Abstract
Carbon dots (CDs), renowned for their distinctive photoluminescence properties, have emerged as a prominent material in the field of luminescence. They are extensively utilized in bioimaging, drug delivery, theranostics, and other applications. In this study, CDs were successfully prepared and isolated from PEC-GS/BG hybrids. Their chemical composition, surface functional groups, and crystal structure were comprehensively characterized. The results demonstrated that the CDs are mainly composed of carbon and oxygen. They exhibit a near-spherical morphology with an average diameter of about 7.4 nm. Then, the fluorescent properties of the CDs were thoroughly assessed. Photoluminescence (PL) measurements revealed that the CDs display intense blue fluorescence upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. This emission is excitation-dependent and shows resilience to variations in pH, high ionic strength, and photobleaching. The quantum yield (QY) was determined to be around 4.5%. Additionally, the synthesized CDs exhibited excellent biocompatibility and cell-labeling capability. These findings indicate that the synthesized CDs hold significant potential for practical applications in various fields.
1 Introduction
Bone tissue engineering (BTE) has drawn considerable interest owing to its remarkable potential in addressing large-scale bone defects and related conditions (Peng et al., 2020; Leonovich et al., 2023). Silicate bioactive glasses (BG) are a promising material in BTE due to their outstanding biocompatibility, bioactivity, and osteoconductivity (Ke et al., 2020; Shearer et al., 2023). Zheng et al. demonstrated that BG could promote angiogenesis by stimulating the release of endogenous bioactive factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) (Zheng et al., 2022). The success of bone repair is highly contingent on the vascularization of the transplanted graft (Zhu et al., 2023; Pan et al., 2024). However, previous research has indicated that the osteogenic capacity of BG alone is insufficient (Putra et al., 2023).
Carbon dots (CDs) are a novel type of carbon nanomaterial, distinguished by their attractive properties that offer significant potential for a wide range of biomedical applications (Yang P. et al., 2019; Yang H. et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2019). CDs typically exhibit excitation-wavelength dependent photoluminescence emission spectra (Liu et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2022), alongside exceptional photostability and strong resistance to photobleaching (Barman et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2023; Ghosal and Ghosh, 2019). Both in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that CDs exhibit excellent cytocompatibility and biological compatibility with no apparent toxic effects (Wei et al., 2024; Dash et al., 2024; Perikala et al., 2023; Dehvari et al., 2020). Moreover, considerable investigations have been conducted into the interactions between CDs and biomacromolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids (Li et al., 2023). Owing to these advantageous properties, CDs have been widely applied in various biomedical fields, such as bioimaging, drug delivery, and therapeutic interventions (Sun et al., 2020; Zhong et al., 2023).
Citric acid is abundant in the skeletal system, accounting for 90% of the total citric acid content in human body, and plays a crucial role in bone metabolism and formation (Książek, 2023; Wang et al., 2023). It has been shown to promote osteogenic differentiation and matrix mineralization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (Zhang et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021). Additionally, it can also serve as a fundamental precursor for the development of CDs (Yang et al., 2022; Otten et al., 2022). In previous studies, our team incorporated citric acid into BG, resulting in the preparation of PEC-GS/BG hybrids that exhibiting enhanced bone-promoting effects (Zhao et al., 2019).
In this study, we synthesized PEC-GS/BG hybrids and identified the presence of fluorescent CDs within them. The structure and fluorescence characteristics of the CDs obtained were systematically investigated. The as-prepared CDs demonstrated near-spherical geometry, excitation-dependent emission, significant quantum yields, excellent photostability, and low toxicity. Additionally, the possible functions of the CDs in cell imaging were also explored.
2 Experimental section
2.1 Materials
Citric acid (>99%) was purchased from J&K Chemical (Beijing, China). Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG300), methoxyethanol (99.8%), calcium 2-methoxyethoxide (CME, ≥98%) and (3-glycidoxypropyl) trimethoxysilane (GS, ≥98%) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, United States). Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, ≥99.0%) was acquired from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All commercial reagents were utilized in the form they were received, without any further purification.
2.2 Preparation of PEC-GS/BG hybrids and CDs
PEC-GS/BG hybrids were prepared using a previously reported procedure (Zhao et al., 2019). At a constant nitrogen flow rate, equal molar amounts of PEG300 and citric acid were introduced into a three-neck round-bottom flask. The mixture was stirred and heated to 180°C for 30 min to yield a poly (ethylene glycol-co-citric acid) (PEC) pre-polymer. The prepared PEC pre-polymers were dissolved in methoxyethanol, resulting in a 50% concentration solution. GS (molar ratio: GS/CA = 0.8/1) was added to the aforementioned solution, and the reaction was conducted at 40°C for 6 h to produce the PEC-GS pre-polymer solution.
TEOS and CME were then sequentially introduced into PEC-GS solution with an organic/inorganic mass ratio of 50:50, while ensuring a Si/Ca molar ratio of 70:30 in the inorganic phase. Specifically, TEOS and PEC-GS were first blended to achieve a colorless solution. Then, CME was added to the mixture and stirred continuously, resulting in the formation of an orange transparent solution. After 12 h of stirring, water droplets were cautiously incorporated into the mixture until a significant increase in viscosity was observed. The mixture was subsequently transferred to a Teflon mold and allowed to gel at room temperature for 24 h, then dried in an oven at 60°C for 7 days. The resulting product is referred to as PEC-GS/BG hybrids.
Subsequently, the hybrids were immersed in distilled water, and CDs were gradually released as the material degraded. The degraded solution, containing CDs, was filtered twice using a 0.22 μm membrane to eliminate any remaining bulk particles. The filtered solution was ultimately dried at 45°C to obtain the CDs.
2.3 Apparatus
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic measurements were performed using a Bruker VECTOR22 spectrometer (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) for elemental analysis was conducted with equipment from Thermoelectricity Instruments, United States. Corresponding energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis was carried out using an EDS detector integrated with a Hitachi S-4800 high-resolution field emission scanning electron microscope. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images were obtained with an FEI Tecnai G20 (FEI, Hillsboro, Oregon, United States) operating at an acceleration voltage of 200 kV. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) experiments were performed in water at room temperature using a 90 Plus particle size analyzer from Brookhaven Instruments Corp (Holtsville, NY, United States). Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra were recorded using a UV-2450 UV-vis spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan). Photoluminescence (PL) spectra were measured at room temperature with an FL-7000 spectrophotometer (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Cell imaging was conducted with an Inverted-BX51 microscope (Olympus, Melville, NY, United States) that utilized a 488 nm laser.
2.4 Assessment of quantum yields
The quantum yield (QY) of the CDs was determined with quinine sulfate (dissolved in 0.1 M H2SO4, QY = 54%) serving as a reference. The QY was calculated according to the following equation (Shen et al., 2021):
In this equation, φ and φ′, I and I′, A and A′ represent the QY, fluorescence intensity, and absorbance of the obtained CDs and the quinine sulfate solution, respectively. Both n and n’ represent the refractive indices of water. Modify the concentrations of the quinine sulfate and CDs solutions to ensure their optical absorbance was below 0.05.
2.5 Cellular toxicity test
The cytotoxicity of CDs was evaluated using an MTT assay (Yang et al., 2023; Zhang W. et al., 2024) on MC3T3-E1 cells, which were obtained from the Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Initially, MC3T3-E1 cells (100 μL) were seeded into 96-well culture plates at a density of 1.0 × 105 cells/mL in α-MEM complete medium. After 12 h, the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing various concentrations of CDs (0, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL), maintaining a total volume of 200 μL per well. Following another 24 h of incubation, 10 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL) was added to each well and incubated for another 4 h. Subsequently, the culture medium was discarded, and 100 μL of DMSO was introduced to dissolve the formazan crystals. The absorbance of each well was measured at a specific wavelength using a microplate reader. Cytotoxicity was assessed using the formula below:where A1 is the absorbance of the wells containing cells exposed to the CDs, and A2 is the absorbance of the wells containing cells not exposed to the CDs. Each control and test concentration was assessed in six replicate wells. Results are presented as means with standard deviations.
2.6 Cell imaging
The potential of CDs for biolabeling was assessed through cell imaging of MC3T3-E1 cells (Sobhanan et al., 2023). In brief, MC3T3-E1 cells were cultured in complete α-MEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 µg/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin. The culture was maintained at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Cells were seeded into well plates at a concentration of 5.0 × 105 cells/mL and incubated for 24 h. Subsequently, cells were incubated with 100 μg/mL CDs for 2 h and washed three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Fluorescence imaging was then performed using an Inverted-BX51 confocal fluorescence microscope with a ×20 objective lens and a 488 nm excitation laser.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Structural characterization
The functional groups of CDs were characterized by FT-IR spectrum (Figure 1A). The broad peak around 3,400 cm−1 is attributed to the N-H or O-H stretching vibrations in amino and hydroxyl groups. The peaks at 2,919 cm−1 and 2,875 cm−1 correspond to the stretching vibrations of the C-H bond. The peak at 1,592 cm−1 can be assigned to the stretching vibration of the C=O bond, while the peaks at 1,413 cm−1 and 1,353 cm−1 are due to the stretching vibrations of the C-N bond. The peaks at 1,065 cm−1 and 1,017 cm−1 are attributed to the C-O bond. The surface composition and elemental analysis of the obtained CDs were characterized using XPS and EDS. The XPS results are shown in Figure 1B. A survey scan was conducted from 0 to 600 eV, revealing primary peaks at 100, 285, 350, and 532 eV, corresponding to Si2p, C1s, Ca2p, and O1s, respectively (with hydrogen not detectable by XPS). Additionally, the EDS results (Figure 1C) indicate that the CDs primarily consist of carbon and oxygen (with a C/O weight ratio of 2.96), along with detectable amounts of silicon. These findings are consistent with the XPS results and suggest the presence of numerous hydrophilic groups on the CD surfaces. The hydrophilic groups evidently stabilize the CDs in aqueous solutions.
FIGURE 1

(A) Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrum, (B) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) survey scan and (C) energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) of CDs.
The size of nanoparticles is crucial for bio-applications (Hu et al., 2022). The TEM image (Figure 2A) demonstrates that the CDs are nearly spherical and well-dispersed. Statistical analysis of the grain size based on the TEM images indicates that the CDs have a size range of 4–10nm, with an average diameter of 7.4 ± 1.4 nm (Figure 2B). However, DLS measurements indicated that the hydrodynamic diameter of the CDs is approximately 24 nm, which is larger than the size determined by TEM. This discrepancy is attributed to the impact of hydration in a water-based solution. While TEM measures the diameter of CDs after being dried on a surface, DLS determines the diameter of hydrated CDs in the solution, reflecting their more “swollen” state (Hu et al., 2022). Therefore, the size of the obtained CDs is appropriate for biological applications. Moreover, the zeta potential of the CDs was measured to be −15.3 mV.
FIGURE 2

(A) Typical TEM image and (B) corresponding particle size distribution of as prepared CDs.
3.2 Fluorescent properties
We measured the UV-vis absorption spectrum of the CDs to determine their band structure. The absorption spectrum, shown in Figure 3A, features two peaks in the 200–300 nm region. The peak at 275 nm is likely due to the π-π* transition of the CDs, while the peak at 207 nm may result from the generation of multiple polyaromatic chromophores. Additionally, as depicted in Figure 3B, the emission spectrum of the CDs was recorded upon excitation with light in the range of 300–380 nm. Both the emission intensity and wavelength are dependent on the excitation wavelength. The emission intensity increases gradually with the excitation wavelength, peaking at 330 nm, and then declines as the excitation wavelength continues to increase. Consistent with previous studies, the emission of the CDs exhibits a notable red-shift property, where the emission wavelength shifts to longer wavelengths as the excitation wavelength increases. This excitation-dependent emission is an inherent characteristic of CDs and has been extensively documented in the literature (Zhang Y. et al., 2024). In addition, the QY of the CDs was calculated to be approximately 4.5% using quinine sulfate solution as a reference.
FIGURE 3

(A) UV-vis absorption spectrum of CDs. Inset: photographs of the CD aqueous solutions under visible light (left) and UV light (right), respectively; (B) Excitation dependent photoluminescence behavior of CDs.
The PL origin of CDs remains under debate, with potential explanations including surface defect states, quantum confinement effects, or other factors. The notion that functional groups act as continuous surface defect states and govern emission properties has gained broad acceptance in the scientific community (Dorontic et al., 2022). The surface defect states on CDs are varied, resulting in heterogeneous emission energy levels and producing excitation-tunable emission (Kaur et al., 2024). Ding et al. also suggested that the photoluminescence of CDs is likely dominated by continuous surface defect states, with different defect states contributing to emissions at different wavelengths (Ding et al., 2024). However, Zhang et al. concluded in their research that the functional groups are non-radiative surface states (Zhang P. et al., 2024). The quantum confinement effect, which is also referred to as the size effect, stands as another broadly recognized mechanism model (Vargas-Reyes et al., 2024). Previous studies have suggested that the strong PL of CDs, observed upon surface passivation, is due to the quantum confinement effect of emissive energy traps on the CD surface (Ayisha Naziba et al., 2024). Rao et al. proposed that the excitation-tunable PL emission of CDs is mainly due to variations in size, rather than the presence of different emission trap sites on particles of similar size (Rao et al., 2023). However, research has indicated that CDs of varying sizes exhibited identical PL emission peaks under a 365 nm UV lamp, which is unexpected given the typical size-dependent emission behavior (Gan et al., 2016). In this study, the excitation wavelength dependence of CD photoluminescence may be attributed to variations in particle size. However, the exact mechanism behind the PL of CDs remains controversial and requires further investigation.
The stability of the as-prepared CDs under various conditions was thoroughly examined. The PL intensity of the CDs exhibited pH independence over a broad range of 2–9, as shown in Figure 4A. Furthermore, the PL intensity remained nearly constant in solutions with NaCl concentrations up to 500 mM, as depicted in Figure 4B. The CDs also demonstrated remarkable stability under UV excitation, with no significant change in PL intensity after 1 hour (Figure 4C), and maintained their PL intensity after 6 months of storage (Figure 4D). These findings indicate that the CDs possess exceptional stability, highlighting their potential for biological applications.
FIGURE 4

(A) Effect of pH on the photoluminescence intensity of CDs; (B) Fluorescence intensity of CDs in NaCl aqueous solution (pH = 7) against the ionic strength; (C) Dependence of the fluorescence intensity of CDs on excitation time under 488 nm irradiation in ultrapure water; (D) Effect of storage time on the photoluminescence intensity of CDs.
3.3 Cytotoxicity and cell-imaging
Cytotoxicity is a critical parameter for evaluating the biocompatibility of biomaterials in cell experiments. In this study, standard MTT assays were performed on MC3T3-E1 cells to assess the cytotoxicity of the synthesized CDs (Yang et al., 2023; Zhang W. et al., 2024). Figure 5A illustrates cell viability following 24-h incubation with CDs at concentrations of 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL. The results clearly indicate that the CDs exhibit low cytotoxicity, even at concentrations as high as 200 μg/mL. Therefore, these CDs demonstrate significant potential for single-molecule imaging and tracking within living cells. To further investigate this application, confocal fluorescence imaging was employed. As shown in Figure 5B, the green emission is predominantly localized within the cytoplasmic region, indicating that the CDs successfully penetrate the cell membrane. The uniform and regular distribution of CDs within the cellular matrix suggests an enhancement in cellular biological activity. These initial findings indicate that the synthesized CDs are promising candidates for use in cell imaging, drug delivery, and bone tissue engineering.
FIGURE 5
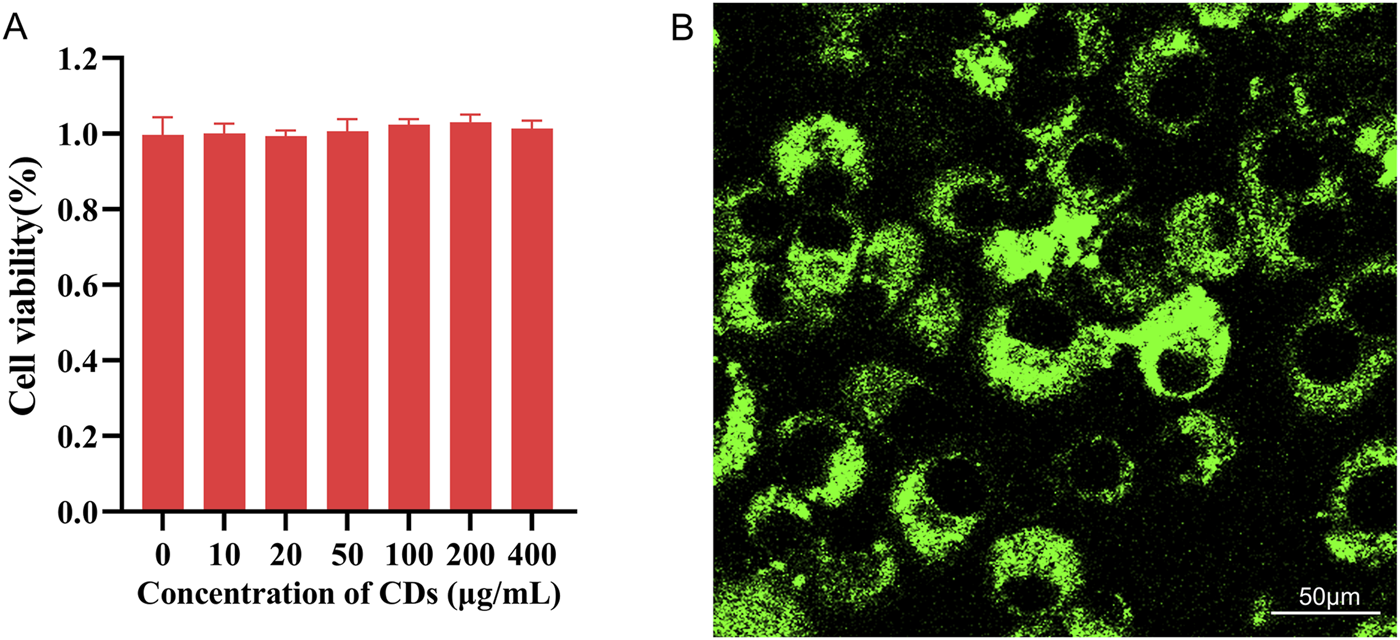
(A) Cell viability of MC3T3-E1 cells after 24-h incubation with various concentrations of CDs; (B) Fluorescence images of MC3T3-E1 cells incubated with CDs for 2 h under 488 nm filter irradiation. Scale bar:50 μm.
4 Conclusion
In the present study, carbon dots (CDs) were successfully synthesized and isolated from PEC-GS/BG hybrids. The CDs exhibit near-spherical geometry with an average diameter of approximately 7.4 nm. They demonstrate strong blue luminescence under ultraviolet irradiation. As the excitation wavelength increases, the emission intensity initially increases and then gradually decreases, with a concurrent red shift in the emission wavelength. Moreover, the CDs exhibit excellent stability and a quantum yield of approximately 4.5%. Cytotoxicity and cell imaging experiments indicate that the CDs exhibit high biocompatibility and uniform intracellular distribution, making them promising candidates for cell-labeling applications.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the studies on animals in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements because only commercially available established cell lines were used.
Author contributions
XZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. JG: Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. HZ: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. XY: Investigation, Resources, Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft. GW: Investigation, Visualization, Data curation, Software, Writing – review and editing. QW: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Software, Writing – review and editing. WL: Formal Analysis, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft. HW: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review and editing. WJ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Project administration. ZZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Research Foundation of YunFu People’s Hospital (Nos A20221002 and A20221003) and Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (2023A1515220002).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Ayisha Naziba T. Praveen Kumar D. Karthikeyan S. Sriramajayam S. Djanaguiraman M. Sundaram S. et al (2024). Biomass derived biofluorescent carbon dots for energy applications: current progress and prospects. Chem. Rec. (New York, NY)24 (6), e202400030. 10.1002/tcr.202400030
2
Barman B. K. Yamada H. Watanabe K. Deguchi K. Ohki S. Hashi K. et al (2024). Rare-earth-metal-Free solid-state fluorescent carbonized-polymer microspheres for unclonable anti-counterfeit whispering-gallery emissions from red to near-infrared wavelengths. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger.11 (30), e2400693. 10.1002/advs.202400693
3
Dash B. S. Lu Y. J. Chen J. P. (2024). Enhancing photothermal/photodynamic therapy for glioblastoma by tumor hypoxia alleviation and heat shock protein inhibition using ir820-conjugated reduced graphene oxide quantum dots. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces16 (11), 13543–13562. 10.1021/acsami.3c19152
4
Dehvari K. Chiu S. H. Lin J. S. Girma W. M. Ling Y. C. Chang J. Y. (2020). Heteroatom doped carbon dots with nanoenzyme like properties as theranostic platforms for free radical scavenging, imaging, and chemotherapy. Acta biomater.114, 343–357. 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.07.022
5
Ding L. Jin X. Gao Y. Kang S. Bai H. Ma X. et al (2024). Precise regulation strategy for fluorescence wavelength of aggregation-induced emission carbon dots. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger.11 (48), e2409345. 10.1002/advs.202409345
6
Dorontic S. Bonasera A. Scopelliti M. Markovic O. Bajuk Bogdanović D. Ciasca G. et al (2022). Gamma-ray-Induced structural transformation of GQDs towards the improvement of their optical properties, monitoring of selected toxic compounds, and photo-induced effects on bacterial strains. Nanomater. Basel, Switz.12 (15), 2714. 10.3390/nano12152714
7
Gan Z. Xu H. Hao Y. (2016). Mechanism for excitation-dependent photoluminescence from graphene quantum dots and other graphene oxide derivates: consensus, debates and challenges. Nanoscale8 (15), 7794–7807. 10.1039/c6nr00605a
8
Ghosal K. Ghosh A. (2019). Carbon dots: the next generation platform for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. and Eng. C, Mater. Biol. Appl.96, 887–903. 10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.060
9
Hu J. Sun Y. Aryee A. A. Qu L. Zhang K. Li Z. (2022). Mechanisms for carbon dots-based chemosensing, biosensing, and bioimaging: a review. Anal. Chim. acta1209, 338885. 10.1016/j.aca.2021.338885
10
Kaur I. Batra V. Bogireddy N. K. R. Baveja J. Kumar Y. Agarwal V. (2024). Chemical- and green-precursor-derived carbon dots for photocatalytic degradation of dyes. iScience27 (2), 108920. 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108920
11
Ke X. Qiu J. Wang X. Yang X. Shen J. Ye S. et al (2020). Modification of pore-wall in direct ink writing wollastonite scaffolds favorable for tuning biodegradation and mechanical stability and enhancing osteogenic capability. FASEB J. official Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol.34 (4), 5673–5687. 10.1096/fj.201903044R
12
Książek E. (2023). Citric acid: properties, microbial production, and applications in industries. Mol. Basel, Switz.29 (1), 22. 10.3390/molecules29010022
13
Leonovich M. Korzhikov-Vlakh V. Lavrentieva A. Pepelanova I. Korzhikova-Vlakh E. Tennikova T. (2023). Poly(lactic acid) and nanocrystalline cellulose methacrylated particles for preparation of cryogelated and 3D-printed scaffolds for tissue engineering. Polymers15 (3), 651. 10.3390/polym15030651
14
Li C. Huang J. Yuan L. Xie W. Ying Y. Li C. et al (2023). Recent progress of emitting long-wavelength carbon dots and their merits for visualization tracking, target delivery and theranostics. Theranostics13 (9), 3064–3102. 10.7150/thno.80579
15
Liu Y. Luo S. Wu P. Ma C. Wu X. Xu M. et al (2019). Hydrothermal synthesis of green fluorescent nitrogen doped carbon dots for the detection of nitrite and multicolor cellular imaging. Anal. Chim. acta.1090, 133–142. 10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.015
16
Liu Y. Wu P. Wu X. Ma C. Luo S. Xu M. et al (2020). Nitrogen and copper (II) co-doped carbon dots for applications in ascorbic acid determination by non-oxidation reduction strategy and cellular imaging. Talanta210, 120649. 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120649
17
Otten M. Hildebrandt M. Kühnemuth R. Karg M. (2022). Pyrolysis and solvothermal synthesis for carbon dots: role of purification and molecular fluorophores. Langmuir ACS J. surfaces colloids38 (19), 6148–6157. 10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c00508
18
Pan Q. Zhang P. Xue F. Zhang J. Fan Z. Chang Z. et al (2024). Subcutaneously engineered decalcified bone matrix xenografts promote bone repair by regulating the immune microenvironment, prevascularization, and stem cell homing. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng.10 (1), 515–524. 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01331
19
Peng Z. Zhao T. Zhou Y. Li S. Li J. Leblanc R. M. (2020). Bone tissue engineering via carbon-based nanomaterials. Adv. Healthc. Mater.9 (5), e1901495. 10.1002/adhm.201901495
20
Perikala M. Valoor R. Bhaskar N. Bhardwaj A. Basu B. (2023). One-step colloidal synthesis of non-toxic electroactive carbon dots with a better threshold cytotoxicity and cytocompatibility. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces15 (1), 281–291. 10.1021/acsami.2c16046
21
Putra N. E. Leeflang M. A. Klimopoulou M. Dong J. Taheri P. Huan Z. et al (2023). Extrusion-based 3D printing of biodegradable, osteogenic, paramagnetic, and porous FeMn-akermanite bone substitutes. Acta biomater.162, 182–198. 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.03.033
22
Rao L. Sun B. Liu Y. Zhang Q. Zhong G. Wen M. et al (2023). Precise regulation of the multicolor spectrum of carbon dots based on the bionic leaf vein ultrasonic microreactor. Ultrason. sonochemistry101, 106674. 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106674
23
Shearer A. Montazerian M. Sly J. J. Hill R. G. Mauro J. C. (2023). Trends and perspectives on the commercialization of bioactive glasses. Acta biomater.160, 14–31. 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.02.020
24
Shen T. Y. Jia P. Y. Chen D. S. Wang L. N. (2021). Hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their application in ion-detection and cell-imaging. Spectrochimica acta Part A, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.248, 119282. 10.1016/j.saa.2020.119282
25
Sobhanan J. Rival J. V. Anas A. Sidharth Shibu E. Takano Y. Biju V. (2023). Luminescent quantum dots: synthesis, optical properties, bioimaging and toxicity. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev.197, 114830. 10.1016/j.addr.2023.114830
26
Sun Y. Qin H. Geng X. Yang R. Qu L. Kani A. N. et al (2020). Rational design of far-red to near-infrared emitting carbon dots for ultrafast lysosomal polarity imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces12 (28), 31738–31744. 10.1021/acsami.0c05005
27
Vargas-Reyes M. Bruna N. Ramos-Zúñiga J. Valenzuela-Ibaceta F. Rivas-Álvarez P. Navarro C. A. et al (2024). Biosynthesis of photostable CdS quantum dots by UV-resistant psychrotolerant bacteria isolated from Union Glacier, Antarctica. Microb. Cell. factories23 (1), 140. 10.1186/s12934-024-02417-x
28
Wang D. Chen Y. Xia T. Claudino M. Melendez A. Ni X. et al (2023). “Citric acid-based intrinsic band-shifting photoluminescent materials,”Research, 6, 0152. 10.34133/research.0152
29
Wei X. Wan C. Peng X. Luo Y. Hu M. Cheng C. et al (2024). Copper-based carbon dots modified hydrogel with osteoimmunomodulatory and osteogenesis for bone regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B12 (23), 5734–5748. 10.1039/d4tb00526k
30
Wu X. Dai H. Yu S. Zhao Y. Long Y. Li W. et al (2021). Citrate regulates extracellular matrix mineralization during osteoblast differentiation in vitro. J. Inorg. Biochem.214, 111269. 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2020.111269
31
Yang H. He L. Pan S. Liu H. Hu X. (2019b). Nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of tannic acid. Spectrochimica acta Part A, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.210, 111–119. 10.1016/j.saa.2018.11.029
32
Yang L. Wang D. Gong Y. Quan T. Tao Y. Liu S. et al (2023). Sulfuric acid induced-synthesis coupled with ethanol extraction-water precipitation purification method for orange fluorescent carbon dots with dual-emission: application for methyl blue detection and cell imaging. Spectrochimica acta Part A, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.286, 121963. 10.1016/j.saa.2022.121963
33
Yang P. Zhu Z. Chen M. Zhou X. Chen W. (2019a). Microwave-assisted synthesis of polyamine-functionalized carbon dots from xylan and their use for the detection of tannic acid. Spectrochimica acta Part A, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.213, 301–308. 10.1016/j.saa.2019.01.043
34
Yang X. Ai L. Yu J. Waterhouse G. I. N. Sui L. Ding J. et al (2022). Photoluminescence mechanisms of red-emissive carbon dots derived from non-conjugated molecules. Sci. Bull.67 (14), 1450–1457. 10.1016/j.scib.2022.06.013
35
Yu X. W. Liu X. Jiang Y. W. Li Y. H. Gao G. Zhu Y. X. et al (2022). Rose bengal-derived ultrabright sulfur-doped carbon dots for fast discrimination between live and dead cells. Anal. Chem.94 (10), 4243–4251. 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04658
36
Zhang L. He J. Li N. Yuan J. Li W. Liu P. et al (2023). Ternary CdS@MoS(2)-Co(3)O(4) multiheterojunction photocatalyst for boosting photocatalytic H(2) evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces15 (37), 43790–43798. 10.1021/acsami.3c09073
37
Zhang P. Zheng Y. Ren L. Li S. Feng M. Zhang Q. et al (2024c). The enhanced photoluminescence properties of carbon dots derived from glucose: the effect of natural oxidation. Nanomater. Basel, Switz.14 (11), 970. 10.3390/nano14110970
38
Zhang W. Smith N. Zhou Y. McGee C. M. Bartoli M. Fu S. et al (2024a). Carbon dots as dual inhibitors of tau and amyloid-beta aggregation for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Acta biomater.183, 341–355. 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.06.001
39
Zhang Y. Fan X. Sun X. Yang X. Li Z. Yang Z. et al (2024b). Synthesis of oil-soluble carbon dots via pyrolysis and their diverse applications in doxycycline detection, fluorescent ink and film. Spectrochimica acta Part A, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.304, 123406. 10.1016/j.saa.2023.123406
40
Zhang Y. Li Y. Liao W. Peng W. Qin J. Chen D. et al (2021). Citrate-stabilized gold nanorods-directed osteogenic differentiation of multiple cells. Int. J. nanomedicine16, 2789–2801. 10.2147/IJN.S299515
41
Zhao H. Ren H. Zhang J. Wang L. Li A. Tang J. et al (2019). Bioactive glass-polycitrate hybrid with osteogenetic ability comparable to autogenous bone. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol.15 (3), 581–592. 10.1166/jbn.2019.2709
42
Zheng W. Bai Z. Huang S. Jiang K. Liu L. Wang X. (2022). The effect of angiogenesis-based scaffold of MesoporousBioactive glass nanofiber on osteogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (20), 12670. 10.3390/ijms232012670
43
Zhong Y. Chen L. Yu S. Yang Y. Liu X. (2023). Advances in magnetic carbon dots: a theranostics platform for fluorescence/magnetic resonance bimodal imaging and therapy for tumors. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng.9 (12), 6548–6566. 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00988
44
Zhu Y. Chen X. Liao Y. (2023). Mesenchymal stem cells-derived apoptotic extracellular vesicles (ApoEVs): mechanism and application in tissue regeneration. Stem cells Dayt. Ohio41 (9), 837–849. 10.1093/stmcls/sxad046
Summary
Keywords
bioimaging, bioactive glass, carbon dots, citric acid, photoluminescence
Citation
Zhang X, Gong J, Zhou H, Yin X, Wu G, Wang Q, Lin W, Wang H, Ji W and Zhang Z (2025) Fluorescent carbon dots in PEC-GS/BG hybrids and their application for bioimaging. Front. Mol. Biosci. 12:1555995. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1555995
Received
06 January 2025
Accepted
02 June 2025
Published
19 June 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Liqiang Zhou, University of Macau, China
Reviewed by
Qian Zhou, Jiangnan University, China
Shichao Wang, Beijing Normal University, Zhuhai, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Gong, Zhou, Yin, Wu, Wang, Lin, Wang, Ji and Zhang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Ji, 276256915@qq.com; Zhongmin Zhang, nfzzm@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.