Abstract
A longstanding enigma in molecular biology is the lack of scaling of protein-coding genes with developmental complexity, referred to as the g-value paradox. On the other hand, a feature of the evolution of multicellular organisms is the emergence of genetic loci termed “enhancers,” which control the spatiotemporal patterns of gene expression during development. Enhancer action has been widely interpreted in terms of an early model that postulated that transcription factors bound at enhancers are brought into juxtaposition with the promoters of target genes. This model tacitly assumed that there is no trans-acting gene product of enhancers, but subsequent studies have shown that enhancers are transcribed in the cells in which they are active. Like protein-coding genes, enhancers produce short bidirectional transcripts and long alternatively spliced RNAs, albeit at lower levels due to their transitory and cell-specific regulatory functions. The evidence indicates that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) expressed from enhancers (elncRNAs) guide the formation of phase-separated transcriptional hubs and the epigenetic modifications to direct cell fate decisions during animal and plant ontogeny. Many, and likely most, lncRNAs are elncRNAs, which should be recognized as a bona fide class of gene products alongside mRNAs, rRNAs, tRNAs, snoRNAs, miRNAs and others of established function, with sequences specifying elncRNAs comprising an increasing fraction of genomic information as developmental complexity increases.
Introduction
Enhancers are genomic sequences in animals and plants that control developmental cell-type-specific spatiotemporal expression patterns of a subset of genes in their neighborhood (Hnisz et al., 2013; Shlyueva et al., 2014; Arnold et al., 2020). Enhancers can be located hundreds of kilobases away from their target genes and are (local) position and orientation-independent (Schoenfelder and Fraser, 2019; Arnold et al., 2020).
Enhancer activity was first observed by Ed Lewis and others in their early studies of the bithorax complex of Drosophila melanogaster (Maeda and Karch, 2006), although it was only in the early 1980s that the term was coined to describe the unexpected ability of certain SV40 virus sequences to increase the expression of a β-globin gene (Banerji et al., 1981). Many tissue-specific enhancers, also referred to as “locus control regions” (Li et al., 2002), were subsequently identified in mammalian immunoglobulin and globin gene loci, as well as in other genes that show restricted expression patterns during development, initially using cloning and deletion approaches (Banerji et al., 1983; Gillies et al., 1983; Whiting et al., 1991; Miyagi et al., 2004; Park et al., 2004; Perry et al., 2011) or insertions of transposons with reporter genes (“enhancer trapping”) in Drosophila (O’Kane and Gehring, 1987; Galloni et al., 1993; McCall et al., 1994; Stathopoulos et al., 2002), plants (Springer, 2000) and other vertebrates (Trinh and Fraser, 2013), lately extended to high throughput CRISPR mutagenesis (Canver et al., 2015; Fulco et al., 2019; Gasperini et al., 2019).
Attempts have been made to typify known enhancers and identify others by their molecular features, including the location of presumed signature proteins (the “transcriptional co-activators” P300/CBP and Mediator), characteristic histone modifications, nucleosome-depleted regions, chromatin topology and/or the expression of “enhancer RNAs” (eRNAs) (Heintzman et al., 2007; Heintzman et al., 2009; De Santa et al., 2010; Wang D et al., 2011; Shen et al., 2012; Whyte et al., 2013; Wu et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2015; Pradeepa et al., 2016; Fulco et al., 2019; Osmala and Lähdesmäki, 2020). Although these features yield somewhat different prediction sets (Hnisz et al., 2013; Heidari et al., 2014; Shlyueva et al., 2014; Rickels and Shilatifard, 2018; Fulco et al., 2019; Halfon, 2019), they have been used to estimate that there are hundreds of thousands of enhancers in the human genome (De Santa et al., 2010; Dunham et al., 2012; Shen et al., 2012; Thurman et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2013; Andersson et al., 2014; Heidari et al., 2014; Arnold et al., 2020; Chen and Liang, 2020), clusters of which have been dubbed “super-enhancers,” “stretch enhancers” or “enhancer jungles” (Hnisz et al., 2013; Parker et al., 2013; Whyte et al., 2013; Pott and Lieb, 2015; Wang et al., 2019; Chen and Liang, 2020; Li and Ovcharenko, 2020).
The appearance of enhancers is associated with the emergence of animal and plant multicellularity and phenotypic diversity (Rubinstein and de Souza, 2013; Villar et al., 2015; Sebé-Pedrós et al., 2016; Rebeiz and Tsiantis, 2017), neuronal expansion in vertebrates (Closser et al., 2021) and the recent evolution of primates (Lagha et al., 2012; Glinsky and Barakat, 2019; Tejada-Martinez et al., 2021). Positive selection for nucleotide changes in enhancers (Whalen and Pollard, 2022), often involving exaptation of transposable elements (Barth et al., 2020), have contributed, for example, to the uniquely human aspects of brain development (Reilly et al., 2015; Mangan et al., 2022), thermoregulation (sweat glands in the skin) (Aldea et al., 2021), and digit and limb patterning, including the increase in size and rotation of the thumb towards the palm for enhanced dexterity (Prabhakar et al., 2008). Many loci contain clusters of enhancers with overlapping activities that are deployed to produce specific patterns of gene expression in different cell types (Whiting et al., 1991; Li et al., 2002; Perry et al., 2011; Malkmus et al., 2021), and it is clear that body plan specification is controlled by multiple enhancers to ensure precise patterns of gene expression during development (Woltering and Duboule, 2010; Perry et al., 2011), the robustness of which is increased by additional so-called “shadow” enhancers that confer increased precision and may provide buffering against noise (Hong et al., 2008; Cannavò et al., 2016; Osterwalder et al., 2018; Waymack et al., 2020; Kvon et al., 2021).
The mechanism of enhancer action.
The mechanism of enhancer action has long been a matter of speculation. A popular model is that put forward in the mid-1980s to reconcile enhancer function with transcription factor control of gene expression, which posits that transcription factor binding sites located in the enhancer are brought into contact with target protein-coding gene promoters by long-distance DNA looping (Dynan and Tjian, 1985; Ptashne, 1986; 1988; Popay and Dixon, 2022). This “crosstalk” model has been described as an example of a founder fallacy, whereby an initial interpretation of limited data is accepted and becomes subject to validation creep (Halfon, 2019).
It is well established that enhancer action alters chromatin topology and the juxtaposition of distal chromosomal sequences in 3-dimensional space, with consequent transcriptional activation of genes in their orbit (Larke et al., 2021; Popay and Dixon, 2022). Enhancer-mediated DNA “loops” may be equivalent to topologically-associated domains (TADs) identified by chromatin conformation capture analysis (Rao et al., 2014; Symmons et al., 2014; Lupianez et al., 2015; Hansen et al., 2018; Souaid et al., 2018) and play a role in the formation and organization of such domains (Furlong and Levine, 2018; Souaid et al., 2018; Lim and Levine, 2021). TAD boundaries are maintained by the interplay of the Cohesin and Mediator complexes and the zinc finger “transcription factor” CTCF (Kagey et al., 2010; Lee and Iyer, 2012; Wutz et al., 2017; Hansen et al., 2018; Popay and Dixon, 2022), all of which bind RNA or RNA/DNA hybrids (Yao et al., 2010; Saldana-Meyer et al., 2014; Kung et al., 2015; Hansen et al., 2019; Pan et al., 2020; Kuru-Schors et al., 2021). Enhancers also play a role in the etiology of complex diseases, developmental disorders and cancer (Hnisz et al., 2013; Smith and Shilatifard, 2014; Herz, 2016; Chen and Liang, 2020; Jindal and Farley, 2021), and disruptions of chromatin topological domains lead to rewiring of gene-enhancer interactions with pathogenic consequences (Smith and Shilatifard, 2014; Lupianez et al., 2015; Krijger and de Laat, 2016; Souaid et al., 2018; Nott et al., 2019; Beagan et al., 2020; Nasser et al., 2021).
There is now considerable evidence that enhancer-driven loop/TAD formation involves the formation of phase-separated biomolecular condensates that act as transcription/splicing hubs (Hnisz et al., 2017; Boehning et al., 2018; Boija et al., 2018; Cho et al., 2018; Hahn, 2018; Sabari et al., 2018; Fang et al., 2019; Nair et al., 2019; Shrinivas et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2019; Jia et al., 2021; Lim and Levine, 2021; Wang J et al., 2021), which are disrupted in developmental disorders and cancer (Kaiser and Semple, 2017; Ahn et al., 2021). In vivo, phase-separated domains (PSDs) are formed by interactions between RNAs and proteins containing intrinsically disordered domains (IDRs) (Järvelin et al., 2016; Fay and Anderson, 2018; Polymenidou, 2018; Protter et al., 2018; Garcia-Jove Navarro et al., 2019; Sanders et al., 2020; Roden and Gladfelter, 2021), which include almost all transcription factors, chromatin-modifying proteins, splicing factors, other RNA binding proteins, Mediator and other complexes involved in TAD formation (Gueroussov et al., 2017; Boija et al., 2018; Hentze et al., 2018; Niklas et al., 2018; Watson and Stott, 2019; Richter et al., 2022), the incidence of which correlates with developmental complexity (Yruela et al., 2017; Kulkarni and Uversky, 2018; Niklas et al., 2018). IDRs determine the localization of transcription factors to target promoters in vivo (Brodsky et al., 2020), and are overrepresented in alternatively spliced exons subject to tissue- and lineage-specific regulation (Romero et al., 2006; Buljan et al., 2012). IDRs are also the major sites of post-translational modifications (Bah and Forman-Kay, 2016), which influence their interactome or “promiscuity” (Cumberworth et al., 2013; Niklas et al., 2015; Wright and Dyson, 2015; Protter et al., 2018; Balcerak et al., 2019; Macossay-Castillo et al., 2019), a central feature of their flexibilities and capabilities, essential to cell state specification during development (see below). Nearly half of RNA-binding sites map to IDRs, which are hotspots of disease due to missense, nonsense and frame-shift mutations (Vacic and Iakoucheva, 2012; Hentze et al., 2018; Meyer et al., 2018; Tsang et al., 2020; Ahmed et al., 2022).
However, there is no evidence that transcription factors bound to enhancer sequences contact the promoters of target genes; rather, this is an enduring assumption. By contrast there is extensive evidence that enhancers are transcribed in the cells in which they are active (Hnisz et al., 2013; Arner et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2015; Li et al., 2016; Hon et al., 2017; Arnold et al., 2020).
Transcription from enhancers
A large fraction of “extragenic” RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers (De Santa et al., 2010). Enhancers express short unstable bi-directional RNAs (sometimes called “eRNAs”) (Koch et al., 2011; Azofeifa et al., 2018). However, short bi-directional unstable RNAs are also produced from active protein-coding genes, and likely have a function in both cases (Seila et al., 2008; Young et al., 2017). Indeed, the epigenetic landscape of, and the features of transcription initiation at, the promoters of enhancers and protein-coding genes are almost indistinguishable (Koch et al., 2011; Core et al., 2014; Arner et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2015; Li et al., 2016; Arnold et al., 2020). Both protein-coding genes and enhancers express long multi-exonic RNAs (Wu et al., 2014; Arner et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2015; Gil and Ulitsky, 2018; Carullo et al., 2020; Sartorelli and Lauberth, 2020), and may not be mutually exclusive, noting the complexity and interleaved nature of mammalian transcription and the fuzzy boundaries of genes (Mattick, 2003; Engstrom et al., 2006; Kapranov et al., 2007), the observations that many enhancers are located in introns or antisense to protein-coding genes (Gillies et al., 1983; Hong et al., 2008; Borsari et al., 2021; Thomas et al., 2021; Bachu et al., 2022), that intronic RNAs constitute the major fraction of the non-coding non-ribosomal RNA in mammalian cells (St Laurent et al., 2012), that antisense RNAs regulate development-specific alternative splicing (Degani et al., 2021; Pérez-Lluch et al., 2021), and that the major transcript from an estimated 17% of human protein-coding genes lacks an annotated coding sequence as indicated by GENCODE (Gonzàlez-Porta et al., 2013).
The long transcripts expressed from enhancers have also been referred to as “eRNAs,” a term that should be reserved for them given that the short bidirectional transcripts also called eRNAs are not specific to enhancers but simply indicative of active promoters. However, to avoid confusion and provide specificity, a better descriptor is “elncRNAs” (enhancer-derived long noncoding RNAs) (Setten et al., 2021; Tan and Marques, 2022), which will be used henceforth. It has been shown that elncRNAs are transcribed by RNA Polymerase II and retained in the nucleus (Koch et al., 2011; Natoli and Andrau, 2012), and that RNA exosome-regulated long non-coding RNA transcription controls super-enhancer activity (Pefanis et al., 2015).
Enhancer transcription is considered the best molecular indicator of enhancer activity in developmental processes (Wu et al., 2014; Arner et al., 2015; Kim et al., 2015; Carullo et al., 2020; Sartorelli and Lauberth, 2020) and cancers (Chen and Liang, 2020). There has been uncertainty about whether the resulting eRNAs are byproducts of TF binding at enhancers or are integral to enhancer action (Li et al., 2016; Schoenfelder and Fraser, 2019), but the evidence is now strongly in favor of the latter, although it is also clear that the act of transcription itself modulates enhancer activity (Pande et al., 2018; Morf et al., 2020; Pande et al., 2020). While genetic analysis by enhancer deletion may not distinguish between the loss of cis-acting DNA regulatory elements and trans-acting elncRNAs (Gao et al., 2020; Andergassen and Rinn, 2021), more incisive strategies such as the insertion of polyA transcription termination sites, removal of elncRNA exons, siRNA- and CRISPRi/Cas13-directed RNA knockdown have shown that elncRNAs are required for enhancer function in diverse contexts (Maass et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013; Melo et al., 2013; Lam et al., 2014; Paralkar et al., 2014; Sun et al., 2014; Xiang et al., 2014; Yin et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016; Isoda et al., 2017; Cajigas et al., 2018; Groff et al., 2018; Fatima et al., 2019; Lewandowski et al., 2019; Allou et al., 2021; Andergassen and Rinn, 2021; Cajigas et al., 2021; Setten et al., 2021; Zibitt et al., 2021). Structural probing and mutational analysis has shown that the elncRNA MUNC, like lncRNAs generally (Mattick et al., 2023), has a defined secondary structure with separate domains that mediate different functions during myogenesis (Przanowska et al., 2022). Indeed, there is strong evidence that lncRNAs have a modular structure, often involving “repeat sequences,” capable of scaffolding chromatin-modifying and other proteins and interacting with genomic target sites via R-loop or triplex formation (Brosius, 2014; Mattick et al., 2023).
Ectopic expression of elncRNAs increases expression of genes targeted by the enhancer (Alvarez-Dominguez et al., 2017; Shii et al., 2017), although there are exceptions (Anderson et al., 2016), and both splicing and modification of elncRNAs modulate enhancer activity (Li et al., 2015; Gil and Ulitsky, 2018; Tan et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2021; Tan and Marques, 2022). Reciprocally, a number of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to emanate from enhancers (Koch et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2015) and/or have enhancer-like developmental effects (Orom et al., 2010; Luo et al., 2016; Alexanian et al., 2017; Barter et al., 2017; Deveson et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2017; Micheletti et al., 2017; Andersen et al., 2019; Field et al., 2019; Ritter et al., 2019; Wilson et al., 2020; Dill et al., 2021; Pal et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2022). Genome-wide enhancer maps have linked disease risk variants to loci identified by genome-wide association studies (Nasser et al., 2021), most of which express lncRNAs (Bartonicek et al., 2017; Hardwick et al., 2019).
There is a striking degree of congruence between the features of elncRNAs and lncRNAs generally (Natoli and Andrau, 2012; Wu et al., 2014; Mattick et al., 2023). Transcriptional data suggest that many if not most lncRNAs are derived from enhancers (Li et al., 2016; Hon et al., 2017). Their numbers are broadly similar: although there are only −20,000 human lncRNA genes annotated in GENCODE1, −100,000 human lncRNA genes have been catalogued in dedicated databases (Fang et al., 2017; The RNAcentral Consortium, 2018; Ma et al., 2019; Volders et al., 2019; Statello et al., 2021); there are likely many more (Deveson et al., 2017), given the under sampling of cells at different developmental stages and the high resolution analyses that have revealed the existence of previously unreported lncRNAs and their isoforms expressed from GWAS regions (Bartonicek et al., 2017; Hardwick et al., 2019), across ch21 (Deveson et al., 2018) and from well-characterized loci, such as those containing p53 and HOX genes (Mercer et al., 2012). While some may be a product of transcriptional noise (Brosius and Raabe, 2016; Xu et al., 2023), thousands of lncRNAs (including many “antisense” RNAs) have been shown to have biological effects when their sequence or expression is perturbed and, while most have not been investigated, indices of their functionality include differential expression, subcellular localization, promoter and splice site conservation, multiexonic structure and extensive alternative splicing (Mattick and Amaral, 2022; Mattick et al., 2023), the latter shown to affect enhancer activity (Tan and Marques, 2022). Like lncRNAs generally (although there are exceptions, such as lncRNAs associated with more generic subnuclear domains such as nucleoli, paraspeckles and neuronal granules (Yamazaki et al., 2021; Yamazaki and Hirose, 2021; Grzejda et al., 2022)), elncRNAs are expressed at relatively low levels and exhibit only modest conservation across species (Deveson et al., 2017; Sartorelli and Lauberth, 2020; Mattick et al., 2023), features consistent with cell- and lineage-specific regulatory functions.
Chromatin modification
High resolution imaging shows the localization of many lncRNAs in punctate domains in the nucleus (Cabili et al., 2015; Quinodoz et al., 2021), with other studies showing widespread chromatin targeting of lncRNAs (Mishra and Kanduri, 2019) and the involvement of lncRNAs [sometimes referred to as “architectural” RNAs (Takeshi et al., 2017)] in the organization of chromosome territories via phase separation (Redrup et al., 2009; Cerase et al., 2019; Li and Fu, 2019; Pessina et al., 2019; Thakur and Henikoff, 2020; Wu et al., 2021a; Bridges et al., 2021; Elguindy and Mendell, 2021; Luo et al., 2021; Wang R et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021). Cohesin, Mediator and CTCF, which determine TAD boundaries, have been shown to be recruited to their target sites by enhancer-derived RNAs (Lai et al., 2013; Li et al., 2013; Tsai et al., 2018; Schoenfelder and Fraser, 2019; Islam et al., 2023). Enhancer function has been shown to require assembly of an enhancer RNA–dependent ribonucleoprotein condensate (Nair et al., 2019), and Mediator complexes with cohesin to form rings that connect two DNA segments and clusters with RNAPII in transcription-dependent condensates (Kagey et al., 2010; Cho et al., 2018). Enhancers also interact with histone modifying proteins and elncRNAs have been shown to modulate DNA and histone modifications and transcription factor binding (Bose et al., 2017; Carullo et al., 2020; Harrison and Bose, 2022). Similarly, lncRNAs associate with chromatin modifying complexes (Dinger et al., 2008; Nagano et al., 2008; Pandey et al., 2008; Khalil et al., 2009), including those identified as elncRNAs involved in the maintenance of stem cell fates and lineage specification (Dinger et al., 2008; Wang K C et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2014; Deng et al., 2016; Subhash et al., 2018).
RNA binding by chromatin-modifying complexes has—like that of IDR-containing proteins generally—been described as “promiscuous” (Davidovich et al., 2013), reflecting their ability to interact with many partners, determined by local concentration, alternative splicing, and post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications (Romero et al., 2006; Buljan et al., 2012; Weatheritt et al., 2012; Cumberworth et al., 2013; Deveson et al., 2018; Protter et al., 2018; Balcerak et al., 2019; Macossay-Castillo et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2021b; Shiau et al., 2022). Cytosine (5mC) and adenosine (m6A) modifications of elncRNAs are known features of active enhancers that regulate their abundance, facilitate transcriptional condensate formation and potentiate co-activator function (Aguilo et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022). RNA modifying enzymes accompany elncRNAs in the formation of PSDs (Harrison and Bose, 2022) and RNA modifications affect a wide range of developmental processes (Mattick and Amaral, 2022). Interestingly, biomolecular condensates also play a role in RNA-directed transgenerational epigenetic inheritance (Wan et al., 2018).
A new model of enhancer action.
As noted already, the popular model for enhancer action posits that transcription factor binding sites located in the enhancer are brought into contact with target protein-coding gene promoters by long-distance DNA looping (Dynan and Tjian, 1985; Ptashne, 1986; Ptashne, 1988; Popay and Dixon, 2022), which is simple to conceive and illustrate. A new schema must consider all of the above information, including the formation of phase-separated topologically-associated domains and the guidance by elncRNAs of TAD boundary proteins, chromatin-modifying complexes and transcription factors to target sites within these domains by RNA-protein and RNA-DNA interactions. A model that attempts to do this is presented in Figure 1, with the important caveat that, while such models can illustrate and expose hypotheses to be tested, they can also constrain and mislead.
FIGURE 1
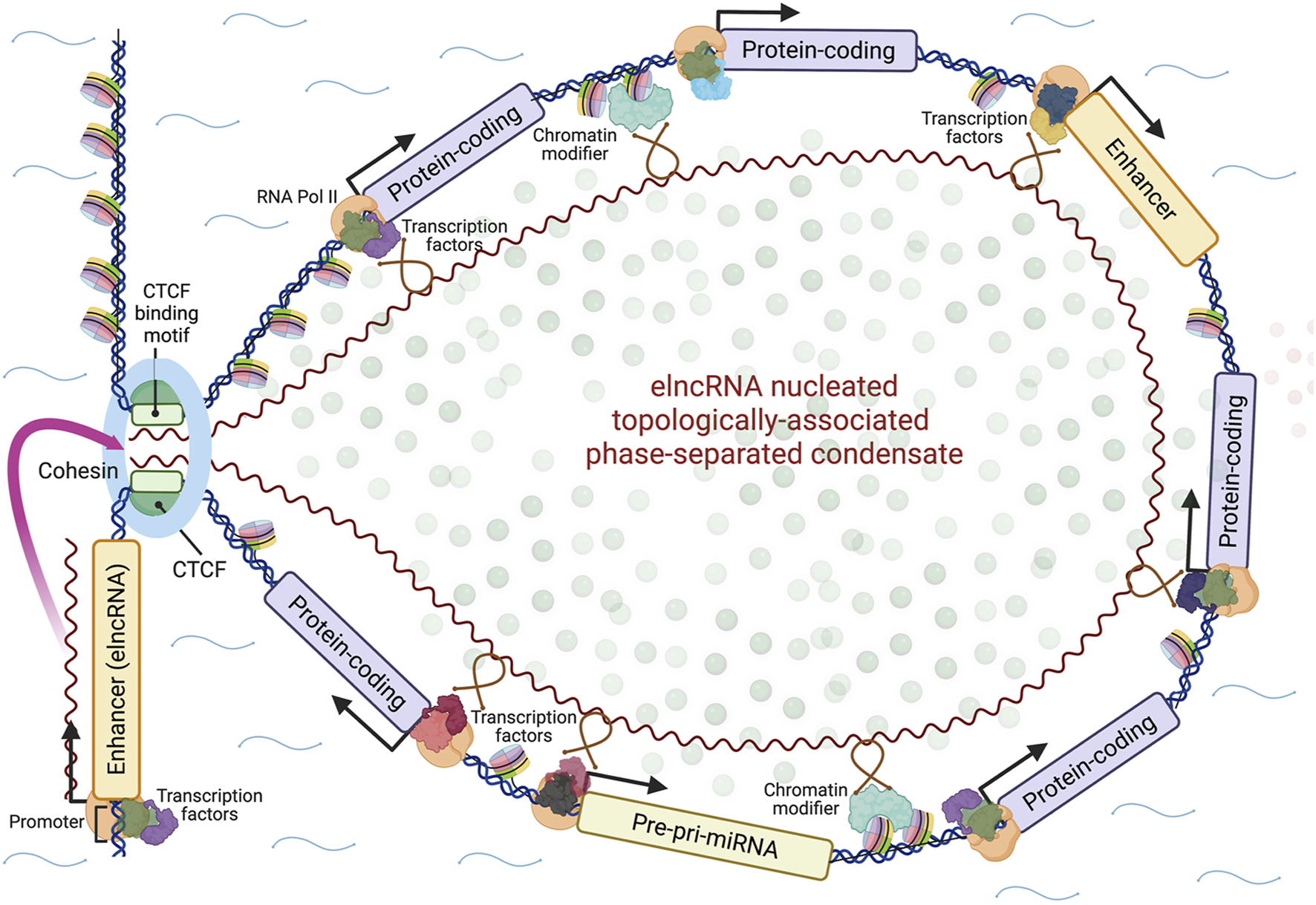
A model for the action of enhancers. Enhancer genes express modular elncRNAs, which nucleate the formation of phase-separated topologically-associated transcription-splicing hubs through their interactions with effector proteins (loop anchoring proteins, chromatin-modifying proteins, transcription factors, splicing factors, other RNA binding proteins) and genomic target sites via RNA-DNA or RNA-DNA-DNA triplex formation. Whether the nucleating elncRNA genes are contained within the looped domain and/or other enhancer loci may be activated within it in a feed-forward fashion is uncertain. The looped domain may also include genes for other regulatory RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs). Created with BioRender.com.
Conclusion
There are two unresolved major features of molecular biology and genetics: lncRNAs and enhancers, both estimated to number in the hundreds of thousands in mammals. The emergent picture is that 1) enhancers comprise their promoters and the RNAs that are transcribed from them and 2) a major subclass of lncRNAs is elncRNAs, whose function is to regulate chromatin architecture and thereby expression of protein-coding and other RNAs (including potentially miRNAs, antisense RNAs and other elncRNAs in a developmental feed-forward fashion), through physical mechanisms that involve recognition of transcription factors, chromatin-modifying complexes, RNA binding and other effector proteins containing IDRs, as well as their genomic target sequences via R-loops or triplexes (Soibam, 2017; Cetin et al., 2019; Mishra and Kanduri, 2019; Cai et al., 2020; Farabella et al., 2021), to form topologically-associated domains that act as developmental stage-specific transcriptional and splicing hubs.
This is not to say that all lncRNAs are elncRNAs; there are many others involved in the formation of specialized domains in the nucleus and the cytoplasm (including metabolic pathways, translation, synapse architecture and autophagy) (Lyon et al., 2021), most of which have yet to be characterized. It is also important to reiterate that, while enhancers and those encoding mRNAs are “genes” in the sense of producing products with phenotypic consequences, they are not discrete entities but rather entangled components of a continuum of genetic information. Moreover, protein-coding loci may also have enhancer activity (Engreitz et al., 2016) and, while it has been observed that transcription affects chromatin architecture (Mele and Rinn, 2016; Creamer et al., 2021), transcription alone does not provide the specificity needed for fine scale control of the epigenetic status and expression of nearby genes.
Enhancers must act transiently at almost every stage of ontogeny [see, e.g. (Bachu et al., 2022; Landshammer et al., 2023)], most of which have not been polled. Humans contain an estimated 30 trillion cells (excluding the microbiome) (Bianconi et al., 2013; Sender et al., 2016), which means that −6 × 1013 binary cell fate (differentiate and/or divide) decisions must be made with high precision and reproducibility to ensure the correct formation of an adult with its myriad of architecturally distinct and correctly wired muscles, bones and organs, exemplified by the phenotypic congruence of monozygotic twins (Mattick and Amaral, 2022).
This number of cell fate decisions is four orders of magnitude greater than the linear information content of the human genome (about × 6109 bits), which implies a dense file structure (Mattick and Amaral, 2022) that may be unzipped by combinatorics of the extensive alternative splicing of lncRNAs (Mercer and Mattick, 2013; Deveson et al., 2018; Rinn and Chang, 2020), RNA modifications, and post-translational modifications of IDRs in interacting proteins and their alternatively spliced exons (Romero et al., 2006; Buljan et al., 2012) to guide the formation, composition and genomic sphere of influence of enhancers at each stage of developmental ontogeny.
It will be a mammoth challenge to decipher the feed-forward program that determines enhancer expression, the structure-function relationships and interactome of elncRNAs during development. It will be an even bigger challenge to understand how regional enhancer action is integrated to inform cell fate decisions, likely by the centrosome2 in animals (itself a phase-separated organelle) (Zwicker et al., 2014; Conduit et al., 2015; Joukov and De Nicolo, 2019) and the mitotic spindle in plants (Liu and Lee, 2022), noting that plant development is more flexible to be responsive to environmental circumstances. Whatever the details, it is evident that the fraction of the genome devoted to enhancers scales with developmental complexity, and that sequences specifying elncRNAs occupy a far greater fraction of animal and plant genomes than those specifying proteins.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and has approved it for publication.
Acknowledgments
JM is supported by SHARP Professorship RG193211 from UNSW Sydney.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; PSD, phase-separated domain; TAD, topologically-associated domain; IDR, intrinsically disordered region; eRNA, enhancer-derived RNA; elncRNA, enhancer-derived lncRNA.
Footnotes
1.^ https://www.gencodegenes.org/human/stats.html.
2.^3′UTRs have been implicated in centrosome localization (Bergalet et al., 2020), an interesting observation in view of the fact that many if not most mammalian genes express 3′UTRs (separately from their normally associated protein-coding sequences) that are chromatin-localized, inhibit cell division and induce differentiation (Mercer et al., 2011; Kocabas et al., 2015; Vilborg et al., 2015), in one case essential for oocyte development (Jenny et al., 2006).
References
1
Aguilo F. Li S. Balasubramaniyan N. Sancho A. Benko S. Zhang F. et al (2016). Deposition of 5-methylcytosine on enhancer RNAs enables the coactivator function of PGC-1α. Cell Rep.14, 479–492. 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.043
2
Ahmed S. S. Rifat Z. T. Lohia R. Campbell A. J. Dunker A. K. Rahman M. S. et al (2022). Characterization of intrinsically disordered regions in proteins informed by human genetic diversity. PLoS Comput. Biol.18, e1009911. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009911
3
Ahn J. H. Davis E. S. Daugird T. A. Zhao S. Quiroga I. Y. Uryu H. et al (2021). Phase separation drives aberrant chromatin looping and cancer development. Nature595, 591–595. 10.1038/s41586-021-03662-5
4
Aldea D. Atsuta Y. Kokalari B. Schaffner S. F. Prasasya R. D. Aharoni A. et al (2021). Repeated mutation of a developmental enhancer contributed to human thermoregulatory evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.118, e2021722118. 10.1073/pnas.2021722118
5
Alexanian M. Maric D. Jenkinson S. P. Mina M. Friedman C. E. Ting C.-C. et al (2017). A transcribed enhancer dictates mesendoderm specification in pluripotency. Nat. Commun.8, 1806. 10.1038/s41467-017-01804-w
6
Allou L. Balzano S. Magg A. Quinodoz M. Royer-Bertrand B. Schöpflin R. et al (2021). Non-coding deletions identify Maenli lncRNA as a limb-specific En1 regulator. Nature592, 93–98. 10.1038/s41586-021-03208-9
7
Alvarez-Dominguez J. R. Knoll M. Gromatzky A. A. Lodish H. F. (2017). The super-enhancer-derived alncRNA-EC7/Bloodlinc potentiates red blood cell development in trans. Cell Rep.19, 2503–2514. 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.082
8
Andergassen D. Rinn J. L. (2021). From genotype to phenotype: Genetics of mammalian long non-coding RNAs in vivo. Nat. Rev. Genet.23, 229–243. 10.1038/s41576-021-00427-8
9
Andersen R. E. Hong S. J. Lim J. J. Cui M. Harpur B. A. Hwang E. et al (2019). The long noncoding RNA Pnky is a trans-acting regulator of cortical development in vivo. Dev. Cell49, 632–642.e7. 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.032
10
Anderson K. M. Anderson D. M. McAnally J. R. Shelton J. M. Bassel-Duby R. Olson E. N. (2016). Transcription of the non-coding RNA upperhand controls Hand2 expression and heart development. Nature539, 433–436. 10.1038/nature20128
11
Andersson R. Gebhard C. Miguel-Escalada I. Hoof I. Bornholdt J. Boyd M. et al (2014). An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature507, 455–461. 10.1038/nature12787
12
Arner E. Daub C. O. Vitting-Seerup K. Andersson R. Lilje B. Drablos F. et al (2015). Transcribed enhancers lead waves of coordinated transcription in transitioning mammalian cells. Science347, 1010–1014. 10.1126/science.1259418
13
Arnold P. R. Wells A. D. Li X. C. (2019). Diversity and emerging roles of enhancer RNA in regulation of gene expression and cell fate. Front. Cell Dev. Biol.7, 377. article 377. 10.3389/fcell.2019.00377
14
Azofeifa J. G. Allen M. A. Hendrix J. R. Read T. Rubin J. D. Dowell R. D. (2018). Enhancer RNA profiling predicts transcription factor activity. Genome Res.28, 334–344. 10.1101/gr.225755.117
15
Bachu V. S. Kandoi S. Park K. U. Kaufman M. L. Schwanke M. Lamba D. A. et al (2022). An enhancer located in a Pde6c intron drives transient expression in the cone photoreceptors of developing mouse and human retinas. Dev. Biol.488, 131–150. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2022.05.012
16
Bah A. Forman-Kay J. D. (2016). Modulation of intrinsically disordered protein function by post-translational modifications. J. Biol. Chem.291, 6696–6705. 10.1074/jbc.R115.695056
17
Balcerak A. Trebinska-Stryjewska A. Konopinski R. Wakula M. Grzybowska E. A. (2019). RNA–protein interactions: Disorder, moonlighting and junk contribute to eukaryotic complexity. Open Biol.9, 190096. 10.1098/rsob.190096
18
Banerji J. Olson L. Schaffner W. (1983). A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell33, 729–740. 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6
19
Banerji J. Rusconi S. Schaffner W. (1981). Expression of a β-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell27, 299–308. 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-X
20
Barter M. J. Gomez R. Hyatt S. Cheung K. Skelton A. J. Xu Y. et al (2017). The long non-coding RNA ROCR contributes to SOX9 expression and chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Development144, 4510–4521. 10.1242/dev.152504
21
Barth N. K. H. Li L. Taher L. (2020). Independent transposon exaptation is a widespread mechanism of redundant enhancer evolution in the mammalian genome. Genome Biol. Evol.12, 1–17. 10.1093/gbe/evaa004
22
Bartonicek N. Clark M. B. Quek X. C. Torpy J. R. Pritchard A. L. Maag J. L. V. et al (2017). Intergenic disease-associated regions are abundant in novel transcripts. Genome Biol.18, 241. article 241. 10.1186/s13059-017-1363-3
23
Beagan J. A. Pastuzyn E. D. Fernandez L. R. Guo M. H. Feng K. Titus K. R. et al (2020). Three-dimensional Genome Res.tructuring across timescales of activity-induced neuronal gene expression. Nat. Neurosci.23, 707–717. 10.1038/s41593-020-0634-6
24
Bergalet J. Patel D. Legendre F. Lapointe C. Benoit Bouvrette L. P. Chin A. et al (2020). Inter-dependent centrosomal co-localization of the cen and Ik2 cis-natural antisense mRNAs in Drosophila. Cell Rep.30, 3339–3352.e6. 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.047
25
Bianconi E. Piovesan A. Facchin F. Beraudi A. Casadei R. Frabetti F. et al (2013). An estimation of the number of cells in the human body. Ann. Hum. Biol.40, 463–471. 10.3109/03014460.2013.807878
26
Boehning M. Dugast-Darzacq C. Rankovic M. Hansen A. S. Yu T. Marie-Nelly H. et al (2018). RNA polymerase II clustering through carboxy-terminal domain phase separation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.25, 833–840. 10.1038/s41594-018-0112-y
27
Boija A. Klein I. A. Sabari B. R. Dall’Agnese A. Coffey E. L. Zamudio A. V. et al (2018). Transcription factors activate genes through the phase-separation capacity of their activation domains. Cell175, 1842–1855.e16. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.042
28
Borsari B. Villegas-Mirón P. Pérez-Lluch S. Turpin I. Laayouni H. Segarra-Casas A. et al (2021). Enhancers with tissue-specific activity are enriched in intronic regions. Genome Res.31, 1325–1336. 10.1101/gr.270371.120
29
Bose D. A. Donahue G. Reinberg D. Shiekhattar R. Bonasio R. Berger S. L. (2017). RNA binding to CBP stimulates histone acetylation and transcription. Cell168, 135–149.e22. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.020
30
Bridges M. C. Daulagala A. C. Kourtidis A. (2021). LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J. Cell Biol.220, e202009045. 10.1083/jcb.202009045
31
Brodsky S. Jana T. Mittelman K. Chapal M. Kumar D. K. Carmi M. et al (2020). Intrinsically disordered regions direct transcription factor in vivo binding specificity. Mol. Cell79, 459–471.e4. 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.05.032
32
Brosius J. Raabe C. A. (2016). What is an RNA? A top layer for RNA classification. RNA Biol.13, 140–144. 10.1080/15476286.2015.1128064
33
Brosius J. (2014). The persistent contributions of RNA to eukaryotic gen(om)e architecture and cellular function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.6, a016089. 10.1101/cshperspect.a016089
34
Buljan M. Chalancon G. Eustermann S. Wagner G. P. Fuxreiter M. Bateman A. et al (2012). Tissue-specific splicing of disordered segments that embed binding motifs rewires protein interaction networks. Mol. Cell46, 871–883. 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.05.039
35
Cabili M. N. Dunagin M. C. McClanahan P. D. Biaesch A. Padovan-Merhar O. Regev A. et al (2015). Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol.16, 20. article 20. 10.1186/s13059-015-0586-4
36
Cai Z. Cao C. Ji L. Ye R. Wang D. Xia C. et al (2020). RIC-seq for global in situ profiling of RNA–RNA spatial interactions. Nature582, 432–437. 10.1038/s41586-020-2249-1
37
Cajigas I. Chakraborty A. Lynam M. Swyter K. R. Bastidas M. Collens L. et al (2021). Sox2-Evf2 lncRNA mechanisms of chromosome topological control in developing forebrain. Development148, dev197202. 10.1242/dev.197202
38
Cajigas I. Chakraborty A. Swyter K. R. Luo H. Bastidas M. Nigro M. et al (2018). The Evf2 ultraconserved enhancer lncRNA functionally and spatially organizes megabase distant genes in the developing forebrain. Mol. Cell71, 956–972.e9. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.024
39
Cannavò E. Khoueiry P. Garfield D. A. Geeleher P. Zichner T. Gustafson E. H. et al (2016). Shadow enhancers are pervasive features of developmental regulatory networks. Curr. Biol.26, 38–51. 10.1016/j.cub.2015.11.034
40
Canver M. C. Smith E. C. Sher F. Pinello L. Sanjana N. E. Shalem O. et al (2015). BCL11A enhancer dissection by Cas9-mediated in situ saturating mutagenesis. Nature527, 192–197. 10.1038/nature15521
41
Carullo N. V. N. Phillips III R. A. Simon R. C. Soto S. A. R. Hinds J. E. Salisbury A. J. et al (2020). Enhancer RNAs predict enhancer–gene regulatory links and are critical for enhancer function in neuronal systems. Nucleic Acids Res.48, 9550–9570. 10.1093/nar/gkaa671
42
Cerase A. Armaos A. Neumayer C. Avner P. Guttman M. Tartaglia G. G. (2019). Phase separation drives X-chromosome inactivation: A hypothesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.26, 331–334. 10.1038/s41594-019-0223-0
43
Chen H. Liang H. (2020). A high-resolution map of human enhancer RNA loci characterizes super-enhancer activities in cancer. Cancer Cell38, 701–715.e5. 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.08.020
44
Cho W.-K. Spille J.-H. Hecht M. Lee C. Li C. Grube V. et al (2018). Mediator and RNA polymerase II clusters associate in transcription-dependent condensates. Science361, 412–415. 10.1126/science.aar4199
45
Chujo T. Hirose T. Tetsuro H. (2017). Nuclear bodies built on architectural long noncoding RNAs: Unifying principles of their construction and function. Mol. cells40, 889–896. 10.14348/molcells.2017.0263
46
Closser M. Guo Y. Wang P. Patel T. Jang S. Hammelman J. et al (2022). An expansion of the non-coding genome and its regulatory potential underlies vertebrate neuronal diversity. Neuron110, 70–85.e6. 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.10.014
47
Conduit P. T. Wainman A. Raff J. W. (2015). Centrosome function and assembly in animal cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.16, 611–624. 10.1038/nrm4062
48
Core L. J. Martins A. L. Danko C. G. Waters C. T. Siepel A. Lis J. T. (2014). Analysis of nascent RNA identifies a unified architecture of initiation regions at mammalian promoters and enhancers. Nat. Genet.46, 1311–1320. 10.1038/ng.3142
49
Creamer K. M. Kolpa H. J. Lawrence J. B. (2021). Nascent RNA scaffolds contribute to chromosome territory architecture and counter chromatin compaction. Mol. Cell81, 3509–3525.e5. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.004
50
Cumberworth A. Lamour G. Babu M. M. Gsponer J. (2013). Promiscuity as a functional trait: Intrinsically disordered regions as central players of interactomes. Biochem. J.454, 361–369. 10.1042/BJ20130545
51
Davidovich C. Zheng L. Goodrich K. J. Cech T. R. (2013). Promiscuous RNA binding by Polycomb repressive complex 2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.20, 1250–1257. 10.1038/nsmb.2679
52
De Santa F. Barozzi I. Mietton F. Ghisletti S. Polletti S. Tusi B. K. et al (2010). A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers. PLoS Biol.8, e1000384. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000384
53
Degani N. Lubelsky Y. Perry R. B.-T. Ainbinder E. Ulitsky I. (2021). Highly conserved and cis-acting lncRNAs produced from paralogous regions in the center of HOXA and HOXB clusters in the endoderm lineage. PLoS Genet.17, e1009681. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009681
54
Deng C. Li Y. Zhou L. Cho J. Patel B. Terada N. et al (2016). HoxBlinc RNA recruits Set1/MLL complexes to activate Hox gene expression patterns and mesoderm lineage development. Cell Rep.14, 103–114. 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.007
55
Deveson I. W. Brunck M. E. Blackburn J. Tseng E. Hon T. Clark T. A. et al (2018). Universal alternative splicing of noncoding exons. Cell Syst.6, 245–255.e5. 10.1016/j.cels.2017.12.005
56
Deveson I. W. Hardwick S. A. Mercer T. R. Mattick J. S. (2017). The dimensions, dynamics, and relevance of the mammalian noncoding transcriptome. Trends Genet.33, 464–478. 10.1016/j.tig.2017.04.004
57
Dill T. L. Carroll A. Pinheiro A. Gao J. Naya F. J. (2021). The long noncoding RNA Meg3 regulates myoblast plasticity and muscle regeneration through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Development148, dev194027. 10.1242/dev.194027
58
Dinger M. E. Amaral P. P. Mercer T. R. Pang K. C. Bruce S. J. Gardiner B. B. et al (2008). Long noncoding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Genome Res.18, 1433–1445. 10.1101/gr.078378.108
59
Dynan W. S. Tjian R. (1985). Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. Nature316, 774–778. 10.1038/316774a0
60
Elguindy M. M. Mendell J. T. (2021). NORAD-induced Pumilio phase separation is required for genome stability. Nature595, 303–308. 10.1038/s41586-021-03633-w
61
Engreitz J. M. Haines J. E. Perez E. M. Munson G. Chen J. Kane M. et al (2016). Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature539, 452–455. 10.1038/nature20149
62
Engstrom P. G. Suzuki H. Ninomiya N. Akalin A. Sessa L. Lavorgna G. et al (2006). Complex loci in human and mouse genomes. PLoS Genet.2, e47. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020047
63
Fang S. Zhang L. Guo J. Niu Y. Wu Y. Li H. et al (2017). NONCODEV5: A comprehensive annotation database for long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.46, D308–D314. 10.1093/nar/gkx1107
64
Fang X. Wang L. Ishikawa R. Li Y. Fiedler M. Liu F. et al (2019). Arabidopsis FLL2 promotes liquid–liquid phase separation of polyadenylation complexes. Nature569, 265–269. 10.1038/s41586-019-1165-8
65
Farabella I. Di Stefano M. Soler-Vila P. Marti-Marimon M. Marti-Renom M. A. (2021). Three-dimensional genome organization via triplex-forming RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.28, 945–954. 10.1038/s41594-021-00678-3
66
Fatima R. Choudhury S. R. Tr D. Bhaduri U. Rao M. R. S. Rao M. (2019). A novel enhancer RNA, Hmrhl, positively regulates its host gene, phkb, in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Non-coding RNA Res.4, 96–108. 10.1016/j.ncrna.2019.08.001
67
Fay M. M. Anderson P. J. (2018). The role of RNA in biological phase separations. J. Mol. Biol.430, 4685–4701. 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.05.003
68
Field A. R. Jacobs F. M. J. Fiddes I. T. Phillips A. P. R. Reyes-Ortiz A. M. LaMontagne E. et al (2019). Structurally conserved primate lncRNAs are transiently expressed during human cortical differentiation and influence cell-type-specific genes. Stem Cell Rep.12, 245–257. 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.12.006
69
Fulco C. P. Nasser J. Jones T. R. Munson G. Bergman D. T. Subramanian V. et al (2019). Activity-by-contact model of enhancer–promoter regulation from thousands of CRISPR perturbations. Nat. Genet.51, 1664–1669. 10.1038/s41588-019-0538-0
70
Furlong E. E. M. Levine M. (2018). Developmental enhancers and chromosome topology. Science361, 1341–1345. 10.1126/science.aau0320
71
Galloni M. Gyurkovics H. Schedl P. Karch F. (1993). The bluetail transposon: Evidence for independent cis-regulatory domains and domain boundaries in the bithorax complex. EMBO J.12, 1087–1097. 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05750.x
72
Gao F. Cai Y. Kapranov P. Xu D. (2020). Reverse-genetics studies of lncRNAs—What we have learnt and paths forward. Genome Biol.21, 93. article 93. 10.1186/s13059-020-01994-5
73
Garcia-Jove Navarro M. Kashida S. Chouaib R. Souquere S. Pierron G. Weil D. et al (2019). RNA is a critical element for the sizing and the composition of phase-separated RNA–protein condensates. Nat. Commun.10, 3230. article 3230. 10.1038/s41467-019-11241-6
74
Gasperini M. Hill A. J. McFaline-Figueroa J. L. Martin B. Kim S. Zhang M. D. et al (2019). A genome-wide framework for mapping gene regulation via cellular genetic screens. Cell176, 377–390.e19. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.029
75
Gil N. Ulitsky I. (2018). Production of spliced long noncoding RNAs specifies regions with increased enhancer activity. Cell Syst.7, 537–547.e3. 10.1016/j.cels.2018.10.009
76
Gillies S. D. Morrison S. L. Oi V. T. Tonegawa S. (1983). A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell33, 717–728. 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4
77
Glinsky G. Barakat T. S. (2019). The evolution of Great Apes has shaped the functional enhancers' landscape in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res.37, 101456. article 101456. 10.1016/j.scr.2019.101456
78
Gonzàlez-Porta M. Frankish A. Rung J. Harrow J. Brazma A. (2013). Transcriptome analysis of human tissues and cell lines reveals one dominant transcript per gene. Genome Biol.14, R70. article R70. 10.1186/gb-2013-14-7-r70
79
Groff A. F. Barutcu A. R. Lewandowski J. P. Rinn J. L. (2018). Enhancers in the Peril lincRNA locus regulate distant but not local genes. Genome Biol.19, 219. article 219. 10.1186/s13059-018-1589-8
80
Grzejda D. Mach J. Schweizer J. A. Hummel B. Rezansoff A. M. Eggenhofer F. et al (2022). The long noncoding RNA mimi scaffolds neuronal granules to maintain nervous system maturity. Sci. Adv.8, eabo5578. 10.1126/sciadv.abo5578
81
Gueroussov S. Weatheritt R. J. O’Hanlon D. Lin Z.-Y. Narula A. Gingras A.-C. et al (2017). Regulatory expansion in mammals of multivalent hnRNP assemblies that globally control alternative splicing. Cell170, 324–339.e23. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.037
82
Hahn S. (2018). Phase separation, protein disorder, and enhancer function. Cell175, 1723–1725. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.034
83
Halfon M. S. (2019). Studying transcriptional enhancers: The founder fallacy, validation creep, and other biases. Trends Genet.35, 93–103. 10.1016/j.tig.2018.11.004
84
Hansen A. S. Cattoglio C. Darzacq X. Tjian R. (2018). Recent evidence that TADs and chromatin loops are dynamic structures. Nucleus9, 20–32. 10.1080/19491034.2017.1389365
85
Hansen A. S. Hsieh T.-H. S. Cattoglio C. Pustova I. Saldaña-Meyer R. Reinberg D. et al (2019). Distinct classes of chromatin loops revealed by deletion of an RNA-binding region in CTCF. Mol. Cell76, 395–411.e13. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.039
86
Hardwick S. A. Bassett S. D. Kaczorowski D. Blackburn J. Barton K. Bartonicek N. et al (2019). Targeted, high-resolution RNA sequencing of non-coding genomic regions associated with neuropsychiatric functions. Front. Genet.10, 309. article 309. 10.3389/fgene.2019.00309
87
Harrison L. J. Bose D. (2022). Enhancer RNAs step forward: New insights into enhancer function. Development149, dev200398. 10.1242/dev.200398
88
Heidari N. Phanstiel D. H. He C. Grubert F. Jahanbani F. Kasowski M. et al (2014). Genome-wide map of regulatory interactions in the human genome. Genome Res.24, 1905–1917. 10.1101/gr.176586.114
89
Heintzman N. D. Hon G. C. Hawkins R. D. Kheradpour P. Stark A. Harp L. F. et al (2009). Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature459, 108–112. 10.1038/nature07829
90
Heintzman N. D. Stuart R. K. Hon G. Fu Y. Ching C. W. Hawkins R. D. et al (2007). Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat. Genet.39, 311–318. 10.1038/ng1966
91
Hentze M. W. Castello A. Schwarzl T. Preiss T. (2018). A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.19, 327–341. 10.1038/nrm.2017.130
92
Herz H.-M. (2016). Enhancer deregulation in cancer and other diseases. Bioessays38, 1003–1015. 10.1002/bies.201600106
93
Hnisz D. Abraham B. J. Lee T. I. Lau A. Saint-André V. Sigova A. A. et al (2013). Super-enhancers in the control of cell identity and disease. Cell155, 934–947. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.053
94
Hnisz D. Shrinivas K. Young R. A. Chakraborty A. K. Sharp P. A. (2017). A phase separation model for transcriptional control. Cell169, 13–23. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.02.007
95
Hon C.-C. Ramilowski J. A. Harshbarger J. Bertin N. Rackham O. J. L. Gough J. et al (2017). An atlas of human long non-coding RNAs with accurate 5′ ends. Nature543, 199–204. 10.1038/nature21374
96
Hong J.-W. Hendrix D. A. Levine M. S. (2008). Shadow enhancers as a source of evolutionary novelty. Science321, 1314. 10.1126/science.1160631
97
Islam Z. Saravanan B. Walavalkar K. Farooq U. Singh A. K. Radhakrishnan S. et al (2023). Active enhancers strengthen insulation by RNA-mediated CTCF binding at chromatin domain boundaries. Genome Res.33, 1–17. 10.1101/gr.276643.122
98
Isoda T. Moore A. J. He Z. Chandra V. Aida M. Denholtz M. et al (2017). Non-coding transcription instructs chromatin folding and compartmentalization to dictate enhancer-promoter communication and T cell fate. Cell171, 103–119.e18. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.001
99
Järvelin A. I. Noerenberg M. Davis I. Castello A. (2016). The new (dis)order in RNA regulation. Cell Commun. Signal.14, 9. article 9. 10.1186/s12964-016-0132-3
100
Jenny A. Hachet O. Zavorszky P. Cyrklaff A. Weston M. D. Johnston D. S. et al (2006). A translation-independent role of oskar RNA in early Drosophila oogenesis. Development133, 2827–2833. 10.1242/dev.02456
101
Jia P. Li X. Wang X. Yao L. Xu Y. Hu Y. et al (2021). ZMYND8 mediated liquid condensates spatiotemporally decommission the latent super-enhancers during macrophage polarization. Nat. Commun.12, 6535. 10.1038/s41467-021-26864-x
102
Jindal G. A. Farley E. K. (2021). Enhancer grammar in development, evolution, and disease: Dependencies and interplay. Dev. Cell56, 575–587. 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.02.016
103
Joukov V. De Nicolo A. (2019). The centrosome and the primary cilium: The yin and yang of a hybrid organelle. Cells8, 701. article 701. 10.3390/cells8070701
104
Kagey M. H. Newman J. J. Bilodeau S. Zhan Y. Orlando D. A. van Berkum N. L. et al (2010). Mediator and cohesin connect gene expression and chromatin architecture. Nature467, 430–435. 10.1038/nature09380
105
Kaiser V. B. Semple C. A. (2017). When TADs go bad: Chromatin structure and nuclear organisation in human disease. F1000Research6, 314. article 314. 10.12688/f1000research.10792.1
106
Kapranov P. Willingham A. T. Gingeras T. R. (2007). Genome-wide transcription and the implications for genomic organization. Nat. Rev. Genet.8, 413–423. 10.1038/nrg2083
107
Khalil A. M. Guttman M. Huarte M. Garber M. Raj A. Rivea Morales D. et al (2009). Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.106, 11667–11672. 10.1073/pnas.0904715106
108
Kim T.-K. Hemberg M. Gray J. M. (2015). Enhancer RNAs: A class of long noncoding RNAs synthesized at enhancers: Figure 1. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.7, a018622. 10.1101/cshperspect.a018622
109
Kocabas A. Duarte T. Kumar S. Hynes M. A. (2015). Widespread differential expression of coding region and 3'UTR sequences in neurons and other tissues. Neuron88, 1149–1156. 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.10.048
110
Koch F. Fenouil R. Gut M. Cauchy P. Albert T. K. Zacarias-Cabeza J. et al (2011). Transcription initiation platforms and GTF recruitment at tissue-specific enhancers and promoters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.18, 956–963. 10.1038/nsmb.2085
111
Krijger P. H. L. de Laat W. (2016). Regulation of disease-associated gene expression in the 3D genome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.17, 771–782. 10.1038/nrm.2016.138
112
Kulkarni P. Uversky V. N. (2018). Intrinsically disordered proteins: The dark horse of the dark proteome. Proteomics18, 1800061. 10.1002/pmic.201800061
113
The ENCODE Project Consortium Kundaje A. Aldred S. F. Collins P. J. Davis C. A. Doyle F. et al (2012). An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature489, 57–74. 10.1038/nature11247
114
Kung J. T. Kesner B. An J. Y. Ahn J. Y. Cifuentes-Rojas C. Colognori D. et al (2015). Locus-specific targeting to the X chromosome revealed by the RNA interactome of CTCF. Mol. Cell57, 361–375. 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.006
115
Kuru-Schors M. Haemmerle M. Gutschner T. (2021). The Cohesin complex and its interplay with non-coding RNAs. Noncoding RNA7, 67. article 67. 10.3390/ncrna7040067
116
Kvon E. Z. Waymack R. Gad M. Wunderlich Z. (2021). Enhancer redundancy in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet.22, 324–336. 10.1038/s41576-020-00311-x
117
Lagha M. Bothma J. P. Levine M. (2012). Mechanisms of transcriptional precision in animal development. Trends Genet.28, 409–416. 10.1016/j.tig.2012.03.006
118
Lai F. Orom U. A. Cesaroni M. Beringer M. Taatjes D. J. Blobel G. A. et al (2013). Activating RNAs associate with Mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature494, 497–501. 10.1038/nature11884
119
Lam M. T. Y. Li W. Rosenfeld M. G. Glass C. K. (2014). Enhancer RNAs and regulated transcriptional programs. Trends Biochem. Sci.39, 170–182. 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.007
120
Landshammer A. Bolondi A. Kretzmer H. Much C. Buschow R. Rose A. et al (2023). T-REX17 is a transiently expressed non-coding RNA essential for human endoderm formation. Elife12, e83077. 10.7554/eLife.83077
121
Larke M. S. C. Schwessinger R. Nojima T. Telenius J. Beagrie R. A. Downes D. J. et al (2021). Enhancers predominantly regulate gene expression during differentiation via transcription initiation. Mol. Cell81, 983–997.e7. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.002
122
Lee B. K. Iyer V. R. (2012). Genome-wide studies of CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and Cohesin provide insight into chromatin structure and regulation. J. Biol. Chem.287, 30906–30913. 10.1074/jbc.R111.324962
123
Lee J.-H. Wang R. Xiong F. Krakowiak J. Liao Z. Nguyen P. T. et al (2021). Enhancer RNA m6A methylation facilitates transcriptional condensate formation and gene activation. Mol. Cell81, 3368–3385.e9. 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.07.024
124
Lewandowski J. P. Lee J. C. Hwang T. Sunwoo H. Goldstein J. M. Groff A. F. et al (2019). The Firre locus produces a trans-acting RNA molecule that functions in hematopoiesis. Nat. Commun.10, 5137. article 5137. 10.1038/s41467-019-12970-4
125
Li P. Tao Z. Dean C. (2015). Phenotypic evolution through variation in splicing of the noncoding RNA COOLAIR. Genes Dev.29, 696–701. 10.1101/gad.258814.115
126
Li Q. Peterson K. R. Fang X. Stamatoyannopoulos G. (2002). Locus control regions. Blood100, 3077–3086. 10.1182/blood-2002-04-1104
127
Li S. Ovcharenko I. (2020). Enhancer jungles establish robust tissue-specific regulatory control in the human genome. Genomics112, 2261–2270. 10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.12.022
128
Li W. Notani D. Ma Q. Tanasa B. Nunez E. Chen A. Y. et al (2013). Functional roles of enhancer RNAs for oestrogen-dependent transcriptional activation. Nature498, 516–520. 10.1038/nature12210
129
Li W. Notani D. Rosenfeld M. G. (2016). Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: Recent insights and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Genet.17, 207–223. 10.1038/nrg.2016.4
130
Li X. Fu X.-D. (2019). Chromatin-associated RNAs as facilitators of functional genomic interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet.20, 503–519. 10.1038/s41576-019-0135-1
131
Lim B. Levine M. S. (2021). Enhancer-promoter communication: Hubs or loops?Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev.67, 5–9. 10.1016/j.gde.2020.10.001
132
Liu B. Lee Y.-R. J. (2022). Spindle assembly and mitosis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol.73, 227–254. 10.1146/annurev-arplant-070721-084258
133
Liu J. Li Y. Lin B. Sheng Y. Yang L. (2017). HBL1 Is a human long noncoding RNA that modulates cardiomyocyte development from pluripotent stem cells by counteracting MIR1. Dev. Cell42, 333–348.e5. 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.07.023
134
Luo J. Qu L. Gao F. Lin J. Liu J. Lin A. (2021). LncRNAs: Architectural scaffolds or more potential roles in phase separation. Front. Genet.12, 626234. article 369. 10.3389/fgene.2021.626234
135
Luo S. Lu J. Y. Liu L. Yin Y. Chen C. Han X. et al (2016). Divergent lncRNAs regulate gene expression and lineage differentiation in pluripotent cells. Cell Stem Cell18, 637–652. 10.1016/j.stem.2016.01.024
136
Lupianez D. G. Kraft K. Heinrich V. Krawitz P. Brancati F. Klopocki E. et al (2015). Disruptions of topological chromatin domains cause pathogenic rewiring of gene-enhancer interactions. Cell161, 1012–1025. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.004
137
Lyon A. S. Peeples W. B. Rosen M. K. (2021). A framework for understanding the functions of biomolecular condensates across scales. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22, 215–235. 10.1038/s41580-020-00303-z
138
Ma L. Cao J. Liu L. Du Q. Li Z. Zou D. et al (2019). LncBook: A curated knowledgebase of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.47, D128–D134. 10.1093/nar/gky960
139
Maass P. G. Rump A. Schulz H. Stricker S. Schulze L. Platzer K. et al (2012). A misplaced lncRNA causes brachydactyly in humans. J. Clin. Invest.122, 3990–4002. 10.1172/JCI65508
140
Macossay-Castillo M. Marvelli G. Guharoy M. Jain A. Kihara D. Tompa P. et al (2019). The balancing act of intrinsically disordered proteins: Enabling functional diversity while minimizing promiscuity. J. Mol. Biol.431, 1650–1670. 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.03.008
141
Maeda R. K. Karch F. (2006). The ABC of the BX-C: The bithorax complex explained. Development133, 1413–1422. 10.1242/dev.02323
142
Malkmus J. Ramos Martins L. Jhanwar S. Kircher B. Palacio V. Sheth R. et al (2021). Spatial regulation by multiple Gremlin1 enhancers provides digit development with cis-regulatory robustness and evolutionary plasticity. Nat. Commun.12, 5557. article 5557. 10.1038/s41467-021-25810-1
143
Mangan R. J. Alsina F. C. Mosti F. Sotelo-Fonseca J. E. Snellings D. A. Au E. H. et al (2022). Adaptive sequence divergence forged new neurodevelopmental enhancers in humans. Cell185, 4587–4603.e23. 10.1016/j.cell.2022.10.016
144
Mattick J. S. Amaral P. P. Carninci P. Carpenter S. Chang H. Y. Chen L.-L. et al (2023). Long noncoding RNAs: Definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.24, 430–447. 10.1038/s41580-022-00566-8
145
Mattick J. S. Amaral P. P. (2022). RNA, the epicenter of genetic information. Boca Raton: CRC Press. 10.1201/9781003109242
146
Mattick J. S. (2003). Challenging the dogma: The hidden layer of non-protein-coding RNAs in complex organisms. Bioessays25, 930–939. 10.1002/bies.10332
147
McCall K. O'Connor M. B. Bender W. (1994). Enhancer traps in the Drosophila bithorax complex mark parasegmental domains. Genetics138, 387–399. 10.1093/genetics/138.2.387
148
Mele M. Rinn J. L. (2016). Cat's cradling" the 3D genome by the act of lncRNA transcription. Mol. Cell62, 657–664. 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.011
149
Melo C. A. Drost J. Wijchers P. J. van de Werken H. de Wit E. Vrielink J. et al (2013). eRNAs are required for p53-dependent enhancer activity and gene transcription. Mol. Cell49, 524–535. 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.021
150
Mercer T. R. Gerhardt D. J. Dinger M. E. Crawford J. Trapnell C. Jeddeloh J. A. et al (2012). Targeted RNA sequencing reveals the deep complexity of the human transcriptome. Nat. Biotechnol.30, 99–104. 10.1038/nbt.2024
151
Mercer T. R. Mattick J. S. (2013). Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.20, 300–307. 10.1038/nsmb.2480
152
Mercer T. R. Wilhelm D. Dinger M. E. Solda G. Korbie D. J. Glazov E. A. et al (2011). Expression of distinct RNAs from 3' untranslated regions. Nucleic Acids Res.39, 2393–2403. 10.1093/nar/gkq1158
153
Meyer K. Kirchner M. Uyar B. Cheng J.-Y. Russo G. Hernandez-Miranda L. R. et al (2018). Mutations in disordered regions can cause disease by creating dileucine motifs. Cell175, 239–253.e17. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.019
154
Micheletti R. Plaisance I. Abraham B. J. Sarre A. Ting C.-C. Alexanian M. et al (2017). The long noncoding RNA Wisper controls cardiac fibrosis and remodeling. Sci. Transl. Med.9, eaai9118. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aai9118
155
Mishra K. Kanduri C. (2019). Understanding long noncoding RNA and chromatin interactions: What we know so far. Noncoding RNA5, 54. article 54. 10.3390/ncrna5040054
156
Miyagi S. Saito T. Mizutani K. Masuyama N. Gotoh Y. Iwama A. et al (2004). The Sox-2 regulatory regions display their activities in two distinct types of multipotent stem cells. Mol. Cell. Biol.24, 4207–4220. 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4207-4220.2004
157
Morf J. Basu S. Amaral P. P. (2020). RNA, genome output and input. Front. Genet.11, 589413. article 1330. 10.3389/fgene.2020.589413
158
Nagano T. Mitchell J. A. Sanz L. A. Pauler F. M. Ferguson-Smith A. C. Feil R. et al (2008). The Air noncoding RNA epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to chromatin. Science322, 1717–1720. 10.1126/science.1163802
159
Nair S. J. Yang L. Meluzzi D. Oh S. Yang F. Friedman M. J. et al (2019). Phase separation of ligand-activated enhancers licenses cooperative chromosomal enhancer assembly. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.26, 193–203. 10.1038/s41594-019-0190-5
160
Nasser J. Bergman D. T. Fulco C. P. Guckelberger P. Doughty B. R. Patwardhan T. A. et al (2021). Genome-wide enhancer maps link risk variants to disease genes. Nature593, 238–243. 10.1038/s41586-021-03446-x
161
Natoli G. Andrau J.-C. (2012). Noncoding transcription at enhancers: General principles and functional models. Annu. Rev. Genet.46, 1–19. 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155459
162
Niklas K. J. Bondos S. E. Dunker A. K. Newman S. A. (2015). Rethinking gene regulatory networks in light of alternative splicing, intrinsically disordered protein domains, and post-translational modifications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol.3, 8. article 8. 10.3389/fcell.2015.00008
163
Niklas K. J. Dunker A. K. Yruela I. (2018). The evolutionary origins of cell type diversification and the role of intrinsically disordered proteins. J. Exp. Bot.69, 1437–1446. 10.1093/jxb/erx493
164
Nott A. Holtman I. R. Coufal N. G. Schlachetzki J. C. M. Yu M. Hu R. et al (2019). Brain cell type-specific enhancer-promoter interactome maps and disease-risk association. Science366, 1134–1139. 10.1126/science.aay0793
165
O’Kane C. J. Gehring W. J. (1987). Detection in situ of genomic regulatory elements in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.84, 9123–9127. 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9123
166
Orom U. A. Derrien T. Beringer M. Gumireddy K. Gardini A. Bussotti G. et al (2010). Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell143, 46–58. 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.001
167
Osmala M. Lähdesmäki H. (2020). Enhancer prediction in the human genome by probabilistic modelling of the chromatin feature patterns. BMC Bioinforma.21, 317. article 317. 10.1186/s12859-020-03621-3
168
Osterwalder M. Barozzi I. Tissières V. Fukuda-Yuzawa Y. Mannion B. J. Afzal S. Y. et al (2018). Enhancer redundancy provides phenotypic robustness in mammalian development. Nature554, 239–243. 10.1038/nature25461
169
Pal D. Neha C. V. Bhaduri U. Zenia Z. Dutta S. Chidambaram S. et al (2021). LncRNA Mrhl orchestrates differentiation programs in mouse embryonic stem cells through chromatin mediated regulation. Stem Cell Res.53, 102250. article 102250. 10.1016/j.scr.2021.102250
170
Pan H. Jin M. Ghadiyaram A. Kaur P. Miller H. E. Ta H. M. et al (2020). Cohesin SA1 and SA2 are RNA binding proteins that localize to RNA containing regions on DNA. Nucleic Acids Res.48, 5639–5655. 10.1093/nar/gkaa284
171
Pande A. Brosius J. Makalowska I. Makalowski W. Raabe C. A. (2018). Transcriptional interference by small transcripts in proximal promoter regions. Nucleic Acids Res.46, 1069–1088. 10.1093/nar/gkx1242
172
Pande A. Makalowski W. Brosius J. Raabe C. A. (2020). Enhancer occlusion transcripts regulate the activity of human enhancer domains via transcriptional interference: A computational perspective. Nucleic Acids Res.48, 3435–3454. 10.1093/nar/gkaa026
173
Pandey R. R. Mondal T. Mohammad F. Enroth S. Redrup L. Komorowski J. et al (2008). Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol. Cell32, 232–246. 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.022
174
Paralkar V. R. Mishra T. Luan J. Yao Y. Kossenkov A. V. Anderson S. M. et al (2014). Lineage and species-specific long noncoding RNAs during erythro-megakaryocytic development. Blood123, 1927–1937. 10.1182/blood-2013-12-544494
175
Park B. K. Sperber S. M. Choudhury A. Ghanem N. Hatch G. T. Sharpe P. T. et al (2004). Intergenic enhancers with distinct activities regulate Dlx gene expression in the mesenchyme of the branchial arches. Dev. Biol.268, 532–545. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.01.010
176
Parker S. C. J. Stitzel M. L. Taylor D. L. Orozco J. M. Erdos M. R. Akiyama J. A. et al (2013). Chromatin stretch enhancer states drive cell-specific gene regulation and harbor human disease risk variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.110, 17921–17926. 10.1073/pnas.1317023110
177
Pefanis E. Wang J. Rothschild G. Lim J. Kazadi D. Sun J. et al (2015). RNA exosome-regulated long non-coding RNA transcription controls super-enhancer activity. Cell161, 774–789. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.04.034
178
Pérez-Lluch S. Klein C. C. Breschi A. Ruiz-Romero M. Abad A. Palumbo E. et al (2020). bsAS, an antisense long non-coding RNA, essential for correct wing development through regulation of blistered/DSRF isoform usage. PLoS Genet.16, e1009245. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009245
179
Perry M. W. Boettiger A. N. Levine M. (2011). Multiple enhancers ensure precision of gap gene-expression patterns in the Drosophila embryo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.108, 13570–13575. 10.1073/pnas.1109873108
180
Pessina F. Giavazzi F. Yin Y. Gioia U. Vitelli V. Galbiati A. et al (2019). Functional transcription promoters at DNA double-strand breaks mediate RNA-driven phase separation of damage-response factors. Nat. Cell Biol.21, 1286–1299. 10.1038/s41556-019-0392-4
181
Polymenidou M. (2018). The RNA face of phase separation. Science360, 859–860. 10.1126/science.aat8028
182
Popay T. M. Dixon J. R. (2022). Coming full circle: On the origin and evolution of the looping model for enhancer–promoter communication. J. Biol. Chem.298, 102117. 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102117
183
Pott S. Lieb J. D. (2015). What are super-enhancers?Nat. Genet.47, 8–12. 10.1038/ng.3167
184
Prabhakar S. Visel A. Akiyama J. A. Shoukry M. Lewis K. D. Holt A. et al (2008). Human-specific gain of function in a developmental enhancer. Science321, 1346–1350. 10.1126/science.1159974
185
Pradeepa M. M. Grimes G. R. Kumar Y. Olley G. Taylor G. C. A. Schneider R. et al (2016). Histone H3 globular domain acetylation identifies a new class of enhancers. Nat. Genet.48, 681–686. 10.1038/ng.3550
186
Protter D. S. W. Rao B. S. Van Treeck B. Lin Y. Mizoue L. Rosen M. K. et al (2018). Intrinsically disordered regions can contribute promiscuous interactions to RNP granule assembly. Cell Rep.22, 1401–1412. 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.036
187
Przanowska R. K. Weidmann C. A. Saha S. Cichewicz M. A. Jensen K. N. Przanowski P. et al (2022). Distinct MUNC lncRNA structural domains regulate transcription of different promyogenic factors. Cell Rep.38, 110361. article 110361. 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110361
188
Ptashne M. (1986). Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature322, 697–701. 10.1038/322697a0
189
Ptashne M. (1988). How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature335, 683–689. 10.1038/335683a0
190
Quinodoz S. A. Jachowicz J. W. Bhat P. Ollikainen N. Banerjee A. K. Goronzy I. N. et al (2021). RNA promotes the formation of spatial compartments in the nucleus. Cell184, 5775–5790.e30. 10.1016/j.cell.2021.10.014
191
Rao S. S. Huntley M. H. Durand N. C. Stamenova E. K. Bochkov I. D. Robinson J. T. et al (2014). A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell159, 1665–1680. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.021
192
Rebeiz M. Tsiantis M. (2017). Enhancer evolution and the origins of morphological novelty. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev.45, 115–123. 10.1016/j.gde.2017.04.006
193
Redrup L. Branco M. R. Perdeaux E. R. Krueger C. Lewis A. Santos F. et al (2009). The long noncoding RNA Kcnq1ot1 organises a lineage-specific nuclear domain for epigenetic gene silencing. Development136, 525–530. 10.1242/dev.031328
194
Reilly S. K. Yin J. Ayoub A. E. Emera D. Leng J. Cotney J. et al (2015). Evolutionary changes in promoter and enhancer activity during human corticogenesis. Science347, 1155–1159. 10.1126/science.1260943
195
Richter W. F. Nayak S. Iwasa J. Taatjes D. J. (2022). The Mediator complex as a master regulator of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.23, 732–749. 10.1038/s41580-022-00498-3
196
Rickels R. Shilatifard A. (2018). Enhancer logic and mechanics in development and disease. Trends Cell Biol.28, 608–630. 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.04.003
197
Rinn J. L. Chang H. Y. (2020). Long noncoding RNAs: Molecular modalities to organismal functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem.89, 283–308. 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012708
198
Ritter N. Ali T. Kopitchinski N. Schuster P. Beisaw A. Hendrix D. A. et al (2019). The lncRNA locus Handsdown regulates cardiac gene programs and is essential for early mouse development. Dev. Cell50, 644–657.e8. 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.07.013
199
Roden C. Gladfelter A. S. (2021). RNA contributions to the form and function of biomolecular condensates. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22, 183–195. 10.1038/s41580-020-0264-6
200
Romero P. R. Zaidi S. Fang Y. Y. Uversky V. N. Radivojac P. Oldfield C. J. et al (2006). Alternative splicing in concert with protein intrinsic disorder enables increased functional diversity in multicellular organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.103, 8390–8395. 10.1073/pnas.0507916103
201
Rubinstein M. de Souza F. S. J. (2013). Evolution of transcriptional enhancers and animal diversity. Philosophical Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci.368, 20130017. 10.1098/rstb.2013.0017
202
S Zibitt M. Hartford C. C. R. Lal A. (2021). Interrogating lncRNA functions via CRISPR/Cas systems. RNA Biol.18, 2097–2106. 10.1080/15476286.2021.1899500
203
Sabari B. R. Dall’Agnese A. Boija A. Klein I. A. Coffey E. L. Shrinivas K. et al (2018). Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers links phase separation and gene control. Science361, eaar3958. 10.1126/science.aar3958
204
Saldana-Meyer R. Gonzalez-Buendia E. Guerrero G. Narendra V. Bonasio R. Recillas-Targa F. et al (2014). CTCF regulates the human p53 gene through direct interaction with its natural antisense transcript, Wrap53. Genes Dev.28, 723–734. 10.1101/gad.236869.113
205
Sanders D. W. Kedersha N. Lee D. S. W. Strom A. R. Drake V. Riback J. A. et al (2020). Competing protein-RNA interaction networks control multiphase intracellular organization. Cell181, 306–324.e28. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.050
206
Sartorelli V. Lauberth S. M. (2020). Enhancer RNAs are an important regulatory layer of the epigenome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.27, 521–528. 10.1038/s41594-020-0446-0
207
Schoenfelder S. Fraser P. (2019). Long-range enhancer–promoter contacts in gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Genet.20, 437–455. 10.1038/s41576-019-0128-0
208
Sebé-Pedrós A. Ballaré C. Parra-Acero H. Chiva C. Tena J. J. Sabidó E. et al (2016). The dynamic regulatory genome of Capsaspora and the origin of animal multicellularity. Cell165, 1224–1237. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.034
209
Seila A. C. Calabrese J. M. Levine S. S. Yeo G. W. Rahl P. B. Flynn R. A. et al (2008). Divergent transcription from active promoters. Science322, 1849–1851. 10.1126/science.1162253
210
Sender R. Fuchs S. Milo R. (2016). Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol.14, e1002533. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002533
211
Sentürk Cetin N. Kuo C.-C. Ribarska T. Li R. Costa I. G. Grummt I. (2019). Isolation and genome-wide characterization of cellular DNA:RNA triplex structures. Nucleic Acids Res.47, 2306–2321. 10.1093/nar/gky1305
212
Setten R. L. Chomchan P. Epps E. W. Burnett J. C. Rossi J. J. (2021). CRED9: A differentially expressed elncRNA regulates expression of transcription factor cebpa. RNA27, 891–906. 10.1261/rna.078752.121
213
Shen Y. Yue F. McCleary D. F. Ye Z. Edsall L. Kuan S. et al (2012). A map of the cis-regulatory sequences in the mouse genome. Nature488, 116–120. 10.1038/nature11243
214
Shiau C.-K. Huang J.-H. Liu Y.-T. Tsai H.-K. (2022). Genome-wide identification of associations between enhancer and alternative splicing in human and mouse. BMC Genomics22, 919. article 919. 10.1186/s12864-022-08537-1
215
Shii L. Song L. Maurer K. Zhang Z. Sullivan K. E. (2017). SERPINB2 is regulated by dynamic interactions with pause-release proteins and enhancer RNAs. Mol. Immunol.88, 20–31. 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.05.005
216
Shlyueva D. Stampfel G. Stark A. (2014). Transcriptional enhancers: From properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat. Rev. Genet.15, 272–286. 10.1038/nrg3682
217
Shrinivas K. Sabari B. R. Coffey E. L. Klein I. A. Boija A. Zamudio A. V. et al (2019). Enhancer features that drive formation of transcriptional condensates. Mol. Cell75, 549–561.e7. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.009
218
Smith E. Shilatifard A. (2014). Enhancer biology and enhanceropathies. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.21, 210–219. 10.1038/nsmb.2784
219
Soibam B. (2017). Super-lncRNAs: Identification of lncRNAs that target super-enhancers via RNA:DNA:DNA triplex formation. RNA23, 1729–1742. 10.1261/rna.061317.117
220
Souaid C. Bloyer S. Noordermeer D. (2018). “Promoter–enhancer looping and regulatory neighborhoods: Gene regulation in the framework of topologically associating domains,” in Nuclear architecture and dynamics. Editors LavelleC.VictorJ.-M. (Boston: Academic Press), 435–456.
221
Springer P. S. (2000). Gene traps: Tools for plant development and genomics. Plant Cell12, 1007–1020. 10.1105/tpc.12.7.1007
222
St Laurent G. Shtokalo D. Tackett M. R. Yang Z. Eremina T. Wahlestedt C. et al (2012). Intronic RNAs constitute the major fraction of the non-coding RNA in mammalian cells. BMC Genomics13, 504. article 504. 10.1186/1471-2164-13-504
223
Statello L. Guo C.-J. Chen L.-L. Huarte M. (2021). Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.22, 96–118. 10.1038/s41580-020-00315-9
224
Stathopoulos A. Van Drenth M. Erives A. Markstein M. Levine M. (2002). Whole-genome analysis of dorsal-ventral patterning in the Drosophila embryo. Cell111, 687–701. 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)01087-5
225
Subhash S. Mishra K. Akhade V. S. Kanduri M. Mondal T. Kanduri C. (2018). H3K4me2 and WDR5 enriched chromatin interacting long non-coding RNAs maintain transcriptionally competent chromatin at divergent transcriptional units. Nucleic Acids Res.46, 9384–9400. 10.1093/nar/gky635
226
Sun J. Li W. Sun Y. Yu D. Wen X. Wang H. et al (2014). A novel antisense long noncoding RNA within the IGF1R gene locus is imprinted in hematopoietic malignancies. Nucleic Acids Res.42, 9588–9601. 10.1093/nar/gku549
227
Sweeney B. A. Petrov A. I. Burkov B. Finn R. D. Bateman A. Szymanski M. et al (2018). RNAcentral: A hub of information for non-coding RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res.47, D221–D229. 10.1093/nar/gky1034
228
Symmons O. Uslu V. V. Tsujimura T. Ruf S. Nassari S. Schwarzer W. et al (2014). Functional and topological characteristics of mammalian regulatory domains. Genome Res.24, 390–400. 10.1101/gr.163519.113
229
Tan J. Y. Biasini A. Young R. S. Marques A. C. (2020). Splicing of enhancer-associated lincRNAs contributes to enhancer activity. Life Sci. Alliance3, e202000663. 10.26508/lsa.202000663
230
Tan J. Y. Marques A. C. (2022). The activity of human enhancers is modulated by the splicing of their associated lncRNAs. PLoS Comput. Biol.18, e1009722. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009722
231
Tejada-Martinez D. Avelar R. A. Lopes I. Zhang B. Novoa G. de Magalhães J. P. et al (2022). Positive selection and enhancer evolution shaped lifespan and body mass in Great Apes. Mol. Biol. Evol.39, msab369. 10.1093/molbev/msab369
232
Thakur J. Henikoff S. (2020). Architectural RNA in chromatin organization. Biochem. Soc. Trans.48, 1967–1978. 10.1042/BST20191226
233
Thomas H. F. Kotova E. Jayaram S. Pilz A. Romeike M. Lackner A. et al (2021). Temporal dissection of an enhancer cluster reveals distinct temporal and functional contributions of individual elements. Mol. Cell81, 969–982.e13. 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.12.047
234
Thurman R. E. Rynes E. Humbert R. Vierstra J. Maurano M. T. Haugen E. et al (2012). The accessible chromatin landscape of the human genome. Nature489, 75–82. 10.1038/nature11232
235
Trinh L. A. Fraser S. E. (2013). Enhancer and gene traps for molecular imaging and genetic analysis in zebrafish. Dev. Growth & Differ.55, 434–445. 10.1111/dgd.12055
236
Tsai P.-F. Dell'Orso S. Rodriguez J. Vivanco K. O. Ko K.-D. Jiang K. et al (2018). A muscle-specific enhancer RNA mediates cohesin recruitment and regulates transcription in trans. Mol. Cell71, 129–141.e8. 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.008
237
Tsang B. Pritišanac I. Scherer S. W. Moses A. M. Forman-Kay J. D. (2020). Phase separation as a missing mechanism for interpretation of disease mutations. Cell183, 1742–1756. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.050
238
Vacic V. Iakoucheva L. M. (2012). Disease mutations in disordered regions—Exception to the rule?Mol. Biosyst.8, 27–32. 10.1039/C1MB05251A
239
Vilborg A. Passarelli M. C. Yario T. A. Tycowski K. T. Steitz J. A. (2015). Widespread inducible transcription downstream of human genes. Mol. Cell59, 449–461. 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.016
240
Villar D. Berthelot C. Aldridge S. Rayner T. F. Lukk M. Pignatelli M. et al (2015). Enhancer evolution across 20 mammalian species. Cell160, 554–566. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.006
241
Volders P.-J. Anckaert J. Verheggen K. Nuytens J. Martens L. Mestdagh P. et al (2019). LNCipedia 5: Towards a reference set of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.47, D135–D139. 10.1093/nar/gky1031
242
Wan G. Fields B. D. Spracklin G. Shukla A. Phillips C. M. Kennedy S. (2018). Spatiotemporal regulation of liquid-like condensates in epigenetic inheritance. Nature557, 679–683. 10.1038/s41586-018-0132-0
243
Wang D. Garcia-Bassets I. Benner C. Li W. Su X. Zhou Y. et al (2011). Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers functionally defined by eRNA. Nature474, 390–394. 10.1038/nature10006
244
Wang J. Yu H. Ma Q. Zeng P. Wu D. Hou Y. et al (2021). Phase separation of OCT4 controls TAD reorganization to promote cell fate transitions. Cell Stem Cell28, 1868–1883.e11. 10.1016/j.stem.2021.04.023
245
Wang K. C. Yang Y. W. Liu B. Sanyal A. Corces-Zimmerman R. Chen Y. et al (2011). A long noncoding RNA maintains active chromatin to coordinate homeotic gene expression. Nature472, 120–124. 10.1038/nature09819
246
Wang R. Cao L. Thorne R. F. Zhang X. D. Li J. Shao F. et al (2021). LncRNA GIRGL drives CAPRIN1-mediated phase separation to suppress glutaminase-1 translation under glutamine deprivation. Sci. Adv.7, eabe5708. 10.1126/sciadv.abe5708
247
Wang X. Cairns M. J. Yan J. (2019). Super-enhancers in transcriptional regulation and genome organization. Nucleic Acids Res.47, 11481–11496. 10.1093/nar/gkz1038
248
Watson M. Stott K. (2019). Disordered domains in chromatin-binding proteins. Essays Biochem.63, 147–156. 10.1042/EBC20180068
249
Waymack R. Fletcher A. Enciso G. Wunderlich Z. (2020). Shadow enhancers can suppress input transcription factor noise through distinct regulatory logic. Elife9, e59351. 10.7554/eLife.59351
250
Weatheritt R. J. Davey N. E. Gibson T. J. (2012). Linear motifs confer functional diversity onto splice variants. Nucleic Acids Res.40, 7123–7131. 10.1093/nar/gks442
251
Whalen S. Pollard K. S. (2022). Enhancer function and evolutionary roles of human accelerated regions. Annu. Rev. Genet.56, 423–439. 10.1146/annurev-genet-071819-103933
252
Whiting J. Marshall H. Cook M. Krumlauf R. Rigby P. W. Stott D. et al (1991). Multiple spatially specific enhancers are required to reconstruct the pattern of Hox-2.6 gene expression. Genes Dev.5, 2048–2059. 10.1101/gad.5.11.2048
253
Whyte W. A. Orlando D. A. Hnisz D. Abraham B. J. Lin C. Y. Kagey M. H. et al (2013). Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell153, 307–319. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.035
254
Wilson K. D. Ameen M. Guo H. Abilez O. J. Tian L. Mumbach M. R. et al (2020). Endogenous retrovirus-derived lncRNA BANCR promotes cardiomyocyte migration in humans and non-human primates. Dev. Cell54, 694–709.e9. 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.07.006
255
Woltering J. M. Duboule D. (2010). The origin of digits: Expression patterns versus regulatory mechanisms. Dev. Cell18, 526–532. 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.04.002
256
Wright P. E. Dyson H. J. (2015). Intrinsically disordered proteins in cellular signalling and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.16, 18–29. 10.1038/nrm3920
257
Wu D. Poddar A. Ninou E. Hwang E. Cole M. A. Liu S. J. et al (2022). Dual genome-wide coding and lncRNA screens in neural induction of induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Genomics2, 100177. article 100177. 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100177
258
Wu H. Nord A. S. Akiyama J. A. Shoukry M. Afzal V. Rubin E. M. et al (2014). Tissue-specific RNA expression marks distant-acting developmental enhancers. PLoS Genet.10, e1004610. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004610
259
Wu M. Xu G. Han C. Luan P.-F. Xing Y.-H. Nan F. et al (2021a). lncRNA SLERT controls phase separation of FC/DFCs to facilitate Pol I transcription. Science373, 547–555. 10.1126/science.abf6582
260
Wu M. Yang L.-Z. Chen L.-L. (2021b). Long noncoding RNA and protein abundance in lncRNPs. RNA27, 1427–1440. 10.1261/rna.078971.121
261
Wutz G. Várnai C. Nagasaka K. Cisneros D. A. Stocsits R. R. Tang W. et al (2017). Topologically associating domains and chromatin loops depend on cohesin and are regulated by CTCF, WAPL, and PDS5 proteins. EMBO J.36, 3573–3599. 10.15252/embj.201798004
262
Xiang J. F. Yin Q. F. Chen T. Zhang Y. Zhang X. O. Wu Z. et al (2014). Human colorectal cancer-specific CCAT1-L lncRNA regulates long-range chromatin interactions at the MYC locus. Cell Res.24, 513–531. 10.1038/cr.2014.35
263
Xu H. Li C. Xu C. Zhang J. (2023). Chance promoter activities illuminate the origins of eukaryotic intergenic transcriptions. Nat. Commun.14, 1826. article 1826. 10.1038/s41467-023-37610-w
264
Xu W. He C. Kaye E. G. Li J. Mu M. Nelson G. M. et al (2022). Dynamic control of chromatin-associated m6A methylation regulates nascent RNA synthesis. Mol. Cell82, 1156–1168.e7. 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.02.006
265
Yamazaki T. Hirose T. (2021). Control of condensates dictates nucleolar architecture. Science373, 486–487. 10.1126/science.abj8350
266
Yamazaki T. Yamamoto T. Yoshino H. Souquere S. Nakagawa S. Pierron G. et al (2021). Paraspeckles are constructed as block copolymer micelles. EMBO J.40, e107270. 10.15252/embj.2020107270
267
Yang Y. Su Z. Song X. Liang B. Zeng F. Chang X. et al (2016). Enhancer RNA-driven looping enhances the transcription of the long noncoding RNA DHRS4-AS1, a controller of the DHRS4 gene cluster. Sci. Rep.6, 20961. 10.1038/srep20961
268
Yang Y. W. Flynn R. A. Chen Y. Qu K. Wan B. Wang K. C. et al (2014). Essential role of lncRNA binding for WDR5 maintenance of active chromatin and embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Elife3, e02046. 10.7554/eLife.02046
269
Yao H. Brick K. Evrard Y. Xiao T. Camerini-Otero R. D. Felsenfeld G. (2010). Mediation of CTCF transcriptional insulation by DEAD-box RNA-binding protein p68 and steroid receptor RNA activator SRA. Genes Dev.24, 2543–2555. 10.1101/gad.1967810
270
Yin Y. Yan P. Lu J. Song G. Zhu Y. Li Z. et al (2015). Opposing roles for the lncRNA Haunt and its genomic locus in regulating HOXA gene activation during embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cell Stem Cell16, 504–516. 10.1016/j.stem.2015.03.007
271
Young R. S. Kumar Y. Bickmore W. A. Taylor M. S. (2017). Bidirectional transcription initiation marks accessible chromatin and is not specific to enhancers. Genome Biol.18, 242. article 242. 10.1186/s13059-017-1379-8
272
Yruela I. Oldfield C. J. Niklas K. J. Dunker A. K. (2017). Evidence for a strong correlation between transcription factor protein disorder and organismic complexity. Genome Biol. Evol.9, 1248–1265. 10.1093/gbe/evx073
273
Zhu J. Adli M. Zou J. Y. Verstappen G. Coyne M. Zhang X. et al (2013). Genome-wide chromatin state transitions associated with developmental and environmental cues. Cell152, 642–654. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.033
274
Zhu P. Lister C. Dean C. (2021). Cold-induced Arabidopsis FRIGIDA nuclear condensates for FLC repression. Nature599, 657–661. 10.1038/s41586-021-04062-5
275
Zwicker D. Decker M. Jaensch S. Hyman A. A. Jülicher F. (2014). Centrosomes are autocatalytic droplets of pericentriolar material organized by centrioles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.111, E2636–E2645. 10.1073/pnas.1404855111
Summary
Keywords
long noncoding RNA, elncRNA, development, chromatin looping, chromatin modification
Citation
Mattick JS (2023) Enhancers are genes that express organizational RNAs. Front. RNA Res. 1:1194526. doi: 10.3389/frnar.2023.1194526
Received
27 March 2023
Accepted
16 May 2023
Published
01 June 2023
Volume
1 - 2023
Edited by
Timofey S. Rozhdestvensky, University of Münster, Germany
Reviewed by
André P. Gerber, University of Surrey, United Kingdom
Juergen Brosius, University of Münster, Germany
Updates
Copyright
© 2023 Mattick.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: John S. Mattick, j.mattick@unsw.edu.au,
†ORCID: John S. Mattick, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7680-7527
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.