- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 2College of Medicine and Biological Information Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 3School of Computer Science and Software Engineering, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
- 4Center for Psychological Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Introduction: The retinal microvasculature has been definitively linked to a variety of diseases, such as ophthalmological, cardiovascular, and other medical conditions. Precisely identifying the retinal microvasculature is crucial for early detection and monitoring of these diseases. While the majority of existing neural network-based research has primarily focused on utilizing the green channel of fundus images for vessel segmentation, it is important to acknowledge the potential value of other channels in this process.
Methods: This study introduces RetinalVasNet, a new method aimed at enhancing the accuracy and effectiveness of retinal vascular segmentation by implementing a sophisticated neural network architecture and incorporating multi-channel fundus images.
Results: Our experimental results demonstrate that RetinalVasNet outperforms previous research in most performance metrics.
Discussion: The findings suggest that each channel provides unique contributions to the vascular segmentation process, emphasizing the importance of incorporating multiple channels for accurate and comprehensive segmentation.
1 Introduction
The retinal microvasculature is closely associated with numerous diseases, serving as a crucial factor in the diagnosis and understanding of ocular and systemic conditions (D'Amico, 1994; Rodríguez-Ramírez et al., 2024; Khalafi et al., 2025). For instance, glaucoma, a progressive optic neuropathy, is characterized by significant morphological changes in the blood vessels within the optic disc region (Zhang et al., 2021; Sharma et al., 2024). These changes play a vital role in the identification and treatment of glaucoma by clinicians. Similarly, the retinal microvasculature is also essential in the diagnosis and management of diabetic angiopathy, a common complication of long-term diabetes (Li et al., 2019; Frazao et al., 2019). Evaluating the deformation of the fundus microvasculature allows for better monitoring and treatment of this condition. Additionally, individuals with blood hypertension may exhibit changes in their retinal microvasculature, serving as potential indicators of the presence or progression of cardiovascular disease (Baker et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). These highlight the significance of the retinal microvasculature in the study and diagnosis of various diseases, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their underlying mechanisms and contributing to improved patient care.
The manual annotation of retinal microvasculature is traditionally carried out by experienced clinical practitioners. However, this method is both labor-intensive and time-consuming, prompting the need for alternative approaches (Ji et al., 2024; Ji et al., 2023). Therefore, the automatic and accurate segmentation of retinal microvasculature is crucial for early diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression in various ophthalmological and cardiovascular conditions (Qin and Chen, 2024; Kovács and Fazekas, 2022). In computing, there are two main types methods: traditional computational algorithms and deep learning techniques (Khandouzi et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2023). Traditional computational algorithms aim to address this issue by relying on pre-existing knowledge of local features. However, they have proven challenging to implement in various scenarios (Soomro et al., 2019). On the other hand, deep learning algorithms have redefined retinal microvasculature detection as a pixel classification problem and have generally outperformed traditional methods. Despite their advantages, deep learning models have a notable limitation - the need for a substantial amount of high-quality training images to effectively train a robust model (Hegde et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). To address the crucial question mentioned above, we present a deep learning method called “RetinalVasNet” based on small samples. The key contributions and innovations of this study can be summarized as follows.
1. Reduce the reliance on high-quality training images: We have implemented a sliding-window technique to minimize the need for high-quality training images. This approach allows for the extraction of a larger number of smaller, overlapping image patches from the original images, effectively augmenting the dataset. This method can significantly improve the training process, resulting in a more robust model with better performance and generalization abilities, even in situations where access to high-quality training images may be limited.
2. Increased Utilization of Color Channels: This study delves into the untapped potential of utilizing all color channels in the segmentation of fundus blood vessels. While most previous studies have primarily focused on the green channel of fundus images, with a few exploring the use of the red channel, the blue channel has been largely neglected. Our findings highlight the valuable information conveyed by each of the three color channels in retinal microvasculature detection, emphasizing the need to consider the contribution of each channel in the development of detection algorithms.
3. Diversified Feature Application: The proposed framework, with its symmetric structure consisting of both down-sampling and up-sampling paths, allows for efficient learning of both low-level and multi-scale features. The down-sampling path extracts essential low-level features, such as edges and textures, while the up-sampling path captures broader contextual and scaled features. The inclusion of DenseBlocks, which provide dense connectivity among layers, enhances the framework’s ability to learn complex patterns at different scales. Additionally, the use of a concatenation operator for skip connections preserves detailed information from lower layers, improving the model’s predictive ability by incorporating both low-level and high-level features.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Overview of the proposed methodology
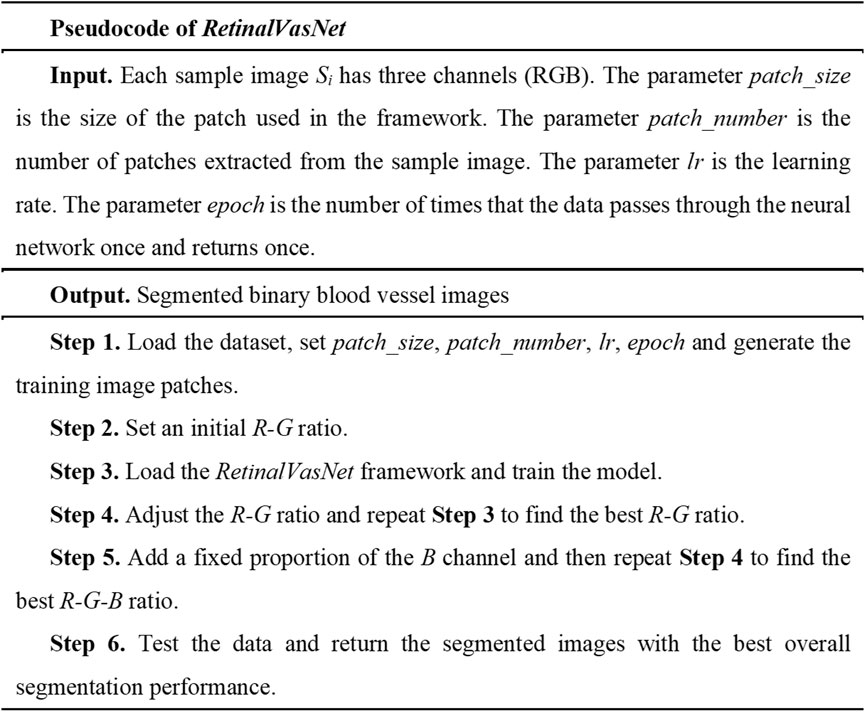
The primary objective of this study is to achieve precise segmentation of blood vessels in fundus images using the proposed framework. The input data comprises an RGB-channel image, and the output is a binary mask. While our framework is also applicable to images in other color modes, the optimized channel ratio will not be utilized in those instances. The pseudocode for RetinalVasNet is presented in Figure 1, with subsequent sections offering a comprehensive explanation of each step in the process.
2.2 Benchmark dataset
This study evaluated the proposed algorithm RetinalVasNet using three popular datasets, i.e., DRIVE (Staal et al., 2004), STARE (Hoover et al., 2000; Hoover and Goldbaum, 2003) CHASE_DB1 (Li et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2025). All these three datasets were publicly available. In order to conduct a fair comparison, this study used the same ratios of the training and testing samples in each dataset. The proposed RetinalVasNet framework takes the fundus images as the input and outputs the binary mask images of the microvasculature. Therefore, we need the datasets of both fundus images and their annotated mask images to train the RetinalVasNet model.
2.3 Framework of RetinalVasNet
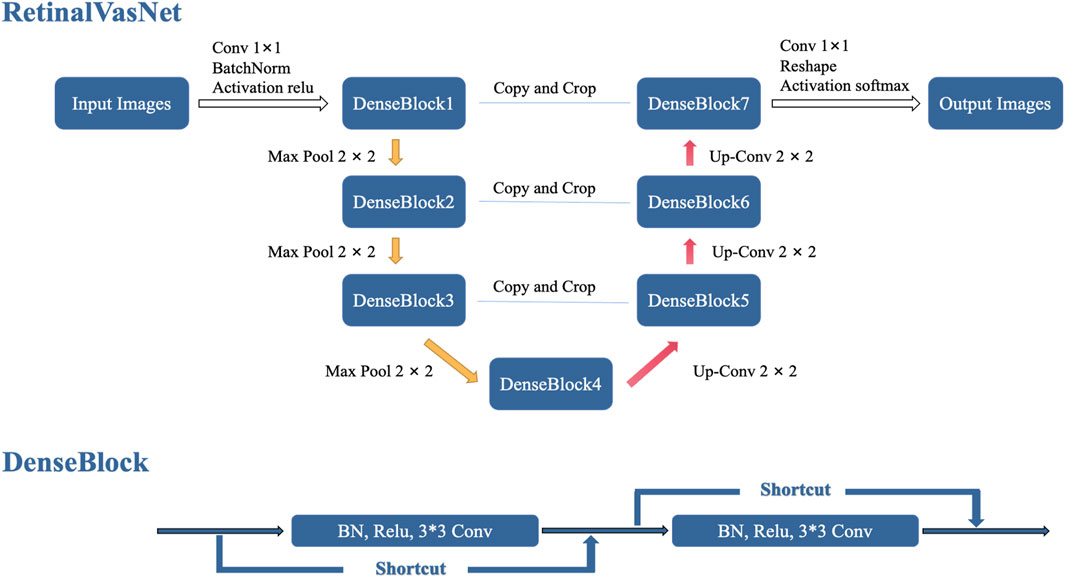
RetinalVasNet adopts a symmetric architecture, comprising two interconnected paths, as illustrated in Figure 2. The down-sampling path links the layers DenseBlock1, DenseBlock2, DenseBlock3, and DenseBlock4, which are responsible for capturing semantic and contextual information. Conversely, the up-sampling path retains spatial details and connects the layers DenseBlock4, DenseBlock5, DenseBlock6, and DenseBlock7. To recover image information lost during pooling or down-sampling, skip connections are incorporated between DenseBlock1 and DenseBlock7, DenseBlock2 and DenseBlock6, as well as DenseBlock3 and DenseBlock5. These skip connections utilize concatenation operations, offering several benefits. They help alleviate the vanishing gradient problem by providing a more direct pathway for gradient flow during backpropagation, allow for the reuse of low-level features in subsequent layers, and enhance the model’s capacity without introducing additional computational burden. Furthermore, concatenating features from various layers facilitates the learning of more diverse and comprehensive feature representations, which may improve performance. The use of concatenation in skip connections also preserves finer, high-resolution details and enables the model to more effectively learn identity functions.
DenseBlock is a module that links the highest layer with the lowest layer in the convolutional neural network. It was originally designed as a part of the DenseNet architecture (Iandola et al., 2025). To preserve the feed-forward style, each layer receives additional inputs from the preceding layers and passes those feature maps onto the next layer. It can be expressed by the formula below:
where
2.4 Data preprocessing
In order to ensure the best possible image quality, this study utilizes standard preprocessing steps, including gray-scale conversion, standardization, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE), and gamma adjustment. When converting an image to grayscale, eight integer bits are used to represent its intensity, providing a range of 256 levels between black and white (0–255). This allows for a diverse range of grey shades, with 0 representing black, 255 representing white, and 1-254 representing various shades of grey. In this study, the RGB mode of the fundus images was utilized and it was suggested that all three channels - red, green, and blue - played a vital role in accurately segmenting the retinal microvasculatures. To achieve this, all RGB-mode images were transformed into grayscale images, with the gray-scale pixel value calculated by adding
2.5 Problem Formulation and evaluation measures
The task of segmenting the retinal microvasculature was approached as a binary classification problem, with vessel pixels as positive samples and all other pixels as negative samples. The number of correctly and incorrectly predicted positive samples were labeled as true positive (TP) and false negative (FN), respectively. Similarly, the number of correctly and incorrectly predicted negative samples were defined as true negative (TN) and false positive (FP). This resulted in
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Assessing the Performance of RetinalVasNet models with Varied ratios of R and G
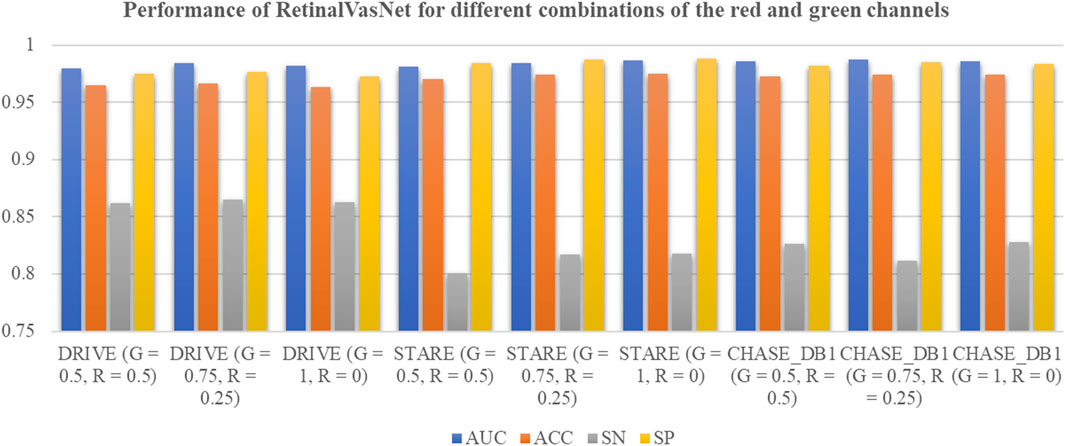
In this study, we tested the widely accepted belief that the green channel is the most effective for segmenting retinal microvasculature, as shown in Figure 3. The channel group “G = 1, R = 0”represents the model performance using the green channel. Interestingly, the green channel produced the best results only for the STARE dataset. In contrast, a combination of “G = 0.75, R = 0.25”achieved the highest performance on the DRIVE and CHASE_DB1 datasets. These results suggest that the red channel may provide valuable complementary information for segmenting retinal microvasculature.
3.2 Fine-tuning the weights of R and G
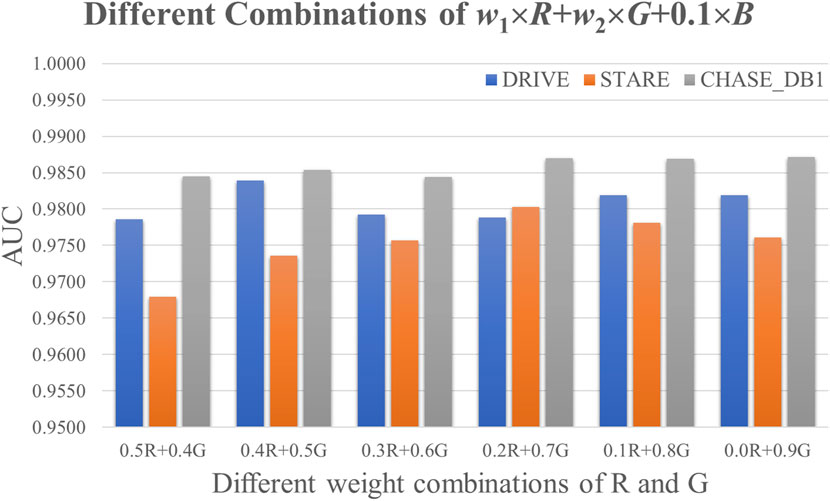
To further investigate the potential of the red and green channels, a comprehensive optimization of their respective weights was conducted, as shown in Figure 4. A grid search methodology was employed to identify the optimal weight configuration for the R and G channels in the formula: GreyPixel = (r - i) × R + (g + i) × G, where i ∈ [-0.05, +0.05] with a step size of 0.01. In this formula, GreyPixel represents the grayscale value of each pixel in the grayscale image used for model training. The values of r and g were determined as r = 0.25 and g = 0.75 for the DRIVE and CHASE_DB1 datasets, and r = 0.00 and g = 1.00 for the STARE dataset, as derived in the previous section. The performance metric, AUC, was utilized as the optimization criterion. The optimal weight combinations were found to be 0.2 4 × R + 0.76 × G for both the DRIVE and CHASE_DB1 datasets, yielding improved AUC values of 0.9845 and 0.9871, respectively, surpassing those from the previous analysis. However, no significant enhancements were observed for the STARE dataset, where the green channel remained the most effective, achieving the highest AUC of 0.9863 for retinal microvascular segmentation.
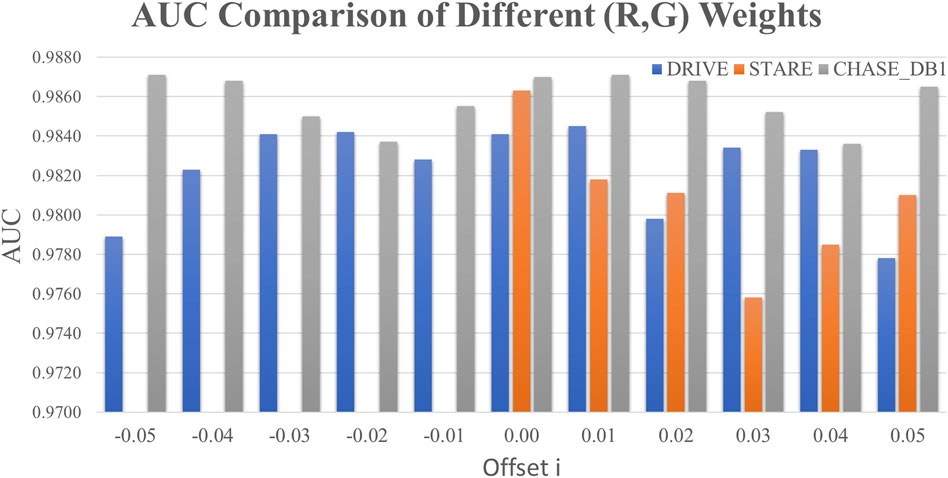
Figure 4. Optimizing the weights of the R and G channels. (The horizontal axis was the offset value i∈[-0.05, +0.05] with the step size 0.01.)
3.3 Combining the R, G, and B channels
The hypothesis of this study posited that all three color channels—R, G, and B—contain valuable information for the segmentation of retinal microvasculature in fundus images. Previous research has predominantly concentrated on the R and G channels as the primary sources for this task. In contrast, this study incorporated the B channel of fundus images, assigning it a fixed weight of
3.4 Evaluating against previous state-of-the-art studies
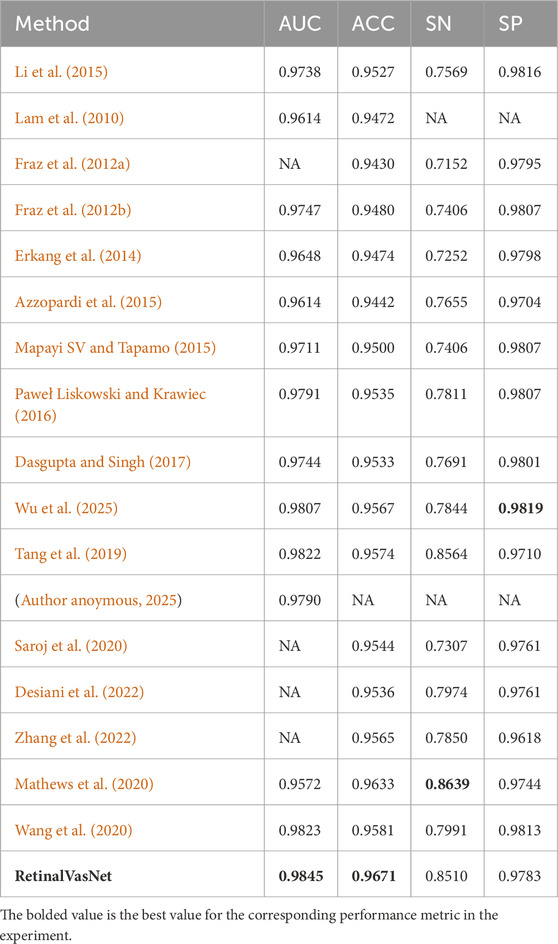
In this section, we demonstrate the superior performance of RetinalVasNet in retinal microvasculature segmentation, particularly in comparison to existing state-of-the-art methods. Our method was evaluated across three prominent datasets—DRIVE, STARE, and CHASE_DB1—and consistently outperformed previous approaches on all metrics, including AUC, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
As shown in Table 1, RetinalVasNet achieved an AUC of 0.9845 on the DRIVE dataset, surpassing all 17 existing methods, with the next best AUC being 0.9807. Notably, RetinalVasNet also excelled in accuracy, achieving 0.9671, while the next best model did not exceed 0.9600 in this metric. Furthermore, our method demonstrated robust performance in sensitivity (SN = 0.8510) and specificity (SP = 0.9783), again outperforming other studies, which underscores its superior ability to detect retinal vessels with higher precision and reliability.
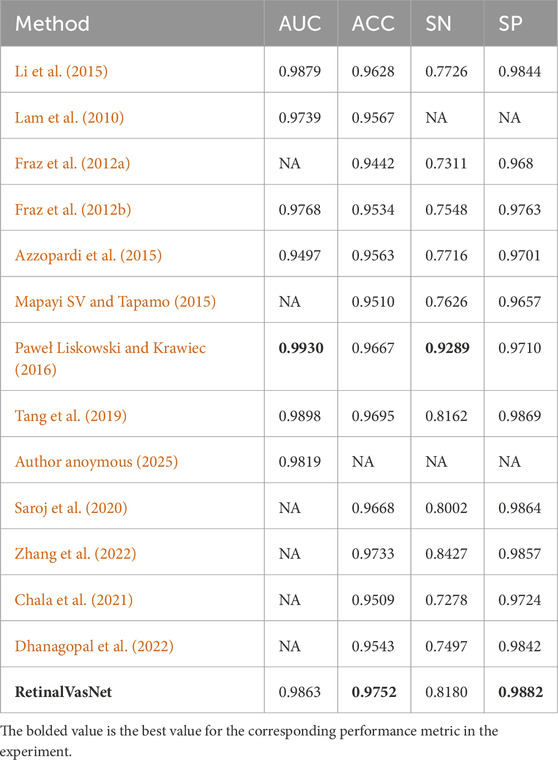
On the STARE dataset, as displayed in Table 2, RetinalVasNet achieved the best specificity (SP = 0.9882) among all competing methods, demonstrating its capacity to minimize false positives and maintain high classification integrity. Despite not achieving the highest AUC, RetinalVasNet’s performance in terms of accuracy (ACC = 0.9752) and sensitivity (SN = 0.8180) showed significant improvements over prior methods, marking a clear advancement in segmentation techniques.
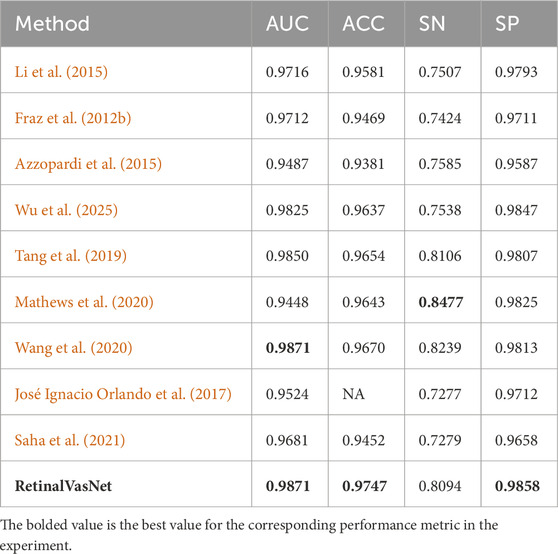
For the CHASE_DB1 dataset, as shown in Table 3, RetinalVasNet again set the bar with an AUC of 0.9871, surpassing all prior methods. Although sensitivity slightly lagged behind the best-performing study, RetinalVasNet’s high specificity (SP = 0.9858) and excellent accuracy (ACC = 0.9747) reinforced its dominance in the segmentation task.
3.5 Comparing cross-training to previous state-of-the-art studies
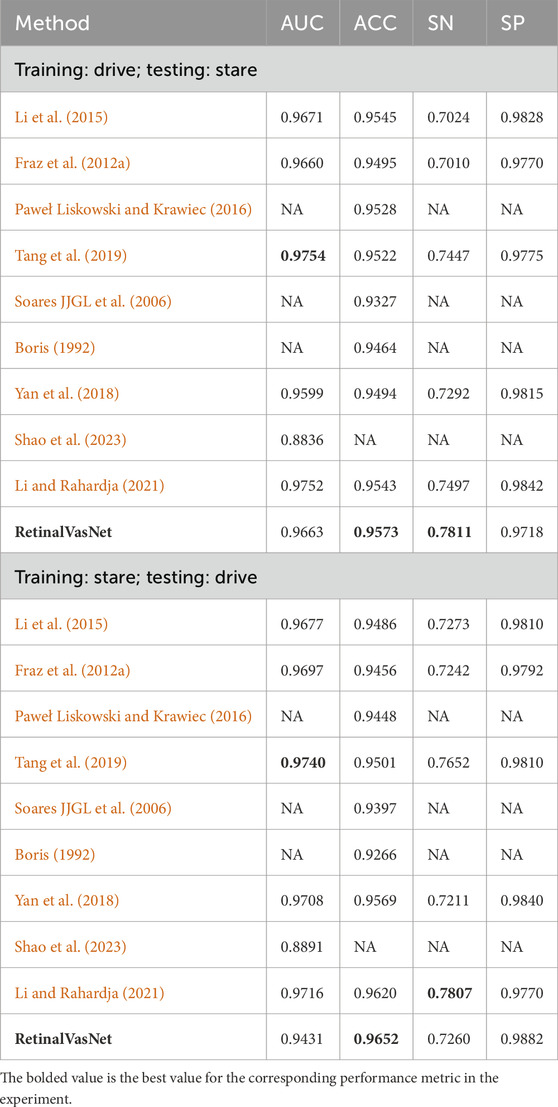
Advancements in AI-driven fundus vascular segmentation have significantly enhanced model accuracy; however, large-scale, real-world clinical validation remains limited. To evaluate RetinalVasNet’s performance on an independent verification dataset, cross-training experiments were conducted using the DRIVE and STARE datasets. As presented in Table 4, RetinalVasNet achieved robust accuracy and sensitivity on the STARE dataset when trained on DRIVE. However, specificity and AUC were slightly lower. Conversely, when trained on STARE and tested on DRIVE, RetinalVasNet attained the highest accuracy but exhibited reduced AUC and sensitivity compared to recent studies, with sensitivity falling below a critical threshold.
These cross-training experiments underscore a key challenge in deploying retinal vessel segmentation models: domain shift. This issue stems from differences in field-of-view and background complexity between datasets. The STARE dataset, with its wider field-of-view, intricate background, thin peripheral vessels, and heterogeneous non-vascular regions, posed challenges not encountered in the DRIVE dataset. Consequently, the model optimized for DRIVE misclassified fine vascular structures as background, reducing sensitivity, and generated false positives in complex backgrounds, lowering specificity. In contrast, the STARE-to-DRIVE transfer yielded high accuracy and specificity but a notable decline in AUC. The DRIVE dataset’s high contrast between vessels and background, coupled with stricter annotation criteria, led to a feature mismatch with STARE-trained models, increasing false negatives for microvessels and consequently impacting AUC by limiting true positive detection.
To address domain discrepancies, we propose multiple strategies: (1) adversarial domain alignment during training to unify feature distributions across datasets, (2) test-time normalization to dynamically adjust to target dataset characteristics, and (3) semi-supervised fine-tuning using pseudo-labels for unlabeled target images. These methods aim to enhance model generalizability, ensuring robust and consistent performance in diverse real-world clinical settings with inherent data variability. In future model development and transfer learning experiments, we will implement and evaluate these strategies to further optimize performance.
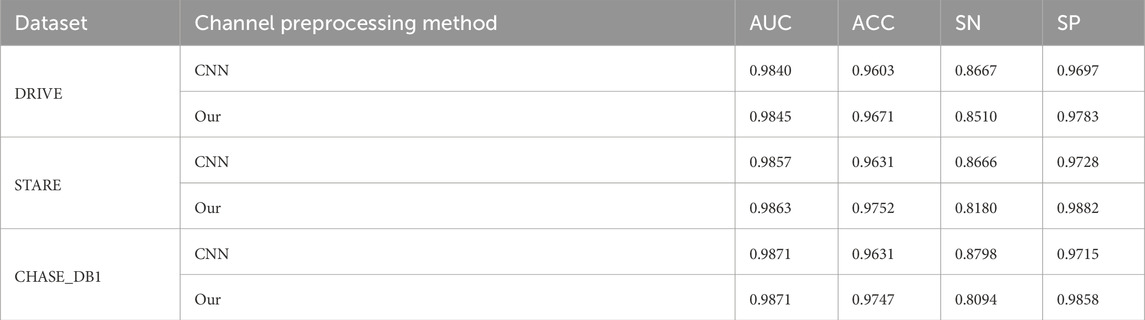
3.6 Assessing the Performance of RetinalVasNet with different Channel Fusion Preprocessing Methods
We conducted a comparison between our method and the traditional convolutional approach, which directly inputs RGB images and learns convolutional filter weights during training. We used a weighted average of the R, G, and B channels as an alternative preprocessing step. Table 5 presents the results of this comparison. Our findings indicate that the Channel Fusion Preprocessing Method outperforms the traditional convolution layer preprocessing across four key metrics, demonstrating its effectiveness and potential advantages over conventional methods.
3.7 Assessing the performance of other datasets
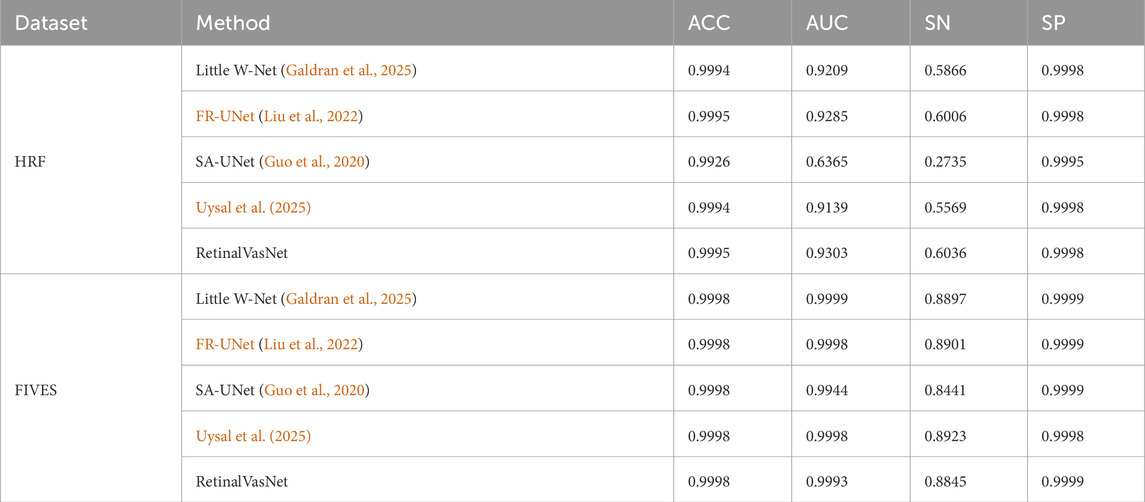
With technological advancements, annotated public fundus image datasets have become more accessible. We compared our results with four state-of-the-art methods using the HRF (Budai et al., 2013) and FIVES (Jin et al., 2022) datasets, Due to large image sizes and server limitations, we downsampled the datasets. The FIVES dataset images, with equal dimensions, were directly downsampled to 224 × 224. For the HRF dataset, we cropped non-essential black areas to achieve a uniform aspect ratio before downsampling to 224 × 224.
As shown in Table 6, For the HRF dataset, RetinalVasNet achieves an accuracy of 0.9995, demonstrating its excellent overall performance. In terms of AUC, it stands at 0.9303, the highest among the methods compared, reflecting its superior ability to distinguish between the foreground (vessels) and background (non-vessels) in retinal images. SN, which measures the true positive rate, is 0.6036 for RetinalVasNet, showing it captures more of the vascular structures compared to others like SA-UNet (0.2735) and Uysal et al. (0.5569), although slightly behind FR-UNet and Little W-Net. The SP of 0.9998 places RetinalVasNet on par with the other methods, indicating its ability to correctly identify non-vessel pixels.
For the FIVES dataset, RetinalVasNet continues to perform exceptionally well. Its accuracy remains 0.9998, indicating that it has maintained high performance across datasets. Its AUC of 0.9993 is slightly lower than FR-UNet and Uysal et al., but still demonstrates a robust ability to distinguish between relevant and irrelevant pixels. Sensitivity increases to 0.8845, outperforming most other methods, including SA-UNet (0.8441), while specificity remains perfect at 0.9999, matching the other state-of-the-art methods in this regard.
In summary, RetinalVasNet consistently delivers high accuracy, AUC, and specificity, with a strong sensitivity score on both the HRF and FIVES datasets. These results highlight its competitive edge in retinal microvasculature segmentation, outperforming or matching many advanced methods, making it a valuable contribution to the field.
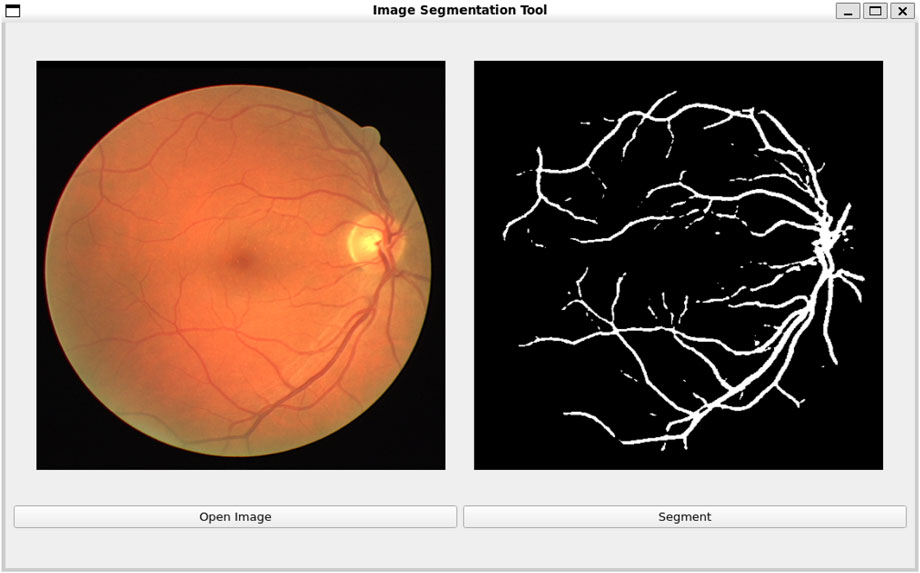
3.8 Visualization experiments
To further demonstrate the practical application and usability of our proposed method, we developed a software tool that allows users to upload fundus images and perform real-time retinal vessel detection. The tool leverages our RetinalVasNet model to generate binary segmentation masks of the microvasculature. As shown in Figure 6, the software interface enables users to input fundus images of different resolutions, and the output clearly visualizes the detected retinal vessels. The usage of the software can be found in Supplementary File 1. The software can be downloaded through the link in Data Availability.
3.9 Principles for designing RetinalVasNet
To effectively segment blood vessels in fundus images, a novel framework must be designed that takes into account their fuzzy boundaries, complex gradients, and biophysical constraints (Orujov et al., 2020; Sidhu et al., 2023). This can be achieved by combining specialized techniques. First, the focus should be on edge detection, as blood vessels follow biophysical rules and have regular shapes despite their fuzzy boundaries (Hakim et al., 2021; Lv et al., 2021). Techniques such as gradient-based methods or advanced convolutional layers can effectively detect these edges. Secondly, a multi-scale approach is necessary due to the complex gradients in fundus images. Implementing a hierarchical structure where the image is processed at different scales can help capture these gradients (Li et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2022). Lastly, a comprehensive preprocessing pipeline is crucial to address variations in image quality and lighting conditions (Huang and Deng, 2023; Zhou et al., 2022). Techniques like contrast enhancement, noise reduction, and histogram equalization can ensure image quality and minimize unwanted variations.
The RetinalVasNet framework is designed with a symmetrical structure that incorporates both down-sampling and up-sampling paths. This allows for efficient learning of low-level and multi-scale features. The down-sampling path focuses on extracting essential features like edges and textures, while the up-sampling path captures broader contextual and scaled features. Additionally, DenseBlocks are used to enhance the framework’s ability to learn intricate patterns at different scales. The use of a concatenation operator for skip connections helps retain detailed information from lower layers, thus improving the model’s predictive capacity by utilizing both low-level and high-level features. Furthermore, the sliding-window technique and a comprehensive preprocessing pipeline provide a diverse and noise-free training dataset, allowing the model to concentrate on learning relevant features. This unique combination of strategies makes RetinalVasNet a powerful tool for segmenting fundus blood vessels, showcasing its potential for superior performance.
Furthermore, RetinalVasNet distinguishes itself from existing “multi-channel/multi-modal” fusion networks through its unique approach to integrating color channels and leveraging them for enhanced segmentation performance. While many current methods focus on simple channel concatenation or basic weighted combinations of channels, RetinalVasNet employs a more sophisticated fusion strategy by incorporating a channel fusion preprocessing step that carefully balances the contributions of each color channel (R, G, B). This method allows the network to capitalize on the distinct information provided by each channel, optimizing their individual strengths for vessel detection. Moreover, unlike traditional multi-modal networks that require the simultaneous processing of diverse types of data (such as combining fundus images with other imaging modalities like OCT or fluorescein angiography), RetinalVasNet solely focuses on RGB fundus images and maximizes their potential without introducing the complexity of multi-modal data fusion. This simplifies the architecture while still enhancing its performance, making it more computationally efficient and easier to implement in clinical settings. By reducing the reliance on additional modalities and focusing on optimizing the inherent information from the RGB channels, RetinalVasNet provides a more streamlined yet powerful solution for retinal microvasculature segmentation.
In the process of optimizing RetinalVasNet, searching for the optimal ratio of RGB channels can be computationally expensive due to the large number of possible combinations and the time required for training multiple models. To address this, we propose several strategies to reduce computational resources and time. First, instead of exhaustively searching across all possible ratios, a more efficient search method such as Bayesian optimization or genetic algorithms can be employed. These methods intelligently explore the search space by using probabilistic models or evolutionary strategies to focus on the most promising ratios, thus reducing the number of evaluations needed. Second, leveraging early stopping during the training process can prevent unnecessary computational costs by halting training once performance plateaus, ensuring that only the most optimal configurations are fully trained. Additionally, adopting transfer learning from pre-trained models can significantly shorten training times, as the model would already have learned low-level features, requiring less fine-tuning for optimal ratio selection. Lastly, the use of parallel processing, where multiple configurations are evaluated simultaneously on separate machines or GPU cores, can speed up the search process. By integrating these approaches, the time and resources required to find the optimal RGB channel ratio can be minimized, making the process more efficient without compromising the model’s performance. All optimization strategies will be implemented and explored in specific directions in our future research to further enhance the efficiency and performance of RetinalVasNet.
4 Conclusion
This study introduces a deep learning framework, RetinalVasNet, for segmenting the retinal microvasculature in fundus images. RetinalVasNet shows superior performance compared to existing studies on the DRIVE and CHASE_DB1 datasets, and performs similarly well on the STARE dataset. In a transfer learning experiment, the method also demonstrates the importance of transferring knowledge from pre-trained models. Our experimental data also suggests that all three color channels of the fundus images contain valuable information for microvasculature segmentation, and a weighted combination of these channels produces satisfactory results. In future studies, we plan to apply the RetinalVasNet framework to other ophthalmological images, such as Ophthalmology Optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: DRIVE can be found at https://drive.grand-challenge.org/, START can be found at https://cecas.clemson.edu/∼ahoover/stare/and CHASE_DB1 can be found at https://blogs.kingston.ac.uk/retinal/chasedb1/.
Author contributions
ZY: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. CX: Methodology, Writing – original draft. GZ: Software, Writing – original draft. WX: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZW: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. ZG: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Northern Theater General Hospital’s independent research projects (ZZKY2024001, ZZKY2024002 and ZZKY2024003).
Acknowledgments
Portions of this work were presented at “Eye3DVas: three-dimensional reconstruction of retinal vascular structures by integrating fundus image features” and “3D-FVS: construction and application of three-dimensional fundus vascular structure model based on single image features”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2025.1562608/full#supplementary-material
References
Azzopardi, G., Strisciuglio, N., Vento, M., and Petkov, N. (2015). Trainable COSFIRE filters for vessel delineation with application to retinal images. Med. image Anal. 19 (1), 46–57. doi:10.1016/j.media.2014.08.002
Baker, S., Xiang, W., and Atkinson, I. (2022). A computationally efficient CNN-LSTM neural network for estimation of blood pressure from features of electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram waveforms. Knowledge-Based Syst. 250, 109151. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109151
Boris, T. (1992). Polyak ABJ: acceleration of stochastic approximation by averaging. SIAM J. Control Optim. 30 (4), 835–855. doi:10.1137/0330046
Budai, A., Bock, R., Maier, A., Hornegger, J., and Michelson, G. (2013). Robust vessel segmentation in fundus images. Int. J. Biomed. imaging 2013, 154860. doi:10.1155/2013/154860
Chala, M., Nsiri, B., El yousfi Alaoui, M. H., Soulaymani, A., Mokhtari, A., and Benaji, B. (2021). An automatic retinal vessel segmentation approach based on convolutional Neural Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 184, 115459. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115459
D'Amico, D. J. (1994). Diseases of the retina. N. Engl. J. Med. 331 (2), 95–106. doi:10.1056/nejm199407143310207
Dasgupta, A. S., and Singh, S. (2017). “Sonam: a fully convolutional neural network based structured prediction approach towards the retinal vessel segmentation,”. IEEE 14th ISBI 248–251. doi:10.1109/isbi.2017.7950512
Desiani, A., Erwin, S. B., Efriliyanti, F., Arhami, M., and Setyaningsih, E. (2022). VG-DropDNet a robust Architecture for blood vessels segmentation on retinal image. IEEE Access 10, 92067–92083. doi:10.1109/access.2022.3202890
Dhanagopal, R., Raj, P. T. V., Suresh Kumar, R., Mohan Das, R., Pradeep, K., and Kwadwo, O.-A. (2022). An efficient retinal segmentation-based deep learning framework for disease prediction. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2022/2013558
Erkang, C. L. D., Wu, Yi, Zhu, Y. J., Zhu, Y. J., Megalooikonomou, V., and Ling, H. (2014). Discriminative vessel segmentation in retinal images by fusing context-aware hybrid features. Mach. Vis. Appl. 25, 1779–1792. doi:10.1007/s00138-014-0638-x
Fraz, M. M., Remagnino, P., Hoppe, A., Uyyanonvara, B., Rudnicka, A. R., Owen, C. G., et al. (2012a). An ensemble classification-based approach applied to retinal blood vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59 (9), 2538–2548. doi:10.1109/TBME.2012.2205687
Fraz, M. M., Remagnino, P., Hoppe, A., Uyyanonvara, B., Rudnicka, A. R., Owen, C. G., et al. (2012b). Blood vessel segmentation methodologies in retinal images–a survey. Comput. methods programs Biomed. 108 (1), 407–433. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2012.03.009
Frazao, L. B., Theera-Umpon, N., and Auephanwiriyakul, S. (2019). Diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy based on holistic texture and local retinal features. Inf. Sci. 475, 44–66. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2018.09.064
Galdran, A., Anjos, A., Dolz, J., Chakor, H., Lombaert, H., and Ayed, I. B. (2025). The little w-net that could: state-of-the-art retinal vessel segmentation with minimalistic models. arXiv preprint arXiv:200901907 2020.
Guo, C., Szemenyei, M., Yi, Y., Wang, W., Chen, B., and Fan, C. (2020). “Sa-unet: spatial attention u-net for retinal vessel segmentation,” in 2020 25th international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR): 2021 (IEEE), 1236–1242.
Hakim, L., Kavitha, M. S., Yudistira, N., and Kurita, T. (2021). Regularizer based on Euler characteristic for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 149, 83–90. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2021.05.023
Hegde, G., Prabhu, S., Gupta, S., Prabhu, G. M., Palorkar, A., Srujan, M. V., et al. (2023). “A systematic review of deep learning approaches for vessel segmentation in retinal fundus images,” in Journal of physics: conference series (IOP Publishing). 012021.
Hoover, A., and Goldbaum, M. (2003). Locating the optic nerve in a retinal image using the fuzzy convergence of the blood vessels. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 22 (8), 951–958. doi:10.1109/TMI.2003.815900
Hoover, A., Kouznetsova, V., and Goldbaum, M. (2000). Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 19 (3), 203–210. doi:10.1109/42.845178
Huang, Y., and Deng, T. (2023). Multi-level spatial-temporal and attentional information deep fusion network for retinal vessel segmentation. Phys. Med. and Biol. 68 (19), 195026. doi:10.1088/1361-6560/acefa0
Iandola, F., Moskewicz, M., Karayev, S., Girshick, R., Darrell, T., and Keutzer, K. (2025). Densenet: implementing efficient convnet descriptor pyramids. arXiv preprint arXiv:14041869 2014.
Ji, Z., Yao, D., Chen, R., Lyu, T., Liao, Q., Zhao, L., et al. (2023). U-Net_dc: a novel U-Net-based model for endometrial cancer cell image segmentation. Information 14 (7), 366. doi:10.3390/info14070366
Ji, Z., Mu, J., Liu, J., Zhang, H., Dai, C., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). ASD-Net: a novel U-Net based asymmetric spatial-channel convolution network for precise kidney and kidney tumor image segmentation. Med. and Biol. Eng. and Comput. 62, 1673–1687. doi:10.1007/s11517-024-03025-y
Jin, K., Huang, X., Zhou, J., Li, Y., Yan, Y., Sun, Y., et al. (2022). FIVES: a fundus image dataset for artificial intelligence based vessel segmentation. Sci. Data 9 (1), 475. doi:10.1038/s41597-022-01564-3
José Ignacio Orlando, E. P., Blaschko, M. B., and Blaschko, M. B. (2017). A discriminatively trained fully connected conditional random field model for blood vessel segmentation in fundus images. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64 (1), 16–27. doi:10.1109/TBME.2016.2535311
Khalafi, P., Morsali, S., Hamidi, S., Ashayeri, H., Sobhi, N., Pedrammehr, S., et al. (2025). Artificial intelligence in stroke risk assessment and management via retinal imaging. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 19, 1490603. doi:10.3389/fncom.2025.1490603
Khandouzi, A., Ariafar, A., Mashayekhpour, Z., Pazira, M., and Baleghi, Y. (2022). Retinal vessel segmentation, a review of classic and deep methods. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 50 (10), 1292–1314. doi:10.1007/s10439-022-03058-0
Kovács, G., and Fazekas, A. (2022). A new baseline for retinal vessel segmentation: numerical identification and correction of methodological inconsistencies affecting 100+ papers. Med. Image Anal. 75, 102300. doi:10.1016/j.media.2021.102300
Lam, B. S. Y., Gao, Y., and Liew, A. W. C. (2010). General retinal vessel segmentation using regularization-based multiconcavity modeling. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 29 (7), 1369–1381. doi:10.1109/TMI.2010.2043259
Li, D., and Rahardja, S. (2021). BSEResU-Net: an attention-based before-activation residual U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 205, 106070. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106070
Li, Q., Feng, B., Xie, L., Liang, P., Zhang, H., and Wang, T. (2015). A cross-modality learning approach for vessel segmentation in retinal images. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 35 (1), 109–118. doi:10.1109/TMI.2015.2457891
Li, T., Gao, Y., Wang, K., Guo, S., Liu, H., and Kang, H. (2019). Diagnostic assessment of deep learning algorithms for diabetic retinopathy screening. Inf. Sci. 501, 511–522. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2019.06.011
Li, W., Wu, C., Cheng, Y., and Yang, Z. (2022). “DM-Net: a Depth-separable convolution and Multi-Scale Network for retinal blood vessel segmentation,” in Journal of physics: conference series (IOP Publishing). 012040.
Liu, W., Yang, H., Tian, T., Cao, Z., Pan, X., Xu, W., et al. (2022). Full-resolution network and dual-threshold iteration for retinal vessel and coronary angiograph segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. health Inf. 26 (9), 4623–4634. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2022.3188710
Lv, Y., Ma, H., Li, J., and Liu, S. (2021). Fusing dense and ReZero residual networks for super-resolution of retinal images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 149, 120–129. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2021.05.019
Mapayi Sv, T., and Tapamo, J. R. (2015). Adaptive thresholding technique for retinal vessel segmentation based on GLCM-energy information. Comput. Math. Methods Med., 0–11. doi:10.1155/2015/597475
Mathews, M. R., Anzar, S. M., Krishnan, R. K., and Panthakkan, A. (2020). “EfficientNet for retinal blood vessel segmentation,” in 2020 3rd international conference on signal processing and information security (ICSPIS), 25–26.
Orujov, F., Maskeliūnas, R., Damaševičius, R., and Wei, W. (2020). Fuzzy based image edge detection algorithm for blood vessel detection in retinal images. Appl. Soft Comput. 94, 106452. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106452
Paweł Liskowski, K. K., and Krawiec, K. (2016). Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35 (11), 2369–2380. doi:10.1109/TMI.2016.2546227
Qin, Q., and Chen, Y. (2024). A review of retinal vessel segmentation for fundus image analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 128, 107454. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107454
Author anoymous, Retina blood vessel segmentation with a convolution neural network (U-net). (2025). Available online at: https://github.com/orobix/retina-unet
Rodríguez-Ramírez, K. T., Norte-Muñoz, M., Lucas-Ruiz, F., Gallego-Ortega, A., Calzaferri, F., García-Bernal, D., et al. (2024). Retinal response to systemic inflammation differs between sexes and neurons. Front. Immunol. 15, 1340013. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1340013
Saha, T. B., Tchiotsop, D., Noubom, M., Louis-Dorr, V., and Wolf, D. (2021). Retinal blood vessels segmentation using classical edge detection filters and the neural network. Inf. Med. Unlocked 23, 100521. doi:10.1016/j.imu.2021.100521
Saroj, S. K., Kumar, R., and Singh, N. P. (2020). Fréchet PDF based matched filter approach for retinal blood vessels segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 194, 105490. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105490
Shao, H. C., Chen, C. Y., Chang, M. H., Yu, C. H., Lin, C. W., and Yang, J. W. (2023). Retina-TransNet: a gradient-guided few-shot retinal vessel segmentation net. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 27 (10), 4902–4913. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2023.3298710
Sharma, S. K., Muduli, D., Priyadarshini, R., Kumar, R. R., Kumar, A., and Pradhan, J. (2024). An evolutionary supply chain management service model based on deep learning features for automated glaucoma detection using fundus images. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 128, 107449. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107449
Sidhu, R., Sachdeva, J., and Katoch, D. (2023). Segmentation of retinal blood vessels by a novel hybrid technique-principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE). Microvasc. Res. 148, 104477. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2023.104477
Soares Jjgl, J. V. B., Cesar, R. M., Cesar Júnior, R. M., Jelinek, H. F., and Cree, M. J. (2006). Retinal vessel segmentation using the 2-D Gabor wavelet and supervised classification. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 25 (9), 1214–1222. doi:10.1109/tmi.2006.879967
Soomro, T. A., Afifi, A. J., Zheng, L., Soomro, S., Gao, J., Hellwich, O., et al. (2019). Deep learning models for retinal blood vessels segmentation: a review. IEEE Access 7, 71696–71717. doi:10.1109/access.2019.2920616
Staal, J., Abràmoff, M. D., Niemeijer, M., Viergever, M. A., and Van Ginneken, B. (2004). Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 23 (4), 501–509. doi:10.1109/TMI.2004.825627
Tang, P., Liang, Q., Yan, X., Zhang, D., Coppola, G., and Sun, W. (2019). Multi-proportion channel ensemble model for retinal vessel segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 111, 103352. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103352
Uysal, E. S., Bilici, M. Ş., Zaza, B. S., Özgenç, M. Y., and Boyar, O. (2025). Exploring the limits of data augmentation for retinal vessel segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:210509365 2021.
Wang, D., Haytham, A., Pottenburgh, J., Saeedi, O., and Tao, Y. (2020). Hard attention net for automatic retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 24 (12), 3384–3396. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2020.3002985
Wang, T., Sun, B., and Jiang, C. (2023). Kernel similarity-based multigranulation three-way decision approach to hypertension risk assessment with multi-source and multi-level structure data. Appl. Soft Comput. 144, 110470. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110470
Wu, Y., Xia, Y., Song, Y., Zhang, Y., and Cai, W. (2025). “Multiscale network followed network model for retinal vessel segmentation,” in International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention: 2018 (Springer), 119–126.
Yan, Z., Yang, X., and Cheng, K. T. (2018). Joint segment-level and pixel-wise losses for deep learning based retinal vessel segmentation. IEEE Trans. bio-medical Eng. 65 (9), 1912–1923. doi:10.1109/TBME.2018.2828137
Zhang, Y., Cai, X., Zhang, Y., Kang, H., Ji, X., and Yuan, X. (2021). TAU: transferable Attention U-Net for optic disc and cup segmentation. Knowledge-Based Syst. 213, 106668. doi:10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106668
Zhang, Y., He, M., Chen, Z., Hu, K., Li, X., and Gao, X. (2022). Bridge-Net: Context-involved U-net with patch-based loss weight mapping for retinal blood vessel segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 195, 116526. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116526
Zhang, T., Zhou, X., Wang, D. D., and Wang, X. (2024). Feature similarity learning based on fuzziness minimization for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Inf. Fusion 106, 102253. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102253
Zhao, H., Huang, J., Zhou, Q., Chen, N., Liu, L., Wang, X., et al. (2022). Deep learning-based optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy for in vivo 3D microvasculature imaging and segmentation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4 (9), 2200004. doi:10.1002/aisy.202200004
Zhou, W.-D., Dong, L., Zhang, K., Wang, Q., Shao, L., Yang, Q., et al. (2022). Deep learning for automatic detection of recurrent retinal detachment after surgery using ultra-widefield fundus images: a single-center Study. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4 (9), 2200067. doi:10.1002/aisy.202200067
Keywords: channel fusion, fundus images, retinal microvasculature, RetinalVasNet, vessel segmentation
Citation: Yao Z, Xing C, Zhu G, Xie W, Wang Z and Zhang G (2025) RetinalVasNet: a deep learning approach for robust retinal microvasculature detection. Front. Mol. Biosci. 12:1562608. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1562608
Received: 17 January 2025; Accepted: 31 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Matteo Becatti, University of Firenze, ItalyReviewed by:
Annagrazia Adornetto, University of Calabria, ItalyJingmin Luan, Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao, China
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Xing, Zhu, Xie, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiguo Wang, d2FuZ3poaWd1bzU3NzhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Guoxu Zhang, emhhbmdndW94dV81MDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Zhaomin Yao
Zhaomin Yao Cengcong Xing3
Cengcong Xing3 Zhiguo Wang
Zhiguo Wang Guoxu Zhang
Guoxu Zhang