- 1FlavinLabs Private Limited, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
- 2Crop Improvement and Biotechnology, ICAR-Central Institute for Subtropical Horticulture, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
- 3Faculty of Science, Bundelkhand University, Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh, India
- 4Nanoscience and Technology Center, University of Central Florida, Florida, FL, United States
- 5Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Chandigarh University, Mohali, Punjab, India
Metal nanoparticles (MNPs) are emerging as powerful inputs for sustainable agriculture due to their high surface reactivity, bioavailability, and controlled release properties leading to better resource availability and higher productivity. This technical review critically examines the application of eight metal nanoparticle (MNP) formulations—zinc, iron, copper, silver, calcium, titanium, gold, and selenium—in enhancing agronomic and economic traits in agriculture. The review highlights the potential of these MNPs to improve crop yield, disease resistance, nutrient uptake, and overall plant health, offering insights into their mechanisms of action and practical applications in sustainable farming. ZnO-NPs, Fe2O3-NPs, Cu-NPs, and Ag-NPs have proven to enhance nutrient use efficiency in crops. ZnO and Fe2O3-NPs improve nutrient uptake, boost photosynthesis, and increase stress tolerance, especially to drought and salinity. Cu-NPs and Ag-NPs stand out for their antibacterial and antifungal properties, offering a novel approach to managing plant diseases. Calcium and titanium nanoparticles boost resilience under salt and oxidative stress. Au-NPs and Se-NPs enhance antioxidant activity and growth, but their effects are dose-dependent. Higher MNP concentrations may cause adverse effects, highlighting the need for careful optimization. In conclusion, while metal nanoparticles (MNPs) hold great potential for enhancing crop plant traits, issues such as dosage optimization, formulation protocols, and environmental and toxicological concerns need careful consideration. To overcome these challenges, the integration of green technologies using microbial and phyto-metabolites could provide safer, more sustainable alternatives, ensuring effective and environmentally friendly use of MNPs in agriculture.
Introduction
Climate change and global warming have significantly affected agricultural crop production worldwide, leading to reduced yields and altered crop viability. The global population has been steadily rising, currently exceeding 8 billion people, and is expected to reach around 9.7 billion by 2050 (UNSD, 2022). This rapid population growth places immense pressure on agriculture: grain production must increase by 60% to meet the global food demand by 2050 (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2020). The current scenario demands sustainable agriculture, i.e., the food resources to be used in a manner that enables minimum waste and maximum agricultural yield (Axelos and Van de Voorde, 2017). Healthy crop and quality food grain and fruit production are essential for ensuring food security, improving nutrition, and supporting sustainable agricultural practices. To achieve this goal a combination of effective farming techniques, precision agriculture technologies, and cultural, agronomical practices such as crop rotation, organic fertilization, and reduced use of inorganic chemicals (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2020) is needed. Additionally, adopting crop varieties that are resilient to biotic stresses (insects, pests, diseases) and tolerant to abiotic stresses (drought, heat, salinity) is crucial for producing healthy crops under changing climatic conditions (Haggag et al., 2015). These integrated approaches would not only boost crop yields but also ensure that food is nutritious, safe, and high-quality, benefiting both consumers and the environment.
Nanotechnology offers the potential to revolutionize agriculture by enhancing crop production, improving resource efficiency, and promoting sustainability (Dziergowska and Michalak, 2022). Through the development and use of nanofertilizers, precise and controlled nutrient delivery to the crop with reduced waste, and minimal environmental pollution concern from excess fertilizer use (Sharma et al., 2022). Nanomaterials can also be used to improve soil health by enhancing water retention and facilitating soil remediation (Raj et al., 2024). These advancements contribute to higher crop yields, reduced chemical inputs, and more sustainable farming practices, addressing the global food demand while minimizing agriculture’s ecological footprint. Nanopesticides, which target specific pests and diseases, offer an eco-friendlier alternative to conventional chemical pesticides, thereby lowering the environmental impact (Upadhyaya et al., 2020). Furthermore, nanotechnology-based formulations have been reported to improve seed treatments, enhance germination rates, boost stress tolerance, and support early plant growth by modulating molecular processes within plants (Nile et al., 2022; Soliman et al., 2016).
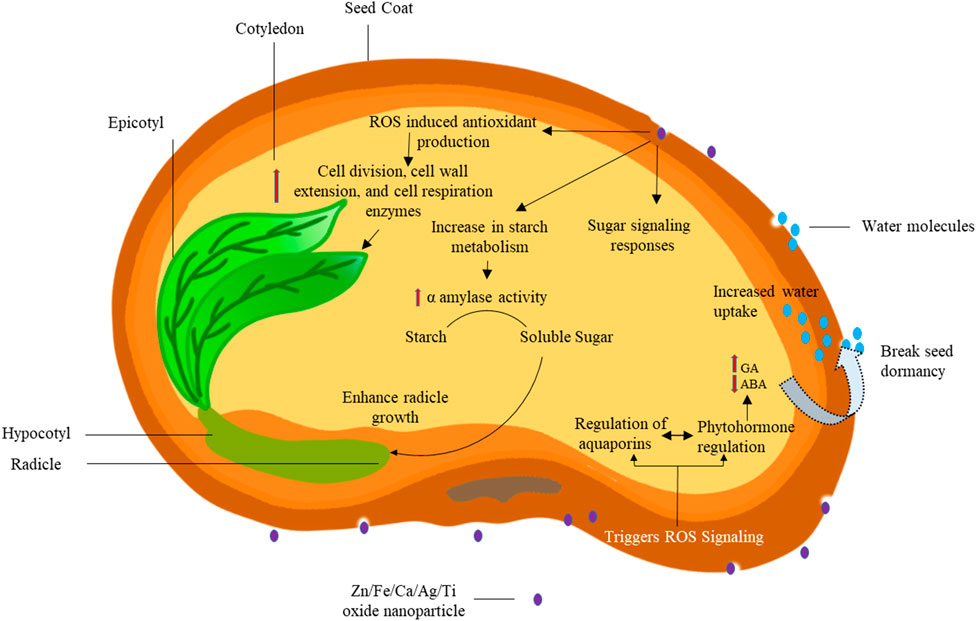
Nanotechnology is a biotechnological advancement with the potential to revolutionize the agriculture sector by enhancing crop production, improving resource efficiency, and fostering sustainability. Through the development and use of nanofertilizers, precise and controlled nutrient delivery is achieved with reduced waste and minimal environmental pollution, addressing key limitations of conventional fertilizers. In addition to nanofertilizers, several other nanotechnological interventions are transforming agricultural practices. Nano-priming represents one such innovation in seed treatment technology. By pre-treating seeds with nanoparticles, nano-priming enhances seed germination and seedling vigor through the modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling and hormonal balances such as gibberellic acid (GA) and abscisic acid (ABA) as shown in Figure 1. This process not only accelerates the initiation of metabolic activities essential for growth but also improves overall stress tolerance during early development.
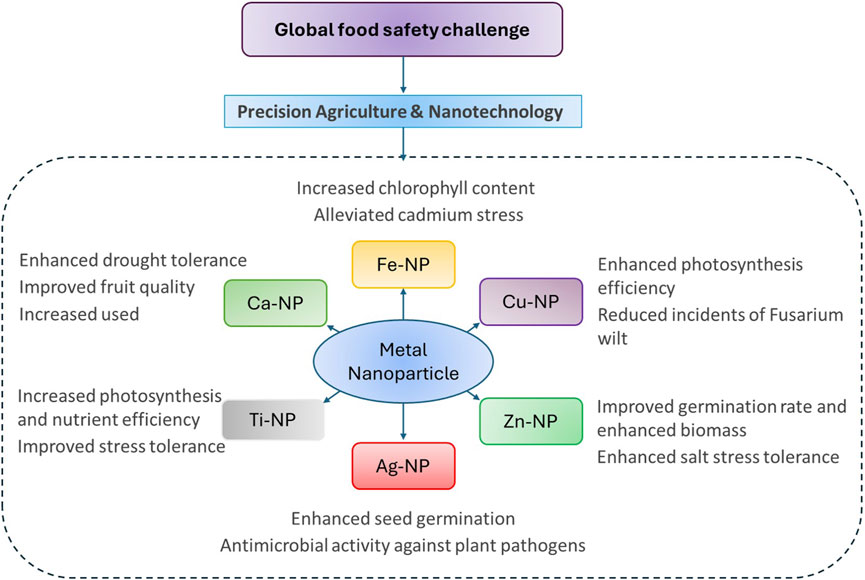
Figure 1. Applications of Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Agriculture: enhancing crop growth, stress tolerance, and food quality through precision agriculture and nanotechnology.
Similarly, nano-pesticides offer an advanced approach to plant protection. Unlike conventional pesticides, nano-pesticides leverage the unique properties of nanoparticles for controlled release and targeted delivery of active ingredients. This improves the specificity of pest control, reduces the required chemical dosage, and minimizes adverse environmental impacts. The enhanced efficiency of nano-pesticides in disease management and pest suppression contributes significantly to sustainable crop protection strategies. Additionally, nano-biosensors are emerging as valuable tools in precision agriculture. These devices, engineered at the nanoscale, enable real-time monitoring of plant physiological states, soil nutrient levels, and the presence of pathogens. By detecting specific biochemical markers, nano-biosensors facilitate timely interventions and data-driven decisions, thus supporting optimal crop management and improving yield outcomes.
Nanotechnological interventions in agriculture also pose significant challenges, including environmental and health risks; their small size and high reactivity can lead to unintended bioaccumulation in soil, water, and organisms (Atanda et al., 2025). Additionally, the high cost of producing nanoparticles and formulating them into practical agricultural products limits their widespread adoption, especially for small, and marginal farmers. Limitations in regulatory frameworks and standardized guidelines for the safe use of nanomaterials in agriculture have hampered their approval and integration into mainstream agronomic practices (Kumari et al., 2024). However, despite these challenges, nanotechnology has been employed in soil nutrition and health management for improving nutrient delivery, pest and disease management, seed treatment, and stress resilience (Sharma et al., 2022). This review critically examines metal-based nanoparticles and their role in improving fertilizer use efficiency, with examples and illustrations.
Metal nanoparticle-based formulations are emerging as transformative tools in agriculture due to their unique characteristics, such as high reactivity, large surface area, and the ability to target specific biological processes. Nanoparticles like silver (Ag), zinc oxide (ZnO), copper (Cu), iron oxide (FeO), and titanium dioxide (TiO2) are being used in fertilizers and pesticides to improve crop growth, pest control, and nutrient delivery (Wani and Kothari, 2018). For instance, zinc oxide nanoparticles act as effective nanofertilizers by promoting nutrient absorption and boosting photosynthetic activity, while silver and copper nanoparticles serve as powerful antimicrobial agents to protect crops from fungal and bacterial infections (Malandrakis et al., 2019). Such formulations are also designed to feature slow-release mechanisms, ensuring sustained delivery of nutrients or pesticides, reducing environmental losses, and minimizing the need for frequent applications (Bajpai et al., 2020). Although challenges such as environmental risks and production costs persist, these innovations have the potential to increase crop yields, improve product quality, and reduce the environmental impact of traditional agricultural practices, promoting more sustainable farming techniques. This review presents an elaborate detailing of the applications of metal nanoparticles-based formulations and their implications on crop growth, reproduction, economic and viable production besides assuring excellent quality produce (Figure 1).
Application of nanotechnology in improving crop growth, and economic yield
Nanoparticle based seed priming technology is the proven nanobiotechnological intervention in breaking dormancy and improving seed germination efficiency. Nanoparticle seed priming (Nano-priming) represents the advancement in agricultural biotechnology, offering innovative approaches to enhance seed germination and seedling development. The process employs nanoparticles that interact with the seed’s biological systems through a sophisticated cascade of cellular and molecular mechanisms. Upon contact with the seed coat, these nanoparticles trigger Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) signaling pathways, initiating a controlled stress response that stimulates antioxidant production within the seed tissues (Nile et al., 2022). This initial response sets in motion a complex series of metabolic events, characterized by enhanced cellular activities including accelerated cell division, cell wall extension, and increased respiratory enzyme function (Nile et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2022; Bajpai et al., 2020). The metabolic shift notably affects starch metabolism, where elevated α-amylase activity facilitates the conversion of stored starch into soluble sugars, providing readily available energy for germination. The process is further regulated by sugar signaling pathways that coordinate with aquaporin-mediated water uptake mechanisms. The significant aspect of this priming technique is that it is influencing the phytohormonal balance, specifically modulating gibberellic acid (GA) and abscisic acid (ABA) levels, which are crucial for breaking seed dormancy (Nile et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2022). The culmination of these synchronized physiological and biochemical modifications manifests in enhanced radicle growth and improved seedling establishment. This intricate interplay between nanomaterials and seed biology demonstrates the potential of nanotechnology in developing more efficient and effective seed treatment methods for modern agriculture (Figure 2).
Nanofertilizers with a particle size of less than 100 nm, serve as macro- or micronutrient fertilizers. They are used for improving as well as increasing agricultural yields. Nanofertilizers are basically nanomaterials which provide nutrients to the growing plants as well as support their growth and improve production. They act in two ways, one is that they supply nutrients to the plants and other is that they can serve as carriers of nutrients and only help in transporting and releasing nutrients (i.e., without being directly utilized as a source of nutrients) (Kaningini et al., 2022). The application of nanofertilizers in crop improvement program is because of their advantageous properties like large surface area, cation exchange capacity, ion adsorption, complexation, etc., and the availability of an unlimited number of nanoparticles on the surface. Different nanoparticles possess different surface compositions having different active sites resulting in different reactivity in context to processes like adsorption and redox reactions. These properties of nanoparticles can be utilized successfully to synthesize nanoparticles for the use in agriculture (Wani and Kothari, 2018).
Metal nanoparticles have been researched for new possibilities in the field of agriculture. This is due to their small size and other unique properties. Nanofertilizers are advantageous over traditional fertilizers because of their large surface area and small size, higher penetration rate, higher solubility, and increased uptake, resulting in the increased growth rate and yield of the plants (Francis et al., 2020). It has also been observed that metal nanofertilizers induce the process of seed germination. Metal nanoparticles have also been studied for their efficiency as pesticides. Therefore, the application of nanofertilizers and nanopesticides will decrease the crop production cost as well as minimize the environmental pollution concerns. Moreover, certain metal nanoparticles can also play a dual role as both fertilizers and pesticides.
Introduction of metal nanoparticles (MNPs) into the plant system, results in physiological changes by interacting with plant cells tissues, stimulates and induces seed germination, enhance photosynthetic pigment content, and improve plant health (Paulami et al., 2023). Various metal ions, metal oxides, polymer-based nanomaterials, carbon nanotubes, engineered nanomaterials, and nanoformulations with active ingredient based nanofertilizers and nanopesticides have showed their potentials in sustainable agriculture production (Chhipa, 2019.).
Some MNPs show promise in suppressing plant disease by directly inhibiting pathogens (e.g., in the case of Ag) or improving delivery of essential micronutrients and stimulating plant defense mechanisms (e.g., in the case of Cu). Metal/metal oxide exposure was found to have a significant positive impact on crop growth and/or plant disease suppression. For instance, nCuO was found to improve disease suppression in eggplants by 69%, while increasing Cu root content by 32% and plant fresh weights by 64%. Several reports have demonstrated the impacts of ENP amendments on soil health and crop yields (Asadishad et al., 2018). This review highlights the fabrication and utilization of different metal nanoparticles and explains the principal and technical considerations for the formulations.
Different type of metal nanoparticles
Significance of Zinc nanoparticles in plant nutrition and physiology
Zinc is one of the essential micronutrients required for plant metabolism which participates in activating enzymes such as RNA polymerase, carbonic anhydrase, and alcohol dehydrogenase. Zn deficiency reduces plant growth, but when present in excess, toxic effects are observed via cytotoxic reactions. Therefore, uptake and transport of zinc by plants should be strictly controlled. Zn ions also have diverse roles and are involved in photosynthesis, lipid, carbohydrate and nucleic acid metabolism. In addition, they act as key component of ‘zinc fingers’, transcription factors, which regulate cell proliferation and differentiation process and also play a critical role in chloroplast development and its associated functions like photosystem II repair process (Sturikova et al., 2018). Zn is also involved in scavenging reactive oxygen species and protecting plants against oxidative damage (Jamal et al., 2018). Zinc plays a pivotal role in stabilization of membranes and structural balancing conformation maintenance of membrane integrity protein by ROS production and scavenging as it is present in superoxide dismutase (Zn-SOD) (Burman et al., 2013). Zinc also regulates growth under drought conditions and dysfunction of antioxidants in plants and helps relieve damage caused by dehydration and enhances plant response during post stress rehydration process (Panda, 2017).
Size of ZnO-NPs and their characterization
The dimensions and structural properties of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) significantly influence their interaction with plant systems. Typically, ZnO-NPs used in agricultural applications range from 10 to 50 nm, which is the optimal size for absorption and eliciting physiological responses. These nanoparticles are evaluated using techniques such as Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), and High-Resolution TEM (HRTEM) to determine their size, shape, crystallinity, and distribution. For instance, 30 nm ZnO-NPs (TEM) enhanced seed germination and seedling vigor in rice (Upadhyaya et al., 2017), while 25 nm particles (HRTEM, SEM) improved water uptake and stress resilience in green gram (Kathiravan et al., 2024). Similarly, particles sized 20–30 nm (SEM, TEM) were associated with increased antioxidative responses in crops like chickpea and pearl millet (Burman et al., 2013; Kumar et al., 2024). However, particles larger than 50 nm or applied at concentrations exceeding 1,500 ppm often led to phytotoxic effects including reduced root length and seedling growth (Rameshraddy et al., 2017; Sarkhosh et al., 2022). Therefore, careful control of nanoparticle dimensions and precise characterization is essential to maximize their benefits while minimizing adverse effects in agricultural applications.
Mode of action of Zn-nanoparticles
(ZnO-NPs) improve plant resistance to abiotic stresses, especially salinity, by influencing various physiological and molecular mechanisms. They enhance antioxidant protection by increasing the levels of enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidases, which reduce oxidative stress (Faizan et al., 2021). ZnO-NPs additionally affect gene expression, modulating more than 1,400 genes related to ion transport, osmotic equilibrium, and stress signal transduction. Significantly, ZnO-NPs improve the absorption of potassium (K+) and calcium (Ca2+) while restricting sodium (Na+) entry, helping to maintain ionic equilibrium during salinity stress (Abideen et al., 2022). These nanoparticles enhance photosynthetic efficiency, chlorophyll levels, and biomass yield by safeguarding chloroplasts against oxidative harm, resulting in increased net photosynthetic rates and improved seedling development (Pérez-Velasco et al., 2021). ZnO-NPs additionally influence hormone signaling, impacting phytohormones such as abscisic acid and auxins that control growth and responses to stress. This leads to enhanced root structure and better water retention during stressful conditions (Abideen et al., 2022). Additionally, ZnO-NPs provide vital zinc, addressing nutrient shortages and enhancing growth, energy metabolism, and resilience to stress (Abideen et al., 2022). In general, ZnO-NPs serve as bio stimulants, improving plant stress resilience and yield via various molecular mechanisms (Figure 3).
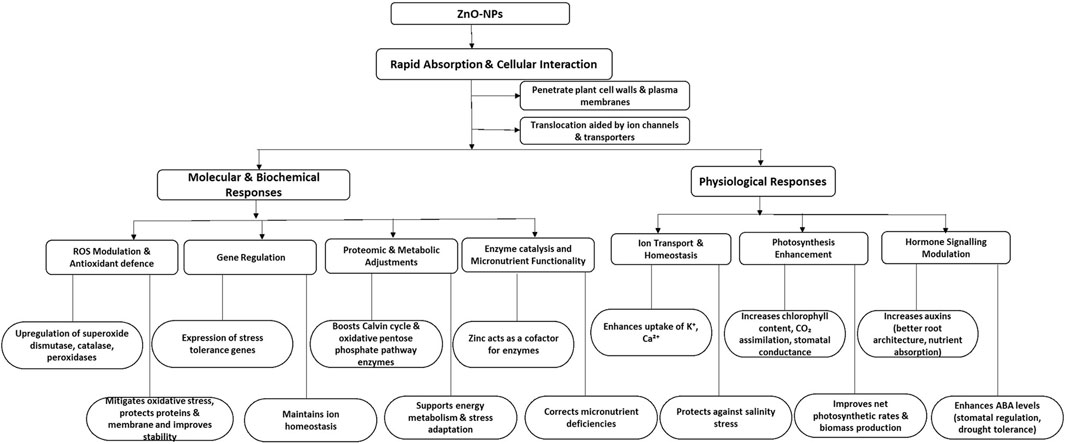
Figure 3. Molecular and physiological responses to application of Zn-NPs in plants. ROS: Reactive oxygen species, K+: Potassium ions, Ca2+: Calcium ions, CO2: Carbon dioxide.
Application of Zn-nanoparticles: case studies
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) have potential to increase food crop yield and improve plant health. Nano-priming of rice seed with ZnO-NPs (up to 1,000 ppm) was reported to have improved germination, biomass, enhanced radicle and plumule length, and increased antioxidant activity, contrary effect such as reduced seed germination and seedling vigor was recorded at higher concentration, i.e., <15,000 ppm (Upadhyaya et al., 2017; Rameshraddy et al., 2017). Foliar spray of Zinc-NPs was found to improve shoot and root growth, increase fresh and dry weight (Farooq et al., 2023; Sohail et al., 2022; Faizan et al., 2021; Rossi et al., 2019; Ralia et al., 2015; Burman et al., 2013; Sabir et al., 2014), and increase chlorophyll content (Sohailet al., 2022; Rossi et al., 2019). Application of ZnO-NPs in salt stress conditions, reduces the deleterious effects of salinity stress in tomato and C. tinctorius by increasing the protein content and antioxidative enzyme activities of peroxidase (POX), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) (Faizan et al., 2021; Yasmin et al., 2021). Ahmed et al. (2021) reported that foliar application of ZnO-NPs on resulted in increased total soluble solids (TSS), induced hardness, besides improving the titratable acidity, ascorbic acid, and lycopene contents. ZnO-NPs have also been reduced to improve salinity stress tolerance trait in many crop plants. For instance, in green gram (Vigna radiata) ZnO-NPs application @ 500ppm resulted in improved water uptake, increased antioxidant activity, and reduced lipid peroxidation (Kathiravan et al., 2024). Similarly, common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris), applications of 100–200 ppm ZnO-NP enhanced salt stress resistance by improving antioxidant enzyme activities and enhanced chlorophyll content (Gupta et al., 2024a). Seed priming with ZnO-NPs increased the rate of germination and also enhanced the radicle and plumule length (Afrayeem and Chaurasia, 2017; Sarkhosh et al., 2022; Panda, 2017; Rameshraddy et al., 2017). However, contrary results have also been with higher ZnO-NP concentration (2,000 ppm in peanut, >250 ppm in tomato, 1,500 ppm in rice, etc.) which includes decreased water content, smaller roots, and marginal cytotoxicity (Burman et al., 2013; Sarkhosh et al., 2022; Rameshraddy et al., 2017). These results indicates that zinc nanoparticles based nanofertilizers have positive effect on crop growth and yield when applied as nanofertilizers in both basal soil application and foliar spray. ZnO-NPs have also shown positive effects on seed germination, as shown in Table 1.
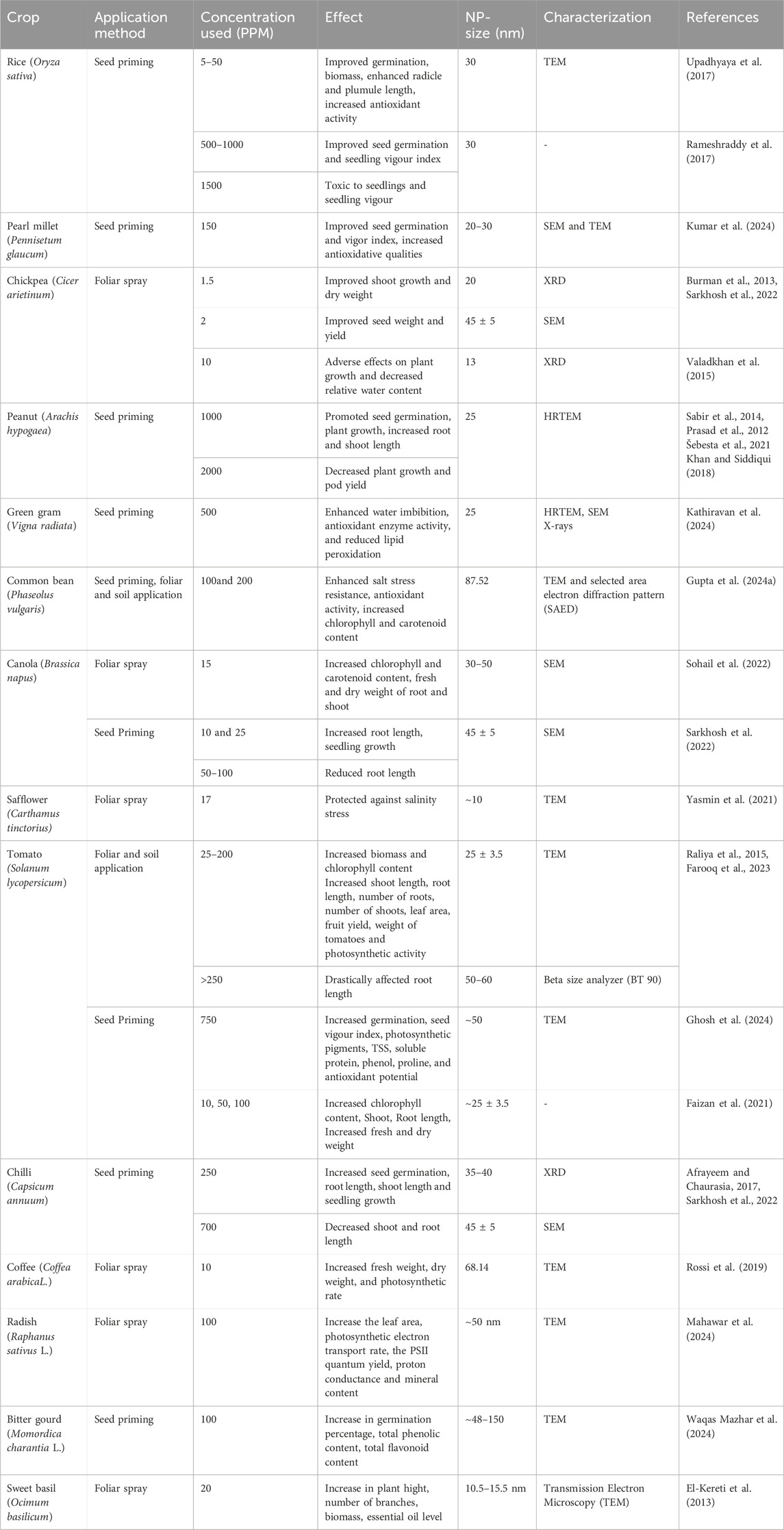
Table 1. Representative examples of effect of application of Zinc Nanoparticles (Zn-NPs) in different crop plants.
Iron nanoparticle significance in physiology and potential application
Iron (Fe) is an essential micronutrient required for plant growth and development which is critical role for chlorophyll synthesis, their structural configuration and functioning. Iron deficiency leads to chlorosis, which affects plant health significantly. Due to the rapid transformation of Fe into plant-unavailable forms like Fe (III) and limited mobility in the phloem cell of plants; the traditional soil application of inorganic Fe fertilizers is unsuccessful (Rengel et al., 1999).
Transcriptomic studies have indicated that Fe-NPs affect genes involved in metal ion balance, cell wall production, and defense signaling pathways, thus enhancing stress resistance (Bidi et al., 2021). In agriculture, Fe-NPs facilitate gene silencing by effectively transporting small interfering RNA (siRNA) to plants. This method assists in silencing genes that hinder growth or disease resistance, thereby improving plant resilience to challenges such as drought, salinity, and pathogen invasions. The capacity of Fe-NPs to enhance gene transfer and increase plant stress resilience underscores their promise in boosting agricultural efficiency and stress control (Shahzad et al., 2025) as shown in Figure 4.
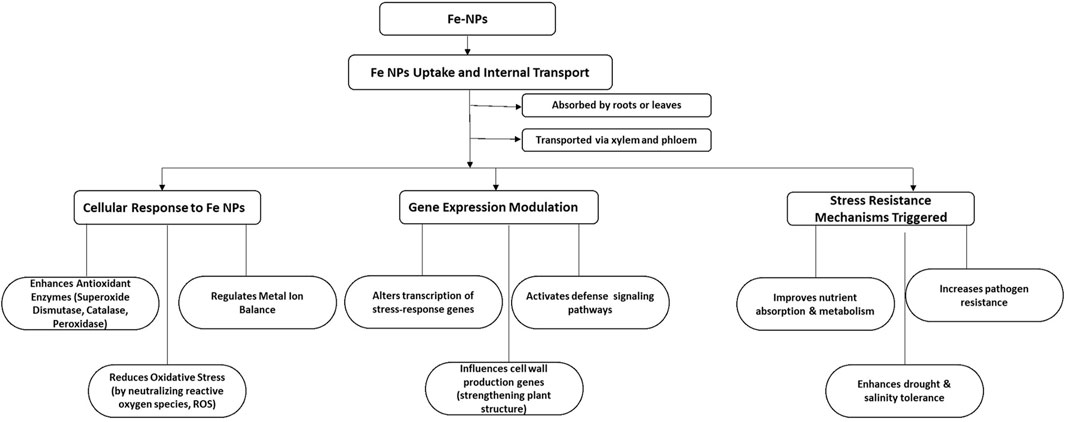
Figure 4. Schematic representation of flow diagram showing the mechanism of action of Fe-NPs in plants.
Iron nanoparticles (Fe-NPs) used in plant systems usually range in size from 4 nm to 100 nm, and their morphology and crystallinity are confirmed using advanced techniques such as TEM, SEM, AFM, and XRD. The most effective Fe-NPs are in the range between 10 and 50 nm, where they promote seed germination, root elongation, and stress resistance. For instance, Fe-NPs measuring 16–20 nm, as confirmed by TEM and FE-SEM, significantly enhanced root development and antioxidative responses in chickpea and gum trees (Palchoudhury et al., 2018; Singh et al., 2021).
Iron nanoparticles, namely, iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3-NPs), are novel innovative formulations that were developed for improving structural stability and biocompatibility (Vázquez-Núñez et al., 2018). Fe2O3-NPs were found to enhance chlorophyll content, root elongation, and seed germination in a variety of crops along with enhanced growth and yield under abiotic stress conditions especially drought, and salinity. In a study done by Adress and coworkers (2020) Fe2O3 nano-coat (20 ppm) application on wheat seeds was observed to have increased biomass and reduced oxidative damage, while soil applications of higher dose (100 ppm) Fe2O3-NPs improved growth and also alleviated cadmium stress. In maize (Zea mays), seed priming with 20 ppm Fe2O3-NPs was reported to have enhanced root elongation, germination index, and vigor, while higher concentrations (50–100 ppm) negatively impacted the seed germination, however, it was found to have improved physiological traits such as enhanced leaf water content, improved photosynthetic efficiency, and good kernel attributes, including cob length and kernel weight (Mazhar et al., 2024; Jalali et al., 2017) (Table 2).
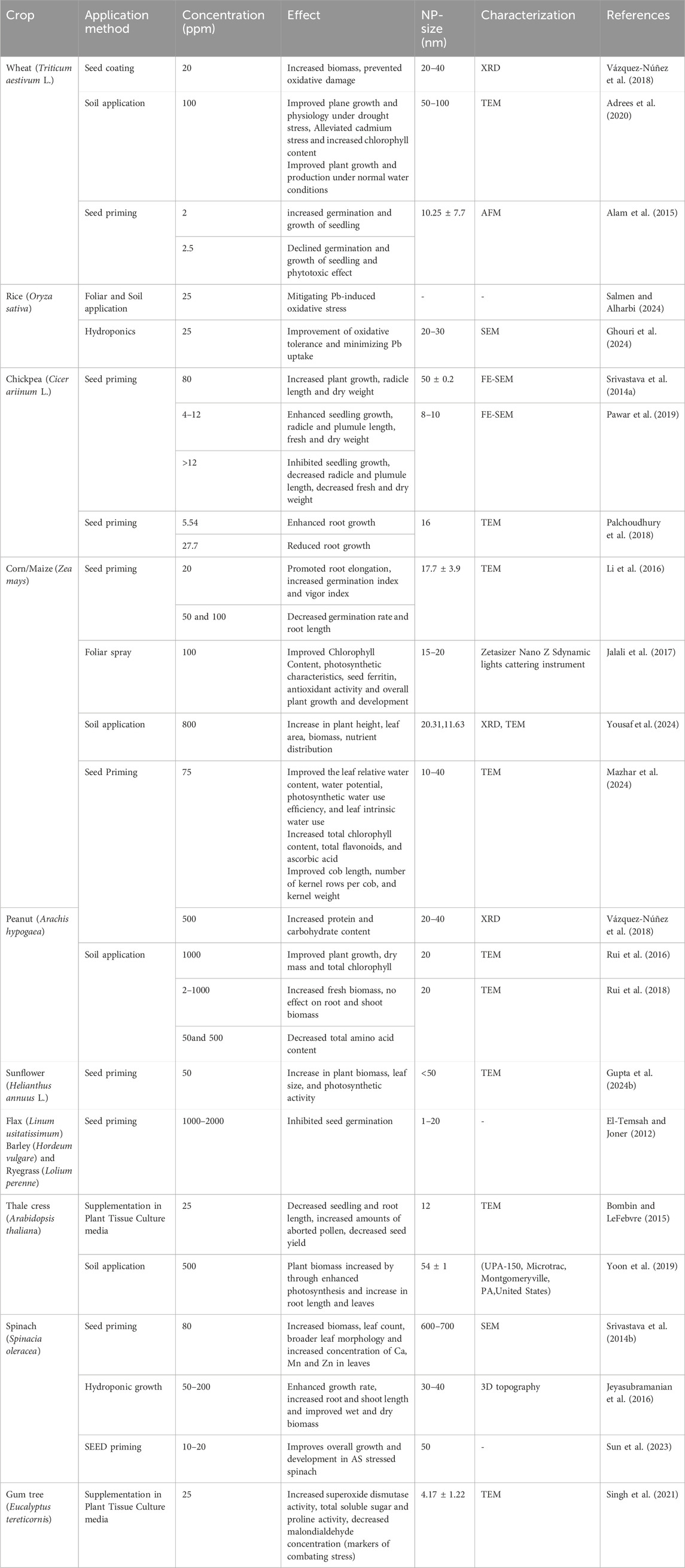
Table 2. Representative examples of the effect of the application of Iron Nanoparticles (Fe-NPs) in different crop plants.
Similarly, in sunflower 50 ppm Fe2O3-NPs application demonstrated an improved biomass, increased leaf size, and photosynthetic activity (Gupta et al., 2024b). In chickpea, seed priming with 4–12 ppm Fe2O3-NPs enhanced radicle and plumule growth, while higher concentrations beyond 12 ppm showed inhibition of growth (Srivastava et al., 2014a; Pawar et al., 2019). Broader leaf morphology, increased biomass, and enhanced mineral content under hydroponic conditions using Fe2O3-NPs in seed priming (10–20 ppm) was proved in spinach with improved overall growth under abiotic stress (Srivastava et al., 2014b; Sun et al., 2023). Peanut treated with 500 ppm Fe2O3-NPs during seed priming showed higher protein and carbohydrate content, and soil application at 1000 mg/kg improved growth and chlorophyll levels, though higher concentrations reduced amino acid content (Rui et al., 2016; Vázquez-Núñez et al., 2018). Even under droughtstress conditions showed less adverse effects was Fe2O3- NPs, as they stabilized heavy metals in the soil and enhance the stress tolerance mechanisms (Lei et al., 2018; Adrees et al., 2020).
Phytotoxic effects were recorded at higher concentrations of Fe2O3-NPs application (>1,000 ppm). For instance, in flax, barley, ryegrass, and Arabidopsis, germination inhibition, decreased seed yield, reduced seedling vigor, and root growth was recorded (Bombin and LeFebvre, 2015). Although Fe2O3-NPs have good potential, it is evident that the fabrication/formulation and conjugation requires systematic study for understanding their absorption, translocation, and potential toxicity mechanisms in order to ensure safe and efficient administration across a range of crops (as mentioned in Table 2).
Copper nanoparticles principles, technical aspects and applications
Copper (Cu) is an important micronutrient for plants, which is mainly found in chloroplasts, accounting for about 70% of the total copper. It is important in chlorophyll synthesis and the synthesis of other pigments and has crucial role in carbohydrate and protein metabolism (Grusak, 2001). Copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) demonstrate potent antimicrobial characteristics by disrupting membranes, releasing Cu2+ ions, generating ROS, and causing DNA damage. They disrupt bacterial membranes, especially in Gram-negative bacteria, enhancing permeability and leading to cell lysis (Hussan et al., 2024; Ingle et al., 2014). Cu2+ ions interfere with protein activity and energy metabolism, whereas ROS induce oxidative stress, harming lipids, proteins, and DNA, resulting in cell death (Rai et al., 2018) as shown in Figure 5. The interplay of these factors renders CuNPs effective against a wide variety of microorganisms. These characteristics render CuNPs promising for use in medicine, agriculture, and environmental remediation; however, additional research is necessary to assess their long-term impact (Ingle et al., 2014).
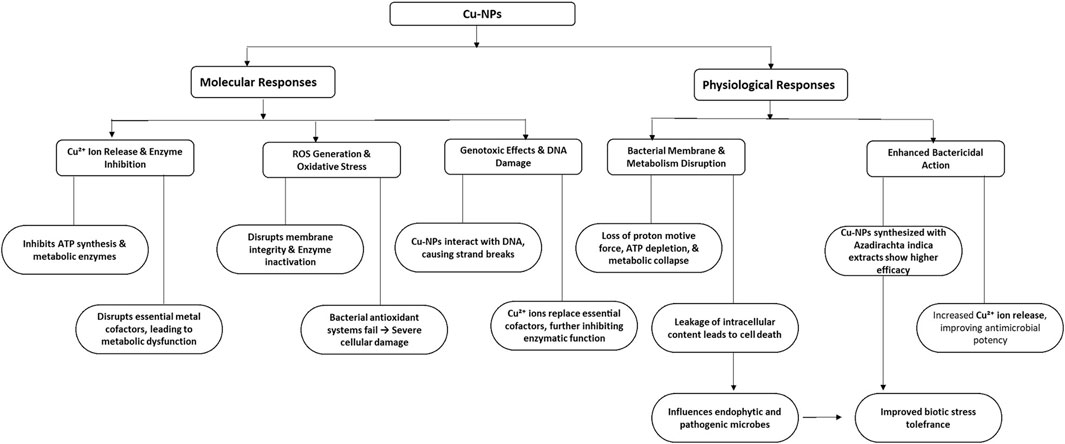
Figure 5. Schematic flow diagram showing molecular and physiological responses of application of Cu-NPs in plants. ROS: Reactive oxygen species, Cu2+: Copper ions.
Copper nanoparticles (Cu-NPs) used in plant studies typically range in size from 10 nm to 100 nm, with certain agglomerates reaching larger sizes depending on synthesis techniques and application conditions. Characterization instruments such as TEM, SEM, Zeta Particle Analyzer, and XRF have been extensively used to evaluate particle shape, size range, and elemental composition. For instance, research involving wheat and mung bean employed Cu-NPs smaller than 50 nm, confirmed by TEM and NTA, and demonstrated improvement in growth and physiological factors (Rai et al., 2018; Jahagirdar et al., 2020). Similarly, Cu-NPs measuring 20–50 nm, as seen via SEM and TEM, were found to enhance antioxidant levels and yield-related characteristics in crops such as tomato and chili (López-Vargas et al., 2018; Uddin et al., 2022). However, at higher doses or larger particle sizes—specifically in the 200–500 nm range used in tomato soil applications—Cu-NPs could potentially cause growth-inhibition or toxic effects, particularly on crops like coriander, barley, and cotton (Lopez-Lima et al., 2021; Zuverza-Mena et al., 2015). The variety of particle sizes and differences in plant reactions underscore the necessity for thorough nanoparticle characterization and dose adjustment when applying Cu-NPs in agriculture.
Cu deficiency leads to reduction in yield and results in physiological disorders such as necrosis, deformation, and discoloration of young leaves, leading to stunted growth. It also affects the development of seeds, grains, and fruits (Lawlor et al., 2004). A prime reason for Cu deficiency in plants is restriction of bioavailability due to its immobilization in soil organic matter (Grusak, 2001).
Copper nanoparticles (Cu-NPs) rank among the most utilized nanoparticles that are used in agriculture. Like all other metal nanoparticles, the efficacy of the Cu-NPs also depends largely on its concentration as the low concentrations of Cu-NPs can promote growth, but higher concentrations show toxic effects. For instance, Adhikari et al. (2012) have demonstrated that Cu-NPs up to 2,000 ppm promoted seed germination in soybean and chickpeas, but beyond this concentration resulted in contrary results. Similarly, 30 ppm Cu-NPs significantly increased the yield, chlorophyll content, spikes per pod number, leaf area, and crop grain weight (Hafeez et al., 2015). López-Vargas et al. (2018) reported higher levels of lycopene, flavonoids, and antioxidant activity in the tomatoes treated with 50–500 ppm of Cu-NP. Uddin et al. (2022) reported that the growth and yield of chilli plants was improved by Cu-NPs (3000ppm). Seed priming of wheat (30 ppm) resulted in increased grain yield, leaf area, chlorophyll content, and growth rates (Hafeez et al., 2015; Rai et al., 2018).
Seed priming with Cu-NPs (100 ppm) improved growth and germination in mung bean (V. radiata), while callus cultures grown on MS media fortified with Cu-NPs (3 ppm) increased phenolic contents (Jahagirdar et al., 2020; Iqbal et al., 2017) (Table 3). In mustard, supplementation of 250–300 ppm Cu-NPs in plant tissue culture media improved in-vitro seed germination efficiency (Tamil Elakkiya et al., 2022). Tomatoes responded positively to foliar sprays of Cu-NPs (50–500 ppm) with increased lycopene content and antioxidant activity (López-Vargas et al., 2018). Supplementation of Cu-NPs in tomato reduced Fusarium wilt disease in greenhouse (Lopez-Lima et al., 2021). In chili (Capsicum frutescens), 300 ppm of foliar application enhanced growth, pod length and yield (Uddin et al., 2022) (Table 3).
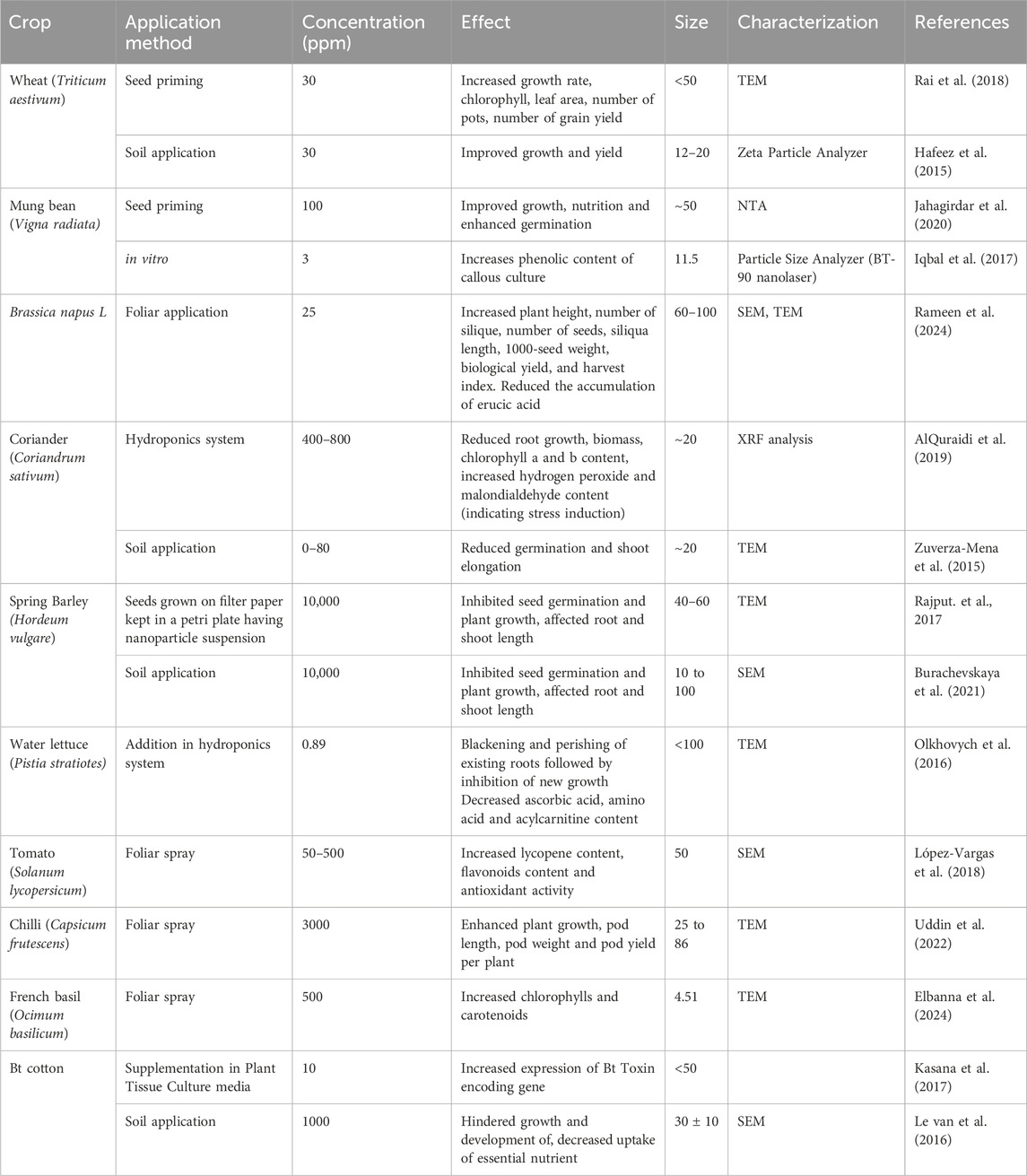
Table 3. Representative examples of effect of application of Copper Nanoparticles (Cu-NPs) in different crop plants.
Notably, Cu-NPs have been known to cause adverse effects in plants such as wheat, yellow squash, and mung beans by perforating their cell membranes and disrupting normal cellular functioning at higher concentrations of (2,000–3,000 ppm) (Lee et al., 2008). Musante and White (2012) found that in sweet potatoes exposure to Cu-NPs had lowered the biomass. These results indicate that concentration-dependent effects of Cu-NPs on plant growth were recorded (Hafeez et al., 2015; Le Van et al., 2016; Zuverza-Mena et al., 2015; Rajput et al., 2018). In Water lettuce application of Cu-NPs (0.89 ppm) resulted in blackened roots and stunted growth at 0.89 ppm in hydroponic systems, along with decreased ascorbic acid and amino acid content (Olkhovych et al., 2016) (Table 3).
Silver nanoparticles and its application in improving crop growth and yield parameters
Silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) are potential agents to enhance agricultural output through better seed germination, growth of plants and defense against several pathogens (Kale et al., 2021). Silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) used in agriculture usually range from 10 to 50 nm, with most characterization performed via TEM, along with occasional use of SEM, XRD, and other methods. Research shows that nanoparticles sized between 20 and 50 nm had significantly benefitted crops such as wheat and lentils, leading to improved growth, enhanced stress resistance, and increased chlorophyll levels (Iqbal et al., 2019; Budhani et al., 2019). However, very small sizes or high concentrations have shown lethality and toxicity effects in sensitive species like Arabidopsis and rice, leading to root damage or hormonal disruptions (Mirzajani et al., 2013; Geisler-Lee et al., 2014). Thus, both the size of the nanoparticles and their application method are vital for the effectiveness and safety of Ag-NPs. Ag-NPs interfere with plant cell membranes via electrostatic interactions, attaching to elements such as lipopolysaccharides and teichoic acids, and aid in penetration. In plants, exposure to AgNP boosts antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and catalase to reduce ROS damage and decreases the expression of genes linked to stress-induced senescence (Jha and Pudake, 2016). AgNPs further boost immunity by regulating phytohormones like salicylic and jasmonic acid, which enhances stress tolerance and disease resistance in agricultural contexts (Sarmast and Salehi, 2016; Mikhailova, 2020) (refer to Figure 6).
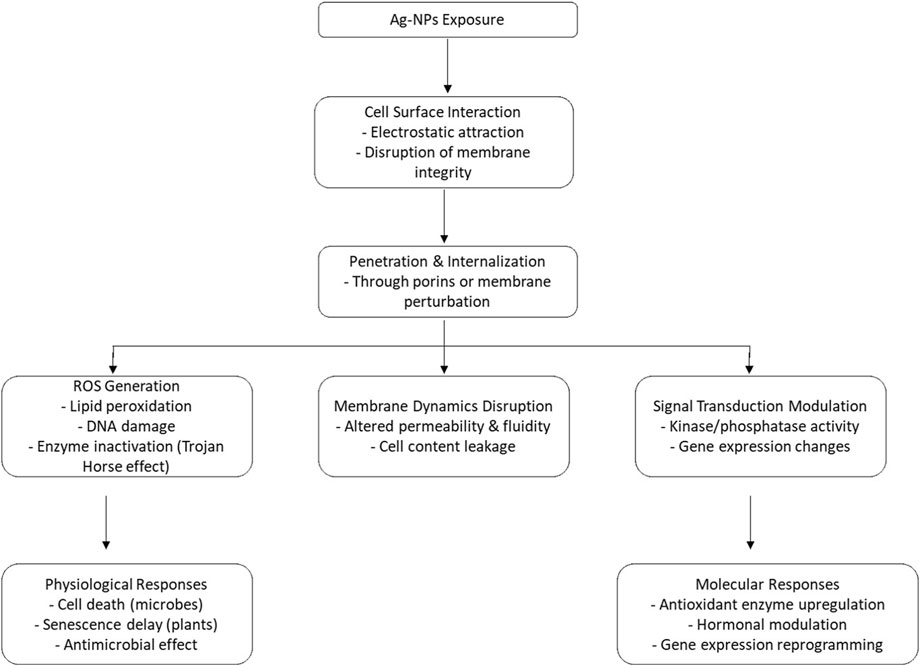
Figure 6. Diagrammatic representation of molecular, biochemical and physiological mechanism of action of Ag-NPs in plants.
The foliar treatment with Ag-NPs has proven to be successful in preventing plant diseases such as molds, rot and wilt. For instance, exposure of Indian mustard to 75 ppm of Ag-NPs enhanced shoot growth, and similar effects were recorded in cowpea (50 ppm) root serve nodulation (Pallavietal., 2016), enhance photosynthetic efficiency, chlorophyll content and plant strength (Hojjat and Kamyab, 2017).
Seed priming with Ag-NPs has significantly enhanced germination rates and plant growth across various species. As an example, Indian mustard seeds treated with Ag-NPs at 100 and 500 ppm increase in length of the root and shoot, total chlorophyll and protein levels (Pandey et al., 2014; Asanova et al., 2019). Similarly, seedling treatments of arugula salad with Ag-NPs (10 ppm) resulted in promotion of root elongation (Vannini et al., 2013). In cowpea seed priming at 750 ppm of Ag-NPs enhanced germination (Maity et al., 2018). In tissue culture and hydroponic systems, Ag-NPs have shown enhanced growth attributes. In vitro germination experiments resulted in higher germination and PDA media enriched with 100 ppm Ag-NPs was phenomenally successful in protecting plants against fungal rot (Kim et al., 2012). Seed priming of Ag-NPs in wheat @ 50 ppm conferred drought tolerance, and foliar application on borage plants at 20–60 ppm increased seed yield, plant height, and leaf count (Elkelish et al., 2024; Seif Sahandi et al., 2011) (Table 4).
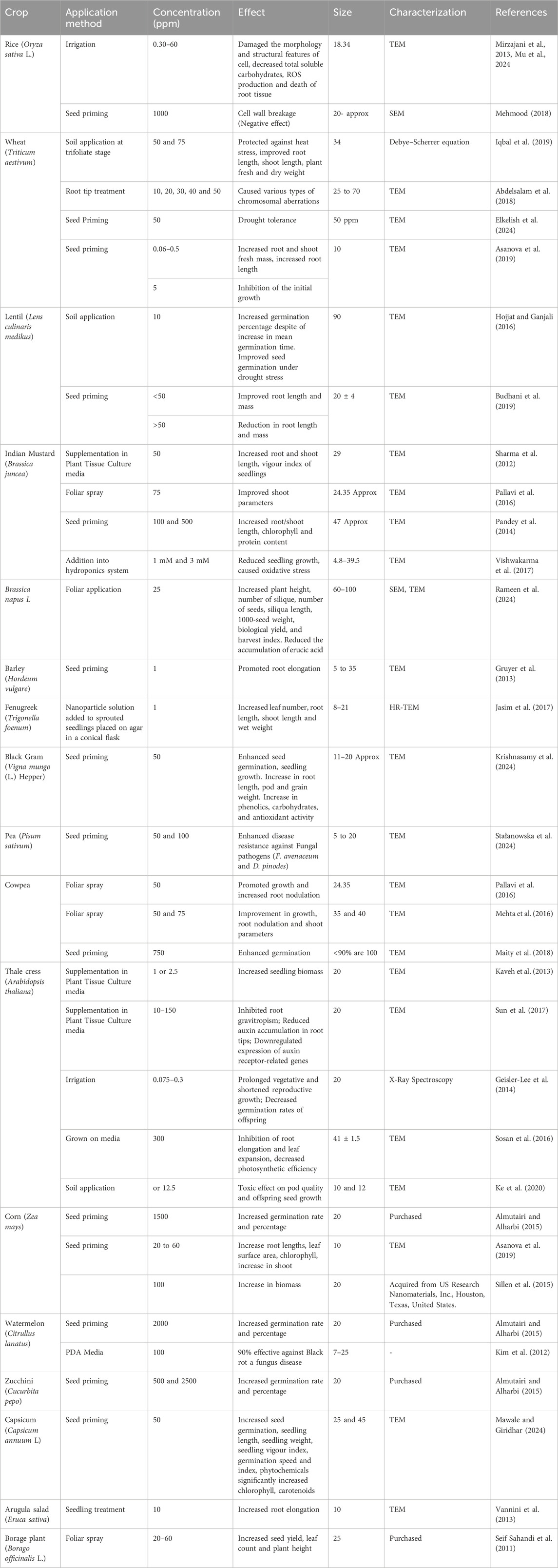
Table 4. Representative examples of effect of application of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) in different crop plants.
Despite its benefits, the effects of Ag-NPs are extremely dose-dependent and differed with plant species, nanoparticle size, and environmental conditions. In general, low to moderate quantities improved growth and yield, while higher doses showed adverse effects. High levels of Ag-NPs in hydroponic systems decreased transcription and biomass in zucchini plants (Almutairi and Alharbi, 2015). Silver, recognized as the second most hazardous metal, has been found to reduce both plant biomass and the transpiration rates in Cucurbita pepo, while also inducing chromosomal abnormalities in Allium cepa root tips (Stampoulis et al., 2009; Kumari et al., 2009). Ag-NPs poses significant environmental concerns as silver ions are released from nanoparticles seep into the surrounding environment. Plants, being primary producers of the food web, are directly affected which disturbs the ecological equilibrium (Yan and Chen, 2019). Although Ag-NPs have shown promise in enhancing crop yield and resilience, their use in agroecosystem needs toxicological analysis (Table 4). Silver nanoparticles seem to have scope for improving crop yields and, diseases management. Nonetheless, environmental consequences function as a setback for its direct utilization. Refinement Ag-NPs formulations, and optimum for field use needs to be worked out for tapping its fullest potential.
Role of Ca-NPs in agricultural production systems
Calcium plays a key role in improving abiotic stress tolerance as Ca2+ regulate affect heavy metal transporter genes, limiting uptake and protecting plants from adverse consequences (Bose and Pottosin, 2011). Calcium serves as both primary and secondary messenger in the signal transduction pathways coordinating the abiotic and biotic stress response pathways, reproductive phase transition and induction of flowering. Ca2+ ions also play major role in conferring microbial competence which is the prime factor exploited for bacterial transformation and genetic engineering studies. Calcium deficiency is characterized by dark-brown lesions on plant tissues and associated physiological functions, thereby retarding growth, development, and progression of phenological stages. (de Freitas and Mitcham, 2012). After absorption, Ca2+ engages with calmodulins and calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs), initiating stress-responsive signaling pathways (Jha and Pudake, 2016). Ca-NPs improve tolerance to salt stress by modulating ion channels, reducing Na+ absorption, and preserving ionic equilibrium, leading to a growth increase of up to 20% in saline environments (Hafez et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2020). They additionally enhance the expression of genes involved in antioxidant protection, modification of the cell wall, and membrane restoration, increasing plant resilience (Jha and Pudake, 2016).
Ca-NPs enhance the cell wall architecture through cross-linking with pectins, boosting rigidity and lowering permeability, which supports pathogen resistance and stress durability. They also regulate hormone signaling, improving water use efficiency, nutrient absorption, and growth during stress (Obomighie et al., 2025) (refer Figure 7). Field experiments indicate that Ca-NPs decrease nutrient leaching by 30% and enhance soil carbon sequestration by 15%, providing environmental advantages (Francis et al., 2024). These effects position Ca-NPs as a valuable resource for enhancing crop yield and promoting sustainable agriculture. Utilization of novel technologies, such as application of CaO-NPs can provide calcium nutrients for optimal requirement for growth, while addressing potential deficiencies.
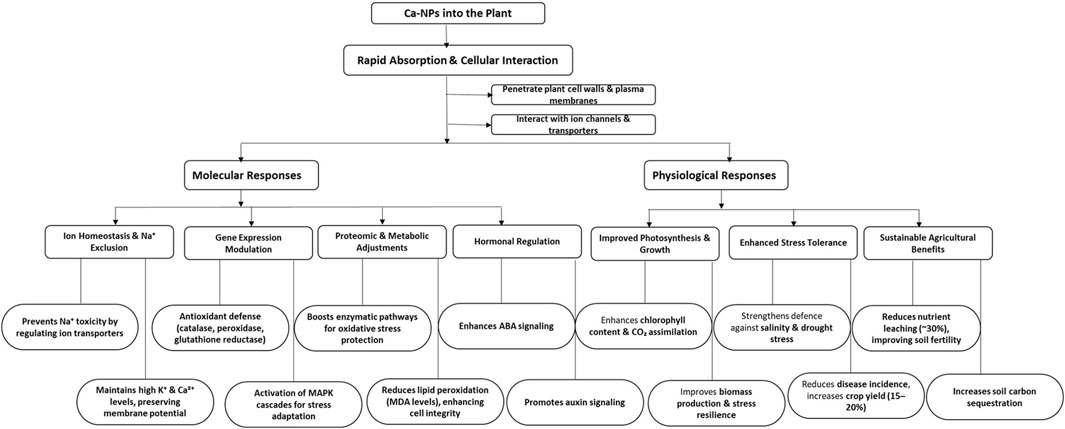
Figure 7. Schematic flow diagram showing effect of application of Ca-NPs in plants in terms of molecular and physiological responses. ROS: Reactive oxygen species, K+: Potassium ions, Ca2+: Calcium ions, Na+: Sodium ions, ABA: Abscisic Acid, MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase, MDA: Malondialdehyde.
Calcium foliar sprays or seed treatments have demonstrated induction of a genetic network governing several biochemical pathways. In strawberries (Fragaria × Ananassa), Ca-NP foliar application @ 100 and 200 ppm, reduced the incidence of Botrytis cinerea. It also improved the levels of essential vitamins (E, C, and A), phenolics, and flavonoids, and increased peroxidase activity leading to enhanced plant health and nutritional quality (Mogazy et al., 2022). Previously Ca-NPs @200 ppm concentration significantly reduced B. cinerea infections, increased growth, and strengthened the plant’s defense mechanisms (Mogazy et al., 2022). Foliar sprays of calcium nanoparticles, at different varying concentrations (50, 100, and 200 ppm) significantly increased shoot and root length, the number of roots and shoots, leaf area, fruit output, and fruit weight in Solanum lycopersicum (tomatoes) for enhanced productivity and economic benefits (Farooq et al., 2023). In canola (Brassica napus L.), foliar application of Ca-NPs (100 ppm) boosted plant biomass, improved nutrient absorption, gas exchange, photosystem II efficiency, and increased antioxidant activity which attributed plant resilience and productivity under water-stressed drought situations (Ayyaz et al., 2022) (as shown in Table 5).
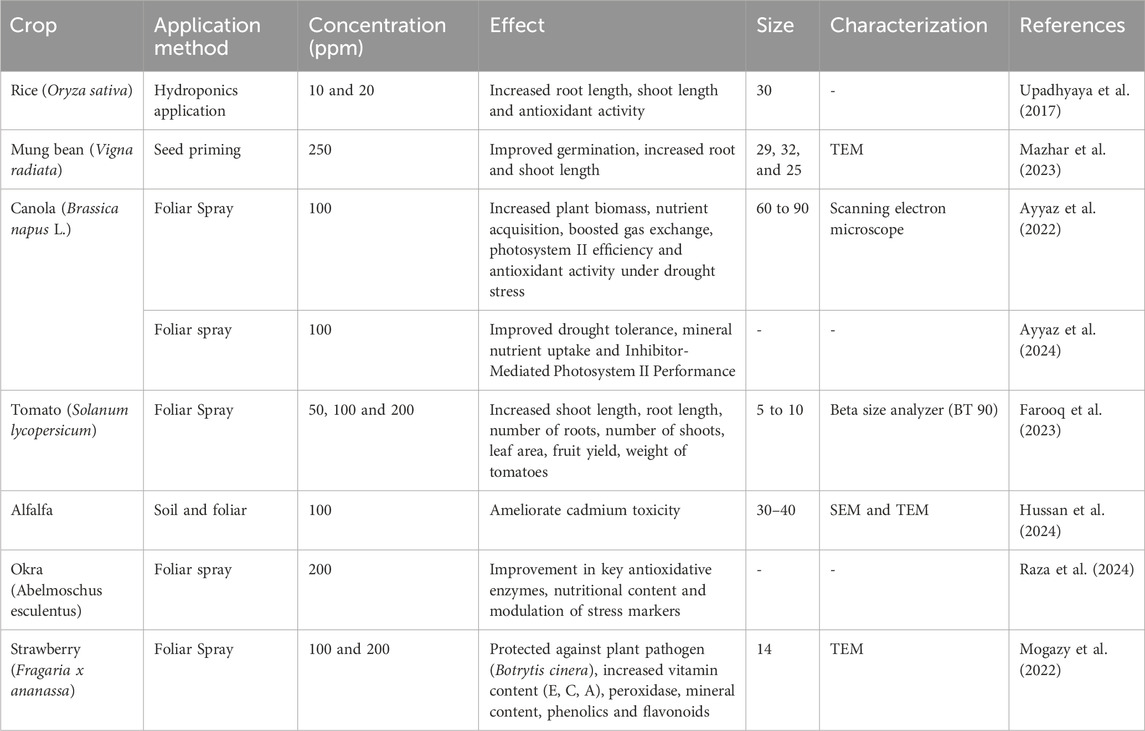
Table 5. Representative examples of effect of application of Calcium Nanoparticles (Ca-NPs) in different crop plants.
Calcium nanoparticles (Ca-NPs) applied in crops typically range from 5 to 90 nm, with most studies uses particles of 10–30 nm size range. These are commonly characterized by TEM or SEM, with occasional use of Beta Size Analyzer (e.g., Farooq et al., 2023). Smaller Ca-NPs (e.g., 5–14 nm) have shown significant benefits in vegetables and fruits, such as tomato and strawberry, enhancing yield, defense against pathogens, and nutrient content (Mogazy et al., 2022; Farooq et al., 2023). In oilseed and legume crops, slightly larger particles (∼25–32 nm) improved germination and growth (Mazhar et al., 2023).
Seed priming with Ca-NPs (250 ppm) enhanced the germination percentage and length of roots and shoots in mung bean (V. radiata) and enhanced early growth promotion (Mazhar et al., 2023). In rice, in vitro in Hogland solution and treated with Ca-NPs (10 and 20 ppm) improved root and shoot length and increasing antioxidant activity conferring stress tolerance (Upadhyaya et al., 2017) (as mentioned in Table 5).
Use of titanium nanoparticles in crop growth and nutrition
Titanium has plant growth promoting effects and providing titanium in the form of nanoparticles to plants can improve plant growth and yield (Faraz et al., 2022). Root or leaves application of Ti in small amounts has been reported to enhance plant performance via stimulation of activities of antioxidant enzymes, increased chlorophyll content and enhanced photosynthetic efficiency hence enhancing nutrient uptake and also improving stress tolerance.
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) used in agriculture generally range from 10 to 115 nm, with most studies reporting effective results at 15–60 nm. These particles are typically characterized using SEM, TEM, and XRD. NPs around 15–30 nm are often associated with enhanced germination, seedling vigor, and stress tolerance, while those larger than 80 nm tend to show negative effects like DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inhibited germination. Thus, TiO2 NPs in the 15–30 nm range are considered optimal for promoting plant growth and minimizing toxicity.
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles(nTiO2) have been hypothesized to function in three different way; 1) pro-oxidant and anti-oxidant roles by modulating reactive oxygen species signaling, 2) manipulation of the nitrogen level in plants via modulation of conversion rate of inorganic to organic nitrogen, and 3)self-modulating role by altering its function and availability by its shape, size and concentration changes. Therefore, in plants, the overall functioning of TiO2 involves a complex interaction. Ti-NPs initiate a series of molecular processes in plants, stimulating essential hormonal pathways, notably abscisic acid (ABA) and salicylic acid (SA), that manage stress responses and boost pathogen defense (Razavizadeh et al., 2023). Ti-NPs also influence membrane-bound ion transporters, enhancing nutrient absorption, particularly for phosphorus, copper, zinc, and calcium, by altering root structure and exudate characteristics. These enhancements lead to a 20% rise in crop yield, elevating photosynthetic efficiency by improving electron transport in chloroplasts and augmenting ATP production, which aids in growth and stress reactions (Francis et al., 2024). Ti-NPs trigger a temporary oxidative burst that is regulated by antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidases, aiding plants in managing oxidative stress (Choudhary et al., 2020). Moreover, Ti-NPs affect the structure of cell walls and the dynamics of ion channels, enhancing resilience to stress.
Genomic research indicates that Ti-NPs enhance the expression of genes associated with metal ion binding, oxidative stress response, and production of secondary metabolites, while reducing the activity of growth-inhibitory genes, thereby altering the plant’s metabolic balance in favor of stress tolerance (Meraj et al., 2020) (Figure 8). TiO2 nanoparticles, a type of Ti-NPs, facilitate effective electron transfer, decrease nutrient loss, and improve soil carbon storage, thereby promoting sustainable agriculture (Francis et al., 2024). The synergy of these effects enhances plant development, output, and adaptability to environmental conditions (Jalil et al., 2019). However, TiO2-NPs also exhibited genotoxic effects as reported in A. cepa, Z. mays, Vicia narbonensis and Nicotiana Tabacum (Cox et al., 2016; Ruffini Castiglione et al., 2011). Foliar application of TiO2-NPs at 2,4, and 6ppm in coriander plants recorded positive effects like increased plant height, fruit yield, no. of branches, amino acid content, total sugars, phenols and chlorophyll contents (Khater, 2015). Similarly in Broad bean and Wheat positive effects with foliar spray of TiO2-NPs were recorded (Abdel Latef et al., 2018; Irshad M. A. et al., 2021). Foliar sprays of TiO2-NPs on Maize plants at 0.02% concentration improved plant growth, dry matter, and final forage yield (Ghooshchi and Lotfi, 2015). In coriander, the root and shoot fresh biomass significantly increased by 50 ppm TiO2-NPs, however use of TiO2-NPs in hydroponics (400 ppm) decreased root length, fresh biomass and water content (Hu et al., 2020). Seed priming at 40 ppm in onion improved storage of onion seed stored in aluminum foil (Khan et al., 2023) (Table 6). It also has been reported that the positive effects of Ti are virtue of its interaction with other nutrients especially Fe. Ti and Fe were reported to have synergistic as well as antagonistic relationships. Perhaps at times of Fe deficiency, Ti induces the expression of genes associated with Fe uptake in plants indicating its alternative role as cofactor for regulating some transcription factor. It was evident from some studies that Ti competes with Fe for proteins or ligands when present in higher concentration (Ruffini Castiglione et al., 2011) (Table 6).
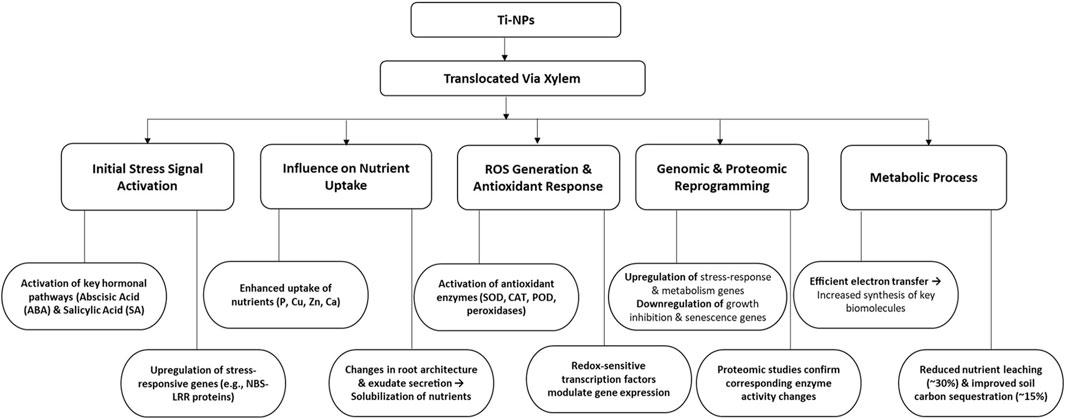
Figure 8. Schematic flow diagram showing mode of action of application of Ti-NPs in plants. P: Phosphorus, Cu: Copper, Zn: Zinc, Ca: Calcium, SOD: Superoxide Dismutase, CAT: Catalase, and POD: Peroxidase.
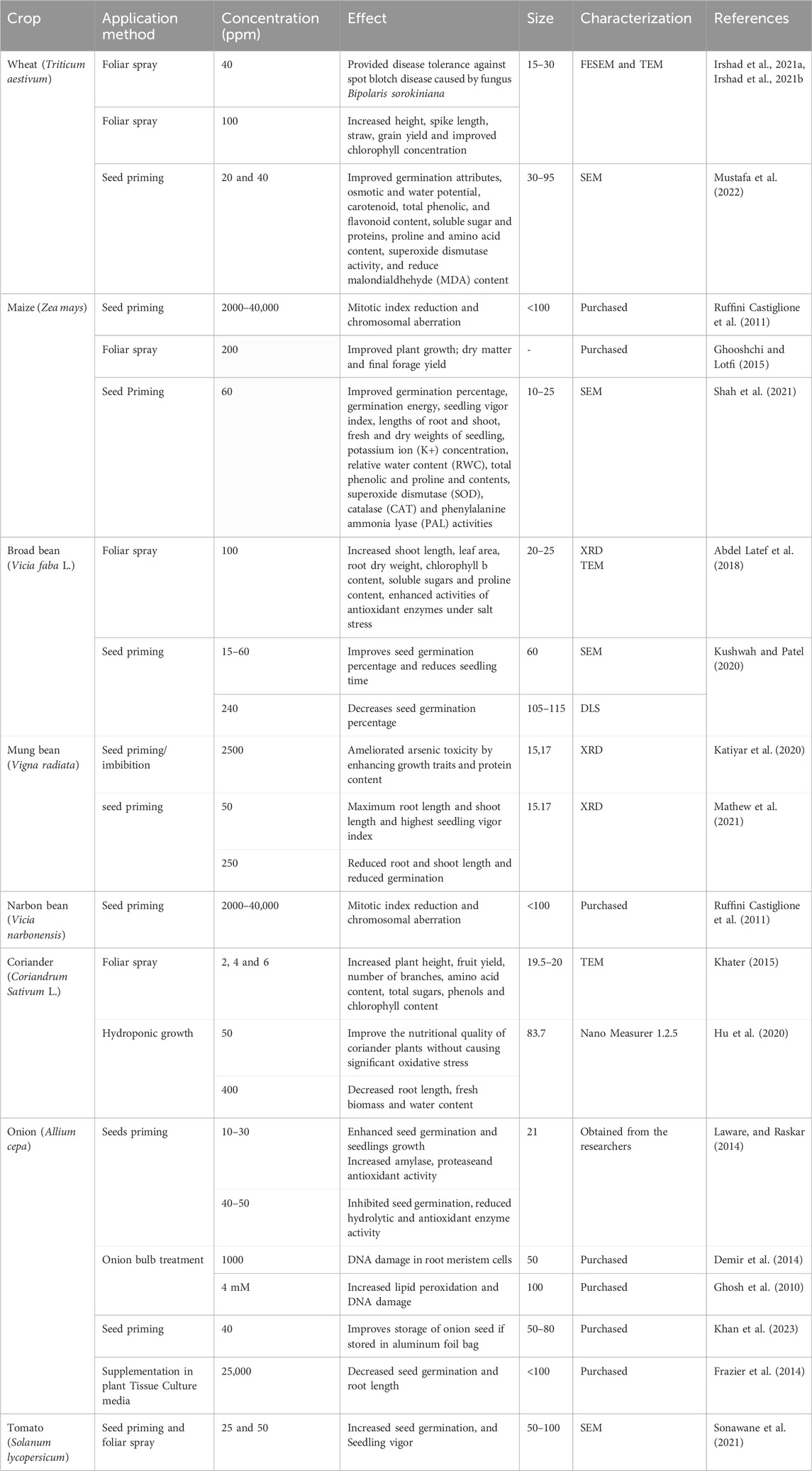
Table 6. Representative examples of effect of application of Titanium Nanoparticles (Ti-NPs) in different crop plants.
Gold nanoparticle (Au-NPs)
Gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) have a vital function in plant nanobiotechnology because of their distinctive characteristics, compatibility with biological systems, and simple functionalization. They mainly penetrate plants through the roots using apoplastic or symplastic pathways and move to above-ground tissues through the xylem. The effectiveness of uptake is influenced by nanoparticle size, charge, and surface chemistry (Zhu et al., 2012; Li et al., 2016). At the molecular level, Au-NPs affect gene expression and metabolic functions, mainly by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS). While low levels of ROS serve as signaling molecules that trigger stress-responsive genes and boost defense strategies, an excessive buildup can result in oxidative stress, which can cause lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and DNA damage. In reaction to this, plants increase the expression of antioxidant defense genes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidases (POD), to mitigate oxidative harm (Li et al., 2016; Zhu et al., 2012) (Figure 9).
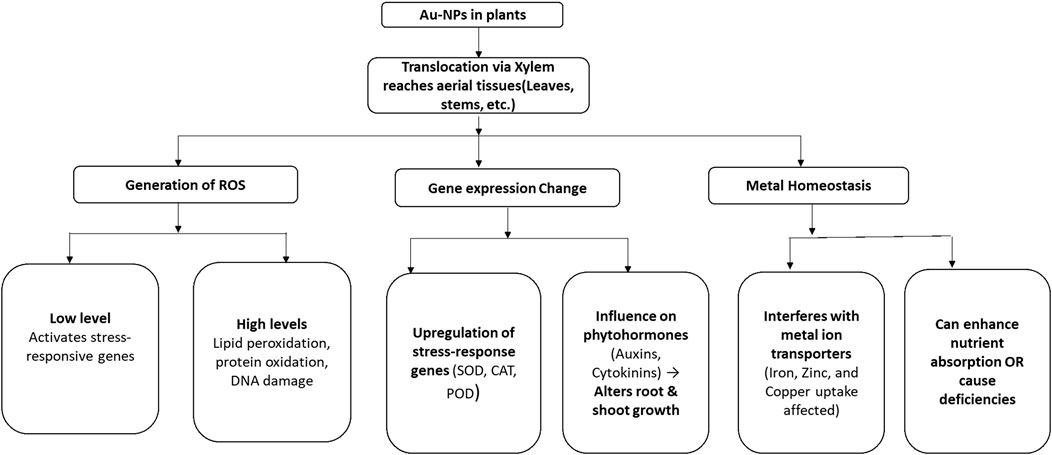
Figure 9. Schematic flow diagram showing molecular and physiological responses of application of Au-NPs in plants. SOD: Superoxide Dismutase, CAT: Catalase, and POD: Peroxidase.
Au-NPs also influence phytohormone signaling, especially auxins and cytokinins, which affect the development of roots and shoots. Furthermore, they modify metal homeostasis by interfering with ion transporters, altering the absorption of micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and copper. This can either enhance nutrient uptake and photosynthesis or lead to imbalances that may cause growth inhibition and metabolic issues (Zhu et al., 2012). In Mentha spicata L. (spearmint), foliar and root applications of Au-NPs (1–100 PPM) resulted in their accumulation in plant tissues, with dose-dependent effects on growth and physiology (Peshkova et al., 2024). Similarly, in parsley, a foliar spray of AuNPs (1–100 PPM) led to their accumulation in aerial parts and a dose-dependent increase in metal content (Peshkova et al., 2025). Wheat subjected to soil applications of Au-NPs (10–100 mg/L) exhibited impacts on seed germination and plant growth parameters (Venzhik et al., 2022) (Table 7).
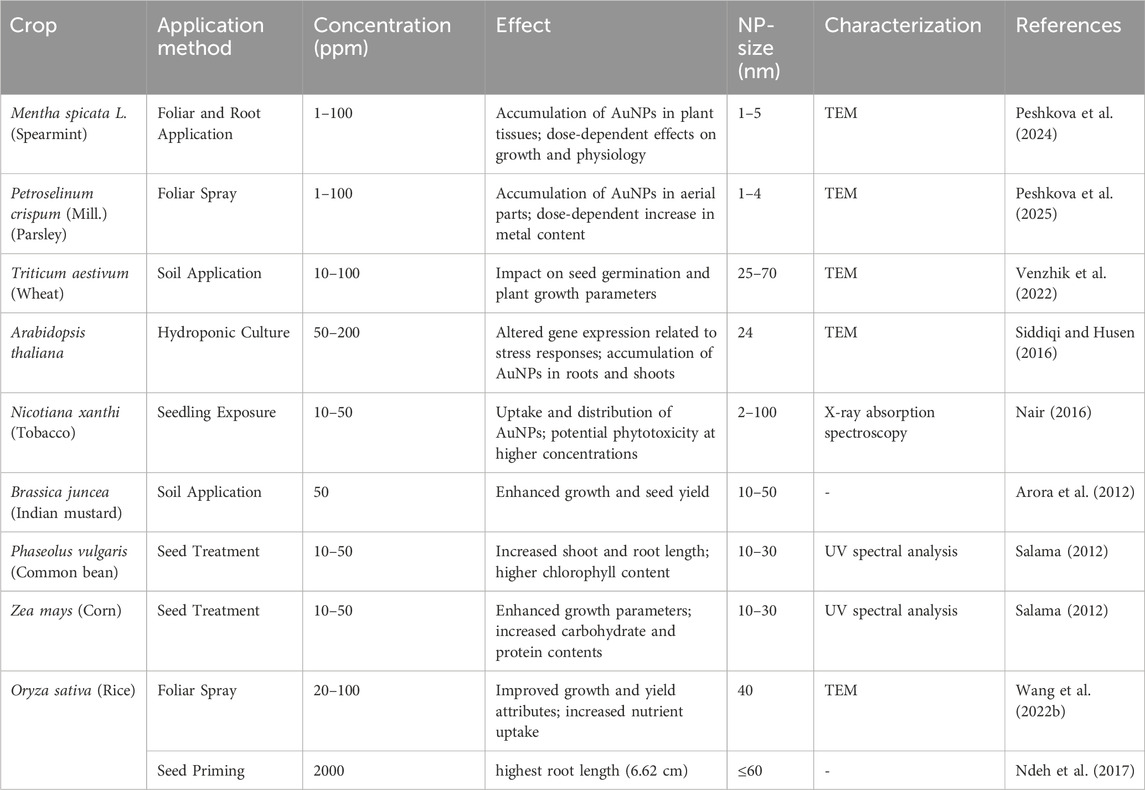
Table 7. Representative examples of the effect of the application of Gold Nanoparticles (Au-NPs) in different crop plants.
In hydroponic culture, Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to Au-NPs (50–200 PPM) showed altered gene expression related to stress responses, along with the accumulation of nanoparticles in roots and shoots (Siddiqi and Husen, 2016). Tobacco seedlings treated with Au-NPs (10–50 PPM) demonstrated uptake and distribution of nanoparticles, though potential phytotoxicity was noted at higher concentrations (Nair, 2016). Brassica juncea grown in soil with 50 PPM Au-NPs experienced enhanced growth and seed yield (Arora et al., 2012)) (Table 7). Seed treatments with Au-NPs (10–50 PPM) positively influenced P. vulgaris (common bean) and Maiz, leading to increased shoot and root length, higher chlorophyll content, and enhanced carbohydrate and protein accumulation (Salama, 2012). In rice, foliar application of AuNPs (20–100 PPM) led to improved growth, yield attributes, and increased nutrient uptake (Wang C. et al., 2022). Furthermore, seed priming of rice with 2,000 ppm Au-NPs resulted in the highest recorded root length (6.62 cm) (Ndeh et al., 2017) (Table 7). These findings suggest that gold nanoparticles can be beneficial in plant growth and stress mitigation; however, their effects vary depending on the plant species, application method, and concentration.
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), typically ranging from 1 to 70 nm, exhibit diverse effects on plants depending on their size, concentration, and method of application. At smaller sizes (1–5 nm), AuNPs accumulate efficiently in tissues of spearmint and parsley, showing dose-dependent physiological effects. In crops like wheat, rice, and corn, sizes between 10 and 50 nm enhance seed germination, shoot/root growth, and nutrient uptake, particularly when applied via foliar spray or seed treatment. However, higher concentrations or larger particle sizes (up to 100 nm) may cause phytotoxicity, as seen in tobacco. Overall, AuNPs around 10–30 nm are generally optimal for promoting plant growth and physiological benefits.
Selenium nanoparticles
Selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) have shown considerable promise in improving plant growth, resilience to stress, and physiological reactions in numerous plant species. Se-NPs improve plant resilience to abiotic and biotic stresses by modulating antioxidant defenses, metabolic processes, and gene regulation. In the face of abiotic stressors like drought, salinity, vanadium, and heavy metal toxicity, Se-NPs—particularly when combined with organic materials such as olive solid waste—aid in regulating ROS levels by boosting antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, APX, GPX) and non-enzymatic antioxidants (ASC, GSH), thus preserving redox balance (Albqmi et al., 2023). They stimulate the phenylpropanoid pathway, boosting secondary antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolics (Ahmad et al., 2021), while also aiding sulfur metabolism to produce glutathione (El Saadony et al., 2021).
Under biotic stress conditions, Phyto-mediated Se-NPs enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes and increase metabolites such as sesamin and γ-tocopherol, thereby improving defense mechanisms and membrane stability (Ahmad A. et al., 2024). They stabilize chlorophyll and regulate phytohormones to improve growth and photosynthesis (Adhikary et al., 2022; Albqmi et al., 2023). Se-NPs are taken up by roots and converted into bioavailable seleno-amino acids, which help in detoxifying heavy metals (Wang C. et al., 2022; Zahedi et al., 2021). The use of phytochemicals in green synthesis enhances the biocompatibility and ROS-scavenging abilities of Se-NP (Sentkowska et al., 2024; Grudniak et al., 2025) as shown in Figure 10. In wheat, the application of Se-NPs on leaves at levels of 0.01%, 0.05%, and 0.1% enhanced growth in saline environments, resulting in greater shoot and root biomass (Zafar et al., 2024). Similarly, Se-NPs administered through foliar spray (25 µM) and at 10 PPMs successfully alleviated drought stress by improving physiological responses and regulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism (Hasanuzzaman et al., 2024).
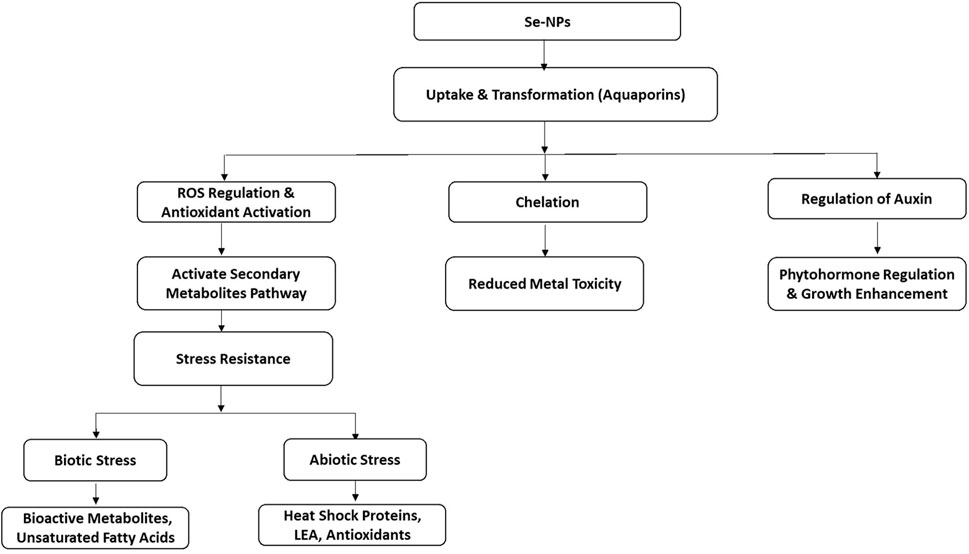
Figure 10. Schematic flow diagram showing physiological and hormonal responses of application of Se-NPs in plants.
In Daucus carota (carrot), a soil application of 20 PPM Se-NPs led to increased growth and better physiological tolerance when exposed to heavy metal stress (El-Batal et al., 2023). Oryza sativa (rice) cultivated in hydroponic systems with 0.5 PPM Se-NPs demonstrated enhanced antioxidant activity; however, at elevated concentrations, selenium nanoparticles revealed a dual effect, promoting growth enhancement and oxidative stress (Freire et al., 2024) (Table 8).
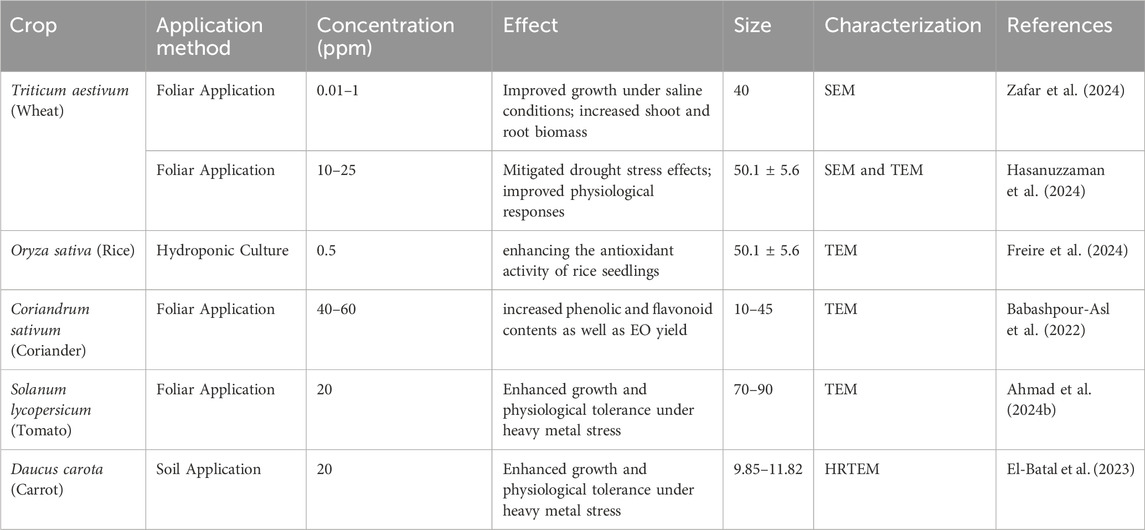
Table 8. Representative examples of effect of application of Selenium Nanoparticles (Se-NPs) in different crop plants.
Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs), typically sized between 10 and 90 nm, have demonstrated significant benefits for various crops under abiotic stress. In wheat, foliar treatments at concentrations of 0.01–25 ppm improved growth and biomass during saline and drought conditions, with optimal effects noted at about 50 nm (Hasanuzzaman et al., 2024; Zafar et al., 2024). Rice seedlings exposed to 0.5 ppm SeNPs in hydroponic systems displayed enhanced antioxidant activity (Freire et al., 2024). Coriander treated with 40–60 ppm SeNPs showed increased levels of phenolic and flavonoid compounds, as well as a higher yield of essential oils (Babashpour-Asl et al., 2022). Similarly, tomato and carrot plants benefited from SeNPs when faced with heavy metal stress, exhibiting improved growth and physiological resilience at nanoparticle sizes ranging from approximately 10–90 nm (Ahmad I. et al., 2024; El-Batal et al., 2023).
The application of Se-NPs on leaves showed positive effects in aromatic and medicinal plants. In coriander, Se-NPs at 40–60 PPM raised the levels of phenolic and flavonoid compounds while boosting essential oil (EO) production under stress conditions (Babashpour-Asl et al., 2022). Likewise, in tomato, a foliar application of 20 PPM Se-NPs enhanced plant growth and heavy metal stress tolerance by modulating secondary metabolites and improving physiological traits (Ahmad A. et al., 2024) (Table 8). These results indicate that selenium nanoparticles may significantly contribute to boosting plant resilience against abiotic stresses, improving antioxidant responses, and fostering growth. Nonetheless, their impacts differ according to species, concentration, and environmental factors, highlighting the necessity for precise optimization of application techniques.
Recent advancements in metal NPs production
The synthesis of metal nanoparticles has been directed to more environmentally friendly and sustainable techniques, such as the use of biological metabolites. Involvement of higher energy, high cost and toxic chemicals are major setbacks of physical and chemical methods of MNPs synthesis. In contrast, the green synthesis approaches using primary and secondary metabolites like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, enzymes, vitamins, organic acids, alkaloids, flavonoids, and terpenes have shown good metal reduction and stabilization properties. Biomolecules work as reducers by different mechanisms that can include deprotonation, nucleophilic reactions, transesterification, ligand binding, or chelation to initiate stable MNPs (Acharya et al., 2025). One of the most prominent examples of this green synthesis approach is the use of microorganisms in the agricultural sector (Bahrulolum et al., 2021). The microbial synthesis of MNPs offers a quick, cost-effective, clean, non-toxic, and environment-friendly alternative over conventional ways. Numerous microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, yeasts, and microalgae, have been used to control plant pathogens as whole cell formulations (Damodaran et al., 2019) or metabolite-based selections using bioimmmunization technology (Damodaran et al., 2023). These studies have implications for the development of metabolite conjugated nano-formulations and nano-biosensors that could be used in disease management and diagnostics of plant pathogens. Green syntheses of nanoparticles which are nontoxic and alsoshows promise in terms of particle sizes, shapes, compositions, and physicochemical properties and thus are amenable to wide-ranging applications in agriculture.
Off-target studies and risk of NPs on pollinator
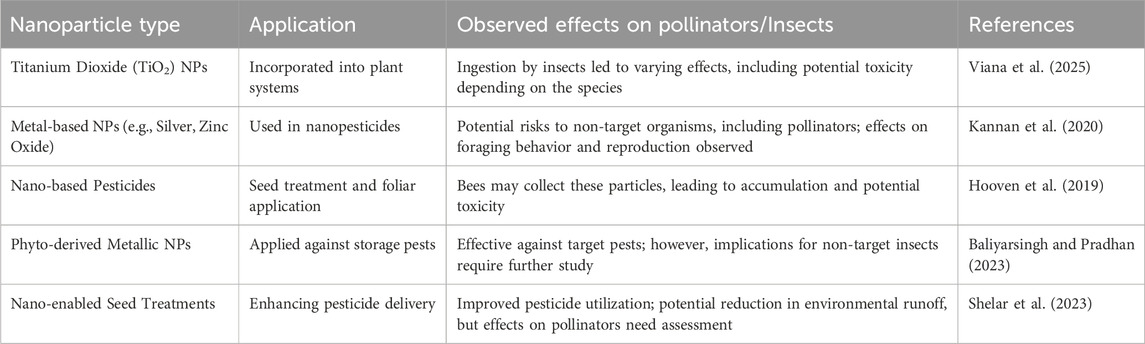
The adoption of engineered nanoparticles (NPs) in agriculture offers potential benefits but also poses emerging risks to non-target insects, especially pollinators. When TiO2-NPs are integrated into plant systems, they can be ingested by insects, leading to a range of responses from harmless interactions to toxic effects, influenced by the species of insect and the levels of exposure (Viana et al., 2025). Metal-based nanoparticles, including silver and zinc oxide NPs, have been linked to potential threats to non-target organisms. Research indicates that these can disrupt foraging behaviors and reproductive success in bees and other beneficial insects (Kannan et al., 2020). Similar concerns arise with nano-based pesticides applied via seed treatments or leaf sprays, where pollinators might inadvertently collect these particles while foraging, potentially accumulating them in their bodies and facing stress or even mortality (Hooven et al., 2019). Plant-derived metal nanoparticles, developed using plant extracts and primarily targeting storage pests, effectively control these pests. Nevertheless, their overall environmental impact remains under-researched. Initial findings suggest they can diminish pest populations, but there may be adverse effects on beneficial insects, necessitating further investigation (Baliyarsingh and Pradhan, 2023). Furthermore, seed treatments employing nanotechnology to enhance pesticide efficacy have contributed to reduced environmental runoff and improved utilization of active ingredients; however, the implications for pollinators are still unclear. Preliminary studies indicate that extensive research is crucial to assess bee exposure levels and potential harm (Shelar et al., 2023) (Table 9). Overall, these findings emphasize the need for a careful risk–benefit analysis prior to implementing nanotechnology in crop protection. While nanoparticles present significant promise for sustainable pest management, safeguarding pollinators will demand comprehensive field trials, established safety assessments, and regulations governing the design and application of nanoparticles to minimize harm to critical ecosystem components.
Conclusion
This review analyzes the use of eight key metal nanoparticles—zinc, iron, copper, silver, calcium, titanium, gold, and selenium—in enhancing crop growth, physiology, and yield. Due to their high surface-area-to-volume ratio and unique properties, these MNPs not only serve as nutrients but also modulate gene expression, hormone activity, and stress responses in crops as outlined in the review. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) boost germination, photosynthesis, and stress tolerance under drought and salinity. Iron oxide (Fe2O3-NPs) promotes chlorophyll synthesis, antioxidant activity, and mitigates heavy metal stress via gene regulation. Copper nanoparticles (Cu-NPs) enhance growth and defense but can be toxic at high doses. Silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) improve germination and vigor through strong antimicrobial action, though their reactivity raises phytotoxicity concerns. Calcium nanoparticles (Ca-NPs) support membrane stability, signaling, and stress resilience. Titanium dioxide (TiO2-NP) improves photosynthesis, nutrient uptake, and regulates stress and hormone pathways. Gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs), though less explored, aid growth and stress tolerance via auxin, cytokinin, and ROS regulation. Selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) enhance stress resistance by activating antioxidant defenses and secondary metabolism.
While metal nanoparticles (MNPs) offer clear agronomic benefits, their effects work in highly dose- and crop-specific manner. Optimal concentrations promote growth and stress tolerance, but excess levels can cause toxicity, hinder germination, and disrupt cellular balance. Determining safe application levels is essential. Ecological concerns such as impacts on soil microbial population and dynamics, nutrient cycling process, and ecosystem stability, highlight the need for robust risk assessments and long-term monitoring trails. Although, high costs are involved in nano-synthesis or nanoformulation’s preparation and poses scalability issues which limits their widespread use, presently the green synthesis using microbes and plant metabolites offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative approach. Bioconjugated MNPs are often more biocompatible and can be tailored for targeted agricultural functions such as integrating them in nutrient management, plant protection, and crop management practices. With responsible innovation and interdisciplinary efforts, MNPs can support climate-resilient and resource-efficient agriculture.
Author contributions
SK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MM: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. KM: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. AB: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. AT: Visualization, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. GS: Writing – review and editing. SB: Writing – review and editing. KC: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. SM: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. TD: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. BK: Writing – review and editing. DR: Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors SK, SS, KM, AT, KC, and SM were employed by FlavinLabs Private Limited.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel Latef, A. A. H., Srivastava, A. K., El-sadek, M. S. A., Kordrostami, M., and Tran, L. S. P. (2018). Titanium dioxide nanoparticles improve growth and enhance tolerance of broad bean plants under saline soil conditions. Land Degrad. Dev. 29, 1065–1073. doi:10.1002/ldr.2780
Abdelsalam, N. R., Abdel-Megeed, A., Ali, H. M., Salem, M. Z., Al-Hayali, M. F., and Elshikh, M. S. (2018). Genotoxicity effects of silver nanoparticles on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) root tip cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 155, 76–85. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.069
Abideen, Z., Waqif, H., Munir, N., El-Keblawy, A., Hasnain, M., Radicetti, E., et al. (2022). Algal-mediated nanoparticles, phycochar, and biofertilizers for mitigating abiotic stresses in plants: a review. Agronomy 12 (8), 1788. doi:10.3390/agronomy12081788
Acharya, C., Mishra, S., Chaurasia, S. K., Pandey, B. K., Dhar, R., and Pandey, J. K. (2025). Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using biometabolites: mechanisms and applications. Biometals 38, 21–54. doi:10.1007/s10534-024-00642-w
Adhikari, T., Kundu, S., Biswas, A. K., Tarafdar, J. C., and Rao, A. S. (2012). Effect of copper oxide nano particle on seed germination of selected crops. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2 (6A), 815. Available online at: https://shorturl.at/K4X4p.
Adhikary, S., Biswas, B., Chakraborty, D., Timsina, J., Pal, S., Chandra Tarafdar, J., et al. (2022). Seed priming with selenium and zinc nanoparticles modifies germination, growth, and yield of direct-seeded rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 7103. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-11307-4
Adrees, M., Khan, Z. S., Ali, S., Hafeez, M., Khalid, S., Rehman, M. Z., et al. (2020). Simultaneous mitigation of cadmium and drought stress in wheat by soil application of iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 238, 124681. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124681
Afrayeem, S. M., and Chaurasia, A. K. (2017). Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on seed germination and seed vigour in chilli (Capsicum annuum L.). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 6 (5), 1564–1566. Available online at: https://www.phytojournal.com/archives/2017/vol6issue5/PartW/6-5-100-866.pdf.
Ahmad, A., Javad, S., Iqbal, S., Shahzadi, K., Gatasheh, M. K., and Javed, T. (2024a). Alleviation potential of green-synthesized selenium nanoparticles for cadmium stress in Solanum lycopersicum L: modulation of secondary metabolites and physiochemical attributes. Plant Cell. Rep. 43 (4), 113. doi:10.1007/s00299-024-03197-9
Ahmad, I., Chen, C., Younas, Z., Yousaf, T., and Mashwani, Z. U. R. (2024b). Seed and foliar application of nano-selenium improves sesame triacylglycerols and oil yield via photosynthetic pigment and enzymatic and chemical antioxidant enhancement revealed by spectrophotometric, UHPLC-Analysis and chemometric modeling. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1431877. doi:10.3389/fpls.2024.1431877
Ahmed, R., Yusoff, A. S. M., Uddin, M. K., Quddus, M. A., and Hossain, M. A. M. (2021). Recent trends in the foliar spraying of zinc nutrient and zinc oxide nanoparticles in tomato production. Agronomy 11, 2074. doi:10.3390/agronomy11102074
Alam, M. J., Sultana, F., and Iqbal, M. T. (2015). Potential of iron nanoparticles to increase germination and growth of wheat seedling. J. Nanosc. Adv. Technol. 1 (3), 14–20. doi:10.24218/jnat.2015.12
Albqmi, M., Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M., Selim, S., Al-Sanea, M. M., Alnusaire, T. S., Almuhayawi, M. S., et al. (2023). Positive interaction of selenium nanoparticles and olive solid waste on vanadium-stressed soybean plant. Agriculture 13 (2), 426. doi:10.3390/agriculture13020426
Almutairi, Z. M., and Alharbi, A. (2015). Effect of silver nanoparticles on seed germination of crop plants. Int. J. Nucl. Quantum. Eng. 9 (6), 280–285. doi:10.24297/jaa.v4i1.4295
AlQuraidi, A. O., Mosa, K. A., and Ramamoorthy, K. (2019). Phytotoxic and genotoxic effects of copper nanoparticles in coriander (coriandrum sativum—Apiaceae). Plants 8 (1), 19. doi:10.3390/plants8010019
Arora, S., Sharma, P., Kumar, S., Nayan, R., Khanna, P. K., and Zaidi, M. G. H. (2012). Gold-nanoparticle induced enhancement in growth and seed yield of Brassica juncea. Plant growth Regul. 66, 303–310. doi:10.1007/s10725-011-9649-z
Asadishad, B., Chahal, S., Akbari, A., Cianciarelli, V., Azodi, M., Ghoshal, S., et al. (2018). Amendment of agricultural soil with metal nanoparticles: effects on soil enzyme activity and microbial community composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52 (4), 1908–1918. doi:10.1021/acs.est.7b05389
Asanova, A. A., Yashin, S. E., Trofimova, T. V., and Polonskiy, V. I. (2019). Application of silver nanoparticles to improve wheat seedlings growth. IOP Conf. Ser. Environ. Earth Sci. 315, 052041. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/315/5/052041
Atanda, S. A., Shaibu, R. O., and Agunbiade, F. O. (2025). Nanoparticles in agriculture: balancing food security and environmental sustainability. Discov. Agric. 3 (1), 26. doi:10.1007/s44279-025-00159-x
M. A. Axelos, and M. Van de Voorde (2017). Nanotechnology in agriculture and food science (New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons). Available online at: https://www.wiley.com/en-it/Nanotechnology+in+Agriculture+and+Food+Science-p-9783527339891.
Ayyaz, A., Fang, R., Ma, J., Hannan, F., Huang, Q., Sun, Y., et al. (2022). Calcium nanoparticles (Ca-NPs) improve drought stress tolerance in Brassica napus by modulating the photosystem II, nutrient acquisition and antioxidant performance. NanoImpact 28, 100423. doi:10.1016/j.impact.2022.100423
Ayyaz, A., Zhou, Y., Batool, I., Hannan, F., Huang, Q., Zhang, K., et al. (2024). Calcium nanoparticles and abscisic acid improve drought tolerance, mineral nutrients uptake and inhibitor-mediated photosystem II performance in Brassica napus. J. Plant Growth Regul. 43, 516–537. doi:10.1007/s00344-023-11108-7
Babashpour-Asl, M., Farajzadeh-Memari-Tabrizi, E., and Yousefpour-Dokhanieh, A. (2022). Foliar-applied selenium nanoparticles alleviate cadmium stress through changes in physio-biochemical status and essential oil profile of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) leaves. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 80021–80031. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-19941-1
Bahrulolum, H., Nooraei, S., Javanshir, N., Tarrahimofrad, H., Mirbagheri, V. S., Easton, A. J., et al. (2021). Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using microorganisms and their application in the agrifood sector. J. Nanobiotechnol 19, 86. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-00834-3
Bajpai, A., Jadhav, K., Muthukumar, M., Kumar, S. S., and Srivatava, G. (2020). “Use of nanotechnology in quality improvement of economically important agricultural crops,” in Biogenic nano-particles and their use in agro-ecosystems (Singapore: Springer), 39–57. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-2985-6
Baliyarsingh, B., and Pradhan, C. K. (2023). Prospects of plant-derived metallic nanopesticides against storage pests-A review. J. Agric. Food Res. 14, 100687. doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100687
Bidi, H., Fallah, H., Niknejad, Y., and Tari, D. B. (2021). Iron oxide nanoparticles alleviate arsenic phytotoxicity in rice by improving iron uptake, oxidative stress tolerance and diminishing arsenic accumulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 163, 348–357. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.04.020
Bombin, S., LeFebvre, M., Sherwood, J., Xu, Y., Bao, Y., and Ramonell, K. (2015). Developmental and reproductive effects of iron oxide nanoparticles in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 (10), 24174–24193. doi:10.3390/ijms161024174
Bose, J., Pottosin, I. I., Shabala, S. S., Palmgren, M. G., and Shabala, S. (2011). Calcium efflux systems in stress signaling and adaptation in plants. Front. Pl. Sci. 2, 85. doi:10.3389/fpls.2011.00085
Budhani, S., Egboluche, N. P., Arslan, Z., Yu, H., and Deng, H. (2019). Phytotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles on seed germination and growth of terrestrial plants. J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part C 37 (4), 330–355. doi:10.1080/10590501.2019.1676600
Burachevskaya, M., Mandzhieva, S., Bauer, T., Minkina, T., Rajput, V., Chaplygin, V., et al. (2021). The effect of granular activated carbon and biochar on the availability of Cu and Zn to Hordeum sativum distichum in contaminated soil. Plants 10 (5), 841. doi:10.3390/plants10050841
Burman, U., Saini, M., and Kumar, P. (2013). Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and antioxidant system of chickpea seedlings. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 95 (4), 605–612. doi:10.1080/02772248.2013.803796
Chhipa, H. (2019). Applications of nanotechnology in agriculture. Methods Microbiol. 46, 115–142. doi:10.1016/bs.mim.2019.01.002
Choudhary, A., Kumar, A., and Kaur, N. (2020). ROS and oxidative burst: roots in plant development. Plant Divers. 42 (1), 33–43. doi:10.1016/j.pld.2019.10.002
Cox, A., Venkatachalam, P., Sahi, S., and Sharma, N. (2016). Silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticle toxicity in plants: a review of current research. Pl. Phy. Bio. 107, 147–163. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.022
Damodaran, T., Mishra, M., Muthukumar, M., Rajan, S., Yadav, K., Kumar, A., et al. (2023). Secondary metabolite induced tolerance to Fusarium oxysporum F. Sp. cubense TR4 in banana cv. grand naine through in vitro bio-immunization: a prospective research translation from induction to field tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1233469. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1233469
Damodaran, T., Mishra, V. K., Jha, S. K., Pankaj, U., Gupta, G., and Gopal, R. (2019). Identification of rhizosphere bacterial diversity with promising salt tolerance, PGP traits and their exploitation for seed germination enhancement in sodic soil. Agric. Res. 8, 36–43. doi:10.1007/s40003-018-0343-5
De Freitas, S. T., and Mitcham, E. I. (2012). 3 factors involved in fruit calcium deficiency disorders. Horti. Rev. 4 (1), 107–146. doi:10.1002/9781118351871
Demir, E., Kaya, N., and Kaya, B. (2014). Genotoxic effects of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on root meristem cells of Allium cepa by comet assay. Turk J. Biol. 38 (1), 31–39. doi:10.3906/biy-1306-11
Dziergowska, K., and Michalak, I. (2022). “The role of nanoparticles in sustainable agriculture,” in Smart agrochem. For susta. Agricul, 225–278. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-817036-6.00007-8
Elbanna, H. M., Ahmed, O. K., Fayed, S. A. K., Hammam, K. A. M., and Yousef, R. S. (2024). Enhancing French basil growth through synergistic foliar treatment with copper nanoparticles and spirulina sp. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 512. doi:10.1186/s12870-024-05153-x
El-Batal, A. I., Ismail, M. A., Amin, M. A., El-Sayyad, G. S., and Osman, M. S. (2023). Selenium nanoparticles induce growth and physiological tolerance of wastewater stressed carrot plants. Biologia 78, 2339–2355. doi:10.1007/s11756-023-01401-x
Elkelish, A., Alqudah, A. M., Alammari, B. S., Alsubeie, M. S., Hamed, S. M., and Thabet, S. G. (2024). Exploring genetic determinants of silver oxide nanoparticle-induced seed priming for drought tolerance in wheat. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 72, 3203–3218. doi:10.1007/s10722-024-02138-5
El-Kereti, M. A., El-feky, S. A., Khater, M. S., Osman, Y. A., and El-sherbini, el-S. A. (2013). ZnOnanofertilizer and he Ne laser irradiation for promoting growth and yield of sweet basil plant. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 5 (3), 169–181. doi:10.2174/2212798405666131112142517
El-Saadony, M. T., Saad, A. M., Najjar, A. A., Alzahrani, S. O., Alkhatib, F. M., Shafi, M. E., et al. (2021). The use of biological selenium nanoparticles to suppress Triticum aestivum L. crown and root rot diseases induced by fusarium species and improve yield under drought and heat stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 28 (8), 4461–4471. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.04.043
El-Temsah, Y. S., and Joner, E. J. (2012). Impact of Fe and Ag nanoparticles on seed germination and differences in bioavailability during exposure in aqueous suspension and soil. Ecotoxicol 27 (1), 42–49. doi:10.1002/tox.20610
Faizan, M., Bhat, J. A., Chen, C., Alyemeni, M. N., Wijaya, L., Ahmad, P., et al. (2021). Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) induce salt tolerance by improving the antioxidant system and photosynthetic machinery in tomato. Pl. Phy. Bioche. 161, 122–130. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.02.002
Faraz, A., Faizan, M., Hayat, S., and Alam, P. (2022). Foliar application of copper oxide nanoparticles increases the photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant activity in Brassica juncea. J. Food Qual. 2022, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2022/5535100
Farooq, A., Javad, S., Jabeen, K., Shah, A. A., Ahmad, A., Shah, A. N., et al. (2023). Effect of calcium oxide, zinc oxide nanoparticles and their combined treatments on growth and yield attributes of Solanum lycopersicum L. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 35 (5), 102647. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2023.102647
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2020). The state of food and agriculture 2020: overcoming water challenges in agriculture [interactive web resource]. Available online at: https://www.fao.org/interactive/state-of-food-agriculture/2020/en/(Accessed June 29, 2025).
Francis, D. V., Abdalla, A. K., Mahakham, W., Sarmah, A. K., and Ahmed, Z. F. (2024). Interaction of plants and metal nanoparticles: exploring its molecular mechanisms for sustainable agriculture and crop improvement. Environ. Int. 190, 108859. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2024.108859
Francis, D. V., Sood, N., and Gokhale, T. (2020). Applications of metal nanoparticles in agriculture. Prog. Prosp. Nanosci. Today 157. Available online at: https://shorturl.at/wmYEl.
Frazier, T. P., Burklew, C. E., and Zhang, B. (2014). Titanium dioxide nanoparticles affect the growth and microRNA expression of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Funct. Integr. Genom 14, 75–83. doi:10.1007/s10142-013-0341-4
Freire, B. M., Lange, C. N., Cavalcanti, Y. T., Monteiro, L. R., Pieretti, J. C., Seabra, A. B., et al. (2024). The dual effect of selenium nanoparticles in rice seedlings: from increasing antioxidant activity to inducing oxidative stress. Plant Stress 11, 100372. doi:10.1016/j.stress.2024.100372
Geisler-Lee, J., Brooks, M., Gerfen, J. R., Wang, Q., Fotis, C., Sparer, A., et al. (2014). Reproductive toxicity and life history study of silver nanoparticle effect, uptake and transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nanomate 4 (2), 301–318. doi:10.3390/nano4020301
Ghooshchi, F., and Lotfi, M. (2015). Impact of titanium on growth and forage production of maize (zea Mays L.) under different growth stage. J. Crop Nutr. Sci. 1, 3–4. Available online at: https://oiccpress.com/jcns/article/view/5825.
Ghosh, M., Bandyopadhyay, M., and Mukherjee, A. (2010). Genotoxicity of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles at two trophic levels: plant and human lymphocytes. Chemosphere 81 (10), 1253–1262. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.022
Ghosh, T., Yadav, S. K., Choudhary, R., Rao, D., Sushma, M. K., Mandal, A., et al. (2024). Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticle-based seed priming for enhancing seed vigour and physio-biochemical quality of tomato seedlings under salinity stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 71, 38. doi:10.1134/S1021443723603609
Ghouri, F., Sarwar, S., Sun, L., Riaz, M., Haider, F. U., Ashraf, H., et al. (2024). Silicon and iron nanoparticles protect rice against lead (pb) stress by improving oxidative tolerance and minimizing Pb uptake. Sci. Rep. 14, 5986. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-55810-2
Grudniak, A., Folcik, J., Szmytke, J., and Sentkowska, A. (2025). Mechanism of antioxidant activity of selenium nanoparticles obtained by green and chemical synthesis. Int. J. Nanomed 20, 2797–2811. doi:10.2147/IJN.S507712
Grusak, M. A. (2001). “Plant macro-And micronutrient minerals,” in Encyclopedia of life sciences (London, UK: Nature Publishing Group). doi:10.1038/npg.els.0001306
Gruyer, N., Dorais, M., Bastien, C., Dassylva, N., and Triffault-Bouchet, G. (2013). Interaction between silver nanoparticles and plant growth. Acta Hortic. 1037, 795–800. doi:10.17660/ActaHortic.2014.1037.105
Gupta, A., Bharati, R., Kubes, J., Popelkova, D., Praus, L., Yang, X., et al. (2024a). Zinc oxide nanoparticles application alleviates salinity stress by modulating plant growth, biochemical attributes and nutrient homeostasis in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1432258. doi:10.3389/fpls.2024.1432258
Gupta, A., Bharati, R., Kubes, J., Vachova, P., Popelkova, D., Mahawar, L., et al. (2024b). Ferric oxide nano-priming enhances photosynthetic and physicochemical properties of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) microgreens. Pl, Soil Enviro. 70 (11), 702–711. doi:10.17221/272/2024-PSE
Hafeez, A., Razzaq, A., Mahmood, T., and Jhanzab, H. M. (2015). Potential of copper nanoparticles to increase growth and yield of wheat. J. Nanosci. Adv. Technol. 1 (1), 6–11. doi:10.24218/jnat.2015.02
Hafez, E. M., Osman, H. S., Gowayed, S. M., Okasha, S. A., Omara, A. E.-D., Sami, R., et al. (2021). Minimizing the adversely impacts of water deficit and soil salinity on maize growth and productivity in response to the application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and silica nanoparticles. Agronomy 11 (4), 676. doi:10.3390/agronomy11040676
Haggag, W. M., Abouziena, H. F., Abd-El-Kreem, F., and El Habbasha, S. (2015). Agriculture biotechnology for management of multiple biotic and abiotic environmental stress in crops. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 7 (10), 882–889.
Hasanuzzaman, M., Raihan, M. R. H., Siddika, A., Bardhan, K., Hosen, M. S., and Prasad, P. V. (2024). Selenium and its nanoparticles modulate the metabolism of reactive oxygen species and morpho-physiology of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to combat oxidative stress under water deficit conditions. BMC Plant Biol. 24 (1), 578. doi:10.1186/s12870-024-05282-3
Hojjat, S. S., and Ganjali, A. (2016). The effect of silver nanoparticles on lentil seed germination under drought stress. Int. J. Farm Allied. Sci. 5 (3), 208–212. Available online at: http://ijfas.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/03/208-212.pdf.
Hojjat, S. S., and Kamyab, M. (2017). The effect of silver nanoparticle on fenugreek seed germination under salinity levels. Russ. Agric. Sci. 43, 61–65. doi:10.3103/S1068367417010189
Hooven, L. A., Chakrabarti, P., Harper, B. J., Sagili, R. R., and Harper, S. L. (2019). Potential risk to pollinators from nanotechnology-based pesticides. Molecules 24 (24), 4458. doi:10.3390/molecules24244458
Hu, J., Wu, X., Wu, F., Chen, W., White, J. C., Yang, Y., et al. (2020). Potential application of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to improve the nutritional quality of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.). J. Hazard. Mat. 389, 121837. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121837
Hussan, M. U., Hussain, S., Hafeez, M. B., Ahmed, S., Hassan, M. U., Jabeen, S., et al. (2024). Comparative role of calcium oxide nanoparticles and calcium bulk fertilizer to alleviate cadmium toxicity by modulating oxidative stress, photosynthetic performance and antioxidant-defense genes expression in alfalfa. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 215, 109002. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.109002
Ingle, A. P., Duran, N., and Rai, M. (2014). Bioactivity, mechanism of action, and cytotoxicity of copper-based nanoparticles: a review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 1001–1009. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5422-8
Iqbal, M., Raja, N. I., Mashwani, Z. U. R., Hussain, M., Ejaz, M., and Yasmeen, F. (2019). Effect of silver nanoparticles on growth of wheat under heat stress. Iran. Jo. Sci. Technol., Trans. A Sci. 43, 387–395. doi:10.1007/s40995-017-0417-4
Iqbal, Z., Javad, S., Naz, S., Shah, A. A., Shah, A. N., Paray, B. A., et al. (2017). Elicitation of the in vitro cultures of selected varieties of Vigna radiata L. with zinc oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles for enhanced phytochemicals production. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 908532. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.908532
Irshad, M. A., Nawaz, R., Ur Rehman, M. Z., Adrees, M., Rizwan, M., Ali, S., et al. (2021b). Synthesis, characterization and advanced sustainable applications of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. safe 212, 111978. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111978
Irshad, M. A., Rehman, M. Z., Anwar-ul-Haq, M., Rizwan, M., Nawaz, R., Shakoor, M. B., et al. (2021a). Effect of green and chemically synthesized titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cadmium accumulation in wheat grains and potential dietary health risk: a field investigation. J. Hazard. Mat. 415, 125585. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125585
Jahagirdar, A. S., Shende, S., Gade, A., and Rai, M. (2020). Bioinspired synthesis of copper nanoparticles and its efficacy on seed viability and seedling growth in mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). Curr. Nanosci. 16 (2), 246–252. doi:10.2174/1573413715666190325170054
Jalali, M., Ghanati, F., Modarres-Sanavi, A. M., and Khoshgoftarmanesh, A. H. (2017). Physiological effects of repeated foliar application of magnetite nanoparticles on maize plants. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 203 (6), 593–602. doi:10.1111/jac.12208
Jalil, S. U., Zahera, M., Khan, M. S., and Ansari, M. I. (2019). Biochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles from leaf protein of Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. xanthi and their physiological, developmental, and ROS scavenging responses on tobacco plant under stress conditions. IET nanobiotechnology 13 (1), 23–29. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5148
Jamal, A., Khan, M. I., Tariq, M., and Fawad, M. (2018). Response of mung bean crop to different levels of applied iron and zinc. Hortic. Plant J. 3 (13), 13–22. doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/JHPR.3.13
Jasim, B., Thomas, R., Mathew, J., and Radhakrishnan, E. K. (2017). Plant growth and diosgenin enhancement effect of silver nanoparticles in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Saudi Pharma. Jo. 25 (3), 443–447. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2016.09.012
Jeyasubramanian, K., Thoppey, U. U. G., Hikku, G. S., Selvakumar, N., Subramania, A., and Krishnamoorthy, K. (2016). Enhancement in growth rate and productivity of spinach grown in hydroponics with iron oxide nanoparticles. Roy. Soc. Chem. Adv. 6 (19), 15451–15459. doi:10.1039/C5RA23425E
Jha, S., and Pudake, R. N. (2016). “Molecular mechanism of plant–nanoparticle interactions,” in Plant nanotechnology. Editors C. Kole, D. Kumar, and M. Khodakovskaya (Cham: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-42154-4_7
Kale, S. K., Parishwad, G. V., and Patil, A. S. (2021). Emerging agriculture applications of silver nanoparticles. ES Food &Agrofor 3, 17–22. doi:10.30919/esfaf438
Kaningini, A. G., Nelwamondo, A. M., Azizi, S., Maaza, M., and Mohale, K. C. (2022). Metal nanoparticles in agriculture: a review of possible use. Coat 12 (10), 1586. doi:10.3390/coatings12101586
Kannan, M., Elango, K., Tamilnayagan, T., Preetha, S., and Kasivelu, G. (2020). “Impact of nanomaterials on beneficial insects in agricultural ecosystems,” in Nanotechnology for food, agriculture, and environment. Nanotechnology in the life sciences. Editors D. Thangadurai, J. Sangeetha, and R. Prasad (Cham: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-3-030-31938-0_16
Kasana, R. C., Panwar, N. R., Kaul, R. K., and Kumar, P. (2017). Biosynthesis and effects of copper nanoparticles on plants. Environ. Chem. Lett. 15, 233–240. doi:10.1007/s10311-017-0615-5
Kathiravan, M., Vanitha, C., Umarani, R., Marimuthu, S., Ayyadurai, P., Sathiya, K., et al. (2024). Seed priming with biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles for enhancing seed germination and vigour through promoting antioxidant and hydrolytic enzyme activity in green gram (Vigna radiata). Agric. Res., 1–13. doi:10.1007/s40003-024-00792-w
Katiyar, P., Yadu, B., Korram, J., Satnami, M. L., Kumar, M., and Keshavkant, S. (2020). Titanium nanoparticles attenuate arsenic toxicity by up-regulating expressions of defensive genes in Vigna radiata L. J. Environ. Sci. Stud. 92, 18–27. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2020.02.013
Kaveh, R., Li, Y. S., Ranjbar, S., Tehrani, R., Brueck, C. L., and Van Aken, B. (2013). Changes in Arabidopsis thaliana gene expression in response to silver nanoparticles and silver ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 (18), 10637–10644. doi:10.1021/es402209w
Ke, M., Li, Y., Qu, Q., Ye, Y., Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M., Zhang, Z., et al. (2020). Offspring toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana flowering and floral development. J. Hazard. Mat. 386, 121975. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121975
Khan, I., Awan, S. A., Rizwan, M., Hassan, Z. U., Akram, M. A., Tariq, R., et al. (2022). Nanoparticles uptake and translocation mechanisms in plants via seed priming, foliar treatment, and root exposure: a review. Enviro. Sci. and Pol. Res. 29 (60), 89823–89833. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-23945-2
Khan, M., and Siddiqui, Z. A. (2018). Zinc oxide nanoparticles for the management of Ralstonia solanacearum, Phomopsis vexans and Meloidogyne incognita incited disease complex of eggplant. Indian Phytopathol. Soc. 71, 355–364. doi:10.1007/s42360-018-0064-5
Khan, S., Dayal, A., Thomas, N., and Shukla, P. K. (2023). Effect of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles on the storability of onion (Allium cepa L.) seeds under ambient condition. Environ. Conserv. J. 24 (2), 1–15. doi:10.36953/ECJ.15132471
Khater, M. S. (2015). Effect of titanium nanoparticles (TiO2) on growth, yield and chemical constituents of coriander plants. J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 48 (4), 187–194.
Kim, S. W., Jung, J. H., Lamsal, K., Kim, Y. S., Min, J. S., and Lee, Y. S. (2012). Antifungal effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) against various plant pathogenic fungi. Mycobiol 40 (1), 53–58. doi:10.5941/MYCO.2012.40.1.053
Krishnasamy, R., Natesh, R., and Obbineni, J. M. (2024). Efficient ros scavenging improves the growth and yield in Black gram (Vigna mungo (L.) hepper) after seed priming and treatment using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles with Pongamia pinnata (L.) pierre leaf extract. J. Plant Growth Regul. 43, 2422–2438. doi:10.1007/s00344-024-11276-0
Kumar, R., Dadhich, A., Dhiman, M., Sharma, L., and Sharma, M. M. (2024). Stimulatory effect of ZnO nanoparticles as a nanofertilizer in seed priming of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) and their bioactivity studies. S. Afr. J. Bot. 165, 30–38. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2023.12.001
Kumari, A., Gupta, A. K., Sharma, S., Jadon, V. S., Sharma, V., Chun, S. C., et al. (2024). Nanoparticles as a tool for alleviating plant stress: mechanisms, implications, and challenges. Plants 13 (11), 1528. doi:10.3390/plants13111528
Kumari, M., Mukherjee, A., and Chandrasekaran, N. (2009). Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa. Sci. Total Environ. 407 (19), 5243–5246. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.06.024
Kushwah, K. S., and Patel, S. (2020). Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) on faba bean (Vicia faba L.) and induced asynaptic mutation: a meiotic study. J. Plant Growth Regul. 39, 1107–1118. doi:10.1007/s00344-019-10046-7
Laware, S. L., and Raskar, S. (2014). Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on hydrolytic and antioxidant enzymes during seed germination in onion. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 3 (7), 749–760.
Lawlor, D. W., Mengel, K., and Kirkby, E. A. (2004). Principles of plant nutrition. Ann. Bot. 93 (4), 479–480. doi:10.1093/aob/mch063
Lee, W. M., An, Y. J., Yoon, H., and Kweon, H. S. (2008). Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (triticum Aestivum): plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 27 (9), 1915–1921. doi:10.1897/07-481.1
Lei, C., Sun, Y., Tsang, D. C., and Lin, D. (2018). Environmental transformations and ecological effects of iron-based nanoparticles. Enviro. Pol. 232, 10–30. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.052
Le Van, N., Ma, C., Shang, J., Rui, Y., Liu, S., and Xing, B. (2016). Effects of CuO nanoparticles on insecticidal activity and phytotoxicity in conventional and transgenic cotton. Chemosphere 144, 661–670. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.028
Li, J., Chang, P. R., Huang, J., Wang, Y., Yuan, H., and Ren, H. (2013). Physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles towards watermelon. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 13 (8), 5561–5567. doi:10.1166/jnn.2013.7533
Li, J., Hu, J., Ma, C., Wang, Y., Wu, C., Huang, J., et al. (2016). Uptake, translocation and physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles in corn (zea Mays L.). Chemosphere 159, 326–334. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.083
Lopez-Lima, D., Mtz-Enriquez, A. I., Carrión, G., Basurto-Cereceda, S., and Pariona, N. (2021). The bifunctional role of copper nanoparticles in tomato: effective treatment for fusarium wilt and plant growth promoter. Sci. Hortic. 277, 109810. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109810
López-Vargas, E. R., Ortega-Ortíz, H., Cadenas-Pliego, G., de Alba Romenus, K., Cabrera de la Fuente, M., Benavides-Mendoza, A., et al. (2018). Foliar application of copper nanoparticles increases the fruit quality and the content of bioactive compounds in tomatoes. Appli. Sci. 8 (7), 1020. doi:10.3390/app8071020
Mahawar, L., Živčák, M., Barboricova, M., Kovár, M., Filaček, A., Ferencova, J., et al. (2024). Effect of copper oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles on photosynthesis and physiology of Raphanus sativus L. under salinity stress. Plant Physiol. biochem. 206, 108281. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108281
Maity, A., Natarajan, N., Pastor, M., Vijay, D., Gupta, C. K., and Wasnik, V. K. (2018). Nanoparticles influence seed germination traits and seed pathogen infection rate in forage sorghum (Sorghum bicolour) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). J. Environ. Biol. 56 (06), 363–372.
Malandrakis, A. A., Kavroulakis, N., and Chrysikopoulos, C. V. (2019). Use of copper, silver and zinc nanoparticles against foliar and soil-borne plant pathogens. Sci. Total Environ. 670, 292–299. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.210
Mathew, S. S., Sunny, N. E., and Shanmugam, V. (2021). Green synthesis of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Cuminum cyminum seed extract; effect on mung bean (Vigna radiata) seed germination. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 126, 108485. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2021.108485
Mawale, K. S., and Giridhar, P. (2024). Green approaches for the synthesis of silver nanoparticle and its augmentation in seed. Germination, growth, and antioxidant level in Capsicum annuum L. Plant Nano Biol. 10, 100107. doi:10.1016/j.plana.2024.100107
Mazhar, M. W., Ishtiaq, M., Maqbool, M., Ajaib, M., Hussain, I., Hussain, T., et al. (2023). Synergistic application of calcium oxide nanoparticles and farmyard manure induces cadmium tolerance in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) by influencing physiological and biochemical parameters. PLoS One 18 (3), e0282531. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282531
Mazhar, M. W., Ishtiaq, M., Maqbool, M., Muzammil, K., Mohieldin, A., Dawria, A., et al. (2024). Optimizing water relations, gas exchange parameters, biochemical attributes and yield of water-stressed maize plants through seed priming with iron oxide nanoparticles. BMC Pl. Biol. 24 (1), 624. doi:10.1186/s12870-024-05324-w
Mehmood, A. (2018). Brief overview of the application of silver nanoparticles to improve growth of crop plants. IET nanobiotechnol 12 (6), 701–705. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0273
Mehta, P., Srivastava, C. M., Arora, R. S., and Sharma, A. K. (2016). Impact assessment of silver nanoparticles on plant growth and soil bacterial diversity. 3 Biotech. 6, 1–10. doi:10.1007/s13205-016-0567-7
Meraj, T. A., Fu, J., Raza, M. A., Zhu, C., Shen, Q., Xu, D., et al. (2020). Transcriptional factors regulate plant stress responses through mediating secondary metabolism. Genes. 11 (4), 346. doi:10.3390/genes11040346
Mikhailova, E. O. (2020). Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of action and probable bio-application. J. Funct. Biomater. 11 (4), 84. doi:10.3390/jfb11040084
Mirzajani, F., Askari, H., Hamzelou, S., Farzaneh, M., and Ghassempour, A. (2013). Effect of silver nanoparticles on Oryza sativa L. and its rhizosphere bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 88, 48–54. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.10.018
Mogazy, A. M., Mohamed, H. I., and El-Mahdy, O. M. (2022). Calcium and iron nanoparticles: a positive modulator of innate immune responses in strawberry against botrytis Cinerea. Process Biochem. 115, 128–145. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2022.02.014
Mu, C., Huang, D., Wang, M., Li, Y., Wang, X., Si, D., et al. (2024). Seed priming with silver ions improves growth and physicochemical features of rice plants (Oryza sativa L.) under copper stress. Agric. Sci. Technol. 4 (7), 711–722. doi:10.1021/acsagscitech.4c00177
Musante, C., and White, J. C. (2012). Toxicity of silver and copper to cucurbitapepo: differential effects of nano and bulk-size particles. Environ. Toxicol. 27 (9), 510–517. doi:10.1002/tox.20667
Mustafa, N., Raja, N. I., Ilyas, N., Abasi, F., Ahmad, M. S., Ehsan, M., et al. (2022). Exogenous application of green titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) to improve the germination, physiochemical, and yield parameters of wheat plants under salinity stress. Molecul 27 (15), 4884. doi:10.3390/molecules27154884
Nair, R. (2016). “Effects of nanoparticles on plant growth and development,” in Plant nanotechnol. Editors C. Kole, D. Kumar, and M. Khodakovskaya (Cham: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-42154-4_5
Ndeh, N. T., Maensiri, S., and Maensiri, D. (2017). Advances in natural sciences: nanoscience and nanotechnology. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8 (3), 035008. doi:10.1088/2043-6254/aa724a
Nile, S. H., Thiruvengadam, M., Wang, Y., Samynathan, R., Shariati, M. A., Rebezov, M., et al. (2022). Nano-priming as emerging seed priming technology for sustainable Agriculture—Recent developments and future perspectives. J. Nanobiotechnol. 20 (1), 254. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01423-8
Obomighie, I., Prentice, I. J., Lewin-Jones, P., Bachtiger, F., Ramsay, N., Kishi-Itakura, C., et al. (2025). Understanding pectin cross-linking in plant cell walls. Commun. Biol. 8 (1), 72. doi:10.1038/s42003-025-07495-0
Olkhovych, O., Volkogon, M., Taran, N., Batsmanova, L., and Kravchenko, I. (2016). The effect of copper and zinc nanoparticles on the growth parameters, contents of ascorbic acid, and qualitative composition of amino acids and acylcarnitines in pistia Stratiotes L. (araceae). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 218–219. doi:10.1186/s11671-016-1422-9
Palchoudhury, S., Jungjohann, K. L., Weerasena, L., Arabshahi, A., Gharge, U., Albattah, A., et al. (2018). Enhanced legume root growth with pre-soaking in α-Fe2O3 nanoparticle fertilizer. Roy. Soc. Chem. Adv. 8 (43), 24075–24083. doi:10.1039/C8RA04680H
Pallavi, C., Joseph, B., Aariff Khan, M. A., and Hemalatha, S. (2016). Effect of integrated nutrient management on nutrient uptake, soil available nutrients and productivity of rainfed finger millet. Inter. J. Sci. Environ. Techno. 5 (5), 2798–2813.
Panda, S. (2017). Physiological impact of zinc nanoparticle on germination of rice (Oryza sativa L) seed. J. Plant Sci. Phytopathol. 1, 062–070. doi:10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001008
Pandey, C., Khan, E., Mishra, A., Sardar, M., and Gupta, M. (2014). Silver nanoparticles and its effect on seed germination and physiology in Brassica juncea L. (Indian mustard) plant. Adv. Sci. Lett. 20 (7-8), 1673–1676. doi:10.1166/asl.2014.5518
Paulami, D. A. M., Paret, M. L., Mondal, R., and Mandal, A. K. (2023). Advancement of noble metallic nanoparticles in agriculture: a promising future. Pedosphere 33 (1), 116–128. doi:10.1016/j.pedsph.2022.06.026
Pawar, V. A., Ambekar, J. D., Kale, B. B., Apte, S. K., and Laware, S. L. (2019). Response in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) seedling growth to seed priming with iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Biosci. 14, 82–91. doi:10.12692/ijb/14.3.82-91
Pérez-Velasco, E. A., Valdez-Aguilar, L. A., Betancourt-Galindo, R., Martínez-Juárez, J., Lozano-Morales, S. A., and González-Fuentes, J. A. (2021). Gas exchange parameters, fruit yield, quality, and nutrient status in tomato are stimulated by ZnO nanoparticles of modified surface and morphology and their application form. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 21, 991–1003. doi:10.1007/s42729-021-00416-0
Peshkova, A., Zinicovscaia, I., Cepoi, L., Rudi, L., Chiriac, T., Yushin, N., et al. (2024). Effects of gold nanoparticles on Mentha spicata L., soil microbiota, and human health risks: impact of exposure routes. Nanomaterials 14 (11), 955. doi:10.3390/nano14110955
Peshkova, A., Zinicovscaia, I., Rudi, L., Chiriac, T., Yushin, N., and Cepoi, L. (2025). Effects of foliar application of copper and gold nanoparticles on Petroselinum crispum (mill.). Nanomaterials 15 (4), 280. doi:10.3390/nano15040280
Prasad, T. N., Sudhakar, P., Sreenivasulu, Y., Latha, P., Munaswamy, V., Reddy, K. R., et al. (2012). Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J. Plant Nutr. 35 (6), 905–927. doi:10.1080/01904167.2012.663443
Rai, M., Ingle, A. P., Pandit, R., Paralikar, P., Shende, S., Gupta, I., et al. (2018). Copper and copper nanoparticles: role in management of insect-pests and pathogenic microbes. Nanotechnol. Rev. 7 (4), 303–315. doi:10.1515/ntrev-2018-0031
Raj, P., Ghosh, A., Jadav, S. K., Patra, H., Panotra, N., Sharma, V., et al. (2024). Nanomaterials for sustainable soil remediation and contaminant immobilization. Asian J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 10 (4), 684–697. doi:10.9734/ajsspn/2024/v10i4439
Rajput, V. D., Minkina, T., Suskova, S., Mandzhieva, S., Tsitsuashvili, V., Chapligin, V., et al. (2018). Effects of copper nanoparticles (cuO NPs) on crop plants: a mini review. BioNanoSci 8, 36–42. doi:10.1007/s12668-017-0466-3
Raliya, R., Nair, R., Chavalmane, S., Wang, W., and Biswas, P. (2015). Mechanistic evaluation of translocation and physiological impact of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles on the tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plant. Metallomi 7 (12), 1584–1594. doi:10.1039/c5mt00168d
Rameen, S., Manaf, A., Bibi, Y., Jhanzab, H. M., Sher, A., Ali, N., et al. (2024). Foliar application of silver (Ag-NPs) and copper (Cu-NPs) nanoparticles enhances phenotypic traits and oil quality in Brassica napus L. Sci. Rep. 14, 27618. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-79269-3
Rameshraddy, G. J., Reddy, R. B. H., Salimath, M., Geetha, K. N., and Shankar, A. G. (2017). Zinc oxide nanoparticles increase zn uptake, translocation in rice with positive effect on growth, yield and moisture stress tolerance. Ind. Jo. Pl. Physiol. 22, 287–294. doi:10.1007/s40502-017-0303-2
Raza, H. Z., Shah, A. A., Noreen, Z., Usman, S., Zafar, S., Yasin, N. A., et al. (2024). Calcium oxide nanoparticles mitigate lead stress in Abelmoschus esculentus though improving the key antioxidative enzymes, nutritional content and modulation of stress markers. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 206, 108171. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.108171
Razavizadeh, R., Adabavazeh, F., and Mosayebi, Z. (2023). Titanium dioxide nanoparticles improve element uptake, antioxidant properties, and essential oil productivity of Melissa officinalis L. seedlings under in vitro drought stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 98020–98033. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29384-x
Rengel, Z., Batten, G. D., and Crowley, D. D. (1999). Agronomic approaches for improving the micronutrient density in edible portions of field crops. Field Crops Res. 60 (1-2), 27–40. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00131-2
Rossi, L., Fedenia, L. N., Sharifan, H., Ma, X., and Lombardini, L. (2019). Effects of foliar application of zinc sulfate and zinc nanoparticles in coffee (coffea Arabica L.) plants. Pl. Physiolo. Biochem. 135, 160–166. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.12.005
Ruffini Castiglione, M., Giorgetti, L., Geri, C., and &Cremonini, R. (2011). The effects of nano-TiO 2 on seed germination, development and mitosis of root tip cells of Vicia narbonensis L. and zea Mays L. J. Nanopart. Res 13, 2443–2449. doi:10.1007/s11051-010-0135-8
Rui, M., Ma, C., Hao, Y., Guo, J., Rui, Y., Tang, X., et al. (2016). Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea). Front. Plant Sci. 7, 815. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00815
Rui, M., Ma, C., White, J. C., Hao, Y., Wang, Y., Tang, X., et al. (2018). Metal oxide nanoparticles alter peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) physiological response and reduce nutritional quality: a life cycle study. Environ. Sci. Nano 5 (9), 2088–2102. doi:10.1039/C8EN00436F
Sabir, S., Arshad, M., and Chaudhari, S. K. (2014). Zinc oxide nanoparticles for revolutionizing agriculture: synthesis and applications. Sci. Wor. J. 1, 1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/925494
Salama, H. M. H. (2012). Effects of silver nanoparticles in some crop plants, common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and corn (zea Mays L.). Int. Res. J. Biotechnol. 3 (10), 190–197. Available online at: https://www.interesjournals.org/articles/effects-of-silver-nanoparticles-in-some-crop-plants-common-bean-phaseolus-vulgaris-l-and-corn--zea-mays-l.pdf#page=2.80.
Salmen, S. H., and Alharbi, S. A. (2024). Mitigating Pb-induced oxidative stress in rice plants by cerium oxide and iron oxide nanoparticles. S Afr. J. Bot. 172, 544–555. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2024.07.039
Sarkhosh, S., Kahrizi, D., Darvishi, E., Tourang, M., Haghighi-Mood, S., Vahedi, P., et al. (2022). Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) on seed germination characteristics in two Brassicaceae family species: camelina sativa and Brassica napus L. J. Nanomater. 1, 1892759. doi:10.1155/2022/1892759
Sarmast, M. K., and Salehi, H. (2016). Silver nanoparticles: an influential element in plant nanobiotechnology. Mol. Biotechnol. 58, 441–449. doi:10.1007/s12033-016-9943-0
Šebesta, M., Kolenčík, M., Sunil, B. R., Illa, R., Mosnáček, J., Ingle, A. P., et al. (2021). Field application of ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles on agricultural plants. Agronomy 11 (11), 2281. doi:10.3390/agronomy11112281
Seif Sahandi, M., Sorooshzadeh, A., Rezazadeh, S., and Naghdibadi, H. A. (2011). Effect of nano silver and silver nitrate on seed yield of borage. J. Med. Plant Res. 5 (2), 171–175.
Sentkowska, A., Konarska, J., Szmytke, J., and Grudniak, A. (2024). Herbal polyphenols as selenium reducers in the green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles: antibacterial and antioxidant capabilities of the obtained SeNPs. Molecules 29 (8), 1686. doi:10.3390/molecules29081686
Shah, T., Latif, S., Saeed, F., Ali, I., Ullah, S., Alsahli, A. A., et al. (2021). Seed priming with titanium dioxide nanoparticles enhances seed vigor, leaf water status, and antioxidant enzyme activities in maize (zea Mays L.) under salinity stress. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 33 (1), 101207. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2020.10.004
Shahzad, R., Koerniati, S., Harlina, P. W., Hastilestari, B. R., Djalovic, I., and Prasad, P. V. (2025). Iron oxide nanoparticles enhance alkaline stress resilience in bell pepper by modulating photosynthetic capacity, membrane integrity, carbohydrate metabolism, and cellular antioxidant defense. BMC Plant Biol. 25 (1), 170. doi:10.1186/s12870-025-06180-y
Sharma, N. K., Vishwakarma, J., Rai, S., Alomar, T. S., AlMasoud, N., and Bhattarai, A. (2022). Green route synthesis and characterization techniques of silver nanoparticles and their biological adeptness. ACS omega 7 (31), 27004–27020. doi:10.1021/acsomega.2c01400
Sharma, P., Bhatt, D., Zaidi, M. G. H., Saradhi, P. P., Khanna, P. K., and Arora, S. (2012). Silver nanoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 167, 2225–2233. doi:10.1007/s12010-012-9759-8
Shelar, A., Nile, S. H., Singh, A. V., Rothenstein, D., Bill, J., Xiao, J., et al. (2023). Recent advances in nano-enabled seed treatment strategies for sustainable agriculture: challenges, risk assessment, and future perspectives. Nano-Micro Lett. 15 (1), 54. doi:10.1007/s40820-023-01025-5
Siddiqi, K. S., and Husen, A. (2016). Engineered gold nanoparticles and plant adaptation potential. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 400. doi:10.1186/s11671-016-1607-2
Sillen, W. M., Thijs, S., Abbamondi, G. R., Janssen, J., Weyens, N., White, J. C., et al. (2015). Effects of silver nanoparticles on soil microorganisms and maize biomass are linked in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol. biochem. 91, 14–22. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.019
Singh, D., Sillu, D., Kumar, A., and Agnihotri, S. (2021). Dual nanozyme characteristics of iron oxide nanoparticles alleviate salinity stress and promote the growth of an agroforestry tree, Eucalyptus tereticornis Sm. Environ. Sci. Nano 8 (5), 1308–1325. doi:10.1039/D1EN00040C
Sohail, L., Ferrari, E., Stierhof, Y. D., Kemmerling, B., and Mashwani, Z. U. R. (2022). Molecular effects of biogenic zinc nanoparticles on the growth and development of Brassica napus L. revealed by proteomics and transcriptomics. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 798751. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.798751
Soliman, A. S., Hassan, M., Abou-Elell, F., Ahmed, A. H., and El-Feky, S. A. (2016). Effect of nano and molecular phosphorus fertilizers on growth and chemical composition of baobab (Adansonia digitata L.). J. Plant Sci. 11, 52–60. doi:10.3923/jps.2016.52.60
Sonawane, H., Arya, S., Math, S., and Shelke, D. (2021). Myco-synthesized silver and titanium oxide nanoparticles as seed priming agents to promote seed germination and seedling growth of solanum Lycopersicum: a comparative study. Internat. Nano Lett. 11 (4), 371–379. doi:10.1007/s40089-021-00346-w
Sosan, A., Svistunenko, D., Straltsova, D., Tsiurkina, K., Smolich, I., Lawson, T., et al. (2016). Engineered silver nanoparticles are sensed at the plasma membrane and dramatically modify the physiology of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The pla. Jo 85 (2), 245–257. doi:10.1111/tpj.13105
Srivastava, G., Das, A., Kusurkar, T. S., Roy, M., Airan, S., Sharma, R. K., et al. (2014a). Iron pyrite, a potential photovoltaic material, increases plant biomass upon seed pretreatment. Mate. Exp. 4 (1), 23–31. doi:10.1166/mex.2014.1139
Srivastava, G., Das, C. K., Das, A., Singh, S. K., Roy, M., Kim, H., et al. (2014b). Seed treatment with iron pyrite (FeS2) nanoparticles increases the production of spinach. Roy. Soc. Che. Adv. 4 (102), 58495–58504. doi:10.1039/C4RA06861K
Stałanowska, K., Railean, V., Pomastowski, P., Pszczółkowska, A., Okorski, A., and Lahuta, L. B. (2024). Seeds priming with bio-silver nanoparticles protects pea (pisum Sativum L.) seedlings against selected fungal pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (21), 11402. doi:10.3390/ijms252111402
Stampoulis, D., Sinha, S. K., and White, J. C. (2009). Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nanoparticles to plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43 (24), 9473–9479. doi:10.1021/es901695c
Sturikova, H., Krystofova, O., Huska, D., and Adam, V. (2018). Zinc, zinc nanoparticles and plants. J. Hazard. Mat. 349, 101–110. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.040
Sun, J., Wang, L., Li, S., Yin, L., Huang, J., and Chen, C. (2017). Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to arabidopsis: inhibition of root gravitropism by interfering with auxin pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 36 (10), 2773–2780. doi:10.1002/etc.3833
Sun, Y., Mfarrej, M. F. B., Song, X., Ma, J., Min, B., and Chen, F. (2023). New insights in to the ameliorative effects of zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles to arsenic stressed spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Plant Physiol. biochem. 199, 107715. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107715
Tamil Elakkiya, V., Meenakshi, R. V., Senthil Kumar, P., Karthik, V., Ravi Shankar, K., Sureshkumar, P., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Sesbania aculeata to enhance the plant growth and antimicrobial activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1313–1322. doi:10.1007/s13762-021-03182-9
Uddin, A. F. M. J., Rakibuzzaman, M., Sabim, M. R., Singh, K., and Mahbuba, S. (2022). Foliar application of copper nanoparticles on growth and yield of chili. Int. J. Bus. Soc. Sci. Res. 10 (1), 18–23.
United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) (2022). The sustainable development goals report 2022. New York: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Available online at: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/(Accessed: 29 June 2025).
Upadhyaya, H., Begum, L., Dey, B., Nath, P. K., and Panda, S. K. (2017). Impact of calcium phosphate nanoparticles on rice plant. J. Plant Sci. Phytopathol. 1 (1), 001–010. doi:10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001001
Upadhyaya, H., Shome, S., Tewari, S., Bhattacharya, M. K., and Panda, S. K. (2020). Responses to ZnO nanoparticles during water stress in Oryza sativa L. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 16 (2), 67–74. Available online at: https://tinyurl.com/562acv9r.
Valadkhan, M., Mohammadi, K., and Nezhad, M. K. (2015). Effect of priming and foliar application of nanoparticles on agronomic traits of chickpea. Biol. Forum. 7 (2), 599–602. Available online at: https://www.researchtrend.net/bfij/pdf/97%20KHOSRO%20MOHAMMADI.pdf.
Vannini, C., Domingo, G., Onelli, E., Prinsi, B., Marsoni, M., Espen, L., et al. (2013). Morphological and proteomic responses of Eruca sativa exposed to silver nanoparticles or silver nitrate. PloS one 8 (7), e68752. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068752
Vázquez-Núñez, E., López-Moreno, M. L., de la Rosa Álvarez, G., and Fernández-Luqueño, F. (2018). Incorporation of nanoparticles into plant nutrients: the real benefits. Agric. nanobiotechnology Mod. Agricul. Sust. Fut., 49–76. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-96719-6_4
Venzhik, Y., Sokolov, A., Sokolov, O., Moshkov, I., and Dykman, L. (2022). “Effects, uptake, and translocation of Au-based nanoparticles in plant,” in Toxicity of nanoparticles in plants, 241–265. doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-90774-3.00016-7
Viana, T. A., Xavier, T. K. D., Barbosa, W. F., do Carmo Cesário, C., Bastos, D. S. S., Bernardes, R. C., et al. (2025). Physiological and behavioral effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticle exposure on stingless bee foragers. J. Hazard Mater 488. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137315
Vijai Anand, K., Reshma, M., Kannan, M., Muthamil Selvan, S., Chaturvedi, S., Shalan, A. E., et al. (2021). Preparation and characterization of calcium oxide nanoparticles from marine molluscan shell waste as nutrient source for plant growth. J. Nanostruc. Chem. 11, 409–422. doi:10.1007/s40097-020-00376-4
Vishwakarma, K., Shweta, , Upadhyay, N., Singh, J., Liu, S., Singh, V. P., et al. (2017). Differential phytotoxic impact of plant mediated silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) on Brassica sp. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 1501. doi:10.3389/fpls.2017.01501
Wang, C., Song, F., Wang, X. L., and Wang, Y. Z. (2022a). A cellulose nanocrystal templating approach to synthesize size-controlled gold nanoparticles with high catalytic activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 209, 464–471. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.046
Wang, Y., Dimkpa, C., Deng, C., Elmer, W. H., Gardea-Torresdey, J., and White, J. C. (2022b). Impact of engineered nanomaterials on rice (Oryza sativa L.): a critical review of current knowledge. Environ. Pollut. 297, 118738. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118738
Wani, K. A., and Kothari, R. (2018). Agricultural nanotechnology: applications and challenges. Ann. Plant Sci. 7 (3), 2146–2148. doi:10.21746/aps.2018.7.3.9
Waqas Mazhar, M., Ishtiaq, M., Maqbool, M., Mahmoud, E. A., Ullah, F., and Elansary, H. O. (2024). Optimizing bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) performance: exploring the impact of varied seed priming durations and zinc oxide nanoparticle concentrations on germination, growth, phytochemical attributes, and agronomic outcomes. Cog. Food Agric. 10 (1), 2313052. doi:10.1080/23311932.2024.2313052
Yan, A., and Chen, Z. (2019). Impacts of silver nanoparticles on plants: a focus on the phytotoxicity and underlying mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (5), 1003. doi:10.3390/ijms20051003
Yasmin, H., Mazher, J., Azmat, A., Nosheen, A., Naz, R., Hassan, M. N., et al. (2021). Combined application of zinc oxide nanoparticles and biofertilizer to induce salt resistance in safflower by regulating ion homeostasis and antioxidant defence responses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 218, 112262. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112262
Yoon, H., Kang, Y. G., Chang, Y. S., and Kim, J. H. (2019). Effects of zerovalent iron nanoparticles on photosynthesis and biochemical adaptation of soil-grown Arabidopsis thaliana. Nanomaterials 9 (11), 1543. doi:10.3390/nano9111543
Yousaf, N., Sardar, M. F., Ishfaq, M., Yu, B., Zhong, Y., Zaman, F., et al. (2024). Insights in to iron-based nanoparticles (hematite and magnetite) improving the maize growth (zea mays L.) and iron nutrition with low environmental impacts. Chemosphere 362, 142781. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142781
Zafar, S., Hasnain, Z., Danish, S., Battaglia, M. L., Fahad, S., Ansari, M. J., et al. (2024). Modulations of wheat growth by selenium nanoparticles under salinity stress. BMC Plant Biol. 24 (1), 35. doi:10.1186/s12870-024-04720-6
Zahedi, S. M., Hosseini, M. S., Daneshvar Hakimi Meybodi, N., and Peijnenburg, W. (2021). Mitigation of the effect of drought on growth and yield of pomegranates by foliar spraying of different sizes of selenium nanoparticles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 101 (12), 5202–5213. doi:10.1002/jsfa.11167
Zhao, L., Lu, L., Wang, A., Zhang, H., Huang, M., Wu, H., et al. (2020). Nano-biotechnology in agriculture: use of nanomaterials to promote plant growth and stress tolerance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68 (7), 1935–1947. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06615
Zhu, Z. J., Wang, H., Yan, B., Zheng, H., Jiang, Y., Miranda, O. R., et al. (2012). Effect of surface charge on the uptake and distribution of gold nanoparticles in four plant species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46 (22), 12391–12398. doi:10.1021/es301977w
Zuverza-Mena, N., Medina-Velo, I. A., Barrios, A. C., Tan, W., Peralta-Videa, J. R., and Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2015). Copper nanoparticles/compounds impact agronomic and physiological parameters in cilantro (Coriandrum sativum). Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 17 (10), 1783–1793. doi:10.1039/C5EM00329F
Keywords: metal nanoparticles, nanofertilizers, crop growth, agronomic traits, economic yields
Citation: Kumar S, Suman S, Muthukumar M, Mishra K, Bajpai A, Tiwari AK, Srivastava G, Bansal S, Chaturvedi K, Maurya S, Damodaran T, Killadi B and Ranjan D (2025) Technical review on different metal nanoparticles and their formulations on growth, agronomic and economic traits of crop plants. Front. Nanotechnol. 7:1576582. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2025.1576582
Received: 14 February 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 28 July 2025.
Edited by:
Ramesh Namdeo Pudake, Amity University, IndiaReviewed by:
Priya Banerjee, Rabindra Bharati University, IndiaSouad Elfeky, Cairo University, Egypt
Copyright © 2025 Kumar, Suman, Muthukumar, Mishra, Bajpai, Tiwari, Srivastava, Bansal, Chaturvedi, Maurya, Damodaran, Killadi and Ranjan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: M. Muthukumar, bXV0aHVrdW1hcmJ0QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; T. Damodaran, dGRhbW9kYXJhbjczQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Sandeep Kumar, orcid.org/0000-0001-6139-1541; Shivangi Suman, orcid.org/0009-0006-8687-3911; M. Muthukumar, orcid.org/0000-0002-0111-7660; Kuldeep Mishra, orcid.org/0009-0007-5673-6745; Ajay Kumar Tiwari, orcid.org/0009-0001-7492-2468; Gaurav Srivastava, orcid.org/0000-0002-3488-6220; ShonakBansal, orcid.org/0000-0002-6551-6011; Kavita Chaturvedi, orcid.org/0009-0006-7114-7941; Shubham Maurya, orcid.org/0009-0005-9371-4575; T. Damodaran, orcid.org/0000-0003-2891-2960; Anju Bajpai, orcid.org/0000-0003-3292-9626; Bharati Killadi, orcid.org/0000-0002-4285-1597; Dipti Ranjan, orcid.org/0009-0000-4373-8409
 Sandeep Kumar
Sandeep Kumar Shivangi Suman
Shivangi Suman M. Muthukumar
M. Muthukumar Kuldeep Mishra
Kuldeep Mishra Anju Bajpai
Anju Bajpai Ajay Kumar Tiwari
Ajay Kumar Tiwari Gaurav Srivastava
Gaurav Srivastava Shonak Bansal
Shonak Bansal Kavita Chaturvedi
Kavita Chaturvedi Shubham Maurya
Shubham Maurya T. Damodaran
T. Damodaran Bharati Killadi
Bharati Killadi Dipti Ranjan
Dipti Ranjan