Abstract
Background:
The clinical and laboratory characteristics of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), particularly indicators related to disease severity, remain inadequately explored in Asian populations.
Objectives:
To characterize the clinical and laboratory features of HS in Chinese patients and to identify risk factors for disease severity.
Methods:
We retrospectively analyzed 197 patients with HS in China. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected. Disease severity was graded using the Hurley staging system. Comprehensive statistical analyses were conducted.
Results:
Among 197 patients, 87.8% were male (male-to-female ratio 7.2:1). Females had a shorter diagnostic delay than males (p = 0.011). Obesity was present in 33.0% of HS patients. Metabolic abnormalities included reduced HDL-c (30.0%), elevated blood glucose (29.1%), increased TG (14.93%), TC (10.31%), and LDL-c (8.96%). Neutrophil-related indices (WBC, ANC, NEUT%) and liver function markers (TP, albumin, ALT, AST, TB) were significantly associated with progression to Hurley stage III. ROC analysis showed modest discrimination for these indicators (AUCs, 0.605–0.652). In multivariable logistic regression analysis, TP remained an independent risk factor for progression to Hurley stage III (OR, 1.240; 95% CI, 1.101–1.397; p = 0.010). A multivariable logistic regression model that integrated significant predictors achieved an AUC of 0.689. This indicated moderate discrimination for advanced disease severity.
Conclusion:
Chinese patients with HS exhibited a pronounced male predominance and relatively mild metabolic abnormalities. Neutrophil-related indices and TP, especially when TP was interpreted together with albumin, were associated with progression to Hurley stage III.
1 Introduction
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), also known as acne inversa (AI), is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by recurrent abscesses, draining tunnels, and hypertrophic scars that predominantly affect the intertriginous region. The global prevalence of HS is ~1%, varying by regions and populations (1). Beyond the skin, HS is associated with systemic inflammation and metabolic comorbidities (1).
The pathogenesis of HS is multifactorial. It has been reported to involve follicular occlusion, immune dysregulation, and cytokine-driven inflammation. Key contributors include IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, IL-23, and TNF-α, while genetic predisposition and microbial dysbiosis further sustain immune cell infiltrates and tissue destruction (2). Mutations in γ-secretase-related genes such as NCSTN and PSENEN have been described in familial HS (3). Variants in immune-regulatory genes (e.g., DEFB104B, GRAMD4), (4) cytochrome P450 pathway genes, (5) and keratinocyte signaling pathways have been implicated in disease chronicity, heterogeneity in clinical course, and differential treatment responses (6, 7).
Epigenetic dysregulation also plays an important role in HS pathogenesis. Recent studies have identified aberrant DNA methylation of cytokine and chemokine genes (e.g., CXCL10, CXCR6), hypermethylation of immune-regulatory pathways such as interferon-γ, JAK-STAT, and IL-17 signaling, as well as disrupted hydroxymethylation and histone acetylation. Together, these alterations may drive chronic inflammation, impaired wound healing, and contribute to systemic immune dysfunction and increased cancer susceptibility in HS (4, 8). In addition, dysregulated expression of genes related to glucose metabolism (POMC, IRS1, GNAS, CACNA1C, AHR, NOTCH3), transporters (ABCC2, ABCG1, SLC39A8, SLC39A9), and metal homeostasis (MMP2, MMP3, SOD2, CP) may promote energy deficiency, ion imbalance, and oxidative stress, thereby amplifying inflammation, enhancing pain sensitization, hindering tissue repair, and ultimately facilitating tunnel formation and fibrosis (9).
The Hurley staging system remains the most widely used tool for assessing HS severity and guiding treatment. However, its reliance on anatomical features limits the ability to capture disease activity and progression, particularly in distinguishing between Hurley stages II and III (6). Therefore, identifying objective markers is crucial for improving disease assessment and management.
A broad range of systemic inflammatory markers has been investigated as potential indicators of HS severity. These include CRP, ESR, NLR, PLR, SII, PIV, SIRI, and SAA, and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, and TNF-α (10–14). Autoantibodies against nuclear antigens (e.g., dsDNA, nucleolin, La/SSB), citrullinated proteins, and extracellular matrix components have also been implicated in HS pathogenesis (14). Serum proteins associated with neutrophil activity, including LCN2, G-CSF, and CXCR, show positive correlations with disease severity (15, 16). Additional biomarkers, such as RBP4, Ang-2, and ANGPTL2, have also been proposed as severity indicators (17). Dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated TG and reduced HDL levels, may also contribute to disease progression (18). However, inconsistent findings and small sample sizes limit their clinical applicability of these indicators, and evidence from Asian populations remains scarce.
To address this gap, we conducted a retrospective study to characterize the clinical and laboratory features of Chinese patients with HS and identified risk factors associated with progression to Hurley stage III, aiming to improve clinical stratification and management strategies.
2 Materials and Methods
This retrospective study analyzed the medical records of 223 Chinese HS patients who visited the outpatient dermatology clinic at the Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, between January 2016 and March 2025. All patients met the diagnostic criteria for HS according to established guidelines, which remained unchanged during the study period (19). Laboratory tests were performed under standardized protocols, and institutional quality assurance records confirmed the consistency of testing platforms and reference ranges over the study years.
Patients were excluded according to the following criteria: (a) receipt of systemic antibiotics or immunosuppressive therapy within the 4 weeks prior to consultation. (b) concurrent acute infections and/or (c) pregnancy or breastfeeding at the consultation. After applying these criteria, 197 patients were included in the final analysis.
Demographic and clinical variables included age, sex, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, age at disease onset, and family history. BMI was categorized according to World Health Organization (WHO) criteria: normal weight (18.5–24.9 kg/m2), overweight (25.0–29.9 kg/m2), and obesity (≥30.0 kg/m2). Laboratory investigations comprised complete blood count, liver and renal function tests, coagulation profile, and inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), serum amyloid A (SAA), and procalcitonin (PCT). Because not all patients underwent every test, missing values were imputed using the mean for continuous variables and the mode for categorical variables, and pairwise deletion was applied in correlation analyses.
Descriptive statistics summarized demographic and clinical variables. Normality of continuous variables was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Normally distributed variables were analyzed using Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA, while non-normally distributed variables were evaluated using the Mann-Whitney U test or Kruskal-Wallis test. Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test.
Correlation analyses examined associations between laboratory markers and clinical indices. Pearson's correlation was applied for normally distributed data, and Spearman's rank correlation for non-normally distributed data. The correlation coefficient (r) was used to quantify the strength and direction of associations. For each correlation, 95% confidence intervals were calculated. Both raw and false discovery rate (FDR)-adjusted p-values (q value) were reported using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure.
Logistic regression identified predictors of severe disease (Hurley stage III vs. Hurley stage I and II). Univariable logistic regression models were first fitted for each demographic, clinical, and laboratory variable. Variables with q < 0.05 in univariable analyses were further considered in multivariable logistic regression. To avoid multicollinearity, highly correlated predictors (r >0.7) were excluded prior to model fitting. Results are presented as odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and corresponding raw and FDR-adjusted p-values (q value).
Model performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. ROC curves and the area under the curve (AUC) values were generated for significant predictors (q < 0.05) from univariable analyses. An overall ROC curve with AUC was calculated for the multivariable model to evaluate combined predictive performance.
All analyses were performed using R software (version 4.4.2). Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05 and/or FDR-adjusted p (q value) <0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Clinical characteristics
Among the 223 HS cases identified in our hospital information system, 197 patients were included in the final analysis, and their clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Most patients were male (87.8%), with a male-to-female ratio of 7.21. The average age was 33.09 ± 10.36 years, with no significant age difference across Hurley stages (p1 = 0.12) or between genders (p2 = 0.82). Males had significantly greater weight and height than females (both p2 <0.001), while BMI did not differ by gender. Smoking was more common in Hurley stage III (64.1%) than in Hurley stage I (42.9%; p1 = 0.09), and was significantly higher in males than females (63.2 vs. 14.3%, p2 <0.001). A positive family history was reported in 24.7% of patients, with no significant differences across Hurley stages (p1 = 0.22) or genders (p2 = 0.32). The mean onset age of disease was 19.85 ± 5.84 years. Diagnostic delay increased with disease severity, with 6.25 ± 5.86 years in Hurley stage I, 8.62 ± 9.83 years in Hurley stage II, and 9.92 ± 9.03 years in Hurley stage III, although the differences were not statistically significant (p = 0.177). However, males experienced significantly longer diagnostic delays than females (9.42 ± 9.31 vs. 6.33 ± 4.57, p = 0.011). In our cohort, 12.6% of patients had Hurley stage I, 30.4% had stage II, and 57.1% had stage III, with no significant gender difference (p2 = 0.13). Notably, none of the patients had concomitant inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Table 1
| Characteristics | Hurley stage I (n = 24) | Hurley stage II (n = 58) | Hurley stage III (n = 109) | p 1 | Male (n = 173) | Female (n = 24) | p 2 | Total (n = 197) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||||||
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 29.83 ± 8.60 | 0.12 | 33.23 ± 10.68 | 32.04 ± 7.84 | 0.82 | 33.09 ± 10.36 | ||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male, n (%) | 20 (83.3) | 47 (81.0) | 100 (91.7) | 0.13 | – | – | – | 171 (87.8) |
| Female, n (%) | 4 (16.7) | 11 (19.0) | 9 (8.3) | – | – | – | 24 (12.2) | |
| Anthropometrics (mean ±SD) | ||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 84.7 ± 19.39 | 85.11 ± 22.26 | 89.21 ± 18.84 | 0.20 | 90.15 ± 19.62 | 72.05 ± 17.55 | <0.001 | 87.02 ± 19.84 |
| Height (m) | 1.77 ± 0.08 | 1.76 ± 0.07 | 1.77 ± 0.08 | 0.37 | 1.78 ± 0.06 | 1.65 ± 0.05 | <0.001 | 1.77 ± 0.08 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.05 ± 5.38 | 27.39 ± 6.49 | 28.32 ± 5.04 | 0.28 | 28.25 ± 5.50 | 26.38 ± 6.01 | 0.32 | 28.03 ± 5.58 |
| Clinical features | ||||||||
| Smoking, n(%) | ||||||||
| Positive | 9 (42.9) | 27 (50.0) | 66 (64.1) | 0.09 | 91 (63.2) | 3 (14.3) | <0.001 | 104 (56.5) |
| Negtive | 12 (57.1) | 27 (50.0) | 37 (35.9) | 53 (36.8) | 18 (85.7) | 80 (44.5) | ||
| Family history, n(%) | ||||||||
| Positive | 9 (42.9) | 10 (18.5) | 26 (25.7) | 0.22 | 39 (27.1) | 3 (14.3) | 0.32 | 45 (24.7) |
| Negative | 12 (57.1) | 44 (81.5) | 75 (74.3) | 105 (72.9) | 18 (85.7) | 137 (75.3) | ||
| Age of onset (years) | 19.83 ± 6.18 | 18.78 ± 4.76 | 20.85 ± 6.77 | 0.10 | 19.87 ± 5.87 | 21.29 ± 7.84 | 0.82 | 19.85 ± 5.84 |
| Diagnostic delay (years, mean ± SD) | 6.25 ± 5.86 | 8.62 ± 9.83 | 9.92 ± 9.03 | 0.177 | 9.42 ± 9.31 | 6.33 ± 4.57 | 0.011 | 9.04 ± 8.92 |
| Hurley stage, n (%) | – | – | – | – | 0.13 | |||
| Hurley stage I | – | – | – | 20 (11.6) | 4 (16.7) | 24 (12.6) | ||
| Hurley stage II | – | – | – | 47 (27.2) | 11 (45.8) | 58 (30.4) | ||
| Hurley stage III | – | – | – | 100 (57.8) | 9 (37.5) | 109 (57.1) | ||
| Inflammatory bowel disease, n(%) | ||||||||
| Positive | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0 (0) |
| Negtive | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 197 (100) |
Characteristics of 197 patients with hidradenitis suppurativa enrolled in the study.
3.2 Metabolic characteristics
In our HS cohort, 58 (29.9%) had a normal BMI, 72 (37.1%) were overweight, and 64 (33.0%) were obese. Overall, 70.1% of patients were overweight or obese. Among metabolic parameters, abnormal HDL-c (30.0%) and blood glucose (29.1%) were most frequent, followed by TG (14.93%), TC (10.31%), and LDL-c (8.96%). TG levels were significantly higher in obese patients compared with both the normal-weight and overweight groups (p < 0.001). No significant BMI-related differences were found for glucose, TC, LDL-c, or HDL-c. Moreover, females showed higher HDL-c levels than males (p = 0.034), with no statistically significant differences in other metabolic indices. No significant differences in glucose or lipid parameters were found across Hurley stages I–III (Table 2).
Table 2
| Variable | Blood glucose (mmol/L) | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | LDL-c (mmol/L) | HDL-c (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abnomal frequency (n%) | 29.10% | 10.31% | 14.93% | 8.96% | 30.00% |
| Gender | |||||
| Male (n = 173, 87.8%) | 5.60 (5.23–6.30) | 4.43 ± 0.98 | 1.31 (0.94–1.80) | 2.96 ± 0.83 | 0.99 (0.85–1.20) |
| Female (n = 24, 12.2%) | 5.70 (5.27–6.35) | 4.52 ± 0.92 | 1.35 (0.74–1.80) | 3.02 ± 0.74 | 1.23 (1.09–1.46) |
| p-Value | 0.918 | 0.756 | 0.510 | 0.765 | 0.034 |
| BMI | |||||
| Normal BMI range, 18.5–24.9 (n = 58, 29.9%) | 5.45 (5.20–5.80) | 4.22 ± 1.04 | 0.95 (0.77–1.33) | 2.90 ± 0.88 | 1.04 (0.87–1.26) |
| Overweight, 25.0–29.9 (n = 72, 37.1%) | 5.60 (5.30–6.20) | 4.50 ± 1.00 | 1.24 (0.95–1.69) | 2.98 ± 0.80 | 1.10 (0.96–1.22) |
| Obesity, 30 or more (n = 64, 33.0%) | 5.80 (5.30–7.60) | 4.56 ± 0.91 | 1.68 (1.23–2.28) | 3.06 ± 0.81 | 0.96 (0.85–1.14) |
| p-Value | 0.067 | 0.327 | <0.001 | 0.687 | 0.27 |
| Hurley stage | |||||
| Hurley stage I (n = 24,12.6%) | 5.80 (5.55–6.55) | 4.34 ± 1.11 | 1.19 (0.83–2.21) | 2.88 ± 0.92 | 1.11 (0.96–1.17) |
| Hurley stage II (n = 58, 30.4%) | 5.40 (5.10–6.08) | 4.42 ± 0.83 | 1.18 (0.89–1.69) | 2.89 ± 0.73 | 1.16 (0.94–1.34) |
| Hurley stage III (n = 109, 57.1%) | 5.60 (5.30–6.30) | 4.49 ± 1.02 | 1.40 (0.96–1.81) | 3.01 ± 0.85 | 0.99 (0.85–1.19) |
| p-Value | 0.352 | 0.858 | 0.476 | 0.743 | 0.451 |
Comparison of metabolic indicators among patients with different groups.
Values are presented as mean ± SD for normally distributed variables or median (Q1–Q3) for non-normally distributed variables.
TG, triglyceride; TC, total cholesterol.
3.3 Correlation analysis
Our correlation analysis revealed a wide range of significant correlations between clinical characteristics and laboratory parameters in HS. These results are detailed in Figures 1, 2 and Supplementary File 1. Males were positively associated with higher WBC, AMC, ANC, RBC, Hemoglobin, and Hematocrit compared with females. Body weight correlated significantly with RBC, Hemoglobin, Hematocrit, ALC, BAS%, ABC, ALT, UA, and TG. Moreover, BMI was positively correlated with ABC, ALT, UA, and TG. Notably, smoking was negatively associated with HDL-c.
Figure 1

The correlation heatmap between clinical and laboratory variables displays only correlations with p < 0.05 and |r| > 0.3. Blue indicates a negative correlation, and red indicates a positive correlation.
Figure 2

The network diagram between clinical and laboratory variables displays only correlations with p < 0.05 and |r| > 0.3.
Furthermore, WBC, ANC, NEUT%, ABC, PLT, and TP increased significantly with disease severity, whereas LY% and MCH showed significant inverse associations. Moreover, correlation analysis also demonstrated that the Hurley stage was positively associated with fibrinogen (r = 0.315, p = 0.035, q = 0.193) and CRP (r = 0.276, p = 0.133, q = 0.416), but negatively with albumin (r = −0.204, p = 0.019, q = 0.132).
3.4 Logistic regression analysis
Using univariable logistic regression analysis with correction for multiple testing, several clinical laboratory values were identified as predictors of advanced HS (q < 0.05; Figure 3; Supplementary File 2). Significant positive associations were observed for neutrophil-related indices, including WBC (OR, 1.250; 95% CI, 1.079–1.447; q = 0.017), ANC (OR, 1.264; 95% CI, 1.080–1.479; q = 0.017), and NEUT% (OR, 1.071; 95% CI, 1.018–1.126; q = 0.028). In addition, LY% (OR, 0.926; 95% CI, 0.875–0.979; q=0.028) and red blood cell indices (hemoglobin, MCV, MCH, MCHC, and RDW) also showed significant associations with disease severity.
Figure 3

Forest plots of univariable logistic regression analyses identifying significant predictors of disease severity in HS, with q values, odds ratios (OR), and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for progression to Hurley stage III.
Biochemical markers of liver function were likewise independently associated with progression to Hurley stage III. Compared with patients in Hurley stages I–II, those with Hurley stage III had higher TP (OR, 1.171; 95% CI, 1.087–1.262; q = 0.0001), but lower albumin (OR, 0.880; 95% CI, 0.794–0.975; q = 0.033), ALT (OR, 0.980; 95% CI, 0.965–0.996; q=0.028), AST (OR, 0.953; 95% CI, 0.918–0.989; q=0.022), and TB (OR, 0.896; 95% CI, 0.824–0.974; q=0.028).
Variables with q < 0.05 in the univariable analysis were then entered into a multivariable logistic regression model. TP (OR, 1.240; 95% CI, 1.101–1.397; q = 0.010) remained an independent risk factor for progression to Hurley stage III (Supplementary File 3).
3.5 Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis
ROC analysis was performed to evaluate the ability of clinical and laboratory markers to discriminate progression to Hurley stage III. Neutrophil-related indices (WBC, NEUT%, and ANC) showed modest predictive ability, with AUCs of 0.610, 0.608, and 0.605, respectively. Liver function markers showed slightly better performance, with AUCs of 0.652 for TP, 0.632 for AST, 0.619 for TB, and 0.612 for ALT (Figure 4a and Supplementary File 4).
Figure 4
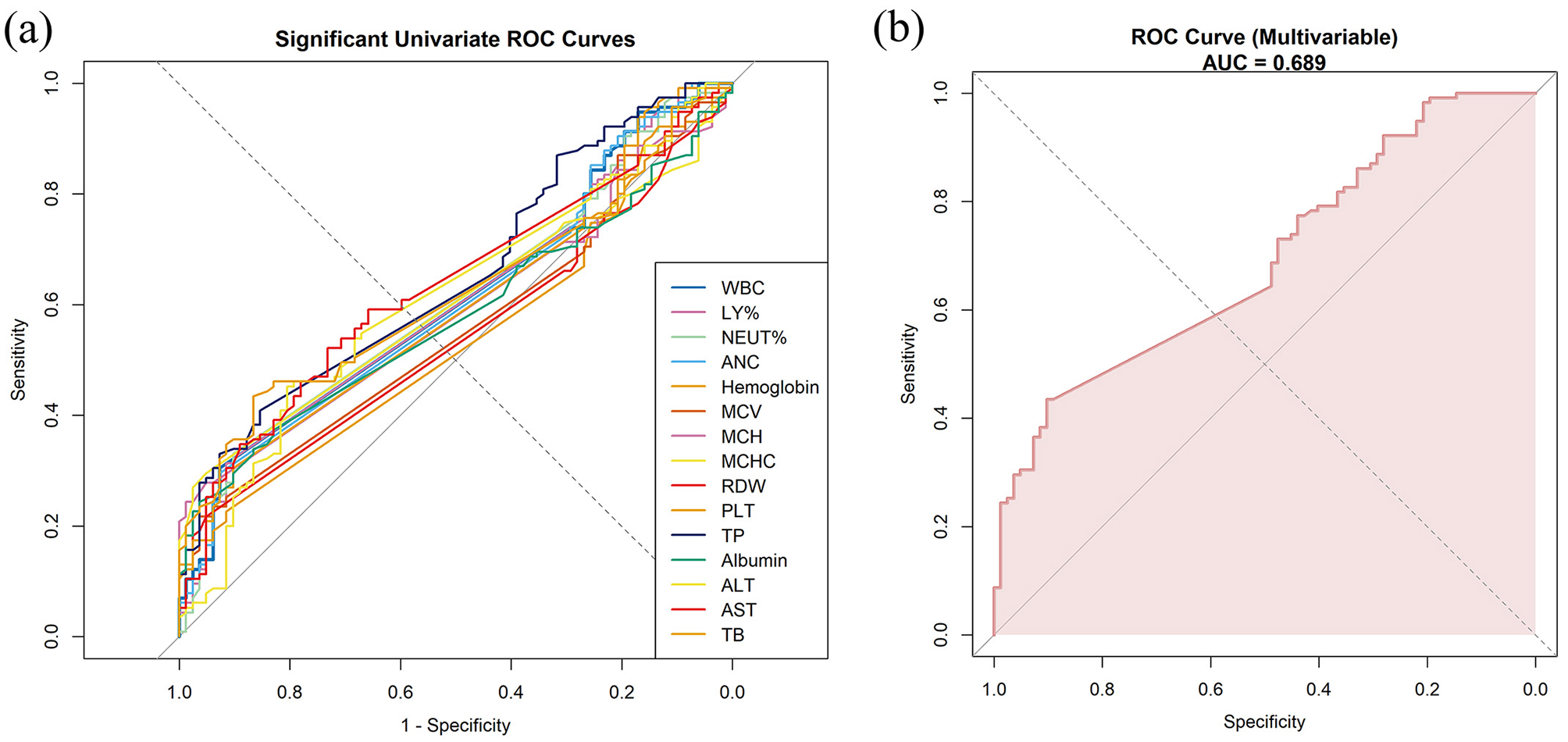
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis demonstrating the predictive performance of clinical and laboratory markers for progression to Hurley stage III, with the area under the curve (AUC). (a) ROC curves based on univariable logistic regression for significant markers. (b) ROC curve based on a multivariable logistic regression model integrating independent predictors (WBC, NEUT%, ANC, TP, and albumin).
Building on these findings, a multivariable logistic regression model incorporating key predictors identified in the univariable analysis demonstrated moderate discrimination, with an AUC of 0.689 (95% CI: 0.617–0.761). At the optimal cut-off (0.621), the model achieved high specificity (0.902) and a high positive predictive value (0.862), supporting its reliability in identifying patients at risk of progression to Hurley stage III (Figure 4b and Supplementary File 5).
4 Discussion
A striking male predominance was observed in this study, contrasting with most Western cohorts but consistent with Asian studies and our prior nationwide findings (male-to-female ratio, 4.7:1) (20–23). Although women represented a smaller proportion, they experienced a shorter diagnostic delay (p = 0.011) than males. This may reflect limited recognition of mild HS in community hospitals, where women with small nodules often receive local treatment rather than being referred, resulting in a referral bias toward more severe cases in our center. Sociocultural factors also play an important role. Women may be reluctant to seek medical care for lesions in intimate areas because of cultural modesty and disease-related stigma, especially when consultations involve male physicians, whereas men generally show less hesitation (24). Moreover, lower estradiol levels in Chinese women may attenuate hormonal sensitivity (25). In contrast, elevated androgen levels in men can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and Th17 responses, enhancing neutrophil recruitment in HS lesions (26). Asian male patients are also more likely to carry γ-secretase variants that impair Notch signaling and promote keratinocyte dysregulation (27). Besides, lifestyle factors appear to amplify these differences. In Western cohorts, the overall smoking prevalence has been reported to reach up to 90%, whereas our cohort showed a lower rate of 56.5%, with a notable predilection for males (p < 0.001) (28). Finally, although obesity is more common in women in Western populations, male patients in our cohort had higher BMI than females (29). This reversal weakens the obesity-related risk for women in Chinese populations, and underscores smoking as the key lifestyle factor behind the male predominance in HS.
Chinese patients with HS showed milder metabolic abnormalities than Western populations (27). In our cohort, obesity, low HDL-c, and hyperglycemia were the most prevalent abnormalities, whereas hypertriglyceridemia, elevated TC, and LDL-c were less frequent. By contrast, in a German population study, central obesity (65.0%), reduced HDL-c levels (50.0%), and hypertriglyceridemia (38.8%) were more common, although the prevalence of hyperglycemia was slightly lower (26.3%) (30). An American study further reported more pronounced metabolic disturbances, with 87.6% of HS patients being obese, 43.8% having hypertriglyceridemia, 46.3% exhibiting low HDL-c, and 61.8% showing glucose intolerance (31). Within our cohort, further analysis showed that low HDL-c did not completely overlap with obesity, suggesting that it may represent an independent metabolic feature of HS. This is consistent with the findings of Hernández et al., (32) who reported that decreased HDL-c in HS cannot be attributed solely to obesity but may result from inflammation-driven mechanisms, such as MMP8-mediated degradation of ApoA1. Moreover, triglyceride levels were significantly higher in obese patients, yet neither TG nor HDL-c levels were independently associated with Hurley stage (31, 33). Taken together, these results suggest that metabolic abnormalities are more likely background comorbidities rather than direct drivers of HS severity, although they may still contribute to systemic inflammatory burden (34).
Neutrophils emerged as key mediators of inflammation in HS. Correlation analyses revealed that neutrophil-related indices, including WBC, ANC, and NEUT%, increased with disease severity, while LY% decreased. Logistic regression and ROC analyses further supported their predictive capacity in identifying patients at risk of progression to Hurley stage III. These results are consistent with previous studies, showing that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) reflects the balance between innate and adaptive immunity. An elevated NLR indicates increased neutrophils with relative lymphopenia, a pattern typical of chronic inflammation (35–37). Mechanistically, sustained neutrophil activation releases proteolytic enzymes and inflammatory mediators such as MMP-9 and IL-1β, leading to local tissue damage. Activated neutrophils also form neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which amplify systemic inflammation and contribute to thrombosis, thereby perpetuating the inflammatory cycle. Persistent neutrophil activation promotes abscess formation, tunnel development, and chronic tissue remodeling, ultimately driving disease progression (36, 38–40). Therapeutically, targeting neutrophils is emerging as a promising strategy in HS. IL-1 inhibitors such as bermekimab and lutikizumab aim to suppress upstream inflammatory pathways, while interventions targeting chemokines, leukotriene B4, or G-CSF signaling seek to limit neutrophil recruitment (1). Historical anti-neutrophilic drugs, including dapsone, colchicine, and tetracyclines, have also shown variable benefit (41). Collectively, these findings emphasize neutrophil-mediated inflammation as a central pathogenic pathway and a promising therapeutic target in HS.
Although total protein (TP) is not a conventional inflammatory marker, it showed notable discriminatory capacity in our cohort. TP levels increased with HS severity, suggesting its potential as a helpful serological indicator. Albumin, in contrast, was negatively associated with Hurley stage, indicating that nutritional decline may accompany disease progression. Conversely, CRP and fibrinogen were positively associated with disease severity, supporting the interpretation that TP elevation largely reflects the accumulation of acute-phase proteins and thus captures the chronic inflammatory burden of HS (42). Previous evidence reported that elevated acute-phase proteins occur in both acute and chronic inflammation and are accompanied by reduced hepatic albumin synthesis (42). In addition, Jennifer Panara et al. (43) reported that the protein gap (total protein minus albumin) correlated strongly with HS severity, with each 1 g/dl increase associated with a 2.24-fold rise in IHS4 score. Accordingly, we speculate that elevated TP with normal albumin may reflect an inflammatory HS subtype (typically Hurley stage II) that mainly responds to anti-inflammatory therapy. In contrast, elevated TP with reduced albumin may indicate a subtype characterized by both inflammation and nutritional depletion (commonly Hurley stage III), which may benefit from combined anti-inflammatory and nutritional interventions.
Several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality. Second, as a single-center study, the generalizability of our findings may be restricted. Third, the predominance of referred patients in our cohort introduces potential referral bias, which may affect the broader applicability of our results. To address this limitation, multi-center collaborations with larger sample sizes are warranted. Additionally, disease severity could not be uniformly assessed using the International Hidradenitis Suppurativa Severity Score System (IHS4) because standardized lesion counts were not consistently available in historical records, which may reduce the precision of severity classification.
In conclusion, Chinese patients with HS exhibited a pronounced male predominance and relatively mild metabolic abnormalities. Neutrophil-related indices and TP, especially when TP was interpreted together with albumin, were associated with progression to Hurley stage III.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants to participate in this study.
Author contributions
QY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Visualization, Methodology. CZ: Validation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. XT: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation. YYang: Validation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Software, Visualization. YYan: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Methodology. BW: Supervision, Resources, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was received for this work and/or its publication. This work was supported by the Special Research Fund for Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College. Number: YSZ2024CG011.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the patients who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared that this work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declared that generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript for language editing (grammar and phrasing).
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1721105/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary File 1Correlation analyses between clinical and laboratory parameters.
Supplementary File 2Univariate logistic regression results.
Supplementary File 3Multivariate logistic regression results.
Supplementary File 4ROC analyses based on univariate models.
Supplementary File 5ROC analyses based on multivariate models.
Abbreviations
BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; IQR, interquartile range; OR, odds ratio; WBC, white blood cell count; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; AMC, absolute monocyte count; ALC, absolute lymphocyte count; ABC, absolute basophil count; LY%, lymphocyte percentage; NEUT%, neutrophil percentage; BAS%, basophil percentage; RBC, red blood cell count; RDW, red cell distribution width; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; PLT, platelet count; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; IL-8, interleukin-8; IL-17, interleukin-17; IL-36, interleukin-36; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-6, interleukin-6; CRP, C-reactive protein; SAA, serum amyloid A; PCT, procalcitonin; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; TB, total bilirubin; TP, total protein; UA, uric acid; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; TG, triglyceride; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; ANGPTL2, angiopoietin-like 2 protein; RBP4, retinol-binding protein 4; Ang-2, angiopoietin-2.
References
1.
Sabat R Alavi A Wolk K Wortsman X McGrath B Garg A et al . Hidradenitis suppurativa. Lancet Lond Engl. (2025) 405:420–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)02475-9
2.
Frew JW . Unravelling the complex pathogenesis of hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. (2025) 192(Supplement_1):i3–14. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae238
3.
Wang B Yang W Wen W Sun J Su B Liu B et al . Gamma-secretase gene mutations in familial acne inversa. Science. (2010) 330:1065. doi: 10.1126/science.1196284
4.
Montoya M Khetani R Martinez R Mayur O Yi JZ McGee JS et al . A genome-wide survey of DNA methylation status in whole blood of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa suggests systemic immune dysregulation and systemic disease burden. Exp Dermatol. (2025) 34:e70065. doi: 10.1111/exd.70065
5.
Radhakrishna U Ratnamala U Jhala DD Vadsaria N Patel M Uppala LV et al . Cytochrome P450 genes mediated by DNA methylation are involved in the resistance to hidradenitis suppurativa. J Invest Dermatol. (2023) 143:670–3.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.08.056
6.
Ovadja ZN Schuit MM van der Horst CMAM Lapid O . Inter- and intrarater reliability of Hurley staging for hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. (2019) 181:344–9. doi: 10.1111/bjd.17588
7.
Jin L Chen Y Muzaffar S Li C Mier-Aguilar CA Khan J et al . Epigenetic switch reshapes epithelial progenitor cell signatures and drives inflammatory pathogenesis in hidradenitis suppurativa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2023) 120:e2315096120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315096120
8.
Burke OM Frerichs VR Garcia DF Stone RC Lev-Tov H Czarnowicki T et al . The impact of innate immunity and epigenetics in the pathogenesis of hidradenitis suppurativa. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1593253. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1593253
9.
Radhakrishna U Kuracha MR Hamzavi I Saiyed N Prajapati J Rawal RM et al . Impaired molecular mechanisms contributing to chronic pain in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: exploring potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26:1039. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031039
10.
Li Y Chuang S Yang H . Systematic review and meta-analysis of peripheral blood inflammatory markers in hidradenitis suppurativa. J Dermatol. (2025) 52:583–92. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.17661
11.
Andriano TM Benesh G Babbush KM Hosgood HD Lin J Cohen SR . Serum inflammatory markers and leukocyte profiles accurately describe hidradenitis suppurativa disease severity. Int J Dermatol. (2022) 61:1270–5. doi: 10.1111/ijd.16244
12.
Akdogan N Dogan S Incel-Uysal P Karabulut E Topcuoglu C Yalcin B et al . Serum amyloid a and C-reactive protein levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are important indicators in hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol Res. (2020) 312:255–62. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-02014-8
13.
Jiménez-Gallo D de la Varga-Martínez R Ossorio-García L Albarrán-Planelles C Rodríguez C Linares-Barrios M . The clinical significance of increased serum proinflammatory cytokines, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Mediators Inflamm. (2017) 2017:2450401. doi: 10.1155/2017/2450401
14.
Carmona-Rivera C O'Neil LJ Patino-Martinez E Shipman WD Zhu C Li QZ et al . Autoantibodies present in hidradenitis suppurativa correlate with disease severity and promote the release of proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages. J Invest Dermatol. (2022) 142(3 Pt B):924–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.07.187
15.
Navrazhina K Garcet S Gonzalez J Grand D Frew JW Krueger JG . In-depth analysis of the hidradenitis suppurativa serum proteome identifies distinct inflammatory subtypes. J Invest Dermatol. (2021) 141:2197–207. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.02.742
16.
Gamell C Bankovacki A Scalzo-Inguanti K Sedgmen B Alhamdoosh M Gail E et al . CSL324, a granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor antagonist, blocks neutrophil migration markers that are upregulated in hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Dermatol. (2023) 188:636–48. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljad013
17.
Hernández JL Ocejo-Vinyals JG Renuncio-García M González-López E Blanco R González-López MA . Angiopoietin-like 2 protein and hidradenitis suppurativa: a new biomarker for disease severity. Biomedicines. (2023) 11:1204. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041204
18.
Li YH Chuang SH Huang YC Yang HJ . A comprehensive systemic review and meta-analysis of the association between lipid profile and hidradenitis suppurativa. Arch Dermatol Res. (2025) 317:225. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03762-y
19.
Fang H Gao XH Geng SM Gu H Gu J He L et al . Diagnosis and treatment of acne inversa/hidradenitis suppurativa in China: an expert consensus statement (2021 version)#. Int J Dermatol Venereol. (2021) 4:100. doi: 10.1097/JD9.0000000000000157
20.
Young KZ Loveless I Su WTK Veenstra J Yin C Dimitrion P et al . A diverse hidradenitis suppurativa cohort: a retrospective cross-sectional study of 13,130 patients from a large US health care system database from 1995 to 2022. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2025) 92:487–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2024.10.073
21.
Killasli H Sartorius K Emtestam L Svensson Å . Hidradenitis suppurativa in Sweden: a registry-based cross-sectional study of 13,538 patients. Dermatology. (2020) 236:281–8. doi: 10.1159/000505545
22.
Lee JH Kwon HS Jung HM Kim GM Bae JM . Prevalence and comorbidities associated with hidradenitis suppurativa in Korea: a nationwide population-based study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2018) 32:1784–90. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15071
23.
Zhong-Shuai W Jing L Qiang J Wei L Song-Mei G Xiao-Jing K et al . Prevalence of acne inversa (hidradenitis suppurativa) in China: a nationwide cross-sectional epidemiological study. Int J Dermatol Venereol. (2022) 5:1–7. doi: 10.1097/JD9.0000000000000204
24.
Ng MSP Lim JG Koh JMY Lee SY Seah CHX Chang SJY et al . Knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions of hidradenitis suppurativa among young adults in Singapore. JAAD Int. (2023) 12:72–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jdin.2023.03.010
25.
Baber RJ . East is east and west is west: perspectives on the menopause in Asia and the west. Climacteric. (2014) 17:23–8. doi: 10.3109/13697137.2013.830607
26.
Abu Rached N Gambichler T Dietrich JW Ocker L Seifert C Stockfleth E et al . The role of hormones in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:15250. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315250
27.
George A . The understudied landscape of hidradenitis suppurativa in Asian skin of colour populations. JEADV Clin Pract. (2025) 4:902–4. doi: 10.1002/jvc2.70065
28.
Happle R König A . Smoker's boils. Dermatol Basel Switz. (2011) 222:282–4. doi: 10.1159/000327923
29.
Sinikumpu SP Jokelainen J Huilaja L . Prevalence and characteristics of hidradenitis suppurativa in the northern Finland birth cohort 1986 study: a cross-sectional study of 2,775 subjects. Acta Derm Venereol. (2024) 104:14732. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v104.14732
30.
Sabat R Tsaousi A Ghoreschi K Wolk K Schneider-Burrus S . Sex-disaggregated population analysis in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Front Med. (2022) 9:1028943. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1028943
31.
Gold DA Reeder VJ Mahan MG Hamzavi IH . The prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2014) 70:699–703. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.11.014
32.
Hernández JL Baldeón C López-Sundh AE Ocejo-Vinyals JG Blanco R González-López MA . Atherogenic index of plasma is associated with the severity of hidradenitis suppurativa: a case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. (2020) 19:200. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01377-6
33.
Molinelli E Morresi C Dragonetti ML De Simoni E Candelora M Marasca S et al . Oxidative stress, high density lipoproteins and hidradenitis suppurativa: a prospective study. Antioxidants. (2025) 14:1014. doi: 10.3390/antiox14081014
34.
Witte K Wolk K Witte-Händel E Krause T Kokolakis G Sabat R . Targeting metabolic syndrome in hidradenitis suppurativa by phytochemicals as a potential complementary therapeutic strategy. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3797. doi: 10.3390/nu15173797
35.
Sánchez-Díaz M Salvador-Rodríguez L Cuenca-Barrales C Arias-Santiago S Molina-Leyva A . Exploring the role of systemic immune-inflammation index and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in cardiovascular risk stratification for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: a cross-sectional study. J Dermatol. (2022) 49:1238–44. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.16558
36.
van Dalen SCM Stein JWJ Bruurmijn T Foster ML Chirivi RGS van der Linden M et al . Neutrophil extracellular traps are widely distributed across lesional and perilesional hidradenitis suppurativa skin, and elevated serum NET markers associate with moderate to severe HS disease. Int J Dermatol. (2025) 64:1234–41. doi: 10.1111/ijd.17706
37.
Gunasinghe SD Peres NG Goyette J Gaus K . Biomechanics of T cell dysfunctions in chronic diseases. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:600829. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.600829
38.
Yaşar NF Uylas MU Baspinar M Sarsilmaz H Ates E Erkasap S et al . Evaluating the use of hematological parameters in staging hidradenitis suppurativa. Wounds Compend Clin Res Pract. (2016) 28:87–91.
39.
Miller IM Ring HC Prens EP Rytgaard H Mogensen UB Ellervik C et al . Leukocyte profile in peripheral blood and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in hidradenitis suppurativa: a comparative cross-sectional study of 462 cases. Dermatology. (2016) 232:511–9. doi: 10.1159/000446021
40.
Öksüm Solak E Baran Ketencioglu B Cinar SL Kartal D Borlu M . The role of new inflammatory markers in determining disease activation and severity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Int J Dermatol. (2023) 62:1076–81. doi: 10.1111/ijd.16744
41.
Franceschin L Guidotti A Mazzetto R Tartaglia J Ciolfi C Alaibac M et al . Repurposing historic drugs for neutrophil-mediated inflammation in skin disorders. Biomolecules. (2024) 14:1515. doi: 10.3390/biom14121515
42.
Mantovani A Garlanda C . Humoral innate immunity and acute-phase proteins. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388:439–52. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2206346
43.
Panara J Jiang SW Liu W Petty AJ Kwock J Liu B et al . Association between protein gap and disease severity of hidradenitis suppurativa. J Integr Dermatol. (2025) 1. doi: 10.64550/joid.kmwfv319
Summary
Keywords
acne inversa, hidradenitis suppurativa, clinical characteristics, laboratory features, disease severity
Citation
Ye Q, Zhang C, Tang X, Yang Y, Li Y, Yan Y and Wang B (2026) Clinical and laboratory characteristics of hidradenitis suppurativa in a Chinese cohort: a retrospective analysis of 197 cases. Front. Med. 12:1721105. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1721105
Received
14 October 2025
Revised
02 December 2025
Accepted
12 December 2025
Published
12 January 2026
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Norbert Kiss, Semmelweis University, Hungary
Reviewed by
Andras Banvolgyi, Semmelweis University, Hungary
Fanni Adél Meznerics, Semmelweis University, Hungary
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Ye, Zhang, Tang, Yang, Li, Yan and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Yan, yanyan@psh.pumc.edu.cn; Baoxi Wang, wangbaoxi@psh.pumc.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡These authors share last authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.