Abstract
MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) and its exosomal variant have gained recognition as pivotal molecular contributors to the etiology and advancement of gastrointestinal (GI) neoplasms, encompassing colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, and esophageal cancers. From a biosciences standpoint, miR-21 operates as a formidable oncomiR by inhibiting tumor suppressor genes, consequently fostering the dysregulated activation of crucial signaling cascades. The exosomal form of miR-21, released through tumor-derived extracellular vesicles, enhances intercellular interactions within the tumor microenvironment, influencing processes such as angiogenesis, immune evasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and metastasis. Clinically, both tissue and circulating (serum/plasma) concentrations of miR-21 exhibit substantial potential as non-invasive biomarkers for the early detection, disease stratification, and prognostic assessment in gastrointestinal malignancies. Increased levels of exosomal miR-21 are associated with diminished overall survival, lymph node dissemination, and resistance to chemotherapeutic agents such as 5-fluorouracil, cisplatin, and gemcitabine. Mechanistically, exosomal miR-21 facilitates drug resistance by inhibiting apoptotic pathways and promoting cellular longevity through the modulation of the tumor microenvironment and stromal-tumor interactions. Therapeutically, bioscience-oriented strategies aimed at targeting miR-21 are currently under scrutiny to counteract chemoresistance and restore therapeutic effectiveness. These methodologies possess significant potential for applications in personalized medicine concerning gastrointestinal cancers. This review synthesizes contemporary biosciences perspectives on the molecular roles of miR-21 and exosomal miR-21, underscoring their diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance in gastrointestinal neoplasms. Particular emphasis is directed toward their involvement in overcoming drug resistance, thereby establishing them as promising targets for forthcoming translational oncology investigations.
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that play crucial roles in post-transcriptional gene regulation. They typically target the 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of messenger RNAs (mRNAs), leading to mRNA degradation or translational repression for approximately 60% of all coding genes (Dhawan et al., 2018). In complex organisms, miRNAs are essential for “fine-tuning” intricate cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and migration (Nagel et al., 2016). Furthermore, miRNAs are key regulators of immunological responses, inflammation, and wound healing processes (Huynh et al., 2019).
Dysregulation of miRNA expression is a common feature in many human diseases, including cancer. Tumors often exploit miRNA-dependent biological mechanisms involved in processes like inflammation and wound healing to drive their own progression (El-Mahdy et al., 2022). Specific miRNAs that promote tumorigenesis are termed “oncomiRs.” Panels of miRNAs have shown potential as diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers across a wide range of malignancies, including breast (Elrebehy et al., 2023), gastric (Zheng et al., 2013), thyroid (Doghish et al., 2023), colorectal (Fathi et al., 2023), kidney (Canatan et al., 2021), and lung cancers (Ahadi, 2021).
OncomiRs function by targeting and inhibiting tumor suppressor (TS) genes, thereby promoting cancer cell survival, proliferation, and metastasis. Common TS genes targeted by various oncomiRs include PTEN, Reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs (RECK), Tropomyosin 1 (TMP1), and Programmed Cell Death 4 (PDCD4) (Park et al., 2021).
Among the most significant and widely studied oncomiRs across the majority of human malignancies is microRNA-21 (miR-21) (Figure 1) (Park et al., 2021). It is noteworthy that most functional studies in this context focus on the miR-21-5p strand as the primary mature, active product, and detailed comparative mechanistic data for the miR-21-3p strand in GI cancers remain limited in the current literature.
FIGURE 1
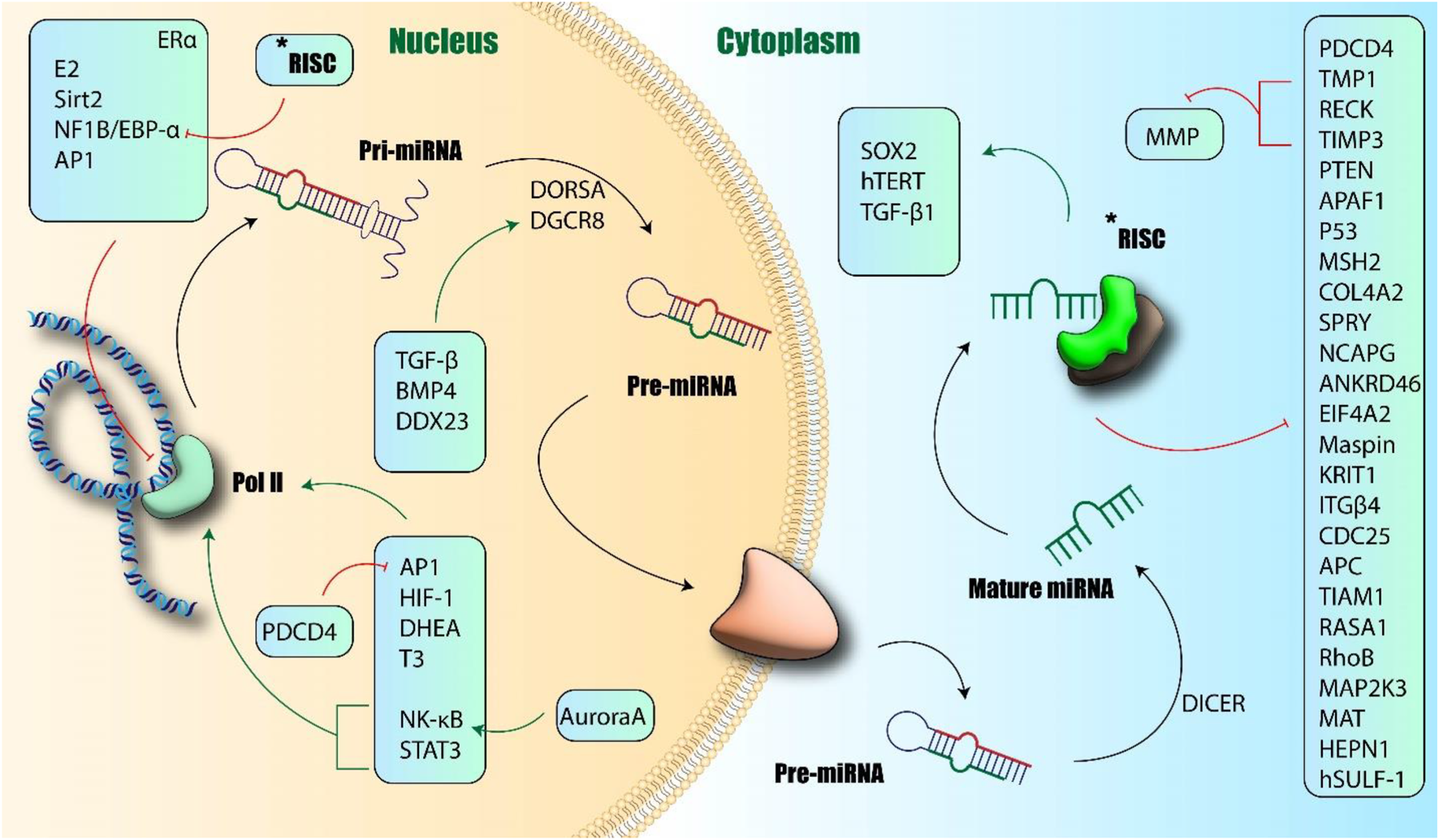
Biogenesis and function of miR-21. Induction of miR-21 transcription occurred via Pol II and further production of Pri-miRNA-21. Different transcriptional factors could induce or inhibit this process. Finally, mature miR-21 changes the transcription of other proteins and induces or inhibits their expression. APAF1: Apoptotic Protease Activating Factor 1; ANKRD46: Ankyrin Repeat Domain 46; APC: Adenomatous Polyposis Coli; AP1: Activator Protein 1; BMP4: Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4; CDC25: Cell Division Cycle 25; COL4A2: Collagen Type IV Alpha 2; DDX23: DEAD-Box Helicase 23; DICER: Dicer Ribonucléase; DHEA: Dehydroepiandrosterone; DGCR8: DiGeorge Syndrome Critical Region Gene 8; DROSHA: Dicer-Related RNA Helicase; EIF4A2: Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4A2; ER-alpha: Estrogen Receptor Alpha; HEPn: Hepatocellular Carcinoma Expressed Protein; HIF-1: Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1; ITGbeta: Integrin Beta; KRIT1: Krit1 Rho GTPase Activating Protein; MAPK: Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; MAT: Methionine Adenosyltransferase; MSH: MutS Homolog; NF1B: Neurofibromin 1; NK-κb: Nuclear Factor kappa B; PDCD4: Programmed Cell Death 4; PTEN: Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog; RASA1: Ras p21 Protein Activator 1; RECK1: Reversion-Inducing Cysteine-Rich Protein with Kazal Motifs 1; RhoB: Ras Homolog Family Member B; SOX2: SRY-Box Transcription Factor 2; SPRY: Sprouty; STAT3: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3; TGF-b: Transforming Growth Factor Beta; TGF-B: Transforming Growth Factor Beta; TIMP3: Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 3; TIAM1: T-Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin-Domain Containing Protein 1 (author-created).
A central mechanism underlying miR-21’s oncogenic activity in numerous cancers involves its regulation of the Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog (PTEN)/Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Protein Kinase B (Akt) signaling pathway. MiR-21 directly binds to the 3′-UTR of PTEN mRNA, leading to translational repression or mRNA degradation, thereby reducing the levels of the PTEN tumor suppressor protein (Zhu et al., 2008; Khan et al., 2016; Meng et al., 2007). Since PTEN normally antagonizes PI3K signaling by dephosphorylating PIP3, its downregulation by miR-21 results in the hyperactivation of PI3K and its downstream effector Akt. Activated Akt promotes cell survival (by inhibiting apoptosis), proliferation, cell growth (partly through mechanistic Target Of Rapamycin (mTOR) signaling), migration, and invasion, and contributes significantly to chemoresistance (Song WF. et al., 2013; Vahidnezhad et al., 2016; Li et al., 2014). This miR-21/PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis represents a core oncogenic signaling node frequently exploited in GI malignancies.
High levels of miR-21 expression are frequently observed in gastric, colorectal, lung, pancreatic, breast, and ovarian cancers, among others (Zhu et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2021a; Huang et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2021; Feng and Tsao, 2016). Clinically, elevated miR-21 expression often correlates with a worse patient prognosis, increased lymph node metastasis (Arisan et al., 2021; Asangani et al., 2008), and the development of chemoresistance (Petrocca et al., 2008). Functional studies support its oncogenic role; induced miR-21 expression can cause malignant B-cell lymphoma in preclinical models, while its genetic silencing reduces carcinogenesis in transgenic mice (Rihane et al., 2022).
It is important to acknowledge, however, that while the vast majority of evidence points to miR-21 acting as a potent oncomiR in GI malignancies, isolated studies have reported potential anti-tumorigenic effects in specific contexts, such as certain models of colon and liver cancer (Xu et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2014). These seemingly contradictory findings underscore the complexity of miRNA function. Such discrepancies might arise from several factors. Cellular and tissue context is paramount; the downstream consequences of miR-21 targeting specific genes (like PTEN or PDCD4) may differ significantly depending on the specific GI cell type, the cancer stage, and the surrounding tumor microenvironment (TME). Furthermore, variations in experimental model systems–ranging from simplified in vitro cultures lacking TME interactions to different types of in vivo animal models (e.g., genetic vs. xenograft) and analyses of heterogeneous human tumor samples–can yield divergent results. Methodological differences, such as the techniques used to modulate miR-21 levels (e.g., mimics vs. inhibitors, transient vs. stable expression) and the specific functional assays employed, can also contribute to variability. Finally, given that miR-21 regulates a complex network of potentially hundreds of target mRNAs, its ultimate biological effect likely represents the net outcome of modulating multiple pathways simultaneously, which could feasibly shift between pro- and anti-tumorigenic depending on the specific cellular state and environmental cues. Understanding these context-dependent factors is crucial for accurately interpreting miR-21’s role and harnessing its therapeutic potential.
This review summarizes the function of miR-21, and particularly its exosomal form, in GI cancers. The literature search for this review was conducted using PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases, covering articles published up to September 2024. Keywords included “miR-21,” “exosomal miR-21,” combined with “esophageal cancer,” “gastric cancer,” “pancreatic cancer,” and “colorectal cancer.” Only English language articles were included.
It is important to acknowledge, however, that while the vast majority of evidence points to miR-21 acting as a potent oncomiR in GI malignancies, isolated studies have reported potential anti-tumorigenic effects in specific contexts, such as certain models of colon and liver cancer (26, 27). These seemingly contradictory findings underscore the complexity of miRNA function. Such discrepancies might arise from several factors. Cellular and tissue context is paramount; the downstream consequences of miR-21 targeting specific genes (like PTEN or PDCD4) may differ significantly depending on the specific GI cell type, the cancer stage, and the surrounding tumor microenvironment (TME). Furthermore, variations in experimental model systems–ranging from simplified in vitro cultures lacking TME interactions to different types of in vivo animal models (e.g., genetic vs. xenograft) and analyses of heterogeneous human tumor samples–can yield divergent results. Methodological differences, such as the techniques used to modulate miR-21 levels (e.g., mimics vs. inhibitors, transient vs. stable expression) and the specific functional assays employed, can also contribute to variability. Finally, given that miR-21 regulates a complex network of potentially hundreds of target mRNAs, its ultimate biological effect likely represents the net outcome of modulating multiple pathways simultaneously, which could feasibly shift between pro- and anti-tumorigenic depending on the specific cellular state and environmental cues. Understanding these context-dependent factors is crucial for accurately interpreting miR-21’s role and harnessing its therapeutic potential.
MicroRNAs and gastrointestinal cancer
MiR-21 and pancreatic cancer
Cancer stem cells, also known as CSCs, have been linked to chemoresistance and are crucial in the development of various cancers, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) (Luo et al., 2020). High autophagic flux in CSCs produces stress in the microenvironment, which in turn increases ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter expression, multidrug resistance genes, and anti-apoptotic proteins (An and Yang, 2020). Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cells (PCSCs), which make up just under one percent of all pancreatic cancer cells, are rare and they promote the growth, preservation, spread, and treatment resistance of PDAC tumors (Vandewalle et al., 2021). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is crucial for cancer cell invasion and metastasis. This process involves increased cell mobility, reduced cell adhesion, the repression of epithelial markers like E-cadherin, and the upregulation of mesenchymal markers including N-cadherin, Vimentin, and transcription factors like Snail and Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 1 (ZEB1) (Wang et al., 2021b). In PDAC, dysregulation of E-cadherin correlates with a worse prognosis, poorer differentiation, and therapy resistance (Medina et al., 2010).
Key regulators of EMT are often overexpressed in PDAC and linked to aggressive phenotypes. For example, Snail expression is elevated in ∼80% of PDAC patients, correlating with higher tumor grade and lymph node invasion (Li et al., 2009). Similarly, ZEB1 overexpression, potentially driven by NF-κB activation, is linked to aggressiveness and poor prognosis (Correia de Sousa et al., 2021). ZEB1 also suppresses miR-200 family members and miR-203, which normally inhibit stemness factors and ZEB1 itself, creating complex feedback loops (Jiang et al., 2020). Vimentin overexpression also promotes PDAC spread, reduces survival, and is linked to gemcitabine resistance (Kim et al., 2011; Klonisch et al., 2008). Non-canonical Wnt-11 expression is another factor associated with advanced staging and poor prognosis (Li et al., 2007). The complex regulation of EMT involves multiple layers, including alternative splicing, post-translational modifications, non-coding RNAs, and chromatin remodeling (Niess et al., 2015). Notably, PDAC cells undergoing EMT often acquire cancer stem cell (CSC) traits, highlighting a close relationship between these two processes (Miranda-Lorenzo et al., 2014).
CD133, CD44, Lgr5, ESA/EpCAM (epithelial-specific antigen), CD24, CXCR4, aldehyde dehydrogenase-1 (ALDH1), and DclK1 are the primary markers of PCSCs. Other markers include (Valle et al., 2018). It's important to note that pathways involving EMT and autophagy are directly related to indications of CSCs as PDAC progresses (Marcato et al., 2011). Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients with the expression of cMet+ CD45+ CD34+CD133 Ter119, CD44, Pdx1, CD13, CD9, CD133, and CD24 had a poor prognosis (PDAC). Recent research has shown that advanced pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia is associated with more CD44, CD24, CXCR4, ESA, and nestin levels (PanIN) (Santamaria et al., 2017).
MiR-21 regulation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and EMT
MiR-21 is strongly expressed in CSCs, and its significance in PDAC was studied by Mortoglou et al. in vitro. After miR-21 was removed from the human PDAC cell lines Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 using a knockout (KO) technique, reversible manifestations of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) along with cancer stem cells’ signs were found. Depending on miR-21 expression levels, the expression patterns of important CSC markers as CD44, CX-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), CD133, and ALDH1 vary. These markers include the CX-C chemokine receptor type 4, CD44, and CD133, as well as ALDH1. Using standard cell viability and invasion assays, Panc-1 and MiaPaCa-2 cell growth as well as their invasive potential were both reduced by miR-21 KO. These findings imply that miR-21 expression correlates with PDAC aggressiveness and may serve as a potential biomarker (Bao et al., 2012; Zhao et al., 2018). Beyond intrinsic cell properties, miR-21 also influences the tumor microenvironment. The PDAC tumor microenvironment has an abundance of immunosuppressive M2 macrophages that serve as a home for parental PDAC cells to proliferate, colonize, and re-generate (Dawood et al., 2014). M2 macrophages are lethal to PDAC patients and reduce the effectiveness of treatment (Lei et al., 2017). M2 macrophage infiltration is also to blame for the paradoxical survival of PDAC cases (Cojoc et al., 2015). By delivering genes into the tumor microenvironment, exosomes encourage tumor progression (Dalla Pozza et al., 2015). Exosomes made by M2 macrophages promote the growth of PDAC cells, which in turn causes the tumor (Kalluri and Weinberg, 2009). Exosomes themselves and exosomal microRNA (miR)-501-3p, which is created by M2 macrophages, are both strong agents that can cause PDAC cells to invade, migrate, spread, and form tumors (Felipe Lima et al., 2016). More specifically, Exosomes produced by M2 macrophages have higher miR-21-5p levels, recommending that such particles might have a role in regulating migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells (Lamouille et al., 2014). Transcriptional factors Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) are important in PDAC. It was discovered that the miR-21 target gene KLF3 controls a subset of KLFs (Iacobuzio-Donahue et al., 2009). Interestingly, it has a connection to esophageal squamous cell cancer’s stem cell-like features (Winter et al., 2008). To add, KLF3 may help with prostate cancer prognosis (Renz et al., 2017).
The study of Chang et al. sought to understand how the miR-21-5p necessary for PDAC stem cell activity and differentiation is carried by M2 macrophage-produced Extracellular Vesicles (EVs), which aid in the development of PDAC. Polarized M2 macrophages were used to extract the EVs. EVs generated from M2 macrophages were examined for miR-21-5p. CD24+CD44+EpCAM+ in vitro co-cultures of M2 macrophages with either high or low miR-21-5p levels and stem cells were carried out. Using assays like qPCR/Western blot for Oct4/Nanog, sphere/colony formation assays, transwell migration/invasion assays, apoptosis assays (e.g., Annexin V staining), and mouse xenograft models for tumorigenicity, the effects of EVs and miR-21-5p were examined. KLF3 expression and miR-21-5p activity were investigated. The increased PDAC stem cell activity is believed to be caused by the EVs that M2 macrophages create. In M2 EVs, miR-21a-5p levels were elevated. PDAC stem cells’ capacities for proliferation, differentiation, colony formation, invasion, migration, and anti-apoptosis were suppressed in vitro and in vivo when expression of Nanog/Oct4 within M2 macrophage-derived EVs has been reduced. In PDAC stem cells, it was obvious that miR-21-5p controlled KLF3 expression and activity. Exosomal miR-21a-5p from M2 macrophages was found to increase PDAC stem cell activity and proliferation while suppressing PDAC stemness by targeting KLF3 (Arumugam et al., 2009).
Other enzymatic pathways within cancer cells are also modulated by miR-21 activity and related inhibitors.
Modulation by peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitors
A class of calcium-dependent enzymes known as peptidylarginine deiminases (PADs) modify target proteins’ structure and function post-translationally by, among other things, having an impact on protein-protein interactions, altering gene regulation and producing new epitopes (Buck et al., 2007). This post-translational change may facilitate protein moonlighting, a phylogenetically evolved mechanism that allows molecules to carry out many roles on the inside of a single polypeptide chain, in terms of both physiological and pathological features (Maier et al., 2010). Five isozyme-specific PADs (Uysal-Onganer et al., 2010), there are known mammalian transcription factors, each having a distinctive affinity for protein targets and pattern of expression. Targeting specific PAD isozymes for different cancer types and subtypes is an active area of research, focusing on the relative significance of the three main isozymes (PAD2, PAD3, and PAD4) in malignancies (Arisan et al., 2020).
In a study by Uysal-Onganer et al., MiaPaCa-2 PDAC and Panc-1 cell lines were handled by the isozyme-specific inhibitors of phosphodiesterase-2 (PAD2), −3, and −4 (PAD2, PAD3, and PAD4) as well as the pan-PAD inhibitor Cl-amidine. The implications for moesin, mitochondrial housekeeping (prohibitin, PHB), and gene regulation were studied in relation to the effects on cellular protein expression. Modifications in EV signatures were also examined (deiminated histone H3, citH3). It was determined that Panc-1 cells expressed PAD2 and PAD3 at higher levels than MiaPaCa-2 cells, indicating that Panc-1 and PAD3 were both identified as pancreatic cancer cell lines. The moesin expression, a protein which has been dysregulated in pancreatic cancer and is related to the severity of the illness, rose in response to therapy with a PAD2 isozyme-specific inhibitor, which proved to be most effective in preventing the invasion of Panc-1 cells. PHB levels decreased as well, albeit the change was not statistically significant, and the results for histone H3 deamination were mixed. Treatment with a PAD inhibitor altered EV signatures, with miR-21 and miR-221, two pro-oncogenic microRNAs, and miR-155, an anti-oncogenic microRNA, being significantly reduced and miR-155 increased, respectively (miR-126). However, blocking PAD4 had no appreciable effect, and blocking all PADs with Cl-amidine had even less of an impact. Limiting PAD4 had no noticeable impact, whereas inhibiting PAD2 and PAD3 had the greatest impact on reducing moesin expression, avoiding cancer cell invasion, and changing EV markers. It is noteworthy that Panc-1 cells also responded strongly to PAD3 inhibitor, validating previous results that Panc-1 cells exhibit more neuronal/stem-like properties than MiaPaCa-2 cells. Their results disclose new regulatory functions for PAD isozymes in PDAC and emphasize the need of tailoring PAD isozyme therapy to the individual disease and cancer subtype being treated (Guo and Wang, 2009). Furthermore, miR-21 interacts with key tumor suppressor pathways sensitive to the hypoxic tumor environment.
Targeting the VHL/HIF-1α axis
VHL is a ubiquitin ligase E3 component of elongin B, elongin C, and cullin-2. When oxygen is plentiful, prolyl hydroxylase proteins hydroxylate hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1, that VHL subsequently ubiquitinates and degrades (Wang L. et al., 2018). Many solid tumors are anoxic, and VHL inactivation may upregulate HIF-1, encouraging tumor growth. VHL might be suppressed in malignancies even though it typically suppresses tumors through mechanisms including microRNA regulation. MiR-101 and (Wang et al., 2016a) miR-155 influence VHL expression (Hotz et al., 2007).
It has been demonstrated that miR-21’s deleterious impact on VHL, its target, is real. MiR-21 inhibition reduced Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and MMP-2 expression plus the HIF-1/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) pathway. MiR-21 silencing inhibited tumor development in vivo. MiR-21 knockdown reduced pancreatic cancer infiltration, motility, and growth through inhibiting the HIF-1/VEGF pathway, MMP-2, and MMP-9 expression. Thus, miR-21/VHL could be used as a viable novel pancreatic cancer therapeutic and preventative target (De Craene and Berx, 2013). Finally, miR-21’s influence extends to stromal components and therapy response.
Role in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and chemoresistance
Several research have demonstrated that miR-21 is crucial for regulating the activation of transforming growth factor beta (TGF) in fibroblasts (Fedele et al., 2017). However, it is unclear if miR-21 in CAFs might change the microenvironment of the PDAC tumor and promote treatment resistance. Using a tumor sample from a patient who had been diagnosed with PDAC, Zhang et al. investigated the connection among CAF activation, miR-21 transcription, and treatment tolerance. They experimented with manipulating miR-21 expression in CAFs to see how it affected CAF function regulation. Gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer patients have been identified as having greater levels of miR-21 expression along with greatly activated CAFs. Strong miR-21 expression in CAFs was found to increase PDAC cell line penetration, MMP-3 and MMP-9 levels and Chemokine Ligand (CCL)-7 as well as Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF), in an in vitro investigation. There in vivo study found that miR-21 downregulation in CAFs decreased desmoplasia and improved the gemcitabine’s benefits, but PDAC desmoplasia was worsened by miR-21 overexpression in CAFs, and the condition was more difficult to cure with gemcitabine. They concluded that miR-21 encouraged CAF activation, that influenced PDAC’s treatment resistance (Klymkowsky and Savagner, 2009). Table 1 lists various researches on miR-21 and pancreatic cancer.
TABLE 1
| Status of expression | Target | Model | Cell line type | Effect | Conclusion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | Snail, ZEB1, Wnt-11, CD24, CD44, CD133, CD13, ALDH1, CXCR4 | In vitro | Panc-1, MiaPaCa-2, BxPC-3, HPDE; H6c7) | Enhanced the expression of biomarkers related to the cancer stemness and progression | Increase of cancer progression and invasion | Plaks et al. (2015) |
| Up | Spry2, MAPK, PI3K | Human serum In vitro, Invivo |
PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, CFPAC-1, HPDE6-c7, SW-1990, AsPC-1 | Enhanced the expression of biomarkers related to the cancer stemness and progression | Promoted EGF-induced proliferation, inhibited cell apoptosis and accelerated cell cycle progression | Traub et al. (1985) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | Increase in pancreatic cancer patients | It could be used as a cancer biomarker for early detection of pancreatic cancer | Yachida and Iacobuzio-Donahue (2009) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | Increase in pancreatic cancer patients | It could be used as a cancer biomarker for early detection of pancreatic cancer |
Javle et al. (2007)
Shibue and Weinberg (2017) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | Increase in pancreatic cancer patients | It could be used as a cancer biomarker for early detection of pancreatic cancer | De Craene and Berx (2013) |
| Up | Mitochondrial pathway | In vitro, In vivo | Mia PaCa-2 Human PDA-derived Capan-2 |
Inhibition of apoptosis | Induction of apoptosis by inhibition of miR-21 expression | Rhim et al. (2012) |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | PSCs, Panc-1 | Increase of cancer stemness and progression via induction of PTEN expression | Increase of cancer progression and invasion | Rao and Mohammed (2015) |
| Up | Slug | In vitro | PANC-1 | Induction of Slug expression | Increase of cancer invasiveness and metastasis | Chalquest (1986) |
| Up | SMAD7 | Human In vitro, In vivo |
- | It inhibits SMAD7 expression | Increase of cancer invasiveness and metastasis | Hruban et al. (2006) |
| Up | KLF3 | In vitro, In vivo | PC-3, Capan-1, AsPC-1, PANC-1, HPC-Y5, THP-1 | Induction of KLF3 expression | Induction of cancer progression | Arumugam et al. (2009) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | Increase in pancreatic cancer patients | It could be used as a cancer biomarker for early detection of pancreatic cancer | Oshima et al. (2007) |
| Up | PTEN, PDCD4 | In vitro | PATU8988, PANC-1, 293 TN | Induction of PTEN and PDCD4 expression | Induction of cancer progression and further metastasis risk | Wang et al. (2019a) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | Increase in pancreatic cancer patients | It could be used as a cancer biomarker for early detection of pancreatic cancer | Lee et al. (2014) |
| Up | FasL | Human, In vitro, In vivo | PANC‐1, BxPC3 | Increase of the expression of FasL along with reduction of miR-21 expression following chemotherapy | Chemotherapy resulted in the reduction of miR-21 while induced FasL expression and further inhibited tumor metastasis | Liu et al. (2018a) |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | HPAC, PANC-1 | Enhanced invasion and metastasis, increased miR-21 expression, decreased PTEN, elevated pAKT level were demonstrated in gemcitabine-resistant HPAC and PANC-1 cells | MiR-21 upregulation induced by histone acetylation in the promoter zone is associated with chemoresistance to gemcitabine and enhanced malignant potential in pancreatic cancer cells | Li et al. (2015a) |
| Up | RECK | Human, In vitro | hTERT-HPNE, Hs27, LPc006, LPc028, LPc033, LPc067, LPc111, LPc167, PP437 | Pre-miR-21 transfection significantly decreased antiproliferative effects and apoptosis | miR-21 expression correlated with outcome in PDAC patients treated with gemcitabine | Mortoglou et al. (2022) |
| Up | Bcl-2 | In vitro | MIA PaCa-2 | Upregulation of Bcl-2 expression was detected in cells transfected with miR-21 mimics, accompanied by downregulated Bax expression, less apoptosis, lower caspase-3 activity, decreased chemosensitivity to gemcitabine and increased proliferation compared with the control cells | Upregulation of Bcl-2 directly induced by miR-21 is associated with apoptosis, chemoresistance and proliferation of MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells | Chandrakesan et al. (2020) |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | MIA Paca-2, CAFs, Panc02 | miR-21 overexpression contributed to the activation of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) by regulating the PDCD4 gene | miR-21 promoted the activation of CAFs and contributed to the drug resistance of PDAC. | Klymkowsky and Savagner (2009) |
| Up | CDK6, IRAK3, NRP1, SMAD7 SOCS6, C5ORF41, KLF12, MAPK10, EFNA1, ZBTB41 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | L3.6 pL | The administration of antagomir-21 significantly induced reduction of L3.6 pL cell proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance against gemcitabine and 5-Fluorouracil | inhibition of miR-21 appear particularly suitable to target stem-like subpopulations and address their specific biological function to promote tumor progression in pancreatic cancer | Hu et al. (2020) |
| Up | PTEN, p85α | In vitro | MiaPaCa-2, PANC-1 | Overexpression of miR-21 resulted in decreased levels of p85α and increased phosphorylation of AKT. | miR-21 can influence PI3K-AKT signaling via its direct regulation of p85α | Yin et al. (2020) |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | HPDE6-C7, SW 1990, CAPAN-1, JF305, PANC-1, BxPC-3 | CACS2 overexpression inhibited the migration and invasion of PANC-1 cells by targeting MiR-21 | A novel regulatory mechanism of the CASC2/miR-21/PTEN axis that may be important in pancreatic cancer | Yin et al. (2019) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | miR-21 could distinguish PC patients from those with other GI cancers or benign pancreatic diseases (BPD) | As new combined microRNA and protein plasmatic biomarker panel for pancreatic cancer | Lan et al. (2019) |
| Up | - | In vitro | AsPC-1, BxPC-3 | Hypoxic conditions resulted in direct binding of HIF-1α to the predicted binding site in miR-21 | MiR-21 overexpression allows cells to avoid apoptosis in a hypoxic microenvironment | Zhai et al. (2019) |
| Up | Tgfbr2, Tgfbi, Sox2, Sox5, Sox7, PTEN, TPM1, PDCD4, Maspin, Rasa1and2, Cstf3 | Human, In vivo | - | The expression of miR-21 was significantly upregulated in human PC tissues as compared to the cancer-adjacent normal tissues | Induction of cancer progression | Liu et al. (2020a) |
| Up | PDCD4, BTG2 | Human, In vitro | PANC-1, MiaPaca-2 | CRISPR-Cas9 cellular model was generated to knock-out the expression of miR-21 in PANC-1 cells | Importance of miR-148a and miR-21 interactions | Meng et al. (2020) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | Increase in mucinous versus nonmucinous cysts | profiling miRNAs in pancreatic cyst fluid samples is feasible and can yield potential biomarkers for the classification of cystic lesions of the pancreas | Vossenaar et al. (2003) |
| Up | - | Human, in vivo | - | increased when comparing normal tissues, premalignant lesions and invasive carcinoma in the mouse model | Circulating miRs could serve as indicators of drug response | György et al. (2006) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | the expressions of miR-21 and miR-155 were associated with tumor stage and poor prognosis | miR-21 and miR-155 renders necessary the revision of use of microRNAs as biological markers | Wang and Wang (2013) |
| Up | PDCD4, TIMP3 | Human tissue | - | PDCD4 (reduced nuclear staining) and TIMP3 (downregulated expression) and increased miR-21 expression | miR-21 downregulates tumor suppressors PDCD4 and TIMP3, causing tumor growth and a poor clinical fate in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Henderson and Martin (2014) |
| Up | BCL-2 | In vitro | PANC-1, CFPAC-1 MIA Paca-2 |
MiR-21 downregulation inhibits BCL-2 expression in PANC-1, CFPAC-1, and MIA Paca-2 cells | Resveratrol inhibits miR-21-regulated BCL-2 expression, affecting apoptosis | Jeffery (2018) |
| Up | - | In vivo | - | PFOS exposure positively regulate apoptosis and cell proliferation in cancer | PFOS exposure altered the expression of a suite of miRNAs | Kosgodage et al. (2018) |
| Up | RECK, PTEN | In vitro | PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, HS766T, SW 1990, PL45, MPanc96, Capan-1 | Gemcitabine was sensitized by miR-21 and miR-221, and antisense-gemcitabine combos were synergistic at high fraction impacted | miR-21 antisense oligonucleotides targeting miRNA kill cells under diverse situations and may be a new pancreatic cancer treatment | Uysal-Onganer et al. (2021) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | miR-21 was significantly increased in cancer fine-needle aspirates | feasibility of miRNA profiling on fine-needle aspirated pancreatic cancer specimens | de Paulsen et al. (2001) |
| Up | - | Human serum/tissue | - | miR-21 is involved in the development of pancreatic cancer critical cancer-associated cellular pathways | miR-21 can be use potential biomarker | Liu et al. (2016a) |
| Up | - | Human tissue/serum | - | miR-21 was overexpressed by cancer- and juxta-tumoral stromal cells | PTEN silencing by miR-21 in cancer promote tumor growth | Kong et al. (2014) |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | - | miR-21 family was markedly over-expressed in chemo-resistant PC cell lines | Mir-21 could serve as potential biomarker for tumor aggressiveness | Sun et al. (2019) |
| Up | PTEN, PDCD4, Maspin, TPM1 | Human, In vitro | MIAPaCa-2, AsPc-1 | borderline significant overexpression of miR-21 was observed in PanIN-3 only | miR-21 abnormalities at the stage of PanIN-3 lesions. and IAP was observed | Yao et al. (2011) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | miR-21 was upregulated in 90.6% of the tumors, no associations with outcomes were found | independent prognostic markers in gastrointestinal cancer patients | Li et al. (2013a) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | - | Can be use as miRNA prediction model differentiate colorectal neoplasia | Liu et al. (2010a) |
| Up | - | In vitro | CAF-19, COLO-357, MIAPaCa-2, nhPSCs | - | targeting these miRNAs could be useful for developing precision medicine for the prevention of tumor progression | Li et al. (2016a) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | specific microRNAs like miR-21, are differentially expressed between tumor buds and main tumor cells | miR-21 could represent a treatment option for aggressive pancreatic cancer | Zhang et al. (2018a) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | miR-21 demonstrating highest relative fold-changes in the precursor lesions | Overexpression of miR-21 is an early event in the multistage progression of pancreatic cancer | Zhao et al. (2018) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | miR-21 were upregulated | Pancreatic cancer tissue expresses microRNA differently from other periampullary tumors | Yu et al. (2021) |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vitro | MIA-Pa-Ca-2, HUP-T3, PSN-1 PDAC | miR-21 levels in the primary tumours correlated with disease stage | miRNA expression profiles may be used as biomarkers for detecting pancreatic cancer | Abue et al. (2015) |
| Up | PDCD4 | In vitro | Panc-1 | Downregulation of miR-21 by I3C was positively-correlated in a time- and dose-dependent manner | I3C would be effective for enhancing sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine via downregulation of miR-21 | Škrha et al. (2015) |
| Up | - | Human saliva | - | hsa-miR-21 being significantly upregulated in saliva of pancreatic cancer patients compared to control | Suggest use of salivary miRNA as biomarker for the early diagnosis of patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer | Yan et al. (2018) |
| Up | - | Human serum | - | miR-21 levels in serum were significantly associated with overall PaC survival | miRNA-based biomarker can serve as a novel noninvasive approach for PaC diagnosis and prognosis | Liu et al. (2016b) |
| Up | - | In vitro | - | miR-21 was significantly overexpressed in PDAC | These markers may distinguish PDAC and its precursor from benign tumors | Tavano et al. (2012) |
| Up | EGFR, HER2 | Human, In vitro | PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, BXCP-3 | miR-21 associated with the EGFR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)2 pathways | Application of the miRNA panel investigated in the present study as a potential predictor of patient responses to anti-EGFR/HER2 treatment | Fang et al. (2022) |
| Up | - | Human tissue | - | Adjuvant gemcitabine after curative resection significantly and independently reduced disease-free survival in pancreatic cancer patients with LNA-ISH-detected miR-21 overexpression | miR-21 may serve as a significant predictor for gemcitabine resistance in patients | Dillhoff et al. (2008) |
miR-21 and pancreatic cancer.
Abbreviations: ALDH1, Aldehyde Dehydrogenase1; BCL-2, B-Cell Lymphoma 2; BTG2, B-cell Translocation Gene 2; C5ORF41, Chromosome 5 Open Reading Frame 41; CD, cluster of differentiation; CDK, Cyclin-Dependent Kinase; Cstf3, Cleavage Stimulation Factor Subunit 3; CXCR4, C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4; EFNA1, Ephrin-A1; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; HPDE, non-tumorigenic human pancreatic ductal epithelial cell line; HER2, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2; IRAK, Interleukin-1, Receptor-Associated Kinase; KLF, Kruppel-Like Factor; MAPK, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; NRP, neuropilin; PDCD4, Programmed Cell Death 4; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Rasa, Ras P21 Protein Activator; RECK, reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with kazal motifs; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling; Sox, SRY (Sex Determining Region Y)-Box; Spry2, Sprouty RTK, Signaling Antagonist 2; TPM, tropomyosin; Tgfbi, Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced; Tgfbr, Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor; VHL, Von Hippel-Lindau; Wnt, Wingless-Type MMTV, integration site family member; ZBTB41, Zinc Finger and BTB, Domain Containing 41.
In pancreatic cancer, miR-21 plays a pivotal role in promoting tumor progression and chemoresistance, particularly through its effects on CSCs and EMT. Overexpression of miR-21 is closely associated with the downregulation of E-cadherin and the upregulation of mesenchymal markers such as N-cadherin, ZEB1, Snail, and vimentin, facilitating the EMT process. This leads to increased cell migration, invasion, and resistance to therapies like gemcitabine. Furthermore, miR-21 contributes to the modulation of key signaling pathways, including NF-B activation and non-canonical Wnt signaling, which in turn promotes the aggressive characteristics of PDAC. Despite the promising findings, there is a gap in understanding the exact molecular mechanisms through which miR-21 regulates EMT and CSCs in PDAC. Future studies should focus on validating these pathways in clinical settings, exploring miR-21 as a therapeutic target, and identifying biomarkers that can aid in the diagnosis and prognosis of PDAC.
MircroRNA-21 and gastric cancer
A collection of genes essential for the onset and spread of cancer are the focus of Mir-21 (Paik et al., 2013). A key mechanism in gastric cancer involves miR-21 targeting PTEN (Wang et al., 2013) leading to activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway which correlates with infiltration, migration, and development (Khan et al., 2016). Qiang et al. look into whether curcumin and PD98059 work together to inhibit gastric cancer growth as a result of the miR-21/PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. At dosages that ranged from 5 to 40 M, it was discovered that curcumin had a time- and dose-dependent inhibitory impact on the proliferation of MGC-803 cells. Strong suppression of p-Akt protein expression was achieved with a high dosage of curcumin. PTEN expression went up and miR-21 went down when curcumin dosage was up. According to their findings, curcumin acted to suppress the miR-21/PTEN/Akt axis. Additionally, cell apoptosis produced by curcumin was substantially amplified after being pretreated with PD98059. The miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway’s inhibition through curcumin has been also dramatically enhanced. Combining curcumin with PD98059 may be a successful stomach cancer treatment plan (Song WF. et al., 2013) (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2
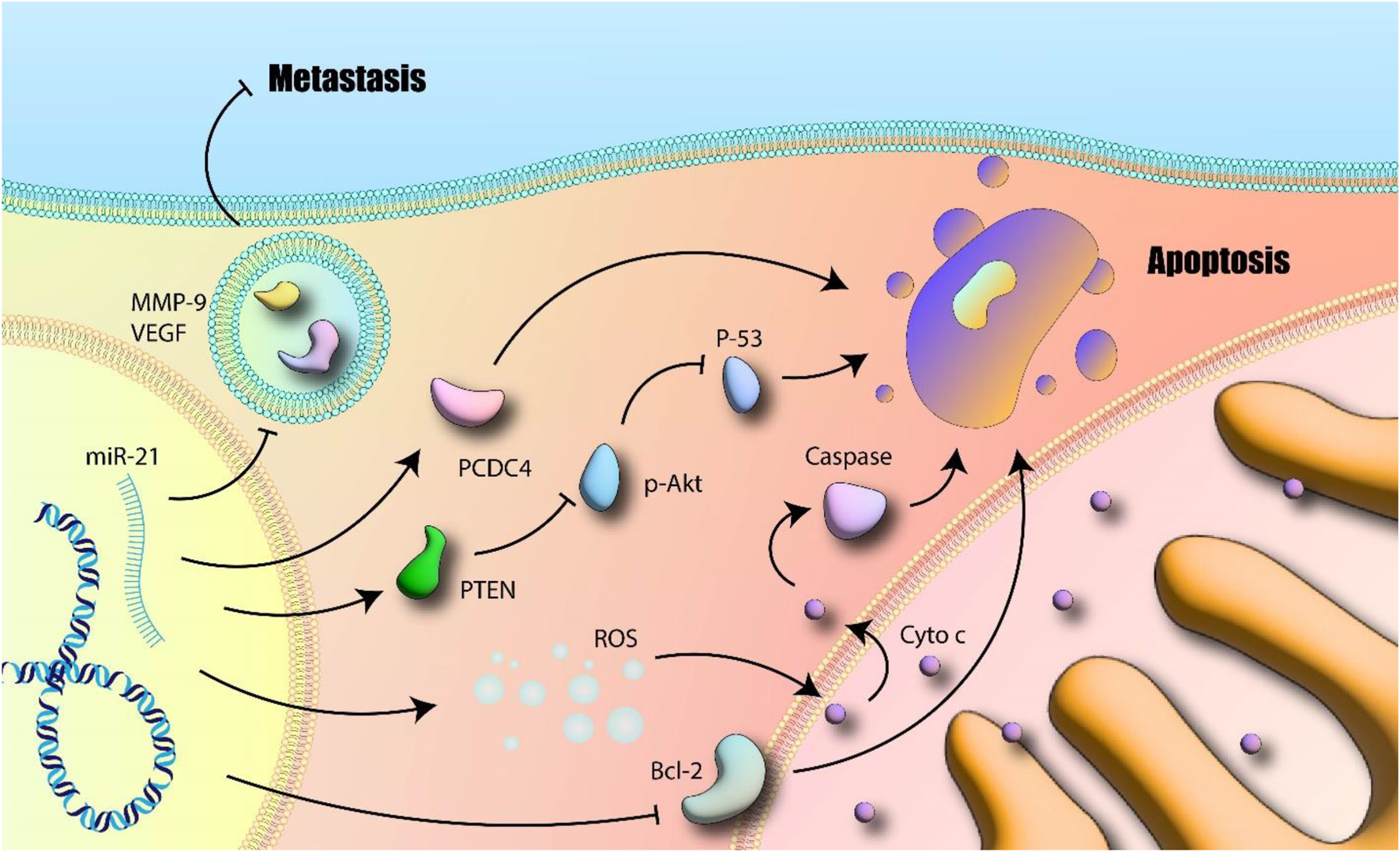
miR-21 and apoptosis: MiR-21 induces MMP-9 and VEGF and further promotes metastasis. Additionally, inhibition of apoptotic related mitochondrial pathway as well as promotion of subcellular signaling pathways which are involved in cell survival and proliferation are other suggested mechanisms. Akt-p: Phosphorylated Akt; BCL-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; Cytoc: Cytotoxic; MMP-9: Matrix Metalloproteinase 9; PTEN: Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog; ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species; VEGF: Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (author-created).
Role in chemoresistance and autophagy via PI3K/Akt/mTOR
MiR-21 has recently been linked to Cisplatin (DDP)-resistant Gastric Cancer (GC) and has been found to be more abundant in these cells than in their parental comparable cells (Dong et al., 2011). Gu et al. investigated the link between miR-21, autophagy, and DDP resistance in vitro. They generated DDP-resistant human gastric adenocarcinoma cell lines by continuous DDP exposure. Western blot analysis confirmed activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in resistant cells. Autophagy levels were assessed by measuring Beclin-1 and LC3 expression (via Western blot) and quantifying autophagosome formation (e.g., via electron microscopy or fluorescent LC3 puncta). Cell survival and apoptosis were quantified using Annexin V-propidium iodide assays. GC cells developed resistance to the growth inhibition and death that the DDP therapy induced. Moreover, DDP-resistant GC cells had increased Akt and mTOR activity. When autophagy was suppressed, GC cells were less sensitive to DDP, but when autophagy was stimulated, the reverse outcome was shown. It was discovered that DDP-resistant GC cells had more microRNA miR-21 than the parent cells did. When DDP-resistant GC cells were transfected with a miR-21 inhibitor, the DDP-resistant GC cells became more sensitive through increasing autophagy, whereas when transfected with miR-21 mimics, DDP resistance has been restored by lowering autophagy. Both of these results were brought about by the miR-21 gene. They discovered that DDP resistance within GC cells is linked to the miR-21, which inhibits autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. This happens because miR-21 suppresses the process. Also, these findings suggested that the therapeutic targets for the successful treatment of DDP resistance within GC cells may include the autophagy-causing substances (Zhao et al., 2015). This study directly links miR-21 overexpression to chemoresistance (specifically to cisplatin) by demonstrating its ability to suppress protective autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, identifying autophagy induction as a potential strategy to overcome miR-21-mediated resistance. Inflammatory signaling pathways are also key regulators and effectors of miR-21 in gastric cancer.
Regulation by inflammatory signaling (NF-κB, IL-6, STAT3)
MiR-21 expression is controlled more than usual by NF-kappaB activation within bone marrow-derived macrophages (Hwang et al., 2010), also through myeloma cells especially inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL)-6 (Toste et al., 2015). Through the related activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) and inactive signal transducer as well as the common gp130 co-receptor subunit, miR-21 expression and IL-6 signaling were related (Zhang et al., 2019a). Stat3 has a substantial impact on the development, stability, and advancement of solid tumors. This is partially because it is a negative regulator of the immune system’s response to malignancies and an intrinsic promoter of neoplastic cells (Yuan et al., 2016). Patients with gastric cancer generally have a worse prognosis when their Stat3 levels are high, and this is especially true if the disease has spread to their lymph nodes (Mace et al., 2013). Tse et al. demonstrated that miR-21 is a Stat3-regulated driver in tumor growth along with enhancement using the development of inflammatory mediator’s gastric cancers in Gp130 F/F mice. This technique was used to demonstrate that Stat3 was necessary for the development of the tumor. Their results were managed to bring into agreement when they identified multiple preserved Stat3 binding sites upstream of the miR-21 gene promoter and demonstrated that systemic administration of a miR-21-specific antisense oligonucleotide antagomir lowered established gastric tumor volume in the Gp130 F/F mouse model of inflammation-associated gastric cancer. Inhibition of miR-21 reduced markers of EMT, decreased ECM remodeling, and restored PTEN function both in cell culture (in vitro) and in the mouse model (in vivo). All of these advantages result from reactivating PTEN. Gastric cancer patients with high levels of STAT3 as well as miR-21 have a worse prognosis, according to preclinical research. A powerful therapeutic target for solid tumors with increased Stat3 activity, miR-21 encourages the development of gastric cancer related to inflammation. For solid tumors with strong Stat3 activation, miR-21 is a potential therapeutic target (Rachagani et al., 2015). The identification of miR-21 as a direct transcriptional target of STAT3 firmly places it within the inflammation-cancer axis, suggesting that the pro-tumorigenic effects of chronic inflammation (e.g., mediated by IL-6) in the stomach may be, at least in part, channeled through miR-21 upregulation. Clinical studies have further explored the potential of miR-21 isoforms as diagnostic and prognostic markers.
Clinical significance of miR-21-3p as a biomarker
Inflammatory illnesses have been shown to have a connection to miR-21-3p, according to earlier research. miR-21-3p is the primary driver of colorectal cancer because it controls the signaling pathways involved in inflammation (Vila-Casadesús et al., 2018). Also, while renal fibrosis is developing, a higher amount of miR-21-3p in the body produces an increase in the inflammatory response (Benesova et al., 2020). According to in human study of Calsina et al., miR-21-3p may influence a patient’s prognosis if they have metastatic paraganglioma or pheochromocytoma (Ryu et al., 2011). In another in human study, Sun et al. investigated the role of miR-21-3p in the occurrence of gastric cancer and the prognosis of the patient (GC). Analyzing One hundred GC patients. miR-21-3p was tested in primary GC and paracancer mucosa. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves for miR-21-predictive 3p in GC. Tumor size, lymph node metastases, and TNM staging subdivided GC patients. GCs produce the miR-21-3p. Stage, size, and lymph node metastases were divided into categories. Patients with big tumors, lymph node metastases, or in the GC tissues of patients with advanced TNM staging, miR-21-3p levels were greater. MiR-21-3p can diagnose GC, per ROC curves. In GC patients overexpressing miR-21-3p, Progression-Free Survival (PFS) and Overall Survival (OS) were worse. Size, lymph node metastases, TNM staging, and miR-21-3p level impacted GC prognosis (LaConti et al., 2011). Consistent clinical findings correlating elevated miR-21 levels (including specific isoforms like miR-21-3p) with advanced stage and poor prognosis reinforce its potential utility as a non-invasive biomarker for gastric cancer diagnosis and patient stratification. Mechanistically, miR-21 also impacts cancer metabolism.
Impact on metabolism via PDHA1 regulation
The enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase alpha 1(PHA1) is essential. This enzyme connects glycolysis with the citric acid cycle in the mitochondria by catalyzing pyruvate decarboxylation. Cancer cells become more lethal when pyruvate dehydrogenase is inhibited, since this enhances the Warburg effect (Papaconstantinou et al., 2013; Nagao et al., 2012). Cancer cells have been shown to undergo metabolic reprogramming when there is deregulation of the gene PDHA1, which has also been discovered (Liu P. et al., 2013). Poor ovarian cancer prognosis has been connected to low PDHA1 expression, according to the literature (Wang F. et al., 2015). Moreover, the more aggressive features of clear cell carcinoma have been associated to low amounts of PDHA1 protein expression (Popov et al., 2015). This work reveals a metabolic dimension to miR-21’s oncogenic function, linking its overexpression to the Warburg effect via suppression of PDHA1 and suggesting that targeting miR-21 might impact tumor metabolism. Beyond metabolism, miR-21 continues to be implicated in EMT regulation within gastric cancer.
Promotion of EMT via TGF-β1/PTEN axis
Li and colleagues found in vitro that miR-21 promotes TGF-β1-induced EMT in gastric cancer cells, an effect linked to regulation of PTEN expression. Inhibition of miR-21 using specific inhibitors led to increased expression of PTEN and E-cadherin, while decreasing the levels of N-cadherin, β-catenin, Vimentin, and Slug, markers associated with EMT. The inhibition of miR-21 significantly reduced cell migration and invasion, both in vitro (through scratch tests) and in vivo (xenograft models), by regulating EMT-related factors. These findings suggest that miR-21 facilitates TGF-β1-induced EMT in GC cells via its known targeting of PTEN, thus promoting tumor progression (Park et al., 2009). Liu et al. looked into gastric cancer by studying the miRNA that controls PDHA1. Researchers found a connection between PDHA1 downregulation and a bad prognosis for gastric cancer. Decreased levels of PDHA1 increased glycolysis, which promoted gastric cancer growth and metastasis. To boost glycolysis and cell growth in gastric cancer, miR-21-5p selectively addressed PDHA1 and downregulated PDHA1 expression. MiR-21-5p was elevated in specimens of gastric cancer, while PDHA1 expression was inversely linked with it. Finally, they suggested that miR-21-5p may target PDHA1 to control a metabolic shift and cancer progression in gastric cancer, suggesting a possible function for this pathway in the therapy of gastric cancer (Hong and Park, 2014). Collectively, the studies on gastric cancer consistently implicate miR-21 in promoting invasion, metastasis, chemoresistance, and metabolic reprogramming, frequently converging on the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway, while also highlighting its connection to inflammatory signaling and its potential as a clinical biomarker. This pathway, essential for cell proliferation and survival, also regulates autophagy, which plays a paradoxical role in cancer progression and therapy response. Targeting the miR-21/PTEN/Akt signaling axis offers a potential therapeutic approach for GC, and further studies are needed to optimize such strategies for clinical application. Table 2 lists various studies on miR-21 and gastric cancer.
TABLE 2
| Type of miR-21 | Status of expression | Target | Model | Cell line type | Effect | Conclusion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Up | KLF5, RECK, TMP1, PDCD4, PTEN, BAX, BCL-2 | In vitro, In vivo | AGS, MKN1 | Inhibition of miR-21 has therapeutic benefits with the functional restoration of PTEN in vitro and in vivo | miR-21 as a robust therapeutic target for solid malignancies characterized by excessive Stat3 activity | Rachagani et al. (2015) |
| miR-21-3p | Up | - | Human, in vitro | SNU-1, AGS, Hs 738.St/Int | He expression levels of miR-21-3p were markedly increased in cancer tissues | Overexpression of miR-21-3p promoted cancer cell migration and invasion | Wang et al. (2009a) |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 and miR-25 were significantly upregulated in GC patients | miR-21 in plasma samples can be served as a potential noninvasive tool in detection of GC | Joshi et al. (2014) | |
| Up | - | In vitro, In vivo | SGC-7901 | The GCIF was able to upregulate the expression of miR-21 in the subcutaneously transplanted tumors | Wartenberg et al. (2016) | ||
| Up | WWP1, SKP2, KLHL42, FBXO11 | Human | - | miR-21 was significantly higher in gastritis group | Overexpression of miR-21may indicate a connection between miRNAs and H. pylori-related problems | Ali et al. (2010) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Significant upregulation of miR-21 in the EGN mucosa | oncogenic potential for miR-21 | Ryu et al. (2010) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | LIFR | In vitro, In vivo | GES-1, AGS, HGC-27 | miR-21-5p overexpression attenuated Lidocaine-induced anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic effects on GC cells | Lidocaine might GC cell malignancy by modulating circ_ANO5/miR-21-5p/LIFR axis, highlighting a novel insight for GC treatment | Valladares-Ayerbes et al. (2011) |
| miR-21-5p | Up | RUNX1 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | AGS, HGC-27, GES-1 | circ_0027599 positively regulated RUNX1 expression via functioning as the sponge for miR-21-5p | Circ_0027599 modulates the miR-21-5p/RUNX1 axis, which may reveal a new GC treatment target. | Carter et al. (2016) |
| miR-21 | Up | APE1, ATM, ATR | In vitro | AGS, HGC-27 | Upregulation miR-21 | It may be a promising strategy for controlling tumor progression | Ali et al. (2015) |
| miR-21-5p | Up | - | Human | - | Higher miR-21-5p expression was associated with T3 + T4 and stage III + IV. | miRNAs may act as potential diagnostic markers | Karamitopoulou et al. (2017) |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | SNU-398, SNU-182 | Upregulating lncRNA CASC11 upregulates miR-21 to cause carboplatin resistance in HCC patients | Habbe et al. (2009) | ||
| Up | PTEN, ERK | Human, In vitro | MKN28, MKN45 | miR-21 expression was upregulated in GC tissues and could be negatively regulated by circHIAT1 | CircHIAT1 downregulated miR-21 to suppress GC cell tumors, suggesting it may be a potential GC therapy target. | Calatayud et al. (2017) | |
| Up | PI3K | In vitro | AGS/DDP | miR-21 mimics contributed to restored DDP resistance by suppressing autophagy | miR-21 is associated with DDP resistance in GC cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | Zhao et al. (2015) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | - | Human, In vitro, In vivo | MKN45, SGC-7901, BGC-823, GES-1 | miR-21 is a GAS5 target and GAS5 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by targeting miR-21 | Targeting miR-21 expression may effect on migration, invasion, and tumor formation, and increase apoptosis | Bhatti et al. (2011) |
| miR-21 | Up | - | In vitro | MGC-803, MKN-28, AGS, BGC-823, GES-1 | miR-21 expression in GC cell lines was higher than in a gastric mucosal epithelial cell line | miR-21 might promote the invasion and metastasis of GC by upregulating EMT. | Paik et al. (2013) |
| miR-21 | Up | KCNK15-AS1 | Human, In vitro | GES-1, BGC-823, SGC-7901 | Knockdown of the expression of miR-21 inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis | KCNK15-AS1 interacted with miR-21 | Duell et al. (2017) |
| Up | - | In vitro | MKN-45 | miR-21, which are involved in stemness and chemo-radioresistance, may provide novel GC therapy insights | Humeau et al. (2015) | ||
| Up | PTEN, NF‐κB | In vitro | MKN-45 | (miR-21) increased cell viability, migration, and invasion | Celastrol reduces MKN45 cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via down-regulating miR-21 and inactivating PTEN/PI3K/AKT and nuclear factor κB signaling pathways | Liu et al. (2012) | |
| Up | SATB1, TIAM1, PDCD4, PTEN, APAF1, TIMP3, TGF-β, PLAG1 | Human | - | miR-21 and miR-222 were significantly higher in GC plasma | miR-21 and miR-222 in plasma samples can be served as a potential noninvasive tool in GC detection | Xue et al. (2013) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | MGC-803 | Colonospheres that are highly enriched in cancer stem/stem like cells reveal increased miR-21 expression and decreased PTEN | CDF normalizes miR-21-PTEN-Akt pathway suggests that the chemical may treat chemotherapy-resistant colorectal cancer | Song et al. (2013a) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | AGS, NCI-N87 | miR-21 inhibited cell cycle progression and enabled apoptosis | miR-21 may provide a therapeutic target for treatment of human gastric cancer | Tian et al. (2016) | |
| Up | 15-PGDH | Human, In vitro | TMK-1, AGS, KATO III, NCI-N87, MKN-1, MKN-28, MKN-45, SNU-1, SNU-5, SNU-216, SNU-484, SNU-601, SNU-638, SNU-668, SNU-719 | miR-21, which was detected in high level in gastric tumors | Loss of 15-PGDH occurs at the very early stage of gastric adenocarcinoma by miR-21. H. pylori infection may affect miR-21 upregulation | Morinaga et al. (2016) | |
| Up | DAXX | Human, In vitro | NCI-N87, KATOIII, AGS, MKN28 | These sponges inhibit cancer cell proliferation and suppress the activity of miR-21 on downstream protein targets | miR-21could be used as potential future therapeutic application in human patients | Zhang et al. (2012) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | PDHA1 | Human, In vitro | GES-1 | miR-21-5p was significantly upregulated in gastric cancer | Potential role of the miR-21-5p/PDHA1 axis in gastric cancer treatment | Hong and Park (2014) |
| Up | - | Human | - | The level of miR-21 showed no significant differences among patients with different clinical and pathological characteristics | The identification of serum miR-378 and miR-21 affects GC diagnosis | Wang et al. (2014) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 were significantly related to an advanced TNM stage in GC patients | Circulating miR-21, could be used as diagnostic plasma biomarkers in gastric cancer patients | Roy et al. (2013) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Increased expression levels of miR-21 in GC samples | Some miR-21 changed in GC may be researched as biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognosis | Qiang et al. (2019) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 and miR-145 was significantly associated with worse prognosis of gastric cancer patients | miR-21 has the potential to serve as relevant diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of GC | Shen et al. (2014) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human | - | miR-21 were upregulated in GC patients with H. pyloriinfection | Suggests that the miRNAs and genes may help diagnose GC. | Liu et al. (2016c) | |
| Up | MMP-3, MMP-9, VEGF | In vitro, In vivo | AGS, NCI-N87, SGC-7901, MKN-45, TMK-1, GES-1 | Overexpression of miR-21 promoted cell mobility of AGS through activation of EMT | MEG3/miR-21 axis participates in the tumor progression and metastasis of gastric cancer through the regulation of EMT. | He et al. (2015) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro, In vivo | MKN74, MKN45, SGC7901, AGS, GES-1 | pcDNA3.1-MEG3 transfection could counteract the promoting role of miR-21 mimic on GC cell proliferation and metastasis | Regulating role of MEG3/miR-21 axis in GC progression and provided a new potential therapeutic strategy for GC treatment | Yang et al. (2013a) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | caspase-8, PI3K, PTEN | In vitro, In vivo | BGC823, SGC7901 | miR-21 regulated by NF-κB mediated the expression of P-gp protein via inhibiting caspase-8, thus regulating Cisplatin-induced cell death | Our results suggest that LV-METase has potential as a therapeutic agent for gastric cancer treatment | Li et al. (2016b) |
| Up | PTEN, P53 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | MKN28, MKN45, SGC-7901, AGS, NCI-N87, HGC-27 | CBX7 was found to upregulate miR-21 via the activation of AKT-NF-κB pathway | CBX7 positively regulates stem cell-like characteristics of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p16 and activating AKT-NF-κB-miR-21 pathway | Vahidnezhad et al. (2016) | |
| Up | p53, PDCD4, Bcl-2 | Human, In vitro | MGC803 | Inhibition of miR-21 reduced the levels of miR-21 and Bcl-2 in MGC803 cells | miR-21 and Bcl-2 may be biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer | Gu et al. (2020) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | PTEN, TIMP3 | Human, In vitro | SGC7901, HEK-293T | Suppressing miR-21-5p expression partially sensitized SGC7901/DOX cells to DOX | Suggests the potential utility of miR-21-5p antagonism to sensitize GC cells to DOX chemotherapy | Sheedy et al. (2010) |
| Up | PTEN | Human | - | - | miR-21 can be use as potential biomarker for GC. | Löffler et al. (2007) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | MKN74 | miR-21 inhibition was associated with increased expression of PTEN | miR-21 inhibitor may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer | Iliopoulos et al. (2010) | |
| Up | 15-PGDH | Human, In vitro | BGC-823, MKN-28, AGS | miR-21 is negatively correlated with 15-PGDH | miR-21 play a role in the progression of gastric cancer | Johnson et al. (2018) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | - | Human | - | miR-21-5p could be detected in small amounts of urine sample | Urine miR-21-5p could be utilized as a novel non-invasive biomarker of gastric cancer detection and monitoring | Deng et al. (2010) |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | MGC-803 | miR-21 and miR-182 in peripheral blood of gastric cancer patients were significantly high | Serve as a target for the clinical treatment of gastric cancer | Tse et al. (2022) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 was significantly higher in the peripheral circulation | Serum miRNA biomarkers may originate from tissues other than the primary tumour | Li et al. (2016b) | |
| Up | Human | - | miR-21 expression in tissue was associated with tumor differentiation | miR-21 could serve as a potential biomarker to identify MGC with chemoresistance | Butz et al. (2016) | ||
| Up | p53, PTEN | Human, In vitro | SGC7901, MKN45, GES-1, AGS | There was a positive correlation between Bmi-1 and miR-21 expression in gastric cancer | Bmi-1 upregulates miR-21 and miR-34a by activating AKT-NF-kB pathway | Calsina et al. (2019) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro, In vivo | SGC-7901, KATO-III | MiR-21 inhibitors significantly inhibit cell migration and invasion in GC cell lines | miR-21 could promote TGF-β1-induced EMT in GC cells through up-regulating PTEN expression | Park et al. (2009) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miRNAs is a novel and noninvasive biomarker for gastric cancer, and could facilitate and simplify its diagnosis | Sun et al. (2020) | ||
| Up | - | Human | - | miRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of patients at early stages | Kim et al. (2006) | ||
| Up | FZD6 | In vitro | SGC-7901, AGS, GES-1 | miR-21- effects in the canonical and non-canonical wnt pathways | May be an important implication for future therapy | Dupuy et al. (2015) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Pregulated in malignant versus adjacent benign gastric mucosa | Suggest the potential for a noninvasive addition to cancer diagnostics | Li et al. (2016c) | |
| Up | Noxa | Human, In vitro | SGC-7901 | An increased miR-21 expression level was identified as a risk factor for advanced stage gastric cancer | miR-21 expression may induce gastric cancer migration and invasion via the downregulation of Noxa expression | Liu et al. (2015) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up | - | Human | - | miR-21-5p may be useful as a predictor of recurrence in young GC patients whose tumors contain a high proportion of intratumoral stroma | Li et al. (2016d) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Lin et al. (2016) | |||
| Up | Bax, Bak, PTEN, Bcl-2 | In vitro | AGS | miR-21 mediates anticancer effects of NS398 in GC cells by regulating apoptosis-related proteins | miR-21 is one of the molecular targets of this specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in the prevention and treatment of GC | Liu et al. (2018b) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Higher tissue hsa-miR-21 level was related to a lower overall survival rate | Can be potentially applied as novel and non-invasive biomarkers for GC. | Li et al. (2022) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Can be used for early detection of gastric cancer | Cuellar-Gomez et al. (2021) | ||
| Up | PTEN | Human | - | miR-21 in both serum and PBMCs increased significantly in GC patients | miR-21 (both in serum and in PBMCs) can serve as a good biomarker for GC and could be used in diagnosis of early (stage I) and late GC (stage IV) | Sun et al. (2021) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Stromal miR-21 is closely related to tumour progression in GC | Stromal miR-21 of tumours might be a target of treatment | Nooh et al. (2021) | |
| Up | PTEN, PDCD4 | In vitro | SGC-7901, MKN-45 | miR-21 inhibitor increased the expression of PTEN and PDCD4 proteins and significantly reduced cell proliferation, migration and invasion | May have important role in gastric cancer growth and dissemination by modulating the expression of the tumor suppressors PTEN and PDCD4 | Pita et al. (2021) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | was significantly overexpressed in gastric tumors compared to normal gastric tissues | Potential as prognostic biomarkers in late stage gastric cancer | Guan et al. (2022) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 level was associated with the tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage, tumor size and tissue categories | miR-21 in peripheral blood as a novel tool for monitoring CTCs in gastric cancer patients | Han et al. (2021a) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 in gastric cancer was significantly high | Potential as prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer | Manoel-Caetano et al. (2020) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vitro | MKN1, MKN7, MKN45, MKN74, NUGC3, NUGC4 AZ521, KATOIII |
An inverse correlation between PDCD4 mRNA and miR-21 was found in gastric cancer | May serve as a target for effective therapies | Zhang et al. (2020) | |
| Up | RECK | Human, In vitro | AGS SGC7901, MKN45, MKN28 GES-1, HEK-293T |
Forced expression of miR-21 significantly enhanced cell proliferation and invasion | miR-21 may be important in the initiation and progression of gastric cancers as an oncomiR | Liu et al. (2020b) | |
| Up | Serpini1 | Human, In vitro | MKN28 | miR-21 and Serpini1 expression levels were inversely correlated in a subgroup of gastric cancers | miR-21 is upregulated, inducing downregulation of Serpini1 | Quan et al. (2020) | |
| Up | PDCD4, RECK, PTEN | Human | - | Li et al. (2020) | |||
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | MKN-45 | Increase in mir-21 and mir-302 expression level in CSCs, relative to cancer cells | May be promising objects for targeting CSCs specifically and efficiently | Xiao and Jie (2019) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | SGC-7901, MKN-28, MKN-45, AGS | The transwell test indicated that cell migration in vitro was notably inhibited with the downregulation of miR-21 | miR-21 suppression may increase PTEN expression, suggesting that gastric cancer may start and progress via PTEN. | Wang et al. (2013) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vitro | AGS, MKN1, SNU216, SNU484, SNU638 | miR-21 overexpression was frequently detected in gastric cancers | May play a role in the development and progression of gastric cancers | Zhang et al. (2019b) | |
| Up | FASLG, BTG2 | In vitro, In vivo | GES-1, AGS, BGC-823, HGC-27, MKN-28, SGC-7901 | miR-21, contribute to the transformation induced by MNNG in GES-1 cells | Offers a new explanation of the mechanisms underlying chemical carcinogenesis | Motamedi et al. (2020) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Expression of miR-21in gastric cancer samples was significantly high | May be applicable to future decisions regarding treatment or as a diagnostic biomarker | Yao et al. (2019a) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | The plasma miR-21 expression was highly associated with differentiation degree and lymph node metastasis rate | miR-21 could be a novel potential biomarker for GC prognosis | Emami et al. (2019) | |
| Up | PI3K | In vitro | GES-1, MGC-803, BGC-823 | miR-21 inhibitor could decrease phospho-Akt expression and NF-κB activity | The effect of celastrol on apoptosis was due to miR-21 inhibiting the PI3K/Akt-dependent NF-κB pathway | Zhou et al. (2019) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 in the serum were associated with an increased tumor size and an advanced pT stage | Serum miR-21 could be exploited as a practical biomarker for monitoring tumor burden in patients with GC. | Park et al. (2018) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | MKN45, NUGC4, NCI-N87 | miR-21/PTEN pathway regulated the sensitivity of HER2-positive GC cell lines to trastuzumab through modulation apoptosis | Suggest miR-21/PTEN pathway may be essential to the trastuzumab resistance mechanism in GC. | Liu et al. (2018c) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 after eradication were significantly higher in the high-risk group than in the controls | May provide a novel and stable marker of increased risk for early gastric cancer after H. pylori eradication | Huang et al. (2018a) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 was detected in patients with low social status | May show homogenous correlations with the existence of common risk factors | Zhao et al. (2018c) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human | - | The relative expression of PDCD4 was negatively correlated with miR-21 | ROS increases gastric carcinogenesis by upregulating miR-21, which downregulates PDCD4 in gastric cancer cells | P et al. (2018) | |
| Up | PTEN, PDCD4, RECK | In vitro, In vivo | U87, LN229, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, SGC7901 | Particular small-molecule miR-21 inhibitor, AC1MMYR2, which prevented Dicer from processing pre-miR-21 to mature miR-21 | Could be used as a broadly useful candidate antitumor drug | Obermannova et al. (2018) | |
| Up | PTEN, RECK, PDCD4 | Human, In vitro | AGS, HGC-27, GES-1 | Caudatin downregulated the expression of oncomir miR-372 and miR-21 | Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a novel mechanism of action for caudatin during therapeutic intervention in gastric cancers | Ranjbar et al. (2018) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | SGC7901 | Dong et al. (2011) | |||
| Up | - | Human | - | Deregulation of miR-21 (upregulation) was detectable in both gastric and esophageal adenocarcinomas | Candidates that can be investigated for their biological functions and for their possible diagnostic | Xu et al. (2018) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 levels in intestinal type gastric cancer specimens were higher than that in diffuse | miRNAs in gastric juice are potential biomarkers that can assist in screening for gastric cancer | Dan et al. (2018) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 were significantly higher in GC patients with stage I | Novel potential biomarkers for GC detection | Xin et al. (2018) | |
| Up | PDCD4, Serpin B5 | Human | - | - | - | ||
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 level and multiple clinicopathological factors | Elevated miR-21 is linked to lymph node metastases, which could be used as a biomarker in GC patients | Gu et al. (2018) | |
| Up | TPM1, PDCD4, PTEN, RECK | Human | - | miR-21 was significantly overexpressed in human solid cancerous serum | MiR-21 may be a broad-spectrum serum biomarker for various solid tumors. | Chen et al. (2018a) |
miR-21 and gastric cancer.
Abbreviations: 15-PGDH, Prostaglandin Dehydrogenase 15; APAF1, Apoptotic Protease Activating Factor 1; APE1, Apurinic/Apyrimidinic Endonuclease 1; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR, Ataxia Telangiectasia and Rad3-Related; Bak, Bcl-2, antagonist killer; BAX, Bcl-2-Associated X Protein; BCL-2, B-Cell Lymphoma 2; BTG-2, B-cell Translocation Gene 2; DAXX, Death Domain-Associated Protein; ERK, Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase; FASLG, fas ligand; FBXO11, F-box Protein 11; FZD6, Frizzled Class Receptor 6; HPDE, non-tumorigenic human pancreatic ductal epithelial cell line; KCNK15-AS1, Potassium Two-Pore Domain Channel Subfamily K Member 15 Antisense RNA, 1; KLF, Kruppel-Like Factor; KLHL42, Kelch Like Family Member 42; LIFR, leukemia inhibitory factor receptor; MAPK, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor Kappa B; PDCD4, Programmed Cell Death 4; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase; PLAG1, PLAG, Transcription Factor 1; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; RECK, reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with kazal motifs; RUNX1, Runt-Related Transcription Factor 1; SATB1, Special AT-rich Sequence-Binding Protein 1; SKP2, S-phase Kinase-Associated Protein 2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; TIAM1, T-Cell Invasive Antigen 1; TIMP3, Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases 3; TPM, tropomyosin; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VHL, Von Hippel-Lindau; Wnt, Wingless-Type MMTV, integration site family member; WWP1, WW, Domain Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase 1.
MircroRNA-21 and esophageal cancer
The cell surface is covered with a protein family called cell adhesion molecules (CADMs). Members of the CADMs family include CADM1, CADM2, CADM3, and CADM4. The CADMs family of genes that inhibit tumors has been discovered (Huang Y. et al., 2018). Some forms of malignant tissue either completely lack or express CADMs at very low levels. For instance, in lung cancer and prostate cancer, promoter methylation prevents the formation of CADM1 (also known as TSLC1) (Wang P. et al., 2018). Also, in prostate cancer, CADM2 expression is downregulated (Li L. et al., 2018). The authors (Li et al.) examine the underlying mechanism of action of CADM2 and its possible significance in ESCC. In this work, In ESCC cell lines and tissues, the scientists discovered that CADM2 expression was comparatively low. The overexpression of CADM2 prevented the growth of ESCC cells and caused them to commit suicide. Additionally, overexpression of CADM2 prevented ESCC cells from using the Akt signaling pathway. Anti-miR-21-5p was observed to limit cell proliferation as well as trigger apoptosis after miR-21-5p has been downregulated, whilst CADM2 knockdown attenuated these effects. Anti-miR-21 transfected cells had decreased levels of p-Akt expression. Si-CADM2 co-transfection increased the expression of p-Akt in the cells within comparison to cells transfected via anti-miR-21-5p. Downregulation of miR-21-5p prevents ESCC cell proliferation as well as death via the CADM2/Akt pathway. According to their research, treating ESCC by focusing on the miR-21-5p/CADM2-Akt axis may offer a fresh, successful method (Kao et al., 2017). These findings identify the miR-21-5p/CADM2/Akt axis as a specific regulatory node controlling ESCC proliferation and apoptosis, offering a potential therapeutic target.
Interaction with the immune microenvironment and T cells
The presence of specific T cell subsets as well as the organized growth and activation of T lymphocytes in the tumor microenvironment are crucial for cancer immunosurveillance (Wang et al., 2017). Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, which form the majority of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, are key effectors of anti-tumor immunity, which may be further subdivided into the following groups: CD8+ Tregs, Tc1, Tc2, Tc17, and Tc18 (Sierzega et al., 2017). Interferon gamma (IFN) as well as tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF) are created by Tc1 cells and have a strong anti-tumor impact, but interleukin (IL)-4, and IL-10, as well as IL-5, secreted through Tc2 cells have a minor to no effect on tumor formation (Qi et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2016b). Because Tc17 CD8+ T cells do not exhibit cytotoxic effects, it is unknown if functional and phenotypic factors contribute to their antitumor activity. In-depth research on Tc17 CD8+ T cells (IL17 secreting) is lacking (Huang et al., 2016; Mirzaei et al., 2016). An increase in CD8+ Treg cells was connected to downregulated anti-tumor immune reactions in some tumour microenvironments (Yan et al., 2016). T-cell regulation is one of the immune cell development and activation mechanisms that microRNAs control (Treece et al., 2016; Sun et al., 2016). The tumor suppressor gene PTEN is primarily targeted by the oncogene miR-21, which encourages the invasion and growth of ESCC cancer cells (Park et al., 2016). This gene was identified as a possible therapeutic target and a promising candidate for the creation of reliable prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers in ESCC due to its high expression (Sisic et al., 2015). MiR-29b, on the other hand, is hypothesized to function as a tumor-suppressor miRNA because it is typically downregulated in ESCC (Li H. et al., 2015). In another study conducted by Samiei et al.; they compared CD3+CD8+ T cells from 34 patients who have ESCC (12 recently diagnosed: ND, 24 under-treated: UT) to CD3+CD8+ T cells from 34 matched healthy donors to ascertain the diagnostic and/or prognostic utilities of IL-10, IFN-γ, and TGF-β, as well as IL-17a producing CD8+ CD3+ T cells (after 160 weeks of follow-up) (Wang D. et al., 2015). Only patients with UT had an increase in Tc17 and CD8+ Treg cell frequency, whereas ND and UT ESCC patients also experienced an increase within IL-10 and TGF-producing CTLs (CD8+ Tregs). Area under the curve [AUC] >0.9 analysis revealed TGF and IL10 expression medians in CTLs to be highly distinguishing biomarkers among ESCC patients and healthy controls. Further, decreased expressions of TGF, IL17a, IL10, and IFN in CTLs were linked to improved prognosis in ESCC. Novel treatment goals in addition potent Predictive and Diagnostic tools for ESCC may be found in the correlation between miR-21 expression and the decreased function of CD3+ CD8+ T cell subsets (Wang D. et al., 2015). This study uniquely links elevated miR-21 expression in ESCC patients to dysregulation of anti-tumor cytotoxic T cell function, suggesting miR-21 contributes to immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment. Returning to intrinsic cellular pathways, the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis is a frequent target.
Regulation of the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway
It is now understood that this signal pathway is aberrant in conditions such thyroid cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, cerebral cavernous malformations, and prostate cancer (Wu et al., 2015). WU et al. investigated how miR-21 regulation influences the biological functions of human esophageal cancer cells. They found miR-21, PI3K, and Akt expression were higher, while PTEN expression was lower, in esophageal cancer tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues. A low positivity for PTEN protein was found in lymph node-metastatic, poorly differentiated esophageal cancer tissues, but positivity for PI3K and AKT proteins was widespread. When compared to the negative and blank groups, we find that inhibition-miR-21 group considerably upregulates the PTEN expression in TE11 cells. Moreover, the Inhibition-miR-21 group drastically decreased TE11 cell invasion, migration, and proliferation in comparison to the empty and negative control groups. The amount of TE11 cells in the cell cycle’s G0/G1 stage was considerably more in the inhibition-miR-21 group comparing to the control group, although the cells’ proportion in S and G2/M phases was considerably lower. TE11 cells have much greater apoptosis rates than the other cell lines examined. The study concluded that miR-21 promotes esophageal cancer cell growth, migration, invasion, and survival while suppressing apoptosis, effects mediated via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway (Jiang et al., 2011). The role of miR-21 in treatment response is also under investigation. Reinforcing findings from other GI cancers, this work confirms the central role of the miR-21/PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway in promoting esophageal cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, while inhibiting apoptosis.
Involvement in radiosensitivity and target gene regulation (PDCD4, KRAS)
The rising amount of research demonstrating that miRNA expression and the prognosis of esophageal cancer are tightly related and it has revealed that miR-21 may promote radiosensitivity in esophageal carcinoma down TE-1 cells (Zheng et al., 2011). The objective of the research conducted by Wen et al. was to examine the miR-21 expression along with the impacts that it has upon cancer cell invasion, apoptosis, and the target genes’ expression in order to better understand its function in esophageal cancer. In order to determine the production of miR-21 in human esophageal tissues, surrounding tissues, as well as an esophageal cancer cell line, a fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction experiment has been conducted. Protein expression levels of the miR-21 targets PDCD4 and PTEN, as well as KRAS, were examined by Western blotting. These findings revealed a large rise in mir-21 expression within TE-13 cells as well as esophageal cancer tissues; however, it was shown that this phenomenon was unrelated to grading or lymph node metastasis. It might be more likely to invade if the antisense TE-13 cells exhibit a lower rate of apoptosis than the control TE-13 cells. PTEN and PDCD4 protein levels were higher in control tissues/cells compared to miR-21-overexpressing conditions whereas K-ras expression levels exhibited the opposite trend. The study suggested that miR-21 promotes ESCC development and spread partly through its regulation of PDCD4 and potential interaction with KRAS signaling (Liu L. et al., 2010).
Together, these studies in esophageal cancer highlight miR-21’s multifaceted roles in regulating cell adhesion, immune responses, core oncogenic pathways like PI3K/Akt, and potentially radiosensitivity, often through established targets like PTEN and PDCD4.
In esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), the cell adhesion molecule CADM2 plays a significant role in tumor suppression. Low CADM2 expression is commonly observed in ESCC tissues, contributing to enhanced tumor growth and resistance to apoptosis. Overexpression of CADM2 in ESCC cells inhibits proliferation and induces cell death by blocking the Akt signaling pathway. This effect is further regulated by miR-21-5p, where its downregulation leads to decreased cell proliferation and increased apoptosis via the CADM2/Akt axis. Additionally, when CADM2 is knocked down, the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of anti-miR-21-5p are attenuated, highlighting the crucial role of the miR-21-5p/CADM2-Akt pathway in regulating ESCC progression. These findings suggest that targeting this pathway could offer a novel therapeutic strategy for ESCC treatment. The researches on miR-21 and esophageal cancer are listed in Table 3.
TABLE 3
| Type of miR-21 | Status of expression | Target | Model | Cell line type | Effect | Conclusion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | - | Human | - | The connection between miR-21 expression and CD3+ CD8+ T cell subgroup dysfunction may represent novel therapeutic targets | Wang et al. (2015b) | ||
| miR-21-5p | Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | EC109, EC9706, THP-1 | THP-1 macrophages generated by phorbol myristate acetate picked up EVs-miR-21-5p from EC109 or EC9706 cells and became M2 macrophages | Positive feedback between M2 polarity of macrophages and esophageal cancer cell EMT in the TME via miR-21-5p shuttling in tumor-derived EVs | Motoyama et al. (2010) |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 increased in endoscopic tissue biopsies | An alternative to histopathological diagnosis as our method provides a quick result following RNA isolation | Zhang et al. (2008) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | HET-1A, ECA109, KYSE150, TE1 | miR-21 were sensitive in the diagnosis of esophageal cancer | Esophageal cancer diagnosis relies on miR-21, which may be novel biomarkers | Yamanaka et al. (2012) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 significantly overexpressed in ESCC cells | miR-21 may serve as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers in patients with ESCC | Shiotani et al. (2012) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | EC-109 | miR-21 in EC-UT were significantly high | miR-21 in serum could serve as potential biomarkers for ESCC | Golestaneh et al. (2012) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | TE11 | miR-21 promotes human esophageal cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle | A novel esophageal cancer treatment target maybe it | Jiang et al. (2011) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | KYSE170 | miR-21 was overexpressed | Plasma miR-21 in ESCC patients may indicate chemoresistance | Cao et al. (2012) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | MiR-21 levels were significantly raised in esophageal tissue and serum | Esophageal cancer may be diagnosed earlier with miR-21 and miR-375 | Yang et al. (2014) | |
| Up | PDCD4, PTEN | In vivo | - | - | May be useful therapeutic targets in ESCC | Guo et al. (2013) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 and miR-375 were of prognostic impact in ESCC | iR-21 was identified as an independent prognostic biomarker for DSS in patients with EAC | Ma et al. (2013) | |
| Up | CADM2 | Human, In vitro | Het-1A, Eca109, TE-1, KYSE140, EC9706 | MiR-21-5p downregulation caused cell death and growth inhibition | miR-21-5p/CADM2/Akt axis may treat ESCC differently | Kao et al. (2017) | |
| Up | PTEN, PDCD4, K-ras | Human, In vitro | TE13 | mir-21 expression significantly increased in esophageal cancer tissues | Interaction with its PDCD4 and K-ras target genes may contribute to esophageal cancer development and metastasis | Liu et al. (2010b) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | increased levels of miR-21 in adenocarcinoma tissues | Esophageal cancer biomarkers may be diagnostic and predictive | Sha et al. (2014) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 over-expressed in esophageal cancer | Could be used as novel molecular markers of esophageal carcinoma | Song et al. (2013b) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | Eca109 | miR-21 was upregulated in Kazakh’s ESCC and that miR-21 played a negative role in regulating PDCD4 | miR-21 may be a potential therapeutic target in management of ESCC | Eto et al. (2014) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 showed a significant positive correlation with that of salivary miR-21 | salivary miR-21 detection may substitute plasma testing for EC diagnosis | Shiotani et al. (2013) | |
| Up | TGF-β | Human, In vitro | EC9706 | Overexpression of miR-21 in esophageal specimens | A novel oncogenic role of nicotine in human esophageal cancer | Stánitz et al. (2013) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | K150, TE-1, EC-9706, EC-1, EC-109 | Rawq01 also inhibited the PI3K-AKT pathway by upregulating PTEN expression via mir-21 inhibition | May help create chemosensitizing tumor therapy techniques by altering microRNA expression | Tu et al. (2014) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | HEEC, EC9706, EC-1, KYSE1170, KYSE410, KYSE180 | Overexpression of miR-21 correlated with tumor status | May be an oncomiR that regulates PTEN and a novel prognostic factor for ESCC patients | Shi et al. (2013) | |
| Up | TPM1, SMAD, TGFβ1, FGF1, STAT3, STAG2, TIMP3, COL4A1 | Human, In vitro | KYSE-30, OE-33, FLO-1 | MiR-21 is primarily expressed in the SCC stroma and released from fibroblasts to affect SCC cell migration and invasion | May contribute to cellular crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment | Li et al. (2013b) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 saliva supernatant were significantly upregulated in patients | Salivary miRNAs may identify esophageal cancer in high-risk locations | Chen et al. (2013) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | hsa-miR-21* was significantly increased in heavy drinking patients | May be useful biomarkers for high-risk population screening and detection | Cui et al. (2013) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | TE-1 | The inhibition of miR-21 significantly increased the cells’ radiosensitivity | To boost esophageal cancer radiosensitivity, miR-21 inhibition may be a novel treatment | Li et al. (2012) | |
| Up | PDCD4, TPM1 | In vivo | - | Overexpression of miR-21 decreased PPP2R2A and PDCD4, their tumor-suppressor targets | miR-21 deregulation linked to inflammation explains how ZD promotes ESCC | Osawa et al. (2011) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 was substantially greater in EC than controls | MiR-21 in saliva may be a new EC biomarker | Xu et al. (2012) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | - | Wang and Zhang (2012) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | Eca109 | Overexpression of MiR-21 in vitro and ESCC increased cell growth | Might target PTEN at post-transcriptional level, and regulated the cancer invasion in Kazakh’s ESCC. | Takai et al. (2003) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | May help assess these individuals and identify those at risk of postsurgical recurrence | miR-21 correlate with tumor location and lymph node status | Kuramochi et al. (2001) | |
| Up | MAPK, TP53INP1, NFIB | Human, In vitro | TE-1, TE-3, TE-7, TE-8, HCE-4, HCE-7, SKGT-4, SKGT-5, Seg-1, Bic-1 | - | - | Fukuhara et al. (2002) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Noncancerous SCC tissue expresses miR-21 more | May help create prognostic biomarkers and new therapeutic targets and therapies | Chang et al. (2010) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | TE1-15, Het-1A | miR-21 expression was substantially higher than in T1 or T2 cancers | May be involved in tumor growth and invasion | Li et al. (2018b) | |
| Up | p10 | Human | - | Both cancers have 3- to 5-fold greater mir_21 expression than normal epithelium | May help identify Barrett esophagus patients at risk for adenocarcinoma | Rahir and Moser (2012) |
miR-21 and esophageal cancer.
Abbreviations: CADM2, Cell Adhesion Molecule 2; COL4A1, Collagen Type IV, Alpha 1 Chain; FGF1, Fibroblast Growth Factor 1; K-ras, Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog; NFIB, Nuclear Factor I B; SMAD, sma and mad related protein; STAG2, Stromal Antigen 2; STAT3, Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3; TGFβ1, Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1; TP53INP1, Tumor Protein P53 Inducible Nuclear Protein 1.
MicroRNA- 21 and colon cancer
In order to learn more about colon cancer formation, invasion and migration, in vitro and in vivo, Wang et al. studied miR-21 along with its unidentified target genes. To modulate miR-21 levels, colon cancer cells were transfected using specific expression vectors: pmiRZip21 (designed to inhibit miR-21 function) or Leti3 (used as a control vector). When miR-21 was repressed in vitro and in vivo, TIMP-3 and RECK have been upregulated at the mRNA as well as protein levels significantly, while PCDH17 and BMPR-II have not been. The capacity of colon cancer cells to penetrate and move both in vitro and in vivo was significantly reduced after pmiRZip21 transfection. The ability of malignancies to penetrate and spread in vitro and in vivo may be restricted through upregulating TIMP-3 and RECK, which could serve to be a target site in anti-tumor treatment (Fridman et al., 2017). Similarly, Ni et al. investigated the molecular basis for Celastrol’s efficacy as an oncotherapy for colon cancer. Western blotting has been utilized to measure the concentrations of PCNA, PI3K, GSK3, and Akt, as well as phosphorylated Akt and GSK3. To find apoptosis, a method called flow cytometry was developed. They discovered that overexpressing a miR-21 mimic increased cell viability, suppressed apoptosis, lowered BCL-2 expression, increased BAX, and enhanced Caspase-3 activity, all of which were blocked by Celastrol. Additionally, Celastrol’s addition only partially prevented the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3 pathway from being activated by miR-21 mimic. Hence, Celastrol may reduce colon cancer cell growth by blocking the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3 pathway and miR-21 (Fridman et al., 2012). These initial studies establish miR-21’s role in promoting colon cancer cell invasion and survival, potentially through targets like TIMP3/RECK and modulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, suggesting inhibitors like Celastrol could counteract its effects.
Regulation of prostaglandin signaling via 15-PGDH
More Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-derived Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was demonstrated to influence a number of cancer-related processes, such as apoptosis evasion, enhanced tumour angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and migration (Yu and Fu, 2006). PGE2 is easily transformed into its inactive state, and this catabolism may have an effect on the quantity of PGE2 in tissues. COX-2 is the enzyme that produces PGE2, and this enzyme has received the most attention for its contribution to the growth of cancer (Mosmann et al., 1997). It is now known that the enzyme 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH; HPGD) is a crucial regulator of prostaglandin amounts since it breaks down PGE2 (Yang et al., 2015). The rate-limiting stage in prostaglandin catabolism, 15-PGDH inactivation, has been associated with PGE2 quantities in the colon (Kemp and Ronchese, 2001). The practically complete loss of 15-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (PGDH) expression along with activity within human colorectal carcinomas when comparing to corresponding healthy tissue emphasizes the significance of PGDH during the initial stages of neoplastic formation (Yen et al., 2009). Poorer patient survival and more highly malignant phenotypes are associated with less 15-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase expression in gastric adenocarcinomas (Liang et al., 2015). 15-PGDH There are various regulatory domains in mRNA’s 3′untranslated region (UTR), namely, potential microRNA-binding sites and AU-rich patterns, which point to a function for post-transcriptional regulation in regulating the production of 15-PGDH (Zhang S. et al., 2018).
The research by Monteleone et al. shows that 15-PGDH can be controlled by miRNAs. These results show an inverse relationship between miR-21 and 15-PGDH in patients with Colorectal Cancer (CRC), with greater miR-21 quantities being linked to lower 15-PGDH expression. Because some locations within its 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) may directly regulate 15-PGDH, the presence of miR-21 within CRC cells lowers 15-PGDH levels while increasing levels of PGE2. Moreover, when epithelial growth factor (EGF) signaling raises miR-21 levels, miR-21 expression is downregulated. Consistent with this, reducing epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling, which normally induces miR-21, complements the anti-proliferative effects of direct miR-21 inhibition in CRC cells. These findings demonstrate a unique method by which miR-21 controls 15-PGDH, as well as the potential role that aberrant miR-21 expression might have in the loss of 15-PGDH expression and the development of CRC (Wang, 2008). This work uncovers a novel link between miR-21, prostaglandin metabolism (via HPGD suppression), and EGFR signaling in CRC, providing a mechanism by which miR-21 can sustain pro-tumorigenic inflammatory signals. Inflammatory mediators are also tightly linked with miR-21 function in colon cancer.
Interaction with inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6)
Inflammation promotes colorectal cancer. Cancer tissue has higher levels of the powerful inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (Aandahl et al., 2008) and promotes cancer (Liu J. et al., 2013). A number of malignancies have high TNF- levels associated with metastasis, including colorectal cancer (Rahmati et al., 2021). Type II transmembrane protein TNF- is synthesized in cells and exists as stable homo-trimers (Li P. et al., 2013). TNF- conversion enzyme proteolytically cleaves TNF- to produce the active soluble homo-trimeric cytokine (TACE). A series of cellular events are triggered when the cytokine binds to TNF- receptors (TNFR). Intriguingly, Cottonham et al. (Tanaka et al., 2013) discovered in colorectal cancer cells that miR-21 is positively controlled by TNF- and TGF-, and that these cells had increased motility and invasiveness in an organoid model. According to Qiu et al. (Samiei et al., 2019) Chen et al. (Samiei et al., 2022), in a diabetic nephropathy model of rat, it was shown that pulling down miR-21 expression decreased TNF- release. Furthermore, he discovered a link among miR-21 as well as TNF- in oral cancer cells, in which it managed proliferative and fatal behavior. As a result, many studies suggest that miR-21 and TNF may interact in an autocrine and paracrine manner.
Trine Mller et al. were interested in the functions of miR-21 in cell viability and TNF- in necrosis at the invasive front of colon tumors. To co-stain miR-21, TNF- mRNA, and cytokeratin, the researchers created an automated method utilizing frozen colon cancer tissue samples (n = 4). TNF- mRNA expression has been only seen in the four instances’ most aggressive cancer cells. Utilizing confocal slide scanning microscopy-produced digital slides, the expression of TNF-mRNA and miR-21 was studied. In developing cancer cells, expression of miR-21 has been observed within both concordant as well as discordant patterns. When comparing to TNF- mRNA, miR-21 was found to be more abundant in cancer cells. Even though miR-21 is unrelated to the expression of mRNA in the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-, they conclude that TNF- and miR-21 simultaneously assist to tumor growth at the tumor’s invasive front in colon cancers. They suggest that miR-21 protects cancer cells and fibroblasts from autocrine and paracrine TNF-induced cell death (Yang et al., 2015). Studies also indicated that there is a mutual relationship between interleukins and miR-21 in the context of cancer development. Saroor and colleagues indicated that immune cells which produced IL-6 in colorectal cancer induced tumor progression and in the presence of this interleukin, cancer cells produced miR-21 and miR-29b to further induce immune cell IL6 production (Bertrand et al., 2014). Many genes linked to cancer have been suggested as potential targets for the miR-21 microRNA. They consist of cell division cycle 25A, tropomyosin 1, protein sprouty homologues one and 2, programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4), and protein sprouty homologues 2 (Wang J. et al., 2015). The maintenance of T cell effects and the control of protracted inflammatory processes are additional functions of miR-21 (de la Chapelle and Jazdzewski, 2011). These studies collectively implicate miR-21 within the complex inflammatory milieu of colon cancer, linking it to key cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 and suggesting it plays a role in both promoting growth and protecting tumor cells from inflammation-induced death, particularly at the invasive margin. This connection between inflammation and miR-21 is particularly relevant in colitis-associated cancer.
Role in colitis-associated cancer (CAC)
The researchers Shi et al. set out to learn more about miR-21’s role in colitis-related colon cancer (CAC) by looking into its molecular underpinnings. MiR-21 expression was investigated in the tumors of 62 Chinese, 37 Japanese, and Austrian individuals with CRC who just had colitis-related neoplasms. Many in vitro and in vivo, as well as clinical methods were used in investigating the biological roles of miR-21. Tumors from 62 CRC patients, 22 CAC patients, and a mouse model of CAC all showed a substantial increase in miR-21. Interleukin (IL) 6, IL-17A, and IL-23, as well as IL-21 production was reduced, and tumour sizes were decreased in miR-21-knockout mice following treatment with azoxymethane and dextran sulphate sodium. Tumor cell proliferation and E-cadherin expression were both suppressed in CAC mouse tumors lacking miR-21, but -catenin and SOX9 levels were increased. Moreover, in miR-21 knockout mice, expression of its target gene PDCD4 was increased, which unexpectedly correlated with enhanced NF-κB activation, highlighting complex downstream effects in the CAC model. In CAC mice, miR-21 removal boosted tumor cell mortality, which was followed by a decline in STAT3 and Bcl-2 activation. Their results indicate for the first time that inhibiting miR-21 is an effective way to reduce CAC levels (Kar et al., 2015). This genetic knockout study provides strong in vivo evidence for miR-21’s causal role in promoting colitis-associated colorectal cancer, linking its function to inflammatory cytokine production, proliferation control via β-catenin/SOX9, target gene PDCD4, and suppression of apoptosis via STAT3/Bcl-2. Finally, miR-21 plays a critical role in chemoresistance and stem cell characteristics in colon cancer. These findings highlight the PTEN/PI3K/Akt axis as a critical downstream pathway modulated by miR-21 in gastric cancer, suggesting that interventions targeting miR-21 (like curcumin) might restore PTEN function and inhibit tumor growth.
Contribution to chemoresistance and cancer stem cells (CSCs)
One of the main factors contributing to the failure of cancer therapy is drug resistance to previously successful cancer treatments. Although the existence of cancer stem cells (CSCs) was theorized as a contributing factor, this is still not fully understood. Colon cancer cells’ stemness is encouraged by miR-21 (Zhang et al., 2010). Additionally, research has shown that 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU)’s therapeutic potency is markedly diminished by miR-21 overexpression (Si et al., 2007). Since the use of the EGFR inhibitor Cetuximab, it has been discovered that EGFR is related to the miR-21 control (mAb to EGFR), and it's been found to reduce miR-21 production (Hong et al., 2013). In contrast to miR-21, miR-145 has been a tumour suppressor that is regulated by p53 and has been linked to a variety of cancers, including colorectal cancer (Yan-nan et al., 2014). By repressing several pluripotent genes, such as OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4, it controls stem cell renewal and pluripotency (Wu et al., 2016).
The research conducted by Yu et al. sought to identify the molecular basis for miR-21’s regulatory role within colon cancer stem cells. The pCMV/miR-145 expression plasmid or transfection of mature, antagonistic miRs were used to regulate the levels of miR-21 and miR-145. Researchers discovered that miR-21 was noticeably increased and miR-145 was noticeably downregulated in CSC-enriched chemoresistant (CR) colon cancer cells. They showed that miR-145s forced expression in colon cancer cells causes the exact opposite effect from that brought on by upregulating the miR-21, considerably inhibiting the growth of CSCs and tumours. Moreover, SCID mice treated with mature antagomir-21 or miR-145 (anti-sense miR-21) exhibit markedly reduced colon cancer cell xenograft development. Because the expression of CD44, Sox-2 and -catenin was lowered and also CK-20 was activated, this shows that antagomir-21 or miR-145 therapy reduces CSC proliferation as well as encourages differentiation. More proof is provided by in vitro studies showing a negative regulatory relationship between miR-145 and miR-21. It seems that k-Ras is important for the control of this process. This is shown by the fact that within CR colon cancer cells, the absence of k-Ras results in a rise in miR-145 production, a decrease in miR-21 production, and an interruption of the collaboration among miR-21 and miR-145, which would typically result in a negative feedback loop. Current research demonstrates the importance of networks that the microRNAs miR-145 and miR-21 are a part in regulating colon cancer chemoresistance as well as the proliferation or/and diversification of cancer stem cells (CSCs) (Hummel et al., 2011). Highlighting the complexity of miRNA networks, these findings demonstrate a reciprocal negative regulation between the oncomiR miR-21 and the tumor suppressor miR-145, modulated by KRAS signaling, which collectively governs CSC properties and chemoresistance in colon cancer. MiR-21 plays a significant role in colon cancer progression, including tumor formation, invasion, and migration. Furthermore, the involvement of COX-2-derived PGE2 in cancer progression underscores its role in colon cancer. PGE2 influences key processes such as cell proliferation and migration, and its catabolism by 15-PGDH regulates its levels in the tumor microenvironment. Loss of 15-PGDH has been linked to elevated PGE2 levels, contributing to colon cancer progression. These insights highlight the potential for targeting miR-21 and related pathways for therapeutic intervention in colon cancer. Table 4 contains a collection of research on miR-21 and colon cancer.
TABLE 4
| Type of miR-21 | Status of expression | Target | Model | Cell line types | Effect | Conclusion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21-3p, miR-21-5p | Up | - | Human, In vivo | - | - | As a potent diagnostic tool for CC determination | Yang et al. (2013b) |
| miR-21-3p | Up | - | Human | - | The early T-stages were related with hsa-miR-21-3p | An innovative approach to CRC diagnosis and therapy | Wen et al. (2015) |
| Up | PDCD4 | In vitro | - | miR-21 overexpression associated with CC | Presents a new theoretical foundation for CC incidence and development | Song et al. (2021) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | Enhance understanding of local tumor molecular differences | Crawford et al. (2020) | |
| Up (stage dependent) | - | Human | - | Levels of miR’s −21increased in non-vesicular to extracellular vesicular | Detect early-stage CRC in a multiethnic, untested population | Yao et al. (2019b) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 were significantly increased | It may be a new colon and breast cancer biomarker, pharmacological target, or gene target | Zhang et al. (2018c) | |
| Up | PI3K | In vitro | HCT-116 | miR-21 mimic overexpression could enhance the cell viability | Celastrol may reduce colon cancer cell growth by affecting miR-21 and the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway | Fridman et al. (2012) | |
| Up | TIMP-3, RECK | In vitro, In vivo | SW480, SW620, HCT-116, LoVo | In colon cancer cells transfected with pmiRZip21 miR-21 expression decreased | potential as a possible target site in anti-tumour therapy | Fridman et al. (2017) | |
| Up (stage dependent) | - | Human | - | miR-21 in stage II was significantly different from stage IV | Can be a good molecular marker for classification of the stages of colon cancer | Wang et al. (2018c) | |
| Up | PDCD4, PTEN | In vitro | HCT-116, CoN ATCC CRL-1790 | bPGN inhibits miR-21 and its target genes such PDCD4 and PTEN, supporting on-target inhibition | As a molecular probe or therapeutic treatment for miRNA-dependent illnesses | Komatsu et al. (2016) | |
| Up | - | In vivo | - | Noninvasive biomarkers can be used as indicators to screen early colon cancer progression | Lv et al. (2016) | ||
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 was more often seen in cancer cells than TNF-α mRNA | miR-21 may shield fibroblasts and cancer cells from TNF-α-induced cell death | Rahmati et al. (2021) | |
| Up | 15-PGDH, PTEN | Human, Invitro | HeLa, HCT-15, LS174T, HT-29, Caco2, HCT-116 | In CRC patients, miR-21 levels are inversely associated to 15-PGDH expression | May reduce 15-PGDH expression and enhance CRC advancement by increasing PGE2 | Mosmann et al. (1997) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | SW480 | Patients with high miR-21 expression had a significantly shorter survival time | May be involved in the regulation of colon cancer cell proliferation | Fong et al. (2016) | |
| Up (stage dependent) | - | Human | - | Some miR-21-positive TBCs also showed laminin-5γ2 positivity | Digital slides from confocal slide scanning microscopy revealed miR-21 expression in TBCs | Winther et al. (2015) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 associated with TNM classification and clinical staging of adenocarcinoma | Possible novel, non-invasive marker for early CRC diagnosis, screening, and prognosis | Hezova et al. (2015) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-221 was significantly higher in rectal cancer than in colonic cancer | - | Stánitz et al. (2015) | |
| miR-21-5p | Down | Tiam1 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | FIHC, HCT-116, HT-29, SW480 | miR-21-5p was expressed at a low level | May offer novel colon cancer treatment targets | Liu et al. (2014) |
| Up | IL6R | Human | - | Restricted EPC behavior, and miR-21 removal eliminated the decreased proliferation | Provide novel treatment targets | Ye et al. (2014) | |
| Up | Wnt | In vitro, In vivo | SW480 | MiR-21 was downregulated by JQ-1 | Mechanism of JQ-1 action is associated with its regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and miR-21 levels | Zhang et al. (2014) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Increased expression in stool of CC patients | - | Weng et al. (2013) | |
| Up | ITGβ4, PDCD4 | In vitro | HCT116 | Berberine’s anti-cancer actions and apoptosis involve miR-21 | - | Li et al. (2013c) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | evaluated in the normal mucosa adjacent to tumor | Can be used as tissue biomarkers also to the tumor-adjacent mucosa | Nouraee et al. (2013) | |
| miR-21-5p | Up (stage dependent) | - | Human | - | Was detected in stage pT1 | Could support risk assessment in stage T1 tumors | Xie et al. (2013) |
| Up | ING3 | Human, In vitro | SW480, HCT-116, FHC | CASC7 suppressed miR-21/ING3-mediated colon cancer cell growth and migration | may be considered as a novel diagnostic marker of CRC | Huang et al. (2013) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | DLD-1, HCT116, HT29, HT55, SW837, VACO4S | May offer translational opportunities | Alder et al. (2012) | ||
| Up | - | In vitro | RKO, HCT 116 | Practical doses of SFN significantly downregulated oncogenic miR-21 | Is a promising approach for delaying and/or preventing CRC | Xie et al. (2012) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | A high miR-21 expression was associated with reduced progression-free survival (PFS) | May predict chemotherapeutic success and survival in unresectable metastatic CC patients | Hamano et al. (2011) | |
| Up | PTGS2 | Human | - | MIR21 expression was associated with CRC-specific mortality in PTGS2-high tumors | Complex immunity and inflammatory roles in tumor progression | Ma et al. (2011) | |
| Up | TNFα | In vitro, In vivo | HCT-116, HCT-8 | A DHA-rich diet reduced miR-21 expression | A novel mechanism for anti-cancer action of DHA | Hu et al. (2011) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human | - | - | may distinguish recurred from non-recurred patients | Mathé et al. (2009) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | CACO2, HT29, HCT116 | In colon cancer cell lines, high folate boosted miR-21 expression | As a colorectal cancer biomarker | Mori et al. (2009) | |
| Up | - | In vitro, In vivo | SW-48 | - | - | Feber et al. (2008) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human | - | The tumor-associated stroma with the greatest rise in miR-21 from adenoma to adenocarcinoma | May play a role in the development of colon cancer | Wang et al. (2019b) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Tumor MIR21 expression was inversely associated with densities of CD3(+) and CD45RO(+) cells | As a potential target for immunotherapy and prevention in colorectal cancer | Ni et al. (2019) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | In vitro | RKO | The apoptosis ratio increased in miR-21 knockout cells | MiR-21 can mediate the drug resistance to 5-FU | Dixon et al. (2013) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro | HCT-116, HT29, SW620, FHC | miR-21 increased the expression of its target molecule PTEN | Therapeutic strategies against clinical colon carcinoma | Sheng et al. (1998) | |
| Up | RECK | In vitro | SW480, LS174 | Blockage of RAGE with anti-RAGE antibody suppresses S100P induction of miR-21 | S100P induces miR-21 expression via ERK and is inhibited by U0126 | Rozic et al. (2001) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vivo | - | miR-21 increased the expression of its target gene PDCD4 | Novel evidence for miR-21 blockade to be a key strategy in reducing CAC. | Kar et al. (2015) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | In vitro, In vivo | HCT-116, HT-29 | miR-21 negatively regulates miR-145 and vice versa | - | Hummel et al. (2011) | |
| Up | RASA1 | In vitro, In vivo | RKO, HCT116, colo205, SW480, HT29, Caco2 | RASA1 is a target gene of miR-21 | Promotes malignant behaviors of RKO cells through regulation of RASA1 expression | Tai et al. (2006) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Defined the CRC metastatic signature | microRNA can distinguish colorectal lymph node and liver | Tai et al. (2002) | |
| Up | hMSH2 TP, DPD |
In vitro | HT-29, HT-29/5-FU | Significantly inhibited apoptosis, enhanced cell proliferation, invasion | May contribute to colon cancer cells’ 5-FU resistance | Myung et al. (2006) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | It may help counsel and personalize disease management | Backlund et al. (2005) | |
| Up | ITGβ4, PDCD4, PTEN | Human, in vitro | Caco-2, DLD-1, HT-29, SW620, HCT116, Colo 205, RKO | miR-21 is a key player in oncogenic EMT | Could be used to predict CRC metastasis | Tatsuwaki et al. (2010) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Associated with poor therapeutic outcome | May also identify adjuvant chemotherapy candidates | Moore et al. (2011) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro, In vivo | HCT-116, HT-29, SW620 | Increased miR-21 expression | May treat chemotherapy-resistant colorectal cancer | Khan et al. (2016) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | In vitro, In vivo | SW480, Caco-2, HT29 | AR inhibition downregulates miR-21 to suppress growth | - | Monteleone et al. (2019) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | - | Old (1985) | |
| Up | PTEN PDCD4, βR2 |
In vitro | HCT-116, HT-29 | Antisense miR-21 induced differentiation | - | Carswell et al. (1975) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Mostly fibroblast-like cells showed miR-21 signal | miR-21 selection of high-risk stage II colon cancer patients is warranted | Arnott et al. (2002) | |
| Up | PTEN | In vitro, In vivo | SW480, Caco-2, HCT116, HT29 | miR-21 expression, suggesting FOXO3a inactivates AP-1 to shut down miR-21 | A novel role of AR in the regulation of miR-21 | Balkwill (2002) | |
| Up | PTEN | Human, In vitro | LoVo, SW480, caco2 | Overexpression of PRL-3 in colon cancer cells activated STAT3 to produce miR-21 | PRL-3-induced miR-21 promotes colon cancer growth and invasion | Guadagni et al. (2007) | |
| Up | - | Human, In vitro | DLD-1 | Overexpression of miR-21 in CRC samples and advanced disease | CRC cells with increased expression of miR-21 have higher migration ability | Grimm et al. (2011) | |
| Up | Spry2, PTEN | In vitro | HCT116 | mir-21 induced upregulation of Spry2 and PTEN | A potential strategy for colon cancer treatment | Ham et al. (2016) | |
| Up | PDCD4, PTEN | In vivo | - | In colon, miR-21 expression rises with age | Could be used as biomarker | Qu et al. (2017) | |
| Up | TGFβR2 | In vitro, In vivo | HCT-116, HT-29 | downregulation of miR-21 enhances luciferase-TGFβR2-3′ UTR activity | Contributes to stemness regulation via altering TGFβR2 signaling | Yu et al. (2015) | |
| Up | PTEN, PPP2CA, SOCS1 | Human, In vitro, In vivo | HCT-116, DLD1, SW480 | NTR1 activation stimulates expression of miR-21 | Correlate with tumor stage | Qiu et al. (2018) | |
| Up | - | In vivo | - | linked to canonical oncogenic signaling pathways | - | Chen et al. (2018b) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Disease-free survival was considerably shorter with miR-21 expression | miR-21 is primarily a stromal microRNA | Møller et al. (2019) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Patients showed higher expression of miR-21 | Could be used as biomarker | Dehghan et al. (2019) | |
| Up | Cdc25A | In vitro | RKO, DLD1 | miR-21 in modulating cell cycle progression | A potential explanation of miR-21 in tumorigenesis | Wang et al. (2009b) | |
| Up | Cdc25A | In vitro | HCT116 | - | - | Asangani et al. (2008) | |
| Up | SPRY2 | In vitro | SW480, SW620 | - | MiR-21 specifically targets and downregulates SPRY2 to promote cellular protrusions | Meng et al. (2007) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | miR-21 to be expressed at high levels in colonic carcinoma cells | miR-21 expression is associated with poor survival and poor therapeutic outcome | Zhu et al. (2007) | |
| Up | - | In vitro | HT-29, HCT-116 | miR-21 that is associated with anti-apoptotic functions characterizing malignant cells | - | Sayed et al. (2008) |
miR-21 and colon cancer.
15-PGDH, Prostaglandin Dehydrogenase 15; Cdc25A, Cell Division Cycle 25A; DPD, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase; IL6R, Interleukin 6 Receptor; ING3, Inhibitor of Growth Family Member 3; ITGβ4, Integrin Beta 4; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase; PPP2CA, Protein Phosphatase 2 Catalytic Subunit Alpha; PTGS2, Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 (Cyclooxygenase-2); PDCD4, Programmed Cell Death 4; RECK, reversion inducing cysteine rich protein with kazal motifs; RASA1, Ras P21 Protein Activator 1; SPRY2, Sprouty RTK, Signaling Antagonist 2; SOCS1, Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1; TGFβR2, Transforming Growth Factor Beta Receptor 2; Tiam1, T-Cell Invasive Antigen 1; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TP, thymidine phosphorylase; Wnt, Wingless-Type MMTV, integration site family member; βR2, Beta Receptor 2; hMSH2, MutS Homolog 2 (Human).
Exosomal miR-21 and gastrointestinal cancers
Beyond its intracellular functions, miR-21 is actively packaged into exosomes—small extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by various cell types, including cancer cells and stromal cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME). These exosomes serve as potent vehicles for intercellular communication, transferring their cargo, including miRNAs like miR-21, to recipient cells (Shi et al., 2016). This transfer allows exosomal miR-21 to exert profound effects on recipient cell behavior, thereby driving key aspects of GI cancer progression. Key roles attributed to exosomal miR-21 include modulating the TME (e.g., influencing macrophage polarization or fibroblast activity), promoting metastasis through processes like EMT, contributing to chemoresistance, and serving as a circulating biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis (Nautiyal et al., 2012; Martínez-Gutierrez et al., 2022; Han Z. et al., 2021). This section will explore the evidence supporting these diverse functions of exosomal miR-21 in GI cancers.
Exosomes are tiny membrane vesicles (30–100 nm) which transport lipids, proteins, messenger RNAs (mRNAs), along with microRNAs (miRNAs) from 1 cell to another (Shi et al., 2016). Research on the biological importance of MV function has increased significantly recently (Yu et al., 2012). It has been shown that some cell types, such as cancer cells, release miRNAs into different physiological fluids via exosomes (Valeri et al., 2010). MiR-21, which is formed from exosomes and was connected to colon cancer cell invasion and proliferation, is studied via researchers Sun et al. to comprehend its mechanisms and how it functions. Human colonic adenocarcinoma cell lines’ culture media were ultracentrifuged to separate exosomes, and several biochemical methods, including Western blotting, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and electron transmission microscopy, were used to measure the expression levels of miR-21. Afterward, using the colon cancer cell lines T84, LS174, and HT29 along with the normal colon epithelial cell line CRL 1831, they carried out in vitro functional assays (proliferation, invasion) and mechanistic studies (Western blot for target genes). Thus, Colon cancer cells expressed significantly more miR-21 exosomes than normal human colon epithelial cells. Genes engaged in cell invasion, and proliferation as well as extracellular matrix synthesis were upregulated when colon cancer cell lines received treatment in vitro with miR-21 mimics or isolated exosomes. Treatment with these exosomes decreased protein levels of miR-21 targets PDCD4, TPM1, and PTEN in recipient cells; notably, direct siRNA silencing of PDCD4 mimicked the pro-invasive and chemoresistance-inducing effects of exosomal miR-21 transfer. Their findings imply that blocking exosomes, and especially those that contain miR-21, might be an effective new way to treat colorectal cancer (Nautiyal et al., 2012). This foundational study demonstrates that colon cancer cells actively release miR-21 via exosomes, which can functionally transfer oncogenic potential (proliferation, invasion, chemoresistance) to recipient cells, partly by suppressing targets like PDCD4.
Mechanisms and role in metastasis (PDAC, ESCC)
Exosome-mediated intercellular communication significantly controls cancer cell activity (Sachdeva et al., 2009; Bandrés et al., 2006). Particularly exosomal microRNAs (miRNAs) encourage tumour growth by inhibiting their natural regulators (Bandrés et al., 2006). miR-21 plays a range of roles in cancer, such as those connected to metastasis. A prometastatic phenotype is brought on by the transfer of miR-21 from hypoxic oral squamous cell carcinoma exosomes to normoxic cells (Yu et al., 2015) Exosomal miR-21 was shown to enhance the invasion as well as migration of esophageal cancer cells through inhibiting programmed cell death (Figure 3) (Martínez-Gutierrez et al., 2022). MiR-21 expression in exosomes generated by pancreatic stellate cells was shown to be greater in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PSCs) (PDAC) (Martínez-Gutierrez et al., 2022). The goal of Ma et al.’s study was to determine how exosomal miR 21 affects PDAC cells’ migration and look into the potential molecular mechanism underlying this link. In people with pancreatic adenocarcinoma, increased miR 21 levels have been related to a weak prognosis, according to analyses of the Ras/ERK signalling pathway as well as the Cancer Genome Atlas database. In vitro migration and invasion assays on PDAC cells demonstrated that internalization of PSC-derived exosomes containing high miR-21 levels stimulated cell motility, raised matrix metalloproteinase 2/9 activity and induced an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Exosomal miR-21 also raised the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK1/2 (measured by Western blot) within PDAC cells. Our findings suggest that exosomal miR 21 produced by PSCs may increase Ras/ERK signalling activity, speed up PDAC cell motility, and trigger EMT. As a result, miR 21 might be a novel therapy target and a reason why certain pancreatic cancer patients have a bad prognosis (Han Z. et al., 2021).
FIGURE 3
Role of exosomal miR-21 in progression of cancer. Exosomal miR-21 regulates the tumor microenvironment via different signaling pathways in endothelial cells, tumor cells, cancer-associated fibroblasts, and immune cells. AKT, RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; BTG, B-cell translocation gene; FASL, Fas ligand; NF1A, nuclear factor 1 A-type; PDCD4, programmed cell death 4; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; RECK, reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TCR: T-cell receptor; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TLR8; Toll-like receptor 8; TPM1, tropomyosin 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor (author-created).
There is evidence that exosome-formed miRNAs made by tumour cells can enter recipient cells and function biologically there. The miR-21 gene was present in the conditioned medium of esophageal cancer cells. Additionally, esophageal cancer cells co-cultured with fibroblasts showed a significant increase in miR-21, facilitating the transfer of miRNAs that shut down exosomes (Eslamizadeh et al., 2021). Liao et al. looked into the significance of the exosome-shuttling miR-21 in the emergence of esophageal cancer in light of the growing body of evidence indicating exosomes may well be employed to transmit genetic data across cells. Using fluorescence microscopy in co-culture experiments, it was discovered that exosomes enter recipient cells. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition showed that neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2) was required for the uptake of exosomal contents like Cy3-labeled miR-21 mimics. Functionally, exosomal miR-21 transfer increased recipient cell motility and invasion, which was mechanistically linked to the suppression of its target PDCD4 and activation of the JNK signaling pathway. Based on their analysis of plasma samples from a cohort of esophageal cancer patients and healthy controls, they discovered that miR-21 has been much greater within plasma from patients with esophageal cancer, indicating a strong risk link with this disease. Their results showed a strong association among exosome-shunting miR-21 as well as esophageal cancer progression and recurrence. As a result, miR-21, which exosomes may carry, has the ability to predict how well esophageal cancer patients would fare (Martínez-Gutierrez et al., 2022). These studies in PDAC and ESCC extend the functional role of exosomal miR-21 to mediating pro-metastatic communication between different cell types in the TME (stromal cells to cancer cells) and promoting migration/invasion through pathways involving Ras/ERK/Akt and PDCD4/JNK, further linking exosomal miR-21 to poor prognosis. Beyond its functional roles, exosomal miR-21 holds promise as a biomarker.
Exosomal miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker (GC, PM)
MicroRNA (miRNA) analysis in exosomes provides valuable data for early detection of cancer without invasive biopsies. Although miRNAs may be useful indicators in the clinic, their modest quantity in exosomes frequently limits their use. Exosomal miR-21 is detected with high sensitivity by a biosensor developed by Xia et al. that uses dual-signal amplification (miR-21). It creates a DNA-RNA heteroduplex in the existence of a cognate target using the biotin-modified capture probe (Cp) and acts as a substrate for such a nuclease that only recognises duplexes (DSN). The DSN performs enzymatic digestion of the Cps, causing the release of numerous DNA catalysts that support the first signal amplification. The DNA catalyst in the supernatant starts a strand displacement reaction employing a nicking-assisted reactant recycling approach to carry out the second stage of signal amplification after magnetic separation. Their biosensor, which employs the dual-signal amplification principle, can detect miR-21 with such a linear range between 0.5 and 100 fM as well as a detection limit of 0.34 fM. Exosomal miR-21 beats serum carcinoembryonic antigen in detecting patients having gastric cancer (GC) as well as patients having precancerous lesions (PC), according to the receiver operating characteristic curve created throughout clinical sample analysis (area under the curve: 0.89 versus 0.74, n = 40). Using a confusion matrix, the proposed biosensor could distinguish between patients who have PC or GC lesions versus normal donors with an accuracy of 83.9%. The suggested biosensor can also distinguish between individuals with GC who have or have not yet developed metastases. DNA-based biosensor-enabled cancer diagnostics may find new uses thanks to their technology (Shiosaki et al., 2020).
Peritoneal metastasis (PM) patients have a poor prognosis despite it being the location where gastric cancer metastasizes most frequently. It may be difficult to recognize peritoneal lesions, making it tough to decide whether to change the course of treatment. Peritoneal metastases are challenging to detect with Computed Tomography (CT) scans because they are frequently too tiny to accurately assess for size reduction, even with advanced technology. Accurate molecular indicators are necessary to determine the volume of tumor inside the peritoneal cavity.
In order to find new markers that indicate the presence of tumors in the peritoneum, Ohzawa et al. studied the exosomal miRNA profile within peritoneal fluids. Exosomes from gastric cancer patients with either microscopic (P0CY1) or macroscopic (P1) peritoneal metastases (PM) were collected, as well as their miRNA expression profiles were carefully examined. TaqMan Advanced miRNA Assays were then used to confirm the expression of putative miRNAs in all 58 samples. After obtaining the peritoneal fluid from 11 individuals who have PM and 14 individuals who do not have PM, they performed a thorough analysis of exosomal miRNA. In PM (+) samples, they found 11 dysregulated miRNAs. The validation study’s findings revealed a connection between the peritoneal cancer index and four miRNAs, whose expression levels were noticeably higher there in 12 p.m. (+) samples (miR-21-5p, miR-223-3p, and miR-92a-3p, as well as miR-342-3p). individuals who have PM (+) samples, in contrast, showed downregulation of such entire miR-29 family. Furthermore, miR-29 at gastrectomy showed significant decrease in 6 individuals who have peritoneal recurrence among 24 patients with pT4 tumors (P = 0.012) due to significant changes in miR-29b-3p. PM management may benefit from using the miRNA expression pattern in peritoneal exosomes, which is highly correlated with the amount of tumor in the peritoneal cavity (Kundaktepe et al., 2020).
Collectively, these biomarker studies highlight the potential of measuring exosomal miR-21 levels in various bodily fluids (plasma, peritoneal fluid) using sensitive detection methods as a non-invasive tool for early diagnosis, monitoring tumor burden (e.g., in peritoneal metastasis), and potentially predicting prognosis in GI cancers.
These findings underscore the pivotal role of exosomal miR-21 in the metastatic spread and resistance of gastrointestinal cancers, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target. Table 5 lists exosomal miR-21 and GI cancers.
TABLE 5
| Type of cancer | Status of expression | Target | Model | Cell line types | Effect | Conclusion | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colon cancer | Up | TPM1, PTEN, PDCD4 | In vitro | HT29, T84, LS174 | Induced resistance against 5-FU | May represent a novel approach for treatment | Nautiyal et al. (2012) |
| Up | - | Human, in vitro | FHC, HCT116, HT-29, RKO, SW48, SW480 | Significant in primary CRC patients, especially early-stage illness | Promising biomarkers for non-invasive diagnosis of the disease | Dehghan et al. (2019) | |
| Gastric cancer | Up | - | Human | - | - | - | Shiosaki et al. (2020) |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | Useful biomarker in the treatment of PM. | Kundaktepe et al. (2020) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human | - | MiR-21 and programmed cell death protein 4 mRNA expression correlated negatively | Useful biomarker in the treatment | Matarlo et al. (2019) | |
| Up | SMAD7 | Human, In vivo, In vitro | MGC803, BGC823, MKN45, HGC27, SGC7901, GES-1, HMrSV5 | Promote tumor peritoneal metastasis | Exosomal miR-21-5p may be a novel therapeutic target for GC peritoneal metastasis | Li et al. (2018c) | |
| Up | - | In vitro | MKN45, SGC7901, NCI-N87, AGS, GES-1 | most abundant sequences among | may make a little contribution to the understanding of exosomal RNA composition | You et al. (2019) | |
| Up | - | Human In vitro |
OCUM-2M, OCUM-2MD3 | Associated with serosal invasion in GC | May serve as biomarkers of peritoneal recurrence after curative GC resection | Knudsen et al. (2018) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | - | Sabry et al. (2019) | |
| Pancreatic cancer | Up | - | Human | - | - | As PC diagnosis and treatment biomarkers and targets | Orosz et al. (2018) |
| Up | Ras | Human, In vitro | PANC-1, MIAPaCa-2 | Promoted cell migration, induced EMT and increased matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 activity | May be a potential cause of poor prognosis in patients | Bandrés et al. (2006) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Candidate prognostic factor for the overall survival | Useful marker | He et al. (2018) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | - | - | Wang et al. (2018d) | |
| Up | - | Human | - | Increased in exosomes | As diagnosis and treatment biomarkers and targets | Zhang et al. (2018d) | |
| Esophageal cancer | Up | PTEN | In vitro, In vivo | EC-9706 | Process of exosomal transfer and promote tumorigenic phenotype | A novel potential therapeutic approach | Ahmed et al. (2018) |
| Up | PDCD4 | In vitro | TE-1, Eca109/DDP, Het-1A | Significantly reduced the invasion ability | Affects the sensitivity of esophageal cancer to cisplatin | Lü et al. (2018) | |
| Up | PDCD4 | Human, In vitro | EC9706 | Promoted the migration and invasion | May become a potential biomarker for prognosis | Grassi et al. (2018) |
Exosomal miR-21 and GI cancers.
PDCD4, Programmed Cell Death 4; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Ras, Ras P21 Protein Activator; SMAD7, SMAD, Family Member 7; TPM1, Tropomyosin 1.
Conclusion
Clinical and experimental data support the importance of MiR-21 in invasion, metastasis, cell growth, and apoptosis. MiR-21 acts as an oncogenic miRNA controlling downstream effectors linked to GI cancers. Solid and hematological cancers have a strong association with miR-21 overexpression. MiR-21 might be a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis, as well as potential therapeutic target for many cancers of various kinds. Based on this hypothesis, new studies on miRNA signaling pathways have begun to examine how they differ from conventional protein signaling pathways. The function of miR-21 in anticancer drug resistance raises the possibility of using targeted therapeutic methods in addition to conventional cytotoxic drugs to inhibit miR-21 in a clinical setting to lessen cancer therapy resistance. Primary liver cancer patients, along with a few other solid tumor and hematological malignancies, are examined for safety following a miRNA-RX34 liposomal injection. We are unaware of any ongoing clinical trials involving miR-21 in cancer patients. Further study must be conducted prior to implementing miRNA-based cancer therapeutic methods in clinical settings. Also, the creation of efficient methods for delivering synthetic therapeutic miRNAs towards particular target tissues might boost the effectiveness of miRNA-mediated therapies, expanding the potential uses of this kind of therapy in the future for the treatment of cancer. While this review highlights the critical roles of miR-21 in gastrointestinal cancer pathogenesis, there are certain limitations that should be acknowledged. The studies referenced primarily focus on experimental models, and while the findings are compelling, their generalizability to broader patient populations remains uncertain. Furthermore, the lack of consistent clinical trial results involving miR-21, particularly in the context of therapeutic applications, highlights the need for more extensive research to better understand its potential as a diagnostic or therapeutic target. Future studies should address these limitations and explore the nuances of miR-21’s involvement in cancer biology across different stages and types of gastrointestinal cancers.
Statements
Author contributions
CW: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Validation, Data curation. MB: Methodology, Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation. XL: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. ZL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Validation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Visualization. HW: Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Validation. SG: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Validation, Methodology, Visualization.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. 1. Youth Found Project of Hebei Education Department (NO. QN2018031). 2. Medical Science Research Project Plan of Hebei Province (NO. 20190873). 3. 2020 Scientific Research Project of Hebei North University (NO. YB2020017).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Aandahl E. M. Torgersen K. M. Taskén K. (2008). CD8+ regulatory T cells-A distinct T-cell lineage or a transient T-cell phenotype?Hum. Immunol.69 (11), 696–699. 10.1016/j.humimm.2008.08.291
2
Abue M. Yokoyama M. Shibuya R. Tamai K. Yamaguchi K. Sato I. et al (2015). Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol.46 (2), 539–547. 10.3892/ijo.2014.2743
3
Ahadi A. (2021). A systematic review of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Immunogenetics73 (2), 155–161. 10.1007/s00251-020-01201-6
4
Ahmed F. E. Ahmed N. C. Gouda M. M. Vos P. W. Bonnerup C. (2018). RT-qPCR for fecal mature MicroRNA quantification and validation. Methods Mol. Biol.1765, 203–215. 10.1007/978-1-4939-7765-9_13
5
Alder H. Taccioli C. Chen H. Jiang Y. Smalley K. J. Fadda P. et al (2012). Dysregulation of miR-31 and miR-21 induced by zinc deficiency promotes esophageal cancer. Carcinogenesis33 (9), 1736–1744. 10.1093/carcin/bgs204
6
Ali S. Almhanna K. Chen W. Philip P. A. Sarkar F. H. (2010). Differentially expressed miRNAs in the plasma may provide a molecular signature for aggressive pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res.3 (1), 28–47.
7
Ali S. Suresh R. Banerjee S. Bao B. Xu Z. Wilson J. et al (2015). Contribution of microRNAs in understanding the pancreatic tumor microenvironment involving cancer associated stellate and fibroblast cells. Am. J. Cancer Res.5 (3), 1251–1264.
8
An Y. Yang Q. (2020). MiR-21 modulates the polarization of macrophages and increases the effects of M2 macrophages on promoting the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer. Life Sci.242, 117162. 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117162
9
Arisan E. D. Rencuzogullari O. Freitas I. L. Radzali S. Keskin B. Kothari A. et al (2020). Upregulated Wnt-11 and miR-21 expression trigger epithelial mesenchymal transition in aggressive prostate cancer cells. Biol. (Basel).9 (3), 52. 10.3390/biology9030052
10
Arisan E. D. Rencuzogullari O. Cieza-Borrella C. Miralles Arenas F. Dwek M. Lange S. et al (2021). MiR-21 is required for the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (4), 1557. 10.3390/ijms22041557
11
Arnott C. H. Scott K. A. Moore R. J. Hewer A. Phillips D. H. Parker P. et al (2002). Tumour necrosis factor-alpha mediates tumour promotion via a PKC alpha- and AP-1-dependent pathway. Oncogene21 (31), 4728–4738. 10.1038/sj.onc.1205588
12
Arumugam T. Ramachandran V. Fournier K. F. Wang H. Marquis L. Abbruzzese J. L. et al (2009). Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res.69 (14), 5820–5828. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2819
13
Asangani I. A. Rasheed S. A. Nikolova D. A. Leupold J. H. Colburn N. H. Post S. et al (2008). MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene27 (15), 2128–2136. 10.1038/sj.onc.1210856
14
Backlund M. G. Mann J. R. Holla V. R. Buchanan F. G. Tai H. H. Musiek E. S. et al (2005). 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is down-regulated in colorectal cancer. J. Biol. Chem.280 (5), 3217–3223. 10.1074/jbc.M411221200
15
Balkwill F. (2002). Tumor necrosis factor or tumor promoting factor?Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.13 (2), 135–141. 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00020-x
16
Bandrés E. Cubedo E. Agirre X. Malumbres R. Zárate R. Ramirez N. et al (2006). Identification by real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral tissues. Mol. Cancer5, 29. 10.1186/1476-4598-5-29
17
Bao B. Ali S. Ahmad A. Azmi A. S. Li Y. Banerjee S. et al (2012). Hypoxia-induced aggressiveness of pancreatic cancer cells is due to increased expression of VEGF, IL-6 and miR-21, which can be attenuated by CDF treatment. PLoS One7 (12), e50165. 10.1371/journal.pone.0050165
18
Benesova L. Halkova T. Bunganic B. Belsanova B. Zavoral M. Traboulsi E. et al (2020). Comparison of native aspirates and cytological smears obtained by EUS-guided biopsies for effective DNA/RNA marker testing in pancreatic cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res.26 (1), 379–385. 10.1007/s12253-018-0490-9
19
Bertrand F. E. McCubrey J. A. Angus C. W. Nutter J. M. Sigounas G. (2014). NOTCH and PTEN in prostate cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul.56, 51–65. 10.1016/j.jbior.2014.05.002
20
Bhatti I. Lee A. James V. Hall R. I. Lund J. N. Tufarelli C. et al (2011). Knockdown of microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Surg.15 (1), 199–208. 10.1007/s11605-010-1381-x
21
Buck E. Eyzaguirre A. Barr S. Thompson S. Sennello R. Young D. et al (2007). Loss of homotypic cell adhesion by epithelial-mesenchymal transition or mutation limits sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Mol. Cancer Ther.6 (2), 532–541. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0462
22
Butz H. Nofech-Mozes R. Ding Q. Khella H. W. Z. Szabó P. M. Jewett M. et al (2016). Exosomal MicroRNAs are diagnostic biomarkers and can mediate cell-cell communication in renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Focus2 (2), 210–218. 10.1016/j.euf.2015.11.006
23
Calatayud D. Dehlendorff C. Boisen M. K. Hasselby J. P. Schultz N. A. Werner J. et al (2017). Tissue MicroRNA profiles as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and periampullary cancers. Biomark. Res.5, 8. 10.1186/s40364-017-0087-6
24
Calsina B. Castro-Vega L. J. Torres-Pérez R. Inglada-Pérez L. Currás-Freixes M. Roldán-Romero J. M. et al (2019). Integrative multi-omics analysis identifies a prognostic miRNA signature and a targetable miR-21-3p/TSC2/mTOR axis in metastatic pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma. Theranostics9 (17), 4946–4958. 10.7150/thno.35458
25
Canatan D. Sönmez Y. Yılmaz Ö. Çim A. Coşkun H. Sezgin G. S. et al (2021). MicroRNAs as biomarkers for breast cancer. Acta Biomed.92 (2), e2021028. 10.23750/abm.v92i2.9678
26
Cao Z. Yoon J. H. Nam S. W. Lee J. Y. Park W. S. (2012). PDCD4 expression inversely correlated with miR-21 levels in gastric cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol.138 (4), 611–619. 10.1007/s00432-011-1140-8
27
Carswell E. A. Old L. J. Kassel R. L. Green S. Fiore N. Williamson B. (1975). An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.72 (9), 3666–3670. 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666
28
Carter J. V. Roberts H. L. Pan J. Rice J. D. Burton J. F. Galbraith N. J. et al (2016). A highly predictive model for diagnosis of colorectal neoplasms using plasma MicroRNA: improving specificity and sensitivity. Ann. Surg.264 (4), 575–584. 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001873
29
Chalquest R. R. (1986). Preveterinary requirements and admission to American veterinary colleges: important changes. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc.189 (1), 27–29. 10.2460/javma.1986.189.01.27
30
Chandrakesan P. Panneerselvam J. May R. Weygant N. Qu D. Berry W. R. et al (2020). DCLK1-Isoform2 alternative splice variant promotes pancreatic tumor immunosuppressive M2-Macrophage polarization. Mol. Cancer Ther.19 (7), 1539–1549. 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0776
31
Chang G. Xu S. Dhir R. Chandran U. O'Keefe D. S. Greenberg N. M. et al (2010). Hypoexpression and epigenetic regulation of candidate tumor suppressor gene CADM-2 in human prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res.16 (22), 5390–5401. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1461
32
Chen Z. Saad R. Jia P. Peng D. Zhu S. Washington M. K. et al (2013). Gastric adenocarcinoma has a unique microRNA signature not present in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer.119 (11), 1985–1993. 10.1002/cncr.28002
33
Chen J. Zhou C. Li J. Xiang X. Zhang L. Deng J. et al (2018a). miR-21-5p confers doxorubicin resistance in gastric cancer cells by targeting PTEN and TIMP3. Int. J. Mol. Med.41 (4), 1855–1866. 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3405
34
Chen X. Zhao L. Xing Y. Lin B. (2018b). RETRACTED: down-regulation of microRNA-21 reduces inflammation and podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by relieving the repression of TIMP3 expression. Biomed. Pharmacother.108, 7–14. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.007
35
Cojoc M. Mäbert K. Muders M. H. Dubrovska A. (2015). A role for cancer stem cells in therapy resistance: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Semin. Cancer Biol.31, 16–27. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.06.004
36
Correia de Sousa M. Calo N. Sobolewski C. Gjorgjieva M. Clément S. Maeder C. et al (2021). Mir-21 suppression promotes mouse hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel)13 (19), 4983. 10.3390/cancers13194983
37
Crawford B. M. Wang H. N. Stolarchuk C. von Furstenberg R. J. Strobbia P. Zhang D. et al (2020). Plasmonic nanobiosensors for detection of microRNA cancer biomarkers in clinical samples. Analyst.145 (13), 4587–4594. 10.1039/d0an00193g
38
Cuellar-Gomez H. Ocharán-Hernández M. E. Calzada-Mendoza C. C. Comoto-Santacruz D. A. (2021). Serum miRNA profile as a potential tool for non-invasive gastric cancer diagnosis in Mexican patients. Cir. Cir.89 (6), 748–754. 10.24875/CIRU.20000963
39
Cui L. Zhang X. Ye G. Zheng T. Song H. Deng H. et al (2013). Gastric juice MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the screening of gastric cancer. Cancer119 (9), 1618–1626. 10.1002/cncr.27903
40
Dalla Pozza E. Dando I. Biondani G. Brandi J. Costanzo C. Zoratti E. et al (2015). Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines display a plastic ability to bi-directionally convert into cancer stem cells. Int. J. Oncol.46 (3), 1099–1108. 10.3892/ijo.2014.2796
41
Dan J. Wang J. Wang Y. Zhu M. Yang X. Peng Z. et al (2018). LncRNA-MEG3 inhibits proliferation and metastasis by regulating miRNA-21 in gastric cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother.99, 931–938. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.164
42
Dawood S. Austin L. Cristofanilli M. (2014). Cancer stem cells: implications for cancer therapy. Oncol. Willist. Park28 (12), 1101–1110.
43
De Craene B. Berx G. (2013). Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer13 (2), 97–110. 10.1038/nrc3447
44
de la Chapelle A. Jazdzewski K. (2011). MicroRNAs in thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.96 (11), 3326–3336. 10.1210/jc.2011-1004
45
de Paulsen N. Brychzy A. Fournier M. C. Klausner R. D. Gnarra J. R. Pause A. et al (2001). Role of transforming growth factor-alpha in von Hippel--Lindau (VHL)(-/-) clear cell renal carcinoma cell proliferation: a possible mechanism coupling VHL tumor suppressor inactivation and tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.98 (4), 1387–1392. 10.1073/pnas.031587498
46
Dehghan F. Boozarpour S. Torabizadeh Z. Alijanpour S. (2019). miR-21: a promising biomarker for the early detection of colon cancer. Onco Targets Ther.12, 5601–5607. 10.2147/OTT.S199508
47
Deng J. Y. Sun D. Liu X. Y. Pan Y. Liang H. (2010). STAT-3 correlates with lymph node metastasis and cell survival in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol.16 (42), 5380–5387. 10.3748/wjg.v16.i42.5380
48
Dhawan A. Scott J. G. Harris A. L. Buffa F. M. (2018). Pan-cancer characterisation of microRNA across cancer hallmarks reveals microRNA-mediated downregulation of tumour suppressors. Nat. Commun.9 (1), 5228. 10.1038/s41467-018-07657-1
49
Dillhoff M. Liu J. Frankel W. Croce C. Bloomston M. (2008). MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J. Gastrointest. Surg.12 (12), 2171–2176. 10.1007/s11605-008-0584-x
50
Dixon D. A. Blanco F. F. Bruno A. Patrignani P. (2013). Mechanistic aspects of COX-2 expression in colorectal neoplasia. Recent Results Cancer Res.191, 7–37. 10.1007/978-3-642-30331-9_2
51
Doghish A. S. El-Husseiny A. A. Abdelmaksoud N. M. El-Mahdy H. A. Elsakka E. G. E. Abdel M. S. S. et al (2023). The interplay of signaling pathways and miRNAs in the pathogenesis and targeted therapy of esophageal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract.246, 154529. 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154529
52
Dong J. Zhao Y. P. Zhou L. Zhang T. P. Chen G. (2011). Bcl-2 upregulation induced by miR-21 via a direct interaction is associated with apoptosis and chemoresistance in MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells. Arch. Med. Res.42 (1), 8–14. 10.1016/j.arcmed.2011.01.006
53
Duell E. J. Lujan-Barroso L. Sala N. Deitz McElyea S. Overvad K. Tjonneland A. et al (2017). Plasma microRNAs as biomarkers of pancreatic cancer risk in a prospective cohort study. Int. J. Cancer141 (5), 905–915. 10.1002/ijc.30790
54
Dupuy F. Tabariès S. Andrzejewski S. Dong Z. Blagih J. Annis M. G. et al (2015). PDK1-Dependent metabolic reprogramming dictates metastatic potential in breast cancer. Cell Metab.22 (4), 577–589. 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.08.007
55
El-Mahdy H. A. Sallam A. M. Ismail A. Elkhawaga S. Y. Elrebehy M. A. Doghish A. S. (2022). miRNAs inspirations in hepatocellular carcinoma: detrimental and favorable aspects of key performers. Pathol. Res. Pract.233, 153886. 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153886
56
Elrebehy M. A. Abdelghany T. M. Elshafey M. M. Gomaa M. H. Doghish A. S. (2023). miR-509-5p promotes colorectal cancer cell ferroptosis by targeting SLC7A11. Pathol. Res. Pract.247, 154557. 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154557
57
Emami S. S. Nekouian R. Akbari A. Faraji A. Abbasi V. Agah S. (2019). Evaluation of circulating miR-21 and miR-222 as diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther.15 (1), 115–119. 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_592_17
58
Eslamizadeh S. Zare A. A. Talebi A. Tabaeian S. P. Eshkiki Z. S. Heydari-Zarnagh H. et al (2021). Differential expression of miR-20a and miR-145 in colorectal tumors as potential location-specific miRNAs. Microrna10 (1), 66–73. 10.2174/2211536609666201221123604
59
Eto K. Iwatsuki M. Watanabe M. Ida S. Ishimoto T. Iwagami S. et al (2014). The microRNA-21/PTEN pathway regulates the sensitivity of HER2-positive gastric cancer cells to trastuzumab. Ann. Surg. Oncol.21 (1), 343–350. 10.1245/s10434-013-3325-7
60
Fang S. Wang L. Luo C. Yi H. Wang X. Ning B. (2022). Curcumol inhibits the growth of xenograft-tumors in mice and the biological activities of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating the miR-21-5p/SMAD7 axis. Cell Cycle21 (12), 1249–1266. 10.1080/15384101.2022.2046983
61
Fathi D. Elballal M. S. Elesawy A. E. Abulsoud A. I. Elshafei A. Elsakka E. G. E. et al (2023). An emphasis on the interaction of signaling pathways highlights the role of miRNAs in the etiology and treatment resistance of gastric cancer. Life Sci.322, 121667. 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121667
62
Feber A. Xi L. Luketich J. D. Pennathur A. Landreneau R. J. Wu M. et al (2008). MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc Surg.135 (2), 255–260. 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2007.08.055
63
Fedele M. Cerchia L. Chiappetta G. (2017). The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer: focus on basal-like carcinomas. Cancers (Basel)9 (10), 134. 10.3390/cancers9100134
64
Felipe Lima J. Nofech-Mozes S. Bayani J. Bartlett J. M. (2016). EMT in breast Carcinoma-A review. J. Clin. Med.5 (7), 65. 10.3390/jcm5070065
65
Feng Y. H. Tsao C. J. (2016). Emerging role of microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed. Rep.5 (4), 395–402. 10.3892/br.2016.747
66
Fong L. Y. Taccioli C. Jing R. Smalley K. J. Alder H. Jiang Y. et al (2016). MicroRNA dysregulation and esophageal cancer development depend on the extent of zinc dietary deficiency. Oncotarget7 (10), 10723–10738. 10.18632/oncotarget.7561
67
Fridman W. H. Pagès F. Sautès-Fridman C. Galon J. (2012). The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer12 (4), 298–306. 10.1038/nrc3245
68
Fridman W. H. Zitvogel L. Sautès-Fridman C. Kroemer G. (2017). The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.14 (12), 717–734. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.101
69
Fukuhara H. Kuramochi M. Fukami T. Kasahara K. Furuhata M. Nobukuni T. et al (2002). Promoter methylation of TSLC1 and tumor suppression by its gene product in human prostate cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res.93 (6), 605–609. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01297.x
70
Golestaneh A. F. Atashi A. Langroudi L. Shafiee A. Ghaemi N. Soleimani M. (2012). miRNAs expressed differently in cancer stem cells and cancer cells of human gastric cancer cell line MKN-45. Cell Biochem. Funct.30 (5), 411–418. 10.1002/cbf.2815
71
Grassi A. Perilli L. Albertoni L. Tessarollo S. Mescoli C. Urso E. D. L. et al (2018). A coordinate deregulation of microRNAs expressed in mucosa adjacent to tumor predicts relapse after resection in localized colon cancer. Mol. Cancer17 (1), 17. 10.1186/s12943-018-0770-8
72
Grimm M. Lazariotou M. Kircher S. Höfelmayr A. Germer C. T. von Rahden B. H. et al (2011). Tumor necrosis factor-α is associated with positive lymph node status in patients with recurrence of colorectal cancer-indications for anti-TNF-α agents in cancer treatment. Cell Oncol. (Dordr)34 (4), 315–326. 10.1007/s13402-011-0027-7
73
Gu J. B. Bao X. B. Ma Z. (2018). Effects of miR-21 on proliferation and apoptosis in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett.15 (1), 618–622. 10.3892/ol.2017.6171
74
Gu Y. Fei Z. Zhu R. (2020). miR-21 modulates cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Anticancer Drugs31 (4), 385–393. 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000886
75
Guadagni F. Ferroni P. Palmirotta R. Portarena I. Formica V. Roselli M. (2007). Review. TNF/VEGF cross-talk in chronic inflammation-related cancer initiation and progression: an early target in anticancer therapeutic strategy. Vivo21 (2), 147–161.
76
Guan E. Liu H. Xu N. (2022). Lidocaine suppresses gastric cancer development through Circ_ANO5/miR-21-5p/LIFR axis. Dig. Dis. Sci.67 (6), 2244–2256. 10.1007/s10620-021-07055-6
77
Guo X. Wang X. F. (2009). Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res.19 (1), 71–88. 10.1038/cr.2008.302
78
Guo B. Li J. Liu L. Hou N. Chang D. Zhao L. et al (2013). Dysregulation of miRNAs and their potential as biomarkers for the diagnosis of gastric cancer. Biomed. Rep.1 (6), 907–912. 10.3892/br.2013.175
79
György B. Tóth E. Tarcsa E. Falus A. Buzás E. I. (2006). Citrullination: a posttranslational modification in health and disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.38 (10), 1662–1677. 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.03.008
80
Habbe N. Koorstra J. B. Mendell J. T. Offerhaus G. J. Ryu J. K. Feldmann G. et al (2009). MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol. Ther.8 (4), 340–346. 10.4161/cbt.8.4.7338
81
Ham B. Fernandez M. C. D'Costa Z. Brodt P. (2016). The diverse roles of the TNF axis in cancer progression and metastasis. Trends Cancer Res.11 (1), 1–27.
82
Hamano R. Miyata H. Yamasaki M. Kurokawa Y. Hara J. Moon J. H. et al (2011). Overexpression of miR-200c induces chemoresistance in esophageal cancers mediated through activation of the Akt signaling pathway. Clin. Cancer Res.17 (9), 3029–3038. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2532
83
Han J. Yang Z. Zhao S. Zheng L. Tian Y. Lv Y. (2021a). Circ_0027599 elevates RUNX1 expression via sponging miR-21-5p on gastric cancer progression. Eur. J. Clin. Invest51 (11), e13592. 10.1111/eci.13592
84
Han Z. Chen H. Guo Z. Zhu J. Xie X. Li Y. et al (2021b). Bioinformatics analysis: the regulatory network of hsa_circ_0007843 and hsa_circ_0007331 in Colon cancer. Biomed. Res. Int.2021, 6662897. 10.1155/2021/6662897
85
He C. Dong X. Zhai B. Jiang X. Dong D. Li B. et al (2015). MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/akt pathway. Oncotarget6 (30), 28867–28881. 10.18632/oncotarget.4814
86
He J. H. Li Y. G. Han Z. P. Zhou J. B. Chen W. M. Lv Y. B. et al (2018). The CircRNA-ACAP2/Hsa-miR-21-5p/Tiam1 regulatory feedback circuit affects the proliferation, migration, and invasion of Colon cancer SW480 cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem.49 (4), 1539–1550. 10.1159/000493457
87
Henderson B. Martin A. C. (2014). Protein moonlighting: a new factor in biology and medicine. Biochem. Soc. Trans.42 (6), 1671–1678. 10.1042/BST20140273
88
Hezova R. Kovarikova A. Srovnal J. Zemanova M. Harustiak T. Ehrmann J. et al (2015). Diagnostic and prognostic potential of miR-21, miR-29c, miR-148 and miR-203 in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Diagn Pathol.10, 42. 10.1186/s13000-015-0280-6
89
Hong T. H. Park I. Y. (2014). MicroRNA expression profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from surgical pancreatic cancer specimens. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res.87 (6), 290–297. 10.4174/astr.2014.87.6.290
90
Hong L. Han Y. Zhang Y. Zhang H. Zhao Q. Wu K. et al (2013). MicroRNA-21: a therapeutic target for reversing drug resistance in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets17 (9), 1073–1080. 10.1517/14728222.2013.819853
91
Hotz B. Arndt M. Dullat S. Bhargava S. Buhr H. J. Hotz H. G. (2007). Epithelial to mesenchymal transition: expression of the regulators snail, slug, and twist in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res.13 (16), 4769–4776. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2926
92
Hruban R. H. Adsay N. V. Albores-Saavedra J. Anver M. R. Biankin A. V. Boivin G. P. et al (2006). Pathology of genetically engineered mouse models of pancreatic exocrine cancer: consensus report and recommendations. Cancer Res.66 (1), 95–106. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2168
93
Hu Y. Correa A. M. Hoque A. Guan B. Ye F. Huang J. et al (2011). Prognostic significance of differentially expressed miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Int. J. Cancer128 (1), 132–143. 10.1002/ijc.25330
94
Hu H. Tu W. Chen Y. Zhu M. Jin H. Huang T. et al (2020). The combination of PKM2 overexpression and M2 macrophages infiltration confers a poor prognosis for PDAC patients. J. Cancer11 (8), 2022–2031. 10.7150/jca.38981
95
Huang S. Li X. Q. Chen X. Che S. M. Chen W. Zhang X. Z. (2013). Inhibition of microRNA-21 increases radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 activation. Dis. Esophagus26 (8), 823–831. 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01389.x
96
Huang S. Wang J. Li J. Luo Q. Zhao M. Zheng L. et al (2016). Serum microRNA expression profile as a diagnostic panel for gastric cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol.46 (9), 811–818. 10.1093/jjco/hyw085
97
Huang S. K. Wang J. Li Y. Lin H. Li D. D. Cui C. J. et al (2018a). Clinical application value of combined detection of serum miR-378 and miR-21 in gastric cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.40 (6), 441–445. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.06.008
98
Huang Y. Zhu J. Li W. Zhang Z. Xiong P. Wang H. et al (2018b). Serum microRNA panel excavated by machine learning as a potential biomarker for the detection of gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep.39 (3), 1338–1346. 10.3892/or.2017.6163
99
Huang M. Zhang T. Yao Z. Y. Xing C. Wu Q. Liu Y. W. et al (2021). MicroRNA related prognosis biomarkers from high throughput sequencing data of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. BMC Med. Genomics14 (1), 72. 10.1186/s12920-021-00932-z
100
Humeau M. Vignolle-Vidoni A. Sicard F. Martins F. Bournet B. Buscail L. et al (2015). Salivary MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer patients. PLoS One10 (6), e0130996. 10.1371/journal.pone.0130996
101
Hummel R. Hussey D. J. Michael M. Z. Haier J. Bruewer M. Senninger N. et al (2011). MiRNAs and their association with locoregional staging and survival following surgery for esophageal carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol.18 (1), 253–260. 10.1245/s10434-010-1213-y
102
Huynh J. Chand A. Gough D. Ernst M. (2019). Therapeutically exploiting STAT3 activity in cancer - using tissue repair as a road map. Nat. Rev. Cancer19 (2), 82–96. 10.1038/s41568-018-0090-8
103
Hwang J. H. Voortman J. Giovannetti E. Steinberg S. M. Leon L. G. Kim Y. T. et al (2010). Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS One5 (5), e10630. 10.1371/journal.pone.0010630
104
Iacobuzio-Donahue C. A. Fu B. Yachida S. Luo M. Abe H. Henderson C. M. et al (2009). DPC4 gene status of the primary carcinoma correlates with patterns of failure in patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol.27 (11), 1806–1813. 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.7188
105
Iliopoulos D. Jaeger S. A. Hirsch H. A. Bulyk M. L. Struhl K. (2010). STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol. Cell.39 (4), 493–506. 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.023
106
Javle M. M. Gibbs J. F. Iwata K. K. Pak Y. Rutledge P. Yu J. et al (2007). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-Erk) in surgically resected pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol.14 (12), 3527–3533. 10.1245/s10434-007-9540-3
107
Jeffery C. J. (2018). Protein moonlighting: what is it, and why is it important?Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci.373 (1738), 20160523. 10.1098/rstb.2016.0523
108
Jiang J. Zheng X. Xu X. Zhou Q. Yan H. Zhang X. et al (2011). Prognostic significance of miR-181b and miR-21 in gastric cancer patients treated with S-1/Oxaliplatin or doxifluridine/oxaliplatin. PLoS One6 (8), e23271. 10.1371/journal.pone.0023271
109
Jiang R. Chen X. Ge S. Wang Q. Liu Y. Chen H. et al (2020). MiR-21-5p induces pyroptosis in colorectal cancer via TGFBI. Front. Oncol.10, 610545. 10.3389/fonc.2020.610545
110
Jiang H. G. Dai C. H. Xu Y. P. Jiang Q. Xia X. B. Shu Y. et al (2021). Four plasma miRNAs act as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett.22 (5), 792. 10.3892/ol.2021.13053
111
Johnson D. E. O'Keefe R. A. Grandis J. R. (2018). Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.15 (4), 234–248. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.8
112
Joshi G. K. Deitz-McElyea S. Johnson M. Mali S. Korc M. Sardar R. (2014). Highly specific plasmonic biosensors for ultrasensitive microRNA detection in plasma from pancreatic cancer patients. Nano Lett.14 (12), 6955–6963. 10.1021/nl503220s
113
Kalluri R. Weinberg R. A. (2009). The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Invest119 (6), 1420–1428. 10.1172/JCI39104
114
Kao H. W. Pan C. Y. Lai C. H. Wu C. W. Fang W. L. Huang K. H. et al (2017). Urine miR-21-5p as a potential non-invasive biomarker for gastric cancer. Oncotarget8 (34), 56389–56397. 10.18632/oncotarget.16916
115
Kar S. Samii A. Bertalanffy H. (2015). PTEN/PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling and the cross talk to KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10 proteins in cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurosurg. Rev.38 (2), 229–236. 10.1007/s10143-014-0597-8
116
Karamitopoulou E. Haemmig S. Baumgartner U. Schlup C. Wartenberg M. Vassella E. (2017). MicroRNA dysregulation in the tumor microenvironment influences the phenotype of pancreatic cancer. Mod. Pathol.30 (8), 1116–1125. 10.1038/modpathol.2017.35
117
Kemp R. A. Ronchese F. (2001). Tumor-specific Tc1, but not Tc2, cells deliver protective antitumor immunity. J. Immunol.167 (11), 6497–6502. 10.4049/jimmunol.167.11.6497
118
Khan K. Cunningham D. Peckitt C. Barton S. Tait D. Hawkins M. et al (2016). miR-21 expression and clinical outcome in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: exploratory analysis of the pancreatic cancer erbitux, radiotherapy and UFT (PERU) trial. Oncotarget7 (11), 12672–12681. 10.18632/oncotarget.7208
119
Kim J. W. Tchernyshyov I. Semenza G. L. Dang C. V. (2006). HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab.3 (3), 177–185. 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.002
120
Kim M. P. Fleming J. B. Wang H. Abbruzzese J. L. Choi W. Kopetz S. et al (2011). ALDH activity selectively defines an enhanced tumor-initiating cell population relative to CD133 expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS One6 (6), e20636. 10.1371/journal.pone.0020636
121
Klonisch T. Wiechec E. Hombach-Klonisch S. Ande S. R. Wesselborg S. Schulze-Osthoff K. et al (2008). Cancer stem cell markers in common cancers - therapeutic implications. Trends Mol. Med.14 (10), 450–460. 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.08.003
122
Klymkowsky M. W. Savagner P. (2009). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher's conceptual friend and foe. Am. J. Pathol.174 (5), 1588–1593. 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080545
123
Knudsen K. N. Lindebjerg J. Kalmár A. Molnár B. Sørensen F. B. Hansen T. F. et al (2018). miR-21 expression analysis in budding Colon cancer cells by confocal slide scanning microscopy. Clin. Exp. Metastasis35 (8), 819–830. 10.1007/s10585-018-9945-3
124
Komatsu S. Ichikawa D. Kawaguchi T. Miyamae M. Okajima W. Ohashi T. et al (2016). Circulating miR-21 as an independent predictive biomarker for chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res.6 (7), 1511–1523.
125
Kong W. He L. Richards E. J. Challa S. Xu C. X. Permuth-Wey J. et al (2014). Upregulation of miRNA-155 promotes tumour angiogenesis by targeting VHL and is associated with poor prognosis and triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene33 (6), 679–689. 10.1038/onc.2012.636
126
Kosgodage U. S. Uysal-Onganer P. MacLatchy A. Kraev I. Chatterton N. P. Nicholas A. P. et al (2018). Peptidylarginine deiminases post-translationally deiminate prohibitin and modulate extracellular vesicle release and MicroRNAs in glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20 (1), 103. 10.3390/ijms20010103
127
Kundaktepe B. P. Sozer V. Papila C. Durmus S. Kocael P. C. Simsek G. et al (2020). Associations between miRNAs and two different cancers: breast and Colon. Cancer Manag. Res.12, 871–879. 10.2147/CMAR.S227628
128
Kuramochi M. Fukuhara H. Nobukuni T. Kanbe T. Maruyama T. Ghosh H. P. et al (2001). TSLC1 is a tumor-suppressor gene in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet.27 (4), 427–430. 10.1038/86934
129
LaConti J. J. Shivapurkar N. Preet A. Deslattes Mays A. Peran I. Kim S. E. et al (2011). Tissue and serum microRNAs in the Kras(G12D) transgenic animal model and in patients with pancreatic cancer. PLoS One6 (6), e20687. 10.1371/journal.pone.0020687
130
Lamouille S. Xu J. Derynck R. (2014). Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.15 (3), 178–196. 10.1038/nrm3758
131
Lan J. Sun L. Xu F. Liu L. Hu F. Song D. et al (2019). M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote cell migration and invasion in Colon cancer. Cancer Res.79 (1), 146–158. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0014
132
Lee S. H. Kim H. Hwang J. H. Shin E. Lee H. S. Hwang D. W. et al (2014). CD24 and S100A4 expression in resectable pancreatic cancers with earlier disease recurrence and poor survival. Pancreas43 (3), 380–388. 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000097
133
Lei Y. Zhang D. Yu J. Dong H. Zhang J. Yang S. (2017). Targeting autophagy in cancer stem cells as an anticancer therapy. Cancer Lett.393, 33–39. 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.012
134
Li C. Heidt D. G. Dalerba P. Burant C. F. Zhang L. Adsay V. et al (2007). Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res.67 (3), 1030–1037. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2030
135
Li C. Lee C. J. Simeone D. M. (2009). Identification of human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Methods Mol. Biol.568, 161–173. 10.1007/978-1-59745-280-9_10
136
Li B. S. Zhao Y. L. Guo G. Li W. Zhu E. D. Luo X. et al (2012). Plasma microRNAs, miR-223, miR-21 and miR-218, as novel potential biomarkers for gastric cancer detection. PLoS One7 (7), e41629. 10.1371/journal.pone.0041629
137
Li Q. Zhang D. Wang Y. Sun P. Hou X. Larner J. et al (2013a). MiR-21/Smad 7 signaling determines TGF-β1-induced CAF formation. Sci. Rep.3, 2038. 10.1038/srep02038
138
Li X. Zhang X. Liu X. Tan Z. Yang C. Ding X. et al (2013b). Caudatin induces cell apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncol. Rep.30 (2), 677–684. 10.3892/or.2013.2495
139
Li P. Mao W. M. Zheng Z. G. Dong Z. M. Ling Z. Q. (2013c). Down-regulation of PTEN expression modulated by dysregulated miR-21 contributes to the progression of esophageal cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci.58 (12), 3483–3493. 10.1007/s10620-013-2854-z
140
Li L. Zhou L. Li Y. Lin S. Tomuleasa C. (2014). MicroRNA-21 stimulates gastric cancer growth and invasion by inhibiting the tumor suppressor effects of programmed cell death protein 4 and phosphatase and tensin homolog. J. Buon19 (1), 228–236.
141
Li X. Zhao H. Gu J. Zheng L. (2015a). Prognostic value of cancer stem cell marker CD133 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol.8 (10), 12084–12092.
142
Li H. Cheng J. Mao Y. Jiang M. Fan X. (2015b). miR-21 inhibits the effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS398 on apoptosis and invasion in gastric cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther.8, 3245–3253. 10.2147/OTT.S90012
143
Li C. Song L. Zhang Z. Bai X. X. Cui M. F. Ma L. J. (2016a). MicroRNA-21 promotes TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer through up-regulating PTEN expression. Oncotarget7 (41), 66989–67003. 10.18632/oncotarget.11888
144
Li Y. Tsang C. K. Wang S. Li X. X. Yang Y. Fu L. et al (2016b). MAF1 suppresses AKT-mTOR signaling and liver cancer through activation of PTEN transcription. Hepatology63 (6), 1928–1942. 10.1002/hep.28507
145
Li Y. Li X. Li X. Zhong Y. Ji Y. Yu D. et al (2016c). PDHA1 gene knockout in prostate cancer cells results in metabolic reprogramming towards greater glutamine dependence. Oncotarget7 (33), 53837–53852. 10.18632/oncotarget.10782
146
Li Y. Huang R. Li X. Li X. Yu D. Zhang M. et al (2016d). Decreased expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase A1 predicts an unfavorable prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res.6 (9), 2076–2087.
147
Li L. Wang X. Li W. Yang L. Liu R. Zeng R. et al (2018a). miR-21 modulates prostaglandin signaling and promotes gastric tumorigenesis by targeting 15-PGDH. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.495 (1), 928–934. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.137
148
Li X. Chen D. Li M. Gao X. Shi G. Zhao H. (2018b). The CADM2/Akt pathway is involved in the inhibitory effect of miR-21-5p downregulation on proliferation and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Chem. Biol. Interact.288, 76–82. 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.04.021
149
Li Q. Li B. Li Q. Wei S. He Z. Huang X. et al (2018c). Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from gastric cancer promotes peritoneal metastasis via mesothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Death and Dis.9 (9), 854. 10.1038/s41419-018-0928-8
150
Li W. Peng X. Wang Z. Zhang H. Huang H. Liu H. et al (2020). The long noncoding RNA, growth arrest-specific 5, suppresses gastric cancer by downregulating miR-21 expression. Pharmacology105 (7-8), 434–444. 10.1159/000504674
151
Li C. Wang H. Meng S. Hong J. Yao L. Shao Y. et al (2022). lncRNA GAS8-AS1 regulates cancer cell proliferation and predicts poor survival of patients with gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett.23 (2), 48. 10.3892/ol.2021.13166
152
Liang Y. Pan H. F. Ye D. Q. (2015). Tc17 cells in immunity and systemic autoimmunity. Int. Rev. Immunol.34 (4), 318–331. 10.3109/08830185.2014.954698
153
Lin C. S. Lee H. T. Lee M. H. Pan S. C. Ke C. Y. Chiu A. W. et al (2016). Role of mitochondrial DNA copy number alteration in human renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci.17 (6), 814. 10.3390/ijms17060814
154
Liu G. Friggeri A. Yang Y. Milosevic J. Ding Q. Thannickal V. J. et al (2010a). miR-21 mediates fibrogenic activation of pulmonary fibroblasts and lung fibrosis. J. Exp. Med.207 (8), 1589–1597. 10.1084/jem.20100035
155
Liu L. Chen Q. Lai R. Wu X. Wu X. Liu F. et al (2010b). Elevated expression of mature miR-21 and miR-155 in cancerous gastric tissues from Chinese patients with gastric cancer. J. Biomed. Res.24 (3), 187–197. 10.1016/S1674-8301(10)60028-0
156
Liu R. Chen X. Du Y. Yao W. Shen L. Wang C. et al (2012). Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Clin. Chem.58 (3), 610–618. 10.1373/clinchem.2011.172767
157
Liu P. Liang H. Xia Q. Li P. Kong H. Lei P. et al (2013a). Resveratrol induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancers cells by inhibiting miR-21 regulation of BCL-2 expression. Clin. Transl. Oncol.15 (9), 741–746. 10.1007/s12094-012-0999-4
158
Liu J. Wu C. P. Lu B. F. Jiang J. T. (2013b). Mechanism of T cell regulation by microRNAs. Cancer Biol. Med.10 (3), 131–137. 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2013.03.002
159
Liu T. Liu Q. Zheng S. Gao X. Lu M. Yang C. et al (2014). MicroRNA-21 promotes cell growth and migration by targeting programmed cell death 4 gene in Kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Markers2014, 232837. 10.1155/2014/232837
160
Liu F. Zhang W. You X. Liu Y. Li Y. Wang Z. et al (2015). The oncoprotein HBXIP promotes glucose metabolism reprogramming via downregulating SCO2 and PDHA1 in breast cancer. Oncotarget6 (29), 27199–27213. 10.18632/oncotarget.4508
161
Liu N. Xia W. Y. Liu S. S. Chen H. Y. Sun L. Liu M. Y. et al (2016a). MicroRNA-101 targets von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor (VHL) to induce HIF1α mediated apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in normoxia condition. Sci. Rep.6, 20489. 10.1038/srep20489
162
Liu Z. Zhang J. Hong G. Quan J. Zhang L. Yu M. (2016b). Propofol inhibits growth and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells through regulation of the miR-21/Slug signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res.8 (10), 4120–4133.
163
Liu D. Yang Z. Wang T. Yang Z. Chen H. Hu Y. et al (2016c). β2-AR signaling controls trastuzumab resistance-dependent pathway. Oncogene35 (1), 47–58. 10.1038/onc.2015.58
164
Liu Y. Wu T. Lu D. Zhen J. Zhang L. (2018a). CD44 overexpression related to lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers33 (3), 308–313. 10.1177/1724600817746951
165
Liu Z. Yu M. Fei B. Fang X. Ma T. Wang D. (2018b). miR-21-5p targets PDHA1 to regulate glycolysis and cancer progression in gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep.40 (5), 2955–2963. 10.3892/or.2018.6695
166
Liu X. Abraham J. M. Cheng Y. Wang Z. Wang Z. Zhang G. et al (2018c). Synthetic circular RNA functions as a miR-21 sponge to suppress gastric carcinoma cell proliferation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids13, 312–321. 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.09.010
167
Liu J. Q. Deng M. Xue N. N. Li T. X. Guo Y. X. Gao L. et al (2020a). lncRNA KLF3-AS1 suppresses cell migration and invasion in ESCC by impairing miR-185-5p-Targeted KLF3 inhibition. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids20, 231–241. 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.020
168
Liu H. Liu T. Zhou Y. Song X. Wei R. (2020b). Overexpression of long non-coding RNA cancer susceptibility 11 is involved in the development of chemoresistance to carboplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett.19 (3), 1993–1998. 10.3892/ol.2020.11265
169
Löffler D. Brocke-Heidrich K. Pfeifer G. Stocsits C. Hackermüller J. Kretzschmar A. K. et al (2007). Interleukin-6 dependent survival of multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood110 (4), 1330–1333. 10.1182/blood-2007-03-081133
170
Lü Y. Han B. Yu H. Cui Z. Li Z. Wang J. (2018). Berberine regulates the microRNA-21-ITGΒ4-PDCD4 axis and inhibits colon cancer viability. Oncol. Lett.15 (4), 5971–5976. 10.3892/ol.2018.7997
171
Luo T. Liu Q. Tan A. Duan L. Jia Y. Nong L. et al (2020). Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted exosome promotes chemoresistance in breast cancer via enhancing miR-21-5p-Mediated S100A6 expression. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics19, 283–293. 10.1016/j.omto.2020.10.008
172
Lv H. He Z. Wang H. Du T. Pang Z. (2016). Differential expression of miR-21 and miR-75 in esophageal carcinoma patients and its clinical implication. Am. J. Transl. Res.8 (7), 3288–3298.
173
Ma W. J. Lv G. D. Tuersun A. Liu Q. Liu H. Zheng S. T. et al (2011). Role of microRNA-21 and effect on PTEN in kazakh's esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep.38 (5), 3253–3260. 10.1007/s11033-010-0480-9
174
Ma G. J. Gu R. M. Zhu M. Wen X. Li J. T. Zhang Y. Y. et al (2013). Plasma post-operative miR-21 expression in the prognosis of gastric cancers. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev.14 (12), 7551–7554. 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.12.7551
175
Mace T. A. Collins A. L. Wojcik S. E. Croce C. M. Lesinski G. B. Bloomston M. (2013). Hypoxia induces the overexpression of microRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Surg. Res.184 (2), 855–860. 10.1016/j.jss.2013.04.061
176
Maier H. J. Schmidt-Strassburger U. Huber M. A. Wiedemann E. M. Beug H. Wirth T. (2010). NF-kappaB promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.295 (2), 214–228. 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.03.003
177
Manoel-Caetano F. S. Rossi A. F. T. Ribeiro M. L. Prates J. Oliani S. M. Silva A. E. (2020). Hydrogen peroxide and Helicobacter pylori extract treatment combined with APE1 knockdown induce DNA damage, G2/M arrest and cell death in gastric cancer cell line. DNA Repair (Amst).96, 102976. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102976
178
Marcato P. Dean C. A. Pan D. Araslanova R. Gillis M. Joshi M. et al (2011). Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity of breast cancer stem cells is primarily due to isoform ALDH1A3 and its expression is predictive of metastasis. Stem Cells29 (1), 32–45. 10.1002/stem.563
179
Martínez-Gutierrez A. Carbajal-Lopez B. Bui T. M. Mendoza-Rodriguez M. Campos-Parra A. D. Calderillo-Ruiz G. et al (2022). A microRNA panel that regulates proinflammatory cytokines as diagnostic and prognosis biomarkers in colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Rep.30, 101252. 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101252
180
Matarlo J. S. Krumpe L. R. H. Heinz W. F. Oh D. Shenoy S. R. Thomas C. L. et al (2019). The natural product butylcycloheptyl prodiginine binds Pre-miR-21, inhibits dicer-mediated processing of Pre-miR-21, and blocks cellular proliferation. Cell Chem. Biol.26 (8), 1133–1142. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.04.011
181
Mathé E. A. Nguyen G. H. Bowman E. D. Zhao Y. Budhu A. Schetter A. J. et al (2009). MicroRNA expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus: associations with survival. Clin. Cancer Res.15 (19), 6192–6200. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1467
182
Medina P. P. Nolde M. Slack F. J. (2010). OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature467 (7311), 86–90. 10.1038/nature09284
183
Meng F. Henson R. Wehbe-Janek H. Ghoshal K. Jacob S. T. Patel T. (2007). MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology133 (2), 647–658. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.05.022
184
Meng J. Lu X. Zhou Y. Zhang M. Gao L. Gao S. et al (2020). Characterization of the prognostic values and response to immunotherapy/chemotherapy of Krüppel-like factors in prostate cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med.24 (10), 5797–5810. 10.1111/jcmm.15242
185
Miranda-Lorenzo I. Dorado J. Lonardo E. Alcala S. Serrano A. G. Clausell-Tormos J. et al (2014). Intracellular autofluorescence: a biomarker for epithelial cancer stem cells. Nat. Methods11 (11), 1161–1169. 10.1038/nmeth.3112
186
Mirzaei H. Khataminfar S. Mohammadparast S. Sales S. S. Maftouh M. Mohammadi M. et al (2016). Circulating microRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in gastric cancer: current status and future perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem.23 (36), 4135–4150. 10.2174/0929867323666160818093854
187
Møller T. James J. P. Holmstrøm K. Sørensen F. B. Lindebjerg J. Nielsen B. S. (2019). Co-Detection of miR-21 and TNF-α mRNA in budding cancer cells in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20 (8), 1907. 10.3390/ijms20081907
188
Monteleone N. J. Moore A. E. Iacona J. R. Lutz C. S. Dixon D. A. (2019). miR-21-mediated regulation of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in colon cancer. Sci. Rep.9 (1), 5405. 10.1038/s41598-019-41862-2
189
Moore A. E. Young L. E. Dixon D. A. (2011). MicroRNA and AU-rich element regulation of prostaglandin synthesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.30 (3-4), 419–435. 10.1007/s10555-011-9300-5
190
Mori Y. Ishiguro H. Kuwabara Y. Kimura M. Mitsui A. Ogawa R. et al (2009). MicroRNA-21 induces cell proliferation and invasion in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep.2 (2), 235–239. 10.3892/mmr_00000089
191
Morinaga S. Nakamura Y. Atsumi Y. Murakawa M. Yamaoku K. Aoyama T. et al (2016). Locked nucleic acid in situ hybridization analysis of MicroRNA-21 predicts clinical outcome in patients after resection for pancreatic cancer treated with adjuvant gemcitabine monotherapy. Anticancer Res.36 (3), 1083–1088.
192
Mortoglou M. Miralles F. Arisan E. D. Dart A. Jurcevic S. Lange S. et al (2022). microRNA-21 regulates stemness in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (3), 1275. 10.3390/ijms23031275
193
Mosmann T. R. Li L. Sad S. (1997). Functions of CD8 T-cell subsets secreting different cytokine patterns. Semin. Immunol.9 (2), 87–92. 10.1006/smim.1997.0065
194
Motamedi M. Razmkhah F. Rezakhani L. Ghasemi S. (2020). Altered expression of CD44, SIRT1, CXCR4, miR-21, miR-34a, and miR-451 genes in MKN-45 cell line after docetaxel treatment. J. Gastrointest. Cancer51 (2), 520–526. 10.1007/s12029-019-00274-1
195
Motoyama K. Inoue H. Mimori K. Tanaka F. Kojima K. Uetake H. et al (2010). Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PDCD4 and microRNA-21 in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol.36 (5), 1089–1095. 10.3892/ijo_00000590
196
Myung S. J. Rerko R. M. Yan M. Platzer P. Guda K. Dotson A. et al (2006). 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is an in vivo suppressor of colon tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.103 (32), 12098–12102. 10.1073/pnas.0603235103
197
Nagao Y. Hisaoka M. Matsuyama A. Kanemitsu S. Hamada T. Fukuyama T. et al (2012). Association of microRNA-21 expression with its targets, PDCD4 and TIMP3, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol.25 (1), 112–121. 10.1038/modpathol.2011.142
198
Nagel R. Semenova E. A. Berns A. (2016). Drugging the addict: non-oncogene addiction as a target for cancer therapy. EMBO Rep.17 (11), 1516–1531. 10.15252/embr.201643030
199
Nautiyal J. Du J. Yu Y. Kanwar S. S. Levi E. Majumdar A. P. (2012). EGFR regulation of colon cancer stem-like cells during aging and in response to the colonic carcinogen dimethylhydrazine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol.302 (7), G655–G663. 10.1152/ajpgi.00323.2011
200
Ni H. Han Y. Jin X. (2019). Celastrol inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation by downregulating miR-21 and PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol.12 (3), 808–816.
201
Niess H. Camaj P. Renner A. Ischenko I. Zhao Y. Krebs S. et al (2015). Side population cells of pancreatic cancer show characteristics of cancer stem cells responsible for resistance and metastasis. Target Oncol.10 (2), 215–227. 10.1007/s11523-014-0323-z
202
Nooh M. Hakemi-Vala M. Nowroozi J. Fatemi S. R. Dezfulian M. (2021). Prediction of blood miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gastric cancer. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol.10 (2), 243–256. 10.52547/rbmb.10.2.243
203
Nouraee N. Van Roosbroeck K. Vasei M. Semnani S. Samaei N. M. Naghshvar F. et al (2013). Expression, tissue distribution and function of miR-21 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One8 (9), e73009. 10.1371/journal.pone.0073009
204
Obermannova R. Redova-Lojova M. Vychytilova-Faltejskova P. Grell P. Cho W. C. Sachlova M. et al (2018). Tumor expression of miR-10b, miR-21, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathological features of gastric cancer in a central European population. Anticancer Res.38 (6), 3719–3724. 10.21873/anticanres.12651
205
Old L. J. (1985). Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science230 (4726), 630–632. 10.1126/science.2413547
206
Orosz E. Kiss I. Gyöngyi Z. Varjas T. (2018). Expression of circulating miR-155, miR-21, miR-221, miR-30a, miR-34a and miR-29a: comparison of colonic and rectal cancer. Vivo32 (6), 1333–1337. 10.21873/invivo.11383
207
Osawa S. Shimada Y. Sekine S. Okumura T. Nagata T. Fukuoka J. et al (2011). MicroRNA profiling of gastric cancer patients from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples. Oncol. Lett.2 (4), 613–619. 10.3892/ol.2011.313
208
Oshima Y. Suzuki A. Kawashimo K. Ishikawa M. Ohkohchi N. Taniguchi H. (2007). Isolation of mouse pancreatic ductal progenitor cells expressing CD133 and c-Met by flow cytometric cell sorting. Gastroenterology132 (2), 720–732. 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.027
209
P L. A. Ahadi A. Zare A. Tarighi S. Zaheri M. Souri M. et al (2018). Up-Regulation of miR-21, miR-25, miR-93, and miR-106b in gastric cancer. Iran. Biomed. J.22 (6), 367–373. 10.29252/.22.6.367
210
Paik W. H. Kim H. R. Park J. K. Song B. J. Lee S. H. Hwang J. H. (2013). Chemosensitivity induced by down-regulation of microRNA-21 in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells by indole-3-carbinol. Anticancer Res.33 (4), 1473–1481.
211
Papaconstantinou I. G. Manta A. Gazouli M. Lyberopoulou A. Lykoudis P. M. Polymeneas G. et al (2013). Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas42 (1), 67–71. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182592ba7
212
Park J. K. Lee E. J. Esau C. Schmittgen T. D. (2009). Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or -221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas38 (7), e190–e199. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181ba82e1
213
Park S. K. Park Y. S. Ahn J. Y. Do E. J. Kim D. Kim J. E. et al (2016). MiR 21-5p as a predictor of recurrence in young gastric cancer patients. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.31 (8), 1429–1435. 10.1111/jgh.13300
214
Park Y. S. Lee J. H. Jung D. B. Kim H. B. Jung J. H. Pak S. et al (2018). MicroRNA-21 induces loss of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in early gastric tubular adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep.8 (1), 17717. 10.1038/s41598-018-36139-z
215
Park J. L. Kim S. K. Jeon S. Jung C. K. Kim Y. S. (2021). MicroRNA profile for diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in thyroid cancer. Cancers (Basel)13 (4), 632. 10.3390/cancers13040632
216
Petrocca F. Visone R. Onelli M. R. Shah M. H. Nicoloso M. S. de Martino I. et al (2008). E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell13 (3), 272–286. 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.02.013
217
Pita I. Libânio D. Dias F. Teixeira A. L. Nogueira I. Medeiros R. et al (2021). Original article: MicroRNA dysregulation in the gastric carcinogenesis Cascade: can we anticipate its role in individualized care?Pathobiology88 (5), 338–350. 10.1159/000515548
218
Plaks V. Kong N. Werb Z. (2015). The cancer stem cell niche: how essential is the niche in regulating stemness of tumor cells?Cell Stem Cell16 (3), 225–238. 10.1016/j.stem.2015.02.015
219
Popov A. Szabo A. Mandys V. (2015). Small nucleolar RNA U91 is a new internal control for accurate microRNAs quantification in pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer15, 774. 10.1186/s12885-015-1785-9
220
Qi M. Liu D. Zhang S. (2017). MicroRNA-21 contributes to the discrimination of chemoresistance in metastatic gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark.18 (4), 451–458. 10.3233/CBM-161732
221
Qiang Z. Meng L. Yi C. Yu L. Chen W. Sha W. (2019). Curcumin regulates the miR-21/PTEN/Akt pathway and acts in synergy with PD98059 to induce apoptosis of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells. J. Int. Med. Res.47 (3), 1288–1297. 10.1177/0300060518822213
222
Qiu Y. F. Wang M. X. Meng L. N. Zhang R. Wang W. (2018). MiR-21 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of oral cancer cells through TNF-α. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.22 (22), 7735–7741. 10.26355/eurrev_201811_16395
223
Qu Y. Zhao G. Li H. (2017). Forward and reverse signaling mediated by transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-alpha and TNF receptor 2: potential roles in an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol.8, 1675. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01675
224
Quan J. Dong D. Lun Y. Sun B. Sun H. Wang Q. et al (2020). Circular RNA circHIAT1 inhibits proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cell lines through downregulation of miR-21. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol.34 (4), e22458. 10.1002/jbt.22458
225
Rachagani S. Macha M. A. Menning M. S. Dey P. Pai P. Smith L. M. et al (2015). Changes in microRNA (miRNA) expression during pancreatic cancer development and progression in a genetically engineered KrasG12D;Pdx1-Cre mouse (KC) model. Oncotarget6 (37), 40295–40309. 10.18632/oncotarget.5641
226
Rahir G. Moser M. (2012). Tumor microenvironment and lymphocyte infiltration. Cancer Immunol. Immunother.61 (6), 751–759. 10.1007/s00262-012-1253-1
227
Rahmati M. Ferns G. A. Mobarra N. (2021). The lower expression of circulating miR-210 and elevated serum levels of HIF-1α in ischemic stroke; possible markers for diagnosis and disease prediction. J. Clin. Lab. Anal.35 (12), e24073. 10.1002/jcla.24073
228
Ranjbar R. Hesari A. Ghasemi F. Sahebkar A. (2018). Expression of microRNAs and IRAK1 pathway genes are altered in gastric cancer patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Cell Biochem.119 (9), 7570–7576. 10.1002/jcb.27067
229
Rao C. V. Mohammed A. (2015). New insights into pancreatic cancer stem cells. World J. Stem Cells7 (3), 547–555. 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i3.547
230
Renz B. W. D'Haese J. G. Werner J. Westphalen C. B. Ilmer M. (2017). Repurposing established compounds to target pancreatic cancer stem cells (CSCs). Med. Sci. (Basel).5 (2), 14. 10.3390/medsci5020014
231
Rhim A. D. Mirek E. T. Aiello N. M. Maitra A. Bailey J. M. McAllister F. et al (2012). EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor formation. Cell148 (1-2), 349–361. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.025
232
Rihane F. E. Erguibi D. Lamsisi M. Chehab F. Ennaji M. M. (2022). RETRACTED ARTICLE: upregulation of miR-21 expression in gastric cancer and its clinicopathological feature Association. J. Gastrointest. Cancer53 (1), 236. 10.1007/s12029-021-00691-1
233
Roy S. Yu Y. Padhye S. B. Sarkar F. H. Majumdar A. P. (2013). Difluorinated-curcumin (CDF) restores PTEN expression in colon cancer cells by down-regulating miR-21. PLoS One8 (7), e68543. 10.1371/journal.pone.0068543
234
Rozic J. G. Chakraborty C. Lala P. K. (2001). Cyclooxygenase inhibitors retard murine mammary tumor progression by reducing tumor cell migration, invasiveness and angiogenesis. Int. J. Cancer93 (4), 497–506. 10.1002/ijc.1376
235
Ryu J. K. Hong S. M. Karikari C. A. Hruban R. H. Goggins M. G. Maitra A. (2010). Aberrant MicroRNA-155 expression is an early event in the multistep progression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology10 (1), 66–73. 10.1159/000231984
236
Ryu J. K. Matthaei H. Dal Molin M. Hong S. M. Canto M. I. Schulick R. D. et al (2011). Elevated microRNA miR-21 levels in pancreatic cyst fluid are predictive of mucinous precursor lesions of ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology11 (3), 343–350. 10.1159/000329183
237
Sabry D. El-Deek S. E. M. Maher M. El-Baz M. A. H. El-Bader H. M. Amer E. et al (2019). Role of miRNA-210, miRNA-21 and miRNA-126 as diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal carcinoma: impact of HIF-1α-VEGF signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem.454 (1-2), 177–189. 10.1007/s11010-018-3462-1
238
Sachdeva M. Zhu S. Wu F. Wu H. Walia V. Kumar S. et al (2009). p53 represses c-Myc through induction of the tumor suppressor miR-145. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.106 (9), 3207–3212. 10.1073/pnas.0808042106
239
Samiei H. Sadighi-Moghaddam B. Mohammadi S. Gharavi A. Abdolmaleki S. Khosravi A. et al (2019). Dysregulation of helper T lymphocytes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients is highly associated with aberrant production of miR-21. Immunol. Res.67 (2-3), 212–222. 10.1007/s12026-019-09079-7
240
Samiei H. Ajam F. Gharavi A. Abdolmaleki S. Kokhaei P. Mohammadi S. et al (2022). Simultaneous disruption of circulating miR-21 and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs): prospective diagnostic and prognostic markers for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). J. Clin. Lab. Anal.36 (1), e24125. 10.1002/jcla.24125
241
Santamaria S. Delgado M. Kremer L. Garcia-Sanz J. A. (2017). Will a mAb-Based immunotherapy directed against cancer stem cells Be feasible?Front. Immunol.8, 1509. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01509
242
Sayed D. Rane S. Lypowy J. He M. Chen I. Y. Vashistha H. et al (2008). MicroRNA-21 targets Sprouty2 and promotes cellular outgrowths. Mol. Biol. Cell19 (8), 3272–3282. 10.1091/mbc.e08-02-0159
243
Sha M. Ye J. Zhang L. X. Luan Z. Y. Chen Y. B. Huang J. X. (2014). Celastrol induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by miR-21 inhibiting PI3K/Akt-NF-κB signaling pathway. Pharmacology93 (1-2), 39–46. 10.1159/000357683
244
Sheedy F. J. Palsson-McDermott E. Hennessy E. J. Martin C. O'Leary J. J. Ruan Q. et al (2010). Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat. Immunol.11 (2), 141–147. 10.1038/ni.1828
245
Shen H. Zhu F. Liu J. Xu T. Pei D. Wang R. et al (2014). Alteration in Mir-21/PTEN expression modulates gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One9 (7), e103305. 10.1371/journal.pone.0103305
246
Sheng H. Shao J. Morrow J. D. Beauchamp R. D. DuBois R. N. (1998). Modulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression by prostaglandin E2 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res.58 (2), 362–366.
247
Shi Z. Zhang J. Qian X. Han L. Zhang K. Chen L. et al (2013). AC1MMYR2, an inhibitor of dicer-mediated biogenesis of oncomir miR-21, reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses tumor growth and progression. Cancer Res.73 (17), 5519–5531. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0280
248
Shi C. Yang Y. Xia Y. Okugawa Y. Yang J. Liang Y. et al (2016). Novel evidence for an oncogenic role of microRNA-21 in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut65 (9), 1470–1481. 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308455
249
Shibue T. Weinberg R. A. (2017). EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol.14 (10), 611–629. 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.44
250
Shiosaki J. Tiirikainen M. Peplowska K. Shaeffer D. Machida M. Sakamoto K. et al (2020). Serum micro-RNA identifies early stage colorectal cancer in a multi-ethnic population. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev.21 (10), 3019–3026. 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.10.3019
251
Shiotani A. Uedo N. Iishi H. Murao T. Kanzaki T. Kimura Y. et al (2012). H. pylori eradication did not improve dysregulation of specific oncogenic miRNAs in intestinal metaplastic glands. J. Gastroenterol.47 (9), 988–998. 10.1007/s00535-012-0562-7
252
Shiotani A. Murao T. Kimura Y. Matsumoto H. Kamada T. Kusunoki H. et al (2013). Identification of serum miRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for detection of high risk for early gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer109 (9), 2323–2330. 10.1038/bjc.2013.596
253
Si M. L. Zhu S. Wu H. Lu Z. Wu F. Mo Y. Y. (2007). miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene26 (19), 2799–2803. 10.1038/sj.onc.1210083
254
Sierzega M. Kaczor M. Kolodziejczyk P. Kulig J. Sanak M. Richter P. (2017). Evaluation of serum microRNA biomarkers for gastric cancer based on blood and tissue pools profiling: the importance of miR-21 and miR-331. Br. J. Cancer117 (2), 266–273. 10.1038/bjc.2017.190
255
Sisic L. Vallböhmer D. Stoecklein N. H. Blank S. Schmidt T. Driemel C. et al (2015). Serum microRNA profiles as prognostic or predictive markers in the multimodality treatment of patients with gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett.10 (2), 869–874. 10.3892/ol.2015.3341
256
Škrha P. Hořínek A. Anděl M. Škrha J. (2015). miRNA-192, miRNA-21 and miRNA-200: new pancreatic cancer markers in diabetic patients?Vnitr Lek.61 (4), 351–354.
257
Song W. F. Wang L. Huang W. Y. Cai X. Cui J. J. Wang L. W. (2013a). MiR-21 upregulation induced by promoter zone histone acetylation is associated with chemoresistance to gemcitabine and enhanced malignancy of pancreatic cancer cells. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev.14 (12), 7529–7536. 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.12.7529
258
Song J. Bai Z. Zhang J. Meng H. Cai J. Deng W. et al (2013b). Serum microRNA-21 levels are related to tumor size in gastric cancer patients but cannot predict prognosis. Oncol. Lett.6 (6), 1733–1737. 10.3892/ol.2013.1626
259
Song J. Yang P. Li X. Zhu X. Liu M. Duan X. et al (2021). Esophageal cancer-derived extracellular vesicle miR-21-5p contributes to EMT of ESCC cells by disorganizing macrophage polarization. Cancers (Basel)13 (16), 4122. 10.3390/cancers13164122
260
Stánitz E. Juhász K. Tóth C. Gombos K. Natali P. G. Ember I. (2013). Evaluation of MicroRNA expression pattern of gastric adenocarcinoma associated with socioeconomic, environmental and lifestyle factors in northwestern Hungary. Anticancer Res.33 (8), 3195–3200.
261
Stánitz É. Juhász K. Gombos K. Gőcze K. Tóth C. Kiss I. (2015). Alteration of miRNA expression correlates with lifestyle, social and environmental determinants in esophageal carcinoma. Anticancer Res.35 (2), 1091–1097.
262
Sun H. Wang P. Zhang Q. He X. Zai G. Wang X. et al (2016). MicroRNA-21 expression is associated with the clinical features of patients with gastric carcinoma and affects the proliferation, invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells by regulating noxa. Mol. Med. Rep.13 (3), 2701–2707. 10.3892/mmr.2016.4863
263
Sun J. Jiang Z. Li Y. Wang K. Chen X. Liu G. (2019). Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits the malignant phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting VHL. Onco Targets Ther.12, 7215–7226. 10.2147/OTT.S211535
264
Sun X. Zhang K. Li D. (2020). Prognostic potential of miR-21-3p in gastric cancer. J. Buon25 (6), 2678–2682.
265
Sun D. Z. Ye M. Ju D. W. Xiu L. J. Pei B. Zhang C. A. et al (2021). The effects of gastric cancer interstitial fluid on tumors based on traditional Chinese medicine 'phlegm' theory and the investigation on the mechanism through microRNA-21 regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.72 (3). 10.26402/jpp.2021.3.07
266
Tai H. H. Ensor C. M. Tong M. Zhou H. Yan F. (2002). Prostaglandin catabolizing enzymes. Prostagl. Other Lipid Mediat68-69, 483–493. 10.1016/s0090-6980(02)00050-3
267
Tai H. H. Cho H. Tong M. Ding Y. (2006). NAD+-linked 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase: structure and biological functions. Curr. Pharm. Des.12 (8), 955–962. 10.2174/138161206776055958
268
Takai Y. Irie K. Shimizu K. Sakisaka T. Ikeda W. (2003). Nectins and nectin-like molecules: roles in cell adhesion, migration, and polarization. Cancer Sci.94 (8), 655–667. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01499.x
269
Tanaka Y. Kamohara H. Kinoshita K. Kurashige J. Ishimoto T. Iwatsuki M. et al (2013). Clinical impact of serum exosomal microRNA-21 as a clinical biomarker in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer119 (6), 1159–1167. 10.1002/cncr.27895
270
Tatsuwaki H. Tanigawa T. Watanabe T. Machida H. Okazaki H. Yamagami H. et al (2010). Reduction of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase expression is an independent predictor of poor survival associated with enhanced cell proliferation in gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci.101 (2), 550–558. 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01390.x
271
Tavano F. di Mola F. F. Piepoli A. Panza A. Copetti M. Burbaci F. P. et al (2012). Changes in miR-143 and miR-21 expression and clinicopathological correlations in pancreatic cancers. Pancreas41 (8), 1280–1284. 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31824c11f4
272
Tian X. Shivapurkar N. Wu Z. Hwang J. J. Pishvaian M. J. Weiner L. M. et al (2016). Circulating microRNA profile predicts disease progression in patients receiving second-line treatment of lapatinib and capecitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett.11 (3), 1645–1650. 10.3892/ol.2016.4101
273
Toste P. A. Li L. Kadera B. E. Nguyen A. H. Tran L. M. Wu N. et al (2015). p85α is a microRNA target and affects chemosensitivity in pancreatic cancer. J. Surg. Res.196 (2), 285–293. 10.1016/j.jss.2015.02.071
274
Traub P. Perides G. Scherbarth A. Traub U. (1985). Tenacious binding of lipids to vimentin during its isolation and purification from ehrlich ascites tumor cells. FEBS Lett.193 (2), 217–221. 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80155-1
275
Treece A. L. Duncan D. L. Tang W. Elmore S. Morgan D. R. Dominguez R. L. et al (2016). Gastric adenocarcinoma microRNA profiles in fixed tissue and in plasma reveal cancer-associated and epstein-barr virus-related expression patterns. Lab. Invest96 (6), 661–671. 10.1038/labinvest.2016.33
276
Tse J. Pierce T. Carli A. L. E. Alorro M. G. Thiem S. Marcusson E. G. et al (2022). Onco-miR-21 promotes Stat3-Dependent gastric cancer progression. Cancers (Basel)14 (2), 264. 10.3390/cancers14020264
277
Tu H. Sun H. Lin Y. Ding J. Nan K. Li Z. et al (2014). Oxidative stress upregulates PDCD4 expression in patients with gastric cancer via miR-21. Curr. Pharm. Des.20 (11), 1917–1923. 10.2174/13816128113199990547
278
Uysal-Onganer P. Kawano Y. Caro M. Walker M. M. Diez S. Darrington R. S. et al (2010). Wnt-11 promotes neuroendocrine-like differentiation, survival and migration of prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cancer9, 55. 10.1186/1476-4598-9-55
279
Uysal-Onganer P. D'Alessio S. Mortoglou M. Kraev I. Lange S. (2021). Peptidylarginine deiminase inhibitor application, using Cl-amidine, PAD2, PAD3 and PAD4 isozyme-specific inhibitors in pancreatic cancer cells, reveals roles for PAD2 and PAD3 in cancer invasion and modulation of extracellular vesicle signatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (3), 1396. 10.3390/ijms22031396
280
Vahidnezhad H. Youssefian L. Uitto J. (2016). Molecular genetics of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in genodermatoses: diagnostic implications and treatment opportunities. J. Invest Dermatol.136 (1), 15–23. 10.1038/JID.2015.331
281
Valeri N. Gasparini P. Braconi C. Paone A. Lovat F. Fabbri M. et al (2010). MicroRNA-21 induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil by down-regulating human DNA MutS homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.107 (49), 21098–21103. 10.1073/pnas.1015541107
282
Valladares-Ayerbes M. Blanco M. Haz M. Medina V. Iglesias-Díaz P. Lorenzo-Patiño M. J. et al (2011). Prognostic impact of disseminated tumor cells and microRNA-17-92 cluster deregulation in gastrointestinal cancer. Int. J. Oncol.39 (5), 1253–1264. 10.3892/ijo.2011.1112
283
Valle S. Martin-Hijano L. Alcalá S. Alonso-Nocelo M. Sainz B. Jr (2018). The ever-evolving concept of the cancer stem cell in pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel)10 (2), 33. 10.3390/cancers10020033
284
Vandewalle V. Essaghir A. Bollaert E. Lenglez S. Graux C. Schoemans H. et al (2021). miR-15a-5p and miR-21-5p contribute to chemoresistance in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia by targeting PDCD4, ARL2 and BTG2. J. Cell Mol. Med.25 (1), 575–585. 10.1111/jcmm.16110
285
Vila-Casadesús M. Vila-Navarro E. Raimondi G. Fillat C. Castells A. Lozano J. J. et al (2018). Deciphering microRNA targets in pancreatic cancer using miRComb R package. Oncotarget9 (5), 6499–6517. 10.18632/oncotarget.24034
286
Vossenaar E. R. Zendman A. J. van Venrooij W. J. Pruijn G. J. (2003). PAD, a growing family of citrullinating enzymes: genes, features and involvement in disease. Bioessays.25 (11), 1106–1118. 10.1002/bies.10357
287
Wang R. F. (2008). CD8+ regulatory T cells, their suppressive mechanisms, and regulation in cancer. Hum. Immunol.69 (11), 811–814. 10.1016/j.humimm.2008.08.276
288
Wang S. Wang Y. (2013). Peptidylarginine deiminases in citrullination, gene regulation, health and pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1829 (10), 1126–1135. 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.07.003
289
Wang B. Zhang Q. (2012). The expression and clinical significance of circulating microRNA-21 in serum of five solid tumors. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol.138 (10), 1659–1666. 10.1007/s00432-012-1244-9
290
Wang J. Chen J. Chang P. LeBlanc A. Li D. Abbruzzesse J. L. et al (2009a). MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila)2 (9), 807–813. 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0094
291
Wang P. Zou F. Zhang X. Li H. Dulak A. Tomko R. J. Jr. et al (2009b). microRNA-21 negatively regulates Cdc25A and cell cycle progression in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res.69 (20), 8157–8165. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1996
292
Wang P. Zhuang L. Zhang J. Fan J. Luo J. Chen H. et al (2013). The serum miR-21 level serves as a predictor for the chemosensitivity of advanced pancreatic cancer, and miR-21 expression confers chemoresistance by targeting FasL. Mol. Oncol.7 (3), 334–345. 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.10.011
293
Wang Z. Cai Q. Jiang Z. Liu B. Zhu Z. Li C. (2014). Prognostic role of microRNA-21 in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Monit.20, 1668–1674. 10.12659/MSM.892096
294
Wang F. Liu W. Jin Y. Wang F. Ma J. (2015a). Prenatal and neonatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonic acid results in aberrant changes in miRNA expression profile and levels in developing rat livers. Environ. Toxicol.30 (6), 712–723. 10.1002/tox.21949
295
Wang D. Fan Z. Liu F. Zuo J. (2015b). Hsa-miR-21 and Hsa-miR-29 in tissue as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem.37 (4), 1454–1462. 10.1159/000438514
296
Wang J. Zhang C. Chen K. Tang H. Tang J. Song C. et al (2015c). ERβ1 inversely correlates with PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway and predicts a favorable prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat.152 (2), 255–269. 10.1007/s10549-015-3467-3
297
Wang X. Liu D. Zhou K. Wang B. Liu Q. Deng F. et al (2016a). Expression of Wnt11 and Rock2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activation of the WNT/PCP pathway and its clinical significance. Pathol. Res. Pract.212 (10), 880–885. 10.1016/j.prp.2016.07.008
298
Wang X. Wang C. Zhang X. Hua R. Gan L. Huang M. et al (2016b). Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating miRNAs. J. Hematol. Oncol.9 (1), 90. 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9
299
Wang X. Wang R. Li F. Wu Y. Liu Y. Zhang W. (2017). Relationship between miR-21 and miR-182 levels in peripheral blood and gastric cancer tissue. Oncol. Lett.14 (2), 1427–1432. 10.3892/ol.2017.6280
300
Wang L. Yao M. Fang M. Zheng W. J. Dong Z. Z. Pan L. H. et al (2018a). Expression of hepatic Wnt5a and its clinicopathological features in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int.17 (3), 227–232. 10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.03.005
301
Wang P. Guan Q. Zhou D. Yu Z. Song Y. Qiu W. (2018b). miR-21 inhibitors modulate biological functions of gastric cancer cells via PTEN/PI3K/mTOR pathway. DNA Cell Biol.37 (1), 38–45. 10.1089/dna.2017.3922
302
Wang K. Chen D. Meng Y. Xu J. Zhang Q. (2018c). Clinical evaluation of 4 types of microRNA in serum as biomarkers of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett.16 (1), 1196–1204. 10.3892/ol.2018.8720
303
Wang W. Yuan X. Xu A. Zhu X. Zhan Y. Wang S. et al (2018d). Human cancer cells suppress behaviors of endothelial progenitor cells through miR-21 targeting IL6R. Microvasc. Res.120, 21–28. 10.1016/j.mvr.2018.05.007
304
Wang V. M. Ferreira R. M. M. Almagro J. Evan T. Legrave N. Zaw T. M. et al (2019a). CD9 identifies pancreatic cancer stem cells and modulates glutamine metabolism to fuel tumour growth. Nat. Cell Biol.21 (11), 1425–1435. 10.1038/s41556-019-0407-1
305
Wang J. Lin Y. Jiang T. Gao C. Wang D. Wang X. et al (2019b). Up-regulation of TIMP-3 and RECK decrease the invasion and metastasis ability of colon cancer. Arab. J. Gastroenterol.20 (3), 127–134. 10.1016/j.ajg.2019.07.003
306
Wang Y. Huang L. Shan N. Ma H. Lu S. Chen X. et al (2021a). Establishing a three-miRNA signature as a prognostic model for colorectal cancer through bioinformatics analysis. Aging (Albany NY)13 (15), 19894–19907. 10.18632/aging.203400
307
Wang Y. Chen G. Dai F. Zhang L. Yuan M. Yang D. et al (2021b). miR-21 induces chemoresistance in ovarian cancer cells via mediating the expression and interaction of CD44v6 and P-gp. Onco Targets Ther.14, 325–336. 10.2147/OTT.S286639
308
Wartenberg M. Centeno I. Haemmig S. Vassella E. Zlobec I. Galván J. A. et al (2016). PTEN alterations of the stromal cells characterise an aggressive subpopulation of pancreatic cancer with enhanced metastatic potential. Eur. J. Cancer65, 80–90. 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.06.013
309
Wen S. W. Zhang Y. F. Li Y. Liu Z. X. Lv H. L. Li Z. H. et al (2015). Characterization and effects of miR-21 expression in esophageal cancer. Genet. Mol. Res.14 (3), 8810–8818. 10.4238/2015.August.3.4
310
Weng W. Wu Q. Yu Y. Mei W. Wang X. (2013). A novel chemotherapeutic arene ruthenium(II) drug Rawq01 altered the effect of microRNA-21 on PTEN/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer cells. Anticancer Res.33 (12), 5407–5414.
311
Winter J. M. Ting A. H. Vilardell F. Gallmeier E. Baylin S. B. Hruban R. H. et al (2008). Absence of E-cadherin expression distinguishes noncohesive from cohesive pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res.14 (2), 412–418. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0487
312
Winther M. Alsner J. Tramm T. Baeksgaard L. Holtved E. Nordsmark M. (2015). Evaluation of miR-21 and miR-375 as prognostic biomarkers in esophageal cancer. Acta Oncol.54 (9), 1582–1591. 10.3109/0284186X.2015.1064161
313
Wu J. Li G. Wang Z. Yao Y. Chen R. Pu X. et al (2015). Circulating MicroRNA-21 is a potential diagnostic biomarker in gastric cancer. Dis. Markers2015, 435656. 10.1155/2015/435656
314
Wu Y. R. Qi H. J. Deng D. F. Luo Y. Y. Yang S. L. (2016). MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol.37 (9), 12061–12070. 10.1007/s13277-016-5074-2
315
Xiao T. Jie Z. (2019). MiR-21 promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Eur. Surg. Res.60 (5-6), 208–218. 10.1159/000504133
316
Xie Z. J. Chen G. Zhang X. C. Li D. F. Huang J. Li Z. J. (2012). Saliva supernatant miR-21: a novel potential biomarker for esophageal cancer detection. Asian Pac J. Cancer Prev.13 (12), 6145–6149. 10.7314/apjcp.2012.13.12.6145
317
Xie Z. Chen G. Zhang X. Li D. Huang J. Yang C. et al (2013). Salivary microRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS One8 (4), e57502. 10.1371/journal.pone.0057502
318
Xin L. Yang W. F. Zhang H. T. Li Y. F. Liu C. (2018). The mechanism study of lentiviral vector carrying methioninase enhances the sensitivity of drug-resistant gastric cancer cells to cisplatin. Br. J. Cancer118 (9), 1189–1199. 10.1038/s41416-018-0043-8
319
Xu Y. Sun J. Xu J. Li Q. Guo Y. Zhang Q. (2012). miR-21 is a promising novel biomarker for lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract.2012, 640168. 10.1155/2012/640168
320
Xu G. Meng L. Yuan D. Li K. Zhang Y. Dang C. et al (2018). MEG3/miR-21 axis affects cell mobility by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep.40 (1), 39–48. 10.3892/or.2018.6424
321
Xue Y. Abou Tayoun A. N. Abo K. M. Pipas J. M. Gordon S. R. Gardner T. B. et al (2013). MicroRNAs as diagnostic markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its precursor, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasm. Cancer Genet.206 (6), 217–221. 10.1016/j.cancergen.2013.05.020
322
Yachida S. Iacobuzio-Donahue C. A. (2009). The pathology and genetics of metastatic pancreatic cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med.133 (3), 413–422. 10.1043/1543-2165-133.3.413
323
Yamanaka S. Olaru A. V. An F. Luvsanjav D. Jin Z. Agarwal R. et al (2012). MicroRNA-21 inhibits Serpini1, a gene with novel tumour suppressive effects in gastric cancer. Dig. Liver Dis.44 (7), 589–596. 10.1016/j.dld.2012.02.016
324
Yan J. Liu T. Zhou X. Dang Y. Yin C. Zhang G. (2016). FZD6, targeted by miR-21, represses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via activating non-canonical wnt pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res.8 (5), 2354–2364.
325
Yan B. Cheng L. Jiang Z. Chen K. Zhou C. Sun L. et al (2018). Resveratrol inhibits ROS-promoted activation and glycolysis of pancreatic stellate cells via suppression of miR-21. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev.2018, 1346958. 10.1155/2018/1346958
326
Yan-nan B. Zhao-yan Y. Li-xi L. jiang Y. Qing-jie X. Yong Z. (2014). MicroRNA-21 accelerates hepatocyte proliferation in vitro via PI3K/Akt signaling by targeting PTEN. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.443 (3), 802–807. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.047
327
Yang S. M. Huang C. Li X. F. Yu M. Z. He Y. Li J. (2013a). miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells by regulating PTEN. Toxicology306, 162–168. 10.1016/j.tox.2013.02.014
328
Yang M. Liu R. Sheng J. Liao J. Wang Y. Pan E. et al (2013b). Differential expression profiles of microRNAs as potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep.29 (1), 169–176. 10.3892/or.2012.2105
329
Yang Q. Xu E. Dai J. Wu J. Zhang S. Peng B. et al (2014). miR-21 regulates N-methyl-N-nitro-N'-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric tumorigenesis by targeting FASLG and BTG2. Toxicol. Lett.228 (3), 147–156. 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.05.005
330
Yang Z. Fang S. Di Y. Ying W. Tan Y. Gu W. (2015). Modulation of NF-κB/miR-21/PTEN pathway sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to cisplatin. PLoS One10 (3), e0121547. 10.1371/journal.pone.0121547
331
Yao Q. Cao S. Li C. Mengesha A. Kong B. Wei M. (2011). Micro-RNA-21 regulates TGF-β-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting PDCD4 in tumor-stroma interaction. Int. J. Cancer128 (8), 1783–1792. 10.1002/ijc.25506
332
Yao S. S. Han L. Tian Z. B. Yu Y. N. Zhang Q. Li X. Y. et al (2019a). Celastrol inhibits growth and metastasis of human gastric cancer cell MKN45 by down-regulating microRNA-21. Phytother. Res.33 (6), 1706–1716. 10.1002/ptr.6359
333
Yao L. H. Wang G. R. Cai Y. Ma Q. Wang D. S. Xu L. et al (2019b). The expressions and diagnostic values of miR-18a and miR-21 in esophageal cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi41 (2), 107–111. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2019.02.006
334
Ye M. Ye P. Zhang W. Rao J. Xie Z. (2014). Diagnostic values of salivary versus and plasma microRNA-21 for early esophageal cancer. Nan Fang. Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao34 (6), 885–889.
335
Yen H. R. Harris T. J. Wada S. Grosso J. F. Getnet D. Goldberg M. V. et al (2009). Tc17 CD8 T cells: functional plasticity and subset diversity. J. Immunol.183 (11), 7161–7168. 10.4049/jimmunol.0900368
336
Yin Z. Ma T. Huang B. Lin L. Zhou Y. Yan J. et al (2019). Macrophage-derived exosomal microRNA-501-3p promotes progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res.38 (1), 310. 10.1186/s13046-019-1313-x
337
Yin Z. Zhou Y. Ma T. Chen S. Shi N. Zou Y. et al (2020). Down-regulated lncRNA SBF2-AS1 in M2 macrophage-derived exosomes elevates miR-122-5p to restrict XIAP, thereby limiting pancreatic cancer development. J. Cell Mol. Med.24 (9), 5028–5038. 10.1111/jcmm.15125
338
You C. Jin L. Xu Q. Shen B. Jiao X. Huang X. (2019). Expression of miR-21 and miR-138 in colon cancer and its effect on cell proliferation and prognosis. Oncol. Lett.17 (2), 2271–2277. 10.3892/ol.2018.9864
339
Yu P. Fu Y. X. (2006). Tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes: friends or foes?Lab. Invest86 (3), 231–245. 10.1038/labinvest.3700389
340
Yu Y. Kanwar S. S. Patel B. B. Oh P. S. Nautiyal J. Sarkar F. H. et al (2012). MicroRNA-21 induces stemness by downregulating transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFβR2) in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis33 (1), 68–76. 10.1093/carcin/bgr246
341
Yu Y. Nangia-Makker P. Farhana L. S G. R. Levi E. Majumdar A. P. (2015). miR-21 and miR-145 cooperation in regulation of colon cancer stem cells. Mol. Cancer14, 98. 10.1186/s12943-015-0372-7
342
Yu J. Yang X. Wu H. Li J. (2021). Clinical significance of color ultrasound, MRI, miR-21, and CA199 in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. J. Oncol.2021, 2380958. 10.1155/2021/2380958
343
Yuan W. Tang W. Xie Y. Wang S. Chen Y. Qi J. et al (2016). New combined microRNA and protein plasmatic biomarker panel for pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget7 (48), 80033–80045. 10.18632/oncotarget.12406
344
Zhai B. Zhang L. Wang C. Zhao Z. Zhang M. Li X. (2019). Identification of microRNA-21 target genes associated with hair follicle development in sheep. PeerJ7, e7167. 10.7717/peerj.7167
345
Zhang Z. Li Z. Gao C. Chen P. Chen J. Liu W. et al (2008). miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab. Invest88 (12), 1358–1366. 10.1038/labinvest.2008.94
346
Zhang J. G. Wang J. J. Zhao F. Liu Q. Jiang K. Yang G. H. (2010). MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Chim. Acta411 (11-12), 846–852. 10.1016/j.cca.2010.02.074
347
Zhang B. G. Li J. F. Yu B. Q. Zhu Z. G. Liu B. Y. Yan M. (2012). microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol. Rep.27 (4), 1019–1026. 10.3892/or.2012.1645
348
Zhang Y. Pan T. Zhong X. Cheng C. (2014). Nicotine upregulates microRNA-21 and promotes TGF-β-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition of esophageal cancer cells. Tumour Biol.35 (7), 7063–7072. 10.1007/s13277-014-1968-z
349
Zhang L. Yao J. Li W. Zhang C. (2018a). Micro-RNA-21 regulates cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Res.26 (6), 827–835. 10.3727/096504017X14934840662335
350
Zhang S. Wu M. Wang F. (2018b). Immune regulation by CD8(+) treg cells: novel possibilities for anticancer immunotherapy. Cell Mol. Immunol.15 (9), 805–807. 10.1038/cmi.2018.170
351
Zhang L. Dong B. Ren P. Ye H. Shi J. Qin J. et al (2018c). Circulating plasma microRNAs in the detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett.16 (3), 3303–3318. 10.3892/ol.2018.8995
352
Zhang Y. Tian S. Xiong J. Zhou Y. Song H. Liu C. (2018d). JQ-1 inhibits Colon cancer proliferation via suppressing Wnt/β-Catenin signaling and miR-21. Chem. Res. Toxicol.31 (5), 302–307. 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.7b00346
353
Zhang H. Feng X. Zhang M. Liu A. Tian L. Bo W. et al (2019a). Long non-coding RNA CASC2 upregulates PTEN to suppress pancreatic carcinoma cell metastasis by downregulating miR-21. Cancer Cell Int.19, 18. 10.1186/s12935-019-0728-y
354
Zhang H. Zhang Z. Wang D. (2019b). Epigenetic regulation of IncRNA KCNKI5-ASI in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag. Res.11, 8589–8602. 10.2147/CMAR.S186002
355
Zhang C. Zhang C. D. Liang Y. Wu K. Z. Pei J. P. Dai D. Q. (2020). The comprehensive upstream transcription and downstream targeting regulation network of miRNAs reveal potential diagnostic roles in gastric cancer. Life Sci.253, 117741. 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117741
356
Zhao Y. Zhao L. Ischenko I. Bao Q. Schwarz B. Nieß H. et al (2015). Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 and microRNA-221 in tumor-initiating stem-like cells modulates tumorigenesis, metastasis, and chemotherapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. Target Oncol.10 (4), 535–548. 10.1007/s11523-015-0360-2
357
Zhao Q. Chen S. Zhu Z. Yu L. Ren Y. Jiang M. et al (2018). miR-21 promotes EGF-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by targeting Spry2. Cell Death and Dis.9 (12), 1157. 10.1038/s41419-018-1182-9
358
Zhao G. Jiang T. Liu Y. Huai G. Lan C. Li G. et al (2018c). Droplet digital PCR-based circulating microRNA detection serve as a promising diagnostic method for gastric cancer. BMC Cancer18 (1), 676. 10.1186/s12885-018-4601-5
359
Zheng Y. Cui L. Sun W. Zhou H. Yuan X. Huo M. et al (2011). MicroRNA-21 is a new marker of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark.10 (2), 71–77. 10.3233/CBM-2011-0231
360
Zheng M. Jiang J. Tang Y. L. Liang X. H. (2013). Oncogene and non-oncogene addiction in inflammation-associated cancers. Future Oncol.9 (4), 561–573. 10.2217/fon.12.202
361
Zhou H. Liu H. Jiang M. Zhang S. Chen J. Fan X. (2019). Targeting MicroRNA-21 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration via PTEN/Akt signaling axis. Cell Transpl.28 (3), 306–317. 10.1177/0963689719825573
362
Zhu S. Si M. L. Wu H. Mo Y. Y. (2007). MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J. Biol. Chem.282 (19), 14328–14336. 10.1074/jbc.M611393200
363
Zhu S. Wu H. Wu F. Nie D. Sheng S. Mo Y. Y. (2008). MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res.18 (3), 350–359. 10.1038/cr.2008.24
Summary
Keywords
gastrointestinal cancers, microRNA-21, exosomes, diagnostics, overcoming drug resistance
Citation
Wang C, Bai M, Liu X, Li Z, Wang H and Guo S (2025) Molecular roles of microRNA-21 and exosomal miR-21 in gastrointestinal cancers: diagnostic, therapeutic, and drug resistance insights. Front. Mol. Biosci. 12:1697875. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1697875
Received
02 September 2025
Revised
29 October 2025
Accepted
03 November 2025
Published
16 December 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Artur Slomka, Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń, Poland
Reviewed by
S. Greeshma, Central University of Kerala, India
Sogand Vahidi, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wang, Bai, Liu, Li, Wang and Guo.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meiling Bai, blxiaobai2022@126.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.