Abstract
Background:
Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs are one of the mainstays of treatment for chronic hepatitis B, but their effects on bone density are highly controversial.
Methods:
In this study, four pharmacovigilance analysis methods and Bonferroni-corrected p-values were used to analyze the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System database to investigate the relationship between adefovir and tenofovir and osteoporosine-related adverse events. In addition, the biological pathways and target proteins were studied by network toxicology and molecular docking techniques.
Results:
Adefovir showed signs of adverse skeletal events at the two PT levels of OSTEOPOROSIS and BONE DENSITY DECREASED, while tenofovir showed signs of adverse skeletal events at the five PT levels of BONE DENSITY DECREASED, BONE LOSS, OSTEOPENIA, OSTEOPOROSIS and OSTEOPOROTIC FRACTURE. Furthermore, at the overall SMQ level, positive signals of adverse skeletal events were also valid. Subgroup analysis showed that adefovir was more likely to cause osteoporosis in the elderly and women, while tenofovir exhibited the opposite trend. Furthermore, GO and KEGG analyses indicated that both drugs may jointly promote osteoporosis through pathways such as cell migration, G protein-coupled receptor and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Molecular docking technology further reveals that the two drugs can produce pathological effects by binding to osteoporosis-related genes such as ADORA1 and JAK1.
Conclusion:
This study comprehensively reported the risk and mechanisms of osteoporosis caused by the clinical use of NAs drugs, and provided more detailed recommendations for clinical improvement and prevention of adverse events.
1 Introduction
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB), a chronic inflammatory disease of the liver caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, has a large patient population (1). According to the World Health Organization, by 2022, 254 million people worldwide will have CHB, with up to 1.2 million new infections each year, making it one of the world’s major health problems (2, 3) As the disease continues to progress, patients with CHB will face the development of advanced liver disease such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer (4). In addition, the total medical cost of hepatitis B related diseases accounts for 151.6% of the annual income of patients’ families, and the annual treatment cost exceeds 700 million US dollars, which seriously affects the quality of life of patients and brings a huge burden to families and society (5, 6).
The primary treatment for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is nucleoside and nucleotide analog (NAs) therapy (7). They are the first-line choice for the treatment of CHB, mainly by inhibiting the activity of HBV deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase, which in turn exerts a good antiviral effect (8, 9). Currently, the NAs commonly used in clinical practice are entecavir, adefovir, telbivudine and tenofovir (10, 11). Among them, adefovir and tenofovir are representative of the first- and second-generation anti-hepatitis drugs, respectively, so this study will focus on adefovir and tenofovir (12).
It is worth noting that there is still controversy about the adverse effects of Adefovir and Tenofovir, and their effects on bone health are high on the list of points of contention (13). Long-term use of both Entecavir and Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is associated with an increased risk of bone and kidney damage, according to an analysis of 211 patients with CHB who received entecavir monotherapy (13). Another retrospective study similarly noted that long-term use of low-dose Adefovir for the treatment of hepatitis B may result in bone pain accompanied by adverse effects such as hypophosphatemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase (14). However, the adverse effects of Adefovir and Tenofovir on bone health are not widely recognized. In some cases, patients with chronic hepatitis with osteoporosis have instead experienced improved bone safety with Tenofovir (15). In addition, a retrospective study with a four to five years follow-up found that patients with CHB treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or entecavir did not have a significant increase in the incidence of bone loss and osteoporosis (16). Therefore, there is an urgent need for real-world evidence to clarify the specific link that exists between Adefovir and Adefovir and bone health.
The FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database is the world’s largest self-reported adverse event database designed to help the FDA better monitor the post-market safety of drugs and therapeutic products (17, 18). In addition, emerging network toxicology translates complex multi-component, multi-target toxicity pathways into intuitive graphical representations that systematically reveal how target toxins trigger pathological mechanisms (19). Molecular docking analysis predicts ligand-protein binding capacity and binding sites, and identifies relevant core active ingredients, providing molecular docking for key targets and actions to further explore the potential mechanism of action of drugs (20).
Therefore, using the FAERS database and molecular docking analysis, the present study focused on the real-world bone health adverse effects profile of Adefovir and Tenofovir esters and clarified the specific mechanisms involved, with the aim of providing a theoretical basis for the rational use of anti-hepatitis virus medications in the clinic and for the prevention and management of associated bone health risks.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Real-world data analysis
2.1.1 Data sources
FAERS is a publicly available database containing data on adverse events (AEs) and medication errors that are spontaneously reported to the FDA. Of these, Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs) from Q1 2004 to Q3 2024 were included in this study and were subjected to pharmacovigilance studies. The FAERS dataset used consists of seven data tables and includes demographic information (DEMO), Drug Information (DRUG), Adverse Event Codes (REAC), Patient Outcomes (OUTC), Reporting Sources (RPSR), Treatment Start and End Dates Associated with Reported Drugs (THER), and Indications for Medication Administration (INDI). The database identifies the content of each record by PRIMARY ID. To minimize data bias, we performed case deduplication prior to statistical analysis according to the FDA-recommended methodology for removing duplicate reports. In addition, subsequent case reports in the FAERS database may contain updated information on the initial case report, so we needed to remove redundancy in this part of the dataset based on a combination of the following six fields: event date, age, gender, adverse event, drug group administered, and country of report, and to select the most recent record from the available cases. As FAERS is a public database containing de-identified data, ethical approval was not required.
2.1.2 Standardized definition of adverse events
Suspected adverse reaction data in the FAERS database were categorized using the Preferred Terminology (PT) levels in the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) version 26.1. The Standardized MedDRA Queries (SMQs) is a comprehensive, proven, predefined set of preferred terminology used to assist regulators and pharmaceutical companies with drug safety issues (21). PT is a term reserved for the specific expression of a single medical concept such as a symptom, sign, disease, diagnosis, indication, examination, surgical and medical operation, medical, social or family history (22). The 10 PTs associated with osteoporosis (“bone density decreased,” “bone formation decreased,” “bone loss,” “bone marrow oedema syndrome,” “osteopenia,” “osteoporosis,” “osteoporosis postmenopausal,” “osteoporotic fracture,” “resorption bone increased” and “senile osteoporosis”) were included in the study and identified in the database. In addition, drugs in the FAERS database are reported using four classifications that designate the role of the drug for the reported adverse event: primary suspect drug, secondary suspect drug, concomitant drug, and interacting drug. We only considered reports labeled as primary suspect drugs based on the “role_code” field.
2.1.3 Statistical analysis
Pharmacovigilance studies were conducted by disproportionate analysis to identify potential drug-adverse event associations after removing duplicate data. Based on disproportionality analysis, four methods of Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR), Proportional Reporting Ratio (PRR), Information Component (IC) and Empirical Bayesian Geometric Mean (EBGM) were used for the study. These four methods were used to detect signals, and according to the pharmacovigilance consensus, the adverse event was considered drug-related when at least one of the signals in the algorithm met the requirements (18). See Supplementary Table 1, for specific equations. The Weber distribution test describes the risk that the AE will increase or decrease over time. Its shape parameter β determines the shape of the distribution function. When the shape parameter β is less than 1 and its 95% CI is less than 1, the risk of adverse events is considered to decrease over time (early failure curve). When the shape parameter β is equal to or close to 1 and its 95% CI includes a value of 1, adverse events continue to occur over time (random failure curves). Finally, when the shape parameter β > 1 and its 95% CI value does not include 1, the incidence of adverse events is thought to increase over time (wear failure curve) (23). The data were organized and statistically analyzed in this study using R (version 4.4.1) and the corresponding version of Rstudio.
2.2 Network toxicology
2.2.1 Screening of drug targets
3D structure and SMILES codes were obtained from PubChem database1 (24). Gene targets of adefovir and tenofovir were screened from Binding DB2 (25), Comparative Toxicogenomics database (CTD)3 (26), and TargetNet4 (27).
2.2.2 Weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA)
GSE56814 analyzed for this study was downloaded from NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. This dataset contained gene expression data of blood mononuclear cells from 80 participants, including 40 women with high bone density and 40 women with low bone density. WGCNA analysis was performed to screen the modules which were significantly associated with osteoporosis. Cluster analysis was performed to detect samples with outliers, which should be removed from the subsequent analysis. The “soft” threshold power (β) and scale-free network coefficients were computed to construct a scale-free network. The modules significantly associated with osteoporosis were then identified. The minimum of genes per module was set to 30. The intersection of significant module genes and drug targets was employed to identify potential gene targets for drugs influencing osteoporosis.
2.2.3 Enrichment analyses
To explore the significantly enriched biological pathways involved in the intersection of adefovir, tenofovir and osteoporosis-related genes, the cluster Profiler R package was used for Gene Ontology (GO) annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Specifically, adefovir and tenofovir target genes were obtained from step 2.2.1. In addition, osteoporosis-related genes were obtained from the GSE56814 dataset (28, 29).
2.3 Molecular docking
The PDB structure files of target proteins were retrieved from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) database5 (30). Using PyMOL 2.3.0, water molecules, heteroatoms and other non-critical non-protein elements were removed to ensure a clean structure of the target protein. The SDF structure files of adefovir and tenofovir were downloaded from PubChem database (see text footnote 1) (24) and then were converted to pdbqt format by AutoDockTools (v1.5.7). Autodock Vina software was used to perform molecular docking process. PyMol 2.3.0 software was used to facilitate the visualization of the docking results pertaining to the optimal conformation.
3 Results
3.1 Real-world data analysis
3.1.1 Descriptive analyses
During the period of testing from Q1 2004 through Q3 2024, the FAERS database recorded 1,834 and 68,862 reports related to adverse reactions triggered by Adefovir and Tenofovir treatment of CHB, respectively (Figure 1). The basic characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. In the gender distribution of treatment with Adefovir, the incidence of AE was significantly higher in the male patient population (n = 1,154, 62.9%) than in the female patient population (n = 454, 24.8%). When specific to osteoporotic events, the number of male patients (n = 163) was approximately three times that of female patients (n = 65). The gender distribution of AEs induced by Tenofovir was similar to that of Adefovir (male n = 42,205, female n = 17,948). In terms of age composition, Adefovir produced adverse reactions that were prevalent in the 18–65-year-old patient population (n = 994, 54.2%). Tenofovir, on the other hand, had a very low incidence in patients aged 18–65 years (n = 70, 0.1%), and was more common in the older patient group aged 65–85 years (n = 36,949, 53.7%). In addition, among patients taking Adefovir or Tenofovir, compared with patients weighing less than 50 kg (Adefovir n = 25; Tenofovir n = 1,325) and more than 100 kg (Adefovir n = 8; Tenofovir n = 998), patients weighing between 50 kg and 100 kg had a larger proportion of people (Adefovir n = 181; Tenofovir n = 6,233).
Figure 1

Schematic illustration of studies of adefovir and tenofovir causing adverse reactions to osteoporosis. GO, Gene Ontology; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
Table 1
| Characteristics | Adefovir | Tenofovir | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | SMQ-Osteoporosis | Total | SMQ-Osteoporosis | |
| Number of events | 1,834 | 254 | 68,862 | 23,579 |
| Sex, n % | ||||
| Female | 454 (24.8%) | 65 (25.6%) | 17,948 (26.1%) | 6,330 (26.8) |
| Male | 1,154 (62.9%) | 163 (64.2%) | 42,205 (61.3%) | 15,621 (66.2) |
| Missing/unknown | 226 (12.3%) | 269 (10.2%) | 8,709 (12.6%) | 1,628 (6.9) |
| Age, n % | ||||
| <18 | 7 (0.4%) | 0 (0%) | 702 (1.0%) | 23 (0.1%) |
| 18–64.9 | 994 (54.2) | 173 (68.1%) | 70 (0.1%) | 5 (0.0%) |
| 65–85 | 245 (13.4%) | 35 (13.8%) | 36,949 (53.7%) | 14,590 (61.9%) |
| >85 | 1 (0.1%) | 1 (0.4%) | 3,337 (4.8%) | 863 (3.7%) |
| Missing/unknown | 587 (32.0%) | 45 (17.7%) | 27,804 (40.4%) | 8,098 (34.3%) |
| Weight, n % | ||||
| <50 kg | 25 (1.4%) | 3 (1.2%) | 1,325 (1.9%) | 73 (0.3%) |
| >100 kg | 8 (0.4%) | 0 (0%) | 998 (1.4%) | 361 (1.5%) |
| 50–100 kg | 181 (9.9%) | 15 (5.9%) | 6,233 (9.1%) | 1,659 (7.0%) |
| Missing/unknown | 1,620 (88.3%) | 236 (92.9%) | 60,306 (87.6%) | 21,486 (91.1%) |
| OUTC_COD | ||||
| CA | 9 (0.5%) | 0 (0%) | 1,444 (2.1%) | 1 (0.0%) |
| DE | 115 (6.3%) | 1 (0.4%) | 3,053 (4.4%) | 244 (1.0%) |
| DS | 45 (2.5%) | 6 (2.4%) | 665 (1.0%) | 40 (0.2%) |
| HO | 566 (30.9%) | 144 (56.7%) | 8,500 (12.3%) | 1,231 (5.2%) |
| LT | 20 (1.1%) | 3 (1.2%) | 699 (1.0%) | 4 (0.0%) |
| OT | 981 (53.5%) | 99 (39.0%) | 39,061 (56.7%) | 18,808 (79.8%) |
| RI | 1 (0.1%) | 0 (0%) | 39 (0.1%) | 1 (0.0%) |
| Missing | 97 (5.3%) | 1 (0.4%) | 15,401 (22.4%) | 3,250 (13.8%) |
| OCCP_COD | ||||
| Consumer | 342 (18.6%) | 26 (10.2%) | 14,933 (21.7%) | 4,021 (17.1%) |
| Health professional | 115 (6.3%) | 14 (5.5%) | 5,452 (7.9%) | 69 (0.3%) |
| Lawyer | – | – | 24,607 (35.7%) | 18,438 (78.2%) |
| Physician | 692 (37.7%) | 110 (43.3%) | 11,400 (16.6%) | 690 (2.9%) |
| Other health-professional | 448 (24.4%) | 101 (39.8%) | 6,054 (8.8%) | 278 (1.2%) |
| Pharmacist | 68 (3.7%) | 1 (0.4%) | 5,075 (7.4%) | 64 (0.3%) |
| Registered Nurse | – | – | 1 (0.0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Missing | 169 (9.2%) | 2 (0.8%) | 5,075 (7.4%) | 64 (0.3%) |
Basic information about adefovir and tenofovir and osteoporosis events.
CA, Congenital Anomaly; DE, Death; DS, Disability; HO, Hospitalization-Initial or Prolonged; LT, Life-Threatening; OT, Other Serious Important Medical Event; RI, Required Intervention to Prevent Permanent.
3.1.2 Signal detection
According to the statistics, a total of 27 organ systems were affected by Adefovir and Tenofovir-related adverse events at the SOC level. The system that was accrued the most was musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders (n = 45,997), while the SOC with the lowest number of accrued SOCs was congenital, familial and genetic disorders (n = 2,620). In terms of signal intensity, renal and urinary disorders showed the strongest positive signals in both drugs, especially in Tenofovir (ROR = 11.23, 95% CI = 11.12–11.34) (Figures 2A,B).
Figure 2

Scanning for adverse osteoporosis events associated with adefovir and tenofovir based on the FAERS database. (A) Bar graph showing the number of AE cases reported for each SOC level of adefovir in the FAERS database. (B) Bar graph showing the number of AE cases reported for tenofovir at each SOC level in the FAERS database. (C) Heatmap showing the ROR of 10 osteoporosis adverse events in the FAERS database under different NAs treatment strategies including adefovir, tenofovir. (D) Risk signal volcano map of adefovir in the North American population. (E) Risk signal volcano plot for tenofovir in the North American population. (F) Adverse event induction time plots for adefovir and tenofovir. NAs, nucleoside/nucleotide analogs; FAERS, Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS); AE, adverse event; SOC, systemic organ classification; ROR, reporting odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
When focusing on osteoporosis-related adverse events caused by Adefovir and Tenofovir, the presence of positive signals was retrieved for both (Figure 2C). Of these, only two positive PTs were retrieved in Adefovir-associated osteoporosis-associated PTs, namely osteoporosis (ROR = 38.42, 95% CI = 33.46–44.13, p = 0) and bone density decreased (ROR = 11.56, 95% CI = 8.78–15.23, p = 7.21E−103) (Figure 2D). Secondly, the highest number of osteoporotic events complicated by Tenofovir administration (n = 45,216) contained five positive PTs. Bone loss (ROR = 579.00, 95%CI = 557.46–601.37, p = 0) was the strongest positive signal intensity for an osteoporosis adverse reaction. In addition, the highest number of occurrences was bone density decreased (n = 19,916), which was also retrieved with a high positive signal. (ROR = 423.92, 95%CI = 413.63–434.46, p = 0) (Figure 2E).
In addition, SMQ further improves the consistency and comparability of the data by having a more rigorous screening and integration mechanism to group multiple PTs with similar presentations or common pathological pathways. Studies based on the SMQ level showed that strong positive signals were detected for both Adefovir and Tenofovir, and the positive signal value for Tenofovir (ROR = 197.88,95% CI = 195.28–200.52) was much greater than that for Adefovir (ROR = 18.96, 95% CI = 16.78–21.42).
Subsequently, we further explored the potential association between Adefovir and Tenofovir induced hair osteoporosis risk in different populations. There were differences in the results of Adefovir versus Tenofovir in different gender populations. The results of SMQ levels showed that in Adefovir, osteoporosis-related adverse events in the female group (female SMQ ROR = 21.49, 95%CI = 16.84–27.43, p < 0.05) presented a stronger signal intensity than in the male group (male SMQ ROR = 14.81, 95%CI = 12.73–17.22, p < 0.05). In contrast, the overall positive signal value for osteoporosis adverse events in women was much lower than the overall positive signal value in men in those treated with Tenofovir. The intensity of positive signals for adverse events in the male group (male SMQ ROR = 349.27, 95%CI = 341.33–357.4, p < 0.05) was approximately two times higher than in the female group (female SMQ ROR = 164.63 95%CI = 161.14–168.2, p < 0.05).
In addition, the study was divided into two cohorts, low (<60 years) and high (≥60 years), for age subgroup analysis. At the SMQ level, the results in Adefovir were opposite to those in Tenofovir. In Adefovir, stronger positive signals were detected in the higher age group (SMQ ROR = 22.87, 95%CI = 18.14–28.84, p < 0.05) than in the lower age group (SMQ ROR = 17.45, 95%CI = 14.82–20.55, p < 0.05) (Figure 3; Table 2).
Figure 3

Differential risk signal analyses for adefovir and tenofovir at the PT and SMQ levels, respectively. PTs, preferred term; SMQ, Standardized MedDRA Queries.
Table 2
| Drug | Category | AEs | N | ROR (95%Cl) | PRR (χ2) | EBGM (EBGM05) | IC (IC025) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adefovir | PT | Bone density decreased | 51 | 11.56 (8.78–15.23) | 11.5 (488.22) | 11.48 (9.12) | 3.52 (3.12) | <0.001 |
| Bone loss | 1 | 0.47 (0.07–3.34) | 0.47 (0.59) | 0.47 (0.09) | −1.09 (−3.13) | >0.99 | ||
| Bone marrow oedema syndrome | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Osteopenia | 7 | 3.35 (1.59–7.02) | 3.34 (11.5) | 3.34 (1.8) | 1.74 (0.72) | >0.99 | ||
| Osteoporosis | 207 | 38.42 (33.46–44.13) | 37.45 (7,308.06) | 37.25 (33.17) | 5.22 (5.02) | <0.001 | ||
| Osteoporotic fracture | 1 | 4.11 (0.58–29.2) | 4.11 (2.35) | 4.11 (0.8) | 2.04 (0) | >0.99 | ||
| Bone formation decreased | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Osteoporosis postmenopausal | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| Resorption bone increased | 1 | 8.82 (1.24–62.73) | 8.82 (6.93) | 8.81 (1.71) | 3.14 (1.1) | >0.99 | ||
| SMQ | SMQ − TOTAL | 268 | 18.96 (16.78–21.42) | 18.35 (4,393.38) | 18.31 (16.53) | 4.19 (4.02) | <0.001 | |
| SMQ − MALE | 175 | 14.81 (12.73–17.22) | 14.36 (2,171.41) | 14.31 (12.61) | 3.84 (3.62) | <0.001 | ||
| SMQ − FEMALE | 67 | 21.49 (16.84–27.43) | 20.74 (16.91) | 4.37 (4.02) | 20.77 (1,261.24) | <0.001 | ||
| SMQ − YOUNGER | 67 | 21.49 (16.84–27.43) | 20.74 (16.91) | 4.37 (4.02) | 20.77 (1,261.24) | <0.001 | ||
| SMQ − OLDER | 74 | 22.87 (18.14–28.84) | 22.2 (1,494.95) | 22.13 (18.22) | 4.47 (4.13) | <0.001 | ||
| Tenofovir | PT | Bone density decreased | 19,916 | 423.92 (413.63–434.46) | 393.37 (2,557,866.25) | 129.69 (127.05) | 7.02 (6.99) | <0.001 |
| Bone loss | 10,533 | 579 (557.46–601.37) | 556.91 (1,498,769.8) | 143.51 (139.03) | 7.17 (7.13) | <0.001 | ||
| Bone marrow oedema syndrome | 3 | 9.76 (3.06–31.14) | 9.76 (22.45) | 3.22 (1.74) | 9.34 (3.54) | 0.59 | ||
| Osteopenia | 5,066 | 111.33 (107.53–115.26) | 109.3 (346,508.18) | 70.01 (68.01) | 6.13 (6.08) | <0.001 | ||
| Osteoporosis | 9,542 | 68.9 (67.29–70.54) | 66.55 (457,793.55) | 49.67 (48.7) | 5.63 (5.6) | <0.001 | ||
| Osteoporotic fracture | 159 | 20.85 (17.7–24.56) | 20.84 (2,708.72) | 18.89 (16.48) | 4.24 (4) | <0.001 | ||
| Bone formation decreased | 1 | 1.35 (0.19–9.66) | 1.35 (0.09) | 0.43 (−1.62) | 1.35 (0.26) | >0.99 | ||
| Osteoporosis postmenopausal | 1 | 1.54 (0.21–10.99) | 1.54 (0.19) | 0.62 (−1.44) | 1.53 (0.3) | >0.99 | ||
| Resorption bone increased | 2 | 0.51 (0.13–2.04) | 0.51 (0.95) | −0.97 (−2.64) | 0.51 (0.16) | >0.99 | ||
| SMQ | SMQ − TOTAL | 45,223 | 197.88 (195.28–200.52) | 165.59 (3,979,447.71) | 89.37 (88.38) | 6.48 (6.46) | <0.001 | |
| SMQ − MALE | 30,091 | 349.27 (341.33–357.4) | 291.21 (2,211,339.52) | 74.58 (73.15) | 6.22 (6.2) | <0.001 | ||
| SMQ − FEMALE | 12,938 | 164.63 (161.14–168.2) | 136.31 (1,298,795.73) | 101.96 (100.14) | 6.67 (6.64) | <0.001 | ||
| SMQ − YOUNGER | 26,387 | 248.53 (243.48–253.69) | 206.45 (2,009,876.54) | 77.37 (76.05) | 6.27 (6.25) | <0.001 | ||
| SMQ − OLDER | 4,778 | 191.88 (185.34–198.66) | 159.01 (582,776.21) | 123.57 (120.04) | 6.95 (6.9) | <0.001 |
Subgroup analysis of adefovir and tenofovir based on age and gender.
ROR, Report Odds Ratio; PRR, Proportional Reporting Ratio; IC, Information Component; EBGM, Empirical Bayesian Geometric Mean; p value, Adjusted p value.
3.1.3 Time-to-onset analysis
In an assessment to evaluate the time to osteoporotic events after Adefovir versus Tenofovir treatment, the mean time to induction for Adefovir was 1,302.48 ± 1,001.47 days and the median time to induction was 1,089 days. The time to induction subgroup showed that approximately 78.26% of Adefovir users experienced osteoporosis adverse events after 1 year. The mean induction time for Tenofovir was 2,123.37 ± 1,567.41 with a median induction time of 1,814 days. As with Adefovir, the majority of its adverse events occurred after 1 year (approximately 90.31%). In addition, we analyzed the time of onset of osteoporosis adverse events associated with both drugs. The results showed a statistically significant difference in the induction time between Adefovir and Tenofovir (p = 0.00092) (Figure 2F). Weibull distribution modeling studies have been used to determine whether the risk of drug-related AE exhibits a time trend. Of these, osteoporosis was mainly randomized after Adefovir treatment and showed a random failure curve. Tenofovir, on the other hand, exhibited a wear failure curve, which suggests that Tenofovir-induced osteoporosis adverse events progressively increase with duration of dosing (Table 3).
Table 3
| Drug | Average (d) ± SD | Median (d) | Scale parameter: α (95% CI) | Shape parameter: β (95% CI) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adefovir | 1,302.48 ± 1,001.47 | 1,089 | 1,331.68 (801.73–1,861.63) | 1.07 (0.70–1.44) | Random failure |
| tenofovir | 2,123.37 ± 1,567.41 | 1,814 | 2,287.95 (2,238.97–2,336.93) | 1.29 (1.26–1.32) | Wear failure |
Weibull shape parameter test for adefovir and tenofovir.
3.2 Network toxicology
3.2.1 Identification of genes related to osteoporosis
GSE56814 dataset, which included 40 women with high bone density and 40 women with low bone density, was downloaded from GEO database and analyzed in this study. Normalization was performed and visualized in Figure 4A. WGCNA was applied to identify the modules significantly associated with osteoporosis. GSM1369791 was identified as abnormal sample and was removed (Figure 4B). A soft threshold power of β = 9 (scale-free R2 = 0.858) was selected (Figure 4C). As shown in Figures 4D,E, 17 co-expression modules were identified, of which the brown module, green module, tan module, gray 60 module, and lightgreen module were significantly associated with osteoporosis. Combine genes in these modules, a total of 1,473 genes were identified as genes closely associated with osteoporosis.
Figure 4

(A) Box plots of raw data normalized between samples. (B) Sample clustering to detect outliers. (C) Determination of the optimal soft threshold. (D) Dendrogram illustrating hierarchical clustering of genes based on their modular characteristics. (E) Correlation analysis between gene modules and clinical traits. The color intensity in the image denotes the strength and direction of the correlation between gene modules and clinical traits: red signifies a positive correlation, blue indicates a negative correlation, and deeper colors reflect stronger correlations. A lower p-value suggests a higher level of significance.
3.2.2 Identification of genes related to drugs influencing osteoporosis
Synthesizing Binding DB, CTD, and TargetNet, a total of 83 genes were identified as the potential targets of adefovir (Supplementary Table 2), 115 genes were identified as the potential targets of tenofovir (Supplementary Table 3). By intersecting these gene targets with 1,473 genes closely associated with osteoporosis, 14 overlapping genes were identified as potential gene targets for adefovir influencing osteoporosis (Figure 5A), and 19 overlapping genes were selected as potential gene targets for tenofovir influencing osteoporosis (Figure 5B). For adefovir, GO enrichment analysis (Figure 5C) suggested that cell migration, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling pathway, sphingolipid mediated signaling pathway, G protein-coupled receptor binding, G protein-coupled amine receptor activity and so on were significantly enriched. KEGG enrichment analysis indicated the significant enrichment of cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway and so on (Figure 5D). For tenofovir, GO enrichment analysis revealed that migration of epithelial cell and endothelial cell, differentiation of endothelial cell, muscle system process, G protein-coupled receptor binding, and cytokine activity, and so on were significantly enriched (Figure 5E). KEGG enrichment analysis suggested that Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, Sphingolipid signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, and IL-17 signaling pathway, and so on were significantly enriched (Figure 5F).
Figure 5
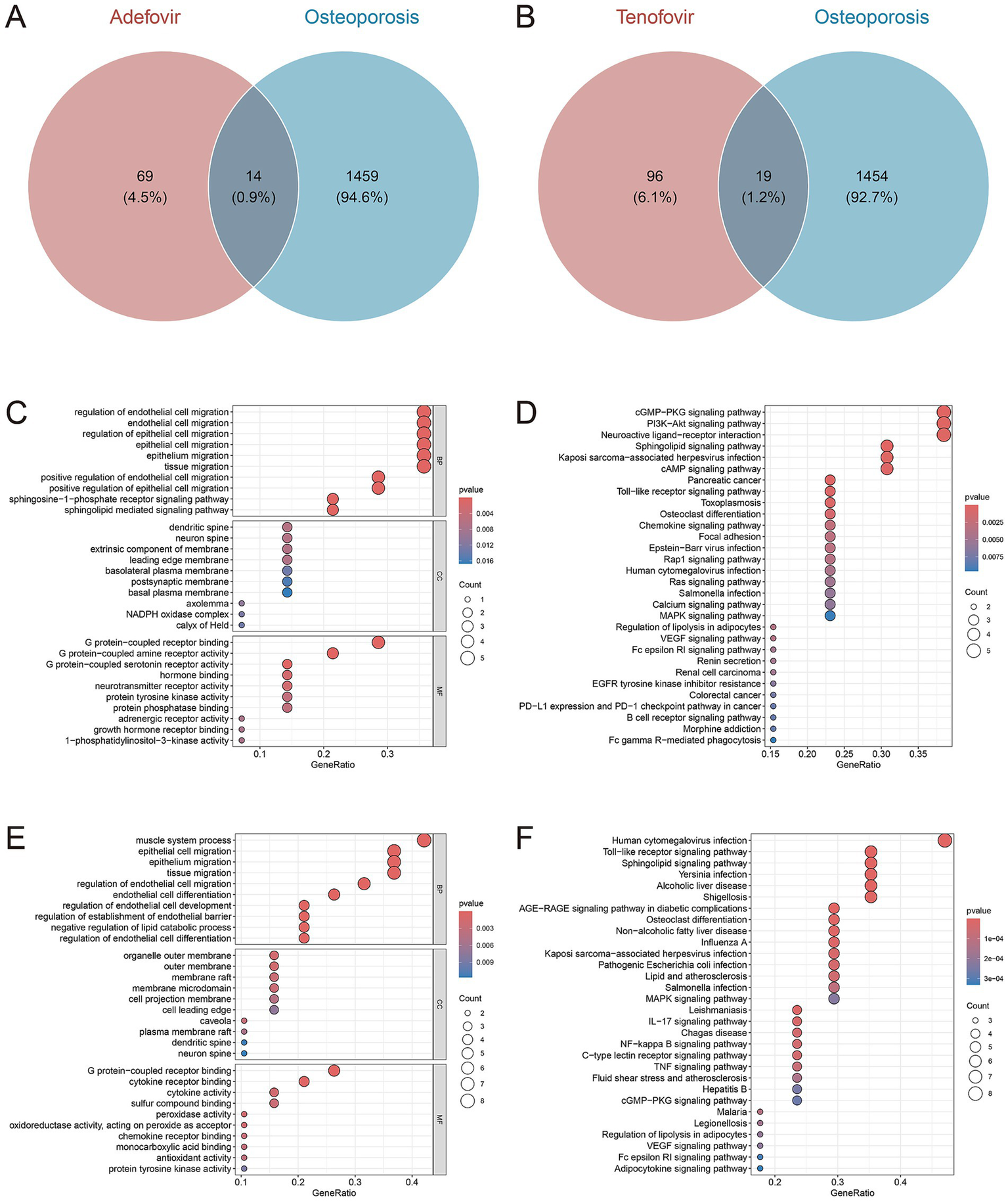
Venn diagrams of gene targets for adefovir (A), and tenofovir (B) influencing osteoporosis. The GO (C) and KEGG (D) plots of the 14 gene targets for adefovir influencing osteoporosis. The GO (E) and KEGG (F) plots of the 19 gene targets for tenofovir influencing osteoporosis.
3.3 Molecular docking
Using molecular docking methods, we further assessed the interaction between adefovir, tenofovir and gene targets of them influencing osteoporosis. As shown in Figure 6, there was a good combination ability between adefovir and ADORA1, HTR5A, JAK1, LCN2, NR2F2, PDE3A, PIK3CG, and RAC1. As shown in Figure 7, the combination between tenofovir and ACACB, ADORA1, CA4, CXCL8, IL1B, JAK1, MPO, NR2F2, PTGS2, RAC1, ROCK1, and TNF was excellent. The detailed information about the binding energies was shown in Table 4.
Figure 6

Molecular docking analyses of adefovir and ADORA1, HTR5A, JAK1, LCN2, NR2F2, PDE3A, PIK3CG, and RAC1.
Figure 7

Molecular docking analyses of tenofovir and ACACB, ADORA1, CA4, CXCL8, IL1B, JAK1, MPO, NR2F2, PTGS2, RAC1, ROCK1, and TNF.
Table 4
| Drug | Targets | PDB ID | Binding affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adefovir | ADORA1 | 5UEN | −5.6 |
| HTR5A | 7UM4 | −6.3 | |
| JAK1 | 4E5W | −6.6 | |
| LCN2 | 3S26 | −5.8 | |
| NR2F2 | 3CJW | −5.8 | |
| PDE3A | 7L27 | −6.5 | |
| PIK3CG | 6AUD | −6.5 | |
| RAC1 | 2NZ8 | −6.3 | |
| Tenofovir | ACACB | 3GLK | −6.5 |
| ADORA1 | 5UEN | −6 | |
| CA4 | 3FW3 | −6.5 | |
| CXCL8 | 6WZM | −5.9 | |
| IL1B | 8C3U | −7 | |
| JAK1 | 4E5W | −7.1 | |
| MPO | 5MFA | −8.2 | |
| NR2F2 | 3CJW | −5.9 | |
| PTGS2 | 5F19 | −7.5 | |
| RAC1 | 2P2L | −6.9 | |
| ROCK1 | 3V8S | −6.9 | |
| TNF | 5M2J | −6.2 |
Results of molecular docking.
4 Discussion
HBV is one of the most important causes of liver disease and poses a major threat to global public health. Currently, NAs drug therapy such as adefovir and tenofovir are recommended as first-line HBV regimens and are widely used in clinical practice (11, 12). However, there is no conclusive information about the effects of these two drugs on bone mineral density (BMD) (31, 32). Therefore, this study confirmed the association between adefovir and tenofovir and osteoporotic events through real-world feedback. This confirmation was based on the assessment of overall SMQ and PT level signaling. In addition, we delved into the specific associations of these drugs through further network toxicology and molecular docking studies.
Specifically, in the present study, there was a signal for skeletal adverse events at the PT level for both adefovir and tenofovir. Subgroup analyses showed that adefovir was more likely to cause osteoporosis in older adults and women, while tenofovir showed the opposite trend. In addition, GO and KEGG analyses showed that both drugs may jointly promote osteoporosis through pathways such as cell migration, G protein-coupled receptor and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways (Figure 8). The latest study further proves our point. Regarding adefovir, several case reports have indicated that patients taking adefovir are prone to bone problems such as osteochondrosis. In addition, patients’ skeletal conditions improved significantly after discontinuing adefovir (33, 34). Also, tenofovir has been found to increase the risk of osteoporosis, which was confirmed by continuous monitoring of bone mineral density in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with tenofovir, which showed a significant decrease in the tenofovir group from the mean percentage of baseline throughout the course of treatment (35).
Figure 8

Schematic diagram of the molecular mechanism of GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis and molecular docking analysis.
Notably, our subgroup analysis of different populations suggests that the bone effects from adefovir and tenofovir accrue to different populations. Adefovir was more likely to affect the elderly and women. Tenofovir, on the contrary, often induces osteoporosis in young people and men. The specific metabolism of the two drugs may play a key role in this particular phenomenon. Adefovir is mainly excreted in its native form via the kidneys, a relatively simple metabolic process that makes renal function crucial for its excretion (36). In the elderly, renal function tends to decline significantly due to reduced renal units, vascular aging, and dysregulation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, which results in the inability to metabolize adefovir properly, leading to a higher signal for adverse events of bone loss (37). In addition, the elderly population is often associated with multiple chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, implying that further impairment of renal function in the elderly due to factors such as high glucose provides a synergistic effect on bone loss due to adefovir (38). Similarly, in the female population, the effects of adefovir on bone mass are also exacerbated by reduced renal blood flow due to decreased ovarian function and estrogen levels during menopause (39). Unlike adefovir, tenofovir has a more complex metabolic pattern, and it has even been able to rescue renal impairment caused by other NAs (40). This causes it to accrue to a population with completely different characteristics than adefovir. A retrospective study from Hong Kong, China suggests that men are more likely to experience osteoporosis and fractures after tenofovir use (41). In addition, in a study of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-negative population using tenofovir, men also showed a predisposition to reduced bone density (42). Furthermore, tenofovir has been observed to exhibit a greater capacity to regulate cytokine and ion levels in comparison to adefovir (43). Furthermore, hormonal secretion regulation mechanisms, such as parathyroid hormone, exhibit heightened sensitivity in younger populations (44). Consequently, when Tenofovir leads to the downregulation of calcium ions and other levels in the body, the younger organism will activate the release of bone calcium levels more quickly than the older group, which will lead to the occurrence of osteoporosis more easily.
Time-series analysis suggested that Adefovir caused osteoporosis to exhibit random failure curve, suggesting that osteoporosis symptoms persisted over time (45). Tenofovir, on the other hand, exhibits a wear failure curve, implying that osteoporosis adverse events progressively increase with Tenofovir dosing time (46). This suggests that long-term use of these two drugs should be avoided as much as possible in the clinic, and when they have to be used, they should be used prophylactically as early as possible with anti-osteoporotic drugs.
GO analysis suggested that cell migration and G-protein-coupled receptor binding are shared pathways by which adefovir and tenofovir trigger osteoporosis. This suggests that adefovir and tenofovir may inhibit endothelial cell migration and the process of neovascularization through mechanisms such as disrupting endothelial cell microfilament structure and producing endothelial cytotoxicity (47, 48). This inhibition leads to a decrease in the production of vascular endothelial growth factor, which decreases the number of cells and new blood vessels reaching the bone-forming region, ultimately resulting in a paucity of blood supply to the bone tissue and a slowing of bone-forming activity (48). In addition, mitochondria play an important role in cell migration. Adefovir and tenofovir induce mitochondrial damage by inhibiting the mitochondrial chaperone TRAP1 and the mtDNA replication protein SSBP1, thereby affecting the energy supply required for cell migration. This cascade of events further impairs osteoblast activity during bone formation, ultimately promoting osteoporosis (49, 50).
Furthermore, upregulation of G protein-coupled receptor binding (GPCR) is another factor in the induction of osteoporosis by adefovir and tenofovir. Among them, 5-hydroxy tryptamine (5-HT) receptor as a GPCR was shown to be widely present in osteoclasts and osteoblasts (51). Up-regulation of 5-HT receptor inhibits the cAMP/PKA pathway, and inhibition of PKA leads to phosphorylation of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), which stimulates osteoclast differentiation and causes a decrease in bone density (52). More in-depth studies of pathway mechanisms have shown that both adefovir and tenofovir have been found to exert their effects on bone density through the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. The Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway is an important pathway for the activation of immune responses, and the majority of TLRs use a MyD88-dependent pathway to activate the transcription factors NF-κB and protein kinase to induce inflammatory cytokine release (53). Among them, the inflammatory response and mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade can promote osteoclast activity, which in turn leads to an imbalance in bone resorption and bone formation, an important causative factor in osteoporosis (54).
In addition to the common pathway, adefovir regulates cell proliferation and differentiation by affecting the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. PI3K activation recruits the downstream signaling molecule protein kinase B (AKT), which promotes mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation, affects osteoblast differentiation and inhibits apoptosis, improves osteoblast survival (55). Whereas, the nucleotide analog Adefovir cellular metabolite can inhibit normal bone formation function by binding to Akt proteins and blocking their movement to the cell membrane and phosphorylation (56). In addition to this, deletion of Akt2, another isoform of AKT, has also been found to decrease the bone resorption capacity of osteoclasts (57). Therefore, when this pathway is upregulated, it increases osteoclast activity and further develops osteoporosis.
Notably, unlike adefovir, tenofovir additionally contributes to the development of osteoporosis by affecting inflammatory cytokine pathways such as IL-17, IL-1β, and TNF. A study on the effects of tenofovir on the mucosal tissue environment likewise found that tenofovir upregulates cytokine gene expression in epithelial cells and fibroblasts, which can increase the level of secretion of inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and IL-8, which in turn can have some negative effects on bone health (58, 59). Further studies found that IL-17 can promote the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in osteoblasts and enhance their ability to degrade bone matrix (60). In addition, IL-1β and TNF-α can also regulate the number of osteoblasts by up-regulating Fas-mediated apoptosis of osteoblasts, which results in an inhibitory effect on the bone formation process (61).
Molecular docking further suggested that adefovir and tenofovir, respectively, could promote the development of osteoporosis by binding to different proteins. Both adefovir and adefovir bind to ADORA1, JAK1, and NR2F2. In addition, adefovir binds well to proteins such as LCN2, PIK3CG, and RAC1, while tenofovir has good binding ability to CXCL8, IL1B, and TNF. The specific mechanisms of some of these related proteins have been elucidated. Adora1 acts as an adenosine receptor and when it is significantly up-regulated, mouse bone density is significantly reduced (62). As a key target, it binds to Adefovir and Tenofovir to promote the development of osteoporosis. Furthermore, when assessing the BMD profile of de-ovulated rats, JAK1 was found to promote bone resorption by co-activation with STAT3 (63). The link between NR2F2 and bone density is unclear, but some studies suggest that its downstream HMGB1 protein may be its core protein affecting bone density (64, 65). In addition to this, adefovir and tenofovir are able to bind specific proteins to act. For example, LCN2 was found to be reduced after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) in obese Chinese women, and hormonally reduced bone density in the patients (66). Adefovir causes increased bone loss in patients by binding to LCN2, while CXCL8, a specific target of tenofovir, interferes with the expression of CXLC8, and patients ultimately experience adverse events of osteoporosis (67). Clarifying the specific protein targets of adefovir and tenofovir-induced osteoporosis will help provide more detailed recommendations for future clinical improvement of the drugs or prevention of adverse events.
Our study has the following strengths, first, we confirmed the presence of osteoporotic adverse events with adefovir and tenofovir treatment using real-world adverse event data. In addition, GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses clarified the biological processes and pathways that play a key role in this. Supplementarily, molecular docking techniques were used to further explore specific protein targets and direct binding processes.
However, this study still has some limitations. First, the FAERS database suffers from many selection biases and contains inaccurate or incomplete information, so we need to conduct more rigorous prospective studies to obtain a more comprehensive and accurate view. Additionally, although relevant targets and pathways can be screened by GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis methods, the specific mechanisms of action of adefovir and tenofovir on these signaling pathways have not been sufficiently investigated, and more experimental evidence is needed to support them in the future. Finally, the molecular docking-based approach has the disadvantage of failing to predict target up-and downregulation, which is detrimental to accurately understanding the mechanism by which chemical components act on disease targets.
5 Conclusion
Our study reveals the effects of Adefovir and Tenofovir on bone health from a real-world perspective and, through further analysis, identifies their core active ingredients and key target pathways that lead to OP. The aim is to provide a theoretical basis for the rational clinical use of anti-hepatitis virus drugs and the prevention and management of associated bone health risks. To provide more detailed recommendations for future clinical improvement of nucleotide analogs or prevention of their adverse events.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SW: Writing – review & editing, Validation. LL: Writing – original draft. LQ: Writing – original draft. ZG: Writing – original draft. YQ: Writing – original draft. CX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Central Guidance of Local Science and Technology Development Funds [No. YDZJSX20231A062] and Shanxi Provincial Scientific and Technological Achievement Transformation Guidance Special Program [No. 202204021301067].
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to FAERS database, PubChem database, Comparative Toxicogenomics database, Gene Expression Omnibus database and Protein Data Bank database provide publicly available data for research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1605024/full#supplementary-material
- 5-HT
5-hydroxy tryptamine
- AEs
Adverse events
- AKT
Protein kinase B
- ATF4
Activating transcription factor 4
- BMD
Bone mineral density
- CaSR
Calcium-sensitive receptor
- CHB
Chronic hepatitis B
- DEMO
Demographic information
- DRUG
Drug Information
- EBGM
Empirical Bayesian Geometric Mean
- FAERS
FDA Adverse Event Reporting System
- GEO
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GPCR
G protein-coupled receptor binding
- HBV
Hepatitis B virus
- HCC
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
- IC
Information Component
- ICSRs
Individual Case Safety Reports
- INDI
Indications for Medication Administration
- LSG
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy
- MAPK
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MedDRA
Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities
- MMP-9
Matrix metalloproteinase-9
- mTOR
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NAs
Nucleotide and nucleoside analogs
- OUTC
Patient Outcomes
- PDB
Protein Data Bank
- PRR
Proportional Reporting Ratio
- PT
Preferred Terminology
- REAC
Adverse Event Codes
- ROR
Reporting Odds Ratio
- RPSR
Reporting Sources
- SMQs
Standardized MedDRA Queries
- THER
Treatment Start and End Dates Associated with Reported Drugs
- TLR
Toll-like receptor
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- WGCNA
Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis
Glossary
References
1.
Chang M . Hepatitis B virus infection. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. (2007) 12:160–7. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2007.01.013
2.
Wang J Li Q Qiu Y Kitanovski S Wang C Zhang C et al . Cell-type-specific expression analysis of liver transcriptomics with clinical parameters to decipher the cause of intrahepatic inflammation in chronic hepatitis B. iMeta. (2024) 3:E221. doi: 10.1002/imt2.221
3.
WHO Hepatitis B fact sheet (2024). Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b
4.
Shih C Yang C Choijilsuren G Chang C Liou A . Hepatitis B virus. Trends Microbiol. (2018) 26:386–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.01.009
5.
Kanwal F Gralnek IM Martin P Dulai GS Farid M Spiegel BM . Treatment alternatives for chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Ann Intern Med. (2005) 142:821–31. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-142-10-200505170-00007
6.
Zhang S Ma Q Liang S Xiao H Zhuang G Zou Y et al . Annual economic burden of hepatitis B virus-related diseases among hospitalized patients in twelve cities in China. J Viral Hepat. (2016) 23:202–10. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12482
7.
Hsu YC Wei MT Nguyen MH . Tenofovir alafenamide as compared to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in the management of chronic hepatitis B with recent trends in patient demographics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 11:999–1008. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2017.1386554
8.
Fung J Lai CL Seto WK Yuen MF . Nucleoside/nucleotide analogues in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2011) 66:2715–25. doi: 10.1093/Jac/Dkr388
9.
Ogunnaike M Das S Raut S Sultana A Nayan MU Ganesan M et al . Chronic hepatitis B infection: new approaches towards cure. Biomol Ther. (2023) 13:1208. doi: 10.3390/Biom13081208
10.
Pisano MB Giadans CG Flichman DM Ré VE Preciado MV Valva P . Viral hepatitis update: progress and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. (2021) 27:4018–44. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i26.4018
11.
European Association for the Study of the Liver . EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. (2017) 67:370–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.021
12.
De Fraga RS Van Vaisberg V Mendes L Carrilho FJ Ono SK . Adverse events of nucleos(t)ide analogues for chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol. (2020) 55:496–514. doi: 10.1007/S00535-020-01680-0
13.
Ning HB Jin H Li K Peng Z Li W Shang J . Analysis of bone mineral density and its influencing factors in 211 patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with long-term entecavir monotherapy. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2021) 29:234–9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20191128-00436
14.
Sun L Yi D Sun W Wang C . Retrospective analysis of the clinical characteristics of Adefovir Dipivoxil-induced Fanconi's syndrome in the Chinese population. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2020) 45:722–8. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13154
15.
Li C Li H Gong M Liu Y Zhang R Geng J et al . A real-world study on safety and efficacy of TAF treatment in HBV patients with high risk of osteoporosis or osteopenia in China. Altern Ther Health Med. (2024) 30:146–51.
16.
Wei M Le A Chang M Hsu H Nguyen P Zhang J et al . Antiviral therapy and the development of osteopenia/osteoporosis among Asians with chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol. (2019) 91:1288–94. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25433
17.
Yang R Yin N Zhao Y Li D Zhang X Li X et al . Adverse events during pregnancy associated with Entecavir and Adefovir: new insights from a real-world analysis of cases reported to FDA adverse event reporting system. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:772768. doi: 10.3389/Fphar.2021.772768
18.
Sakaeda T Tamon A Kadoyama K Okuno Y . Data mining of the public version of the FDA adverse event reporting system. Int J Med Sci. (2013) 10:796–803. doi: 10.7150/Ijms.6048
19.
Huang S . Analysis of environmental pollutant bisphenol F elicited prostate injury targets and underlying mechanisms through network toxicology, molecular docking, and multi-level bioinformatics data integration. Toxicology. (2024) 506:153847. doi: 10.1016/J.Tox.2024.153847
20.
Fu S Zhou Y Hu C Xu Z Hou J . Network pharmacology and molecular docking technology-based predictive study of the active ingredients and potential targets of rhubarb for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Bmc Complement Med Ther. (2022) 22:210. doi: 10.1186/S12906-022-03662-6
21.
She X Yin D Guo Q Tang Y Wang S Wang X . Electrolyte disorders induced by six multikinase inhibitors therapy for renal cell carcinoma: a large-scale pharmacovigilance analysis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:5592. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56335-4
22.
Meddra . Meddra (2024). Available at: https://www.meddra.org/how-to-use/support-documentation
23.
Lv L Wu X Ren Y Guo Y Wang H Li X . Postmarketing safety evaluation of pemetrexed using FAERS and JADER databases. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:18738. doi: 10.1038/S41598-025-02426-9
24.
PubChem . (2024). Available online at: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
25.
Liu T Lin Y Wen X Jorissen R Gilson M . BindingDB: a web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities. Nucleic Acids Res. (2007) 35:D198–201. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl999
26.
Ap D Tc W Rj J Sciaky D Wiegers J Cj M . Comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD): update 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:D1257–62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac833
27.
Yao Z Dong J Che Y Zhu M Wen M Wang N et al . Targetnet: a web service for predicting potential drug-target interaction profiling via multi-target SAR models. J Comput Aided Mol Des. (2016) 30:413–24. doi: 10.1007/s10822-016-9915-2
28.
Kanehisa M Furumichi M Tanabe M Sato Y Morishima K . KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. (2017) 45:D353–d361. doi: 10.1093/Nar/Gkw1092
29.
Yu G Wang L Han Y He Q . clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. (2012) 16:284–7. doi: 10.1089/Omi.2011.0118
30.
Berman HM Westbrook J Feng Z Gilliland G Bhat TN Weissig H et al . The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. (2000) 28:235–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235
31.
Marcellin P Wong D Sievert W Buggisch P Petersen J Flisiak R et al . Ten-year efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Liver Int. (2019) 39:1868–75. doi: 10.1111/Liv.14155
32.
Maggi P Montinaro V Leone A Fasano M Volpe A Bellacosa C et al . Bone and kidney toxicity induced by nucleotide analogues in patients affected by HBV-related chronic hepatitis: a longitudinal study. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2015) 70:1150–4. doi: 10.1093/Jac/Dku502
33.
He Y Huang X Ye Y Xu H . Clinical management of hypophosphatemic osteomalacia induced by Adefovir and Tenofovir: insights from a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). (2024) 103:E40746. doi: 10.1097/Md.0000000000040746
34.
Li L Wang S Wu H Luo D Dong G Feng Y et al . Acquired hypophosphatemic osteomalacia is easily misdiagnosed or neglected by rheumatologists: a report of 9 cases. Exp Ther Med. (2018) 15:5389–93. doi: 10.3892/Etm.2018.6106
35.
Huang PY Chiu SY Chang KC Tseng PL Yen YH Tsai MC et al . A novel evidence of serial changes of bone mineral density in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with Entecavir. Hepatol Int. (2021) 15:310–7. doi: 10.1007/S12072-021-10148-Z
36.
Zhou Y Wei M Zhang M Zhang J Tang F Wu X . Adefovir accumulation in the renal interstitium triggers mast cell degranulation and promotes renal interstitial fibrosis. Toxicol Lett. (2022) 359:10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2022.01.018
37.
Baylis C . Changes in renal hemodynamics and structure in the aging kidney; sexual dimorphism and the nitric oxide system. Exp Gerontol. (2005) 40:271–8. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2005.01.008
38.
Liu M Yao Y Tan F Wang J Hu R Du J et al . Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (Sglt-2) inhibitors ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (Iri) by modulating autophagic processes. Transl Res. (2025) 277:27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2024.12.006
39.
Rf S Schibalski R Ia Y Stadler K Dv I . Sex differences in renal mitochondrial function: a hormone-gous opportunity for research. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2020) 319:F1117–24. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00320.2020
40.
Hong X Cai Z Zhou F Jin X Wang G Ouyang B et al . Improved pharmacokinetics of Tenofovir ester prodrugs strengthened the inhibition of HBV replication and the rebalance of hepatocellular metabolism in preclinical models. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:932934. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.932934
41.
Yip T Lai J Yam T Tse Y Hui V Lai M et al . Long-term use of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate increases fracture risk in elderly patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. (2024) 80:553–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.12.001
42.
Liu A Vittinghoff E Sellmeyer D Irvin R Mulligan K Mayer K et al . Bone mineral density in HIV-negative men participating in a tenofovir pre-exposure prophylaxis randomized clinical trial in San Francisco. PLoS One. (2011) 6:E23688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023688
43.
Dumitriu L Ursu H . Hyperthyroidism in the elderly. I. Clinical manifestations. Endocrinologie. (1985) 23:83–90.
44.
Seelaar H Hj S Azmani A Küsters B Rosso S Majoor-Krakauer D et al . TDP-43 pathology in familial frontotemporal dementia and motor neuron disease without Progranulin mutations. Brain. (2007) 130:1375–85. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm024
45.
Sauzet O Carvajal A Escudero A Molokhia M Cornelius V . Illustration of the Weibull shape parameter signal detection tool using electronic healthcare record data. Drug Saf. (2013) 36:995–1006. doi: 10.1007/S40264-013-0061-7
46.
Mazhar F Battini V Gringeri M Pozzi M Mosini G Marran A et al . The impact of anti-TNFα agents on weight-related changes: new insights from a real-world pharmacovigilance study using the FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) database. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2021) 21:1281–90. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2021.1948529
47.
Song L Ding S Ge Z Zhu X Qiu C Wang Y et al . Nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors attenuate angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis by impairing receptor tyrosine kinases signalling in endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. (2018) 175:1241–59. doi: 10.1111/bph.14036
48.
Wilkins H Knerler S Warshanna A Ortiz R Haas K Orsburn B et al . Drug metabolism and transport capacity of endothelial cells, pericytes, and astrocytes: implications for CNS drug disposition. Biorxiv. (2024). doi: 10.1101/2024.08.01.606165
49.
Birkus G Hitchcock M Cihlar T . Assessment of mitochondrial toxicity in human cells treated with tenofovir: comparison with other nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2002) 46:716–23. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.3.716-723.2002
50.
Zhao X Sun K Lan Z Song W Cheng L Chi W et al . Tenofovir and Adefovir down-regulate mitochondrial chaperone Trap1 and succinate dehydrogenase subunit B to metabolically reprogram glucose metabolism and induce nephrotoxicity. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:46344. doi: 10.1038/srep46344
51.
Vestergaard P . Serotonin: a new potential risk factor for falls, low BMD, and fracture. J Bone Miner Res. (2018) 33:1558–9. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3560
52.
Weerasinghe DK Hodge JM Pasco JA Samarasinghe RM Azimi Manavi B Williams LJ . Antipsychotic-induced bone loss: the role of dopamine, serotonin and adrenergic receptor signalling. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2023) 11:1184550. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1184550
53.
Tsai ST Yang CC Liao HY Lin YW . Electroacupuncture reduces fibromyalgia pain via neuronal/microglial inactivation and toll-like receptor 4 in the mouse brain: precise interpretation of chemogenetics. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:387. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020387
54.
Zhang Y He Y Zong Y Guo J Sun L Ma Y et al . 17β-estradiol attenuates homocysteine-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response as well as MAPKs cascade via activating Pi3-K/Akt signal transduction pathway in raw 264.7 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai. (2015) 47:65–72. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmu124
55.
Zhao J Lin F Liang G Han Y Xu N Pan J et al . Exploration of the molecular mechanism of Polygonati Rhizoma in the treatment of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:815891. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.815891
56.
Duan Y Chen Z Ren H Hu P . Impact of nucleosides analogues and nucleotide analogues on the outcomes related to chronic hepatitis B based on non-antiviral effects. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. (2023) 31:880–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20221231-00616
57.
Ilyas S Lee J Lee D . Emerging roles of natural compounds in osteoporosis: regulation, molecular mechanisms and bone regeneration. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). (2024) 17:984. doi: 10.3390/ph17080984
58.
Biswas N Rodriguez-Garcia M Shen Z Crist S Bodwell J Fahey J et al . Effects of tenofovir on cytokines and nucleotidases in HIV-1 target cells and the mucosal tissue environment in the female reproductive tract. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2014) 58:6444–53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03270-14
59.
Kany S Vollrath J Relja B . Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:6008. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236008
60.
Samarpita S Doss H Ganesan R Rasool M . Interleukin 17 under hypoxia mimetic condition augments osteoclast mediated bone erosion and expression of HIF-1α and MMP-9. Cell Immunol. (2018) 332:39–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.07.005
61.
Tsuboi M Kawakami A Nakashima T Matsuoka N Urayama S Kawabe Y et al . Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta increase the FAS-mediated apoptosis of human osteoblasts. J Lab Clin Med. (1999) 134:222–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2143(99)90201-9
62.
Wang Y Di Y Li Y Lu J Ji B Zhang Y et al . Role of sphingolipid metabolism signaling in a novel mouse model of renal osteodystrophy based on transcriptomic approach. Chin Med J. (2025) 138:68–78. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003261
63.
Zhang Z Song C Zhang F Xiang L Chen Y Li Y et al . Rhizoma dioscoreae extract protects against alveolar bone loss in ovariectomized rats via micrornas regulation. Nutrients. (2015) 7:1333–51. doi: 10.3390/nu7021333
64.
Guo Y Ge X Wang W Wang R Chen Q Wang H . Epimedium applied in the clinical treatment of osteoporosis patients with periodontitis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2024) 103:E40837. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040837
65.
Sun H Feng Q Qin B Guo X Liu X Song J et al . Bruceine a attenuates fibrogenesis and inflammation through NR2F2-regulated HMGB1 inflammatory signaling cascades in hepatic fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol. (2025) 987:177164. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177164
66.
Wen X Zhu B Zhang Y Mei F Cheng X Qian C et al . Alterations in fat mass and bone mineral density are associated with decreased lipocalin-2 after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in obese Chinese women. Obes Surg. (2019) 29:2862–8. doi: 10.1007/s11695-019-03914-4
67.
Yanchen F Yali L Xue D Zixuan L Yunke Z Zhiying C et al . Exploring the multicomponent synergy mechanism of Zuogui wan on postmenopausal osteoporosis by a systems pharmacology strategy. J Tradit Chin Med. (2024) 44:489–95. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231204.005
Summary
Keywords
adefovir, tenofovir, osteoporosis, G protein-coupled receptor, IL-17
Citation
Di J, Wang S, Liu L, Qi L, Guo Z, Qin Y and Xiang C (2025) An in-depth investigation of NAs-induced osteoporosis adverse events: a real-world, network toxicology and molecular docking analysis. Front. Med. 12:1605024. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1605024
Received
11 April 2025
Accepted
23 June 2025
Published
04 July 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Min-Cong He, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, China
Reviewed by
Bangjian He, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, China
He Haijun, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Di, Wang, Liu, Qi, Guo, Qin and Xiang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chuan Xiang, chuanxiang@sxmu.edu.cn
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.