Abstract
Background:
Crigler-Najjar syndrome (CNS) is caused by mutations in uridine 5′-diphosphate glucuronyltransferase (UGT1A1) resulting in enzyme deficiency and hyperbilirubinemia. Type II CNS patients could respond to phenobarbital treatment and survive. This study presents a rare case of type II CNS.
Case summary:
The proband was a 29-year-old male patient admitted with severe jaundice. A hepatic biopsy showed bullous steatosis of the peri-central veins of the hepatic lobule, sediment of bile pigment, and mild periportal inflammation with normal liver plate structure. The type II CNS was diagnosed by routine genomic sequencing which found that the proband with the Gry71Arg/Tyr486Asp compound heterozygous mutations in the UGT1A1 gene. After treatment with phenobarbital (180 mg/day), his bilirubin levels fluctuated between 100 and 200 μmol/L for 6 months and without severe icterus.
Conclusion:
Type II CNS could be diagnosed by routine gene sequencing and treated by phenobarbital.
Introduction
Crigler-Najjar syndrome (CNS) is an inherited deficiency of uridine 5′-diphosphate glucuronyltransferase (UGT1A1) enzyme and is characterized by hyperbilirubinemia. The complete absence of the UGT1A1 enzyme activity results in type I, which does not respond to phenobarbital and was reported in 1952 by Crigler and Najjar, while a partial loss of UGT1A1 activity results in type II, first found by Arias and that can respond to phenobarbital treatment (1, 2). The major manifestation of CNS is jaundice. Type I CNS patients usually die in infancy, but type II CNS patients survive despite long-term icterus and pruritus. This study presents a rare case of type II CNS.
Case presentation
The proband was a 29-year-old male patient admitted to First Affiliated hospital of Dalian Medical University with severe jaundice. His parents claimed that he had icterus and pruritus from birth, without any treatment. He was 163 cm in height and 81 kg in weight. All hemolytic anemia parameters, including Hemoglobin, coagulation function, thyroid function, ceruloplasmin, and immunoglobulin was normal. Total bilirubin was 237.8 μmol/L, among which unconjugated bilirubin was 228.8 μmol/L, other parameters of liver function were all in normal range. Hepatitis, Epstein–Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus tests were negative. Computed tomography (CT) scan showed a low density and normal shape of the liver. The CT index was 50 HU, suggesting fatty liver (Figure 1). A hepatic biopsy showed bullous steatosis of the peri-central veins of the hepatic lobule, bile pigment sedimentation, and mild periportal inflammation with normal liver plate structure (Figure 2).
Figure 1

The CT scan of the proband. Lower density and normal shape of the liver (CT index is 50 U).
Figure 2
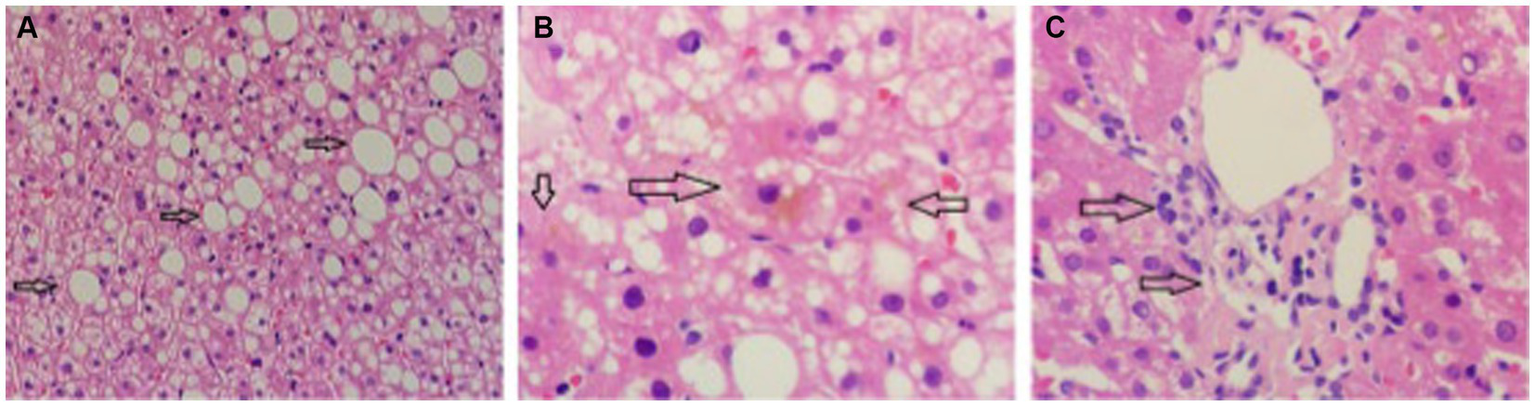
The pathology of liver biopsy. (A) Normal hepatic plate structure with bullous steatosis of peri-central veins of hepatic lobule (indicated by arrow). (B) Sediment of bile pigment (indicated by arrow). (C) Mild periportal inflammation.
There is no consanguinity between the proband’s parents. To confirm the diagnosis of type II CNS, blood genomic DNA from the proband and his parents was routinely extracted and sequenced. The genetic test results showed two suspected homozygous pathogenic mutations. One mutation was the c.1456 T > G p.Y486D homozygous mutation. Y486D is located on exon 5, changing the 1,456 thymine (T) into guanine (G) and changing residue 486 tyrosine (Tyr) into aspartic acid (Asp). His parents were c.1456 T > G p.Y486D heterozygous carriers (Supplementary Figures S1A–C). The other mutation was the c.211G > A p.G71R homozygous mutation. G71R is located in exon 1, mutating the 211 guanine (G) into adenine (A) and changing residue 71 from glycine (Gly) to arginine (Arg). His father was a c.211G > A p.G71R homozygous carrier without any symptoms, and his mother was a heterozygosis carrier (Supplementary Figures S1D–F).
The patient was therefore diagnosed with type II CNS. He received phenobarbital treatment (180 mg/day) since then to reduce bilirubin levels associated with jaundice. After that, his mean total bilirubin levels fluctuated between 100 and 200 μmol/L during the next 6 months and without severe icterus and pruritus without severe side effects.
Discussion
This study presents a rare case of type II CNS. Hepatic biopsy showed bullous steatosis of the peri-central veins of the hepatic lobule, sediment of bile pigment, and mild periportal inflammation with normal liver plate structure. The type II CNS was diagnosed by routine genomic sequencing which found that the proband with the Gry71Arg/Tyr486Asp compound heterozygous mutations in the UGT1A1 gene. After treatment with phenobarbital, the bilirubin levels fluctuated between 100 and 200 μmol/L for 6 months and without severe icterus.
The molecular basis of type II CNS is mainly missense UGT1A1 gene mutations resulting in the partial lack of UGT enzyme activity (3). Many single-nucleotide mutations are responsible for type II CNS in East Asians, particularly in the first exon with the Gry71Arg mutation. The carrier rate in the East Asian people is as high as 15.2% and even 30% in the Chinese people (4). Multiple mutations in different areas of the UGT1A1 gene and compound heterozygous mutations can cause type II CNS (5). Yamamoto et al. reported that different combinations of the Gry71Arg and Tyr486Asp mutations could result in different enzymatic activities. The UGT activity levels in patients with the Gry71Arg heterozygous, Gry71Arg homozygous, Tyr486Asp homozygous, and Gry71Arg/Tyr486Asp compound heterozygous mutations were reported to be 60.2, 32.2, 7.62%, and 6.2 ± 1.6%, respectively (6). In the case reported here, the patient had the compound heterozygous mutations Gry71Arg + Tyr486Asp. Both Gry71Arg and Try 486Asp were detected in an adult with normal promoter area and continuous jaundice. Therefore, type II NCS could be confirmed. This study summarized the polymorphism markers in the UGT1A1 gene found in type II CNS (Table 1).
Table 1
| Author | Date | Country | Mutation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labrune et al. | 1994 | France | G308E Q357R S381R A401P Q357X W335X+ A368T W335X+ 1223insG A291V K437X |
(35) |
| Kadakol et al. | 2000 | United States | c. 115C > G c. 222C > A c. 517delC c. 722-723delAG c. 1046delA c. 1223delA/N c. 1451G > A c.1452G > A c. 1,490 T > A/N |
(3) |
| Maruo et al. | 2006 | Turkey | T-3279G A(TA)7TAA p.H39D |
(37) |
| Huang et al. | 2006 | Taiwan, China | c.479 T > A c.610A > G c.1465 T > G + c.211G > A |
(34) |
| D’Apolito et al. | 2007 | Italy | c.835A > T c.1381 T > C c.1328 T > C c.1223–1,224 ins G + c.1184G > T c.1060 T > A |
(38) |
| Sneitz et al. | 2010 | Finland | c.44 T > G c.1489delG c.1160C > A c.211G4A, c1456T4G, c.1220delA c.625C > T c.572C > T c.1328 T > C c.1006C > A |
(39) |
| Maruo et al. | 2011 | Turkey | p.K402T + p.G71R;Y486D | (40) |
| Nakagawa et al. | 2011 | Japan | c.1456 T > G | (41) |
| Minucci et al. | 2013 | Italy, | c.1099C > T+ c.508_510delTTC | (42) |
| Nilyanimit et al. | 2013 | Thailand | [A(TA)7TAA] | (43) |
| Zheng et al. | 2014 | China | c.211G > A + c.508_510delTTC + c.1456 T > G | (44) |
| Maruo et al. | 2015 | Iran | p.V225G | (45) |
| Tesapirat et al. | 2015 | Thailand | c.1069-1070insC + c.1456 T > G | (36) |
| Wu et al. | 2016 | China | c.610 A > G+ c.1091 C > T | (20) |
Reported mutations in UGT1A1 gene in Crigler-Najjar syndrome II.
Both types I and II CNS can occur in children and adults, with clinical jaundice due to elevated total bilirubin, while transaminase can be normal. Due to severe reduction or even complete lack of the UGT, type I CNS can manifest with bilirubin >342 μmol/L and deteriorate with kernicterus and death within 2 years after birth. In type II CNS, jaundice is usually lighter, and total bilirubin is usually <342 μmol/L, but the levels fluctuate because of stress, fatigue, infection, pregnancy, or drug use. Genetic testing helps with the diagnosis. Serum bilirubin levels can decrease by >30% with phenobarbital treatment, with a relatively far better prognosis (20–22). Type II CNS can increase the risk of gallbladder stones. Recently, Fernandes et al. (23) reported that the disease is associated with acute cholangitis. Zhang et al. (24) reported a patient with stenosing papillitis and acute biliary pancreatitis. Regarding the hepatic pathology findings, most cases show small amounts of cystic granules sediment in liver cells under the light microscope, and bile embolism can be found with both electron and light microscope (24). Elfar et al. (25) presented a patient with persistent unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, clinically diagnosed as type II CNS, who underwent liver transplantation due to liver cirrhosis. They reported that CNS could progress to hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis (25).
Gilbert’s syndrome is another hereditary condition that affects bilirubin processing by the liver, similar to Crigler-Najjar syndrome, but it is much more common and generally milder. It results from a variation in the same UGT1A1 gene responsible for Crigler-Najjar syndrome, but the impact on bilirubin processing is less severe. Individuals with Gilbert’s syndrome typically have slightly higher bilirubin levels, which may lead to mild jaundice, especially during times of illness, fasting, or stress. However, Gilbert’s syndrome is often considered a benign condition that does not require treatment and does not lead to serious health problems.
The mention of Gilbert’s syndrome is relevant because it lies on the same spectrum of bilirubin metabolism disorders as Crigler-Najjar syndrome, with Gilbert’s at the milder end and Type I Crigler-Najjar at the most severe (26). Type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome falls in between these two. Understanding Gilbert’s syndrome can help clarify the range of genetic variations affecting bilirubin metabolism and their impacts (2).
Regarding consanguinity, this is a relevant consideration for genetic disorders like Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Consanguinity (marriage or reproduction between closely related individuals) increases the likelihood of both parents carrying the same genetic mutation and, therefore, increases the risk of their children inheriting autosomal recessive conditions like Type I Crigler-Najjar syndrome or, to a lesser extent, the genetic variations responsible for Type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome and Gilbert’s syndrome (27). While Gilbert’s syndrome often results from a common variation in the UGT1A1 gene promoter region and might not be directly tied to consanguinity, Type I and Type II Crigler-Najjar syndromes result from more specific mutations that could indeed have a higher incidence in populations or families where consanguinity is more common. Genetic counseling can provide families with information on the risk of inherited conditions and guidance on management and prevention (28).
In a cohort of 22 older patients with type I CNS, nine (41%) were found with histological fibrosis discovered in the explants at the time of liver transplantation. In addition, portal, pericentral, and mixed fibrosis could be seen. Moreover, fibrotic individuals were notably older than those without fibrosis, suggesting that the injury might be incrementally acquired (29).
First and the basic management of CNS is avoiding drugs like penicillin, sulphonamides, salicylates, ceftriaxone, and furosemide that can displace bilirubin from albumin (30). The management of type II CNS is relatively easier and more effective because of the partial activity of the UGT enzyme. Phototherapy and phenobarbital are the most common and effective ones (31). The management of type I CNS is very complicated, and transplantation and gene therapy were only experimental treatments for type I CNS (32). Phototherapy acts by converting bilirubin without the conjugation in the liver. The bilirubin can be excreted in the bile directly. Bilirubin levels over 171 μmol/L are an indication for phototherapy in term infants without risk factors, while the threshold is 4 mg/dL (68.4 μmol/L) in infants with high risk for kernicterus (preterm, low birth weight) (33). This technique involves the patient’s exposure to light for 10–12 h, even 14 h, per day (19, 34, 35). Oral calcium supplementation makes phototherapy more efficient (36). Phenobarbital can induce UGT1A1 activity, and it is the most effective drug for CNS, especially type II CNS. The dose is 3–5 mg/kg/day, usually 60–180 mg/day (5). The dose can be reduced (below 60 mg/day, 30–60 mg/day recommended) in pregnancy to avoid its teratogenic side effects. A response usually can be seen within 2–3 weeks. In addition, calcium supplementation has also been found to increase the gut excretion of bilirubin. Maternal bilirubin serum levels should be below 10 mg/dL (171 μmol/L). Furthermore, folic acid at a dose of 10 mg is recommended during pregnancy (37). Orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) can offer an option in genetic diseases involving the liver, and many monogenic diseases can be cured by liver transplantation. Kayler et al. (38) firstly retrospectively analyzed the efficiency of OLT in metabolic liver disease, including CNS, and proved beneficial in a 78-month follow-up. Bayram et al. (39) conducted a 24-month research and suggested that OLT should be performed before neurobehavioral abnormalities occur. The mortality is up to 10% in the first post-transplantation year, and lifelong immunosuppressive drugs are needed (2). In a 26-month follow-up, OLD could maintain normal serum bilirubin and no requirement for phototherapy (38). Apart from liver transplantation, liver cell transplantation (LCT) is a promising technique and is less invasive. Chen et al. (39) reported a decline of serum bilirubin by 30–60%, and biliary excretion of bilirubin glucuronides indicated that transplanted iHeps expressed UGT1A1 activity, a postnatal function of hepatocytes. In another research, the efficacy and overall safety of heterologous human adult liver-derived progenitor cell (HepaStem) were confirmed after 12 months (40). A phase I/II prospective, open-label, multicenter, randomized trial aimed primarily at evaluating the safety of HepaStem in pediatric patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs) or CNS 6 months post-transplantation. The secondary objective included the assessment of safety up to 12 months post-infusion and of preliminary efficacy (41). Table 2 presents the studies of liver transplantation in CNS. Gene therapy can modify the genome, and it is a promising approach to cure gene-related diseases such as CNS. Bellodi-Privato et al. (58) reported a successful gene therapy of the Gunn rat by in vivo neonatal hepatic gene transfer using murine oncoretroviral vectors. In the report, the Gunn rats were injected with viruses carrying a functional UGT1 gene, and bilirubinemia was normal after 6 weeks (3 μmol/L) and remained in the normal range (i.e., <10 μmol/L) for more than 34 weeks (58). Many studies confirmed the efficacy of gene therapy with adeno-associated viruses, including AVV1, AVV2, AVV6, AVV8, VV9, AVV5 (59–61).
Table 2
| Author | Date | Number of cases | Follow up | Result | OLT/LCT* | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kadakol et al. | 2000 | 1 | 3 years | Beneficial | OLT | (3) |
| Schauer et al | 2002 | 2 | 27 months | Beneficial | OLT | (46) |
| Al Shurafa et al. | 2002 | 6 | 1 year | Beneficial and curative | OLT | (47) |
| Kayler et al. | 2002 | 1 | 78 months | Beneficial | OLT | (23) |
| Schauer et al. | 2003 | 3 | 36 months | Beneficial/Improved | OLT | (48) |
| Darwish et al. | 2004 | 1 | 12-month | Beneficial on plasma bilirubin level | LCT | (49) |
| Ambrosino et al. | 2005 | 1 | 24 months | Good liver function | LCT | (50) |
| Broering et al. | 2005 | 2 | 8 months | Normal total bilirubin and liver function | OLT | (51) |
| Morioka et al. | 2005 | 2 | 14 months | Beneficial | OLT | (52) |
| Strauss et al. | 2006 | 4 | 20-month | Beneficial | OLT | (20) |
| Quaglia et al. | 2008 | 1 | Not mentioned | Partially Improved | LCT | (53) |
| Allen et al. | 2008 | 1 | 26 months | Normal serum bilirubin | OLT | (26) |
| Khan et al. | 2008 | 1 | 2 months | Safety, feasibility, and efficacy | LCT | (54) |
| Ozçay et al. | 2009 | 4 | 24 months | Curative and beneficial | OLT | (55) |
| Meyburg et al. | 2010 | 1 | 15 months | Beneficial | LCT | (56) |
| Shanmugam et al. | 2011 | 1 | 18 months | Beneficial | OLT | (57) |
| Tu et al. | 2012 | 1 | 12 months | Beneficial | OLT | (58) |
| Bayram et al. | 2013 | 2 | 24 months | Successful but irreversible neurobehavioral abnormalities | OLT | (24) |
| Mauruo et al. | 2015 | 2 | — | Death | OLT | (45) |
| Jorns et al | 2015 | 1 | 1 year/2 weeks | Good condition with excellent graft function. | LCT | (59) |
| Baris et al | 2018 | 1 | 3 months | Beneficial | OLT | (60) |
| Mitchell et al. | 2018 | 22 | 5.8 years(mean) | Beneficial | OLT | (13) |
| Nader et al. | 2018 | 1 | 6 months | Death of sepsis | OLT | (61) |
| Elfar et al. | 2019 | 1 | Not mentioned | Beneficial | OLT | (12) |
Liver transplantation in the Crigler-Najjar syndrome patient.
*OLT, Orthotopic liver transplantation; LCT, liver cell transplantation.
Gilbert syndrome is an another Missense UGT1A1 gene mutations resulting in the partial lack of UGT enzyme activity.
In conclusion, for type II CNS, phototherapy therapy and drug therapy like phenobarbital are effective, and the prognosis can be satisfying. On the other hand, for type I CNS patients, liver transplantation may be needed eventually. Many new therapeutic approaches are being pursued in preclinical research for developing safe and effective treatments for CNS. Gene therapy has been successfully performed in animals, and the safety and efficacy issues are being identified. Gene therapy might be a promising and realistic modality for the treatment of CNS in the following decades.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
TH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Methodology, Data curation. XG: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation. LZ: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization. XL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology. LW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the help of the profonde and his parents.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1354514/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Crigler JF Najjar VA . Congenital familial nonhemolytic jaundice with kernicterus. Pediatrics. (1952) 10:169–80. PMID:
2.
Strassburg CP . Hyperbilirubinemia syndromes (Gilbert-Meulengracht, Crigler-Najjar, Dubin-Johnson, and rotor syndrome). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. (2010) 24:555–71. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2010.07.007
3.
Kadakol A Ghosh SS Sappal BS Sharma G Chowdhury JR Chowdhury NR . Genetic lesions of bilirubin uridine-diphosphoglucuronate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1) causing Crigler-Najjar and Gilbert syndromes: correlation of genotype to phenotype. Hum Mutat. (2000) 16:297–306. doi: 10.1002/1098-1004(200010)16:4<297::AID-HUMU2>3.0.CO;2-Z
4.
Teng HC Huang MJ Tang KS Yang SS Tseng CS Huang CS . Combined UGT1A1 and UGT1A7 variant alleles are associated with increased risk of Gilbert's syndrome in Taiwanese adults. Clin Genet. (2007) 72:321–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00873.x
5.
Ranjan P Kohli S Saxena R Thakur S . Mutation analysis in Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II-case report and literature review. J Clin Exp Hepatol. (2011) 1:204–6. doi: 10.1016/S0973-6883(11)60239-9
6.
Yamamoto K Sato H Fujiyama Y Doida Y Bamba T . Contribution of two missense mutations (G71R and Y486D) of the bilirubin UDP glycosyltransferase (UGT1A1) gene to phenotypes of Gilbert's syndrome and Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Biochim Biophys Acta. (1998) 1406:267–73. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(98)00013-1
7.
Labrune P Myara A Hadchouel M Ronchi F Bernard O Trivin F et al . Genetic heterogeneity of Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I: a study of 14 cases. Hum Genet. (1994) 94:693–7. Epub 1994/12/01. doi: 10.1007/BF00206965
8.
Maruo Y Topaloglu AK Takahashi H Mori A Iwai M Duzovali O et al . Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II caused by a homozygous triple mutation [T-3279G, A(TA)7TAA, and H39D] of UGT1A1. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2006) 42:236–9. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000184922.09389.0a
9.
Huang CS Tan N Yang SS Sung YC Huang MJ . Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2. Journal of the Formosan medical association =. Taiwan yi zhi. (2006) 105:950–3. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(09)60182-0
10.
D’Apolito M Marrone A Servedio V Vajro P De Falco L Iolascon A . Seven novel mutations of the UGT1A1 gene in patients with unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Haematologica. (2007) 92:133–4. doi: 10.3324/haematol.10585
11.
Sneitz N Bakker CT de Knegt RJ Halley DJ Finel M Bosma PJ . Crigler-Najjar syndrome in the Netherlands: identification of four novel UGT1A1 alleles, genotype-phenotype correlation, and functional analysis of 10 missense mutants. Hum Mutat. (2010) 31:52–9. doi: 10.1002/humu.21133
12.
Maruo Y Ozgenc F Mimura Y Ota Y Matsui K Takahashi H et al . Compound heterozygote of a novel missense mutation (p.K402T) and a double missense mutation (p.[G71R;Y486D]) in type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2011) 52:362–5. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3181fcafb8
13.
Nakagawa T Mure T Yusoff S Ono E Kusuma Harahap IS Morikawa S et al . A homozygous mutation in UGT1A1 exon 5 may be responsible for persistent hyperbilirubinemia in a Japanese girl with Gilbert’s syndrome. Kobe J Med Sci. (2011) 57:E26–31. PMID:
14.
Minucci A Canu G Gentile L Cimino V Giardina B Zuppi C et al . Identification of a novel mutation in UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1) gene in a child with neonatal unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Clin Biochem. (2013) 46:170–2. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.10.007
15.
Nilyanimit P Krasaelap A Foonoi M Chongsrisawat V Poovorawan Y . Role of a homozygous A(TA)(7)TAA promoter polymorphism and an exon 1 heterozygous frameshift mutation UGT1A1 in Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II in a Thai neonate. Genet Mol Res. (2013) 12:3391–7. doi: 10.4238/2013.September.4.5
16.
Zheng B Hu G Yu J Liu Z . Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II in a Chinese boy resulting from three mutations in the bilirubin uridine 5′-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1) gene and a family genetic analysis. BMC Pediatr. (2014) 14:267. Epub 2014/10/17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-267
17.
Maruo Y Behnam M Ikushiro S Nakahara S Nouri N Salehi M . Two different UGT1A1 mutations causing Crigler-Najjar syndrome types I and II in an Iranian family. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. (2015) 24:523–6. doi: 10.15403/jgld.2014.1121.244.ugt
18.
Tesapirat L Nilyanimit P Wanlapakorn N Poovorawan Y . Compound heterozygosity of a novel exon 3 frameshift (p.R357P fs*24) mutation and Y486D mutation in exon 5 of the UGT1A1 gene in a Thai infant with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2. Genet Mol Res. (2015) 14:3293–9. doi: 10.4238/2015.April.13.8
19.
Strauss KA Robinson DL Vreman HJ Puffenberger EG Hart G Morton DH . Management of hyperbilirubinemia and prevention of kernicterus in 20 patients with Crigler-Najjar disease. Eur J Pediatr. (2006) 165:306–19. doi: 10.1007/s00431-005-0055-2
20.
Wu Y Li G Zhou Y Li J Hu Y . Genetic analysis of a child affected with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Zhonghua yi xue yi chuan xue za zhi = Zhonghua yixue yichuanxue zazhi = Chinese journal of medical genetics. (2016) 33:328–31. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1003-9406.2016.03.011
21.
Kumar P Sasmal G Gupta S Saxena R Kohli S . Crigler Najjar syndrome type 2 (CNS type 2): an unwonted cause of jaundice in adults. J Clin Diagn Res. (2017) 11:OD05–6. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/28195.10221
22.
Seppen J Bosma PJ Goldhoorn BG Bakker CT Chowdhury JR Chowdhury NR et al . Discrimination between Crigler-Najjar type I and II by expression of mutant bilirubin uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase. J Clin Invest. (1994) 94:2385–91. doi: 10.1172/JCI117604
23.
Fernandes SR Moura CM Rodrigues B Correia LA Cortez-Pinto H Velosa J . Acute cholangitis in an old patient with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II—a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. (2016) 16:33. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0449-9
24.
He ZY You H Zhao XY . Clinical and pathological features of inherited metabolic liver disease in adults. Zhonghua gan zang bing za zhi = Zhonghua ganzangbing zazhi = Chinese journal of hepatology. (2018) 26:889–93. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.12.003
25.
Elfar W Jarvinen E Ji W Mosorin J Sega AG Iuga AC et al . A novel pathogenic UGT1A1 variant in a Sudanese child with type 1 Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Drug Metab Dispos. (2019) 47:45–8. doi: 10.1124/dmd.118.084368
26.
Bosma PJ Chowdhury JR Bakker C Gantla S de Boer A Oostra BA et al . The genetic basis of the reduced expression of bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 in Gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. (1995) 333:1171–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511023331802
27.
Kapitulnik J . Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and bilirubin toxicity in the preterm infant. Clin Chem. (2004) 50:1452–5. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.035352
28.
Rok K Klemen Š . Possible health effects of consanguineous marriage. Acta Dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica. (2011) 20:93–7.
29.
Mitchell E Ranganathan S McKiernan P Squires RH Strauss K Soltys K et al . Hepatic parenchymal injury in Crigler-Najjar type I. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2018) 66:588–94. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001843
30.
Nair KM Lohse P Nampoothiri S . Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 2: novel UGT1A1 mutation. Indian J Hum Gen. (2012) 18:233–4. doi: 10.4103/0971-6866.100776
31.
Vianello E Tiribelli C Gazzin S . Histone acetylation in hyperbilirubinemia: an unexplored mechanism for bilirubin-induced encephalopathy and kernicterus. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. (2012) 5:190–208.
32.
D'Antiga L Beuers U Ronzitti G Brunetti-Pierri N Baumann U Di Giorgio A et al . Gene therapy in patients with the Crigler-Najjar syndrome. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389:620–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2214084
33.
Agati G Fusi F Pratesi S Galvan P Donzelli GP . Bilirubin photoisomerization products in serum and urine from a Crigler—Najjar type I patient treated by phototherapy. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol. (1998) 47:181–9. doi: 10.1016/S1011-1344(98)00221-8
34.
Wilson JH Sinaasappel M Lotgering FK Langendonk JG . Recommendations for pregnancies in patients with crigler-najjar syndrome. JIMD Rep. (2013) 7:59–62. doi: 10.1007/8904_2012_142
35.
Nydegger A Bednarz A Hardikar W . Use of daytime phototherapy for Crigler-Najjar disease. J Paediatr Child Health. (2005) 41:387–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.2005.00642.x
36.
Jansen PL . Diagnosis and management of Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. (1999) 158:S089–94. doi: 10.1007/pl00014330
37.
Chaubal AN Patel R Choksi D Shah K Ingle M Sawant P . Management of pregnancy in Crigler Najjar syndrome type 2. World J Hepatol. (2016) 8:530–2. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i11.530
38.
Kayler LK Merion RM Lee S Sung RS Punch JD Rudich SM et al . Long-term survival after liver transplantation in children with metabolic disorders. Pediatr Transplant. (2002) 6:295–300. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3046.2002.02009.x
39.
Bayram E Ozturk Y Hiz S Topcu Y Kilic M Zeytunlu M . Neurophysiological follow-up of two siblings with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I and review of literature. Turk J Pediatr. (2013) 55:349–53. PMID:
40.
Meyburg J Schmidt J Hoffmann GF . Liver cell transplantation in children. Clin Transpl. (2009) 23:75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0012.2009.01113.x
41.
Allen KJ Mifsud NA Williamson R Bertolino P Hardikar W . Cell-mediated rejection results in allograft loss after liver cell transplantation. Liver Transplant. (2008) 14:688–94. doi: 10.1002/lt.21443
42.
Schauer R Lang T Zimmermann A Stangl M Da Silva L Schildberg FW et al . Successful liver transplantation of two brothers with crigler-najjar syndrome type 1 using a single cadaveric organ. Transplantation. (2002) 73:67–9. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200201150-00012
43.
Al Shurafa H Wali S Chehab MS Al Shahed M Jawdat M Djurberg H et al . Living-related liver transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome in Saudi Arabia. Clin Transplant. (2002) 16:222–6. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0012.2002.01140.x
44.
Schauer R Stangl M Lang T Zimmermann A Chouker A Gerbes AL et al . Treatment of Crigler-Najjar type 1 disease: relevance of early liver transplantation. J Pediatr Surg. (2003) 38:1227–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(03)00273-2
45.
Darwish AA Sokal E Stephenne X Najimi M de Goyet JV Reding R . Permanent access to the portal system for cellular transplantation using an implantable port device. Liver Transplant. (2004) 10:1213–5. doi: 10.1002/lt.20228
46.
Ambrosino G Varotto S Strom SC Guariso G Franchin E Miotto D et al . Isolated hepatocyte transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1. Cell Transplant. (2005) 14:151–7. doi: 10.3727/000000005783983250
47.
Broering DC Walter J Bassas AF . Overcoming the portal steal phenomenon in auxiliary partial orthotopic liver transplantation by modulation of the venous outflow of the native liver. Liver Transplant. (2005) 11:1140–3. doi: 10.1002/lt.20535
48.
Morioka D Kasahara M Takada Y Corrales JP Yoshizawa A Sakamoto S et al . Living donor liver transplantation for pediatric patients with inheritable metabolic disorders. Am J Transplant. (2005) 5:2754–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01084.x
49.
Quaglia A Lehec SC Hughes RD Mitry RR Knisely AS Devereaux S et al . Liver after hepatocyte transplantation for liver-based metabolic disorders in children. Cell Transplant. (2008) 17:1403–14. doi: 10.3727/096368908787648083
50.
Khan AA Parveen N Mahaboob VS Rajendraprasad A Ravindraprakash HR Venkateswarlu J et al . Treatment of Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1 by hepatic progenitor cell transplantation: a simple procedure for management of hyperbilirubinemia. Transplant Proc. (2008) 40:1148–50. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2008.03.022
51.
Ozcay F Alehan F Sevmis S Karakayali H Moray G Torgay A et al . Living related liver transplantation in Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1. Transplant Proc. (2009) 41:2875–7. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.07.025
52.
Meyburg J Hoerster F Schmidt J Poeschl J Hoffmann GF Schenk JP . Monitoring of intraportal liver cell application in children. Cell Transplant. (2010) 19:629–38. doi: 10.3727/096368909X485058
53.
Shanmugam NP Perumalla R Gopinath R Olithselvan A Varghese J Kapoor D et al . Auxiliary liver transplantation: a form of gene therapy in selective metabolic disorders. J Clin Exp Hepatol. (2011) 1:118–20. doi: 10.1016/S0973-6883(11)60132-1
54.
Tu ZH Shang DS Jiang JC Zhang W Zhang M Wang WL et al . Liver transplantation in Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. (2012) 11:545–8. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(12)60222-7
55.
Jorns C Nowak G Nemeth A Zemack H Mork LM Johansson H et al . De novo donor-specific HLA antibody formation in two patients with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I following human hepatocyte transplantation with partial hepatectomy preconditioning. Am J Transplant. (2016) 16:1021–30. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13487
56.
Baris Z Ozcay F Usta Y Ozgun G . Liver cirrhosis in a patient with Crigler Najjar syndrome. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. (2018) 37:301–6. doi: 10.1080/15513815.2018.1492053
57.
Shakibazad N Kamali K Honar N Bordbar M Mohazabieh E . Rigler sign in a child with Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease: A sign that should not be missed. Exp Clin Transplant. (2018) 16:352–4. doi: 10.6002/ect.2016.0006
58.
Chen Y Li Y Wang X Zhang W Sauer V Chang CJ et al . Amelioration of hyperbilirubinemia in Gunn rats after transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes. Stem Cell Rep. (2015) 5:22–30. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.04.017
59.
Lysy PA Najimi M Stephenne X Bourgois A Smets F Sokal EM . Liver cell transplantation for Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I: update and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. (2008) 14:3464–70. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.3464
60.
Smets F Dobbelaere D McKiernan P Dionisi-Vici C Broue P Jacquemin E et al . Phase I/II trial of liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells in pediatric liver-based metabolic disorders: a prospective, open label, multicenter, partially randomized, safety study of one cycle of heterologous human adult liver-derived progenitor cells (HepaStem) in urea cycle disorders and Crigler-Najjar syndrome patients. Transplantation. (2019) 103:1903–15. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002605
61.
Bellodi-Privato M Aubert D Pichard V Myara A Trivin F Ferry N . Successful gene therapy of the Gunn rat by in vivo neonatal hepatic gene transfer using murine oncoretroviral vectors. Hepatology. (2005) 42:431–8. doi: 10.1002/hep.20794
Summary
Keywords
Crigler-Najjar syndrome, hyperbilirubinemia, UGT1A1, phenobarbital, case report
Citation
He T, Geng X, Zhu L, Lin X and Wang L (2024) Type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome: a case report and literature review. Front. Med. 11:1354514. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1354514
Received
12 December 2023
Accepted
16 April 2024
Published
09 May 2024
Volume
11 - 2024
Edited by
Roberto Gramignoli, Karolinska Institutet (KI), Sweden
Reviewed by
Stefania Bunduc, Fundeni Clinical Institute, Romania
Ahmad Karadagi, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 He, Geng, Zhu, Lin and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Zhu, zhuleiphd@163.comLixia Wang, wenwensl@yeah.net
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.