Abstract
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a rare, aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that can affect the kidneys. In this research, we described a very rare case of secondary membranous nephropathy (MN) associated with MCL. A 67-year-old man manifested with impaired renal function and nephrotic syndrome (NS). Kidney biopsy revealed atypical MN and MCL cell infiltration. After eight rounds of modified R-CHOP therapy, which includes rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone, the patient achieved complete remission, accompanied by improved renal function and a reduction in proteinuria. This case demonstrates the precise diagnosis and treatment of the primary disease, which can lead to favorable outcomes.
Introduction
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is a mature B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that accounts for approximately 5 to 7% of all lymphoma cases (1). The median age at diagnosis is between 60 and 70 years, with a higher prevalence in men than in women (1). MCL is typically diagnosed based on morphologic features and immunophenotyping. The neoplastic cells are small-to-medium lymphocytes expressing CD20, CD5, and cyclin D1. The cells are negative for CD10 and Bcl-6 and usually do not express CD23 (2).
Membranous nephropathy (MN) is a common glomerular disease. It is characterized histomorphologically by the presence of immune deposits in the subepithelial space of the glomerular filtration barrier, accompanied by diffuse thickening of the basement membrane (3, 4). The clinical manifestation of MN is nephrotic range proteinuria with edema (3, 4). The etiology and pathogenesis of MN are not fully understood. The primary MN (PMN), which is also called idiopathic MN (IMN), accounts for 70% of all MN (5). In PMN, circulating autoantibodies, mostly of the IgG4 subclass [e.g., anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (anti-PLA2R) and anti-thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A (THSD7A)], bind to endogenous antigens on podocytes and are assumed to be the first step of pathophysiological changes (5, 6). In secondary MN, antibodies might bind to neoantigens or planted antigens to cause the following kidney lesions (3).
There is very limited literature on kidney lesions associated with MCL. Renal involvement in MCL patients can exhibit diverse histopathological characteristics, and damage resulting from direct tumor infiltration is rarely identified as the underlying cause, as observed in a cohort of patients with NHLs (7). In this research, we demonstrate a rare case of MN secondary to MCL.
Case presentation
A 67-year-old Chinese man presented to our department with a history of foamy urine and lower extremity edema for more than 10 months. Upon admission, physical examination revealed a blood pressure of 118/85 mmHg, a pulse of 95/min, a temperature of 36.6°C, a respiratory rate of 18/min, a height of 170 cm, and a weight of 72.3 kg. On physical examination, the patient showed slight edema of both lower limbs and palpable enlargement of peripheral lymph nodes, which included both cervical lymph nodes, occipital nodes, supraclavicular lymph nodes, axillary lymph nodes, and inguinal lymph nodes. Splenomegaly was also detected. Laboratory investigations revealed an elevated serum creatinine (SCr) level of 210.4 μmol/L (normal range: 57–111 μmol/L, corresponding to an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 27.36 mL/min/1.73 m2, as calculated by the CKD-EPI equation) and decreased serum albumin level of 26.6 g/L. Urinalysis showed proteinuria and microscopic hematuria (579 RBCs/μl). The 24-h proteinuria was 3.8 g (total urine volume: 1650 mL) (Figure 1). His blood leukocyte count was 6.85 × 109/L, hemoglobin was 85 g/L (normocytic normochromic anemia), and platelet count was 159 × 109/L. Serum globulin was increased to 51.2 g/L. Elevated IgG of 33.9 g/L and IgA of 8.26 g/L were observed. Complement 3 was 0.85 g/L, which was within the normal range, while Complement 4 was slightly decreased at 0.14 g/L. Antinuclear antibodies were positive at a dilution of 1:100 and could not be further typed. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCAs), anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibodies, serum immunofixation electrophoresis, and anti-PLA2R antibodies were all negative. Additionally, hepatitis B, C, and HIV serology were negative. Renal ultrasound revealed two normal-sized kidneys.
Figure 1

The clinical course of the case. R-CHOP indicates rituximab (375 mg/m2), cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2), doxorubicin (60 mg/m2), vincristine (1.4 mg/m2), and prednisolone (100 mg/d × 5d).
Flow cytometry of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) found 10.07% abnormal B-cell clones. Bone marrow biopsy and axillary lymph node biopsy were subsequently performed. Bone marrow flow cytometry revealed abnormal B-cell clones comprising 16.94% of cells. Immunohistopathology examination of the axillary lymph node confirmed a diagnosis of MCL, classified as Stage IVa according to the Ann Arbor staging system (8) and the Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of MCL (9). (18)F-FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) was performed to evaluate the lymph node and organ involvement (10). It revealed multiple enlarged lymph nodes of varying sizes across several regions of the body. The largest lymph node was located in the axillary region, measuring 3.9 cm × 2.1 cm, with a maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of 8.0. These lymph nodes exhibited varying degrees of increased FDG metabolism, consistent with the metabolic pattern of lymphoma. Furthermore, nodular FDG-avid foci were observed in the upper limb muscles and subcutaneous tissue of the right shoulder. Splenomegaly with diffusely increased FDG uptake (SUVmax 5.8) was also noted. A renal biopsy was subsequently performed. Light microscopy revealed 20 glomeruli, including 3 with atherosclerosis and 1 with segmental cellular crescent formation. The remaining glomeruli showed mild proliferation of mesangial cells and matrix. Multifocal lymphocyte infiltration was observed in the tubulointerstitial area, with partial nodular formation (Figures 2A–D, 3A,B). The nodular regions were positive for CD20, CD5, and cyclin D1, which indicated MCL cell infiltration (Figures 2E–G). The GBM thickened diffusely. The tubule displayed multifocal atrophy. Direct immunofluorescence showed granular capillary loop staining for IgG (2+), C3 (2+), C1q (3+), IgG1 (3+), kappa (2+), and lambda (1+), but glomerular staining for IgA, IgM, C4, fibrin, HBs, HBc, IgG1, IgG2, and IgG3 were all negative (Figures 3C–F). PMN-associated antigens PLA2R and THSD7A staining were negative. Electron microscopy showed extensive foot process effacement and dense deposits in the subepithelial, basement membrane, and mesangial areas. It also indicated segmental uniform thickening of the basement membrane, reaching a thickness of up to 1,000 nm (Figure 3G). Based on these findings, the patient was diagnosed with atypical MN with MCL.
Figure 2
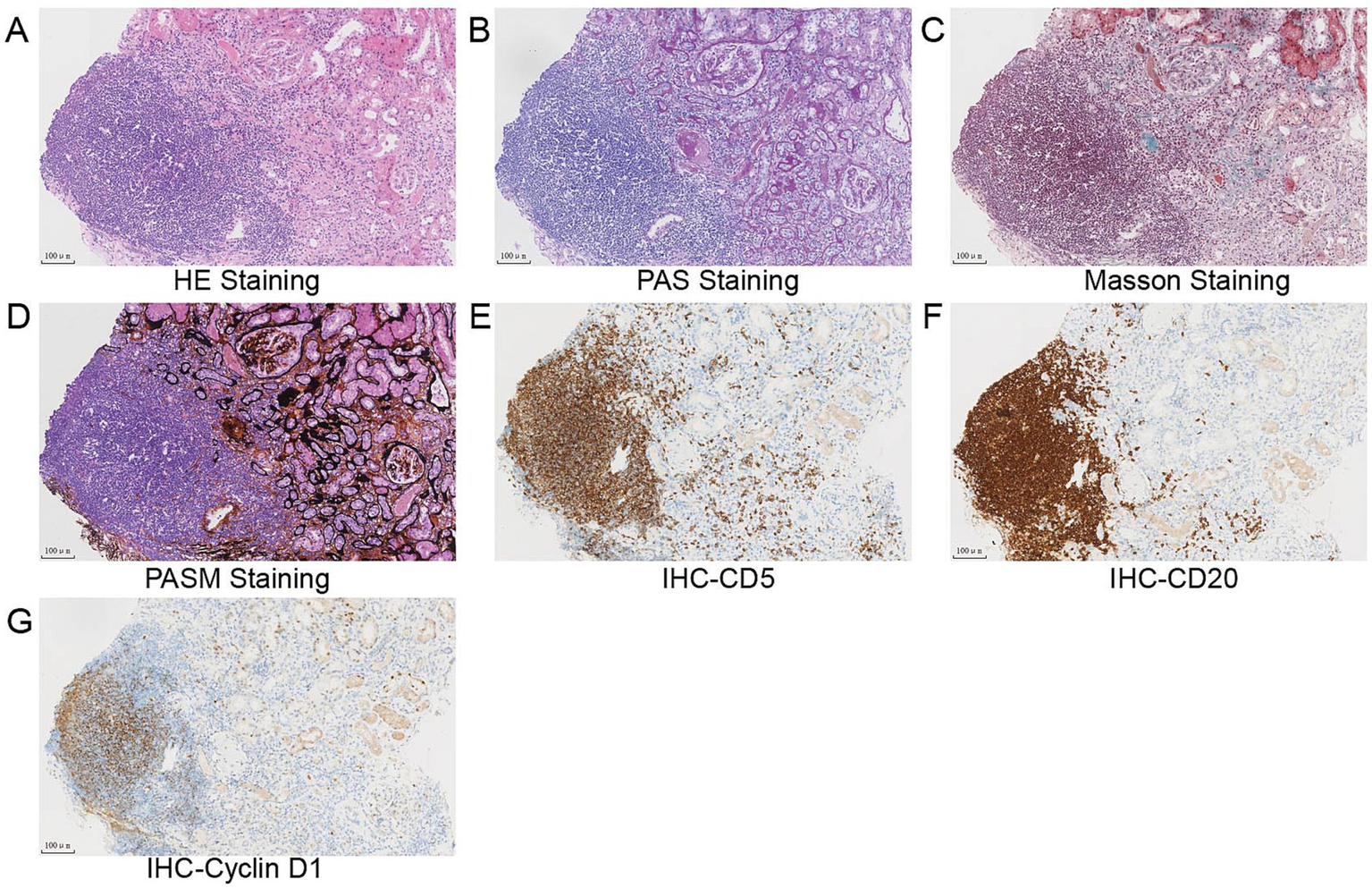
(A–D) Light microscopy study of the renal biopsy specimen revealed mild proliferation of mesangial cells and matrix, diffuse thickening of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), multifocal atrophy of the tubule, and nodular lymphocytes infiltration in the tubulointerstitial (A) hematoxylin and eosin staining, (B) periodic acid–Schiff staining, (C) Masson trichrome staining, (D) periodic acid silver methenamine staining, and (E–H) immunohistochemical analysis revealed that lymphoblasts were strongly positive for CD5 (E), CD20 (F), and cyclin D1 (G). Scale bars, 100 μm.
Figure 3
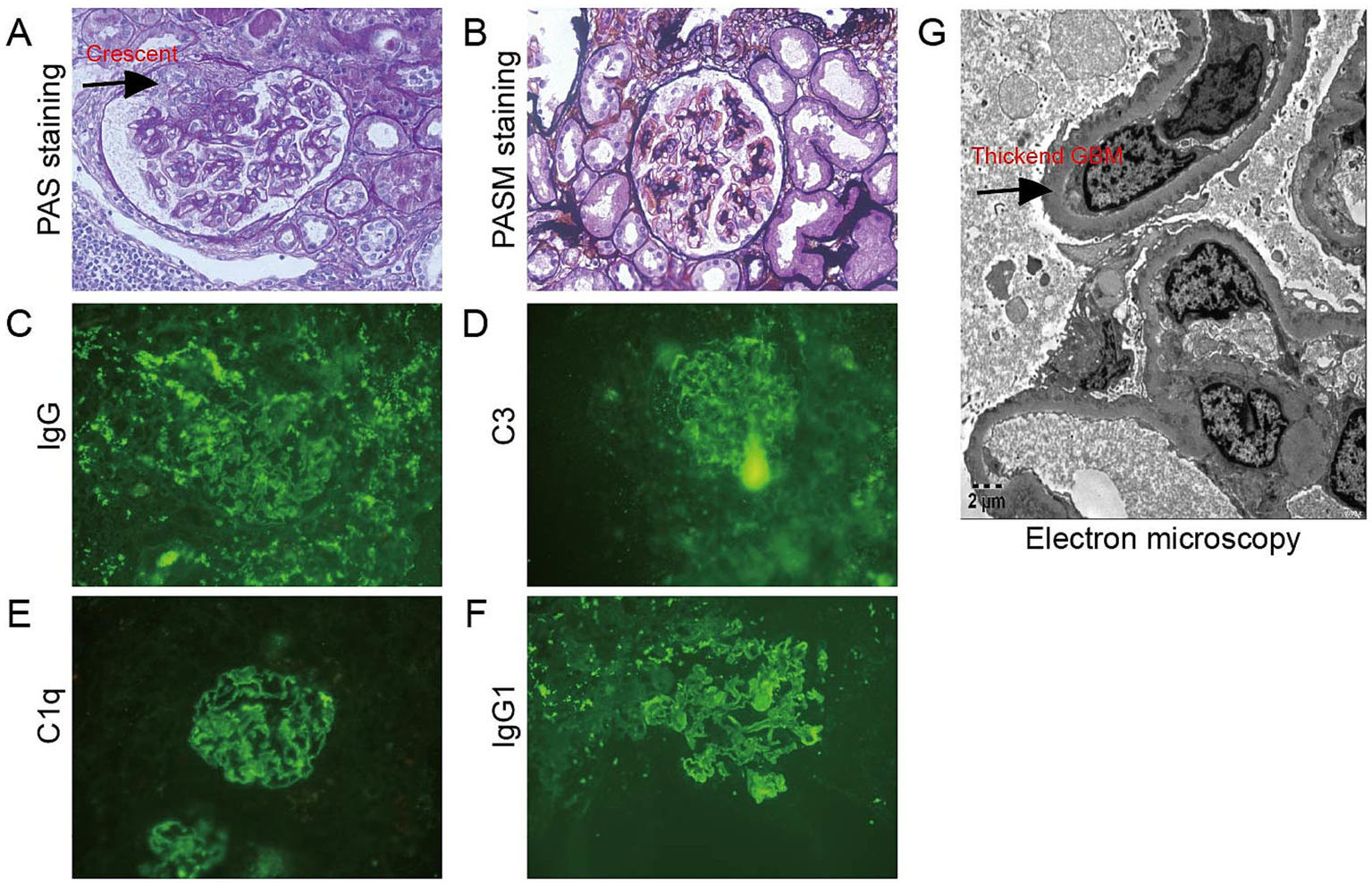
Histopathological findings in the glomerulus. (A,B) The glomeruli showed mild proliferation of mesangial cells and matrix, and there was one segmental cellular crescent formed (arrow) (A) Periodic acid–Schiff staining, ×400; (B) Periodic acid silver methenamine staining, ×400; (C–F) IgG, C3, C1q, and IgG1 granular deposits along the glomerular capillary loops direct immunofluorescence, (C) IgG staining; (D) C3 staining; (E) C1q staining; and (F) IgG1 staining; (G) Electron microscopy showed segmental homogenous thickening of the GBM, with thickness measuring up to 1,000 nm (arrow) (electron microscopy, ×5,000).
The patient’s Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG) performance status was 1. He received chemotherapy with modified R-CHOP, which consists of rituximab (375 mg/m2), cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2), doxorubicin (60 mg/m2), vincristine (1.4 mg/m2), and prednisolone (100 mg, once daily for 5 days). The standard interval between cycles was 28 days. After one round of chemotherapy, the patient’s SCr level decreased to 178.3 μmol/L with an eGFR of 33.19 mL/min/1.73 m2 as calculated by the CKD-EPI equation. The treatment of round 2 was delayed by 28 days due to pneumonia. After the eighth round of R-CHOP therapy, the SCr was 118.2 μmol/L with an eGFR of 54.55 mL/min/1.73 m2. The 24-h proteinuria was 0.68 g (total urine volume: 1,650 mL) (Figure 1). Post-treatment PET/CT revealed a significant reduction in size and FDG uptake of previously involved lymph nodes. The largest lymph node of the axillary region was 1.2 cm × 0.6 cm (SUVmax 0.9). The Deauville score was 2. No enlargement or abnormal FDG uptake was observed in the spleen. The latest follow-up was 1 year post-treatment. The patient’s SCr was 139.5 μmol/L, with an eGFR of 35.4 mL/min/1.73 m2. The 24-h proteinuria was 0.29 g/24 h. (Figure 1).
Discussion
MCL is a rare, aggressive lymphoma. Renal involvement of MCL has been reported previously. The histopathological features include membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) (11), minimal change disease (MCD) (12), ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis (13), lupus nephritis (14), and lymphoma infiltrating the kidney parenchyma. MN secondary to MCL is indeed rare.
In this study, we present the case of a 67-year-old man with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma and MN secondary to MCL. Renal impairment was significantly improved by chemotherapy for MCL. It is well known that MN is the most frequent renal injury associated with solid tumors, but only a few cases have reported the association between MN and lymphoma (15, 16). As in Hodgkin’s disease, the most common renal lesion is minimal-change nephrotic syndrome (17), whereas the association of MN with non-Hodgkin lymphomas has been rarely reported (18). Nie’s study showed that renal amyloidosis and MN were the most common glomerular diseases in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (19). Another study found that the most common glomerular lesion is membranoproliferative GN, followed by MN in NHL and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (7). In a multi-institutional study, the authors retrospectively reviewed patients’ kidney biopsy samples of those who had active and treated MCL (20). There were 20 patients who had active MCL at the time of biopsy, of which 14 presented with acute kidney injury, proteinuria, and/or hematuria due to MCL. Kidney pathology revealed that two patients had proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal immunoglobulin deposits (PGNMID), two had C3GN, three had secondary MN, two had tubular basement membrane deposits, and two had modest lupus-like GN (20). Several case reports have described kidney involvement in MCL; however, only a few have reported MN associated with MCL (21).
In MN, a high level of serum anti-PLA2R antibodies and the presence of PLA2R antigen in the kidney are usually associated with primary forms of MN (22). THSD7A is currently believed to be used to assess PMN activity and patient prognosis (23). PLA2R and THSD7A have diagnostic significance for PMN (22, 23). For secondary MN, several new target antigens, such as neural epidermal growth factor-like 1 protein (NELL-1), exostosin 1 (EXT1), EXT2, semaphorin 3B (SEMA3B), and serine protease HTRA1, have been found in recent years (3). However, these newly found target antigens have not yet been widely applied in clinical practice. In our case, PLA2R and THSD7A were negative, indicating that the patient likely had secondary MN. Kidney immunohistochemistry (IHC) revealed positive expression of CD5, CD19, and cyclin D1, meeting the most recent MCL diagnostic criteria (9). Based on these findings, we diagnosed the patient with secondary MN due to MCL. The precise pathologic mechanisms and target antigens responsible for disease in secondary MN are less well understood. It is assumed that circulating antigens, immune complexes, or monoclonal immunoglobulins may “plant” on the subepithelial side of the GBM by virtue of size and/or charge and thereby initiate immune complex formation in the subepithelial position (24). Researchers found that RAS signaling via the Wnt1/β-catenin pathway, gut microbiota, oxidative stress, and inflammation were involved in MN pathogenesis (25–27). However, no study, to date, has reported a specific mechanism of MCL-induced MN. It still needs to be explored.
For PMN, all patients should receive supportive management, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin-receptor blockers, blood pressure control, and sodium intake restriction (24). Based on the disease classification, PMN patients will receive different treatment strategies, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. There are also some traditional Chinese medicines (e.g., Tripterygium wilfordii multiglucoside) that have been found to be effective in MN (28). However, the general treatment principle for secondary MN is to treat the underlying disease. In patients with malignancy-associated MN, treating the malignancy should be paramount (24). Older patients and those with serious coexisting conditions may not be candidates for autologous transplantation (1). In our case, the patient was elderly and had significant renal impairment at diagnosis, making him unsuitable for autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). According to the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of MCL in China (5), patients over 65 years of age, those with poor general condition, or those unsuitable for ASCT should receive non-intensive regimens such as R-CHOP, bendamustine-rituximab (B-R), or Venetoclax-Rituximab-Cyclophosphamide-Doxorubicin-Prednisone (VR-CAP). In addition to chemotherapy, several trials have investigated “chemotherapy-free” regimens as initial treatments for MCL. A study evaluating lenalidomide plus rituximab as first-line treatment reported a response rate of 92%, with a complete response rate of 64% (29). In the US, the combination of ibrutinib and rituximab was studied, achieving a complete response rate of 71% (30). Additionally, numerous treatment approaches have emerged in recent years, including targeted therapies such as BTK and BCL2 inhibitors, which have demonstrated durable responses (31, 32). Cellular therapies, such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells and bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE) antibodies, have shown promising results (33, 34). However, it is essential to note that these pilot studies included a limited number of highly selected patients. More time and research are needed to prove the efficacy of these therapeutic approaches. In our case, the patient chose to receive R-CHOP therapy for MCL, which resulted in complete remission. His creatinine and proteinuria decreased significantly, demonstrating the treatment’s effectiveness.
Conclusion
In summary, we reported the case of an old male patient who presented with nephrotic syndrome and impaired kidney function attributed to MCL. Renal biopsy showed atypical MN with concomitant interstitial infiltration from lymphoid cells. This case was diagnosed as MN secondary to mantle cell lymphoma. A longer follow-up is necessary to evaluate the long-term outcomes of treatment. Additionally, further research is needed to elucidate the pathogenesis of lymphoma-associated MN.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The requirement of ethical approval was waived by the committee of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital for the studies involving humans because Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board also waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants; legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
MR: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Writing – original draft. LC: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. QS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JW: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Medical and Health Research Project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2024KY028).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Jianguang Gong of the Nephrology Department and Yuan Chen of the Pathology Department of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital for the pathological staining and diagnosis of the kidney.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Armitage JO Longo DL . Mantle-cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386:2495–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2202672
2.
Cheah CY Opat S Trotman J Marlton P . Front-line management of indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma in Australia. Part 2: mantle cell lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma. Intern Med J. (2019) 49:1070–80. doi: 10.1111/imj.14268
3.
Hoxha E Reinhard L Stahl RAK . Membranous nephropathy: new pathogenic mechanisms and their clinical implications. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2022) 18:466–78. doi: 10.1038/s41581-022-00564-1
4.
Bi Jingru Wenkai G Pengcheng J Xinhui W Yuansheng X . Diagnosis and treatment of membranous nephropathy in integrative medicine. Integrat Med Nephrol Androl. (2024) 11:e23–e00014. doi: 10.1097/IMNA-D-23-00014
5.
Duan Y Yue Q Jing Z Rziwanguli A Changrong Z Tian X et al . IgG4-related disease with IgG1-dominant membranous nephropathy: a rare case report. Integrat Med Nephrol Androl. (2023) 10:e00007. doi: 10.1097/IMNA-D-23-00007
6.
Tesar V Hruskova Z . Autoantibodies in the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of membranous nephropathy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:593288. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.593288
7.
Da'as N Polliack A Cohen Y Amir G Darmon D Kleinman Y et al . Kidney involvement and renal manifestations in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and lymphocytic leukemia: a retrospective study in 700 patients. Eur J Haematol. (2001) 67:158–64. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0609.2001.5790493.x
8.
Carbone PP Kaplan HS Musshoff K Smithers DW Tubiana M . Report of the committee on Hodgkin's disease staging classification. Cancer Res. (1971) 31:1860–1. PMID:
9.
Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. Hematology oncology Committee of China Anti Cancer a, Society of Hematology at Chinese medical a, Union for China Lymphoma Investigator at Chinese Society of Clinical O: [the guideline of the diagnosis and treatment of mantle cell lymphoma in China (2022)]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. (2022) 43:529–36. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2022.07.001
10.
Cheson BD Fisher RI Barrington SF Cavalli F Schwartz LH Zucca E et al . Eastern cooperative oncology G et al: recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32:3059–67. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.8800
11.
Lubas A Mroz A Smoszna J Niemczyk S . Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, mantle cell lymphoma infiltration, and acute kidney injury. Int Urol Nephrol. (2013) 45:1489–94. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0210-4
12.
Khow KS Yong AS Yong TY Kuss BJ Barbara JA Li JY . Minimal change disease associated with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma. Ren Fail. (2014) 36:634–7. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2014.883905
13.
Miyata KN Siddiqi NA Kiss LP Harbord NB Winchester JF . Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive pauci-immune glomerulonephritis associated with mantle cell lymphoma. Clin Nephrol Case Stud. (2017) 5:9–15. doi: 10.5414/CNCS109036
14.
Bao D Tan Y Yu X Wang B Wang H Xu R et al . Case report: a rare case of lupus nephritis associated with mantle cell Lymphoma. Front Med. (2021) 8:759279. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.759279
15.
Hotta O Taguma Y Kurosawa K Sudo K Takahashi H . Membranous nephropathy associated with nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease. Nephron. (1993) 63:347–50. doi: 10.1159/000187221
16.
Gomez-Campdera FJ Lopez-Gomez JM Jofre R Flores E . Membranous nephropathy in Hodgkin's disease in complete remission. Nephron. (1994) 68:392. doi: 10.1159/000188411
17.
Dabbs DJ Striker LM Mignon F Striker G . Glomerular lesions in lymphomas and leukemias. Am J Med. (1986) 80:63–70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90049-5
18.
Strippoli GF Manno C Rossini M Occhiogrosso G Maiorano E Schena FP . Primary cerebral lymphoma and membranous nephropathy: a still unreported association. Am J Kidney Dis. (2002) 39:E22. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2002.33413 PMID:
19.
Nie G Sun L Zhang C Yuan Y Mao H Wang Z et al . Clinicopathological features and individualized treatment of kidney involvement in B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:903315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.903315
20.
Andeen NK Abdulameer S Charu V Zuckerman JE Troxell M Kambham N et al . A diverse Spectrum of immune complex- and complement-mediated kidney diseases is associated with mantle cell Lymphoma. Kidney Int Rep. (2022) 7:568–79. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.12.020
21.
Qin B Li Y Kuang D Yang X Pan C Cai X et al . Diagnosis and treatment of secondary nephrotic syndrome with rash as the first symptom: a case report. BMC Nephrol. (2024) 25:225. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03665-0
22.
Murt A Berke I Bruchfeld A Caravaca-Fontan F Floege J Frangou E et al . Malignancies and glomerulonephritis: when to suspect and when to screen?Clin Kidney J. (2025) 18:sfaf101. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaf101
23.
Jiang S Jiang D Lian Z Huang X Li T Zhang Y . THSD7A as a promising biomarker for membranous nephrosis. Mol Biotechnol. (2024) 66:3117–35. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00934-5
24.
Alsharhan L Beck LH Jr . Membranous nephropathy: Core curriculum 2021. Am J Kidney Dis. (2021) 77:440–53. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.10.009
25.
Miao H Wang YN Su W Zou L Zhuang SG Yu XY et al . Sirtuin 6 protects against podocyte injury by blocking the renin-angiotensin system by inhibiting the Wnt1/beta-catenin pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2024) 45:137–49. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01148-w
26.
Miao H Wang YN Yu XY Zou L Guo Y Su W et al . Lactobacillus species ameliorate membranous nephropathy through inhibiting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway via tryptophan-produced indole metabolites. Br J Pharmacol. (2024) 181:162–79. doi: 10.1111/bph.16219
27.
Wang YN Miao H Yu XY Guo Y Su W Liu F et al . Oxidative stress and inflammation are mediated via aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 207:89–106. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.07.014
28.
Zhu H Xiao Y Ji Y . Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicines combined with biomedicine in the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1391675. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1391675
29.
Ruan J Martin P Shah B Schuster SJ Smith SM Furman RR et al . Lenalidomide plus rituximab as initial treatment for mantle-cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:1835–44. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1505237
30.
Jain P Zhao S Lee HJ Hill HA Ok CY Kanagal-Shamanna R et al . Ibrutinib with rituximab in first-line treatment of older patients with mantle cell Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40:202–12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01797
31.
Eyre TA Cheah CY Sarkozy C Kumar A Le Gouill S . Mantle cell Lymphoma: optimal treatment with Bruton tyrosine kinase-targeted approaches. J Clin Oncol. (2025):JCO2500146. doi: 10.1200/JCO-25-00146
32.
Tam CS Anderson MA Pott C Agarwal R Handunnetti S Hicks RJ et al . Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax for the treatment of mantle-cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:1211–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1715519
33.
Minson A Hamad N Cheah CY Tam C Blombery P Westerman D et al . CAR T cells and time-limited ibrutinib as treatment for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: the phase 2 TARMAC study. Blood. (2024) 143:673–84. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021306
34.
Goebeler ME Bargou R . Blinatumomab: a CD19/CD3 bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) with unique anti-tumor efficacy. Leuk Lymphoma. (2016) 57:1021–32. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2016.1161185
Summary
Keywords
membranous nephropathy, mantle cell lymphoma, nephrotic syndrome, secondary nephropathy, non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Citation
Ren M, Cao L, Shen Q, Zhu B and Wu J (2025) Case Report: Membranous nephropathy associated with mantle cell lymphoma: a rare case. Front. Med. 12:1627010. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1627010
Received
13 May 2025
Accepted
24 July 2025
Published
15 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Ying-Yong Zhao, Northwest University, China
Reviewed by
Neha Manhas, Medanta The Medicity Hospital, India
Xinhui Wang, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, China
Osman Radhwi, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Ren, Cao, Shen, Zhu and Wu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Wu, qieziwujuan18@163.com
†ORCID: Juan Wu, orcid.org/0000-0002-2660-0587
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.