- 1Department of Rheumatology, NHO Tokyo National Hospital, Kiyose, Japan
- 2Clinical Research Center for Allergy and Rheumatology, NHO Sagamihara National Hospital, Sagamihara, Japan
- 3Department of Rheumatology, NHO Sagamihara National Hospital, Sagamihara, Japan
- 4Department of Rheumatic Diseases, Tokyo Metropolitan Tama Medical Center, Fuchu, Japan
- 5Department of Rheumatology, NHO Himeji Medical Center, Himeji, Japan
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Sagami Seikyou Ganka Naika, Sagamihara, Japan
- 7Department of Clinical Laboratory, NHO Sagamihara National Hospital, Sagamihara, Japan
- 8Department of Orthopedics/Rheumatology, NHO Miyakonojo Medical Center, Miyakonojo, Japan
- 9Tanimura Hospital, Nobeoka, Japan
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, NHO Nagoya Medical Center, Nagoya, Japan
- 11Department of Life Sciences, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
- 12Clinical Research Center, NHO Nagasaki Medical Center, Omura, Japan
- 13Department of Gastroenterology and Rheumatology, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine, Fukushima, Japan
- 14Department of Internal Medicine, St. Francis Hospital, Nagasaki, Japan
Objective: Lung diseases that are chronic (emphysema [EMP], airway disease, interstitial lung disease) can complicate rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as extra-articular manifestations. Anti-Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) antibody (Ab) has been analyzed for the diagnosis of periodontal disease and RA patients showed increased anti-P. gingivalis Ab levels. However, amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab in RA complicated with chronic lung disease (CLD) are unknown. We measured anti-P. gingivalis Ab in cases of RA with CLD.
Methods: Anti-P. gingivalis lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Ab were measured in RA patient sera by enzyme immunoassay.
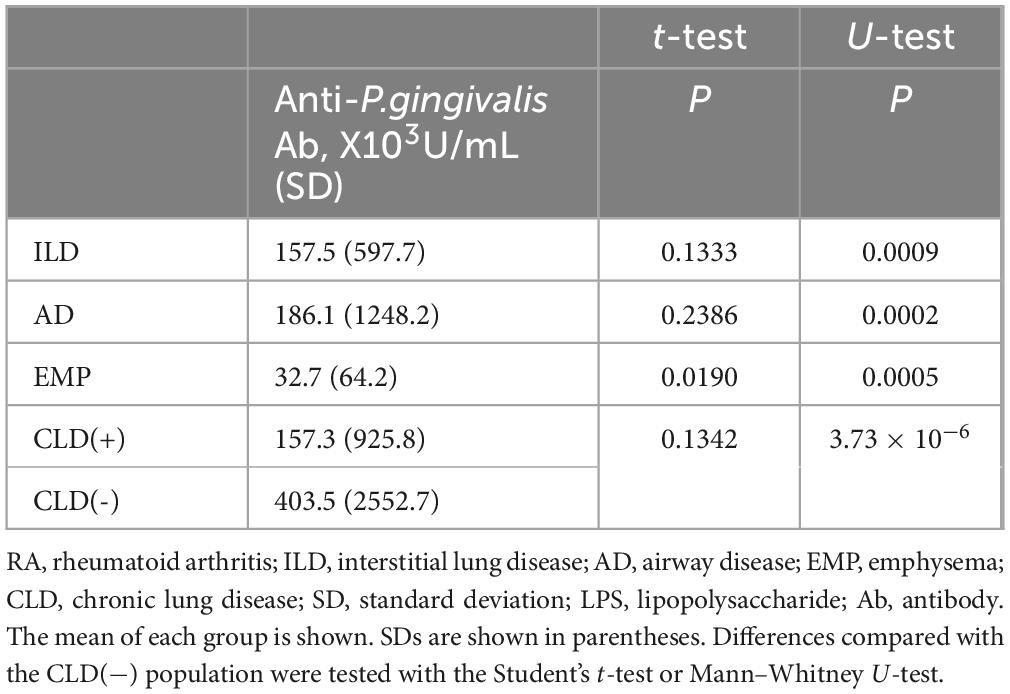
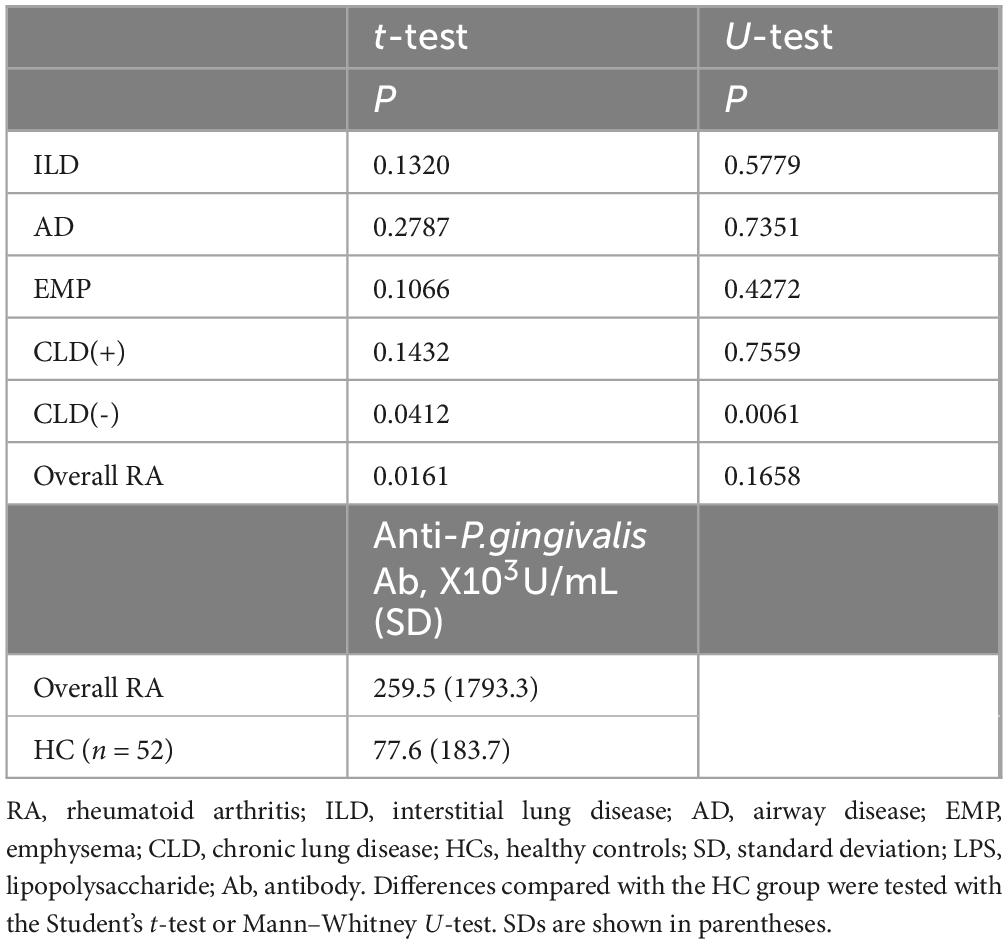
Results: Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab levels in RA with EMP were significantly lower than in RA cases without CLD (P = 0.0190, mean ± standard deviation [SD], 32.7 ± 64.2 [×103U/mL] vs. 403.5 ± 2552.7 [×103U/mL]). Multiple logistic regression analyses revealed the independence of this association. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts were increased in RA without CLD (P = 0.0412) compared with healthy controls (77.6 ± 183.7 [×103U/mL]).
Conclusion: Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab levels in RA with EMP were lower compared with RA without CLD. Citrullinated peptides were mainly generated in the lungs of RA with EMP and the oral cavity of RA without CLD, suggesting the heterogeneity of RA.
Introduction
Pathogenic factors of the chronic autoimmune disease rheumatoid arthritis (RA) featuring destruction of synovial joints (1), are poorly understood. Chronic lung diseases (CLD) (emphysema [EMP], airway disease [AD], interstitial lung disease [ILD]) (2), can frequently complicate RA, which results in a poor prognosis (3–8).
Rheumatoid arthritis patients generate many autoreactive antibodies, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA), which are thought to be pathogenic. Citrullinated peptides generated in lungs under the influence of smoking, lead to the production of ACPA. Smoking also confers a poor prognosis in RA patients (9). Periodontal disease, associated with infection by Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) has links to RA (10). Endogenous peptidyl-arginine-deiminase from P. gingivalis mediates oral cavity citrullinated peptide production, leading to the generation of ACPA (1, 11).
Anti-P. gingivalis antibody (Ab) analysis for the diagnosis of periodontal disease (12) showed anti-P. gingivalis Ab titers were decreased after treatment (13, 14). The levels of anti-P. gingivalis whole-cell Ab highly correlated to anti-P. gingivalis lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Ab levels (15). Anti-P. gingivalis Ab levels are increased in atherosclerosis (16), hyperlipidemia (17), RA (10), and chronic kidney disease (18). However, treatment of periodontal disease did not alter RA disease activity (19, 20).
Serum anti-P. gingivalis Ab levels might reflect P. gingivalis infection, which increases the risk of developing some diseases. The amounts of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab in RA complicated with CLD could be lower than those without CLD, since citrullinated peptides might be generated in lung of RA with CLD and in oral cavity of RA without CLD, respectively. However, there are few reports on amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab in RA complicated by CLD. This investigation measured anti-P. gingivalis Ab in RA complicated by CLD.
Material and methods
Patients
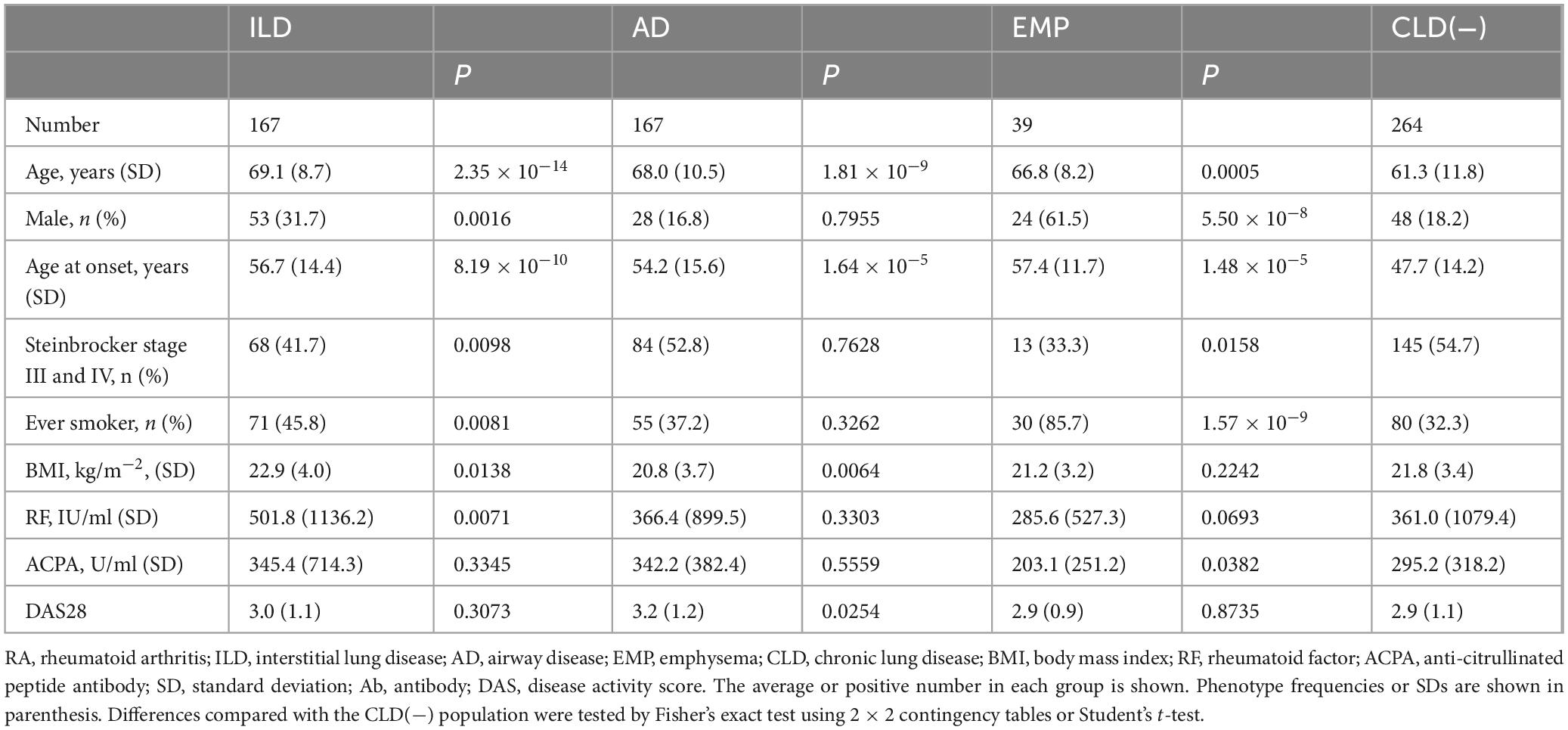
Overall, 637 RA patients with chest computed tomography findings and 52 healthy controls (HCs) at Miyakonojo Medical Center, Himeji Medical Center, Nagasaki Medical Center, Tokyo National Hospital, Nagoya Medical Center, and Sagamihara National Hospital were recruited. All RA cases fulfilled the RA criteria (21, 22). Those with ILD, AD, EMP, or no CLD [CLD(−)] were diagnosed using chest computed tomography as described elsewhere (23–25): ILD (irregular linear opacities and honeycombing, bilateral ground-glass attenuation patterns predominantly in subpleural and basal regions), AD (centrilobular or peribronchial nodules and branching linear structures, bronchial dilatation, bronchial wall thickening, or atelectasis), EMP (low attenuation area or bullae), or CLD(−) (no abnormalities in computed tomography images). RA patients with the other chest computed tomography patterns were excluded from this study. Steinbrocker stages were evaluated as described (26).
This study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study received approval from the Research Ethics Committee of Tokyo National Hospital (190010) and Research Ethics Committees of the institutes involved. Informed written consent was attained from all participants.
Detection of serum anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab
Serum anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab was measured by a Human anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab ELISA kit (Chondrex, Inc., Woodinville, WA, USA), as instructed by the manufacturer (27–29).
Statistical analysis
Rheumatoid arthritis patient clinical characteristics were compared using the Student t-test or Fisher’s exact test with the use of a 2 × 2 contingency table. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts were compared by Student’s t-test or Mann–Whitney U-test. Correlations between anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts, ACPA titers, and disease activity score 28 (DAS28) were evaluated with Pearson correlation coefficient values. Independent associations of amounts of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab with EMP in RA were evaluated by multiple logistic regression. The associations of amounts of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab with EMP were evaluated when conditioned on each clinical manifestation. The associations of each clinical manifestation with EMP were evaluated when conditioned on amounts of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab.
Results
Clinical characteristics of RA patient subsets
Comparisons of RA subset clinical characteristics were compared to those with RA cases without CLD (Table 1). Mean ages, male percentages, onset age, ever smoker percentage, and percentage of Steinbrocker stages III or IV, were higher in RA complicated with ILD or EMP. The body mass index (BMI) was lower and the age at onset as well as the mean age were higher for RA with AD. Increased RF levels were observed for RA with ILD, and ACPA levels were decreased in RA with EMP.
Detection of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab in RA
Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab was detected in RA patient sera (Figure 1) and comparisons of titers of each RA subset with those without CLD were performed (Table 2). Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab levels in RA with EMP (P = 0.0190, mean ± standard deviation [SD], 32.7 ± 64.2 [×103U/mL]) were significantly lower than those in CLD(−)RA (403.5 ± 2552.7 [×103U/mL]).
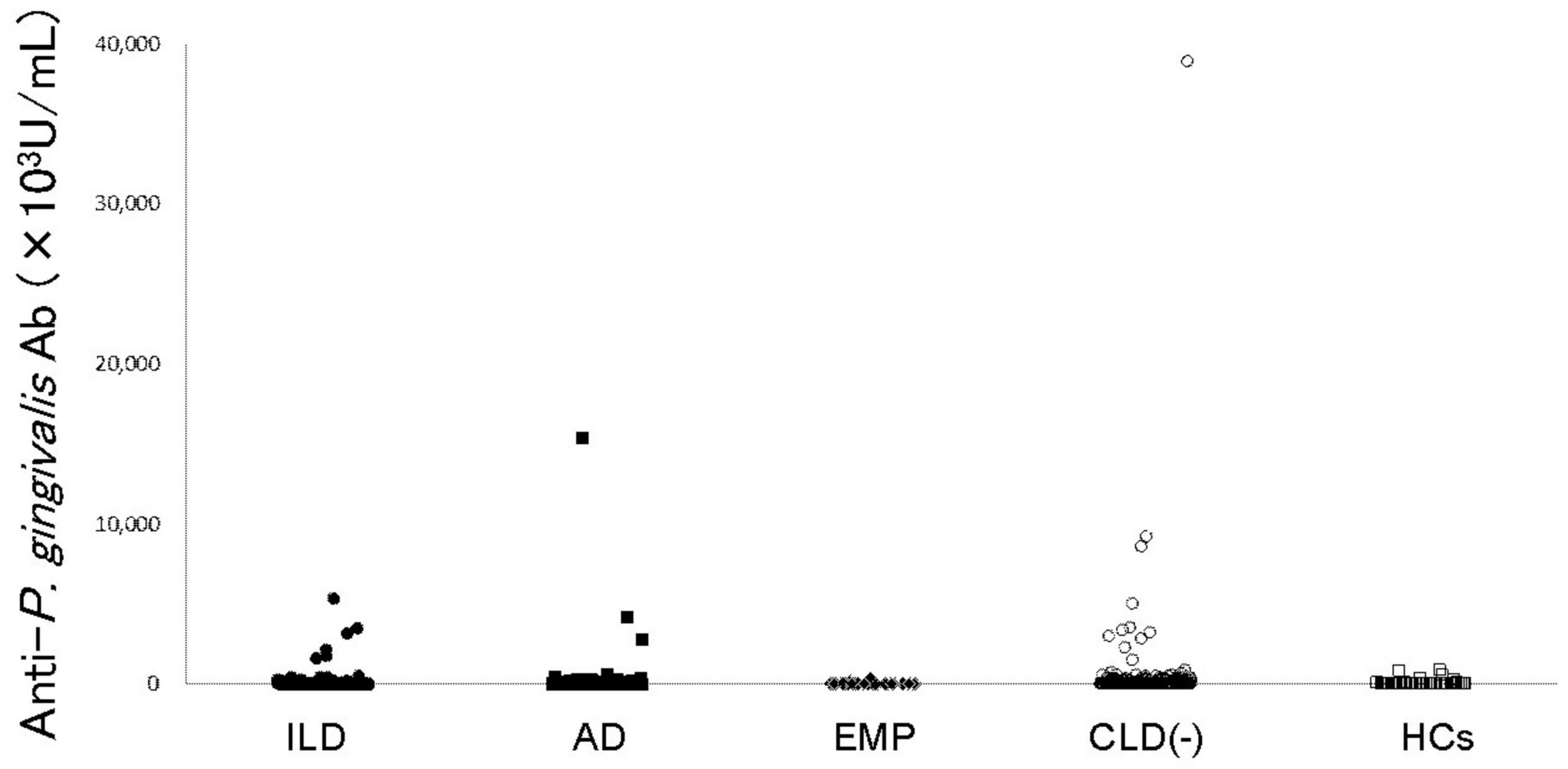
Figure 1. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS antibody levels in RA patients and controls. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS antibody levels are shown. Filled circles, filled squares, filled diamonds, empty circles, and empty squares represent RA with ILD, RA with AD, RA with EMP, RA without CLD, and HCs, respectively. RA: rheumatoid arthritis, ILD: interstitial lung disease, AD: airway disease, EMP: emphysema, CLD: chronic lung disease, HCs: healthy controls, LPS: lipopolysaccharide.
The correlation of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers, ACPA levels, and DAS28 were showed in Supplementary Table 1. The weak correlation of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts and DAS28 was detected in the RA patients (correlation coefficient 0.09, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.00–0.17, P = 0.0470), especially in CLD(−)RA (correlation coefficient 0.14, 95% CI 0.02–0.26, P = 0.0225).
The effects of smoking on anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers were analyzed and the results were shown in Supplementary Table 2. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers were not different between ever and never smoker groups, though anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers in RA with EMP (P = 0.0003, mean ± SD, 18.9 ± 16.4 [×103U/mL]) were significantly lower than CLD(−)RA (240.2 ± 1088.6 [×103U/mL]) in never smoker group. The effects of smoking on ACPA titers were also analyzed (Supplementary Table 3), and no association was detected in this subgroup analysis.
Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab is independently related to EMP in RA
Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to omit the impact of patient clinical characteristics on anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab linked to EMP in RA (Table 3). Univariate analysis demonstrated anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab was significantly linked to EMP (P = 0.0123, odds ratio [OR] 0.99, 95% CI 0.98–1.00) and this persisted to be significant when conditioned on age (Padjusted = 0.0172, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.99–1.00), sex (Padjusted = 0.0243, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.99–1.00), age at onset (Padjusted = 0.0221, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.99–1.00), Steinbrocker stage (Padjusted = 0.0141, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.98–1.00), smoking status (Padjusted = 0.0231, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.99–1.00), BMI (Padjusted = 0.0135, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.98–1.00), RF (Padjusted = 0.0164, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.98–1.00), or ACPA (Padjusted = 0.0193, OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.99–1.00), respectively. Thus, these data suggested that anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab was independently associated with EMP in RA.
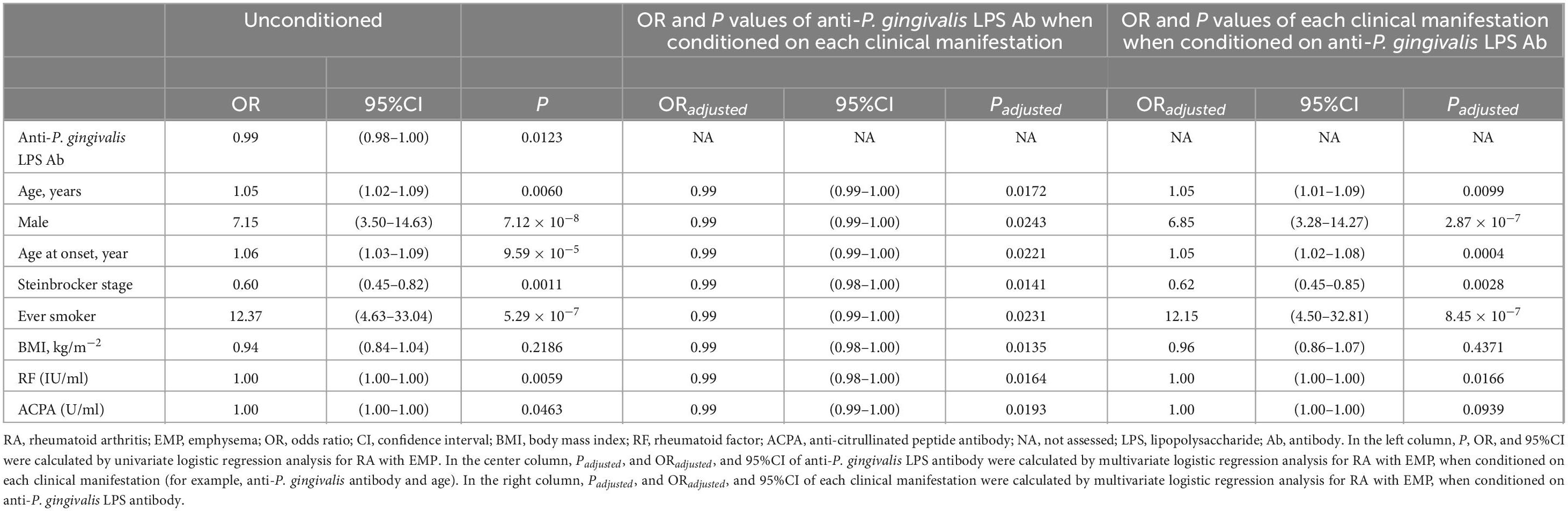
Table 3. Multiple logistic regression analysis of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab and each clinical manifestation for RA with EMP.
Comparison of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab between RA subsets and controls
Measurement of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab indicated increased levels in RA patients without CLD, and overall RA patients, compared with HCs (Table 4). Thus, compared with HCs, higher anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts were noted in overall RA cases, especially CLD(−)RA.
Discussion
In this study, it was revealed that anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts reported for RA with EMP were lower compared with RA without CLD and this association was independent. Additionally, higher anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts were observed for RA cases without CLD compared with HCs. In RA without CLD, citrullinated peptides are mainly generated in the oral cavity under the influence of periodontal disease, leading to the production of ACPA. In RA with CLD, especially with EMP, citrullinated peptides are mainly generated in the lung under the influence of smoking leading to the production of ACPA. These findings indicate the pathogenesis of RA might be heterogeneous. It was reported that the endogenous peptidyl-arginine-deiminase of P. gingivalis develops citrullinated peptides as autoantigens of ILD, leading to the production of ACPA (30). However, our data did not support that hypothesis. RA without CLD, “oral cavity RA”, would be partially overlapped with younger age onset RA populations and RA patients with CLD, “lung RA”, would be partially overlapped with elder age onset RA populations. The precise information of these heterogeneous features of RA should be investigated and would help to establish personalized medicine of RA.
In previous studies, increased amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab were reported for RA cases compared to HCs (10). We confirmed increased amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab in RA cases, per se, and they were extremely elevated in the CLD(−)RA group. Because few studies of anti-P. gingivalis Ab amounts in RA with CLD have been reported, our study results could not be precisely compared with previous reports. Amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab in cases with EMP or bronchitis were reported to be comparable (31). However, significantly lower amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab were reported for RA with EMP than for RA without CLD in this study. Because a similar pathogenesis is suspected to be involved in periodontal disease and EMP (32), these two disorders might have a similar role in RA pathogenesis in patients without CLD or with EMP, respectively.
Amounts of anti-P. gingivalis Ab in RA might be influenced by clinical manifestations. However, the relationship between anti-P. gingivalis Ab levels and EMP remained significant, even after clinical manifestation effects were adjusted for multiple logistic regression analyses. Thus, the amount of anti-P. gingivalis Ab measured was independently linked to EMP in RA.
It was known that ILD and AD resulted in a poor prognosis in RA (3–7). The coexistence of EMP and ILD conferred a poorer prognosis in RA (8). However, few studies on the prognosis of RA patients with EMP were conducted. Thus, the precise characterization of the RA subpopulation with EMP should be performed.
This study reports previously unknown findings related to anti-P. gingivalis Ab amounts in RA cases with EMP including low levels in RA complicated by EMP. However, anti-P. gingivalis Ab amounts in RA with other CLD including AD and ILD were lower than CLD(−)RA, when examined with U-test. The stratified analyses of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab or ACPA titers on smoking status were conducted, and anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers in RA with EMP were lower than CLD(−)RA in never smoker group. However, anti-P. gingivalis Ab amounts in RA with other CLD including AD and ILD were lower than CLD(−)RA, when examined with U-test. ACPA titers in ever smoker group were higher than those in never smoker group in CLD(−)RA, when examined with U-test. The correlations of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers with ACPA or DAS28 were also analyzed and the correlation of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers and DAS28 was found in the RA patients. Since considerable variations of anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab titers between individuals were detected in this study and sample size of the present study was modest, statistical powers were not enough for these subgroup analyses. Study limitations included the modest sample size and the fact that only Japanese populations were included. Thus, large-scale studies of different ethnic populations should be undertaken. Information on periodontal disease reported for patients with RA was not attained here; thus, putative direct correlations between periodontal disease and EMP in RA patients require further examination.
Conclusion
We investigated anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab in RA with or without CLD. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab levels in RA with EMP were lower compared with RA without CLD. Multiple logistic regression analyses showed the independence of this association. Anti-P. gingivalis LPS Ab amounts were increased in RA without CLD compared with healthy controls. Citrullinated peptides were mainly generated in the lung of RA with CLD, “lung RA”, and in the oral cavity of RA without CLD, “oral cavity RA”. RA without CLD would be partially overlapped with younger age onset RA populations and RA patients with CLD would be partially overlapped with elder age onset RA populations. These data suggested the heterogeneity of RA and the precise information of these heterogeneous features of RA would help to establish personalized medicine of RA.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by this study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study received approval from the Research Ethics Committee of Tokyo National Hospital (190010) and Research Ethics Committees of the institutes involved. Informed written consent was attained from all participants. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SO: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. TH: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. KSh: Resources, Writing – review & editing. MF: Resources, Writing – review & editing. AH: Writing – review & editing, Resources. AK: Resources, Writing – review & editing. KSa: Writing – review & editing, Resources. NY: Writing – review & editing, Resources. MS: Resources, Writing – review & editing. TM: Resources, Writing – review & editing. NF: Writing – review & editing, Resources. KM: Resources, Writing – review & editing. ST: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Resources. HF: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Resources, Conceptualization, Investigation, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B, C) (26293123, 15K09543, 18K08402, 22591090) and Young Scientists (B) (24791018) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Grants-in-Aid for Clinical Research from the National Hospital Organization, Health and Labor Science Research Grants from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan, Grants-in-Aid of the Practical Research Project for Allergic Diseases and Immunology (Research on Allergic Diseases and Immunology) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and Research Grants from The Nakatomi Foundation, Bristol-Myers K.K., Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Welfare Foundation, Takeda Science Foundation, Daiwa Securities Health Foundation, and the Japan Research Foundation for Clinical Pharmacology. An RA Clinical Investigation Grant was received from Bristol-Myers Squibb Co. The following pharmaceutical companies provided research grants: Astellas Pharma Inc., Merck Sharp and Dohme Inc., Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Pfizer Japan Inc., Teijin Pharma Limited, and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
Conflict of interest
HF and the following funders are supported wholly, or partly, by the following. The Takeda Science Foundation is supported by endowments from the Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. The Nakatomi Foundation was established by Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co, and the Japan Research Foundation for Clinical Pharmacology is related to Daiichi Sankyo. The Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Welfare Foundation was established by Mitsui Sumitomo Insurance Co., Ltd, and The Daiwa Securities Health Foundation was established by Daiwa Securities Group Inc. HF received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb Co and honoraria from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ajinomoto Co., Inc., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., Luminex Japan Corporation Ltd, Ayumi Pharmaceutical Corporation, and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. ST received research grants from Astellas Pharma Inc., Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Merck Sharp and Dohme Inc., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Teijin Pharma Limited, and Pfizer Japan Inc. and honoraria from Astellas Pharma Inc., Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., AbbVie GK., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., and Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1654271/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Smolen J, Aletaha D, McInnes I. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. (2016) 388:2023–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
2. Stainer A, Tonutti A, De Santis M, Amati F, Ceribelli A, Bongiovanni G, et al. Unmet needs and perspectives in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a critical review. Front Med. (2023) 10:1129939. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1129939
3. Hakala M. Poor prognosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis hospitalized for interstitial lung fibrosis. Chest. (1988) 93:114–8. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.1.114
4. Koduri G, Norton S, Young A, Cox N, Davies P, Devlin J, et al. Interstitial lung disease has a poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis: results from an inception cohort. Rheumatology. (2010) 49:1483–9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq035
5. Kim E, Elicker B, Maldonado F, Webb W, Ryu J, Van Uden J, et al. Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. (2010) 35:1322–8. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00092309
6. Vergnenègre A, Pugnere N, Antonini M, Arnaud M, Melloni B, Treves R, et al. Airway obstruction and rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Respir J. (1997) 10:1072–8. doi: 10.1183/09031936.97.10051072
7. Swinson D, Symmons D, Suresh U, Jones M, Booth J. Decreased survival in patients with co-existent rheumatoid arthritis and bronchiectasis. Br J Rheumatol. (1997) 36:689–91. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.6.689
8. Kim H, Lee J, Lee E, Ha Y, Chae E, Han M, et al. Risk prediction model in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Respirology. (2020) 25:1257–64. doi: 10.1111/resp.13848
9. Ren J, Ding Y, Zhao J, Sun Y. Impact of cigarette smoking on rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung diseases: a retrospective case control study on clinical and radiological features and prognosis. Rheumatol Int. (2023) 43:293–301. doi: 10.1007/s00296-022-05219-9
10. Bender P, Bürgin W, Sculean A, Eick S. Serum antibody levels against Porphyromonas gingivalis in patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. (2017) 21:33–42. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1938-5
11. Arleevskaya M, Takha E, Petrov S, Kazarian G, Novikov A, Larionova R, et al. Causal risk and protective factors in rheumatoid arthritis: a genetic update. J Transl Autoimmun. (2021) 4:100119. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100119
12. Mouton C, Hammond P, Slots J, Genco R. Serum antibodies to oral Bacteroides asaccharolyticus (Bacteroides gingivalis): relationship to age and periondontal disease. Infect Immun. (1981) 31:182–92. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.182-192.1981
13. Schenck K, Helgeland K, Tollefsen T. Antibodies against lipopolysaccharide from Bacteroides gingivalis before and after periodontal treatment. Scand J Dent Res. (1987) 95:112–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1987.tb01816.x
14. Murayama Y, Nagai A, Okamura K, Kurihara H, Nomura Y, Kokeguchi S, et al. Serum immunoglobulin G antibody to periodontal bacteria. Adv Dent Res. (1988) 2:339–45. doi: 10.1177/08959374880020022401
15. Guo S, Takahashi K, Kokeguchi S, Takashiba S, Kinane D, Murayama Y. Antibody responses against Porphyromonas gingivalis infection in patients with early-onset periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. (2000) 27:769–77. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2000.027010769.x
16. Chen Y, Umeda M, Nagasawa T, Takeuchi Y, Huang Y, Inoue Y, et al. Periodontitis may increase the risk of peripheral arterial disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2008) 35:153–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2007.08.016
17. Cutler C, Shinedling E, Nunn M, Jotwani R, Kim B, Nares S, et al. Association between periodontitis and hyperlipidemia: cause or effect? J Periodontol. (1999) 70:1429–34. doi: 10.1902/jop.1999.70.12.1429
18. Iwasaki M, Taylor G, Manz M, Kaneko N, Imai S, Yoshihara A, et al. Serum antibody to Porphyromonas gingivalis in chronic kidney disease. J Dent Res. (2012) 91:828–33. doi: 10.1177/0022034512455063
19. Möller B, Kollert F, Sculean A, Villiger P. Infectious triggers in periodontitis and the gut in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a complex story about association and causality. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01108
20. Monsarrat P, Fernandez de Grado G, Constantin A, Willmann C, Nabet C, Sixou M, et al. The effect of periodontal treatment on patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the ESPERA randomised controlled trial. Joint Bone Spine. (2019) 86:600–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2019.02.006
21. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman A, Funovits J, Felson D, Bingham C, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:2569–81. doi: 10.1002/art.27584
22. Arnett F, Edworthy S, Bloch D, McShane D, Fries J, Cooper N, et al. The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (1988) 31:315–24. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302
23. Tanaka N, Kim J, Newell J, Brown K, Cool C, Meehan R, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-related lung diseases: ct findings. Radiology. (2004) 232:81–91. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2321030174
24. Mori S, Cho I, Koga Y, Sugimoto M. Comparison of pulmonary abnormalities on high-resolution computed tomography in patients with early versus longstanding rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. (2008) 35:1513–21.
25. Oka S, Furukawa H, Shimada K, Sugii S, Hashimoto A, Komiya A, et al. Association of human leukocyte antigen alleles with chronic lung diseases in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. (2016) 55:1301–7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew025
26. Steinbrocker O, Traeger C, Batterman R. Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Med Assoc. (1949) 140:659–62. doi: 10.1001/jama.1949.02900430001001
27. Terato K, Waritani T, Fukai R, Shionoya H, Itoh H, Katayama K. Contribution of bacterial pathogens to evoking serological disease markers and aggravating disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0190588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190588
28. Kitamura K, Shionoya H, Suzuki S, Fukai R, Uda S, Abe C, et al. Oral and intestinal bacterial substances associated with disease activities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional clinical study. J Immunol Res. (2022) 2022:6839356. doi: 10.1155/2022/6839356
29. Fu K, Chiu M, Wara-Aswapati N, Yang C, Chang L, Guo Y, et al. Oral microbiome and serological analyses on association of Alzheimer’s disease and periodontitis. Oral Dis. (2023) 29:3677–87. doi: 10.1111/odi.14348
30. Jenning M, Marklein B, Ytterberg J, Zubarev R, Joshua V, van Schaardenburg D, et al. Bacterial citrullinated epitopes generated by Porphyromonas gingivalis infection-a missing link for ACPA production. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:1194–202. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216919
31. Lund Håheim A, Olsen I, Thelle D, Rønningen K. Comparative analysis of antibodies to four major periodontal bacteria in respiratory diseases: a cohort study. BMJ Open. (2024) 14:e082116. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-082116
Keywords: rheumatoid arthritis, anti-Porphyromonas gingivalis antibodies, emphysema, chronic lung disease, citrullinated peptides
Citation: Oka S, Higuchi T, Shimada K, Fujimori M, Hashimoto A, Komiya A, Saisho K, Yoshikawa N, Suzuki M, Matsui T, Fukui N, Migita K, Tohma S and Furukawa H (2025) Anti-Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide antibody in rheumatoid arthritis patients with emphysema. Front. Med. 12:1654271. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1654271
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 04 September 2025;
Published: 22 September 2025.
Edited by:
Yonggang Qu, Shihezi University, ChinaReviewed by:
M. Faizan Siddiqui, Osh State University, KyrgyzstanMayra Mejia, Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Respiratorias, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Oka, Higuchi, Shimada, Fujimori, Hashimoto, Komiya, Saisho, Yoshikawa, Suzuki, Matsui, Fukui, Migita, Tohma and Furukawa. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hiroshi Furukawa, ZnVydWthd2EtdGt5QHVtaW4ub3Jn
 Shomi Oka1,2
Shomi Oka1,2 Toshihiro Matsui
Toshihiro Matsui Kiyoshi Migita
Kiyoshi Migita Hiroshi Furukawa
Hiroshi Furukawa