- 1Food Science and Quality Control, Halabja Technical College, Sulaimani Polytechnic University, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq
- 2Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Institute of Pharmacy, University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria
- 3Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Pakistan
- 4Food Science Department, College of Agriculture, University of Basrah, Basrah, Iraq
- 5College of Medicine, University of Warith Al-Anbiyaa, Karbala, Iraq
- 6Medical Laboratory Science Department, Halabja Technical College, Sulaimani Polytechnic University, Sulaymaniya, Iraq
- 7Medical Laboratory Techniques Department, Halabja Technical Institute, Research Center, Sulaimani Polytechnic University, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq
- 8Nursing Department, Halabja Technical Institute, Sulaimani Polytechnic University, Sulaimani, Iraq
- 9Department of Food Science and Technology, University of West Attica, Egaleo, Greece
- 10Department of Chemical Engineering, BioTeC+ Chemical and Biochemical Process, KU Leuven, Gent, Belgium
- 11Dairy Science Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
- 12Department of Supply Chain, University of Management and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan
- 13Food Science Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Cairo University, Giza, Egypt
This comprehensive review explores nanobubbles (NBs) technology advancements for improving drug and nutraceutical delivery and promoting human health. NBs are gas-filled nanocarriers owing to unique structures, excellent stability, flexibility, biocompatibility, and precise targeting abilities that stand out as promising drug delivery systems that improve bioavailability and enable controlled drug release. NBs demonstrate various applications, such as cancer therapy and cardiovascular health treatment, addressing neurodegenerative disorders, and aiding nutrient absorption. A significant advantage of NBs is their ultrasound-triggered cavitation, which enables targeted delivery with minimal systemic toxicity. In nutraceuticals, NBs enhance the absorption of vital nutrients, primarily those with poor bioavailability, by stabilizing and effectively targeting these compounds in the gastrointestinal system. However, long-term safety issues demand thorough preclinical studies, including bioaccumulation and cytotoxicity. The review examines important ethical, safety, and regulatory factors which must be addressed to advance NB technology in clinical and nutritional applications. The potential of these systems exists, but scalability and sustainability pose significant challenges. The full potential of nanocarriers in healthcare and nutrition depends on ongoing research into biodegradable materials and scalable production alongside the development of eco-friendly nanocarrier systems. Research results show NBs are fundamental to precision medicine and personalized nutrition, establishing a base for innovative drug and nutraceutical delivery systems.
1 Introduction
The convergence of nanotechnology, therapeutic, and nutritional sciences is resulting in more efficient and precise drug delivery methods, improving bioavailability, stability, and safety. Nonpharmaceuticals have emerged as transformative drug delivery technologies, providing increased stability, targeted therapy, bioavailability, and controlled release of bioactive substances. Such systems cover sensitive pharmaceuticals with polymeric matrices, thereby regulating their release and enhancing their absorption at target areas (Noreen et al., 2024). One of the latest advancements in this field involves using nanobubbles (NBs). These gas-filled particles are smaller than 1 μm, demonstrating high efficiency in precision drug and nutraceutical delivery (Cavalli et al., 2016). NBs are considered a transformative tool for overcoming the limitations of traditional delivery methods because of their small size, high stability, and customizable surface qualities. Nanofibers may flow through blood arteries, overcome biological barriers, and transfer bioactive substances directly to target tissues (Jin et al., 2022).
NBs are tiny gas core nanocarriers stabilized by surfactant or polymeric shells, which enhance encapsulation efficiency, biocompatibility, and controlled release properties. Recent advances in nanobubble design have focused on improving bio-degradability and reducing long-term toxicity risks, making them appropriate for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical uses (Pandey and Pandey, 2024). Figure 1 depicts the structural representation of the nanobubble and its role as a targeted and drug delivery carrier. Modifying the surface composition of NBs allows for site-specific drug delivery while decreasing systemic exposure and off-target effects. This property will enable them to respond to external stimuli such as ultrasound, temperature, or pH changes, permitting targeted and triggered medication release (Xiong et al., 2021). In therapeutics and nutraceutical applications, NBs provide a new paradigm for improving bioavailability and controlled release, ensuring enhanced absorption at the target by minimizing degradation and toxicity (Gul et al., 2024). The emergence of stimuli-responsive features permits their application in precision medicine, specifically cancer therapy, cardiovascular therapies, and immunological regulation. In nutraceutical distribution, tailored NBs increase the absorption of bioactive substances in the gastrointestinal system, shielding sensitive components from enzymatic destruction and increasing therapeutic efficacy (Noreen and Bernkop-Schnürch, 2024).
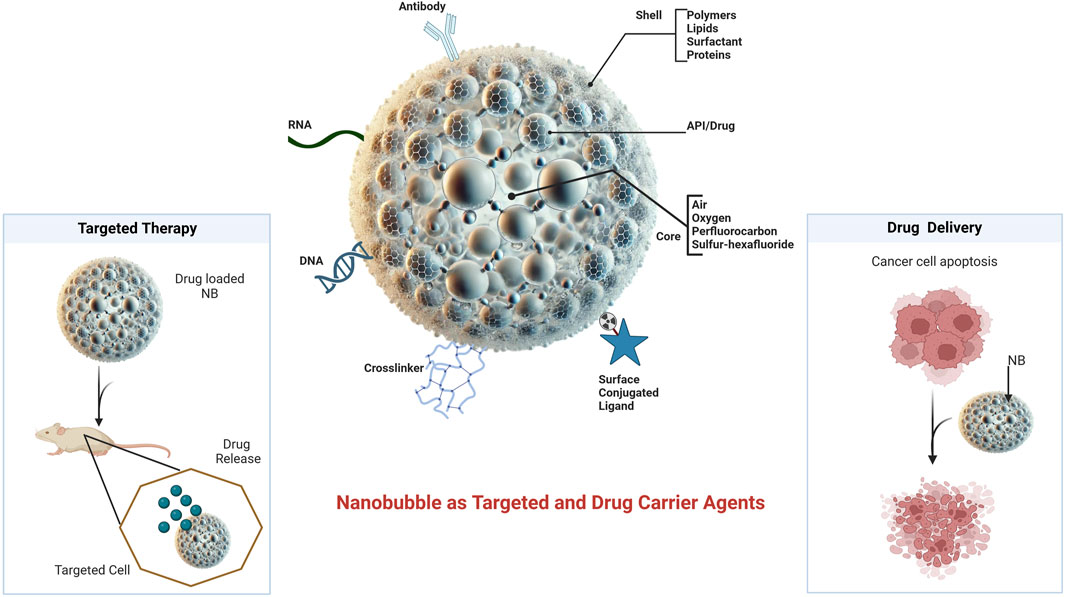
Figure 1. Structural representation of a nanobubble and its role as a targeted and drug delivery carrier.
This comprehensive review explores the development mechanisms, safety problems, scalability challenges, and sustainability properties of NBs that make them suitable for drugs and nutraceutical delivery systems. One of the most significant advantages of NBs is their ability to selectively accumulate in diseased tissues, making them valuable tools in precision medicine. NBs can use ultrasound or other external stimuli to control the release of their payload, which improves therapeutic effects while reducing systemic toxicity. This technique is particularly essential in cancer since NBs allow for the localized administration of chemotherapeutic medicines while reducing harm to healthy tissues (Shah et al., 2023). In nutraceutical applications, targeted NB systems improve nutrient absorption efficiency, particularly for compounds with solubility and bioavailability. This property benefits from dietary supplements, functional foods, and deficiency treatments (Wang et al., 2023). NB formulations provide an innovative approach over traditional nutraceutical delivery methods by increasing solubility, stability, and transport efficiency. Through the investigation of recent advancements, this review discusses the safety profiles, scalability innovations, and sustainability considerations to show the promise of NBs in transforming pharmaceutical and nutraceutical delivery. Special emphasis was placed on biodegradable and ecologically friendly NB formulations addressing long-term toxicity, bioaccumulation, and large-scale manufacturing practicality. NB technology is set to change the future of medicine and nutrition by providing precise, efficient, and sustainable delivery systems. Moreover, we focus on some of the specific uses of NBs in areas such as cancer treatment, cardio health, and dietary supplementation, where NBs make possible the accurate conveyance of drugs and nutrients (Kulkarni et al., 2022; Soyluoglu et al., 2021).
Nutraceuticals and therapeutic compounds that are the most susceptible to environmental degradation are among those that, after being encapsulated by nanobubbles, have protection afforded to them. However, they are also transported safely orally or intravenously. Moreover, NBs search for and interact with biological and physical stimuli due to their qualities. Thus, they constantly evolve contact tools for precision medicine and individualized nutrition (Mcclements, 2020). Nanoscale NBs have enormous potential in drug and nutraceutical delivery, thus making significant changes in the healthcare field, increasing the therapeutic effect, and improving patients’ health outcomes. At the same time, the science of nanotechnology keeps developing. This review aims to enable the innately NB-based applications and benefits of NB technology for therapeutics and nutraceuticals, and it will show the development of human health through innovative and efficient delivery methods.
2 Nanobubbles: structure, properties, and formation
One of the distinguishing features of NBs is their high surface area-to-volume ratio, which contributes to improved gas solubility, higher internal pressure, and the production of reactive species due to surface charge interactions (Wang et al., 2019; Bai et al., 2023; Takahashi et al., 2007). Their near-neutral (typically pH 6.8–7.4) stability enables sustained circulation in biological systems, making them particularly efficient in precision medicine, environmental remediation (Li et al., 2021), groundwater remediation, and targeted drug delivery (Kwon et al., 2020).
Nanobubbles often face challenges like coalescence (merging) or dissolution due to their small size and high internal pressure. Near-neutral stability implies that these nanobubbles.
• Maintain their structure effectively in physiological or slightly varying pH conditions
• Do not burst or dissolve rapidly, especially in biological environments (which are usually near pH 7),
• They are suitable for longer circulation in the body, targeted drug delivery, or environmental applications like water treatment.
Besides, external factors such as temperature, pressure, and surfactant concentration all impact NB stability. Variations in these factors can change their size, responsiveness, and functional behavior, influencing their usefulness in specific applications. The incorporation of polymeric coatings considerably improves the stability of NB, improves circulation duration, and improves the efficacy of drug/nutrient administration. Polymeric coatings like chitosan (CS), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) also have a significant impact on augmenting the NB biocompatibility and preventing premature release by the immune system. For instance, by PEGylation of nanocarriers, opsonization was reduced by creating a steric barrier, leading to an increased drug stock at the target site and prolonged systemic circulation (Qaiser et al., 2024). Additionally, chitosan-coated nanoparticles enhance mucoadhesion, augmenting the bioavailability of therapeutics administered via the oral and pulmonary routes. Therefore, NBs stabilized with polymeric coatings exhibit extended longevity, while those formed in high-pressure environments may experience size fluctuations and coalescence over time (Wang and Wang, 2023). In medicine, using vapor NBs on nanoparticle areas has transformed the development of accurate transport techniques for cancer therapy, demonstrating improved penetration into tumor tissues and controlled drug release upon external stimuli activation (Lee E. et al., 2020). NBs could be indirectly made during the laser fabrication procedure and the production of two-dimensional substances (Lei et al., 2024). NBs are gaseous compounds with radii ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers. Due to their small size, they require advanced microscopy techniques for visualization. The advanced atomic force microscope images show that the nanotubules are mainly composed of spherical caps, without knowing their exact shape (An et al., 2015). Surface NBs can be found under various microscopy techniques, most commonly the atomic force microscope (Hampton and Nguyen, 2009). NBs are highly stable adsorbed substances and spread out as pancake-like or liquid dispersions. The first evidence of interfacial NBs is a scientific study that worked on the attractive force among hydrophobic areas immersed in water. Based on this, this character is similar to the separation distance among the different surfaces (Par et al., 1994). It has recently analyzed the intricate behavior and characteristics of NBs across various procedures. The study confirmed the substantiated NBs’ remarkable stability in the medium, preserving over an extended time, even with dissolution (Tan et al., 2021). NBs have properties of high stability and longevity and can easily bind to hydrophobic surfaces of various materials. These characteristics can increase the range of use of NBs in many applications, such as surface coating and cleaning, removing polluting materials, medicine, and agriculture (Ushida et al., 2012; Zimmerman et al., 2011).
2.1 Types of nanobubbles
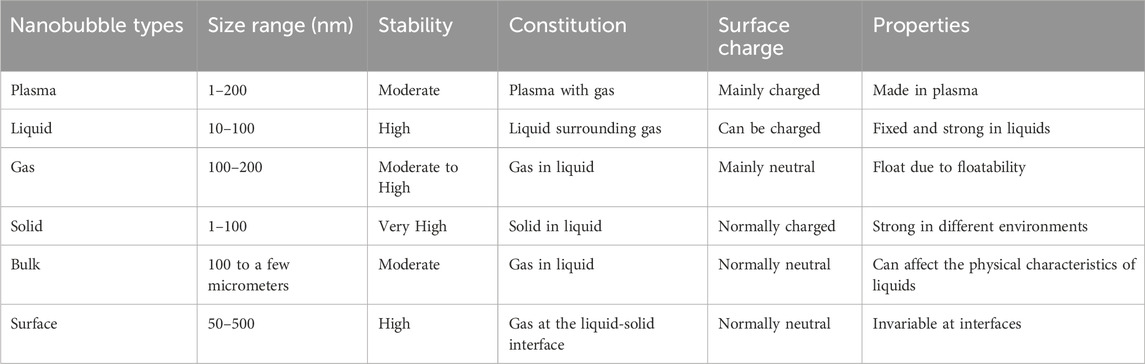
NBs, specified by their tiny size and specific gas content, have drawn significant attention in different applications of medical and environmental sciences. NBs are classified into different sorts according to their gas content (O2, N2, and CO2), size, and stability; each provides specific characteristics and behaviors. The most critical NBs identified, which are plasma, liquid, gas, solid, surface, and bulk NBs, are shown in Table 1. (Sharma et al., 2024; Bunkin et al., 2021). Size also has a crucial role in their functionality. NBs typically range from 50 to 500 nm in diameter, with smaller bubbles (around 50–100 nm) showing enhanced stability and extending residence times in liquids.
In contrast, larger ones might make more productive gas transfer possible, enhance reactivity and stability, and extend residence times in liquids. Furthermore, stability can be improved by integrating surface materials or polymeric coatings, resulting in stabilized NBs that withstand coalescence and sedimentation. These and other parameters have a considerable impact on NB behavior and use, making them a versatile instrument in medicine delivery and water treatment (Javed et al., 2023; Huang et al., 2023). Thus, knowing NBs is essential; these NB properties are vital for enhancing their design and utilization in various fields.
2.2 Techniques of nanobubble formation
Preparing NBs is a complex process influenced by various physical, chemical, and engineering factors. NBs are typically generated through gas dissolution, cavitation, and bubble nucleation, each affecting their size, stability, and functionality. The two main pathways for NB formation are:
Gas dissolution method–This dissolution pathway requires the step-by-step dissolution of gas into a liquid, then oversaturation and nucleation. This commonly occurs at interfaces or bulk solutions and is affected by gas solubility pressure, temperature, and surfactant concentration.
Collapse of large bubbles (cavitation method) –Collapse of giant bubbles under high shear stress or acoustic cavitation, forming smaller and stable NBs. This process is augmented by ultrasound, high-pressure shearing, or microfluidic mixing (Ji et al., 2021).
External factors such as shear stress, ultrasound frequency, and pressure gradient play a critical role in NBs formation, directly influencing their size distribution and stability. Comprehending these pathways improves NB formation efficiency, optimizing their use in drug delivery, environmental remediation, and diagnostics (Sharma et al., 2024; Che and Theodorakis, 2017). Comprehension of these pathways can assist in understanding based on the feature of nanobubble behavior and help in improving their production for different industrial and biomedical uses.
When exposed to ultrasound, NBs are presently being studied for their potential in the targeted delivery of medicines, proteins, and nucleic acids. The preferred medicine is encapsulated in the inner core, and upon irradiation with ultrasound or extracorporeal shock waves, the drug is released from the NBs into the target cells (Batchelor et al., 2022). Furthermore, chemical methods can be used to make NBs, in which the solubility and stability of gases within a liquid are quickly accelerated. Apart from the above essential methods, microfluidics and high shear mixing are two other creative techniques for exploring the making of NBs. These techniques are critical for making nanobubbles across different fields (Nazari et al., 2022).
2.2.1 Scalability and reproducibility of production processes of NBs
The shift from laboratory-scale NB manufacturing to large-scale industrial production encompasses several hurdles, including batch-to-batch variability, limited scalability, and variable drug-loading efficiency. Traditional procedures, such as probe sonication and gas dissolution, have low repeatability and significant energy consumption (Rosselló and Ohl, 2023).
To overcome these limitations, several scalable NB production techniques have emerged:
• Microfluidic-Based Nanobubble Production - A simple and scalable method for continuous, size-controlled synthesis of NBs. Unlike conventional approaches, microfluidics produces monodisperse bubbles, which improves reproducibility in clinical and pharmaceutical applications.
• High-Pressure Homogenization - A process in which gas-liquid mixtures are driven through tight channels with high shear, resulting in homogenous NB formation. This approach improves drug encapsulation efficiency, making it suitable for industrial-scale NB production.
• Electrostatic Self-Assembly–This method improves NB stability and drug-binding efficiency by modifying their surface charge characteristics. This approach is helpful for tailored drug delivery applications. To ensure batch-to-batch consistency in NB formulations, real-time monitoring and quality control are required, using:
∘ Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) – These techniques provide real-time measurements of NB size, stability, and concentration.
∘ Zeta Potential measurements analyze surface charge, which impacts NB stability and drug-binding efficiency.
∘ AI-driven automated feedback systems are being integrated into NB manufacturing settings to optimize synthesis parameters and reduce unpredictability.
Additionally, lyophilization (freeze-drying) techniques have been incorporated to enhance long-term storage stability, reduce aggregation, and maintain NB functionality for extended periods. By integrating scalable synthesis methods, real-time monitoring, and automated quality control, NB technology can effectively translate from laboratory research to large-scale applications (Kida et al., 2023).
2.2.2 Optimization of production processes of NBs
The productivity and efficiency of NBs can be increased by optimizing the manufacturing process. NBs are widely used in drug delivery, water treatment, and oil recovery, but their production must be fine-tuned for different applications. Many essential electrolysis, cavitation, and microfluidic methods have been established to make optimized NBs. In everyday situations, each technique has provided positive and negative effectiveness across its applications. For example, electrolysis can create a distinct gas that is appropriate for the desired use, even though this technique might use high energy. In a different example, the cavitation technique can make many NBs quickly. However, its pressure and temperature parameters must be controlled carefully to ensure size distribution consistency. In addition, in microfluidic techniques, bubble size and gas composition are controlled, but these methods might not be applicable in all areas and face some challenges (Silva et al., 2024; Paknahad et al., 2021). Additionally, NBs can be stabilized using polymer coatings and biocompatible surfactants (such as PEG and phospholipids), lessening coalescence and lengthening their circulation period in biomedical applications. As a result, optimizing these different techniques by improving their processes and real-time monitoring will give more chances for using NBs in various areas and increase outcomes (Jin et al., 2022).
2.2.3 Strategies for drug loading in NBs
Four primary strategies exist for loading drugs into NBs (Figure 2). The initial loading strategy focused on the encapsulation of gases within the core. This method allows for controlled drug release when exposed to ultrasound or external stimuli. This technique is primarily used in ultrasound-triggered delivery systems, in which NBs emit gas in response to acoustic stimulation (Figure 2A) (Nittayacharn et al., 2019). The alternative method involves the direct attachment of drug-conjugated nanoparticles to the surface of NBs, subsequently enhancing targeted delivery while maintaining NB stability in circulation (Figure 2B) (Kancheva et al., 2023). The third technique involves the potential binding of the drug within or beneath the NB shell. This strategy provides better protection for sensitive drugs and ensures gradual, sustained release (Figure 2C) (Dasgupta et al., 2023). The fourth option for drug loading in NBs is the nesting approach. This involves layering multiple drug-loaded NBs, increasing therapeutic payload capacity (Figure 2D) (Batchelor et al., 2020). All these techniques provide high-efficiency drug loading while preserving NB stability, making them adaptable carriers for targeted therapy applications.
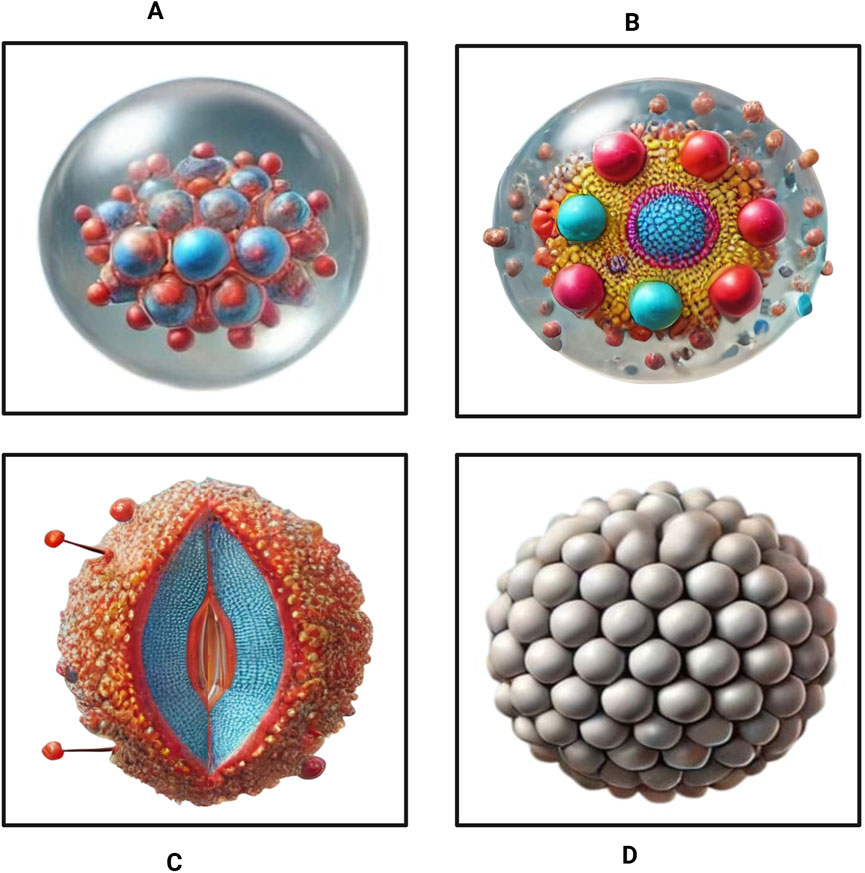
Figure 2. Strategies for drug loading in NBs. (A) Encapsulating gases in the bubble core (B) attaching drug-conjugated nanoparticles to the bubble shell, (C) encapsulation within or directly beneath the NB shell, and (D) the nesting structure loading.
3 Mechanisms of nanobubble-enhanced delivery systems
NBs interact primarily with cell membranes and tissues through mechanisms that enhance permeability, facilitate intracellular drug transport or nutraceutical delivery, and improve bioavailability. These include sonoporation, endosomal escape, localized oxygen release (oxygenation) to improve hypoxic conditions, and controlled release triggered by external stimuli such as ultrasound, temperature, pH, or light. These mechanisms are summarized in Table 2, which outlines their applications in drug and nutraceutical delivery.
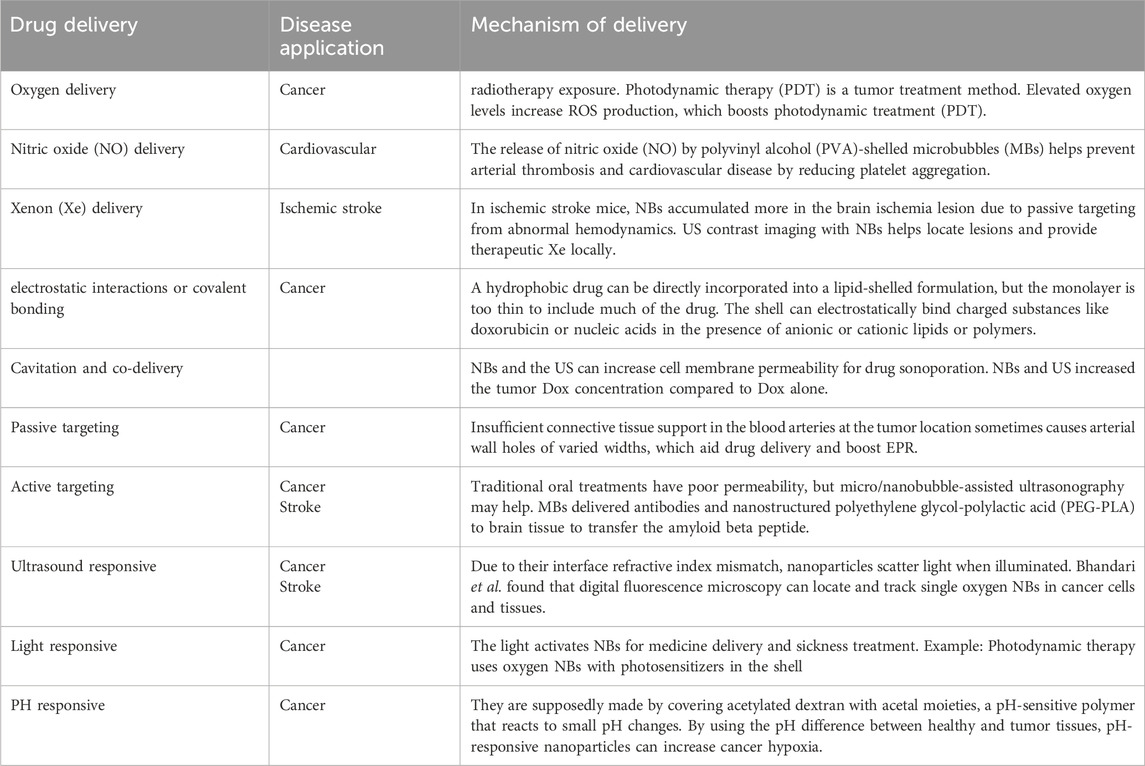
Table 2. Overview of key mechanisms and applications of NBs and microbubbles in drug and nutraceutical delivery.
3.1 Sonoporation and ultrasound trigger delivery
Ultrasound is widely used to induce oscillations in NBs, causing mechanical effects that open temporary pores in cell membranes. This process, known as sonoporation, enhances cell membrane permeability, allowing drugs or nutrients to enter cells more efficiently and with minimal cytotoxicity. Studies have shown that oscillating NBs create transient pores in the membrane, which reseal after drug delivery, minimizing cellular damage. This technique benefits targeted cancer therapy as API may be administered directly to tumor cells while preserving healthy tissues. Additionally, the cavitation effect can be modulated by varying the ultrasound’s frequency and strength, which will regulate the extent of cellular uptake and the depth of drug penetration. NBs may collapse (inertial cavitation) in high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) applications, resulting in localized medication release and improved therapeutic results (De Cock et al., 2015).
3.2 Endosomal escape via vapor nanobubbles (VNBs)
Vapor nanobubbles (VNBs) offer a promising strategy for bypassing the endosomal degradation pathways. When supported by laser beams, VNBs create mechanical forces that break endosomal membranes, freeing the encapsulated material and enabling direct cytoplasmic delivery. This approach is very suitable for gene therapy, silencing RNA interference (RNAi), and CRISPR-based genetic modifications, as it prevents enzymatic degradation in lysosomal compartments (Fraire et al., 2020). According to recent research, laser-activated VNBs have the potential to be used in immunotherapy applications since they not only promote intracellular drug release but also strengthen immune response activation.
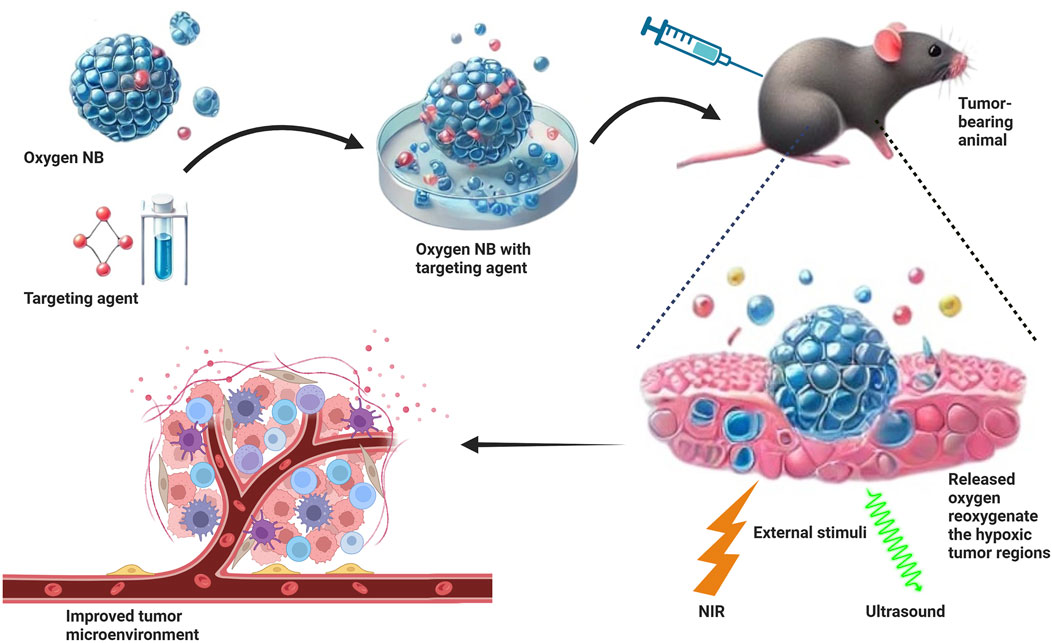
3.3 Oxygen nanobubbles (OnBs) and hypoxia mitigation
The OnB is considered an adjunct therapy for hypoxia and mitochondrial dysfunction. Such as ischemic illnesses, stroke, and cancer. By delivering extremely concentrated oxygen to hypoxic areas, these NBs improve cellular metabolism and increase the effectiveness of oxygen-dependent treatments. In tumor microenvironments, where hypoxia leads to treatment resistance, OnBs are very helpful. OnBs can decrease tumor survival rates by improving the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiation therapy by raising local oxygenation (Messerschmidt et al., 2023).
3.4 Drug and nutraceutical encapsulation techniques
NBs enhance bioavailability through mechanisms such as sonoporation or endocytosis-mediated internalization (e.g., clathrin-mediated or caveolae-mediated pathways), allowing for controlled and efficient intracellular delivery of drugs and nutritional supplements. Furthermore, drug and nutraceutical encapsulation techniques using NBs can be accomplished using different strategies, including lipid-based, polymer-based, and hybrid nanobubble carriers. (a) The lipid-based NBs are usually applied due to their resemblance to cell membranes, which makes them biocompatible and less toxic. The lipid layer acts as a protective hull by maintaining NBs under physiological conditions and preventing encapsulated substances from being broken down by enzymes (Pasupathy et al., 2022). (b) Polymer-based NBs are yet another option that provides surface modification for active targeting and regulated drug release. Polymeric shells decrease off-target effects and increase medication stability by prolonging circulation time. PEGylated NBs, for instance, increase systemic retention and improve therapeutic efficacy by decreasing immune recognition. (c) In hybrid NBs, lipids and polymers can be combined to encapsulate hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules, increasing the variety of medications and nutraceuticals that can be delivered. These hybrid formulations improve solubility and absorption, which is especially helpful for medications not very soluble in water (Yurkin and Wang, 2017).
3.5 Stimuli-responsive release mechanism for precision therapy
NBs can be engineered to expel payloads in response to specific external stimuli, providing spatiotemporal control over medication delivery. Therefore, for release mechanisms and targeted delivery, NB delivery systems are fabricated to release their contents in response to definite stimuli, such as ultrasound, pH change, or temperature shift, thereby enabling precise control over the drug release time and location (Figure 3). (a) The ultrasound-triggered release method is the most widely used non-invasive technique. NBs vibrate, collapse under ultrasound waves, and release drugs at target sites inside the tumor or inflamed tissue. The method has been deemed particularly successful in treating cancer, where ultrasound-NBs are burst to preferentially deliver drugs to the cancer cells instead of the healthy cells. To provide site-specific delivery and reduce systemic toxicity (Roovers et al., 2019). (b) pH-sensitive NBs react to acidic surroundings, such as tumor locations or inflammatory tissues. The shell degrades in response to pH, allowing targeted drug release while avoiding damage to healthy cells. This method improves precision therapy while reducing unwanted effects (Fan et al., 2019). (c) Temperature-sensitive NBs, when exposed to heat, certain NBs undergo phase changes, making them ideal for thermoresponsive drug release in localized hyperthermia treatments. (d) Magnetically responsive NBs are the type in which magnetic nanoparticles can be integrated into NBs, enabling externally controlled, targeted medication delivery using magnetic fields.
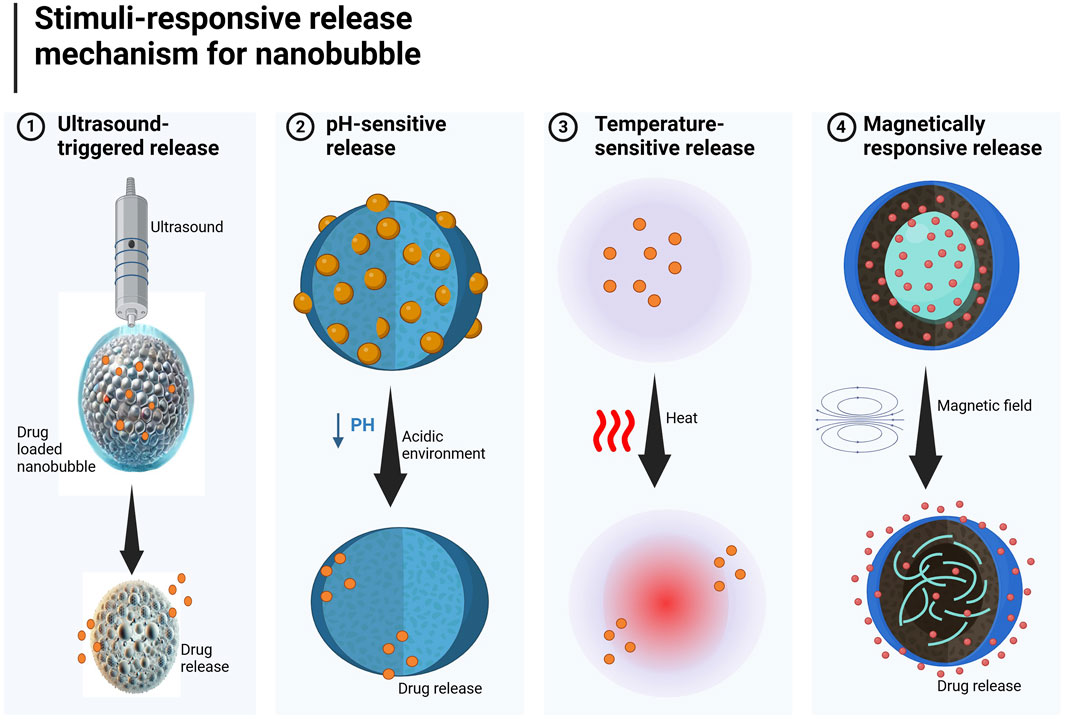
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of stimuli-responsive nanobubbles (NBs) for precision drug delivery (1). Ultrasound-triggered NBs (2). pH-sensitive NBs (3). Temperature-sensitive NBs (4). Magnetically responsive NBs.
3.6 Environmental sensitivity and control targeting
NBs target to minimize off-target effects while increasing therapy efficacy. Their environmental sensitivity guarantees that pharmaceuticals are only given in diseased areas, preventing premature release. Furthermore, environmentally sensitive NBs provide a way of controlled release dependent on certain physical conditions. Furthermore, NBs are important in nutraceutical applications by shielding bioactive chemicals from environmental degradation, particularly in the gastrointestinal system. Encapsulation within NBs protects delicate compounds, including vitamins, probiotics, and polyphenols, from enzymatic degradation or chemical instability in the upper gastrointestinal tract, resulting in regulated release at the targeted absorption location. This extends shelf life and enhances bioavailability, resulting in increased therapeutic advantages. Among these smart NBs are tumor-targeted NBs and inflammation-responsive NBs (English, 2022). (a) In the tumor-targeted NBs, incorporating tumor-specific ligands or monoclonal antibodies into NB surfaces increases selective tumor targeting and medication accumulation at malignant locations. This focused method improves therapeutic efficacy while reducing systemic medication exposure, resulting in fewer side effects (Chen et al., 2022). (b) Meanwhile, inflammation-responsive NBs are specifically programmed to release medicines in response to oxidative stress or inflammatory signals. They show promise in treating autoimmune illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease by delivering anti-inflammatory medicines directly to afflicted tissues. Recent research has shown that hydrogen-loaded nanobubbles can substantially reduce virus-induced inflammation by decreasing proinflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species (ROS) buildup, as evidenced in a zebrafish model of viral infection (Li et al., 2022), Figure 4.
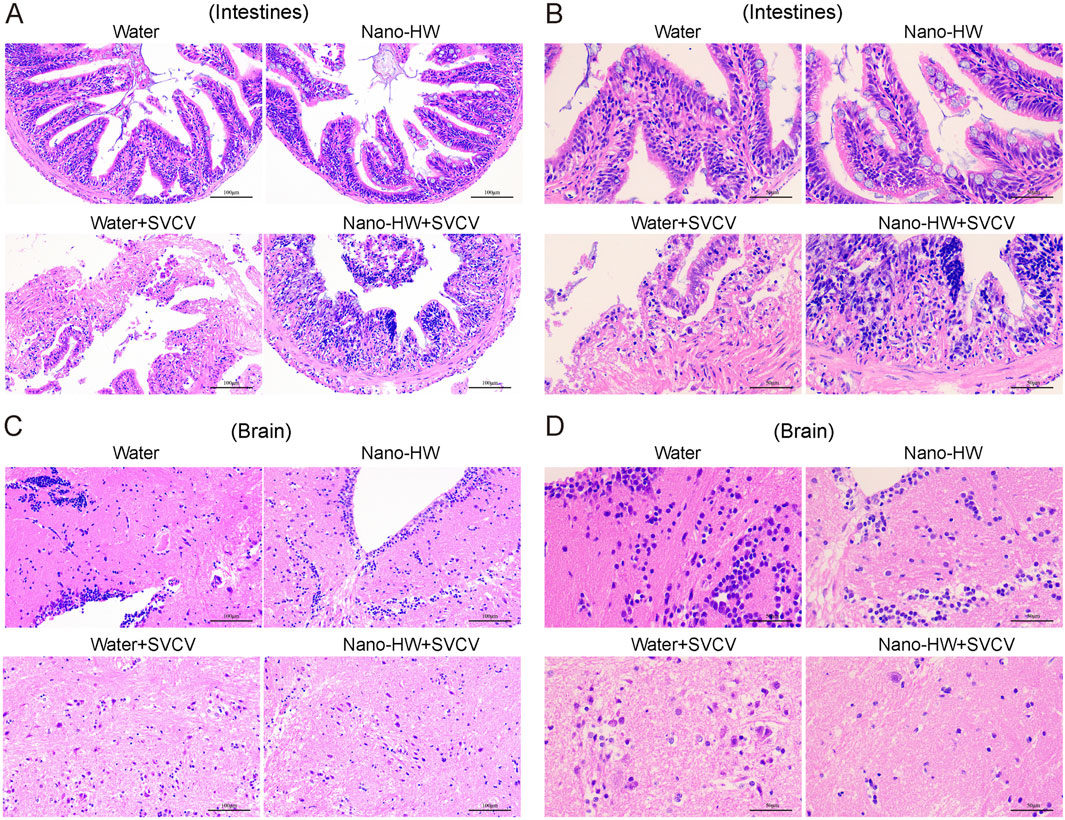
Figure 4. Histopathological analysis of intestinal (A and B) and brain (C and D) tissues from nano-HW-treated and untreated zebrafish. Tissue sections were collected on day 5 post-infection and subjected to H&E staining. The results indicate that SVCV infection caused severe tissue damage in the intestines and brain, which was significantly alleviated in the nano-HW-treated group. Reprinted with permission from Li et al. (2022). Copyright (2025) Elsevier.
4 Applications of NBs
4.1 Applications of NBs in drug delivery
A drug delivery system (DDS) utilizes various methods to deliver the appropriate prescription dosage to the correct place within a set timeframe, boosting utilization efficiency and lowering side effects. Unlike traditional drug delivery systems, stimuli-responsive innovative drug delivery systems that respond to endogenous and/or external stimuli offer significant advantages, including reduced drug concentration variability, decreased medication toxicity, and improved therapeutic efficacy (K et al., 2024). Ultrasound (US) exhibits significant characteristics among various external stimuli, including optical, electrical, magnetic, thermal, and mechanical stimuli, particularly in clinical medical applications. Gas systems, including microbubbles (MBs) and NBs, have attracted considerable attention as a novel drug delivery system (DDS) due to their advantageous scattering properties, high harmonic generation, and the bursting behavior induced by ultrasonic pressure (Jin et al., 2022). This section outlines the strategies and designs of DDSs utilizing NBs, including direct delivery, co-delivery, targeted delivery, and stimulus-responsive delivery. The following subsections will discuss the significant applications of NBs in drug delivery, focusing on tumor Theranostics, drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for brain diseases, vascular diagnosis and treatment, neurodegenerative disease therapy, and anticancer drug delivery.
4.1.1 Tumor theranostics
Despite the significant morbidity and mortality associated with cancer, it is imperative to pursue effective therapeutic strategies (Siegel et al., 2019). The current preferred clinical interventions for cancer are surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy (Li X. et al., 2018). While these possess a specific therapeutic action, they fail to target tumor tissue, resulting in toxicity and adverse effects on normal tissue. The low local medication concentration in the tumor results in a heightened risk of long-term metastasis (Kalbasi et al., 2017). Micro/NBs support the site-targeted delivery of antineoplastic drugs to tumors, which solves the problems that cause the limitations in traditional therapeutic modalities (Kaneko and Willmann, 2012). For instance, Gao et al. developed an innovative in vivo delivery method for anticancer drugs that uses bifunctional nanodroplets as the carriers that act smartly (Gao et al., 2021). Even though cancer is the second leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the world, the point made here is that healthcare professionals need to come up with therapies that are truly effective for cancer patients. The currently preferred methods of the treatment of cancer that are being used in clinics include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. While acting as directional treatment effects, these are not specific to cancerous tissue, resulting in toxicity and damage to the normal tissues, which are the side effects. The low local medication concentration in the tumor results in a heightened risk of long-term metastasis. Micro/NBs enable the site-specific release of anticancer drugs at cancerous sites, which consequently deals with the limitations of the usual therapy options (Browning and Stride, 2018). Nanodroplets using perfluorohexane (PFH) to encapsulate bubble cores with chitosan/alginate complexes were influenced by the endogenous local tumor microenvironment pH and stimulated by exogenous ultrasound irradiation, with both factors synergistically facilitating localized drug release (Gao et al., 2021). Scientists found that this new droplet had a powerful effect on fighting tumors. This means that ultrasound-assisted drug delivery for tumor treatment has come a long way. Furthermore, the phase transition of the nanodroplets into bubbles augmented the disparity in acoustic impedance between the bubbles and the surrounding medium, laying the groundwork for image surveillance to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy (Cao et al., 2018). In a separate investigation, researchers engineered bubbles with a poly (amino acid) shell enclosing perfluoropentane (PFP), pentafluorobutane (PFB), and doxorubicin (DOX) (Zhang et al., 2018). Once at the tumor site, the local acidic microenvironment supports tumor cell proliferation and tumor growth, which also contributes to a reduced cavitation threshold Low-frequency ultrasound continuously creates inertial cavitation in air bubbles, making it easier for DOX to reach the deep tumor site. Because the area around a tumor often lacks oxygen, using carrier cells such as macrophages or mesenchymal stem cells to load drugs, combined with ultrasound-assisted irradiation, increase the drug accumulation in hypoxic tumor regions, enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy (Zhao et al., 2012). Huang et al. used monocytes and macrophages to surround polymer-shelled bubbles and vesicles loaded with doxorubicin. They then used ultrasound to control the release of the drugs. The findings indicated that integrating US-assisted bubbles and drug-loaded cells significantly enhanced drug transport to hypoxic tumor locations and increased chemotherapeutic efficacy (Huang et al., 2015). The unique vascular milieu of the tumor, characterized by vascular tortuosity, elevated fluid pressure, growth-induced angiogenesis, and solid hypoxia, intrinsically links the efficacy of infusions (Lugano et al., 2020). The primary impediments to drug delivery at the tumor site are aberrant tumor vasculature and elevated interstitial pressure (Nakamura et al., 2016). When there is insufficient connective tissue support in the blood vessels near the tumor, holes of different sizes often form in the vessels’ walls. It makes it easier to give medications and boosts the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR). Hence, Nanoparticles with a size of less than 1 μm have recently garnered significant attention in cancer imaging and treatment due to their ability to accumulate at the target location via the EPR effect. Nanoparticles’ improved ability to permeate and retain matter makes it possible to use specific ligand-binding bubbles to image tumors only. Lipid shells and functional imaging agents, such as porphyrins or fluorescent dyes, comprise the transport platform, enabling simultaneous optical imaging and immunohistochemistry. Mai et al. produced biocompatible cyanine 5.5 (cy5.5) NBs, which serve as a dual ultrasound fluorescence contrast agent. The experimental data in vivo and in vitro demonstrate that Cy5.5-NBs facilitate tumor-selective imaging. Due to their nanoscale size (typically <500 nm), the advent of NBs presents a viable approach for advancing targeted ultrasound molecular imaging (Mai et al., 2013). Gao et al. found that attaching CA-125 antibodies to NBs for US molecular imaging might help find epithelial ovarian cancer more easily (Gao et al., 2017). Using contrast-enhanced ultrasound, Johansen et al. (2021) conducted’ imaging of nanoparticles toward a cancer biomarker associated with targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase mu (PTPmu), with nontargeted imaging conducted in vitro and murine models. The signal of PTPmu-targeted nanoparticles in the tumor remains elevated at the following point, suggesting that molecular ultrasound imaging can identify tumors using PTPmu-targeted nanoparticles, potentially assisting in diagnosis and therapy. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an efficacious treatment modality with negligible adverse effects. It uses photosensitizers activated by light to change dissolved oxygen into reactive oxygen species (ROS) or singlet oxygen (1 O2), killing cells nearby. Owing to its excellent specificity and minimal side effects, photodynamic therapy (PDT) has emerged as a viable approach for tumor treatment. The increased effectiveness of near-infrared-induced photodynamic treatment in NBs has been attributed to nanoscopic gaseous cavities, the ability to deliver drugs, and the ability to transmit sound waves. Tumor hypoxia is a limiting factor in the efficacy of oxygen-utilizing cancer therapies, potentially diminishing patient survival rates (Yang et al., 2022). One effective approach to mitigate hypoxia within the tumor microenvironment is to enhance oxygen levels at the tumor location. Engineers have engineered oxygenated MNBs to deliver oxygen and enhance tumor therapies such as radiation and photodynamic therapy. As an innovative oxygen transporter, biological gas vesicles (GVS) can mitigate tumor hypoxia (Zhao et al., 2021; So et al., 2020). A layer of liposomes alters the surface of GVS, a naturally occurring gas-filled chamber in a protein shell. In vitro and in vivo investigations, photodynamic treatment with lipid GVS (O2) demonstrates a notable increase in tumor cell apoptosis and necrosis. They formulated an ICG-NBs-O2 aqueous solution to enhance the PDT impact of ICG, allowing free ICG molecules to self-assemble at the gas-liquid interface of free nano-oxygen bubbles (NBs-O2) (Song et al., 2017). The results show that the quantum yield of singlet oxygen (1 O2) for ICG-NBs-O2 is eight times higher than that for free ICG in water. In vivo and in vitro tests demonstrate that the ICG-NBs-O2 aqueous solution markedly enhances the PDT’s efficacy against tumors compared to the free ICG aqueous solution. Li et al. (2021) facilitated in vivo bubble burst and photodynamic treatment for several centimeters deep tumors using US/PAI imaging. The mechanical impact of an explosion can augment the discharge of a photosensitizer. The US revealed the shape of the tumor and demonstrated the rapid perfusion of neuroblastomas. The mechanical damage and release of the combination demonstrated a notable synergistic anticancer effect on deep-seated tumors. Song et al. made lipid-polymer bilayer oxygen NBs by attaching chlorine-e6 (CE6) to the polymeric shell. These NBs are a new source of oxygen for photodynamic therapy (PDT). The synthesized NBs exhibit exceptional stability, minimizing the risk of premature oxygen release, and are preserved as lyophilized powder to circumvent storage issues. The tests, both in vitro and in vivo, showed that NBs were better at targeting tumors and absorbing cells than free CE6. Using oxygen NBs in photodynamic therapy can greatly improve the treatment’s effectiveness and survival rate in the CE6 glioma-bearing mouse model, with no noticeable side effects. The reason is that the encapsulated oxygen NBs help make more singlet oxygen. Using fluorescence imaging and ultrasound imaging together takes advantage of the best parts of both, making up for the fact that fluorescence imaging has a limited penetration depth and ultrasound imaging does not have enough resolution (Chan et al., 2018). The new dual-mode angiography enhances resolution and signal-to-noise ratio with its dual imaging mode. The article shows how to make a two-mode angiography system called UCNP-CN@NBs by combining upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) with graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots (CNS) and putting them inside NBs. 808 nm light irradiation of UCNPs can excite and emit visible and ultraviolet (UV) light, transferring the UV light’s energy to CNs to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) for photodynamic treatment. Ultrasound enhances the detonation of NBs and the liberation of reactive oxygen species in photodynamic therapy, thereby leading to the demise of cancer cells (Huang et al., 2020).
4.1.2 Drug delivery across the BBB for brain diseases
Tight connections between endothelial cells in vessel walls form the blood-brain barrier, which prevents potentially dangerous substances from entering the brain. Furthermore, the blood-brain barrier constitutes the principal impediment to medicine delivery for neurological disorders. Reports indicate that the blood-brain barrier can impede the extravasation of approximately 98% of small molecules (under 600 Da) and 100% of macromolecules into the brain (Åslund et al., 2017; Hu et al., 2020). Focused ultrasound (FUS) and microbubble nucleation bubbles (MNBs) show much promise for breaking down the blood-brain barrier (BBB) because it is safe, precise, temporary, and do not involve any invasive procedures (Deprez et al., 2021). Ultrasound can produce cavitation of microbubbles, facilitating the opening of the blood-brain barrier. The inertial cavitation of bubble collapse often leads to microjetting and shock waves, potentially damaging the vascular endothelium. The steady cavitation of bubbles frequently produces mechanical stress, which might compromise tight junctions and enhance blood-brain barrier permeability (Lee et al., 2017). MBs can reduce the energy required by the US to open the BBB by a factor of 100 (Hynynen et al., 2001). Small animals and nonhuman primates have extensively validated the safety of FUS-mediated BBB disruption (Downs et al., 2015a; Downs et al., 2015b). Furthermore, Phase I and II clinical trials have validated the safety of FUS-mediated blood-brain barrier rupture (Dauba et al., 2020).
A combination of FUS and MNBs can independently treat illness. Researchers have reported that FUS, combined with MBs, can trigger neurogenesis (Mooney et al., 2016). Alternatively, reduce the amyloid load in Alzheimer’s disease (Burgess et al., 2014).
Nanobubbles (NBs) have shown considerable promise in improving drug and nutraceutical delivery by breaking down biological barriers that traditionally limit therapeutic access. In comparison, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) has been extensively investigated; other essential physiological barriers present obstacles in drug administration. Recent research reveals that NBs can be tailored to effectively bypass these obstacles, resulting in improved bioavailability and focused therapy by crossing these physiological barriers, as shown in Figure 5.
• Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) – As previously discussed, targeted ultrasound and NB-mediated cavitation can temporarily break the blood-brain barrier (BBB), providing regulated drug administration to the central nervous system while reducing neurotoxicity (Gattegno et al., 2024).
• Lung Barrier (Alveolar-Capillary Barrier) – Several drugs are unable to penetrate deep lung tissues due to the tight connections of alveolar epithelial cells. NB-based aerosols have shown promise for improved pulmonary drug delivery by increasing cellular absorption and extending retention in the lungs. This is especially important for treating respiratory conditions, including pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer (Huang et al., 2024).
• Blood-Eye Barrier (BEB) – The blood-retinal and blood-aqueous barriers prevent drugs from penetrating ocular tissues, making retinal disease therapy difficult. NBs functionalized with mucoadhesive polymers have been studied to improve corneal permeability and hence drug delivery for ocular illnesses like as macular degeneration and glaucoma (Bisen et al., 2024).
• Gastrointestinal (GI) – Enzymatic breakdown and inadequate intestinal absorption frequently reduce the bioavailability of oral drugs and nutraceuticals. NBs encapsulating bioactive chemicals can improve their stability in the digestive tract and enable targeted absorption in the colon, increasing systemic bioavailability (Čolić et al., 2024).
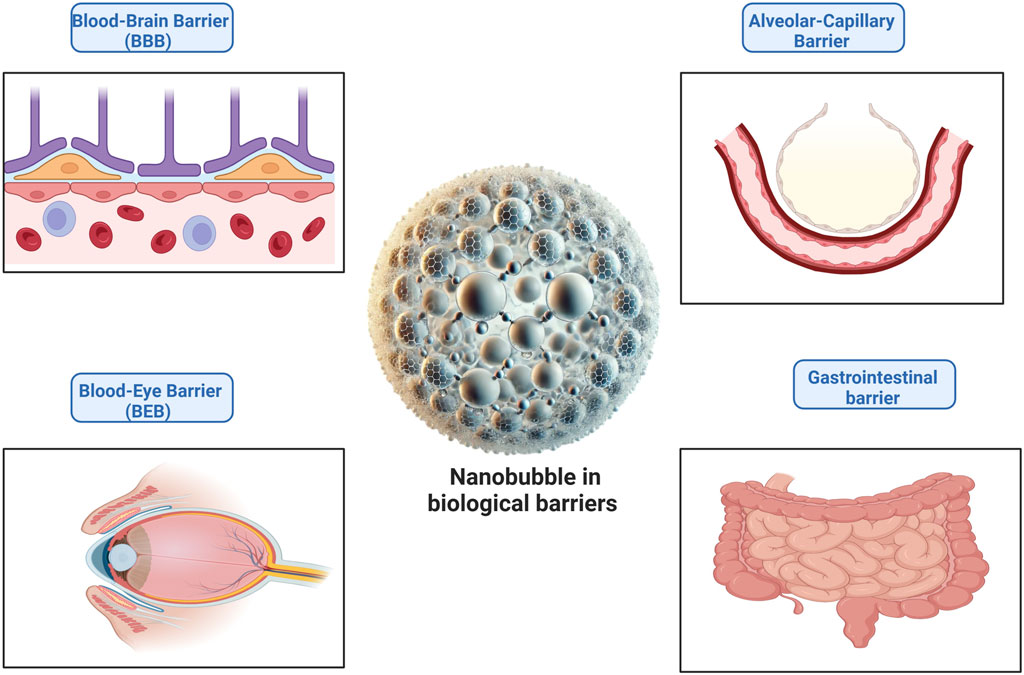
Figure 5. Nanobubbles (NBs) in biological barriers, including the blood-brain barrier (BBB), lung alveolar-capillary barrier, blood-eye barrier (BEB), and gastrointestinal barrier, for targeted drug delivery.
Researchers can broaden the therapeutic and nutraceutical applications of NBs by utilizing their ability to permeate many biological barriers in neurological, respiratory, ophthalmic, and gastrointestinal illnesses. Continued progress in NB surface modifications, stimuli-responsive characteristics, and targeted release mechanisms will be important for increasing their effectiveness in overcoming these hurdles.
The application of NBs in conjunction with FUS for drug delivery systems primarily targets the treatment of cerebral disorders such as glioblastoma (GBM), neurodegenerative illnesses, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease (PD) (Burgess et al., 2014). Yan et al. encapsulated curcumin in lipid-PLGA nanoparticles (Cur-NBs), demonstrating significant potential for treating Parkinson’s disease. The researchers used Cur-NBs in combination with low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) to treat PD mice. The results showed that 400-nm Cur-NBs can cross the blood-brain barrier to deliver curcumin to deep brain nuclei when exposed to low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) radiation. Within 6 h, they achieved a cumulative release rate of 30% for curcumin, which markedly improved effectiveness in the Parkinson C57BL/6J mouse model (Yan et al., 2021).
Chan et al. developed an NB-based DDS, encapsulating FePt nanoparticles within the hydrophobic core alongside doxorubicin. The nanoparticles’ surface was functionalized with the targeted ligand transferrin (Dox-FePt@NB-Tf) to facilitate targeted drug delivery, as shown in Figure 6. A magnetic field was employed in the NBs-based device to actively target Tf to the tumor site. Additionally, T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) enabled real-time monitoring of the targeted NBs. To enhance drug penetration across the blood-brain barrier (BBB), high-intensity focused ultrasound oscillation (FUS) was applied to induce NB oscillation and cavitation. This transient disruption of the BBB facilitated the efficient transport of doxorubicin to the brain tumor. The Dox-FePt@NB-Tf system represents a significant advancement in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) treatment by improving drug delivery and enabling real-time tumor imaging (Chan et al., 2021).
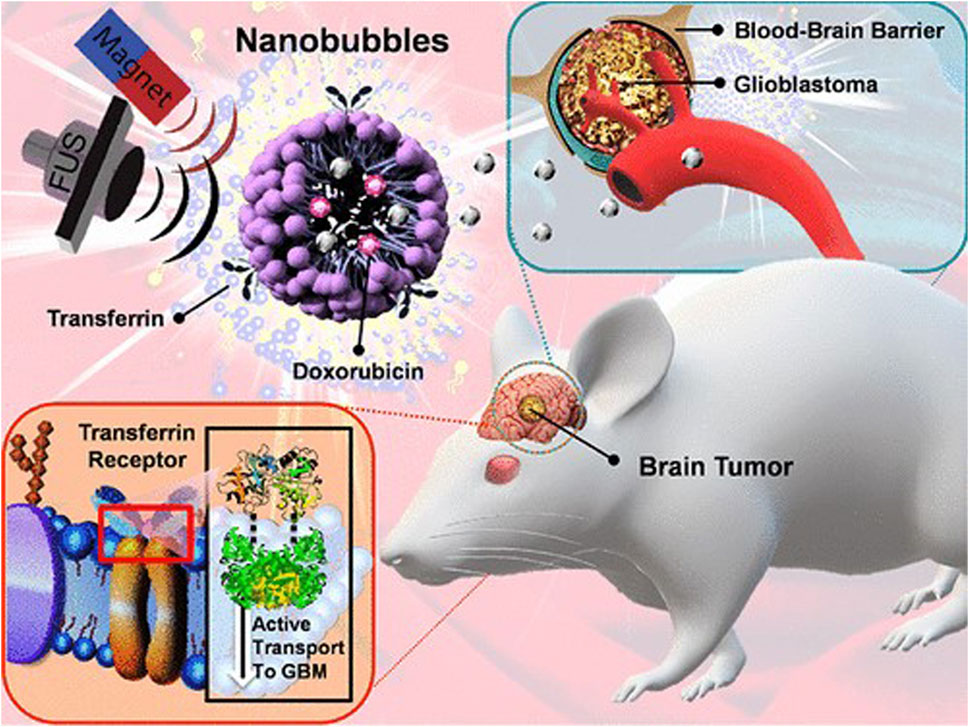
Figure 6. Schematic representation of a nanobubble-based targeted drug delivery system for glioblastoma treatment. The system utilizes FePt nanoparticles and doxorubicin, functionalized with transferrin for tumor targeting. Reprinted with permission from Chan et al. (2021). Copyright (2025) American Chemical Society.
Most drug delivery techniques employing nanobubbles’ cavitation in the brain require the rupture of the NBs to release the therapeutic chemicals. While NBs and focused ultrasound have confirmed the safety of disrupting the blood-brain barrier without causing acute or chronic inflammation, a thorough investigation into the potential risks of brain damage, including hemorrhage, is necessary. Only a few studies have included evaluations of cavitation thresholds or stability performance in the design of BBB apertures (Choi et al., 2009).
Furthermore, various studies have progressed worldwide to develop a clinical approach for penetrating the blood-brain barrier. Researchers have clinically examined magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound and microbubbles to treat glioblastoma and other ailments (Gasca-Salas et al., 2021; Lipsman et al., 2018). Without surgical intervention, placing an ultrasound device on the head and using its low frequency to penetrate the skull transcranially. Conversely, researchers have developed non-focused ultrasound to manage glioblastoma (Carpentier et al., 2016). Here, the surgical position is the transducer beneath the cranial vault. Consequently, it demonstrates invasiveness; however, it is not necessary for application in every therapy and can be executed in simple ways. A specialist ultrasonic device is developed to detect inertial cavitation and adjust acoustic power to prevent it, ensuring safe therapy (Sun et al., 2017). Researchers have examined the potential of microbubbles to deliver effective and safe treatment. The lipid composition of the shell, the encapsulated gas, and the microbubbles’ particle size may affect the blood-brain barrier’s permeability (Omata et al., 2019; Song et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2015). Therefore, producing optimized microbubbles to enhance blood-brain barrier permeability is essential for developing a therapeutic system for neurological illnesses. Even though some problems need to be considered, the progress made in ultrasonic devices and microbubbles will allow the creation of effective and safe blood-brain barrier systems, which will help treat brain and central nervous system diseases.
4.1.3 Vascular diagnosis and treatment
Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases have become the primary cause of death in human health. The Global Health Metrics published by The Lancet in 1990–2021 projects the burden to 2050, demonstrating that mortality rates from various diseases vary by geography, gender, and age. Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are identified as the most lethal noncommunicable diseases, responsible for nearly 18 million deaths. Numerous studies have examined the utilization of NBs in the early identification and treatment of vascular disorders. Precision medicine is an innovative medical paradigm rooted in personalized medicine that enables the accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment of diseases at the molecular level. Using molecular imaging technologies and drug delivery systems makes it easier to find molecular diseases early, give targeted therapy, track how well it works in real-time, and make accurate predictions about the prognosis (Liu et al., 2016). Since nanoparticles generate backscattered ultrasound, and the acoustic signal correlates positively with bubble concentration, they serve as ultrasound contrast agents for molecular imaging, enabling real-time, noninvasive visualization to monitor therapeutic administration at an early stage. Myocardial infarction (MI) is a significant societal burden characterized by myocardial ischemic necrosis resulting from coronary artery blockage and inadequate blood supply. The primary etiology of myocardial infarction is the thrombotic obstruction of a coronary artery (Frangogiannis, 2011). Since myocardial infarction can cause significant metabolic and ionic disturbances in the impacted myocardium, it is crucial to avert the rapid decline of systolic function. Notwithstanding advancements in myocardial infarction treatment options, myocardial cell dysfunction and fibrous composition formation remain a risk for the development of congestive heart failure. Consequently, enhanced blood perfusion and restoring damaged cardiac cells are crucial for a better prognosis. Micro/nanobubble-assisted ultrasound therapy works by (1) breaking up clots, (Cavalli et al., 2016), changing blood vessels to improve blood flow, and (Jin et al., 2022) healing heart tissue that has been damaged. Micro/nanobubble-assisted ultrasound improves blood flow by making arteries wider and the walls of blood vessels less stiff. This is made easier by the release of endothelial-derived vasodilators by inertial cavitation (Suchkova et al., 2002). Cavitation produces augmented blood flow, which enables the endothelium and erythrocytes to release substantial amounts of adenosine triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate can enhance the endothelial release of prostaglandin and nitric oxide. Adenosine converts nitric oxide and prostaglandins, relaxing smooth muscle cells and reducing inflammation and platelet aggregation (Belcik et al., 2017). Li et al. employed a canine coronary microthrombi model. They found that the combination of ultrasound and microbubble drug delivery significantly enhanced myocardial perfusion, compared to the control group, and significantly improved myocardial function (Li H. et al., 2018). Moreover, studies have documented the potential of using stem cells to rehabilitate impaired cardiomyocytes in managing myocardial infarction. Kokhuis et al. examined a novel approach integrating stem cells with MBs (Kokhuis et al., 2015). Researchers found that the method efficiently restored damaged myocardial tissue and enhanced cardiac function. Cell transplantation has utilized microbubbles with nitric oxide in their center to enhance the homing of stem cells to the infarcted myocardium (Dörner et al., 2013). Tong et al. showed that mesenchymal stem cells could move more easily, and the number of capillaries was much higher in the US + NO MBs group than in the control group. This suggests that cardiac function has significantly improved (Tong et al., 2013). Vascular disease frequently targets molecular targets such as intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), selectins, oxidized lipids, thin fibrous caps, and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) (English, 2022). Nanoparticles attach ligands or antibodies to their surface for specific purposes. The aggregation of NBs at specified locations results in a steady rise in their acoustic signals, facilitating tailored enhancement of ultrasound imaging, which is applicable for image-guided drug delivery and therapy for vascular diseases (Tong et al., 2013). Targeted NBs frequently use the robust interaction between receptors and ligands for molecular imaging. The primary pathogenic characteristic of atherosclerosis is angiogenesis, where endothelial cells overexpress VEGF. Zhang et al. created ligand-conjugated lipid NBs for the molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaque by employing the noncovalent biotin-avidin linker technique to attach anti-VEGFR-2 ligands to the nanobubbles. The targeted NBs demonstrated an average diameter of 320 nm, with a ligand conjugation efficiency of 36.16%. In a rabbit kidney model, findings indicated that the targeted NBs enabled site-specific recognition of atherosclerosis for ultrasound molecular imaging. Bioorthogonal coupling chemistry represents an effective strategy for molecular imaging. Using a two-step pretargeting bioorthogonal chemistry approach, we presented tetrazine-modified microbubbles for acute thrombus ultrasound molecular imaging (Lipsman et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2017). P-selectin is exposed on the platelet surface when platelets activate during thrombus formation. The CD62p antibody targets it. Synthesized and preinjected CD62p antibodies modified with trans-cyclooctene (TCO) bind to thrombi noncovalently. Using click chemistry with s-tetrazine and TCO, CD62p antibody-targeted thrombi could capture Tetra-MBs quickly and specifically. US real-time molecular imaging of thrombi is possible with click chemistry and quick microbubble capture. A bio-orthogonal targeted molecular ultrasound imaging technique can quickly, easily, and effectively identify thrombosis, indicating the promise of nanoparticle-based medication delivery. Targeted nanoparticles for gas, medication, and gene delivery in vascular disease treatment have improved with molecular imaging. Sono thrombolysis is a common vascular disease treatment that uses nanobubble cavitation to destroy fibrin mesh (Wijaya et al., 2020). Ling et al. created cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp-targeted PLGA microbubbles and NBs and evaluated their efficacy in clot disruption when combined with urokinase (Ma et al., 2019). Laboratory researchers found that NBs-cRGD with urokinase dissolved clots better than MBs-cRGD. Fibrin network disruption was greatest with NBs-cRGD. Researchers believe targeted NB cavitation improves thromboembolism penetration and urokinase thrombolysis. Targeted NBs enable safe, efficient, and effective thrombolytic treatments for thromboembolism (Ma et al., 2019). Functional NBs improve ischemic stroke therapy, according to researchers. Encapsulating sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) in platelet membrane vesicles, our lab has created biomimetic NBs for ischemic stroke Theranostics (Suchkova et al., 2002). The platelet-bio-NBs demonstrated precise lesion-targeting capability. The heightened buildup of PNBs in the lesion can facilitate the real-time monitoring of stroke progression by contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging. Additionally, the platelet-bio-NBs could change the microvascular structure of the lesion, which could protect the brain cells near the ischemic area and help treat ischemic stroke. Theranostics approaches to vascular disorders based on biomimetic nanoparticles made from cell membranes are a new idea that could have a lot of clinical uses.
4.1.4 Delivering drugs for neurodegenerative disease therapy
Neurodegenerative diseases are intricate, severe conditions with a significant prevalence. It is imperative to identify novel and effective therapies to inhibit the advancement of these diseases (Gitler et al., 2017). Lewy bodies form within alpha-synuclein-rich neurons in Parkinson’s disease (PD), a prevalent progressive neurodegenerative disorder, due to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain (Lee BE. et al., 2020). The primary treatment method involves increasing the body’s natural supply of dopamine. However, this does not stop neuronal damage that’s already happening and may lead to a recurrence (Pinto et al., 2019). Using micro/NBs along with transcranial low-intensity focused ultrasound can get through the blood-brain barrier. This makes micro/nanobubble-assisted ultrasound a rapidly improving way to treat Parkinson’s disease (Kinfe et al., 2020). Yan et al. investigated a novel platform for the targeted delivery of curcumin into the murine brain as depicted in Figure 7. They employed melt crystallization techniques to improve the solubility of curcumin in water and facilitate the formation of curcumin-loaded lipid-poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles (Cur-NBs) by encapsulating curcumin within the core of lipid-PLGA nanoparticles in a murine model. The findings showed that using low-intensity focused ultrasound along with Cur-NBs could help curcumin get deeper into brain tissue by making it easier for the BBB to open. This significantly increased the treatment’s efficacy over using Cur-NBs alone. The Cur-NBs platform intends to overcome the limitations of the BBB in drug delivery for central nervous system disorders. In addition, employing low-intensity focused ultrasound in conjunction with bubble-gene complexes has been demonstrated to help treat Parkinson’s disease without causing any damage to the cells (Yan et al., 2021).
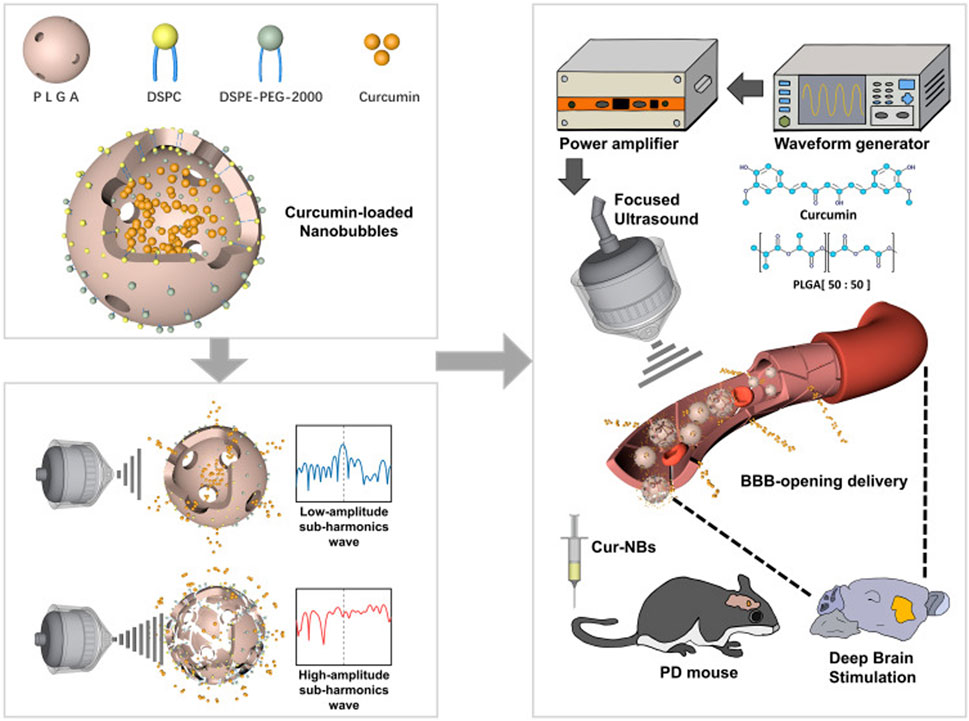
Figure 7. Diagrammatic representation of Cur-NBs and LIFU’s noninvasive localized delivery of curcumin for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Reprinted with permission from Yan et al. (2021). Copyright (2025) Dove Medical Press Limited.
In another study, Fan et al. investigated cationic microbubbles as gene carriers to enhance the stability of the bubble-gene combination (Fan et al., 2016). A transcranial-focused ultrasonic interacted with the bubble-gene complex, facilitating therapeutic gene transitory penetration and promoting localized expression. Besides Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease is another prevalent neurodegenerative condition, marked by impaired neurogenesis in the dorsal hippocampus, accompanied by amyloid accumulation and neurofibrillary tangles (Bloom, 2014). Because the lesion is in deep brain tissue, Researchers anticipate that micro/nanobubble-assisted ultrasonography will mitigate the limitations of inadequate permeability associated with conventional oral medications. Researchers used MBs to transport amyloid beta peptide into cerebral tissue by delivering antibodies and nanostructured polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid (PEG-PLA) (Yao et al., 2014). The irradiation of MBs in the US prompted the polymer nanoparticles to release beta peptides and target biomarkers associated with Alzheimer’s disease. This approach can significantly enhance the therapeutic efficacy of nanomaterials in treating brain disorders.
4.1.5 Anticancer drug delivery
Initially, researchers suggested using a combination of drug-loaded NBs and ultrasound as a therapeutic approach for cancer chemotherapy. Suzuki et al. (2005) described how NBs and ultrasound can make it easier for four cancer cells to pass through and improve the killing power of anticancer drugs (cisplatin and 5-FU). NBs and ultrasonics significantly enhanced the sensitivity of cells to cisplatin and 5-FU. Ultrasonic technology can vaporize perfluorocarbon nanodroplets, transforming them into micron-scale gas bubbles in situ. Following the vaporization of PFC nanodroplets, the micron-scale gas bubbles can engage robustly with ultrasound radiation, enabling their application in cancer imaging and therapy. Gao et al. (2008) developed a polymeric nanobubble system to enhance the doxorubicin sensitivity of cancer cells in conjunction with ultrasound. The developed systems comprise perfluorocarbon nanodroplets stabilized by a biodegradable block copolymer shell (PEG-PLLA or PEG-PCL). Upon exposure to physiological temperatures, the nanodroplets transform into nano/microbubbles. When ultrasound is focused on a tumor, doxorubicin-filled NBspop falls apart; this lets the medicine inside them escape and improves the effectiveness of chemotherapy in living tumors (Gao et al., 2008). Rapoport et al. employed polymeric micelles to encapsulate liquid perfluoropropane (PFP) containing doxorubicin. In this system, elevating the temperature to 37°C resulted in the vaporization of PFP nanodrops into larger bubbles. The authors suggested that ultrasound targeting the tumor could produce larger microbubbles through the coalescence of vaporized nano drops. The authors illustrated the viability of employing polymer-stabilized PFP nanodroplets for the delivery of doxorubicin to xenograft tumors, demonstrating that this approach might inhibit tumor growth (Rapoport et al., 2007). The administration of paclitaxel using perfluoropentane nanodroplets stabilized by amphiphilic block copolymers yielded favorable in vitro and in vivo outcomes. Using 1-MHz ultrasound and paclitaxel-loaded PFP nanoemulsions all over the body significantly decreased tumor size in breast, ovarian, and pancreatic cancer models in mice (Rapoport et al., 2009). Rapoport’s findings indicate that the transition from droplet to bubble and subsequent bubble oscillation facilitates encapsulated medicines’ release and improves intracellular absorption. The proposed process for ultrasound-mediated drug administration utilizing polymer-stabilized perfluorocarbon nanodroplets relies on the transition from droplets to bubbles (Rapoport, 2012). The particle volume significantly rises during the transition from droplet to bubble, reducing droplet shell thickness. The researchers anticipate that this will improve the release of the encapsulated medication, especially when ultrasonic action separates the drug from the droplet surface. The augmentation of surface area reduces copolymer concentration on the surface and may generate ‘bare’ patches that could enhance drug release. Du et al. (2011) conducted a separate investigation that synthesized polymeric micelles from poly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)-methoxy-poly (ethylene glycol) (PLGA-mPEG) to encapsulate doxorubicin. The introduction of perfluoropentane transformed the micelles into nanodroplets, stabilized the PEG shell, and subsequently transformed them into NBs at 37°C. The significant pH dependence of the ultrasound-induced release of doxorubicin (40 kHz, 0.7 W/cm2) from NBs was documented. Doxorubicin-encapsulated nanodroplets showed better anticancer activity and lower toxicity in a murine tumor model. This is because they were better at targeting the tumor and less likely to leak into healthy tissues. Deng et al. recently created NBs by putting doxorubicin hydrochloride inside poly (lactic-co-glycollic acid) (PLGA) shells so that cancer cells can get the medicine they need. HeLa cells internalized doxorubicin-loaded NBs in a concentration- and time-dependent manner, demonstrating a superior inhibitory effect on cell growth in vitro compared to free doxorubicin.
Wu et al. reviewed the progress of nanobubble technology in tumor diagnosis and treatment, highlighting their role as contrast agents for tumor visualization and their potential in drug delivery due to high solubility, stability, and drug loading capacity. The study discusses oxygen NBs for targeted reoxygenation and chemotherapeutic enhancement and vapor NBs for drug release through external stimuli. It explores the use of NBs in combination therapy for tumors (Wu et al., 2021) Figure 8.
Zhang et al. utilized poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) NBs as a targeted medication carrier, an effective ultrasound contrast agent, and a synergistic agent for high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation of choriocarcinoma. The researchers synthesized and infused methotrexate (MTX)-loaded NBs with perfluorocarbon gas using a double emulsion evaporation technique. Investigators subsequently attached the active tumor-targeting monoclonal anti-HLAG antibodies (mAbHLA-G) to the surface of the nanobubbles. The mAbHLA-G/MTX/PLGA NBs showed targeted effectiveness against tumor tissues both in vitro and in vivo, which led to better ultrasound imaging of tumors. Later tests showed that the targeted NBs work with focused ultrasound to make HIFU ablation more effective by changing the acoustic environment. This is made possible by the focused ultrasound, which also helps the controlled release of MTX that is part of the system (Zhang et al., 2014). Engineered novel multifunctional nanodroplets of perfluoropentane stabilized by an amphiphilic block copolymer (polyethylene glycol block-polycaprolactone) for ultrasound-mediated delivery of curcumin.
Nanodroplets effectively held the encapsulated curcumin in vivo and released the medication under ADV, facilitating precise targeting for the tumor. Following the injection of curcumin-loaded nanodroplets in conjunction with ultrasound, researchers noted a significant decrease in tumor growth in S180 tumor-bearing mice (Ji et al., 2014). Also, Lin et al. (2016) created a novel drug-targeting method utilizing a combination of ultrasound-sensitive NBs and cell-permeable peptides (CPPs). The asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) peptide-modified NBs (CPP-DOX/NGRNB) encapsulated the CPP-doxorubicin conjugate (CPPDOX), integrating the specific targeting efficacy of NGR, the cell-penetrating capabilities of CPPs, and the ultrasound-triggered drug release properties of nanobubbles. Local ultrasonic stimulation may induce CPPDOX release from NB and enhance its penetration. This approach exhibited significant tumor inhibitory effects, both in vitro and in vivo, with improved efficacy due to ultrasound stimulation.
Xie et al. encapsulated CPPs in NBs as CPP-CPT conjugates to facilitate intracellular administration of CPT to tumor locations and improve delivery efficiency. The investigator employed an ultrasonography of the local tumor to facilitate the targeted delivery of CPP-CPT to the tumor cells. CPP-CPTNB demonstrated efficient cellular absorption and notable cytotoxic efficacy in HeLa cells in vitro. Furthermore, following systemic dosing in mice, CPP-CPTNB combined with ultrasound demonstrated a superior tumor reduction effect in nude mice with xenografted HeLa cell tumors and outstanding safety profiles compared to the standard CPT injection group (Xie et al., 2016). Recently, researchers have suggested Extracorporeal Shock Waves (ESWs), acoustic waves commonly used in lithotripsy without adverse consequences, as a novel method to enhance medication release from anticancer drug-loaded nanobubbles. ESWs precisely focus on varying depths and generate cavitation without thermal effects, leading to the permeabilization of plasma membranes. These attributes render ESWs a superior alternative to ultrasounds in medication delivery strategies. Researchers developed novel glycol chitosan nanoparticles infused with perfluoropentane to administer doxorubicin. The synergy between doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles and electroswelling specifically targets doxorubicin and enhances its anticancer efficacy in anaplastic thyroid cancer cell lines. The combined use of doxorubicin-loaded nanoparticles and electro-switched waves showed higher cytotoxicity than free doxorubicin, leading to a 40% drop in the drug’s GI50. ESWs increased the uptake of drug-loaded NBs inside cells and raised the amount of doxorubicin in the nucleus (Rychak and Klibanov). In conclusion, NBs may provide many advantages for anticancer medication delivery, enhancing the uptake of chemotherapeutic agents by cancer cell lines. This technique can effectively target anticancer drug delivery due to low exposure of healthy tissues, which are not the targets, thus diminishing the adverse systemic effects and decreasing the therapeutic doses.
4.2 Applications of NBs in nutraceutical delivery
Nutraceuticals usually experience poor bioavailability issues caused mainly by the low solubility of the compound, its instability in the gastrointestinal tract, and its weak absorption. NBs can solve such problems by increasing stability and enabling the proper delivery of substances to the intestinal cells. Thus, they can enhance the bioavailability of essential nutrients, e.g., vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Nanobubble systems have been used to encapsulate hydrophobic nutrients, thereby allowing their dissolution in aqueous environments and thus increasing the transportation through biological barriers (Yao et al., 2015). The nanobubbles, produced from biopolymers like chitosan, have mucoadhesive properties, allowing the retention of the compound for a longer time in the gastrointestinal tract and improving absorption (Hu and Huang, 2013). Numerous case studies have confirmed the effectiveness of the nanobubble methodology for antioxidants and vitamins. According to the nanobubble approach, the vitamin B12 and folic acid are trapped within the NBs and processed quickly by the stable gastrointestinal wall; hence, the absorption is thereby increased, and thus, health benefits are brought to governance (Ar et al., 2021).
Table 3 provides an overview of different nutraceuticals that increase stability and absorption. Besides these, NB technology allows nutraceuticals to be more stable and long-lasting by protecting the highly sensitive chemical compounds from such atmospheric parameters as light, oxygen, and temperature. A new approach to nutritive product citation uses an encapsulation process of nanobubbles; hence, it is possible to prevent oxidative degradation, which is the most typical problem of some bioactive compounds, including polyphenols and omega-3 fatty acids. NBs with an outer shell are involved and act as a barrier in enclosing the protected material within the shell, thereby increasing the product’s longevity. One of the methods used to maintain the stability of the bubbles, such as lipid jackets that are resistant to environmental factors and, hence, hold for a long duration, is the lipid encapsulation technique (Pasupathy et al., 2022). Besides, incorporating NBs with ultrasound-motivated discharge mechanisms has led to the precise dispersion of nutraceuticals, thus maintaining the stability of the active ingredients within the bubble until they are transported to the specified place. Therefore, this site-specific release of nutrients before absorption extends the product’s lifespan and potency (Cavalli et al., 2016).
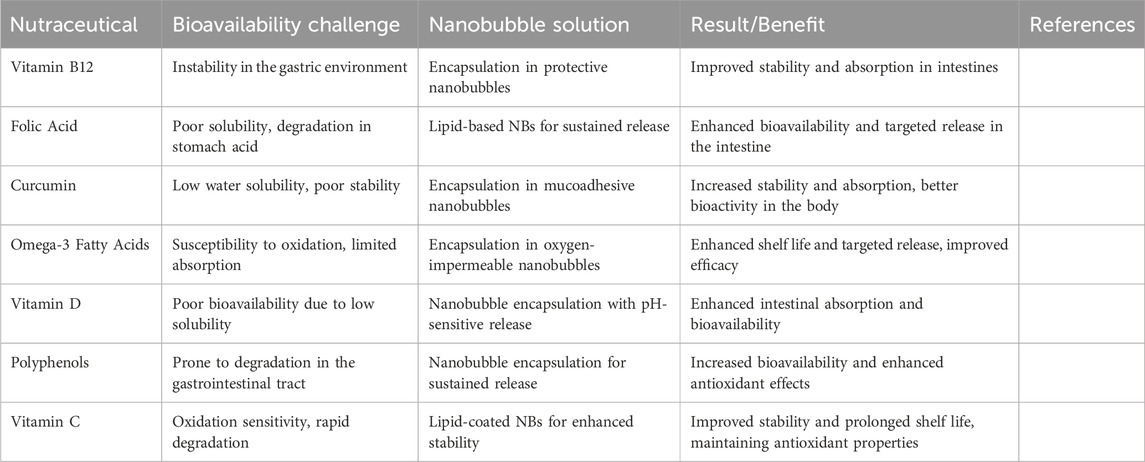
Table 3. It discusses the different nutraceuticals, their encapsulation challenges, and the beneficial effects that can be obtained via nanobubble-based delivery systems.
In their research, Tarhan and Spotti (2021) investigated nanoemulsions, which are vehicles for the delivery of nutraceuticals, and discovered that they use comparable electrostatic and repulsive forces to encapsulate hydrophobics substances such as cell membranes and nanoshells, making them very stable. The authors thus concluded that besides enhancing bioavailability, nanoemulsions could also potentially improve nutraceutical foods’ therapeutic performance (Tarhan and Spotti, 2021). Moreover, Singh et al. emphasize using nanotechnology-based methods to deliver nutraceuticals to ensure bioavailability. Central to their investigation was how nanobubbles, an essential part of this technology, increase the stability and ability to prolong the shelf life of food products (Singh et al., 2021). On the contrary, Favvas et al. concentrated on the production and stability of NBs in large quantities. Their work was mainly on how they can be used to increase nutritional efficiency. The findings suggested that bulk NBs can substantially increase the stabilization and transmission of nutrients in any of the two applications, namely, food and agri-products (Favvas et al., 2021). Zimmerman et al. found that the developments in energy-efficient nanobubble-generating techniques could open their usage in the food and nutraceutical industries. It was suggested that energy-efficient production, which reduces electricity consumption, could be a more cost-effective way for nanobubble synthesis, which in turn might benefit the production of food products with firmly inserted bioactive elements (Zimmerman et al., 2011).
5 Safety, regulatory, and ethical considerations
Nanobubble technology offers great promise in drug and nutraceutical delivery, but the potential risks associated with toxicity, long-term bioaccumulation, and regulatory approvals require careful evaluation. While many studies have demonstrated the biocompatibility of NBs, their effects at high concentrations or with repeated exposure remain a concern.
5.1 Toxicity concerns and long-term bioaccumulation
Research indicates that certain types of nanoparticles, such as cationic NBs, may exhibit cytotoxic effects if used in high doses, particularly in liver and kidney cells, due to oxidative stress, membrane damage, and inflammatory response. Long-term exposure to NBs with synthetic shells, particularly those encapsulating persistent gases like perfluoropentane in their cores, has raised concerns regarding potential bioaccumulation and systemic toxicity. Some studies suggest that persistent nanomaterials could accumulate in tissues, leading to chronic inflammation or immune system activation (Pan et al., 2012). Recent in vivo research shows that polymer-based NBs exhibit lower toxicity than non-degradable equivalents, especially those with biodegradable coatings (such as PEG or PLGA). However, buildup has been seen in animal models in the brain, liver, and spleen, which calls for more in-depth research on clearance mechanisms. The excretion pathways of NBs remain under investigation, with preliminary findings suggesting elimination through renal and hepatic routes. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that gas-core NBs (such as NBs filled with oxygen and nitric oxide) change cellular oxygenation and metabolism, which may have unforeseen physiological consequences if improperly managed. These hazards emphasize how crucial it is to do thorough preclinical safety evaluations prior to clinical implementation.
Immune responses are critical in the clinical translation of NB-based drug delivery systems. While PEGylation and polymer coatings help reduce immune recognition, some studies have reported activation of the complement system and innate immune response upon repeated NB exposure. This may result in accelerated blood clearance (ABC phenomenon) and reduced therapeutic efficacy. Advanced surface modifications, including zwitterionic polymers and bioinspired coatings, are being investigated to improve stealth properties and minimize immune recognition. Evaluating immunotoxicity and cytokine profiling in preclinical studies ensures safety in future clinical applications (Argenziano et al., 2025; Chen et al., in press; Argenziano et al., 2022).
5.2 FDA and EMA regulatory perspectives
Regulatory approval of NB-based therapeutics and nutraceuticals faces challenges due to limited historical data and evolving guidelines for nanotechnology-based formulations. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies NBs under nanomedicine regulations, requiring extensive pharmacokinetic, biodistribution, and toxicity profiling before clinical approval. The FDA evaluates nanomaterials on a case-by-case basis, meaning that each NB formulation must undergo rigorous scrutiny for safety and efficacy before approval.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) follows a similar approach, focusing on nanocarriers’ Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) profile. Recent EMA guidelines emphasize the need for precise characterization of NB formulations, including stability, degradation pathways, and potential immunogenic responses. Given concerns over nanomaterials accumulating in ecosystems, EMA regulations also require long-term environmental impact assessments.
The FDA and the EMA are increasing their focus on the potential risks of NBs crossing biological barriers, such as the BBB, and their interactions with immune cells. Regulatory bodies recommend standardized safety protocols before granting clinical trial approvals, including in vitro and in vivo models that mimic human exposure scenarios.
5.3 Ethical and transparency consideration
Beyond regulatory concerns, public perception and ethical transparency play a crucial role in accepting NB-based products. Many consumers remain skeptical of nanotechnology in pharmaceuticals and food products, emphasizing the need for clear labeling and risk disclosure. Ethical guidelines recommend detailed public communication regarding NB technology’s safety, benefits, and limitations to foster informed decision-making.
Additionally, the impact of NBs on the environment must be considered, particularly for industrial-scale production and wastewater contamination risks. The potential release of engineered nanomaterials into ecosystems requires further investigation to ensure biodegradability and minimize unintended ecological effects.
6 Challenges, limitations and sustainability considerations
Despite their promising applications, NB formulations face several key challenges linked with biodegradability, scalability, clinical translation, and sustainability. Although significant progress has been made, addressing these limitations is crucial for their widespread adoption in medicine, nutraceuticals, and environmental applications.
6.1 Biodegradable and long-term stability
A significant issue for NB-based DDs is biodegradability and clearance from the body. Synthetic polymer-based NB, such as perfluorocarbon-based shells, are likely to accumulate to an unacceptable level in biological tissues, and long-term accumulation is a concern. There are reports that the nonbiodegradable carrier that is used in this study could be the cause of systemic toxicity and chronic inflammation in the long term.
To reduce these risks, biodegradable polymeric NBs, containing, for instance, poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and chitosan, have been formulated to improve both safety and biosorption. These materials are degraded to non-toxic metabolites expelled by natural metabolic routes. However, their degradation rate must be precisely controlled to maintain stability in circulation while providing controllable drug release. Emerging strategies to improve NB biodegradability include:
• Beyond such lipids and polymers, hybrid NB systems with adsorbed lipid and polymer coatings increase depolymerization (breakdown) without losing structural integrity.
• Stimuli-responsive NBs are degraded depending on local pH, temperature, or enzymatic activity at their indicated location.
• The creation of bio-inspired NBs with naturally occurring lipids and proteins minimizes the potential for immune activation and long-term deposition.
Besides, recent studies suggest that combining nanoparticles and targeted ultrasound can transiently alter the BBB, allowing medication to be delivered to the brain while reducing overall exposure. However, BBB disruption must be carefully controlled, as severe or sustained permeability can cause neuroinflammation, edema, and irreparable pathological damage. Low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) and nanobubble-assisted cavitation have been the focus of research to address these safety issues since they enable site-specific, reversible BBB opening with minimal tissue damage. To guarantee that BBB permeability is transient and minimize neurotoxicity concerns, ultrasonic parameters including frequency, intensity, and pulse duration must be optimized (Perolina et al., 2024). Furthermore, using biodegradable nanobubbles with controlled drug release mechanisms improves safety by limiting exposure time and avoiding unwanted effects on adjacent tissues (Pasupathy et al., 2022). Recent preclinical investigations show that BBB control with ultrasound and nanobubbles is only transitory, with permeability often returning within a few hrs. This controlled method not only lowers the potential of long-term injury but also improves drug penetration into the central nervous system (CNS). Continued research is required to improve safety measures and discover the best circumstances for clinical applications of this developing technology (Burgess and Hynynen, 2014).
Although these approaches have potential, additional investigations are warranted to guarantee complete detoxification without leftover toxicity.
6.2 Scalability and manufacturing challenges
Another complex challenge in translating the NB to commercial applications is scalability. Traditional NB production methods, like probe sonication, microfluidics, and gas dissolving, often lead to inconsistent results or poor output. Many methods that can be used on a larger scale are being studied to solve this. These include using high-pressure homogenization to make many nanoparticles with controlled sizes and electrostatic self-assembly to make the particles precisely and repeatedly. In addition, microfluidic systems that run continuously help keep the nanoparticles stable and improve how well they hold other substances, all while keeping costs down. Keeping the nanoparticles stable while they are stored and moved is also essential. Many mixtures need special handling (for example, keeping them cold or protecting them from force), which can reduce how long they last. Drying them by freezing them is a helpful way to keep them stable for a long time and quickly make them ready for use.
6.3 Sustainability and environmental impact
The sustainability of NB technology relies on environmentally friendly production techniques, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and reduced environmental toxicity. Although NBs have potential in biomedical, culinary, and water treatment applications, their extensive utilization prompts worry over sustainability and ecological consequences. The challenges are high cost due to existing NB synthesis techniques, like sonication and cavitation. Hence, researchers are exploring low-energy microfluidic approaches and renewable energy-powered NB production to reduce their carbon footprint. Many NB designs use artificial plastics that do not break down naturally. Changing to materials from plants, such as alginate or cellulose, may boost lasting use while keeping them strong and good at carrying drugs. Waste management and bioaccumulation are other challenges for these NBs. Hence, Persistent nanomaterials can accumulate in wastewater, soil, and marine ecosystems. Studies focus on biodegradable coatings that degrade naturally after serving their medicinal purpose, lowering long-term pollution issues. Therefore, there is a need for emerging sustainable solutions, such as green synthesis techniques, such as enzymatic self-assembly and bio-fabrication, which minimize chemical waste. Natural or bio-renewable materials, including lipid-based NBs and protein-stabilized nanocarriers, are now in practice to reduce toxicity and enhance biodegradability. Another solution is the studies, including Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), to evaluate the NB formulations carbon footprint and environmental impact. While retaining efficacy in medicine and nutraceutical delivery, NB technology can reduce its environmental impact by incorporating sustainable materials and energy-efficient production methods.
6.4 Clinical translation and regulatory challenges
Apart from encouraging preclinical investigations, regulatory obstacles and safety concerns have restricted the clinical translation of NBs. The intricacy of NB behavior in vivo and the absence of consistent safety evaluations are why so few NB-based treatments have progressed to human trials. Assuring uniform drug loading and regulated release across various NB formulations is one of the main problems in clinical translation, as is the variability in NB interactions with biological systems, such as immune detection and clearance. Additionally, there are obstacles to regulatory approval because NBs must satisfy strict safety and effectiveness standards set by organizations like the FDA and EMA.
Researchers are investigating various strategies to aid clinical translation, including personalized medicine techniques, in which NBs are delivered utilizing biomarker-guided delivery and customized for patient profiles. Cutting-edge imaging methods, such as following NBs in real-time with MRI and ultrasound, are used to watch their behavior in vivo. Working with regulatory bodies to create precise standards for toxicity testing, clinical assessment, and NB characterization. Although NBs have enormous potential for nutraceutical applications, cancer treatment, and targeted drug administration, their effective incorporation into mainstream healthcare depends on resolving issues with biodegradability, scalability, sustainability, and clinical efficacy.
7 Future trends and concluding remarks
NBs offer a revolutionary approach to drug and nutraceutical delivery, addressing key limitations of traditional methods through enhanced stability, targeted release, and stimuli-responsive properties. This review highlights the versatility of NBs across diverse applications, from cancer therapy and cardiovascular treatments to enhancing nutraceutical bioavailability. Despite the promising advancements, challenges remain, particularly in optimizing NB formulations for specific applications, ensuring reproducibility in large-scale manufacturing, and addressing long-term safety concerns. Future research should focus on refining synthesis techniques, improving NB circulation time, and minimizing potential toxicity, particularly in clinical applications. Standardizing characterization techniques and scaling up production while maintaining reproducibility and regulatory compliance will be critical next steps. Continued research and development, along with robust regulatory frameworks, are crucial to realizing the full potential of NBs in advancing human health. Future studies should focus on refining NB production techniques and exploring their impacts on various biological systems, paving the way for safer, more effective delivery systems in clinical and nutritional fields.
Developing biodegradable, biocompatible, and hybrid NB is a critical aspect of developing NB technology. By combining NBs with advanced surface modifications, such as polymeric stabilizers or ligand-functionalized coatings, their targeting effectiveness may be improved, and unwanted systemic interactions may be decreased. Moreover, improving drug-loading capacity, guaranteeing long-term stability, and boosting repeatability in large-scale manufacturing are critical to NB-based therapies’ clinical translation.
Using targeting ligands and stimuli-responsive techniques to facilitate site-specific drug delivery and precision medicine is another exciting avenue. This strategy would improve the targeting of damaged tissues, such as inflammatory or malignant cells, lowering systemic toxicity and enhancing therapeutic results. Moreover, the investigation into hybrid systems combining NBs with other nanomaterials, such as liposomes or nanoparticles, could have positive implications for diagnostic imaging and drug delivery. Combining NBs with AI-driven drug delivery platforms may further refine treatment personalization, optimizing dosage and timing based on real-time patient data.
Furthermore, the delivery of nutraceuticals by NBs is rapidly evolving. Emerging trends in functional foods and personalized nutrition highlight the need for NB-based carriers to enhance bioactive compounds’ stability and absorption, particularly for conditions requiring precise dietary interventions. For instance, future research should cover how these systems could be enhanced to improve the bioavailability of bioactive chemicals in specific cases where the traditional mode of delivery is ineffective. Finally, strict safety and regulatory requirements must be laid down to enable the NBs to find widespread application in clinics and nutrition. The field will further evolve by integrating multi-disciplinary aspects related to pharmacology, material sciences, and nanotechnology to fully explore the therapeutic aspects of NBs.
Author contributions
FA: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. SN: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Visualization. AA: Writing – review and editing. OM: Writing – review and editing. SQ: Writing – review and editing. DA: Writing – review and editing. ZA: Writing – review and editing. ET: Writing – review and editing. JV: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. DK: Writing – review and editing. AAE-M: Writing – review and editing. MA: Writing – review and editing. TA: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We are highly thankful to Hassan Mahmood (MS English literature and linguistics) for critically reviewing the text of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Correction note
A correction has been made to this article. Details can be found at: 10.3389/fnano.2025.1655276.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors appreciate the use of technical support (AI-assisted technologies/BioRender for images).
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, H., Liu, G., and Craig, V. S. (2015). Wetting of nanophases: nanobubbles, nanodroplets and micropancakes on hydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 222, 9–17. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2014.07.008
Argenziano, M., Occhipinti, S., Scomparin, A., Angelini, C., Novelli, F., Soster, M., et al. (2022). Exploring chitosan-shelled nanobubbles to improve HER2+ immunotherapy via dendritic cell targeting. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 12 (8), 2007–2018. doi:10.1007/s13346-022-01185-8
Argenziano, M., Spagnolo, R., and Cavalli, R. (2025). What are the future applications of chitosan nanobubbles in drug delivery? Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 22 (3), 307–309. doi:10.1080/17425247.2025.2462761
Arshad, R., Gulshad, L., Haq, I.-U., Farooq, M. A., Al-Farga, A., Siddique, R., et al. (2021). Nanotechnology: a novel tool to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients. Food Sci. Nutr. 9, 3354–3361. doi:10.1002/fsn3.2311
Åslund, A. K., Snipstad, S., Healey, A., Kvåle, S., Torp, S. H., Sontum, P. C., et al. (2017). Efficient enhancement of blood-brain barrier permeability using Acoustic Cluster Therapy (ACT). Theranostics 7 (1), 23–30. doi:10.7150/thno.16577
Bai, M., Liu, Z., Zhan, L., Yuan, M., and Yu, H. (2023). Effect of pore size distribution and colloidal fines of porous media on the transport behavior of micro-nano-bubbles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 660, 130851. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130851
Batchelor, D. V., Abou-Saleh, R. H., Coletta, P. L., McLaughlan, J. R., Peyman, S. A., and Evans, S. D. (2020). Nested nanobubbles for ultrasound-triggered drug release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12 (26), 29085–29093. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c07022
Batchelor, D. V., Armistead, F. J., Ingram, N., Peyman, S. A., McLaughlan, J. R., Coletta, P. L., et al. (2022). The influence of nanobubble size and stability on ultrasound enhanced drug delivery. Langmuir 38 (45), 13943–13954. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c02303
Belcik, J. T., Davidson, B. P., Xie, A., Wu, M. D., Yadava, M., Qi, Y., et al. (2017). Augmentation of muscle blood flow by ultrasound cavitation is mediated by ATP and purinergic signaling. Circulation 135 (13), 1240–1252. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.116.024826
Bisen, A. C., Biswas, A., Dubey, A., Sanap, S. N., Agrawal, S., Yadav, K. S., et al. (2024). A review on polymers in ocular drug delivery systems. MedComm–Biomaterials Appl. 3 (2), e77. doi:10.1002/mba2.77
Bloom, G. S. (2014). Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA neurol. 71 (4), 505–508. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847
Browning, R. J., and Stride, E. P. J. (2018). Microbubble-mediated delivery for cancer therapy. Fluids 3, 74. doi:10.3390/fluids3040074
Bunkin, N. F., Shkirin, A. V., Penkov, N. V., Goltayev, M. V., Ignatiev, P. S., Gudkov, S. V., et al. (2021). Effect of gas type and its pressure on nanobubble generation. Front. Chem. 9, 630074. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.630074
Burgess, A., Dubey, S., Yeung, S., Hough, O., Eterman, N., Aubert, I., et al. (2014). Alzheimer disease in a mouse model: MR imaging–guided focused ultrasound targeted to the hippocampus opens the blood-brain barrier and improves pathologic abnormalities and behavior. Radiology 273 (3), 736–745. doi:10.1148/radiol.14140245
Burgess, A., and Hynynen, K. (2014). Drug delivery across the blood–brain barrier using focused ultrasound. Expert Opin. drug Deliv. 11 (5), 711–721. doi:10.1517/17425247.2014.897693
Cao, Y., Chen, Y., Yu, T., Guo, Y., Liu, F., Yao, Y., et al. (2018). Drug release from phase-changeable nanodroplets triggered by low-intensity focused ultrasound. Theranostics 8, 1327–1339. doi:10.7150/thno.21492
Carpentier, A., Canney, M., Vignot, A., Reina, V., Beccaria, K., Horodyckid, C., et al. (2016). Clinical trial of blood-brain barrier disruption by pulsed ultrasound. Sci. Transl. Med. 8 (343), 343re2–re2. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf6086
Cavalli, R., Soster, M., and Argenziano, M. (2016). Nanobubbles: a promising efficient tool for therapeutic delivery. Ther. Deliv. 7 (2), 117–138. doi:10.4155/tde.15.92
Chan, M.-H., Chen, W., Li, C.-H., Fang, C.-Y., Chang, Y.-C., Wei, D.-H., et al. (2021). An advanced in situ magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonic theranostics nanocomposite platform: crossing the blood–brain barrier and improving the suppression of glioblastoma using iron-platinum nanoparticles in nanobubbles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (23), 26759–26769. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c04990
Chan, M.-H., Pan, Y.-T., Chan, Y.-C., Hsiao, M., Chen, C.-H., Sun, L., et al. (2018). Nanobubble-embedded inorganic 808 nm excited upconversion nanocomposites for tumor multiple imaging and treatment. Chem. Sci. 9 (12), 3141–3151. doi:10.1039/c8sc00108a
Che, Z., and Theodorakis, P. E. (2017). Formation, dissolution and properties of surface nanobubbles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 487, 123–129. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.027
Chen, X., Xu, L., Chen, C., Huang, Q., and Hu, J. (in press). Recent advances in ultrasound-targeted nanobubbles combined with cancer immunotherapy: mechanisms, applications, and challenges. Fundam. Res. doi:10.1016/j.fmre.2024.10.017
Chen, Y., Luo, X., Liu, Y., Zou, Y., Yang, S., Liu, C., et al. (2022). Targeted nanobubbles of PD-L1 mAb combined with doxorubicin as a synergistic tumor repressor in hepatocarcinoma. Int. J. Nanomedicine 17, 3989–4008. doi:10.2147/ijn.s376172
Choi, J. J., Feshitan, J. A., Baseri, B., Wang, S., Tung, Y.-S., Borden, M. A., et al. (2009). Microbubble-size dependence of focused ultrasound-induced blood–brain barrier opening in mice in vivo. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57 (1), 145–154. doi:10.1109/tbme.2009.2034533
Čolić, M., Kraljević Pavelić, S., Peršurić, Ž., Agaj, A., Bulog, A., and Pavelić, K. (2024). Enhancing the bioavailability and activity of natural antioxidants with nanobubbles and nanoparticles. Redox Rep. 29 (1), 2333619. doi:10.1080/13510002.2024.2333619
Dasgupta, A., Sun, T., Palomba, R., Rama, E., Zhang, Y., Power, C., et al. (2023). Nonspherical ultrasound microbubbles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120 (13), e2218847120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2218847120
Dauba, A., Delalande, A., Kamimura, H. A., Conti, A., Larrat, B., Tsapis, N., et al. (2020). Recent advances on ultrasound contrast agents for blood-brain barrier opening with focused ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 12 (11), 1125. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12111125
De Cock, I., Zagato, E., Braeckmans, K., Luan, Y., de Jong, N., De Smedt, S. C., et al. (2015). Ultrasound and microbubble mediated drug delivery: acoustic pressure as determinant for uptake via membrane pores or endocytosis. J. Control. Release 197, 20–28. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.10.031
Deprez, J., Lajoinie, G., Engelen, Y., De Smedt, S., and Lentacker, I. (2021). Opening doors with ultrasound and microbubbles: beating biological barriers to promote drug delivery. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 172, 9–36. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2021.02.015
Dörner, J., Struck, R., Zimmer, S., Peigney, C., Duerr, G. D., Dewald, O., et al. (2013). Ultrasound-mediated stimulation of microbubbles after acute myocardial infarction and reperfusion ameliorates left-ventricular remodelling in mice via improvement of borderzone vascularization. PLoS One 8 (2), e56841. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0056841
Downs, M. E., Buch, A., Karakatsani, M. E., Konofagou, E. E., and Ferrera, V. P. (2015a). Blood-brain barrier opening in behaving non-human primates via focused ultrasound with systemically administered microbubbles. Sci. Rep. 5 (1), 15076. doi:10.1038/srep15076
Downs, M. E., Buch, A., Sierra, C., Karakatsani, M. E., Chen, S., Konofagou, E. E., et al. (2015b). Long-term safety of repeated blood-brain barrier opening via focused ultrasound with microbubbles in non-human primates performing a cognitive task. PLoS One 10 (5), e0125911. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0125911
Du, L., Jin, Y., Zhou, W., and Zhao, J. (2011). Ultrasound-triggered drug release and enhanced anticancer effect of doxorubicin-loaded poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide)-methoxy-poly (ethylene glycol) nanodroplets. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 37 (8), 1252–1258. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2011.05.012
English, N. J. (2022). Environmental exploration of ultra-dense nanobubbles: rethinking sustainability. Environments 9 (3), 33. doi:10.3390/environments9030033
Fan, C.-H., Ting, C.-Y., Lin, C. Y., Chan, H.-L., Chang, Y.-C., Chen, Y.-Y., et al. (2016). Noninvasive, targeted and non-viral ultrasound-mediated GDNF-plasmid delivery for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 6 (1), 19579. doi:10.1038/srep19579
Fan, P., Yang, D., Wu, J., Yang, Y., Guo, X., Tu, J., et al. (2019). Cell-cycle-dependences of membrane permeability and viability observed for HeLa cells undergoing multi-bubble-cell interactions. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 53, 178–186. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.01.005
Favvas, E. P., Kyzas, G. Z., Efthimiadou, E. K., and Mitropoulos, A. C. (2021). Bulk nanobubbles, generation methods and potential applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 54, 101455. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2021.101455
Fraire, J. C., Houthaeve, G., Liu, J., Raes, L., Vermeulen, L. M. P., Stremersch, S., et al. (2020). Vapor nanobubble is the more reliable photothermal mechanism for inducing endosomal escape of siRNA without disturbing cell homeostasis. J. Control. Release 319, 262–275. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.050
Frangogiannis, N. G. (2011). Pathophysiology of myocardial infarction. Compr. Physiol. 5 (4), 1841–1875. doi:10.1002/cphy.c150006
Gao, Y., Hernandez, C., Yuan, H.-X., Lilly, J., Kota, P., Zhou, H., et al. (2017). Ultrasound molecular imaging of ovarian cancer with CA-125 targeted nanobubble contrast agents. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 13 (7), 2159–2168. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2017.06.001
Gao, Y., Ma, Q., Cao, J., Shi, Y., Wang, J., Ma, H., et al. (2021). Bifunctional alginate/chitosan stabilized perfluorohexane nanodroplets as smart vehicles for ultrasound and pH responsive delivery of anticancer agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 191, 1068–1078. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.166
Gao, Z., Kennedy, A. M., Christensen, D. A., and Rapoport, N. Y. (2008). Drug-loaded nano/microbubbles for combining ultrasonography and targeted chemotherapy. Ultrasonics 48 (4), 260–270. doi:10.1016/j.ultras.2007.11.002
Gasca-Salas, C., Fernández-Rodríguez, B., Pineda-Pardo, J. A., Rodríguez-Rojas, R., Obeso, I., Hernández-Fernández, F., et al. (2021). Blood-brain barrier opening with focused ultrasound in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 779. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21022-9
Gattegno, R., Arbel, L., Riess, N., Shinar, H., Katz, S., and Ilovitsh, T. (2024). Enhanced capillary delivery with nanobubble-mediated blood-brain barrier opening and advanced high resolution vascular segmentation. J. Control. Release 369, 506–516. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.04.001
Gitler, A. D., Dhillon, P., and Shorter, J. (2017). Neurodegenerative disease: models, mechanisms, and a new hope. Dis. models Mech. 10 (5), 499–502. doi:10.1242/dmm.030205
Gul, S., Miano, T. F., Mujeeb, A., Chachar, M., Majeedano, M. I., Murtaza, G., et al. (2024). Advancements in nutraceutical delivery: integrating nanotechnology and microencapsulation for enhanced efficacy and bioavailability. Matrix Sci. Pharma 8, 1–6. doi:10.4103/mtsp.mtsp_1_24
Hampton, M. A., and Nguyen, A. V. (2009). Accumulation of dissolved gases at hydrophobic surfaces in water and sodium chloride solutions: implications for coal flotation. Miner. Eng. 22 (9-10), 786–792. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2009.02.006
Hu, B., and Huang, Q. (2013). Biopolymer based nano-delivery systems for enhancing bioavailability of nutraceuticals. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 31, 1190–1203. doi:10.1007/s10118-013-1331-7
Hu, C., Tao, L., Cao, X., and Chen, L. (2020). The solute carrier transporters and the brain: physiological and pharmacological implications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 15 (2), 131–144. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2019.09.002
Huang, B., Yang, L., Yu, W., Li, Y., Li, L., and Gu, N. (2023). Advances of therapeutic microbubbles and nanobubbles. Natl. Sci. Open 2 (5), 20220062. doi:10.1360/nso/20220062
Huang, W.-C., Chiang, W.-H., Cheng, Y.-H., Lin, W.-C., Yu, C.-F., Yen, C.-Y., et al. (2015). Tumortropic monocyte-mediated delivery of echogenic polymer bubbles and therapeutic vesicles for chemotherapy of tumor hypoxia. Biomaterials 71, 71–83. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.08.033
Huang, W. T., Chan, M. H., Chen, X., Hsiao, M., and Liu, R. S. (2020). Theranostic nanobubble encapsulating a plasmon-enhanced upconversion hybrid nanosystem for cancer therapy. Theranostics 10, 782–796. doi:10.7150/thno.38684
Huang, Y., Guo, X., Wu, Y., Chen, X., Feng, L., Xie, N., et al. (2024). Nanotechnology’s frontier in combatting infectious and inflammatory diseases: prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9 (1), 34. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01745-z
Hynynen, K., McDannold, N., Vykhodtseva, N., and Jolesz, F. A. (2001). Noninvasive MR imaging–guided focal opening of the blood-brain barrier in rabbits. Radiology 220 (3), 640–646. doi:10.1148/radiol.2202001804
Javed, M., Matloob, A., Ettoumi, F.-e., Sheikh, A. R., Zhang, R., and Xu, Y. (2023). Novel nanobubble technology in food science: application and mechanism. Food Innovation Adv. 2 (2), 135–144. doi:10.48130/fia-2023-0014
Ji, G., Yang, J., and Chen, J. (2014). Preparation of novel curcumin-loaded multifunctional nanodroplets for combining ultrasonic development and targeted chemotherapy. Int. J. Pharm. 466 (1-2), 314–320. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.03.030
Ji, Y., Guo, Z., Tan, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Hu, J., et al. (2021). Generating bulk nanobubbles in alcohol systems. ACS Omega 6 (4), 2873–2881. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c05222
Jin, J., Yang, L., Chen, F., and Gu, N. (2022). Drug delivery system based on nanobubbles. Interdiscip. Mater. 1, 471–494. doi:10.1002/idm2.12050
Johansen, M. L., Perera, R., Abenojar, E., Wang, X., Vincent, J., Exner, A. A., et al. (2021). Ultrasound-based molecular imaging of tumors with PTPmu biomarker-targeted nanobubble contrast agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (4), 1983. doi:10.3390/ijms22041983
Kalbasi, A., Komar, C., Tooker, G. M., Liu, M., Lee, J. W., Gladney, W. L., et al. (2017). Tumor-derived CCL2 mediates resistance to radiotherapy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 23 (1), 137–148. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-0870
Kallepalli, B., Garg, U., Jain, N., Nagpal, R., Malhotra, S., Tiwari, T., et al. (2024). Intelligent drug delivery: pioneering stimuli-responsive systems to revolutionize disease management- an in-depth exploration. Curr. drug Deliv. 22, 195–214. doi:10.2174/0115672018278641231221051359
Kancheva, M., Aronson, L., Pattilachan, T., Sautto, F., Daines, B., Thommes, D., et al. (2023). Bubble-based drug delivery systems: next-generation diagnosis to therapy. J. Funct. Biomaterials 14 (7), 373. doi:10.3390/jfb14070373
Kaneko, O. F., and Willmann, J. K. (2012). Ultrasound for molecular imaging and therapy in cancer. Quantitative Imaging Med. Surg. 2 (2), 87–97. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2012.06.06
Kida, H., Yamasaki, Y., Feril, Jr L. B., Endo, H., Itaka, K., and Tachibana, K. (2023). Efficient mRNA delivery with lyophilized human serum albumin-based nanobubbles. Nanomaterials 13 (7), 1283. doi:10.3390/nano13071283
Kinfe, T., Stadlbauer, A., Winder, K., Hurlemann, R., and Buchfelder, M. (2020). Incisionless MR-guided focused ultrasound: technical considerations and current therapeutic approaches in psychiatric disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 20 (7), 687–696. doi:10.1080/14737175.2020.1779590
Kokhuis, T., Skachkov, I., Naaijkens, B., Juffermans, L., Kamp, O., Kooiman, K., et al. (2015). Intravital microscopy of localized stem cell delivery using microbubbles and acoustic radiation force. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 112 (1), 220–227. doi:10.1002/bit.25337
Kulkarni, A. D., Gulecha, V. S., Dolas, R., Zalte, A. G., Deore, S. R., Deore, S. S., et al. (2022). Nanobubbles: fundamentals and recent drug delivery applications. Int. J. Health Sci., 1004–1025. doi:10.53730/ijhs.v6ns8.11598
Kwon, H., Mohamed, M. M., Annable, M. D, and Kim, H. (2020). Remediation of NAPL-contaminated porous media using micro-nano ozone bubbles: Bench-scale experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 228, 103563.
Lee, B. E., Kim, H. Y., Kim, H.-J., Jeong, H., Kim, B.-G., Lee, H.-E., et al. (2020b). O-GlcNAcylation regulates dopamine neuron function, survival and degeneration in Parkinson disease. Brain 143 (12), 3699–3716. doi:10.1093/brain/awaa320
Lee, E., Huang, D., and Luo, T. (2020a). Ballistic supercavitating nanoparticles driven by single Gaussian beam optical pushing and pulling forces. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 2404. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16267-9
Lee, H., Kim, H., Han, H., Lee, M., Lee, S., Yoo, H., et al. (2017). Microbubbles used for contrast enhanced ultrasound and theragnosis: a review of principles to applications. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 7, 59–69. doi:10.1007/s13534-017-0016-5
Lei, J., Huang, D., Zhao, W., Liu, S., and Yue, Y. (2024). Investigating the stability mechanisms of single bulk Nanobubbles: a molecular dynamics perspective. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 225, 125407. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2024.125407
Li, C., Cao, Y., Kohei, F., Hao, H., Peng, G., Cheng, C., et al. (2022). Nano-bubble hydrogen water: an effective therapeutic agent against inflammation related disease caused by viral infection in zebrafish model. Virol. Sin. 37 (2), 277–283. doi:10.1016/j.virs.2022.01.023
Li, H., Lu, Y., Sun, Y., Chen, G., Wang, J., Wang, S., et al. (2018b). Diagnostic ultrasound and microbubbles treatment improves outcomes of coronary no-reflow in canine models by sonothrombolysis. Crit. Care Med. 46 (9), e912–e920. doi:10.1097/ccm.0000000000003255
Li, H., Wu, Z., Zhang, J., Sun, X., Duan, F., Yao, J., et al. (2021). Instant ultrasound-evoked precise nanobubble explosion and deep photodynamic therapy for tumors guided by molecular imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (18), 21097–21107. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c05517
Li, X., Lee, S., and Yoon, J. (2018a). Supramolecular photosensitizers rejuvenate photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47 (4), 1174–1188. doi:10.1039/c7cs00594f
Lin, W., Xie, X., Deng, J., Liu, H., Chen, Y., Fu, X., et al. (2016). Cell-penetrating peptide-doxorubicin conjugate loaded NGR-modified nanobubbles for ultrasound triggered drug delivery. J. Drug Target. 24 (2), 134–146. doi:10.3109/1061186x.2015.1058802
Lipsman, N., Meng, Y., Bethune, A. J., Huang, Y., Lam, B., Masellis, M., et al. (2018). Blood–brain barrier opening in Alzheimer’s disease using MR-guided focused ultrasound. Nat. Commun. 9 (1), 2336. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04529-6
Liu, D., Yang, F., Xiong, F., and Gu, N. (2016). The smart drug delivery system and its clinical potential. Theranostics 6 (9), 1306–1323. doi:10.7150/thno.14858
Lugano, R., Ramachandran, M., and Dimberg, A. (2020). Tumor angiogenesis: causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 1745–1770. doi:10.1007/s00018-019-03351-7
Ma, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Qian, X., Xue, N., Jiang, Z., et al. (2019). Deep penetration of targeted nanobubbles enhanced cavitation effect on thrombolytic capacity. Bioconjugate Chem. 31, 369–374. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00653
Mai, L., Yao, A., Li, J., Wei, Q., Yuchi, M., He, X., et al. (2013). Cyanine 5.5 conjugated nanobubbles as a tumor selective contrast agent for dual ultrasound-fluorescence imaging in a mouse model. PLoS One 8 (4), e61224. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061224
Mcclements, D. J. (2020). Nano-enabled personalized nutrition: developing multicomponent-bioactive colloidal delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 282, 102211. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2020.102211
Messerschmidt, V., Ren, W., Tsipursky, M., and Irudayaraj, J. (2023). Characterization of oxygen nanobubbles and in vitro evaluation of retinal cells in hypoxia. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 12 (2), 16. doi:10.1167/tvst.12.2.16
Mooney, S. J., Shah, K., Yeung, S., Burgess, A., Aubert, I., and Hynynen, K. (2016). Focused ultrasound-induced neurogenesis requires an increase in blood-brain barrier permeability. PLoS One 11 (7), e0159892. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159892
Nakamura, Y., Mochida, A., Choyke, P. L., and Kobayashi, H. (2016). Nanodrug delivery: is the enhanced permeability and retention effect sufficient for curing cancer? Bioconjugate Chem. 27 (10), 2225–2238. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00437
Nazari, S., Hassanzadeh, A., He, Y., Khoshdast, H., and Kowalczuk, P. B. (2022). Recent developments in generation, detection and application of nanobubbles in flotation. Minerals 12 (4), 462. doi:10.3390/min12040462
Nittayacharn, P., Yuan, H.-X., Hernandez, C., Bielecki, P., Zhou, H., and Exner, A. A. (2019). Enhancing tumor drug distribution with ultrasound-triggered nanobubbles. J. Pharm. Sci. 108 (9), 3091–3098. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2019.05.004
Noreen, S., and Bernkop-Schnürch, A. (2024). Thiolated poly-and oligosaccharide-based hydrogels for tissue engineering and wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34 (4), 2310129. doi:10.1002/adfm.202310129
Noreen, S., Pervaiz, F., Ijaz, M., Hanif, M. F., Hamza, J. R., Mahmood, H., et al. (2024). pH-sensitive docetaxel-loaded chitosan/thiolated hyaluronic acid polymeric nanoparticles for colorectal cancer. Nanomedicine 19 (9), 755–777. doi:10.2217/nnm-2023-0318
Omata, D., Maruyama, T., Unga, J., Hagiwara, F., Munakata, L., Kageyama, S., et al. (2019). Effects of encapsulated gas on stability of lipid-based microbubbles and ultrasound-triggered drug delivery. J. Control. Release 311, 65–73. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.08.023
Paknahad, A. A., Kerr, L., Wong, D. A., Kolios, M. C., and Tsai, S. S. (2021). Biomedical nanobubbles and opportunities for microfluidics. RSC Adv. 11 (52), 32750–32774. doi:10.1039/d1ra04890b
Pan, T.-L., Wang, P.-W., Al-suwayeh, S. A., Huang, Y., and Fang, J.-Y. (2012). Toxicological effects of cationic nanobubbles on the liver and kidneys: biomarkers for predicting the risk. Food Chem. Toxicol. 50 (11), 3892–3901. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.07.005
Pandey, V., and Pandey, T. (2024). Chitosan-functionalized nanobubbles for precision oncology: advances in targeted cancer therapeutics. J. Mater. Chem. B 12, 11076–11088. doi:10.1039/d4tb01930j
Parker, J. L., Claesson, P. M., and Attard, P. (1994). Bubbles, cavities, and the long-ranged attraction between hydrophobic surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 98 (34), 8468–8480. doi:10.1021/j100085a029
Pasupathy, R., Pandian, P. M., and Selvamuthukumar, S. (2022). Nanobubbles: a novel targeted drug delivery system. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 58. doi:10.1590/s2175-97902022e19604
Perolina, E., Meissner, S., Raos, B., Harland, B., Thakur, S., and Svirskis, D. (2024). Translating ultrasound-mediated drug delivery technologies for CNS applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 208, 115274. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2024.115274
Pinto, M., Fernandes, C., Martins, E., Silva, R., Benfeito, S., Cagide, F., et al. (2019). Boosting drug discovery for Parkinson’s: enhancement of the delivery of a monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor by brain-targeted PEGylated polycaprolactone-based nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 11 (7), 331. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics11070331
Qaiser, R., Pervaiz, F., Noreen, S., Hanan, H., Shoukat, H., Mahmood, H., et al. (2024). Optimizing lornoxicam-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) and (polyethylene glycol) nanoparticles for transdermal delivery: ex vivo/in vivo inflammation evaluation. Nanomedicine 19 (16), 1471–1485. doi:10.1080/17435889.2024.2359356
Rapoport, N., Gao, Z., and Kennedy, A. (2007). Multifunctional nanoparticles for combining ultrasonic tumor imaging and targeted chemotherapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 99 (14), 1095–1106. doi:10.1093/jnci/djm043
Rapoport, N. Y. (2012). Phase-shift, stimuli-responsive perfluorocarbon nanodroplets for drug delivery to cancer. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 4 (5), 492–510. doi:10.1002/wnan.1176
Rapoport, N. Y., Kennedy, A. M., Shea, J. E., Scaife, C. L., and Nam, K.-H. (2009). Controlled and targeted tumor chemotherapy by ultrasound-activated nanoemulsions/microbubbles. J. Control. Release 138 (3), 268–276. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.05.026
Roovers, S., Lajoinie, G. P. R., De Cock, I., Brans, T., Dewitte, H., Braeckmans, K., et al. (2019). Sonoprinting of nanoparticle-loaded microbubbles: unraveling the multi-timescale mechanism. Biomaterials 217, 119250. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119250
Rosselló, J. M., and Ohl, C.-D. (2023). Clean production and characterization of nanobubbles using laser energy deposition. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 94, 106321. doi:10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106321
Rychak, J. J., and Klibanov, A. L. (2014). Nucleic acid delivery with microbubbles and ultrasound. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 72, 82–93. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.01.009
Shah, R., Phatak, N., Choudhary, A., Gadewar, S., Uddin, A., and Bhattacharya, S. (2023). Exploring the theranostic applications and prospects of nanobubbles. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 25, 1167–1181. doi:10.2174/0113892010248189231010085827
Sharma, H., Nirmalkar, N., and Zhang, W. (2024). Nanobubbles produced by nanopores to probe gas-liquid mass transfer characteristics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 665, 274–285. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2024.03.080
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., and Jemal, A. (2019). Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69 (1), 7–34. doi:10.3322/caac.21551
Silva, J., Arias-Torres, L., Carlesi, C., and Aroca, G. (2024). Use of nanobubbles to improve mass transfer in bioprocesses. Processes 12 (6), 1227. doi:10.3390/pr12061227
Singh, A., Desu, P. K., Nakkala, R. K., Kondi, V., Devi, S., Alam, M. S., et al. (2021). Nanotechnology-based approaches applied to nutraceuticals. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 12, 485–499. doi:10.1007/s13346-021-00960-3
Song, K.-H., Fan, A. C., Hinkle, J. J., Newman, J., Borden, M. A., and Harvey, B. K. (2017). Microbubble gas volume: a unifying dose parameter in blood-brain barrier opening by focused ultrasound. Theranostics 7 (1), 144–152. doi:10.7150/thno.15987
Song, L., Wang, G., Hou, X., Kala, S., Qiu, Z., Wong, K. F., et al. (2020). Biogenic nanobubbles for effective oxygen delivery and enhanced photodynamic therapy of cancer. Acta Biomater. 108, 313–325. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.03.034
Soyluoglu, M., Kim, D., Zaker, Y., and Karanfil, T. (2021). Stability of oxygen nanobubbles under freshwater conditions. Water Res. 206, 117749. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2021.117749
Suchkova, V. N., Baggs, R. B., Sahni, S. K., and Francis, C. W. (2002). Ultrasound improves tissue perfusion in ischemic tissue through a nitric oxide dependent mechanism. Thrombosis Haemostasis 88 (11), 865–870. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1613315
Sun, T., Zhang, Y., Power, C., Alexander, P. M., Sutton, J. T., Aryal, M., et al. (2017). Closed-loop control of targeted ultrasound drug delivery across the blood–brain/tumor barriers in a rat glioma model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (48), E10281–E10290. doi:10.1073/pnas.1713328114
M. Suzuki, K. Koshiyama, F. Shinohara, S. Mori, M. Ono, Y. Tomitaet al. (2005). “Nanobubbles enhanced drug susceptibility of cancer cells using ultrasound.” in International Congress Series. Elsevier 1284, 338–339.
Takahashi, M., Chiba, K., and Li, P. (2007). Free-radical generation from collapsing microbubbles in the absence of a dynamic stimulus. J. Phys. Chem. B 111 (6), 1343–1347. doi:10.1021/jp0669254
Tan, B. H., An, H., and Ohl, C.-D. (2021). Stability of surface and bulk nanobubbles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 53, 101428. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2021.101428
Tarhan, O., and Spotti, M. J. (2021). Nutraceutical delivery through nano-emulsions: general aspects, recent applications and patented inventions. Colloids Surfaces B, Biointerfaces 200, 111526. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111526
Tong, J., Ding, J.-d., Shen, X.-x., Chen, L., Bian, Y.-p., Ma, G., et al. (2013). Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation enhancement in myocardial infarction rat model under ultrasound combined with nitric oxide microbubbles. PLoS One 8, e80186. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080186
Ushida, A., Hasegawa, T., Takahashi, N., Nakajima, T., Murao, S., Narumi, T., et al. (2012). Effect of mixed nanobubble and microbubble liquids on the washing rate of cloth in an alternating flow. J. Surfactants Deterg. 15 (6), 695–702. doi:10.1007/s11743-012-1348-x
Wang, Q., Zhao, H., Qi, N., Qin, Y., Zhang, X., and Li, Y. (2019). Generation and stability of size-adjustable bulk nanobubbles based on periodic pressure change. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 1118. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-38066-5
Wang, T., Yuan, C., Dai, B., Liu, Y., Li, M., Feng, Z., et al. (2017). Click-chemistry-mediated rapid microbubble capture for acute thrombus ultrasound molecular imaging. ChemBioChem 18 (14), 1364–1368. doi:10.1002/cbic.201700068
Wang, X., Shi, G., Fan, S., Ma, J., Yan, Y., Wang, M.-m., et al. (2023). Targeted delivery of food functional ingredients in precise nutrition: design strategy and application of nutritional intervention. Crit. Rev. food Sci. Nutr. 64, 7854–7877. doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2193275
Wang, Y., and Wang, T. (2023). Preparation method and application of nanobubbles: a review. Coatings 13 (9), 1510. doi:10.3390/coatings13091510
Wijaya, A., Maruf, A., Wu, W., and Wang, G. (2020). Recent advances in micro-and nano-bubbles for atherosclerosis applications. Biomaterials Sci. 8 (18), 4920–4939. doi:10.1039/d0bm00762e
Wu, R., Yang, X., Dong, N., Liu, Y., and Zhang, P. (2021). Nanobubbles for tumors: imaging and drug carriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 65, 102749. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2021.102749
Wu, S.-Y., Chen, C. C., Tung, Y.-S., Olumolade, O. O., and Konofagou, E. E. (2015). Effects of the microbubble shell physicochemical properties on ultrasound-mediated drug delivery to the brain. J. Control. Release 212, 30–40. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.06.007
Xie, X., Lin, W., Liu, H., Deng, J., Chen, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2016). Ultrasound-responsive nanobubbles contained with peptide–camptothecin conjugates for targeted drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 23 (8), 2756–2764. doi:10.3109/10717544.2015.1077289
Xiong, R., Xu, R. X., Huang, C., De Smedt, S. C., and Braeckmans, K. (2021). Stimuli-responsive nanobubbles for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50 (9), 5746–5776. doi:10.1039/c9cs00839j
Yan, Y., Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Cai, F., Niu, W., Song, L., et al. (2021). Brain delivery of curcumin through low-intensity ultrasound-induced blood–brain barrier opening via lipid-plga nanobubbles. Int. J. Nanomedicine 16, 7433–7447. doi:10.2147/ijn.s327737
Yang, L., Huang, B., Hu, S., An, Y., Sheng, J., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Indocyanine green assembled free oxygen-nanobubbles towards enhanced near-infrared induced photodynamic therapy. Nano Res. 15 (5), 4285–4293. doi:10.1007/s12274-022-4085-0
Yao, L., Song, Q., Bai, W., Zhang, J., Miao, D., Jiang, M., et al. (2014). Facilitated brain delivery of poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (lactic acid) nanoparticles by microbubble-enhanced unfocused ultrasound. Biomaterials 35 (10), 3384–3395. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.12.043
Yao, M., Mcclements, D. J., and Xiao, H. (2015). Improving oral bioavailability of nutraceuticals by engineered nanoparticle-based delivery systems. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2, 14–19. doi:10.1016/j.cofs.2014.12.005
Yurkin, S. T., and Wang, Z. (2017). Cell membrane-derived nanoparticles: emerging clinical opportunities for targeted drug delivery. Nanomedicine 12 (16), 2007–2019. doi:10.2217/nnm-2017-0100
Zhang, L., Yin, T., Li, B., Zheng, R., Qiu, C., Lam, K. S., et al. (2018). Size-modulable nanoprobe for high-performance ultrasound imaging and drug delivery against cancer. Acs Nano 12 (4), 3449–3460. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b00076
Zhang, X., Zheng, Y., Wang, Z., Huang, S., Chen, Y., Jiang, W., et al. (2014). Methotrexate-loaded PLGA nanobubbles for ultrasound imaging and synergistic targeted therapy of residual tumor during HIFU ablation. Biomaterials 35 (19), 5148–5161. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.02.036
Zhao, M., Yang, X., Fu, H., Chen, C., Zhang, Y., Wu, Z., et al. (2021). Immune/hypoxic tumor microenvironment regulation-enhanced photodynamic treatment realized by pH-responsive phase transition-targeting nanobubbles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (28), 32763–32779. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c07323
Zhao, Y.-z., Dai, Dd, Lu, C.-t., Lv, H.-F., Zhang, Y., Li, X., et al. (2012). Using acoustic cavitation to enhance chemotherapy of DOX liposomes: experiment in vitro and in vivo. Drug Dev. Industrial Pharm. 38, 1090–1098. doi:10.3109/03639045.2011.640332
Keywords: nanobubbles (NBs), drug delivery, nutraceutical delivery, neurodegenerative disease, sustainability
Citation: Awlqadr FH, Noreen S, Altemimi AB, Mohammed OA, Qadir SA, Ahmed DH, Alkanan ZT, Tsakali E, Van Impe JFM, Kozak D, Abd El-Maksoud AA, Ashraf MA and Abedelmaksoud TG (2025) Advancement in nanobubble technology: enhancing drug and nutraceutical delivery with focus on bioavailability, targeted therapy, safety, and sustainability. Front. Nanotechnol. 7:1548593. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2025.1548593
Received: 19 December 2024; Accepted: 05 June 2025;
Published: 25 June 2025; Corrected: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Caterina Guiot, University of Turin, ItalyReviewed by:
Liangcan He, Harbin Institute of Technology, ChinaYasmeen ismail Al-Hadidy, University of Tikrit, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Awlqadr, Noreen, Altemimi, Mohammed, Qadir, Ahmed, Alkanan, Tsakali, Van Impe, Kozak, Abd El-Maksoud, Ashraf and Abedelmaksoud. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sobia Noreen, c29iaWFub3JlZW4wN0BnbWFpbC5jb20=; Jan F. M. Van Impe, amFuLnZhbmltcGVAa3VsZXV2ZW4uYmU=
 Farhang Hameed Awlqadr
Farhang Hameed Awlqadr Sobia Noreen
Sobia Noreen Ammar B. Altemimi4,5
Ammar B. Altemimi4,5 Othman Abdulrahman Mohammed
Othman Abdulrahman Mohammed Syamand Ahmed Qadir
Syamand Ahmed Qadir Efstathia Tsakali
Efstathia Tsakali Jan F. M. Van Impe
Jan F. M. Van Impe Ahmed A. Abd El-Maksoud
Ahmed A. Abd El-Maksoud Muhammad Azeem Ashraf
Muhammad Azeem Ashraf Tarek Gamal Abedelmaksoud
Tarek Gamal Abedelmaksoud