The initial step involved eliminating duplicate literature, followed by a detailed review of the article’s title and abstract for preliminary screening. Upon obtaining the full text, a secondary filtration process was carried out. Any discrepancies encountered during the screening process were resolved through negotiation or consultation with a third party. The extracted data were meticulously recorded in tabular form, capturing key details such as the first author, year of publication, country of publication, experimental design, basic characteristics of study subjects, sample size, intervention measures, outcome indicators, duration of disease, and the incidence of MACEs during the trial.
2.6 Assessment of risk of bias for included studies
The methodological rigor of the incorporated studies was assessed utilizing the bias risk assessment tool designed for randomized controlled trials, as stipulated in the Cochrane Manual of Systematic Reviewers 5.1.0.
2.7 Statistical analysis
The comparison of MACEs between secukinumab and ixekizumab, as well as their comparison with a placebo was conducted using RevMan 5.4 software. Relative risk served as the effect statistic for dichotomous variables was expressed as the relative risk (RR), and a 95% confidence interval (CI) was employed for interval estimation. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the chi-square test, and the extent of heterogeneity was measured using I2 test. If no significant heterogeneity was observed (p > 0.10, I2 ≤ 50%), the fixed-effects model was applied. In case of where heterogeneity was present, a thorough analysis of its potential causes was conducted, and subsequently, the random-effects model was implemented.
3 Results
3.1 Study characteristics
Through a systematic search, a total of 1,129 articles were retrieved, distributed across PubMed (n = 181), Embase (n = 655), and the Cochrane Library (n = 293). After initial screening, 81 articles were selected for further evaluation. Following a rigorous secondary screening process, 20 articles were included for both qualitative and quantitative analysis. It worth noting that all of included articles were in English (Figure 1).
3.2 Risk of bias
In conclusion, the analysis included a total of 20 studies, encompassing 23 randomized controlled trials, which involved 10,746 participants. The experimental group consisted of 7,738 participants, while the control group included 3,008 participants. The essential information from these studies is presented in Table 1.
Table 1
| First Author, surname, and Year | Country | Design | Group | Sample size | Male | MACEs | Age, y | Duration of psoriasis, y | treatment period, w |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bagel, J., 2017 | United States | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 51 | 27 | 0 | 42.7 ± 13.4 | NA | 12 |
| (2) Placebo control group | 51 | 24 | 0 | 41.1 ± 14.2 | |||||
| Nash, P., 2018 | Australia | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 139 | 67 | 0 | 49.3 ± 12.9 | NA | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 138 | 61 | 0 | 50.1 ± 11.7 | |||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 137 | 59 | 0 | 50.1 ± 12.6 | |||||
| Papp, K., 2013 | Canada | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 450 mg treatment group | 27 | 21 | 0 | 45.4 ± 11.64 | 16.2 ± 10.41 | 12 |
| (2) Secukinumab 225 mg treatment group | 21 | 14 | 1 | 45.8 ± 12.36 | 17.1 ± 9.01 | ||||
| (3) Secukinumab 75 mg treatment group | 26 | 22 | 3 | 46.3 ± 13.43 | 17.7 ± 11.53 | ||||
| (4) Secukinumab 25 mg treatment group | 29 | 20 | 1 | 46.1 ± 12.65 | 19.8 ± 12.66 | ||||
| (5) Placebo control group | 22 | 14 | 3 | 45.9 ± 10.88 | 21.4 ± 14.80 | ||||
| Paul, C., 2015 | France | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 60 | 46 | 0 | 46.6 ± 14.23 | 21.0 ± 13.51 | 12 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 61 | 41 | 0 | 43.9 ± 14.41 | 20.6 ± 14.54 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 61 | 38 | 0 | 43.7 ± 12.74 | 19.86 ± 12.20 | ||||
| Blauvelt, A., 2015 | United States | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 59 | 38 | 2 | 45.1 ± 12.57 | 18.0 ± 11.86 | 12 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 59 | 40 | 0 | 46.0 ± 15.09 | 20.4 ± 12.97 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 59 | 39 | 0 | 46.5 ± 14.14 | 20.2 ± 14.22 | ||||
| Ohtsuki, M., 2014 | Japan | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 29 | 26 | 0 | 51.9 ± 11.77 | 15.6 ± 10.30 | 12 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 29 | 23 | 1 | 48.2 ± 13.08 | 15.6 ± 10.41 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 29 | 23 | 0 | 50.2 ± 13.62 | 14.1 ± 10.91 | ||||
| Mrowietz, U., 2019 | United States | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 79 | 15 | 0 | 50.6 ± 14.8 | NA | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 80 | 17 | 0 | 50.7 ± 13.7 | |||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 78 | 19 | 1 | 52.9 ± 11.3 | |||||
| Langley, R., 2014 | United Kingdom | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 245 | 169 | 0 | 44.9 ± 13.5 | 17.4 ± 11.1 | 12 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 245 | 168 | 0 | 44.9 ± 13.3 | 17.5 ± 12.0 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 248 | 172 | 0 | 45.4 ± 12.6 | 17.3 ± 12.4 | ||||
| Nguyen, T., 2022 | California | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 103 | 53 | 0 | 51.9 ± 12.6 | NA | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 103 | 56 | 1 | 51.3 ± 14.6 | |||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 52 | 23 | 1 | 53.1 ± 12.7 | |||||
| Mease, P. J., 2015 | United Kingdom | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 202 | 96 | 0 | 49.6 ± 11.8 | NA | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 75 mg treatment group | 202 | 84 | 1 | 48.8 ± 12.2 | |||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 202 | 96 | 0 | 48.5 ± 11.2 | |||||
| Gottlieb, A., 2017 | United States | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 69 | 38 | 0 | 48.8 ± 14.2 | NA | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 68 | 40 | 0 | 52.4 ± 12.6 | |||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 68 | 34 | 0 | 50.9 ± 13.0 | |||||
| McInnes, I. B., 2015 | United Kingdom | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 100 | 51 | 0 | 46.9 ± 12.6 | NA | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 100 | 55 | 0 | 46.5 ± 11.7 | |||||
| (3) Secukinumab 75 mg treatment group | 99 | 47 | 1 | 48.6 ± 11.4 | |||||
| (4) Placebo control group | 98 | 39 | 0 | 49.9 ± 12.5 | |||||
| Reich, K., 2019 | Germany | RCT | (1) Secukinumab 300 mg treatment group | 66 | 53 | 0 | 45.1 ± 12.9 | 18.01 | 16 |
| (2) Secukinumab 150 mg treatment group | 67 | 55 | 0 | 43.5 ± 10.9 | 20.02 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 65 | 52 | 0 | 43.6 ± 11.2 | 17.35 | ||||
| Kemény, L., 2019 | Hungary | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group | 734 | NA | 3 | 45.4 ± 13.1 | 18.4 ± 12.3 | 12 |
| (2) Placebo control group | 360 | 1 | |||||||
| Ryan, C., 2018 | Ireland | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group | 75 | 56 | 0 | 43.1 ± 13.0 | 16.9 ± 12.8 | 12 |
| (2) Placebo control group | 74 | 57 | 0 | 44.4 ± 12.6 | 16.1 ± 12.5 | ||||
| Nash, P., 2017 | Australia | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q4W) | 122 | 59 | 0 | 52.6 ± 13.6 | 15·7 ± 12.3 | 24 |
| (2) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q2W) | 123 | 73 | 0 | 51·7 ± 11.9 | 16.5 ± 13.0 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 118 | 62 | 2 | 51·5 ± 10.4 | 15.3 ± 12.6 | ||||
| Mease, P. J., 2017 | United States | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q4W) | 107 | 45 | 0 | 49.1 ± 10.1 | 16.5 ± 13.8 | 24 |
| (2) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q2W) | 103 | 48 | 0 | 49.8 ± 12.6 | 17.0 ± 14.0 | ||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 106 | 48 | 0 | 50.6 ± 12.3 | 16.0 ± 13.8 | ||||
| Gordon, K. B., 2016 | United States | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q4W) | 1,165 | 791 | 2 | * | * | 12 |
| (2) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q2W) | 1,169 | 766 | 0 | ||||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 792 | 560 | 1 | ||||||
| Griffiths, C. E. M., 2015 | United Kingdom | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q4W) | 733 | 502 | 1 | * | * | 12 |
| (2) Ixekizumab treatment group (Q2W) | 736 | 475 | 0 | ||||||
| (3) Placebo control group | 361 | 257 | 1 | ||||||
| Leonardi, C., 2012 | United States | RCT | (1) Ixekizumab treatment group | 115 | 67 | 0 | * | * | 20 |
| (2) Placebo control group | 27 | 27 | 0 |
Characteristics of the included studies.
*Details are provided in the Supplementary Table S1; NA, Not mentioned.
All of the studies adhered to a randomized double-blind trial design. However, four studies (9–12) exhibited had unclear randomization methods, one study (11) lacked clarity in outcome index evaluation methods, and 12 studies (13–24) utilized distributive hiding. Apart from one study (20), the remaining 19 studies were conducted at multiple centers. It should be noted that all studies experienced participant due to adverse reactions, such as psoriatic erythroderma, alopecia, herpes and others. A detailed breakdown of the bias risk assessment results is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2
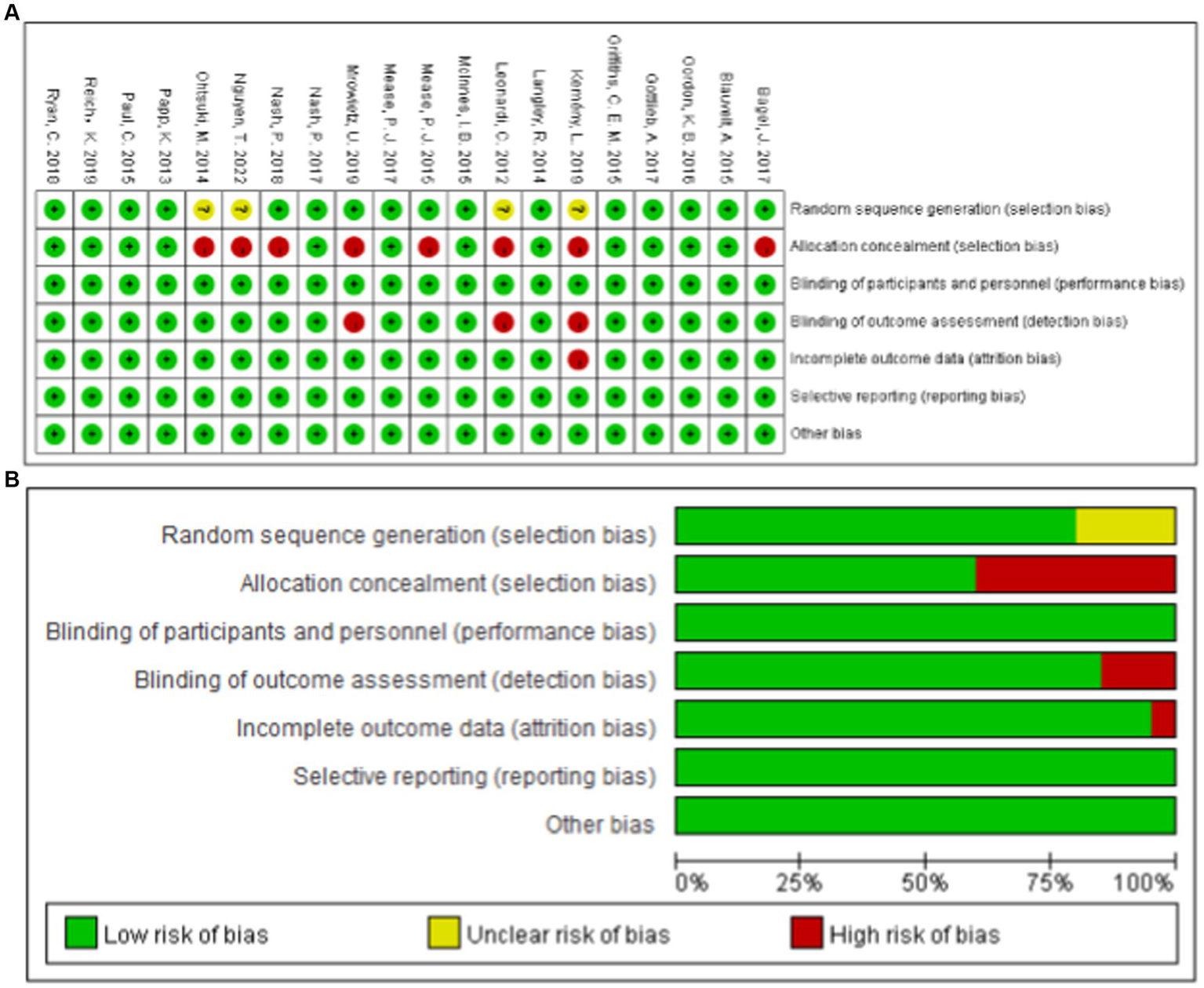
Summary of Cochrane risk of Bias for the RCTs.
3.3 Meta-analysis
3.3.1 Incidence of MACEs in patients with psoriasis using secukinumab
Thirteen studies reported MACEs in patients treated with secukinumab (9, 10, 13–19, 25–28). The results of meta-analysis showed that there was no increase in the incidence of MACEs in patients treated with secukinumab. Furthermore, there was no significant difference between the experimental group and the control group [RR = 0.61, 95%CI (0.26, 1.44), p = 0.26] as depicted in Figure 3.
Figure 3

Forest plots of the incidence of MACEs between secukinumab and placebo groups.
3.3.2 Comparison of secukinumab in the incidence of 300 mg and 150 mg MACEs
Ten studies (9, 10, 14–19, 26, 27) have reported a direct comparison of the incidence of MACEs in patients treated with secukinumab at different doses of 300 mg and 150 mg. The meta-analysis results showed that there was no significant difference between the two groups [RR = 1.00, 95%CI (0.23, 4.35) p = 1.00] as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4

Forest plot of the incidence of MACEs between the 300 mg and 150 mg secukinumab groups.
3.3.3 Incidence of MACEs in patients with psoriasis using ixekizumab
The incidence of MACEs in patients with psoriasis treated with ixekizumab was reported in seven studies (11, 12, 20–24). The meta-analysis results showed that ixekizumab did not increase the incidence of MACEs in patients. Additionally, there was no significant difference between the experimental group and the control group [RR = 0.47, 95%CI (0.15, 1.47), p = 0.20] as depicted in Figure 5.
Figure 5
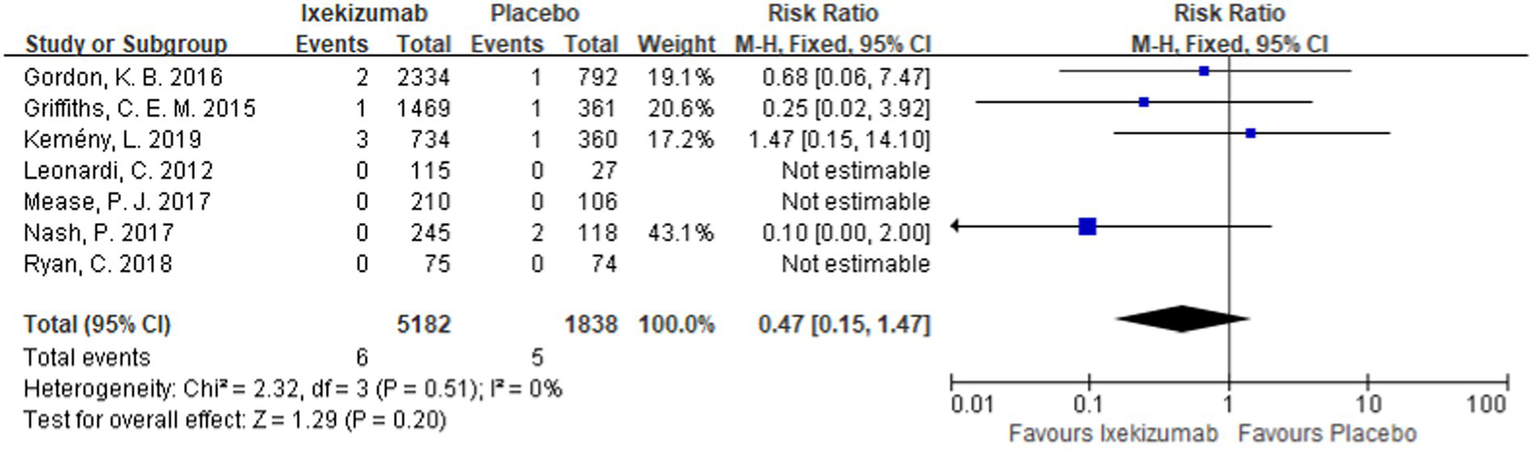
Forest plot of incidence of MACEs between ixekizumab and placebo groups.
3.3.4 Comparison of the incidence of different frequencies of administration of ixekizumab
A direct comparison of the incidence of MACEs in patients treated with different frequencies of administration of ixekizumab (receive subcutaneous injections of ixekizumab every 2 weeks and every 4 weeks) was reported in four studies (21–24). The meta-analysis results showed that there was no significant difference between the two groups [RR = 4.01, 95%CI (0.45, 35.89) p = 0.21] as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6
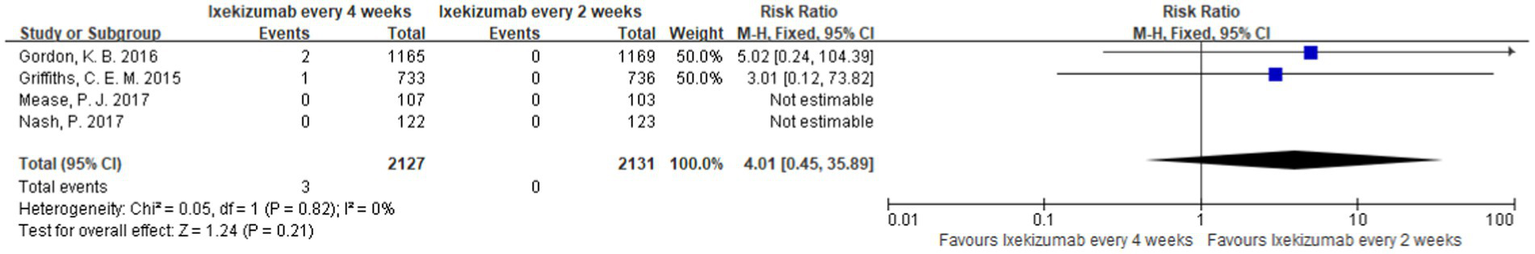
Forest map of the incidence of MACEs between the different frequencies of administration of ixekizumab.
3.4 Bias in publication
Funnel plots were used to analyze publication bias in the literatures reporting the incidence of MACEs in each group (Figure 7). The results showed that all funnel plots had good symmetry, suggesting that the study results were less affected by publication bias.
Figure 7
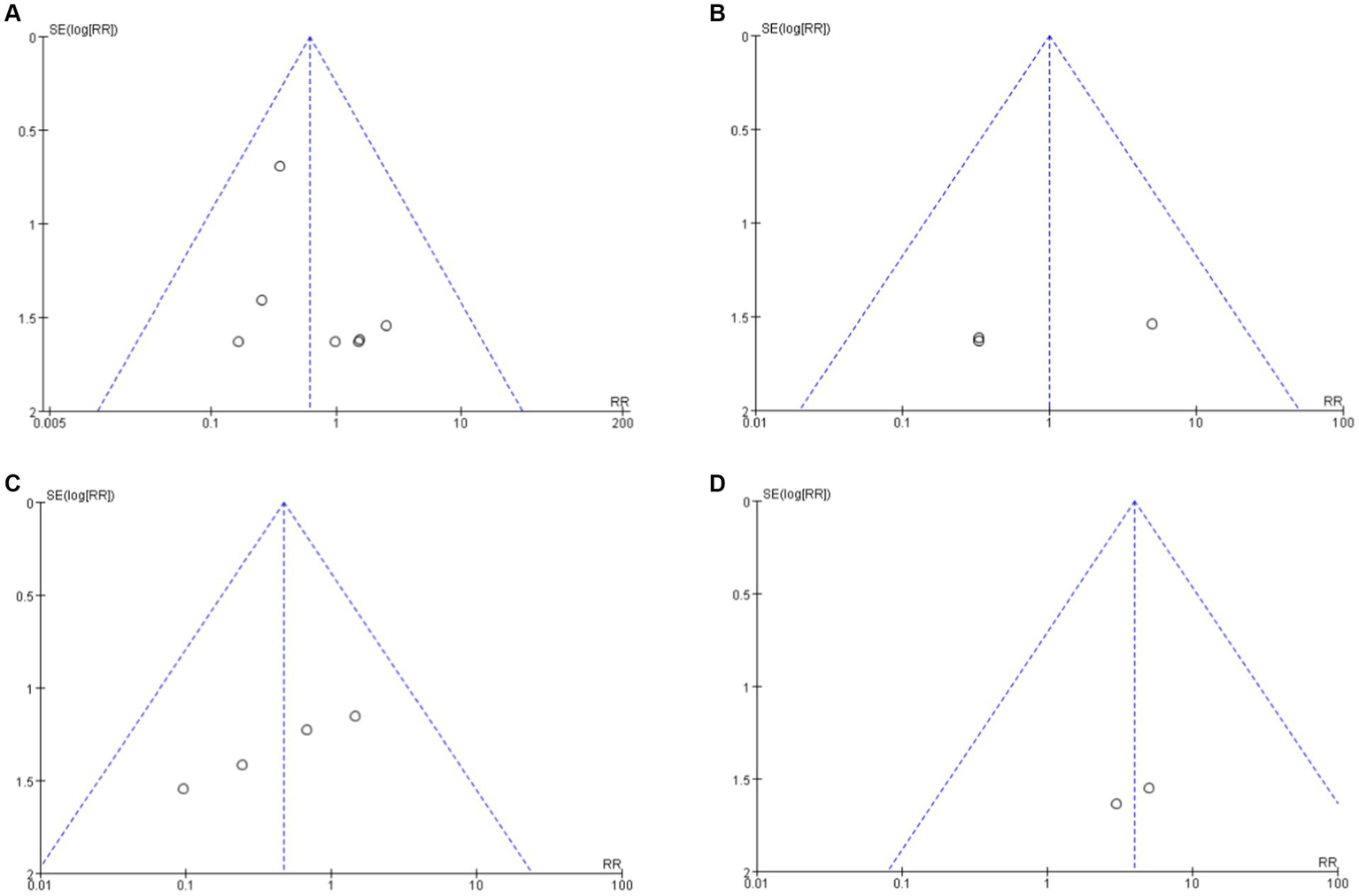
Funnel plot analysis of clinical indicators among each group. (A) Secukinumab vs. Placebo. (B) Secukinumab 300 mg vs. 150 mg. (C) Ixekuzumab vs. Placebo. (D) Ixekizumab Every 4 Weeks vs. Every 2 Weeks.
4 Discussion
4.1 Quality of the studies
The search strategy employed is robust and designed to minimize the likelihood of overlooking eligible studies. Most of the included studies exhibit a clear and high risk of bias (ROB), with explicit references to randomization and blinding strategies. For example, Nash et al. (21) implemented treatment allocation concealment and generated a random sequence using a computer. The study ensured that investigators, study site staff, and patients remained unaware of treatment allocations until the initial data analysis. However, a few studies lack clarity in their descriptions of randomization and blinding methods. In the study conducted by Nguyen et al. (10), for instance, the randomization method was unclear, and no specific treatment allocation scheme was specified.
4.2 Outcome
Psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin disease, has a significant impact on both the physical and mental well-being of individuals affected by it. Emerging evidence suggests that severe psoriasis is not only linked to metabolic disorders, obesity, and heightened mortality but also serve as an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke (29). The condition is associated with various comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, cancer, gastrointestinal disorders, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (30). A recent study conducted in UK revealed that individuals with moderate to severe psoriasis had a lifespan that was approximately 6 years shorter than their healthy counterparts, possibly attributed to inflammation-induced cardiovascular diseases (CVD), such as myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction (31).
Furthermore, research indicates a 57% increased risk of cardiovascular (CV) death among patients with severe psoriasis compared to those with traditional CV risk factors. Notably, while the majority of CV death risks are typically attributed to explained by major cardiac risk factors, this association is not consistently observed in severe psoriasis cases, implying an independent association between severe psoriasis and CV death (32). Additionally, Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is linked to a higher incidence of CVD complications in Western countries and Japan. Recent analyses of cytokines from psoriasis patients suggest that certain cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-17, and IL-23, have cardiovascular effects (31).
The IL-17A inhibitors such as secukinumab and ixekizumab have been approve for the treatment of psoriasis in China. Many studies have shown that the efficacy and safety of these two drugs in treating psoriasis, but their impact on psoriasis comorbidities, particularly cardiovascular disease has received less attention. Therefore, studies have been conducted to investigated the effect of IL-17A inhibitors on cardiovascular events in patients with psoriasis.
This study included 20 studies to investigate the association between IL-17A inhibitors and psoriasis comorbidities (specifically cardiovascular disease) based on the occurrence of MACEs in patients with psoriasis treating with secukinumab and ixekizumab. With the exception of one study, the other included studies were multi-center randomized double-blind controlled trials with well-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Among the 20 studies, only 4 studies had a large bias due to unclear randomization methods, while most of the studies had a low risk of bias. The meta-analysis results of this study showed no significant difference in the incidence of MACEs between secukinumab and ixekizumab compared to placebo, and the difference between the two groups was not statistically significant. The findings were consistent with the study by Rungapiromnan et al. (33) which demonstrated that secukinumab and ixekizumab did not significantly affect the risk of MACEs in adult patients with psoriasis in the short term, and there was no dose-dependent increase in the incidence of adverse events.
4.3 Limitation
The baseline characteristics of the included literature in this study were comparable, ensuring reliable results, high literature quality, and a large sample size. However, certain limitations should be acknowledged:
-
Methodological Heterogeneity: The use of diverse follow-up treatment regimens introduced substantial methodological heterogeneity. Ethical considerations prevented the long-term use of a placebo, resulting in a relatively short trial period focused solely on MACEs during the double-blind phase, without further analysis.
-
Age Representation: The predominantly middle-aged participants included in this study may not accurately represent the true incidence across all age groups. The incidence of such events tends to increase with age, and therefore, the finding may be limited in their generalizability to different age ranges.
-
Cardiovascular Risk Factors: It’s essential to note that most patients had pre-existing cardiovascular risk factors. While myocardial infarction and stroke were identified as the most common cardiovascular events, the occurrence of these events may not be solely attributable to the administered drugs. The presence of these pre-existing risk factors introduces a potential confounding factor should be taken into consideration when interpreting the results.
4.4 Recommendations
Future research directions should encompass RCTs involve a broader spectrum of age groups among patients. This would help provide more comprehensive insights into the impact of IL-17A inhibitors on cardiovascular events across different age range. Furthermore, there is a need for more direct comparisons between different drugs to enhance the understanding of their relative efficacy in treating psoriasis and their effect on CV outcomes. Additionally, it would be valuable to conduct additional trials with consistent follow-up regimens, allowing for a more in-depth exploration of associated long-term and post-discontinuation safety concerns with IL-17A inhibitors. It is imperative that these studies are substantiated by an increased number of high-quality clinical trials to ensure the reliability and robustness of the findings.
5 Conclusion
A meta-analysis was undertaken to explore the impact of IL-17A inhibitors (secukinumab and ixekizumab) on serious cardiovascular adverse events in adult patients with psoriasis. To ensure the validity and reliability of the clinical evidence in this study, only randomized controlled trials were included, minimizing the potential sources of bias. This rigorous approach provides a solid foundation for assessing the short-term effects of IL-17A inhibitors on cardiovascular disease in individuals with psoriasis. Furthermore, the majority of the incorporated studies featured substantial sample sizes, enhancing the study’s utility as a valuable guide for informed decision-making, particularly when addressing comorbidities associated with psoriasis.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YZ: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Resources. ZY: Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. JG: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Conceptualization. DS: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NM 82272358), Key Research and Development Plan of Jining (2022YXNS127 and 2023YXNS001), Medicine health science and technology development plan of Shandong Province (202202070556).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1353893/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Augustin M Sator PG von Kiedrowski R Conrad C Rigopoulos D Romanelli M et al . Secukinumab demonstrated sustained retention, effectiveness and safety in a real-world setting in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: long-term results from an interim analysis of the SERENA study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2022) 36:1796–804. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18329
2.
Chi CC Wu YW Chao TH Chen CC Chen YJ Cheng HM et al . 2022 Taiwanese Dermatological Association (TDA), Taiwanese Association for Psoriasis and Skin Immunology (TAPSI), and Taiwan Society of cardiology (TSOC) joint consensus recommendations for the management of psoriatic disease with attention to cardiovascular comorbidities. J Formos Med Assoc. (2023) 122:442–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2022.10.010
3.
Ogdie A Yu Y Haynes K Love TJ Maliha S Jiang Y et al . Risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:326–32. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205675
4.
Patrick MT Li Q Wasikowski R Mehta N Gudjonsson JE Elder JT et al . Shared genetic risk factors and causal association between psoriasis and coronary artery disease. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:10.1038/s41467-022-34323-4:6565.
5.
Merola JF McInnes IB Deodhar AA Dey AK Adamstein NH Quebe-Fehling E et al . Effect of Secukinumab on traditional cardiovascular risk factors and inflammatory biomarkers: post hoc analyses of pooled data across three indications. Rheumatol Ther. (2022) 9:935–55. doi: 10.1007/s40744-022-00434-z
6.
Eshwar V Kamath A Shastry R Shenoy AK Kamath P . A Review of the Safety of Interleukin-17A Inhibitor Secukinumab. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). (2022) 15:1365. doi: 10.3390/ph15111365
7.
Zeng JX Luo Q Wen J Tian X Zhou X Li W et al . Real-world investigation of the efficacy and safety of secukinumab for psoriasis treatment in a Chinese population. Chin Med J. (2020) 134:117–9. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001179
8.
Golhen K Winskill C Theiler M Buettcher M Yeh YH Zhang N et al . Understanding efficacy-safety balance of biologics in moderate-to-severe pediatric psoriasis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:944208. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.944208
9.
Ohtsuki M Morita A Abe M Takahashi H Seko N Karpov A et al . Secukinumab efficacy and safety in Japanese patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: subanalysis from ERASURE, a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. J Dermatol. (2014) 41:1039–46. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12668
10.
Nguyen T Churchill M Levin R Valenzuela G Merola JF Ogdie A et al . Secukinumab in United States biologic-naive patients with psoriatic arthritis: results from the randomized, placebo-controlled CHOICE study. J Rheumatol. (2022) 49:894–902. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.210912
11.
Kemeny L Berggren L Dossenbach M Dutronc Y Paul C . Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab in patients with plaque psoriasis across different degrees of disease severity: results from UNCOVER-2 and UNCOVER-3. J Dermatolog Treat. (2019) 30:19–26. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2018.1473551
12.
Leonardi C Matheson R Zachariae C Cameron G Li L Edson-Heredia E et al . Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:1190–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1109997
13.
Papp KA Langley RG Sigurgeirsson B Abe M Baker DR Konno P et al . Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II dose-ranging study. Br J Dermatol. (2013) 168:412–21. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12110
14.
Paul C Lacour JP Tedremets L Kreutzer K Jazayeri S Adams S et al . Efficacy, safety and usability of secukinumab administration by autoinjector/pen in psoriasis: a randomized, controlled trial (JUNCTURE). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2015) 29:1082–90. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12751
15.
Blauvelt A Prinz JC Gottlieb AB Kingo K Sofen H Ruer-Mulard M et al . Secukinumab administration by pre-filled syringe: efficacy, safety and usability results from a randomized controlled trial in psoriasis (FEATURE). Br J Dermatol. (2015) 172:484–93. doi: 10.1111/bjd.13348
16.
Langley RG Elewski BE Lebwohl M Reich K Griffiths CE Papp K et al . Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis--results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:326–38. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1314258
17.
Gottlieb A Sullivan J van Doorn M Kubanov A You R Parneix A et al . Secukinumab shows significant efficacy in palmoplantar psoriasis: Results from GESTURE, a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2017) 76:70–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.07.058
18.
McInnes IB Mease PJ Kirkham B Kavanaugh A Ritchlin CT Rahman P et al . Secukinumab, a human anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriatic arthritis (FUTURE 2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2015) 386:1137–46. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61134-5
19.
Reich K Sullivan J Arenberger P Mrowietz U Jazayeri S Augustin M et al . Effect of secukinumab on the clinical activity and disease burden of nail psoriasis: 32-week results from the randomized placebo-controlled TRANSFIGURE trial. Br J Dermatol. (2019) 181:954–66. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17351
20.
Ryan C Menter A Guenther L Blauvelt A Bissonnette R Meeuwis K et al . Efficacy and safety of ixekizumab in a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase IIIb study of patients with moderate-to-severe genital psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. (2018) 179:844–52. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16736
21.
Nash P Kirkham B Okada M Rahman P Combe B Burmester GR et al . Ixekizumab for the treatment of patients with active psoriatic arthritis and an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: results from the 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled period of the SPIRIT-P2 phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2017) 389:2317–27. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31429-0
22.
Mease PJ van der Heijde D Ritchlin CT Okada M Cuchacovich RS Shuler CL et al . Ixekizumab, an interleukin-17A specific monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of biologic-naive patients with active psoriatic arthritis: results from the 24-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active (adalimumab)-controlled period of the phase III trial SPIRIT-P1. Ann Rheum Dis. (2017) 76:79–87. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209709
23.
Gordon KB Blauvelt A Papp KA Langley RG Luger T Ohtsuki M et al . Phase 3 trials of Ixekizumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:345–56. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1512711
24.
Griffiths CE Reich K Lebwohl M van de Kerkhof P Paul C Menter A et al . Comparison of ixekizumab with etanercept or placebo in moderate-to-severe psoriasis (UNCOVER-2 and UNCOVER-3): results from two phase 3 randomised trials. Lancet. (2015) 386:541–51. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60125-8
25.
Bagel J Duffin KC Moore A Ferris LK Siu K Steadman J et al . The effect of secukinumab on moderate-to-severe scalp psoriasis: Results of a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3b study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2017) 77:667–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.05.033
26.
Nash P Mease PJ McInnes IB Rahman P Ritchlin CT Blanco R et al . Efficacy and safety of secukinumab administration by autoinjector in patients with psoriatic arthritis: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (FUTURE 3). Arthritis Res Ther. (2018) 20:47. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1551-x
27.
Mrowietz U Bachelez H Burden AD Rissler M Sieder C Orsenigo R et al . Secukinumab for moderate-to-severe palmoplantar pustular psoriasis: Results of the 2PRECISE study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2019) 80:1344–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.066
28.
Mease PJ McInnes IB Kirkham B Kavanaugh A Rahman P van der Heijde D et al . Secukinumab inhibition of interleukin-17A in patients with psoriatic arthritis. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1329–39. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1412679
29.
Kurd SK Gelfand JM . The prevalence of previously diagnosed and undiagnosed psoriasis in US adults: results from NHANES 2003-2004. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2009) 60:218–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.09.022
30.
Abuabara K Azfar RS Shin DB Neimann AL Troxel AB Gelfand JM . Cause-specific mortality in patients with severe psoriasis: a population-based cohort study in the U.K. Br J Dermatol. (2010) 163:586–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09941.x
31.
Yamazaki F Takehana K Tanaka A Son Y Ozaki Y Tanizaki H . relationship between psoriasis and prevalence of cardiovascular disease in 88 Japanese patients. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:3640. doi: 10.3390/jcm10163640
32.
Mehta NN Azfar RS Shin DB Neimann AL Troxel AB Gelfand JM . Patients with severe psoriasis are at increased risk of cardiovascular mortality: cohort study using the General Practice Research Database. Eur Heart J. (2010) 31:1000–6. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp567
33.
Rungapiromnan W Yiu Z Warren RB Griffiths C Ashcroft DM . Impact of biologic therapies on risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with psoriasis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br J Dermatol. (2017) 176:890–901. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14964
Summary
Keywords
secukinumab, ixekizumab, psoriasis, major adverse cardiovascular events, adverse event
Citation
Zhang Y, Yang Z, Gong J and Shi D (2024) Effects of secukinumab and ixekizumab on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with psoriasis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Med. 11:1353893. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1353893
Received
10 January 2024
Accepted
20 February 2024
Published
06 March 2024
Volume
11 - 2024
Edited by
Laura Atzori, University of Cagliari, Italy
Reviewed by
Annunziata Dattola, Policlinico Tor Vergata, Italy
Gabriele Biondi, Azienda Ospedaliero Universitaria Sassari, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Zhang, Yang, Gong and Shi.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongmei Shi, shidongmei28@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.