Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a complex clinical disease characterized by sophisticated molecular pathways. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including lncRNAs, miRNAs, and circRNAs, play a pivotal role. This review focuses on the role of ncRNAs in AKI pathogenesis and their potential as biomarkers for early detection and therapeutic intervention. We carried out an extensive examination of the expression patterns, functional roles, and molecular mechanisms of lncRNAs, miRNAs, and circRNAs in AKI, as well as their relevance to treatments with natural medicines. Our findings underscore the dualistic nature of ncRNAs in AKI, acting as both protective and detrimental factors that influence key biological processes includes inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. We also point out the possible importance of other ncRNA types, such as snoRNAs and snRNAs, in AKI pathophysiology. This review provides a holistic perspective on the role of ncRNAs in AKI and lays the theoretical groundwork for the creation of innovative therapeutic strategies and biomarkers.
Graphical Abstract
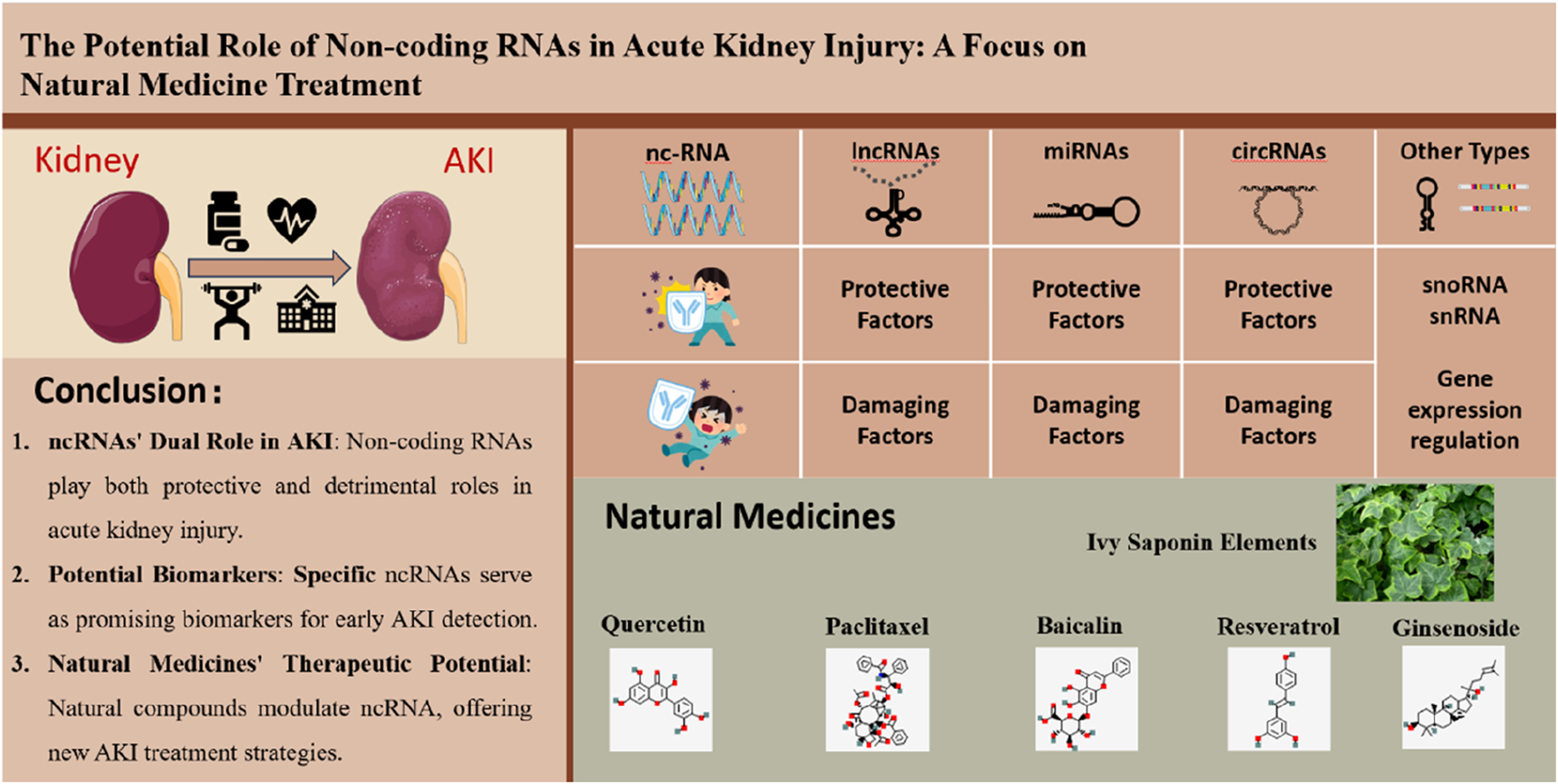
The figure illustrates the potential role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in acute kidney injury (AKI) and their relevance to natural medicine treatment. On the left side, it shows a kidney and AKI, with key conclusions listed below, including the dual role of ncRNAs in AKI, their potential as biomarkers, and the therapeutic potential of natural medicines. The right side categorizes ncRNAs into lncRNAs, miRNAs, circRNAs, and other types like snoRNAs and snRNAs, highlighting their protective and damaging factors. At the bottom, it displays natural medicines such as Ivy Saponin Elements, Quercetin, Paclitaxel, etc., indicating their therapeutic potential in AKI by modulating ncRNAs.
1 Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) occurs when blood creatinine levels rise rapidly in a short time, often with symptoms like oliguria or anuria. It is associated with renal damage, an elevated risk of coronary artery disease and chronic renal disease, affecting around 20% of hospitalized patients (Peerapornratana et al., 2019). Despite this significant incidence, AKI management is often inadequate, and reliable early identification markers are lacking. Thus, it is essential to pinpoint effective biological markers for AKI’s onset and progression for timely intervention. Non-coding RNA (ncRNA), which is a potential therapeutic target and diagnostic biomarker for AKI, is increasingly shown to be important in this process. The goal of this paper is to give a thorough overview of ncRNAs in AKI, focusing on lncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs, and evaluates their potential to serve as trustworthy biomarkers for the condition.
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have emerged as pivotal regulators in various biological processes, with lncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs being the most extensively studied types. These ncRNAs have been well-documented to play crucial roles in kidney physiology and pathophysiology, making them promising candidates for biomarker discovery and therapeutic development. Accumulating evidence has highlighted their involvement in the complex mechanisms underlying AKI. For instance, lncRNAs have been reported to regulate kidney cell proliferation and apoptosis, circRNAs have been implicated in modulating renal inflammatory responses, and miRNAs have been linked to kidney fibrosis and repair processes (Chang et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2020). In light of this growing body of evidence, we focus on these three types of ncRNAs to provide a comprehensive understanding of their roles in AKI and to explore their potential clinical applications.
2 Classification and role of noncoding RNAs
Advancements in high-throughput sequencing have increased interest in ncRNAs, which make up over 90% of RNAs in the human genome. They can be classified into structural and regulatory categories. Small ncRNAs are defined as those under 50 nucleotides, including small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs), and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs). Intermediate-length ncRNAs include small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA). Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have a closed-loop structure, whereas long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are longer than 200 nucleotides (Good, 2023). Compared to messenger RNAs (mRNAs), ncRNAs are often more crucial in disease development. Acting as competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs), they influence various physiopathologic processes; for example, circPDK1 enhances glucose metabolism in pancreatic cancer by sponging miR-628-3p (Lin et al., 2022). Moreover, ncRNAs can interact with proteins; lncRNA SNHG17 stabilizes c-Myc proteins, promoting cell proliferation (Liu J. Y. et al., 2021). NcRNAs also influence protein translation, with modifications such as N6-methyladenosine affecting circRNA function in response to cellular stress, which may impact miRNA interactions (Wang X. et al., 2021). Recent studies suggest some lncRNAs and circRNAs may also perform translational functions, marking a new area of research (Wu et al., 2020). Their diverse roles extend to various diseases, including renal disease, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
3 ncRNA and AKI
Recent studies have emphasized the regulatory functions of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the transcription and translation of proteins, with a particular focus on their altered expression patterns in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (SA-AKI). Evidence suggests that abnormal levels of lncRNAs, miRNAs, and circRNAs play a role in the development and course of AKI. This paper summarizes current research on these ncRNA types, describing the molecular mechanisms, functional roles, and expression patterns of each. NcRNAs are anticipated to become novel therapeutic targets or biomarkers for early detection and prognostic assessment of AKI (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1

Dual Role of Non-coding RNAs in Acute Kidney Injury. The figure shows the dual role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in acute kidney injury (AKI). On the left are protective ncRNAs like lncRNA, miRNA, and circRNA that help reduce kidney damage and aid recovery. On the right are damaging ncRNAs that may worsen kidney injury and contribute to AKI’s progression. It lists specific ncRNAs and their roles in AKI. (Created with FigDraw).
3.1 lncRNA
Initially, lncRNAs were considered transcriptional noise from RNA polymerase II due to their lack of an open reading frame (Uszczynska-Ratajczak et al., 2018). However, high-throughput sequencing has revealed their significance at various embryonic stages. The subcellular localization of lncRNAs determines their functional roles: nuclear lncRNAs regulate mRNA translation, splicing, localization, and transcription, while cytoplasmic lncRNAs can act as “miRNA sponges” to control mRNA degradation (Gil and Ulitsky, 2020). It's getting clearer how lncRNAs function in the pathophysiology of AKI. As summarized in Table 1, we classified findings from studies on lncRNAs in AKI into protective and detrimental factors based on their effects.
TABLE 1
| lncRNA | Sample type | Expression | Functional role | Signaling pathway/target gene | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DANCR | Serum and cellular | Downregulates | Increases cell viability and prevents inflammatory reaction and apoptosis caused by LPS | miR-214/KLF6 | Zhao et al. (2020) |
| GAS5 | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulates | Inhibits cellular pyroptosis | miR-579-3p/SIRT1/PGC-1alpha/Nrf2 | Ling et al. (2021) |
| GAS5 | Kidney tissues and cells | Upregulates | Promotes apoptosis | miR-1/TSP-1 | Geng et al. (2020) |
| 9935 | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulates | Inhibits p53-mediated apoptosis | HuR/Tp53 | Ding et al. (2021) |
| LINC00052 | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulates | Promotes cell proliferation and inhibits hypoxia-induced apoptosis | miR-532-3p/Wnt/β-linker protein | Li et al. (2020) |
| DLX6-AS1 | Serum and cells | Upregulation | Releases inflammatory factors and promotes cellular pyroptosis | miR-223-3p/NLRP3 | Tan et al. (2020) |
| RMRP | Serum and cellular | Upregulates | Promotes LPS-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response | NLRP3/miR-206/DDX5 | Zhang et al. (2021a) |
| PVT1 | Kidney tissue, serum and cells | Upregulates | Inhibits cell viability and promotes cellular pyroptosis, apoptosis and inflammatory responses | miR-20a-5p/NLRP3 miR-17-5p/NF-κB | Deng et al. (2021), Yuan et al. (2021) |
| SNHG14 | Kidney tissue, serum and cells | Upregulation | Inhibits cell viability and promotes inflammation and oxidative stress | miR-124-3p/MMP2 | Xue et al. (2021) |
| XIST | Kidney tissues and cells | Upregulates | Delays cellular damage | miR-142-5p/PDCD4 | Tang et al. (2020) |
| LINC00963 | Kidney tissues and cells | Upregulates | Promotes apoptosis | miR-128-3p/JAK2/STAT1 | Xie et al. (2020) |
| MEG3 | Cells | Upregulates | Activates cellular autophagy and induces apoptosis | MEG3/miR-145-5p/RTKN/Wnt/β-catenin/c-MYC | Liu et al. (2021b) |
The possible molecular mechanisms and functional roles of lncRNA in AKI.
3.1.1 lncRNAs as protective factors
Multiple studies report altered lncRNA expression in AKI contexts. Evidence quality varies across experimental models. Human biomarker studies show that DANCR serum levels are downregulated in AKI patients versus controls. Zhao et al. reported that DANCR “sponges” miR-214 in vitro (Zhao et al., 2020). Its clinical utility as a biomarker requires validation of sensitivity and specificity. LINC00052 plasma levels are reduced in AKI patients. Li et al. found that LINC00052’s correlation with hypoxia and Wnt/β-catenin signaling remains unvalidated in human tissues (Li et al., 2020).
Rodent models provide mechanistic insights. GAS5 is downregulated in SA-AKI mouse kidneys and LPS-HK2 cells. Ling et al. observed that this correlates with cell death via the miR-579-3p/SIRT1 axis (Ling et al., 2021). However, Geng et al. discovered that GAS5 is upregulated in I/R-AKI kidneys and promotes apoptosis via miR-21/TSP-1 (Geng et al., 2020). This discrepancy highlights model dependence. NONRATG019935.2 (9935) is downregulated in SA-AKI rat kidneys. Ding et al. demonstrated that overexpression of 9935 prevents kidney tubular epithelial cells from undergoing apoptosis. It interacts with p53 and stabilizes Tp53 mRNA (Ding et al., 2021).
Critical knowledge gaps remain. No established lncRNA “signature” for AKI staging exists due to fragmented studies. The origin of circulating lncRNAs, such as DANCR and LINC00052, is unclear. They may result from passive leakage due to kidney damage or active secretion. Therapeutic modulation, such as LINC00052 overexpression in rodents, lacks in vivo delivery strategies and safety data.
3.1.2 lncRNAs as damaging factors
Conversely, certain lncRNAs exhibit elevated expression in AKI and may drive inflammation and renal damage (Table 1). Evidence from human studies provides initial biomarker insights. In SA-AKI patients, serum DLX6-AS1 levels rise and correlate with creatinine—a clinical indicator of kidney dysfunction (Tan et al., 2020). This suggests DLX6-AS1 could serve as a liquid biopsy biomarker. Similarly, RMRP increases in patient serum and LPS-exposed HK-2 cells. When silenced, RMRP reduces inflammation and cell death in mice, hinting at its pathogenic role (Zhang X. et al., 2021).
Animal and cellular models reveal mechanistic actions. PVT1, overexpressed in SA-AKI mouse kidneys and human serum, “recruits” miR-20a-5p to activate NLRP3, fueling pyroptosis and inflammation (Deng et al., 2021; Yuan et al., 2021). In HK-2 cells, SNHG14 acts as a miR-124-3p “sponge” to elevate MMP2, worsening ischemia-reperfusion injury (Xue et al., 2021). XIST, upregulated in I/R-AKI, suppresses miR-142-5p and elevates PDCD4—a cell death promoter (Tang et al., 2020).
Controversies and knowledge gaps persist. LINC00963 targets miR-128-3p to block apoptosis in AKI (Xie et al., 2020), while MEG3 activates Wnt/β-catenin to exacerbate injury (Liu D. et al., 2021). These opposing roles highlight context-dependent functions. Most mechanisms (e.g., PVT1/NF-κB (Yuan et al., 2021)) are cell-derived; their relevance in human tissues remains unverified. Critically, these lncRNAs are detected in blood, but further research is needed to determine whether they originate from damaged kidneys or actively signal disease progression. Future studies should focus on validating these lncRNAs in larger human cohorts and exploring their potential as therapeutic targets.
3.2 miRNA
MiRNAs target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and regulate their expression, playing a crucial role in various pathogenic diseases. Changes in miRNA expression levels reflect disease activity and can serve as biomarkers for diagnosing conditions such as inflammation and cancer (Condrat et al., 2020). Studies have confirmed alterations in serum and urine miRNA levels in acute kidney injury (AKI), suggesting their potential as biotherapeutic agents and their significance in AKI development. Monitoring miRNA expression could aid in the identification and management of AKI (Mahtal et al., 2022).
3.2.1 miRNAs as protective factors
In the context of AKI, blood-derived and tissue-derived miRNAs reach renal tissues, binding to target genes to suppress apoptotic signals and inflammatory mediators. In the rat model of SA-AKI, miR-22-3p is significantly diminished, reducing inflammation and apoptosis by targeting PTEN (Wang X. et al., 2020). Zhang et al. found that SA-AKI patients have downregulated miR-22-3p in serum and urine, with a negative correlation between miR-22-3p levels and renal impairment indicators, suggesting it as a prognostic biomarker for 28-day survival (Zhang H. et al., 2021).
miR-93 protects kidney tubular epithelial cells from LPS-induced apoptosis via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway (Zhan et al., 2021). Antioxidant miRNAs like miR-30c-5p and miR-223-3p inhibit cellular pyroptosis (Li et al., 2021; Gao M. et al., 2022). However, Liu et al. found no association between renal damage biomarkers and miR-574-5p, indicating that miRNAs could aid in AKI diagnosis and management (Liu S. et al., 2021).
In bone marrow-derived dendritic cells, I/R injury reduces miR-21 expression, but miR-21 overexpression decreases renal injury and I/R-AKI by reducing proinflammatory factor synthesis and release (Jia et al., 2020). A recent study showed that NF-κB activation and elevated miR-26a-5p levels suppress renal inflammation by inhibiting IL-6 (Chen et al., 2022). These findings indicate that specific miRNAs act as protective factors and valuable biomarkers for AKI.
3.2.2 miRNAs as damaging factors
Conversely, certain miRNAs overexpression can activate inflammatory pathways and accelerate AKI progression. According to a large dataset study, serum miR-452 levels are elevated in SA-AKI patients, demonstrating 63.83% diagnostic sensitivity. These levels show a positive correlation with serum creatinine and urinary miR-452 (Liu et al., 2020a). Similarly, increased blood miR-210 and miR-494 levels predict poor AKI patient prognosis (Lin et al., 2019).
Animal and cellular studies provide mechanistic insights. In LPS-induced SA-AKI rats, elevated miR-128-3p levels correlate with increased inflammatory mediators and apoptosis. Notably, inhibiting miR-128-3p exacerbates inflammation (Wang L. et al., 2020). miR-376b collaborates with NF-κB to promote cell death in mice, and its decrease in SA-AKI mice’s urine and renal tubular cells is linked to NF-κB activation (Liu et al., 2020b). miR-543 and miR-199b-3p are upregulated in serum, renal tissues, and cells, worsening AKI inflammation and cell death (Zhang et al., 2022; Tian et al., 2021) (Table 2).
TABLE 2
| miRNA | Sample type | Expression | Functional role | Signaling pathway/target gene | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-22-3p | Kidney tissue and cells | Downregulates | Inhibits inflammation and apoptosis | miR-22-3p/PTEN | Wang et al. (2020a) |
| miR-93 | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulated | Inhibits apoptosis and inflammatory reactions | PTEN/AKT/mTOR | Zhan et al. (2021) |
| miR-30c-5p | Renal tissues and cells | Downregulation | Inhibits cellular pyroptosis | miR-30c-5p/TXNIP | Li et al. (2021) |
| miR-223-3p | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulated | Inhibition of cellular pyroptosis | NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β | Gao et al. (2022a) |
| miR-574-5p | Cellular | Downregulates | Increased cell viability | Scr, Cys-C, KIM-1 | Liu et al. (2021c) |
| miR-21 | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulates | Reduces inflammatory response | miR-21/CCR7 | Jia et al. (2020) |
| miR-26a-5p | Kidney tissues and cells | Downregulates | Inhibition of renal inflammatory response | NF-κB/miR-26a-5p/IL-6 | Chen et al. (2022) |
| miR-128-3p | Renal tissues and cells | Upregulates | Promotes inflammatory infiltration, increases inflammatory factor expression and decreases cell viability | miR-128-3p/NPR1 | Wang et al. (2020b) |
| miR-452 | Serum, urine and cells | Upregulates | Induction of septic AKI | NF-κB | Liu et al. (2020a) |
| miR-210, miR-494 | serum | Upregulation | Induces septic AKI | -- | Lin et al. (2019) |
| miR-376b | Urine and cells | Upregulates | Promotes inflammation and cell necrosis, exacerbates kidney injury | NF-κB/miR-376b/NFKBIZ | Liu et al. (2020b) |
| miR-543 | Cellular | Upregulated | Promotes inflammation and apoptosis | miR-543/Bcl-2 | Zhang et al. (2022) |
| miR-199b-3p | Kidney tissues and cells | Upregulated | Promotes renal tubular cell edema and necrosis, inflammatory infiltration | miR-199b-3p/Nrf2 | Tian et al. (2021) |
The possible molecular mechanisms and functional roles of miRNA in AKI.
Despite these findings, significant gaps remain. The origin of circulating miRNAs—whether from kidney leakage or active signaling—requires further investigation. Species differences, such as miR-376b′s divergent trends in mice and humans, highlight the need for cross-species validation. Most mechanistic insights, including miR-376b/NF-κB interactions, derive from cellular studies and require human tissue validation. Future research should focus on validating these miRNAs in larger human cohorts and exploring their therapeutic potential. Addressing these gaps will enhance our understanding of miRNAs in AKI and facilitate their translation into clinical applications.
MiRNAs play a complex dual role in AKI. By targeting specific genes, they regulate inflammation and cell death, exhibiting either protective effects or disease-promoting activities. While current evidence supports the potential of miRNAs in AKI diagnosis and prognosis, further research is required to fully elucidate their mechanisms of action and origin prior to clinical application. Moreover, the consistency of data across species requires additional validation. Future studies should aim to confirm the roles of these miRNAs in larger patient populations and investigate their potential as therapeutic targets, with the goal of achieving new breakthroughs in AKI treatment.
3.3 circRNAs
Because circRNAs are more stable than other non-coding RNAs, they are becoming more and more popular as indicators for diagnosis and prognosis, such as miRNAs. Their differential expression in AKI and association with competitive endogenous RNAs make circRNAs promising candidates for therapeutic targeting. To facilitate circRNA-based therapies, new delivery methods are necessary for effective translation into target organs. As our understanding of circRNA’s role in AKI pathophysiology grows, it may significantly impact the assessment and management of the condition.
3.3.1 circRNAs as protective factors
Some circRNAs function as protective factors in AKI, delivering protective signals in blood tests and acting as cellular shields. For example, circ-0091702 levels decrease in the serum of LPS-AKI patients. When active, it serves as a sponge for miR-545-3p, protecting THBS2 and shielding kidney cells from damage (Tan and Bei, 2021). Similarly, circ-YAP1 levels decline in the serum of AKI patients and in injured cells. Enhancing circ-YAP1 helps mitigate fibrosis and inflammation via the miR-21-5p/PI3K pathway (Huang et al., 2020).
These circRNAs also function as cellular guardians. circ-VMA21 exerts protective effects in HK-2 cells by regulating the miR-7-5p/PPARA axis, thereby combating oxidative stress and cell death (Wang et al., 2022). circ-PRKCI binds to miR-106b-5p, freeing GAB1 to aid in cell repair (Xiong et al., 2021). Additionally, circ-0068888 and circ-0008882 jointly inhibit inflammation by respectively targeting miR-21-5p and miR-155-5p (Wei et al., 2021; You and Kuang, 2023).
However, most evidence originates from cellular studies rather than patient-based research. For instance, the protective roles of circ-VMA21 and circ-PRKCI have been predominantly demonstrated in cell models. While the decrease of circ-YAP1 in serum suggests its potential as an AKI biomarker, large-scale patient studies are still required to confirm this.
In summary, these circRNAs show potential as protective factors in AKI, but further validation in patient cohorts is necessary to solidify their role as diagnostic tools.
3.3.2 circRNAs as damaging factors
Some circRNAs act as damaging factors in AKI, serving as both circulating biomarkers and intracellular molecular saboteurs. Clinical studies have shown that circ-0020339 is significantly upregulated in the serum of patients with sepsis-associated AKI (SA-AKI), and its levels correlate with creatinine concentrations. Silencing circ-0020339 improves survival in murine models and reduces LPS-induced cell death and inflammation in HK-2 cells, highlighting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker (Wang et al., 2023). Similarly, the elevation of circ_0114427 in patient blood worsens inflammation through the miR-495-3p/TRAF6/NF-κB axis (Xu L. et al., 2022).
At the cellular level, these circRNAs drive renal injury through distinct pathological mechanisms. Circ-RASGEF1B promotes inflammation and apoptosis via the miR-146a-5p/Pdk1 axis, directly reducing tubular cell viability (Cao et al., 2021). Circ-UBE2D2 sponges miR-370-3p to upregulate NR4A3, triggering apoptosis in LPS-exposed HK-2 cells (Huang and Zheng, 2022). Circ-AKT3 impairs cellular repair by disrupting the miR-144-5p/Wnt/β-catenin pathway, exacerbating ischemic tubular damage (Xu Y. et al., 2022). Circ-ITGB1, activated by GATA-binding protein, induces inflammatory responses through the miR-328-3p/PIM1 axis (Gao Y. et al., 2022). The mouse-specific mmu_circ_0000943 aggravates oxidative stress and apoptosis by sponging miR-377-3p and overexpressing Egr2 (Huang et al., 2022). Circ-SNRK activates MAPK signaling (p-JNK/p38), promoting inflammation and apoptosis in renal tissues (Meng et al., 2022). Notably, context-dependent roles exist. For example, circ_0023404 suppresses inflammation by targeting IL-6R in some settings (Xu et al., 2021), yet may promote damage in others—underscoring microenvironmental influences on circRNA functionality (Table 3).
TABLE 3
| circRNA | Sample type | Expression | Functional role | Signaling pathway/target gene | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circ-0091702 | Cellular | Downregulates | Attenuates cellular damage | miR-545-3p/THBS2 | Tan and Bei (2021) |
| circ-VMA21 | Cells | Downregulates | Inhibits oxidative damage, inflammatory processes, and cell death | miR-7-5p/PPARA | Wang et al. (2022) |
| circ-PRKCI | Cells | Downregulates | Inhibits apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress | miR-106b-5p/GAB1 | Xiong et al. (2021) |
| circ-YAP1 | Serum and cells | Downregulates | Reduces inflammatory response, inhibits cellular damage | miR-21-5p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR | Huang et al. (2020) |
| circ-0068888 | Cellular | Downregulation | Inhibits inflammatory response and oxidative stress | miR-21-5p/NF-κB | Wei et al. (2021) |
| circ-0008882 | Cells | Downregulates | Attenuates cellular damage | miR-155-5p/PDE7A | You and Kuang (2023) |
| circ-RASGEF1B | cellular | Upregulates | Encourages inflammatory cell response and cell death | MicroRNA-146a-5p/Pdk1 | Cao et al. (2021) |
| circ-UBE2D2 | Cells | Upregulates | Inhibits cell viability, promotes apoptosis | miR-370-3p/NR4A3 | Huang and Zheng (2022) |
| circ-0020339 | Serum and cells | Upregulates | Promotes apoptosis and inflammatory responses | miR-17-5p/IPMK TRAF6/p-AKT/p-IKK/p-IκBα/p-p65 | Wang et al. (2023) |
| circ_0023404 | Cell | Upregulation | Stimulates secretion of inflammatory factors and promotes inflammatory responses | miR-136/IL-6R | Xu et al. (2021) |
| Circ_0114427 | Serum and cellular | Upregulates | Inhibits cell viability and promotes inflammation responses and necrosis | miR-495-3p/TRAF6/NF-κB/p65 | Xu et al. (2022a) |
| Circ-AKT3 | Renal tissues and cells | Upregulated | Promotes oxidative damage and apoptosis | miR-144-5p/Wnt/β-catenin | Xu et al. (2022b) |
| circ-ITGB1 | Cells | Upregulated | Promotes inflammation responses and necrosis | miR-328-3p/PIM1 | Gao et al. (2022b) |
| mmu_circ_0000943 | Kidney tissue and cells | Upregulated | Stimulates inflammatory response and promotes apoptosis | miR-377-3p/Egr2 | Huang et al. (2022) |
| circ-SNRK | Kidney tissue, serum and cells | Upregulates | Promotes inflammatory factor secretion and apoptosis | MAPK/p-JNK, p-38 | Meng et al. (2022) |
The possible molecular mechanisms and functional roles of circRNA in AKI.
In summary, these circRNAs play a significant role in AKI by influencing various pathological processes such as inflammation, apoptosis, and cellular repair. Their dual role as biomarkers and active participants in disease progression makes them potential targets for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in AKI. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate their mechanisms and clinical applications.
3.4 Other types of ncRNA in AKI
In addition to lncRNAs, other non-coding RNAs, such as small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), warrant exploration for their potential roles in acute kidney injury (AKI) (Zhu et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2019). SnoRNAs primarily function in the chemical modification of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and have been implicated in various cellular processes, including gene expression regulation. Emerging evidence suggests that specific snoRNAs may influence renal cell survival and apoptosis during AKI by modulating rRNA stability and facilitating ribosome biogenesis. Changes in snoRNA expression profiles have been linked to inflammatory responses in kidney tissues, indicating a potential role in AKI pathophysiology.
In a similar vein, snRNAs are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing, which results in the production of functional mRNA. Anomalies in the splicing of genes related to stress responses and renal function may arise from dysregulation of snRNA, contributing to AKI development. However, research on snoRNAs and snRNAs in AKI is limited, and this section does not serve as the primary focus of this study. Future investigations will aim to provide further insights into the contributions of these ncRNAs, enhancing our understanding of renal injury mechanisms and improving clinical management strategies.
4 Developments in the research of natural medicines controlling ncRNA for the therapy of AKI
Research on non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) is gaining traction in the field of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Various natural compounds and herbal extracts show promise in mitigating renal injury and apoptosis by modulating ncRNA activity (Figure 2). This section summarizes the effects of these herbal extracts on protein expression via ncRNA and their potential for treating acute kidney injury (AKI).
FIGURE 2

Illustration of Non-coding RNA Functions and Natural Medicine Regulations in Acute Kidney Injury. The figure illustrates the roles of natural medicines in modulating ncRNAs for the therapy of acute kidney injury (AKI). Various natural compounds, including quercetin, paclitaxel, ginsenosides, baicalin, and resveratrol, are shown to influence ncRNA activity. These compounds can affect lncRNAs and circRNAs, which in turn regulate inflammation, apoptosis, and other cellular processes. (Created with FigDraw).
4.1 Quercetin
Quercetin, abundant in Chinese herbs like Radix Bupleuri and mulberry leaf, offers anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and antioxidant benefits. It protects kidneys by raising glutathione (GSH) levels and cutting lipid ROS and malondialdehyde, thus easing ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) -induced AKI. Quercetin also inhibits HIF-1α in the NEAT1/HMGB1 pathway, reducing cell damage. This suggests quercetin could be a new therapeutic target (Wang Y. et al., 2020; Luo et al., 2022).
It is interesting to note that quercetin’s ability to modulate the NEAT1/HMGB1 pathway may have broader implications for AKI treatment. By targeting this pathway, quercetin not only reduces oxidative stress but also attenuates inflammation, which are both critical factors in the progression of AKI. However, further research is required to fully understand the extent of quercetin’s effects and its potential for clinical application.
4.2 Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel, the first plant-derived chemotherapeutic agent from the redbud tree bark, is widely used in oncology. Recent studies show it enhances cell proliferation and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Paclitaxel mitigates LPS-induced AKI by altering the lnc-MALAT1/miR-370-3p/HMGB1 axis, suggesting a potential therapy for sepsis -associated AKI (Xu et al., 2020).
Paclitaxel’s role in regulating the lnc-MALAT1/miR-370-3p/HMGB1 axis highlights its potential as a therapeutic agent for AKI. The ability to modulate this specific axis could provide a targeted approach to reducing inflammation and preventing further kidney damage in patients with sepsis. However, the long-term effects and safety of paclitaxel in AKI treatment need to be further evaluated.
4.3 Ivy saponin elements
Ivy saponinogenin (HDG), a pentacyclic triterpenoid saponin in astragalus mongholicus, shows strong anti-inflammatory properties across various diseases. Kehuan Xie used HDG to treat LPS-induced kidney inflammation in renal tubular epithelial cells, both in vivo and in vitro. Transcriptome sequencing revealed significant changes in lncRNA expression, especially lncRNA-A330074k22Rik (A33). Ivy saponins also reduce cisplatin-induced renal injury via the A330074k22Rik/Axin2/β-catenin pathway (Xie et al., 2022).
The significant changes in lncRNA expression observed with HDG treatment indicate a potential therapeutic mechanism for ivy saponins in AKI. By targeting specific lncRNAs and their associated signaling pathways, ivy saponins may offer a novel approach to reducing renal injury.
4.4 Baicalin
Baicalin, a bioactive flavonoid from Scutellaria baicalensis, is known for its anti-inflammatory, diuretic, and antibacterial properties. It significantly improved HK-2 cell viability and reduced levels of inflammatory markers such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Baicalin downregulates cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, TXNIP, NLRP3, and miR-223-3p. Its mechanism likely involves suppressing the TXNIP/NLRP3/miR-223-3p pathway (Sun et al., 2020).
Baicalin’s multi-faceted approach to reducing inflammation and improving cell viability makes it a promising candidate for AKI treatment. By targeting multiple components of the inflammatory pathway, baicalin may provide a more comprehensive therapeutic effect. However, the clinical feasibility of baicalin as a treatment option in AKI patients remains to be determined through further studies.
4.5 Resveratrol
Resveratrol, present in over 70 plant species, has diverse biological effects. It lowers TNF-α in AKI rat models and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines. Resveratrol inhibits MALAT1 expression, protecting kidneys via the lncRNA MALAT1/miR-205 axis (Wang B. et al., 2021). It also regulates pathways linked to circ_0074371, which is elevated in LPS-treated HK-2 cells and AKI patients. Resveratrol exerts nephroprotective effects through the circ_0074371/miR-145-5p/IPMK pathway, reducing cellular apoptosis and oxidative stress (Zhu and Wu, 2024).
Resveratrol’s ability to modulate both lncRNA and circRNA pathways offers a dual therapeutic approach for AKI. By targeting these specific RNA networks, resveratrol may provide a more effective treatment strategy. However, the translation of these findings into clinical practice requires additional research to confirm resveratrol’s efficacy and safety in human subjects.
4.6 Ginsenoside
Ginsenosides, the main active components of ginseng, are used in TCM for their anti-cancer and immunomodulatory effects. Ginsenoside Rd protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing FoxO1 and stimulating the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Other ginsenosides like Rg1 and Rg3 decrease renal injury markers such as creatinine and urea nitrogen (Yao et al., 2022; Chang et al., 2023).
Ginsenosides’ dual action of reducing renal injury markers and protecting renal structures makes them potential therapeutic agents for AKI. Their ability to modulate both the FoxO1 and Nrf2 pathways suggests a comprehensive approach to reducing kidney damage. However, the specific mechanisms and optimal dosages for different ginsenosides in AKI treatment need to be further explored.
In summary, several ncRNAs show potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in AKI. Natural compounds like quercetin, paclitaxel, and resveratrol modulate specific RNA networks, offering new therapeutic approaches for AKI. However, the connection between natural medicine and ncRNA regulation needs more concrete evidence. Future studies should build on these examples and explore additional natural compounds that can specifically target ncRNA networks involved in AKI.
5 Discussion
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have shown significant promise as biomarkers and therapeutic targets for acute kidney injury (AKI). However, there are also limitations and inconsistencies in the current research that need to be critically evaluated.
5.1 Challenges in clinical applicability of ncRNA biomarkers
The translation of ncRNA biomarkers from preclinical models to clinical practice faces several unresolved challenges. In terms of sensitivity and specificity, such as miR-452 in serum showing 63.83% sensitivity for AKI diagnosis (Liu et al., 2020a), this finding lack validation in large human cohorts. Moreover, cross-reactivity with non-renal conditions like systemic inflammation may compromise the specificity of ncRNA biomarkers.
Diagnostic standardization is another major challenge. Current AKI diagnostics mainly rely on serum creatinine and urine output. However, ncRNA-based detection requires standardized protocols for sample collection, RNA isolation, and quantification. The variability in techniques, such as RNA-seq versus qPCR, contributes to inconsistent thresholds, as seen in the upregulation of circ-0020339 in sepsis-associated AKI (SA-AKI) (Wang et al., 2023).
Additionally, the dynamic range of ncRNAs poses a challenge. The levels of ncRNA may fluctuate with different stages of AKI; however, longitudinal studies defining its temporal dynamics are still scarce.
5.2 Mechanistic gaps and conflicting findings
There are several pathways where the mechanistic depth is lacking or contradictory roles are observed. Crucially, the dysregulation of ncRNAs is intrinsically linked to the development of hallmark AKI pathological features, including acute tubular injury (ATI), interstitial inflammation, and the initiation of maladaptive repair processes that can lead to fibrosis. The dualistic functions of ncRNAs are evident. For instance, GAS5 acts as a protective factor in SA-AKI by inhibiting pyroptosis via the miR-579-3p/SIRT1 pathway, yet it promotes apoptosis in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-AKI through the miR-21/TSP-1 pathway (Ling et al., 2021; Geng et al., 2020). This discrepancy may arise from model-specific stressors, such as sepsis versus ischemia, highlighting the need for context-dependent pathway validation.
Similarly, miR-128-3p exacerbates inflammation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced AKI but attenuates injury in I/R models via JAK/STAT modulation (Xie et al., 2020; Wang L. et al., 2020). These contrasting roles suggest that the microenvironment significantly influences ncRNA functionality and its downstream pathological consequences. The net effect on tubular cell survival, inflammatory infiltration, and interstitial damage varies depending on the ncRNA and the injury context.
Furthermore, the link between ncRNA dysregulation and the progression towards fibrosis, although more characteristic of CKD, is an emerging concern in AKI recovery. Some ncRNAs implicated in sustained inflammation and impaired tubular repair could potentially lay the groundwork for interstitial fibrosis if the injury persists or repair is dysregulated. While not the primary focus of acute injury, understanding how early ncRNA changes might predispose to or initiate fibrotic pathways is a critical mechanistic gap.
Unresolved issues also exist in pathway crosstalk relevant to pathology. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is frequently linked to lncRNAs and miRNAs (Zhang X. et al., 2021; Gao M. et al., 2022). However, upstream regulators and feedback loops remain underexplored. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is also variably reported as protective or damaging, indicating cell-type-specific signaling outcomes that influence tubular repair versus dysrepair and potential fibrotic transformation (Li et al., 2020; Liu D. et al., 2021).
In summary, while numerous ncRNAs are dysregulated in AKI, explicitly linking their altered expression to the causation and progression of specific pathological hallmarks—such as acute tubular necrosis/apoptosis, interstitial inflammatory cell influx, oxidative stress-mediated damage, and the nascent stages of fibrosis—remains an area requiring deeper investigation.
5.3 Barriers to therapeutic translation
When it comes to therapeutic translation, there are several barriers to consider. Delivery and specificity are key challenges. While natural medicines like baicalin and resveratrol have shown efficacy in modulating ncRNAs in vitro, targeted delivery to renal tubules in vivo remains unresolved (Sun et al., 2020; Wang B. et al., 2021; Zhu and Wu, 2024). Additionally, off-target effects of ncRNA inhibitors, such as antagomiRs, may disrupt physiological gene networks.
Another barrier is compensatory mechanisms. Silencing a single ncRNA often does not fully rescue AKI phenotypes, suggesting redundant roles within competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks. This implies that combinatorial targeting strategies may need to be investigated.
5.4 Future perspectives
Despite the limitations and challenges, the potential of ncRNAs in AKI research remains promising. In the future, we need large-scale trials to validate ncRNA therapies and develop better delivery systems. We must deeply explore ncRNA regulatory networks to understand AKI better and find new treatments. Also, it's key to link ncRNA signatures to specific AKI pathological features. Using techniques like in situ hybridization on kidney tissue can map ncRNA expression in damaged areas, inflammation, or early fibrosis. This will clarify ncRNAs’ role in AKI pathology and improve their use as biomarkers.
6 Summary
This review has provided a comprehensive overview of the role of ncRNAs in AKI, focusing on lncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs. We have highlighted their dualistic nature in AKI pathogenesis, acting as both protective and detrimental factors. The integration of natural medicine with ncRNA regulation offers a novel perspective for the development of therapeutic strategies. Moreover, it is important to critically evaluate the limitations and inconsistencies in the current research. Future studies should aim to bridge the translational gap between preclinical models and clinical practice, address the challenges in using ncRNAs as biomarkers, and explore the potential of ncRNA-targeting natural compounds through well-designed clinical trials. Furthermore, the application of bioinformatics and systems biology approaches will be instrumental in unraveling the complex ncRNA networks in AKI. Continued research in this field has the potential to significantly advance our understanding of AKI pathogenesis and pave the way for innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Ultimately, this could enhance patient outcomes and provide a clearer understanding of the complex mechanisms governing kidney injury.
Research into herbal treatments in the context of ncRNA regulation in AKI is still in its early phases. Current research primarily focuses on isolated compounds and extracts derived from Chinese herbs, with less emphasis on complex herbal formulations or proprietary Chinese medicines that are frequently employed in clinical settings. This gap highlights the need for more comprehensive studies that investigate the synergistic effects of multi-ingredient herbal formulations on ncRNA regulation and their subsequent impact on AKI outcomes. Furthermore, bioinformatics tools can play a crucial role in advancing this field. By predicting gene interactions with ncRNAs, bioinformatics approaches could accelerate the identification of potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. These insights can lead to the development of innovative diagnostic applications and targeted treatments for AKI.
Statements
Author contributions
YG: Writing – original draft. YZ: Writing – original draft, Data curation. HZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YX: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YF: Methodology, Writing – original draft. DZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology. HY: Writing – original draft, Investigation. YQ: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. BY: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Based on HIF-1α/Wnt signaling pathway to explore the role and mechanism of Kidney Supporting Formula in intervening the transformation of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease No.: 2022KJ168.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Cao J. Shi D. Zhu L. Song L. (2021). Circ_RASGEF1B promotes LPS-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response by targeting MicroRNA-146a-5p/Pdk1 axis in septic acute kidney injury cell model. Nephron145 (6), 748–759. 10.1159/000517475
2
Chang S. Chang M. Liu G. Xu D. Wang H. Sun R. et al (2022). LncRNA OIP5-AS1 reduces renal epithelial cell apoptosis in cisplatin-induced AKI by regulating the miR-144-5p/PKM2 axis. Biomed. J.45 (4), 642–653. 10.1016/j.bj.2021.07.005
3
Chang S. N. Park J. G. Kang S. C. (2023). Therapeutic propensity of ginsenosides Rg1 and Rg3 in rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury and renohepatic crosstalk in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol.115, 109602. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109602
4
Chen Y. Zhou X. Wu Y. (2022). The miR-26a-5p/IL-6 axis alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting renal inflammation. Ren. Fail.44 (1), 551–561. 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2056486
5
Condrat C. E. Thompson D. C. Barbu M. G. Bugnar O. L. Boboc A. Cretoiu D. et al (2020). miRNAs as biomarkers in disease: latest findings regarding their role in diagnosis and prognosis. Cells9 (2), 276. 10.3390/cells9020276
6
Deng L. T. Wang Q. L. Yu C. Gao M. (2021). lncRNA PVT1 modulates NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in septic acute kidney injury by targeting miR-20a-5p. Mol. Med. Rep.23 (4), 271. 10.3892/mmr.2021.11910
7
Ding Y. Zhou D. Y. Yu H. Zhu T. Guo F. He Y. et al (2021). Upregulation of lncRNA NONRATG019935.2 suppresses the p53-mediated apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in septic acute kidney injury. Cell death and Dis.12 (8), 771. 10.1038/s41419-021-03953-9
8
Gao M. Li H. Liu Q. Ma N. Zi P. Shi H. et al (2022a). KLF6 promotes pyroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in septic acute kidney injury. Shock (Augusta, Ga.)57 (3), 417–426. 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001881
9
Gao Y. Xu W. Guo C. Huang T. (2022b). GATA1 regulates the microRNA-328-3p/PIM1 axis via circular RNA ITGB1 to promote renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in HK-2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med.50 (2), 100. 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5156
10
Geng X. Song N. Zhao S. Xu J. Liu Y. Fang Y. et al (2020). LncRNA GAS5 promotes apoptosis as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-21 via thrombospondin 1 in ischemic AKI. Cell death Discov.6, 19. 10.1038/s41420-020-0253-8
11
Gil N. Ulitsky I. (2020). Regulation of gene expression by cis-acting long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet.21 (2), 102–117. 10.1038/s41576-019-0184-5
12
Good D. J. (2023). Non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases. Genes14 (7), 1429. 10.3390/genes14071429
13
Huang T. Cao Y. Wang H. Wang Q. Ji J. Sun X. et al (2020). Circular RNA YAP1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-21-5p to secure HK-2 cells from ischaemia/reperfusion-induced injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med.24 (8), 4707–4715. 10.1111/jcmm.15142
14
Huang T. Gao Y. Cao Y. Wang Q. Dong Z. (2022). Downregulation of mmu_circ_0000943 ameliorates renal ischemia reperfusion-triggered inflammation and oxidative stress via regulating mmu-miR-377-3p/Egr2 axis. Int. Immunopharmacol.106, 108614. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108614
15
Huang Y. Zheng G. (2022). Circ_UBE2D2 attenuates the progression of septic acute kidney injury in rats by targeting miR-370-3p/NR4A3 axis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.32 (6), 740–748. 10.4014/jmb.2112.12038
16
Jia P. Pan T. Xu S. Fang Y. Song N. Guo M. et al (2020). Depletion of miR-21 in dendritic cells aggravates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB J. official Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol.34 (9), 11729–11740. 10.1096/fj.201903222RR
17
Jiang Z. H. Tang Y. Z. Song H. N. Yang M. Li B. Ni C. L. (2020). miRNA-342 suppresses renal interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by targeting SOX6. Int. J. Mol. Med.45 (1), 45–52. 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4388
18
Li X. Yao L. Zeng X. Hu B. Zhang X. Wang J. et al (2021). miR-30c-5p alleviated pyroptosis during sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via targeting TXNIP. Inflammation44 (1), 217–228. 10.1007/s10753-020-01323-9
19
Li X. Zheng P. Ji T. Tang B. Wang Y. Bai S. (2020). LINC00052 ameliorates acute kidney injury by sponging miR-532-3p and activating the wnt signaling pathway. Aging13 (1), 340–350. 10.18632/aging.104152
20
Lin J. Wang X. Zhai S. Shi M. Peng C. Deng X. et al (2022). Hypoxia-induced exosomal circPDK1 promotes pancreatic cancer glycolysis via c-myc activation by modulating miR-628-3p/BPTF axis and degrading BIN1. J. Hematol. and Oncol.15 (1), 128. 10.1186/s13045-022-01348-7
21
Lin Y. Ding Y. Song S. Li M. Wang T. Guo F. (2019). Expression patterns and prognostic value of miR-210, miR-494, and miR-205 in middle-aged and old patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Bosnian J. basic Med. Sci.19 (3), 249–256. 10.17305/bjbms.2019.4131
22
Ling H. Li Q. Duan Z. P. Wang Y. J. Hu B. Q. Dai X. G. (2021). LncRNA GAS5 inhibits miR-579-3p to activate SIRT1/PGC-1α/Nrf2 signaling pathway to reduce cell pyroptosis in sepsis-associated renal injury. Am. J. physiology. Cell physiology321 (1), C117–C133. 10.1152/ajpcell.00394.2020
23
Liu D. Liu Y. Zheng X. Liu N. (2021b). c-MYC-induced long noncoding RNA MEG3 aggravates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury through activating mitophagy by upregulation of RTKN to trigger the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell death and Dis.12 (2), 191. 10.1038/s41419-021-03466-5
24
Liu J. Y. Chen Y. J. Feng H. H. Chen Z. L. Wang Y. L. Yang J. E. et al (2021a). LncRNA SNHG17 interacts with LRPPRC to stabilize c-Myc protein and promote G1/S transition and cell proliferation. Cell death and Dis.12 (11), 970. 10.1038/s41419-021-04238-x
25
Liu S. Zhao L. Zhang L. Qiao L. Gao S. (2021c). Downregulation of miR-574-5p inhibits HK-2 cell viability and predicts the onset of acute kidney injury in sepsis patients. Ren. Fail.43 (1), 942–948. 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1939051
26
Liu Z. Tang C. He L. Yang D. Cai J. Zhu J. et al (2020b). The negative feedback loop of NF-κB/miR-376b/NFKBIZ in septic acute kidney injury. JCI insight5 (24), e142272. 10.1172/jci.insight.142272
27
Liu Z. Wang Y. Shu S. Cai J. Tang C. Dong Z. (2019). Non-coding RNAs in kidney injury and repair. Am. J. physiology. Cell physiology317 (2), C177-C188–C188. 10.1152/ajpcell.00048.2019
28
Liu Z. Yang D. Gao J. Xiang X. Hu X. Li S. et al (2020a). Discovery and validation of miR-452 as an effective biomarker for acute kidney injury in sepsis. Theranostics10 (26), 11963–11975. 10.7150/thno.50093
29
Luo M. Liu Z. Hu Z. He Q. (2022). Quercetin improves contrast-induced acute kidney injury through the HIF-1α/lncRNA NEAT1/HMGB1 pathway. Pharm. Biol.60 (1), 889–898. 10.1080/13880209.2022.2058558
30
Ma T. Wu J. Chen Z. (2023). Regulatory networks of circRNA-centred ceRNAs in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Epigenetics18 (1), 2278960. 10.1080/15592294.2023.2278960
31
Mahtal N. Lenoir O. Tinel C. Anglicheau D. Tharaux P. L. (2022). MicroRNAs in kidney injury and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol.18 (10), 643–662. 10.1038/s41581-022-00608-6
32
Meng F. Chen Q. Gu S. Cui R. Ma Q. Cao R. et al (2022). Inhibition of circ-snrk ameliorates apoptosis and inflammation in acute kidney injury by regulating the MAPK pathway. Ren. Fail.44 (1), 672–681. 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2032746
33
Peerapornratana S. Manrique-Caballero C. L. Gómez H. Kellum J. A. (2019). Acute kidney injury from sepsis: current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int.96 (5), 1083–1099. 10.1016/j.kint.2019.05.026
34
Sun Y. Liu M. W. Zhao Y. H. Lu Y. X. Wang Y. A. Tong C. W. (2020). Baicalin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury by inhibiting the TXNIP/NLRP3 signalling pathway via increasing miR-223-3p expression. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. agents34 (1), 69–82. 10.23812/19-502-A
35
Tan J. Fan J. He J. Zhao L. Tang H. (2020). Knockdown of LncRNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits HK-2 cell pyroptosis via regulating miR-223-3p/NLRP3 pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. J. bioenergetics Biomembr.52 (5), 367–376. 10.1007/s10863-020-09845-5
36
Tan M. Bei R. (2021). Circ_0091702 serves as a sponge of miR-545-3p to attenuate sepsis-related acute kidney injury by upregulating THBS2. J. Mol. histology52 (4), 717–728. 10.1007/s10735-021-09991-z
37
Tang B. Li W. Ji T. Li X. Qu X. Feng L. et al (2020). Downregulation of XIST ameliorates acute kidney injury by sponging miR-142-5p and targeting PDCD4. J. Cell. physiology235 (11), 8852–8863. 10.1002/jcp.29729
38
Tian X. Liu Y. Wang H. Zhang J. Xie L. Huo Y. et al (2021). The role of miR-199b-3p in regulating Nrf2 pathway by dihydromyricetin to alleviate septic acute kidney injury. Free Radic. Res.55 (7), 842–852. 10.1080/10715762.2021.1962008
39
Uszczynska-Ratajczak B. Lagarde J. Frankish A. Guigó R. Johnson R. (2018). Towards a complete map of the human long non-coding RNA transcriptome. Nat. Rev. Genet.19 (9), 535–548. 10.1038/s41576-018-0017-y
40
Wang B. Wang Y. Xu K. Zeng Z. Xu Z. Yue D. et al (2021b). Resveratrol alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by deactivating the lncRNA MALAT1/MiR-205 axis. Central-European J. Immunol.46 (3), 295–304. 10.5114/ceji.2021.109195
41
Wang F. Zhang F. Tian Q. Sheng K. (2022). CircVMA21 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced HK-2 cell injury depending on the regulation of miR-7-5p/PPARA. Autoimmunity55 (2), 136–146. 10.1080/08916934.2021.2012764
42
Wang L. Bayinchahan B. Zhang D. Wang Z. Xiao D. (2023). The novel biomarker circ_0020339 drives septic acute kidney injury by targeting miR-17-5p/IPMK axis. Int. urology Nephrol.55 (2), 437–448. 10.1007/s11255-022-03331-0
43
Wang L. Wang K. Tian Z. (2020b). miR-128-3p inhibits NRP1 expression and promotes inflammatory response to acute kidney injury in sepsis. Inflammation43 (5), 1772–1779. 10.1007/s10753-020-01251-8
44
Wang X. Ma R. Zhang X. Cui L. Ding Y. Shi W. et al (2021a). Crosstalk between N6-methyladenosine modification and circular RNAs: current understanding and future directions. Mol. cancer20 (1), 121. 10.1186/s12943-021-01415-6
45
Wang X. Wang Y. Kong M. Yang J. (2020a). MiR-22-3p suppresses sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by targeting PTEN. Biosci. Rep.40 (6), BSR20200527. 10.1042/BSR20200527
46
Wang Y. Quan F. Cao Q. Lin Y. Yue C. Bi R. et al (2020c). Quercetin alleviates acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. J. Adv. Res.28, 231–243. 10.1016/j.jare.2020.07.007
47
Wei W. Yao Y. Bi H. Xu W. Gao Y. (2021). Circular RNA circ_0068,888 protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced HK-2 cell injury via sponging microRNA-21-5p. Biochem. biophysical Res. Commun.540, 1–7. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.12.018
48
Wu P. Mo Y. Peng M. Tang T. Zhong Y. Deng X. et al (2020). Emerging role of tumor-related functional peptides encoded by lncRNA and circRNA. Mol. cancer19 (1), 22. 10.1186/s12943-020-1147-3
49
Xie K. H. Liu X. H. Jia J. Zhong X. Han R. Y. Tan R. Z. et al (2022). Hederagenin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via inhibiting long non-coding RNA A330074k22Rik/Axin2/β-catenin signalling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol.112, 109247. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109247
50
Xie L. B. Chen B. Liao X. Chen Y. F. Yang R. He S. R. et al (2020). LINC00963 targeting miR-128-3p promotes acute kidney injury process by activating JAK2/STAT1 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med.24 (10), 5555–5564. 10.1111/jcmm.15211
51
Xiong Y. Wang Y. Tian H. Li Y. Xu Q. He Z. (2021). Circ-PRKCI alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced human kidney 2 cell injury by regulating miR-106b-5p/GAB1 axis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol.78 (4), 523–533. 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001031
52
Xu L. Cao H. Xu P. Nie M. Zhao C. (2022a). Circ_0114427 promotes LPS-Induced septic acute kidney injury by modulating miR-495-3p/TRAF6 through the NF-κB pathway. Autoimmunity55 (1), 52–64. 10.1080/08916934.2021.1995861
53
Xu L. Hu G. Xing P. Zhou M. Wang D. (2020). Paclitaxel alleviates the sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via lnc-MALAT1/miR-370-3p/HMGB1 axis. Life Sci.262, 118505. 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118505
54
Xu Y. Jiang W. Zhong L. Li H. Bai L. Chen X. et al (2022b). circ-AKT3 aggravates renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury via regulating miR-144-5p/Wnt/β-catenin pathway and oxidative stress. J. Cell. Mol. Med.26 (6), 1766–1775. 10.1111/jcmm.16072
55
Xu Y. Li X. Li H. Zhong L. Lin Y. Xie J. et al (2021). Circ_0023404 sponges miR-136 to induce HK-2 cells injury triggered by hypoxia/reoxygenation via up-regulating IL-6R. J. Cell. Mol. Med.25 (11), 4912–4921. 10.1111/jcmm.15986
56
Xue Q. Yang L. Wang H. Han S. (2021). Silence of long noncoding RNA SNHG14 alleviates Ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating miR-124-3p/MMP2 axis. BioMed Res. Int.2021, 8884438. 10.1155/2021/8884438
57
Yao Y. Hu S. Zhang C. Zhou Q. Wang H. Yang Y. et al (2022). Ginsenoside Rd attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by exerting an anti-pyroptotic effect via the miR-139-5p/FoxO1/Keap1/Nrf2 axis. Int. Immunopharmacol.105, 108582. 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108582
58
You T. Kuang F. (2023). CIRC_0008882 stimulates pde7a to suppress septic acute kidney injury progression by sponging mir-155-5P. Shock (Augusta, Ga.)59 (4), 657–665. 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002093
59
Yuan W. Xiong X. Du J. Fan Q. Wang R. Zhang X. (2021). LncRNA PVT1 accelerates LPS-Induced septic acute kidney injury through targeting miR-17-5p and regulating NF-κB pathway. Int. urology Nephrol.53 (11), 2409–2419. 10.1007/s11255-021-02905-8
60
Zhan Y. Zhu M. Liu S. Lu J. Ni Z. Cai H. et al (2021). MicroRNA-93 inhibits the apoptosis and inflammatory response of tubular epithelial cells via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in acute kidney injury. Mol. Med. Rep.24 (3), 666. 10.3892/mmr.2021.12305
61
Zhang H. Che L. Wang Y. Zhou H. Gong H. Man X. et al (2021b). Deregulated microRNA-22-3p in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury serves as a new biomarker to predict disease occurrence and 28-day survival outcomes. Int. Urol. Nephrol.53(10):2107–2116. 10.1007/s11255-021-02784-z
62
Zhang W. Q. Wang H. J. Li Y. Z. Du X. F. Hao X. L. Jiang H. M. et al (2022). Inhibition of microRNA-543 alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via targeting Bcl-2. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.26 (7), 2305–2312. 10.26355/eurrev_202204_28460
63
Zhang X. Huang Z. Wang Y. Wang T. Li J. Xi P. (2021a). Long non-coding RNA RMRP contributes to sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Yonsei Med. J.62 (3), 262–273. 10.3349/ymj.2021.62.3.262
64
Zhao H. Chen B. Li Z. Wang B. Li L. (2020). Long noncoding RNA DANCR suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced septic acute kidney injury by regulating miR-214 in HK-2 cells. Med. Sci. Monit.26, e921822. 10.12659/MSM.921822
65
Zhu D. Wu X. (2024). Resveratrol inhibits circ_0074371-related pathway to alleviate sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Biochem. Genet.62 (3), 1779–1794. 10.1007/s10528-023-10517-3
66
Zhu H. Wang J. Miao J. Shen M. Wang H. Huang X. et al (2024). SNORD3A regulates STING transcription to promote ferroptosis in acute kidney injury. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger.11 (33), e2400305. 10.1002/advs.202400305
Summary
Keywords
acute kidney injury, non-coding RNA, natural medicine, biomarkers, LncRNA-long noncoding RNA
Citation
Guo Y, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Xing Y, Fang Y, Zheng D, Yang H, Qiao Y and Yang B (2025) The potential role of non-coding RNAs in acute kidney injury: a focus on natural medicine treatment. Front. Mol. Biosci. 12:1648526. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1648526
Received
17 June 2025
Accepted
21 July 2025
Published
07 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Artur Slomka, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Poland
Reviewed by
Assunta Sellitto, Italian Institute of Technology, Italy
Rakhee Rathnam Kalari Kandy, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United States
Jeane Silva, Augusta State University, United States
Huang Pengfei, First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Guo, Zhao, Zhang, Xing, Fang, Zheng, Yang, Qiao and Yang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bo Yang, yb8203@126.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.