- 1Chengdu National Agricultural Science and Technology Center, Institute of Urban Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Chengdu, China
- 2Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Functional Agriculture and Bio-intelligent Manufacturing, Kizilsu Vocational Technical College, Atushi, China
- 3Zhengzhou Research Base, State Key Laboratory of Cotton Biology, School of Agricultural Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 4Nutrition and Bromatology Group, Department of Analytical Chemistry and Food Science, Faculty of Sciences, Universidade de Vigo, Ourense, Spain
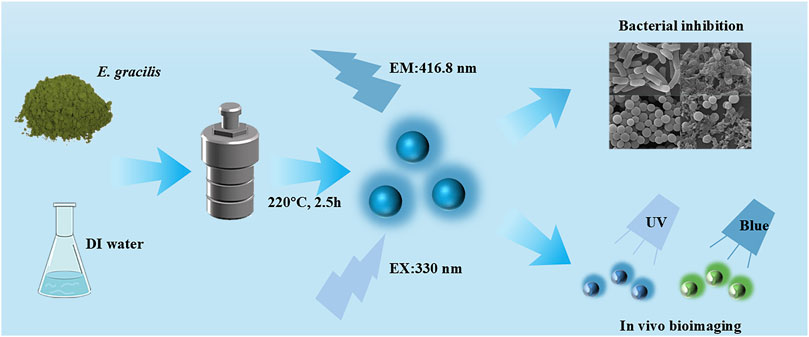
Introduction: Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are a promising class of zero-dimensional carbon nanomaterials (<10 nm) that can be synthesized from organic precursors. They have attracted intense attentions due to their high water solubility, nontoxicity, excellent biocompatibility, and strong optical properties. Microalgae offer a low-cost, renewable, and eco-friendly source of carbon for CQD synthesis. Their high carbon content, functionalization potential, and biocompatibility make them ideal precursors for producing CQDs with excellent properties and versatile applications.
Methods: In this study, we explored the synthesis of Euglena gracilis-derived CQDs (E-CQDs) via a one-step hydrothermal green synthesis method and investigated their potential application in bioimaging and antibacterial materials. The synthesized E-CQDs were comprehensively characterized using TEM, XRD, FTIR, XPS, and UV-vis analysis.
Results: The TEM images showed that E-CQDs had a spherical shape with diameters ranging from 6.5 to 10.5 nm. The XRD patterns indicated that the E-CQDs were crystalline in nature. The FTIR results suggested that E-CQDs were functionalized with C-N and N-H bonds. XPS analysis showed that the E-CQDs were mainly composed of carbon,nitrogen, oxygen and silicon. The UV-vis spectra exhibited a peak at a wavelength of 252 nm, indicating strong absorption in the ultraviolet region. The antibacterial activity test demonstrated that E-CQDs had high inhibitory activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, causing damage to their cell membranes. Additionally, the bioimaging assay indicated E-CQDs possessed the capacity for bioimaging applications in cells, such as Chlorella.
Discussion: This work presents a green synthesis approach for microalgae-derived CQDs, overcoming some environmental drawbacks of traditional chemical methods. It validates the dual-function paradigm where a single nanomaterial can simultaneously suppress bacterial growth and enable bioimaging.
Highlights
Euglena gracilis powder can be used as raw materials for the fabrication of CQDs via a one-step hydrothermal green synthesis method.
E-CQDs exhibited a spherical shape with diameters ranging from 6.5 to 10.5 nm, and displayed high fluorescence emission intensity.
Green synthesized E-CQDs have remarkable potential in antibacterial and bioimaging applications.
1 Introduction
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are widely regarded as a novel class of polychromatic luminescent carbon nanoparticles with sp2/sp3 hybrid carbon nuclei, typically characterized by diameters of less than 10 nm (Jia et al., 2012; Pandya et al., 2024). They have abundant hydroxyl or carboxyl functional groups. CQDs are primarily composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). To enhance their properties, researchers have introduced various heteroatoms such as nitrogen (N), sulfur (S), and phosphorus (P) to create doped CQDs (e.g., N-CQDs, S-CQDs, and P-CQDs). These doped CQDs exhibit significantly higher fluorescence emission intensity and display a range of colorful luminescence. Specifically, the emission wavelength of doped CQDs tends to shift towards the near-infrared or blue regions, which is a notable change compared to their non-doped counterparts (Torres et al., 2023). The nanoparticles have recently received a lot of attention due to their outstanding biocomcompatibility, tunable photoluminescence, versatile surface chemistry, electrochemical luminescence, high solubility in aqueous solutions, and low toxicity (Dong et al., 2021). It makes them suitable for applications in many fields, including metal ion detection, bioimaging, water treatment, biosensing, antibacterial materials, cancer therapy, gene delivery, and drug delivery (Ma et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2023).
The global deployment of CQDs is catalyzing a paradigm shift in multiple industries. For example, according to recent reports, global solid waste (SW) generation has escalated due to urbanization and population expansion, with forecasts predicting a staggering 3.40 billion tons by 2050. Notably, CQDs and their derivatives-applicable in energy storage, chemical sensing, and drug delivery-can be efficiently synthesized from SWs, indicating the approach’s economic and ecological potential (Das et al., 2023). Annual global food waste reaches 1.43 billion metric tons, representing approximately 33% of total production, with consequent economic damages estimated at USD 940 billion. The integration of CQDs into biopolymer-based active packaging containing antioxidants and antimicrobials is a promising solution (Singh et al., 2024). In 2024, the global carbon nanotubes market achieved a valuation of USD 1.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 2.6 billion by 2029. Concurrently, several CQDs have been progressively incorporated into dental applications over the past two decades, demonstrating substantial improvements in treatment efficacy and clinical outcomes (Vasluianu et al., 2025). The compound annual growth rate of the CQDs market is projected to exceed 25% by 2030, reflecting their transformative impact on emerging industries (Tu et al., 2023).
Recently, CQDs has been used in antibacterial agent and bioimaging applications. For instance, novel quaternized CQDs were synthesized using curcumin and glycidyl trimethylammonium chloride, resulting in high solubility and stability. These quaternized CQDs exhibited excellent electrical conductivity and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity (Wu et al., 2022). Spermidine-capped CQDs were also prepared using polyethyleneimine and spermidine, which demonstrated antibacterial activity against both Escherichia coli and multidrug-resistant E. coli (Cui et al., 2023). The antibacterial mechanisms of CQDs primarily involve the physical disruption of biofilms and oxidative damage to bacterial nucleic acids (Tejwan et al., 2021). Additionally, L-CQDs from lotus plumules were synthesized and their potential in biological imaging were also evaluated. The results indicated that these L-CQDs possessed significant imaging capabilities (Liu et al., 2025).
CQDs can be synthesized using two primary approaches. The first is the top-down method, which involves techniques like arc discharge, laser ablation, electrochemical processes, and acid-reflux. The second is the bottom-up method, which includes hydrothermal treatment, microwave irradiation, thermal decomposition, and plasma treatment from molecular precursors such as glucose, sucrose, citric acid, fruit juices, and plant extracts (Krishna Saraswat et al., 2024). Several conventional methods need many chemical agents and instrument facilities while bio-fabrication of CQDs has a lot of benefits due to its simple fabrication and eco-friendly. Hydrothermal method is most commonly used for the generation of CQDs (Manikandan and Min, 2023).
In general, natural resources, such as plant leaves and peels, are widely used as sustainable carbon sources in environmentally friendly synthetic processes (Mindivan and Göktaş, 2023). Currently, a diverse range of biological materials are being utilized for the environmentally friendly synthesis of CQDs. These materials include Malva sylvestris flowers (Blancas et al., 2024), bamboo (Wang et al., 2018), rice straw (Kaur et al., 2024), and various other biological substances. For instance, lignin presents as a renewable source of carbon nanoparticles. A novel biobased material was synthesized via Fenton reaction, employing lignin as natural grafting additives onto nanocellulose surfaces through in situ polymerization of coniferyl alcohol. The material exhibited dual antioxidant properties and organic radical stabilization in cellulose nanocomposite films (Gerbin et al., 2020). The synthesis of novel kraft softwood lignin-derived CQDs was also reported, and the CQDs promote cell attachment within 24 h and sustain it for at least 7 days without any adverse or toxic effects. The data suggested that the CQDs could be suitable for in vivo cell culture applications (Christoph et al., 2024). Microalgae, photosynthetic microorganisms, are regarded as another sustainable resource with potential applications across various fields. These organisms exhibit remarkable species diversity and are rich in valuable bioactive compounds (Guehaz et al., 2023). Compared to other materials employed in the synthesis of carbon quantum dots (CQDs), microalgae offer several distinct advantages. These include diminutive size, rapid reproduction rates, environmental friendliness, and ease of cultivation, rendering them highly suitable for the “bottom-up” synthesis strategy (Ortiz Montoya et al., 2014). Notably, Chlorella has been extensively utilized as a green biological material for CQD synthesis, yielding CQDs with commendable properties (Dong et al., 2021; Wang L. et al., 2024). It was reported that the fabrication of nitrogen selfdoped carbon dots (CDs) via Chlorella pyrenoidosa and its use as a fluorescent link were carried out, and the material has a spherical morphology of the particles with sizes ranging from 3 to 6.5 nm (Guo et al., 2021). Another CDs were fabricated via the hydrothermal treatment of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and the ability for the Fe3+ ion is also further analyzed. The particles were emitted blue fluorescence under UV exposure (365 nm) (Zhang et al., 2022a). Moreover, microalgae-derived CQDs have also been employed as an eco-friendly modifier to facilitate the formation of nano-MnS/FeS composites, thereby significantly enhancing the removal efficiency of Cd2+ ions. This application underscores the potential of microalgae-CQDs to serve as a versatile and sustainable green modifier for mediating the synthesis of various metal sulfides, opening new avenues for environmental remediation and material science (Wang et al., 2023).
Euglena gracilis is a unicellular protist and one of the most prevalent and extensively utilized microalgal species (Farjallah et al., 2024). As a model organism, its cell size typically between 35 and 50 µm in length and 8–20 µm in diameter, which is larger than that of Chlorella (2–4 µm) (Yan et al., 2023; Ortiz Montoya et al., 2014). The obvious distinguishable size affects the separation process, which makes E. gracilis have better filterability and dehydration (Jutidamrongphan et al., 2015). Euglena gracilis is easier to culture and separate than Chlorella vulgaris. Morever, it is rich in fatty acids and thus holds great potential as a biodiesel feedstock (Chen et al., 2022). Besides, other advantages like no cell wall and strong environmental adaptability could also make the microalgae serve as excellent precursors for CQD synthesis. However, there is no studies exploring the synthesis of CQDs from E. gracilis in recent years. The synthesis method and their potential application in bioimaging and antibacterial materials have not been reported.
Hence, in this study, E. gracilis were used as precursors for CODs without any additional chemicals. Euglena gracilis-drived CQDs (E-CQDs) with down-conversion effects were firstly synthesized using a one-step and a low cost hydrothermal procedure. The structural, composition, and properties of the prepared CQDs were thoroughly investigated. Biological applications including antibacterial effects and bioimaging were carried out. This research not only provides a novel approach for preparing CQDs using E. gracilis as a new microalgal material but also offers valuable insights into their potential applications in antibacterial and bioimaging fields.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials and reagents
The E. gracilis powder was purchased from Yunnan Baoshan Zeyuan Algal Health Technology Co., Ltd. Deionized (DI) water was prepared in the laboratory. A poly (tetrafluoroethylene) Teflon-lined autoclave was purchased from Beijing Kemet Technology Co., Ltd.
2.2 Synthesis of E-CQDs
To synthesize E-CQDs, 4.8 g of dry E. gracilis powder was thoroughly mixed with 60 mL of DI water and stirred for 10 min. The resulting was then transferred to 100 mL Teflon-lined autoclave and heated it at 220 °C for 2.5 h in an electrothermal constant temperature drying oven. After cooling the autoclave to room temperature, the solution was filtered through a sulfone filter membrane with a 0.45 µm pore size to remove any insoluble residues. The filtrate was subsequently freeze-dried to yield a brown powder. The CQDs obtained from this process were designated as E-CQDs.
2.3 Optimization of synthesis method of E-CQDs
To optimize the synthesis of E-CQDs, we systematically varied the ratios of E. gracilis powder (2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, 10%), reaction temperatures (140 °C, 160 °C, 180 °C, 200 °C, 220 °C), and reaction times (0.5 h, 1.0 h, 1.5 h, 2.0 h, 2.5 h). The resulting solutions were filtered, and the filtrates were subsequently diluted to a suitable concentration. The absorbance and fluorescence of the diluted E-CQDs were measured at an excitation wavelength of 380 nm, following the standardized procedure outlined by Dong et al. (2021). Specifically, the absorbance at 380 nm was meticulously adjusted to fall within the range of 0.06–0.10 to ensure precise and reliable measurements. Thereafter, the absorbance and relative fluorescence intensity were comprehensively analyzed using a Spark Multifunctional Enzyme Marker (Tecan A-5082, Made in Austria) to thoroughly evaluate the optical properties of the synthesized E-CQDs. Relative Fluorescence Units (RFU) was used to qualitatively asses the efficiency of the synthesis method.
2.4 Characterization
Fluorescence emission spectroscopy was performed using an F-4700 spectrophotometer (Hitachi, Tokyo). The crystalline phase was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using an Ultima IV instrument (Rigaku Corp.). Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra were acquired using a LAMBDA 1050+ UV/Vis Spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed at 200 kV using a JEM-F200 microscope (JEOL). TEM image was analyzed using ImageJ® software version 1.54 m. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were recorded within the range of 4,000–500 cm-1 using a Nicolet iS10 FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed using an AXIS Supra + spectrometer (Shimadzu).
2.5 Antibacterial activity of E-CQDs
2.5.1 Disk diffusion assay
This study utilized the research methodology of Amoon et al. (2024) with some modifications. The disc diffusion method was employed to explore the inhibitory ability of E-CQDs against E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus were activated at 180 rpm for 12 h at 37 °C. Subsequently, the bacterial suspensions were centrifuged at 6,000 rpm for 1 min to collect the precipitates, which were then resuspended in sterile water. A volume of 100 µL of the bacterial suspension, adjusted to an absorbance of 0.1 at 600 nm, was spread evenly onto LB solid medium. Blank discs (6 mm in diameter) were prepared by immersing them in sterile water (serving as a negative control) and E-CQDs solutions (concentrations ranging from 5 to 200 mg/mL) for over 30 min to ensure complete absorption. These discs were then placed at various locations on the LB solid medium inoculated with either E. coli or S. aureus. The petri dishes were sealed and incubated at 37 °C. After 12 h of incubation, the diameters of the inhibition zones were measured using a vernier caliper to assess the antibacterial efficacy of the E-CQDs.
2.5.2 Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum bactericidal concentration
The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) refers to the lowest concentration of CQDs that prevents the growth of a specific microorganism. The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) is defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent required to kill 99.9% of the initial inoculum after incubation for 24 h under standardized conditions (Balouiri et al., 2016). The antibacterial efficiency was evaluated through the two key quantitative parameters: MIC and MBC following the broth microdilution methods described by Zeng et al. (2024). Five different dilutions of E-CQDs diluents were prepared in 1,000 µL of LB broth medium, with a negative control containing no E-CQDs. Each dilution was inoculated with 1,000 µL of a suspension of S. aureus or E. coli at a concentration of 1 × 108 CFU/mL. After incubating the samples at 37 °C for 4 h, 20 µL aliquots were spread onto LB agar plates and further incubated at 37 °C for 15 h. After incubation, the absence of microbial growth on these plates indicates the number of surviving cells (CFU/mL) and confirms the MBC. The antibacterial ratio was calculated using the formula: Antibacterial Ratio (%)=(A-B)/A × 100%, where A represents the colony count in the blank control group, and B represents the colony count in the treatment group.
2.5.3 Bacterial morphological characteristics
The morphological characteristics in bacteria before and after E-CQDs treatment were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). After treatment with E-CQDs at 37 °C for 4 h, E. coli and S. aureus cells were harvested by centrifugation until visible pellets formed. These pellets were gently resuspended in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged again under the same conditions. The supernatant was then discarded, and the cells were fixed in 3% glutaraldehyde for 10 h at 4 °C. The fixed cells were subsequently washed three times with ultrapure water (10 min per wash), then post-fixed with 1% osmium tetroxide for 1–2 h. After additional ultrapure water washes (3
2.6 In vivo bioimaging assay
To assess the bioimaging potential of E-CQDs, Chlorella, a widely recognized single-celled algal model organism, was selected for fluorescence imaging assays. Previous work by Nam et al. (2019) has demonstrated the utility of Chlorella as an organism model for fluorescence imaging. Based on this foundation, the present study utilized E-CQDs to conduct fluorescence imaging of Chlorella, thereby assessing the viability of CQDs for bioimaging applications.
Two 1 mL tubes of Chlorella suspensions were prepared and labeled as tube A (control) and tube B (E-CQDs treated). A solution of 20 mg/L E-CQDs was added to tube B, while DI water was added to tube A as a negative control. Both tubes were incubated at 25 °C with continuous shaking at 180 rpm. After 24 h of incubation, the culture solution was removed by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm then resuspended in DI water. The fluorescence effect was observed under a fluorescence microscope (Leica Microsystems CMS GmbH) after 30 min of Uv irradiation.
2.7 Statistical analysis
All experimental data were processed using Microsoft Excel 2021 (Microsoft Corp., United States) for preliminary calculations and normalization. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) performed with IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0 (IBM Corp., United States) at a 95% confidence level (p < 0.05 considered significant). Graphical representations were generated using OriginPro 2021 (OriginLab Corp., United States) with error bars denoting standard deviations (n ≥ 3).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Optimization of synthesis method for E-CQDs
E-CQDs were synthesized using a direct hydrothermal method with E. gracilis powder as the raw material. The schematic illustration of the synthesis process was summarized in Figure 1a. The synthesis parameters of E-CQD including additional amount, reaction temperature, and reaction time were optimized.
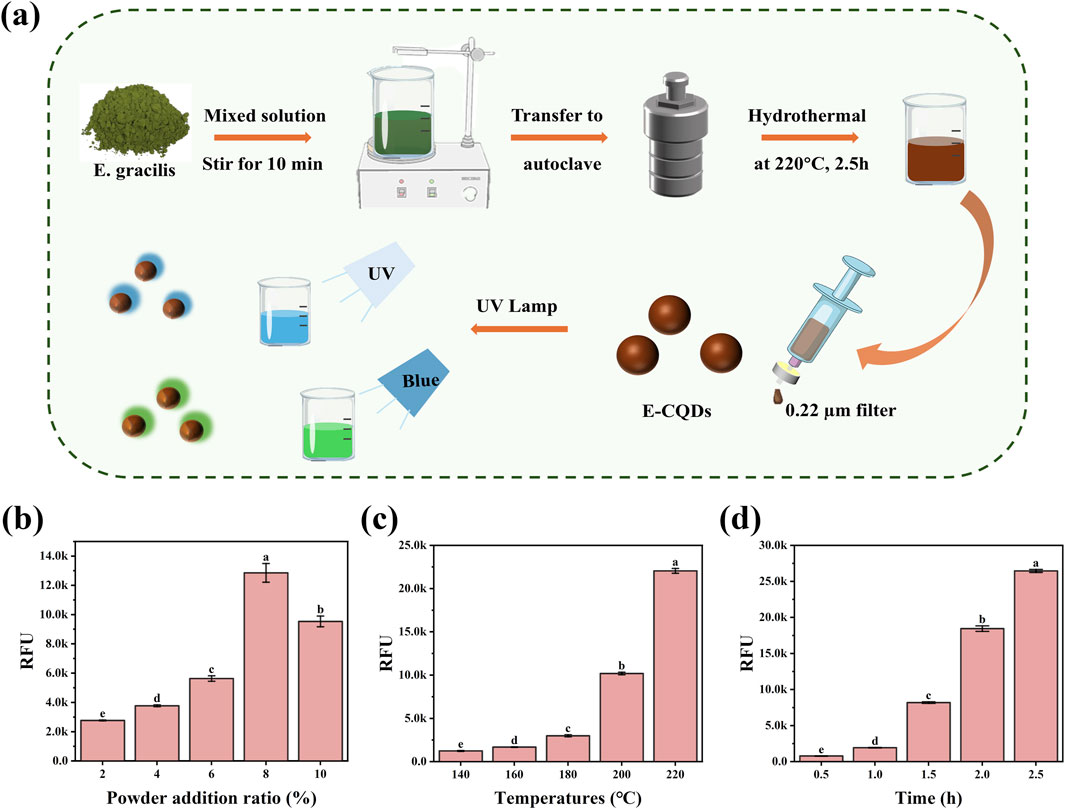
Figure 1. The optimization of the synthesis method for E-CQDs. (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis process for E-CQDs. (b) Effects of different E. gracilis powder addition ratio, (c) reaction temperature, and (d) incubation time on the fluorescence intensity of E-CQDs. The letters (a–e) in (b–d) indicate significant differences between groups. Different letters denote significant differences (p < 0.05), while the same letters indicate no significant differences.
The influence of E. gracilis powder addition ratio ranging from 2% to 10% on the fluorescence intensity of E-CQDs was studied. As shown in Figure 1b, with reacting at 200 °C for 2 h, the fluorescence intensity first increased and then decreased with increasing E. gracilis powder addition ratio. The maximum value of RFU is obtained at 8% E. gracilis powder addition, which was adopted for further experiments. The influences of incubation temperature ranging from 140 °C to 220 °C were also examined, and the results are shown in Figure 1c. As the reaction temperature increased, a concomitant increase in the RFU of the E-CQDs was observed. When the reaction temperature was set at 220 °C, the RFU of the E-CQDs reached their maximum value. When the reaction was conducted at 220 °C, the influence of different reaction time (0.5 h–2.5 h) on RFU was also investigated. As depicted in Figure 1d, with the increase of incubation time, RFU of E-CQDs also significantly increased. As the reaction time was 2.5 h, maximum RFU could be obtained. To achieve the highest RFU and ensure a stable signal, the optimized synthesis conditions were determined to be the addition of 8% E. gracilis powder, followed by a reaction at 220 °C for 2.5 h. All E-CQDs used for subsequent in-depth studies were synthesized under these optimized conditions. It’s reported that the aggregation and interactions of CQD species in solution could inhibit full potential of light emitters, which named aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) effect (Adsetts et al., 2020). The complex of CQDs and phthalimide crystals (CQDs/PC) could prevent CQDs from touching directly by embedding the CQDs in phthalimide crystal matrix in situ, which effectively reduced the ACQ effect (Zheng et al., 2020). In this study, concentration-dependent sedimentation was observed in the E-CQDs stock solution while diluted E-CQDs solutions maintained colloidal stability with no observed aggregation. In terms of reducing ACQ effect, the E-CQDs embedded in situ within PC may be also suggested.
3.2 Structural characterization
The CQDs prepared by the hydrothermal method were observed with TEM. Figure 2a shows that the E-CQDs exhibited a globular morphology, with a relatively uniform distribution of particles and absence of distinct lattice fringes. A histogram of the size distribution was derived by counting 100 particles, revealing that the diameter distribution of the E-CQDs ranged from 6.5 to 10.5 nm, with an average diameter of 9.2 nm. These results indicated that the materials can be classified as CQDs. The crystalline phase purity of E-CQDs was elucidated via XRD analysis. Figure 2b depicts the XRD crystalline profile of E-CQDs. There is a broad peak at 23.89 °, which is attributed to the partial ordering in the carbon dots. This ordering may arise from the covalent crosslinking of the skeletal structure during the polymerization process. (Huang et al., 2024; Miao et al., 2025). The FTIR spectrum was recorded to explore the surface functional groups of the E-CQDs. As illustrated in Figure 2c, the FTIR spectrum of the synthesized E-CQDs exhibits peaked at 3,238.9 cm−1, which is linked to the stretching vibrations of O-H or N-H bonds. Meanwhile, the peak of E-CQDs at 2,964.87 cm−1 may show the presence of the stretching vibrations of C-H (Bao et al., 2015; Qandeel et al., 2024). The 1,667.13 cm−1 peak is attributed to the absorption bands of C=O. It may originate from the amid bond (-CONH -) or the -COOH group (Hua et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2013). The peak at 1,454.94 cm−1 corresponds to C-H stretching vibration and the peak at 1,118.71 cm−1 corresponds to C-N stretching vibration (Li et al., 2024; Mmelesi et al., 2024).
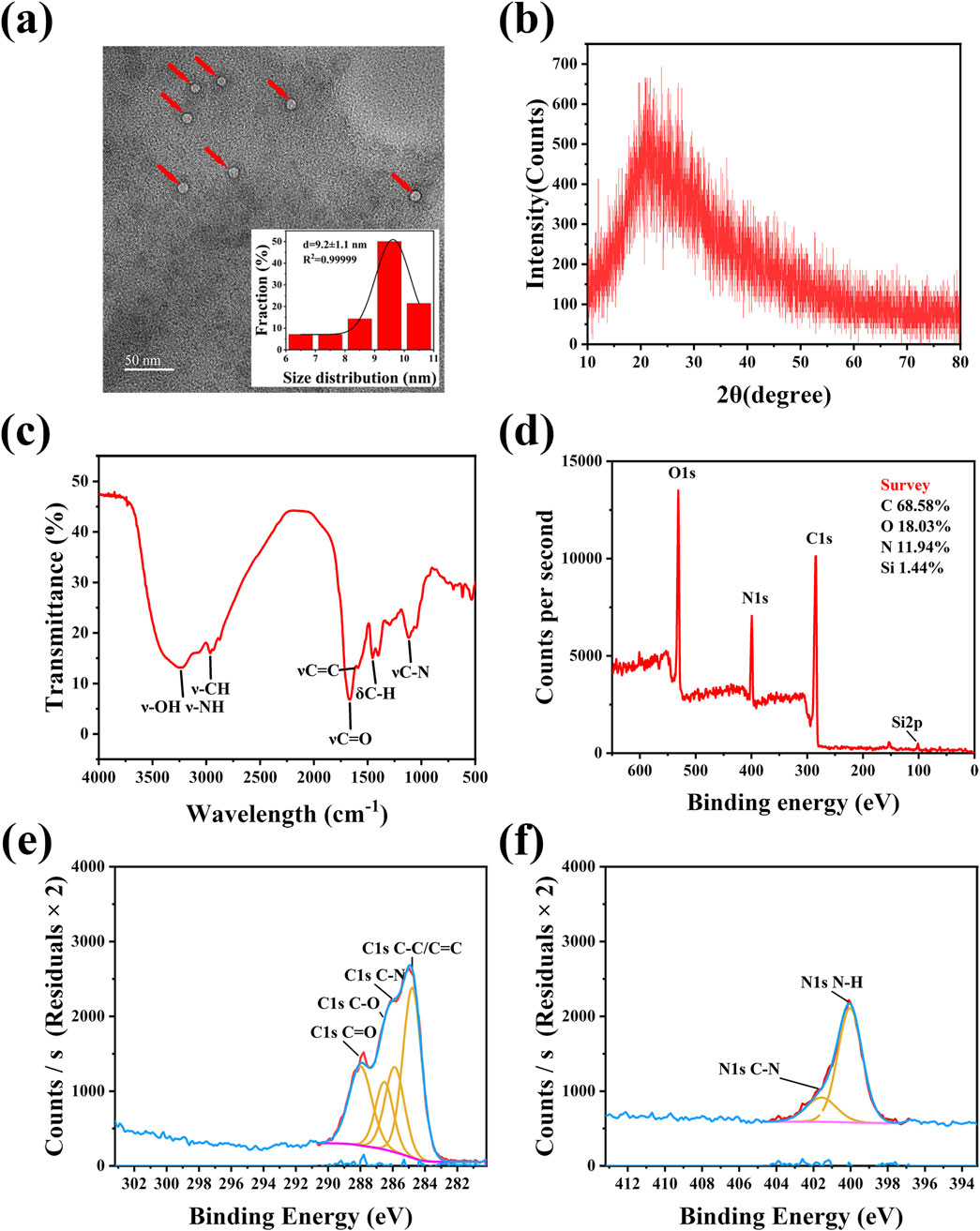
Figure 2. Structural Characterization of E-CQDs. (a) TEM image and size distribution of E-CQDs.The red arrows represent the E-CQDs; (b) XRD pattern of E-CQDs; (c) FTIR spectra of E-CQDs; (d) XPS survey spectra; (e) C 1s XPS spectra of E-CQDs; (f) N 1s XPS spectra of E-CQDs.
XPS was employed to analyze the microstructures and elemental composition of the synthesized CQDs. As depicted in Figure 2d, the four main peaks in this spectrum include C 1s, N 1s, O 1s, and Si 2p, which can be seen at 284, 399, 531, and 101 eV binding energies, respectively. The elemental composition of E-CQDs was determined to be C (68.58%), O (18.03%), N (11.94%), and Si (1.44%). Figure 2e shows the C 1s spectrum of the E-CQDs. The C 1s XPS spectrum reveals multiple peaks at 284.8 eV, 285.9 eV, 286.5 eV, and 288 eV, corresponding to C-C/C=C, C-N, C-O, and C=O bonds (Fatima et al., 2024; Gawal and Golder, 2024), respectively. The two peaks of N 1s at 400 eV and 401.6 eV, as shown in Figure 2f, are attributed to the C-N and N-H bonds, respectively (Tao et al., 2018). XPS analysis revealed that the surface composition of E-CQDs aligns well with the findings from FTIR spectroscopy. It suggests that E-CQDs possess a high density of oxygen- and nitrogen-containing functional groups, including hydroxyl, carboxyl, and amine groups. These functional groups endow E-CQDs with excellent water solubility.
3.3 Optical properties of E-CQDs
Figure 3 shows the optical properties of the E-CQD. As shown in Figure 3a, the original synthesized aqueous solution of E-CQDs (prepared from a mixture of 4.8 g of dry E. gracilis powder and 60 mL of DI water) was filtered, and initially appeared brownish-black. However, upon dilution by a factor of 100, the solution turned light yellow. Figure 3b shows an image of the E-CQDs samples under UV light irradiation. Upon exposure to 365 nm ultraviolet (UV) light, the sample exhibited bright blue fluorescence. Consistent with the literature (Zapata-Hernandez et al., 2024), the blue luminescence of E-CQDs is likely attributed to the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups. These groups create distinct sp2 energy levels between the π and π* bands, as evidenced by the FTIR spectrum of the CQDs. Figure 3c depicts the E-CQD’s photoluminescence with excitation wavelength variations ranging from 300 to 400 nm. The most significant emission peak was observed at 416.8 nm when an excitation wavelength of 330 nm was used. The photoluminescence in E-CQDs may stem from the separation of sp2 domains by sp3 domains. The formation of sp3 domains is supported by the presence of oxygen-containing functional groups. Additionally, the excitation-wavelength-dependent emission behavior could be attributed to oxygen functionalities that induce surface defects, acting as surface energy traps (Zapata-Hernandez et al., 2024). The E-CQD’s UV-Vis absorption spectrum (Figure 3d) evidenced a peak in the UV region at approximately 252 nm, with a tail extending into the visible range. The absorbance band at 252 nm is related to the π–π* transition of the aromatic C=C bonds (Hua et al., 2017).
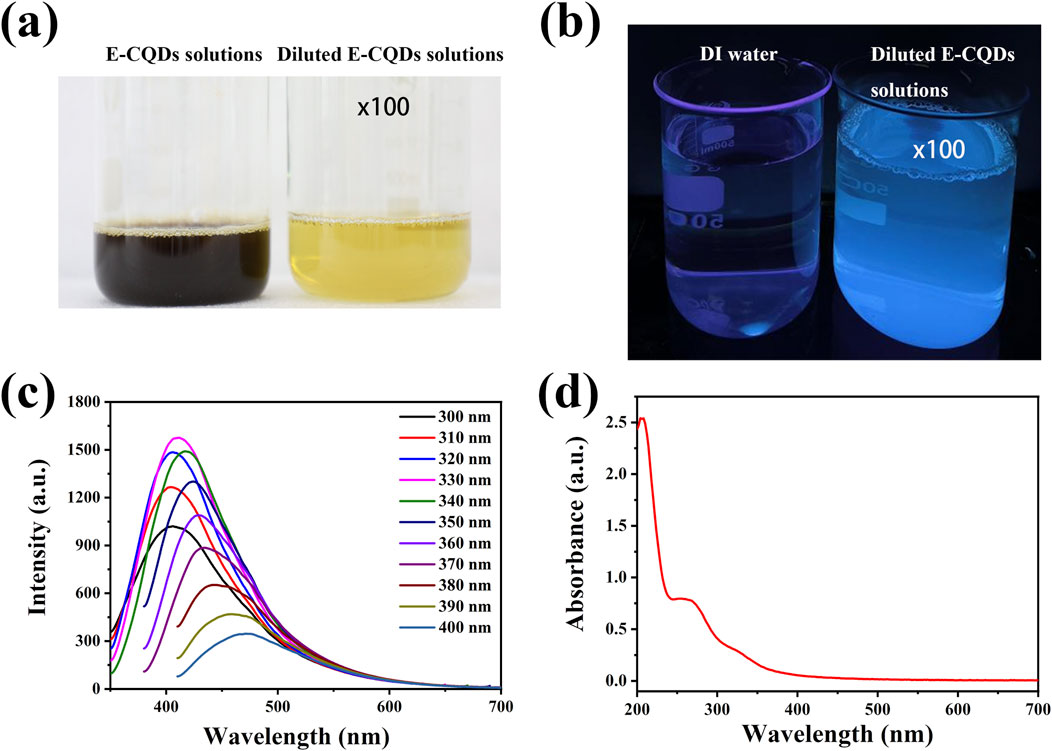
Figure 3. Optical properties of E-CQDs. (a) The image of the filtered original synthesized aqueous solution of E-CQDs (prepared from a mixture of 4.8 g of dry Euglena gracilis powder and 60 mL of DI water) and the 100x diluted E-CQDs solution; (b) The image of DI water and 100x diluted E-CQDs solutions under Uv; (c) Photoluminescence of E-CQDs with different excitation wavelength; (d) UV-vis absorption spectra of E-CQDs.
3.4 Antibacterial activity in vitro
Disk diffusion assays, MIC, MBC, together with image analysis, were employed to evaluate the antibacterial activity of E-CQDs against E. coli (Gram-negative bacteria) and S. aureus (Gram-positive bacteria) (Figure 4). Figures 4a,b illustrate the observed inhibition zone diameters for different concentrations (0, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 mg/mL) of E-CQDs against E. coli and S. aureus, respectively. When the concentration is below 50 mg/mL, E-CQDs display no antibacterial activity against E. coli. However, at concentrations of 50, 100, and 200 mg/mL, distinct inhibition zones are observed (Figure 4a). At a concentration of 200 mg/mL, E-CQDs showed an inhibition zone value of 7.5 mm. Differently, There is no significant antibacterial activity against S. aureus when the concentration is below 100 mg/mL (Figure 4b). The 200 mg/mL E-CQDs inhibited the S. aureus growth with inhibition zone of 9 mm. The results were consistent with those reported by Amoon et al. (2024) and Ma et al. (2020), both of whom demonstrated that bacterial growth could be inhibited by treatment with suitable concentrations of CQDs. Figures 4c,e show MIC of the E-CQDs against E. coli while Figures 4d,f depict MBC of the E-CQDs against S. aureus, using broth microdilution method. As the concentration of E-CQDs increased, the antibacterial effect became increasingly pronounced. MIC of the E-CQDs against E. coli and S. aureus were determined to be 100 mg/mL. At a concentration of 200 mg/mL, only a minimal number of colonies were observable on LB agar plates, indicating bactericidal activities exceeding 95% against E. coli and 90% against S. aureus. In terms of MBC, Both E. coli and S. aureusdid can not grow at a concentration of 250 mg/mL and above, indicating the value of MBC was 250. mg/mL.
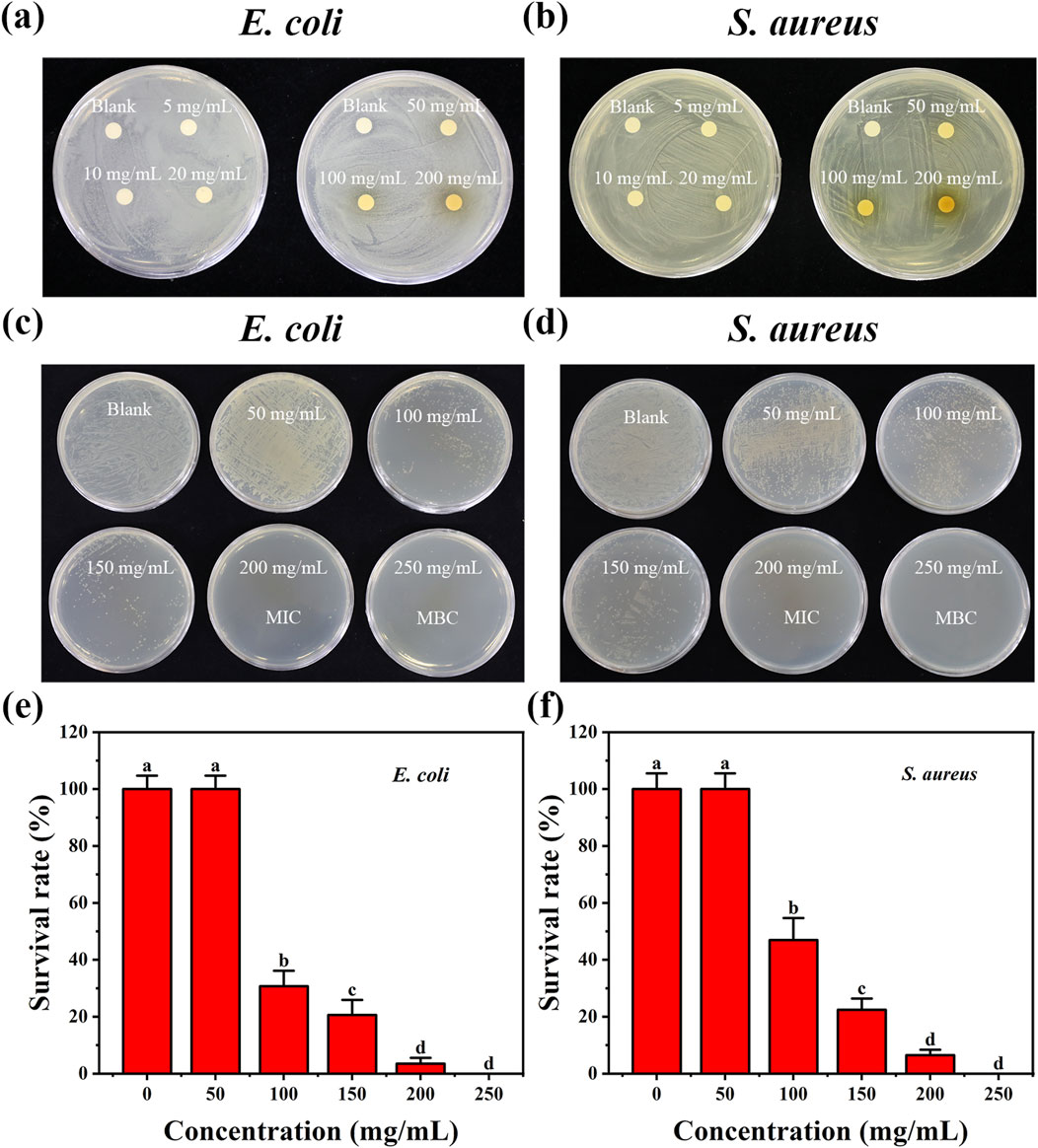
Figure 4. Antibacterial effects of E-CQDs at various concentrations on (a) E. coli and (b) Staphylococcus aureus as determined by disk diffusion assay, corresponding minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBC) for (c) Escherichia coli (E.coli) and (d) Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). Survival rates of (e) E. coli and (f) S. aureus exposed to different concentrations of E-CQDs. The letters (a–d) in (e–f) indicate significant differences between groups. Different letters denote significant differences (p < 0.05), while the same letters indicate no significant differences.
Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (N-CQDs) with excellent antifungal performance were synthesized using chitosan quaternary ammonium salt (HACC) as the raw material, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 1.8 mg/mL (Wang Y. et al., 2024). Phosphorus-doped CQDs were prepared by a simple hydrothermal method using valine as a carbon source, triethylamine as a nitrogen source, and phosphoric acid as a phosphorus source. Their MIC values decreased from 0.71 to 0.51 to 0.18 mg/mL on E. coli and S. aureus with increasing phosphorus content (Chai et al., 2022). N-CQDs derived from Hedyotis diffusa Willd. Exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against both S. aureus and E. coli, with MIC values of 0.055 mg/mL and 0.038 mg/mL, respectively (Pei et al., 2025). Additionally, novel CMC/CuO NPs/CQDs were effective against S. aureus and E. coli, with MIC values of 25 mg/mL and >50 mg/mL, respectively (Amoon et al., 2024). Compared to these CQDs, the concentration of E-CQDs (100 mg/L) required to inhibit bacterial growth is higher, likely due to the absence of amino acids (e.g., Arg/Lys), metal doping (e.g., zinc (Zn), and copper (Cu)), or nanocomposite formation in E-CQDs. Certainly, the antibacterial activity of E-CQDs can not be denied. MIC of E-CQDs is relatively high compared to other natural extracts. For instance, the MIC of E-CQDs is significantly lower than that of arum ethanolic extracts (MIC: 500 mg/mL) (Al-Daghistani et al., 2021) and Scorzonera mackmeliana extracts (MIC: 341.85 mg/mL) (Sweidan et al., 2020), indicating the potential of E-CQDs as an effective antibacterial agent. Future research may explore the doping of E-CQDs with compounds such as valine, triethylamine, phosphoric acid, Zn, Fe, and Cu to enhance their antibacterial capabilities.
It is reported that the bactericidal mechanism of CQDs can be characterized by the disruption of the bacterial membrane, leading to the leakage of cytoplasmic contents and ultimately culminating in cell apoptosis (Pant et al., 2023). SEM was used to image the bacteria in the presence of the E-CQDs (Figure 5). The morphology of E. coli and S. aureus changed significantly prior to and post the treatment with E-CQDs. In the absence of CQDs, the bacteria exhibited their typical sizes and morphologies: E. coli appears as rod-shaped bacteria (Figure 5a), whereas S. aureus has a spherical appearance and formed grape-like clusters (Figure 5c). Both types of bacteria presented smooth, intact surfaces. The cell membrane of the bacterial group treated with E-CQDs exhibited severe damage, with the surface becoming rough, deformed and significantly shrunken (Figures 5b,d). These changes may strongly suggest cell membrane damage (Bacellar et al., 2014). There was a hypothesis that S. aureus was less susceptible after treatment of CQDs than E. coli (Nie et al., 2020). Consistent with this supposition, intact S. aureus was still observable in Figure 5d while E. coli was seriously damaged (Figure 5b). It could be explained by the fact that E-CQDs may have a reduced ability to penetrate into the interior of S. aureus. Thus, the observed morphological changes in the bacteria may indicate alterations in the permeability of their membranes, which would affect the regulation of transmembrane transport and result in cell death.
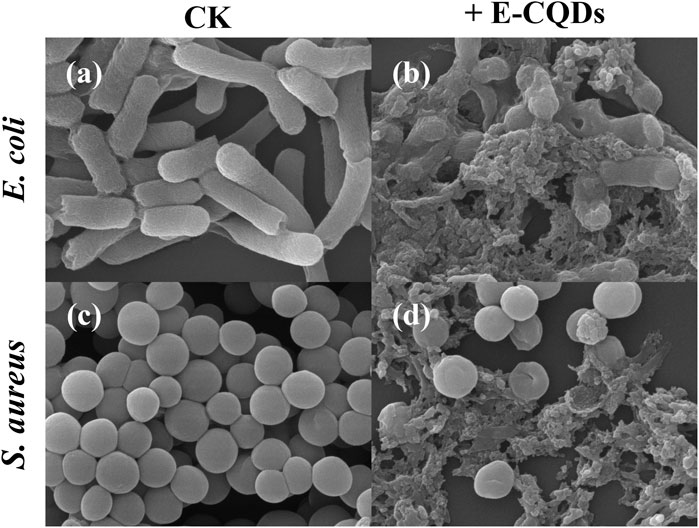

Figure 5. SEM images of E. coli (a,b) and S. aureus (c,d). Panel a and c depict the untreated cells, and panels b and d are the cells after incubation with E-CQDs.
3.5 In vivo bioimaging effect
CQDs with multicolor fluorescence emissions may show great potential in applications such as molecular imaging and in vivo molecular tracking. For instance, in a study conducted by Manjubaashini et al. (2024), CQDs were utilized for in vivo bioimaging in zebrafish to evaluate their potential for bioimaging applications. Moreover, it has been reported that unicellular algae, as autotrophic biosystems, uniquely possess multiple functions, including oxygen generation, dynamic motility, fluorescence imaging, and programmable biosynthesis (Wang et al., 2025). Chlorella, a widely utilized single-celled alga, is a model organism commonly employed in biological and biotechnological studies.
In this research, Chlorella pyrenoidosa was employed, and fluorescence imaging was performed using E-CQD, and the imaging effects of the E-CQDs under varied excitation irradiation towards C. pyrenoidosa cells were depicted in Figure 6. As shown in Figures 6a,b, there was no difference in the morphology of the cells under bright field conditions. No fluorescence of C. pyrenoidosa in the absence of E-CQDs was observed under the UV, blue light or green light illumination (Figure 6c,e,g). Obviously, Upon treatment with E-CQDs, Chlorella exhibited blue fluorescence under UV excitation within the wavelength range of 327–383 nm (Figure 6d) and green fluorescence under blue excitation within the range of 460–500 nm (Figure 6f). Similar to C. pyrenoidosa in the absence of E-CQDs (Figure 6g), no fluorescence was observed under green excitation within the range of 541–551 nm (Figure 6h). E-CQDs treatment didn’t affect the growth of Chlorella cells. Moreover, the observed fluorescence was found to be located in the whole cell, which was different from the finding that internalized nitrogen-doped carbon dots were concentrated in the nucleus (Zhang et al., 2020b). These findings suggested that E-CQDs may bioaccumulate within Chlorella cells, which implies that E-CQDs hold practical value as imaging agents for live-cell studies and have the potential to serve as a probe for in vivo bioimaging applications.
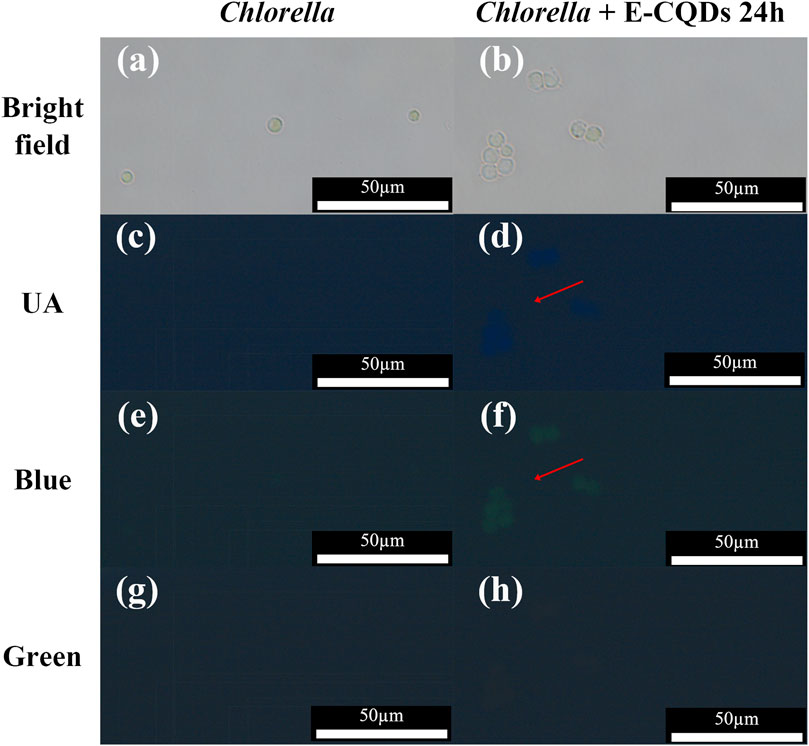
Figure 6. Fluorescent images of Chlorella cells with and without E-CQDs under different excitation wavelengths. (a) Bright-field image of Chlorella cells without E-CQDs; (b) Bright-field image of Chlorella cells with E-CQDs; (c) Fluorescent image of Chlorella cells without E-CQDs under UV irradiation; (d) Fluorescent image of Chlorella cells with E-CQDs under UV irradiation; (e) Fluorescent image of Chlorella cells without E-CQDs under blue light irradiation; (f) Fluorescent image of Chlorella cells with E-CQDs under blue light irradiation; (g) Fluorescent image of Chlorella cells without E-CQDs under green light irradiation; (h) Fluorescent image of Chlorella cells with E-CQDs under green light irradiation.
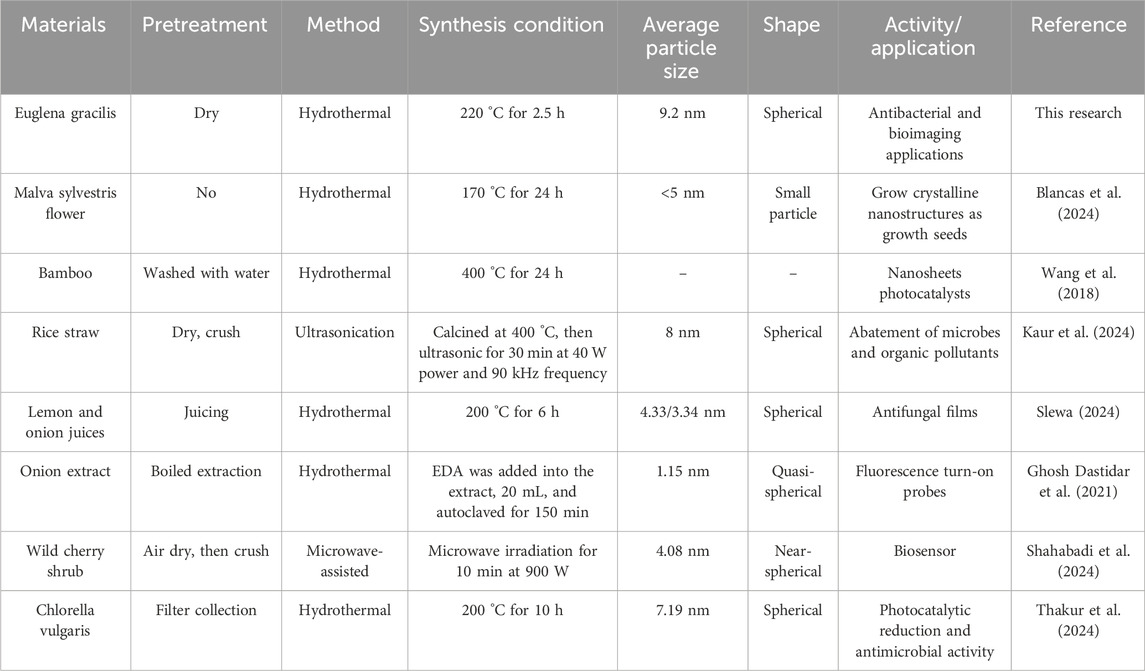
The environmentally friendly synthesis of CQDs using various biological materials was compared (Table 1). Blancas et al. (2024) carried out synthesis of CQDs by Hydrothermal method using of Malva sylvestris flower. It required about 24 h for the synthesis, and showed small particle with a 5 nm size. The CQDs form M. sylvestris flower could grow crystalline nanostructures as growth seeds. Wang et al. (2018) developed a novel approach for CQDs fabrication by the use of bamboo biomass. It was heated for 24 h at 400 °C. Comparing with these CQDs reported, the method of preparing E-CQDs using E. gracilis powder as the raw material offers several advantages. It facilitates the acquisition of raw materials, simplifies pretreatment, and streamlines preparation procedures. The average particle size of the resulting E-CQDs was comparable to that of CQDs prepared using rice straw and Chlorella vulgaris as raw materials (Kaur et al., 2024; Thakur et al., 2024). Besides, CQDs from rice straw (Kaur et al., 2024), lemon and onion juices (Slewa, 2024), onion extract (Ghosh Dastidar et al., 2021),wild cherry shrub (Shahabadi et al., 2024), and C. vulgaris (Thakur et al., 2024) exhibited the potential application in abatement of microbes and organic pollutants, antifungal films, fluorescence turn-on probes, biosensor, and photocatalytic reduction and antimicrobial activity, respectively. In this study, E-CQDs have dual-functions that include antibacterial effects and bioimaging applications, which indicated that the nanomatrials could serve as next-generation antibacterial materials and nanotheranostics. However, the antibacterial effects of E-CQDs is relatively low, and the fabrication of elements-doped like N, silicon (Si), cadmium sulphide, cerium oxide, and silver) carbon dots (N-CDs) may be investigated in future, which can increase the activities of E-CQDs. Interestingly, polysaccharides found in marine environments can serve as carbon-rich precursors for synthesizing CQDs. Marine polysaccharides have a distinct advantage over other CQD precursors because they contain multiple heteroatoms, including N, S, and O (Torres et al., 2023). Euglena gracilis can accumulate large amounts of beta-1, 3-glucan paramylon, a polysaccharide (Lee et al., 2024). Therefore, E. gracilis polysaccharides may also possess the potential of CQDs with applications in various fields, including biomedicine (e.g., drug delivery, bioimaging, and biosensing), photocatalysis, water quality monitoring, and the food industry. Sensing, photocatalysis, diagnostics and therapy of E-CQDs could be also studied in the next step.
4 Conclusion
In this study, we developed a sustainable and resource-efficient method to synthesize dual-functional CQDs from the microalga E. gracilis. Through hydrothermal optimization, the resulting E-CQDs displayed exceptional fluorescence properties (excitation/emission wavelength = 330/416.8 nm) with an average diameter of 9.2 nm. Additionally, they exhibited potent broad-spectrum antibacterial activity against both E. coli and S. aureus, with MIC of 100 mg/mL. Importantly, E-CQDs demonstrated in vivo bioimaging capabilities upon UV/blue-light excitation, confirming their cellular uptake and luminescence emission within biological systems. This work presents a green synthesis approach for microalgae-derived CQDs, overcoming the environmental drawbacks of traditional chemical methods. It validates the dual-functionality concept where a single nanomaterial can simultaneously suppress bacterial growth and enable bioimaging. Furthermore, it establishes E. gracilis as a viable bioresource for high-value nanomaterial production due to its robustness and metabolic flexibility. The E-CQDs platform holds significant promise for applications in antibacterial coatings, diagnostic imaging probes, and theranostic nanomedicine. In the future, further research should be conducted to enhance the antibacterial activity of E-CQDs by increasing the P-doping ratio, introducing metal doping, or combining them with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and chitosan (CS). In addition, the in vitro cytocompatibility of E-CQDs with human mesenchymal stem cells, the WRL-68 cell line, the HT1080 cell line, or zebrafish embryos could be investigated to promote their potential biomedical applications. Future studies should also aim to achieve a high quantum yield and improved stability of E-CQDs for bioimaging, as well as to develop E-CQDs with clearly defined geometry, composition, and structure.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
HC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Supervision, Methodology, Project administration. CY: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Visualization. WX: Writing – review and editing, Resources, Supervision, Methodology. ZD: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Validation. GG: Writing – review and editing. HZ: Writing – review and editing. YL: Writing – review and editing. BH: Writing – review and editing. ZQ: Writing – review and editing. MR: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Project administration, Conceptualization, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (34-IUA-02), the Local Financial Project of the National Agricultural Science and Technology Center (NASC2024TD02), the Xinjiang Science and Technology Program (ZYYD2024CG09) (ZYYD2025CG10), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2024NSFC1261), and Key Laboratory of Se-enriched Products Development and Quality Control, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs/National-Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Se-enriched Food Development (Se-2023C01).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adsetts, J. R., Hoesterey, S., Gao, C., Love, D. A., and Ding, Z. (2020). Electrochemiluminescence and photoluminescence of carbon quantum dots controlled by aggregation-induced emission, aggregation-caused quenching, and interfacial reactions. Langmuir 36 (47), 14432–14442. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02886
Al-Daghistani, H. I., Abu-Niaaj, L. F., Bustanji, Y., Al-Hamaideh, K. D., Al-Salamat, H., Nassar, M. N., et al. (2021). Antibacterial and cytotoxicity evaluation of Arum hygrophilum bioss. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 25 (23), 7306–7316. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202112_27424
Amoon, H., Moghadam, A., and Hajkarim, M. C. (2024). Synthesis, characterization, and investigation of antibacterial activity of novel CMC/CuO NPs/CQDs bionanocomposite coating. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 268 (Pt 2), 131922. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131922
Bacellar, I. O., Pavani, C., Sales, E. M., Itri, R., Wainwright, M., and Baptista, M. S. (2014). Membrane damage efficiency of phenothiazinium photosensitizers. Photochem. Photobiol. 90 (4), 801–813. doi:10.1111/php.12264
Balouiri, M., Sadiki, M., and Ibnsouda, S. K. (2016). Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J. Pharm. Anal. 6 (2), 71–79. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
Bao, L., Liu, C., Zhang, Z. L., and Pang, D. W. (2015). Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv. Mat. 27 (10), 1663–1667. doi:10.1002/adma.201405070
Blancas, J., Cayetano-Castro, N., Pérez, R., and Rosas, G. (2024). A novel hydrothermal approach to preparing ZnO flower-like using CQDs as growth seeds. Mat. Sci. Eng. B 309 (000), 117654. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2024.117654
Chai, S., Zhou, L., Chi, Y., Chen, L., Pei, S., and Chen, B. (2022). Enhanced antibacterial activity with increasing P doping ratio in CQDs. RSC Adv. 12 (43), 27709–27715. doi:10.1039/d2ra04809d
Chen, Z., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Qin, H., He, J., Zheng, Z., et al. (2022). Evaluation of Euglena gracilis 815 as a new candidate for biodiesel production. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 827513. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.827513
Christoph, E., Yu, L., Newby, S. D., Rivera Orsini, M. A., Scroggins, J., Keffer, D. J., et al. (2024). Novel kraft softwood lignin-derived carbon quantum dots: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro cytocompatibility. Nanomater. (Basel) 14 (12), 1029. doi:10.3390/nano14121029
Cui, T., Wu, Y., Peng, Z., Ban, Q., Wang, M., Cheng, J., et al. (2023). Spermidine-capped carbon dots as potent antimicrobial nanomaterials against Escherichia coli. Lwt 187, 115359. doi:10.1016/j.lwt.2023.115359
Das, C., Sillanpää, M., Zaidi, S. A., Khan, M. A., and Biswas, G. (2023). Current trends in carbon-based quantum dots development from solid wastes and their applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 30 (16), 45528–45554. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-25822-y
Dong, D., Liu, T., Liang, D., Jin, X., Qi, Z., Li, A., et al. (2021). Facile hydrothermal synthesis of chlorella-derived environmentally friendly fluorescent carbon dots for differentiation of living and dead chlorella. ACS Appl. Bio Mat. 4 (4), 3697–3705. doi:10.1021/acsabm.1c00178
Farjallah, A., Fillion, M., and Guéguen, C. (2024). Metabolic responses of Euglena gracilis under photoheterotrophic and heterotrophic conditions. Protist 175 (3), 126035. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2024.126035
Fatima, T., Husain, S., and Khanuja, M. (2024). Novel ternary Z scheme carbon quantum dots (CQDs) decorated WS2/PANI ((CQDs@WS2/PANI):0D:2D:1D) nanocomposite for the photocatalytic degradation and electrochemical detection of pharmaceutical drugs. Nano Mat. Sci. 7, 259–275. doi:10.1016/j.nanoms.2024.04.005
Gawal, P. M., and Golder, A. K. (2024). Vegetal route for synthesis of CQDs/CdS nanocomposites for photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to methanol under visible light. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 683 (000), 133068. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.133068
Gerbin, E., Frapart, Y. M., Marcuello, C., Cottyn, B., Foulon, L., Pernes, M., et al. (2020). Dual antioxidant properties and organic radical stabilization in cellulose nanocomposite films functionalized by in situ polymerization of coniferyl alcohol. Biomacromolecules 21 (8), 3163–3175. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00583
Ghosh Dastidar, D., Mukherjee, P., Ghosh, D., and Banerjee, D. (2021). Carbon quantum dots prepared from onion extract as fluorescence turn-on probes for selective estimation of Zn2+ in blood plasma. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 611 (000), 125781. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125781
Guehaz, K., Boual, Z., Abdou, I., Telli, A., and Belkhalfa, H. (2023). Microalgae's polysaccharides, are they potent antioxidants? Critical review. Arch. Microbiol. 206 (1), 14. doi:10.1007/s00203-023-03738-y
Guo, D., Lyu, Y., Gao, Y., Lin, Y., Zhang, X., Pan, Y., et al. (2021). Synthesis, solution and solid-state fluorescence of nitrogen self-doped carbon dots derived from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 631, 127741. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127741
Hua, X.-W., Bao, Y.-W., Wang, H.-Y., Chen, Z., and Wu, F.-G. (2017). Bacteria-derived fluorescent carbon dots for microbial live/dead differentiation. Nanoscale 9 (6), 2150–2161. doi:10.1039/c6nr06558a
Huang, K., Lin, L., Zhang, L., Zhao, M., Dai, X., Jiang, Y., et al. (2024). Rapid synthesis of ultra-bright blue and cyan CQDs fluorescent powders based on chemical dispersion and concentration effects. Ceram. Int. 50 (2 Pt.B), 4046–4052. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.11.173
Jia, X., Li, J., and Wang, E. (2012). One-pot green synthesis of optically pH-sensitive carbon dots with upconversion luminescence. Nanoscale 4 (18), 5572–5575. doi:10.1039/c2nr31319g
Jutidamrongphan, W., Park, K. Y., Lee, K., Kim, D., Lim, B. R., and Lee, J. W. (2015). Effect of carbon dioxide injection on photosynthetic wastewater treatment using microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Euglena gracilis. Desalin. Water Treat. 54, 3654–3660. doi:10.1080/19443994.2014.923197
Kaur, A., Kaur, M., and Vyas, P. (2024). Abatement of microbes and organic pollutants using heterostructural nanocomposites of rice straw CQDs with substituted strontium ferrite. Chemosphere 359, 142310. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.142310
Krishna Saraswat, S., Ahmed Mustafa, M., Kamil Ghadir, G., Kaur, M., Guamán Lozada, D. F., Hasen shuhata alubiady, M., et al. (2024). Carbon quantum dots: a comprehensive review of green synthesis, characterization and investigation their applications in bioimaging. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 162 (000), 112279. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2024.112279
Lee, H. H., Seong, J. Y., Kang, H., and Cho, H. (2024). Euglena gracilis enhances innate and adaptive immunity through specific expression of Dectin-1 in CP-induced immunosuppressed mice. Nutr. 16 (18), 3158. doi:10.3390/nu16183158
Li, X., Chen, C. C., Wu, L., Zhou, J., Huang, Y., and Zhu, X. (2024). Neglected negative effect of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) entering the ocean on marine organisms living in different water layers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 199, 115921. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115921
Liu, Y., Wang, X., Wang, G., Liu, B., Zhang, X., Chen, J., et al. (2025). Green biosynthesis of carbon quantum dots from lotus seed plumules for folic acid detection and bioimaging applications. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 332, 125825. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2025.125825
Ma, Y., Zhang, M., Wang, H., Wang, B., Huang, H., Liu, Y., et al. (2020). N-doped carbon dots derived from leaves with low toxicity via damaging cytomembrane for broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. Mat. Today Commun. 24, 101222. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101222
Manikandan, V., and Min, S. C. (2023). Biofabrication of carbon quantum dots and their food packaging applications: a review. Food. Sci. Biotechnol. 32 (9), 1159–1171. doi:10.1007/s10068-023-01309-x
Manjubaashini, N., Bargavi, P., and Balakumar, S. (2024). Carbon quantum dots derived from agro waste biomass for pioneering bioanalysis and in vivo bioimaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 454 (000), 115702. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2024.115702
Miao, Y., Zhang, T., Zhao, X., Sun, X., and Lv, J. (2025). Gadolinium doped carbon dots for anti-gram-negative bacteria and visible light photodynamic enhancement of antibacterial effect. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 326, 125158. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2024.125158
Mindivan, F., and Göktaş, M. (2023). The green synthesis of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) and characterization of polycaprolactone (PCL/CQDs) films. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Chem. Eng. Asp. 677, 132446. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132446
Mmelesi, O. K., Ammar-Merah, S., Nkambule, T. T. I., Nkosi, B., Liu, X., Kefeni, K. K., et al. (2024). The photodegradation of naproxen in an aqueous solution employing a cobalt ferrite-carbon quantum dots (CF/N-CQDs) nanocomposite, synthesized via microwave approach. J. Water Process Eng. 59 (000), 104968. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.104968
Nam, S. H., Lee, J., and An, Y. J. (2019). Quantitative assessment of photosynthetic activity of Chlorella (class Trebouxiophyceae) adsorbed onto soil by using fluorescence imaging. Environ. Pollut. 254 (Pt A), 112942. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2019.07.110
Nie, X., Jiang, C., Wu, S., Chen, W., Lv, P., Wang, Q., et al. (2020). Carbon quantum dots: a bright future as photosensitizers for in vitro antibacterial photodynamic inactivation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 206, 111864. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.111864
Ortiz Montoya, E. Y., Casazza, A. A., Aliakbarian, B., Perego, P., Converti, A., and de Carvalho, J. C. M. (2014). Production of Chlorella vulgaris as a source of essential fatty acids in a tubular photobioreactor continuously fed with air enriched with CO2 at different concentrations. Biotechnol. Prog. 30 (4), 916–922. doi:10.1002/btpr.1885
Pandya, P., Webster, T. J., and Ghosh, S. (2024). Nanobioprospecting of photoautotrophs for the fabrication of quantum dots: mechanism and applications. Front. Chem. 12, 1458804. doi:10.3389/fchem.2024.1458804
Pant, M., Kumar, S., Kiran, K., Bisht, N. S., Pande, V., and Dandapat, A. A. (2023). A universal green approach for the synthesis of NPS-codoped carbon quantum dots with enhanced broad-spectrum antibacterial and antioxidant activities. RSC Adv. 13 (14), 9186–9194. doi:10.1039/d2ra08103b
Pei, S., Cai, S., Yan, K., Zhou, J., Luo, K., and Chen, X. (2025). Synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots as an effective fluorescent sensor of Fe3+ ions and a potent antibacterial agent. J. Fluoresc. 35, 7339–7348. doi:10.1007/s10895-024-04112-x
Qandeel, N. A., El-Shaheny, R., El-Masry, A. A., Eid, M., and Moustafa, M. A. (2024). Valorization of cantaloupe waste for green microwave-driven synthesis of N-self doped CQDs as a fluorescence sensor for nizatidine in urine and pharmaceuticals. A step ahead for circular economy practice. Microchem. J. 199 (000), 110047. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2024.110047
Shahabadi, N., Omidfar, K., and Zendehcheshm, S. (2024). Hemoglobin-capped carbon dots synthesized via microwave green approach as a biosensor for specific cholesterol detection. Microchem. J. 207, 111652. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2024.111652
Singh, A. K., Itkor, P., Lee, M., Saenjaiban, A., and Lee, Y. S. (2024). Synergistic integration of carbon quantum dots in biopolymer matrices: an overview of current advancements in antioxidant and antimicrobial active packaging. Molecules 29 (21), 5138. doi:10.3390/molecules29215138
Slewa, L. H. (2024). Antifungal films for strawberry packaging using carbon quantum dots derived from lemon and onion juice via green hydrothermal method. Food Biosci. 61, 104653. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104653
Sweidan, A., El-Mestrah, M., Kanaan, H., Dandache, I., Merhi, F., and Chokr, A. (2020). Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Scorzonera mackmeliana. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 33 (1), 199–206. doi:10.36721/PJPS.2020.33.1.REG.199-206.1
Tao, S., Lu, S., Geng, Y., Zhu, S., Redfern, S. A. T., Song, Y., et al. (2018). Design of metal-free polymer carbon dots: a new class of room-temperature phosphorescent materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57 (9), 2393–2398. doi:10.1002/anie.201712662
Tejwan, N., Saini, A. K., Sharma, A., Singh, T. A., Kumar, N., and Das, J. (2021). Metal-doped and hybrid carbon dots: a comprehensive review on their synthesis and biomedical applications. J. Control. Release. 330, 132–150. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.023
Thakur, S., Bains, A., Kumar, A., Goksen, G., Dhull, S. B., Ali, N., et al. (2024). Biomass-derived carbon quantum dots from Chlorella vulgaris: photocatalytic reduction of malachite green dye coupled with anti-quorum sensing and antimicrobial activity against food pathogens. Food Biosci. 62, 105272. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2024.105272
Torres, F. G., Gonzales, K. N., Troncoso, O. P., and Cañedom, V. S. (2023). Carbon quantum dots based on marine polysaccharides: types, synthesis, and applications. Mar. Drugs. 21 (6), 338. doi:10.3390/md21060338
Tu, L., Li, Q., Qiu, S., Li, M., Shin, J., Wu, P., et al. (2023). Recent developments in carbon dots: a biomedical application perspective. J. Mat. Chem. B 11 (14), 3038–3053. doi:10.1039/d2tb02794a
Vasluianu, R. I., Dima, A. M., Bobu, L., Murariu, A., Stamatin, O., Baciu, E. R., et al. (2025). Dentistry insights: single-walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, carbon dots, and the rise of hybrid materials. J. Funct. Biomater. 16 (3), 110. doi:10.3390/jfb16030110
Wang, T., Liu, X., Ma, C., Zhu, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2018). Bamboo prepared carbon quantum dots (CQDs) for enhancing Bi3Ti4O12 nanosheets photocatalytic activity. J. Alloys Compd. 752, 106–114. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.04.085
Wang, C., Bi, L., Liu, J., Huang, B., Wang, F., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Microalgae-derived carbon quantum dots mediated formation of metal sulfide nano-adsorbents with exceptional cadmium removal performance. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 629 (Pt A), 994–1002. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.188
Wang L., L., Wang, T., Hao, R., and Wang, Y. (2024). Construction strategy and mechanism of a novel wood preservative with excellent antifungal effects. Molecules 29 (5), 1013. doi:10.3390/molecules29051013
Wang, Y., Gu, Z., Dong, J., Zhu, J., Liu, C., Li, G., et al. (2024). Green synthesis of chlorella-derived carbon dots and their fluorescence imaging in zebrafish. RSC Adv. 14 (2), 1459–1463. doi:10.1039/d3ra07623g
Wang, J., Li, H., Su, Q., Liu, J., Li, K., Wang, Z., et al. (2025). Living photosynthetic micro/nano-platforms: engineering unicellular algae for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mat. 51, 575–597. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.023
Wu, L., Gao, Y., Zhao, C., Huang, D., Chen, W., Lin, X., et al. (2022). Synthesis of curcumin-quaternized carbon quantum dots with enhanced broad-spectrum antibacterial activity for promoting infected wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 133, 112608. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2021.112608
Yan, K. T. H., Hie, I. S. Y., Samaranayake, E. A., Chang, J. L. K., and Wang, A. Z. H. (2023). Medium and process optimizations for Euglena gracilis with high biomass production enriched with protein. Algal Res. 75, 103265. doi:10.1016/j.algal.2023.103265
Zapata-Hernandez, C., Durango-Giraldo, G., Gomez-Echeverri, M., Buitrago-Sierra, R., Herrera, B., and Cacua, K. (2024). The impact of carbon quantum dots derived from spent coffee grounds on the droplet combustion of diesel/n-butanol blend. Heliyon 10 (21), e39671. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39671
Zeng, R., Gao, Q., Xiao, L., Wang, W., Gu, Y., Huang, H., et al. (2024). Precise tuning of the d-band center of dual-atomic enzymes for catalytic therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 146 (14), 10023–10031. doi:10.1021/jacs.4c00791
Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Shi, Y., Sun, C., Zhou, N., and Wen, H. (2020b). The synthesis and functional study of multicolor nitrogen-doped carbon dots for live cell nuclear imaging. Molecules 25 (2), 306. doi:10.3390/molecules25020306
Zhang, J., Xia, A., Chen, H., Nizami, A. S., Huang, Y., Zhu, X., et al. (2022a). Biobased carbon dots production via hydrothermal conversion of microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Sci. Total Environ. 839, 156144. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156144
Zheng, Y., Zheng, J., Wang, J., Yang, Y., Lu, T., and Liu, X. (2020). Facile preparation of stable solid-state carbon quantum dots with multi-peak emission. Nanomater. (Basel) 10 (2), 303. doi:10.3390/nano10020303
Zhu, S., Meng, Q., Wang, L., Zhang, J., Song, Y., Jin, H., et al. (2013). Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52 (14), 3953–3957. doi:10.1002/anie.201300519
Keywords: Euglena gracilis, hydrothermal green synthesis, carbon quantum dots, bacterial inhibition, bioimaging
Citation: Cheng H, Yang C, Xu W, Deng Z, Guan G, Zahid H, Liu Y, Hu B, Qin Z and Ren M (2025) Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots from Euglena gracilis for antibacterial and bioimaging applications. Front. Nanotechnol. 7:1634916. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2025.1634916
Received: 25 May 2025; Accepted: 30 September 2025;
Published: 22 October 2025.
Edited by:
Vijay Bhooshan Kumar, Los Alamos National Laboratory (DOE), United StatesReviewed by:
Carlos Marcuello, Instituto de Nanociencia y Materiales de Aragón (INMA), SpainVarsha Sahu, Utkal University Department of Pharmacy, India
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Yang, Xu, Deng, Guan, Zahid, Liu, Hu, Qin and Ren. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhanke Qin, cWtfMDEyQDE2My5jb20=; Maozhi Ren, cmVubWFvemhpMDFAY2Fhcy5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hao Cheng
Hao Cheng Chenglong Yang1,3†
Chenglong Yang1,3† Yi Liu
Yi Liu Maozhi Ren
Maozhi Ren